REV PrM 04/02
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
=
Low Power, +2.3 V to +5.5 V, 50 MHz
Complete DDS
Preliminary Technical Data AD9834
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106,U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
FEATURES
+2.3 V to +5.5 V Power Supply
50 MHz Speed
Low Jitter Clock Output
Sine Output/Triangular Output
Serial Loading
Power-Down Option
Narrowband SFDR > 72 dB
20 mW Power Consumption at 3 V
20-Pin TSSOP
APPLICATIONS
Test Equipment
Slow Sweep Generator
DDS Tuning
Digital Modulation
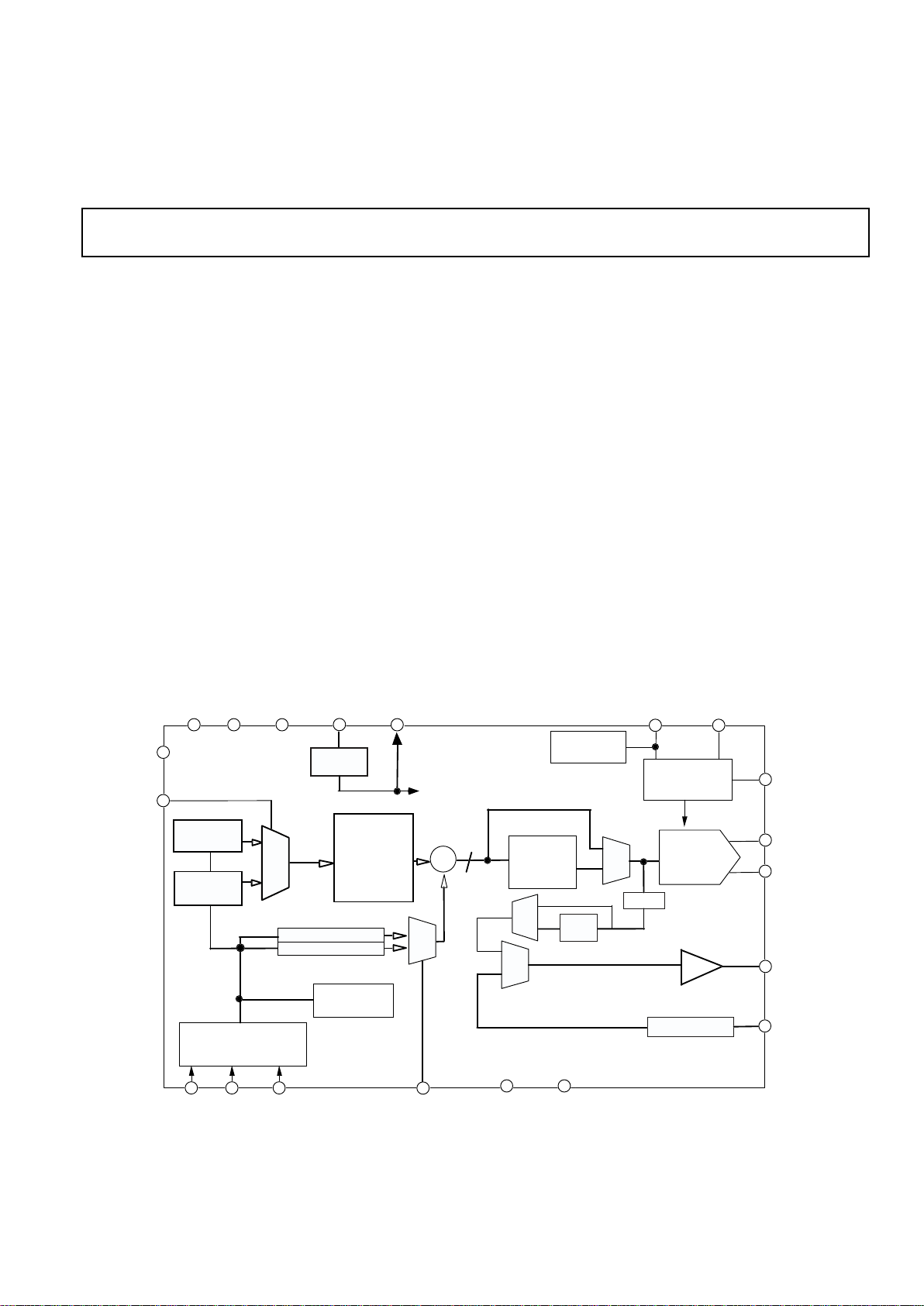
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9834 is a numerically controlled oscillator
employing a phase accumulator, a SIN ROM and a
10-bit D/A converter integrated on a single CMOS
chip. Clock rates up to 50 MHz are supported with a
power supply from 2.3 V to 5.5 V.
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
10-Bit
DAC
IOUT
COMP
REFOUT
FullScale
Control
FS ADJUST
AD9834
IOUTB
SIGN BIT OUT
COMPARATOR
VIN
MUX
Serial Interface
&
Control Logic
SCLK
SDATAFSYNC
12 Bit PHASE1 REG
SLEEPPSELECT
16 Bit Control
Register
SIN
ROM
MUX
28 Bit
FREQ0 REG
MCLK
FSELECT
28 Bit
FREQ1 REG
12
On-Board
Reference
AGNDAVDD DGND DVDD
Phase
Accumulator
(28 Bit)
MUX
Regulator
CAP/2.5V
VCC
2.5V
RESET
12 Bit PHASE0 REG
MSB
MUX
DIV BY
2
MUX
Capability for phase modulation and frequency modulation is provided. Frequency accuracy can be controlled to
one part in 0.25 billion. Modulation is effected by loading
registers through the serial interface.
The AD9834 offers the user a variety of output
waveforms. The SIN ROM can be bypassed so that a
linear up/down ramp is output from the DAC. If the SIN
ROM is not by-passed, a sinusoidal output is available.
Also, if a clock output is required, the MSB of the DAC
data can be output, or the on-chip comparator can be
used.
The digital section is driven by an on-board regulator
which steps down the applied DVDD to +2.5 V when
DVDD exceeds +2.5 V. The analog and digital sections
are independent and can be run from different power
supplies e.g. AVDD can equals 5 V with DVDD equal to
3 V, etc.
The AD9834 has a power-down pin (SLEEP) which
allows external control of a power-down mode. Sections of
the device which are not being used can be powered down to
minimise the current consumption e.g. the DAC can be
powered down when a clock output is being generated.
The part is available in a 20-pin TSSOP package.
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A

