14-Bit, 165 MSPS
TxDAC
®
D/A Converter
FEATURES
High Performance Member of Pin Compatible
TxDAC Product Family
Excellent Spurious-Free Dynamic Range Performance
SFDR to Nyquist:
83 dBc @ 5 MHz Output
80 dBc @ 10 MHz Output
73 dBc @ 20 MHz Output
SNR @ 5 MHz Output, 125 MSPS: 77 dB
Twos Complement or Straight Binary Data Format
Differential Current Outputs: 2 mA to 20 mA
Power Dissipation: 135 mW @ 3.3 V
Power-Down Mode: 15 mW @ 3.3 V
On-Chip 1.2 V Reference
CMOS Compatible Digital Interface
28-Lead SOIC, 28-Lead TSSOP, and 32-Lead LFCSP
Packages
Edge-Triggered Latches
APPLICATIONS
Wideband Communication Transmit Channel:
Direct IF
Base Stations
Wireless Local Loop
Digital Radio Link
Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS)
Instrumentation
R
SET
CLOCK
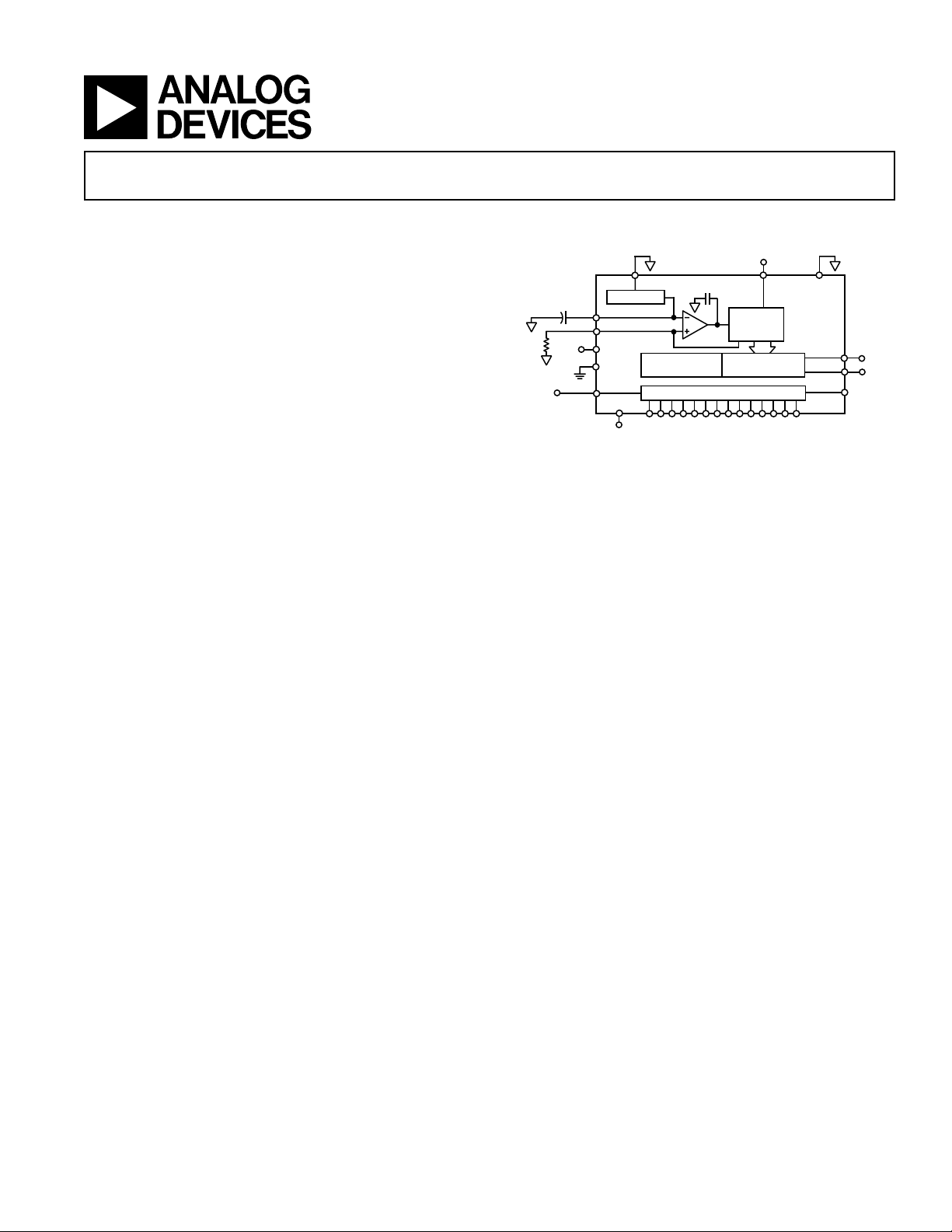
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
0.1F
3.3V
REFLO
+1.2V REF
REFIO
FS ADJ
DVDD
DCOM
CLOCK
DIGITAL DATA INPUTS (DB13–DB0)
SLEEP
150pF
SEGMENTED
SWITCHES
LATCHES
CURRENT
SOURCE
ARRAY
SWITCHES
AD9744
3.3V
AVDD
ACOM
AD9744
LSB
IOUTA
IOUTB
*
MODE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9744 is a 14-bit resolution, wideband, third generation
member of the TxDAC series of high performance, low power
CMOS digital-to-analog converters (DACs). The TxDAC family,
consisting of pin compatible 8-, 10-, 12-, and 14-bit DACs, is
specifically optimized for the transmit signal path of communication systems. All of the devices share the same interface options,
small outline package, and pinout, providing an upward or downward component selection path based on performance, resolution,
and cost. The AD9744 offers exceptional ac and dc performance
while supporting update rates up to 165 MSPS.
The AD9744’s low power dissipation makes it well suited for
portable and low power applications. Its power dissipation can
be further reduced to a mere 60 mW with a slight degradation
in performance by lowering the full-scale current output. Also,
a power-down mode reduces the standby power dissipation to
approximately 15 mW. A segmented current source architecture is combined with a proprietary switching technique to
reduce spurious components and enhance dynamic performance.
*Protected by U.S. Patent Numbers 5568145, 5689257, and 5703519.
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
Edge-triggered input latches and a 1.2 V temperature compensated band gap reference have been integrated to provide a
complete monolithic DAC solution. The digital inputs support
3V CMOS logic families.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The AD9744 is the 14-bit member of the pin compatible
TxDAC family, which offers excellent INL and DNL
performance.
2. Data input supports twos complement or straight binary
data coding.
3. High speed, single-ended CMOS clock input supports
165 MSPS conversion rate.
4. Low power: Complete CMOS DAC function operates on
135 mW from a 2.7 V to 3.6 V single supply. The DAC
full-scale current can be reduced for lower power operation,
and a sleep mode is provided for low power idle periods.
