REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
a
AD9873
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2000
Analog Front End Converter for
Set-Top Box, Cable Modem
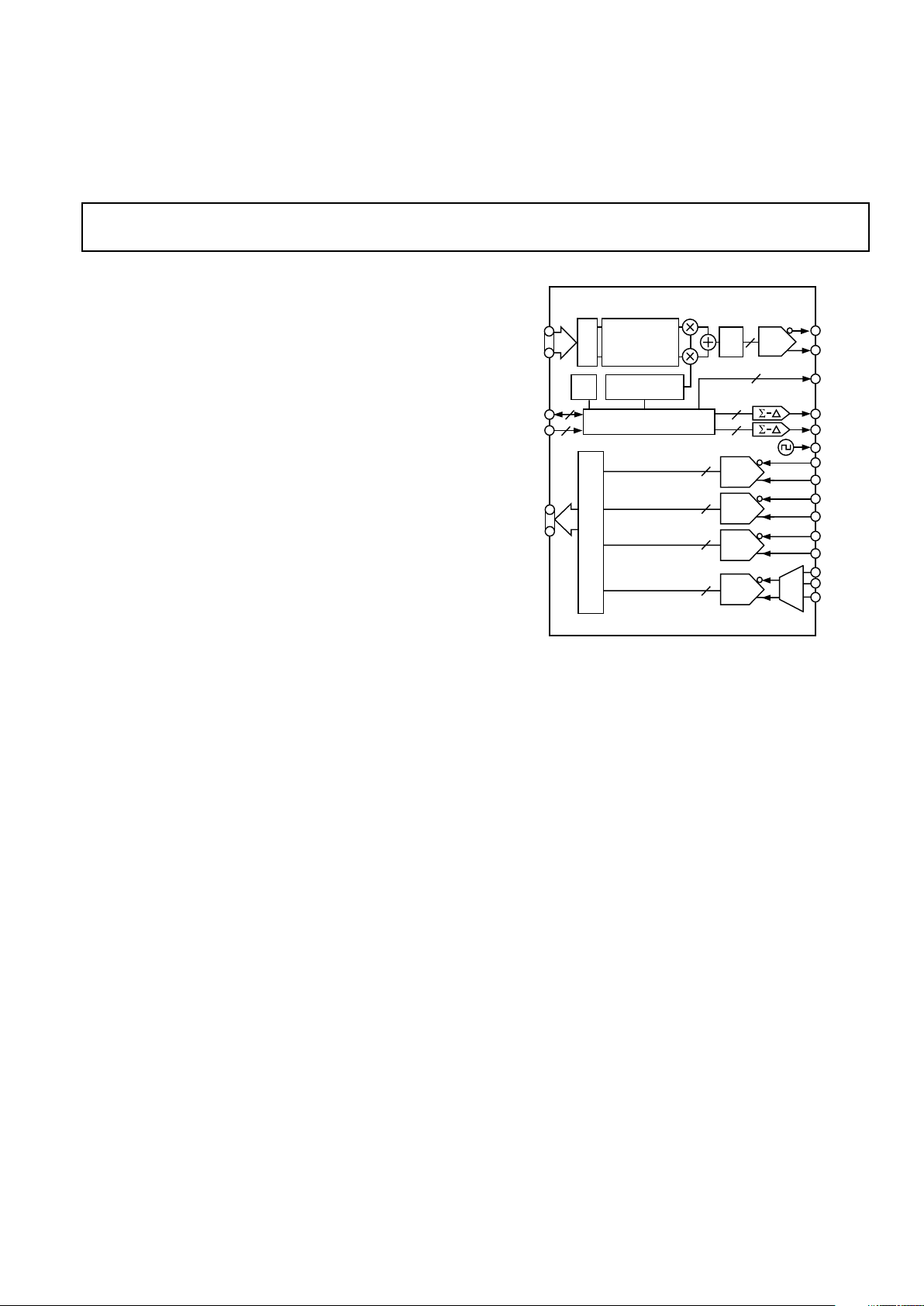
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DAC
INV
SINC
12
Tx
INTERPOLATOR
FILTER
PLL DDS
SIN
COS
3
12
12
4
2
MUX
8
8
10
12
Tx IQ
Tx SYNC
SERIAL ITF
PROFILE
Rx SYNC
Rx IQ
Rx IF
AD9873
CA
SDELTA0
SDELTA1
REF CLK
I
IN
Q
IN
IF10
IF12
VIDEO
Tx
CONTROL FUNCTIONS
Rx
ADC
ADC
ADC
ADC
FEATURES
Low-Cost 3.3 V CMOS Analog Front End Converter for
MCNS-DOCSIS, DVB, DAVIC-Compliant
Set-Top Box, Cable Modem Applications
232 MHz Quadrature Digital Upconverter
DC to 65 MHz Output Bandwidth
12-Bit Direct IF D/A Converter (TxDAC+
®
)
Programmable Reference Clock Multiplier (PLL)
Direct Digital Synthesis
Interpolator
SIN(x)/x Compensation Filter
Four Programmable, Pin-Selectable Modulator Profiles
Single-Tone Mode for Frequency Synthesis Applications
12-Bit, 33 MSPS Sampling Direct IF A/D Converter with
Auxiliary Automatic Clamp Video Input Multiplexer
10-Bit, 33 MSPS Sampling Direct IF A/D Converter
Dual 8-Bit, 16.5 MSPS Sampling IQ A/D Converter
Two Independently Programmable Sigma-Delta
Converters
Direct Interface to AD8321/AD8323 PGA Cable Driver
Programmable Frequency Output
Power-Down Modes
APPLICATIONS
Cable and Satellite Systems
PC Multimedia
Digital Communications
Data and Video Modems
Cable Modem
Set-Top Boxes
Powerline Modem
Broadband Wireless Communication
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9873 integrates a complete 232 MHz quadrature
digital transmitter and a multichannel receiver with four highperformance analog-to-digital converters (ADC) for various
video and digital data signals. The AD9873 is designed for cable
modem set-top box applications, where cost, size, power dissipation, and dynamic performance are critical attributes. A single
external crystal is used to control all internal conversion and
data processing cycles.
The transmit section of the AD9873 includes a high-speed
direct digital synthesizer (DDS), a high-performance, high-speed
12-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC), programmable clock
multiplier circuitry, digital filters, and other digital signal
processing functions, to form a complete quadrature digital
up-converter device.
On the receiver side, two 8-bit ADCs are optimized for IQ
demodulated “out-of band” signals. An on-chip 10-bit ADC
is typically used as a direct IF input of 256 QAM modulated
signals in cable modem applications. A second direct IF input
and an auxiliary video input with automatic programmable clamp
function are multiplexed to a high-performance 12-bit video ADC.
The chip’s programmable sigma-delta modulated outputs and
an output clock may be used to control external components
such as programmable gain amplifiers (PGA) and mixer stages.
Three pins provide a direct interface to the AD8321/AD8323
programmable gain amplifier (PGA) cable driver.
The AD9873 is available in a space-saving 100-lead MQFP package.
TxDAC+ is a registered trademark of Analog Devices, Inc.

