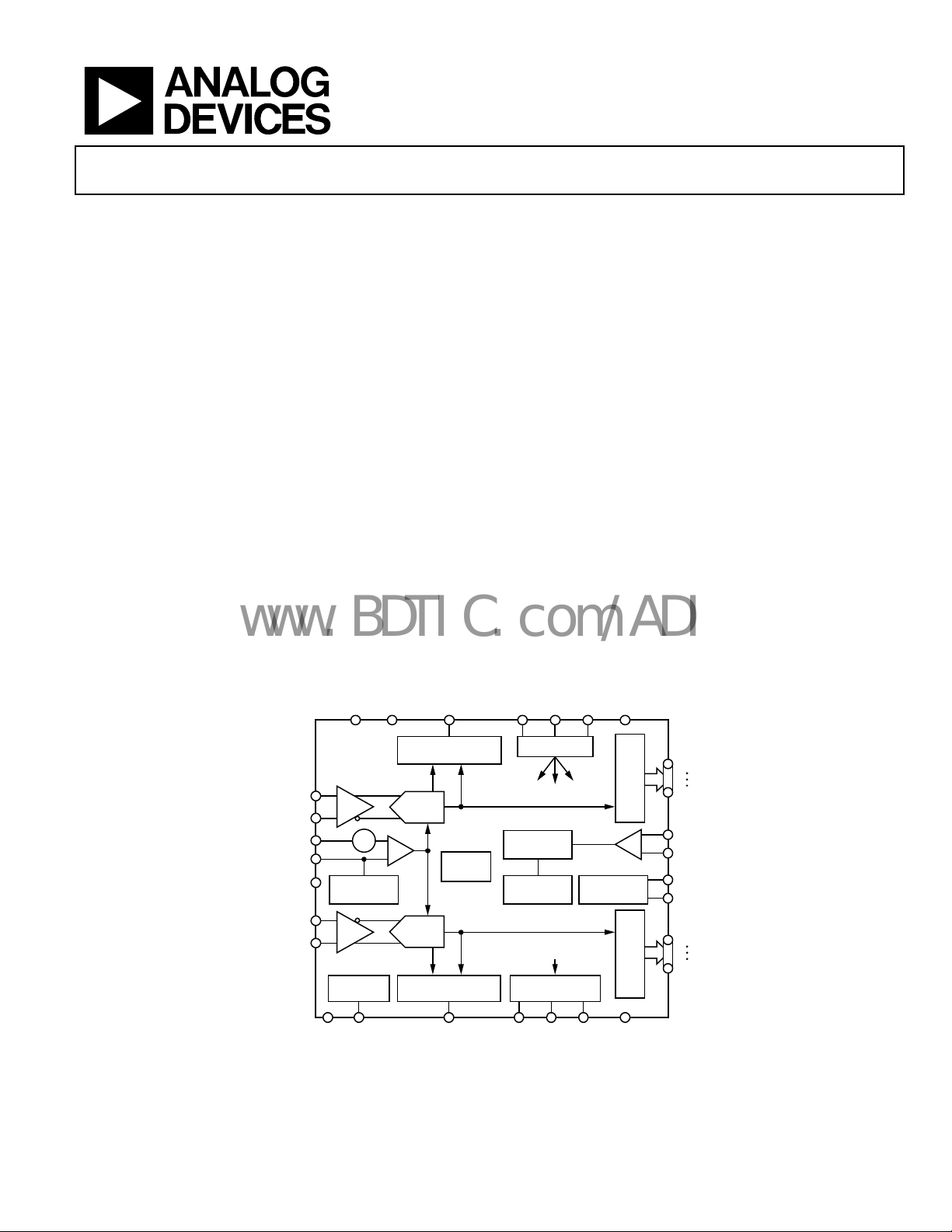
10-Bit, 105 MSPS/125 MSPS/150 MSPS,
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
1.8 V Dual Analog-to-Digital Converter
FEATURES
SNR = 60.6 dBc (61.6 dBFS) to 70 MHz at 150 MSPS
SFDR = 81 dBc to 70 MHz at 150 MSPS
Low power: 825 mW at 150 MSPS
1.8 V analog supply operation
1.8 V to 3.3 V CMOS output supply or 1.8 V LVDS supply
Integer 1 to 8 input clock divider
Intermediate frequency (IF) sampling frequenci
Internal analog-to-digital converter (ADC) voltage reference
Integrated ADC sample-and-hold inputs
Flexible analog input: 1 V p-p to 2 V p-p range
Differential analog inputs with 650 MHz bandwidth
ADC clock duty cycle stabilizer
95 dB channel isolation/crosstalk
Serial port control
User-configurable built-in self-test (BIST) capability
Energy-saving power-down modes
Integrated receive features
Fast detect/threshold bits
Composite signal monitor
APPLICATIONS
Point-to-point radio receivers (GPSK, QAM)
Diversity radio systems
es up to 450 MHz
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
FD[0:3]A
AD9600
I/Q demodulation systems
Smart antenna systems
Digital predistortion
General-purpose software radios
Broadband data applications
Data acquisition
Nondestructive testing
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Integrated dual, 10-bit, 150 MSPS/125 MSPS/105 MSPS ADC.
ast overrange detect and signal monitor with serial output.
2. F
3. Si
gnal monitor block with dedicated serial output mode.
4. P
roprietary differential input maintains excellent SNR
performance for input frequencies up to 450 MHz.
5. The AD9600 op
features a separate digital output driver supply to
accommodate 1.8 V to 3.3 V logic families.
6. A st
andard serial port interface supports various product
features and functions, such as data formatting (offset
binary, twos complement, or gray coding), enabling the
clock DCS, power-down mode, and voltage reference mode.
7. Th
e AD9600 is pin compatible with the AD9627-11, AD9627,
AD9640, allowing a simple migration from 10 bits to
and
11 b
its, 12 bits, or 14 bits.
SCLK/
SDIO/
DFS
DCS
erates from a single 1.8 V supply and
DRVDDDVDDAVDD CSB
FD BITS/THRESHOLD
AD9600
VIN + A
VIN – A
VREF
SENSE
CML
VIN – B
VIN + B
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
SHA ADC
–+
REFERENCE
SELECT
SHA
MULTICHIP
SYNC
NOTES
1. PIN NAMES ARE F OR THE CMOS PIN CONFIGURATION O NLY;
SEE FIGURE 7 FOR LVDS PIN NAMES.
DETECT
SIGNAL
MONITOR
ADC
FD BITS/THRESHOLD
DETECT
FD[0:3]B
SPI
D9A
PROGRAMMING DATA
DIVIDE 1
TO 8
DUTY CYCLE
STABLIZER
SERIAL MONITOR
DATA
SERIAL MONITOR
INTERFACE
SMI
SMI
SDFS
Figure 1.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
SCLK/
PDWN
SDO/
OEB
CMOS/LV DS
DCO
GENERATION
CMOS/ LVDS
DRGNDSYNCAGND SMI
D0A
OUTPUT BUFFER
CLK+
CLK–
DCOA
DCOB
D9B
D0B
OUTPUT BUFF ER
6909-001

