Page 1
14-Bit, 80 MSPS, A/D Converter
FEATURES
80 MSPS guaranteed sampling rate
100 dB two-tone SFDR with 69.3 MHz and 70.3 MHz
73.1 dB SNR with 70 MHz input
97 dBc SFDR with 70 MHz input
Excellent linearity
DNL = ±0.4 LSB typical
INL = ±0.6 LSB typical
1.2 W power dissipation
3.3 V and 5 V supply operation
2.0 V p-p differential full-scale input
LVDS outputs (ANSI-644 compatible)
Data format select
Output clock available
APPLICATIONS
Multicarrier, multimode cellular receivers
Antenna array positioning
Power amplifier linearization
Broadband wireless
Radar, infared imaging
Communications instrumentation
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9444 is a 14-bit monolithic, sampling analog-to-digital
converter (ADC) with an on-chip, track-and-hold circuit and is
optimized for power, small size, and ease of use. The product
operates at up to an 80 MSPS conversion rate and is optimized
for multicarrier, multimode receivers, such as those found in
cellular infrastructure equipment.
The ADC requires 3.3 V and 5.0 V power supplies and a low
voltage differential input clock for full performance operation.
No external reference or driver components are required for
many applications. Data outputs are LVDS-compatible (ANSI-
644) or CMOS-compatible and include the means to reduce
the overall current needed for short trace distances.
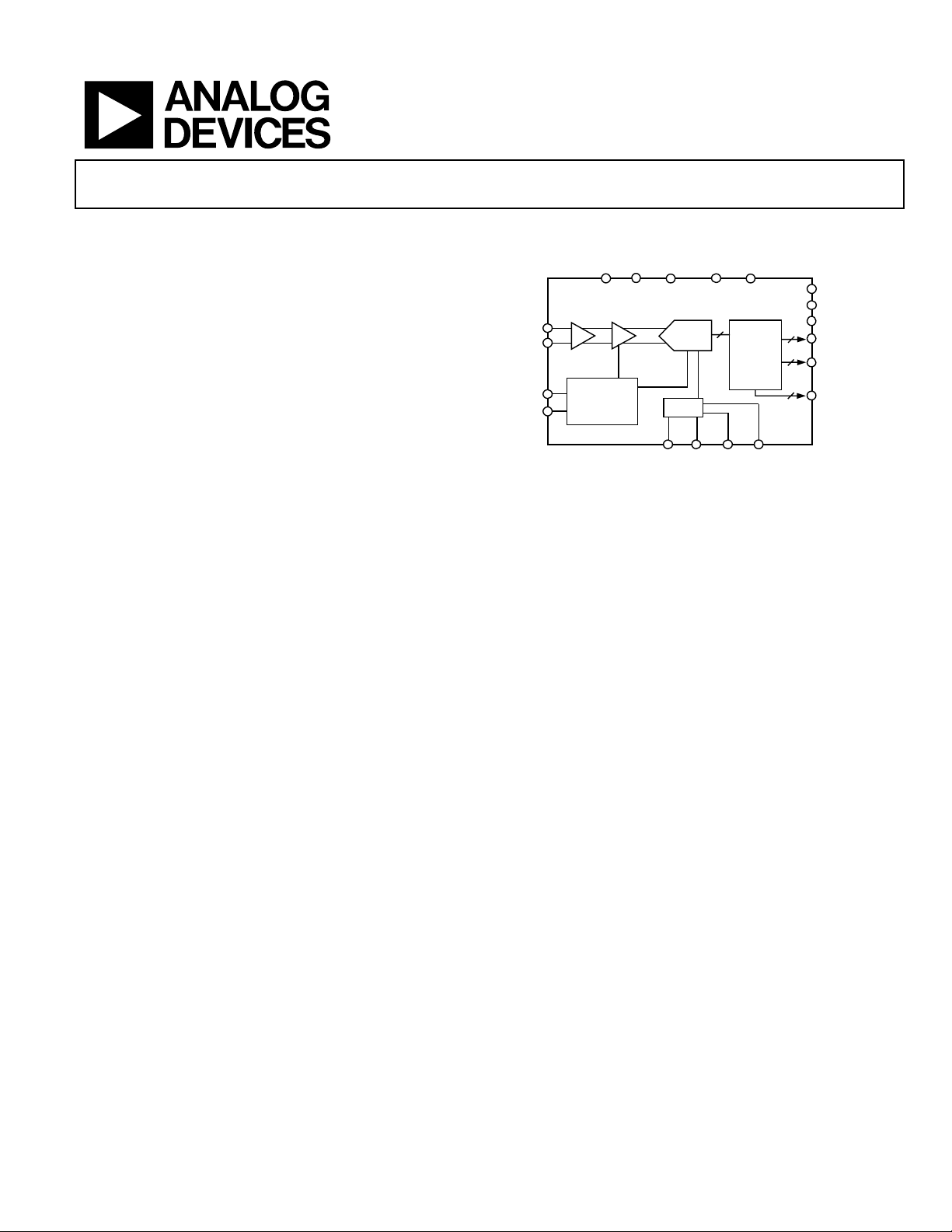
AD9444
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AGND DRGND DRVDD
AVDD1 AVDD2
2
28
2
DFS
DCS MODE
OUTPUT MODE
OR
D13–D0
DCO
AD9444
VIN+
VIN–
CLK+
CLK–
BUFFER
CLOCK
AND TIMING
MANAGEMENT
T/H
VREF
PIPELINE
ADC
REF
Figure 1.