REV. 0
AD9873
–2–
Page
FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
PIN CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
REGISTER BIT DEFINITIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS . . . 14
Typical Power Consumption Characteristics . . . . . . . . . 14
Dual Sideband Transmit Spectrum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Single Sideband Transmit Spectrum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Typical QAM Transmit Performance Characteristics . . 16
Typical ADC Performance Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . 18
THEORY OF OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Transmit Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
OSC IN Clock Multiplier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Receive Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
CLOCK AND OSCILLATOR CIRCUITRY . . . . . . . . . . 22
PROGRAMMABLE CLOCK OUTPUT REF CLK . . . . 23
SIGMA-DELTA OUTPUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
SERIAL INTERFACE FOR REGISTER CONTROL . . . 23
General Operation of the Serial Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Instruction Byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Serial Interface Port Pin Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
MSB/LSB Transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Notes on Serial Port Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Page
TRANSMIT PATH (Tx) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Transmit Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Data Assembler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Half-Band Filters (HBFs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Cascaded Integrator—COMB (CIC) Filter . . . . . . . . . . 25
Combined Filter Response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Inverse SINC Filter (ISF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Tx Signal Level Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Tx Throughput and Latency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
D/A Converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
PROGRAMMING/WRITING THE AD8321/AD8323
CABLE DRIVER AMPLIFIER GAIN CONTROL . . . 29
RECEIVE PATH (Rx) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
ADC Theory of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Receive Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Driving the Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Op Amp Selection Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
ADC Differential Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
ADC Voltage References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Video Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
POWER AND GROUNDING CONSIDERATIONS . . . 32
EVALUATION BOARD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
TABLE OF CONTENTS
REV. 0
–3–
AD9873
(VAS = 3.3 V ⴞ 5%, VDS = 3.3 V ⴞ 10%, f
OSCIN
= 27 MHz, f
SYSCLK
= 216 MHz, f
MCLK
= 54 MHz
(M = 8, N = 4), ADC Sample Rate derived from PLL f
MCLK
, R
SET
= 10 k⍀, 75 ⍀ DAC Load)
Test
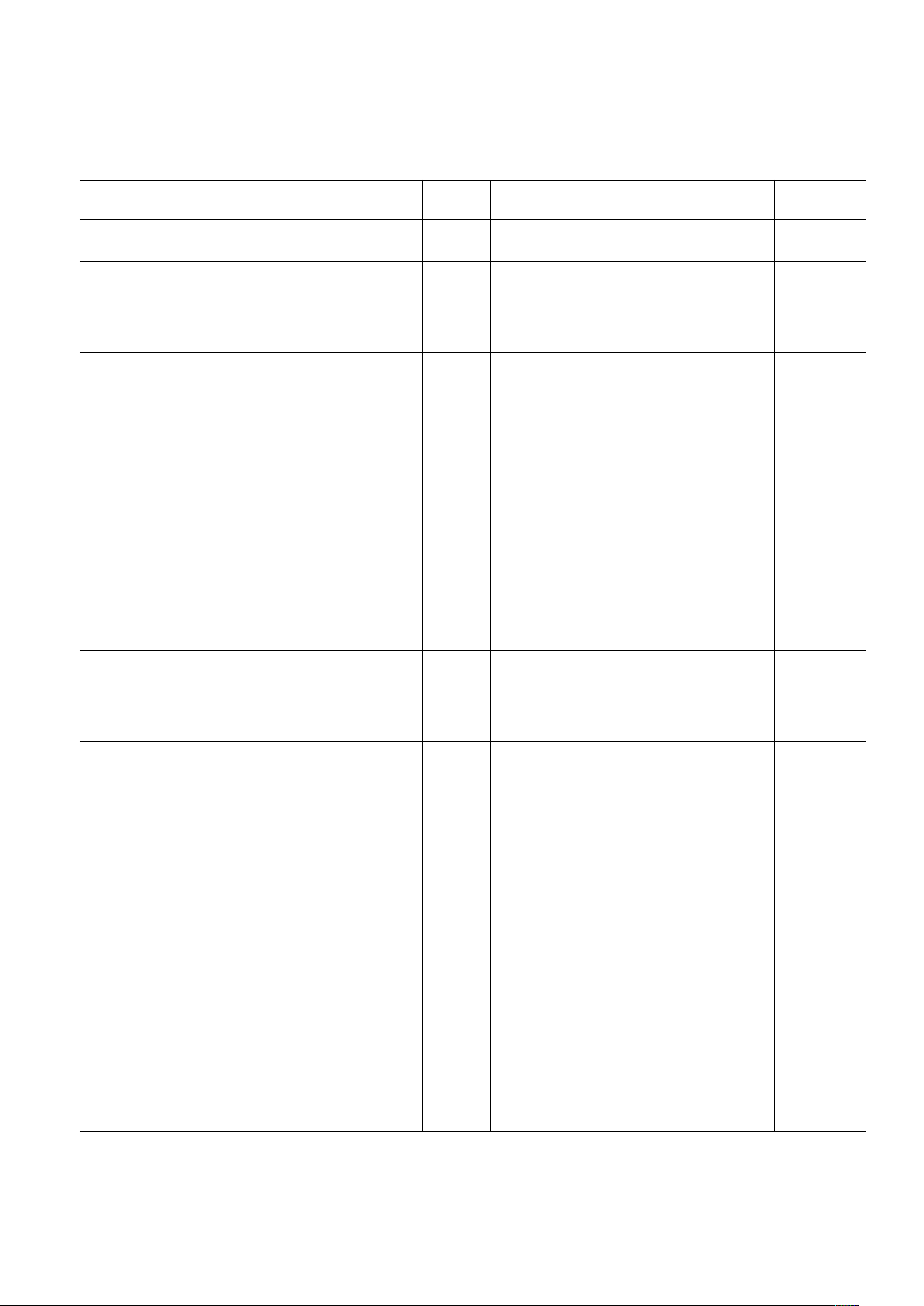
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
SYSTEM CLOCK, DAC SAMPLING f
SYSCLK
Frequency Range Full III 232 MHz
OSC IN and XTAL CHARACTERISTICS
Frequency Range Full III 3 33 MHz
Duty Cycle 25C III 35 50 65 %
Input Capacitance 25CIV 3 pF
Input Resistance 25C IV 100 MΩ
MCLK OUT JITTER (f
MCLK
Derived from PLL) 25C IV 6 ps rms
TxDAC CHARACTERISTICS
1
Resolution N/A N/A 12 Bits
Full-Scale Output Current Full III 2 4 20 mA
Gain Error (Using Internal Reference) 25C I –3 0.14 +3 % FS
Output Offset 25C I –1 +1 % FS
Reference Voltage (REFIO Level) 25°C I 1.18 1.23 1.28 V
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) 25CIV ±2.5 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity (INL) 25CIV ±8 LSB
Output Capacitance 25CIV 5 pF
Phase Noise @ 1 kHz Offset, 42 MHz 25C IV –113 dBc/Hz
Output Voltage Compliance Range Full III –0.5 +1.5 V
