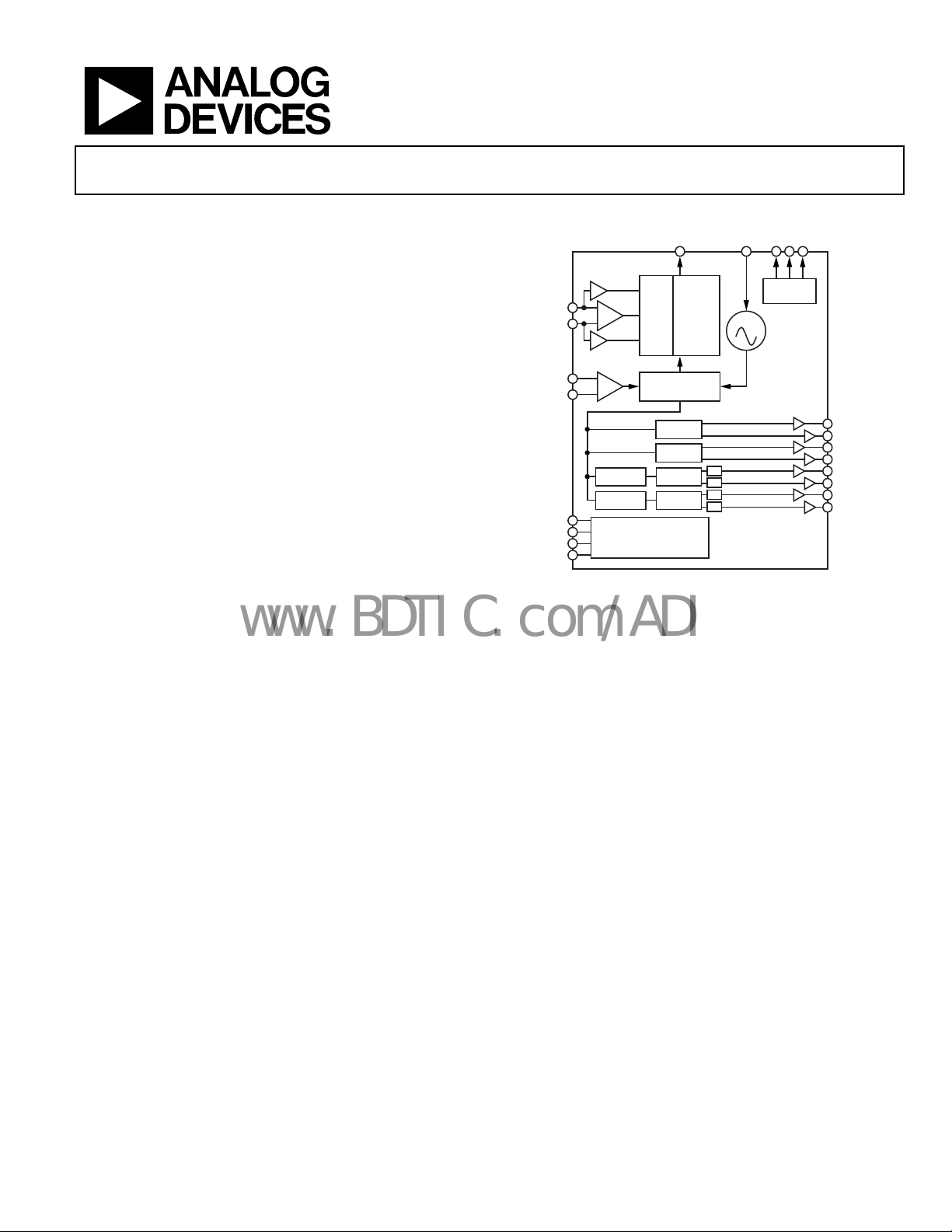
12-Output Clock Generator with
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES
Low phase noise, phase-locked loop
On-chip VCO tunes from 1.75 GHz to 2.25 GHz
External VCO/VCXO to 2.4 GHz optional
1 differential or 2 single-ended reference inputs
Reference monitoring capability
Auto and manual reference switchover/holdover modes
Autorecover from holdover
Accepts references to 250 MHz
Programmable delays in path to PFD
Digital or analog lock detect, selectable
2 pairs of 1.6 GHz LVPECL outputs
Each pair shares 1 to 32 dividers with coarse phase delay
Additive output jitter 225 f
Channel-to-channel skew paired outputs <10 ps
2 pairs of 800 MHz LVDS clock outputs
Each pair shares two cascaded 1 to 32 dividers with coarse
phase del
ay
Additive output jitter 275 f
Fine delay adjust (ΔT) on each LVDS output
Eight 250 MHz CMOS outputs (two per LVDS output)
Automatic synchronization of all outputs on power-up
Manual synchronization of outputs as needed
Serial control port
48-lead LFCSP
APPLICATIONS
Low jitter, low phase noise clock distribution
Clocking high speed ADCs, DACs, DDSs, DDCs, DUCs, MxFEs
High performance wireless transceivers
High performance instrumentation
Broadband infrastructure
AT E
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9517-31 provides a multi-output clock distribution
function with subpicosecond jitter performance, along with an
on-chip PLL and VCO. The on-chip VCO tunes from 1.75 GHz
to 2.25 GHz. Optionally, an external VCO/VCXO of up to
2.4 GHz may be used.
The AD9517-3 emphasizes low jitter and phase noise to
max
imize data converter performance, and it can benefit other
applications with demanding phase noise and jitter requirements.
rms
S
rms
S
Integrated 2.0 GHz VCO
AD9517-3
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
PLL
ΔT
ΔT
ΔT
ΔT
LF
STATUS
MONITOR
VCO
LVPECL
LVPECL
LVDS/CMOS
LVDS/CMOS
AD9517-3
CP
REF1
REFIN
REF2
SWITCHOVER
AND MONITOR
CLK
DIV/Φ DIV/Φ
DIV/Φ DIV/Φ
SERIAL CONT ROL PORT
DIVIDER
AND MUXs
DIV/Φ
DIV/Φ
AND
DIGITAL LOGIC
Figure 1.
The AD9517-3 features four LVPECL outputs (in two pairs);
four LVDS outputs (in two pairs); and eight CMOS outputs
(two per LVDS output). The LVPECL outputs operate to 1.6 GHz,
the LVDS outputs operate to 800 MHz, and the CMOS outputs
operate to 250 MHz.
Each pair of outputs has dividers that allow both the divide
atio and coarse delay (or phase) to be set. The range of division
r
for the LVPECL outputs is 1 to 32. The LVDS/CMOS outputs
allow a range of divisions up to a maximum of 1024.
The AD9517-3 is available in a 48-lead LFCSP and can be
op
erated from a single 3.3 V supply. An external VCO, which
requires an extended voltage range, can be accommodated
by connecting the charge pump supply (VCP) to 5.5 V. A
separate LVPECL power supply can be from 2.375 V to 3.6 V.
The AD9517-3 is specified for operation over the standard
ustrial range of −40°C to +85°C.
ind
1
AD9517 is used throughout to refer to all the members of the AD9517
family. However, when AD9517-3 is used, it is referring to that specific
member of the AD9517 family.
OUT0
OUT1
OUT2
OUT3
OUT4
OUT5
OUT6
OUT7
06427-001
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 3
Specifications..................................................................................... 4
Power Supply Requirements ....................................................... 4
PLL Characteristics ...................................................................... 4
Clock Inputs.................................................................................. 6
Clock Outputs............................................................................... 6
Timing Characteristics ................................................................ 7
Clock Output Additive Phase Noise (Distribution Only; VCO
Divider Not Used) ........................................................................ 8
Clock Output Absolute Phase Noise (Internal VCO Used).... 9
Clock Output Absolute Time Jitter (Clock Generation Using
Internal VCO) ............................................................................. 10
Clock Output Absolute Time Jitter (Clock Cleanup Using
Internal VCO) ............................................................................. 10
Clock Output Absolute Time Jitter (Clock Generation Using
External VCXO) ......................................................................... 10
Clock Output Additive Time Jitter (VCO Divider Not Used)
....................................................................................................... 11
Clock Output Additive Time Jitter (VCO Divider Used)..... 11
Delay Block Additive Time Jitter.............................................. 12
Serial Control Port .....................................................................12
,
, and
SYNC
PD
LD, STATUS, REFMON Pins.................................................... 13
Power Dissipation....................................................................... 14
Timing Diagrams............................................................................ 15
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 16
Thermal Resistance .................................................................... 16
ESD Caution................................................................................ 16
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 17
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 19
Te r mi n ol o g y .................................................................................... 25
Detailed Block Diagram ................................................................ 26
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 27
Operational Configurations...................................................... 27
High Frequency Clock Distribution—CLK or External
VCO >1600 MHz ...................................................................27
Internal VCO and Clock Distribution.................................29
Pins ..................................................... 13
RESET
Clock Distribution or External VCO <1600 MHz ............ 31
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) .................................................... 33
Configuration of the PLL ...................................................... 33
Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) ........................................ 33
Charge Pump (CP)................................................................. 34
On-Chip VCO ........................................................................ 34
PLL External Loop Filter....................................................... 34
PLL Reference Inputs............................................................. 34
Reference Switchover............................................................. 35
Reference Divider R............................................................... 35
VCXO/VCO Feedback Divider N: P, A, B, R ..................... 35
Digital Lock Detect (DLD) ....................................................... 37
Analog Lock Detect (ALD)................................................... 37
Current Source Digital Lock Detect (DLD) ....................... 37
External VCXO/VCO Clock Input (CLK/
Holdover .................................................................................. 38
Manual Holdover Mode ........................................................ 38
Automatic/Internal Holdover Mode.................................... 38
Frequency Status Monitors................................................... 39
VCO Calibration .................................................................... 40
Clock Distribution ..................................................................... 41
Internal VCO or External CLK as Clock Source ............... 41
CLK or VCO Direct to LVPECL Outputs........................... 41
Clock Frequency Division..................................................... 42
VCO Divider ........................................................................... 42
Channel Dividers—LVPECL Outputs................................. 42
Channel Dividers—LVDS/CMOS Outputs........................ 44
Synchronizing the Outputs—SYNC Function ................... 47
Clock Outputs......................................................................... 49
LVPECL Outputs: OUT0 to OUT3 ..................................... 49
LVDS/CMOS Outputs: OUT4 to OUT7............................. 50
Reset Modes ................................................................................ 50
Power-On Reset—Start-Up Conditions When VS Is
Applied .................................................................................... 50
Asynchronous Reset via the
Soft Reset via 0x00<5> .......................................................... 50
Power-Down Modes .................................................................. 50
Chip Power-Down via
PLL Power-Down................................................................... 51
Distribution Power-Down .................................................... 51
RESET
PD
.................................................... 50
CLK
)................ 37
Pin ............................. 50
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Individual Clock Output Power-Down................................51
Individual Circuit Block Power-Down ................................51
Serial Control Port ..........................................................................52
Serial Control Port Pin Descriptions........................................52
General Operation of Serial Control Port ...............................52
Communication Cycle—Instruction Plus Data..................52
Wr it e .........................................................................................52
Read ..........................................................................................53
The Instruction Word (16 Bits).................................................53
MSB/LSB First Transfers............................................................53
REVISION HISTORY
7/07—Revision 0: Initial Version
Register Map Overview ..................................................................56
Register Map Descriptions.............................................................60
Application Notes............................................................................78
Using the AD9517 Outputs for ADC Clock Applications ....78
LVPECL Clock D i s t ribut io n ......................................................78
LVDS Clock Distribution...........................................................78
CMOS Clock Distribution.........................................................79
Outline Dimensions........................................................................80
Ordering Guide...........................................................................80
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
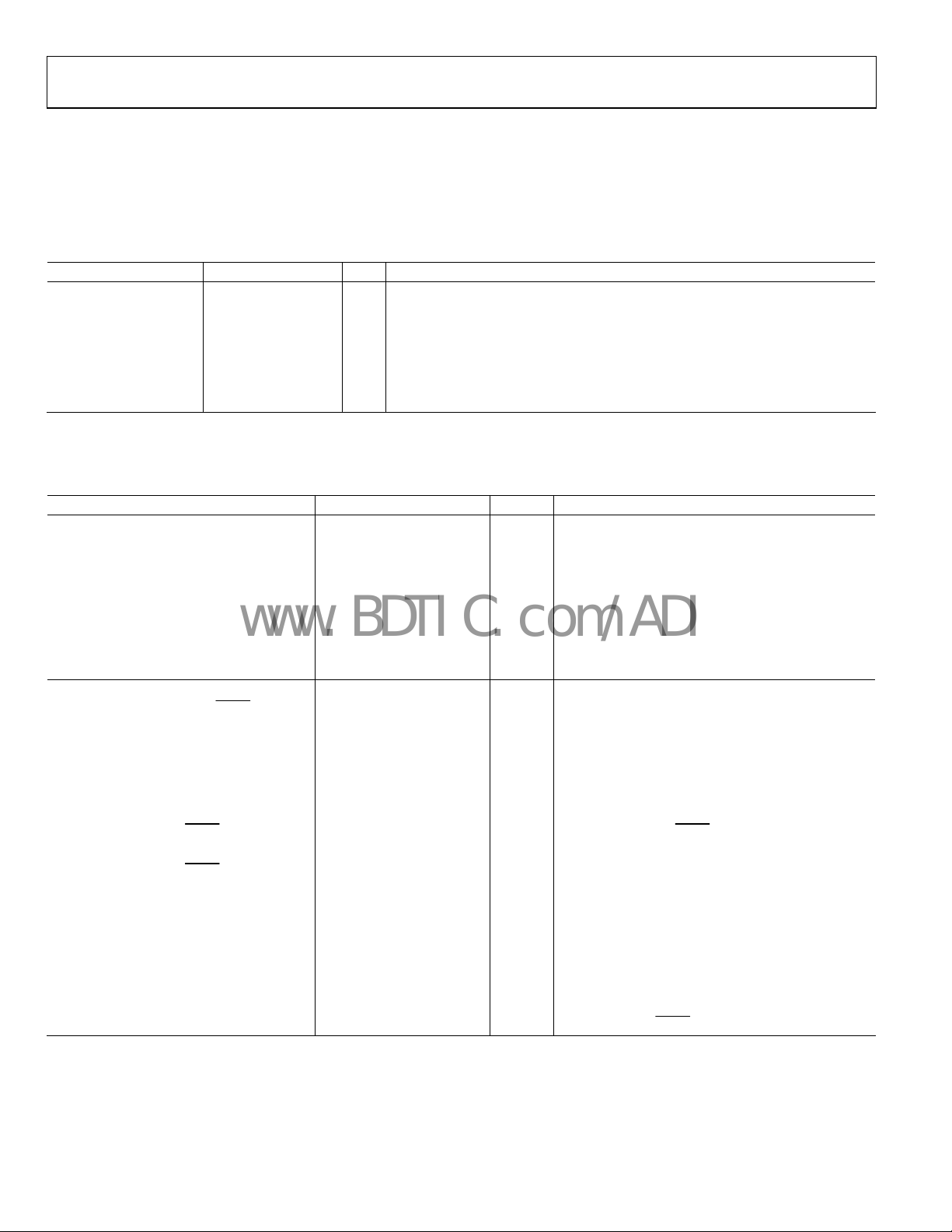
SPECIFICATIONS
Typical (typ) is given for VS = V
unless otherwise noted. Minimum (min) and maximum (max) values are given over full V
POWER SUPPLY REQUIREMENTS
Table 1.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
V
S
V
S_LVPECL
V
CP
3.135 3.3 3.465 V This is 3.3 V ± 5%
2.375 V
V
S
RSET Pin Resistor 4.12 kΩ Sets internal biasing currents; connect to ground
CPRSET Pin Resistor 5.1 kΩ
BYPASS Pin Capacitor 220 nF Bypass for internal LDO regulator; necessary for LDO stability; connect to ground
PLL CHARACTERISTICS
Table 2.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
VCO (ON-CHIP)
Frequency Range 1750 2250 MHz See Figure 15
VCO Gain (K
Tunin g Volt age (VT) 0.5 VCP − 0.5 V
Frequency Pushing (Open-Loop) 1 MHz/V
Phase Noise @ 100 kHz Offset −108 dBc/Hz f = 2000 MHz
Phase Noise @ 1 MHz Offset −126 dBc/Hz f = 2000 MHz
REFERENCE INPUTS
Differential Mode (REFIN, REFIN)
Input Frequency 0 250 MHz
Input Sensitivity 250 mV p-p
Self-Bias Voltage, REFIN 1.35 1.60 1.75 V Self-bias voltage of REFIN
Self-Bias Voltage, REFIN
Input Resistance, REFIN 4.0 4.8 5.9 kΩ Self-biased
Input Resistance, REFIN
Dual Single-Ended Mode (REF1, REF2) Two single-ended CMOS-compatible inputs
Input Frequency (AC-Coupled) 20 250 MHz Slew rate > 50 V/μs
Input Frequency (DC-Coupled) 0 250 MHz Slew rate > 50 V/μs; CMOS levels
Input Sensitivity (AC-Coupled) 0.8 V p-p Should not exceed VS p-p
Input Logic High 2.0 V
Input Logic Low 0.8 V
Input Current −100 +100 μA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
) 50 MHz/V See Figure 10
VCO
= 3.3 V ± 5%; VS ≤ VCP ≤ 5.25 V; TA = 25°C; RSET = 4.12 kΩ; CPRSET = 5.1 kΩ,
S_LVPECL
and TA (−40°C to +85°C) variation.
S
V This is nominally 2.5 V to 3.3 V ± 5%
S
5.25 V This is nominally 3.3 V to 5.0 V ± 5%
Sets internal CP current range, nominally 4.8 mA (CP_lsb = 600 μA);
tual current can be calculated by: CP_lsb = 3.06/CPRSET; connect to ground
ac
≤ VS when using internal VCO; outside of this
V
CP
range, the CP spurs may increase due to CP up/
down mismatch
Differential mode (can accommodate singleended input by ac grounding undriven input)
Frequencies below about 1 MHz should be
coupled; be careful to match V
dcPLL figure of merit increases with increasing
te; see Figure 14
slew ra
1.30 1.50 1.60 V
4.4 5.3 6.4 kΩ Self-biased
Self-bias voltage of REFIN
1
1
Each pin, REFIN/REFIN
CM
1
1
(REF1/REF2)
(self-bias voltage)
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
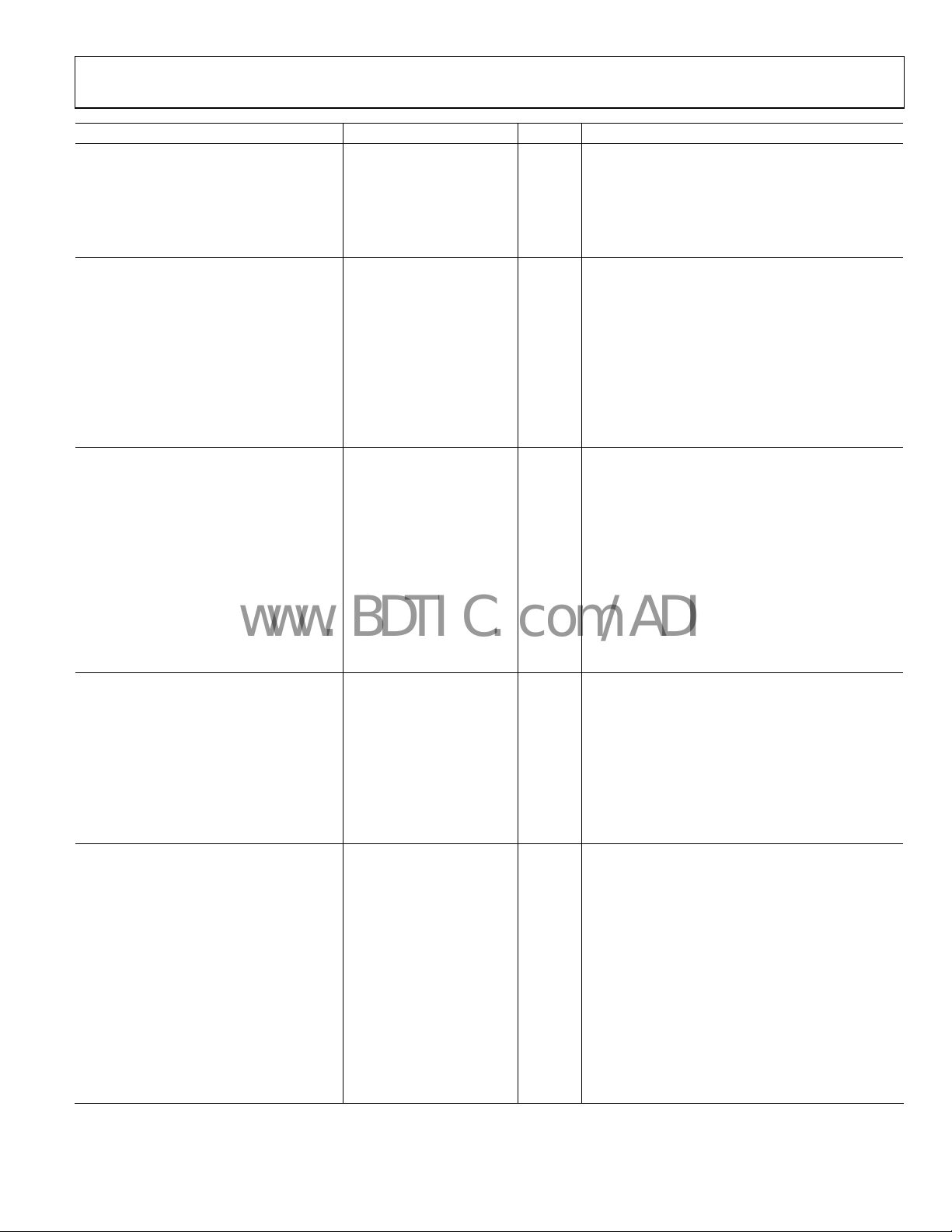
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
PHASE/FREQUENCY DETECTOR (PFD)
PFD Input Frequency 100 MHz Antibacklash pulse width = 1.3 ns, 2.9 ns
45 MHz Antibacklash pulse width = 6.0 ns
Antibacklash Pulse Width 1.3 ns 0x17<1:0> = 01b
2.9 ns 0x17<1:0> = 00b; 0x17<1:0> = 11b
6.0 ns 0x17<1:0> = 10b
CHARGE PUMP (CP)
ICP Sink/Source Programmable
High Value 4.8 mA
Low Value 0.60 mA
Absolute Accuracy 2.5 % CPV = VCP /2 V
CPRSET Range 2.7/10 kΩ
ICP High Impedance Mode Leakage 1 nA
Sink-and-Source Current Matching 2 % 0.5 < CPV < VCP − 0.5 V
ICP vs. V
CP
ICP vs. Temperature 2 % CPV = VCP /2 V
PRESCALER (PART OF N DIVIDER)
Prescaler Input Frequency
P = 1 FD 300 MHz
P = 2 FD 600 MHz
P = 3 FD 900 MHz
P = 2 DM (2/3) 600 MHz
P = 4 DM (4/5) 1000 MHz
P = 8 DM (8/9) 2400 MHz
P = 16 DM (16/17) 3000 MHz
P = 32 DM (32/33) 3000 MHz
Prescaler Output Frequency 300 MHz
PLL DIVIDER DELAYS Register 0x19: R<5:3>, N<2:0>; see Tab le 53
000 Off
001 330 ps
010 440 ps
011 550 ps
100 660 ps
101 770 ps
110 880 ps
111 990 ps
NOISE CHARACTERISTICS
In-Band Phase Noise of the Charge
Pump/Phase Frequency Detector
(In-Band Means Within the LBW
of the PLL)
@ 500 kHz PFD Frequency −165 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz PFD Frequency −162 dBc/Hz
@ 10 MHz PFD Frequency −151 dBc/Hz
@ 50 MHz PFD Frequency −143 dBc/Hz
PLL Figure of Merit (FOM) −220 dBc/Hz
1.5 % 0.5 < CPV < VCP − 0.5 V
With CPRSET = 5.1 kΩ
A, B counter input frequency (prescaler
equency divided by P)
input fr
The PLL in-band phase noise floor is estimated
by measuring the in-band phase noise at the
output of the VCO and subtracting 20 log(N)
(where N is the value of the N divider)
Reference slew rate > 0.25 V/ns. FOM + 10 log(f
is an approximation of the PFD/CP in-band
phase noise (in the flat region) inside the PLL
loop bandwidth; when running closed loop,
the phase noise, as observed at the VCO output,
is increased by 20 log(N)
PFD
)
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
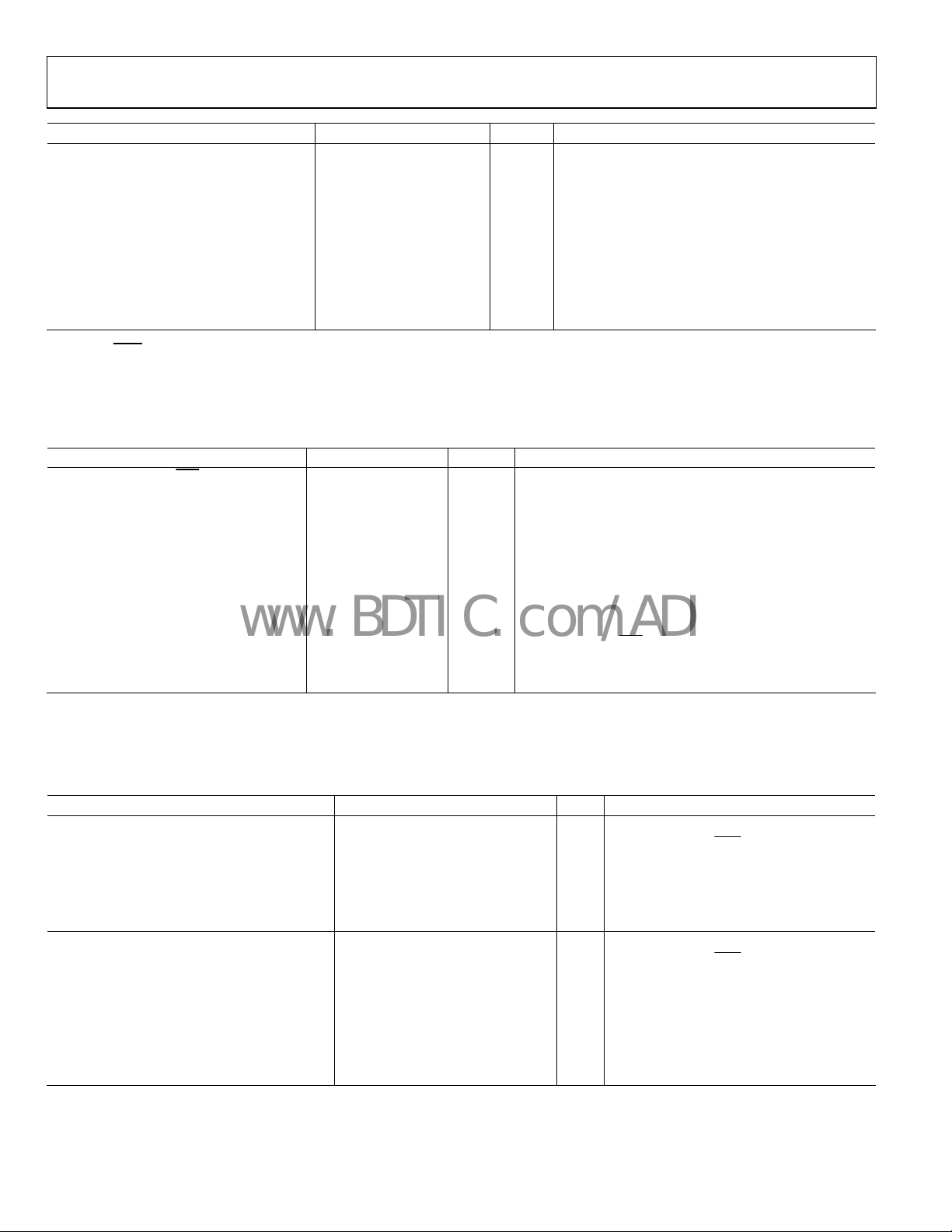
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
PLL DIGITAL LOCK DETECT WINDOW
Required to Lock (Coincidence of Edges) Selected by 0x17<1:0> and 0x18<4>
Low Range (ABP 1.3 ns, 2.9 ns) 3.5 ns 0x17<1:0> = 00b, 01b,11b; 0x18<4> = 1b
High Range (ABP 1.3 ns, 2.9 ns) 7.5 ns 0x17<1:0> = 00b, 01b, 11b; 0x18<4> = 0b
High Range (ABP 6 ns) 3.5 ns 0x17<1:0> = 10b; 0x18<4> = 0b
To Unlock After Lock (Hysteresis)
Low Range (ABP 1.3 ns, 2.9 ns) 7 ns 0x17<1:0> = 00b, 01b, 11b; 0x18<4> = 1b
High Range (ABP 1.3 ns, 2.9 ns) 15 ns 0x17<1:0> = 00b, 01b, 11b; 0x18<4> = 0b
High Range (ABP 6 ns) 11 ns 0x17<1:0> = 10b; 0x18<4> = 0b
1
REFIN and
2
For reliable operation of the digital lock detect, the period of the PFD frequency must be greater than the unlock-after-lock time.
REFIN
self-bias points are offset slightly to avoid chatter on an open input condition.
CLOCK INPUTS
Table 3.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CLOCK INPUTS (CLK, CLK)
Input Frequency 0
0
Input Sensitivity, Differential 150 mV p-p
Input Level, Differential 2 V p-p
Input Common-Mode Voltage, V
Input Common-Mode Range, V
Input Sensitivity, Single-Ended 150 mV p-p
Input Resistance 3.9 4.7 5.7 kΩ Self-biased
Input Capacitance 2 pF
1
Below about 1 MHz, the input should be dc-coupled. Care should be taken to match VCM.
CMR
2
2
Signal available at LD, STATUS, and REFMON pins
when se
lected by appropriate register settings
Differential input
1
2.4 GHz High frequency distribution (VCO divider)
1
1.6 GHz Distribution only (VCO divider bypassed)
Measured at 2.4 GHz; jitter performance is improved
w rates > 1 V/ns
with sle
Larger voltage swings may turn on the protection
diodes and can degr
CM
1.3 1.57 1.8 V Self-biased; enables ac coupling
ade jitter performance
1.3 1.8 V With 200 mV p-p signal applied; dc-coupled
CLK ac-coupled; CLK
ac-bypassed to RF ground
CLOCK OUTPUTS
Table 4.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL CLOCK OUTPUTS Termination = 50 Ω to VS − 2 V
OUT0, OUT1, OUT2, OUT3
Differential (OUT,
Output Frequency, Maximum 2950 MHz Using direct to output; see Figure 25
Output High Voltage (VOH) VS − 1.12 VS − 0.98 VS − 0.84 V
Output Low Voltage (VOL) VS − 2.03 VS − 1.77 VS − 1.49 V
Output Differential Voltage (VOD) 550 790 980 mV
LVDS CLOCK OUTPUTS Differential termination 100 Ω @ 3.5 mA
OUT4, OUT5, OUT6, OUT7
Differential (OUT,
Output Frequency 800 MHz See Figure 26
Differential Output Voltage (VOD) 247 360 454 mV
Delta V
OD
25 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS) 1.125 1.24 1.375 V
Delta V
OS
25 mV
Short-Circuit Current (ISA, ISB) 14 24 mA Output shorted to GND
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 80
OUT
OUT
)
)
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CMOS CLOCK OUTPUTS
OUT4A, OUT4B, OUT5A, OUT5B, OUT6A,
OUT6B, OUT7A, OUT7B
Output Frequency 250 MHz See Figure 27
Output Voltage High (VOH) VS − 0.1 V @ 1 mA load
Output Voltage Low (VOL) 0.1 V @ 1 mA load
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Table 5.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL Termination = 50 Ω to VS − 2 V; level = 810 mV
Output Rise Time, t
Output Fall Time, t
PROPAGATION DELAY, t
High Frequency Clock Distribution Configuration 835 995 1180 ps See Figure 42
Clock Distribution Configuration 773 933 1090 ps See Figure 44
Variation with Temperature 0.8 ps/°C
OUTPUT SKEW, LVPECL OUTPUTS
LVPECL Outputs That Share the Same Divider 5 15 ps
LVPECL Outputs on Different Dividers 13 40 ps
All LVPECL Outputs Across Multiple Parts 220 ps
LVDS Termination = 100 Ω differential; 3.5 mA
Output Rise Time, t
Output Fall Time, t
PROPAGATION DELAY, t
For All Divide Values 1.4 1.8 2.1 ns
Variation with Temperature 1.25 ps/°C
OUTPUT SKEW, LVDS OUTPUTS
LVDS Outputs That Share the Same Divider 6 62 ps
LVDS Outputs on Different Dividers 25 150 ps
All LVDS Outputs Across Multiple Parts 430 ps
CMOS Termination = open
Output Rise Time, t
Output Fall Time, t
PROPAGATION DELAY, t
For All Divide Values 1.6 2.1 2.6 ns
Variation with Temperature 2.6 ps/°C
OUTPUT SKEW, CMOS OUTPUTS
CMOS Outputs That Share the Same Divider 4 66 ps
All CMOS Outputs on Different Dividers 28 180 ps
All CMOS Outputs Across Multiple Parts 675 ps
DELAY ADJUST
Shortest Delay Range
Zero Scale 50 315 680 ps 0xA2 (0xA5) (0xA8) (0xAB) <5:0> 000000b
Full Scale 540 880 1180 ps 0xA2 (0xA5) (0xA8) (0xAB) <5:0> 101111b
Longest Delay Range
Zero Scale 200 570 950 ps 0xA2 (0xA5) (0xA8) (0xAB) <5:0> 000000b
Quarter Scale 1.72 2.31 2.89 ns 0xA2 (0xA5) (0xA8) (0xAB) <5:0> 001100b
Full Scale 5.7 8.0 10.1 ns 0xA2 (0xA5) (0xA8) (0xAB) <5:0> 101111b
RP
FP
, CLK-TO-LVPECL OUTPUT
PECL
1
RL
FL
, CLK-TO-LVDS OUTPUT Delay off on all outputs
LVDS
1
RC
FC
, CLK-TO-CMOS OUTPUT Fine delay off
CMOS
1
3
4
4
Single-ended; termination = 10 pF
70 180 ps 20% to 80%, measured differentially
70 180 ps 80% to 20%, measured differentially
170 350 ps 20% to 80%, measured differentially
160 350 ps 20% to 80%, measured differentially
2
2
Delay off on all outputs
495 1000 ps 20% to 80%, C
475 985 ps 80% to 20%, C
LOAD
LOAD
= 10 pF
= 10 pF
Fine delay off
LVDS and CMOS
0xA1 (0xA4) (0xA7) (0xAA) <5:0> 101111b
0xA1 (0xA4) (0xA7) (0xAA) <5:0> 000000b
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Delay Variation with Temperature
Short Delay Range
Zero Scale 0.23 ps/°C
Full Scale −0.02 ps/°C
Long Delay Range
Zero Scale 0.3 ps/°C
Full Scale 0.24 ps/°C
1
This is the difference between any two similar delay paths while operating at the same voltage and temperature.
2
Corresponding CMOS drivers set to A for noninverting, and B for inverting.
3
The maximum delay that can be used is a little less than one-half the period of the clock. A longer delay disables the output.
4
Incremental delay; does not include propagation delay.
5
All delays between zero scale and full scale can be estimated by linear interpolation.
CLOCK OUTPUT ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE (DISTRIBUTION ONLY; VCO DIVIDER NOT USED)
Table 6.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CLK-TO-LVPECL ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE
CLK = 1 GHz, OUTPUT = 1 GHz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns
Divider = 1
@ 10 Hz Offset −109 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −118 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −130 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −139 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −144 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −146 dBc/Hz
@ 10 MHz Offset −147 dBc/Hz
@ 100 MHz Offset −149 dBc/Hz
CLK = 1 GHz, OUTPUT = 200 MHz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns
Divider = 5
@ 10 Hz Offset −120 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −126 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −139 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −150 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −155 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −157 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −157 dBc/Hz
CLK-TO-LVDS ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE
CLK = 1.6 GHz, OUTPUT = 800 MHz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns
Divider = 2
@ 10 Hz Offset −103 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −110 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −120 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −127 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −133 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −138 dBc/Hz
@ 10 MHz Offset −147 dBc/Hz
@ 100 MHz Offset −149 dBc/Hz
5
5
Distribution section only; does not
include PLL and
VCO
Distribution section only; does not
include PLL and
VCO
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CLK = 1.6 GHz, OUTPUT = 400 MHz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns
Divider = 4
@ 10 Hz Offset −114 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −122 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −132 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −140 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −146 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −150 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −155 dBc/Hz
CLK-TO-CMOS ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE
CLK = 1 GHz, OUTPUT = 250 MHz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns
Divider = 4
@ 10 Hz Offset −110 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −120 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −127 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −136 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −144 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −147 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −154 dBc/Hz
CLK = 1 GHz, OUTPUT = 50 MHz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns
Divider = 20
@ 10 Hz Offset −124 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −134 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −142 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −151 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −157 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −160 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −163 dBc/Hz
Distribution section only; does not
include PLL and
VCO
CLOCK OUTPUT ABSOLUTE PHASE NOISE (INTERNAL VCO USED)
Table 7.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL ABSOLUTE PHASE NOISE Internal VCO; direct to LVPECL output
VCO = 2.25 GHz; OUTPUT = 2.25 GHz
@ 1 kHz Offset −49 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −79 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −104 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −123 dBc/Hz
@ 10 MHz Offset −143 dBc/Hz
@ 40 MHz Offset −147 dBc/Hz
VCO = 2.00 GHz; OUTPUT = 2.00 GHz
@ 1 kHz Offset −53 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −83 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −108 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −126 dBc/Hz
@ 10 MHz Offset −142 dBc/Hz
@ 40 MHz Offset −147 dBc/Hz
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
VCO = 1.75 GHz; OUTPUT = 1.75 GHz
@ 1 kHz Offset −54 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −88 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −112 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −130 dBc/Hz
@ 10 MHz Offset −143 dBc/Hz
@ 40 MHz Offset −147 dBc/Hz
CLOCK OUTPUT ABSOLUTE TIME JITTER (CLOCK GENERATION USING INTERNAL VCO)
Table 8.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL OUTPUT ABSOLUTE TIME JITTER
VCO = 1.97 GHz; LVPECL = 245.76 MHz; PLL LBW = 143 kHz 129 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 10 MHz
303 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
VCO = 1.97 GHz; LVPECL = 122.88 MHz; PLL LBW = 143 kHz 135 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 10 MHz
302 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
VCO = 1.97 GHz; LVPECL = 61.44 MHz; PLL LBW = 143 kHz 179 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 10 MHz
343 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Application example based on a typical
setup wher
clean, so a wider PLL loop bandwidth is
used; reference = 15.36 MHz; R = 1
e the reference source is
CLOCK OUTPUT ABSOLUTE TIME JITTER (CLOCK CLEANUP USING INTERNAL VCO)
Table 9.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL OUTPUT ABSOLUTE TIME JITTER
VCO = 1.87 GHz; LVPECL = 622.08 MHz; PLL LBW = 125 Hz 400 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
VCO = 1.87 GHz; LVPECL = 155.52 MHz; PLL LBW = 125 Hz 390 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
VCO = 1.97 GHz; LVPECL = 122.88 MHz; PLL LBW = 125 Hz 485 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Application example based on a typical
setup wher
jittery, so a narrower PLL loop bandwidth
is used; reference = 10.0 MHz; R = 20
e the reference source is
CLOCK OUTPUT ABSOLUTE TIME JITTER (CLOCK GENERATION USING EXTERNAL VCXO)
Table 10.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL OUTPUT ABSOLUTE TIME JITTER
LVPECL = 245.76 MHz; PLL LBW = 125 Hz 54 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 5 MHz
77 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 10 MHz
109 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
LVPECL = 122.88 MHz; PLL LBW = 125 Hz 79 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 5 MHz
114 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 10 MHz
163 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
LVPECL = 61.44 MHz; PLL LBW = 125 Hz 124 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 5 MHz
176 fS rms Integration BW = 200 kHz to 10 MHz
259 fS rms Integration BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Application example based on a typical setup using an
ternal 245.76 MHz VCXO (Toyocom TCO-2112);
ex
reference = 15.36 MHz; R = 1
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
CLOCK OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER (VCO DIVIDER NOT USED)
Table 11.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK = 622.08 MHz; LVPECL = 622.08 MHz; Divider = 1 40 fS rms BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
CLK = 622.08 MHz; LVPECL = 155.52 MHz; Divider = 4 80 fS rms BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
CLK = 1.6 GHz; LVPECL = 100 MHz; Divider = 16 215 fS rms
CLK = 500 MHz; LVPECL = 100 MHz; Divider = 5 245 fS rms
LVDS OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK = 1.6 GHz; LVDS = 800 MHz; Divider = 2; VCO Divider Not Used 85 fS rms BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
CLK = 1 GHz; LVDS = 200 MHz; Divider = 5 113 fS rms BW = 12 kHz to 20 MHz
CLK = 1.6 GHz; LVDS = 100 MHz; Divider = 16 280 fS rms
CMOS OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK = 1.6 GHz; CMOS = 100 MHz; Divider = 16 365 fS rms
Distribution section only; does not
include PLL and
clock signal
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
C not used for even divides
DC
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
C on
DC
Distribution section only; does not
include PLL and
clock signal
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
C not used for even divides
DC
Distribution section only; does not
include PLL and
clock signal
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
C not used for even divides
DC
VCO; rising edge of
VCO; rising edge of
VCO; rising edge of
CLOCK OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER (VCO DIVIDER USED)
Table 12.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK = 2.4 GHz; VCO DIV = 2; LVPECL = 100 MHz;
Divider = 12; Duty-Cycle Correction = Off
LVDS OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK = 2.4 GHz; VCO DIV = 2; LVDS = 100 MHz;
Divider = 12; Duty-Cycle Correction = Off
CMOS OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK = 2.4 GHz; VCO DIV = 2; CMOS = 100 MHz;
Divider = 12; Duty-Cycle Correction = Off
210 f
285 f
350 f
S
S
S
Distribution section only; does not include PLL and VCO;
ising edge of clock signal
uses r
rms Calculated from SNR of ADC method
Distribution section only; does not include PLL and VCO;
ising edge of clock signal
uses r
rms Calculated from SNR of ADC method
Distribution section only; does not include PLL and VCO;
ising edge of clock signal
uses r
rms Calculated from SNR of ADC method
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DELAY BLOCK ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
Table 13.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DELAY BLOCK ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
100 MHz Output
Delay (1600 μA, 1C) Fine Adj. 000000 0.54 ps rms
Delay (1600 μA, 1C) Fine Adj. 101111 0.60 ps rms
Delay (800 μA, 1C) Fine Adj. 000000 0.65 ps rms
Delay (800 μA, 1C) Fine Adj. 101111 0.85 ps rms
Delay (800 μA, 4C) Fine Adj. 000000 0.79 ps rms
Delay (800 μA, 4C) Fine Adj. 101111 1.2 ps rms
Delay (400 μA, 4C) Fine Adj. 000000 1.2 ps rms
Delay (400 μA, 4C) Fine Adj. 101111 2.0 ps rms
Delay (200 μA, 1C) Fine Adj. 000000 1.3 ps rms
Delay (200 μA, 1C) Fine Adj. 101111 2.5 ps rms
Delay (200 μA, 4C) Fine Adj. 000000 1.9 ps rms
Delay (200 μA, 4C) Fine Adj. 101111 3.8 ps rms
1
This value is incremental. That is, it is in addition to the jitter of the LVDS or CMOS output without the delay. To estimate the total jitter, the LVDS or CMOS output jitter
should be added to this value using the root sum of the squares (RSS) method.
1
Incremental additive jitter
SERIAL CONTROL PORT
Table 14.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CS (INPUT)
Input Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Input Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Input Logic 1 Current 3 μA
Input Logic 0 Current 110 μA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
SCLK (INPUT) SCLK has an internal 30 kΩ pull-down resistor
Input Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Input Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Input Logic 1 Current 110 μA
Input Logic 0 Current 1 μA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
SDIO (WHEN INPUT)
Input Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Input Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Input Logic 1 Current 10 nA
Input Logic 0 Current 20 nA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
SDIO, SDO (OUTPUTS)
Output Logic 1 Voltage 2.7 V
Output Logic 0 Voltage 0.4 V
CS has an internal 30 kΩ pull-up resistor
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
TIMING
Clock Rate (SCLK, 1/t
Pulse Width High, t
Pulse Width Low, t
SDIO to SCLK Setup, t
SCLK to SDIO Hold, t
SCLK to Valid SDIO and SDO, t
CS to SCLK Setup and Hold, tS, t
CS Minimum Pulse Width High, t
PD
,
SYNC
, AND
Table 15.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS These pins each have a 30 kΩ internal pull-up resistor
Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Logic 1 Current 110 μA
Logic 0 Current 1 μA
Capacitance 2 pF
RESET TIMING
Pulse Width Low 50 ns
SYNC TIMING
Pulse Width Low 1.5 High speed clock cycles High speed clock is CLK input signal
LD, STATUS, REFMON PINS
) 25 MHz
SCLK
HI
LO
DS
DH
RESET
DV
H
PWH
PINS
16 ns
16 ns
2 ns
1.1 ns
8 ns
2 ns
3 ns
Table 16.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High (VOH) 2.7 V
Output Voltage Low (VOL) 0.4 V
MAXIMUM TOGGLE RATE 100 MHz
ANALOG LOCK DETECT
Capacitance 3 pF
REF1, REF2, AND VCO FREQUENCY STATUS MONITOR
Normal Range 1.02 MHz
Extended Range 8 kHz
LD PIN COMPARATOR
Trip Point 1.6 V
Hysteresis 260 mV
When selected as a digital output (CMOS); there are other
modes in whic
see Tab le 53, 0x17, 0x1A, and 0x1B
Applies when mux is set to any divider or counter output,
or PFD up/d
mode; usually debug mode only; beware that spurs may
couple to output when any of these pins are toggling
On-chip capacitance; used to calculate RC time constant
or analog lock detect readback; use a pull-up resistor
f
Frequency above which the monitor indicates the
esence of the reference
pr
Frequency above which the monitor indicates the
esence of the reference
pr
h these pins are not CMOS digital outputs;
own pulse; also applies in analog lock detect
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
POWER DISSIPATION
Table 17.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
POWER DISSIPATION, CHIP
Power-On Default 1.0 1.2 W
Full Operation; CMOS Outputs at 225 MHz 1.4 2.0 W
Full Operation; LVDS Outputs at 225 MHz 1.4 2.1 W
PD
Power-Down
PD
Power-Down, Maximum Sleep
VCP Supply 1.5 mW PLL operating; typical closed-loop configuration
POWER DELTAS, INDIVIDUAL FUNCTIONS Power delta when a function is enabled/disabled
VCO Divider 30 mW VCO divider not used
REFIN (Differential) 20 mW All references off to differential reference enabled
REF1, REF2 (Single-Ended) 4 mW
VCO 70 mW CLK input selected to VCO selected
PLL 75 mW PLL off to PLL on, normal operation; no reference enabled
Channel Divider 30 mW Divider bypassed to divide-by-2 to divide-by-32
LVPECL Channel (Divider Plus Output Driver) 160 mW No LVPECL output on to one LVPECL output on
LVPECL Driver 90 mW Second LVPECL output turned on, same channel
LVDS Channel (Divider Plus Output Driver) 120 mW No LVDS output on to one LVDS output on
LVDS Driver 50 mW Second LVDS output turned on, same channel
CMOS Channel (Divider Plus Output Driver) 100 mW Static; no CMOS output on to one CMOS output on
CMOS Driver (Second in Pair) 0 mW Static; second CMOS output, same pair, turned on
CMOS Driver (First in Second Pair) 30 mW Static; first output, second pair, turned on
Fine Delay Block 50 mW
75 185 mW
31 mW
No clock; no programming; defa
does not include power dissipated in external resistors
PLL on; internal VCO = 2250 MHz; VCO divider = 2;
annel dividers on; six LVPECL outputs @ 562.5 MHz;
all ch
eight CMOS outputs (10 pF load) @ 225 MHz; all fine
delay on, maximum current; does not include power
dissipated in external resistors
PLL on; internal VCO = 2250 MHz, VCO divider = 2;
all channel dividers on; six L
four LVDS outputs @ 225 MHz; all fine delay on,
maximum current; does not include power dissipated
in external resistors
PD
pin pulled low; does not include power dissipated
in terminations
PD
pin pulled low; PLL power-down 0x10<1:0> = 01b;
SYNC power-down 0x230<2> = 1b; REF for distribution
power-down 0x230<1> = 1b
All references off to REF1 or REF2 enabled; differential
ference not enabled
re
Delay block off to delay block enabled; maximum
ent setting
curr
ult register values;
VPECL outputs @ 562.5 MHz;
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 80
AD9517-3
K
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
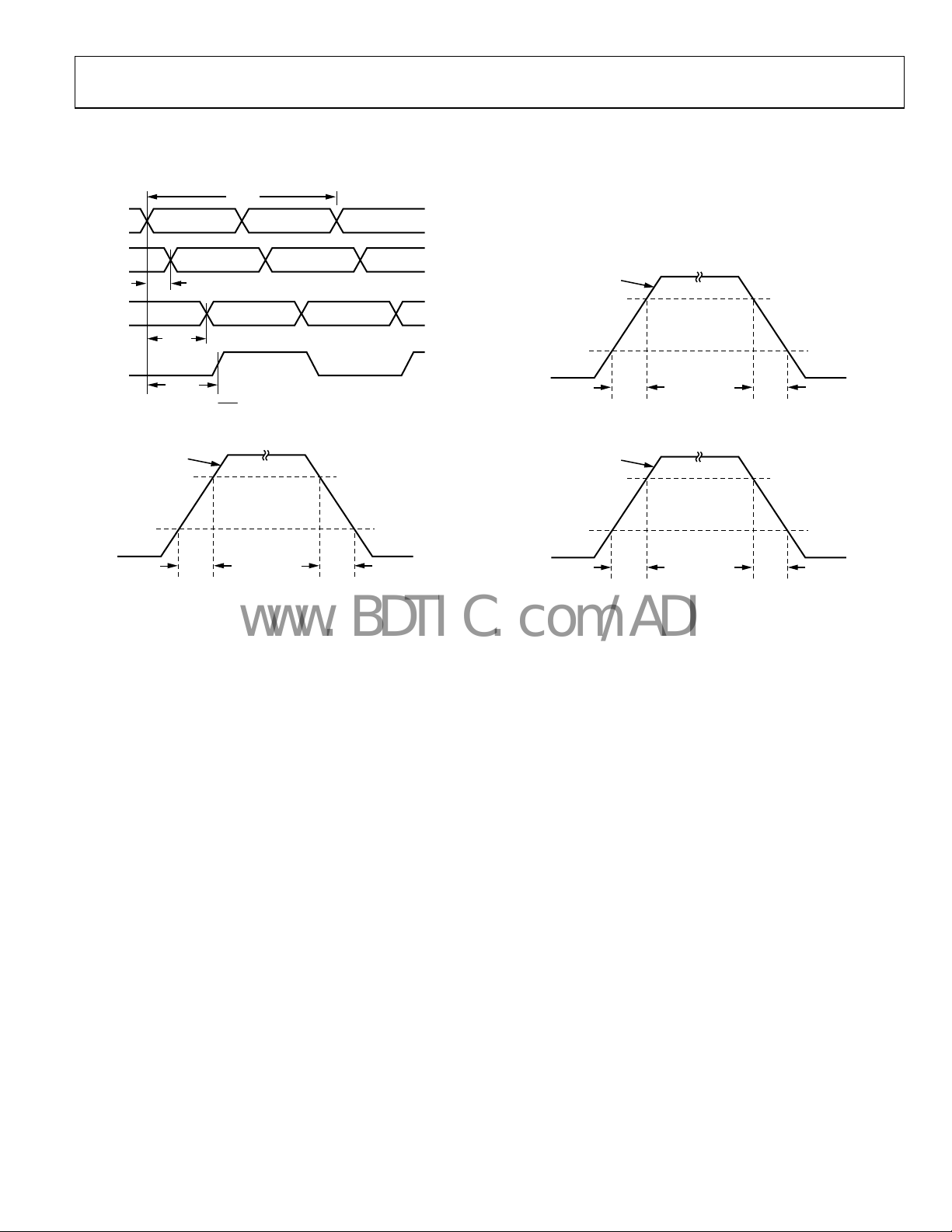
TIMING DIAGRAMS
t
CLK
CL
t
t
LVDS
t
CMOS
Figure 2. CLK/
DIFFERENTIAL
80%
20%
Figure 3. LVPECL Timing, Differential
PECL
CLK
to Clock Output Timing, DIV = 1
LVPECL
t
RP
06427-060
t
FP
06427-061
DIFFERENTIAL
80%
LVDS
20%
t
RL
Figure 4. LVDS Timing, Differential
SINGL E-ENDE D
80%
CMOS
10pF LOAD
20%
t
RC
Figure 5. CMOS Timing, Single-End
t
FL
t
FC
ed, 10 pF Load
06427-062
06427-063
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 18.
With
Parameter or Pin
VS, VS_LVPECL GND −0.3 V to +3.6 V
VCP GND −0.3 V to +5.8 V
REFIN, REFIN
REFIN
RSET GND −0.3 V to VS + 0.3 V
CPRSET GND −0.3 V to VS + 0.3 V
CLK, CLK
CLK
SCLK, SDIO, SDO, CS
OUT0, OUT0, OUT1, OUT1,
OUT2, OUT2
OUT4, OUT4, OUT5, OUT5,
OUT6, OUT6, OUT7, OUT7
SYNC
REFMON, STATUS, LD GND −0.3 V to VS + 0.3 V
Junction Temperature
Storage Temperature
Range
Lead Temperature (10 sec) 300°C
1
See Table 19 for θJA.
, OUT3, OUT3,
Respec
t To Rating
GND −0.3 V to VS + 0.3 V
REFIN
GND −0.3 V to VS + 0.3 V
CLK
GND −0.3 V to VS + 0.3 V
GND −0.3 V to VS + 0.3 V
GND −0.3 V to VS + 0.3 V
1
150°C
−65°C to +150°C
−3.3 V to +3.3 V
−1.2 V to +1.2 V
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Table 19.
Package Type
48-Lead LFCSP 28.5 °C/W
1
Thermal impedance measurements were taken on a 4-layer board in still air
in accordance with EIA/JESD51-7.
1
θ
JA
Unit
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
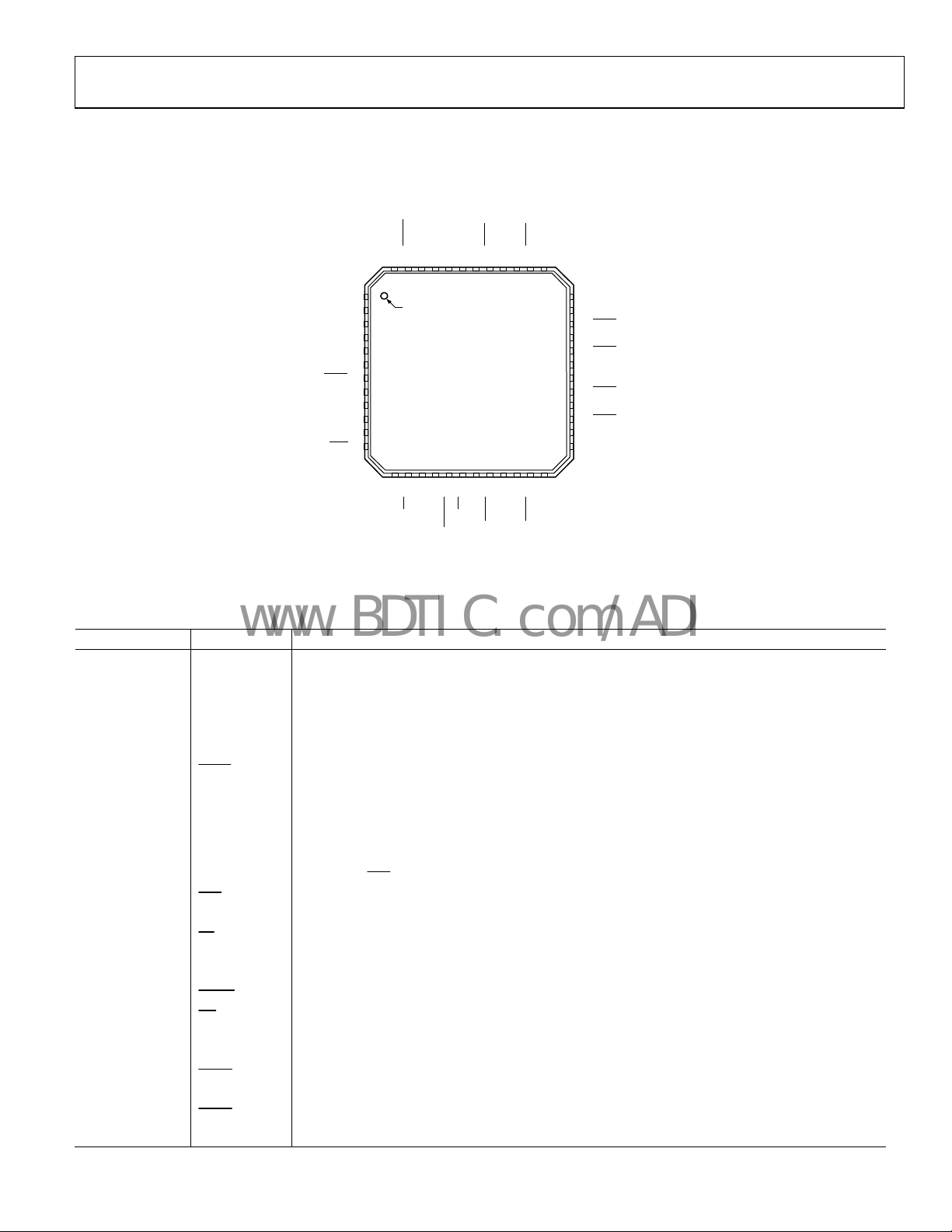
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
REFIN (REF 1)
REFIN (REF 2)
CPRSETVSRSETVSOUT0
4847464544434241403938
OUT0
VS_LVPECL
OUT1
OUT1
VS
37
REFMON
LD
VCP
CP
STATUS
REF_SEL
SYNC
BYPASS
VS
CLK
CLK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LF
9
10
11
12
PIN 1
INDICAT OR
AD9517-3
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
13141516171819
CS
SCLK
PD
SDO
SDIO
RESET
2021222324
OUT2
OUT2
S_LVPECL
OUT3
36
S
V
35
OUT4 (OUT4A)
34
OUT4 (OUT4B)
33
OUT5 (OUT5A)
32
OUT5 (OUT5B)
31
VS
30
VS
29
OUT7 (OUT7B)
28
OUT7 (OUT7A)
27
OUT6 (OUT6B)
26
OUT6 (OUT6A)
25
S
V
VS
OUT3
06427-003
Figure 6. Pin Configuration
Table 20. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 REFMON Reference Monitor (Output). This pin has multiple selectable outputs; see Table 53 0x1B.
2 LD Lock Detect (Output). This pin has multiple selectable outputs; see Tabl e 53 0x1A.
3 VCP
4 CP
5 STATUS
6 REF_SEL
7
SYNC
Power Supply for Charge Pump (CP); VS < VCP < 5.0 V.
Charge Pump (Output). Connects to external loop filter.
Status (Output). This pin has multiple selectable outputs; see Table 53 0x17.
Reference Select. Selects REF1 (low) or REF2 (high). This pin has an internal 30 kΩ pull-down resistor.
Manual Synchronizations and Manual Holdover. This pin initiates a manual synchronization and is
also used for manual holdover. Active low. This pin has an internal 30 kΩ pull-up resistor.
8 LF
9 BYPASS
10, 24, 25, 30, 31,
VS
Loop Filter (Input). Connects to VCO control voltage node internally.
This pin is for bypassing the LDO to ground with a capacitor.
3.3 V Power Pins.
36, 37, 43, 45
11 CLK
12
CLK
13 SCLK
14
CS
Along with CLK
Along with CLK, this is the differential input for the clock distribution section.
Serial Control Port Data Clock Signal.
Serial Control Port Chip Select; Active Low. This pin has an internal 30 kΩ pull-up resistor.
, this is the differential input for the clock distribution section.
15 SDO Serial Control Port Unidirectional Serial Data Out.
16 SDIO
17
18
RESET
PD
21, 40 VS_LVPECL
42 OUT0
41
OUT0
39 OUT1
38
OUT1
Serial Control Port Bidirectional Serial Data In/Out.
Chip Reset; Active Low. This pin has an internal 30 kΩ pull-up resistor.
Chip Power Down; Active Low. This pin has an internal 30 kΩ pull-up resistor.
Extended Voltage 2.5 V to 3.3 V LVPECL Power Pins.
LVPECL Output; One Side of a Differential LVPECL Output.
LVPECL Output; One Side of a Differential LVPECL Output.
LVPECL Output; One Side of a Differential LVPECL Output.
LVPECL Output; One Side of a Differential LVPECL Output.
19 OUT2 LVPECL Output; One Side of a Differential LVPECL Output.
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 80
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
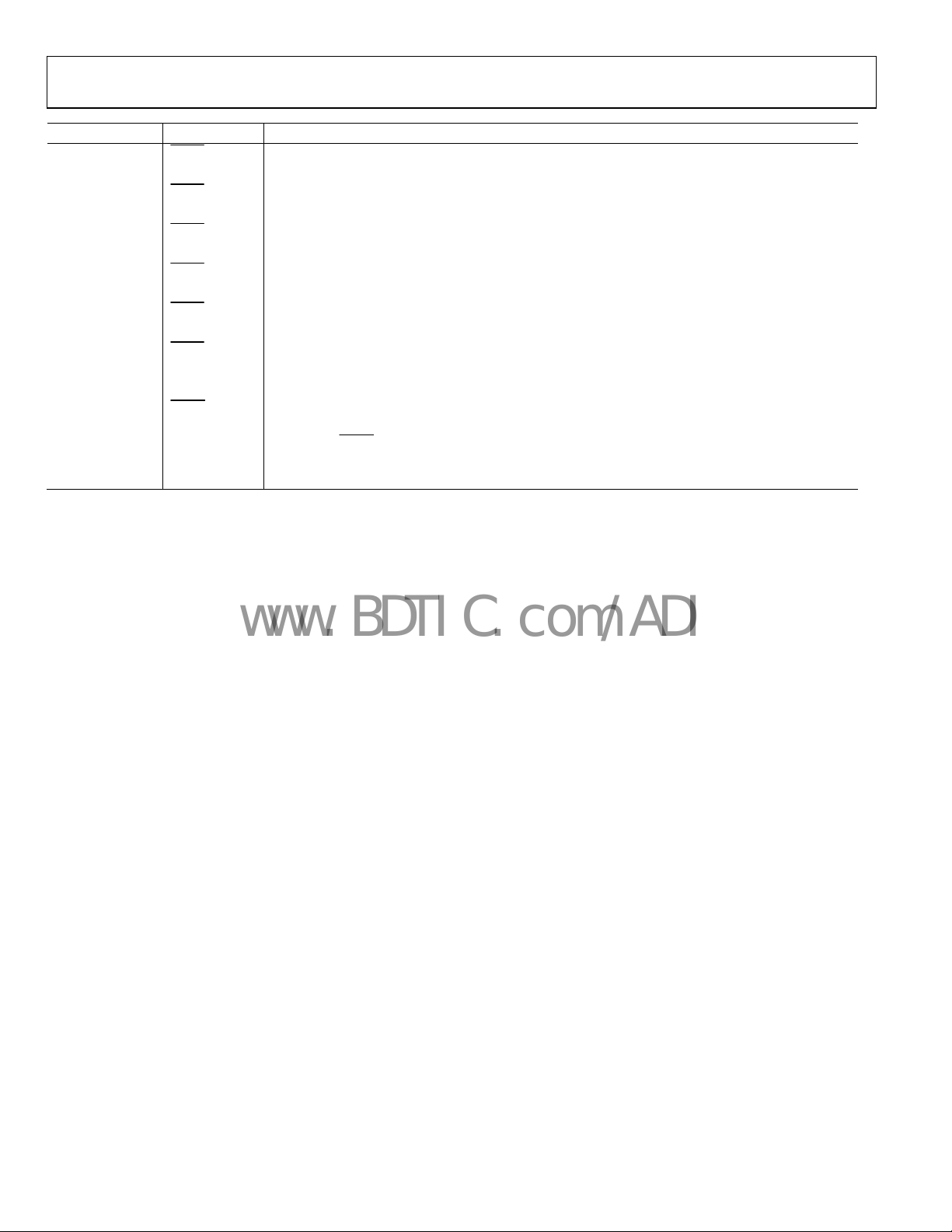
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
20
22 OUT3 LVPECL Output; One Side of a Differential LVPECL Output.
23
35 OUT4 (OUT4A) LVDS/CMOS Output; One Side of a Differential LVDS Output, or a Single-Ended CMOS Output.
34
33 OUT5 (OUT5A) LVDS/CMOS Output; One Side of a Differential LVDS Output, or a Single-Ended CMOS Output.
32
26 OUT6 (OUT6A) LVDS/CMOS Output; One Side of a Differential LVDS Output, or a Single-Ended CMOS Output.
27
28 OUT7 (OUT7A) LVDS/CMOS Output; One Side of a Differential LVDS Output, or a Single-Ended CMOS Output.
29
44 RSET Resistor connected here sets internal bias currents. Nominal value = 4.12 kΩ.
46 CPRSET Resistor connected here sets the CP current range. Nominal value = 5.1 kΩ.
47
48 REFIN (REF1)
EPAD GND Ground; External Paddle (EPAD). This is the only ground for the part.
OUT2
OUT3
(OUT4B)
OUT4
(OUT5B)
OUT5
(OUT6B)
OUT6
(OUT7B)
OUT7
(REF2) Along with REFIN, this is the differential input for the PLL reference. Alternatively, this pin is a
REFIN
LVPECL Output; One Side of a Differential LVPECL Output.
LVPECL Output; One Side of a Differential LVPECL Output.
LVDS/CMOS Output; One Side of a Differential LVDS Output, or a Single-Ended CMOS Output.
LVDS/CMOS Output; One Side of a Differential LVDS Output, or a Single-Ended CMOS Output.
LVDS/CMOS Output; One Side of a Differential LVDS Output, or a Single-Ended CMOS Output.
LVDS/CMOS Output; One Side of a Differential LVDS Output, or a Single-Ended CMOS Output.
single-ended input for REF2.
Along with REFIN
single-ended input for REF1.
, this is the differential input for the PLL reference. Alternatively, this pin is a
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 80
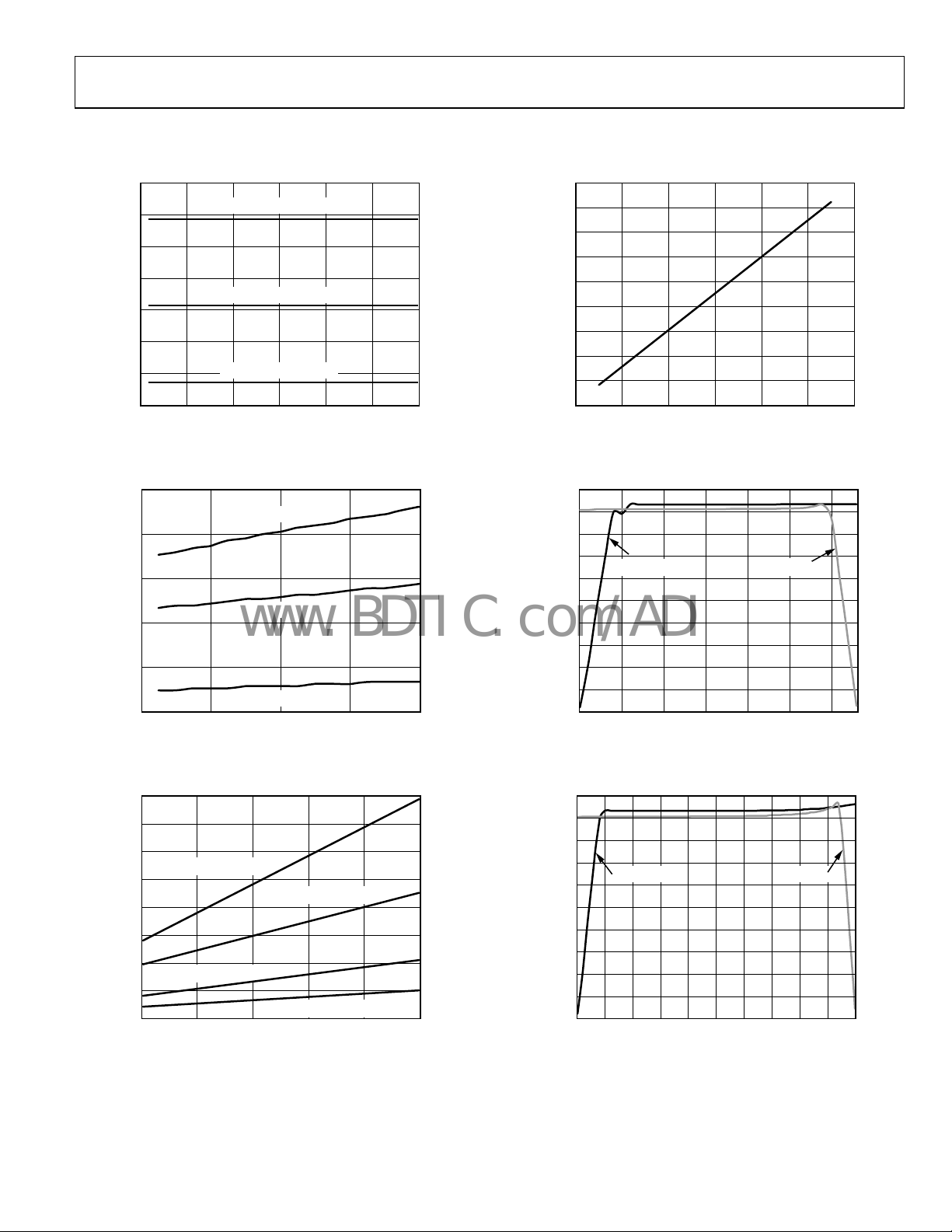
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
240
220
200
180
160
CURRENT (mA)
140
120
100
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
Figure 7. Current vs. Frequency, Direct
2 CHANNELS—4 LVPE CL
2 CHANNELS—2 LVPE CL
1 CHANNEL—1 LVPECL
FREQUENCY (MHz)
to Output, LVPECL Outputs
06427-007
180
2 CHANNELS—4 LVDS
160
140
120
CURRENT (mA)
100
80
0 200 400 600 800
2 CHANNELS—2 LVDS
1 CHANNEL—1 LVDS
FREQUENCY (MHz )
06427-008
Figure 8. Current vs. Frequency—LVDS Outputs
240
220
200
180
160
140
CURRENT (mA)
120
100
2 CHANNELS—8 CMOS
2 CHANNELS—2 CMOS
1 CHANNEL—2 CMOS
80
02
FREQUENCY (MHz )
1 CHANNEL—1 CMOS
010050
5020015
06427-009
Figure 9. Current vs. Frequency—CMOS Outputs
70
65
60
55
50
(MHz/V)
45
VCO
K
40
35
30
25
1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3
VCO FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 10. VCO K
vs. Frequency
VCO
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
CURRENT FROM CP P IN (mA)
1.0
0.5
PUMP DOWN PUMP UP
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
VOLTAGE ON CP PIN (V)
Figure 11. Charge Pump Characteristics @ VCP = 3.3 V
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
CURRENT FROM CP P IN (mA)
1.0
0.5
0
PUMP DOWN PUMP UP
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 3.0 4.02.5 3.5 5.04.5
VOLTAGE ON CP PIN (V)
Figure 12. Charge Pump Characteristics @ VCP = 5.0 V
06427-010
06427-011
06427-012
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 80
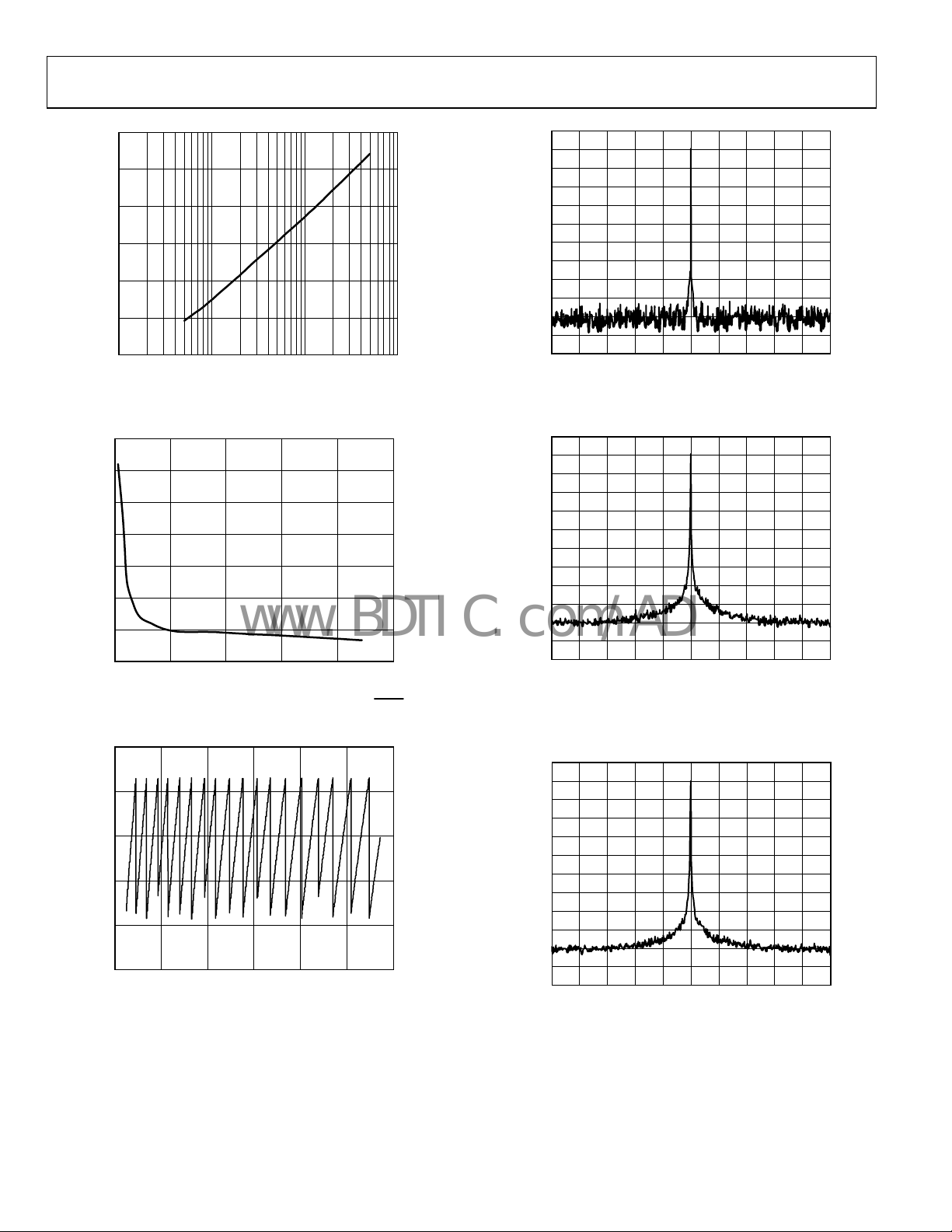
AD9517-3
–
–
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
140
–145
–150
–155
(dBc/Hz)
–160
–165
PFD PHASE NOI SE REFERRED TO PFD INPUT
–170
0.1 1 10010
PFD FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 13. PFD Phase Noise Referred to PFD Input vs. PFD Frequency
210
–212
–214
–216
–218
–220
PLL FIGURE OF MERIT (dBc/ Hz)
–222
–224
02
Figure 14. PLL Figure
SLEW RATE (V/n s)
of Merit (FOM) vs. Slew Rate at REFIN/
1.9
1.7
1.5
1.3
VCO TUNING V OLTAGE (V)
1.1
0.9
1.71.81.92.02.12.22.3
VCO FREQUENCY ( GHz)
Figure 15. VCO Tuning Voltage vs. Frequency
REFIN
10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
RELATIVE POWER (dB)
–80
–90
–100
–110
CENTER 122.88MHz SPAN 50MHz5MHz/DIV
06427-013
06427-137
Figure 16. PFD/CP Spurs; 122.88 MHz; PFD = 15.36 MHz;
= 127 kHz; I
LBW
10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
RELATIVE POWER (dB)
–80
–90
–100
–110
.52.01.51.00.5
06427-136
06427-138
CENTER 122.88MHz SPAN 1MHz100kHz/DIV
Figure 17. Output Spectrum, LVPECL; 122.88 MHz; PFD = 15.36 MHz;
= 127 kHz; I
LBW
10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
RELATIVE POWER (dB)
–80
–90
–100
–110
CENTER 122. 88MHz SPAN 1M Hz100kHz/DIV
= 3.0 mA; F
CP
= 3.0 mA; F
CP
= 2.21 GHz
VCO
= 2.21 GHz
VCO
06427-135
06427-134
Figure 18. Output Spectrum, LVDS; 122.88 MHz; PFD = 15.36 MHz;
= 127 kHz; I
LBW
= 3.0 mA; F
CP
= 2.21 GHz
VCO
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 80
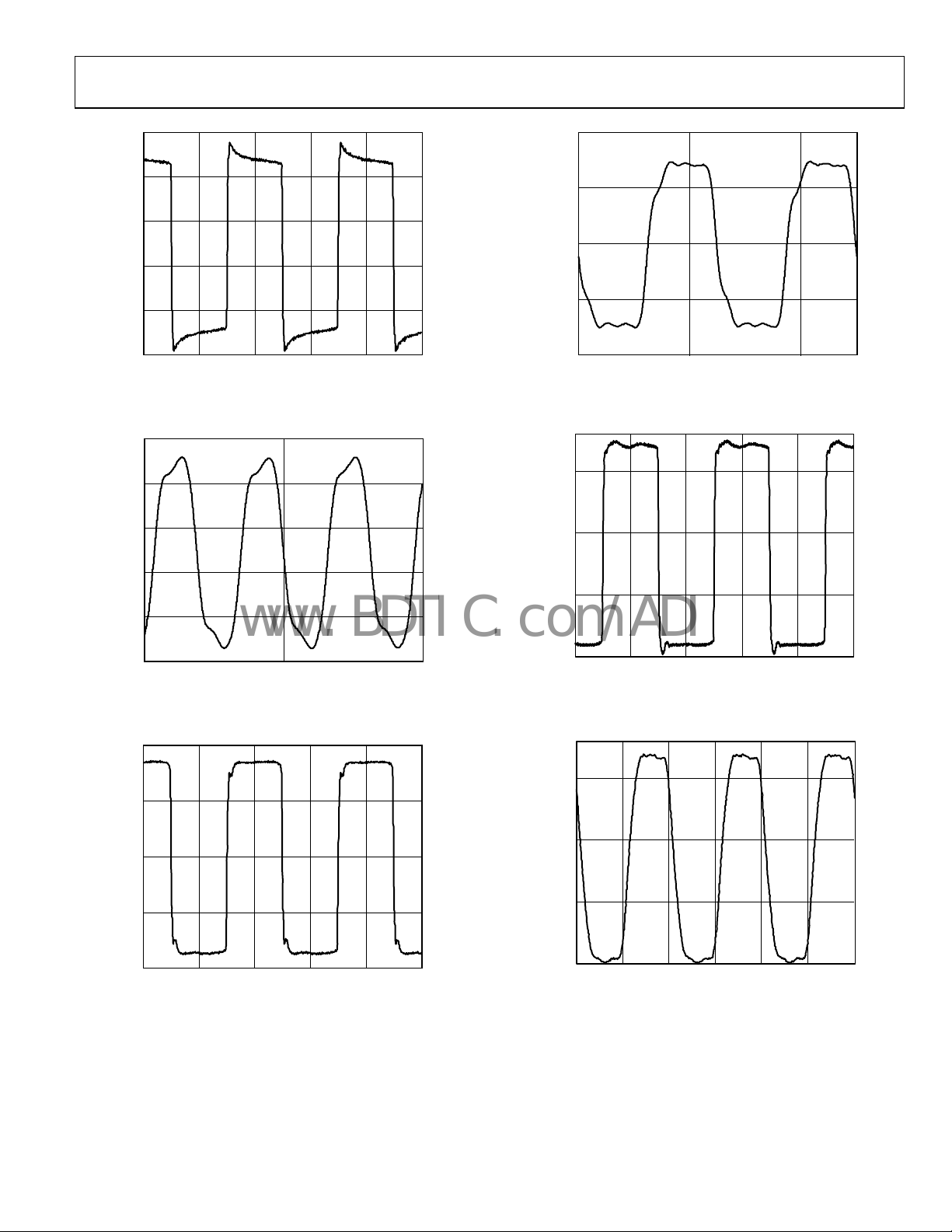
AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
1.0
0.
0.2
6
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT (V)
–0.6
–1.0
02
TIME (ns)
2015105
5
06427-014
Figure 19. LVPECL Output (Differential) @ 100 MHz
–0.2
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT (V)
–0.4
021
Figure 22. LVDS Output (Differential) @ 800 MHz
1.0
0.6
0.2
–0.2
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT (V)
–0.6
–1.0
021
TIME (ns)
Figure 20. LVPECL Output (Differential) @ 1600 MHz
06427-015
2.8
1.8
OUTPUT (V)
0.8
–0.2
0860 1004020
Figure 23. CMOS Output @ 25 MHz
0.4
TIME (ns)
TIME (ns)
06427-017
0
06427-018
0.2
0
–0.2
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT (V)
–0.4
02
TIME (ns)
2015105
5
06427-016
Figure 21. LVDS Output (Differential) @ 100 MHz
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 80
OUTPUT (V)
2.8
1.8
0.8
–0.2
086121042
Figure 24. CMOS Output @ 250 MHz
TIME (ns)
06427-019
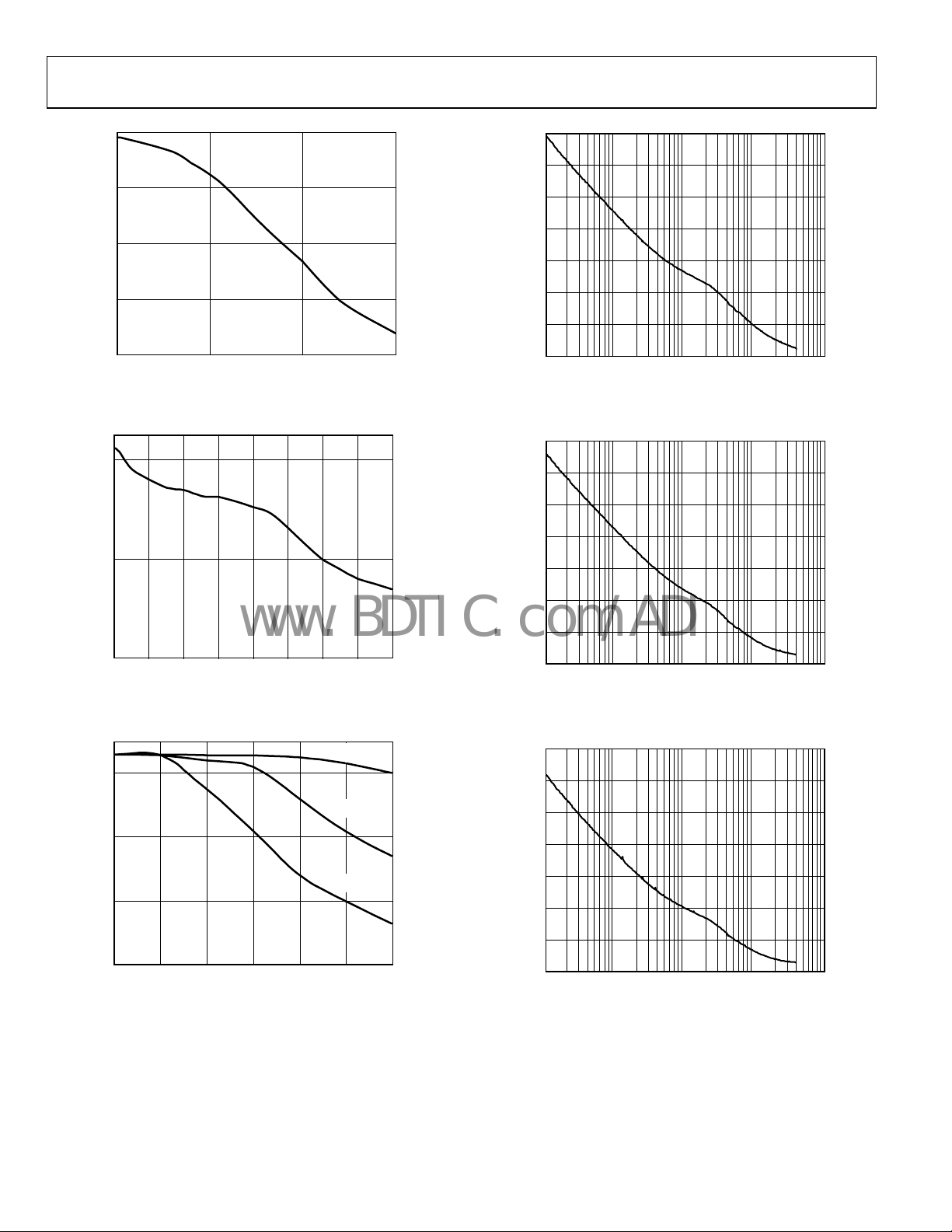
AD9517-3
–
–
–
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
1600
1400
80
–90
–100
1200
1000
DIFFERENTIAL SWING (mV p-p)
800
0321
FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 25. LVPECL Differential Swing vs. Frequency
700
600
DIFFERENTIAL SWING (mV p-p)
500
080070060050
FREQUENCY (MHz )
Figure 26. LVDS Differential Swing vs. Frequency
3
–110
–120
–130
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–140
–150
10k 100M10M1M100k
06427-020
FREQUENCY (Hz)
06427-023
Figure 28. Internal VCO Phase Noise (Absolute) Direct to LVPECL @ 2250 MHz
80
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–140
0400300200100
06427-021
–150
10k 100M10M1M100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
06427-024
Figure 29. Internal VCO Phase Noise (Absolute) Direct to LVPECL @ 2000 MHz
CL = 2pF
80
–90
C
= 10pF
L
2
= 20pF
C
OUTPUT SWING (V)
1
0
0 600500400300200100
OUTPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 27. CMOS Output Swing vs. Frequency
L
and Capacitive Load
06427-133
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 80
–100
–110
–120
–130
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–140
–150
10k 100M10M1M100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
06427-025
Figure 30. Internal VCO Phase Noise (Absolute) Direct to LVPECL @ 1750 MHz
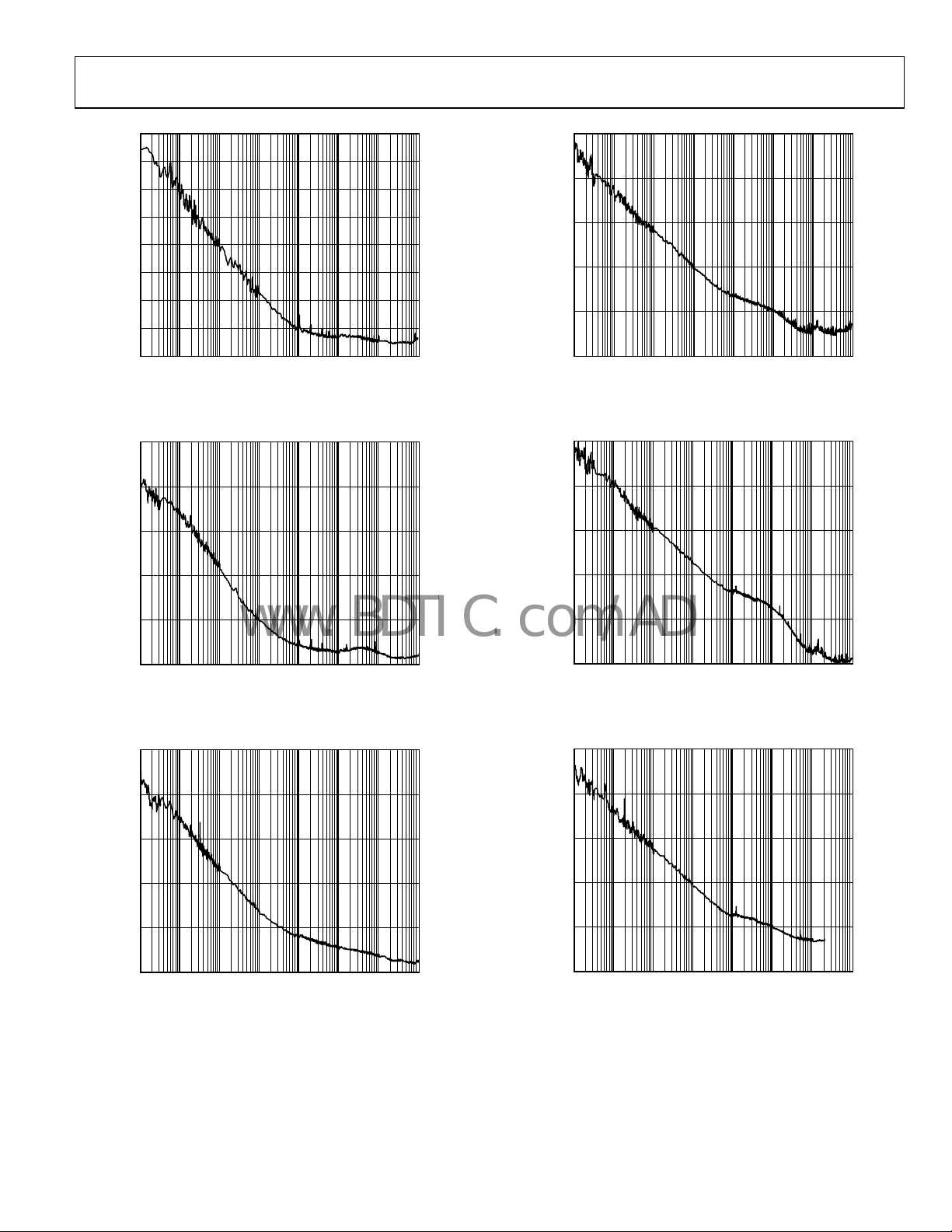
AD9517-3
–
–
–
–
–
–
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
120
–125
–130
110
–120
–135
–140
–145
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–150
–155
–160
10 100M10M1M100k10k1k100
Figure 31. Phase Noise (Additive) LV
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PECL @ 245.76 MHz, Divide-by-1
110
–120
–130
–140
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
10 100M10M1M100k10k1k100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 32. Phase Noise (Additive) LVPECL @ 200 M
100
Hz, Divide-by-5
–130
–140
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
10 100M1k 10k 100k 1M 10M100
06427-026
Figure 34. Phase Noise (Additive) LVD
FREQUENCY (Hz)
S @ 200 MHz, Divide-by-1
06427-142
100
–110
–120
–130
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–140
–150
10 100M10M1M100k10k1k100
06427-027
Figure 35. Phase Noise (Additive) LVD
FREQUENCY (Hz)
S @ 800 MHz, Divide-by-2
06427-130
120
–110
–120
–130
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–140
–150
10 100M10M1M100k10k1k100
Figure 33. Phase Noise (Additive) LVPECL @ 1600 MHz, D
FREQUENCY (Hz)
ivide-by-1
06427-128
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 80
–130
–140
–150
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–160
–170
10 100M10M1M100k10k1k100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 36. Phase Noise (Additive) CM
OS @ 50 MHz, Divide-by-20
06427-131
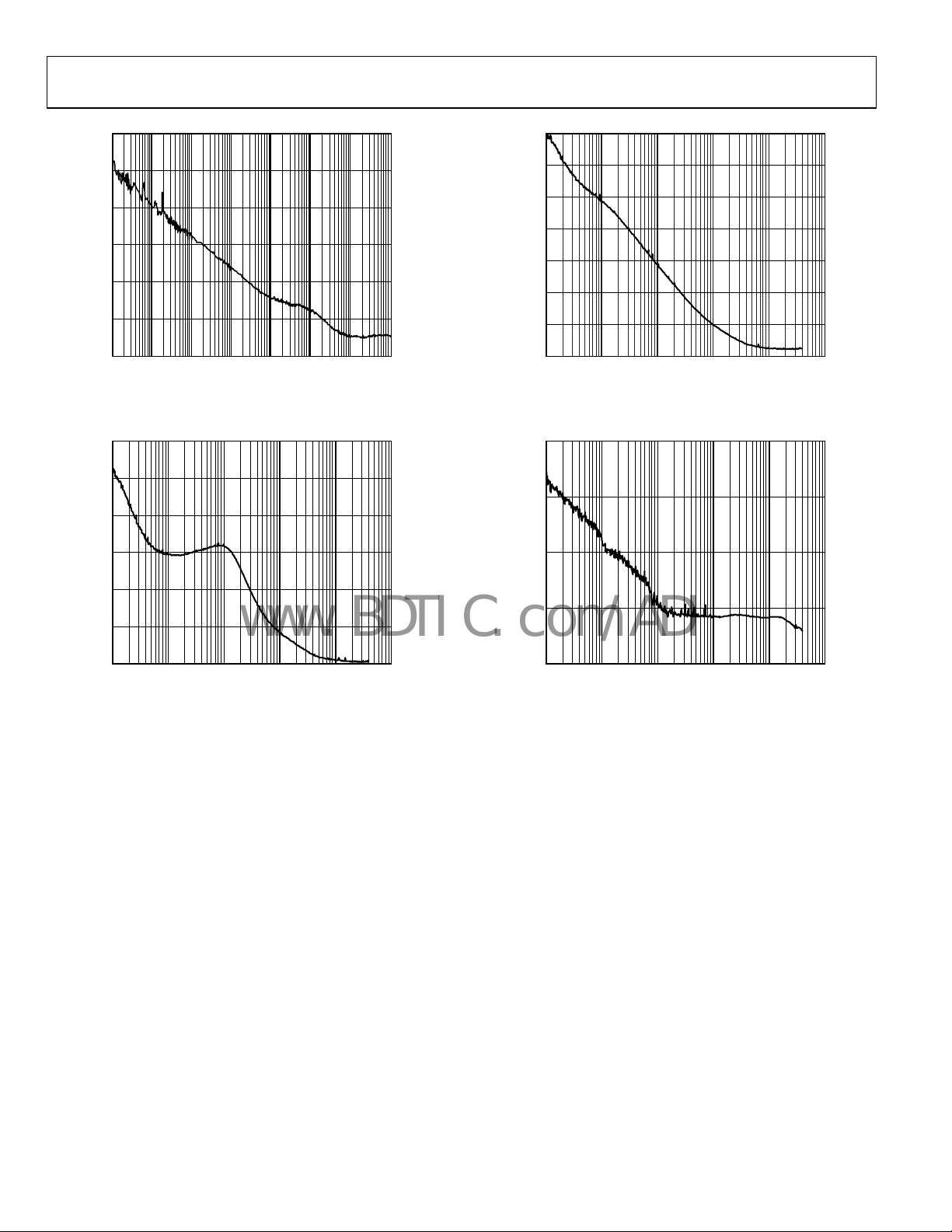
AD9517-3
–
–
–
–
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
100
90
–110
–120
–130
–140
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
10 100M10M1M100k10k1k100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 37. Phase Noise (Additive) CM
100
–110
–120
–130
–140
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–150
OS @ 250 MHz, Divide-by-4
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
1k 100M10M1M100k10k
06427-132
FREQUENCY (Hz)
06427-139
Figure 39. Phase Noise (Absolute) Clock Cleanup; Internal VCO @ 1.87 GHz;
P
FD = 19.44 MHz; LBW = 12.8 kHz; LVPECL Output = 155.52 MHz
120
–130
–140
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
1k 100M10M1M100k10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 38. Phase Noise (Absolute) Clock Generation; Internal VCO @
1.9
7 GHz; PFD = 15.36 MHz; LBW = 143 kHz; LVPECL Output = 122.88 MHz
–160
1k 100M10M1M100k10k
06427-141
Figure 40. Phase Noise (Absolute), Ex
FREQUENCY (Hz)
ternal VCXO (Toyocom TCO-2112)
06427-140
@ 245.76 MHz; PFD = 15.36 MHz; LBW = 250 Hz; LVPECL Output = 245.76 MHz
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TERMINOLOGY
Phase Jitter and Phase Noise
An ideal sine wave can be thought of as having a continuous
nd even progression of phase with time from 0° to 360° for
a
each cycle. Actual signals, however, display a certain amount
of variation from ideal phase progression over time. This
phenomenon is called phase jitter. Although many causes can
contribute to phase jitter, one major cause is random noise,
which is characterized statistically as being Gaussian (normal)
in distribution.
This phase jitter leads to a spreading out of the energy of the
sin
e wave in the frequency domain, producing a continuous
power spectrum. This power spectrum is usually reported as a
series of values whose units are dBc/Hz at a given offset in
frequency from the sine wave (carrier). The value is a ratio
(expressed in dB) of the power contained within a 1 Hz
bandwidth with respect to the power at the carrier frequency.
For each measurement, the offset from the carrier frequency is
also given.
It is meaningful to integrate the total power contained within
ome interval of offset frequencies (for example, 10 kHz to
s
10 MHz). This is called the integrated phase noise over that
frequency offset interval and can be readily related to the time
jitter due to the phase noise within that offset frequency interval.
Phase noise has a detrimental effect on the performance of
Cs, DACs, and RF mixers. It lowers the achievable dynamic
AD
range of the converters and mixers, although they are affected
in somewhat different ways.
Time Jitter
Phase noise is a frequency domain phenomenon. In the time
do
main, the same effect is exhibited as time jitter. When
observing a sine wave, the time of successive zero crossings
varies. In a square wave, the time jitter is a displacement of the
edges from their ideal (regular) times of occurrence. In both
cases, the variations in timing from the ideal are the time jitter.
Because these variations are random in nature, the time jitter is
specified in units of seconds root mean square (rms) or 1 sigma
of the Gaussian distribution.
Time jitter that occurs on a sampling clock for a DAC or an
C decreases the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and dynamic
AD
range of the converter. A sampling clock with the lowest possible
jitter provides the highest performance from a given converter.
Additive Phase Noise
Additive phase noise is the amount of phase noise that is
ttributable to the device or subsystem being measured. The
a
phase noise of any external oscillators or clock sources iss
subtracted. This makes it possible to predict the degree to which
the device impacts the total system phase noise when used in
conjunction with the various oscillators and clock sources, each
of which contributes its own phase noise to the total. In many
cases, the phase noise of one element dominates the system
phase noise. When there are multiple contributors to phase
noise, the total is the square root of the sum of squares of the
individual contributors.
Additive Time Jitter
Additive time jitter is the amount of time jitter that is
ttributable to the device or subsystem being measured. The
a
time jitter of any external oscillators or clock sources is subtracted.
This makes it possible to predict the degree to which the device
impacts the total system time jitter when used in conjunction with
the various oscillators and clock sources, each of which
contributes its own time jitter to the total. In many cases, the
time jitter of the external oscillators and clock sources dominates
the system time jitter.
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 80