5. On-chip voltage reference: The AD9744 includes a 1.2 V
temperature compensated band gap voltage reference.
6. Industry-standard 28-lead SOIC, 28-lead TSSOP, and 32-lead
LFCSP packages.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
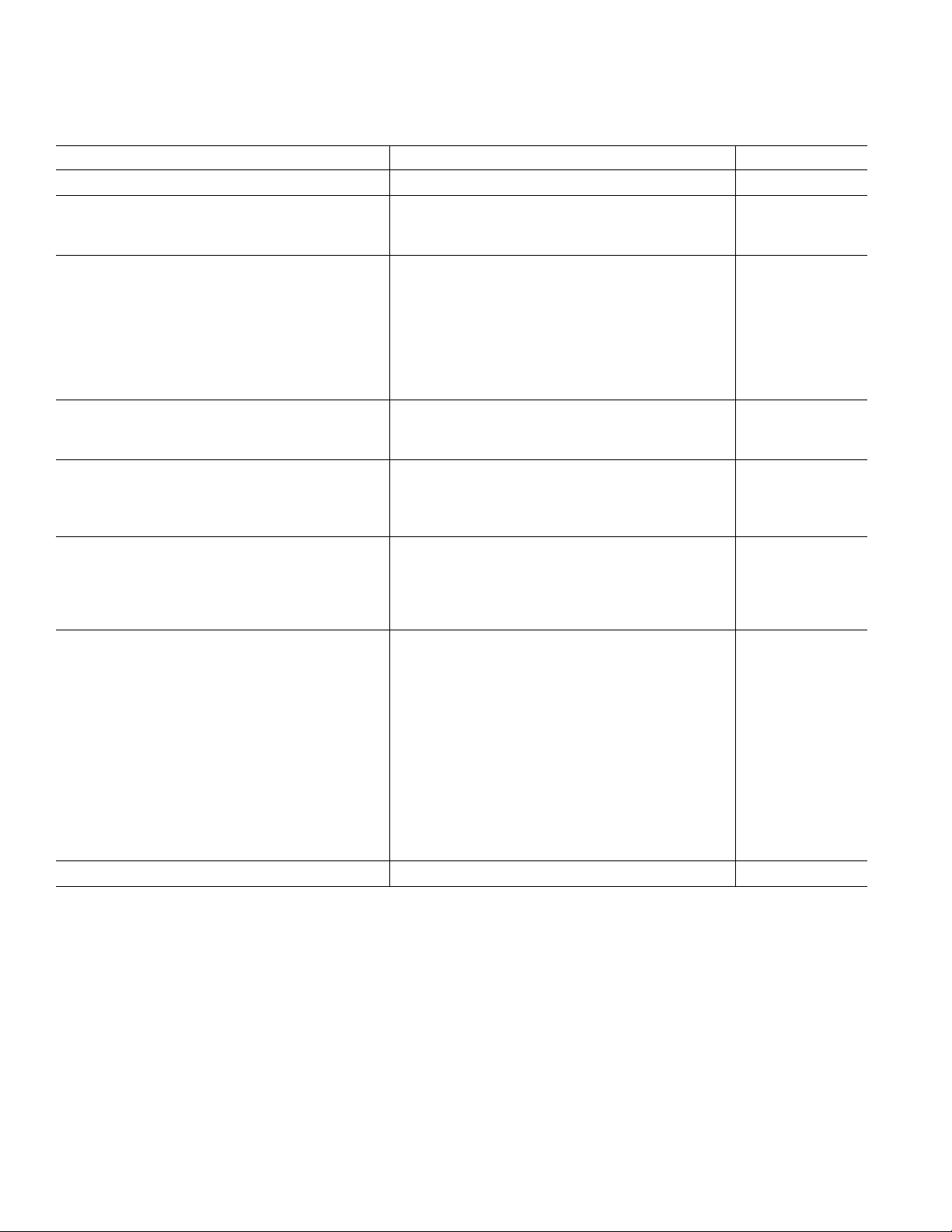
AD9744–SPECIFICATIONS
(T
to T
DC SPECIFICATIONS
MIN
, AVDD = 3.3 V, DVDD = 3.3 V, CLKVDD = 3.3 V, I
MAX
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 14 Bits
DC ACCURACY
1
Integral Linearity Error (INL) –5 ± 0.8 +5 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) –3 ± 0.5 +3 LSB
ANALOG OUTPUT
Offset Error –0.02 +0.02 % of FSR
Gain Error (Without Internal Reference) –0.5 ± 0.1 +0.5 % of FSR
Gain Error (With Internal Reference) –0.5 ± 0.1 +0.5 % of FSR
Full-Scale Output Current
2
220mA
Output Compliance Range –1 +1.25 V
Output Resistance 100 kW
Output Capacitance 5 pF
REFERENCE OUTPUT
Reference Voltage 1.14 1.20 1.26 V
Reference Output Current
3
REFERENCE INPUT
Input Compliance Range 0.1 1.25 V
Reference Input Resistance (Ext. Reference) 1 MW
Small Signal Bandwidth 0.5 MHz
TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENTS
Offset Drift 0 ppm of FSR/∞C
Gain Drift (Without Internal Reference) ± 50 ppm of FSR/∞C
Gain Drift (With Internal Reference) ± 100 ppm of FSR/∞C
Reference Voltage Drift ± 50 ppm/∞C
POWER SUPPLY
Supply Voltages
AVDD 2.7 3.3 3.6 V
DVDD 2.7 3.3 3.6 V
CLKVDD 2.7 3.3 3.6 V
Analog Supply Current (I
Digital Supply Current (I
Clock Supply Current (I
Supply Current Sleep Mode (I
Power Dissipation
Power Dissipation
4
5
Power Supply Rejection Ratio—AVDD
Power Supply Rejection Ratio—DVDD
)3336mA
AVDD
4
)
DVDD
)56mA
CLKVDD
)56mA
AVDD
6
6
–1 +1 % of FSR/V
–0.04 +0.04 % of FSR/V
OPERATING RANGE –40 +85 ∞C
NOTES
1
Measured at IOUTA, driving a virtual ground.
2
Nominal full-scale current, I
3
An external buffer amplifier with input bias current <100 nA should be used to drive any external load.
4
Measured at f
5
Measured as unbuffered voltage output with I
6
± 5% power supply variation.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
= 25 MSPS and f
CLOCK
, is 32 times the I
OUTFS
OUT
= 1 MHz.
OUTFS
current.
REF
= 20 mA and 50 W R
at IOUTA and IOUTB, f
LOAD
CLOCK
= 20 mA, unless otherwise noted.)
OUTFS
100 nA
89mA
135 145 mW
145 mW
= 100 MSPS and f
= 40 MHz.