AD9834
–2–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions/Comments
SIGNAL DAC SPECIFICATIONS
Resolution 10 Bits
Update Rate (f
MAX
) 50 MSPS
I
OUT
Full Scale 2.8 mA
Output Compliance
2
0.8 V
DC Accuracy:
Integral Nonlinearity ±1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity ±0.5 LSB
DDS SPECIFICATIONS
Dynamic Specifications:
Signal to Noise Ratio 50 dB f
MCLK
= 50 MHz, f
OUT
= f
MCLK
/4096
Total Harmonic Distortion -53 dBc f
MCLK
= 50 MHz, f
OUT
= f
MCLK
/4096
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR):
Wideband (0 to Nyquist) 50 dBc f
MCLK
= 50 MHz, f
OUT
= f
MCLK
/7
NarrowBand (± 200 kHz) 72 dBc f
MCLK
= 50 MHz, f
OUT
= f
MCLK
/7
Clock Feedthrough –55 dBc
Wake Up Time 1 ms
COMPARATOR
Input Voltage Range 1 V p-p ac-coupled internally
Input Capacitance 10 pF
Input HighPass Cutoff Frequency 4 MHz
Input DC Resistance 1 M Ω
Input DC Current 10 µA
OUTPUT BUFFER
Output Rise/Fall Time 20 ns Using a 15 pF Load
Output Jitter 100 ps rms When DAC data MSB is output
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Internal Reference 1.116 1.2 1.284 V 1.2 V ± 7%
REFOUT Input Impedance
3
1KΩ
Reference TC 100 ppm/°C
LOGIC INPUTS
V
INH
, Input High Voltage D
VDD
–0.9 V +3.6 V to +5.5 V Power Supply
D
VDD
- 0.5 V +2.7 V to +3.6 V Power Supply
2 V +2.3 V to + 2.7 V Power Supply
V
INL
, Input Low Voltage 0.9 V +3.6 V to +5.5 V Power Supply
0.5 V +2.3 V to + 3.6 V Power Supply
I
INH
, Input Current 1 µA
CIN, Input Capacitance 10 pF
POWER SUPPLIES f
MCLK
= 50 MHz, f
OUT
= f
MCLK
/7
AVDD 2.3 5.5 V
DVDD 2.3 5.5 V
I
AA
4
5mA
I
DD
4
0.5 + 0.04/MHz mA
I
AA
+ I
DD
4
7 10 mA 3 V Power Supply
10 15 mA 5 V Power Supply
Low Power Sleep Mode
4
0.25 mA DAC and Internal Clock Powered Down
NOTES
1
Operating temperature range is as follows: B Version: –40°C to +85°C; typical specifications are at 25ⴗC
2
Guaranteed by Design.
3
Applies when REFOUT is sourcing current. The impedance is higher when REFOUT is sinking current.
4
Measured with the digital inputs static and equal to 0 V or DVDD.
Specifications subject to change without notice. There is 95% test coverage of the digital circuitry.
SPECIFICATIONS
1
(VDD = +2.3 V to +5.5 V; AGND = DGND = 0 V; TA = T
MIN
to T
MAX
; R
SET
= 6.8 k
Ω;Ω;
Ω;Ω;
Ω;
R
LOAD
= 200
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω for IOUT and IOUTB unless otherwise noted)
AD9834
–3–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
1
(VDD = +2.3 V to +5.5 V; AGND = DGND = 0 V, unless otherwise noted)
Parameter Limit at T
MIN
to T
MAX
Units Test Conditions/Comments
t
1
20 ns min MCLK Period
t
2
8 ns min MCLK High Duration
t
3
8 ns min MCLK Low Duration
t
4
25 ns min SCLK Period
t
5
10 ns min SCLK High Duration
t
6
10 ns min SCLK Low Duration
t
7
5 ns min FSYNC to SCLK Falling Edge Setup Time
t
8
10 ns min FSYNC to SCLK Hold Time
t
4
- 5 ns max
t
9
5 ns min Data Setup Time
t
10
3 ns min Data Hold Time
t
11
8 ns min FSELECT, PSELECT Setup Time Before MCLK Rising Edge
t
11A
*
8 ns min FSELECT, PSELECT Setup Time After MCLK Rising Edge
1
Guaranteed by design, not production tested.
*See Pin Description Section.
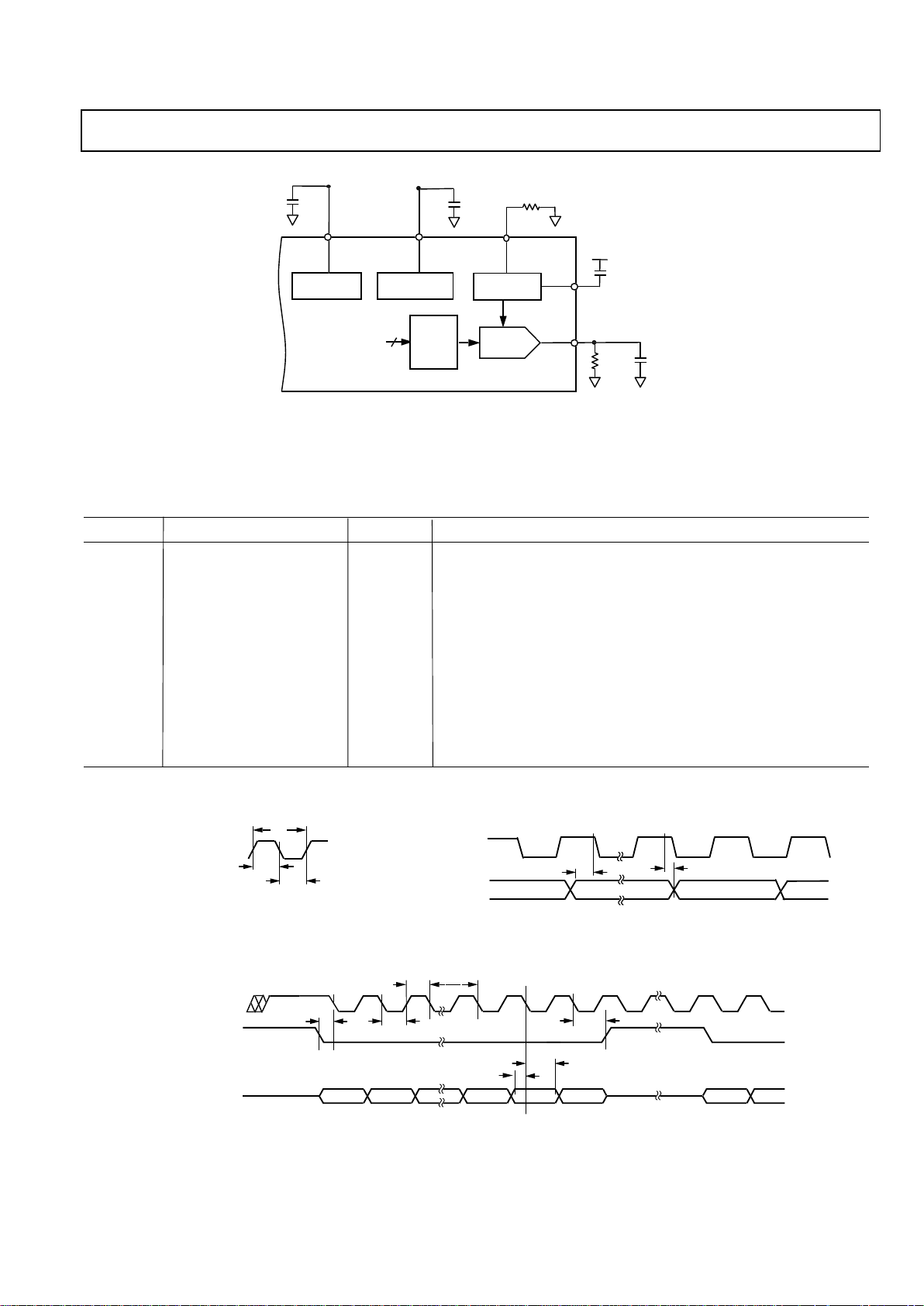
Figure 3. Control Timing
Figure 2. Master Clock
Figure 4. Serial Timing
Figure 1. Test Circuit With which Specifications are tested.
IOUT
COMP
FS
ADJUST
REFOUT
12
AD9834
ON-BOARD
REFERENCE
10-BIT DAC
SIN
ROM
FULL-SCALE
CONTROL
200R 20pF
R
SET
6.8 K
10nF
10nF
AVDD
REGULATOR
100nF
CAP/2.5V
MCLK
t
2
t
1
t
3
t
11A
t
11
VALIDDATA VALIDDATA VALIDDATA
MCLK
FSELECT,
PSELECT
SCLK
FSYNC
SDATA
t
5
t
4
t
6
t
7
t
8
t
10
t
9
D15 D14 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14
AD9834
–4–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
(TA = +25°C unless otherwise noted)
AVDD to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +6 V
DVDD to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +6 V
AVDD to DVDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +0.3 V
AGND to DGND. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +0.3 V
CAP/2.5V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.75 V
Digital I/O Voltage to DGND –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Analog I/O Voltage to AGND –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial (B Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD9834BRU –40°C to +85°C 20-Pin TSSOP (
Thin Shrink Small Outline Package
) RU-20
EVAL-AD9834EB Evaluation Board
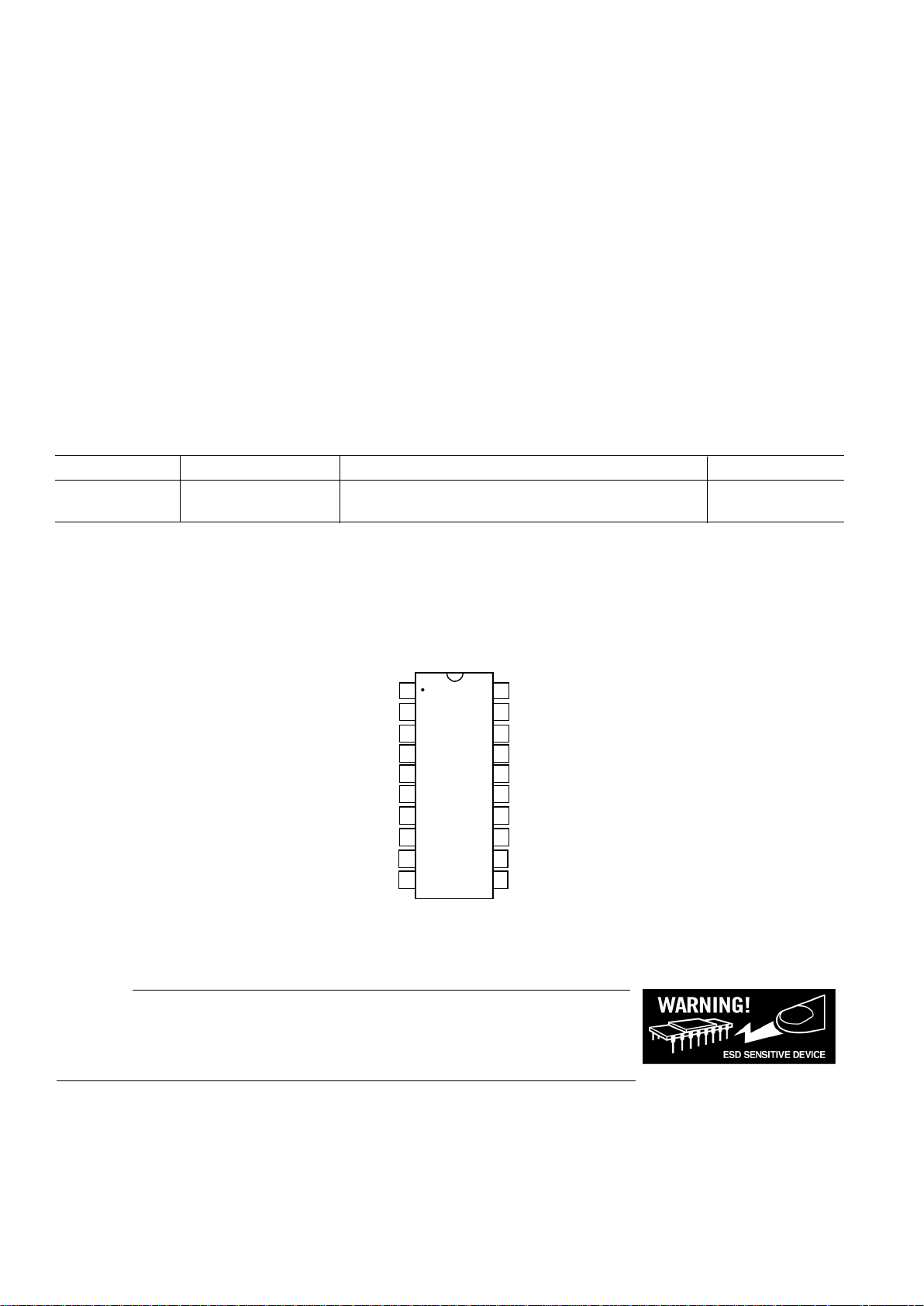
PIN CONFIGURATION
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . .–65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . +150°C
TSSOP Package
θ
JA
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .143°C/W
θ
JC
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45°C/W
Lead Temperature, Soldering (10 sec) . . . . . . . . . 300°C
IR Reflow, Peak Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220°C
*Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent
damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device
at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational sections of this
specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD9834 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
TOP VIEW
(Notto Scale)
O
FS ADJUST
REFOUT
AVDD
DVDD
CAP/+2.5V
DGND
MCLK
IOUTB
IOUT
AGND
VIN
SIGNBITOUT
FSYNC
SCLK
SDATA
AD9834
FSELECT
PSELECT
12
11
10
9
COMP
SLEEP
RESET
AD9834
–5–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
PIN FUNCTIONS DESCRIPTIONS
Pin # Mnemonic Function
ANALOG SIGNAL AND REFERENCE
1 FS ADJUST Full-Scale Adjust Control. A resistor (R
SET
) is connected between this pin and AGND. This
determines the magnitude of the full-scale DAC current. The relationship between R
SET
and
the full-scale current is as follows:
IOUT
FULL-SCALE
= 18 x V
REFOUT/RSET
V
REFOUT
= 1.20 V nominal, R
SET
= 6.8 kΩ typical
2 REFOUT Voltage Reference Output. The AD9834 has an internal 1.20 V reference, which is made
available at this pin.
3 COMP A DAC Bias Pin. This pin is used for de-coupling the DAC bias voltage.
17 VIN Input to comparator. The comparator can be used to generate a square wave from the
sinusoidal DAC output. The DAC output should be filtered appropriately before being applied
to the comparator to improve jitter. When bits OPBITEN and SIGNPIB in the control
register are set to 1, the comparator input is connected to VIN.
19,20 IOUT, IOUTB Current Output. This is a high impedance current source. A load resistor of nominally 200 Ω
should be connected between IOUT and AGND. IOUTB should preferably be tied through an
external load resistor of 200 Ω to AGND but can be tied directly to AGND. A 20pF capacitor
to AGND is also recommended to prevent clock feedthrough.
POWER SUPPLY
4 AVDD Positive power supply for the analog section. AVDD can have a value from +2.3 V to +5.5 V.
A 0.1 µF decoupling capacitor should be connected between AVDD and AGND.
5 DVDD Positive power supply for the digital section. DVDD can have a value from +2.3 V to +5.5 V.
A 0.1 µF decoupling capacitor should be connected between DVDD and DGND.
6 CAP/2.5V The digital circuitry operates from a +2.5 V power supply. This +2.5 V is generated from
DVDD using an on board regulator (when DVDD exceeds +2.7 V). The regulator requires a
decoupling capacitor of typically 100 nF which is connected from CAP/2.5V to DGND. If
DVDD is equal to or less than +2.7 V, CAP/2.5 V should be shorted to DVDD.
7 DGND Digital Ground.
18 AGND Analog Ground.
DIGITAL INTERFACE AND CONTROL
8 MCLK Digital Clock Input. DDS output frequencies are expressed as a binary fraction of the
frequency of MCLK. The output frequency accuracy and phase noise are determined by this
clock.
9 FSELECT Frequency Select Input. FSELECT controls which frequency register, FREQ0 or FREQ1, is
used in the phase accumulator. The frequency register to be used can be selected using the pin
FSELECT or the bit FSEL. When the bit FSEL is being used to select the frequency register,
this pin, FSELECT, should be tied to CMOS high or low.
10 PSELECT Phase Select Input. PSELECT controls which phase register, PHASE0 or PHASE1, is added
to the phase accumulator output. The phase register to be used can be selected using the pin
PSELECT or the bit PSEL. When the phase registers are being controlled by the bit PSEL,
this pin, PSELECT, should be tied to CMOS high or low.
11 RESET Active high digital input. RESET resets appropriate internal registers to zero which
corresponds to an analog output of midscale. RESET does not affect any of the addressable
registers.
12 SLEEP Active high digital input. When this pin is high, the DAC is powered down. This pin has the
same function as control bit SLEEP12.
13 SDATA Serial Data Input. The 16-bit serial data word is applied to this input.
14 SC L K Serial Clock Input. Data is clocked into the AD9834 on each falling SCLK edge.
15 FSYNC Active Low Control Input. This is the frame synchronisation signal for the input data. When
FSYNC is taken low, the internal logic is informed that a new word is being loaded into
the device.
16 SIGN BIT OUT Logic Output. The comparator output is available on this pin or, alternatively, the MSB from
the NCO can be output on this pin. Setting bit OPBITEN in the control register to 1 enables
this output pin. Bit SIGNPIB determines whether the comparator output or the MSB from
the NCO is output on the pin.