AD9517-3
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DETAILED BLOCK DIAGRAM
REFIN ( REF1)
REFIN ( REF2)
BYPASS
CLK
CLK
PD
SYNC
RESET
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
CS
REF1
REF2
REGULATOR ( LDO)
LF
REF_ SEL CPRSETVCP
REFERENCE
SWITCHOVER
STATUS
STATUS
LOW DROPOUT
VCO
DIGITAL
LOGIC
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
S GND RSET
DISTRIBUTI ON
REFERENCE
R
DIVIDER
VCO STATUS
P, P + 1
PRESCALER
DIVIDE BY
2, 3, 4, 5, OR 6
01
N DIVIDE R
A/B
COUNTERS
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
REFMO N
PROGRAMMABLE
R DELAY
PROGRAMMABLE
N DELAY
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
LOCK
DETECT
PHASE
FREQUENCY
DETECTOR
PLL
REFERENCE
CHARGE
ΔT
ΔT
PUMP
LVDS/CMOS
HOLD
LVPECL
LVPECL
LD
CP
STATUS
OUT0
OUT0
OUT1
OUT1
OUT2
OUT2
OUT3
OUT3
OUT4 (OUT4A)
OUT4 (OUT4B)
OUT5 (OUT5A)
OUT5 (OUT5B)
AD9517-3
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
Figure 41. Detailed Block Diagram
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 80
1 TO 32
ΔT
ΔT
LVDS/CMOS
OUT6 (OUT6A)
OUT6 (OUT6B)
OUT7 (OUT7A)
OUT7 (OUT7B)
6427-002