OUT
REV. A–2–
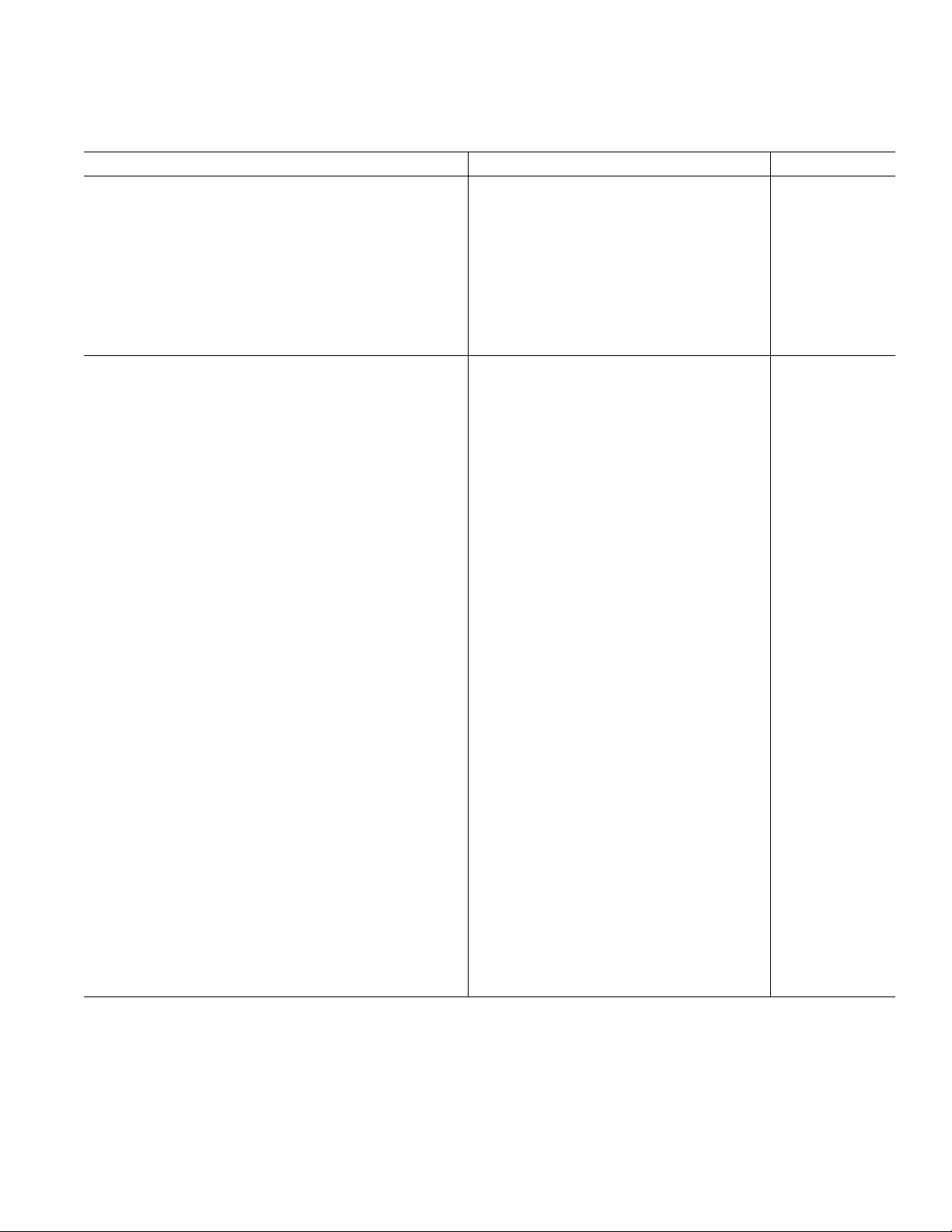
AD9744
(T
to T
, AVDD = 3.3 V, DVDD = 3.3 V, CLKVDD = 3.3 V, I
MAX
DYNAMIC SPECIFICATIONS
MIN
transformer coupled output, 50 doubly terminated, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Maximum Output Update Rate (f
Output Settling Time (t
Output Propagation Delay (t
) (to 0.1%)
ST
)1ns
PD
Glitch Impulse 5 pV-s
Output Rise Time (10% to 90%)
Output Fall Time (10% to 90%)
Output Noise (I
Output Noise (I
Noise Spectral Density
OUTFS
OUTFS
= 20 mA)
= 2 mA)
3
2
) 165 MSPS
CLOCK
1
1
1
2
11 ns
2.5 ns
2.5 ns
50 pA/÷Hz
30 pA/÷Hz
–155 dBm/Hz
AC LINEARITY
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range to Nyquist
= 25 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 1.00 MHz
OUT
0 dBFS Output 77 90 dBc
–6 dBFS Output 87 dBc
–12 dBFS Output 82 dBc
–18 dBFS Output 82 dBc
= 65 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
f
= 65 MSPS; f
CLOCK
= 65 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 65 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
f
= 65 MSPS; f
CLOCK
= 165 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 165 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 1.00 MHz 85 dBc
OUT
= 2.51 MHz 84 dBc
OUT
= 10 MHz 80 dBc
OUT
= 15 MHz 75 dBc
OUT
= 25 MHz 74 dBc
OUT
= 21 MHz 73 dBc
OUT
= 41 MHz 60 dBc
OUT
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range within a Window
= 25 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 50 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
f
= 65 MSPS; f
CLOCK
= 125 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 1.00 MHz; 2 MHz Span 84 90 dBc
OUT
= 5.02 MHz; 2 MHz Span 90 dBc
OUT
= 5.03 MHz; 2.5 MHz Span 87 dBc
OUT
= 5.04 MHz; 4 MHz Span 87 dBc
OUT
Total Harmonic Distortion
= 25 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 50 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 65 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
f
= 125 MSPS; f
CLOCK
= 1.00 MHz –86 –77 dBc
OUT
= 2.00 MHz –77 dBc
OUT
= 2.00 MHz –77 dBc
OUT
= 2.00 MHz –77 dBc
OUT
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
= 65 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
f
= 65 MSPS; f
CLOCK
= 125 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 125 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
f
= 165 MSPS; f
CLOCK
= 165 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 5 MHz; I
OUT
= 5 MHz; I
OUT
= 5 MHz; I
OUT
= 5 MHz; I
OUT
= 5 MHz; I
OUT
= 5 MHz; I
OUT
= 20 mA 82 dB
OUTFS
= 5 mA 88 dB
OUTFS
= 20 mA 77 dB
OUTFS
= 5 mA 78 dB
OUTFS
= 20 mA 70 dB
OUTFS
= 5 mA 70 dB
OUTFS
Multitone Power Ratio (8 Tones at 400 kHz Spacing)
= 78 MSPS; f
f
CLOCK
= 15.0 MHz to 18.2 MHz
OUT
0 dBFS Output 66 dBc
–6 dBFS Output 68 dBc
–12 dBFS Output 62 dBc
–18 dBFS Output 61 dBc
NOTES
1
Measured single-ended into 50 W load.