14
CMOS
OR
LVDS
OUTPUT
STAGING
REFBSENSE REFT
Optional features allow users to implement various selectable
operating conditions, including data format select and output
data mode.
The AD9444 is available in a 100-lead surface-mount plastic
package (100-lead TQFP/EP) specified over the industrial
temperature range (−40°C to +85°C).
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. High performance: Outstanding SFDR performance for mul-
ticarrier, multimode 3G and 4G cellular base station
receivers.
2. Ease of use: On-chip reference and track-and-hold. An
output clock simplifies data capture.
3. Packaged in a Pb-free, 100-lead TQFP/EP.
4. Clock DCS maintains overall ADC performance over a wide
range of clock pulse widths.
5. OR (out-of-range) outputs indicate when the signal is beyond
the selected input range.
05089-001
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com
Page 2

AD9444
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DC Specifications ............................................................................. 3
Clock Input Considerations...................................................... 22
AC Specifications.............................................................................. 4
Digital Specifications........................................................................ 5
Switching Specifications .................................................................. 6
Explanation of Test Levels........................................................... 7
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 8
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 8
Definitions of Specifications........................................................... 9
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions .........................10
Equivalent Circuits......................................................................... 14
Typical Performance Characteristics........................................... 15
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 20
Analog Input and Reference Overview ...................................20
REVISION HISTORY
10/04—Revision 0: Initial Version
Power Considerations................................................................ 23
Digital Outputs ........................................................................... 23
Timing ......................................................................................... 23
Operational Mode Selection ..................................................... 23
Evaluation Board ........................................................................ 24
LVDS Evaluation Board Schematics........................................ 25
LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Bill of Materials (BOM) ...... 30
CMOS Evaluation Board Schematics...................................... 32
CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Bill of Materials (BOM)..... 37
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 39
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 39
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 40
Page 3
AD9444
DC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD1 = 3.3 V, AVDD2 = 5.0 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, LVDS mode, sample rate = 80 MSPS, 2 V p-p differential input, internal trimmed
reference (1.0 V mode), A
Table 1.
Parameter Temp Test Level
RESOLUTION Full VI 14 Bits
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes Full VI Guaranteed
Offset Error Full VI 6 ±0.3 6 mV
Gain Error
1
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)2 25°C I −1.3 ±0.6 +1.3 LSB
Full VI −1.7 +1.7 LSB
TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset Error Full V 12 µV/°C
Gain Error Full V 0.002 %FS/°C
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Output Voltage1 Full VI 0.87 1.0 1.13 V
Load Regulation @ 1.0 mA Full V ±2 mV
Reference Input Current (External 1.0 V Reference) Full VI 80 125 µA
INPUT REFERRED NOISE 25°C V 1.0 LSB rms
ANALOG INPUT
Input Span Full V 2 V p-p
Input Common-Mode Voltage Full V 3.5 V
Input Resistance
3
Input Capacitance3 Full V 2.5 pF
POWER SUPPLIES
Supply Voltage
AVDD1 Full IV 3.14 3.3 3.46 V
AVDD2 Full IV 4.75 5.0 5.25 V
DRVDD—LVDS Outputs Full IV 3.0 3.6 V
DRVDD—CMOS Outputs Full IV 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
Supply Current
AVDD1 Full VI 217 240 mA
AVDD22 Full VI 71 80 mA
IDRVDD2—LVDS Outputs Full VI 55 62 mA
IDRVDD2—CMOS Outputs Full V 12 mA
PSRR
Offset Full V 1 mV/V
Gain Full V 0.2 %/V
POWER CONSUMPTION
DC Input—LVDS Outputs Full VI 1.21 1.4 W
DC Input—CMOS Outputs Full V 1.07 W
Sine Wave Input2—LVDS Outputs Full VI 1.25 W
Sine Wave Input2—CMOS Outputs Full V 1.11 W
1
The internal voltage reference is trimmed at final test to minimize the gain error of the AD9444.
2
Measured at the maximum clock rate, fIN = 15 MHz, full-scale sine wave, with a 100 Ω differential termination on each pair of output bits for LVDS output mode and
approximately 5 pF loading on each output bit for CMOS output mode.
3
Input capacitance or resistance refers to the effective impedance between one differential input pin and AGND. Refer to for the equivalent analog input
structure.
= −0.5 dBFS, DCS on, unless other wise note d.