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
THEORY OF OPERATION
OPERATIONAL CONFIGURATIONS
The AD9517 can be configured in several ways. These
configurations must be set up by loading the control registers
(see Tabl e 51 and Ta bl e 52 through Tabl e 61 ). Each section or
f
unction must be individually programmed by setting the
appropriate bits in the corresponding control register or registers.
High Frequency Clock Distribution—CLK or External VCO >1600 MHz
The AD9517 power-up default configuration has the PLL
powered off and the routing of the input set so that the
CLK
CLK/
through the VCO divider (divide-by-2/divide-by-3/divide-by-4/
divide-by-5/divide-by-6). This is a distribution only mode that
allows for an external input up to 2400 MHz (see
max
is 1600 MHz; therefore, higher input frequencies must be
divided down before reaching the channel dividers. This input
routing can also be used for lower input frequencies, but the
minimum divide is 2 before the channel dividers.
When the PLL is enabled, this routing also allows the use of the
PLL
2400 MHz. In this configuration, the internal VCO is not used,
and is powered off. The external VCO/VCXO feeds directly into
the prescaler.
The register settings shown in Table 2 1 are the default values of
hese registers at power-up or after a reset operation. If the
t
contents of the registers are altered by prior programming after
power-up or reset, these registers may also be set intentionally
to these values.
input is connected to the distribution section
Table 3 ). The
imum frequency that can be applied to the channel dividers
with an external VCO or VCXO with a frequency less than
Table 21. Default Settings of Some PLL Registers
Register Function
0x10<1:0> = 01b PLL asynchronous power-down (PLL off)
0x1E0<2:0> = 010b Set VCO divider = 4
0x1E1<0> = 0b Use the VCO divider
0x1E1<1> = 0b CLK selected as the source
When using the internal PLL with an external VCO, the PLL
must be turned on.
Table 22. Settings When Using an External VCO
Register Function
0x10 to 0x1E PLL normal operation (PLL on).
0x1E1<1> = 0b
An external VCO requires an external loop filter that must be
connected between CP and the tuning pin of the VCO. This
loop filter determines the loop bandwidth and stability of the
PLL. Make sure to select the proper PFD polarity for the VCO
being used.
Table 23. Setting the PFD Polarity
Register Function
0x10<7> = 0b
0x10<7> = 1b
PLL settings. Select and enable a reference
input; set R, N
according to the intended loop configuration.
PFD polarity positive (higher control
oltage produces higher frequency)
v
PFD polarity negative (higher control
oltage produces lower frequency)
v
(P, A, B), PFD polarity, and I
CP
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 80