2
Output noise is measured with a full-scale output set to 20 mA with no conversion activity. It is a measure of the thermal noise only.
3
Noise spectral density is the average noise power normalized to a 1 Hz bandwidth, with the DAC converting and producing an output tone.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
= 20 mA, differential
OUTFS
REV. A
–3–
AD9744
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
(T
to T
MIN
, AVDD = 3.3 V, DVDD = 3.3 V, CLKVDD = 3.3 V, I
MAX
= 20 mA, unless otherwise noted.)
OUTFS
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
DIGITAL INPUTS
1
Logic 1 Voltage 2.1 3 V
Logic 0 Voltage 0 0.9 V
Logic 1 Current –10 +10 mA
Logic 0 Current –10 +10 mA
Input Capacitance 5 pF
Input Setup Time (t
Input Hold Time (t
Latch Pulsewidth (t
CLK INPUTS
2
) 2.0 ns
S
) 1.5 ns
H
) 1.5 ns
LPW
Input Voltage Range 0 3 V
Common-Mode Voltage 0.75 1.5 2.25 V
Differential Voltage 0.5 1.5 V
NOTES
1
Includes CLOCK pin on SOIC/TSSOP packages and CLK+ pin on LFCSP package in single-ended clock input mode.
2
Applicable to CLK+ and CLK– inputs when configured for differential or PECL clock input mode.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
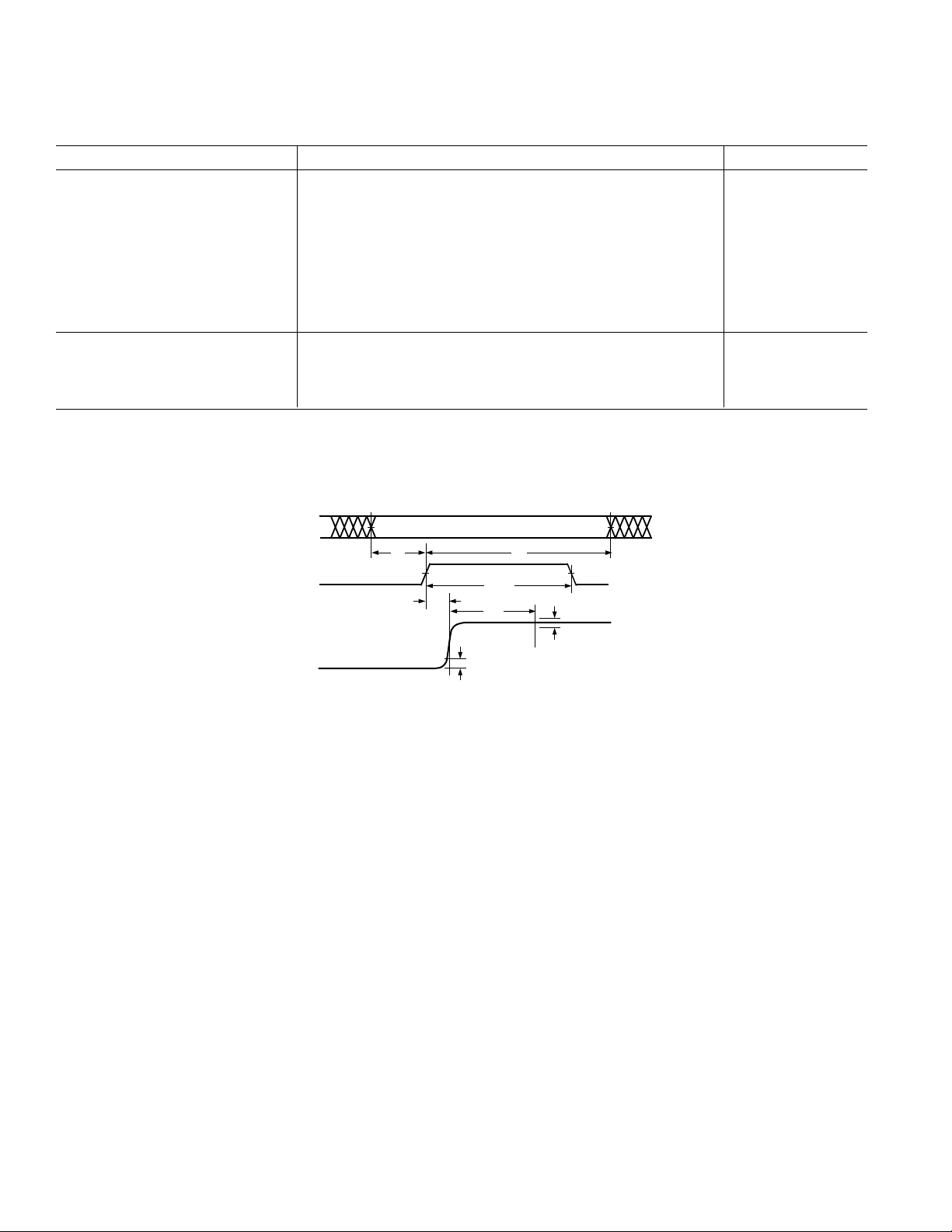
DB0–DB13
CLOCK
IOUTA
OR
IOUTB
t
S
t
PD
0.1%
t
H
t
LPW
t
ST
0.1%
Figure 1. Timing Diagram
REV. A–4–
AD9744
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
With
Parameter Respect to Min Max Unit
AVDD ACOM –0.3 +3.9 V
DVDD DCOM –0.3 +3.9 V
CLKVDD CLKCOM –0.3 +3.9 V
ACOM DCOM –0.3 +0.3 V
ACOM CLKCOM –0.3 +0.3 V
DCOM CLKCOM –0.3 +0.3 V
AVDD DVDD –3.9 +3.9 V
AVDD CLKVDD –3.9 +3.9 V
DVDD CLKVDD –3.9 +3.9 V
CLOCK, SLEEP DCOM –0.3 DVDD + 0.3 V
Digital Inputs, MODE DCOM –0.3 DVDD + 0.3 V
IOUTA, IOUTB ACOM –1.0 AVDD + 0.3 V
REFIO, REFLO, FS ADJ ACOM –0.3 AVDD + 0.3 V
CLK+, CLK–, CMODE CLKCOM –0.3 CLKVDD + 0.3 V
Junction Temperature 150 ∞C
Storage Temperature –65 +150 ∞C
Lead Temperature (10 sec) 300 ∞C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings
for extended periods may effect device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS* Thermal Resistance
28-Lead 300-Mil SOIC
= 55.9∞C/W
JA
28-Lead TSSOP
= 67.7∞C/W
JA
32-Lead LFCSP
= 32.5∞C/W
JA
*Thermal impedance measurements were taken on a 4-layer board in still air,