AD9834
–6–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
Typical Performance Characteristics
TPC 1. Typical Current Consumption
vs. MCLK Frequency
TPC 4. Wide Band SFDR vs. f
OUT/fMCLK
for Various MCLK Frequencies
TPC 7. Wake-Up Time vs.
Temperature
TPC 2. Narrow Band SFDR vs. MCLK
Frequency
TPC 5. SNR vs. MCLK Frequency
TPC 8. V
REFOUT
vs. Temperature
TPC 3. Wide Band SFDR vs. MCLK
Frequency
TPC 6. SNR vs. f
OUT/fMCLK
for
Various MCLK Frequencies

AD9834
–7–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
Typical Performance Characteristics
TPC 9. f
MCLK
= 10 MHz; f
OUT
= 2.4 kHz;
Frequency Word = 000FBA9
TPC 12. f
MCLK
= 50 MHz; f
OUT
= 12 kHz;
Frequency Word =
000FBA9
TPC 15. f
MCLK
= 50 MHz; f
OUT
= 4.8
MHz; Frequency Word =
189374C
TPC 10. f
MCLK
= 10 MHz; f
OUT
= 1.43 kHz
= f
MCLK
/7 ;
Frequency Word = 2492492
TPC 13. f
MCLK
= 50 MHz; f
OUT
= 120 kHz;
Frequency Word =
009D496
TPC 16. f
MCLK
= 50 MHz;
f
OUT
= 7.143 MHz = f
MCLK
/7 ;
Frequency Word = 2492492
TPC 11. f
MCLK
= 10 MHz; f
OUT
= 3.33 kHz
= f
MCLK
/3 ;
Frequency Word = 5555555
TPC 14. f
MCLK
= 50 MHz; f
OUT
= 1.2
MHz; Frequency Word =
0624DD3
TPC 17. f
MCLK
= 50 MHz;
f
OUT
= 16.667 MHz = f
MCLK
/3 ;
Frequency Word = 5555555