AD9517-3
V
T
R
)
VCO
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REFIN (REF 1)
REFIN (REF 2)
BYPASS
CLK
CLK
PD
SYNC
RESET
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
CS
LF
REF_ SEL CPRSETVCP
REFERENCE
SWITCHOVER
REF1
REF2
STATUS
LOW DROPOU
EGULATOR (LDO
DIGITAL
LOGIC
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
STATUS
S GND RSET
DISTRI BUTION
REFERENCE
R
DIVIDE R
VCO STATUS
P, P + 1
PRESCALER
DIVIDE BY
2, 3, 4, 5, OR 6
01
N DIVIDER
A/B
COUNTERS
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
REFMON
PROGRAMMABLE
R DELAY
PROGRAMMABLE
N DELAY
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
LOCK
DETECT
PHASE
FREQUENCY
DETECTOR
PLL
REFERENCE
CHARGE
ΔT
ΔT
PUMP
LVDS/CMOS
HOLD
LVPECL
LVPECL
LD
CP
STATUS
OUT0
OUT0
OUT1
OUT1
OUT2
OUT2
OUT3
OUT3
OUT4 (OUT4A)
OUT4 (OUT4B)
OUT5 (OUT5A)
OUT5 (OUT5B)
AD9517-3
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
Figure 42. High Frequency Clock Distribution or External VCO > 1600 MHz
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 80
ΔT
ΔT
LVDS/CMOS
OUT6 (OUT6A)
OUT6 (OUT6B)
OUT7 (OUT7A)
OUT7 (OUT7B)
06427-029

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Internal VCO and Clock Distribution
When using the internal VCO and PLL, the VCO divider must
be employed to ensure that the frequency presented to the
channel dividers does not exceed its specified maximum
frequency (1600 MHz, see
ernal loop filter to set the loop bandwidth. The external loop
ext
filter is also crucial to the loop stability.
When using the internal VCO, it is necessary to calibrate the
V
CO (0x18<0>) to ensure optimal performance.
For internal VCO and clock distribution applications, the
re
gister settings shown in Ta b le 2 4 should be used.
Tabl e 3). The internal PLL uses an
Table 24. Settings When Using Internal VCO
Register Function
0x10<1:0> = 00b PLL normal operation (PLL on).
0x10 to 0x1E
0x18<0> = 0,
0x232<0> = 1
0x18<0> = 1,
0x232<0> = 1
0x1E0<2:0>
0x1E1<0> = 0b
0x1E1<1> = 1b VCO selected as the source.
PLL settings. Select and enable a reference
input; set R, N
according to the intended loop configuration.
Reset VCO calibration (first time after
power-up, this does not have to be done,
but must be done subsequently).
Initiate VCO calibration.
VCO divider set to divide-by-2, divide-by-3,
-by-4, divide-by-5, and divide-by-6.
divide
Use the VCO divider as source for
istribution section.
d
(P, A, B), PFD polarity, and I
CP
Rev. 0 | Page 29 of 80

AD9517-3
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REFIN ( REF1)
REFIN ( REF2)
BYPASS
CLK
CLK
PD
SYNC
RESET
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
CS
REF1
REF2
REGULATOR ( LDO)
LF
REF_ SEL CPRSETVCP
REFERENCE
SWITCHOVER
STATUS
STATUS
LOW DROPOUT
VCO
DIGITAL
LOGIC
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
S GND RSET
DISTRIBUTI ON
REFERENCE
R
DIVIDER
VCO STATUS
P, P + 1
PRESCALER
DIVIDE BY
2, 3, 4, 5, OR 6
01
N DIVIDE R
A/B
COUNTERS
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
REFMO N
PROGRAMMABLE
R DELAY
PROGRAMMABLE
N DELAY
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
LOCK
DETECT
PHASE
FREQUENCY
DETECTOR
PLL
REFERENCE
CHARGE
ΔT
ΔT
PUMP
LVDS/CMOS
HOLD
LVPECL
LVPECL
LD
CP
STATUS
OUT0
OUT0
OUT1
OUT1
OUT2
OUT2
OUT3
OUT3
OUT4 (OUT4A)
OUT4 (OUT4B)
OUT5 (OUT5A)
OUT5 (OUT5B)
OUT6 (OUT6A)
OUT6 (OUT6B)
OUT7 (OUT7A)
OUT7 (OUT7B)
06427-030
AD9517-3
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
ΔT
LVDS/CMOS
ΔT
Figure 43. Internal VCO and Clock Distribution
Rev. 0 | Page 30 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Clock Distribution or External VCO <1600 MHz
When the external clock source to be distributed or the external
VCO/VCXO is <1600 MHz, a configuration that bypasses the
VCO divider can be used. This only differs from the High
F
requency Clock Distribution—CLK or External VCO >1600 MHz
s
ection in that the VCO divider (divide-by-2, divide-by-3,
divide-by-4, divide-by-5, and divide-by-6) is bypassed. This
limits the frequency of the clock source to <1600 MHz (due to
the maximum input frequency allowed at the channel dividers).
Configuration and Register Settings
For clock distribution applications where the external clock is
<1600 MHz, the register settings shown in Tab le 2 5 should be used.
Table 26. Settings for Using Internal PLL with External VCO
<1600 MH
Register Function
0x1E1<0> = 1b
0x10<1:0> = 00b
An external VCO/VCXO requires an external loop filter that
must be connected between CP and the tuning pin of the
VCO/VCXO. This loop filter determines the loop bandwidth
and stability of the PLL. Make sure to select the proper PFD
polarity for the VCO/VCXO being used.
z
Bypass the VCO divider as source for
istribution section
d
PLL normal operation (PLL on) along with
other ap
propriate PLL settings in 0x10 to 0x1E
Table 25. Settings for Clock Distribution <1600 MHz
Register Function
0x10<1:0> = 01b PLL asynchronous power-down (PLL off)
0x1E1<0> = 1b
0x1E1<1> = 0b CLK selected as the source
When using the internal PLL with an external VCO <1600 MHz,
the PLL must be turned on.
Bypass the VCO divider as source for
istribution section
d
Table 27. Setting the PFD Polarity
Register Function
0x10<7> = 0
0x10<7> = 1
PFD polarity positive (higher control voltage
oduces higher frequency)
pr
PFD polarity negative (higher control
oltage produces lower frequency)
v
Rev. 0 | Page 31 of 80

AD9517-3
V
LO
OUT
R
)
VCO
DIVIDE BY
2, 3, 4
6
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REFIN (REF1)
REFIN (REF2)
BYPASS
CLK
CLK
PD
SYNC
RESET
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
CS
LF
REF_ SEL CPRSETVCP
REFERENCE
SWITCHOVER
REF1
STATUS
REF2
W DROP
EGULATOR (LDO
DIGITAL
LOGIC
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
STATUS
S GND RSET
DISTRIBUTI ON
REFERENCE
R
DIVIDER
VCO STATUS
P, P + 1
PRESCALER
, 5, OR
01
N DIVIDER
A/B
COUNTERS
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
REFMON
PROGRAMMABLE
R DELAY
PROGRAMMABLE
N DELAY
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
LOCK
DETECT
PHASE
FREQUENCY
DETECTOR
PLL
REFERENCE
CHARGE
ΔT
ΔT
PUMP
LVDS/CMOS
HOLD
LVPECL
LVPECL
LD
CP
STATUS
OUT0
OUT0
OUT1
OUT1
OUT2
OUT2
OUT3
OUT3
OUT4 (OUT4A)
OUT4 (OUT4B)
OUT5 (OUT5A)
OUT5 (OUT5B)
OUT6 (OUT6A)
OUT6 (OUT6B)
OUT7 (OUT7A)
OUT7 (OUT7B)
06427-028
AD9517-3
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
DIVIDE BY
1 TO 32
ΔT
LVDS/CMOS
ΔT
Figure 44. Clock Distribution or External VCO <1600 MHz
Rev. 0 | Page 32 of 80

AD9517-3
VCPV
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL)
REF_SEL
SGND
RSET
REFMO N
CPRSET
N DIVIDER
DIST
REF
R DIVIDER
A/B
COUNTERS
0
1
Figure 45. PLL Functional Blocks
REFIN ( REF1)
REFIN ( REF2)
BYPASS
CLK
CLK
REGULATOR (LDO)
LF
REFERENCE
SWITCHOVER
REF1
REF2
LOW DROPOUT
VCO
STATUS
STATUS
P, P + 1
PRESCALER
DIVIDE BY
2, 3, 4, 5, OR 6
01
The AD9517 includes an on-chip PLL with an on-chip VCO.
LL blocks can be used either with the on-chip VCO to
The P
create a complete phase-locked loop or with an external VCO
or VCXO. The PLL requires an external loop filter, which
usually consists of a small number of capacitors and resistors.
The configuration and components of the loop filter help to
establish the loop bandwidth and stability of the operating PLL.
The AD9517 PLL is useful for generating clock frequencies
rom a supplied reference frequency. This includes conversion
f
of reference frequencies to much higher frequencies for subsequent
division and distribution. In addition, the PLL can be exploited to
clean up jitter and phase noise on a noisy reference. The exact
choices of PLL parameters and loop dynamics are application
specific. The flexibility and depth of the AD9517 PLL allow the
part to be tailored to function in many different applications
and signal environments.
Configuration of the PLL
The AD9517 allows flexible configuration of the PLL,
accommodating various reference frequencies, PFD comparison
frequencies, VCO frequencies, internal or external VCO/VCXO,
and loop dynamics. This is accomplished by the various settings
that include the R divider, the N divider, the PFD polarity (only
applicable to external VCO/VCXO), the antibacklash pulse
width, the charge pump current, the selection of internal VCO
or external VCO/VCXO, and the loop bandwidth. These are
managed through programmable register settings (see
nd Tabl e 53 ) and by the design of the external loop filter.
a
Tabl e 51
PROGRAMMABLE
R DELAY
PROGRAMMABLE
N DELAY
VCO STATUS
Su
are highly dependent upon proper configuration of the PLL
settings. The design of the external loop filter is crucial to the
proper operation of the PLL. A thorough knowledge of PLL
theory and design is helpful.
ADIsimCLK™ (V1.2 o
with the design and exploration of the capabilities and features
of the AD9517, including the design of the PLL loop filter. It is
available at www.analog.com/clocks.
Phase Frequency Detector (PFD)
The PFD takes inputs from the R counter and N counter and
produces an output proportional to the phase and frequency
difference between them. The PFD includes a programmable
delay element that controls the width of the antibacklash pulse.
This pulse ensures that there is no dead zone in the PFD
transfer function and minimizes phase noise and reference
spurs. The antibacklash pulse width is set by 0x17<1:0>.
An important limit to keep in mind is the maximum frequency
a
PFD is a function of the antibacklash pulse setting, as specified
in the phase/frequency detector section of
LOCK
DETECT
PHASE
FREQUENCY
DETECTOR
PLL
REF
CHARGE PUMP
HOLD
LD
CP
STATUS
06427-064
ccessful PLL operation and satisfactory PLL loop performance
r later) is a free program that can help
llowed into the PFD. The maximum input frequency into the
Tabl e 2.
Rev. 0 | Page 33 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Charge Pump (CP)
The charge pump is controlled by the PFD. The PFD monitors
the phase and frequency relationship between its two inputs
and tells the CP to pump up or pump down to charge or
discharge the integrating node (part of the loop filter). The
integrated and filtered CP current is transformed into a voltage
that drives the tuning node of the internal VCO through the LF
pin (or the tuning pin of an external VCO) to move the VCO
frequency up or down. The CP can be set (0x10<6:4>) for high
impedance (allows holdover operation), for normal operation
(attempts to lock the PLL loop), for pump up, or for pump
down (test modes). The CP current is programmable in eight
steps from (nominally) 600 μA to 4.8 mA. The exact value of
the CP current LSB is set by the CP_RSET resistor, which is
nominally 5.1 kΩ.
On-Chip VCO
The AD9517 includes an on-chip VCO covering the frequency
range shown in Tab le 2 . Achieving low VCO phase noise was a
riority in the design of the VCO.
p
To tune over the wide range of frequencies covered by this
V
CO, ranges are used. This is largely transparent to the user but
is the reason that the VCO must be calibrated when the PLL
loop is first set up. The calibration procedure ensures that the
VCO is operating within the correct band range for the frequency
that it is asked to produce. See the
itional information.
add
VCO Calibration section for
The on-chip VCO is powered by an on-chip, low drop out
(LD
O), linear voltage regulator. The LDO provides some
isolation of the VCO from variations in the power supply
voltage level. The BYPASS pin should be connected to ground
by a 220 nF capacitor to ensure stability. This LDO employs the
same technology used in the anyCAP® line of regulators from
Analog Devices, Inc., making it insensitive to the type of
capacitor used. Driving an external load from the BYPASS pin
is not supported.
PLL External Loop Filter
When using the internal VCO, the external loop filter should be
referenced to the BYPASS pin for optimal noise and spurious
performance. An example of an external loop filter for the PLL
is shown in
desir
depend upon the VCO frequency, the K
Figure 46. A loop filter must be calculated for each
ed PLL configuration. The values of the components
, the PFD frequency,
VCO
the CP current, the desired loop bandwidth, and the desired
phase margin. The loop filter affects the phase noise, the loop
settling time, and the loop stability. A knowledge of PLL theory
is necessary for understanding the subject of loop filter design.
There are tools available, such as ADIsimCLK, that can help
with the calculation of a loop filter according to the application
requirements.
PLL Reference Inputs
The AD9517 features a flexible PLL reference input circuit that
allows either a fully differential input or two separate singleended inputs. The input frequency range for the reference
inputs is specified in
e single-ended inputs are self-biased, allowing for easy
th
ac coupling of input signals.
The differential input and the single-ended inputs share the two
ns, REFIN (REF1)/
pi
type is selected and controlled by 0x1C (see Tab l e 5 1 and Tab l e 5 3).
When the differential reference input is selected, the self-bias
lev
el of the two sides is offset slightly (~100 mV, see Ta b le 2 ) to
p
revent chattering of the input buffer when the reference is slow
or missing. This increases the voltage swing required of the
driver and overcomes the offset.
The single-ended inputs can be driven by either a dc-coupled
C
MOS level signal or an ac-coupled sine wave or square wave.
Each single-ended input can be independently powered down
when not needed to increase isolation and reduce power. Either
a differential or a single-ended reference must be specifically
enabled. All PLL reference inputs are off by default.
The differential reference input is powered down whenever the
PLL is p
not selected. The single-ended buffers power down when the
PLL is powered down and when their individual power-down
registers are set. When the differential mode is selected, the
single-ended inputs are powered down.
In differential mode, the reference input pins are internally selfbiased so that they can be ac-coupled via capacitors. It is possible to
dc couple to these inputs. If the differential REFIN is driven by
a single-ended signal, the unused side (
decoupled via a suitable capacitor to a quiet ground. Figure 47
s
hows the equivalent circuit of REFIN.
AD9517-3
LF
VCO
CHARGE
PUMP
Figure 46. Example of External Loop Filter for PLL
CP
BYPASS
C
= 220nF
BP
R2
R1
C1 C2 C3
06427-065
Tabl e 2. Both the differential and
REFIN
(REF2). The desired reference input
owered down or when the differential reference input is
) should be
REFIN
Rev. 0 | Page 34 of 80

AD9517-3
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REF1
10kΩ 12kΩ
REFIN
REFIN
10kΩ 10kΩ
REF2
Figure 47. REFIN Equivalent C
85kΩ
85kΩ
S
150Ω
150Ω
V
S
ircuit
V
S
06427-066
Reference Switchover
The AD9517 supports dual single-ended CMOS inputs, as well
as a single differential reference input. In the dual single-ended
reference mode, the AD9517 supports automatic and manual
PLL reference clock switching between REF1 (on Pin REFIN)
and REF2 (on Pin
REFIN
). This feature supports networking
and other applications that require redundant references. When
using reference switchover, the single-ended reference inputs
should be dc-coupled CMOS levels and never be allowed to go
to high impedance. If these inputs are allowed to go to high
impedance, noise may cause the buffer to chatter, causing a false
detection of the presence of a reference.
There are several configurable modes of reference switchover.
The s
witchover can be performed manually or automatically.
The manual switchover is done either through a register setting
(0x1D) or by using the REF_SEL pin. The automatic switchover
occurs when REF1 disappears. There is also a switchover deglitch
feature that ensures that the PLL does not receive rising edges that
are far out of alignment with the newly selected reference.
There are two reference automatic switchover modes (0x1C):
• P
refer REF1: Switch from REF1 to REF2 when REF1
disappears. Return to REF1 from REF2 when REF1 returns.
tay on REF2: Automatically switch to REF2 if REF1 disappears,
• S
but do not switch back to REF1 if it reappears. The reference
can be set back to REF1 manually at an appropriate time.
In automatic mode, REF1 is monitored by REF2. If REF1
isappears (two consecutive falling edges of REF2 without an
d
edge transition on REF1), REF1 is considered missing. Upon
the next subsequent rising edge of REF2, REF2 is used as the
reference clock to the PLL. If 0x1C<3> = 0b (default), when
REF1 returns (four rising edges of REF1 without two falling
edges of REF2 between the REF1 edges), the PLL reference
switches back to REF1. If 0x1C<3> = 1b, the user can control
when to switch back to REF1. This is done by programming the
part to manual reference select mode (0x1C<4> = 0b) and by
ensuring that the registers and/or REF_SEL pin are set to select
the desired reference. Automatic mode can be re-enabled when
REF1 is reselected.
Manual switchover requires the presence of a clock on the
r
eference input that is being switched to, or that the deglitching
feature be disabled (0x1C<7>).
Reference Divider R
The reference inputs are routed to the reference divider, R.
R (a 14-bit counter) can be set to any value from 0 to 16383 by
writing to 0x11 and 0x12. (Both R = 0 and R = 1 give divide-by-1.)
The output of the R divider goes to one of the PFD inputs to be
compared with the VCO frequency divided by the N divider.
The frequency applied to the PFD must not exceed the
maximum allowable frequency, which depends on the
antibacklash pulse setting (see
Tabl e 2).
The R counter has its own reset. The R counter can be reset
g the shared reset bit of the R, A, and B counters. It can also
usin
be reset by a
SYNC
operation.
VCXO/VCO Feedback Divider N: P, A, B, R
The N divider is a combination of a prescaler (P) and two
counters, A and B. The total divider value is
N = (P ×
where P ca
B) + A
n be 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32.
Prescaler
The prescaler of the AD9517 allows for two modes of operation:
a fixed divide (FD) mode of 1, 2, or 3, and dual modulus (DM)
mode where the prescaler divides by P and (P + 1) {2 and 3, 4
and 5, 8 and 9, 16 and 17, or 32 and 33}. The prescaler modes of
operation are given in
ailable at all frequencies (see Tabl e 2).
av
Tabl e 53 , 0x16<2:0>. Not all modes are
When operating the AD9517 in dual modulus mode (P//P + 1),
t
he equation used to relate input reference frequency to VCO
output frequency is
= (f
f
VCO
/R) × (P × B + A) = f
REF
× N/R
REF
However, when operating the prescaler in FD mode 1, 2, or 3,
th
e A counter is not used (A = 0) and the equation simplifies to
f
= (f
VCO
/R) × (P × B) = f
REF
× N/R
REF
When A = 0, the divide is a fixed divide of P = 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32,
which case the previous equation also applies.
in
Rev. 0 | Page 35 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
By using combinations of DM and FD modes, the AD9517 can
achieve values of N all the way down to N = 1. Tabl e 28 shows
h
ow a 10 MHz reference input may be locked to any integer
multiple of N.
Note that the same value of N may be derived in different ways,
as i
llustrated by the case of N = 12. The user may choose a fixed
divide mode P = 2 with B = 6, or use the dual modulus mode
2/3 with A = 0, B = 6, or use the dual modulus mode 4/5 with
A = 0, B = 3.
A and B Counters
The AD9517 B counter can be bypassed (B = 1). This B counter
bypass mode is only valid when using the prescaler in FD mode.
When A = 0, the divide is a fixed divide of P = 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32.
Unlike the R counter, an A = 0 is actually a zero. The B counter
ust be ≥3 or bypassed.
m
Table 28. How a 10 MHz Reference Input May Be Locked to Any Integer Multiple of N
FREF R P A B N FVCO Mode Notes
10 1 1 X 1 1 10 FD P = 1, B = 1 (bypassed)
10 1 2 X 1 2 20 FD P = 2, B = 1 (bypassed)
10 1 1 X 3 3 30 FD P = 1, B = 3
10 1 1 X 4 4 40 FD P = 1, B = 4
10 1 1 X 5 5 50 FD P = 1, B = 5
10 1 2 X 3 6 60 FD P = 2, B = 3
10 1 2 0 3 6 60 DM P and P + 1 = 2 and 3, A = 0, B = 3
10 1 2 1 3 7 70 DM P and P + 1 = 2 and 3, A = 1, B = 3
10 1 2 2 3 8 80 DM P and P + 1 = 2 and 3, A = 2, B = 3
10 1 2 1 4 9 90 DM P and P + 1 = 2 and 3, A = 1, B = 4
10 1 2 X 5 10 100 FD P = 2, B = 5
10 1 2 0 5 10 100 DM P and P + 1 = 2 and 3, A = 0, B = 5
10 1 2 1 5 11 110 DM P and P + 1 = 2 and 3, A = 1, B = 5
10 1 2 X 6 12 120 FD P = 2, B = 6
10 1 2 0 6 12 120 DM P and P + 1 = 2 and 3, A = 0, B = 6
10 1 4 0 3 12 120 DM P and P + 1 = 4 and 5, A = 0, B = 3
10 1 4 1 3 13 130 DM P and P + 1 = 4 and 5, A = 1, B = 3
The maximum input frequency to the A/B counter is reflected
he maximum prescaler output frequency specified in
in t
s the prescaler input frequency (VCO or CLK) divided by P.
This i
Although manual reset is not normally required, the A/B counters
ha
ve their own reset bit. A and B counters can be reset using the
shared reset bit of the R, A, and B counters. They may also be
reset through a
R, A, and B Counters:
The R, A and B counters may also be reset simultaneously
through the
(see Tabl e 53 ). The
SYNC
operation.
SYNC
Pin Reset
SYNC
pin. This function is controlled by 0x19<7:6>
SYNC
pin reset is disabled by default.
Tabl e 2.
R and N Divider Delays
Both the R and N dividers feature a programmable delay cell.
These delays may be enabled to allow adjustment of the phase
relationship between the PLL reference clock and the VCO or
CLK. Each delay is controlled by three bits. The total delay
range is about 1 ns. See 0x19 in
Tabl e 53 .
Rev. 0 | Page 36 of 80