Wideband SFDR
5 MHz Analog Out, I
OUT
= 4 mA 25C IV 59 dBc
65 MHz Analog Out, I
OUT
= 4 mA 25C IV 54 dBc
Narrowband SFDR (100 kHz Window)
65 MHz Analog Out, I
OUT
= 4 mA 25C IV 79 dBc
Tx MODULATOR CHARACTERISTICS
I/Q Offset Full III 50 55 dB
Pass Band Amplitude Ripple (f < f
IQCLK
/8) Full III 0.1 dB
Pass Band Amplitude Ripple (f < f
IQCLK
/4) Full III 0.5 dB
Stop Band Response (f > f
IQCLK
× 3/4) Full III –63 dB
8-BIT ADC CHARACTERISTICS
Resolution N/A N/A 8 Bits
Conversion Rate Full III 16.5 MHz
Pipeline Delay N/A N/A 3.5 ADC Cycles
DC Accuracy
Differential Nonlinearity 25CIV 0.5 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity 25CIV 0.5 LSB
Offset Error for Each 8-Bit ADC 25CIV 0.75 % FSR
Gain Error for Each 8-Bit ADC 25CIV 4 % FSR
Offset Matching Between 8-Bit ADCs Full IV 3 LSB
Gain Matching Between 8-Bit ADCs Full IV 4.5 LSB
Analog Input
Input Voltage Range Full IV 1 V p-p
Input Capacitance 25C IV 1.4 pF
Differential Input Resistance 25CIV 4 kΩ
Aperture Delay 25C IV 2.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) 25C IV 1.2 ps rms
Input Bandwidth (–3 dB) 25C IV 90 MHz
Input Referred Noise 25C IV 600 µV
Reference Voltage Error
REFT8–REFB8 (0.5 V) 25CI ±4 ±92 mV
Dynamic Performance (A
IN
= –0.5 dB FS, f = 5 MHz)
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio (SINAD) Full II 43.5 48 dB
SPECIFICATIONS
REV. 0
–4–
AD9873–SPECIFICATIONS
Test
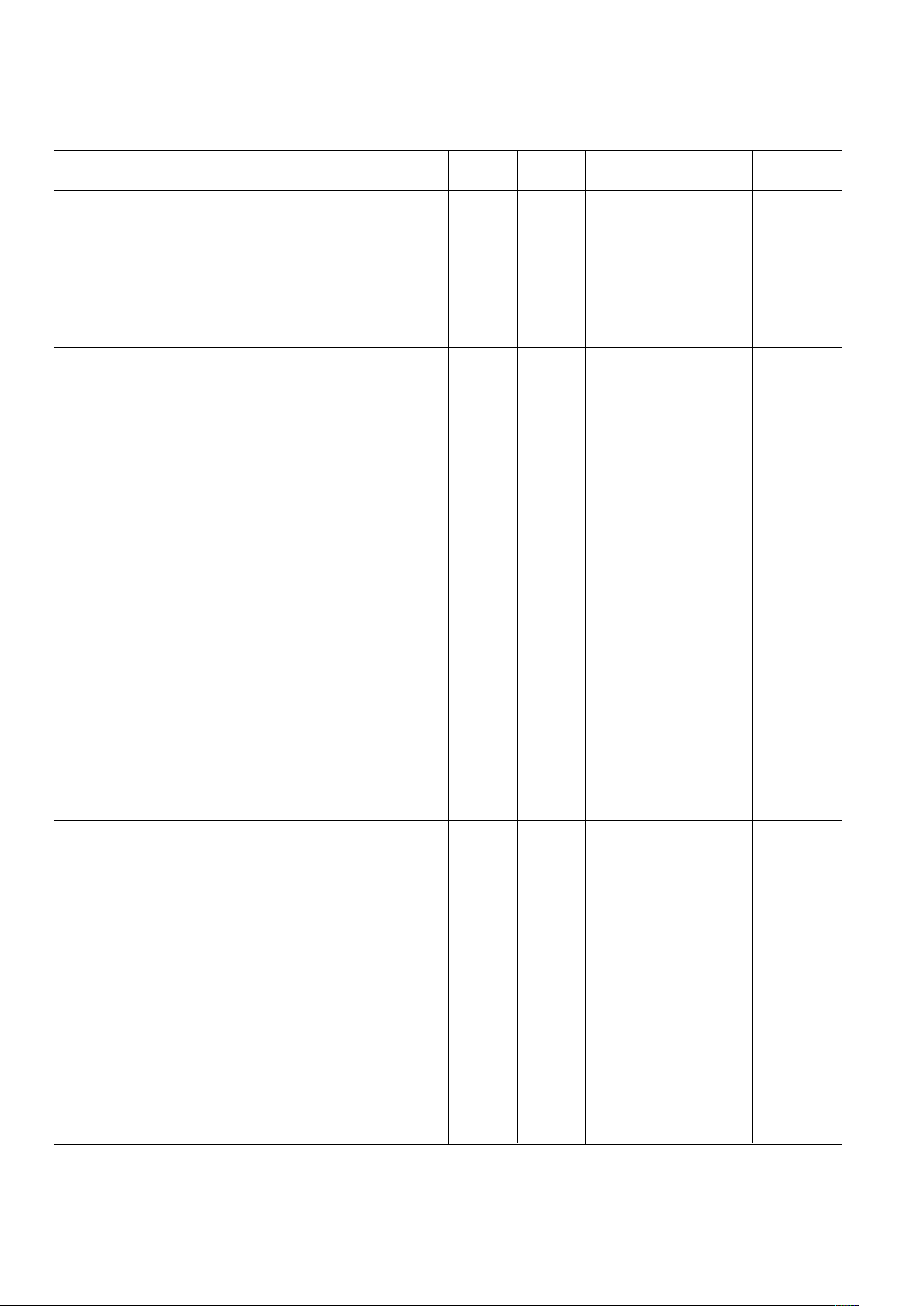
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
8-BIT ADC CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Dynamic Performance (A
IN
= –0.5 dB FS, f = 5 MHz)
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB) Full II 6.9 7.68 Bits
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
2
Full IV 7.68 Bits
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Full II 43.5 48 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) Full II –66 –57 dB
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) Full II 58 64 dB
Differential Phase 25C IV <0.1 Degree
Differential Gain 25C IV 1 LSB
10-BIT ADC CHARACTERISTICS
Resolution N/A N/A 10 Bits
Conversion Rate Full III 33 MHz
Pipeline Delay N/A N/A 5.5 ADC Cycles
DC Accuracy
Differential Nonlinearity 25CIV 0.75 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity 25CIV 0.5 LSB
Offset Error 25CIV 0.5 % FSR
Gain Error 25CIV 3 % FSR
Analog Input
Input Voltage Range Full IV 2 V p-p
Input Capacitance 25C IV 1.4 pF
Differential Input Resistance 25CIV 4 kΩ
Aperture Delay 25C IV 2.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) 25C IV 1.2 ps rms
Input Bandwidth (–3 dB) 25C IV 95 MHz
Input Referred Noise 25C IV 350 µV
Reference Voltage
REFT10–REFB10 (1 V) 25CI ±6 ±200 mV
Dynamic Performance (A
IN
= –0.5 dB FS, f = 5 MHz)
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio (SINAD) Full II 57.9 60.1 dB
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB) Full II 9.3 9.7 Bits
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
3
Full IV 9.8 Bits
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Full II 58.2 60.1 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) Full II –75.8 –63.9 dB
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) Full II 65.7 80 dB
Differential Phase 25C IV <0.1 Degree
Differential Gain 25C IV <1 LSB
12-BIT ADC CHARACTERISTICS
Resolution N/A N/A 12 Bits
Conversion Rate Full III 33 MHz
Pipeline Delay N/A N/A 5.5 ADC Cycles
DC Accuracy
Differential Nonlinearity 25CIV 0.75 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity 25CIV 1.5 LSB
Offset Error 25CIV 1 % FSR
Gain Error 25CIV 2 % FSR
Analog Input
Input Voltage Range Full IV 2 V p-p
Input Capacitance 25C IV 1.4 pF
Differential Input Resistance 25CIV 4 kΩ
Aperture Delay 25C IV 2.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) 25C IV 1.2 ps rms
Input Bandwidth (–3 dB) 25C IV 85 MHz
Input Referred Noise 25CIV 75 µV
Reference Voltage
REFT12–REFB12 (1 V) 25CI ±6 ±200 mV
REV. 0
–5–
AD9873
Test
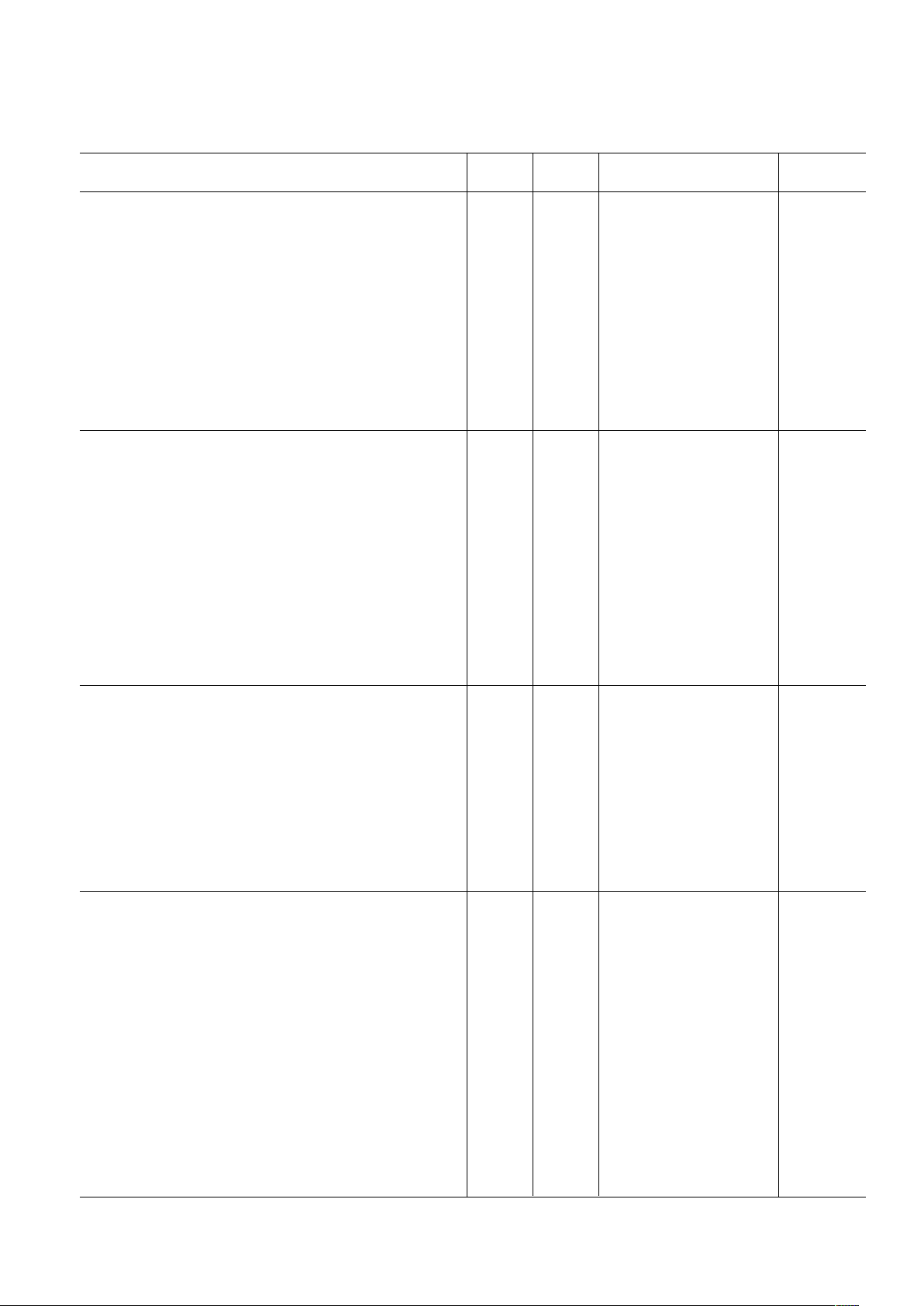