in accordance with EIA/JESD51-7.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Options*
AD9744AR –40∞C to +85∞C 28-Lead 300-Mil SOIC R-28
AD9744ARRL –40∞C to +85∞C 28-Lead 300-Mil SOIC R-28
AD9744ARU –40∞C to +85∞C 28-Lead TSSOP RU-28
AD9744ARURL7 –40∞C to +85∞C 28-Lead TSSOP RU-28
AD9744ACP –40∞C to +85∞C 32-Lead LFCSP CP-32
AD9744ACPRL7 –40∞C to +85∞C 32-Lead LFCSP CP-32
AD9744-EB Evaluation Board (SOIC)
AD9744ACP-PCB Evaluation Board (LFCSP)
*R = Small Outline IC; RU = Thin Shrink Small Outline Package; CP = Lead Frame Chip Scale Package
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the
AD9744 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended
to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. A
–5–
AD9744
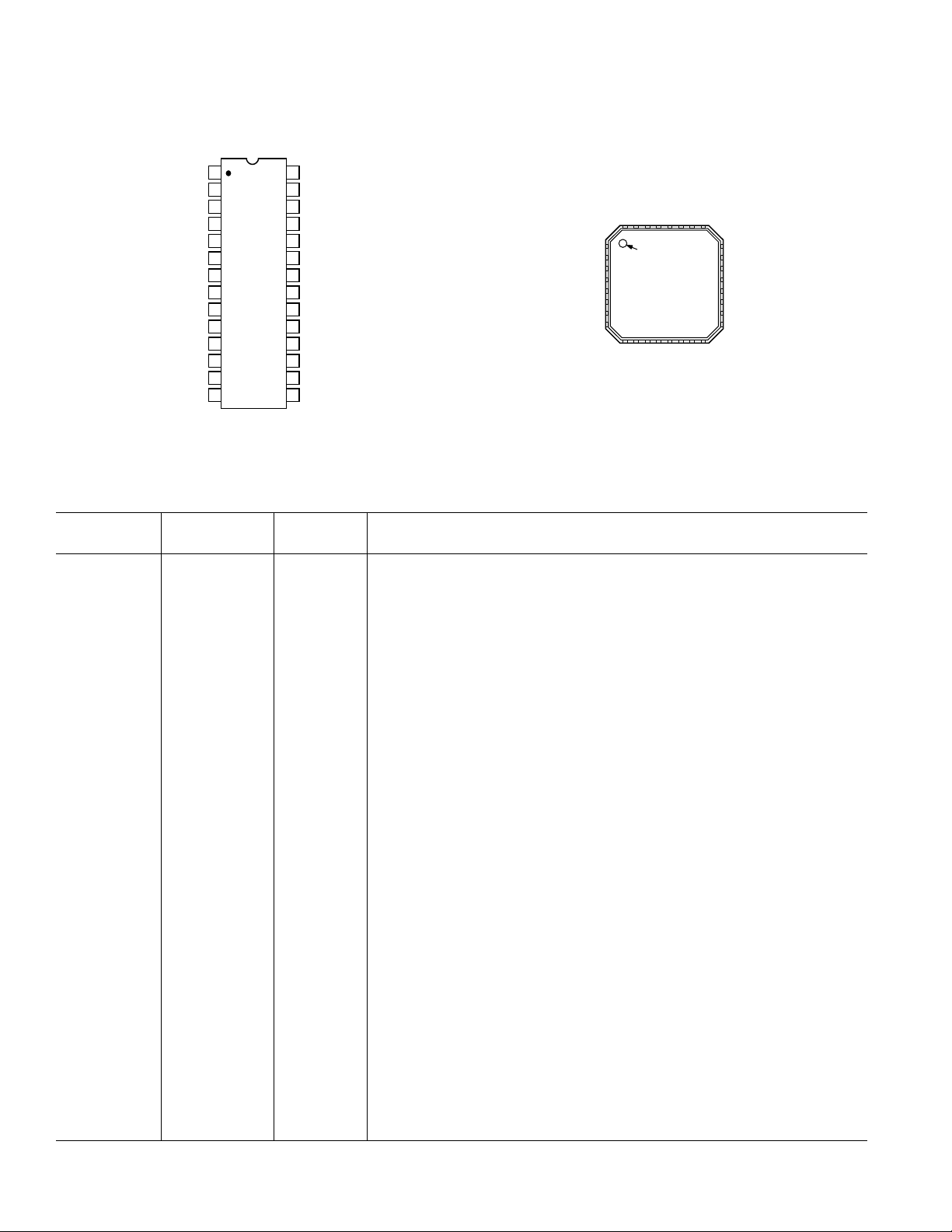
28-Lead SOIC and TSSOP
PIN CONFIGURATION
32-Lead LFCSP
(MSB) DB13
DB12
DB11
DB10
DB9
DB8
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
(LSB ) DB0
1
2
3
4
5
AD9744
6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
NC = NO CONNECT
28
CLOCK
27
DVDD
26
DCOM
25
MODE
AVDD
24
23
RESERVED
22
IOUTA
21
IOUTB
20
ACOM
19
NC
FS ADJ
18
REFIO
17
REFLO
16
SLEEP
15
DB7 1
DB6 2
DVDD 3
DB5 4
DB4 5
DB3 6
DB2 7
DB1 8
32 DB8
31 DB9
30 DB10
29 DB11
28 DB12
PIN 1
INDICATOR
AD9744
TOP VIEW
CLK 12
CLK 13
DCOM 10
CLKVDD 11
(LSB) DB0 9
NC = NO CONNECT
27 DB13 (MSB)
26 DCOM
25 SLEEP
24 FS ADJ
23 REFIO
22 ACOM
21 IOUTA
20 IOUTB
19 ACOM
18 AVDD
17 AVDD
MODE 16
CMODE 15
CLKCOM 14
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
SOIC/TSSOP LFCSP
Pin No. Pin No. Mnemonic Description
127DB13 Most Significant Data Bit (MSB).
2–13 28–32, 1, 2, 4–8 DB12–DB1 Data Bits 12–1.
14 9 DB0 Least Significant Data Bit (LSB).
15 25 SLEEP Power-Down Control Input. Active high. Contains active pull-down circuit;
it may be left unterminated if not used.
16 N/A REFLO Reference Ground when Internal 1.2 V Reference Used. Connect to AVDD to
disable internal reference.
17 23 REFIO Reference Input/Output. Serves as reference input when internal reference disabled
(i.e., tie REFLO to AVDD). Serves as 1.2 V reference output when internal
reference activated (i.e., tie REFLO to ACOM). Requires 0.1 mF capacitor to
ACOM when internal reference activated.
18 24 FS ADJ Full-Scale Current Output Adjust.
19 N/A NC No Internal Connection.
20 19, 22 ACOM Analog Common.