IN
Full VI −3.0 ±0.4 +3.0 % FSR
2
Full VI −0.8 ±0.4 +0.8 LSB
Full V 1 kΩ
AD9444BSVZ-80
Min Typ Max
Figure 6
Unit
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 40
Page 4
AD9444
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD1 = 3.3 V, AVDD2 = 5.0 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, LVDS mode, sample rate = 80 MSPS, 2 V p-p differential input, internal trimmed
reference (1.0 V mode), A
Table 2.
Parameter Temp Test Level
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE-RATIO (SNR)
fIN = 10 MHz 25°C IV 73.0 74.0 dB
Full IV 72.7 dB
fIN = 35 MHz 25°C I 72.4 73.7 dB
Full IV 72.3 dB
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C IV 72.3 73.1 dB
Full IV 72.0 dB
fIN = 100 MHz 25°C V 72.3 dB
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE-AND DISTORTION (SINAD)
fIN = 10 MHz 25°C IV 73.0 74.0 dB
Full IV 72.7 dB
fIN = 35 MHz 25°C I 72.4 73.7 dB
Full IV 72.2 dB
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C IV 72.2 73.1 dB
Full IV 72.0 dB
fIN = 100 MHz 25°C V 72.3 dB
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS (ENOB)
fIN = 10 MHz 25°C V 12.1 Bits
fIN = 35 MHz 25°C V 12.0 Bits
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C V 11.9 Bits
fIN = 100 MHz 25°C V 11.8 Bits
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
fIN = 10 MHz 25°C IV 91 97 dBc
Full IV 87 dBc
fIN = 35 MHz 25°C I 91 97 dBc
Full IV 87 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C IV 90 97 dBc
Full IV 87 dBc
fIN = 100 MHz 25°C V 96 dBc
WORST HARMONIC, SECOND OR THIRD
fIN = 10 MHz 25°C IV −97 −91 dBc
Full IV −87 dBc
fIN = 35 MHz 25°C I −97 −91 dBc
Full IV −87 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C IV −97 −90 dBc
Full IV −87 dBc
fIN = 100 MHz 25°C V −96 dBc
WORST SPUR EXCLUDING SECOND OR HARMONICS
fIN = 10 MHz 25°C IV −102 −93 dBc
Full IV −93 dBc
fIN = 35 MHz 25°C I −103 −93 dBc
Full IV −93 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C IV −102 −93 dBc
Full IV −93 dBc
fIN = 100 MHz 25°C V −99 dBc
TWO-TONE SFDR
fIN = 10.8 MHz @ −7 dBFS, 9.8 MHz @ −7 dBFS 25°C V −102 dBFS
fIN = 70.3 MHz @ −7 dBFS, 69.3 MHz @ −7 dBFS 25°C V −100 dBFS
ANALOG BANDWIDTH Full V 650 MHz
= −0.5 dBFS, DCS on, unless other wise note d.
IN
AD9444BSVZ-80
Min Typ Max
Unit
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 40
Page 5
AD9444
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD1 = 3.3 V, AVDD2 = 5.0 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, R
Table 3.
Parameter Temp Test Level
CMOS LOGIC INPUTS (DFS, DCS MODE, OUTPUT MODE)
High Level Input Voltage Full IV 2.0 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full IV 0.8 V
High Level Input Current Full VI +200 µA
Low Level Input Current Full VI −10 +10 µA
Input Capacitance Full V 2 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUT BITS—CMOS Mode (D0 to D13, OTR)
DRVDD = 3.3 V
High Level Output Voltage Full IV 3.25 V
Low Level Output Voltage Full IV 0.2 V
DIGITAL OUTPUT BITS LVDS Mode (D0 to D13, OTR)
VOD Differential Output Voltage
2
VOS Output Offset Voltage Full VI 1.125 1.375 V
CLOCK INPUTS (CLK+, CLK−)
Differential Input Voltage Full IV 0.2 V
Common-Mode Voltage Full VI 1.3 1.5 1.6 V
Differential Input Resistance Full V 8 10 12 kΩ
Differential Input Capacitance Full V 4 pF
1
Output voltage levels measured with 5 pF load on each output.
2
LVDS R
= 100 Ω.
TERM
= 3.74 kΩ, unless otherwise noted.