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
12-BIT ADC CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Dynamic Performance (A
IN
= –0.5 dB FS, f = 5 MHz)
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio (SINAD) Full III 62.3 65 dB
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio (SINAD)
3
Full IV 67.4 dB
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB) Full III 10.0 10.5 Bits
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
3
Full IV 10.8 Bits
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Full III 63.3 65.3 dB
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
3
Full IV 67.4 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) Full III –77.6 –65.4 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
3
Full IV –77.6 dB
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) Full III 65.7 80 dB
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
3
Full IV 80 dB
Differential Phase 25C IV <0.1 Degree
Differential Gain 25C IV <1 LSB
VIDEO CLAMP INPUT
Input Voltage Range Full IV 2 V
Clamp Current Positive 25C IV 1.3 mA
Clamp Droop Current 25CIV 2 A
Clamp Level Offset Programming Range 25C III 256 512 2032 LSB
Clamp Level Resolution 25C IV 16 LSB
Carrier Rejection Filter Bandwidth (–3 dB) 25C IV 0.6 MHz
Dynamic Performance (A
IN
= –0.5 dB FS, f = 5 MHz)
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio (SINAD) Full IV 52 dB
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB) Full IV 8.34 Bits
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Full IV 61.0 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) Full IV –53.0 dB
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) Full IV 55.0 dB
Differential Phase 25°C IV <0.1 Degree
Differential Gain 25°C IV <8 LSB
CHANNEL-TO-CHANNEL ISOLATION
Tx DAC-to-ADC Isolation
(5 MHz Analog Output)
Isolation Between Tx and 8-Bit ADCs 25C IV >80 dB
Isolation Between Tx and 10-Bit ADC 25C IV >85 dB
Isolation Between Tx and 12-Bit ADC 25C IV >90 dB
ADC-to-ADC Isolation
(A
IN
= –0.5 dB FS, f = 5 MHz)
Isolation Between IF12 and Video 25C III 70 >70 dB
Isolation Between IF10 and IF12 25C IV >80 dB
Isolation Between Q in and IF10 25C IV >80 dB
Isolation Between Q in and I Inputs 25C IV >70 dB
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
(20 pF Load)
Wake-Up Time N/A N/A 200 t
MCLK
Cycles
Minimum RESET Pulsewidth Low (t
RL
) N/A N/A 5 t
MCLK
Cycles
Digital Output Rise/Fall Time 25C III 2.8 4 ns
Tx/Rx Interface
MCLK Frequency (f
MCLK
)25C III 66 MHz
TxSYNC/TxIQ Set Up Time (t
SU
)25C III 3 ns
TxSYNC/TxIQ Hold Time (t
HD
)25C III 3 ns
RxSYNC/RxIQ/IF to Valid Time (t
TV
)25C III 5.2 ns
RxSYNC/RxIQ/IF Hold Time (t
HT
)25C III 0.2 ns
Serial Control Bus
SCLK Frequency (f
SCLK
) Full III 15 MHz
Clock Pulsewidth High (t
PWH
) Full III 30 ns
Clock Pulsewidth Low (t
PWL
) Full III 30 ns
Clock Rise/Fall Time Full III 1 ms
Data/Chip-Select Setup Time (t
DS
) Full III 25 ns
Data Hold Time (t
DH
) Full III 0 ns
Data Valid Time (tDV) Full III 30 ns
REV. 0
–6–
AD9873–SPECIFICATIONS
Test
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
CMOS LOGIC INPUTS
Logic “1” Voltage 25C III 2.0 V
Logic “0” Voltage 25C III 0.8 V
Logic “1” Current 25C III 12 A
Logic “0” Current 25C III 12 A
Input Capacitance 25CIV 3 pF
CMOS LOGIC OUTPUTS (1 mA Load)
Logic “1” Voltage 25C III 2.4 V
Logic “0” Voltage 25C III 0.4 V
POWER SUPPLY
Analog Supply Current I
AS
25C II 91 115 mA
Digital Supply Current I
DS
Full Operating Conditions4 (Register 02h = 00h) 25C IV 250 mA
Zero Input Tx
4
(Register 02h = 00h) 25C II 175 205 mA
25% Tx Burst Duty Cycle
4
(Register 02h = 00h) 25C IV 210 mA
Power-Down Digital Tx (Register 02h = 20h) 25°CII 42 55 mA
Power Supply Rejection (Differential Signal)
Tx DAC 25C IV <0.25 % FS
8-Bit ADC 25C IV <0.004 % FS
10-Bit ADC 25C IV <0.002 % FS
12-Bit ADC 25C IV <0.0004 % FS
NOTES
1
Single tone generated by applying a 1.6875 MHz sine signal to the Q Channel and the 90 degree phase shifted (cosine) signal to the I Channel.