AD9834
–8–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
TERMINOLOGY
Integral Nonlinearity
This is the maximum deviation of any code from a
straight line passing through the endpoints of the transfer
function. The endpoints of the transfer function are zero
scale, a point 0.5 LSB below the first code transition
(000 . . . 00 to 000 . . . 01) and full scale, a point 0.5 LSB
above the last code transition (111 . . . 10 to 111 . . . 11).
The error is expressed in LSBs.
Differential Nonlinearity
This is the difference between the measured and ideal 1
LSB change between two adjacent codes in the DAC. A
specified differential nonlinearity of
±1 LSB maximium ensures
monotonicity.
Output Compliance
The output compliance refers to the maximum voltage
that can be generated at the output of the DAC to meet
the specifications. When voltages greater than that specified for the output compliance are generated, the AD9834
may not meet the specifications listed in the data sheet.
Spurious Free Dynamic Range
Along with the frequency of interest, harmonics of the
fundamental frequency and images of the these frequencies
are present at the output of a DDS device. The spurious
free dynamic range (SFDR) refers to the largest spur or
harmonic which is present in the band of interest. The
wide band SFDR gives the magnitude of the largest harmonic or spur relative to the magnitude of the fundamental
frequency in the 0 to Nyquist bandwidth. The narrow band
SFDR gives the attenuation of the largest spur or harmonic
in a bandwidth of ±200 kHz about the fundamental frequency.
Total Harmonic Distortion
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) is the ratio of the rms
sum of harmonics to the rms value of the fundameltal. For
the AD9834, THD is defined as:
THD = 20 log√(V
2
2
+ V
3
2
+ V
4
2
+ V
5
2
+ V
6
2
)/V
1
where V1 is the rms amplitude of the fundamental and V2,
V
3
, V4, V5 and V6 are the rms amplitudes of the second
through thre sixth harmonic.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
S/N is the ratio of the rms value of the measured output
signal to the rms sum of all other spectral components
below the Nyquist frequency, excluding the first six harmonics and dc. The value for SNR is expressed in
decibels.
Clock Feedthrough
There will be feedthrough from the MCLK input to the
analog output. Clock feedthrough refers to the magnitude
of the MCLK signal relative to the fundamental frequency
in the AD9834’s output spectrum.
THEORY OF OPERATION
Sine waves are typically thought of in terms of their
magnitude form a(t) = sin (ωt). However, these are
nonlinear and not easy to generate except through piece
wise construction. On the other hand, the angular
information is linear in nature. That is, the phase angle
rotates through a fixed angle for each unit of time. The
angular rate depends on the frequency of the signal by the
traditional rate of ω = 2πf.
Figure 5. Sine Wave
Knowing that the phase of a sine wave is linear and given
a reference interval (clock period), the phase rotation for
that period can be determined.
∆Phase = ωδt
Solving for ω
ω = ∆
Phase
/δt = 2πf
Solving for f and substituting the reference clock
frequency for the reference period (1/f
MCLK
= δt)
f = ∆Phase x f
MCLK
/2π
The AD9834 builds the output based on this simple
equation. A simple DDS chip can implement this
equation with three major subcircuits:
Numerical Controlled Oscillator + Phase Modulator
SIN ROM
Digital- to- Analog Convertor.
Each of these sub-circuits are discussed in the following
section.
MAGNITUDE
PHASE
+1
0
-1
2
π
0

AD9834
–9–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The AD9834 is a fully integrated Direct Digital Synthesis
(DDS) chip. The chip requires one reference clock, one
low precision resistor and eight decoupling capacitors to
provide digitally created sine waves up to 25 MHz. In
addition to the generation of this RF signal, the chip is
fully capable of a broad range of simple and complex
modulation schemes. These modulation schemes are fully
implemented in the digital domain allowing accurate and
simple realization of complex modulation algorithms using DSP techniques.
The internal circuitry of the AD9834 consists of the following main sections: a Numerical Controlled Oscillator
(NCO), Frequency and Phase Modulators, SIN ROM, a
Digital-to-Analog Converter, a Comparator and a
Regulator.
Numerical Controlled Oscillator + Phase Modulator
This consists of two frequency select registers, a phase
accumulator, two phase offset registers and a phase offset
adder. The main component of the NCO is a 28-bit phase
accumulator which assembles the phase component of the
output signal. Continuous time signals have a phase range
of 0 to 2. Outside this range of numbers, the sinusoid
functions repeat themselves in a periodic manner. The
digital implementation is no different. The accumulator
simply scales the range of phase numbers into a multibit
digital word. The phase accumulator in the AD9834 is
implemented with 28 bits. Therefore, in the AD9834, 2
= 2
28
. Likewise, the ∆Phase term is scaled into this range
of numbers 0 < ∆Phase < 2
28
– 1. Making these substitu-
tions into the equation above
f = ∆Phase x f
MCLK
/2
28
where 0 < ∆Phase < 228 - 1.
The input to the phase accumulator (i.e., the phase step)
can be selected either from the FREQ0 Register or
FREQ1 Register and this is controlled by the FSELECT
pin or the FSEL bit. NCOs inherently generate
continuous phase signals, thus avoiding any output
discontinuity when switching between frequencies.
Following the NCO, a phase offset can be added to
perform phase modulation using the 12-bit Phase
Registers. The contents of one of these phase registers is
added to the most significant bits of the NCO. The
AD9834 has two Phase registers, the resolution of these
registers being 2π/4096.
SIN ROM
To make the output from the NCO useful, it must be
converted from phase information into a sinusoidal value.
Since phase information maps directly into amplitude, the
SIN ROM uses the digital phase information as an address to a look-up table, and converts the phase
information into amplitude. Although the NCO contains a
28-bit phase accumulator, the output of the NCO is truncated to 12 bits. Using the full resolution of the phase
accumulator is impractical and unnecessary as this would
require a look-up table of 2
28
entries. It is necessary only
to have sufficient phase resolution such that the errors due
to truncation are smaller than the resolution of the 10-bit
DAC. This requires the SIN ROM to have two bits of
phase resolution more than the 10-bit DAC.
The SIN ROM is enabled using bits MODE and
OPBITEN in the control register. This is explained further in Table 14.
Digital-to-Analog Converter
The AD9834 includes a high impedance current source
10-bit DAC, capable of driving a wide range of loads.
Full-scale output current can be adjusted, for optimum
power and external load requirements, through the use of
a single external resistor (R
SET
).
The DAC can be configured for either single-ended or
differential operation. IOUT and IOUTB can be connected through equal external resistors to AGND to
develop complementary output voltages. The load resistors can be any value required, as long as the full-scale
voltage developed across it does not exceed the voltage
compliance range. Since full-scale current is controlled by
R
SET
, adjustments to R
SET
can balance changes made to the
load resistors.
Comparator
The AD9834 can be used to generate synthesised digital
clock signals. This can be done by using the on-board
self-biasing comparator, which converts the DAC's sinusoidal signal to a square wave. The output from the DAC
may be filtered externally before being applied to the
comparator input. The comparator reference voltage is the
time-average of the signal applied to V
IN
. The comparator
can accept a signal of 1 Vpp. As the comparator's input is
ac-coupled, to operate correctly as a zero crossing
dectector, it requires a minimum input frequency of 3
MHz. The comparator's output will be a square wave with
an amplitude from 0 V to DVDD.
To enable the comparator, bits SIGNPIB and OPBITEN
in the control resister are set to '1'. This is explained further in Table 13.
Regulator
The AD9834 has separate power supplies for the analog
and digital section. AVDD provides the power supply
required for the analog section, while DVDD provides the
power supply for the digital section. Both of these supplies
can have a value of +2.3V to +5.5V, and are independant
of each other e.g. the analog section can be operated at 5V
and the digital section can be operated at 3V or vice versa.
The internal digital section of the AD9834 is operated at
2.5 V. An on-board regulator steps down the voltage applied at DVDD to 2.5 V. The digital inteface (serial port)
of the AD9834 is also operated from DVDD. These digital signals are level shifted within the AD9834 to make
them 2.5V compatible.
When the applied voltage at the DVDD pin of the
AD9834 is equal to or less than 2.5V, the pins CAP/2.5V
and DVDD should be tied together, thus by-passing the
on-board regulator.