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Product Highlights........................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
General Description......................................................................... 3
Specifications..................................................................................... 4
DC Specifications ......................................................................... 4
AC Specifications.......................................................................... 5
Digital Specifications ................................................................... 6
Switching Specifications .............................................................. 8
Timing Characteristics ................................................................ 9
Timing Diagrams.......................................................................... 9
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 11
Thermal Characteristics ............................................................ 11
ESD Caution................................................................................ 11
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 12
Equivalent Circuits......................................................................... 16
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 17
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 22
ADC Architecture ...................................................................... 22
Analog Input Considerations....................................................22
Volt a ge R e fer e nce ....................................................................... 24
Clock Input Considerations...................................................... 25
Power Dissipation and Standby Mode..................................... 27
Digital Outputs ........................................................................... 27
Timing.......................................................................................... 28
ADC Overrange and Gain Control.............................................. 29
Fast Detect Overview................................................................. 29
ADC Fast Magnitude................................................................. 29
ADC Overrange (OR)................................................................ 30
Gain Switching............................................................................ 30
Signal Monitor ................................................................................ 32
Peak Detector Mode................................................................... 32
RMS/MS Magnitude Mode....................................................... 32
Threshold Crossing Mode......................................................... 33
Additional Control Bits ............................................................. 33
DC Correction............................................................................ 34
Signal Monitor SPORT Output ................................................ 34
Built-In Self-Test (BIST) and Output Test .................................. 35
Built-In Self-Test (BIST)............................................................ 35
Output Test Modes..................................................................... 35
Channel/Chip Synchronization.................................................... 36
Serial Port Interface (SPI).............................................................. 37
Configuration Using the SPI..................................................... 37
Hardware Interface..................................................................... 37
Configuration Without the SPI................................................ 38
SPI Accessible Features.............................................................. 38
Memory Map .................................................................................. 39
Reading the Memory Map Table.............................................. 39
Memory Map .............................................................................. 40
Memory Map Register Description ......................................... 43
Applications..................................................................................... 46
Design Guidelines ...................................................................... 46
Evaluation Board ............................................................................ 47
Power Supplies ............................................................................ 47
Input Signals................................................................................ 47
Output Signals ............................................................................ 47
Default Operation and Jumper Selection Settings................. 48
Alternative Clock Configurations ............................................ 48
Alternative Analog Input Drive Configuration...................... 49
Schematics................................................................................... 50
Evaluation Board Layouts ......................................................... 60
Bill of Materials........................................................................... 68
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 70
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 70
REVISION HISTORY
11/07—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9600 is a dual, 10-bit, 105 MSPS/125 MSPS/150 MSPS
ADC. It is designed to support communications applications
where low cost, small size, and versatility are desired.
The dual ADC core features a multistage, differential pipelined
rchitecture with integrated output error correction logic. Each
a
ADC features wide bandwidth, differential sample-and-hold
analog input amplifiers supporting a variety of user-selectable
input ranges. An integrated voltage reference eases design
considerations. A duty cycle stabilizer is provided to compensate for variations in the ADC clock duty cycle, allowing the
converters to maintain excellent performance.
The AD9600 has several functions that simplify the automated
ga
in control (AGC) function in a communications receiver. For
example, the fast detect feature allows fast overrange detection
by outputting four bits of input level information with very
short latency.
In addition, the programmable threshold detector allows monit
oring the amplitude of the incoming signal with short latency,
using the four fast detect bits of the ADC. If the input signal level
exceeds the programmable threshold, the fine upper threshold
indicator goes high. Because this threshold is set from the four
MSBs, the user can quickly adjust the system gain to avoid an
overrange condition.
Another AGC-related function of the AD9600 is the signal
onitor. This block allows the user to monitor the composite
m
magnitude of the incoming signal, which aids in setting the gain
to optimize the dynamic range of the overall system.
The ADC output data can be routed directly to the two external
10-b
it output ports. These outputs can be set from 1.8 V to 3.3 V
CMOS or 1.8 V LVDS. In addition, flexible power-down options
allow significant power savings.
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
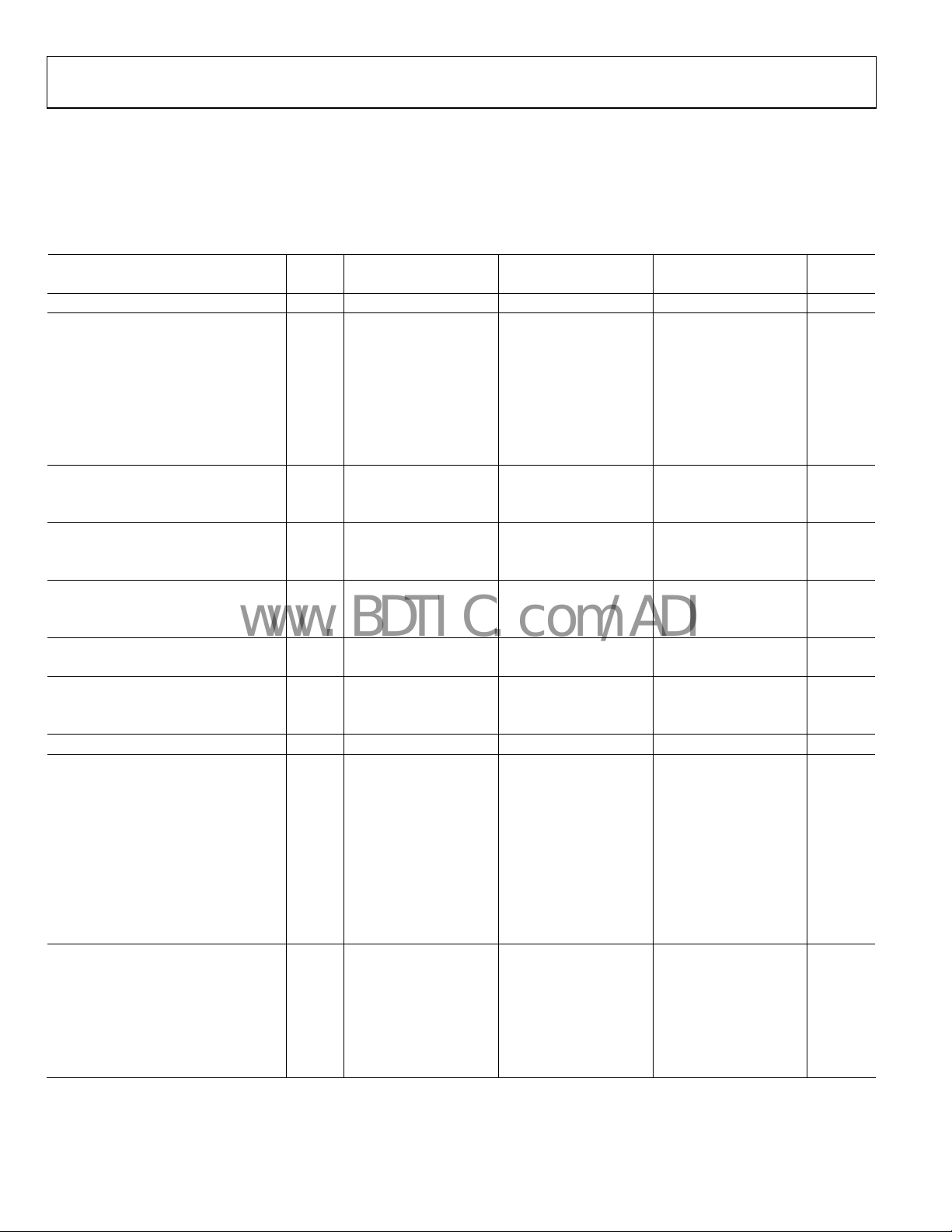
SPECIFICATIONS
DC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, DCS
enabled, fast detect output pins disabled, signal monitor disabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
AD9600BCPZ-105 AD9600BCPZ-125 AD9600BCPZ-150
Parameter Temp
RESOLUTION Full 10 10 10 Bits
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes Full Guaranteed Guaranteed Guaranteed
Offset Error Full ±0.3 ±0.7 ±0.3 ±0.7 ±0.3 ±0.7 % FSR
Gain Error Full −3.6 −2.2 −1.0 −4.0 −2.5 −1.3 −4.3 −3.0 −1.6 % FSR
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
1
Full ±0.2 ±0.2 ±0.2 LSB
25°C ±0.1 ±0.1 ±0.1 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
1
Full ±0.3 ±0.3 ±0.4 LSB
25°C ±0.1 ±0.1 ±0.1 LSB
MATCHING CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Error Full ±0.3 ±0.7 ±0.3 ±0.7 ±0.2 ±0.7 % FSR
Gain Error Full ±0.2 ±0.8 ±0.3 ±0.8 ±0.2 ±0.8 % FSR
TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset Error Full ±15 ±15 ±15 ppm/°C
Gain Error Full ±95 ±95 ±95 ppm/°C
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Output Voltage Error (1 V Mode) Full ±5 ±16 ±5 ±16 ±5 ±16 mV
Load Regulation @ 1.0 mA Full 7 7 7 mV
INPUT-REFERRED NOISE
VREF = 1.0 V 25°C 0.1 0.1 0.1 LSB rms
ANALOG INPUT
Input Span, VREF = 1.0 V Full
Input Capacitance
2
Full
VREF INPUT RESISTANCE Full 6 6 6 kΩ
POWER SUPPLIES
Supply Voltage
AVDD, DVDD Full 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
DRVDD (CMOS Mode) Full 1.7 3.3 3.6 1.7 3.3 3.6 1.7 3.3 3.6 V
Supply Current
1, 3
I
AVDD
4
1, 3,
I
DVDD
I
(3.3 V CMOS) Full
DRVDD
I
(1.8 V CMOS) Full
DRVDD
I
(1.8 V LVDS)
DRVDD
Full
Full
POWER CONSUMPTION
DC Input Full
Sine Wave Input
1
DRVDD = 1.8 V Full
DRVDD = 3.3 V Full
Standby Power
4
Full
Power-Down Power Full
1
Measured with a low input frequency, full-scale sine wave, with approximately 5 pF loading on each output bit.
2
Input capacitance refers to the effective capacitance between one differential input pin and AGND. Refer to Figure 8 for the equivalent analog input structure.
3
The maximum limit applies to the combination of I
4
Standby power is measured with a dc input and the CLK+ and CLK− pins inactive (set to AVDD or AGND).
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
and I
DVDD
currents.
AVDD
2
8
310 365 385 455 419 495 mA
34 365 42 455 50 495 mA
35
15
42
600 650 750 800 825 890 mW
645
740
68
2.5 6 2.5 6 2.5 6 mW
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 72
2 2 V p-p
8 8 pF
36 42 mA
18 22 mA
44 46 mA
813 892 mW
900 990 mW
77 77 mW
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
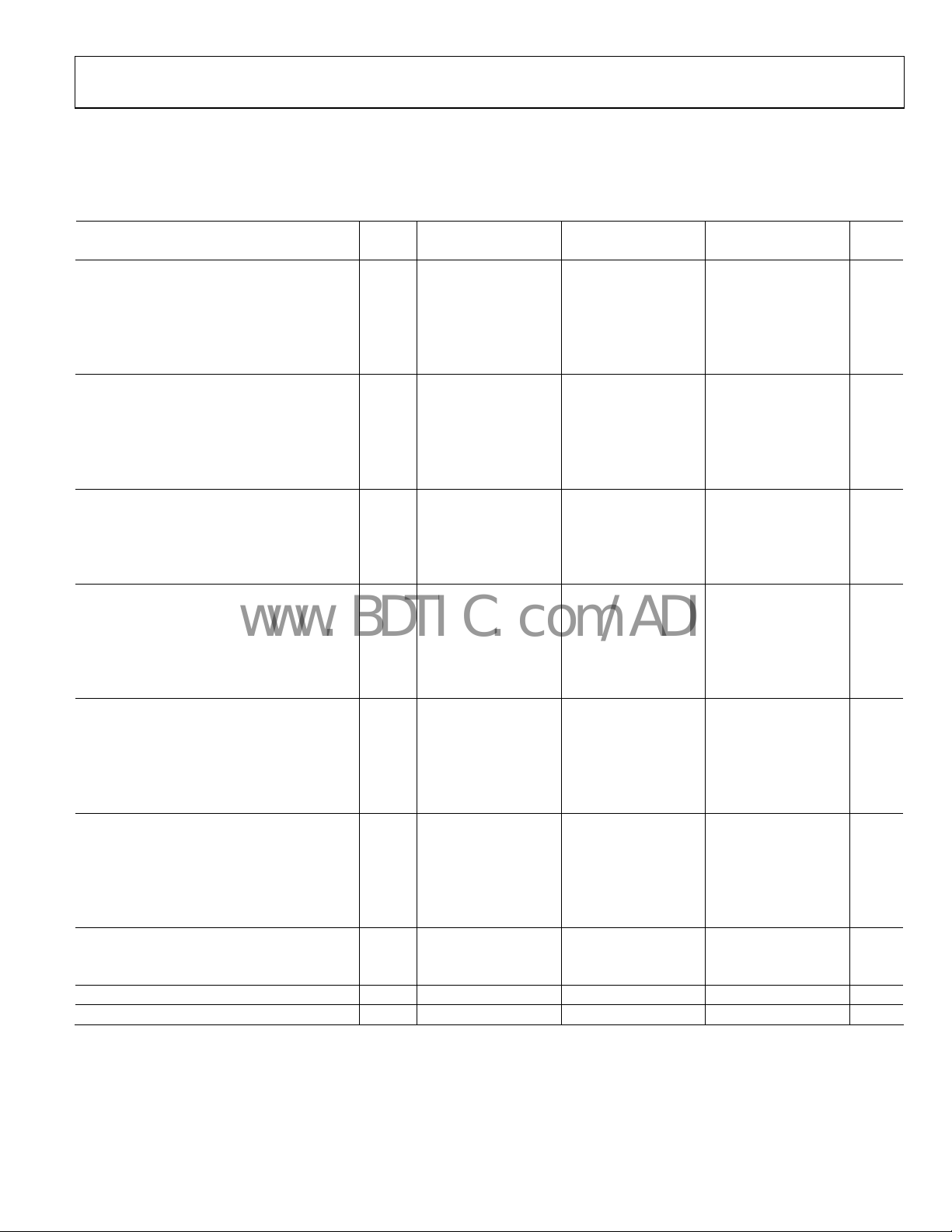
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, DCS
enabled, fast detect output pins disabled, signal monitor disabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO (SNR)
fIN = 2.3 MHz 25°C 60.7 60.6 60.6 dB
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 60.6 60.6 60.6 dB
Full 60.3 60.3
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 60.6 60.6 60.5 dB
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE AND DISTORTION (SINAD)
fIN = 2.3 MHz 25°C 60.6
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 60.5
Full 60.2
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 60.5
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C 60.4 60.4 60.3 dB
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS (ENOB)
fIN = 2.3 MHz 25°C
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C
WORST SECOND OR THIRD HARMONIC
fIN = 2.3 MHz 25°C
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C
Full
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
fIN = 2.3 MHz 25°C
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C
Full 72.0
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C
WORST OTHER HARMONIC OR SPUR
fIN = 2.3 MHz 25°C
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C
Full
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C
fIN = 220 MHz 25°C
TWO-TONE SFDR
fIN = 29.1 MHz, 32.1 MHz (−7 dBFS ) 25°C
fIN = 169.1 MHz, 172.1 MHz (−7 dBFS ) 25°C
CROSSTALK
ANALOG INPUT BANDWIDTH 25°C
1
See AN-835 Application Note, Understanding High Speed ADC Testing and Evaluation, for a complete set of definitions.
2
Crosstalk is measured at 100 MHz with −1 dBFS on one channel and no input on the alternate channel.
1
2
Temp
Full
AD9600BCPZ-105 AD9600BCPZ-125 AD9600BCPZ-150
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
60.5
9.9
9.9
9.9
9.9
−87.0
−85.0
−84.0
−83.0
85.5
85.0
83.0
81.0
−92
−88
−86
−86
84
82
95
650
−72.0
−81
60.5 60.4 dB
60.5 60.5 dB
60.5 60.5 dB
60.2
60.5 60.4 dB
9.9
9.9
9.9
9.9
−86.5
−85.0
−84.0
−83.0
85.5
85.0
72.0
84.0
81.0
−92
-88
−86
−86
84
82
95
650
60.3 dB
60.1 dB
−72.0
72.0
−81
9.9
9.9
9.9
9.9
−88.5
−84.0
−83.5
−77
85.5
84.0
83.5
77
−92
−88
−86
−86
84
82
95
650
−72.0 dBc
−80 dBc
Unit
Bits
Bits
Bits
Bits
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
dB
MHz
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
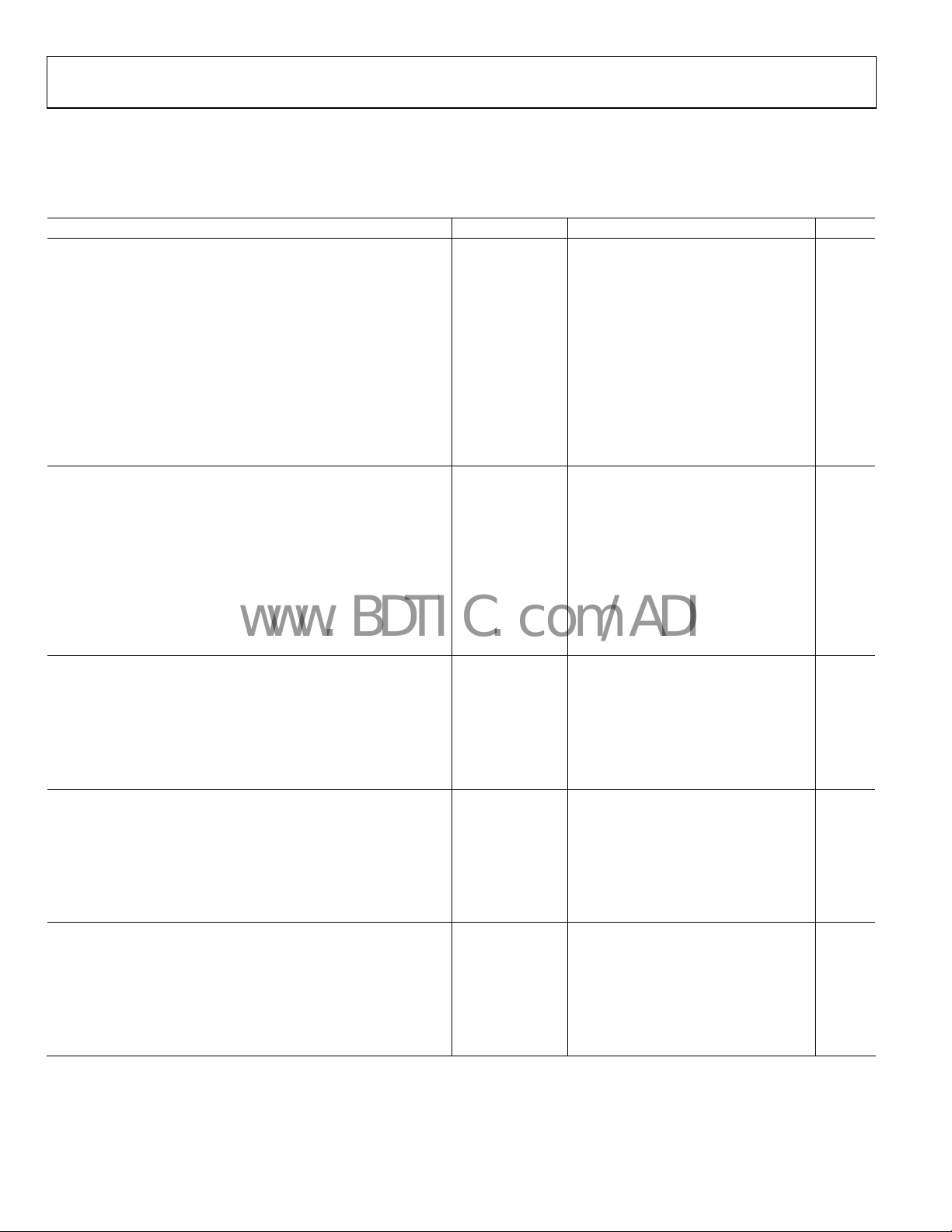
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, maximum sample rate, −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, DCS
enabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
DIFFERENTIAL CLOCK INPUTS (CLK+, CLK−)
Logic Compliance CMOS/LVDS/LVPECL
Internal Common-Mode Bias Full 1.2 V
Differential Input Voltage Full 0.2 6 V p-p
Input Voltage Range Full GND − 0.3 AVDD + 1.6 V
Input Common-Mode Range Full 1.1 AVDD V
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.2 3.6 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.8 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Input Capacitance Full 4 pF
Input Resistance Full 8 10 12 kΩ
SYNC INPUT
Logic Compliance CMOS
Internal Bias Full 1.2 V
Input Voltage Range Full GND − 0.3 AVDD + 1.6 V
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.2 3.6 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.8 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Input Capacitance Full 4 pF
Input Resistance Full 8 10 12 kΩ
LOGIC INPUT (CSB)1
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 3.6 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full 40 132 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 2 pF
LOGIC INPUT (SCLK/DFS)2
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 3.6 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current (VIN = 3.3 V) Full −92 −135 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 2 pF
LOGIC INPUTS/OUTPUTS (SDIO/DCS, SMI SDFS)
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 3.6 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full 38 128 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 5 pF
1
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
LOGIC INPUTS/OUTPUTS (SMI SDO/OEB, SMI SCLK/PDWN)
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 3.6 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current (VIN = 3.3 V) Full −90 −134 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 5 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
CMOS Mode—DRVDD = 3.3 V
High Level Output Voltage (IOH = 50 μA) Full 3.29 V
High Level Output Voltage (IOH = 0.5 mA) Full 3.25 V
Low Level Output Voltage (IOL = 1.6 mA) Full 0.2 V
Low Level Output Voltage (IOL = 50 μA) Full 0.05 V
CMOS Mode—DRVDD = 1.8 V
High Level Output Voltage (IOH = 50 μA) Full 1.79 V
High Level Output Voltage (IOH = 0.5 mA) Full 1.75 V
Low Level Output Voltage (IOL = 1.6 mA) Full 0.2 V
Low Level Output Voltage (IOL = 50 μA) Full 0.05 V
LVDS Mode—DRVDD = 1.8 V
Differential Output Voltage (VOD), ANSI Mode Full 250 350 450 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS), ANSI Mode Full 1.15 1.25 1.35 V
Differential Output Voltage (VOD), Reduced Swing Mode Full 150 200 280 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS), Reduced Swing Mode Full 1.15 1.25 1.35 V
1
Pull up.
2
Pull down.
2
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, maximum sample rate, −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, DCS
enabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
AD9600BCPZ-105 AD9600BCPZ-125 AD9600BCPZ-150
Parameter Temp
CLOCK INPUT PARAMETERS
Input Clock Rate Full 625 625 625 MHz
Conversion Rate
DCS Enabled Full 20 105 20 125 20 150 MSPS
DCS Disabled Full 10 105 10 125 10 150 MSPS
CLK Period (t
CLK Pulse Width High
Divide-by-1 Mode,
DCS Enabled
Divide-by-1 Mode,
DCS Disabled
Divide-by-2 Mode,
DCS Enabled
Divide-by-3 Through Divide-
by-8 Modes, DCS Enabled
DATA OUTPUT PARAMETERS
CMOS Mode—DRVDD = 3.3 V
Data Propagation Delay (tPD)1Full 2.2 4.5 6.4 2.2 4.5 6.4 2.2 4.5 6.4 ns
DCO Propagation Delay (t
Setup Time (tS) Full 5.25 4.5 3.83 ns
Hold Time (tH) Full 4.25 3.5 2.83 ns
CMOS Mode—DRVDD = 1.8 V
Data Propagation Delay (tPD)1
DCO Propagation Delay (t
Setup Time (tS) Full 5.25 4.5 3.83 ns
Hold Time (tH) Full 4.25 3.5 2.83 ns
LVDS Mode—DRVDD = 1.8 V Full
Data Propagation Delay (tPD)1
DCO Propagation Delay (t
CMOS Mode Pipeline Delay
(Latency)
LVDS Mode Pipeline Delay
(Latency) Channel A/Channel B
Aperture Delay (tA) Full 1.0 1.0 1.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter, tJ) Full 0.1 0.1 0.1 ps rms
Wake-Up Time
OUT-OF-RANGE RECOVERY TIME Full 2 3 3 Cycles
1
Output propagation delay is measured from the CLK+ and CLK− pins 50% transition to the output data pins 50% transition, with 5 pF load.
2
Wake-up time is dependent on the value of the decoupling capacitors.
) Full 9.5 8 6.66 ns
CLK
Full 2.85 4.75 6.65 2.4 4 5.6 2.0 3.33 4.66 ns
Full 4.28 4.75 5.23 3.6 4 4.4 3.0 3.33 3.66 ns
Full 1.6 1.6 1.6 ns
Full 0.8 0.8 0.8 ns
) Full 3.8 5.0 6.8 3.8 5.0 6.8 3.8 5.0 6.8 ns
DCO
Full 2.4 5.2 6.9 2.4 5.2 6.9 2.4 5.2 6.9 ns
) Full 4.0 5.6 7.3 4.0 5.6 7.3 4.0 5.6 7.3 ns
DCO
2.0 4.8 6.3 2.0 4.8 6.3 2.0 4.8 6.3 ns
) Full 5.2 7.3 9.0 5.2 7.3 9.0 5.2 7.3 9.0 ns
DCO
Full 12 12 12 Cycles
Full 12/12.5 12/12.5 12/12.5 Cycles
2
Full 350 350 350 μs
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 72
AD9600
A
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Table 5.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
SYNC TIMING REQUIREMENTS
t
SSYNC
t
HSYNC
SPI TIMING REQUIREMENTS
t
DS
t
DH
t
CLK
t
S
t
H
t
HIGH
t
LOW
t
EN_SDIO
t
DIS_SDIO
SPORT TIMING REQUIREMENTS
t
CSSCLK
t
SSCLKSDO
t
SSCLKSDFS
Setup time between SYNC and the rising edge of CLK+ 0.24 ns
Hold time between SYNC and the rising edge of CLK+ 0.40 ns
Setup time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK 2 ns
Hold time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK 2 ns
Period of the SCLK 40 ns
Setup time between CSB and SCLK 2 ns
Hold time between CSB and SCLK 2 ns
SCLK pulse width high 10 ns
SCLK pulse width low 10 ns
Time required for the SDIO pin to switch from an input to an output
10 ns
relative to the SCLK falling edge
Time required for the SDIO pin to switch from an output to an input
10 ns
relative to the SCLK rising edge
Delay from the rising edge of CLK+ to the rising edge of SMI SCLK 3.2 4.5 6.2 ns
Delay from the rising edge of SMI SCLK to SMI SDO −0.4 0 0.4 ns
Delay from the rising edge of SMI SCLK to SMI SDFS −0.4 0 0.4 ns
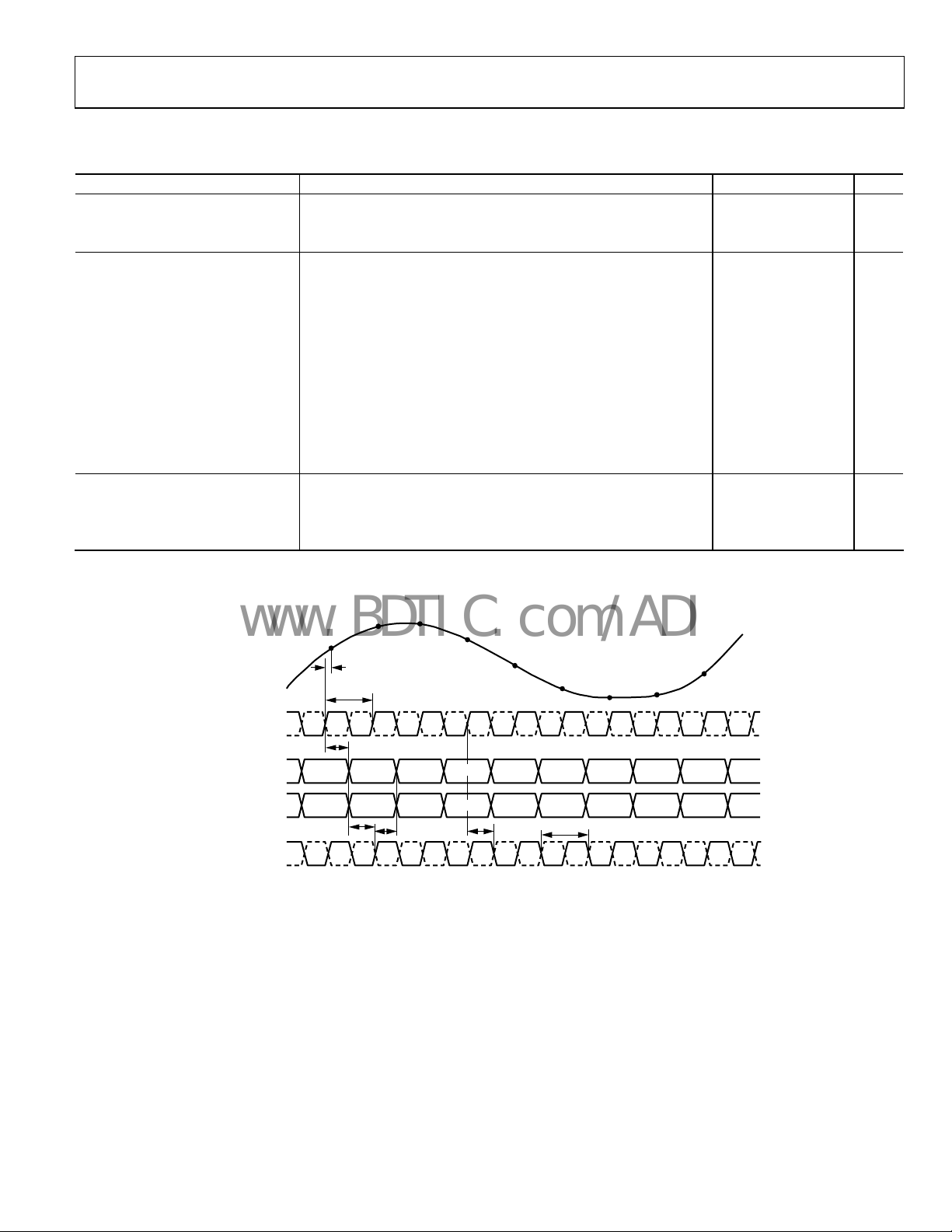
TIMING DIAGRAMS
CH A/CH B DAT
CH A/CH B FAST
CLK+
CLK–
DETECT
DCOA/DCOB
N+2
N+ 1
N
t
A
t
CLK
t
PD
N – 12 N – 11 N – 9 N – 8 N – 7 N – 6 N – 5 N – 4
N – 13
N – 1 N + 2 N + 3 N + 4 N + 5 N + 6N – 3 N – 2
t
S
t
H
N+ 3
N – 10
N
t
N + 1
DCO
N+ 4
N+ 5
N+ 6
t
CLK
N+ 7
Figure 2. CMOS Output Mode Data and Fast Detect Output Timing
N+ 8
06909-012
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 72
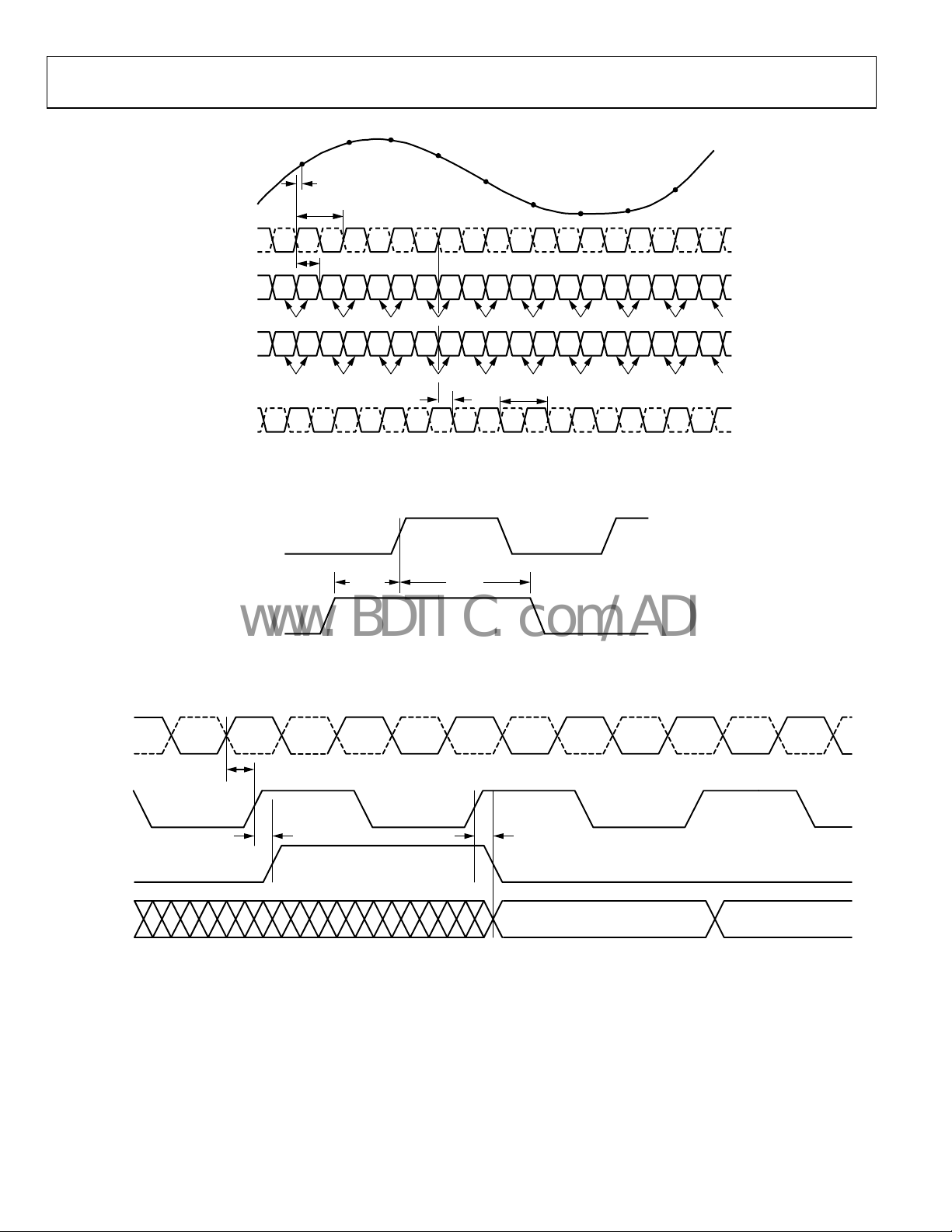
AD9600
S
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
N
t
A
CLK+
CLK–
CH A/CH B DATA
CH A/CH B FAS T
DETECT
DCO+
DCO–
t
PD
ABABABABABABABABA AB
N – 12 N – 11 N – 9 N – 8 N – 7 N – 6 N – 5 N – 4
N – 13
ABABABABABABABABA AB
N – 6 N – 5 N – 3 N – 2 N – 1 N N + 1 N + 2N – 7
Figure 3. LVDS Mode Data and Fast Detect Output T
N+ 1
t
CLK
N+2
N+ 3
N – 10
N – 4
N+ 4
t
DCO
N+ 5
t
CLK
N+ 6
N+ 7
iming (Fast Detect Mode Select Bits = 000)
N+ 8
06909-089
CLK+
CLK+
CLK–
MI SCLK/PDWN
SMI SDFS
t
SSYNC
SYNC
Figure 4. SYNC Input Timing Requirements
t
CSSCLK
t
SSCLKSDFS
Figure 5. Signal Monitor SPORT Outpu
t
HSYNC
t
SSCLKSDO
DATA DATASMI SDO/OEB
t Timing (Divide-by-2 Mode)
06909-072
06909-082
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 6.
Parameter Rating
ELECTRICAL
AVDD, DVDD to AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
DRVDD to DRGND −0.3 V to +3.9 V
AGND to DRGND −0.3 V to +0.3 V
AVDD to DRVDD −3.9 V to +2.0 V
VIN + A/VIN + B, VIN − A/VIN − B to
−0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
AGND
CLK+, CLK− to AGND −0.3 V to +3.9 V
SYNC to AGND −0.3 V to +3.9 V
VREF to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
SENSE to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
CML to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
RBIAS to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
CSB to AGND −0.3 V to +3.9 V
SCLK/DFS to DRGND −0.3 V to +3.9 V
SDIO/DCS to DRGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
SMI SDO/OEB −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
SMI SCLK/PDWN −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
SMI SDFS −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
Output Data Pins to DRGND
Fast Detect Output Pins to DRGND
Data Clock Output Pins to DRGND
1
−0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
2
−0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
3
−0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
ENVIRONMENTAL
Operating Temperature Range
−40°C to +85°C
(Ambient)
Maximum Junction Temperature
150°C
Under Bias
Storage Temperature Range
−65°C to +150°C
(Ambient)
1
The output data pins are D0A/D0B to D9A/D9B for the CMOS configuration
and D0+/D0− to D9+/D9− for the LVDS configuration.
2 The fast detect output pins are FD0A/FD0B to FD3A/FD3B for the CMOS
configuration and FD0+/FD0− to FD3+/FD3−.
3
The data clock output pins are DCOA and DCOB for the CMOS configuration
and DCO+ and DCO− for the LVDS configuration.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
The exposed paddle must be soldered to the ground plane for
the LFCSP package. Soldering the exposed paddle to the
customer board increases the reliability of the solder joints,
maximizing the thermal capability of the package.
Table 7. Thermal Resistance
Airflow
locity
Package Type
64 Lead, 9 mm × 9 mm
LFCSP (CP-64-3)
Ve
(m/s)
0 18.8 0.6 6.0 °C/W
1.0 16.5 °C/W
1, 2
1, 3
θ
θ
JA
JC
1, 4
θ
Unit
JB
2.0 15.8 °C/W
1
Per JEDEC 51-7 standard and JEDEC 25-5 2S2P test board.
2
Per JEDEC JESD51-2 (still air) or JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air).
3
Per MIL-Std 883, Method 1012.1.
4
Per JEDEC JESD51-8 (still air).
Typical θJA and θJC are specified for a 4-layer board in still air.
Airflow increases heat dissipation, effectively reducing θ
JA
. In
addition, metal (such as metal traces through holes, ground,
and power planes) that is in direct contact with the package
leads reduces the θ
.
JA
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
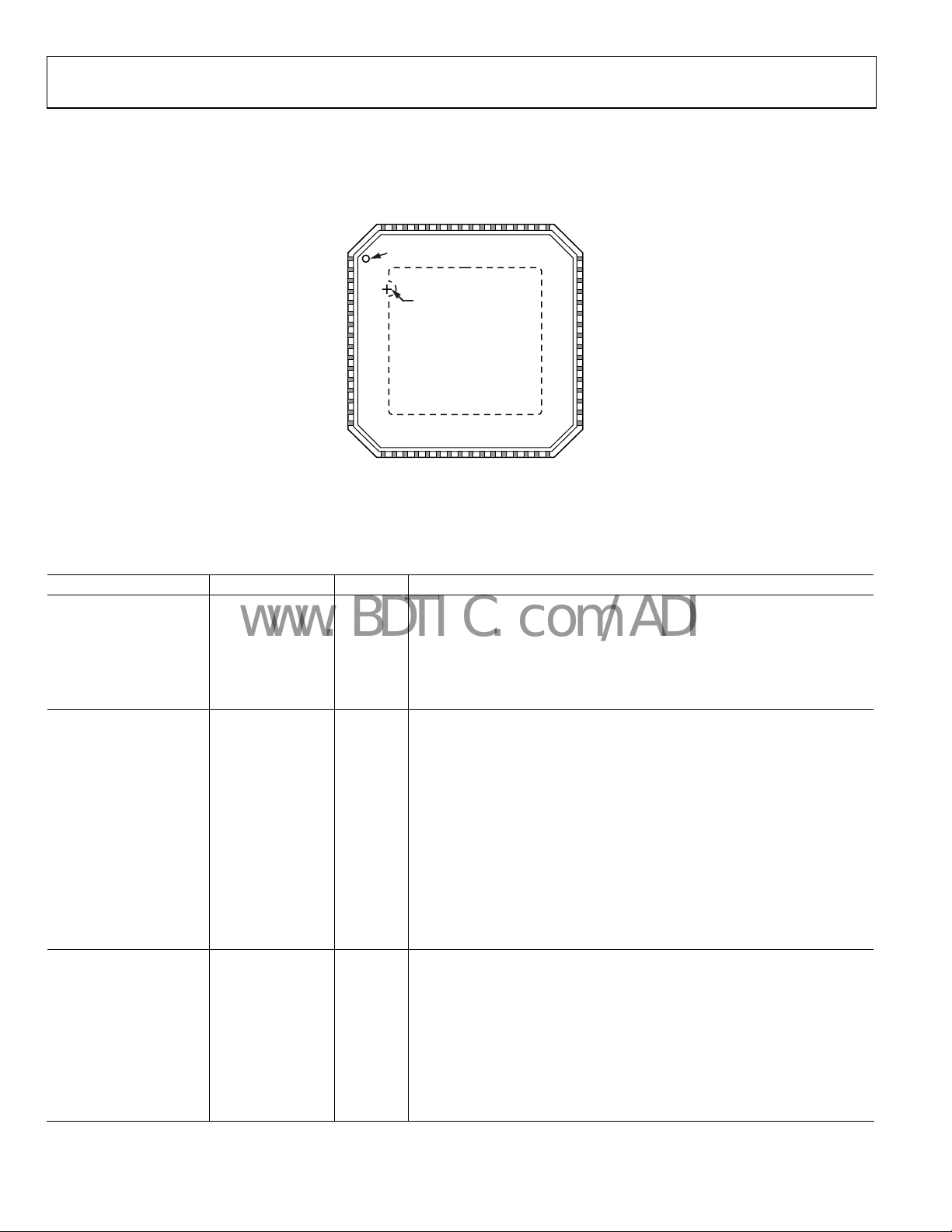
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
DRGND
D1B
D0B (LSB)
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DVDD
FD3B
FD2B
FD1B
FD0B
SYNC
CSB
CLK–
CLK+
49
48
SCLK/DFS
47
SDIO/DCS
46
AVDD
45
AVDD
44
VIN + B
43
VIN – B
42
RBIAS
41
CML
40
SENSE
39
VREF
38
VIN – A
37
VIN + A
36
AVDD
35
SMI SDFS
34
SMI SCLK/PDWN
33
SMI SDO/OEB
DRVDD
D2B
D3B
D4B
D5B
D6B
D7B
D8B
(MSB) D9B
DCOB
DCOA
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
(LSB) D0A
646362616059585756555453525150
PIN 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
INDICATO R
EXPOSED PADDLE, PIN 0
(BOTTOM OF PACKAGE)
AD9600
PARALLEL CMOS
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
DNC = DO NOT CONNECT
171819202122232425262728293031
D1A
D2A
D3A
D4A
D5A
D6A
D7A
D8A
FD0A
DRGND
DVDD
DRVDD
FD1A
(MSB) D9A
32
FD2A
FD3A
06909-002
Figure 6. Parallel CMOS Mode Pin Configuration (Top View)
Table 8. Parallel CMOS Mode Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
ADC Power Supplies
20, 64 DRGND Ground Digital Output Ground.
1, 21 DRVDD Supply Digital Output Driver Supply (1.8 V to 3.3 V).
24, 57 DVDD Supply Digital Power Supply (1.8 V Nominal).
36, 45, 46 AVDD Supply Analog Power Supply (1.8 V Nominal).
0 AGND Ground Analog Ground. Pin 0 is the exposed thermal pad on the bottom of the package.
ADC Inputs
37 VIN + A Input Differential Analog Input Pin (+) for Channel A.
38 VIN − A Input Differential Analog Input Pin (−) for Channel A.
44 VIN + B Input Differential Analog Input Pin (+) for Channel B.
43 VIN − B Input Differential Analog Input Pin (−) for Channel B.
39 VREF I/O Voltage Reference Input/Output.
40 SENSE Input Voltage Reference Mode Select (see Tab le 11 for details).
42 RBIAS Input External Reference Bias Resistor.
41 CML Output Common-Mode Level Bias Output for Analog Inputs.
49 CLK+ Input
ADC Master Clock True. The ADC clock can be driven using a single-ended
CMOS (see Figure 60 and Figure 61 for the recommended connection).
50 CLK− Input
ADC Master Clock Complement. The ADC clock can be driven using a single-
nded CMOS (see Figure 60 and Figure 61 for the recommended connection).
e
ADC Fast Detect Outputs
29 FD0A Output Channel A Fast Detect Indicator (see Tab le 14 for details).
30 FD1A Output Channel A Fast Detect Indicator (see Tab le 14 for details).
31 FD2A Output Channel A Fast Detect Indicator (see Tab le 14 for details).
32 FD3A Output Channel A Fast Detect Indicator (see Tab le 14 for details).
53 FD0B Output Channel B Fast Detect Indicator (see Tab le 14 for details).
54 FD1B Output Channel B Fast Detect Indicator (see Tab le 14 for details).
55 FD2B Output Channel B Fast Detect Indicator (see Tab le 14 for details).
56 FD3B Output Channel B Fast Detect Indicator (see Tab le 14 for details).
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
Digital Inputs
52 SYNC Input Digital Synchronization Pin (Slave Mode Only).
Digital Outputs
16 to 19, 22, 23,
25 to 28
62, 63, 2 to 9 D0B to D9B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
11 DCOA Output Channel A Data Clock Output.
10 DCOB Output Channel B Data Clock Output.
SPI Control
48 SCLK/DFS Input SPI Serial Clock/Data Format Select Pin in External Pin Mode.
47 SDIO/DCS I/O SPI Serial Data Input and Output/Duty Cycle Stabilizer in External Pin Mode.
51 CSB Input SPI Chip Select (Active Low).
Signal Monitor Port
33 SMI SDO/OEB I/O
35 SMI SDFS Output Signal Monitor Serial Data Frame Sync.
34 SMI SCLK/PDWN I/O Signal Monitor Serial Clock Output/Power-Down Input in External Pin Mode.
Do Not Connect
12 to 15, 58 to 61 DNC N/A Do Not Connect.
D0A to D9A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
Signal Monitor Serial Data Output/Output Enable I
External Pin Mode.
nput (Active Low) in
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DRGND
DNC
DNC
FD3+
FD3–
FD2+
FD2–
DVDD
FD1+
FD1–
FD0+
FD0–
SYNC
CSB
CLK–
CLK+
49
48
SCLK/DFS
47
SDIO/DCS
46
AVDD
45
AVDD
44
VIN + B
43
VIN – B
42
RBIAS
41
CML
40
SENSE
39
VREF
38
VIN – A
37
VIN + A
36
AVDD
35
SMI SDFS
34
SMI SCLK/PDWN
33
SMI SDO/OEB
DRVDD
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
(LSB) D0–
D0+
DCO–
DCO+
D1–
D1+
D2–
D2+
D3–
646362616059585756555453525150
PIN 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
INDICATO R
EXPOSED PADDLE, PIN 0
(BOTTOM OF PACKAGE)
AD9600
PARALLEL LVDS
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
DNC = DO NOT CONNECT
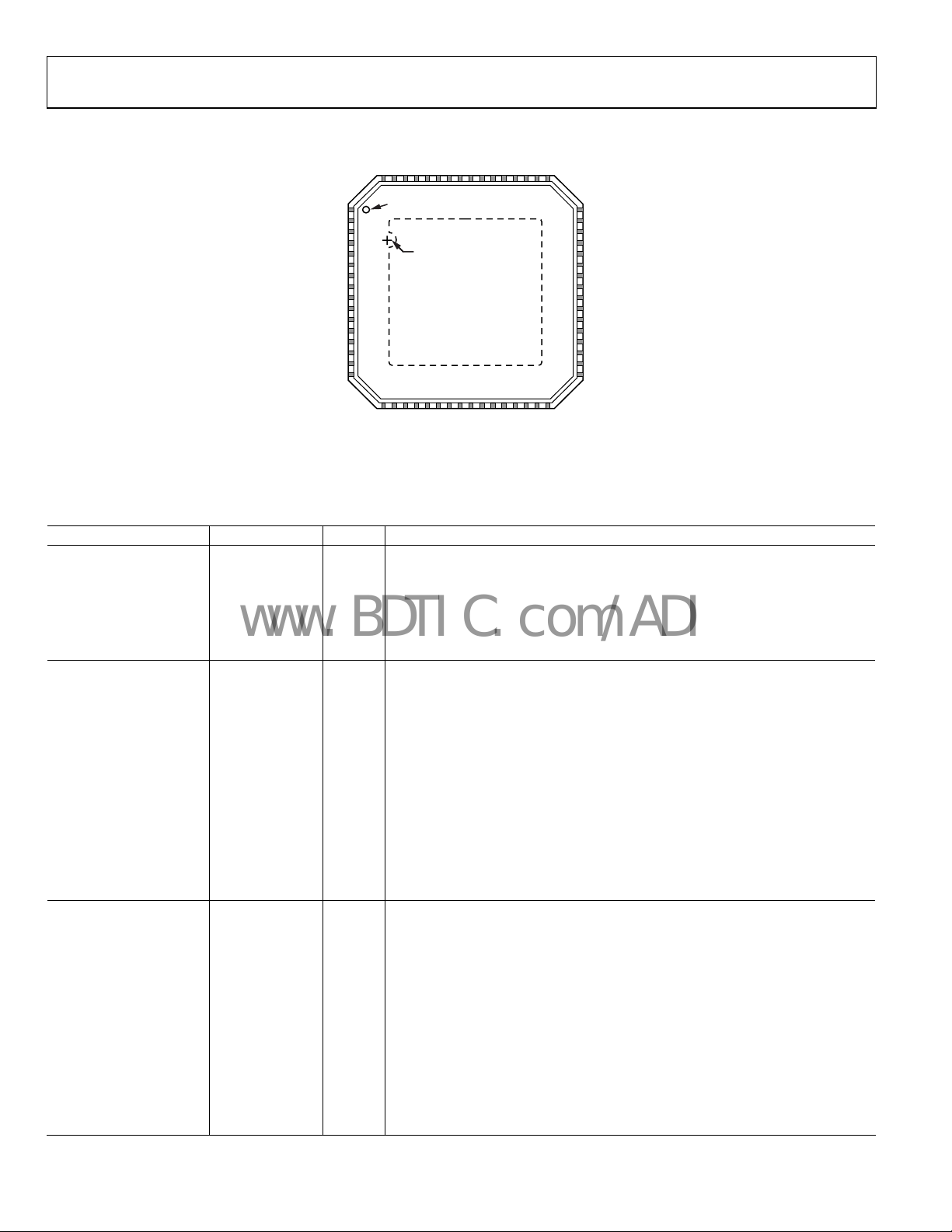
Figure 7. Interleaved Parallel LVDS M
171819202122232425262728293031
D5–
D6–
D7–
D4–
D3+
D5+
D4+
DRGND
DRVDD
DVDD
D8–
D6+
D7+
D8+
ode Pin Configuration (Top View)
32
D9–
(MSB) D9+
06909-003
Table 9. Interleaved Parallel LVDS Mode Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
ADC Power Supplies
20, 64 DRGND Ground Digital Output Ground.
1, 21 DRVDD Supply Digital Output Driver Supply (1.8 V to 3.3 V).
24, 57 DVDD Supply Digital Power Supply (1.8 V Nominal).
36, 45, 46 AVDD Supply Analog Power Supply (1.8 V Nominal).
0 AGND Ground Analog Ground. Pin 0 is the exposed thermal pad on the bottom of the package.
ADC Inputs
37 VIN + A Input Differential Analog Input Pin (+) for Channel A.
38 VIN − A Input Differential Analog Input Pin (−) for Channel A.
44 VIN + B Input Differential Analog Input Pin (+) for Channel B.
43 VIN − B Input Differential Analog Input Pin (−) for Channel B.
39 VREF I/O Voltage Reference Input/Output.
40 SENSE Input Voltage Reference Mode Select (see Table 11 for details).
42 RBIAS Input External Reference Bias Resistor.
41 CML Output Common-Mode Level Bias Output for Analog Inputs.
49 CLK+ Input
ADC Master Clock True. The ADC clock can be driven using a single-ended CMOS
(see Figure 60 and Figure 61 for the recommended connection).
50 CLK− Input
ADC Master Clock Complement. The ADC clock can be driven using a single-ended
CMOS (see Figure 60 and Figure 61 for the recommended connection).
ADC Fast Detect Outputs
54 FD0+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Fast Detect Indicator 0 True (see Table 1 4 for full details).
53 FD0− Output
Channel A/Channel B LVDS Fast Detect Indicator 0 Complement (see Tabl e 14
or details).
f
56 FD1+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Fast Detect Indicator 1 True (see Table 1 4 for details).
55 FD1− Output
Channel A/Channel B LVDS Fast Detect Indicator 1 Complement (see Table 14
or details).
f
59 FD2+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Fast Detect Indicator 2 True (see Table 1 4 for details).
58 FD2− Output
Channel A/Channel B LVDS Fast Detect Indicator 2 Complement (see Table 14
or details).
f
61 FD3+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Fast Detect Indicator 3 True (see Table 1 4 for details).
60 FD3− Output
Channel A/Channel B LVDS Fast Detect Indicator 3 Complement (see Tabl e 14
or details).
f
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
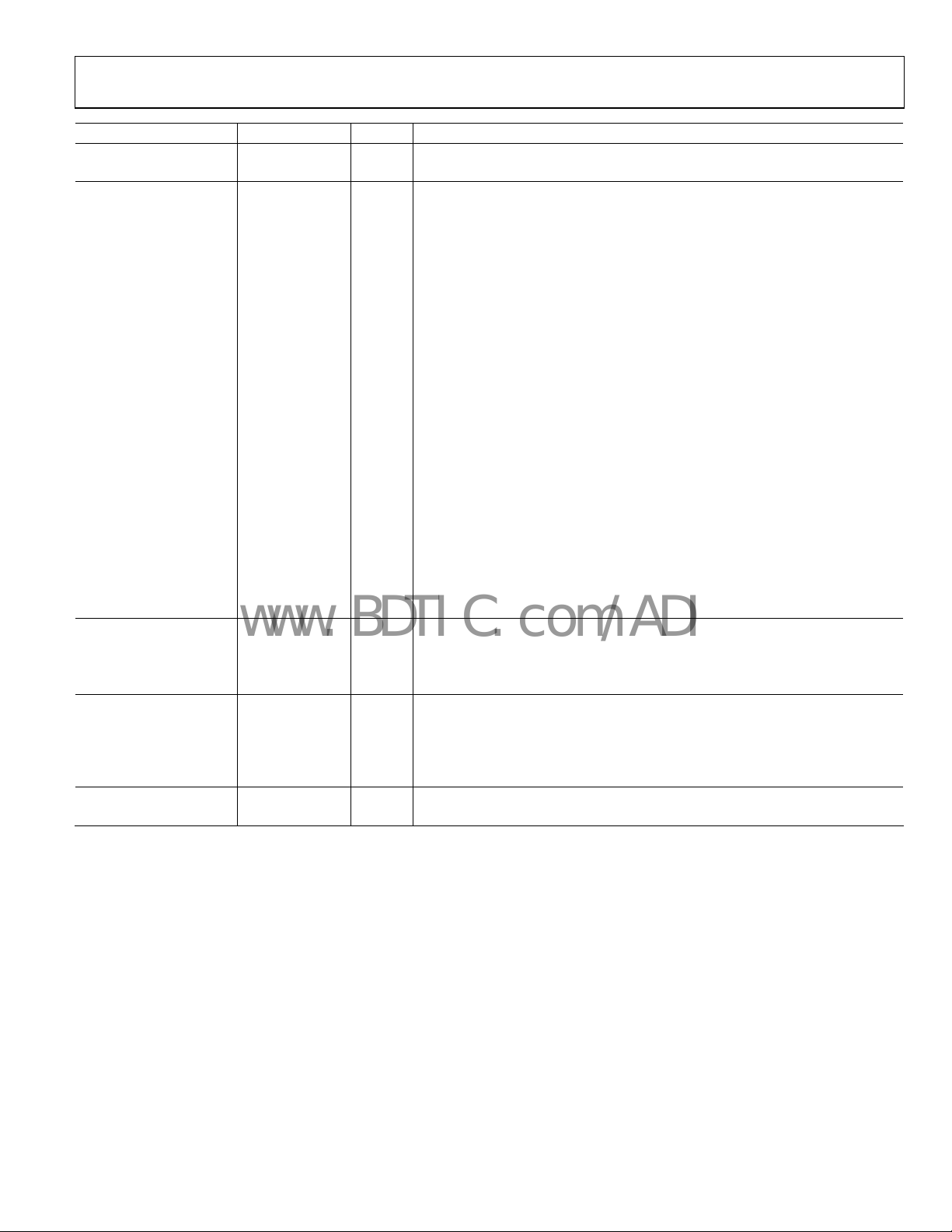
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
Digital Inputs
52 SYNC Input Digital Synchronization Pin (Slave Mode Only).
Digital Outputs
9 D0+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 0 True.
8 D0− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 0 Complement.
13 D1+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 1 True.
12 D1− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 1 Complement.
15 D2+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 2 True.
14 D2− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 2 Complement.
17 D3+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 3 True.
16 D3− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 3 Complement.
19 D4+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 4 True.
18 D4− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 4 Complement.
23 D5+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 5 True.
22 D5− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 5 Complement.
26 D6+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 6 True.
25 D6− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 6 Complement.
28 D7+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 7 True.
27 D7− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 7 Complement.
30 D8+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 8 True.
29 D8− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 8 Complement.
32 D9+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 9 True.
31 D9− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 9 Complement.
11 DCO+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Data Clock Output True.
10 DCO− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Data Clock Output Complement.
SPI Control
48 SCLK/DFS Input SPI Serial Clock/Data Format Select Pin in External Pin Mode.
47 SDIO/DCS I/O SPI Serial Data Input and Output/Duty Cycle Stabilizer in External Pin Mode.
51 CSB Input SPI Chip Select (Active Low).
Signal Monitor Port
33 SMI SDO/OEB I/O
35 SMI SDFS Output Signal Monitor Serial Data Frame Sync.
34 SMI SCLK/PDWN I/O Signal Monitor Serial Clock Output/Power-Down Input in External Pin Mode.
Do Not Connect
2 to 7, 62, 63 DNC N/A Do Not Connect.
Signal Monitor Serial Data Output/Output Enable I
External Pin Mode.
nput (Active Low) in
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 72
AD9600
V
C
A
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS
26kΩ
1kΩ
1kΩ
06909-008
LK+
IN
Figure 8. Analog Input Circuit
AVDD
1.2V
10kΩ 10kΩ
SCLK/DFS
06909-004
Figure 12. Equivalent SCLK/DFS Input Circuit
SENSE
CLK–
Figure 9. Equivalent Clock Input Circu
DRVDD
DRGND
Figure 10. Digital Output
DRVDD
DRVDD
26kΩ
SDIO/DCS
1kΩ
6909-005
it
6909-081
Figure 13. Equivalent SENSE Circuit
VDD
26kΩ
CSB
1kΩ
06909-009
06909-010
Figure 14. Equivalent CSB Input Circuit
AVDD
REF
06909-007
Figure 11. Equivalent SDIO/DCS Input Circuit
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 72
6kΩ
Figure 15. Equivalent VREF Circuit
06909-011