LVD SB IA S
1
Full VI 247 545 mV
AD9444BSVZ-80
Min Typ Max
Unit
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 40
Page 6
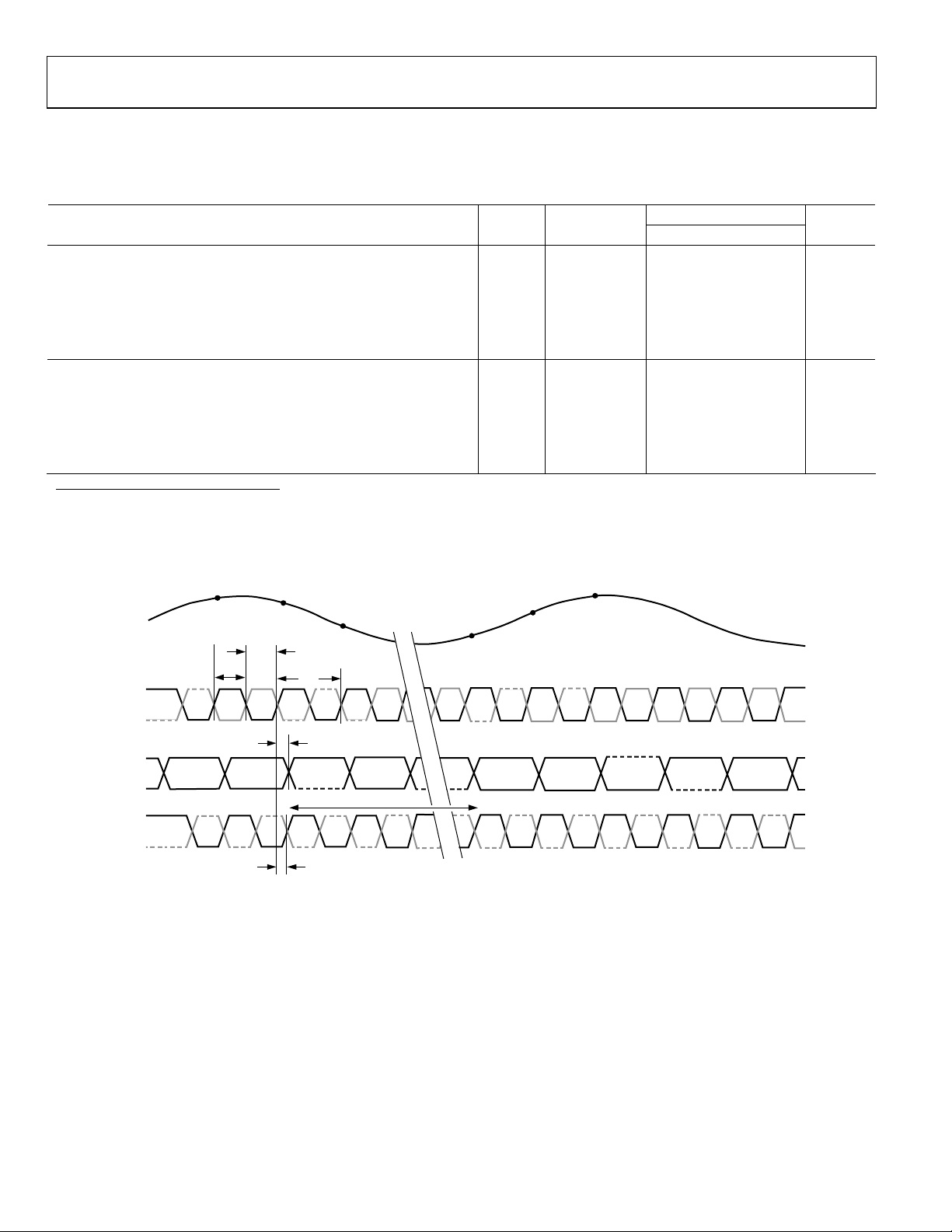
AD9444
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD1 = 3.3 V, AVDD2 = 5.0 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
AD9444BSVZ-80
Parameter Temp Test Level
Min Typ Max
CLOCK INPUT PARAMETERS
Maximum Conversion Rate Full VI 80 MSPS
Minimum Conversion Rate Full V 10 MSPS
CLK Period Full V 12.5 ns
CLK Pulse Width High1 (t
CLK Pulse Width Low1 (t
) Full V 4 ns
CLKH
) Full V 4 ns
CLKL
DATA OUTPUT PARAMETERS
Output Propagation Delay—CMOS (tPD)2 (DX, DCO+) Full IV 3 5.25 8 ns
Output Propagation Delay—LVDS (tPD)3 (DX+, DCO+) Full VI 3 5 7.5 ns
Pipeline Delay (Latency) Full V 12 Cycles
Aperture Delay (tA) Full V ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter, tJ) Full V 0.2 ps rms
1
With duty cycle stabilizer (DCS) enabled.
2
Output propagation delay is measured from clock 50% transition to data 50% transition, with 5 pF load.
3
LVDS R
= 100 Ω. Measured from the 50% point of the rising edge of CLK+ to the 50% point of the data transition.