AD9517-3
V
V
CLKC
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DIGITAL LOCK DETECT (DLD)
By selecting the proper output through the mux on each pin,
the DLD function is available at the LD, STATUS, and
REFMON pins. The DLD circuit indicates a lock when the time
difference of the rising edges at the PFD inputs is less than a
specified value (the lock threshold). The loss of a lock is
indicated when the time difference exceeds a specified value
(the unlock threshold). Note that the unlock threshold is wider
than the lock threshold, which allows some phase error in
excess of the lock window to occur without chattering on the
lock indicator.
The lock detect window timing depends on three settings: the
LD window bit (0x18<4>), the antibacklash pulse width
D
setting (0x17<1:0>, see Tab l e 2 ), and the lock detect counter
(0x18<6:5>). A
programmable number of consecutive PFD cycles with a time
difference less than the lock detect threshold. The lock detect
circuit continues to indicate a lock until a time difference
greater than the unlock threshold occurs on a single subsequent
cycle. For the lock detect to work properly, the period of the
PFD frequency must be greater than the unlock threshold. The
number of consecutive PFD cycles required for lock is
programmable (0x18<6:5>).
Analog Lock Detect (ALD)
The AD9517 provides an ALD function that may be selected for
use at the LD pin. There are two versions of ALD:
• N-cha
pull-up resistor to the positive supply, VS. The output is
normally high with short, low-going pulses. Lock is indicated
by the minimum duty cycle of the low-going pulses.
-channel open-drain lock detect. This signal requires a pull-
• P
down resistor to GND. The output is normally low with
short, high-going pulses. Lock is indicated by the minimum
duty cycle of the high-going pulses.
The analog lock detect function requires an R-C filter to
p
rovide a logic level indicating lock/unlock.
Current Source Digital Lock Detect (DLD)
During the PLL locking sequence, it is normal for the DLD
signal to toggle a number of times before remaining steady
when the PLL is completely locked and stable. There may be
applications where it is desirable to have DLD asserted only
after the PLL is solidly locked. This is possible by using the
lock is not indicated until there is a
nnel open-drain lock detect. This signal requires a
= 3.3
S
AD9517-3
ALD
Figure 48. Example of Analog Lock Detect Filter, Using
an N-Ch
LD
annel Open-Drain Driver
R2
V
R1
OUT
C
06427-067
current source lock detect function. This function is set by
selecting it as the output from the LD pin control (0x1A<5:0>).
The current source lock detect provides a current of 110 μA
when D
LD is true and shorts to ground when DLD is false.
If a capacitor is connected to the LD pin, it charges at a rate
determined by the current source during the DLD true time
but is discharged nearly instantly when DLD is false. By
monitoring the voltage at the LD pin (top of the capacitor), it is
only possible to get a Logic High level after the DLD has been
true for a sufficiently long time. Any momentary DLD false
resets the charging. By selecting a properly sized capacitor, it is
possible to delay a lock detect indication until the PLL is stably
locked, and the lock detect does not chatter.
The voltage on the capacitor can be sensed by an external
co
mparator connected to the LD pin. However, there is an
internal LD pin comparator that can be read at the REFMON
pin control (0x1B<4:0>) or the STATUS pin control (0x17<7:2>)
as an active high signal. It is also available as an active low signal
(REFMON, 0x1B<4:0> and STATUS, 0x17<7:2>). The internal
LD pin comparator trip point and hysteresis are given in
AD9517-3
110µA
C
V
OUT
CLK
DLD
LD PIN
COMPARAT OR
Figure 49. Current Source Lock Detect
LD
REFMON
OR
STATUS
External VCXO/VCO Clock Input (CLK/
)
Table 1 6.
06427-068
CLK is a differential input that can be used as an input to drive
the AD9517 clock distribution section. This input can receive
up to 2.4 GHz. The pins are internally self-biased, and the input
signal should be ac-coupled via capacitors.
CLOCK INPUT
STAGE
06427-032
The CLK/
V
S
LK
2.5kΩ 2.5kΩ
5kΩ
5kΩ
Figure 50. CLK Equivalent Input Circuit
CLK
input can be used either as a distribution only
input (with the PLL off ), or as a feedback input for an external
VCO/VCXO using the internal PLL, when the internal VCO is
not used. The CLK/
CLK
input can be used for frequencies up
to 2.4 GHz.
Rev. 0 | Page 37 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Holdover
The AD9517 PLL has a holdover function. Holdover is
implemented by putting the charge pump into a high
impedance state. This is useful when the PLL reference clock is
lost. Holdover mode allows the VCO to maintain a relatively
constant frequency even though there is no reference clock.
Without this function, the charge pump is placed into a constant
pump-up or pump-down state, resulting in a massive VCO
frequency shift. Because the charge pump is placed in a high
impedance state, any leakage that occurs at the charge pump
output or the VCO tuning node causes a drift of the VCO
frequency. This can be mitigated by using a loop filter that
contains a large capacitive component because this drift is
limited by the current leakage induced slew rate (I
LEAK
/C)
of the VCO control voltage.
SYNC
Both a manual holdover, using the
pin, and an automatic
holdover mode are provided. To use either function, the holdover
function must be enabled (0x1D<0> and 0x1D<2>).
[Note that the VCO cannot be calibrated with the holdover
ena
bled because the holdover resets the N divider during
calibration, which prevents proper calibration. Disable holdover
before issuing a VCO calibration.]
Manual Holdover Mode
A manual holdover mode can be enabled that allows the user to
place the charge pump into a high impedance state when the
SYNC
pin is asserted low. This operation is edge sensitive not
level sensitive. The charge pump immediately enters a high
impedance state. To take the charge pump out of a high
impedance state take the
SYNC
pin high. The charge pump
then leaves high impedance state synchronously with the next
PFD rising edge from the reference clock. This prevents
extraneous charge pump events from occurring during the time
between
SYNC
going high and the next PFD event. This also
means that the charge pump stays in a high impedance state as
long as there is no reference clock present.
The B counter (in the N divider) is reset synchronously with the
cha
rge pump leaving the high impedance state on the reference
path PFD event. This helps align the edges out of the R and N
dividers for faster settling of the PLL. Because the prescaler is
not reset, this feature works best when the B and R numbers are
close because this results in a smaller phase difference for the
loop to settle out.
When using this mode, the channel dividers should be set to
SYNC
nore the
ig
pin (at least after an initial
dividers are not set to ignore the
SYNC
SYNC
event). If the
pin, any time
SYNC
is
taken low to put the part into holdover, the distribution outputs
turn off.
Automatic/Internal Holdover Mode
When enabled, this function automatically puts the charge
pump into a high impedance state when the loop loses lock.
The assumption is that the only reason the loop loses lock is due
to the PLL losing the reference clock; therefore, the holdover
function puts the charge pump into a high impedance state to
maintain the VCO frequency as close as possible to the original
frequency before the reference clock disappears.
A flow chart of the automatic/internal holdover function
peration is shown in Figure 51.
o
PLL ENABLED
LOOP OUT OF LOCK. DIGITAL LOCK
DETECT SIGNAL GOES LOW WHEN THE
LOOP LEA VES LOCK AS DET ERMINED
BY THE PHASE DIFFERENCE AT THE
INPUT OF THE PFD.
NO
ANALOG LO CK DETECT PIN INDICATES
LOCK WAS PREVIOUSLY ACHIEVED.
(0x1D<3> = 1: USE L D PIN VOLT AGE
WITH HOLDOVER.
0x1D<3> = 0: IGNO RE LD PIN VOLTAGE,
TREAT LD PIN AS ALWAYS HIGH.)
CHARGE PUMP IS MADE
HIGH IMPEDANCE .
PLL COUNT ERS CONTINU E
OPERATING NORMALLY.
CHARGE PUMP REM AINS HIGH
IMPEDANCE UNTIL THE REFERENCE
HAS RETURNED.
YES
TAKE CHARGE PUMP OUT OF
HIGH IMPEDANCE . PLL CAN
NOW RESETTLE.
WAIT FOR DLD TO GO HIGH. THIS TAKES
5 TO 255 CYCLES ( PROGRAMMING OF THE DLD
DELAY COUNTE R) WITH THE REFERENCE AND
FEEDBACK CLOCKS INSIDE THE LOCK WINDOW AT
THE PFD. THIS ENSURES THAT THE HOLDOVER
FUNCTION WAITS FOR THE PLL TO SETTLE AND LOCK
BEFORE THE HOLDOVER F UNCTION CAN BE
RETRIGGE RED.
DLD == LOW
YES
WAS
LD PIN == HIGH
WHEN DLD WENT
LOW?
YES
HIGH IMPEDANCE
CHARGE PUMP
YES
REFERENCE
EDGE AT PFD?
YES
RELEASE
CHARGE PUMP
HIGH IMPEDANCE
YES
DLD == HIGH
NO
NO
NO
Figure 51. Flow Chart of Automatic/Internal Holdover Mode
The holdover function senses the logic level of the LD pin as a
condition to enter holdover. The signal at LD can be from the
DLD, ALD, or current source LD mode. It is possible to disable
the LD comparator (0x1D<3>), which causes the holdover
function to always sense LD as high. If DLD is used, it is
possible for the DLD signal to chatter some while the PLL is
reacquiring lock. The holdover function may retrigger, thereby
preventing the holdover mode from terminating. Use of the
current source lock detect mode is recommended to avoid this
situation (see the
Current Source Digital Lock Detect section).
6427-069
Rev. 0 | Page 38 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Once in holdover mode, the charge pump stays in a high
impedance state as long as there is no reference clock present.
As in the external holdover mode, the B counter (in the N
divider) is r
high impedance state on the reference path PFD event. This
helps to align the edges out of the R and N dividers for faster
settling of the PLL and to reduce frequency errors during
settling. Because the prescaler is not reset, this feature works
best when the B and R numbers are close, resulting in a smaller
phase difference for the loop to settle out.
After leaving holdover, the loop then reacquires lock and the
LD p
holdover (CP high impedance).
The holdover function always responds to the state of the
urrently selected reference (0x1C). If the loop loses lock during
c
a reference switchover (see the Reference Switchover section),
oldover is triggered briefly until the next reference clock edge
h
at the PFD.
The following registers affect the automatic/internal holdover
nction:
fu
• 0x18<6:5>—lo
consecutive PFD cycles with edges inside the lock detect
window are required for the DLD indicator to indicate lock.
This impacts the time required before the LD pin can begin
to charge as well as the delay from the end of a holdover
event until the holdover function can be re-engaged.
• 0x18<3>—disable digital lock detect. This bit must be set to a
0 to enable the DLD circuit. Automatic/internal holdover
does not operate correctly without the DLD function enabled.
• 0x1A<5:0>—L
the current source lock detect mode if using the LD pin
comparator. Load the LD pin with a capacitor of an
appropriate value.
eset synchronously with the charge pump leaving
in must charge (if 0x1D<3> = 1) before it can re-enter
ck detect counter. This changes how many
D pin control. Set this to 000100b to put it in
For example, to use automatic holdover with:
utomatic reference switchover, prefer REF1.
• A
• Dig
ital lock detect: five PFD cycles, high range window.
utomatic holdover using the LD pin comparator.
• A
The following registers are set (in addition to the normal PLL
gisters):
re
• 0x18<6:5> = 00b; lo
• 0x18<4> = 0b; l
• 0x18<3> = 0b;
• 0x1A<5
• 0x1C<
• 0x1C<3> = 0b;
• 0x1C<
• 0x1D<3> = 1b;
• 0x1D<2> = 1b;
• 0x1D<
• 0x1D<0> = 1b;
:0> = 000100b; current source lock detect mode.
4> = 1b; automatic reference switchover enabled.
2:1> = 11b; enable REF1 and REF2 input buffers.
1> = 0b; use internal/automatic holdover mode.
ck detect counter = five cycles.
ock detect window = high range.
DLD normal operation.
prefer REF1.
enable LD pin comparator.
enable the holdover function.
enable the holdover function.
Frequency Status Monitors
The AD9517 contains three frequency status monitors that are
used to indicate if the PLL reference (or references in the case of
single-ended mode) and the VCO have fallen below a threshold
frequency. A diagram showing their location in the PLL is
shown in Figure 52.
The PLL reference monitors have two threshold frequencies:
n
ormal and extended (see Ta b le 1 6). The reference frequency
m
onitor thresholds are selected in 0x1F.
<3>—LD pin comparato enable r. 1 = enable; 0 = disable.
• 0x1D
When disabled, the holdover function always senses the LD
pin as high.
• 0x1D<1>— exter
• 0x1D<0> an
disabled, both external and automatic/internal holdover are
disabled.
nal holdover control.
d 0x1D<2>—holdover enable. If holdover is
Rev. 0 | Page 39 of 80

AD9517-3
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REFIN ( REF1)
REFIN ( REF2)
BYPASS
CLK
CLK
REF1
REF2
REGULATOR ( LDO)
LF
REF_SEL CPRSETVCP
REFERENCE
SWITCHOVER
STATUS
STATUS
LOW DROPOUT
VCO
S GND RSET
DISTRIBUTI ON
REFERENCE
R
DIVIDER
N DIVIDE R
P, P + 1
PRESCALER
DIVIDE BY
2, 3, 4, 5, OR 6
01
Figure 52. Reference and VCO Status Monitors
A/B
COUNTERS
VCO Calibration
The AD9517 on-chip VCO must be calibrated to ensure proper
operation over process and temperature. The VCO calibration
is controlled by a calibration controller running off a divided
REFIN clock. The calibration requires that the PLL be set up
properly to lock the PLL loop and that the REFIN clock be
present. During the first initialization after a power-up or a
reset of the AD9517, a VCO calibration sequence is initiated by
setting 0x18<0> = 1b. This can be done as part of the initial
setup before executing an update registers (0x232<0> = 1b).
Subsequent to the initial setup, a VCO calibration sequence is
initiated by resetting 0x18<0> = 0b, executing an update registers
operation, setting 0x18<0> = 1b, and executing another update
registers operation. A readback bit (0x1F<6>) indicates when a
VCO calibration is finished by returning a logic true (that is, 1b).
The sequence of operations for the VCO calibration is:
• Pr
ogram the PLL registers to the proper values for the PLL loop.
• F
or the initial setting of the registers after a power-up or
reset, initiate VCO calibration by setting 0x18<0> = 1b.
Subsequently, whenever a calibration is desired, set 0x18<0> =
0b, update registers, and set 0x18<0> = 1b, update registers.
YNC operation is initiated internally, causing the outputs
• A S
to go to a static state determined by normal SYNC function
operation.
• V
CO calibrates to the desired setting for the requested VCO
frequency.
nternally, the SYNC signal is released, allowing outputs to
• I
continue clocking.
• P
LL loop is closed.
• P
LL locks.
PROGRAMMABLE
PROGRAMMABLE
VCO STATUS
0
1
REFMO N
LD
CP
STATUS
R DELAY
N DELAY
LOCK
DETECT
PHASE
FREQUENCY
DETECT OR
PLL
REFERENCE
CHARGE
PUMP
HOLD
A SYNC is executed during the VCO calibration; therefore, the
o
utputs of the AD9517 are held static during the calibration,
which prevents unwanted frequencies from being produced.
However, at the end of a VCO calibration, the outputs may
resume clocking before the PLL loop is completely settled.
The VCO calibration clock divider is set as shown in Tabl e 53
(0x18<2:1>).
The calibration divider divides the PFD frequency (reference
f
requency divided by R) down to the calibration clock. The
calibration occurs at the PFD frequency divided by the
calibration divider setting. Lower VCO calibration clock
frequencies result in longer times for a calibration to be
completed.
The VCO calibration clock frequency is given by
= f
f
CAL_CLOCK
/(R × cal_div)
REFIN
where:
f
is the frequency of the REFIN signal.
REFIN
R is the value of the R divider.
cal_div is the division set for the VCO calibration divider
(0x18<2:1>).
The VCO calibration takes 4400 calibration clock cycles.
Ther
efore, the VCO calibration time in PLL reference clock
cycles is given by
Time to Calibrate VCO =
4400 × R × cal_
div PLL Reference Clock Cycles
Table 29. Example Time to Complete a VCO Calibration with
ifferent f Frequencies
D
f
REFIN
REFIN
(MHz) R Divider PFD Time to Calibrate VCO
100 1 100 MHz 88 μs
10 10 1 MHz 8.8 ms
10 100 100 kHz 88 ms
06427-070
Rev. 0 | Page 40 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VCO calibration must be manually initiated. This allows for
flexibility in deciding what order to program registers and when
to initiate a calibration, instead of having it happen every time
certain PLL registers have their values change. For example, this
allows for the VCO frequency to be changed by small amounts
without having an automatic calibration occur each time; this
should be done with caution and only when the user knows the
VCO control voltage is not going to exceed the nominal best
performance limits. For example, a few 100 kHz steps are fine,
but a few MHz might not be. Additionally, because the
calibration procedure results in rapid changes in the VCO
frequency, the distribution section is automatically placed in
SYNC until the calibration is finished. Therefore, this
temporary loss of outputs must be expected.
A VCO calibration should be initiated under the following
nditions:
co
ter changing any of the PLL R, P, B, and A divider settings,
• Af
or after a change in the PLL reference clock frequency. This,
in effect, means any time a PLL register or reference clock is
changed such that a different VCO frequency results.
henever system calibration is desired. The VCO is designed
• W
to operate properly over extremes of temperatures even when
it is first calibrated at the opposite extreme. However, a VCO
calibration can be initiated at any time, if desired.
CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
A clock channel consists of a pair (or double pair, in the case of
CMOS) of outputs that share a common divider. A clock output
consists of the drivers that connect to the output pins. The clock
outputs have either LVPECL or LVDS/CMOS signal levels at
the pins.
The AD9517 has four clock channels: two channels are LVPECL
(
four outputs); two channels are LVDS/CMOS (up to four
LVDS outputs or up to eight CMOS outputs).
Each channel has its own programmable divider that divides
he clock frequency applied to its input. The LVPECL channel
t
dividers contain a divider that can divide by any integer from
1 to 32. Each LVDS/CMOS channel divider contains two
cascaded dividers that can be set to divide by any integer from
1 to 32. The total division of the channel is the product of the
divide value of the two cascaded dividers. This allows divide
values of (1 to 32) × (1 to 32), or up to 1024 (notice that this is
not all values from 1 to 1024 but only the set of numbers that
are the product of the two dividers).
Because the internal VCO frequency is above the maximum
c
hannel divider input frequency (1600 MHz), the VCO divider
must be used after the on-chip VCO. The VCO divider can be
set to divide by 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. External clock signals connected
to the CLK input also require the VCO divider if the frequency
of the signal is greater than 1600 MHz.
The channel dividers allow for a selection of various duty cycles,
dep
ending on the currently set division. That is, for any specific
division, D, the output of the divider can be set to high for
N + 1 input clock cycles and low for M + 1 input clock cycles
(where D = N + M + 2). For example, a divide-by-5 can be high
for one divider input cycle and low for four cycles, or a divideby-5 can be high for three divider input cycles and low for two
cycles. Other combinations are also possible.
The channel dividers include a duty-cycle correction function
tha
t can be disabled. In contrast to the selectable duty cycle
just described, this function can correct a non-50% duty cycle
caused by an odd division. However, this requires that the
division be set by M = N + 1.
In addition, the channel dividers allow a coarse phase offset or
y to be set. Depending on the division selected, the output
dela
can be delayed by up to 31 input clock cycles. The divider
outputs can also be set to start high or to start low.
Internal VCO or External CLK as Clock Source
The clock distribution of the AD9517 has two clock input
sources: an internal VCO and an external clock connected to
the CLK/
chosen as the source of the clock signal to distribute. When the
internal VCO is selected as the source, the VCO divider must be
used. When CLK is selected as the source, it is not necessary to
use the VCO divider if the CLK frequency is less than the
maximum channel divider input frequency (1600 MHz);
otherwise, the VCO divider must be used to reduce the
frequency to one acceptable by the channel dividers.
s
hows how the VCO, CLK, and VCO divider are selected.
0x1E1<1:0> selects the channel divider source and determines
whether the VCO divider is used. It is not possible to select the
VCO without using the VCO divider.
Table 30. Selecting VCO or CLK as Source for Channel
Di
<1> <0>
0 0 CLK Used
0 1 CLK Not used
1 0 VCO Used
1 1 Not allowed Not allowed
CLK
pins. Either the internal VCO or CLK must be
vider and Whether VCO Divider Is Used
0x1E1
Channel Divider Source VCO Divider
Tabl e 30
CLK or VCO Direct to LVPECL Outputs
It is possible to connect either the internal VCO or the CLK
(whichever is selected as the input to the VCO divider) directly
to the LVPECL outputs, OUT0 to OUT3. This configuration
can pass frequencies up to the maximum frequency of the VCO
directly to the LVPECL outputs. The LVPECL outputs may not
be able to provide a full voltage swing at the highest frequencies.
Rev. 0 | Page 41 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
To connect the LVPECL outputs directly to the internal VCO or
CLK, the VCO divider must be selected as the source to the
distribution section, even if no channel uses it.
Either the internal VCO or the CLK can be selected as the
s
ource for the direct-to-output routing.
Table 31. Settings for Routing VCO Divider Input Directly
to LVPECL
Register Setting Selection
0x1E1<1:0> = 00b CLK is the source; VCO divider selected
0x1E1<1:0> = 10b VCO is the source; VCO divider selected
0x192<1> = 1b Direct to output (OUT0, OUT1)
0x198<1> = 1b Direct to output (OUT2, OUT3)
Outputs
Clock Frequency Division
The total frequency division is a combination of the VCO
divider (when used) and the channel divider. When the VCO
divider is used, the total division from the VCO or CLK to the
output is the product of the VCO divider (2, 3, 4, 5, and 6) and
the division of the channel divider.
indi
cate how the frequency division for a channel is set. For the
Table 3 2 and Tab l e 3 3
LVPECL outputs, there is only one divider per channel. For the
LVDS/CMOS outputs, there are two dividers (X.1, X.2)
cascaded per channel.
Table 32. Frequency Division for Divider 0 and Divider 1
CLK or VCO
Selected
CLK/VCO 2 to 6 1 (bypassed) Yes 1
CLK/VCO 2 to 6 1 (bypassed) No (2 to 6) × (1)
CLK/VCO 2 to 6 2 to 32 No
CLK
CLK
VCO Divider
Not
used
Not
used
Channel
Divider
1 (bypassed) No 1
2 to 32 No 2 to 32
Direct to
Output
Frequency
Division
(2 to 6) ×
(2 to 32)
Table 33. Frequency Division for Divider 2 and Divider 3
CLK or
VCO
Selected
CLK/VCO 2 to 6
CLK/VCO 2 to 6 2 to 32
CLK/VCO 2 to 6 2 to 32 2 to 32
CLK
CLK
CLK
VCO
Div
Not
used
Not
used
Not
used
ider
Channel Divider
X.1 X.2
1
ypassed) 1 (bypassed)
(b
1
ypassed)
(b
1 1 1
2 to 32 1 (2 to 32) × (1)
2 to 32 2 to 32
Frequency
Division
(2 to 6) ×
(1) × (1)
(2 to 6) ×
(2 to 32) × (1)
(2 to 6) ×
to 32) ×
(2
(2 to 32)
2 to 32 ×
(2 to 32)
The channel dividers feeding the LVPECL output drivers
contain one 2-to-32 frequency divider. This divider provides for
division by 1 to 32. Division by 1 is accomplished by bypassing
the divider. The dividers also provide for a programmable duty
cycle, with optional duty-cycle correction when the divide ratio
is odd. A phase offset or delay in increments of the input clock
cycle is selectable. The channel dividers operate with a signal at
their inputs up to 1600 MHz. The features and settings of the
dividers are selected by programming the appropriate setup
and control registers (see
Tabl e 51 through Tab le 6 1).
VCO Divider
The VCO divider provides frequency division between the
internal VCO or the external CLK input and the clock
distribution channel dividers. The VCO divider can be set
to divide by 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 (see Tab le 5 9 , 0x1E0<2:0>).
Channel Dividers—LVPECL Outputs
Each pair of LVPECL outputs is driven by a channel divider.
There are two channel dividers (0, 1) driving four LVPECL
outputs (OUT0 to OUT3). Tabl e 34 gives the register locations
u
sed for setting the division and other functions of these
dividers. The division is set by the values of M and N. The
divider can be bypassed (equivalent to divide-by-1, divider circuit
is powered down) by setting the bypass bit. The duty-cycle
correction can be enabled or disabled according to the setting of
the DCCOFF bits.
Table 34. Setting D
Low Cycles M High Cycles
Divider
0 0x190<7:4> 0x190<3:0> 0x191<7> 0x192<0>
1 0x196<7:4> 0x196<3:0> 0x197<7> 0x198<0>
for Divider 0 and Divider 1
X
N Bypass DCCOFF
Channel Frequency Division (0, 1)
For each channel (where the channel number is x: 0, 1), the
frequency division, D
, is set by the values of M and N
X
(four bits each, representing Decimal 0 to Decimal 15), where
Number of Low Cycles = M + 1
Number of High Cycles = N + 1
The cycles are cycles of the clock signal currently routed to the
in
put of the channel dividers (VCO divider out or CLK).
When a divider is bypassed, D
Otherwise, D
= (N + 1) + (M + 1) = N + M + 2. This allows
X
= 1.
X
each channel divider to divide by any integer from 1 to 32.
Rev. 0 | Page 42 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Duty Cycle and Duty-Cycle Correction (0, 1)
The duty cycle of the clock signal at the output of a channel is a
result of some or all of the following conditions:
hat are the M and N values for the channel?
• W
• I
s the DCC enabled?
• I
s the VCO divider used?
• Wh
at is the CLK input duty cycle? (The internal VCO has a
50% duty cycle.)
The DCC function is enabled by default for each channel
er. However, the DCC function can be disabled
divid
individually for each channel divider by setting the
DCCOFF bit for that channel.
Certain M and N values for a channel divider result in a non50% d
uty cycle. A non-50% duty cycle can also result with an
even division if M ≠ N. The duty-cycle correction function
automatically corrects non-50% duty cycles at the channel
divider output to 50% duty cycle. Duty-cycle correction
requires the following channel divider conditions:
• A
n even division must be set as M = N
• An o
dd division must be set as M = N + 1
When not bypassed or corrected by the DCC function, the duty
ycle of each channel divider output is the numerical value of
c
(N + 1)/(N + M + 2) expressed as a %.
The duty cycle at the output of the channel divider for various
co
nfigurations is shown in Tabl e 3 5 to Ta ble 37.
Table 35. Duty Cycle with VCO Divider, Input Duty Cycle Is 50%
Divider
Even
Odd = 3
Odd = 5
Even, Odd Even
Even, Odd Odd
N + M + 2 DCCOFF = 1 DCCOFF = 0
1 (divider
ypassed)
b
1 (divider
ypassed)
b
1 (divider
ypassed)
b
D
X
50% 50%
33.3% 50%
40% 50%
(N + 1)/
(N +
(N + 1)/
(N +
Output Duty Cycle VCO
50%; requires M = N
M + 2)
50%; requires M = N + 1
M + 2)
Table 36. Duty Cycle with VCO Divider, Input Duty Cycle Is X%
D
Divider
Even
Odd = 3
Odd = 5
Even Even
Odd
Odd = 3 Even
Odd = 3 Odd
Odd = 5 Even
Odd = 5 Odd
X
N + M + 2 DCCOFF = 1 DCCOFF = 0
1 (divider
ypassed)
b
1 (divider
ypassed)
b
1 (divider
ypassed)
b
50% 50%
33.3% (1 + X%)/3
40% (2 + X%)/5
(N + 1)/
(N +
(N + 1)/
(N +
(N + 1)/
(N +
(N + 1)/
(N +
(N + 1)/
(N +
(N + 1)/
(N +
M + 2)
M + 2)
M + 2)
M + 2)
M + 2)
M + 2)
Output Duty Cycle VCO
50%,
requires M = N
50%,
requires M = N + 1
50%,
requires M = N
(3N + 4 + X%)/(6N + 9),
requires M = N + 1
50%,
requires M = N
(5N + 7 + X%)/(10N + 15),
requires M = N + 1
Table 37. Channel Divider Output Duty Cycle When the
VCO Divider Is Not Used
D
Duty Cycle
Any 1
Any Even
50% Odd
X% Odd
X
N + M + 2 DCCOFF = 1 DCCOFF = 0
1 (divider
b
(N + 1)/
M + N + 2)
(
(N + 1)/
M + N + 2)
(
(N + 1)/
M + N + 2)
(
ypassed)
Output Duty Cycle Input Clock
Same as input
duty cycle
50%, requires M = N
50%, requires
M = N + 1
(N + 1 + X%)/(2 × N + 3),
requires M = N + 1
The internal VCO has a duty cycle of 50%. Therefore, when the
VCO is connected directly to the output, the duty cycle is 50%.
If the CLK input is routed directly to the output, the duty cycle of
the output is the same as the CLK input.
Rev. 0 | Page 43 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Phase Offset or Coarse Time Delay (0, 1)
Each channel divider allows for a phase offset, or a coarse time
delay, to be programmed by setting register bits (see Ta b le 3 8).
Th
ese settings determine the number of cycles (successive
rising edges) of the channel divider input frequency by which to
offset, or delay, the rising edge of the output of the divider. This
delay is with respect to a nondelayed output (that is, with a
phase offset of zero). The amount of the delay is set by five bits
loaded into the phase offset (PO) register plus the start high
(SH) bit for each channel divider. When the start high bit is set,
the delay is also affected by the number of low cycles (M)
programmed for the divider.
It is necessary to use the SYNC function to make phase offsets
fective (see the Synchronizing the Outputs—SYNC Function
ef
secti
on).
Table 38. Setting Phase Offset and Division for Divider 0 and
Divider
Divider
1
Start
High (SH)
Phase
Of
fset (PO)
Low Cycles M High Cycles
N
0 0x191<4> 0x191<3:0> 0x190<7:4> 0x190<3:0>
1 0x197<4> 0x197<3:0> 0x196<7:4> 0x196<3:0>
Let
= delay (in seconds).
Δ
t
Δ
= delay (in cycles of clock signal at input to DX).
c
T
= period of the clock signal at the input of the divider, DX
X
(in seconds).
Φ =
16 × SH<4> + 8 × PO<3> + 4 × PO<2> + 2 × PO<1> + 1 × PO<0>.
The channel divide-by is set as N = high cycles and M = low cycles.
Case 1
For Φ ≤ 15:
Δ
= Φ × TX
t
Δ
= Δt/TX = Φ
c
Case 2
For Φ ≥ 16:
Δ
= (Φ − 16 + M + 1) × T
t
Δc = Δt/T
X
X
By giving each divider a different phase offset, output-to-output
delays can be set in increments of the channel divider input
clock cycle. Figure 53 shows the results of setting such a coarse
of
fset between outputs.
CHANNEL
DIVIDER INP UT
DIVIDER 0
DIVIDER 1
DIVIDER 2
0123456789101112131415
Tx
SH = 0
PO = 0
SH = 0
PO = 1
SH = 0
PO = 2
Figure 53. Effect of Coarse Phase Offset (or Delay)
L
I
D
V
I
D
E
N
N
A
H
C
I
D
V
=
4
1 × Tx
2 × Tx
T
U
S
T
U
P
R
O
E
5
0
,
%
T
U
D
Y
=
06427-071
Rev. 0 | Page 44 of 80
Channel Dividers—LVDS/CMOS Outputs
Channel Divider 2 and Channel Divider 3 each drive a pair of
LVDS out p uts , g i v i n g f ou r LV D S o utputs (OUT4 to OUT7).
Alternatively, each of these LVDS differential outputs can be
configured individually as a pair (A and B) of CMOS singleended outputs, providing for up to eight CMOS outputs. By
default, the B output of each pair is off but can be turned on as
desired.
Channel Divider 2 and Channel Divider 3 each consist of two
caded, 1 to 32, frequency dividers. The channel frequency
cas
division is D
X.1
× D
or up to 1024. Both of the dividers also
X.2
have DCC enabled by default, but this function can be disabled,
if desired, by setting the DCCOFF bit of the channel. A coarse
phase offset or delay is also programmable (see the
o
r Coarse Time Delay (Divider 2 and Divider 3) section). The
c
hannel dividers operate up to 1600 MHz. The features and
Phase Offset
settings of the dividers are selected by programming the
appropriate setup and control registers (see
Tabl e 51 and Tab l e
52 through Tabl e 61 ).
Table 39. Setting Division (D
) for Divider 2, Divider 3
X
Divider M N Bypass DCCOFF
2 2.1 0x199<7:4> 0x199<3:0> 0x19C<4> 0x19D<0>
2.2 0x19B<7:4> 0x19B<3:0> 0x19C<5> 0x19D<0>
3 3.1 0x19E<7:4> 0x19E<3:0> 0x1A1<4> 0x1A2<0>
3.2 0x1A0<7:4> 0x1A0<3:0> 0x1A1<5> 0x1A2<0>
Channel Frequency Division (Divider 2 and Divider 3)
The division for each channel divider is set by the bits in the
registers for the individual dividers (X.Y = 2.1, 2.2, 3.1, and 3.2)
Number of Low Cycles = M
Number of High Cycles = N
When both X.1 and X.2 are bypassed, D
When only X.2 is bypassed, D
When both X.1 and X.2 are not bypassed, D
(N
+ M
X.2
+ 2).
X.2
X.Y
X.Y
= (N
X
+ 1
+ 1
X.1
= 1 × 1 = 1.
X
+ M
+ 2) × 1.
X.1
= (N
X
X.1
+ M
+ 2) ×
X.1
By cascading the dividers, channel division up to 1024 can be
tained. However, not all integer value divisions from 1 to
ob
1024 are obtainable; only the values that are the product of the
separate divisions of the two dividers (D
X.1
× D
X.2
) can be realized.
If only one divider is needed when using Divider 2 and Divider 3,
e the first one (X.1) and bypass the second one (X.2). Do not
us
bypass X.1 and use X.2.