21 20 IOUTB Complementary DAC Current Output. Full-scale current when all data bits are 0s.
22 21 IOUTA DAC Current Output. Full-scale current when all data bits are 1s.
23 N/A RESERVED Reserved. Do Not Connect to Common or Supply.
24 17, 18 AVDD Analog Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
25 16 MODE Selects Input Data Format. Connect to DCOM for straight binary, DVDD for
twos complement.
N/A 15 CMODE Clock Mode Selection. Connect to CLKCOM for single-ended clock receiver
(drive CLK+ and float CLK–). Connect to CLKVDD for differential receiver.
Float for PECL receiver (terminations on-chip).
26 10, 26 DCOM Digital Common.
27 3 DVDD Digital Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
28 N/A CLOCK Clock Input. Data latched on positive edge of clock.
N/A 12 CLK+ Differential Clock Input.
N/A 13 CLK– Differential Clock Input.
N/A 11 CLKVDD Clock Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
N/A 14 CLKCOM Clock Common.
REV. A–6–
AD9744
DEFINITIONS OF SPECIFICATIONS
Linearity Error (Also Called Integral Nonlinearity or INL)
Linearity error is defined as the maximum deviation of the
actual analog output from the ideal output, determined by a
straight line drawn from zero to full scale.
Differential Nonlinearity (or DNL)
DNL is the measure of the variation in analog value, normalized
to full scale, associated with a 1 LSB change in digital input code.
Monotonicity
A D/A converter is monotonic if the output either increases or
remains constant as the digital input increases.
Offset Error
The deviation of the output current from the ideal of zero is
called the offset error. For IOUTA, 0 mA output is expected
when the inputs are all 0s. For IOUTB, 0 mA output is expected
when all inputs are set to 1s.
Gain Error
The difference between the actual and ideal output span. The
actual span is determined by the output when all inputs are set
to 1s minus the output when all inputs are set to 0s.
Output Compliance Range
The range of allowable voltage at the output of a current output
DAC. Operation beyond the maximum compliance limits may
cause either output stage saturation or breakdown, resulting in
nonlinear performance.
Temperature Drift
Temperature drift is specified as the maximum change from the
ambient (25∞C) value to the value at either T
MIN
or T
MAX
. For
offset and gain drift, the drift is reported in ppm of full-scale
range (FSR) per ∞C. For reference drift, the drift is reported in
ppm per ∞C.
Power Supply Rejection
The maximum change in the full-scale output as the supplies