AD9834
–10–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Serial Interface
The AD9834 has a standard 3-wire serial interface, which
is compatible with SPI, QSPI, MICROWIRE and DSP
interface standards.
Data is loaded into the device as a 16-bit word under the
control of a serial clock input, SCLK. The timing diagram for this operation is given in Figure 4.
The FSYNC input is a level triggered input that acts as a
frame synchronisation and chip enable. Data can only be
transferred into the device when FSYNC is low. To start
the serial data transfer, FSYNC should be taken low, observing the minimum FSYNC to SCLK falling edge setup
time, t
7
. After FSYNC goes low, serial data will be shifted
into the device's input shift register on the falling edges of
SCLK for 16 clock pulses. FSYNC may be taken high
after the sixteenth falling edge of SCLK, observing the
minimum SCLK falling edge to FSYNC rising edge time,
t
8
. Alternatively, FSYNC can be kept low for a multiple of
16 SCLK pulses, and then brought high at the end of the
data transfer. In this way, a continuous stream of 16 bit
words can be loaded while FSYNC is held low, FSYNC
only going high after the 16th SCLK falling edge of the
last word loaded.
The SCLK can be continuous or, alternatively, the SCLK
can idle high or low between write operations.
Powering up the AD9834
The flow chart in Figure 7 shows the operating routine for
the AD9834. When the AD9834 is powered up, the part
should be reset. This will reset appropriate internal registers to zero to provide an analog output of midscale. To
avoid spurious DAC outputs while the AD9834 is being
initialized, the RESET bit/pin should be set to 1 until the
part is ready to begin generating an output. RESET does
not reset the phase, frequency or control registers. These
registers will contain invalid data and, therefore, should be
set to a known value by the user. The RESET bit/pin
should then be set to 0 to begin generating an output. A
signal will appear at the DAC output 7 MCLK cycles after
RESET is set to 0.
Latency
Associated with each operation is a latency. When the pins
FSELECT and PSELECT change value there is a pipeline delay before control is transfered to the selected
register. When the timing specifications t11 and t11A are
met (see figure 3) FSELECT and PSELECT have latencies of 7 MCLK cycles. When the timing specifications
t11 and t11A are not met, the latency is increased by one
MCLK cycle.
Similarly there is a latency associated with each asynchronous write operation. If a selected frequency/phase register
is loaded with a new word there is a delay of 7 to 8 MCLK
cycles before the analog output will change. (There is an
uncertainty of one MCLK cycle as it depends on the position of the MCLK rising edge when the data is loaded into
the destination register.)
The negative transition of the RESET and SLEEP functions are sampled on the internal falling edge of MCLK,
therefore also have a latency associated with them.
The Control Register
The AD9834 contains a 16-bit control register which sets
up the AD9834 as the user wishes to operate it. All control
bits, except MODE, are sampled on the internal negative
edge of MCLK.
Table 2, on the following page, describes the individual
bits of the control register. The different functions and the
various output options from the AD9834 are described in
more detail in the section following Table 2.
To inform the AD9834 that you wish to alter the contents
of the Control register, D15 and D14 must be set to '0' as
shown below.
Table 1. Control Register
D15 D14 D13 D0
0 0 CONTROL BITS
Figure 6. Function of Control Bits
1
MUX
0
Div
by 2
DIV2
MODE + O PBITEN
SIGNPIB
SLEEP12
SLEEP1
Pha se
Accumulator
(28 B i t)
SIN
ROM
1
MUX
0
1
MUX
0
COMPARATOR
(Low P ower)
10 - Bit DAC
AD9834
DIGITAL
OUTPUT
(enable)
IOUT
IOUTB
VIN
SIGN BIT OUT
OPBITEN

AD9834
–11–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
Table 2. Description of bits in the Control Register
Bit Name Function
D13 B28 Two write operations are required to load a complete word into either of the Frequency registers.
B28 = '1' allows a complete word to be loaded into a frequency register in two consecutive
writes. The first write contains the 14 LSBs of the frequency word and the next write will
contain the 14 MSBs. The first two bits of each sixteen-bit word define the frequency register to
which the word is loaded, and should therefore be the same for both of the consecutive writes.
Refer to table 6 for the appropriate addresses. The write to the frequency register occurs after both
words have been loaded, so the register never holds an intermediate value. An example of a complete 28-bit write is shown in table 7.
When B28 = '0' the 28-bit frequency register operates as 2 14-bit registers, one containing the 14
MSBs and the other containing the 14 LSBs. This means that the 14 MSBs of the frequency
word can be altered independent of the 14 LSBs and vice versa. To alter the 14 MSBs or the 14
LSBs, a single write is made to the appropriate Frequency address. The control bit D12 (HLB)
informs the AD9834 whether the bits to be altered are the 14 MSBs or 14 LSBs.
D12 HLB This control bit allows the user to continuously load the MSBs or LSBs of a frequency regiser
while ignoring the remaining 14 bits. This is useful if the complete 28 bit resolution is not required. HLB is used in conjunction with D13 (B28). This control bit indicates whether the 14 bits
being loaded are being transferred to the 14 MSBs or 14 LSBs of the addressed frequency register. D13 (B28) must be set to '0' to be able to change the MSBs and LSBs of a frequency word
seperately. When D13 (B28) = '1', this control bit is ignored.
HLB = '1' allows a write to the 14 MSBs of the addressed frequency register.
HLB = '0' allows a write to the 14 LSBs of the addressed frequency register.
D11 FSEL The FSEL bit defines whether the FREQ0 register or the FREQ1 register is used in the phase
accumulator. See table 4 on selecting a frequency register.
D10 PSEL The PSEL bit defines whether the PHASE0 register or the PHASE1 register data is added to the
output of the phase accumulator. See Table 5 on selecting a phase register.
D9 PIN/SW Functions that select frequency and phase registers, reset internal registers, and power down the
DAC can be implemented using either software or hardware. PIN/SW selects the source of
control for these functions.
PIN/SW = '1' implies that the functions are being controlled using the appropriate control pins.
PIN/SW = '0' implies that the functions are being controlled using the appropriate control bits.
D8 RESET RESET = '1' resets internal registers to zero, which corresponds to an analog output of midscale.
RESET = '0' disables Reset. This function is explained further in Table 11.
D7 SLEEP1 When SLEEP1 = '1', the internal MCLK clock is disabled. The DAC output will remain at its
present value as the NCO is no longer accumulating.
When SLEEP1 = '0' MCLK is enabled. This function is explained further in Table 12.
D6 SLEEP12 SLEEP12 = '1' powers down the on-chip DAC. This is useful when the AD9834 is used to output
the MSB of the DAC data.
SLEEP12 = '0' implies that the DAC is active. This function is explained further in Table 12.
D5 OPBITEN The function of this bit is to control whether there is an output at the pin SIGN BIT OUT. This
bit should remain at '0' if the user is not using the pin SIGN BIT OUT.
OPBITEN = '1' enables the pin SIGN BIT OUT.
When OPBITEN equals 0, the SIGN BIT OUT output buffer is put into a high impedance state
and, therefore, no output is available at the SIGN BIT OUT pin.
D4 SIGNPIB The function of this bit is to control what is output at the pin SIGN BIT OUT.
When SIGNPIB = '1', the on board comparator is connected to SIGN BIT OUT. After filtering
the sinusoidal output from the DAC, the waveform can be applied to the comparator to generate a
square waveform. This is explained futher in Table 13.
When SIGNPIB = '0', the MSB (or MSB/2) of the DAC data is connected to the pin SIGN BIT
OUT. The bit DIV2 controls whether it is the MSB or MSB/2 that is ouput.
D3 DIV2 DIV2 is used in association with SIGNPIB and OPBITEN. This is fully explained in Table 13.
When DIV2 = '1', the digital output is passed directly to the SIGN BIT OUT pin.
When DIV2 = '0', the digital output/2 is passed directly to the SIGN BIT OUT pin.
D2 Reserved This bit must always be set to 0.
D1 MODE The function of this bit is to control what is output at the IOUT/IOUT pins. This bit should be
set to '0' if the control bit OPBITEN = '1'.
When MODE = '1', the SIN ROM is bypassed, resulting in a ramp output from the DAC.
When MODE = '0' the SIN ROM is used to convert the phase information into amplitude infor-
mation which results in a sinusoidal signal at the output (See table 14).
D0 Reserved This bit must always be set to 0.