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, sample rate = 150 MSPS, DCS enabled, 1 V internal reference, 2 V p-p differential input,
VIN = −1.0 dBFS, 64k sample, and T
0
–20
–40
= 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
A
150MSPS
2.3MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 60.6dB (61. 6dBFS)
ENOB = 9.9 BITS
SFDR = 85.5dBc
–20
–40
0
150MSPS
140MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 60.5dB (61. 5dBFS)
ENOB = 9.8 BITS
SFDR = 83.5d Bc
–60
SECOND HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
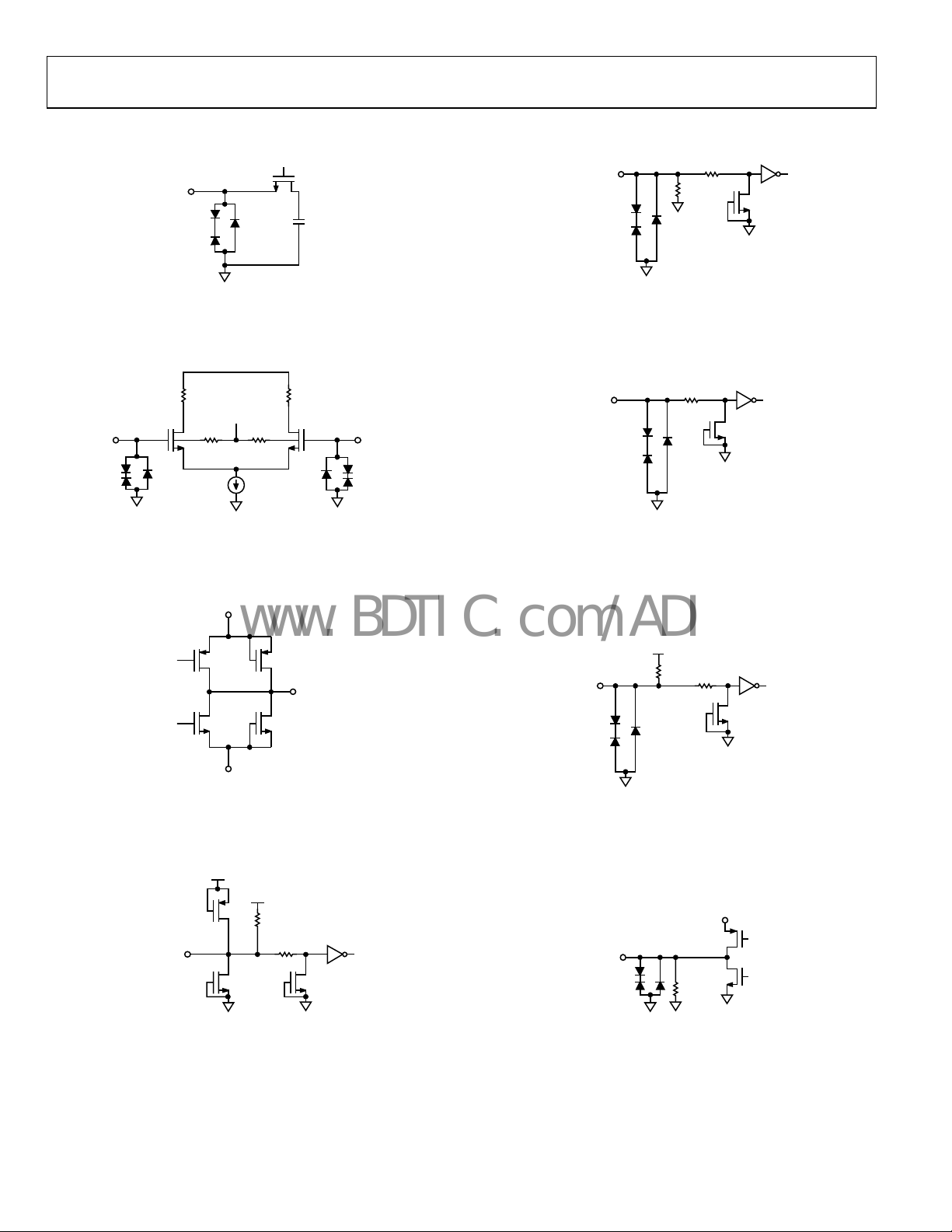
Figure 16. AD9600-150 Single-Tone FFT with f
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
Figure 17. AD9600-150 Single-Tone FFT with f
THIRD HARMONIC
0 10203040506070
0 10203040506070
FREQUENCY (MHz)
150MSPS
30.3MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 60.6dB (61. 6dBFS)
ENOB = 9.9 BITS
SFDR = 84.0dBc
THIRD HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
= 2.3 MHz
IN
= 30.3 MHz
IN
SECOND
HARMONIC
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
06909-029
Figure 19. AD9600-150 Single-Tone FFT with f
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
06909-030
Figure 20. AD9600-150 Single-Tone FFT with f
SECOND HARMONIC
0 10203040506070
150MSPS
220MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 60.4dB (61. 4dBFS)
ENOB = 9.7 BITS
SFDR = 77.0dBc
SECOND HARMONIC
0 10203040506070
THIRD HARMONIC
FREQUE NCY (MHz )
FREQUE NCY (MHz )
= 140 MHz
IN
THIRD HARMONIC
= 220 MHz
IN
06909-119
06909-120
0
150MSPS
70MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 60.6dB (61. 6dBFS)
–20
ENOB = 9.8 BITS
SFDR = 84.0dBc
–40
–60
SECOND HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
0 10203040506070
FREQUE NCY (MHz )
Figure 18. AD9600-150 Single-Tone FFT with f
THIRD HARMONIC
IN
= 70 MHz
06909-118
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 72
0
150MSPS
337MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 60.2dB (61. 2dBFS)
–20
ENOB = 9.7 BITS
SFDR = 74.0dBc
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
0 10203040506070
FREQUE NCY (MHz )
Figure 21. AD9600-150 Single-Tone FFT with f
THIRD HARMONIC
SECOND HARMONIC
IN
= 337 MHz
06909-121
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
0
–20
–40
SECOND HARMONIC
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
THIRD HARMONIC
150MSPS
440MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 60.0dB (61. 0dBFS)
ENOB = 9.6 BITS
SFDR = 70.0dBc
0
125MSPS
70.1MHz @ –1dBF S
SNR = 60.6dB (61. 6dBFS)
–20
ENOB = 9.8 BITS
SFDR = 85.0dBc
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
THIRD HARMONIC
SECOND HARMONIC
–100
–120
0 10203040506070
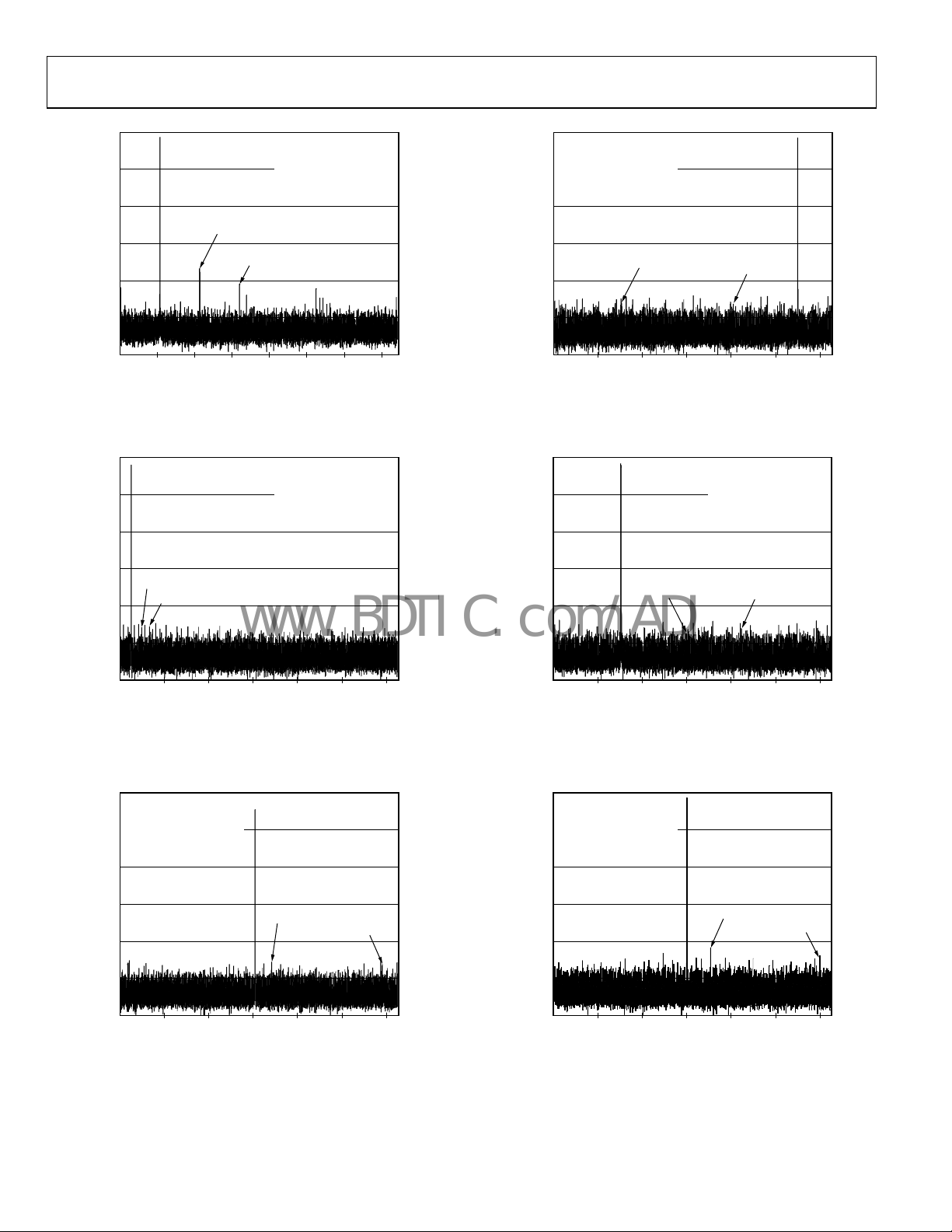
Figure 22. AD9600-150 Single-Tone FFT with f
0
–20
–40
–60
SECOND HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
THIRD HARMONIC
0 102030405060
Figure 23. AD9600-125 Single-Tone FFT with f
FREQUENCY (MHz)
125MSPS
2.3MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 60.6dB (61. 6dBFS)
ENOB = 9.8 BITS
SFDR = 86.5dBc
FREQUENCY (MHz)
= 440 MHz
IN
= 2.3 MHz
IN
–100
–120
0 102030405060
06909-122
Figure 25. AD9600-125 Single-Tone FFT with f
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
0 102030405060
06909-123
Figure 26. AD9600-125 Single-Tone FFT with f
FREQUENCY (MHz)
125MSPS
140.1MHz @ –1dBF S
SNR = 60.6dB (61. 6dBFS)
ENOB = 9.8 BITS
SFDR = 84.0dBc
SECOND HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
= 70.1 MHz
IN
THIRD HARMONIC
= 140.1 MHz
IN
06909-125
06909-126
0
125MSPS
30.3MHz @ –1dBF S
SNR = 60.6dB (61. 6dBFS)
–20
ENOB = 9.8 BITS
SFDR = 85.0dBc
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
0 102030405060
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 24. AD9600-125 Single-Tone FFT with f
THIRD HARMONIC
SECOND HARMONIC
= 30.3 MHz
IN
06909-124
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 72
0
125MSPS
220.1MHz @ –1dBF S
SNR = 60.5dB (61. 5dBFS)
–20
ENOB = 9.7 BITS
SFDR = 81.0dBc
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
0 102030405060
Figure 27. AD9600-125 Single-Tone FFT with f
THIRD HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SECOND HARMONIC
= 220.1 MHz
IN
06909-127
AD9600
–
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
120
95
100
80
60
85dB REFERENCE L INE
40
SNR/SFDR (dBc AND d Bm)
20
0
–60 –10–20–30–40–50 0
SNR (dBFS)
SNR (dBc)
AMPLITUDE (dBm)
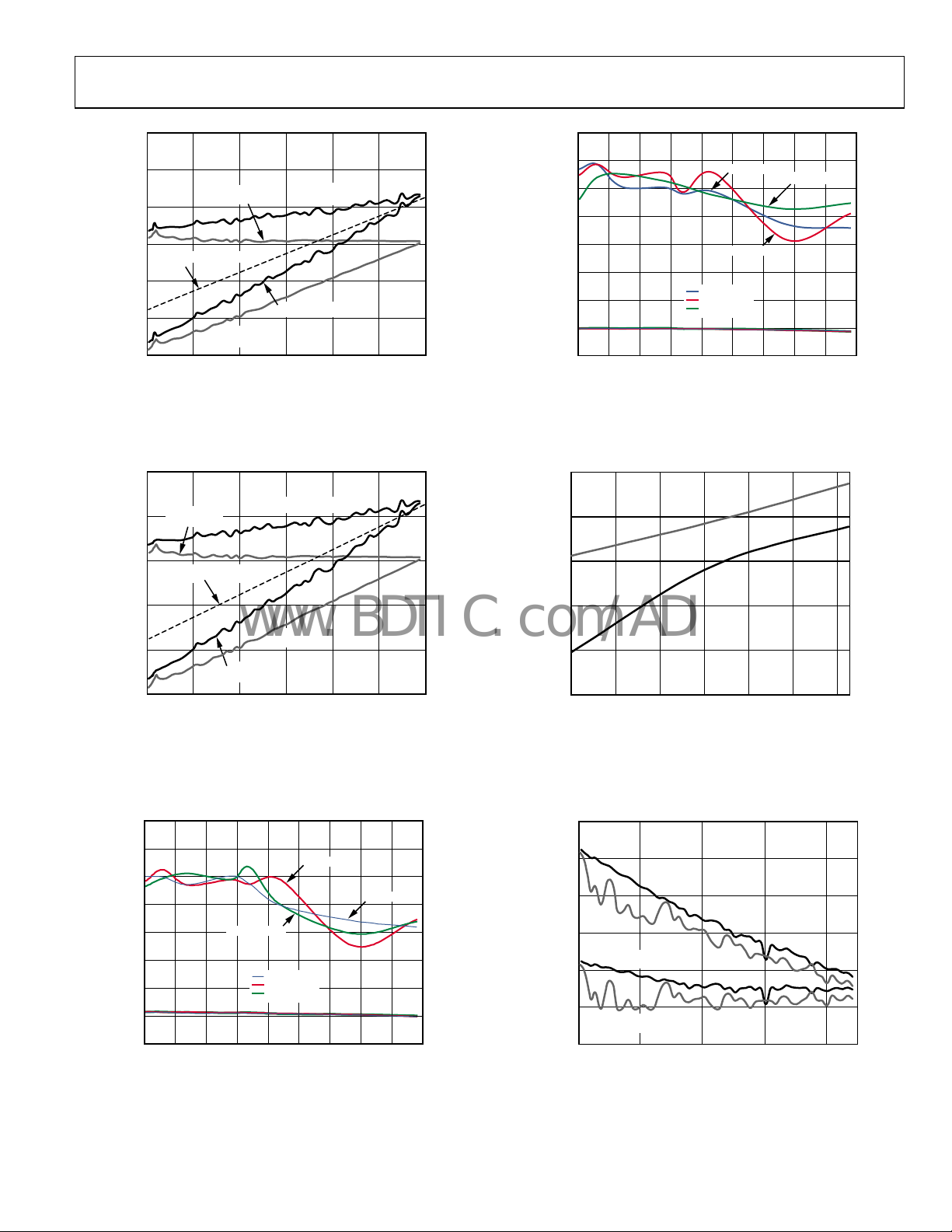
Figure 28. AD9600-150 Single-Tone S
= 2.4 MHz
f
IN
100
80
SNR (dBFS)
60
85dB REFERENCE L INE
40
SNR/SFDR (dBc AND dBm)
20
SFDR (dBc)
0
–60 –10–20–30–40–50 0
AMPLI TUDE (d Bm)
Figure 29. AD9600-150 Single-Tone S
= 98.12 MHz
f
IN
SFDR (dBFS)
SFDR (dBc)
NR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (A
SFDR (dBFS)
SNR (dBc)
NR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (A
) with
IN
) with
IN
90
85
80
75
70
SNR/SFDR (d Bc)
65
60
55
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
06909-031
INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 31. AD9600-150 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (f
SFDR +25°C
SFDR +85°C
SNR +25°C
SNR +85°C
SNR –40°C
SFDR –40°C
) and
IN
06909-034
Temperature with12 V p-p Full Scale
2.5
–3.0
–3.5
–4.0
GAIN ERROR (%F SR)
–4.5
–5.0
–40 806040
06909-032
TEMPERATURE (°C)
GAIN
OFFSET
200–20
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
OFFSET ERROR (%FSR)
06909-132
Figure 32. AD9600-150 Gain and Offset vs. Temperature
95
90
85
80
75
70
SNR/SFDR (d Bc)
65
60
55
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
SFDR –40°C
INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 30. AD9600-150 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (f
SNR +25°C
SNR +85°C
SNR –40°C
SFDR +85°C
SFDR +25°C
) and
IN
06909-033
Temperature with 2 V p-p Full Scale
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 72
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
SFDR/IMD3 ( dBc AND dBFS)
–100
–120
–60 –12–24–36–48
IMD3 (dBc)
SFDR (dBc)
SFDR (dBFS)
IMD3 (dBFS )
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBF S)
Figure 33. AD9600-150 Two-Tone SFDR/IMD3 vs. Input Amplitude (A
= 29.1 MHz, f
f
IN1
= 32.1 MHz, fS = 150 MSPS
IN2
) with
IN
06909-133
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
–20
0
150MSPS
169.1MHz @ –7dBF S
172.1MHz @ –7dBF S
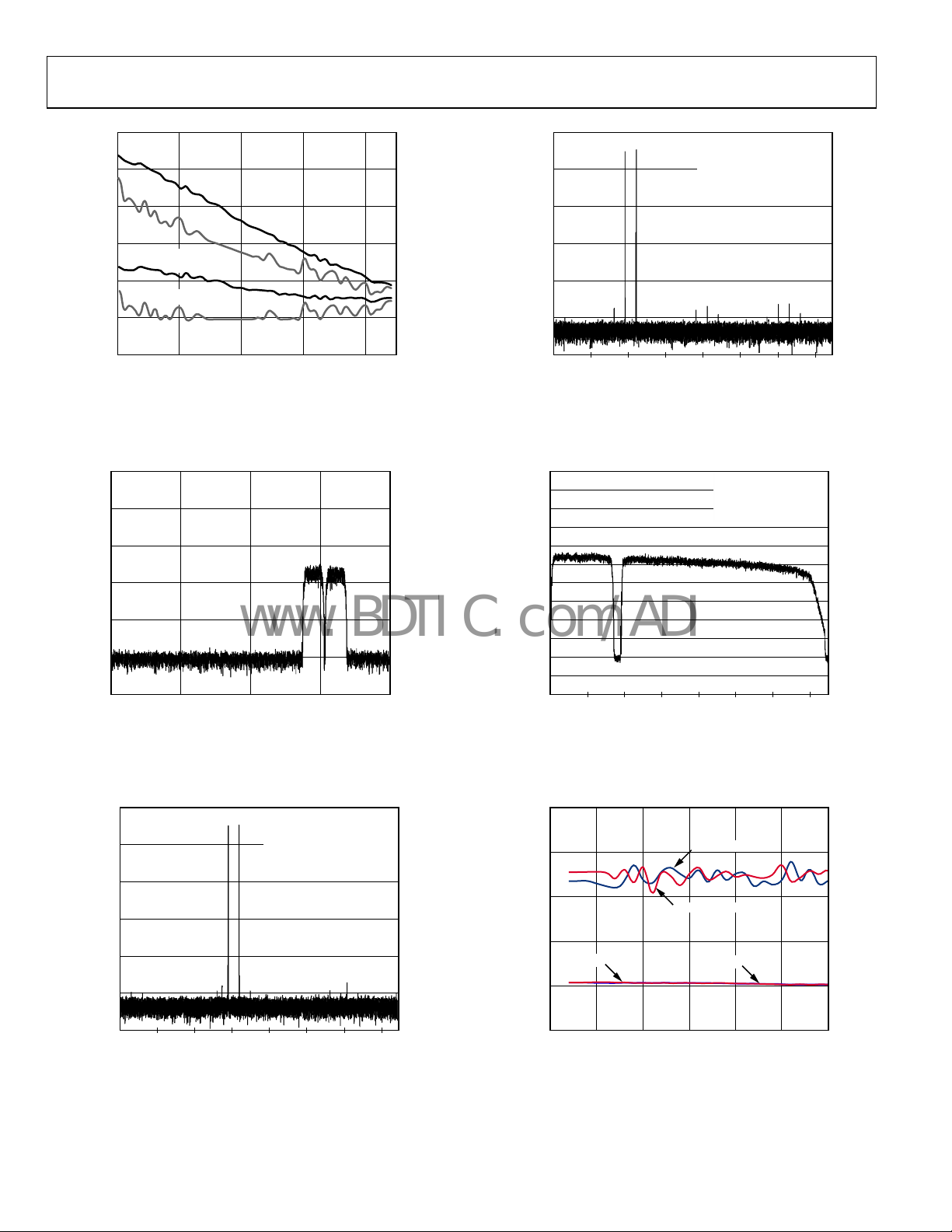
SFDR = 83.1dBc (90.1dBFS )
0
SFDR (dBc)
–20
–40
IMD3 (dBc)
–60
SFDR (dBFS)
–80
SFDR/IMD3 ( dBc AND dBFS)
–100
–120
IMD3 (dBFS)
–60 –12–24–36–48
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
Figure 34. AD9600-150 Two-Tone SFDR/IMD3 vs. Input Amplitude (A
= 169.1 MHz, f
f
IN1
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
= 172.1 MHz, fS = 150 MSPS
IN2
) with
IN
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
0 10203040506070
06909-134
Figure 37. AD9600-150 Two-Tone SFDR/IMD3 vs. Input Frequency (f
= 169.1 MHz, f
f
IN1
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
= 172.1 MHz, fS = 150 MSPS
IN2
NPR = 54.3dBc
NOTCH @ 18. 5MHz
NOTCH WIDTH = 3M Hz
) with
IN
06909-137
–120
0 15.36 30.72 46.08 61. 44
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 35. AD9600-125 Two 64k WCDMA Carriers with
= 170 MHz, fS = 125 MSPS
f
IN
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
0 10203040506070
INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
150MSPS
29.1MHz @ –7dBF S
32.1MHz @ –7dBF S
SFDR = 86.1dBc (93.1dBFS )
Figure 36. AD9600-150 Two-Tone SFDR/IMD3 vs. Input Frequency (f
= 29.1 MHz, f
f
IN1
= 32.1 MHz, fS = 150 MSPS
IN2
) with
IN
–120
07605040302010
06909-135
FREQUENCY (MHz)
0
06909-138
Figure 38. AD9600-150 Noise Power Ratio (NPR)
100
90
80
70
SNR/SFDR (dBc)
06909-136
SNR—SIDE A
60
50
0 25 50 75 100 125 150
Figure 39. AD9600-150 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Clock Frequency (f
f
SFDR—SIDE B
SFDR—SIDE A
SNR—SIDE B
ENCODE (MSPS)
= 2.3 MHz
IN1
) with
S
06909-035
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 72
AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
12
10
8
0.10 LSB rms
100
95
SFDR DCS ON
90
85
6
4
NUMBER OF HIT S (1M)
2
0
OUTPUT CODE
Figure 40. AD9600 Grounded Input Histogram
0.10
0.05
0
INL ERROR (LSB)
–0.05
–0.10
0 128 256 384 512 640 768 896 1024
Figure 41. AD9600 INL with f
OUTPUT CODE
= 10.3 MHz
IN1
80
75
SNR/SFDR (d Bc)
SNR DCS ON
70
65
N + 3N + 2N + 1NN – 1N – 2N – 3
06909-140
60
20 806040
Figure 43. AD9600-150 SNR/SFDR vs. Duty Cycle with f
95
90
85
80
75
70
SNR/SFDR (d Bc)
65
60
55
0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1. 1 1.2 1.3
06909-036
INPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 44. AD9600-150 SNR/SFDR vs. Input
f
IN1
SFDR DCS OFF
SNR DCS OFF
DUTY CYCLE (%)
SFDR
SNR
Common-Mode Voltage (V
= 30 MHz
= 10.3 MHz
IN1
CM
06909-143
06909-144
) with
0.100
0.075
0.050
0.025
0
–0.025
DNL ERROR (LSB)
–0.050
–0.075
–0.100
0 128 256 384 512 640 768 896 1024
Figure 42. AD9600 DNL with f
OUTPUT CO DE
= 10.3 MHz
IN1
06909-037
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
THEORY OF OPERATION
The AD9600 dual ADC design can be used for diversity
reception of signals, where the ADCs are operating identically
on the same carrier but from two separate antennae. The ADCs
can also be operated with independent analog inputs. The user
can sample any f
/2 frequency segment from dc to 200 MHz
S
using appropriate low-pass or band-pass filtering at the ADC
inputs with little loss in ADC performance. Although operation
of up to 450 MHz analog input is permitted, ADC distortion
increases at frequencies toward the higher end of this range.
In nondiversity applications, the AD9600 can be used as a
eband receiver where one ADC is used for I input data and
bas
the other used for Q input data.
Synchronization capability is provided to allow synchronized
g among multiple channels or multiple devices.
timin
Programming and control of the AD9600 is accomplished using
a 3-b
it SPI-compatible serial interface.
ADC ARCHITECTURE
The AD9600 architecture consists of a dual front-end sampleand-hold amplifier (SHA) followed by a pipelined switchedcapacitor ADC. The quantized outputs from each stage are
combined into a final 10-bit result in the digital correction
logic. The pipelined architecture permits the first stage to
operate on a new input sample while the remaining stages
operate on preceding samples. Sampling occurs on the rising
edge of the clock.
Each stage of the pipeline excluding the last consists of a low
esolution flash ADC connected to a switched-capacitor digital-
r
to-analog converter (DAC) and an interstage residue amplifier
(a multiplying digital-to-analog converter (MDAC)). The residue
amplifier magnifies the difference between the reconstructed
DAC output and the flash input for the next stage in the
pipeline. One bit of redundancy is used in each stage to
facilitate digital correction of flash errors. The last stage simply
consists of a flash ADC.
The input stage of each channel contains a differential SHA that
ca
n be ac- or dc-coupled in differential or single-ended modes.
The output-staging block aligns the data, corrects errors, and
passes the data to the output buffers. The output buffers are
powered from a separate supply, allowing adjustment of the
output voltage swing. During power-down, the output buffers
go into a high impedance state.
ANALOG INPUT CONSIDERATIONS
The analog input to the AD9600 is a differential switchedcapacitor SHA that has been designed for optimum
performance while processing a differential input signal.
The clock signal alternatively switches the SHA between sample
ode and hold mode (see Figure 45). When the SHA is
m
swi
tched into sample mode, the signal source must be capable
of charging the sample capacitors and settling within one-half
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 72
of a clock cycle. A small resistor in series with each input can
help reduce the peak transient current required from the output
stage of the driving source. A shunt capacitor can be placed
across the inputs to provide dynamic charging currents. This
passive network creates a low-pass filter at the ADC’s input;
therefore, the precise values are dependent on the application.
In undersampling (IF sampling) applications, any shunt capacitors
ould be reduced. In combination with the driving source
sh
impedance, the shunt capacitors limit the input bandwidth. See
the
AN-742 Application Note, F
requency Domain Response of
Switched-Capacitor ADCs; the AN-827 Application Note, A
esonant Approach to Interfacing Amplifiers to Switched-Capacitor
R
ADCs; and the Analog Dialogue article “Tr an s fo r me r- C o up le d
F
ront-End for Wideband A/D Converters” (Volume 39, April
2005
) for more information. In general, the precise values are
dependent on the application.
S
C
H
C
H
S
06909-013
VIN+
C
PIN, PAR
VIN–
C
PIN, PAR
Figure 45. Switched-Capac
S
S
C
S
H
C
S
itor SHA Input
For best dynamic performance, the source impedances driving
VIN+ and VIN− should be matched.
An internal differential reference buffer creates positive and nega
tive reference voltages that define the input span of the ADC core.
The span of the ADC core is set by the buffer to 2 × VREF.
Input Common Mode
The analog inputs of the AD9600 are not internally dc-biased.
Therefore, in ac-coupled applications, the user must provide this
bias externally. Setting the device so that V
= 0.55 × AVDD is
CM
recommended for optimum performance, but the device can
function over a wider range with reasonable performance (see
Figure 44). An on-board common-mode voltage reference is
cluded in the design and is available from the CML pin.
in
Optimum performance is achieved when the common-mode
voltage of the analog input is set by the CML pin voltage (typically
0.55 × AVDD). The CML pin must be decoupled to ground by a
0.1 F capacitor as described in the
Applications section.
Differential Input Configurations
Optimum performance is achieved while driving the AD9600
in a differential input configuration. For baseband applications,
the AD8138, ADA4937-2, and ADA4938-2 differential drivers
p
rovide excellent performance and a flexible interface to the
ADC. The output common-mode voltage of the AD8138 is