are varied from nominal to minimum and maximum specified
voltages.
Settling Time
The time required for the output to reach and remain within a
specified error band about its final value, measured from the
start of the output transition.
Glitch Impulse
Asymmetrical switching times in a DAC give rise to undesired
output transients that are quantified by a glitch impulse. It is
specified as the net area of the glitch in pV-s.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range
The difference, in dB, between the rms amplitude of the output
signal and the peak spurious signal over the specified bandwidth.
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
THD is the ratio of the rms sum of the first six harmonic components to the rms value of the measured input signal. It is expressed
as a percentage or in decibels (dB).
Multitone Power Ratio
The spurious-free dynamic range containing multiple carrier
tones of equal amplitude. It is measured as the difference between
the rms amplitude of a carrier tone to the peak spurious signal
in the region of a removed tone.
DVDD
DCOM
R
SET
2k
RETIMED
CLOCK
OUTPUT*
LECROY 9210
PULSE GENERATOR
3.3V
0.1F
3.3V
50
+1.2V REF
REFIO
FS ADJ
DVDD
DCOM
CLOCK
SLEEP
REFLO
SEGMENTED SWITCHES
FOR DB13–DB5
CLOCK
OUTPUT
150pF
LATCHES
DIGITAL
DATA
TEKTRONIX AWG-2021
WITH OPTION 4
AVDD ACOM
PMOS
CURRENT SOURCE
ARRAY
LSB
SWITCHES
AD9744
IOUTA
IOUTB
MODE
50
50
*AWG2021 CLOCK RETIMED
SO THAT THE DIGITAL DATA
TRANSITIONS ON FALLING EDGE
OF 50% DUTY CYCLE CLOCK.
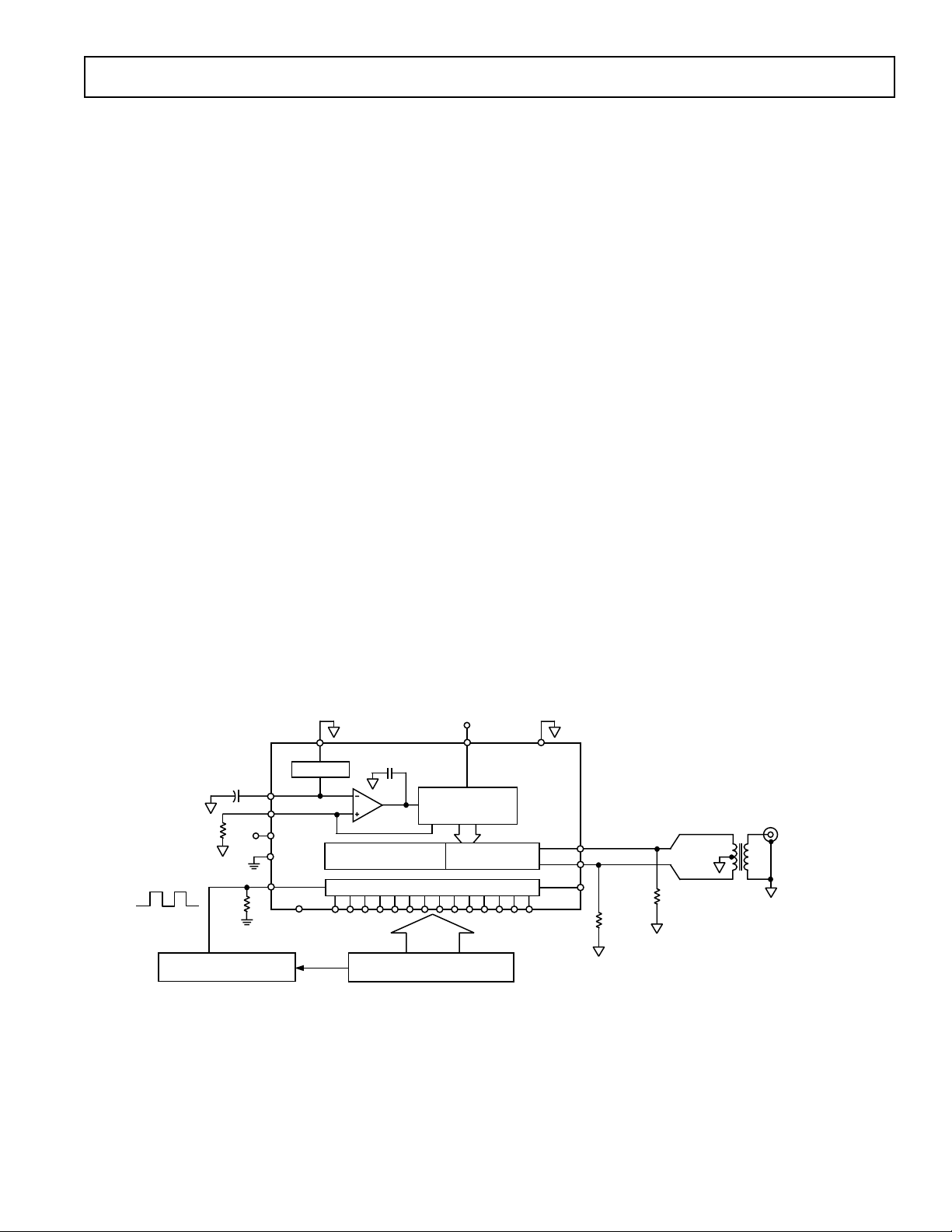
Figure 2. Basic AC Characterization Test Set-Up (SOIC/TSSOP Packages)
MINI-CIRCUITS
T1-1T
RHODE & SCHWARZ
FSEA30
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
REV. A
–7–
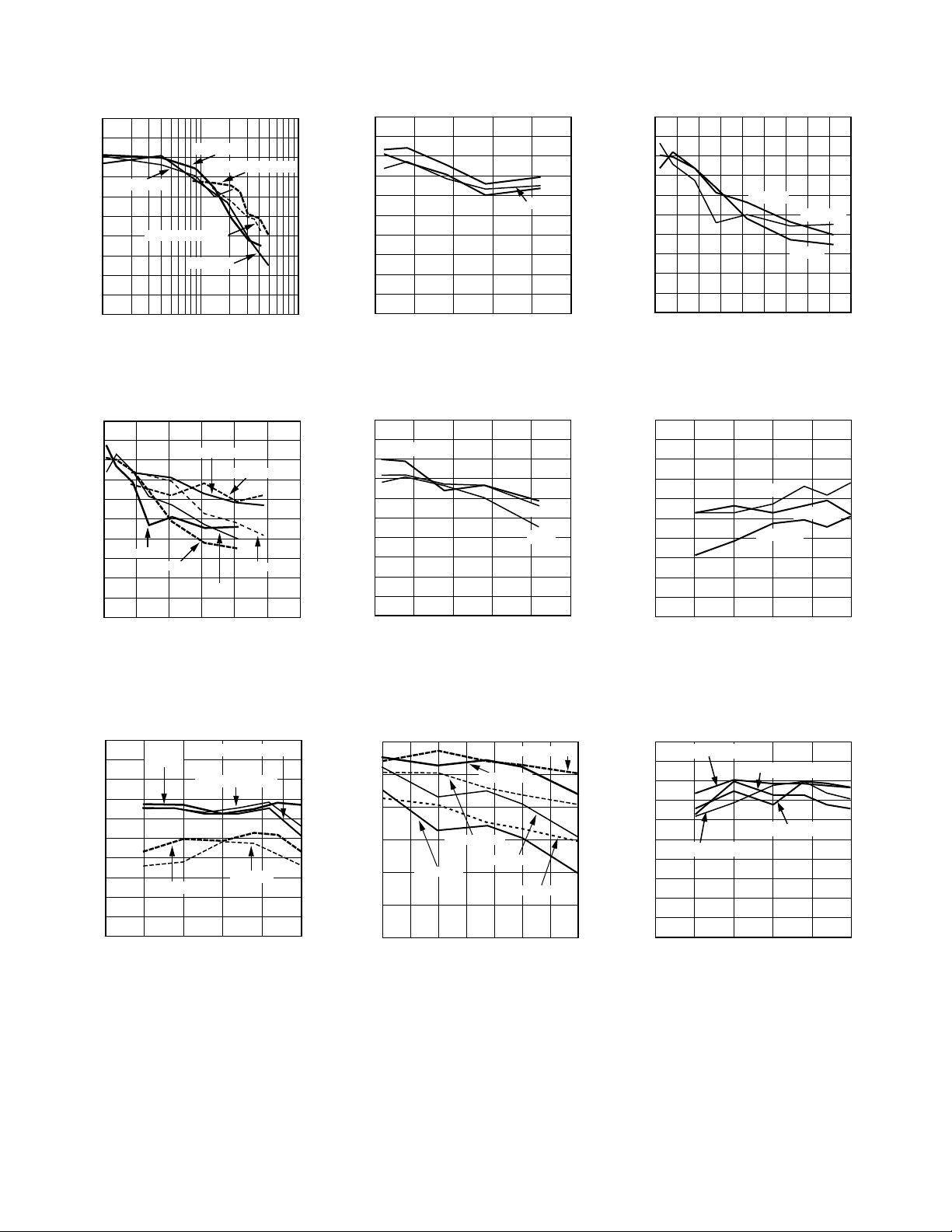
AD9744–Typical Performance Characteristics
95
90
85
80
65MSPS
75
70
65
SFDR (dBc)
60
55
50
45
125MSPS (LFCSP)
110
TPC 1. SFDR vs. f
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
SFDR (dBc)
–12dBFS
65
55
50
45
0102030
TPC 4. SFDR vs. f
125MSPS
165MSPS
f
(MHz)
OUT
OUT
–6dBFS (LFCSP)
0dBFS
–6dBFS
(MHz)
f
OUT
@ 165 MSPS
OUT
165MSPS (LFCSP)
@ 0 dBFS
100
–12dBFS (LFCSP)
0dBFS (LFCSP)
40 50 60
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
SFDR (dBc)
60
55
50
45
05 2510 15 20
TPC 2. SFDR vs. f
95
90
20mA
85
80
75
70
65
SFDR (dBc)
60
55
50
45
05 2510 15 20
TPC 5. SFDR vs. f
f
f
OUT
OUT
0dBFS
(MHz)
OUT
(MHz)
OUT
–6dBFS
@ 65 MSPS
and I
@ 65 MSPS and 0 dBFS
–12dBFS
10mA
5mA
OUTFS
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