TERM
Unit
A
CLK+
CLK–
DATA OUT
DCO+
DCO–
N–1
IN
t
CLKH
t
CLKL
t
CPD
N
N+1
1/f
S
t
PD
N–12
12 CLOCK CYCLES
N–11
N
N+1
05089-002
Figure 2. LVDS Mode Timing Diagram
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 40
Page 7
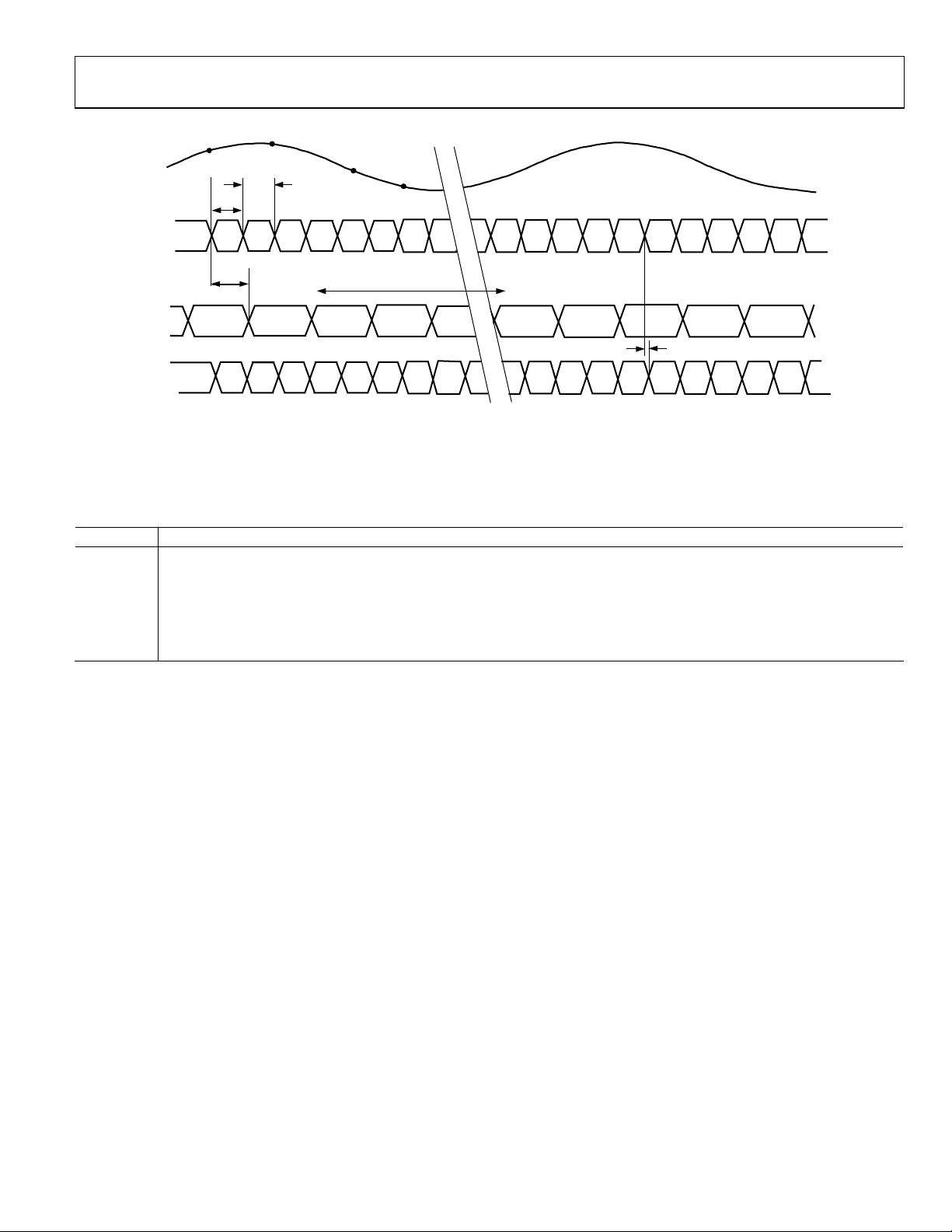
AD9444
N
N+1
t
CLKL
t
PD
N+2
12 CYCLES
VIN
CLK–
CLK+
N–1
t
CLKH
DX
DCO+
DCO–
N-12 N-11 N-1 N
t
DCOPD
Figure 3. CMOS Timing Diagram
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
Test Level Definitions
I 100% production tested.
II 100% production tested at 25°C and sample tested at specified temperatures.
III Sample tested only.
IV Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization testing.
V Parameter is a typical value only.
VI 100% production tested at 25°C and guaranteed by design and characterization for industrial temperature range.
05089-003
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 40
Page 8
AD9444
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5.
With
Parameter
ELECTRICAL
AVDD1 AGND −0.3 +4 V
AVDD2 AGND −0.3 +6 V
DRVDD DGND −0.3 +4 V
AGND DGND −0.3 +0.3 V
AVDD1 DRVDD −4 +4 V
AVDD2 DRVDD −4 +6 V
AVDD2 AVDD1 −4 +6 V
D0 to D13 DGND –0.3 DRVDD + 0.3 V
CLK, MODE AGND –0.3 AVDD1 + 0.3 V
VIN+, VIN− AGND –0.3 AVDD2 + 0.3 V
VREF AGND –0.3 AVDD1 + 0.3 V
SENSE AGND –0.3 AVDD1 + 0.3 V
REFT, REFB AGND –0.3 AVDD1 + 0.3 V
ENVIRONMENTAL
Storage Temperature –65 +125 °C
Operating Temperature Range –40 +85 °C
Lead Temperature Range
(Soldering 10 sec)
Junction Temperature 150 °C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
Respect to
Min Max Unit
300 °C
Thermal Resistance
The heat sink of the AD9444 package must be soldered to
ground.