AD9600
2
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
easily set with the CML pin of the AD9600 (see Figure 46), and
the driver can be configured in a Sallen-Key filter topology to
band limit the input signal.
1V p-p
49.9Ω
0.1µF
499Ω
523Ω
499Ω
AD8138
499Ω
R
C
R
AVDD
VIN+
AD9600
VIN–
CML
Figure 46. Differential Input Configuration Using the AD8138
06909-014
For baseband applications where SNR is a key parameter,
differential transformer coupling is the recommended input
configuration. An example is shown in Figure 47. The CML
v
oltage can be connected to the center tap of the transformer’s
secondary winding to bias the analog input.
The signal characteristics must be considered when selecting a
nsformer. Most RF transformers saturate at frequencies
tra
below a few megahertz. Excessive signal power can cause core
saturation, which leads to distortion.
R
V p-p
49.9Ω
R
0.1µF
Figure 47. Differential Transformer-Coupled Configuration
VIN+
AD9600
C
VIN–
CML
06909-015
At input frequencies in the second Nyquist zone and above, the
noise performance of most amplifiers is not adequate to achieve
the true SNR performance of the AD9600. For applications where
SNR is a key parameter, differential double-balun coupling is
the recommended input configuration. An example is shown
in
Figure 49.
2V p-p
0.1µF
SP
A
S
Figure 49. Differential Double-Balun Input Configuration
0.1µF
P
0.1µF
CC
An alternative to using a transformer-coupled input at
requencies in the second Nyquist zone is to use the
f
ferential driver. An example is shown in Figure 50. See the
dif
AD8352
AD8352 data sheet for more information.
In any configuration, the value of the shunt capacitor, C, is
dep
endent on the input frequency and source impedance and may
need to be reduced or removed. Ta b le 1 0 lists the recommended
val
ues to set the RC network. However, the actual values are
dependent on the input signal; therefore,
e used as a starting guide.
b
Tabl e 10 should only
Table 10. Example RC Network
Frequency Range (MHz) R Series (Ω, Each) C Differential (pF)
0 to 70 33 15
70 to 200 33 5
200 to 300 15 5
>300 15 Open
Single-Ended Input Configuration
A single-ended input can provide adequate performance in
cost-sensitive applications. In this configuration, SFDR and
distortion performance degrade due to the large input commonmode swing. If the source impedances on each input are matched,
there should be little effect on SNR performance.
d
etails a typical single-ended input configuration.
AVDD
10µF
1kΩ
25Ω
25Ω
2V p-p
0.1µF
49.9Ω
10µF
R
C
R
0.1µF
1kΩ
AVDD
1kΩ
1kΩ
0.1µF
Figure 48. Single-Ended Input Configuration
VIN+
AD9600
VIN–
CML
R
C
R
06909-228
Figure 48
VIN+
ADC
AD9600
VIN–
06909-018
ANALOG INPUT
ANALOG INPUT
16
1
2
R
C
D
0.1µF
R
D
G
3
4
5
0Ω
8, 13
AD8352
10
14
0.1µF
0.1µF
0Ω
Figure 50. Differential Input Configuration Using the AD8352
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 72
0.1µF
0.1µF
11
200Ω
200Ω
0.1µF
R
R
0.1µF
VIN+
C
AD9600
VIN–
CML
06909-270

AD9600
F
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
A stable and accurate voltage reference is built into the AD9600.
The input range can be adjusted by varying the reference voltage
applied to the AD9600, using either the internal reference or an
externally applied reference voltage. The input span of the ADC
tracks reference voltage changes linearly. The various reference
modes are summarized in this section. The
Deco
upling section describes the best PCB layout practices for
t
he reference.
Internal Reference Connection
A comparator within the AD9600 detects the potential at the
SENSE pin and configures the reference into four possible modes,
which are summarized in Tabl e 1 1 . If SENSE is grounded, the
re
ference amplifier switch is connected to the internal resistor
divider (see
ENSE pin to VREF switches the reference amplifier output to
S
Figure 51), setting VREF to 1.0 V. Connecting the
the SENSE pin, completing the loop and providing a 0.5 V
reference output. If a resistor divider is connected external to
the chip as shown in
S
ENSE pin. This puts the reference amplifier in a noninverting
Figure 52, the switch again selects the
mode with the VREF output defined as
R2
⎞
⎛
VREF 15.0
+×=
⎟
⎜
R1
⎠
⎝
The input range of the ADC always equals twice the voltage at
he reference pin for either an internal or an external reference.
t
Reference
If the internal reference of the AD9600 is used to drive multiple
converters to improve gain matching, the loading of the reference
by the other converters must be considered. Figure 53 depicts
ow the internal reference voltage is affected by loading.
h
0
–0.25
–0.50
–0.75
VIN + A/VIN + B
VIN – A/VIN – B
ADC
CORE
VREF
0.1µF1µ
Figure 52. Programmable Reference Configuration
R2
SENSE
R1
SELECT
LOGIC
VREF = 1.0V
0.5V
AD9600
VREF = 0.5V
06909-020
VIN + A/VIN + B
VIN – A/V IN – B
ADC
CORE
VREF
0.1µF1µF
SENSE
Figure 51. Internal Reference Configuration
SELECT
LOGIC
0.5V
AD9600
06909-019
–1.00
REFERENCE VO LTAGE ERROR (%)
–1.25
02
0.5 1. 0 1.5
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 53. VREF Accuracy vs. Load
.0
Table 11. Reference Configuration Summary
Selected Mode SENSE Voltage Resulting VREF (V) Resulting Differential Span (V p-p)
External Reference AVDD N/A 2 × external reference
Internal Fixed Reference VREF 0.5 1.0
Programmable Reference 0.2 V to VREF
R2
⎞
⎛
15.0
⎜
⎝
+×
⎟
R1
⎠
(see Figure 52)
2 × VREF
Internal Fixed Reference AGND to 0.2 V 1.0 2.0
6909-280
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 72

AD9600
A
C
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
External Reference Operation
The use of an external reference may be necessary to enhance
the gain accuracy of the ADC or to improve the thermal drift
characteristics. Figure 54 shows the typical drift characteristics
f the internal reference in 1.0 V mode.
o
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
REFERENCE VO LTAGE ERROR (mV)
–2.0
–2.5
–40
–200 20406080
TEMPERATURE (° C)
06909-299
Figure 54. Typical VREF Drift
When the SENSE pin is tied to AVDD, the internal reference is
disabled, allowing the use of an external reference. An internal
reference buffer loads the external reference with an equivalent
6 kΩ load (see Figure 15). The internal buffer generates the
ositive and negative full-scale references for the ADC core.
p
Therefore, the external reference must be limited to a maximum
of 1.0 V.
CLOCK INPUT CONSIDERATIONS
For optimum performance, the AD9600 sample clock inputs
(CLK+ and CLK−) should be clocked with a differential signal.
The signal is typically ac-coupled into the CLK+ and CLK− pins
via a transformer or capacitors. These pins are biased internally
(see Figure 55) and require no external bias.
AVDD
1.2V
CLK+
2pF
Figure 55. Equivalent Clock Input Circuit
Clock Input Options
The AD9600 has a very flexible clock input structure. The clock
input can be a CMOS, LVDS, LVPECL, or sine wave signal.
Regardless of the type of signal being used, the jitter of the clock
source is of the most concern, as described in the Jitter
onsiderations
C
section.
Figure 56 and Figure 57 show preferred methods for clocking the
AD9600
(at clock rates of up to 625 MHz). A low jitter clock source
is converted from a single-ended signal to a differential signal
using either an RF balun or an RF transformer.
2pF
CLK–
06909-023
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 72
The RF balun configuration is recommended for clock
requencies between 125 MHz and 625 MHz, and the RF
f
transformer is recommended for clock frequencies from 10 MHz
to 200 MHz. The back-to-back Schottky diodes across the
secondary transformer or balun limit clock excursions into the
AD9600 to approximately 0.8 V p-p differential.
This helps prevent the large voltage swings of the clock from
f
eeding through to other portions of the AD9600 while
preserving the fast rise and fall times of the signal that are
critical to low jitter performance.
XFMR
0.1µF
®
0.1µF0.1µF
0.1µF
0.1µF1nF
0.1µF
SCHOTTKY
DIODES :
HSMS2822
SCHOTTKY
DIODES :
HSMS2822
CLK+
ADC
AD9600
CLK–
CLK+
ADC
AD9600
CLK–
06909-057
Mini-Circuits
ADT1-1WT, 1:1Z
CLK+
50Ω
100Ω
Figure 56. Transformer-Coupled Differential Clock (up to 200 MHz)
CLK+
50Ω
1nF
Figure 57. Balun-Coupled Differential Clock (up to 625 MHz)
If a low jitter clock source is not available, another option is to
ac-couple a differential PECL signal to the sample clock input
pins as shown in Figure 58. The AD9510/AD9511/AD9512/
AD9513/AD9514/AD9515 family of clock drivers offers excellent
tter performance.
ji
D9510/AD9511/AD9512/
AD9513/AD9514/AD9515
LK+
CLK–
50kΩ 50kΩ
0.1µF
0.1µF
PECL
DRIVER
0.1µF
CLK+
100Ω
0.1µF
240Ω240Ω
ADC
AD9600
CLK–
Figure 58. Differential PECL Sample Clock (up to 150 MSPS)
A third option is to ac-couple a differential LVDS signal to the
sample clock input pins as shown in Figure 59. The AD9510/
AD9511/AD9512/AD9513/AD9514/AD9515 family of clock
rivers offer excellent jitter performance.
d
AD9510/AD9511/AD9512/
AD9513/AD9514/AD9515
CLK+
CLK–
50kΩ
0.1µF
0.1µF
50kΩ
LVDS
DRIVER
Figure 59. Differential LVDS Sample Clock (up to 150 MSPS)
0.1µF
100Ω
0.1µF
CLK+
ADC
AD9600
CLK–
06909-024
06909-025
06909-026