2
Sampling directly with f
OSCCIN
/2. No degradation due to Clock Multiplier PLL. ADC Clock Select Register 08h, Bits 5 and 7 set to “1.”
3
Sampling directly with f
OSCCIN
. No degradation due to Clock Multiplier PLL. ADC Clock Select Register 08h, Bits 5 and 7 set to “1.”
4
See performance graph TPC 2 for power saving in burst mode operation.
REV. 0
AD9873
–7–
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Power Supply (VAS, VDS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.9 V
Digital Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 mA
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to AVDD (IQ) +0.3 V
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0C to 70C
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150C
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65C to +150C
Lead Temperature (Soldering 10 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300C
*Absolute maximum ratings are limiting values, to be applied individually, and
beyond which the serviceability of the circuit may be impaired. Functional
operability under any of these conditions is not necessarily implied. Exposure of
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods of time may affect
device reliability.
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
I – 100% production tested.
II – Devices are 100% production tested at 25C and guaran-
teed by design and characterization testing for commercial
operating temperature range (0C to 70C).
III – Parameter is guaranteed by design and/or characteriz-
ation testing.
IV – Parameter is a typical value only.
N/A – Test level definition is not applicable.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Thermal Resistance
100-Lead MQFP
JA
= 40.5C/W
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD9873 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Description Option
AD9873JS 0C to 70C Metric Quad Flatpack (MQFP) S-100C
AD9873-EB Evaluation Board

REV. 0
AD9873
–8–
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY ERROR (DNL, NO
MISSING CODES)
An ideal converter exhibits code transitions that are exactly 1 LSB
apart. DNL is the deviation from this ideal value. Guaranteed
no missing codes to 10-bit resolution indicates that all 1024 codes
respectively, must be present over all operating ranges.
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY ERROR (INL)
Linearity error refers to the deviation of each individual code
from a line drawn from “negative full scale” through “positive
full scale.” The point used as “negative full scale” occurs 1/2 LSB
before the first code transition. “Positive full scale” is defined as
a level 1 1/2 LSB beyond the last code transition. The deviation
is measured from the middle of each particular code to the true
straight line.
PHASE NOISE
Single-sideband phase noise power density is specified relative to
the carrier (dBc/Hz) at a given frequency offset (1 kHz) from
the carrier. Phase noise can be measured directly in single tone
transmit mode with a spectrum analyzer that supports noise
marker measurements. It detects the relative power between the
carrier and the offset (1 kHz) sideband noise and takes the resolution bandwidth (rbw) into account by subtracting 10 log (rbw).
It also adds a correction factor that compensates for the implementation of the resolution bandwidth, log display and detector
characteristic.
OUTPUT COMPLIANCE RANGE
The range of allowable voltage at the output of a current-output
DAC. Operation beyond the maximum compliance limits may
cause either output stage saturation, resulting in nonlinear performance or breakdown.
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
The difference, in dB, between the rms amplitude of the DACs
output signal (or ADC’s input signal) and the peak spurious
signal over the specified bandwidth (Nyquist bandwidth unless
otherwise noted).
PIPELINE DELAY (LATENCY)
The number of clock cycles between conversion initiation and the
associated output data being made available.
OFFSET ERROR
First transition should occur for an analog value 1/2 LSB above
negative full scale. Offset error is defined as the deviation of the
actual transition from that point.
GAIN ERROR
The first code transition should occur at an analog value 1/2 LSB
above negative full scale. The last transition should occur for an
analog value 1 1/2 LSB below the nominal full scale. Gain error
is the deviation of the actual difference between first and last
code transitions and the ideal difference between first and last
code transitions.
APERTURE DELAY
Aperture delay is a measure of the Sample-and-Hold Amplifier
(SHA) performance and specifies the time delay between the
rising edge of the sampling clock input to when the input signal
is held for conversion.
APERTURE UNCERTAINTY (JITTER)
Aperture jitter is the variation in aperture delay for successive
samples and is manifested as noise on the input to the ADC.
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE + DISTORTION (SINAD) RATIO
SINAD is the ratio of the rms value of the measured input signal
to the rms sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, including harmonics but excluding dc. The value for
SINAD is expressed in decibels.
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS (ENOB)
For a sine wave, SINAD can be expressed in terms of the number
of bits. Using the following formula,
N = (SINAD – 1.76) dB/6.02
it is possible to obtain a measure of performance expressed as N,
the effective number of bits.
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO (SNR)
SNR is the ratio of the rms value of the measured input signal to
the rms sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, excluding harmonics and dc. The value for SNR is
expressed in decibels.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION (THD)
THD is the ratio of the rms sum of the first six harmonic components to the rms value of the measured input signal and is
expressed as a percentage or in decibels.
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION
Power supply rejection specifies the converters maximum full-scale
change when the supplies are varied from nominal to minimum
and maximum specified voltages.
CHANNEL-TO-CHANNEL ISOLATION (CROSSTALK)
In an ideal multichannel system, the signal in one channel will
not influence the signal level of another channel. The channelto-channel isolation specification is a measure of the change that
occurs to a grounded channel as a full-scale signal is applied to
another channel.