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Duty Cycle and Duty-Cycle Correction (Divider 2 and Divider 3)
The same duty cycle and DCC considerations apply to Divider 2
and Divider 3 as to Divider 0 and Divider 1 (see Duty Cycle and
ty-Cycle Correction (0, 1)); however, with these channel
Du
ers, the number of possible configurations is even more
divid
complex.
Duty-cycle correction on Divider 2 and Divider 3 requires the
lowing channel divider conditions:
fol
• A
n even D
must be set as M
X.Y
X.Y
= N
(low cycles = high
X.Y
cycles).
• An o
must be set as M
dd D
X.Y
X.Y
= N
+ 1 (the number of
X.Y
low cycles must be one greater than the number of high cycles).
f only one divider is bypassed, it must be the second
• I
divider, X.2.
f only one divider has an even divide-by, it must be the
• I
second divider, X.2.
The possibilities for the duty cycle of the output clock from
D
ivider 2 and Divider 3 are shown in Tabl e 4 0 through Tab le 4 4.
Table 40. Divider 2 and Divider 3 Duty Cycle
; VCO Divider
Used; Duty Cycle Correction Off (DCCOFF = 1)
VCO
Divider
D
X.1
+ M
N
X.1
+ 2 N
X.1
X.2
D
+ M
X.2
Output Duty Cycle
+ 2
X.2
Even 1 1 50%
Odd = 3 1 1 33.3%
Odd = 5 1 1 40%
Even Even, Odd 1
Odd Even, Odd 1
Even Even, Odd Even, Odd
Odd Even, Odd Even, Odd
(N
(N
(N
(N
(N
(N
(N
(N
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.2
X.2
X.2
X.2
+ 1)/
+ M
+ 1)/
+ M
+ 1)/
+ M
+ 1)/
+ M
X.1
X.1
X.2
X.2
+ 2)
+ 2)
+ 2)
+ 2)
Table 41. Divider 2 and Divider 3 Duty Cycle; VCO Divider
Not Used; Duty Cycle Correction Off (DCCOFF = 1)
Input Clock
Duty Cycle
D
X.1
N
+ M
X.1
+ 2 N
X.1
X.2
D
+ M
X.2
X.2
+ 2
Output
ty Cycle
Du
50% 1 1 50%
X% 1 1 X%
50% Even, Odd 1
X% Even, Odd 1
50% Even, Odd Even, Odd
X% Even, Odd Even, Odd
(N
(N
(N
(N
(N
(N
(N
(N
+ 1)/
X.1
+ M
X.1
+ 1)/
X.1
+ M
X.1
+ 1)/
X.2
+ M
X.2
+ 1)/
X.2
+ M
X.2
X.1
X.1
X.2
X.2
+ 2)
+ 2)
+ 2)
+ 2)
Table 42. Divider 2 and Divider 3 Duty Cycle; VCO Divider
Used; Duty Cycle Correction Is On (DCCOFF = 0); VCO
Divider Input Duty Cycle = 50%
VCO
Divider
D
X.1
N
+ M
X.1
+ 2 N
X.1
X.2
+ M
D
X.2
+ 2
X.2
Output
Duty Cycle
Even 1 1 50%
Odd 1 1 50%
Even Even (N
Odd Even (N
Even Odd (M
Odd Odd (M
Even Even (N
Odd Even (N
Even Odd (M
Odd Odd (M
Even Odd (M
Odd Odd (M
= M
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
) 1 50%
X.1
= M
) 1 50%
X.1
= N
+ 1) 1 50%
X.1
= N
+ 1) 1 50%
X.1
= M
X.1
= M
X.1
= N
+ 1) Even (N
X.1
= N
+ 1) Even (N
X.1
= N
+ 1) Odd (M
X.1
= N
+ 1) Odd (M
X.1
) Even (N
) Even (N
X.2
X.2
X.2
X.2
X.2
X.2
= M
= M
= M
= M
= N
= N
) 50%
X.2
) 50%
X.2
) 50%
X.2
) 50%
X.2
+ 1) 50%
X.2
+ 1) 50%
X.2
Rev. 0 | Page 45 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Table 43. Divider 2 and Divider 3 Duty Cycle; VCO Divider
Used; Duty Cycle Correction On (DCCOFF = 0); VCO
Divider Input Duty Cycle = X%
VCO
Divider
D
X.1
N
+ M
X.1
+ 2 N
X.1
X.2
D
+ M
X.2
X.2
+ 2
Output
Duty Cycle
Even 1 1 50%
Odd = 3 1 1 (1 + X%)/3
Odd = 5 1 1 (2 + X%)/5
Even
Odd
Even
Odd = 3
Odd = 5
Even
Odd
Even
Odd
Even
Odd = 3
Odd = 5
Even
(N
X.1
Even
(N
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Even
(N
X.1
Even
(N
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
= M
= M
= N
= N
= N
= M
= M
= N
= N
= N
= N
= N
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
1 50%
)
1 50%
)
1 50%
+ 1)
+ 1)
+ 1)
)
)
+ 1)
+ 1)
+ 1)
+ 1)
1
1
Even
(N
X.2
Even
(N
X.2
Even
(N
X.2
Even
(N
X.2
Odd
(M
X.2
Odd
(M
X.2
= M
= M
= M
= M
= N
= N
X.2
X.2
X.2
X.2
X.2
X.2
)
)
)
)
+ 1)
+ 1)
(3N
(6N
(5N
(10N
50%
50%
50%
50%
50%
(6N
9N
X.2
(3(2N
(2N
+ 1)
Odd
(M
X.2
= N
X.2
+ 1)
(10N
15N
(5(2 N
(2 N
+ 4 + X%)/
X.1
+ 9)
X.1
+ 7 + X%)/
X.1
+ 15)
X.1
+ 9N
X.1NX.2
+ 13 + X%)/
+ 3)
X.1
+ 3))
X.2
+ 15N
X.1NX.2
+ 22 + X%)/
X.2
+ 3)
X.1
+ 3))
X.2
+
X.1
X.1
+
Table 44. Divider 2 and Divider 3 Duty Cycle
Not Used; Duty Cycle Correction On (DCCOFF = 0)
Input
Clock
D
X.1
D
X.2
Duty
Cycle N
X.1
+ M
+ 2 N
X.1
X.2
+ M
X.2
+ 2
50% 1 1 50%
50%
Even
(N
X.1
= M
X.1
1 50%
)
X% 1 1 X% (High)
X%
50%
X%
50%
X%
50%
X%
50%
X%
Even
(N
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Even
(N
X.1
Even
(N
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
Odd
(M
X.1
= M
= N
= N
= M
= M
= N
= N
= N
= N
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
X.1
1 50%
)
1 50%
+ 1)
1
+ 1)
Even
)
(N
= M
X.2
)
X.2
Even
)
(N
= M
X.2
)
X.2
Even
+ 1)
(N
= M
X.2
)
X.2
Even
+ 1)
(N
= M
X.2
)
X.2
Odd
+ 1)
(M
= N
+ 1)
X.2
X.2
Odd
+ 1)
(M
= N
+ 1)
X.2
X.2
Phase Offset or Coarse Time Delay (Divider 2 and Divider 3)
Divider 2 and Divider 3 can be set to have a phase offset or
delay. The phase offset is set by a combination of the bits in the
phase offset and start high registers (see Tab l e 4 5 ).
Table 45. Setting Phase Offset and Division for Divider 2 and
Divider
Divider
3
Start
High (SH)
Phase
Of
fset (PO)
Low
Cycles M
2 2.1 0x19C<0> 0x19A<3:0> 0x199<7:4> 0x199<3:0>
2.2 0x19C<1> 0x19A<7:4> 0x19B<7:4> 0x19B<3:0>
3 3.1 0x1A1<0> 0x19F<3:0> 0x19E<7:4> 0x19E<3:0>
3.2 0x1A1<1> 0x19F<7:4> 0x1A0<7:4> 0x1A0<3:0>
Let:
= delay (in seconds).
Δ
t
Φ
= 16 × SH<0> + 8 × PO<3> + 4 × PO<2> + 2 × PO<1> +
x.y
1 × PO<0>.
T
= period of the clock signal at the input to D
X.1
T
= period of the clock signal at the input to D
X.2
; VCO Divider
Output
Duty Cycle
+ 1 + X%)/
(N
X.1
+ 3)
(2N
X.1
50%
50%
50%
50%
50%
(2N
3N
((2N
+ 3N
X.1NX.2
+ 4 + X%)/
X.2
+ 3)(2N
X.1
High
Cycles N
(in seconds).
X.1
(in seconds).
X.2
X.1
X.2
+
+ 3))
Rev. 0 | Page 46 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Case 1
When Φ
Δ
= Φ
t
≤ 15 and Φ
x.1
× T
x.1
X.1
+ Φ
X.2
x.2
× T
≤ 15:
x.2
Case 2
When Φ
Δ
= Φ
t
≤ 15 and Φ
x.1
× T
X.1
X.1
+ (Φ
≥ 16:
x.2
− 16 + M
X.2
+ 1) × T
X.2
X.2
Case 3
When Φ
Δ
= (Φ
t
≥ 16 and Φ
X.1
− 16 + M
X.1
X.2
+ 1) × T
X.1
≤ 15:
X.1
+ Φ
X.2
× T
X.2
Case 4
When Φ
Δ
=
t
(Φ
− 16 + M
X.1
≥ 16 and Φ
X.1
X.1
X.2
+ 1) × T
≥ 16:
+ (Φ
X.1
− 16 + M
X.2
+ 1) × T
X.2
X.2
Fine Delay Adjust (Divider 2 and Divider 3)
Each AD9517 LVDS/CMOS output (OUT4 to OUT7) includes
an analog delay element that can be programmed to give
variable time delays (Δ
VCO
CLK
DIVIDER
DIVIDE R
X.1
) in the clock signal at that output.
t
BYPASS
ΔT
FINE DELAY
DIVIDER
X.2
Figure 54. Fine Delay (OUT4 to OUT7)
ADJUST
BYPASS
ΔT
FINE DELAY
ADJUST
CMOS
LVDS
CMOS
CMOS
LVDS
CMOS
OUTM
OUTM
OUTPUT
DRIVERS
OUTN
OUTN
06427-072
The amount of delay applied to the clock signal is determined
by programming four registers per output (see Tabl e 46 ).
Table 46. Setting Analog Fine Delays
OUTPUT
(LVDS/CMOS)
Ramp
Capacitors
Ramp
Current
Delay
Fraction
Delay
Bypass
OUT4 0xA1<5:3> 0xA1<2:0> 0xA2<5:0> 0xA0<0>
OUT5 0xA4<5:3> 0xA4<2:0> 0xA5<5:0> 0xA3<0>
OUT6 0xA7<5:3> 0xA7<2:0> 0xA8<5:0> 0xA6<0>
OUT7 0xAA<5:3> 0xAA<2:0> 0xAB<5:0> 0xA9<0>
Calculating the Fine Delay
The following values and equations are used to calculate the
delay of the delay block:
I
(μA) = 200 × (Ramp Current + 1)
RAMP
Number of Capacitors = Number of
Bits = 0 in Ramp Capacitors + 1
Example: 101 = 1 + 1 = 2; 110 = 1 + 1 = 2; 100 = 2 + 1 = 3;
001 = 2 + 1 = 3;
Delay Range (ns
()
111 = 0 + 1 = 1.
) = 200 × ((No. of Caps + 3)/(I
()
IOffset
RAMP
1016000.34ns
RAMP
⎛−
4
−
⎜
+×−+=
⎜
⎝
)) × 1.3286
CapsofNo.
I
RAMP
1
⎞
⎟
6
×
⎟
⎠
Delay Full Scale (ns) = Delay Range + Offset
Fine Delay (ns)
= Delay Range × Delay Fraction × (1/63) + Offset
Note that only delay fraction values up to 47 decimals (101111b;
re supported.
0x2F) a
In no case can the fine delay exceed one-half of the output clock
p
eriod. If a delay longer than half of the clock period is attempted,
the output stops clocking.
The delay function adds some jitter greater than that specified
r the nondelayed output. This means that the delay function
fo
should be used primarily for clocking digital chips, such as
FPGA, ASIC, DUC, and DDC. An output with this delay
enabled may not be suitable for clocking data converters. The
jitter is higher for long full scales because the delay block uses a
ramp and trip points to create the variable delay. A slower ramp
time produces more time jitter.
Synchronizing the Outputs—SYNC Function
The AD9517 clock outputs can be synchronized to each other.
Outputs can be individually excluded from synchronization.
Synchronization consists of setting the nonexcluded outputs to
a preset set of static conditions and subsequently releasing these
outputs to continue clocking at the same instant with the preset
conditions applied. This allows for the alignment of the edges of
two or more outputs or for the spacing of edges according to the
coarse phase offset settings for two or more outputs.
Rev. 0 | Page 47 of 80

AD9517-3
S
R
R
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Synchronization of the outputs is executed in several ways:
SYNC
• Th
e
pin is forced low and then released (manual SYNC).
• B
y setting and then resetting any one of the following three
bits: the soft SYNC bit (0x230<0>), the soft reset bit (0x00<5>
[mirrored]), or the distribution power-down bit (0x230<1>).
ynchronization of the outputs can be executed as part of the
• S
chip power-up sequence.
RESET
• The
e
• Th
henever a VCO calibration is completed, an internal SYNC
• W
pin is forced low and then released (chip reset).
PD
pin is forced low and then released (chip power-down).
signal is automatically asserted at the beginning and released
upon the completion of a VCO calibration.
CHANNEL DIVIDE
OUTPUT CLOCKING
CHANNEL DIVIDER O UTPUT STAT IC
The most common way to execute the SYNC function is to use
SYNC
th
e
pin to do a manual synchronization of the outputs.
This requires a low-going signal on the
SYNC
pin, which is held
low and then released when synchronization is desired. The
timing of the SYNC operation is shown in
CO divider) and Figure 56 (VCO divider not used). There is
V
a
n uncertainty of up to one cycle of the clock at the input to the
Figure 55 (using
channel divider due to the asynchronous nature of the SYNC
signal with respect to the clock edges inside the AD9517. The
delay from the
SYNC
rising edge to the beginning of synchronized
output clocking is between 14 and 15 cycles of clock at the
channel divider input, plus either one cycle of the VCO divider
input (see
Figure 55), or one cycle of the channel divider input
(see Figure 56), depending on whether the VCO divider is used.
C
ycles are counted from the rising edge of the signal.
Another common way to execute the SYNC function is by
se
tting and resetting the soft SYNC bit at 0x230<0> (see Tabl e 52
th
rough Ta ble 61 for details). Both setting and resetting of the
oft SYNC bit require an update all registers (0x232<0> = 1)
s
operation to take effect.
CHANNEL DIVIDE
OUTPUT CLOCKING
INPUT TO VCO DIVIDER
INPUT TO CHANNEL DIVIDER
YNC PIN
OUTPUT OF
CHANNEL DIVIDER
123 456 78910
14 TO 15 CYCLES AT CHANNEL DIVIDER INPUT + 1 CYCLE AT VCO DIVIDER I NPUT
Figure 55. SYNC Timing When VCO Divider Is Used—CLK or VCO Is Input
1
11
13 14
12
06427-073
Rev. 0 | Page 48 of 80

AD9517-3
R
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
CHANNEL DIVIDER
OUTPUT CLOCKING
CHANNEL DIVIDER O UTPUT ST ATIC
CHANNEL DIVIDE
OUTPUT CLOCKING
INPUT TO CLK
IINPUT TO CHANNEL DIVI DER
SYNC PIN
OUTPUT OF
CHANNEL DIVIDER
12345678910
14 TO 15 CYCLES AT CHANNEL DIVIDER INPUT + 1 CYCLE AT CLK I NPUT
Figure 56. SYNC Timing When VCO Divider Is Not Used—CLK Input Only
A SYNC operation brings all outputs that have not been
uded (by the nosync bit) to a preset condition before
excl
allowing the outputs to begin clocking in synchronicity. The
preset condition takes into account the settings in each of the
channel’s start high bit and its phase offset. These settings
govern both the static state of each output when the SYNC
operation is happening and the state and relative phase of the
outputs when they begin clocking again upon completion of the
SYNC operation. Between outputs and after synchronization,
this allows for the setting of phase offsets.
The AD9517 outputs are in pairs, sharing a channel divider per
p
air (two pairs of pairs, four outputs, in the case of CMOS). The
synchronization conditions apply to both outputs of a pair.
Each channel (a divider and its outputs) can be excluded from
ny SYNC operation by setting the nosync bit of the channel.
a
Channels that are set to ignore SYNC (excluded channels) do
not set their outputs static during a SYNC operation, and their
outputs are not synchronized with those of the nonexcluded
channels.
Clock Outputs
The AD9517 offers three output level choices: LVPECL, LVDS,
and CMOS. OUT0 to OUT3 are LVPECL differential outputs;
and OUT4 to OUT7 are LVDS/CMOS outputs. These outputs
can be configured as either LVDS differential or as pairs of
single-ended CMOS outputs.
1
11
13 14
12
6427-074
LVPECL Outputs: OUT0 to OUT3
The LVPECL differential voltage (VOD) is selectable from
~400 mV to ~960 mV (see 0xF0:0xF5<3:2>). The LVPECL
outputs have dedicated pins for power supply (VS_LVPECL),
allowing a separate power supply to be used. V
S_LVPECL
can be
from 2.5 V to 3.3 V.
The LVPECL output polarity can be set as noninverting or
in
verting, which allows for the adjustment of the relative
polarity of outputs within an application without requiring a
board layout change. Each LVPECL output can be powered
down or powered up as needed. Because of the architecture of
the LVPECL output stages, there is the possibility of electrical
overstress and breakdown under certain power-down conditions.
For this reason, the LVPECL outputs have several power-down
modes. This includes a safe power-down mode that continues
to protect the output devices while powered down, although it
consumes somewhat more power than a total power-down. If
the LVPECL output pins are terminated, it is best to select the
safe power-down mode. If the pins are not connected (unused),
it is acceptable to use the total power-down mode.
3.3
OUT
OUT
Rev. 0 | Page 49 of 80
GND
Figure 57. LVPECL Output Simplified Equivalent Circuit
06427-033

AD9517-3
3
A
3
A
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
LVDS/CMOS Outputs: OUT4 to OUT7
OUT4 to OUT7 can be configured as either an LVDS
differential output or as a pair of CMOS single-ended outputs.
The LVDS outputs allow for selectable output current from
~1.75 mA to ~7 mA.
The LVDS output polarity can be set as noninverting or
in
verting, which allows for the adjustment of the relative
polarity of outputs within an application without requiring a
board layout change. Each LVDS output can be powered down
if not needed to save power.
.5m
OUT
OUT
.5m
Figure 58. LVDS Output Simplified Equivalent Circuit with
3.5
mA Typical Current Source
06427-034
OUT4 to OUT7 can also be CMOS outputs. Each LVDS output
can be configured to be two CMOS outputs. This provides for
up to eight CMOS outputs: OUT4A, OUT4B, OUT5A, OUT5B,
OUT6A, OUT6B, OUT7A, and OUT7B. When an output is
configured as CMOS, the CMOS Output A is automatically
turned on. The CMOS Output B can be turned on or off
independently. The relative polarity of the CMOS outputs can also
be selected for any combination of inverting and noninverting. See
Tabl e 56 , 0x140<7:5>, 0x141<7:5>, 0x142<7:5>, and 0x143<7:5>.
Each LVDS/CMOS output can be powered down as needed to
ave power. The CMOS output power-down is controlled by the
s
same bit that controls the LVDS power-down for that output.
This power-down control affects both the CMOS A and
CMOS B outputs. However, when the CMOS A output is powered
up, the CMOS B output can be powered on or off separately.
S
OUT
06427-035
Figure 59. CMOS Equivalent Output C
ircuit
RESET MODES
The AD9517 has several ways to force the chip into a reset
condition that restores all registers to their default values and
makes these settings active.
Power-On Reset—Start-Up Conditions When VS Is Applied
A power-on reset (POR) is issued when the VS power supply is
turned on. This initializes the chip to the power-on conditions
that are determined by the default register settings. These are
indicated in the Default Value (Hex) column of Tab l e 5 1 . At
p
ower-on, the AD9517 also executes a SYNC operation, which
brings the outputs into phase alignment according to the default
settings.
Asynchronous Reset via the
RESET
Pin
An asynchronous hard reset is executed by momentarily pulling
RESET
low. A reset restores the chip registers to the default
settings.
Soft Reset via 0x00<5>
A soft reset is executed by writing 0x00<5> and 0x00<2> = 1b.
This bit is not self-clearing; therefore, it must be cleared by
writing 0x00<5> and 0x00<2> = 0b to reset it and complete the
soft reset operation. A soft reset restores the default values to
the internal registers. The soft reset bit does not require an
update registers command (0x232) to be issued.
POWER-DOWN MODES
Chip Power-Down via PD
The AD9517 can be put into a power-down condition by
PD
pulling the
functions and currents inside the AD9517. The chip remains in
this power-down state until
When woken up, the AD9517 returns to the settings programmed
into its registers prior to the power-down, unless the registers
are changed by new programming while the
PD
The
except the bias current necessary to maintain the LVPECL
outputs in a safe shutdown mode. This is needed to protect the
LVPECL output circuitry from damage that could be caused by
certain termination and load configurations when tristated.
Because this is not a complete power-down, it can be called
sleep mode.
When the AD9517 is in a
following state:
he PLL is off (asynchronous power-down).
• T
• The V
• The CL
• Al
• A
• Al
• The s
commands.
pin low. Power-down turns off most of the
PD
is brought back to Logic High.
PD
pin is held low.
power-down shuts down the currents on the chip,
PD
power-down, the chip is in the
CO is off.
K input buffer is off.
l dividers are off.
ll LVDS/CMOS outputs are off.
l LVPECL outputs are in safe off mode.
erial control port is active, and the chip responds to
Rev. 0 | Page 50 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
If the AD9517 clock outputs must be synchronized to each
other, a SYNC is required upon exiting power-down (see the
Synchronizing the Outputs—SYNC Function section). A VCO
libration is not required when exiting power-down.
ca
PLL Power-Down
The PLL section of the AD9517 can be selectively powered
down. There are three PLL operating modes set by 0x10<1:0>,
as shown in Tab l e 5 3 .
In asynchronous power-down mode, the device powers down as
oon as the registers are updated.
s
In synchronous power-down mode, the PLL power-down is
ga
ted by the charge pump to prevent unwanted frequency
jumps. The device goes into power-down on the occurrence of
the next charge pump event after the registers are updated.
Distribution Power-Down
The distribution section can be powered down by writing
0x230<1> = 1b. This turns off the bias to the distribution
section. If the LVPECL power-down mode is normal operation
(00b), it is possible for a low impedance load on that LVPECL
output to draw significant current during this power-down. If
the LVPECL power-down mode is set to 11b, the LVPECL
output is not protected from reverse bias and can be damaged
under certain termination conditions.
Individual Clock Output Power-Down
Any of the clock distribution outputs may be powered down
individually by writing to the appropriate registers. The register
map details the individual power-down settings for each output
(see
Tabl e 51 ). The LVDS/CMOS outputs may be powered
wn, regardless of their output load configuration.
do
The LVPECL outputs have multiple power-down modes
(see Tabl e 55 ), which give some flexibility in dealing with the
va
rious output termination conditions. When the mode is set to
10b, the LVPECL output is protected from reverse bias to
2 VBE + 1 V. If the mode is set to 11b, the LVPECL output is
not protected from reverse bias and can be damaged under
certain termination conditions. This setting also affects the
operation when the distribution block is powered down with
0x230<1> = 1b (see the
Individual Circuit Block Power-Down
Other AD9517 circuit blocks (such as CLK, REF1, and REF2)
can be powered down individually. This gives flexibility in
configuring the part for power savings whenever certain chip
functions are not needed.
Distribution Power-Down section).
Rev. 0 | Page 51 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SERIAL CONTROL PORT
The AD9517 serial control port is a flexible, synchronous, serial
communications port that allows an easy interface with many
industry-standard microcontrollers and microprocessors. The
AD9517 serial control port is compatible with most synchronous
transfer formats, including both the Motorola SPI® and Intel®
SSR® protocols. The serial control port allows read/write access
to all registers that configure the AD9517. Single- or multiplebyte transfers are supported, as well as MSB first or LSB first
transfer formats. The AD9517 serial control port can be
configured for a single bidirectional I/O pin (SDIO only) or
for two unidirectional I/O pins (SDIO/SDO). By default, the
AD9517 is in bidirectional mode, long instruction (long
instruction is the only instruction mode supported).
SERIAL CONTROL PORT PIN DESCRIPTIONS
SCLK (serial clock) is the serial shift clock. This pin is an input.
SCLK is used to synchronize serial control port reads and
writes. Write data bits are registered on the rising edge of this
clock, and read data bits are registered on the falling edge. This
pin is internally pulled down by a 30 kΩ resistor to ground.
SDIO (serial data input/output) is a dual-purpose pin and acts
ther an input only (unidirectional mode) or as both an
as ei
input/output (bidirectional mode). The AD9517 defaults to the
bidirectional I/O mode (0x00<7> = 0).
SDO (s
erial data out) is used only in the unidirectional I/O
mode (0x00<7>) as a separate output pin for reading back data.
(chip select bar) is an active low control that gates the read
CS
and write cycles. When
is high, SDO and SDIO are in a high
CS
impedance state. This pin is internally pulled up by a 30 kΩ
resistor to VS.
13
SCLK
SDO
SDIO
Figure 60. Serial Control Port
CS
AD9517-3
14
SERIAL
15
CONTRO L
16
PORT
06427-036
GENERAL OPERATION OF SERIAL CONTROL PORT
A write or a read operation to the AD9517 is initiated by
pulling
CS
bytes of data (plus instruction data) are transferred (see Tab le 47 ).
In
these modes,
boundary, allowing time for the system controller to process the
next byte.
high during either part (instruction or data) of the transfer.
low.
CS
stalled high is supported in modes where three or fewer
can temporarily return high on any byte
CS
can go high on byte boundaries only and can go
CS
During this period, the serial control port state machine enters
a wai
t state until all data is sent. If the system controller decides
to abort the transfer before all of the data is sent, the state machine
must be reset by either completing the remaining transfers or by
returning the
less than eight SCLK cycles). Raising the
low for at least one complete SCLK cycle (but
CS
on a nonbyte
CS
boundary terminates the serial transfer and flushes the buffer.
In the streaming mode (see Ta b l e 47 ), any number of data bytes
an be transferred in a continuous stream. The register address
c
is automatically incremented or decremented (see the
rst Transfers section).
Fi
must be raised at the end of the last
CS
MSB/LSB
byte to be transferred, thereby ending the stream mode.
Communication Cycle—Instruction Plus Data
There are two parts to a communication cycle with the AD9517.
The first writes a 16-bit instruction word into the AD9517,
coincident with the first 16 SCLK rising edges. The instruction
word provides the AD9517 serial control port with information
regarding the data transfer, which is the second part of the
communication cycle. The instruction word defines whether
the upcoming data transfer is a read or a write, the number of
bytes in the data transfer, and the starting register address for
the first byte of the data transfer.
Write
If the instruction word is for a write operation, the second part
is the transfer of data into the serial control port buffer of the
AD9517. Data bits are registered on the rising edge of SCLK.
The length of the transfer (1, 2, 3 bytes or streaming mode) is
cated by two bits (W1:W0) in the instruction byte. When
indi
the transfer is 1, 2, or 3 bytes, but not streaming,
CS
can be
raised after each sequence of eight bits to stall the bus (except
after the last byte, where it ends the cycle). When the bus is
stalled, the serial transfer resumes when
is lowered. Raising CS
CS
on a nonbyte boundary resets the serial control port. During a
write, streaming mode does not skip over reserved or blank
registers; therefore, the user must know what bit pattern to
write to the reserved registers to preserve proper operation of
the part. It does not matter what data is written to blank registers.
Because data is written into a serial control port buffer area, not
dir
ectly into the actual control registers of the AD9517, an
additional operation is needed to transfer the serial control port
buffer contents to the actual control registers of the AD9517,
thereby causing them to become active. The update registers
operation consists of setting 0x232<0> = 1b (this bit is selfclearing). Any number of bytes of data can be changed before
executing an update registers. The update registers simultaneously
actuates all register changes that have been written to the buffer
since any previous update.
Rev. 0 | Page 52 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Read
If the instruction word is for a read operation, the next N × 8
SCLK c
ycles clock out the data from the address specified in the
instruction word, where N is 1 to 3 as determined by W1:W0.
If N = 4, the read operation is in streaming mode, continuing
until
is raised. Streaming mode does not skip over reserved
CS
or blank registers. The readback data is valid on the falling
edge of SCLK.
The default mode of the AD9517 serial control port is the
idirectional mode. In bidirectional mode, both the sent data
b
and the readback data appear on the SDIO pin. It is also possible to
set the AD9517 to unidirectional mode (SDO enable register,
0x00<7>). In unidirectional mode, the readback data appears
on the SDO pin.
A readback request reads the data that is in the serial control
po
rt buffer area, or the data in the active registers (see Figure 61).
Re
adback of the buffer or active registers is controlled by 0x04<0>.
The AD9517 supports only the long instruction mode; therefore,
0x00<4:3> m
ust be set to 11b (this register uses mirrored bits).
Long instruction mode is the default at power-up or reset.
The AD9517 uses Register Address 0x00 to Register
A
ddress 0x232.
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
CS
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
WRITE RE GISTE R 0x232 = 0x01
TO UDATE REG ISTERS
Figure 61. Relationship Between Serial Control Port Buffer Registers and
Active Registers of the AD9517
UPDATE
REGISTERS
BUFFER REGI STERS
ACTIVE REGI STERS
06427-037
THE INSTRUCTION WORD (16 BITS)
The MSB of the instruction word is R/W, which indicates
whether the instruction is a read or a write. The next two bits,
W1:W0, indicate the length of the transfer in bytes. The final
13 bits are the address (A12:A0) at which to begin the read or
write operation.
For a write, the instruction word is followed by the number of
b
ytes of data indicated by Bits W1:W0 (see Tab l e 4 7 ).
Table 47. Byte Transfer Count
W1
0 0 1
0 1 2
1
1 1 Streaming mode
W0 Bytes to Transfer
0 3
A12:A0: These 13 bits select the address within the register map
that is written to or read from during the data transfer portion
of the communications cycle. Only Bits<A9:A0> are needed to
cover the range of the 0x232 registers used by the AD9517.
Bits<A12:A10> must always be 0b. For multibyte transfers, this
address is the starting byte address. In MSB first mode,
subsequent bytes increment the address.
MSB/LSB FIRST TRANSFERS
The AD9517 instruction word and byte data can be MSB first
or LSB first. Any data written to 0000 must be mirrored; the
upper four bits (7:4) must mirror the lower four bits (3:0). This
makes it irrelevant whether LSB first or MSB first is in effect. As
an example of this mirroring, see the default setting for this
register: 0x18, which mirrors Bit 4 and Bit 3. This sets the long
instruction mode (default, and is the only mode supported).
The default for the AD9517 is MSB first.
When LSB first is set by 0x00<2> and 0x00<6>, it takes effect
ediately, because it only affects the operation of the serial
imm
control port and does not require that an update be executed.
When MSB first mode is active, the instruction and data bytes
m
ust be written from MSB to LSB. Multibyte data transfers in
MSB first format start with an instruction byte that includes the
register address of the most significant data byte. Subsequent
data bytes must follow in order from the high address to the low
address. In MSB first mode, the serial control port internal
address generator decrements for each data byte of the
multibyte transfer cycle.
When LSB first is active, the instruction and data bytes must be
written from LSB to MSB. Multibyte data transfers in LSB first
format start with an instruction byte that includes the register
address of the least significant data byte followed by multiple
data bytes. The internal byte address generator of the serial
control port increments for each byte of the multibyte
transfer cycle.
The AD9517 serial control port register address decrements
f
rom the register address just written toward 0x00 for multibyte
I/O operations if the MSB first mode is active (default). If the
LSB first mode is active, the register address of the serial control
port increments from the address just written toward 0x232 for
multibyte I/O operations.
Streaming mode always terminates when it hits Address 0x232.
Note that unused addresses are not skipped during multibyte
I/O operations.
Table 48. Streaming Mode (No Addresses Are Skipped)
Write Mode
LSB first
MSB first Decrement 0x01, 0x00, 0x232, stop
Address Direction Stop Sequence
Increment 0x230, 0x231, 0x232, stop
Rev. 0 | Page 53 of 80