AD9600
C
(
)
×π−
=
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
In some applications, it is acceptable to drive the sample clock
inputs with a single-ended CMOS signal. In such applications,
CLK+ should be driven directly from a CMOS gate, and the
CLK− pin should be bypassed to ground with a 0.1 µF capacitor
in parallel with a 39 kΩ resistor (see Figure 60). Although the
CLK+ in
put circuit supply is AVDD (1.8 V), this input is designed
to withstand input voltages of up to 3.6 V and therefore offers
several selections for the drive logic voltage.
AD9510/AD9511/AD9512/
AD9513/AD9514/AD9515
VCC
0.1µF
OPTIONAL
100Ω
OPTIONAL
100Ω
39kΩ
0.1µF
0.1µF
0.1µF
CLK+
ADC
AD9600
CLK–
CLK+
ADC
AD9600
CLK–
0.1µF
1kΩ
CLK+
50Ω
Figure 60. Single-Ended 1.8 V CMOS Sample Clock (up to 150 MSPS)
VCC
LK+
0.1µF
50Ω
Figure 61 Single-Ended 3.3 V CMOS Sample Clock (up to 150 MSPS)
CMOS
DRIVER
1kΩ
AD9510/AD9511/AD9512/
AD9513/AD9514/AD9515
1kΩ
CMOS
DRIVER
1kΩ
Input Clock Divider
The AD9600 contains an input clock divider with the ability to
divide the input clock by integer values between 1 and 8. If a
divide ratio other than 1 is selected, the duty cycle stabilizer is
automatically enabled.
The AD9600 clock divider can be synchronized by using the
ernal SYNC input. Bit 1 and Bit 2 of Register 0x100 allow the
ext
clock divider to be resynchronized either on every SYNC signal
or on only the first SYNC signal after the register is written. A
valid SYNC causes the clock divider to reset to its initial state.
This synchronization feature allows aligning the clock dividers of
multiple devices to guarantee simultaneous input sampling.
Clock Duty Cycle
Typical high speed ADCs use both clock edges to generate a
variety of internal timing signals. As a result, these ADCs may
be sensitive to the clock duty cycle. Commonly, a ±5% tolerance
is required on the clock duty cycle to maintain dynamic
performance characteristics. The AD9600 contains a duty cycle
stabilizer (DCS) that retimes the nonsampling (or falling) edge,
providing an internal clock signal with a nominal 50% duty
cycle. This allows the user to provide a wide range of clock
input duty cycles without affecting the performance of the
AD9600. When the SDIO/DCS pin functions as DCS, noise and
distortion performance are nearly flat for a wide range of duty
cycles, as shown in
Figure 43.
06909-027
06909-028
Jitter in the rising edge of the input is an important concern, and it
is
not reduced by the internal stabilization circuit. The duty cycle
control loop does not function for clock rates less than 20 MHz
nominally. The loop has a time constant associated with it that
needs to be considered if the clock rate may change dynamically.
This requires a wait time of 1.5 s to 5 s after a dynamic clock
frequency increase or decrease before the DCS loop is relocked
to the input signal. During this time, the loop is not locked, the
DCS loop is bypassed, and the internal device timing is dependent
on the duty cycle of the input clock signal. In such applications,
it may be appropriate to disable the duty clock stabilizer. In all
other applications, enabling the DCS circuit is recommended to
maximize ac performance.
Jitter Considerations
High speed, high resolution ADCs are sensitive to the quality of
the clock input. The degradation in SNR at a given input
frequency (f
) due to jitter (tJ) can be calculated as
IN
tfSNR
2log20
JIN
In this equation, the rms aperture jitter represents the root
m
ean square of all jitter sources, including the clock input,
analog input signal, and ADC aperture jitter. IF undersampling
applications are particularly sensitive to jitter (see
65
60
MEASURED
55
SNR (dBc)
50
45
1 10 100 1000
Figure 62. SNR vs. Input Frequency and Jitter
INPUT FREQ UENCY (MHz)
Figure 62).
0.05ps
0.20ps
0.5ps
1.0ps
1.50ps
2.00ps
2.50ps
3.00ps
06909-162
The clock input should be treated as an analog signal in cases
where aperture jitter may affect the dynamic range of the AD9600.
Power supplies for clock drivers should be separated from the
ADC output driver supplies to avoid modulating the clock signal
with digital noise. Low jitter, crystal-controlled oscillators make
the best clock sources. If the clock is generated from another
type of source (by gating, dividing, or another method), it
should be retimed by the original clock during the last step.
Refer to the AN-501 Application Note and the AN-756
pplication Note for more in-depth information about jitter
A
erformance as it relates to ADCs.
p
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
POWER DISSIPATION AND STANDBY MODE
As shown in Figure 63, the power dissipated by the AD9600 is
proportional to its sample rate. In CMOS output mode, the
digital power dissipation is determined primarily by the
strength of the digital drivers and the load on each output bit.
The maximum DRVDD current (I
DRVDDDRVDD
where N is t
he number of output bits (22 in the case of AD9600
with the fast detect output pins disabled).
This maximum current occurs when every output bit switches
n every clock cycle, that is, a full-scale square wave at the
o
Nyquist frequency, f
/2. In practice, the DRVDD current is
CLK
established by the average number of output bits switching,
which is determined by the sample rate and the characteristics
of the analog input signal. Reducing the capacitive load presented
to the output drivers can minimize digital power consumption.
The data in
c
onditions as the Typical Performance Characteristics, with a 5
pF lo
TOTAL POWER (W)
TOTAL POWER (W)
Figure 63 was taken with the same operating
ad on each output driver.
1.25
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
0 255075100125150
Figure 63. AD9600-150 Power and Current vs. Sample Rate
1.25
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
0 25 50 75 100 125
Figure 64. AD9600-125 Power and Current vs. Sample Rate
TOTAL POWER
I
ENCODE (MSPS)
I
AVDD
TOTAL POWER
ENCODE (MSPS)
DVDD
I
DVDD
) can be calculated as
DRVDD
NfCVI
×××=
AVDD
I
DRVDD
I
DRVDD
CLKLOAD
I
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
SUPPLY CURRENT (A)
0.1
0
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
SUPPLY CURRENT (A)
0.1
0
1.00
0.75
0.50
TOTAL POWER (W)
0.25
0
0 100755025
I
TOTAL POWER
I
DRVDD
I
DVDD
ENCODE (MSPS)
AVDD
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
SUPPLY CURRENT (A)
06909-999
Figure 65. AD9600-105 Power and Current vs. Sample Rate
By asserting the PDWN mode (either through the SPI port or
by asserting the PDWN pin high), the AD9600 is placed into
power-down mode. In this state, the ADC typically dissipates
2.5 mW. During power-down, the output drivers are placed in a
high impedance state. Asserting the PDWN pin low returns the
AD9600 to its normal operating mode. Note that PDWN is
referenced to the digital output driver supply (DRVDD) and
should not exceed that supply voltage.
In power-down mode, low power dissipation is achieved by
utting down the reference, reference buffer, biasing networks,
sh
and clock. Internal capacitors are discharged when entering
power-down mode and must be recharged when returning to
normal operation. As a result, the wake-up time is related to the
time spent in power-down mode: shorter power-down cycles
result in proportionally shorter wake-up times.
When using the SPI port interface, the user can place the ADC
in
to power-down or standby mode. Standby mode allows the
user to keep the internal reference circuitry powered when
06909-038
faster wake-up times are required. See the
Reg
ister Description
section for more details.
Memor y Map
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
The AD9600 output drivers can be configured to interface with
1.8 V to 3.3 V logic families by matching DRVDD to the digital
supply of the interfaced logic.
In CMOS output mode, the output drivers are sized to provide
ufficient output current to drive a wide variety of logic
s
families. However, large drive currents tend to cause current
glitches on the supplies and may affect converter performance.
Applications requiring the ADC to drive large capacitive loads
or large fanouts may require external buffers or latches.
The output data format can be selected for either offset binary
o
r twos complement by setting the SCLK/DFS pin when
06909-039
operating in the external pin mode (see Tabl e 12 ). As detailed in
e Memory Map Register Description section, the data format
th
n be selected for offset binary, twos complement, or gray code
ca
when using the SPI control.
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Table 12. SCLK/DFS Mode Selection (External Pin Mode)
Voltage at Pin SCLK/DFS SDIO/DCS
AGND (default) Binary DCS disabled
AVDD Twos complement DCS enabled
Digital Output Enable Function (OEB)
The AD9600 has a flexible three-state ability for the digital
output pins. The three-state mode can be enabled by using the
SMI SDO/OEB pin or the SPI interface. If the SMI SDO/OEB pin
is low, the output data drivers are enabled. If the SMI SDO/OEB pin
is high, the output data drivers are placed into a high impedance
state. This output enable function is not intended for rapid access
to the data bus. Note that OEB is referenced to the digital output
driver supply (DRVDD) and should not exceed that supply voltage.
When the device uses the SPI interface, each channel’s data and
fast de
tect output pins can be independently three-stated by
using the output enable bar bit in Register 0x14.
Table 13. Output Data Format
Input (V) Condition (V) Binary Output Mode Twos Complement Mode Overrange
(VIN+ ) − (VIN− ) < −VREF − 0.5 LSB 00 0000 0000 10 0000 0000 1
(VIN+ ) − (VIN− ) = –VREF 00 0000 0000 10 0000 0000 0
(VIN+ ) − (VIN− ) = 0 10 0000 0000 00 0000 0000 0
(VIN+ ) − (VIN− ) = +VREF − 1.0 LSB 11 1111 1111 01 1111 1111 0
(VIN+ ) − (VIN− ) > +VREF − 0.5 LSB 11 1111 1111 01 1111 1111 1
TIMING
The AD9600 provides latched data with a pipeline delay of
12 clock cycles. Data outputs are available one propagation
delay (t
The length of the output data lines and the loads placed on them
s
hould be minimized to reduce transients within the AD9600.
These transients can degrade the dynamic performance of the
converter. The lowest typical conversion rate of the AD9600 is
typically 10 MSPS. At clock rates below 10 MSPS, dynamic
performance may degrade.
Data Clock Output (DCO)
The AD9600 provides two data clock output (DCO) signals
intended for capturing the data in an external register. The data
outputs are valid on the rising edge of DCO, unless the polarity has
been changed via the SPI. See the timing diagrams shown in
Figure 2 and Figure 3 for more information.
) after the rising edge of the clock signal.
PD
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ADC OVERRANGE AND GAIN CONTROL
In receiver applications, it is desirable to have a mechanism to
reliably determine when the converter is about to be clipped.
The standard overflow indicator provides after-the-fact information on the state of the analog input that is of limited usefulness.
Therefore, it is helpful to have a programmable threshold below
full scale that allows time to reduce the gain before the clip
actually occurs. In addition, because input signals can have
significant slew rates, latency of this function is of major concern.
Highly pipelined converters can have significant latency. A good
compromise is to use the output bits from the first stage of the
ADC for this function. Latency for these output bits is very low,
and overall resolution is not highly significant. Peak input signals
are typically between full scale and 6 dB to 10 dB below full
scale. A 3-bit or 4-bit output provides adequate range and
resolution for this function.
Via the SPI port, the user can provide a threshold above which
n overrange output would be active. As long as the signal is below
a
that threshold, the output should remain low. The fast detect
output pins can also be programmed via the SPI port so that one of
the pins functions as a traditional overrange pin for customers
who currently use this feature. In this mode, all 12 bits of the
converter are examined in the traditional manner, and the output is
high for the condition normally defined as overflow. In either
mode, the magnitude of the data is considered in the calculation
of the condition (but the sign of the data is not considered). The
threshold detection responds identically to positive and negative
signals outside the desired magnitude range.
FAST DETECT OVERVIEW
The AD9600 contains circuitry to facilitate fast overrange detection, allowing very flexible external gain control implementations.
Each ADC has four fast detect output pins that are used to output
information about the current state of the ADC input level. The
function of these pins is programmable via the fast detect mode
select bits and the fast detect enable bit in Register 0x104, allowing
range information to be output from several points in the internal
datapath. These pins can also be set up to indicate the presence of
overrange or underrange conditions, according to programmable
threshold levels.
r the fast detect pins.
fo
Tabl e 14 shows the six configurations available
Table 14. Fast Detect Mode Select Bits Settings
Fast Detect
Mode Select Bits
(Register 0x104 [3:1])
000
001 ADC fast magnitude
010 ADC fast magnitude
011 ADC fast magnitude
100 OR C_UT F_UT F_LT
101 OR F_UT IG DG
1
The fast detect pins are FD0A/FD0B to FD9A/FD9B for the CMOS mode
configuration and FD0+/FD0− to FD9+/FD9− for the LVDS mode
configuration.
2
See the ADC Overrange (OR) and Gain Switching sections for more
information about OR, C_UT, F_UT, F_LT, IG, and DG.
Information Presented on
Fast Detect (FD) Pins of Each ADC
FD [3] FD [2] FD [1] FD [0]
ADC fast magnitude (see
Table 16)
(see
(see
(see
Table 17)
Table 17)
OR F_LT
C_UT F_LT
1, 2
Table 15)
OR
ADC FAST MAGNITUDE
When the fast detect output pins are configured to output the ADC
fast magnitude (that is, when the fast detect mode select bits are
set to 0b000), the information presented is the ADC level from an
early converter stage with only a two-clock-cycle latency (when
in CMOS output mode). Using the fast detect output pins in
this configuration provides the earliest possible level indication
information. Because this information is provided early in the
datapath, there is a significant uncertainty in the level indicated.
The nominal levels, along with the uncertainty indicated by the
ADC fast magnitude, are shown in
Table 15. ADC Fast Magnitude Nominal Levels with
Fast Detect Mode Select Bits = 000
Nominal Input
ADC Fast Magnitude on
FD [3:0] Pins
0000 <−24 Minimum to −18.07
0001 −24 to −14.5 −30.14 to −12.04
0010 −14.5 to −10 −18.07 to −8.52
0011 −10 to −7 −12.04 to −6.02
0100 −7 to −5 −8.52 to −4.08
0101 −5 to −3.25 −6.02 to −2.5
0110 −3.25 to −1.8 −4.08 to −1.16
0111 −1.8 to −0.56 −2.5 to FS
1000 −0.56 to 0 −1.16 to 0
Ma
Below FS (dB)
Tabl e 15 .
gnitude
Nominal Input
Ma
gnitude
Uncertainty (dB)
Rev. 0 | Page 29 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
When the fast detect mode select bits are set to 0b001, 0b010, or
0b011, a subset of the fast detect output pins is available. In these
modes, the fast detect output pins have a latency of six clock cycles.
Tabl e 16 shows the corresponding ADC input levels when the
fas
t detect mode select bits are set to 0b001 (that is, when ADC
fast magnitude is presented on the FD [3:1] pins).
Table 16. ADC Fast Magnitude Nominal Levels with
Fast Detect Mode Select Bits = 001
Nominal Input
gnitude
ADC Fast Magnitude on
FD [3:1] Pins
000 <−24 Minimum to −18.07
001 −24 to −14.5 −30.14 to −12.04
010 −14.5 to −10 −18.07 to −8.52
011 −10 to −7 −12.04 to −6.02
100 −7 to −5 −8.52 to −4.08
101 −5 to −3.25 −6.02 to −2.5
110 −3.25 to −1.8 −4.08 to −1.16
111 −1.8 to 0 −2.5 to 0
Ma
Below FS (dB)
Nominal Input
Ma
gnitude
Uncertainty (dB)
When the fast detect mode select bits are set to 0b010 or 0b011
(that is, when ADC fast magnitude is presented on the FD [3:2]
pins), the LSB is not provided. The input ranges for this mode
are shown in
Tabl e 17 .
Table 17. ADC Fast Magnitude Nominal Levels with
Fast Detect Mode Select Bits = 010 or 011
Nominal Input
ADC Fast Magnitude on
FD [3:2] Pins
00 <−14.5 Minimum to −12.04
01 −14.5 to −7 −18.07 to −6.02
10 −7 to −3.25 −8.52 to −2.5
11 −3.25 to 0 −4.08 to 0
gnitude
Ma
Below FS (dB)
Nominal Input
Magnitude
Uncertainty (dB)
ADC OVERRANGE (OR)
The ADC overrange indicator is asserted when an overrange is
detected on the input of the ADC. The overrange condition is
determined at the output of the ADC pipeline and therefore is
subject to the 12-clock-cycle latency. An overrange at the input
would be indicated by this bit 12 clock cycles after it occurred.
GAIN SWITCHING
The AD9600 includes circuitry that is useful in applications
either where large dynamic ranges exist or where gain ranging
converters are employed. This circuitry allows digital thresholds
to be set such that an upper threshold and a lower threshold can
be programmed. Fast detect mode select bit = 010 through fast
detect mode select bit = 101 support various combinations of the
gain switching options.
One such use is to detect when an ADC is about to reach full
s
cale with a particular input condition. The result is to provide
an indicator that can be used to quickly insert an attenuator that
prevents ADC overdrive.
Coarse Upper Threshold (C_UT)
The coarse upper threshold indicator is asserted if the ADC fast
magnitude input level is greater than the level programmed in the
coarse upper threshold register at Address 0x105 [2:0]. The coarse
upper threshold output is output two clock cycles after the level
is exceeded at the input and therefore provides a fast indication of
the input signal level. The coarse upper threshold levels are
shown in
mini
Tabl e 18 . This indicator remains asserted for a
mum of two ADC clock cycles or until the signal drops
below the threshold level.
Table 18. Coarse Upper Threshold Levels
C_UT Is Active When Signal
gnitude Below FS
Coarse Upper Threshold
(Register 0x105 [2:0])
000 <−24
001 −24
010 −14.5
011 −10
100 −7
101 −5
110 −3.25
111 −1.8
Ma
Is Greater Than (dB)
Fine Upper Threshold (F_UT)
The fine upper threshold indicator is asserted if the input magnitude exceeds the value programmed in the fine upper threshold
register located at Address 0x106 and Address 0x107. The 13-bit
threshold register is compared with the signal magnitude at the
output of the ADC. This comparison is subject to the ADC clock
latency but is accurate in terms of the converter resolution. The
fine threshold magnitude is defined by the following equation:
dBFS = 20 log(Thresho
ld Magnitude/2
13
) (1)
Fine Lower Threshold (F_LT)
The fine lower threshold indicator is asserted if the input magni
tude is less than the value programmed in the fine lower threshold
register located at Address 0x108 and Address 0x109. The fine
lower threshold register is a 13-bit register that is compared with
the signal magnitude at the output of the ADC. This comparison
is subject to the ADC clock latency but provides a comparison
accurate to the converter resolution. The fine threshold magnitude
is defined in Equation 1.
The operation of the F_UT and F_LT indicators is shown in
Figure 66.
Rev. 0 | Page 30 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Increment Gain (IG) and Decrement Gain (DG)
The increment gain and decrement gain indicators are intended
to be used together to provide information to enable external gain
control. The decrement gain indicator works in conjunction with
the coarse upper threshold bits, asserting when the input
magnitude is greater than the 3-bit value in the coarse upper
threshold register (Address 0x105). The increment gain indicator,
similarly, corresponds with the fine lower threshold bits, except
that it is asserted only if the input magnitude is less than the
value programmed in the fine lower threshold register after the
dwell time elapses. This dwell time is set by the 16-bit increase
gain dwell time register (Address 0x10A and Address 0x10B) and
is in units of ADC input clock cycles ranging from 1 to 65,535. The
TIMER RESET BY
RISE ABOVE F _LT
fine lower threshold register is a 13-bit register that is compared
wi
th the magnitude at the output of the ADC. This comparison
is subject to the ADC clock latency but allows a finer, more
accurate comparison. The fine threshold magnitude is defined
in Equation 1 (see the
Fine Upper Threshold (F_UT) section).
The decrement gain output is influenced by the fast detect output
p
ins, which provide a fast indication of potential overrange
conditions. Assertion of the increment gain indicator is based
on the comparison at the output of the ADC, requiring the input
magnitude to remain below an accurate, programmable level for a
predefined period before signaling external circuitry to increase
the gain.
The operation of the IG and DG indicators is shown in Figure 66.
UPPER THRESHOL D (COARSE OR FINE)
DWELL TIME
FINE LO WER THRESHO LD
C_UT OR F_UT *
F_LT
DG
IG
*C_UT AND F_UT DIF FER ONLY IN ACCURACY AND LATENCY.
NOTE: OUTPUTS FOLLOW THE INSTANTANEOUS SIGNAL LEVEL AND NOT THE ENVELOPE BUT ARE GUARANTEE D ACTIVE FOR A MINIMUM OF TWO ADC CLOCK CYCLES.
Figure 66. Threshold Settings for C_UT
, F_UT, F_LT, IG, and DG
DWELL TIME
TIMER COMPLETES BEFORE
SIGNAL RISES ABOVE F_LT
6909-097
Rev. 0 | Page 31 of 72

AD9600
*
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SIGNAL MONITOR
The signal monitoring block provides additional information about
the signal being digitized by the ADC. The signal monitor computes
the rms input magnitude, the peak magnitude, and/or the number
of samples by which the magnitude exceeds a particular threshold.
Together, these functions can be used to gain insight into the
signal characteristics and to estimate the peak/average ratio or
even the shape of the complementary cumulative distribution
function (CCDF) curve of the input signal. This information
can be used to drive an AGC loop to optimize the range of the
ADC in the presence of real-world signals.
The signal monitor result values can be obtained from the part by
re
ading back Register 0x116 to Register 0x11B, using the SPI port
or the signal monitor SPORT output. The output contents of the
SPI-accessible signal monitor registers are set via the two signal
monitor mode bits of the signal monitor control register
(Address 0x112). Both ADC channels must be configured for
the same signal monitor mode. Separate SPI-accessible, 20-bit
signal monitor result (SMR) registers (Address 0x116 to Address
0x11B) are provided for each ADC channel. Any combination of
the signal monitor functions can also be output to the user via
the serial SPORT interface. These outputs are enabled using the
peak detector output enable, rms magnitude output enable, and
threshold crossing output enable bits in the signal monitor
SPORT control register (Address 0x111).
For each of the signal monitor measurements, a programmable
s
ignal monitor period register (SMPR) controls the duration of
the measurement. This period is programmed as the number of
input clock cycles in the 24-bit signal monitor period register
located at Address 0x113, Address 0x114, and Address 0x115.
This register can be programmed with a period from 128 samples
24
to 16.78 (2
) million samples.
Because the dc offset of the ADC can be significantly larger
t
han the signal of interest (affecting the results from the signal
monitor), a dc correction circuit is included as part of the signal
monitor block to null the dc offset before measuring the power.
PEAK DETECTOR MODE
The magnitude of the input port signal is monitored over a
programmable period (determined by SMPR) to give the peak
value detected. This function is enabled by programming a
Logic 1 in the signal monitor mode bits of the signal monitor
control register (Address 0x112) or by setting the peak detector
output enable bit in the signal monitor SPORT control register
(Address 0x111). The 24-bit SMPR must be programmed before
activating this mode.
After enabling this mode, the value in the SMPR is loaded into
a moni
tor period timer and the countdown is started. The magnitude of the input signal is compared with the value in the
internal peak level holding register (not accessible to the user),
and the greater of the two values is updated as the current peak
level. The initial value in the peak level holding register is set to
Rev. 0 | Page 32 of 72
the current ADC input signal magnitude, and the comparison
continues until the monitor period timer reaches a count of 1.
When the monitor period timer reaches a count of 1, the 13-bit
val
ue in the peak level holding register is transferred to the signal
monitor holding register (not accessible to the user) and can be
read through the SPI port or output through the SPORT serial
interface. The monitor period timer is reloaded with the value in
the SMPR, and the countdown is restarted. In addition, the value in
the peak level holding register is reset to the magnitude of the
first input sample, and the previously explained comparison and
update procedure continues.
Figure 67 is a block diagram of the peak detector logic. The
MR register contains the absolute magnitude of the peak
S
detected by the peak detector logic.
FROM
MEMORY
MAP
SIGNAL MONITOR
PERIOD REGI STER
FROM
INPUT
PORTS
THESE ARE INTERNAL REGISTERS. THEY ARE NOT IN THE REGISTER
MAP AND CANNOT BE ACCESSED BY USERS.
MAGNITUDE
STORAGE
REGISTER*
LOAD LOAD
COMPARE
A>B
Figure 67. ADC Input Peak Detector Block Diagram
LOAD
CLEAR
DOWN
COUNTER
IS COUNT = 1?
SIGNAL MONITOR
HOLDING
REGISTER (SMR)*
TO
MEMORY
MAP/SPORT
6909-044
RMS/MS MAGNITUDE MODE
In this mode, the root-mean-square (rms) or mean-square (ms)
magnitude of the input port signal is integrated (by adding an
accumulator) over a programmable period (determined by SMPR)
to give the rms or ms magnitude of the input signal. This mode
is set by programming Logic 0 in the signal monitor mode bits
of the signal monitor control register (Address 0x112) or by setting
the rms magnitude output enable bit in the signal monitor
SPORT control register (Address 0x111). The 24-bit SMPR,
representing the period over which integration is performed,
must be programmed before activating this mode.
After enabling the rms/ms magnitude mode, the value in the SMPR
s loaded into a monitor period timer, and the countdown is started
i
immediately. Each input sample is converted to floating-point
format and squared. It is then converted to an 11-bit fixed-point
format and added to the contents of the 24-bit accumulator. The
integration continues until the monitor period timer reaches a
count of 1.
When the monitor period timer reaches a count of 1, the square
r
oot of the value in the accumulator is taken and transferred
(after some formatting) to the signal monitor holding register,
which can be read through the SPI port or output through the
SPORT serial port. The monitor period timer is reloaded with
the value in the SMPR, and the countdown is restarted. In addition,