AD9834
–12–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
The Frequency and Phase Resisters
The AD9834 contains 2 frequency registers and 2 phase
registers. These are described in Table 3 below.
Table 3. Frequency/Phase Registers
Register Size Description
FREQ0 28 Bits Frequency Register 0. When FSEL
bit or FSELECT pin = 0, this register defines the output frequency as a
fraction of the MCLK frequency.
FREQ1 28 Bits Frequency Register 1. When FSEL
bit or FSELECT pin = 1, this register defines the output frequency as a
fraction of the MCLK frequency.
PHASE0 12 Bits Phase Offset Register 0. When PSEL
bit or PSELECT pin = 0, the contents of this register are added to the
output of the phase accumulator.
PHASE1 12 Bits Phase Offset Register 1. When PSEL
bit or PSELECT pin = 1, the contents of this register are added to the
output of the phase accumulator.
The analog output from the AD9834 is
f
MCLK
/2
28
x FREQREG
where FREQREG is the value loaded into the selected
frequency register. This signal will be phase shifted by
2π/4096 x PHASEREG
where PHASEREG is the value contained in the selected
phase register.
Access to the frequency and phase registers is controlled
by both the FSELECT/PSELECT pins and the FSEL/
PSEL control bits. If the control bit PIN/SW = 1, the
pins controls the function, whereas if PIN/SW = 0, the
bits control the function. This is outlined in tables 4 and 5
below. If the FSEL/PSEL bits are being used, the pins
should preferably be held at CMOS logic high or low.
Control of the frequency/phase registers can be interchanged from the pins to the bits.
Table 4: Selecting a Frequency Register
FSELECT FSEL PIN/SW Selected Register
0 X 1 FREQ0 REG
1 X 1 FREQ1 REG
X 0 0 FREQ0 REG
X 1 0 FREQ1 REG
Table 5: Selecting a Phase Register
PSELECT PSEL PIN/SW Selected Register
0 X 1 PHASE0 REG
1 X 1 PHASE1 REG
X 0 0 PHASE0 REG
X 1 0 PHASE1 REG
The FSELECT and PSELECT pins are sampled on the
internal falling edge of MCLK. It is recommended that
the data on these pins does not change within a time window of the falling edge of MCLK (see Figure 3 for
timing). If FSELECT/PSELECT changes value when a
falling edge occurs, there is an uncertainty of one MCLK
cycle as to when control is transferred to the other frequency/phase register.
The flow charts in Figures 8 and 9 show the routine for
selecting and writing to the frequency and phase registers
of the AD9834.
Writing to a Frequency Register:
When writing to a frequency register, bits D15 and D14
give the address of the frequency register.
Table 6. Frequency Register Bits
D15 D14 D13 D0
0 1 MSB 14 FREQ0 REG BITS LSB
1 0 MSB 14 FREQ1 REG BITS LSB
If the user wishes to alter the entire contents of a frequency register, two consecutive writes to the same
address must be performed, as the frequency registers are
28 bits wide. The first write will contain the 14 LSBs
while the second write will contain the 14 MSBs. For this
mode of operation, the control bit B28 (D13) should be
set to 1. An example of a 28-bit write is shown in Table 7
below.
Table 7: Writing 3FFF0000 to FREQ0 REG
SDATA input Result of input word
0010 0000 0000 0000 Control word write (D15, D14 = 00);
B28 (D13) = 1; HLB (D12) = X
0100 0000 0000 0000 FREQ0 REG write (D15, D14 = 01);
14 LSBs = 0000
0111 1111 1111 1111 FREQ0 REG write (D15, D14 = 01);
14 MSBs = 3FFF
In some applications, the user does not need to alter all 28
bits of the frequency register. With coarse tuning, only
the 14 MSBs are altered while with fine tuning, only the
14 LSBs are altered. By setting the control bit B28 (D13)
to 0, the 28-bit frequency register operates as 2 14-bit
registers, one containing the 14 MSBs and the other containing the 14 LSBs. This means that the 14 MSBs of the
frequency word can be altered independent of the 14 LSBs
and vice versa. Bit HLB (D12) in the control register
identifies which 14 bits are being altered. Examples of this
are shown over.

AD9834
–13–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
Table 8: Writing 3FFF to the 14 LSBs of FREQ1 REG
SDATA input Result of input word
0000 0000 0000 0000 Control word write (D15, D14 = 00);
B28 (D13) = 0; HLB (D12) = 0, i.e. LSBs
1011 1111 1111 1111 FREQ1 REG write (D15, D14 = 10);
14 LSBs = 3FFF
Table 9: Writing 3FFF to the 14 MSBs of FREQ0 REG
SDATA input Result of Input word
0001 0000 0000 0000 Control word write (D15, D14 = 00);
B28 (D13) = 0; HLB (D12) = 1, i.e. MSBs
0111 1111 1111 1111 FREQ0 REG write (D15, D14 = 01);
14 MSBs = 3FFF
Writing to a Phase Register:
When writing to a phase register, bits D15 and D14 are
set to 11. Bit D13 identifies which phase register is being
loaded.
Table 10. Phase Register Bits
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D0
1 1 0 X MSB 12 PHASE0 BITS LSB
1 1 1 X MSB 12 PHASE1 BITS LSB
The RESET Function
The RESET function resets appropriate internal registers
to zero to provide an analog output of midscale. RESET
does not reset the phase, frequency or control registers.
When the AD9834 is powered up, the part should be reset. To reset the AD9834, set the RESET pin/bit to 1. To
take the part out of reset, set the pin/bit to 0. A signal will
appear at the DAC output 7 MCLK cycles after RESET is
set to 0.
The RESET function is controlled by both the RESET
pin and the RESET control bit. If the control bit PIN/SW
= 0, the RESET bit controls the function, whereas if PIN/
SW = 1, the pin control the function.
Table 11: Applying RESET
RESET pin RESET bit PIN/SW Result
0 X 1 No Reset Applied
1 X 1 Internal Registers Reset
X 0 0 No Reset Applied
X 1 0 Internal Registers Reset
The effect of asserting the RESET pin is seen immediately at the output, i.e. the zero to one transition of this
pin is not sampled. However, the negative transition of
RESET is sampled on the internal falling edge of MCLK.
The Sleep Function
Sections of the AD9834 which are not in use can be powered down minimise power consumption. This is done
using the Sleep Function. The parts of the chip that can
be powered down are the Internal clock and the DAC.
The DAC can be powered down through hardware or
software. The pin/bits required for the Sleep Function are
outlined in Table 12.
Table 12: Applying the SLEEP Function
SLEEP SLEEP1 SLEEP12 PIN/SW Result
pin bit bit bit
0 X X 1 No powerdown
1 X X 1 DAC Powered Down
X 0 0 0 No powerdown
X 0 1 0 DAC Powered Down
X 1 0 0 Internal Clock disabled
X 1 1 0 Both the DAC powered
down and the Internal
Clock disabled
DAC Powered Down: This is useful when the AD9834 is
used to output the MSB of the DAC data only. In this
case, the DAC is not required so it can be powered down
to reduce power consumption.
Internal Clock disabled: When the internal clock of the
AD9834 is disabled the DAC output will remain at its
present value as the NCO is no longer accumulating. New
frequency, phase and control words can be written to the
part when the SLEEP1 control bit is active. The
synchronising clock is still active which means that the
selected frequency and phase registers can also be changed
either at the pins or by using the control bits. Setting the
SLEEP1 bit equal to 0 enables the MCLK. Any changes
made to the registers while SLEEP1 was active will be
seen at the output after a certain latency.
The effect of asserting the SLEEP pin is seen immediately
at the output, i.e. the zero to one transition of this pin is
not sampled. However, the negative transition of SLEEP
is sampled on the internal falling edge of MCLK.
The SIGN BIT OUT Pin
The AD9834 offers a variety of outputs from the chip.
The digital outputs are available from the SIGN BIT
OUT pin. The available outputs are the comparator output or the MSB of the DAC data.
This pin must be enabled before use. The enabling/disabling of this pin is controlled by the bit OPBITEN (D5)
in the control register. When OPBITEN = 1, this pin is
enabled. Note that the MODE bit (D1) in the control
register should be set to '0' if OPBITEN = '1'.