Table 6.
Package Type θ
100-Lead TQFP/EP 19.8 8.3 2 °C/W
JA
θ
JB
θ
JC
Unit
Typical θ
= 19.8°C/W (heat-sink soldered) for multilayer
JA
board in still air.
Typical θ
= 8.3°C/W (heat-sink soldered) for multilayer board
JB
in still air.
Typical θ
= 2°C/W (junction to exposed heat sink) represents
JC
the thermal resistance through heat-sink path.
Airflow increases heat dissipation effectively reducing θ
. Also,
JA
more metal directly in contact with the package leads, from
metal traces, through holes, ground, and power planes, reduces
. It is required that the exposed heat sink be soldered to
the θ
JA
the ground plane.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the
human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic
discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of
functionality.
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 40
Page 9

AD9444
DEFINITIONS OF SPECIFICATIONS
Analog Bandwidth (Full Power Bandwidth)
The analog input frequency at which the spectral power of the
fundamental frequency (as determined by the FFT analysis) is
reduced by 3 dB.
Minimum Conversion Rate
The clock rate at which the SNR of the lowest analog signal
frequency drops by no more than 3 dB below the guaranteed
limit.
Aperture Delay (t
)
A
The delay between the 50% point of the rising edge of the clock
and the instant at which the analog input is sampled.
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter, t
)
J
The sample-to-sample variation in aperture delay.
Clock Pulse Width and Duty Cycle
Pulse width high is the minimum amount of time that the
clock pulse should be left in the Logic 1 state to achieve rated
performance. Pulse width low is the minimum time the clock
pulse should be left in the low state. At a given clock rate, these
specifications define an acceptable clock duty cycle.
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL, No Missing Codes)
An ideal ADC exhibits code transitions that are exactly 1 LSB
apart. DNL is the deviation from this ideal value. Guaranteed no
missing codes to 14-bit resolution indicates that all 16384 codes
must be present over all operating ranges.
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
The effective number of bits for a sine wave input at a given
input frequency can be calculated directly from its measured
SINAD using the following formula
()
SINAD
=
ENOB
1.76−
6.02
Gain Error
The first code transition should occur at an analog value ½ LSB
above negative full scale. The last transition should occur at an
analog value 1 ½ LSB below the positive full scale. Gain error is
the deviation of the actual difference between first and last code
transitions and the ideal difference between first and last code
transitions.
Offset Error
The major carry transition should occur for an analog value
½ LSB below VIN+ = VIN−. Offset error is defined as the
deviation of the actual transition from that point.
Out-of-Range Recovery Time
The time it takes for the ADC to reacquire the analog input
after a transition from 10% above positive full scale to 10%
above negative full scale, or from 10% below negative full scale
to 10% below positive full scale.
Output Propagation Delay (tPD)
The delay between the clock rising edge and the time when all
bits are within valid logic levels.
Power-Supply Rejection Ratio
The change in full scale from the value with the supply at the
minimum limit to the value with the supply at its maximum limit.
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion (SINAD)
The ratio of the rms input signal amplitude to the rms value of
the sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, including harmonics but excluding dc.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
The ratio of the rms input signal amplitude to the rms value of
the sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, excluding the first six harmonics and dc.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the
peak spurious spectral component. The peak spurious component may or may not be a harmonic. May be reported in dBc
(i.e., degrades as signal level is lowered) or dBFS (always related
back to converter full scale).
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
The deviation of each individual code from a line drawn from
negative full scale through positive full scale. The point used as
negative full scale occurs ½ LSB before the first code transition.
Positive full scale is defined as a level 1 ½ LSBs beyond the last
code transition. The deviation is measured from the middle of
each particular code to the true straight line.
Maximum Conversion Rate
The clock rate at which parametric testing is performed.
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 40
Temperature Drift
The temperature drift for offset error and gain error specifies
the maximum change from the initial (25°C) value to the value
at T
MIN
or T
MAX
.
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
The ratio of the rms input signal amplitude to the rms value of
the sum of the first six harmonic components.
Two -Ton e SFDR
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value
of the peak spurious component. The peak spurious component
may or may not be an IMD product.