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
the value of the accumulator is reset to the first input sample
signal power, and the accumulation continues with the
subsequent input samples.
Figure 68 illustrates the rms magnitude monitoring logic.
FROM
MEMORY
MAP
SIGNAL MONITOR
PERIOD REGISTER
FROM
INPUT
PORTS
*THIS IS AN I NTERNAL REG ISTER. IT IS NOT IN THE REGIST ER
MAP AND CANNOT BE ACCESSED BY USERS.
Figure 68. ADC Input RMS Magnitude Monitoring Block Diagram
ACCUMULATOR
DOWN
COUNTER
LOAD
CLEAR LOAD
IS COUNT = 1?
SIGNAL MO NITOR
HOLDING
REGISTER (SMR)*
TO
MEMORY
MAP/SPORT
For rms magnitude mode, the value in the signal monitor result
(SMR) register is a 20-bit fixed-point number. The following
equation can be used to determine the rms magnitude in decibels
full scale (dBFS) from the MAG value in the register:
RMS Magnitude = 20 log
SMPMAG
⎞
⎛
⎟
⎜
20
2
⎠
⎝
⎡
log10
−
[]
⎢
2
⎣
⎤
)(log
SMPceil
⎥
2
⎦
where if the signal monitor period (SMP) is a power of 2, the
econd term in the equation becomes 0.
s
For ms magnitude mode, the value in the SMR is a 20-bit fixed-
oint number. The following equation can be used to determine
p
the ms magnitude in decibels full scale (dBFS) from the MAG
value in the register:
MS Magnitude
= 10 log
SMPMAG
⎞
⎛
⎜
⎝
−
⎟
20
2
⎠
⎡
log10
[]
⎢
2
⎣
⎤
)(log
SMPceil
⎥
2
⎦
where if the SMP is a power of 2, the second term in the
uation becomes 0.
eq
THRESHOLD CROSSING MODE
In the threshold crossing mode of operation, the magnitude of
the input port signal is monitored over a programmable period
(determined by SMPR) to count the number of times it crosses a
certain programmable threshold value. This mode is set by
programming Logic 1x (where x is a don’t care bit) in the signal
monitor mode bits of the signal monitor control register
(Address 0x112) or by setting the threshold crossing output
enable bit in the signal monitor SPORT control register
(Address 0x111). Before activating this mode, the user needs to
program the 24-bit signal monitor period register (Address 0x113
to Address 0x115) and the 13-bit fine upper threshold register
(Address 0x106 and Address 0x107) for each individual input
port. The same fine upper threshold register is used for both
signal monitoring and gain control (see the
nd Gain Control
a
section).
After entering this mode, the value in the SMPR is loaded
i
nto a monitor period timer and the countdown is started. The
magnitude of the input signal is compared with the previously
programmed fine upper threshold register on each input clock
ADC Overrange
06909-092
cycle. If the input signal has a magnitude greater than the value
set in the fine upper threshold register, the value in the internal
count register (not accessible to the user) is incremented by 1.
The initial value of the internal count register is set to 0. The
mparison and incrementing of this value continues until the
co
monitor period timer reaches a count of 1.
When the monitor period timer reaches a count of 1, the value
he internal count register is transferred to the signal monitor
in t
holding register (not accessible to the user), which can be read
through the SPI port or output through the SPORT serial port.
The monitor period timer is reloaded with the value in the SMPR,
nd the countdown is restarted. The internal count register is
a
also cleared to a value of 0.
cr
ossing logic. The value in the SMR register is the number of
Figure 69 illustrates the threshold
samples that have a magnitude greater than the fine upper
threshold register.
FROM
MEMORY
MAP
SIGNAL MO NITOR
PERIOD REGIS TER
FROM
INPUT
PORTS
FROM
MEMORY
MAP
*THIS IS AN INTERNAL REGISTER. IT IS NOT IN THE REGISTER
MAP AND CANNOT BE ACCESS ED BY USERS.
A
COMPARE
A > B
FINE UPPER
THRESHOLD
REGISTER
Figure 69. ADC Input Threshold Crossing Block Diagram
B
DOWN
COUNTER
LOAD
CLEAR
COMPARE
A > B
IS COUNT = 1?
LOAD
SIGNAL MO NITOR
HOLDING
REGISTER (SMR)*
TO
MEMORY
MAP/SPORT
ADDITIONAL CONTROL BITS
For additional flexibility in the signal monitoring process, two
control bits are provided in the signal monitor control register
(Address 0x112). They are the signal monitor enable bit and the
complex power calculation mode enable bit.
Signal Monitor Enable Bit
The signal monitor enable bit, located in Bit 0 of Register 0x112,
enables operation of the signal monitor block. If the signal monitor
function is not needed in a particular application, this bit should
be cleared (default) to conserve power.
Complex Power Calculation Mode Enable Bit
When this bit is set, the part assumes that Channel A is digitizing
the I data and Channel B is digitizing the Q data for a complex
input signal (or vice versa). In this mode, the power reported is
equal to
22
QI +
This result is presented in the signal monitor DC value Channel A
egister (Address 0x10D and Address 0x10E) if the signal monitor
r
mode bits are set to 00. The signal monitor DC value Channel B
register (Address 0x10F and Address 0x110) continues to compute
the Channel B value.
06909-046
Rev. 0 | Page 33 of 72

AD9600
S
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DC CORRECTION
Because the dc offset of the ADC may be significantly larger
than the signal being measured, a dc correction circuit is included
to null the dc offset before measuring the power. The dc correction
circuit can also be switched into the main signal path, but this
may not be appropriate if the ADC is digitizing a time-varying
signal with significant dc content, such as GSM.
DC Correction Bandwidth
The dc correction circuit is a high-pass filter with a programmable
bandwidth (ranging between 0.15 Hz and 1.2 kHz at 125 MSPS).
The bandwidth is controlled by writing the 4-bit dc correction
bandwidth register located at Register 0x10C, Bits [5:2].
The following equation can be used to compute the bandwidth
value for the dc correction circuit:
f
−−
14
BWCorrDC
k
2__
where:
he 4-bit value programmed in Register 0x10C, Bits [5:2]
k is t
(values between 0 and 13 are valid for k; programming 14 or
15 provides the same result as programming 13).
is the AD9600 ADC sample rate in hertz.
f
CLK
DC Correction Readback
The current dc correction value can be read back in Register 0x10D
and Register 0x10E for Channel A and Register 0x10F and
Register 0x110 for Channel B. The dc correction value is a 10-bit
value that can span the entire input range of the ADC.
DC Correction Freeze
Setting the dc correction freeze bit (Bit 6 of Register 0x10C) halts
the dc correction at its current state and continues to use the last
updated value as the dc correction value. Clearing this bit restarts
dc correction and adds the currently calculated value to the data.
CLK
×=
π×
2
DC Correction Enable Bits
Setting Bit 0 (the dc correction for SM enable bit) of Register 0x10C
enables the dc correction for use in the signal monitor calculations.
Setting Bit 1 (the dc correction for signal path enable bit) of
Register 0x10C enables the calculated dc correction value to
be added to the output data signal path.
SIGNAL MONITOR SPORT OUTPUT
The SPORT is a serial interface with three output pins:
SMI SCLK (SPORT clock), SMI SDFS (SPORT frame sync), and
SMI SDO (SPORT data). The SPORT is the master and drives
all three SPORT output pins on the chip.
SMI SCLK
The data and frame sync are driven on the positive edge of the
SMI SCLK. The SMI SCLK has three possible baud rates: 1/2, 1/4,
or 1/8 the ADC clock rate, based on the SPORT controls. In
addition, by using the SPORT SMI SCLK sleep bit, the SMI SCLK
can be gated to remain low when the signal monitor block is not
sending any data. Using this bit to disable the SMI SCLK when it is
not needed can reduce coupling errors in the return signal path.
Doing so, however, has the disadvantage of spreading the
frequency content of the clock; if desired, the SMI SCLK can be
left enabled to ease frequency planning.
SMI SDFS
The SMI SDFS is the serial data frame sync. It defines the start
o
f a frame. One SPORT frame includes data from both
datapaths. The data from Datapath A is sent just after the frame
sync, followed by data from Datapath B.
SMI SDO
The SMI SDO is the serial data output of the block. The data is sent
SB first on the first positive edge after the SMI SDFS. Each data
M
output block includes one or more rms magnitude value, peak level
value, and threshold crossing value from each datapath in the stated
order. If enabled, the data is sent, rms first, followed by the peak
value and the threshold crossing value, as shown in Figure 70.
GATED, BASED ON CONTRO L
SMI SCLK/PDWN
SMI SDFS
SMI SDO/OEB
MI SCLK/PDWN
SMI SDFS
SMI SDO/OEB
RMS/MS CH A
MSB MSB
20 CYCLES 16 CYCL ES16 CYCLES 20 CYCLES 16 CYCL ES 16 CYCLE S
MSB MSBRMS/MS CH A RMS/MS CH ALSB THR CH A RMS/MS CH B LSB THR CH B
LSB LSBTHR CH A
PK CH A
Figure 70. Signal Monitor SPORT Output Timing (RMS, Peak, and Threshold Enabled)
20 CYCLES 16 CYCLES 20 CYCLES 16 CYCLES
Figure 71. Signal Monitor SPORT Output Ti
Rev. 0 | Page 34 of 72
PK CH B THR CH BRMS/MS CH B
GATED, BASED O N CONTROL
ming (RMS and Threshold Enabled)
RMS/MS CH A
06909-094
6909-095