AD9834
–14–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
Comparator Output: The AD9834 has an on-board
comparator. To connect this comparator to the SIGN
BIT OUT pin, the SIGNPIB (D4) control bit must be set
to 1. After filtering the sinusoidal output from the DAC,
the waveform can be applied to the comparator to generate
a square waveform.
MSB from the NCO: The MSB from the NCO can be
output from the AD9834. By setting the SIGNPIB (D4)
control bit to 0, the MSB of the DAC data is available at
the SIGN BIT OUT pin. This is useful as a coarse clock
source. This square wave can also be divided by 2 before
being output. The bit DIV2 (D3) in the control register
controls the frequency of this output from the SIGN BIT
OUT pin.
Table 13: Various Outputs from SIGN BIT OUT
OPBITEN MODE SIGNPIB DIV2 SIGN BIT OUT
Bit Bit Bit Bit Pin
0 X X X High Impedance
1 0 0 0 DAC data MSB / 2
1 0 0 1 DAC data MSB
1 0 1 0 Reserved
1 0 1 1 Comparator Output
1 1 X X Reserved
The IOUT/IOUTB Pins
The analog outputs from the AD9834 are available from
the IOUT/IOUTB pins. The available outputs are a
sinuoidal output or a ramp output.
Sinusoidal Output: The SIN ROM is used to convert the
phase information from the frequency and phase registers
into amplitude information which results in a sinusoidal
signal at the output. To have a sinusoidal output from the
IOUT/IOUTB pins set the bt MODE (D1) = 1.
Up/Down Ramp Output: The SIN ROM can be bypassed
so that the truncated digital output from the NCO is sent
to the DAC. In this case, the output is no longer sinusoidal. The DAC will produce a ramp up/down function. To
have a ramp output from the IOUT/IOUTB pins set the
bt MODE (D1) = 0.
Note that the SLEEP pin/SLEEP12 bit must be 0 (i.e. the
DAC is enabled) when using these pins.
Table 14: Various Outputs from IOUT/IOUTB
OPBITEN Bit MODE Bit I OUT / IOUTB Pins
0 0 Sinusoid
0 1 Up/Down Ramp
1 0 Sinusoid
1 1 Reserved
APPLICATIONS
Because of the various output options available from the
part, the AD9834 can be configured to suit a wide variety
of applications.
One of the areas where the AD9834 is suitable is in modulation applications. The part can be used to perform
simple modulation such as FSK. More complex modulation schemes such as GMSK and QPSK can also be
implemented using the AD9834.
In an FSK application, the two frequency registers of the
AD9834 are loaded with different values; one frequency
will represent the space frequency while the other will
represent the mark frequency. The digital data stream is
fed to the FSELECT pin which will cause the AD9834 to
modulate the carrier frequency between the two values.
The AD9834 has two phase registers; this enables the part
to perform PSK. With phase shift keying, the carrier frequency is phase shifted, the phase being altered by an
amount which is related to the bit stream being input to
the modulator.
The AD9834 is also suitable for signal generator applications. With the on-board comparator, the device can be
used to generate a square wave.
With its low current consumption, the part is suitable for
applications in which it can be used as a local oscillator.

AD9834
–15–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
Figure 7. Flow Chart for AD9834 Initialisation and Operation
Figure 8. Initialisation
WAIT 7/8 MCLK
CYCLES
See Timing Diagram Fig. 2
V
OUT
= V
REFOUT
* 18 * R
LOAD/RSET *
(1+ (SIN(2p(FREQREG * F
MCLK *
t/2
28 +
PHASEREG/212)))
DAC OUTPUT
DATA WRITE
SELECT DATA
SOURCES
INITIALISATION
See Figure 8 below
CHANGE PHASE?
CHANGE FREQUENCY?
CHANGE FSEL/
FSELECT?
CHANGE FREQ
REGISTER?
CHANGE DAC OUTPUT
FROM SIN TO RAMP?
CONTROL
REGISTER
WRTE?
CHANGE OUTPUT AT
SIGN BIT OUT PIN?
CHANGE PSEL/
PSELECT?
CHANGE PHASE
REGISTER?
See Figure 9
See Figure 10
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
YES
INITIALISATION
APPLY RESET
USING PIN
USING CONTROL
BIT
WRITE TO FREQUENCY AND PHASE REGISTERS
FREQ0 REG = F
OUT0
/ f
MCLK
* 2
28
FREQ1 REG = F
OUT1
/ f
MCLK
* 2
28
PHASE 0 & PHASE1 REG = (PhaseShift * 212) / 2p
(See Figure 9 Below)
SET RESET PIN = 1
SET RESET = 0
SELECT FREQUENCY REGISTERS
SELECT PHASE REGISTERS
USING PIN
USING CONTROL
BIT
(CONTROL REGISTER WRITE)
RESET bit = 0
FSEL = Selected Freq Register
PSEL = Selected Phase Register
PIN/SW = 0
(APPLY SIGNALS AT PINS)
RESET pin = 0
FSELECT = Selected Freq Register
PSELECT = Selected Phase Register
(CONTROL REGISTER WRITE)
RESET = 1
PIN/SW = 0
(CONTROL REGISTER WRITE)
PIN/SW = 1

AD9834
–16–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
Figure 9. Data Writes
Figure 10. Selecting Data Sources
DA T A WRITE
WRITE A FULL 28-BIT WORD
TO A FREQUENCY REGISTER?
WRITE 14 MSBs OR LSBs
TO A FREQUENCY REGISTER?
WRITE TO PHASE
REGISTER?
(CONTROL REGISTER WRITE)
B28 (D13) = 1
WRITE 2 CONSECUTIVE
16-BIT WORDS
(See Table 7 for Example)
WRITE A 16-BIT WORD
(See Tables 8 & 9 for
examples)
(CONTROL REGISTER WRITE)
B28 (D13) = 0
HLB (D12) = 0 / 1
WRITE ANOTHER FULL
28 BITS TO A
FREQUENCY REGISTER?
WRITE 14 MSBs OR LSBs
TO A
FREQUENCY REGISTER?
(16 - Bit Write)
D15, D14 = 11
D13 = 0/1 (chooses the
phase register)
D12 = X
D11 ... D0 = Phase Data
WRITE TO ANOTHER
PHASE REGISTER?
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
SELECT DATA SOURCES
FSELECT AND PSELECT
PINS BEING USED?
SET FSELECT
AND PSELECT
(CONTROL REGISTER WRITE)
PIN/SW = 0
SET FSEL Bit
SET PSEL Bit
(CONTROL REGISTER WRITE)
PIN/SW = 1
YES
NO

AD9834
–17–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
INTERFACING TO MICROPROCESSORS
The AD9834 has a standard serial interface which allows
the part to interface directly with several microprocessors.
The device uses an external serial clock to write the data/
control information into the device. The serial clock can
have a frequency of 40 MHz maximum. The serial clock
can be continuous or, it can idle high or low between
write operations. When data/control information is being
written to the AD9834, FSYNC is taken low and is held
low while the 16 bits of data are being written into the
AD9834. The FSYNC signal frames the 16 bits of information being loaded into the AD9834.
AD9834 to ADSP-21xx Interface
Figure 12 shows the serial interface between the AD9834
and the ADSP-21xx. The ADSP-21xx should be set up to
operate in the SPORT Transmit Alternate Framing Mode
(TFSW = 1). The ADSP-21xx is programmed through
the SPORT control register and should be configured as
follows:
Internal clock operation (ISCLK = 1)
Active low framing (INVTFS = 1)
16-bit word length (SLEN = 15)
Internal frame sync signal (ITFS = 1)
Generate a frame sync for each write (TFSR = 1).
Transmission is initiated by writing a word to the Tx register after the SPORT has been enabled. The data is
clocked out on each rising edge of the serial clock and
clocked into the AD9834 on the SCLK falling edge.
Figure 11. ADSP2101/ADSP2103 to AD9834 Interface
AD9834 to 68HC11/68L11 Interface
Figure 13 shows the serial interface between the AD9834
and the 68HC11/68L11 microcontroller. The
microcontroller is configured as the master by setting bit
MSTR in the SPCR to 1 and, this provides a serial clock
on SCK while the MOSI output drives the serial data line
SDATA. Since the microcontroller does not have a dedicated frame sync pin, the FSYNC signal is derived from a
port line (PC7). The set up conditions for correct operation of the interface are as follows:
SCK idles high between write operations (CPOL = 0)
data is valid on the SCK falling edge (CPHA = 1).
When data is being transmitted to the AD9834, the
FSYNC line is taken low (PC7). Serial data from the
68HC11/68L11 is transmitted in 8-bit bytes with only 8
falling clock edges occuring in the transmit cycle. Data is
transmitted MSB first. In order to load data into the
AD9834, PC7 is held low after the first 8 bits are transferred and a second serial write operation is performed to
the AD9834. Only after the second 8 bits have been trans-
GROUNDING AND LAYOUT
The printed circuit board that houses the AD9834 should
be designed so that the analog and digital sections are
separated and confined to certain areas of the board. This
facilitates the use of ground planes which can be separated
easily. A minimum etch technique is generally best for
ground planes as it gives the best shielding. Digital and
analog ground planes should only be joined in one place.
If the AD9834 is the only device requiring an AGND to
DGND connection, then the ground planes should be
connected at the AGND and DGND pins of the AD9834.
If the AD9834 is in a system where multiple devices require AGND to DGND connections, the connection
should be made at one point only, a star ground point that
should be established as close as possible to the AD9834.
Avoid running digital lines under the device as these will
couple noise onto the die. The analog ground plane should
be allowed to run under the AD9834 to avoid noise coupling. The power supply lines to the AD9834 should use
as large a track as is possible to provide low impedance
paths and reduce the effects of glitches on the power supply line. Fast switching signals such as clocks should be
shielded with digital ground to avoid radiating noise to
other sections of the board. Avoid crossover of digital and
analog signals. Traces on opposite sides of the board
should run at right angles to each other. This will reduce
the effects of feedthrough through the board. A microstrip
technique is by far the best but is not always possible with
a double-sided board. In this technique, the component
side of the board is dedicated to ground planes while signals are placed on the other side.
Good decoupling is important. The analog and digital
supplies to the AD9834 are independent and separately
pinned out to minimize coupling between analog and digital sections of the device. All analog and digital supplies
should be decoupled to AGND and DGND respectively
with 0.1 µF ceramic capacitors in parallel with 10 µF
tantalum capacitors. To achieve the best from the
decoupling capacitors, they should be placed as close as
possible to the device, ideally right up against the device.
In systems where a common supply is used to drive both
the AVDD and DVDD of the AD9834, it is recommended
that the system’s AVDD supply be used. This supply
should have the recommended analog supply decoupling
between the AVDD pins of the AD9834 and AGND and
the recommended digital supply decoupling capacitors
between the DVDD pins and DGND.