AD9517-3
K
K
K
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Table 49. Serial Control Port, 16-Bit Instruction Word, MSB First
MSB LSB
I15 I14 I13 I12 I11 I10 I9 I8 I7 I6 I5 I4 I3 I2 I1 I0
R/W
CS
SCL
DON'T CARE
W1 W0 A12 = 0 A11 = 0 A10 = 0 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
SDIO A12W0W1R/W A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
16-BIT INST RUCTION HEADE R REGISTE R (N) DATA REG ISTER (N – 1) DATA
Figure 62. Serial Control Port Write—MSB First, 16
-Bit Instruction, Two Bytes Data
CS
SCL
DON'T CARE
SDIO
SDO
DON'T CARE
A12W0W1R/W A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Figure 63. Serial Control Port Read—MSB Firs
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
REGISTE R (N) DATA16-BIT INST RUCTION HE ADER REGIST ER (N – 1) DATA RE GISTER ( N – 2) DATA REG ISTER ( N – 3) DATA
t, 16-Bit Instruction, Four Bytes Data
t
CS
SCLK
SDIO
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
DS
t
S
R/W
t
DH
W1W0A12A11A10A9A8A7A6A5D4D3D2D1D0
Figure 64. Serial Control Port Write—MSB First, 1
t
HI
t
CLK
t
LO
t
C
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
6-Bit Instruction, Timing Measurements
CS
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
DON'T
CARE
6427-040
6427-038
06427-039
SCLK
t
DV
SDIO
SDO
Figure 65. Timing Diagram for Serial Control Port Register Read
CS
DON'T CARE
SCL
SDIO
DON'T CARE
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 D1D0R/WW1W0 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
16-BIT INST RUCTION HEADE R REGISTE R (N) DATA REG ISTER (N + 1) DATA
Figure 66. Serial Control Port Write—LSB First, 16
Rev. 0 | Page 54 of 80
DATA BIT N – 1DATA BIT N
-Bit Instruction, Two Bytes Data
06427-041
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
6427-042

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
CS
SCLK
t
S
t
CLK
t
HI
t
DS
t
DH
t
LO
t
C
SDIO
BIT N BIT N + 1
Figure 67. Serial Control Port Timing—Write
Table 50. Serial Control Port Timing
Parameter Description
t
DS
t
DH
t
CLK
t
S
t
C
t
HI
t
LO
t
DV
Setup time between data and rising edge of SCLK
Hold time between data and rising edge of SCLK
Period of the clock
Setup time between CS falling edge and SCLK rising edge (start of communication cycle)
Setup time between SCLK rising edge and CS rising edge (end of communication cycle)
Minimum period that SCLK should be in a Logic High state
Minimum period that SCLK should be in a Logic Low state
SCLK to valid SDIO and SDO (see Figure 65)
06427-043
Rev. 0 | Page 55 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER MAP OVERVIEW
Table 51. Register Map Overview
Default
Addr
(Hex)
Serial Port Configuration
00 Serial Port
01 Blank
02 to
03
04 Read Back
PLL
10 PFD and
11 R Counter 14-Bit R Divider Bits<7:0> (LSB) 01
12 Blank 14-Bit R Divider Bits<13:8> (MSB) 00
13 A Counter Blank 6-Bit A Counter 00
14 13-Bit B Counter Bits<7:0> (LSB) 03
15
16 PLL Control 1 Set CP Pin
17 PLL Control 2 STATUS Pin Control Antibacklash Pulse Width 00
18 PLL Control 3 Reserved Lock Detect Counter Digital Lock
19 PLL Control 4
1A PLL Control 5 Reserved Reference
1B PLL Control 6 VCO
1C PLL Control 7 Disable
1D PLL Control 8 Reserved PLL Status
1E PLL Control 9
1F PLL Readback Reserved VCO Cal
20 to
4F
Parameter
Configuration
Control
Charge Pump
B Counter
Bit 7
(MSB)
SDO
Active
PFD
Polarity
to V
/2
CP
R, A, B Counters
Pin Reset
Frequency
Monitor
Switchover
Deglitch
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
LSB First Soft Reset Long
Charge Pump Current Charge Pump Mode PLL Power-Down 7D
Blank 13-Bit B Counter Bits<12:8> (MSB) 00
r
)
Reset A and
B Counters
REF1 (REFIN)
Fr
equency
Monitor
Use
REF_SEL Pin
Holdover
Active
Reset R
Counte
SYNC
Frequency
Monitor
Threshold
REF2
REFIN
(
Frequency
Monitor
Select
F2
RE
Finished
Instruction
Reserved
Blank Read Back
Reset All
Counters
Detect
Window
R Path Delay N Path Delay 00
Automatic
Reference
Switchover
Register
Disable
REF2
Selected
Blank
Long
Instruction
B Counter
Bypass
Disable
ital Lock
Dig
Detect
Stay on
F2
RE
LD Pin
Comparato
Enable
Reserved
VCO
Frequency
> Threshold
Soft Reset LSB First SDO Active 18
Active
Registers
Prescaler P 06
VCO Calibration Divider VCO Cal
LD Pin Control 00
REFMON Pin Control 00
r
REF2
Power On
Holdover
le
Enab
REF2
equency
Fr
> Threshold
REF1
Power On
External
Holdover
Control
REF1
equency
Fr
>Threshold
Now
Differential
Reference
Holdover
le
Enab
Digital
Lock
Detect
Value
(Hex)
00
06
00
00
00
--
Rev. 0 | Page 56 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Default
Addr
(Hex)
Fine Delay Adjust: OUT4 to OUT7
A0 OUT4 Delay
A1 OUT4 Delay
A2 OUT4 Delay
A3 OUT5 Delay
A4 OUT5 Delay
A5 OUT5 Delay
A6 OUT6 Delay
A7 OUT6 Delay
Parameter
Bypass
Full-Scale
Fraction
Bypass
Full-Scale
Fraction
Bypass
Full-Scale
Bit 7
(MSB)
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 (LSB)
Blank OUT4 Delay
Bypass
Blank OUT4 Ramp Capacitors OUT4 Ramp Current 00
Blank OUT4 Delay Fraction 00
Blank OUT5 Delay
Bypass
Blank OUT5 Ramp Capacitors OUT5 Ramp Current 00
Blank OUT5 Delay Fraction 00
Blank OUT6 Delay
Bypass
Blank OUT6 Ramp Capacitors OUT6 Ramp Current 00
Value
(Hex)
01
01
01
A8 OUT6 Delay
Fraction
A9 OUT7 Delay
Bypass
AA OUT7 Delay
Full-Scale
AB OUT7 Delay
Fraction
AC to
EF
LVPECL Outputs
F0 OUT0 Blank OUT0
F1 OUT1 Blank OUT1
F2 to
F3
F4 OUT2 Blank OUT2
F5 OUT3 Blank OUT3
F6 to
13F
LVDS/CMOS Outputs
140 OUT4 OUT4 CMOS Output
Polarity
141 OUT5 OUT5 CMOS Output
Polarity
142 OUT6 OUT6 CMOS Output
Polarity
143 OUT7 OUT7 CMOS Output
Polarity
144 to
18F
Blank OUT6 Delay Fraction 00
Blank OUT7 Delay
Blank OUT7 Ramp Capacitors OUT7 Ramp Current 00
Blank OUT7 Delay Fraction 00
Blank
Invert
Invert
Reserved
Invert
Invert
Blank
OUT4 LVDS/
CMOS
Output
Polarity
OUT5 LVDS/
CMOS
Output
Polarity
OUT6 LVDS/
CMOS
Output
Polarity
OUT7 LVDS/
CMOS
Output
Polarity
OUT4
CMOS B
OUT5
CMOS B
OUT6
CMOS B
OUT7
CMOS B
Blank
OUT0 LVPECL
Differential Voltage
OUT1 LVPECL
Differential Voltage
OUT2 LVPECL
Differential Voltage
OUT3 LVPECL
Differential Voltage
OUT4 Select
/CMOS
LVDS
OUT5 Select
/CMOS
LVDS
OUT6 Select
/CMOS
LVDS
OUT7 Select
/CMOS
LVDS
OUT0 Power-Down 08
OUT1 Power-Down A
OUT2 Power-Down 08
OUT3 Power-Down 0A
OUT4 LVDS Output
Current
OUT5 LVDS Output
Current
OUT6 LVDS Output
Current
OUT7 LVDS Output
Current
Bypass
OUT4
Power-Down
OUT5
Power-Down
OUT6
Power-Down
OUT7
Power-Down
01
42
43
42
43
Rev. 0 | Page 57 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Default
Addr
(Hex)
LVPECL Channel Dividers
190 Divider 0
191 Divider 0
192 Blank Reserved Divider 0
193
to
195
196 Divider1
197 Divider 1
198 Blank Reserved Divider 1
LVDS/CMOS Channel Dividers
199 Divider 2
19A Phase Offset Divider 2.2 Phase Offset Divider 2.1 00
19B Low Cycles Divider 2.2 High Cycles Divider 2.2 11
19C Reserved Bypass
19D Blank Reserved Divider 2
19E Divider 3
19F Phase Offset Divider 3.2 Phase Offset Divider 3.1 00
1A0 Low Cycles Divider 3.2 High Cycles Divider 3.2 11
1A1 Reserved Bypass
1A2 Blank Reserved Divider 3
1A3 Reserved
1A4
to
1DF
VCO Divider and CLK Input
1E0 VCO Divider Blank Reserved VCO Divider 02
Parameter
(PECL)
(PECL)
(LVDS/CMOS)
(LVDS/CMOS)
Bit 7
(MSB)
Bypass
Bypass
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
Divider 0 Low Cycles Divider 0 High Cycles 00
Divider 0
Nosync
Divider 1 Low Cycles Divider 1 High Cycles 00
Divider 1
Nosync
Low Cycles Divider 2.1 High Cycles Divider 2.1 22
Low Cycles Divider 3.1 High Cycles Divider 3.1 22
Divider 0
Force High
Divider 1
Force High
Divider 2.2
Divider 3.2
Divider 0
Start High
Reserved
Divider 1
Start High
Bypass
Divider 2.1
Bypass
Divider 3.1
Blank
Divider 2
Nosync
Divider 3
Nosync
Divider 0 Phase Offset 80
Direct to
Output
Divider 1 Phase Offset 00
Direct to
Output
Divider 2
Force High
Divider 3
Force High
Start High
Divider 2.2
Start High
Divider 3.2
Bit 0 (LSB)
Divider 0
DCCOFF
Divider 1
DCCOFF
Start High
Divider 2.1
DCCOFF
Start High
Divider 3.1
DCCOFF
Value
(Hex)
00
00
00
00
00
00
1E1 Input CLKs Reserved Power-
1E2
to
22A
Down
Clock
Input
Section
Blank
Rev. 0 | Page 58 of 80
Power-Down
lock
VCO C
Interface
PowerDown VCO
and CLK
Select
VCO o
r CLK
Bypass
VCO
Divider
00

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Default
Addr
(Hex)
System
230 Power-Down
231 Blank Reserved 00
Update All Registers
232 Update All
Parameter
and Sync
Registers
Bit 7
(MSB)
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
Reserved Power-
Down Sync
Blank Update All
PowerDown
Distribution
Reference
Bit 0 (LSB)
Soft Sync 00
Registers
(Self-Clearing
Bit)
Value
(Hex)
00
Rev. 0 | Page 59 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER MAP DESCRIPTIONS
Tabl e 52 through Tab le 6 1 provide a detailed description of each of the control register functions. The registers are listed by hexadecimal
address. Reference to a specific bit or range of bits within a register is indicated by angle brackets. For example, <3> refers to Bit 3, and
<5:2> refers to the range of bits from Bit 5 through Bit 2.
Table 52. Serial Port Configuration
Reg. Addr (Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
00 <7> SDO Active Selects unidirectional or bidirectional data transfer mode.
<7> = 0; SDIO pin used for write and read; SDO set high impedance; bidirectional mode.
<7> = 1; SDO used for read; SDIO used for write; unidirectional mode.
00 <6> LSB First MSB or LSB data orientation.
<6> = 0; data-oriented MSB first; addressing decrements.
<6> = 1; data-oriented LSB first; addressing increments.
00 <5> Soft Reset Soft Reset.
00 <4> Long Instruction
<4> = 0; 8-bit instruction (short).
<4> = 1; 16-bit instruction (long).
00 <3:0> Mirror<7:4>
<0> = <7>.
<1> = <6>.
<2> = <5>.
<3> = <4>.
04 <0> Read Back Active Registers Select register bank used for a readback.
<0> = 0; read back buffer registers.
<0> = 1; read back active registers.
<5> = 1 (not self-clearing). Soft reset; restores default values to internal registers.
Not self-
Short/long instruction mode (this part uses long
should always be = 1).
Bits<3:0> should always mirror Bits<7:4> so that it does not ma
part is in MSB or LSB first mode (see Register 0x00<6>). User should set bits as follows:
clearing. Must be cleared to 0b to complete reset operation.
instruction mode only, so this bit
tter whether the
Rev. 0 | Page 60 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Table 53. PLL
Reg.
Addr
(Hex)
Bit(s) Name Description
10 <7> PFD Polarity
<7> = 0; positive (higher control voltage produces higher frequency).
<7> = 1; negative (higher control voltage produces lower frequency).
10 <6:4> CP Current Charge pump current (with CPRSET = 5.1 kΩ).
0 0 0 0.6
0 0 1 1.2
0 1 0 1.8
0 1 1 2.4
1 0 0 3.0
1 0 1 3.6
1 1 0 4.2
1 1 1 4.8
10 <3:2> CP Mode Charge pump operating mode.
0 0 High impedance state.
0 1 Force source current (pump up).
1 0 Force sink current (pump down).
1 1 Normal operation.
10 <1:0> PLL Power- PLL operating mode.
Down
0 0 Normal operation.
0 1 Asynchronous power-down.
1 0 Normal operation.
1 1 Synchronous power-down.
11 <7:0>
12 <5:0>
13 <5:0>
14 <7:0>
15 <4:0>
16 <7> Set CP Pin Set the CP pin to one-half of the VCP supply voltage.
to VCP/2 <7> = 0; CP normal operation.
<7> = 1; CP pin set to VCP/2.
16 <6> Reset R Reset R counter (R divider).
Counter <6> = 0; normal.
<6> = 1; reset R counter.
16 <5> Reset A and B Reset A and B counters (part of N divider).
Counters <5> = 0; normal.
<5> = 1; reset A and B counters.
14-Bit
R Divider
Bits<7:0>
(LSB)
14-Bit
R Divider
Bits<1
(MSB)
6-Bit
A C
ounter
13-Bit
B C
ounter
Bits<7:0>
(LSB)
13-Bit
B C
ounter
Bits<12:8>
(MSB)
Sets the PFD polarity. Negative polarity is for use
The on-chip VCO requires positive polarity <7> = 0.
<6> <5> <4> ICP (mA)
<3> <2> Charge Pump Mode
<1> <0> Mode
R divider LSBs—lower eight bits.
R divider MSBs—upper six bits.
3:8>
A counter (part of N divider).
B counter (part of N divider)—lower eight bits.
B counter (part of N divider)—upper five bits.
Rev. 0 | Page 61 of 80
(if needed) with external VCO/VCXO only.

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
16 <4> Reset All Reset R, A, and B counters.
Counters <4> = 0; normal.
<4> = 1; reset R, A, and B counters.
16 <3> B Counter B counter bypass. This is valid only when operating the prescaler in FD mode.
Bypass <3> = 0; normal.
16 <2:0> Prescaler P Prescaler: DM = dual modulus and FD = fixed divide.
0 0 0 FD Divide-by-1.
0 0 1 FD Divide-by-2.
0 1 0 DM Divide-by-2 and divide-by-3 when A ≠ 0; divide-by-2 when A = 0.
0 1 1 DM Divide-by-4 and divide-by-5 when A ≠ 0; divide-by-4 when A = 0.
1 0 0 DM Divide-by-8 and divide-by-9 when A ≠ 0; divide-by-8 when A = 0.
1 0 1 DM Divide-by-16 and divide-by-17 when A ≠ 0; divide-by-16 when A = 0.
1 1 0 DM Divide-by-32 and divide-by-33 when A ≠ 0; divide-by-32 when A = 0.
1 1 1 FD Divide-by-3.
17 <7:2> STATUS Select the signal that is connected to the STATUS pin
Pin Control
0 0 0 0 0 0 LVL Ground (dc).
0 0 0 0 0 1 DYN N divider output (after the delay).
0 0 0 0 1 0 DYN R divider output (after the delay).
0 0 0 0 1 1 DYN A divider output.
0 0 0 1 0 0 DYN Prescaler output.
0 0 0 1 0 1 DYN PFD up pulse.
0 0 0 1 1 0 DYN PFD down pulse.
0 X X X X X LVL Ground (dc); for all other cases of 0XXXXX not specified.
The selections that follow are the same as REFMON.
1 0 0 0 0 0 LVL Ground (dc).
1 0 0 0 0 1 DYN REF1 clock (differential reference when in differential mode).
1 0 0 0 1 0 DYN REF2 clock (N/A in differential mode).
1 0 0 0 1 1 DYN
1 0 0 1 0 0 DYN
1 0 0 1 0 1 LVL
1 0 0 1 1 0 LVL
1 0 0 1 1 1 LVL Status REF1 frequency (active high).
1 0 1 0 0 0 LVL Status REF2 frequency (active high).
1 0 1 0 0 1 LVL (Status REF1 frequency) AND (status REF2 frequency).
1 0 1 0 1 0 LVL (DLD) AND (status of selected reference) AND (status of VCO).
1 0 1 0 1 1 LVL Status of VCO frequency (active high).
1 0 1 1 0 0 LVL Selected reference (low = REF1, high = REF2).
1 0 1 1 0 1 LVL Digital lock detect (DLD); active high.
1 0 1 1 1 0 LVL Holdover active (active high).
1 0 1 1 1 1 LVL LD pin comparator output (active high).
1 1 0 0 0 0 LVL VS (PLL supply).
<3> = 1; B counter is set to divide-by-1. This allows the prescaler setting to determine the divide for
the N divider
<2> <1> <0> Mode Prescaler
<7> <6> <5> <4> <3> <2>
.
Level or
Dynamic
Signal
Signal at STATUS Pin
Selected reference to PLL (differential reference when in
erential mode).
diff
Unselected reference to PLL (not available in differential
mode).
Status of selected reference (status of differential reference);
tive high.
ac
Status of unselected reference (not available in differential
mode); ac
tive high.
Rev. 0 | Page 62 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
<7> <6> <5> <4> <3> <2>
1 1 0 0 0 1 DYN
1 1 0 0 1 0 DYN
1 1 0 0 1 1 DYN
1 1 0 1 0 0 DYN
1 1 0 1 0 1 LVL
1 1 0 1 1 0 LVL
1 1 0 1 1 1 LVL Status of REF1 frequency (active low).
1 1 1 0 0 0 LVL Status of REF2 frequency (active low).
1 1 1 0 0 1 LVL
1 1 1 0 1 0 LVL
1 1 1 0 1 1 LVL Status of VCO Frequency (active low).
1 1 1 1 0 0 LVL Selected reference (low = REF2, high = REF1).
1 1 1 1 0 1 LVL Digital lock detect (DLD) (active low).
1 1 1 1 1 0 LVL Holdover active (active low).
1 1 1 1 1 1 LVL LD pin comparator output (active low).
17 <1:0> Antibacklash
Pulse Width 0 0 2.9
0 1 1.3
1 0 6.0
1 1 2.9
18 <6:5>
0 0 5
0 1 16
1 0 64
1 1 255
18 <4>
Window <4> = 0; high range.
<4> = 1; low range.
18 <3> Disable Digital lock detect operation.
Digital <3> = 0; normal lock detect operation.
Lock Detect <3> = 1; disable lock detect.
18 <2:1> VCO Cal VCO Calibration Divider. Divider used to generate the VCO calibration clock from the PLL reference clock.
Divider
0 0 2
0 1 4
1 0 8
1 1 16 (default)
18 <0>
Lock Detect
unter
Co
Digital Lock
tect
De
VCO Cal
w
No
<1> <0> Antibacklash Pulse Width (ns)
Required consecutive number of PFD cycles with edges inside lock detect window before the DLD indicates
a locked condition.
<6> <5> PFD Cycles to Determine Lock
If the time difference of the rising edges at the inputs to the PFD are less than the lock detect window time, the
digital lock detect flag is set. The flag remains set until the time difference is greater than the loss-of-lock threshold.
<2> <1> VCO Calibration Clock Divider
Bit used to initiate the VCO calibration. This bit must be toggled from 0 to 1 in the active registers. The sequence
to initiate a calibration is: program to a 0, followed by an update bit (Register 0x232<0>); then programmed to
1, followed by another update bit (Register 0x232<0>). This sequence gives complete control over when the
VCO calibration occurs relative to the programming of other registers that can impact the calibration.
Level or
Dynamic
Signal
Signal at STATUS Pin
REF1 clock
REF2 clock
Selected reference to PLL
differential mode).
Unselected reference to PLL
differential mode).
Status of selected reference (status of differential reference);
tive low.
ac
Status of unselected reference (not available in differential
mode); ac
(Status of REF1 frequency) AND (status of REF2 frequency)
(DLD) AND (status of selected reference) AND (status of VCO)
(differential reference when in differential mode).
(not available in differential mode).
(differential reference when in
(not available when in
tive low.
.
.
Rev. 0 | Page 63 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
19 <7:6> R, A, B
Counters 0 0
Reset 1 0 Synchronous reset.
1 1
19 <5:3> R Path Delay <5:3> R Path Delay (see Table 2).
19 <2:0> N Path Delay <2:0> N Path Delay (see Table 2 ).
1A <6>
Monitor <6> = 0; frequency valid if frequency is above the higher frequency threshold.
Threshold <6> = 1; frequency valid if frequency is above the lower frequency threshold.
1A <5:0> LD Pin Select the signal that is connected to the LD pin.
Control
0 0 0 0 0 0 LVL Digital lock detect (high = lock, low = unlock).
0 0 0 0 0 1 DYN P-channel, open-drain lock detect (analog lock detect).
0 0 0 0 1 0 DYN N-channel, open-drain lock detect (analog lock detect).
0 0 0 0 1 1 HIZ High-Z LD pin.
0 0 0 1 0 0 CUR Current source lock detect (110 μA when DLD is true).
0 X X X X X LVL Ground (dc); for all other cases of 0XXXXX not specified.
The selections that follow are the same as REFMON.
1 0 0 0 0 0 LVL Ground (dc).
1 0 0 0 0 1 DYN REF1 clock (differential reference when in differential mode).
1 0 0 0 1 0 DYN REF2 clock (N/A in differential mode).
1 0 0 0 1 1 DYN
1 0 0 1 0 0 DYN Unselected reference to PLL (not available in differential mode).
1 0 0 1 0 1 LVL
1 0 0 1 1 0 LVL
1 0 0 1 1 1 LVL Status REF1 frequency (active high).
1 0 1 0 0 0 LVL Status REF2 frequency (active high).
1 0 1 0 0 1 LVL (Status REF1 frequency) AND (status REF2 frequency).
1 0 1 0 1 0 LVL (DLD) AND (status of selected reference) AND (status of VCO).
1 0 1 0 1 1 LVL Status of VCO frequency (active high).
1 0 1 1 0 0 LVL Selected reference (low = REF1, high = REF2).
1 0 1 1 0 1 LVL Digital lock detect (DLD); active high.
1 0 1 1 1 0 LVL Holdover active (active high).
1 0 1 1 1 1 LVL N/A—do not use.
1 1 0 0 0 0 LVL VS (PLL supply).
1 1 0 0 0 1 DYN
1 1 0 0 1 0 DYN
1 1 0 0 1 1 DYN
1 1 0 1 0 0 DYN
1 1 0 1 0 1 LVL
SYNC
Pin
Reference
requency
F
<7> <6> Action
Do nothing on
0 1 Asynchronous reset.
Do nothing on
Sets the reference (REF1/REF2) frequency monitor’s detection threshold frequency. This does not affect
the VCO frequency monitor’s detection threshold (see Table 16 , REF1, REF2, and VCO Frequency Status Monitor).
<5> <4> <3> <2> <1> <0>
SYNC
(default).
SYNC
.
Level or
Dynamic
Signal Signal at LD Pin
Selected reference to PLL (differential reference when in
diff
Status of selected reference (status of differential reference);
ac
Status of unselected reference (not available in differential
mode); ac
REF1 clock
REF2 clock
Selected reference to PLL
differential mode).
Unselected reference to PLL
mode).
Status of selected reference (status of differential reference);
ac
erential mode).
tive high.
tive high.
(differential reference when in differential mode).
(not available in differential mode).
(differential reference when in
(not available when in differential
tive low.
Rev. 0 | Page 64 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
<5> <4> <3> <2> <1> <0>
1 1 0 1 1 0 LVL
1 1 0 1 1 1 LVL Status of REF1 frequency (active low).
1 1 1 0 0 0 LVL Status of REF2 frequency (active low).
1 1 1 0 0 1 LVL
1 1 1 0 1 0 LVL
1 1 1 0 1 1 LVL Status of VCO frequency (active low).
1 1 1 1 0 0 LVL Selected reference (low = REF2, high = REF1).
1 1 1 1 0 1 LVL Digital lock detect (DLD); active low.
1 1 1 1 1 0 LVL Holdover active (active low).
1 1 1 1 1 1 LVL N/A—do not use.
1B <7> VCO Enable or disable VCO frequency monitor.
Frequency <7> = 0; disable VCO frequency monitor.
Monitor <7> = 1; enable VCO frequency monitor.
1B <6>
Frequency <6> = 0; disable REF2 frequency monitor.
Monitor <6> = 1; enable REF2 frequency monitor.
1B <5>
Monitor <5> = 0; disable REF1 (REFIN) frequency monitor.
<5> = 1; enable REF1 (REFIN) frequency monitor.
1B <4:0> REFMON Pin Select the signal that is connected to the REFMON pin.
Control
0 0 0 0 0 LVL Ground (dc).
0 0 0 0 1 DYN REF1 clock (differential reference when in differential mode).
0 0 0 1 0 DYN REF2 clock (N/A in differential mode).
0 0 0 1 1 DYN
0 0 1 0 0 DYN Unselected reference to PLL (not available in differential mode).
0 0 1 0 1 LVL
0 0 1 1 0 LVL
0 0 1 1 1 LVL Status REF1 frequency (active high).
0 1 0 0 0 LVL Status REF2 frequency (active high).
0 1 0 0 1 LVL (Status REF1 frequency) AND (status REF2 frequency).
0 1 0 1 0 LVL (DLD) AND (status of selected reference) AND (status of VCO).
0 1 0 1 1 LVL Status of VCO frequency (active high).
0 1 1 0 0 LVL Selected reference (low = REF1, high = REF2).
0 1 1 0 1 LVL Digital lock detect (DLD); active low.
0 1 1 1 0 LVL Holdover active (active high).
0 1 1 1 1 LVL LD pin comparator output (active high).
1 0 0 0 0 LVL VS (PLL supply).
1 0 0 0 1 DYN
1 0 0 1 0 DYN
1 0 0 1 1 DYN
REF2 (
REF1 (REFIN)
requency
F
Enable or disable REF2 frequency monitor.
REFIN
)
REF1 (REFIN) frequency monitor enable; this is for both REF1 (single-ended) and REFIN (differential) inputs
(as selected by differential reference mode).
<4> <3> <2> <1> <0>
Level or
Dynamic
Signal
Level or
Dynamic
Signal Signal at REFMON Pin
Signal at LD Pin
Status of unselected reference (not available in differential
mode); ac
(Status of REF1 frequency) AND (status of REF2 frequency)
(DLD) AND (status of selected reference) AND (status of VCO)
Selected reference to PLL (differential reference when in
erential mode).
diff
Status of selected reference (status of differential reference);
tive high.
ac
Status of unselected reference (not available in differential mode);
tive high.
ac
REF1 clock
REF2 clock
Selected reference to PLL
differential mode).
tive low.
(differential reference when in differential mode).
(not available in differential mode).
.
(differential reference when in
.
Rev. 0 | Page 65 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
<4> <3> <2> <1> <0>
1 0 1 0 0 DYN
1 0 1 0 1 LVL
1 0 1 1 0 LVL
1 0 1 1 1 LVL Status of REF1 frequency (active low).
1 1 0 0 0 LVL Status of REF2 frequency (active low).
1 1 0 0 1 LVL
1 1 0 1 0 LVL
1 1 0 1 1 LVL Status of VCO frequency (active low).
1 1 1 0 0 LVL Selected reference (low = REF2, high = REF1).
1 1 1 0 1 LVL Digital lock detect (DLD); active low.
1 1 1 1 0 LVL Holdover active (active low).
1 1 1 1 1 LVL LD pin comparator output (active low).
1C <7> Disable Disable or enable the switchover deglitch circuit.
Switchover <7> = 0; enable switchover deglitch circuit.
Deglitch <7> = 1; disable switchover deglitch circuit.
1C <6> Select REF2 If Register 0x1C<5> = 0, select reference for PLL.
<6> = 0; select REF1.
<6> = 1; select REF2.
1C <5> Use REF_SEL If Register 0x1C<4> = 0 (manual), set method of PLL reference selection.
Pin <5> = 0; use Register 0x1C<6>.
<5> = 1; use REF_SEL pin.
1C <4>
Switchover <4> = 0; manual reference switchover.
<4> = 1; automatic reference switchover.
1C <3> Stay on REF2 Stay on REF2 after switchover.
<3> = 0; return to REF1 automatically when REF1 status is good again.
<3> = 1; stay on REF2 after switchover. Do not automatically return to REF1.
1C <2> REF2 When automatic reference switchover is disabled, this bit turns the REF2 power on.
Power-On <2> = 0; REF2 power-off.
<2> = 1; REF2 power-on.
1C <1> REF1 When automatic reference switchover is disabled, this bit turns the REF1 power on.
Power-On <1> = 0; REF1 power-off.
<1> = 1; REF1 power-on.
1C <0>
<0> = 0; single-ended reference mode.
<0> = 1; differential reference mode.
1D <4> PLL Status Disables the PLL status register readback.
Register <4> = 0; PLL status register enable.
Disable <4> = 1; PLL status register disable.
Automatic
ference
Re
Differential
ference
Re
Automatic or manual reference switchover. Single-ended reference mode must be selected by
Register 0x1C<0> = 0.
Selects the PLL reference mode, differential or single-ended. Single-ended must be selected for the
automatic switchover for REF1 and REF2 to work.
Level or
Dynamic
Signal
Signal at REFMON Pin
Unselected reference to PLL
differential mode).
Status of selected reference (status of differential reference);
tive low.
ac
Status of unselected reference (not available in differential mode);
tive low.
ac
(Status of REF1 frequency) AND (status of REF2 frequency)
(DLD) AND (status of selected reference) AND (status of VCO)
(not available when in
.
.
Rev. 0 | Page 66 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
1D <3>
<3> = 0; disable LD pin comparator; internal/automatic holdover controller treats this pin as true (high).
<3> = 1; enable LD pin comparator.
1D <2> Holdover Along with <0> enables the holdover function.
Enable <2> = 0; holdover disabled.
<2> = 1; holdover enabled.
1D <1> External
Holdover <1> = 0; automatic holdover mode—holdover controlled by automatic holdover circuit.
Control
1D <0> Holdover Along with <2> enables the holdover function.
Enable <0> = 0; holdover disabled.
<0> = 1; holdover enabled.
1F <6> VCO Cal Readback register: status of the VCO calibration.
Finished <6> = 0; VCO calibration not finished.
<6> = 1; VCO calibration finished.
1F <5>
<5> = 0; not in holdover.
<5> = 1; holdover state active.
1F <4> REF2 Readback register: indicates which PLL reference is selected as the input to the PLL.
Selected <4> = 0; REF1 selected (or differential reference if in differential mode).
<4> = 1; REF2 selected.
1F <3>
Threshold <3> = 0; VCO frequency is less than the threshold.
<3> = 1; VCO frequency is greater than the threshold.
1F <2>
Threshold <2> = 0; REF2 frequency is less than threshold frequency.
<2> = 1; REF2 frequency is greater than threshold frequency.
1F <1>
Threshold <1> = 0; REF1 frequency is less than threshold frequency.
<1> = 1; REF1 frequency is greater than threshold frequency.
1F <0> Digital Lock Readback register: digital lock detect.
Detect <0> = 0; PLL is not locked.
<0> = 1; PLL is locked.
LD Pin
mparator
Co
Enable
Holdover
tive
Ac
VCO
requency >
F
REF2
requency >
F
REF1
requency >
F
Enables the LD pin voltage comparator. This is used with the LD pin current source lock detect mode.
When in the internal (automatic) holdover mode, this enables the use of the voltage on the LD pin to
determine if the PLL was previously in a locked state (see Figure 51). Otherwise, this can be used with
MON and STATUS pins to monitor the voltage on this pin.
the REF
Enables the external hold control through the SYNC
<1> = 1; external holdover mode—holdover controlled by SYNC
Readback register: indicates if the part is in the holdover state (see Figure 51). This is not the same as holdover
enabled
Readback register: indicates if the VCO frequency is greater than the threshold (see Table 16, REF1, REF2, and VCO
F
Readback register: indicates if the frequency of the signal at REF2 is greater than the threshold frequency
set by Register 0x1A<6>.
Readback register: indicates if the frequency of the signal at REF2 is greater than the threshold frequency
set by Register 0x1A<6>.
.
requency Status Monitor).
pin. (This disables the internal holdover mode.)
pin.
Rev. 0 | Page 67 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Table 54. Fine Delay Adjust: OUT4 to OUT7
Reg.
Addr
(Hex)
Bit(s) Name Description
A0 <0> OUT4 Delay Bypass or use the delay function.
Bypass <0> = 0; use delay function.
<0> = 1; bypass delay function.
A1 <5:3>
0 0 0 4
0 0 1 3
0 1 0 3
0 1 1 2
1 0 0 3
1 0 1 2
1 1 0 2
1 1 1 1
A1 <2:0>
0 0 0 200
0 0 1 400
0 1 0 600
0 1 1 800
1 0 0 1000
1 0 1 1200
1 1 0 1400
1 1 1 1600
A2 <5:0>
A3 <0> OUT5 Delay Bypass or use the delay function.
Bypass <0> = 0; use delay function.
<0> = 1; bypass delay function.
A4 <5:3>
0 0 0 4
0 0 1 3
0 1 0 3
0 1 1 2
1 0 0 3
1 0 1 2
1 1 0 2
1 1 1 1
OUT4 Ramp
itors
Capac
OUT4 Ramp
rrent
Cu
OUT4
y Fraction
Dela
OUT5 Ramp
itors
Capac
Selects the number of ramp capacitors used by the delay function. The combination of the number of the
capacitors and the ramp current sets the delay full scale.
<5> <4> <3> Number of Capacitors
Ramp current for the delay function. The combination of the number of capacitors and the ramp current
sets the delay full scale.
<2> <1> <0> Current (μA)
Selects the fraction of the full-scale delay desired (6-bit binary).
000000 gives zero delay.
Only delay values up to 47 decimals (101111b; 0x2F) are supported.
Selects the number of ramp capacitors used by the delay function. The combination of the number of the
capacitors and the ramp current sets the delay full scale.
<5> <4> <3> Number of Capacitors
Rev. 0 | Page 68 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
A4 <2:0>
0 0 0 200
0 0 1 400
0 1 0 600
0 1 1 800
1 0 0 1000
1 0 1 1200
1 1 0 1400
1 1 1 1600
A5 <5:0>
A6 <0> OUT6 Delay Bypass or use the delay function.
Bypass <0> = 0; use delay function.
<0> = 1; bypass delay function.
A7 <5:3>
0 0 0 4
0 0 1 3
0 1 0 3
0 1 1 2
1 0 0 3
1 0 1 2
1 1 0 2
1 1 1 1
A7 <2:0>
0 0 0 200
0 0 1 400
0 1 0 600
0 1 1 800
1 0 0 1000
1 0 1 1200
1 1 0 1400
1 1 1 1600
A8 <5:0>
A9 <0> OUT7 Delay Bypass or use the delay function.
Bypass <0> = 0; use delay function.
<0> = 1; bypass delay function.
OUT5 Ramp
rrent
Cu
OUT5 Delay
action
Fr
OUT6 Ramp
itors
Capac
OUT6 Ramp
rrent
Cu
OUT6 Delay
action
Fr
Ramp current for the delay function. The combination of the number of capacitors and the ramp
current sets the delay full scale.
<2> <1> <0> Current (μA)
Selects the fraction of the full-scale delay desired (6-bit binary).
000000 give zero delay.
Only delay values up to 47 decimals (101111b; 0x2F) are supported.
Selects the number of ramp capacitors used by the delay function. The combination of the number of
capacitors and the ramp current sets the delay full scale.
<5> <4> <3> Number of Capacitors
Ramp current for the delay function. The combination of the number of capacitors and the ramp
current sets the delay full scale.
<2> <1> <0> Current (μA)
Selects the fraction of the full-scale delay desired (6-bit binary).
000000 gives zero delay.
Only delay values up to 47 decimals (101111b; 0x2F) are supported.
Rev. 0 | Page 69 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
AA <5:3>
0 0 0 4
0 0 1 3
0 1 0 3
0 1 1 2
1 0 0 3
1 0 1 2
1 1 0 2
1 1 1 1
AA <2:0>
0 0 0 200
0 0 1 400
0 1 0 600
0 1 1 800
1 0 0 1000
1 0 1 1200
1 1 0 1400
1 1 1 1600
AB <5:0>
OUT7 Ramp
itors
Capac
OUT7 Ramp
rrent
Cu
OUT7 Delay
action
Fr
Selects the number of ramp capacitors used by the delay function. The combination of the number of
capacitors and the ramp current sets the delay full scale.
<5> <4> <3> Number of Capacitors
Ramp current for the delay function. The combination of the number of capacitors and the ramp
current sets the delay full scale.
<2> <1> <0> Current Value (μA)
Selects the fraction of the full-scale delay desired (6-bit binary).
000000 gives zero delay.
Only delay values up to 47 decimals (101111b; 0x2F) are supported.
Table 55. LVPECL Outputs
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
F0 <4> OUT0 Invert Sets the output polarity.
<4> = 0; noninverting.
<4> = 1; inverting.
F0 <3:2> OUT0 LVPECL Sets the LVPECL output differential voltage (VOD).
Differential
Voltage 0 0 400
0 1 600
1 0 780
1 1 960
F0 <1:0> OUT0 LVPECL power-down modes.
Power-Down
0 0 Normal operation. On
0 1 Partial power-down, reference on; use only if there are no external load resistors. Off
1 0 Partial power-down, reference on, safe LVPECL power-down. Off
1 1 Total power-down, reference off; use only if there are no external load resistors. Off
F1 <4> OUT1 Invert Sets the output polarity.
<4> = 0; noninverting.
<4> = 1; inverting.
<3> <2> V
<1> <0> Mode Output
OD
(mV)
Rev. 0 | Page 70 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
F1 <3:2> OUT1 LVPECL Sets the LVPECL output differential voltage (VOD).
Differential
Voltage 0 0 400
0 1 600
1 0 780
1 1 960
F1 <1:0> OUT1 LVPECL power-down modes.
Power-Down
0 0 Normal operation. On
0 1 Partial power-down, reference on; use only if there are no external load resistors. Off
1 0 Partial power-down, reference on, safe LVPECL power-down. Off
1 1 Total power-down, reference off; use only if there are no external load resistors. Off
F4 <4> OUT2 Invert Sets the output polarity.
<4> = 0; noninverting.
<4> = 1; inverting.
F4 <3:2> OUT2 LVPECL Sets the LVPECL output differential voltage (VOD).
Differential
Voltage 0 0 400
0 1 600
1 0 780
1 1 960
F4 <1:0> OUT2 LVPECL power-down modes.
Power-Down
0 0 Normal operation. On
0 1 Partial power-down, reference on; use only if there are no external load resistors. Off
1 0 Partial power-down, reference on, safe LVPECL power-down. Off
1 1 Total power-down, reference off; use only if there are no external load resistors. Off
F5 <4> OUT3 Invert Sets the output polarity.
<4> = 0; noninverting.
<4> = 1; inverting.
F5 <3:2> OUT3 LVPECL Sets the LVPECL output differential voltage (VOD).
Differential
Voltage 0 0 400
0 1 600
1 0 780
1 1 960
F5 <1:0> OUT3 LVPECL power-down modes.
Power-Down
0 0 Normal operation. On
0 1 Partial power-down, reference on; use only if there are no external load resistors. Off
1 0 Partial power-down, reference on, safe LVPECL power-down. Off
1 1 Total power-down, reference off; use only if there are no external load resistors. Off
<3> <2> V
<1> <0> Mode Output
<3> <2> VOD (mV)
<1> <0> Mode Output
<3> <2> V
<1> <0> Mode Output
OD
OD
(mV)
(mV)
Rev. 0 | Page 71 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Table 56. LVDS/CMOS Outputs
Reg.
Addr
(Hex)
Bit(s) Name Description
140 <7:5>
0 0 0 Noninverting Inverting Noninverting
0 1 0 Noninverting Noninverting Noninverting
1 0 0 Inverting Inverting Noninverting
1 1 0 Inverting Noninverting Noninverting
0 0 1 Inverting Noninverting Inverting
0 1 1 Inverting Inverting Inverting
1 0 1 Noninverting Noninverting Inverting
1 1 1 Noninverting Inverting Inverting
140 <4> OUT4 CMOS B In CMOS mode, turn on/off the CMOS B output. There is no effect in LVDS mode.
<4> = 0; turn off the CMOS B output.
<4> = 1; turn on the CMOS B output.
140 <3> OUT4 Select LVDS/CMOS Select LVDS or CMOS logic levels.
<3> = 0; LVDS.
<3> = 1; CMOS.
140 <2:1> OUT4 LVDS Output Current Set output current level in LVDS mode. This has no effect in CMOS mode.
0 0 1.75 100
0 1 3.5 100
1 0 5.25 50
1 1 7 50
140 <0> OUT4 Power-Down Power-down output (LVDS/CMOS).
<0> = 0; power on.
<0> = 1; power off.
141 <7:5> OUT5 Output Polarity
0 0 0 Noninverting Inverting Noninverting
0 1 0 Noninverting Noninverting Noninverting
1 0 0 Inverting Inverting Noninverting
1 1 0 Inverting Noninverting Noninverting
0 0 1 Inverting Noninverting Inverting
0 1 1 Inverting Inverting Inverting
1 0 1 Noninverting Noninverting Inverting
1 1 1 Noninverting Inverting Inverting
141 <4> OUT5 CMOS B In CMOS mode, turn on/off the CMOS B output. There is no effect in LVDS mode.
<4> = 0; turn off the CMOS B output.
<4> = 1; turn on the CMOS B output.
141 <3> OUT5 Select LVDS/CMOS Select LVDS or CMOS logic levels.
<3> = 0; LVDS.
<3> = 1; CMOS.
141 <2:1> OUT5 LVDS Output Current Set output current level in LVDS mode. This has no effect in CMOS mode.
0 0 1.75 100
0 1 3.5 100
1 0 5.25 50
1 1 7 50
OUT4 Output Polarity
In CMOS mode, <7:5> select the output polarit
In LVDS mode, only <5> determines LVDS polarity.
<7> <6> <5> OUT4A (CMOS) OUT4B (CMOS) OUT4 (LVDS)
<2> <1> Current (mA) Recommended Termination (Ω)
In CMOS mode, <7:5> select the output polarit
In LVDS mode, only <5> determines LVDS polarity.
<7> <6> <5> OUT5A (CMOS) OUT5B (CMOS) OUT5 (LVDS)
<2> <1> Current (mA) Recommended Termination (Ω)
Rev. 0 | Page 72 of 80
y of each CMOS output.
y of each CMOS output.