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
BUILT-IN SELF-TEST (BIST) AND OUTPUT TEST
The AD9600 includes built-in test features to enable verification
of the integrity of each channel as well as to facilitate board level
debugging. A BIST feature is included that verifies the integrity
of the digital datapath of the AD9600. Various output test options
are also provided to place predictable values on the outputs of
the AD9600.
BUILT-IN SELF-TEST (BIST)
The BIST is a thorough test of the digital portion of the selected
AD9600 signal path. When enabled, the test runs from an internal
pseudorandom noise (PN) source through the digital datapath,
starting at the ADC block output. The BIST sequence runs for
512 cycles and then stops. The BIST signature value for Channel
A or Channel B is placed in Register 0x24 and Register 0x25. If
one channel is chosen, its BIST signature is written to the two
registers. If both channels are chosen, the results of the two
channels are XOR’ed and placed in the BIST signature registers.
The outputs are not disconnected during this test; therefore, the PN
s
equence can be observed as it runs. The PN sequence can be
continued from its last value or started from the beginning, based
on the value programmed in Bit 2 of Register 0x0E. The BIST
signature result varies depending on the channel configuration.
OUTPUT TEST MODES
The output test options are shown in Tab l e 2 2 . When an output
test mode is enabled, the analog section of the ADC is disconnected from the digital back end blocks, and the test pattern is run
through the output formatting block. Some of the test patterns are
subject to output formatting, and some are not. The seed value for
the PN sequence tests can be forced by setting Bit 4 or Bit 5 of
the test mode register (Address 0x0D) to hold the generator in
reset mode. These tests can be performed with or without an
analog signal (if present, the analog signal is ignored), but they
do require an encode clock. For more information, see AN-877
plication Note, I
Ap
nterfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI.
Rev. 0 | Page 35 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
CHANNEL/CHIP SYNCHRONIZATION
The AD9600 has a SYNC input that offers the user flexible
synchronization options for synchronizing the internal blocks.
The clock divider sync feature is useful to guarantee synchronized
sample clocks across multiple ADCs. The signal monitor block can
also be synchronized using the SYNC input, allowing properties of
the input signal to be measured during a specific period. The
input clock divider can be enabled to synchronize on a single
occurrence of the sync signal or on every occurrence. The signal
monitor block is synchronized on every SYNC input signal.
The SYNC input is internally synchronized to the sample clock;
owever, to ensure there is no timing uncertainty between
h
multiple parts, the SYNC input signal should be externally
synchronized to the input clock signal, meeting the setup and
hold times shown in Table 5. The SYNC input should be driven
usin
g a single-ended CMOS-type signal.
Rev. 0 | Page 36 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SERIAL PORT INTERFACE (SPI)
The AD9600 SPI allows the user to configure the converter for
specific functions or operations through a structured register
space provided inside the ADC. This may provide the user
with additional flexibility and customization, depending on the
application. Addresses are accessed via the serial port and can
be written to or read from via the port. Memory is organized
into bytes that can be further divided into fields, which are documented in the Memory Map section. For detailed operational
rmation, see AN-877 Application Note, I
info
Speed ADCs via SPI.
nterfacing to High
CONFIGURATION USING THE SPI
There are three pins that define the SPI: SCLK, SDIO, and CSB
(see Tabl e 19 ). The SCLK pin is used to synchronize the read
a
nd write data presented from and to the ADC. The SDIO pin is
a dual-purpose pin that allows data to be sent to and read from
the internal ADC memory map registers. The CSB pin is an activelow control that enables or disables the read and write cycles.
Table 19. Serial Port Interface Pins
Pin Function
SCLK
Serial Clock. The serial shift clock input, which is used to
synchroniz
SDIO
Serial Data Input/Output. A
typically serves as an input or an output, depending on
the instruction being sent and the relative position in the
timing frame.
CSB
Chip Select Bar. An active-low control that gates the read
and wr
The falling edge of the CSB in conjunction with the rising edge
of the SCLK determines the start of the framing. An example of
the serial timing and its definitions can be found in Figure 72
an
d Tab l e 5 .
Other modes involving the CSB are available. The CSB can be
w indefinitely, which permanently enables the device;
held lo
this is called streaming. The CSB can stall high between bytes to
allow for additional external timing. When CSB is tied high, SPI
functions are placed in high impedance mode. This mode turns
on any secondary functions of the SPI pin.
During an instruction phase, a 16-bit instruction is transmitted.
ta follows the instruction phase, and its length is determined
Da
by the W0 and W1 bits. W0 and W1 represent the number of
data bytes to transfer for either a read or a write. The value
represented by W1:W0 + 1 is the number of bytes to transfer.
e serial interface reads and writes.
dual-purpose pin that
ite cycles.
All data is composed of 8-bit words. The first bit of each individual
b
yte of serial data indicates whether a read command or a write
command is issued. This allows the SDIO pin to change direction
from an input to an output.
In addition to word length, the instruction phase determines if
t
he serial frame is a read or write operation, allowing the serial
port to be used to both program the chip and read the contents
of the on-chip memory. If the instruction is a readback operation,
performing a readback causes the SDIO pin to change direction
from an input to an output at the appropriate point in the
serial frame.
Data can be sent in MSB-first mode or LSB-first mode. MSB-first
m
ode is the default on power-up and can be changed via the SPI
port configuration register (Address 0x00). For more information
about this and other features, see AN-877 Application Note,
I
nterfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI.
HARDWARE INTERFACE
The pins described in Ta b le 1 9 constitute the physical interface
between the user programming device and the serial port of the
AD9600. The SCLK pin and the CSB pin function as inputs
when using the SPI interface. The SDIO pin is bidirectional,
functioning as an input during write phases and as an output
during readback.
The SPI interface is flexible enough to be controlled by either
FPGA
s or microcontrollers. One method for SPI configuration
is described in detail in AN-812 Application Note, M
Based Serial Port Interface (SPI) Boot Circuit.
The SPI port should not be active during periods when the full
ynamic performance of the converter is required. Because the
d
SCLK, CSB, and SDIO signals are typically asynchronous to the
ADC clock, noise from these signals can degrade converter
performance. If the on-board SPI bus is used for other devices, it
may be necessary to provide buffers between this bus and the
AD9600 to keep these signals from transitioning at the converter
inputs during critical sampling periods.
Some pins serve a dual function when the SPI interface is not
b
eing used. When the pins are strapped to AVDD or ground
during device power-on, they are associated with a specific
function. The Theory of Operation section describes the
s
trappable functions supported on the AD9600.
icrocontroller-
Rev. 0 | Page 37 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
CONFIGURATION WITHOUT THE SPI
In applications that do not interface to the SPI control registers,
the SDIO/DCS pin, the SCLK/DFS pin, the SMI SDO/OEB pin,
and the SMI SCLK/PDWN pin serve as standalone CMOScompatible control pins. When the device is powered up, it is
assumed that the user intends to use the pins as static control
lines for the duty cycle stabilizer, output data format, output
enable, and power-down feature control. In this mode, the CSB
chip select should be connected to AVDD, which disables the
serial port interface.
Table 20. Mode Selection
External
Pin
SMI SCLK/PDWN
V
oltage Configuration
AVDD (default) Duty cycle stabilizer enabled SDIO/DCS
AGND Duty cycle stabilizer disabled
AVDD Twos complement enabled SCLK/DFS
AGND (default) Offset binary enabled
AVDD Outputs in high impedance SMI SDO/OEB
AGND (default) Outputs enabled
AVDD
Chip in power-down or
by
stand
AGND (default) Normal operation
SPI ACCESSIBLE FEATURES
Brief descriptions of the general features available on many
Analog Devices, Inc., high speed ADCs, including the AD9600,
that are accessible via the SPI are included in Tab le 2 1. These
fe
atures are described in detail in the AN-877 Application Note,
nterfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI. The AD9600 part-specific
I
features are described in the Memory Map Register Description
secti
on.
Table 21. Features Accessible Using the SPI
Feature Name Description
Modes
Clock Allows the user to access the DCS via the SPI
Offset
Tes t I /O
Output Mode Allows the user to set up the outputs
Output Phase Allows the user to set the output clock polarity
Output Delay Allows the user to vary the DCO delay
VREF Allows the user to set the reference voltage
Allows the user to set either the power-down
or the standby mode
mode
Allows the user to digitally adjust the
onverter offset
c
Allows the user to set the test modes to have
nown data on the output bits
k
CSB
SCLK
SDIO
DON’T CARE
t
t
DS
t
S
R/W W1 W0 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7
t
DH
HIGH
t
LOW
Figure 72. Serial Port Interface Timing Diagram
t
CLK
D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
t
H
DON’T CARE
DON’T C AREDON’T CARE
06909-049
Rev. 0 | Page 38 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
MEMORY MAP
READING THE MEMORY MAP TABLE
Each row in the memory map registers table (Tabl e 22 ) has eight
bit locations. The memory map is divided into four sections: the
chip configuration registers (Address 0x00 to Address 0x02), the
channel index and transfer registers (Address 0x05 and Address
0xFF), the ADC functions registers (Address 0x08 to Address
0x25), and the digital feature control registers (Address 0x100 to
Address 0x11B).
The leftmost column of the memory map indicates the register
addr
ess number, and the default value is shown in the second
rightmost column. The (MSB) Bit 7 column is the start of the
default hexadecimal value given. For example, Address 0x18, the
VREF select register, has a default value of 0xC0, meaning that
Bit 7 = 1, Bit 6 = 1, and the remaining bits are 0s. This setting is the
default reference selection setting. The default value uses a 2.0 V
peak-to-peak reference. For more information on this function and
others, see the AN-877 Application Note, I
ADCs via SPI. This application note details the functions controlled
by Register 0x00 to Register 0xFF. The remaining registers
(from Register 0x100 to Register 0x11B) are documented in the
Memory Map Register Description section.
Open Locations
All address and bit locations that are not included in Tab l e 2 2
are currently not supported for this device. Unused bits of a
valid address location should be written with 0s. Writing to these
locations is required only when part of an address location is
open (for example, Address 0x18). If the entire address location
is open (for example, Address 0x13), this address location should
not be written.
Default Values
When the AD9600 comes out of a reset, critical registers are
loaded with default values. The default values for the registers
are given in the memory map registers table (Tabl e 22).
nterfacing to High Speed
Logic Levels
An explanation of logic level terminology follows:
• “Bit is set” is synonymous with “bit is set to Logic 1” or
“writing Logic 1 for the bit.”
• “Clear a bit” is synonymous with “bit is set to Logic 0” or
“writing Logic 0 for the bit.”
Transfer Register Map
Address 0x08 to Address 0x18 are shadowed. Writes to these
addresses do not affect part operation until a transfer command
is issued by writing 0x01 to Address 0xFF, setting the transfer bit.
This allows these registers to be updated internally and simultaneously when the transfer bit (Bit 0 of Register 0xFF) is set. The
internal update takes place when the transfer bit is set, and the
bit autoclears.
Channel-Specific Registers
Some channel setup functions, such as the signal monitor
thresholds, can be individually programmed for each channel.
In these cases, channel address locations are internally
duplicated for each channel. These registers are designated as
local registers in Tab l e 2 2 and can be accessed by setting the
a
ppropriate Channel A or Channel B bits in Register 0x05. If
both bits are set, the subsequent write affects the registers of
both channels. In a read cycle, only Channel A or Channel B
should be set to read one of the two registers. If both bits are set
during an SPI read cycle, the part returns the value for
Channel A.
On the other hand, registers that are designated as global registers
in
Tabl e 2 2 affect the entire part or the channel features for which
pendent settings are not allowed between the channels. The
inde
settings in Register 0x05 do not affect the global registers.
Rev. 0 | Page 39 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
MEMORY MAP
All address and bit locations that are not included in Tab l e 2 2 are currently not supported for this device.
Table 22. Memory Map Registers
Addr
Register
(Hex)
Name
Chip Configuration Registers
0x00
SPI Port
Configuration
(Global)
0x01 Chip ID
(Global)
0x02 Chip Grade
(Global)
Channel Index and Transfer Registers
0x05 Channel Index Open Open Open Open Open Open
0xFF Transfer Open Open Open Open Open Open Open Transfer 0x00
ADC Functions Registers
0x08 Power Modes Open Open
0x09 Global Clock
(Global)
0x0B Clock Divide
(Global)
0x0D
Test Mode
(Local)
Bit 7
(MSB)
0 LSB first Soft reset 1 1 Soft reset LSB first 0 0x18
Open Open Speed grade ID
Open Open Open Open Open Open Open
Open Open Open Open Open Clock divide ratio
Open Open
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
8-bit Chip ID [7:0]
(AD9600 = 0x12)
(default)
00 = 150 MSPS
01 = 125 MSPS
10 = 105 MSPS
11 = 80 MSPS
External
powerdown pin
function
(global)
0 = powerdown
1 = standby
Reset PN23
gen
Open Open Open
Reset
PN9 gen
Open Open Open Open
Data
Channel B
(default)
Internal power-down
mode (local)
00 = normal operation
01 = full power-down
10 = standby
11 = normal operation
000 = divide by 1
001 = divide by 2
010 = divide by 3
011 = divide by 4
100 = divide by 5
101 = divide by 6
110 = divide by 7
111 = divide by 8
Open Output test mode
000 = off (default)
001 = midscale short
010 = positive FS
011 = negative FS
100 = alternating checkerboard
101 = PN 23 sequence
110 = PN 9 sequence
111 = one/zero word toggle
Bit 0
(LSB)
Data
Channel A
(default)
Duty cycle
stabilizer
(default)
Default
Value
(Hex)
0x12
Read
only
Read
only
0x03
0x00
0x01
0x00
0x00
Default
Notes/
Comments
The nibbles
are mirrored
so that LSB- or
MSB-first mode
is set correctly,
regardless of
shift mode.
Read only.
Speed grade
ID used to
differentiate
devices.
Bits are set
to determine
which on-chip
device receives
the next write
command;
applies to local
registers.
Synchronously
transfers data
from the
master shift
register to the
slave.
Determines
various generic
modes of chip
operation.
Clock divide
values other
than 000
automatically
cause the duty
cycle stabilizer
to become
active.
When this
register is set,
the test data is
placed on the
output pins in
place of normal
data.
Rev. 0 | Page 40 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Addr
Register
(Hex)
Name
0x0E BIST Enable
(Local)
0x10 Offset Adjust
(Local)
0x14 Output Mode
0x16
Clock Phase
Control
(Global)
0x17
DCO Output
Delay (Global)
0x18 VREF Select
(Global)
0x24
BIST Signature
LSB (Local)
0x25
BIST Signature
MSB (Local)
Digital Feature Control Registers
0x100 Sync Control
(Global)
0x104
Fast Detect
Control (Local)
0x105
Coarse Upper
Threshold
(Local)
0x106
Fine Upper
Threshold
Register 0
(Local)
0x107
Fine Upper
Threshold
Register 1
(Local)
0x108
Fine Lower
Threshold
Register 0
(Local)
0x109
Fine Lower
Threshold
Register 1
(Local)
Bit 7
(MSB)
Open Open Open Open Open
Open Open
Drive
strength
0 V to 3.3 V
CMOS or
ANSI
LVDS:
1 V to 1.8 V
CMOS or
reduced:
LVDS
(global)
Invert DCO
clock
Open Open Open
Reference voltage selection
00 = 1.25 V p-p
01 = 1.5 V p-p
10 = 1.75 V p-p
11 = 2.0 V p-p (default)
Signal
monitor
sync
enable
Open Open Open Open Fast Detect Mode Select [2:0]
Open Open Open Open Open Coarse Upper Threshold [2:0] 0x00
Open Open Open Fine Upper Threshold [12:8] 0x00
Open Open Open Fine Lower Threshold [12:8] 0x00
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
Reset BIST
sequence
Offset adjust in LSBs from +31 to −32
(twos complement format)
Output type
0 = CMOS
1 = LVDS
(global)
Open Open Open Open Input clock divider phase adjust
Open Open Open Open
Open
Open Open Open Open Open Open 0xC0
Output
enable bar
(local)
DCO clock delay
(delay = 2500 ps × register value/31)
00000 = 0 ps
00001 = 81 ps
00010 = 161 ps
…
11110 = 2419 ps
11111 = 2500 ps
BIST signature [7:0] 0x00 Read only.
BIST signature [15:8] 0x00 Read only.
Fine Upper Threshold [7:0] 0x00
Fine Lower Threshold [7:0] 0x00
Open
Output
invert
(local)
000 = no delay
001 = 1 input clock cycle
010 = 2 input clock cycles
011 = 3 input clock cycles
100 = 4 input clock cycles
101 = 5 input clock cycles
110 = 6 input clock cycles
111 = 7 input clock cycles
Clock
divider
next sync
only
Open BIST enable 0x00
00 = offset binary
01 = twos complement
01 = gray code
11 = offset binary
(local)
Clock
divider
sync
enable
Bit 0
(LSB)
Master
sync
enable
Fast detect
enable
Default
Value
(Hex)
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
Default
Notes/
Comments
Configures the
outputs and
the format of
the data.
Allows
selection of
clock delays
into the input
clock divider.
Rev. 0 | Page 41 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Addr
(Hex)
0x10A
0x10B
0x10C
0x10D
0x10E
0x10F
0x110
0x111
0x112
0x113
0x114
0x115
0x116
0x117
Register
Name
Increase Gain
Dwell Time
Register 0
(Local)
Increase Gain
Dwell Time
Register 1
(Local)
Signal Monitor
DC Correction
Control
(Global)
Signal Monitor
DC Value
Channel A
Register 0
(Global)
Signal Monitor
DC Value
Channel A
Register 1
(Global)
Signal Monitor
DC Value
Channel B
Register 0
(Global)
Signal Monitor
DC Value
Channel B
Register 1
(Global)
Signal Monitor
SPORT Control
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Control
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Period
Register 0
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Period
Register 1
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Period
Register 2
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Result
Channel A
Register 0
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Result
Channel A
Register 1
(Global)
Default
Bit 7
(MSB)
Open
Open Open DC Value Channel A [13:8] Read only.
Open Open DC Value Channel A [13:8] Read only
Open
Complex
power
calculation
mode
enable
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
Increase Gain Dwell Time [7:0] 0x00
Increase Gain Dwell Time [15:8] 0x00
DC
correction
freeze
RMS/MS
magnitude
output
enable
Open Open Open
Peak
detector
output
enable
DC Correction Bandwidth [3:0]
DC Value Channel A [7:0] Read only.
DC Value Channel B [7:0] Read only.
Threshold
crossing
output
enable
Signal Monitor Period [7:0] 0x80
Signal Monitor Period [15:8] 0x00
Signal Monitor Period [23:16] 0x00
Signal Monitor Result Channel A [7:0] Read only.
Signal Monitor Result Channel A [15:8] Read only.
SPORT SMI
SCLK divide
00 = undefined
01 = divide by 2
10 = divide by 4
11 = divide by 8
Signal
monitor
rms/ms
select
0 = rms
1 = ms
Signal monitor mode
00 = rms/ms magnitude
01 = peak power
10 = threshold crossing
11 = threshold crossing
DC
correction
for signal
path
enable
SPORT
SMI SCLK
sleep
Bit 0
(LSB)
DC
correction
for signal
monitor
enable
Signal
monitor
SPORT
output
enable
Signal
monitor
enable
Value
(Hex)
0x00
0x04
0x00
Default
Notes/
Comments
In ADC clock
cycles.
In ADC clock
cycles.
In ADC clock
cycles.
In ADC clock
cycles.
In ADC clock
cycles.
Rev. 0 | Page 42 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Addr
(Hex)
0x118
0x119
0x11A
0x11B
Register
Name
Signal Monitor
Result
Channel A
Register 2
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Result
Channel B
Register 0
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Result
Channel B
Register 1
(Global)
Signal Monitor
Result
Channel B
Register 2
(Global)
Default
Bit 7
(MSB)
Open Open Open Open Signal Monitor Value Channel A [19:16] Read only.
Open Open Open Open Signal Monitor Result Channel B [19:16] Read only.
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
Signal Monitor Result Channel B [7:0] Read only.
Signal Monitor Result Channel B [15:8] Read only.
Bit 0
(LSB)
Value
(Hex)
Default
Notes/
Comments
MEMORY MAP REGISTER DESCRIPTION
For information about functions controlled in Register 0x00 to
Register 0xFF, see Application Note AN-877, Interfacing to High
Speed ADCs via SPI.
Sync Control (Register 0x100)
Bit 7—Signal Monitor Sync Enable
Bit 7 enables the sync pulse from the external sync input to the
signal monitor block. The sync signal is passed when both Bit 7
and Bit 0 are high. This is continuous sync mode.
Bits [6:3]—Reserved
Bit 2—Clock Divider Next Sync Only
If the master sync enable bit (Address 0x100 [0]) is high and the
clock divider sync enable bit (Address 0x100 [1]) is high, the
clock divider next sync only bit (Address 0x100 [2]) allows the
clock divider to sync to the first sync pulse it receives and ignore
the rest. The clock divider sync enable bit (Address 0x100 [1])
resets after it syncs.
Bit 1—Clock Divider Sync Enable
Bit 1 gates the sync pulse to the clock divider. The sync signal is
passed when both Bit 1 and Bit 0 are high. This is continuous
sync mode.
Bit 0—Master Sync Enable
Bit 0 must be high to enable the sync functions.
Fast Detect Control (Register 0x104)
Bits [7:4]—Reserved
Bits [3:1]—Fast Detect Mode Select
These bits set the mode of the fast detect output pins according
to Tab l e 1 4 .
Bit 0—Fast Detect Enable
Bit 0 is used to enable the fast detect output pins. When the fast
detect output pins are disabled, the outputs go into a high
impedance state. In LVDS mode, when the fast detect output
pins are interleaved, the outputs go high-Z only if both channels
are turned off (power-down/standby/output disabled). If only one
channel is turned off (power-down/standby/output disabled), the
fast detect output pins repeat the data of the active channel.
Coarse Upper Threshold (Register 0x105)
Bits [7:3]—Reserved
Bits [2:0]—Coarse Upper Threshold
These bits set the level required to assert the coarse upper
threshold indication (see Ta bl e 18 ).
Fine Upper Threshold (Register 0x106 and Register 0x107)
Register 0x106, Bits [7:0]—Fine Upper Threshold [7:0]
Register 0x107, Bits [7:5]—Reserved
Register 0x107, Bits [4:0]—Fine Upper Threshold [12:8]
These registers provide the fine upper limit threshold. This 13-bit
value is compared with the 10-bit magnitude from the ADC
block. If the ADC magnitude exceeds this threshold value, the
F_UT indicator is set.
Fine Lower Threshold (Register 0x108 and Register 0x109)
Register 0x108, Bits [7:0]—Fine Lower Threshold [7:0]
R
egister 0x109, Bits [7:5]—Reserved
Register 0x109, Bits [4:0]—Fine Lower Threshold [12:8]
These registers provide a fine lower limit threshold. This 13-bit
value is compared with the 10-bit magnitude from the ADC
block. If the ADC magnitude is less than this threshold value,
the F_LT indicator is set.
Rev. 0 | Page 43 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Increase Gain Dwell Time (Register 0x10A and Register 0x10B)
Register 0x10A, Bits [7:0]—Increase Gain Dwell Time [7:0]
egister 0x10B, Bits [7:0]—Increase Gain Dwell Time [15:8]
R
These registers are programmed with the dwell time in ADC
clock cycles. The signal must be below the fine lower threshold
value before the increase gain (IG) indicator is asserted.
Signal Monitor DC Correction Control (Register 0x10C)
Bit 7—Reserved
B
it 6—DC Correction Freeze
When Bit 6 is set high, the dc correction is not updated to the
signal monitor block; therefore, the block continues to hold the last
dc value that it calculated.
Bits [5:2]—DC Correction Bandwidth
These bits set the averaging time of the power monitor dc
correction function. This 4-bit word sets the bandwidth of the
correction block according to the following equation:
f
−−
14
BWCorrDC
where:
he 4-bit value programmed in Register 0x10C, Bits [5:2]
k is t
(values between 0 and 13 are valid for k; programming 14 or
15 provides the same result as programming 13).
is the AD9600 ADC sample rate in hertz.
f
CLK
k
2__
CLK
×=
π×
2
Bit 1—DC Correction for Signal Path Enable
Setting Bit 1 high causes the output of the dc measurement block to
be summed with the data in the signal path to remove the dc offset
from the signal path.
Bit 0—DC Correction for Signal Monitor Enable
Bit 0 enables the dc correction function in the signal monitor block.
The dc correction is an averaging function that can be used by
the signal monitor to remove dc offset in the signal. Removing
this dc from the measurement allows a more accurate reading.
Signal Monitor DC Value Channel A (Register 0x10D and Register 0x10E)
Register 0x10D, Bits [7:0]—DC Value Channel A [7:0]
Register 0x10E, Bits [7:6]—Reserved
Register 0x10E, Bits [5:0]—DC Value Channel A [13:8]
These read-only registers hold the latest dc offset value computed
by the signal monitor for Channel A.
Signal Monitor DC Value Channel B (Register 0x10F and Register 0x110)
Register 0x10F Bits [7:0]—DC Value Channel B [7:0]
Register 0x110 Bits [7:6]—Reserved
Register 0x110 Bits [5:0]—DC Value Channel B [13:8]
These read-only registers hold the latest dc offset value computed
by the signal monitor for Channel B.
Signal Monitor SPORT Control (Register 0x111)
Bit 7—Reserved
Bit 6—RMS/MS Magnitude Output Enable
These bits enable the 20-bit rms or ms magnitude measurement
as output on the SPORT.
Bit 5—Peak Detector Output Enable
Bit 5 enables the 10-bit peak measurement as output on the SPORT.
Bit 4—Threshold Crossing Output Enable
Bit 4 enables the 10-bit threshold measurement as output on
the SPORT.
Bits [3:2]—SPORT SMI SCLK Divide
The values of these bits set the SPORT SMI SCLK divide ratio
from the input clock. A value of 0x01 sets divide by 2 (default),
a value of 0x10 sets divide by 4, and a value of 0x11 sets divide by 8.
Bit 1— SPORT SMI SCLK Sleep
Setting Bit 1 high causes the SMI SCLK to remain low when the
signal monitor block has no data to transfer.
Bit 0—Signal Monitor SPORT Output Enable
When set, Bit 0 enables the SPORT output of the signal monitor
to begin shifting out the result data from the signal monitor block.
Signal Monitor Control (Register 0x112)
Bit 7—Complex Power Calculation Mode Enable
This mode assumes that I data is present on one channel and
Q data is present on the opposite channel. The result reported
is the complex power, measured as
22
QI +
Bits [6:4]—Reserved
Bit 3—Signal Monitor RMS/MS Select
Setting Bit 3 low selects rms power measurement mode. Setting
Bit 3 high selects ms power measurement mode.
Bits [2:1]—Signal Monitor Mode
Bit 2 and Bit 1 set the mode of the signal monitor for the data
output of Register 0x116 to Register 0x11B. Setting Bit 2 and Bit 1
to 00 selects rms/ms magnitude output, setting these bits to 01
selects peak power output, and setting to 10 or 11 selects threshold
crossing output.
Bit 0—Signal Monitor Enable
Setting Bit 0 high enables the signal monitor block.
Rev. 0 | Page 44 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Signal Monitor Period (Register 0x113 to Register 0x115)
Register 0x113, Bits [7:0]—Signal Monitor Period [7:0]
Register 0x114, Bits [7:0]—Signal Monitor Period [15:8]
Register 0x115, Bits [7:0]—Signal Monitor Period [23:16]
This 24-bit value sets the number of clock cycles over which
the signal monitor performs its operation. The minimum value
for this register is 128 cycles; programmed values less than 128
revert to 128.
Signal Monitor Result Channel A (Register 0x116 to Register 0x118)
Register 0x116, Bits [7:0]—S
Channel A [7:0]
Register 0x117, Bits [7:0]—S
Channel A [15:8]
Register 0x118, Bits [7:4]—Reserved
Register 0x118, Bits [3:0]—S
Channel A [19:16]
This 20-bit value contains the result calculated by the signal
monitoring block for Channel A. The content is dependent on the
settings in Bits [2:1] of Register 0x112.
ignal Monitor Result
ignal Monitor Result
ignal Monitor Result
Signal Monitor Result Channel B (Register 0x119 to Register 0x11B)
Register 0x119, Bits [7:0]— Signal Monitor Result
hannel B [7:0]
C
Register 0x11A, Bits [7:0]—Signal Monitor Result
C
hannel B [15:8]
Register 0x11B, Bits [7:4]—Reserved
Register 0x11B, Bits [3:0]—Signal Monitor Result
C
hannel B [19:16]
This 20-bit value contains the result calculated by the signal
monitoring block for Channel B. The content is dependent on
the settings in Bits [2:1] of Register 0x112.
Rev. 0 | Page 45 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
DESIGN GUIDELINES
When designing the AD9600 into a system, the designer
should, before starting design and layout, become familiar with
these guidelines, which discuss the special circuit connections
and layout requirements for certain pins.
Power and Ground Recommendations
When connecting power to the AD9600, the designer should use
two separate 1.8 V supplies: one supply should be used for AVDD
and DVDD and a separate supply for DRVDD. The AVDD and
DVDD supplies, although derived from the same source, should be
isolated with a ferrite bead or filter choke and have separate
decoupling capacitors. The user can employ several different
decoupling capacitors to cover both high and low frequencies.
These should be located close to the point of entry at the PC
board level and close to the part’s pins with minimal trace
length.
A single PC board ground plane should be sufficient when
u
sing the AD9600. With proper decoupling and smart partitioning of the PC board’s analog, digital, and clock sections,
optimum performance can be easily achieved.
Exposed Paddle Thermal Heat Slug Recommendations
To achieve the best electrical and thermal performance of the
AD9600, the exposed paddle on the underside of the ADC must
be connected to analog ground (AGND). A continuously exposed
(no solder mask) copper plane on the PCB should mate to the
exposed paddle, Pin 0, of the AD9600. In addition, the copper
plane should have several vias to achieve the lowest possible
resistive thermal path for heat dissipation to flow through the
bottom of the PCB, and these vias should be filled or plugged
with nonconductive epoxy.
To maximize the coverage and adhesion between the ADC and
, overlay a silkscreen to partition the continuous plane on
PCB
the PCB into several uniform sections. This provides several tie
points between the ADC and PCB during the reflow process.
Using one continuous plane with no partitions guarantees only
one tie point between the ADC and PCB. See the evaluation board
layout figures (Figure 84 to Figure 91) for an example of a PCB
yout. For detailed information on packaging and the PCB layout
la
of chip scale packages, see the AN-772 Application Note, A D
and Manufacturing Guide for the Lead Frame Chip Scale Package
(LFCSP).
CML
The CML pin should be decoupled to ground with a 0.1 µF
capacitor, as shown in Figure 47.
RBIAS
The AD9600 requires the user to place a 10 kΩ resistor between
the RBIAS pin and ground. This register sets the master current
reference of the ADC core and should have at least a 1% tolerance.
Reference Decoupling
The VREF pin should be externally decoupled to ground with a
low-ESR 1.0 µF capacitor in parallel with a 0.1 µF ceramic lowESR capacitor.
SPI Port
The SPI port should not be active during periods when the full
dynamic performance of the converter is required. Because the
SCLK, CSB, and SDIO signals are typically asynchronous to the
ADC clock, noise from these signals can degrade the converter’s
performance. If the on-board SPI bus is used for other devices,
it may be necessary to provide buffers between this bus and the
AD9600 in order to keep these signals from transitioning at the
converter inputs during critical sampling periods.
esign
Rev. 0 | Page 46 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
EVALUATION BOARD
The AD9600 evaluation board provides all of the support
circuitry required to operate the ADC in its various modes and
configurations. The converter can be driven differentially using the
double-balun configuration (default) or an AD8352 differential
iver. The ADC can also be driven in a single-ended fashion.
dr
Separate power pins are provided to isolate the DUT from the
AD8352 drive circuitry. Each input configuration can be selected
b
y properly connecting various components (see Figure 74 to
Figure 83). Figure 73 shows the typical bench characterization
etup used to evaluate the ac performance of the AD9600.
s
It is critical that the signal sources used for the analog input and
clo
ck have very low phase noise (<<1 ps rms jitter) to realize the
optimum performance of the converter. Proper filtering of the
analog input signal to remove harmonics and lower the integrated
or broadband noise at the input is also necessary to achieve the
specified noise performance.
See Figure 74 to Figure 91 for the complete schematics and
l
ayout diagrams that demonstrate the routing and grounding
techniques that should be applied at the system level.
POWER SUPPLIES
The evaluation board comes with a wall-mountable switching
power supply that provides a 6 V, 2 A maximum output. Connect
the supply to the rated 100 V ac to 240 V ac wall outlet at 47 Hz
to 63 Hz. The output of the supply is a 2.1 mm inner diameter
circular jack that connects to the PCB at J16. Once on the PC
board, the 6 V supply is fused and conditioned before connecting
to six low dropout linear regulators that supply the proper bias
to each of the various sections of the board.
WALL OUTLET
100V AC TO 240V AC
47Hz TO 63Hz
6V DC
2A MAX
SWITCHING
POWER
SUPPLY
ROHDE & SCHWARZ,
SMA100A,
2V p-p SIG NAL
SYNTHESIZ ER
ROHDE & SCHWARZ,
SMA100A,
2V p-p SIG NAL
SYNTHESIZ ER
ROHDE & SCHWARZ,
SMA100A,
2V p-p SIGNAL
SYNTHESIZER
BAND-PASS
FILTER
BAND-PASS
FILTER
AINA
AINB
CLK
5.0V
–+
GND
1.8V
GND
AVDD IN
AMP VDD
AD9600
EVALUAT ION BO ARD
Figure 73. Evaluation Board Connection
–+–+
3.3V
GND
The evaluation board can be operated using external supplies by
emoving L1, L3, L4, and L13 to disconnect the voltage
r
regulators supplied from the switching power supply. This
enables the user to individually bias each section of the board.
Use P3 and P4 to connect a different supply for each section. At
least one 1.8 V supply is needed with a 1 A current capability
for AVDD and DVDD; a separate 1.8 V to 3.3 V supply is
recommended for DRVDD. To operate the evaluation board
using the AD8352 driver, a separate 5.0 V supply (AMP VDD)
ith a 1 A current capability is needed. To operate the evaluation
w
board using the alternative SPI options, a separate 3.3 V analog
supply (VS) is needed in addition to the other supplies. The 3.3
V supply (VS) should also have a 1 A current capability. Using
Solder Jumper SJ35 allows the user to separate AVDD and
DVDD if desired.
INPUT SIGNALS
When connecting the clock and analog sources to the evaluation
board, use clean signal generators with low phase noise, such as
Rohde & Schwarz SMA100A or Agilent HP8644 signal generators
or the equivalent, as well as a 1 m, shielded, RG-58, 50 Ω coaxial
cable. Enter the desired frequency and amplitude for the ADC.
The AD9600 evaluation board from Analog Devices can accept
a ~2.8 V p-p or a 13 dBm sine wave input for the clock. When
connecting the analog input source, it is recommended to use a
multipole, narrow-band, band-pass filter with 50 Ω terminations.
Good choices of such band-pass filters are available from TTE,
Allen Avionics, and K&L Microwave, Inc. Connect the filter
directly to the evaluation board, if possible.
OUTPUT SIGNALS
The parallel CMOS outputs interface directly with the Analog
Devices standard ADC data capture board (HSC-ADCEVALCZ). For more information on the ADC data capture
boards and their optional settings, visit www.analog.com/FIFO.
–+
DRVDD IN
3.3V
GND
VS
PARALLEL
PARALLEL
3.3V
–+
VCP
GND
10-BIT
CMOS
10-BIT
CMOS
SPI SPI
HSC-ADC-EVALCZ
FPGA BASED
DATA
CAPTURE BOARD
USB
CONNECTION
PC RUNNING
VISUAL ANALOG
AND SPI
CONTROLL ER
SOFTWARE
06909-300
Rev. 0 | Page 47 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DEFAULT OPERATION AND JUMPER SELECTION SETTINGS
The following is a list of the default and optional settings, or
modes, allowed on the AD9600 evaluation board.
POWER
Connect the switching power supply that is provided with the
evaluation kit between a rated 100 V ac to 240 V ac wall outlet
at 47 Hz to 63 Hz and P500.
VIN
The evaluation board is set up for a double-balun configuration analog input with an optimum 50 Ω impedance matching
from 70 MHz to 200 MHz. For more bandwidth response, the
differential capacitor across the analog inputs can be changed or
removed (see Tabl e 1 0 ). The common mode of the analog inputs is
eveloped from the center tap of the transformer via the CML
d
pin of the ADC (see the Analog Input Considerations section).
VREF
VREF is set to 1.0 V by tying the SENSE pin to ground and
adding a jumper on Header J5 (Pin 1 to Pin 2). This causes the
ADC to operate in the 2.0 V p-p full-scale range. To place the
ADC in the 1.0 V p-p mode (VREF = 0.5 V), a jumper should
be placed on Header J4. A separate external reference option is
also included on the evaluation board. To use an external reference,
connect Pin 1 of J6 to Pin 2 of J6 and provide an external
reference at TP5. Proper use of the VREF options is detailed in
the Vol ta g e Re f er e nce section.
RBIAS
RBIAS requires that a 10 kΩ resistor (R503) be connected to
ground. This pin is used to set the ADC core bias current.
CLOCK
The default clock input circuitry is derived from a simple baluncoupled circuit using a high bandwidth 1:1 impedance ratio balun
(T5) that adds a very low amount of jitter to the clock path. The
clock input is 50 Ω terminated and ac-coupled to handle singleended sine wave inputs. The transformer converts the single-ended
input to a differential signal that is clipped before entering the
ADC clock inputs. When the AD9600 input clock divider is used,
clock frequencies up to 625 MHz can be input into the evaluation
board through Connector S5.
PDWN
To enable the power-down feature, connect J7, shorting the
PDWN pin to AVDD.
CSB
The CSB pin is internally pulled up, setting the chip into
external pin mode, to ignore the SDIO and SCLK information.
To connect the control of the CSB pin to the SPI circuitry on the
evaluation board, connect Pin 1 of J21 to Pin 2 of J21.
SCLK/DFS
If the SPI port is in external pin mode, the SCLK/DFS pin sets the
data format of the outputs. If the pin is left floating, the pin is
internally pulled down, setting the default data format condition
to offset binary. Connecting Pin 1 of J2 to Pin 2 of J2 sets the
format to twos complement. If the SPI port is in serial pin mode,
connecting Pin 2 of J2 to Pin 3 of J2 connects the SCLK pin to the
on-board SPI circuitry (see the Serial Port Interface (SPI)
on).
secti
SDIO/DCS
If the SPI port is in external pin mode, the SDIO/DCS pin acts
to set the duty cycle stabilizer. If the pin is left floating, the pin is
internally pulled up, setting the default condition to DCS enabled.
To disable the DCS, connect Pin 1 of J1 to Pin 2 of J1. If the SPI
port is in serial pin mode, connecting Pin 2 of J1 to Pin 3 of J1
connects the SDIO pin to the on-board SPI circuitry (see the
Serial Port Interface (SPI) section).
ALTERNATIVE CLOCK CONFIGURATIONS
Two clocking options are provided on the AD9600 evaluation
board. The first option is to use the on-board crystal oscillator
(Y1) to provide the clock input to the part. To enable this
crystal, Resistors R8 (0 Ω) and R85 (10 kΩ) should be installed
and Resistors R82 and R30 should be removed.
The second option is to use a differential LVPECL clock to
d
rive the ADC input using the AD9516-4 (U2). When using
th
is option, the AD9516-4 charge-pump filter components need
be populated (see Figure 78). Consult the AD9516-4 data
to
eet for more information.
sh
To configure the clock input (from S5) to drive the AD9516
re
ference input instead of directly driving the ADC, the
ollowing components need to be added, removed, and/or
f
changed.
1.
Remove R32, R33, R99, and R101 in the default clock path.
2.
Populate C78 and C79 with 0.001 µF capacitors and R78
and R79 with 0 Ω resistors in the clock path.
Additionally, unused AD9516 outputs (one LVDS and one
VPECL) are routed to optional Connectors S8 through S11 on
L
the evaluation board.
Rev. 0 | Page 48 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Remove C1, C17, C18, and C117 in the default analog
ALTERNATIVE ANALOG INPUT DRIVE CONFIGURATION
This section provides a brief description of the alternative analog
input drive configuration using the AD8352. When using this
d
rive option, some additional components need to be populated.
For more details on the AD8352 differential driver, including
how
it works and its optional pin settings, consult the AD8352
ta sheet.
da
To configure the analog input to drive the AD8352 instead of
th
e default transformer option, the following components need
to be added, removed, and/or changed for Channel A. In addition,
the corresponding components for Channel B should be changed.
1.
input path.
2.
Populate C8 and C9 with 0.1 µF capacitors in the analog
input path. To drive the AD8352 in the differential input
ode populate Transformer T10; Resistors R1, R37, R39,
m
R126, and R127; and Capacitors C10, C11, and C125.
3.
Populate the optional amplifier output path with the
desired components, including an optional low-pass filter.
Install 0 Ω Resistors R44 and R48. Resistors R43 and R47
should be increased (typically to 100 Ω) to increase the
output impedance seen by the AD8352 to 200 Ω.
Rev. 0 | Page 49 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SCHEMATICS
DNPDNP
C139
AMP-A
12PF
AMP+A
AVDD
AVDD
06909-301
DNPDNP
L16
180NH
12
IND0603
C4
18PF
120NH
12
L14
IND0603
C12
C2
0.1U
10KOHM
R41
AMPVDD
BA
W1
R40
10KOHM
R38
R37
0OHM
AMPVDD
C10
0.1U
R31
0OHM
C8
0.1U
0.001U
12
11
GND
VON 10
VOP
VCC
13
VCM
14
15
16
DNP
Z1
ENB
VIP
RGN
RGP
RDP
3
2
1
100OHM
R127
C125
.3PF
4.12K
R126
DNP
R36
24.9OHM
R29
123
ETC1-1-13
PS
5
C9
OPTIONAL AMPLIFIER INPUT PATH
INA-
12
L17
12
L15
C16
9
GND
VCC
AD8352
GND
VIN
RDN
4
R35
F
T10
R54
4
0.1U
INA+
DNP
180NH
IND0603
DNP
120NH
IND0603
0.001U
8
67
5
24.9OHM
0OHM
R49
0OHM
1
TP14
AMPVDD
C27
10U
C23
0.1U
C22
0.1U
R39
0OHM
C11
0.1U
R26
AMP-A
R44
0OHM
C17
CML
T7
R110
0OHM
R50
VIN-A
33OHM
0OHM
1
TP15
C5
4.7PF
33OHM
R43
R42
CML
0.1U
4
T2
F
3
654
F
T1
ADT1_1W T
123
57.6OHM
R5
C3
0.1U
0OHM
C18
5
PS
1
2
PS
4
VIN+A
R27
33OHM
33OHM
R47
AMP+A
R48
0OHM
0.1U
0OHM
ETC1-1-1 3
123
ETC1-1-1 3
5
R4
DEFAULT AMPLIFIER INPUT PATH
0.1U
R2
INA-
C47
0.1U
C117
R120
0OHM
1
2
S1
0OHM
C1
0.1U
R121
0OHM
57.6OHM
R28
RES0402
1
S2
INA+
57.6OHM
R1
2
Figure 74. Evaluation Board Schematic, Channel A Analog Inputs
Rev. 0 | Page 50 of 72
AIN-
AIN+

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
AVDD
R80
C29
12PF
C19
18PF
10
VON
Z2
RGN
AMP-B
DNPDNP
12
L21
12
L19
C140
9
GND
VCC
AD8352
GND
VIN
RDN
413
180NH
IND0603IND0603
120NH
DNP DNP
0.001U
8
67
5
AMPVDD
AMP+B
DNP
180NH
12
L20
DNP
120NH
12
L18
IND0603 IND0603
C46
0.001U
C24
0.1U
12
10KOHM
R53
AMPVDD
BA
R131
10KOHM
W2
11
GND
VOP
VCC
13
VCM
15
ENB
16 14
VIP
RGP
RDP
2
0OHM
1
TP16
R73
C62
10U
C61
0.1U
C60
0.1U
AMP-B
R94
0OHM
AVDD
VIN-B
R81
0OHM
1
TP17
C84
33OHM
33OHM
R70
R96
VIN+B
4.7PF
R74
33OHM
57.6OHM
R72
C83
0.1U
33OHM
R71
0OHM
CML
AMP+B
R95
0OHM
06909-302
C82
321
F
T4
4
PS
5
C6
R123
1
S3
0.1U
0OHM
R69
321
F
T3
4
0.1U
INB+
0OHM
RES0402
57.6OHM
R52
2
100OHM
AMPVDD
R132
C38
R66
DNP
R133
0OHM
0.1U
0OHM
R129
C128
.3PF
4.12K
R128
DNP
R68
24.9OHM
R134
321
F
ETC1-1-13
T11
PS
4
5
R6
0OHM
C39
0.1U
24.9OHM
R135
R55
0OHM
DEFAULT AMPLIFIER INPUT PATH
OPTIONAL AMPLIFIER INPUT PATH
C30
0.1U
INB+
C31
0.1U
INB-
C7
0.1U
ETC1-1-13
PS
CML
R111
0OHM
ADT1_1WT
INB-
C28
R122
1
S4
5
456
T8
321
ETC1-1-13
0.1U
C51
R67
0.1U
0OHM
RES0402
0OHM
57.6OHM
R51
2
Figure 75. Evaluation Board Schematic, Channel B Analog Inputs
Rev. 0 | Page 51 of 72
AIN-
AIN+