AD9834
–18–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
ferred should FSYNC be taken high again.
Figure 12. 68HC11/68L11 to AD9834 Interface
AD9834 to 80C51/80L51 Interface
Figure 14 shows the serial interface between the AD9834
and the 80C51/80L51 microcontroller. The
microcontroller is operated in mode 0 so that TXD of the
80C51/80L51 drives SCLK of the AD9834 while RXD
drives the serial data line SDATA. The FSYNC signal is
again derived from a bit programmable pin on the port
(P3.3 being used in the diagram). When data is to be
transmitted to the AD9834, P3.3 is taken low. The
80C51/80L51 transmits data in 8 bit bytes thus, only 8
falling SCLK edges occur in each cycle. To load the remaining 8 bits to the AD9834, P3.3 is held low after the
first 8 bits have been transmitted and a second write operation is initiated to transmit the second byte of data.
P3.3 is taken high following the completion of the second
write operation. SCLK should idle high between the two
write operations. The 80C51/80L51 outputs the serial
data in a format which has the LSB first. The AD9834
accepts the MSB first (the 4 MSBs being the control information, the next 4 bits being the address while the 8
LSBs contain the data when writing to a destination register). Therefore, the transmit routine of the 80C51/80L51
must take this into account and re-arrange the bits so that
the MSB is output first.
Figure 13. 80C51/80L51 to AD9834 Interface
AD9834 to DSP56002 Interface
Figure 15 shows the interface between the AD9834 and
the DSP56002. The DSP56002 is configured for normal
mode asynchronous operation with a Gated internal clock
(SYN = 0, GCK = 1, SCKD = 1). The frame sync pin is
generated internally (SC2 = 1), the transfers are 16 bits
wide (WL1 = 1, WL0 = 0) and the frame sync signal will
frame the 16 bits (FSL = 0). The frame sync signal is
available on pin SC2 but, it needs to be inverted before
being applied to the AD9834. The interface to the
DSP56000/DSP56001 is similar to that of the DSP56002.
Figure 14. AD9834 to DSP56002 Interface
AD9834 EVALUATION BOARD
The AD9834 Evaluation Board allows designers to evaluate the high performance AD9834 DDS modulator with
minimum of effort.
To prove that this device will meet the user's waveform
synthesis requirements, the user only require's a powersupply, an IBM-compatible PC and a spectrum analyser
along with the evaluation board.
The DDS evaluation kit includes a populated, tested
AD9834 printed circuit board. The evaluation board interfaces to the parallel port of an IBM compatible PC.
Software is available with the evaluation board which allows the user to easily program the AD9834. A schematic
of the Evaluation board is shown in Figure 24. The software will run on any IBM compatible PC which has
Microsoft Windows95, Windows98 or Windows ME 2000
NT™ installed.
Using the AD9834 Evaluation Board
The AD9834 Evaluation kit is a test system designed to
simplify the evaluation of the AD9834. An application
note is also available with the evaluation board and gives
full information on operating the evaluation board.
Prototyping Area
An area is available on the evaluation board for the user to
add additional circuits to the evaluation test set. Users
may want to build custom analog filters for the output or
add buffers and operational amplifiers to be used in the
final application.
XO vs. External Clock
The AD9834 can operate with master clocks up to
50MHz. A 50MHz oscillator is included on the evaluation
board. However, this oscillator can be removed and, if
required, an external CMOS clock connected to the part.
Power Supply
Power to the AD9834 Evaluation Board must be provided
externally through pin connections. The power leads
should be twisted to reduce ground loops.

AD9834
–19–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DA TA
Figure 15. AD9834 Evaluation Board Layout
Integrated Circuits
U3 OSC XTAL 50 MHz
U1 AD9834BRU
U2 74HCT244
Capacitors
C1 C2 C5 C6 C7 C9 C14 100nF Ceramic Capacitor
C3 C4 C13 10nF ceramic Capacitor
C8 C10 10uF Tantalum Capacitor
C11 C12 C15 C16 Option for extra
decoupling capacitors
Resistors
R1 R2 10 KΩ Resistor
R3 51 Ω Resistor
R4 6.8 kΩ Resistor
R5 R6 200 Ω Resistor
R7 300 Ω Resistor
Links
Lk1 Lk2 Lk5 3 pin sil header
Lk3 Lk4 2 pin sil header
Switch
S W End Stackable Switch (SDC
Double Throw)
Sockets
PSEL1; FSEL1; CLK1; Sub Minature BNC
IOUT; IOUTB; SBOUT; Connector
Connectors
J1 36-Pin Edge Connector
J2, J3 PCB Mounting Terminal
Block
C8
10µFC70.1µF
DVDD
J2 J3
C9
0.1µF
C10
10µF
AVDD
C1
0.1µF
DVDD AVDD
C2
0.1µF
5
4
DVDD
AVDD
3
2
12
1
20
COMP
REFOUT
SLEEP
FSADJUST
IOUTB
AVDD
C3
10nF
C11
LK5
6.8k
IOUTB
R6
200R
DGND AGND
718
10
9
8
15
13
14
MCLK
FSELECT
PSELECT
FSYNC
SDATA
SCLK
18
16
14
1
6
4
2
DVDD
C6
0.1µF
U2
J1
SCLK
SDATA
FSYNC
R1
10K
R2
10K
PSELECT
FSELECT
LK1
LK2
SW
DVDD
MCLK
50R
DGND
DVDD
OUT
DVDD
C5
0.1µF
U3
SCLK
SDATA
FSYNC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
U1
AD9834
0.1µF
C4
DVDD
R4
19
IOUT
C12
IOUT
R5
200R
C11
300R
R7
C11
VIN
17
SIGNBITOUT
SBOUT
16
R3
LK3
7
14
8
RESET
RESET
11
12
8
RESET
CAP
LK4
C13
0.01µF
C14
0.01µF
6

AD9834
–20–
REV PrM
PRELIMINAR Y TECHNICAL DAT A
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
20-Lead Small Outline Package (TSSOP)
(RU-20)
20
11
10
1
0.260 (6.60)
0.252 (6.40)
0.256 (6.50)
0.246 (6.25)
0.177 (4.50)
0.169 (4.30)
PIN 1
SEATING
PLANE
0.006 (0.15)
0.002 (0.05)
0.0118 (0.30)
0.0075 (0.19)
0.0256 (0.65)
BSC
0.0433
(1.10)
MAX
0.0079 (0.20)
0.0035 (0.090)
0.028 (0.70)
0.020 (0.50)
8
o
0
o
 Loading...
Loading...