Page 10
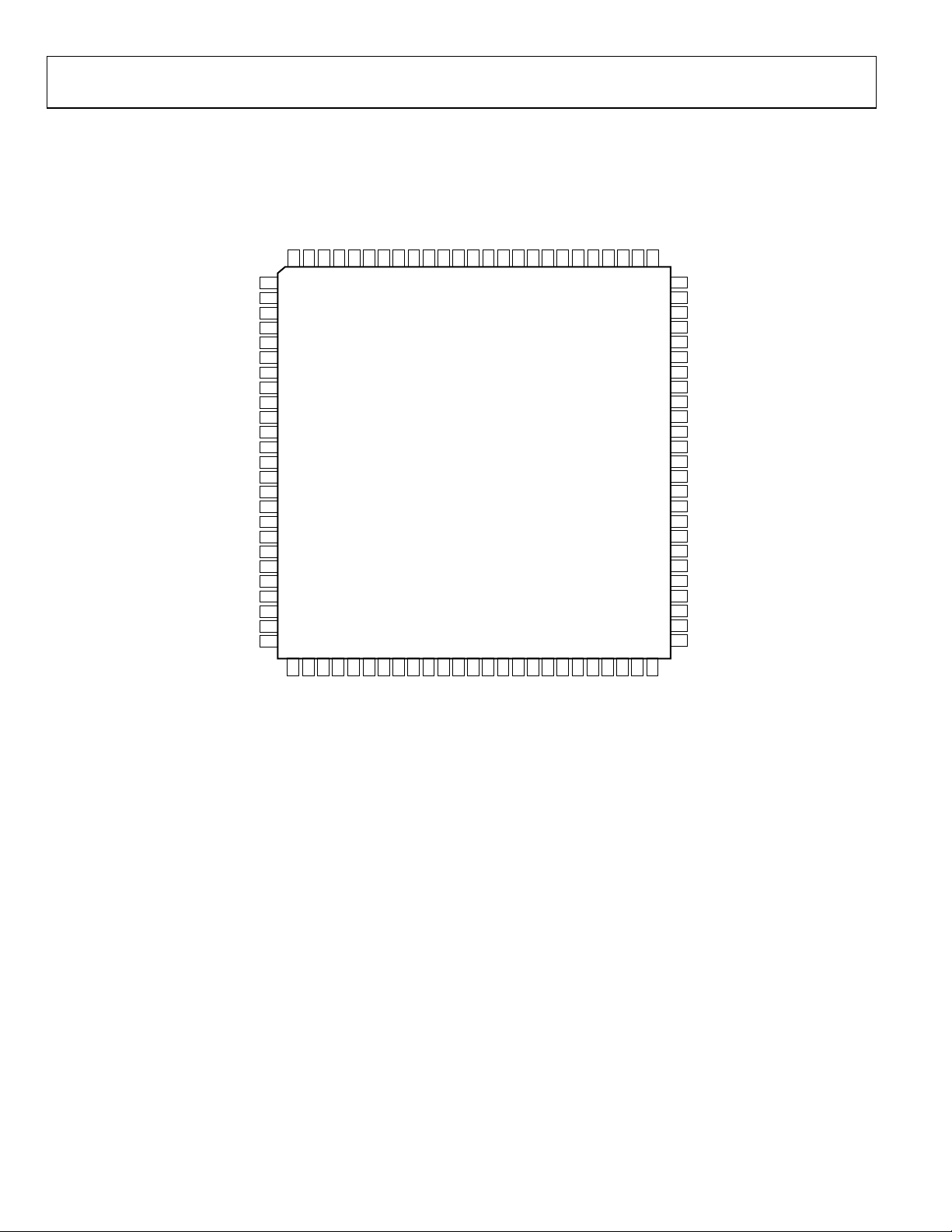
AD9444
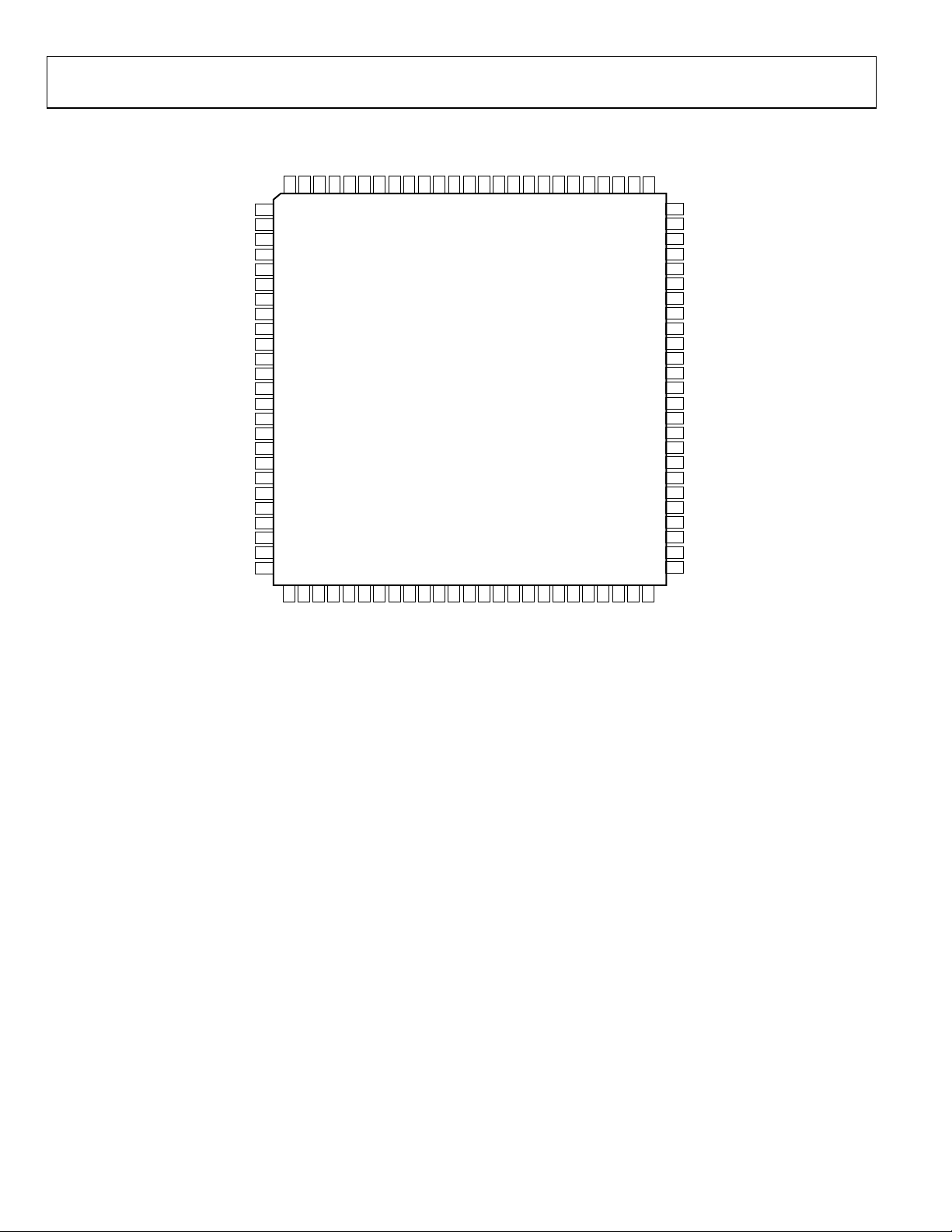
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
DCS MODE
AGND
AVDD1
AGND
AGND
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AGND
AVDD1
AGND
OR+
OR–
AVDD1
DNC
DNC
DNC
OUTPUT MODE
DFS
LVDSBIAS
AVDD1
AVDD1
SENSE
VREF
AGND
REFT
REFB
AGND
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD2
AGND
VIN+
VIN–
AGND
AVDD1
AVDD1
99989796959493
100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
929190
89
88
AD9444
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
8786858483
DRVDD
DRGND
82
D13+ (MSB)
D13–79D12+78D12–77D11+76D11–
81
80
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
DRVDD
DRGND
D10+
D10–
D9+
D9–
D8+
D8–
DRGND
D7+
D7–
DCO+
DCO–
DRVDD
DRGND
D6+
D6–
D5+
D5–
D4+
D4–
DRVDD
DRGND
D3+
D3–
2627282930
AVDD1
AVDD1
DNC = DO NOT CONNECT
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD2
31
AVDD2
32
C1
AGND
33
343536
AVDD1
AVDD1
CLK+
37
39
40
38
414243
4445464748
D1–
D0+
CLK–
AVDD1
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD1