REV. 0
AD9873
–9–
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin No. Mnemonic Pin Function
1, 84, 87 AVDD Analog Supply Voltage
92, 95 10-/12-Bit ADC
2, 21, 70 DRGND Pin Driver Digital Ground
3, 22, 72 DRVDD Pin Driver Digital Supply Voltage
4–15 IF11–IF0 Multiplexed Output of IF10-
and IF12-Bit ADCs
16–19 Rx IQ 3 Multiplexed Output of I and
–Rx IQ 0 Q 8-Bit ADCs
20 Rx SYNC Demultiplexer Synchronization
Output for IF and IQ ADCs
23 MCLK Master Clock Output
Demultiplexer
24, 33, 38 DVDD Digital Supply Voltage
25, 34, DGND Digital Ground
39, 40
26 Tx SYNC Synchronization Input for
Transmitter
27–32 Tx IQ 5 Multiplexed I and Q Input
–Tx IQ 0 Data for Transmitter (Two’s
Complement)
35, 36 PROFILE[1:0] Profile Selection Inputs
37 RESET Master Reset Input, Reset applies
for all Interfaces and Registers
41 SCLK Serial Interface Input Clock
42 CS Serial Interface Chip Select
43 SDIO Serial Interface Data I/O
44 SDO Serial Interface Data Output
45 DGND Tx Digital Ground Tx Section
46 DVDD Tx Digital Supply Voltage Tx
47 PWR DOWN Transmit Power-Down
Control Input
48 REFIO DAC Bandgap requires 0.1 µF
Capacitor to Ground
49 FSADJ Full-Scale DAC Current Output
Adjust with External Resistor
50 AGND Tx Analog Ground Tx Section
51 Tx– Transmitter DAC Output–
52 Tx+ Transmitter DAC Output+
53 AVDD Tx Analog Supply Voltage Tx
54 DGND PLL PLL Digital Ground
55 DVDD PLL PLL Digital Supply Voltage
56 AVDD PLL PLL Analog Supply Voltage
57 PLL FILTER PLL Loop Filter Connection
58 AGND PLL PLL Analog Ground
59 DGND OSC Digital Ground Oscillator
60 XTAL Crystal Oscillator Inv. Output
61 OSC IN Oscillator Clock Input
62 DVDD OSC Digital Supply Oscillator
63 CA CLK Cable Amplifier Control
Clock Output
Pin No. Mnemonic Pin Function
64 CA DATA Cable Amplifier Control Data
Output
65 CA ENABLE Cable Amplifier Control Enable
Output
66 DVDD SD Supply Voltage Sigma Delta
67 SDELTA1 Sigma Delta Output Stream 1
68 SDELTA0 Sigma Delta Output Stream 0
69 DGND SD Ground Sigma Delta
71 REF CLK Programmable Reference Clock
Output Derived from MCLK
73 AVDD IQ Analog Supply 8-Bit ADCs
74, 77, 80 AGND IQ Analog Ground 8-Bit ADCs
75 REFB8 Bottom Reference Decoupling
IQ 8-Bit ADC’s Reference
76 REFT8 Top Reference Decoupling
IQ 8-Bit ADC’s Reference
78 I IN– Inverting I Analog Input
79 I IN+ Noninverting I Analog Input
81 Q IN– Inverting Q Analog Input
82 Q IN+ Noninverting Q Analog Input
83, 88, 91, AGND Analog Ground 10-/12-Bit ADC
96, 99
85 REFB10 Bottom Reference Decoupling
IF 10-Bit ADC’s Reference
86 REFT10 Top Reference Decoupling
IF 10-Bit ADC’s Reference
89 IF10– Noninverting IF10 Analog Input
90 IF10+ Inverting IF10 Analog Input
93 REFB12 Bottom Reference Decoupling
IF 12-Bit ADC’s Reference
94 REFT12 Top Reference Decoupling
IF 12-Bit ADC’s Reference
97 IF12– Inverting IF12 Analog Input
98 IF12+ Noninverting IF12 Analog Input
100 VIDEO IN Single-Ended Video Input
REV. 0
AD9873
–10–
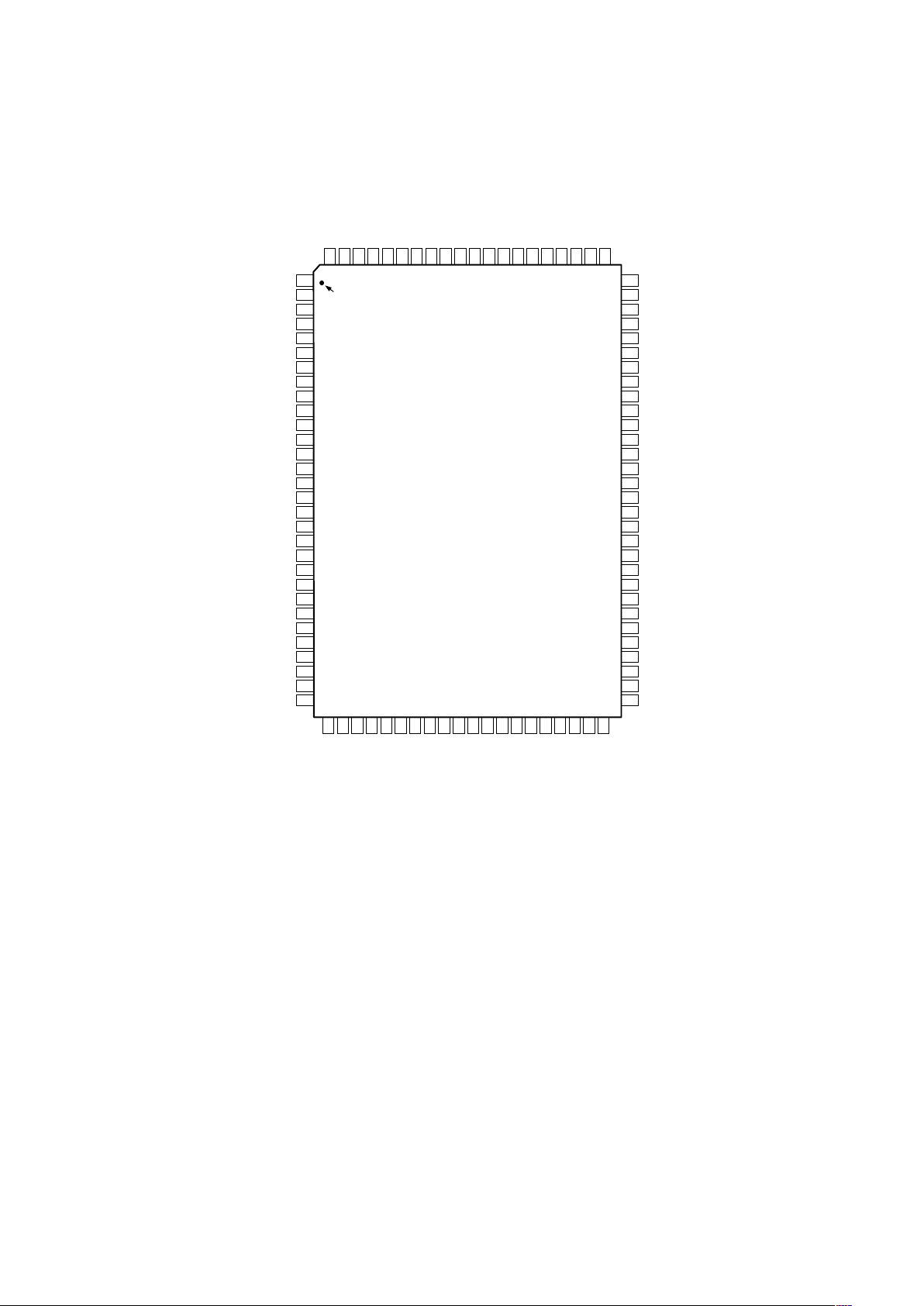
PIN CONFIGURATION
5
4
3
2
7
6
9
8
1
11
10
16
15
14
13
18
17
20
19
22
21
12
24
23
26
25
28
27
30
29
32
33
34
35
36
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
31
37
76
77
78
79
74
75
72
73
70
71
80
65
66
67
68
63
64
61
62
59
60
69
57
58
55
56
53
54
51
52
100
99989796959493929190898887868584838281