AD9600
0
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
CLK+
24.9OHM
C20
0.1U
R78
0OHM
ALTCLK+
VS
0.1U
C145
C64
R99
OPT_CLK+
C78
0.001U
456
C56
0.1U
321
OPT_CLK+
0.001U
R83
0OHM
R32
0OHM
R33
0OHM
T9
C63
ADT1_1WT
5
0.001U
321
F
T5
PS
4
TP2
21
DNP
R34
OPT_CLK -
C79
0.001U
ETC1-1-13
C94
OPT_CLK-
C77
0.001U
0.001U
R84
R79
R101
0OHM
ALTCLK-
6909-303
CLK -
C21
0.1U
24.9OHM
0OHM
10KOHM
R85
10KOHM
R82
R8
R90
0OHM
0OHM
R30
1
2
S5
SMA200UP
ENC
R3
0OHM
57.6OHM
S6
SMA200UP
57.6OHM
R7
1
2
ENC\
Figure 76. Evaluation Board Schematic, DUT Clock Input
Rev. 0 | Page 52 of 72

AD9600
T
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
LVDS
OUTPU T
S8
1
S9
2
2
1
100OHM
S10
1
LVPECL
OUTPU
S11
2
2
1
06909-304
R75
C88
0.1U
C87
0.1U
C85
0.1U
C86
0.1U
SYNC
200
C141
0.001U
100OHM
R9
OUT6P
OUT6N
VS
49
5031
51
52
OUT1B
53
OUT1
54
55
VS_OUT_DR
4.12K
VS
R12
AGND
VS
5.1K
R11
OUT0B
56
OUT0
57
VS_REF
58
59
60
61
VS_PLL_2
62
CP_RSET
63
REFINB
64
REFIN
TP8
1
48
OUT6
TOADC
LVPECL
ALTCLK-
ALTCLK+
200
R86
200
R88
AGNDCP
44
43
46
47
OUT7
OUT6B
42
45
OUT2
OUT2B
OUT7B
GND_ESD
VS
VS_OUT_DR
41
VS_OUT23_DRV
AGND
37
40
39
OUT3
OUT3B
35
38
36
OUT9
OUT9B
VS_OUT23_DIV
GND_OUT89_DIV
VS_OUT67_1
VS_OUT67_2
VS_OUT01_DIV
VS_OUT01_DRV
U2
RSET_CLOCK
GND_REF
AD9516_64LFCSP
VS_PRESCALER
R91
200
R92R125
33
34
OUT8
OUT8B
VS
PAD
VS_OUT89_2
32
VS_OUT89_1
VS_OUT45_DIV
30
OUT5B
29
OUT5
28
VS_OUT45_DRV
27
OUT4B
26
OUT4
25
PDB
24
RESETB
23
SDIO
22
SDO
21
NC4
20
NC3
19
NC2
18
CSB
17
VS_OUT_DR
PDB
RESETB
SDI
SDO
CSB_2
OPT_CLK+
OPT_CLK-
VS_PLL_1
1
VS
TP19
CP
LD
REFMON
2
STATUS
VCP
3
6
4
5
STATUS
REFMON
VCP
1
TEST
R10
TEST
TP18
0OHM
C104
0.1U
LD
1
TEST
TP20
Figure 77. Evaluation Board Schematic, Optional AD9516 Clock Circuit
Rev. 0 | Page 53 of 72
C97
0.1U
C96
BYPASS_LDO
LF
REF_SEL
SYNCB
7
9
8
CLK
NC1
VS_CLK_DIST
VS_VCO
12
10
11
SCLK
CLKB
15
16
13
14
0.1U
VCP
BYPASS_LDO
VS
LF
SYNCB
1
REF_SEL
C80
18PF
VCXO_CLK +
S7
AD9516
CLKIN
SCLK
C99
0.1U
C98
0.1U
0.1U
C143
C142
49.9OHM
R89
R124
0OHM
RES0402
1
2
0OHM
RES0402
0.1U
C101
0.1U
C100
0.1U
VCXO_CLK -
VS_OUT_DR

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
RESET BSYNC BPDBREF_SE L
RES0402
10KOHM
VSVSVSVS
R105
RES0402
10KOHM
R103
RES0402
10KOHM
R102
VCXO_CLK -
RES0402
10KOHM
R100
VCP
SYNC
24.9OHM
R87
RES0402
10KOHM
R107
RES0402
10KOHM
R106
VCXO_CLK +
R139
R114
VCP
6
VCC
0OHM
0OHM
RES0402
RES0402
RES0402
10KOHM
R109
RES0402
10KOHM
R108
4
5
OUT2
OUT1
06909-305
R104
0OHM
RES0402
1
R46
33OHM
RES0402
456
Y2
VCC
NL27WZ04
GND
A2
321
C25
0.1U
RES0603
57.6OHM
R45
1
2
S12
SMA200UP
AC
TP1
C26
0.1U
Y1
U3
A1
LD
VS
200
R76
VS
SYNC
OSCVECTRON_VS500
FREQ_CTRL_V
1
LF
R116
0OHM
0OHM
RES0402
RES0402
C92
VALVALVA L
C91
Charge Pump Filter
C90
R136 R137 R97 R117
CP
VS-500
GND
OUT_DISABLE
3
2
SEL
SEL
C89
R93
VAL
SEL
SEL
Figure 78. Evaluation Board Schematic, Optional AD9516 Loop Filter/VCO and SYNC Input
U25
C144
SEL
VAL
R98
BYPASS_LDO
Rev. 0 | Page 54 of 72

AD9600
S
O
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
D3A
SPARE5
SPARE6
SPARE7
SPARE8
DCOB
DCOA
D2A
1
D2A
D3A
D4A
D5A
D6A
D7A
D8A
D9A
8765432
RPAK8
8765432
22ohm
9
10111213141516
0.1U
C36
C35
0.001U
DRVD D
TP3
1
RES0402
R115
0OHM
RPAK8
22ohm
FD0A
FD1A
FD2A
FD3A
PWR_SD
PWR_SCLK
PWR_SDF
R62
16
1
15
2
14
3
13
4
12
5
11
6
10
7
9
8
RES0402
RES0402
R113
0OHM
0OHM
R112
DVDD
22ohm
1
RPAK8
R61
20
21
22
24
27
28
29
30
31
32
D0A
(LSB)
17
D1A
18
D2A
D3A
DRGND
DRVDD
D4A
D5A
DVDD
D6A
D7A
D8A
D9A(MSB)
FD0A
FD1A
FD2A
FD3A
SMI_SDO/OEB
9
10111213141516
16
NC
NCNCNC
SMI_SCLK/PDW N
SMI_SDF S
333534
146015
13
AVDD
36
NC
VIN+A
1
121011
DCOA
VIN-A
1
1
R60
DCOB
D9B(MSB)
SENSE
VREF
3943384437
9
AD9600
40
D9B
8765432
RPAK8
22ohm
9
10111213141516
7266255234
8
D7B
D8B
CML
RBIAS
42
41
D6B
D7B
D8B
D2B
D3B
D4B
D5B
1
SPARE3
SPARE4
D0B
D1B
1
R59
0.001U
C33
3192
1
D6B
VIN-B
D2B
D3B
D4B
D5B
VIN+B
DRVDD
64
DRGND
63
D1B
62
D0B(LSB)
61
NC
NC
59
NC
58
57
DVDD
56
FD3B
55
FD2B
54
FD1B
53
FD0B
52
SYNC
51
SPI_CSB
50
CLK-
49
CLK+
AVDD2
AVDD3
SPI_SCLK/DFS
SPI_SDIO/DCS
47
48
46
45
432
1
RPAK4
22ohm
567
8
0.1U
C34
R58
DRVDD
DVDD
SYNC
SPI_CSB
CLKCLK+
U1
FD1B
FD2B
FD3B
SPARE1
SPARE2
8765432
9
10111213141516
FD0B
06909-306
1
RPAK8
R57
22ohm
CM L
VIN-A
AVDD
VIN+ A
DRVDD
J7- INSTALL FOR PDWN
J8- INSTALLFOROUTPUTDISABLE
C14
0.1U
J5- INSTALLFORIVVREF/2VINPUTSPAN
J4- INSTALLFOR0.5VVREF/IV INPUTSPAN
J6- INSTALLFOREXTERNALREFERENCEMODE
C15
1U
VIN-B
VIN+ B
AVDD
AVDD
SPI_SDIO
SPI_SCLK
C137
C120
0.1U
0.1U
C32
RES0402
RES0402
R63
R64
0OHM
10KOHM
1
TP6
AVDD
TP5
1
C40
0.1U
C126
0.001U
C127
0.001U
DVDD
0.001U
C121
0.1U
C109
0.1U
C122
0.001U
AVDD
Figure 79. Evaluation Board Schematic, DUT
Rev. 0 | Page 55 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
C71
0.1U
C76
0.1U
C70
0.1U
C75
0.1U
C69
0.1U
C68
0.1U
C67
0.1U
C66
0.1U
C65
0.1U
V_DIG
J12
A1
A2
B2
B3
C1
C2
D1
D2
TYCO_HM-ZD
RES0402
10KOHM
VS
R118
R143
R119
0OHM
1
RES0402
TEST
TP21
SDO
RESETB
VS
C74
0.1U
C73
0.1U
C72
0.1U
V_DIG
DG10
DG9
DG8
DG7
DG6
DG5
DG4
DG3
DG2
DG1
BG10
BG9
BG8
BG7
BG6
BG5
BG4
BG3
BG2
BG1
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
B4
B5
B6
B7
C3
C4
D3
0OHM
C5
D4
D5
A10
B10
R142
0OHM
SDFS_OUT
RES0402
RES0402
SDI
R141
0OHM
SCLK_OUT
RES0402
RES0402
10KOHM
R140
R144
0OHM
B8
C6
C7
D6
R145
RES0402
C8
D7
D8
VAL
R130R77
1
1
TEST
TEST
TP24
TP23
SYNC
0OHM
RES0402
B1
B9
C9
D9
C10
D10
SDO_OUT
1
TEST
TP22
100OHM
OUT6P
06909-307
OUT6N
CSB_2
DG10
DG9
DG8
DG7
DG6
DG5
DG4
DG3
DG2
DG1
BG10
BG9
BG8
BG7
BG6
BG5
BG4
BG3
BG2
BG1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
B1
C9
CHANNELA
C10
D10
SCLK_OUT
SDFS_OUT
DIGITAL/HSC-ADC-EVALCZ INTERFACE
24
U15
25
PWR_SCLK
PWR_SDFS
B8
B9
C7
C8
D8
D9
V_DI G
SDO_OUT
V_DI G
FD3A
PWR_SDO
B6
B7
D7
FD2A
FD1A
C5
C6
D6
A10
B10
D6A
D7A
D8A
D9A
FD0A
V_DI G
B4
B5
C3
C4
D4
D5
1234567891011121314151617181920212223
U16
74VCX162244MTD
4847464544434241403938373635343332313029282726
D4A
D5A
B2
B3
C1
C2
D2
D3
V_DIG
24
25
D0A
D1A
D2A
D3A
V_DI G
SPARE8
Figure 80. Evaluation Board Schema
CSB
SCLK
J10
A1
D1
B1
C10
D10
TYCO_HM-ZD
OUT6N
DCOB
DCOA
SPARE7
D9B
SPARE5
SPARE6
A8
A9
B9
C8
C9
D8
D9
1234567891011121314151617181920212223
4847464544434241403938373635343332313029282726
V_DI G
D4B
D5B
D6B
D7B
D8B
BG6
BG5
BG4
BG3
BG2
BG1
A7
B7
B8
C6
C7
D6
D7
24
U17
74VCX162244MTD
25
DG3
DG2
DG1
BG10
BG9
BG8
BG7
A5
A6
B6
C5
D5
A10
B10
V_DI G
D0B
D1B
D2B
D3B
V_DI G
SPARE4
DG10
DG9
DG8
DG7
DG6
DG5
DG4
J11
CHANNELB
A1
A2
A3
A4
B4
B5
C3
C4
D4
FD2B
FD3B
SPARE3
SPARE1
SPARE2
B2
B3
C1
C2
D1
D2
D3
V_DI G
FD0B
FD1B
V_DI G
TYCO_HM-ZD
OUT6P
1234567891011121314151617181920212223
74VCX162244MTD
4847464544434241403938373635343332313029282726
tic, Digital Output Interface
Rev. 0 | Page 56 of 72

AD9600
T
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
JUMPER PINS 1 TO 2 FOR DCS ENABLE
JUMPER PINS 1 TO 2 FOR T WOS COMP LE M E NT OUTPU
J1 - JUMPER PINS 2 TO 3 FOR SPI OPERATION
J2 - JUMPER PINS 2 TO 3 FOR SPI OPERATION
1
J1
3
V_DI G
J21 - INSTALL JUMPER FOR SPI OPERATION
SPI_SCLK
SPI_SDIO
1
J2
3
R22
R23
100KOHM
RES0603
SPI_CSBV_DIG
100KOHM
RES0603
06909-308
R17
V_DI G
VCC
GND
100KOHM
RES0603
456
Y2
NC7WZ16P6 X
A2
321
CSB
RES040 2
10KOHM
R65
V_DIG
R20
R19
U7
SDI
VS
R21
1KOHM
RES0603
1KOHM
RES0603
R18
1KOHM
RES0603
V_DIG
SDO
4
5
6
Y1
Y2
VCC
NC7WZ07P6 X
A1
GND
A2
3
2
1
C13
0.1U
10KOHM
RES0402
V_DI G
V_DIG
C81
0.1U
Y1
U8
R24
CSB_2
A1
10KOHM
RES0402
SCLK
CSB
SDI
SDO
SCLK
Figure 81. Evaluation Board Schematic, SPI Circuitry
Rev. 0 | Page 57 of 72

AD9600
N
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DRVDDI
21
L4
10uh
IND1210
C45
AVDDI N
21
L3
10uh
IND1210
C43
1U
ADP3339
OUT
GND
4
1
PAD
VR3
IN
3
C42
1U
21
CR12
S2A_RECT
21
CR11
S2A_RECT
VR1
ADP3334
1U
C93
0.001U
140KOHM
R13
1
2
3
FB
GND
OUT
IN2
IN
8
7
5
OUT2
SD
6
C44
1U
78.7KOHM
R14
DRVDDSETTING
147K
78.7K
94.0K
140K
107K
76.8K
3.3
1.8
2.5
DRVDD R13 R1 4
TP4
TP9
1
1
1
TP131TP121TP10
GNDTEST POINT S
06909-309
1
1
21
CR10
S2A_RECT
RES0603
AC
PWR_IN
21
CR8
SHOT_RECT
245
6
CG
CG
CB
CG
F1
BIAS
PSG
1
3
CR7
21
S2A_RECT
F2
SMDC110F
C41
10U
2
J16
POWER_JAC K
6V,2A MAX
3
1
POWERINPUT
261OHM
R16
AVDD
C57
0.1U
C52
L6
IND1210
10UH
12
SJ35
10U
BNX-016
AVDDIN
1P12P23P34P45P56
P3
DVDD
C103
0.1U
C102
10U
21
L9
IND1210
10UH
P6
OPTIONALPOWERSUPPLYINPUTS
1
TP25
DRVDD
21
IND1210
DRVDDIN
P4
V_DI G
C59
C54
21
L11
IND1210
10uh
C58
0.1U
C53
10U
L10
10uh
VS
P1P2P3
0.1U
10U
VCP
P4
Figure 82. Evaluation Board Schematic, Power Supply
Rev. 0 | Page 58 of 72

AD9600
5
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
C10
AMPVDD
21
L1
IND1210
10UH
C130
1U
OUT
GND
4
1
PAD
ADP3339
IN
VR4
3
C129
1U
PWR_IN
VS_OUT_DR
21
L12
IND1210
10uh
VS
21
L13
IND1210
10uh
0.1U
C116
0.1U
C107
0.1U
C113
0.1U
C114
0.1U
C115
0.1U
C111
0.1U
C108
0.1U
C112
0.1U
C110
0.1U
VS
VCP
21
L8
IND1210
10UH
C131
1U
06909-310
OUT
IN
PWR_IN
SJ37
C95
0.001U
140KOHM
C136
1U
GND
1
C135
1U
VR2
ADP3334
R25
1
2
3
FB
5
GND
OUT
OUT2
6
SD
IN2
IN
8
7
C132
1U
PWR_IN
78.7KOHM
R15
C118
10U
VS
C124
10U
VS_OUT_DR
C119
10U
VCP
VCP
Power Supply ByPass Capacitors
SJ36
C134
1U
OUT
GND
4
1
PAD
ADP3339
IN
VR5
3
C133
1U
PWR_IN
4
PAD
ADP3339
VR6
3
Figure 83. Evaluation Board Schematic, Power Supply Cont.
Rev. 0 | Page 59 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
EVALUATION BOARD LAYOUTS
Figure 84. Evaluation Board Layout, Primary Side
Rev. 0 | Page 60 of 72
06909-185

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Figure 85. Evaluation Board Layout, Ground Plane
Rev. 0 | Page 61 of 72
6909-186

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Figure 86. Evaluation Board Layout, Power Plane
Rev. 0 | Page 62 of 72
6909-187

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Figure 87. Evaluation Board Layout, Power Plane
Rev. 0 | Page 63 of 72
6909-188

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Figure 88. Evaluation Board Layout, Ground Plane
Rev. 0 | Page 64 of 72
06909-189

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Figure 89. Evaluation Board Layout, Secondary Side (Mirrored Image)
Rev. 0 | Page 65 of 72
6909-190

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Figure 90. Evaluation Board Layout, Silkscreen, Primary Side
Rev. 0 | Page 66 of 72
06909-191

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Figure 91. Evaluation Board Layout, S
Rev. 0 | Page 67 of 72
ilk Screen, Secondary Side
6909-192

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
BILL OF MATERIALS
Table 23. Evaluation Board Bill of Materials (BOM)
Reference
gnator
Item Qty
1 1 AD9600CE_REVB PCB PCB Analog Devices
2 55 C1 to C3, C6, C7,
3 1 C80 18 pF, COG, 50 V, 5% ceramic
4 2 C5 , C84 4.7 pF, COG, 50 V, 5% ceramic
5 10 C33, C35, C63,
6 13 C15, C42 to C45,
7 10 C27, C41, C52 to
8 1 CR5 Schottky diode HSMS2822, SOT23 SOT23 Avago Technologies HSMS-2822-BLKG
9 2 CR6, CR9 LED RED, SMT, 0603, SS-type LED0603 Panasonic LNJ208R8ARA
Desi
C13, C14, C17, C18,
C20 to C26, C32,
C57 to C61, C65
to C76, C81 to
C83, C96 to C101,
C103, C105, C107,
C108, C110 to
C116, C145
C93 to C95, C122,
C126, C127, C137
C129 to C136
C54, C62, C102,
C118, C119, C124
Description Package Manufacturer Mfg. Part Number
0.1 μF, 16 V ceramic
capacitor,
capacitor, SMT 0402
capacitor, SMT 0402
0.001 μF, X7R, 25 V, 10%
cer
1 μF, X5R, 25 V, 10% ceramic
capacitor, SMT 0805
10 μF, X5R, 10 V, 10% ceramic
capacitor,
SMT 0402
amic capacitor, SMT 0402
SMT 1206
1, 2
C0402SM Murata GRM155R71C104KA88D
C0402SM Murata GJM1555C1H180JB01J
C0402SM Murata GJM1555C1H4R7CB01J
C0402SM Murata GRM155R71H102KA01D
C0805 Murata GR4M219R61A105KC01D
C1206 Murata GRM31CR61C106KC31L
10 4 CR7, CR10 to CR12 50 V, 2 A diode DO_214AA Micro Commercial Components S2A-TP
11 1 CR8 30 V, 3 A diode DO_214AB Micro Commercial Components SK33-TP
12 1 F1 EMI filter FLTHMURATABNX01 Murata BNX016-01
13 1 F2 6.0 V, 3.0 A, trip current
14 2 J1 to J2 3-pin, male, single row,
15 9 J4 to J9, J18, J19,
J21
16 3 J10 to J12 Interface connector TYCO_HM_ZD Tyco 6469169-1
17 1 J14 8-pin, male, double row,
18 1 J16 DC power jack connector PWR_JACK1 Cui Stack PJ-002A
19 10 L1, L3, L4, L6, L8
to L13
20 1 P3 6-terminal connector PTMICRO6 Weiland Electric, Inc. Z5.531.3625.0
21 1 P4 4-terminal connector PTMICRO4 Weiland Electric, Inc. Z5.531.3425.0
22 3 R7, R30, R45 57.6 Ω, 0603, 1/10 W,
23 27 R2, R3, R4, R32,
R33, R42, R64,
R67, R69, R90,
R96, R99, R101,
R104, R110 to
R113, R115, R119,
R121, R123, R141
to R145
24 2 R13, R25 140 kΩ, 0603, 1/10 W,
25 2 R14, R15 78.7 kΩ, 0603, 1/10 W,
resettable fuse
straight header
2-pin, male, straight header HDR2 Samtec TWS-102-08-G-S
straight header
10 μH, 2 A bead core, 1210 1210 Panasonic EXC-CL3225U1
1% resistor
0 Ω, 1/16 W, 5% resistor R0402SM NIC Components NRC04ZOTRF
1% resistor
1% resistor
L1206 Tyco Raychem NANOSMDC150F-2
HDR3 Samtec TWS-1003-08-G-S
CNBERG2X4H350LD Samtec TSW-104-08-T-D
R0603 NIC Components NRC06F57R6TRF
R0603 NIC Components NRC06F1403TRF
R0603 NIC Components NRC06F7872TRF
Rev. 0 | Page 68 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reference
gnator
Item Qty
26 1 R16 261 Ω, 0603, 1/10 W,
27 3 R17, R22, R23 100 kΩ, 0603, 1/10 W,
28 7 R18, R24, R63, R65,
29 3 R19, R20, R21 1 kΩ, 0603, 1/10 W,
30 9 R26, R27, R43,
31 5 R57, R59 to R62 22 Ω, 16-pin, 8-resistor,
32 1 R58 22 Ω, 8-pin, 4-resistor,
33 1 R76 200 Ω, 0402, 1/16 W,
34 4 S2, S3, S5 ,S12 SMA, inline, male,
35 1 SJ35 0 Ω, 1/8 W, 1% resistor SLDR_PAD2MUYLAR NIC Components NRC10ZOTRF
36 5 T1 to T5 Balun TRAN6B M/A-COM MABA-007159-000000
37 1 U1 IC, AD9600 LFCSP64-9X9-9E Analog Devices AD9600BCPZ
38 1 U2 Clock distribution, PLL IC LFCSP64-9X9 Analog Devices AD9516-4BCPZ
39 1 U3 Dual inverter IC SC70_6 Fairchild Semiconductor NC7WZ04P6X_NL
40 1 U7 Dual buffer IC,
41 1 U8 UHS dual buffer IC SC70_6 Fairchild Semiconductor NC7WZ16P6X_NL
42 3 U15 to U17 16-bit CMOS buffer IC TSOP48_8_1MM Fairchild Semiconductor 74VCX16244MTDX_NL
43 2 VR1, VR2 Adjustable regulator LFCSP8-3X3 Analog Devices ADP3334ACPZ
44 1 VR3 1.8 V high accuracy regulator SOT223-HS Analog Devices ADP3339AKCZ-1.8
45 1 VR4 5.0 V high accuracy regulator SOT223-HS Analog Devices ADP3339AKCZ-5.0
46 2 VR5, VR6 3.3 V high accuracy regulator SOT223-HS Analog Devices ADP3339AKCZ-3.3
47 1 Y1 Oscillator clock, VFAC3 OSC-CTS-CB3 Valpey Fisher VFAC3-BHL
48 2 Z1, Z2 High speed IC, op amp LFCSP16-3X3-PAD Analog Devices AD8352ACPZ
1
This bill of materials is RoHS compliant.
2
The bill of materials lists only those items that are normally installed in the default condition. Items that are not installed are not included in the BOM.
Desi
R82, R118, R140
R46, R47, R70,
R71, R73, R74
Description Package Manufacturer Mfg. Part Number
1% resistor
1% resistor
10 kΩ, 0402, 1/16 W,
1% resistor
1% resistor
33 Ω, 0402, 1/16 W,
% resistor
5
resistor array
resistor array
1% resistor
coaxial connector
open-drain circuits
R0603 NIC Components NRC06F2610TRF
R0603 NIC Components NRC06F1003TRF
R0402SM NIC Components NRC04F1002TRF
R0603 NIC Components NRC06F1001TRF
R0402SM NIC Components NRC04J330TRF
R_742 CTS Corporation 742C163220JPTR
RES_ARRY CTS Corporation 742C083220JPTR
R0402SM NIC Components NCR04F2000TRF
SMA_EDGE Emerson Network
Power
SC70_6 Fairchild Semiconductor NC7WZ07P6X_NL
142-0701-201
Rev. 0 | Page 69 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
49
48
0.60 MAX
EXPOSED PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
PIN 1
64
INDICATOR
1
7.25
7.10 SQ
6.95
PIN 1
INDICATOR
9.00
BSC SQ
TOP VIEW
8.75
BSC SQ
0.60
MAX
0.50
BSC
1.00
0.85
0.80
SEATING
PLANE
12° MAX
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.30
0.23
0.18
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC ST ANDARDS MO-220-VMM D-4
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.20 REF
33
32
7.50
REF
16
17
0.25 MIN
051007-C
Figure 92. 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
9
mm × 9 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-64-3)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD9600BCPZ-150
AD9600BCPZ-125
AD9600BCPZ-105
AD9600-150EBZ
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
1
−40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-3
1
−40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-3
1
−40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-3
1
Evaluation Board with AD9600 and Software
Rev. 0 | Page 70 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
Rev. 0 | Page 71 of 72

AD9600
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
©2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D06909-0-11/07(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 72 of 72
 Loading...
Loading...