SFDR (dBc)
60
55
50
45
05 4510 15 35
TPC 3. SFDR vs. f
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
SFDR (dBc)
60
55
50
45
–6dBFS
(MHz)
f
OUT
@ 125 MSPS
OUT
65MSPS
165MSPS
A
(dBFS)
OUT
–12dBFS
0dBFS
403020 25
125MSPS
TPC 6. Single-Tone SFDR vs. A
@ f
OUT
= f
CLOCK
/11
0–5–25 –10–15–20
OUT
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
SFDR (dBc)
60
55
50
45
–25 –20 –15 –10
65MSPS
125MSPS
165MSPS (LFCSP)
125MSPS (LFCSP)
A
(dBFS)
OUT
165MSPS
–5 0
TPC 7. Single-Tone SFDR vs. A
@ f
OUT
= f
CLOCK
/5
OUT
80
75
70
65
SNR (dB)
60
55
50
5mA SOIC
25 45 65 85
TPC 8. SNR vs. f
@ f
= 5 MHz and 0 dBFS
OUT
20mA SOIC
10mA LFCSP
105 125 145 165
(MSPS)
f
CLOCK
CLOCK
20mA LFCSP
10mA SOIC
5mA LFCSP
and I
OUTFS
95
65MSPS (8.3,10.3)
90
85
80
75
70
125MSPS (16.9, 18.9)
65
SFDR (dBc)
60
55
50
45
165MSPS (22.6, 24.6)
78MSPS (10.1, 12.1)
A
(dBFS)
OUT
TPC 9. Dual-Tone IMD vs. A
@ f
OUT
= f
CLOCK
/7
0–5–25 –10–15–20
OUT
REV. A–8–
AD9744
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
ERROR (LSB)
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
4096 8192 12288 16384
0
CODE
TPC 10. Typical INL
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
MAGNITUDE (dBm)
–80
–90
–100
16 2611 16 21
f
CLOCK
f
= 15.0MHz
OUT
SFDR = 79dBc
AMPLITUDE = 0dBFS
FREQUENCY (MHz)
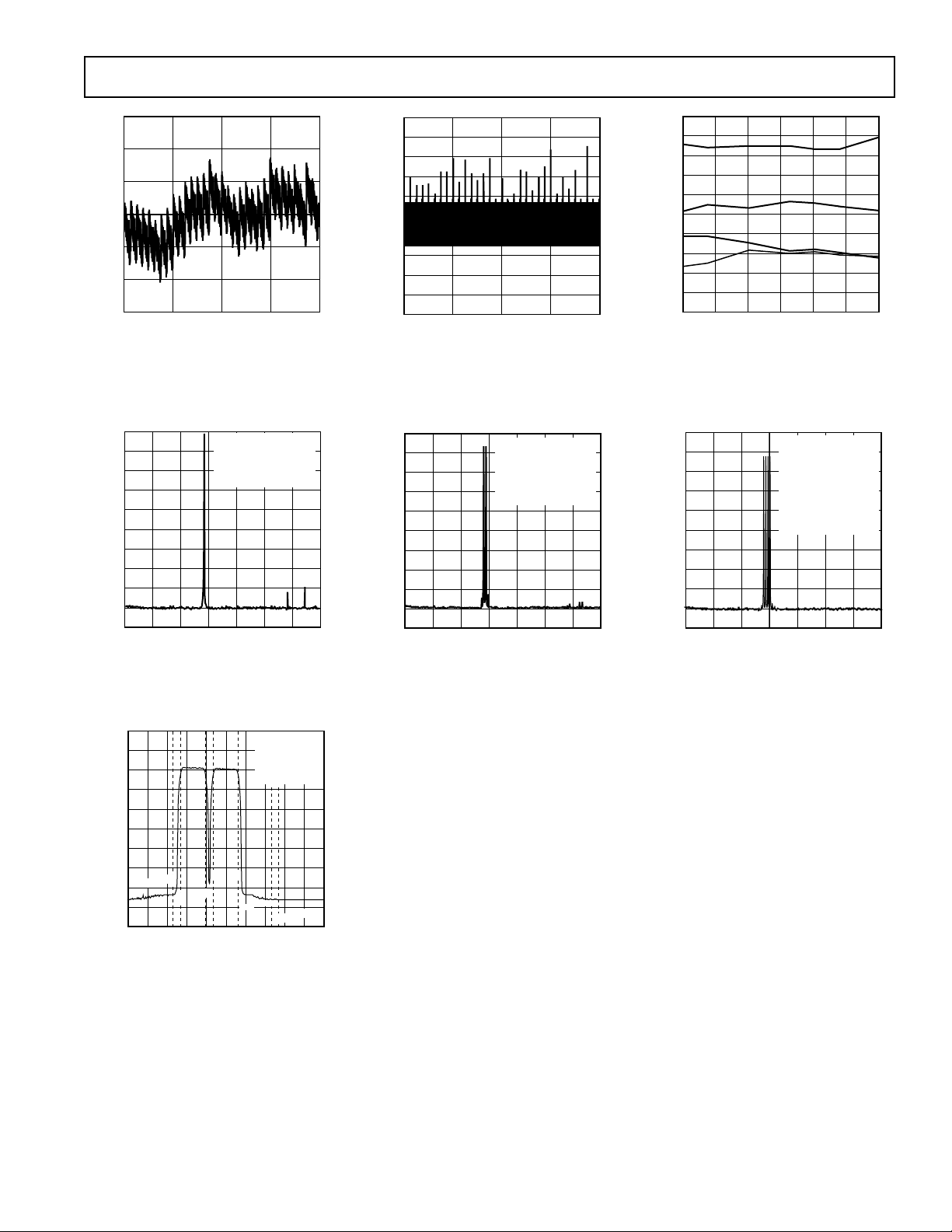
TPC 13. Single-Tone SFDR
= 78MSPS
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
ERROR (LSB)
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0 4096
8192 12288 16384
CODE
TPC 11. Typical DNL
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
SFDR (dBc)
34MHz
60
55
50
45
–40 –20 6002040
4MHz
19MHz
49MHz
TEMPERATURE (C)
TPC 12. SFDR vs. Temperature
80
@ 165 MSPS, 0 dBFS
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
MAGNITUDE (dBm)
–80
–90
31
36
–100
16 2611 16 21
f
= 78MSPS
CLOCK
f
= 15.0MHz
OUT1
f
= 15.4MHz
OUT2
SFDR = 77dBc
AMPLITUDE = 0dBFS
FREQUENCY (MHz)
31
36
TPC 14. Dual-Tone SFDR
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
MAGNITUDE (dBm)
–80
–90
–100
16 2611 16 21
f
f
f
f
f
SFDR = 75dBc
AMPLITUDE = 0dBFS
FREQUENCY (MHz)
TPC 15. Four-Tone SFDR
CLOCK
OUT1
OUT2
OUT3
OUT4
= 78MSPS
= 15.0MHz
= 15.4MHz
= 15.8MHz
= 16.2MHz
31
36
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
MAGNITUDE (dBm)
C12
–100
–110
–120
CENTER 33.22MHz
C12
C0
C11
C11
3MHz SPAN 30MHz
C0
CU1
TPC 16. Two-Carrier UMTS
Spectrum (ACLR = 64 dB)
–39.01dBm
29.38000000MHz
CH PWR –19.26dBm
ACP UP –64.98dB
ACP L OW +0.55dB
ALT1 UP –66.26dB
ALT1 LOW –64.23dB
CU1
CU2
CU2
REV. A
–9–
 Loading...
Loading...