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
TOP VIEW
(Pins Down)
VIDEO IN
AGND
IF12+
IF12–
AGND
AVDD
REFT12
REFB12
AVDD
AGND
IF10+
IF10–
AGND
AVDD
REFT10
REFB10
AVDD
AGND
Q IN+
Q IN–
TxIQ(1)
TxIQ(0)
DVDD
DGND
PROFILE(1)
PROFILE(0)
RESET
DVDD
DGND
DGND
SCLK
CS
SDIO
SDO
DGND Tx
DVDD Tx
PWR DOWN
REFIO
FSADJ
AGND Tx
AGND IQ
I IN+
I IN–
AGND IQ
REFT8
REFB8
AGND IQ
AVDD IQ
DRVDD
REF CLK
DRGND
DGND SD
SDELTA 0
SDELTA 1
DVDD SD
CA ENABLE
CA DATA
CA CLK
DVDD OSC
OSC IN
XTAL
DGND OSC
AGND PLL
PLL FILTER
AVDD PLL
DVDD PLL
DGND PLL
AVDD Tx
Tx+
Tx–
DRGND
DRVDD
(MSB) IF(11)
IF(10)
IF(9)
IF(8)
IF(7)
IF(6)
IF(5)
IF(4)
IF(3)
IF(2)
IF(1)
IF(0)
(MSB) RxIQ(3)
RxIQ(2)
RxIQ(1)
RxIQ(0)
RxSYNC
DRGND
DRVDD
MLCK
DVDD
DGND
TxSYNC
(MSB) TxIQ(5)
TxIQ(4)
TxIQ(3)
TxIQ(2)
AD9873
AVDD
REV. 0
AD9873
–11–
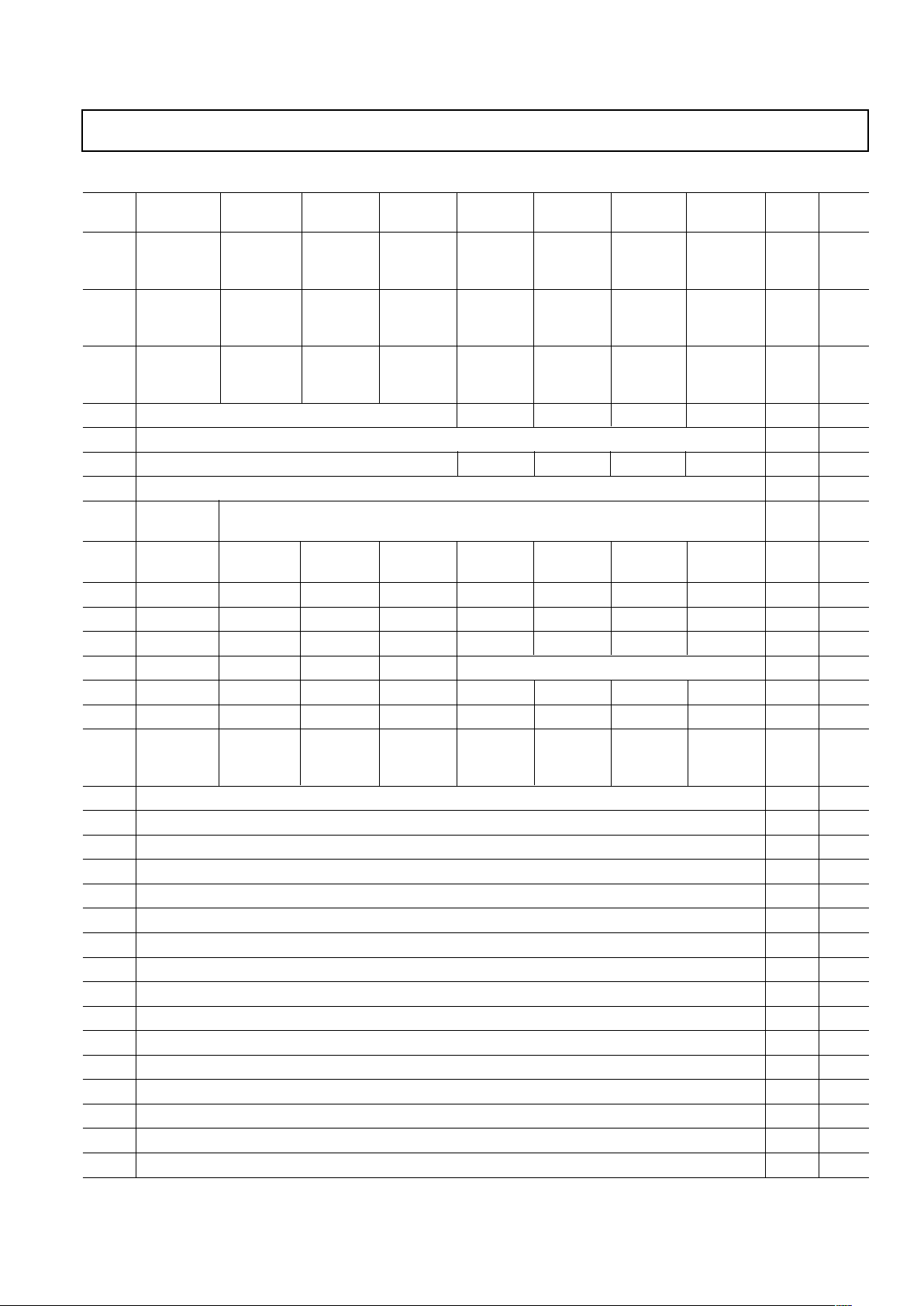
Table I. Register Map
Address Default
(Hex) Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (Hex) Type
00 SDIO LSB/MSB RESET OSC IN OSC IN OSC IN OSC IN OSC IN 10 rw
Bidirectional First Multiplier Multiplier Multiplier Multiplier Multiplier
M <4> M <3> M <2> M <1> M <0>
01 PLL OSC IN MCLK MCLK MCLK MCLK MCLK MCLK 09 rw
Lock Divider Divider Divider Divider Divider Divider Divider
Detect N = 3 (4) R <5> R <4> R <3> R <2> R <1> R <0>
02 Power-Down Power-Down Power-Down Power-Down Power-Down Power-Down Power-Down Power-Down 00 rw
PLL DAC Tx Digital Tx 12-Bit ADC Reference 10-Bit ADC Reference 8-Bit ADC
12-Bit ADC 10-Bit ADC
03 Sigma-Delta Output 0 Control Word <3:0> LSB 000000rw
04 Sigma-Delta Output 0 Control Word <11:4> MSB 00 rw
05 Sigma-Delta Output 1 Control Word <3:0> LSB 000000rw
06 Sigma-Delta Output 1 Control Word <11:4> MSB 00 rw
07 Video Input Clamp Level Control for Video Input <6:0> 20 rw ADC
Enable
08 ADC Clock 0 ADC Clock 0 0 0 Test Test 00 rw ADC
Select Select 12-Bit ADC 10-Bit ADC
090 0 00000000rw
0A0 0 00000000rw
0B0 0 0 0000000rw
0C 0 0 0 0 Version <3:0> 0X r
0D0 0 00000000r
0E0 0 0 0000000r
0F 0 0 Profile Profile 0 Bypass Spectral Single-Tone 00 rw Tx
Select <1> Select <0> Inv. Sinc Inversion Tx Tx Mode
Tx Filter
10 Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 0 <7:0> 00 rw Tx
11 Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 0 <15:8> 00 rw Tx
12 Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 0 <23:16> 00 rw Tx
13 Cable Driver Amplifier Gain Control Profile 0 <7:0> 00 rw Tx
14 Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 1 <7:0> 00 rw Tx
15 Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 1 <15:8> 00 rw Tx
16 Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 1 <23:16> 00 rw Tx
17 Cable Driver Amplifier Gain Control Profile 1 <7:0> 00 rw Tx
18 Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 2 <7:0> 00 rw Tx
19 Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 2 <15:8> 00 rw Tx
1A Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 2 <23:16> 00 rw Tx
1B Cable Driver Amplifier Gain Control Profile 2 <7:0> 00 rw Tx
1C Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 3 <7:0> 00 rw Tx
1D Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 3 <15:8> 00 rw Tx
1E Tx Frequency Turning Word Profile 3 <23:16> 00 rw Tx
1F Cable Driver Amplifier Gain Control Profile 3 <7:0> 00 rw Tx
“0” register bits should not be programmed with 1.