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
141 <0> OUT5 Power-Down Power-down output (LVDS/CMOS).
<0> = 0; power on.
<0> = 1; power off.
142 <7:5> OUT6 Output Polarity
0 0 0 Noninverting Inverting Noninverting
0 1 0 Noninverting Noninverting Noninverting
1 0 0 Inverting Inverting Noninverting
1 1 0 Inverting Noninverting Noninverting
0 0 1 Inverting Noninverting Inverting
0 1 1 Inverting Inverting Inverting
1 0 1 Noninverting Noninverting Inverting
1 1 1 Noninverting Inverting Inverting
142 <4> OUT6 CMOS B In CMOS mode, turn on/off the CMOS B output. There is no effect in LVDS mode.
142 <3> OUT6 Select LVDS/CMOS Select LVDS or CMOS logic levels.
142 <2:1> OUT6 LVDS Output Current Set output current level in LVDS mode. This has no effect in CMOS mode.
142 <0> OUT6 Power-Down Power-down output (LVDS/CMOS).
<0> = 0; power on.
<0> = 1; power off.
143 <7:5> OUT7 Output Polarity
0 0 0 Noninverting Inverting Noninverting
0 1 0 Noninverting Noninverting Noninverting
1 0 0 Inverting Inverting Noninverting
1 1 0 Inverting Noninverting Noninverting
0 0 1 Inverting Noninverting Inverting
0 1 1 Inverting Inverting Inverting
1 0 1 Noninverting Noninverting Inverting
1 1 1 Noninverting Inverting Inverting
143 <4> OUT7 CMOS B In CMOS mode, turn on/off the CMOS B output. There is no effect in LVDS mode.
<4> = 0; turn off the CMOS B output.
<4> = 1; turn on the CMOS B output.
143 <3> OUT7 Select LVDS/CMOS Select LVDS or CMOS logic levels.
<3> = 0; LVDS.
<3> = 1; CMOS.
In CMOS mode, <7:5> select the output polarit
In LVDS mode, only <5> determines LVDS polarity.
<7> <6> <5> OUT6A (CMOS) OUT6B (CMOS) OUT6 (LVDS)
<4> = 0; turn off the CMOS B output.
<4> = 1; turn on the CMOS B output.
<3> = 0; LVDS.
<3> = 1; CMOS.
<2> <1> Current (mA) Recommended Termination (Ω)
0 0 1.75 100
0 1 3.5 100
1 0 5.25 50
1 1 7 50
In CMOS mode, <7:5> select the output polarit
In LVDS mode, only <5> determines LVDS polarity.
<7> <6> <5> OUT7A (CMOS) OUT7B (CMOS) OUT7 (LVDS)
y of each CMOS output.
y of each CMOS output.
Rev. 0 | Page 73 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
143 <2:1> OUT7 LVDS Output Current Set output current level in LVDS mode. This has no effect in CMOS mode.
0 0 1.75 100
0 1 3.5 100
1 0 5.25 50
1 1 7 50
143 <0> OUT7 Power-Down Power-down output (LVDS/CMOS).
<0> = 0; power on.
<0> = 1; power off.
Table 57. LVPECL Channel Dividers
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
190 <7:4> Divider 0 Low Cycles Number of clock cycles of the divider input during which divider output stays low.
190 <3:0> Divider 0 High Cycles Number of clock cycles of the divider input during which divider output stays high.
191 <7> Divider 0 Bypass Bypass and power-down the divider; route input to divider output.
<7> = 0; use divider.
<7> = 1; bypass divider.
191 <6> Divider 0 Nosync Nosync.
<6> = 0; obey chip-level SYNC signal.
<6> = 1; ignore chip-level SYNC signal.
191 <5> Divider 0 Force High Force divider output to high. This requires that nosync also be set.
<5> = 0; divider output forced to low.
<5> = 1; divider output forced to high.
191 <4> Divider 0 Start High Selects clock output to start high or start low.
<4> = 0; start low.
<4> = 1; start high.
191 <3:0> Divider 0 Phase Offset Phase offset.
192 <1> Divider 0 Direct to Output Connect OUT0 and OUT1 to Divider 0 or directly to VCO or CLK.
<1> = 0: OUT0 and OUT1 are connected to Divider 0.
192 <0> Divider 0 DCCOFF Duty-cycle correction function.
<0> = 0; enable duty-cycle correction.
<0> = 1; disable duty-cycle correction.
196 <7:4> Divider 1 Low Cycles Number of clock cycles of the divider input during which divider output stays low.
196 <3:0> Divider 1 High Cycles Number of clock cycles of the divider input during which divider output stays high.
197 <7> Divider 1 Bypass Bypass and power-down the divider; route input to divider output.
<7> = 0; use divider.
<7> = 1; bypass divider.
197 <6> Divider 1 Nosync Nosync.
<6> = 0; obey chip-level SYNC signal.
<6> = 1; ignore chip-level SYNC signal.
197 <5> Divider 1 Force High Force divider output to high. This requires that nosync also be set.
<5> = 0; divider output forced to low.
<5> = 1; divider output forced to high.
<2> <1> Current (mA) Recommended Termination (Ω)
<1> = 1:
f 0x1E1<1:0> = 10b, the VCO is routed directly to OUT0 and OUT1.
I
If 0x1E1<1:0> = 00b, the CLK is routed directly to OUT0 and OUT1.
If 0x1E1<1:0> = 01b, there is no effect.
Rev. 0 | Page 74 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
197 <4> Divider 1 Start High Selects clock output to start high or start low.
<4> = 0; start low.
<4> = 1; start high.
197 <3:0> Divider 1 Phase Offset Phase offset.
198 <1> Divider 1 Direct to Output Connect OUT2 and OUT3 to Divider 2 or directly to VCO or CLK.
<1> = 0; OUT2 and OUT3 are connected to Divider 1.
198 <0> Divider 1 DCCOFF Duty-cycle correction function.
<0> = 0; enable duty-cycle correction.
<0> = 1; disable duty-cycle correction.
Table 58. LVDS/CMOS Channel Dividers
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
199 <7:4> Low Cycles Divider 2.1 Number of clock cycles of 2.1 divider input during which 2.1 output stays low.
199 <3:0> High Cycles Divider 2.1 Number of clock cycles of 2.1 divider input during which 2.1 output stays high.
19A <7:4> Phase Offset Divider 2.2 Refer to LVDS/CMOS channel divider function description.
19A <3:0> Phase Offset Divider 2.1 Refer to LVDS//CMOS channel divider function description.
19B <7:4> Low Cycles Divider 2.2 Number of clock cycles of 2.2 divider input during which 2.2 output stays low.
19B <3:0> High Cycles Divider 2.2 Number of clock cycles of 2.2 divider input during which 2.2 output stays high.
19C <5> Bypass Divider 2.2 Bypass (and power-down) 2.2 divider logic, route clock to 2.2 output.
<5> = 0; do not bypass.
<5> = 1; bypass.
19C <4> Bypass Divider 2.1 Bypass (and power-down) 2.1 divider logic, route clock to 2.1 output.
<4> = 0; do not bypass.
<4> = 1; bypass.
19C <3> Divider 2 Nosync Nosync.
<3> = 0; obey chip-level SYNC signal.
<3> = 1; ignore chip-level SYNC signal.
19C <2> Divider 2 Force High Force Divider 2 output high. Requires that nosync also be set.
<2> = 0; force low.
<2> = 1; force high.
19C <1> Start High Divider 2.2 Divider 2.2 start high/low.
<1> = 0; start low.
<1> = 1; start high.
19C <0> Start High Divider 2.1 Divider 2.1 start high/low.
<0> = 0; start low.
<0> = 1; start high.
19D <0> Divider 2 DCCOFF Duty-cycle correction function.
<0> = 0; enable duty-cycle correction.
<0> = 1; disable duty-cycle correction.
19E <7:4> Low Cycles Divider 3.1 Number of clock cycles of divider 3.1 input during which 3.1 output stays low.
19E <3:0> High Cycles Divider 3.1 Number of clock cycles of 3.1 divider input during which 3.1 output stays high.
19F <7:4> Phase Offset Divider 3.2 Refer to LVDS/CMOS channel divider function description.
<1> = 1:
f 0x1E1<1:0> = 10b, the VCO is routed directly to OUT2 and OUT3.
I
If 0x1E1<1:0> = 00b, the CLK is routed directly to OUT2 and OUT3.
If 0x1E1<1:0> = 01b, there is no effect.
Rev. 0 | Page 75 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
19F <3:0> Phase Offset Divider 3.1 Refer to LVDS/CMOS channel divider function description.
1A0 <7:4> Low Cycles Divider 3.2 Number of clock cycles of 3.2 divider input during which 3.2 output stays low.
1A0 <3:0> High Cycles Divider 3.2 Number of clock cycles of 3.2 divider input during which 3.2 output stays high.
1A1 <5> Bypass Divider 3.2 Bypass (and power-down) 3.2 divider logic, route clock to 3.2 output.
<5> = 0; do not bypass.
<5> = 1; bypass.
1A1 <4> Bypass Divider 3.1 Bypass (and power-down) 3.1 divider logic, route clock to 3.1 output.
<4> = 0; do not bypass.
<4> = 1; bypass.
1A1 <3> Divider 3 Nosync Nosync.
<3> = 0; obey chip-level SYNC signal.
<3> = 1; ignore chip-level SYNC signal.
1A1 <2> Divider 3 Force High Force Divider 3 output high. Requires that nosync also be set.
<2> = 0; force low.
<2> = 1; force high.
1A1 <1> Start High Divider 3.2 Divider 3.2 start high/low.
<1> = 0; start low.
<1> = 1; start high.
1A1 <0> Start High Divider 3.1 Divider 3.1 start high/low.
<0> = 0; start low.
<0> = 1; start high.
1A2 <0> Divider 3 DCCOFF Duty-cycle correction function.
<0> = 0; enable duty-cycle correction.
<0> = 1; disable duty-cycle correction.
Table 59. VCO Divider and CLK Input
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
1E0 <2:0> VCO Divider
0 0 0 2
0 0 1 3
0 1 0 4
0 1 1 5
1 0 0 6
1 0 1 Output static
1 1 0 Output static
1 1 1 Output static
1E1 <4> Power-Down Clock Input Section Power down the clock input section (including CLK buffer, VCO divider, and CLK tree).
<4> = 0; normal operation.
<4> = 1; power-down.
1E1 <3> Power-Down VCO Clock Interface Power down the interface block between VCO and clock distribution.
<3> = 0; normal operation.
<3> = 1; power-down.
1E1 <2> Power-Down VCO and CLK Power down both VCO and CLK input.
<2> = 0; normal operation.
<2> = 1; power-down.
<2> <1> <0> Divide
Rev. 0 | Page 76 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
1E1 <1> Select VCO or CLK Select either the VCO or the CLK as the input to VCO divider.
<1> = 0; select external CLK as input to VCO divider.
<1> = 1; select VCO as input to VCO divider; cannot bypass VCO divider when this is selected.
1E1 <0> Bypass VCO Divider Bypass or use the VCO divider.
<0> = 0; use VCO divider.
<0> = 1; bypass VCO divider; cannot select VCO as input when this is selected.
Table 60. System
Reg.
Addr
(Hex) Bit(s) Name Description
230 <2> Power-Down SYNC Power down the SYNC function.
<2> = 0; normal operation of the SYNC function.
<2> = 1; power-down SYNC circuitry.
230 <1> Power-Down Distribution Reference Power down the reference for distribution section.
<1> = 0; normal operation of the reference for the distribution section.
<1> = 1; power down the reference for the distribution section.
230 <0> Soft SYNC
The soft SYNC bit works the same as the SYNC
is reversed. That is, a high level forces selected channels into a predetermined static
state, and a 1-to-0 transition triggers a SYNC.
<0> = 0; same as SYNC
<0> = 1; same as SYNC
high.
low.
pin, except that the polarity of the bit
Table 61. Update All Registers
Reg.
Addr
(Hex)
Bit(s) Name Description
232 <0>
<0> = 1 (self-clearing); update all active registers to the contents of the buffer registers.
Update All
egisters
R
This bit must be set to 1 to transfer the contents of the buffer registers into the active registers. This happens
on the next SCLK rising edge. This bit is self-clearing; that is, it does not have to be set back to 0.
Rev. 0 | Page 77 of 80

AD9517-3
V
V
V
V
V
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
APPLICATION NOTES
USING THE AD9517 OUTPUTS FOR ADC CLOCK APPLICATIONS
Any high speed ADC is extremely sensitive to the quality of its
sampling clock. An ADC can be thought of as a sampling mixer,
and any noise, distortion, or timing jitter on the clock is
combined with the desired signal at the analog-to-digital
output. Clock integrity requirements scale with the analog input
frequency and resolution, with higher analog input frequency
applications at ≥14-bit resolution being the most stringent. The
theoretical SNR of an ADC is limited by the ADC resolution
and the jitter on the sampling clock. Considering an ideal ADC
of infinite resolution where the step size and quantization error
can be ignored, the available SNR can be expressed
approximately by
⎛
⎜
SNR
×=
log20(dB)
⎜
⎝
where:
is the highest analog frequency being digitized.
f
A
is the rms jitter on the sampling clock.
t
J
Figure 68 shows the required sampling clock jitter as a function
o
f the analog frequency and effective number of bits (ENOB).
110
100
90
80
70
SNR (dB)
60
50
40
30
10 1k100
Figure 68. SNR and ENOB vs. Analog Input Frequency
See the AN-756 application note and the AN-501 application note
www.analog.com.
at
Many high performance ADCs feature differential clock inputs
t
o simplify the task of providing the required low jitter clock on
a noisy PCB. (Distributing a single-ended clock on a noisy PCB
can result in coupled noise on the sample clock. Differential
distribution has inherent common-mode rejection that can
provide superior clock performance in a noisy environment.)
The AD9517 features both LVPECL and LVDS outputs that
provide differential clock outputs, which enable clock solutions
that maximize converter SNR performance. The input
requirements of the ADC (differential or single-ended, logic
level termination) should be considered when selecting the best
clocking/converter solution.
⎞
1
⎟
⎟
π
tf
2
J
A
⎠
18
2πf
1
AtJ
16
14
12
ENOB
10
8
6
06427-044
f
A
(MHz)
SNR = 20log
t
J
=
1
0
2
0
0
f
S
4
0
0
f
S
1
p
s
2
p
s
1
0
p
s
0
f
S
LVPECL CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
The LVPECL outputs of the AD9517 provide the lowest jitter
clock signals available from the AD9517. The LVPECL outputs
(because they are open emitter) require a dc termination to bias
the output transistors. The simplified equivalent circuit in
Figure 57 shows the LVPECL output stage.
In most applications, an LVPECL far-end Thevenin termination
ecommended, as shown in Figure 69. The resistor network is
is r
desig
ned to match the transmission line impedance (50 Ω) and
the switching threshold (V
S_LVPECL
LVPECL
S_LVPECL
LVPECL
200Ω 200Ω
Figure 70. LVPECL with Parallel Transmission Line
(NOT CO UPLED)
V
Figure 69. LVPECL Far-End Thevenin Termination
0.1nF
0.1nF
− 1.3 V).
S
50Ω
SINGLE-E NDED
50Ω
= VS – 1.3V
T
100Ω DIFFERENTIAL
(COUPLED)
TRANSMISSION LINE
S_LVPECL
100Ω
127Ω127Ω
83Ω83Ω
V
S
LVPECL
S_LVPECL
LVPECL
6427-045
06427-046
LVDS CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
The AD9517 provides four clock outputs (OUT4 to OUT7) that
are selectable as either CMOS or LVDS level outputs. LVDS is a
differential output option that uses a current mode output stage.
The nominal current is 3.5 mA, which yields 350 mV output
swing across a 100 Ω resistor. The LVDS output meets or
exceeds all ANSI/TIA/EIA-644 specifications.
A recommended termination circuit for the LVDS outputs is
shown i
n Figure 71.
S
LVDS
DIFFERENTIAL (COUPLED)
100Ω
100Ω
Figure 71. LVDS Output Termination
See the AN-586 application note at www.analog.com for more
information on LVDS.
S
LVDS
06427-047
Rev. 0 | Page 78 of 80

AD9517-3
V
Ω
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
CMOS CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
The AD9517 provides four clock outputs (OUT4 to OUT7)
that are selectable as either CMOS or LVDS level outputs.
When selected as CMOS, each output becomes a pair of CMOS
outputs, each of which can be individually turned on or off and
set as noninverting or inverting. These outputs are 3.3 V CMOS
compatible.
Whenever single-ended CMOS clocking is used, some of the
lowing general guidelines should be used.
fol
Point-to-point nets should be designed such that a driver has
only one receiver on the net, if possible. This allows for simple
termination schemes and minimizes ringing due to possible
mismatched impedances on the net. Series termination at the
source is generally required to provide transmission line
matching and/or to reduce current transients at the driver.
The value of the resistor is dependent on the board design and
timing requirements (typically 10 Ω to 100 Ω is used). CMOS
outputs are also limited in terms of the capacitive load or trace
length that they can drive. Typically, trace lengths less than
3 inches are recommended to preserve signal rise/fall times and
preserve signal integrity.
60.4
(1.0 INCH)
10Ω
CMOS CMOS
Figure 72. Series Termination of CMOS Output
MICROSTRIP
06427-076
Termination at the far-end of the PCB trace is a second option.
The CMOS outputs of the AD9517 do not supply enough
current to provide a full voltage swing with a low impedance
resistive, far-end termination, as shown in
en
d termination network should match the PCB trace impedance
Figure 73. The far-
and provide the desired switching point. The reduced signal
swing may still meet receiver input requirements in some
applications. This can be useful when driving long trace
lengths on less critical nets.
S
10Ω
CMOS CMOS
Figure 73. CMOS Output with Far-End Termination
50Ω
100Ω
100Ω
6427-077
Because of the limitations of single-ended CMOS clocking,
consider using differential outputs when driving high speed
signals over long traces. The AD9517 offers both LVPECL and
LVDS outputs that are better suited for driving long traces
where the inherent noise immunity of differential signaling
provides superior performance for clocking converters.
Rev. 0 | Page 79 of 80

AD9517-3
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
0.30
0.23
0.18
PIN 1
48
INDICATOR
1
BSC SQ
PIN 1
INDICATOR
7.00
0.60 MAX
37
36
0.60 MAX
1.00
0.85
0.80
12° MAX
SEATING
PLANE
TOP
VIEW
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VKKD-2
6.75
BSC SQ
0.20 REF
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
COPLANARITY
0.08
25
24
EXPOSED
PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
5.50
REF
13
5.25
5.10 SQ
4.95
12
0.25 MIN
Figure 74. 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
7
mm × 7 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
CP-48-1
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD9517-3BCPZ
AD9517-3BCPZ-REEL7
AD9517-3/PCBZ
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
1
1
1
−40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VQ) CP-48-1
−40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VQ) CP-48-1
Evaluation Board
©2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D06427-0-7/07(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 80 of 80
 Loading...
Loading...