REV. 0
AD9873
–12–
REGISTER BIT DEFINITIONS
00h, Bits 0–4: OSC IN Multiplier–Register Address
This register field is used to program the on-chip multiplier (PLL)
that generates the chip’s high-frequency system clock, f
SYSCLK
.
For example, to multiply the external crystal clock f
OSCIN
by 19
decimal, program register address 00h, Bits 5–1 as 13h. Default
value is M = 16 = 10h. Valid entries range from M = 1 to 31.
M = 1 (no PLL) requires a very stable, high-frequency clock at
OSC IN. A changed f
SYSCLK
frequency is stable (PLL locked)
after a maximum of 200 f
MCLK
cycles (= Wake-Up Time).
00h, Bit 5: RESET
Writing a one to this bit resets the registers to their default values and restarts the chip. The RESET bit always reads back
0. Register address 00h bits are not cleared by this software reset.
However, a low level at the RESET pin would force all registers,
including all bits in address 00h, to their default state.
00h, Bit 6: LSB/MSB First
Active high indicates SPI serial port access of instruction byte
and data registers is least significant bit (LSB) first. Default low
indicates most significant bit (MSB) first format.
00h, Bit 7: SDIO Bidirectional
Default low indicates SPI serial port uses dedicated input/output
lines (SDIO and SDO pin). High configures serial port as single
line I/O (SDIO pin is used bidirectional).
01h, Bits 0–5: MCLK Divider
This register is used to divide the chip’s master clock by R, where
R is an integer between 2 and 63. The generated reference clock,
REF CLK, can be used for external frequency-controlled
devices. Default value is R = 9.
01h, Bit 6: OSC IN Divider
The OSC IN multiplier output clock can be divided by 4 or 3 to
generate the chip’s master clock. Active high indicates a divide
ratio of N = 3. Default low configures a divide ratio of N = 4.
01h, Bit 7: PLL Lock Detect
If this bit is set to 1, REF CLK pin is disabled from the normal usage. In this mode REF CLK high signals that the internal
phase lock loop (PLL) is in lock with CLK IN.
02h Bits 0–7: Power-Down
Sections of the chip that are not used can be put in a power saving
mode when the corresponding bits are set to 1. This register has
a default value of 00h with all sections active.
Bit 0: Power-Down 8-bit ADC powers down the 8-bit ADC
and stops RxSYNC framing signal.
Bit 1: Power-Down 10-bit ADC reference powers down the
internal 10-bit ADC reference.
Bit 2: Power-Down 10-bit ADC powers down the 10-bit ADC.
Bit 3: Power-Down 12-bit ADC reference powers down the
internal 12-bit ADC reference.
Bit 4: Power-Down 12-bit ADC powers down the 12-bit ADC.
Bit 5: Power-Down Tx powers down the transmit section of
the chip.
Bit 6: Power-Down DAC Tx powers down the DAC.
Bit 7: Power-Down PLL powers down the CLK IN Multiplier.
03h to 06h: Sigma-Delta Output Control Words
The Sigma-Delta Output Control Words –0 and –1 are 12 bits
wide and split in MSB bits <11:4> and LSB bits <3:0>. Changes
to the sigma-delta outputs take effect immediately for every MSB
or LSB register write. Sigma-delta output control words have a
default value of 0. The smaller the programmed values in these
registers, the lower are the integrated (low-pass filtered) sigma
delta output levels (straight binary format).
07h, Bits 0–6: Clamp Level Control for Video Input
A 7-bit clamp level offset can be set for the internal automatic
clamp level control loop of the Video Input.
Clamp level offset = Clamp level control × 16.
This register defaults to 32 = 20h, which amounts to a clamp
level offset of 512 LSB = 200h. Valid clamp level control values
are 16 to 127.
07h, Bit 7: Video Input Enable
This bit controls the multiplexer to the 12-bit ADC and determines if IF12 input or Video input is used. The bit is default set
to 0 for the IF12 input.
08h, Bit 0: Test 10-Bit ADC
Active high allows nonmultiplexed 10-bit ADC data only to be
read at IF outputs. Output data changes at half MCLK clock rate.
This bit defaults to 0.
08h, Bit 1: Test 12-Bit ADC
Active high allows nonmultiplexed 12-bit ADC data only to be
read at IF outputs. Output data changes at half MCLK clock rate.
This bit defaults to 0.
08h, Bit 5 and Bit 7: ADC Clock Select
Active high indicates that the frequency at OSC IN is directly used
to sample the on chip ADCs. Default low indicates that the on
chip ADCs generate their sampling frequencies from the internally
generated master clock MCLK. Both Bit 5 and Bit 7 need to be
programmed with the same values.
0Ch, Bits 0–3: Version
This register stores the die version of the chip. It can only be read.
0Fh, Bit 0: Single-Tone Tx Mode
Active high configures the AD9873 for single-tone applications.
The AD9873 will supply a single frequency output as determined
by the frequency tuning word (FTW) selected by the active
profile. In this mode, the Tx IQ input data pins are ignored
but should be tied high or low. Default value of single-tone
Tx mode is 0 (inactive).
0Fh, Bit 1: Spectral Inversion Tx
When set to 1, inverted modulation is performed
(I cos (ωt) + Q sin (ωt)).
Default is logic zero, noninverted modulation
(I cos (ωt) – Q sin (ωt)).
0Fh, Bit 2: Bypass Inv Sinc Tx Filter
Active high, configures the AD9873 to bypass the SIN(X)/X
compensation filter. Default value is 0 (inverse sinc filter enabled).
 Loading...
Loading...