AVDD1
D1+
(LSB) D0–
DRVDD
49
D2–
DRGND
50
D2+
05089-004
Figure 4. 100-Lead TQFP/EP Pin Configuration in LVDS Mode
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 40
Page 11
AD9444
Table 7. Pin Function Descriptions—100-Lead TQFP/EP in LVDS Mode
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1, 8 to 9,
16 to 18,
24 to 27,
34 to 35, 38,
41 to 42, 87,
89 to 95, 98
2 to 4 DNC
5
6 DFS
7 LVDSBIAS
10 SENSE
11 VREF
12, 15, 20,
23, 32, 86,
88, 96 to 97,
99, Exposed
Heat Sink
13 REFT
14 REFB
19, 28 to 31,
39 to 40
21 VIN+ Analog Input—True.
22 VIN− Analog Input—Complement.
33 C1
36 CLK+ Clock Input—True.
37 CLK− Clock Input—Complement.
43 D0− (LSB)
AVDD1 3.3 V (±5%) Analog Supply.
Do Not Connect. These pins
should float.
OUTPUT
MODE
AGND
AVDD2 5.0 V Analog Supply (±5%).
CMOS Compatible Output Logic
Mode Control Pin. OUTPUT MODE
= 0 for CMOS mode, and OUTPUT
MODE = 1 (AVDD1) for LVDS
outputs.
Data Format Select Pin. CMOS
control pin that determines the
format of the output data. DFS =
high (AVDD1) for twos complement, DFS = low (ground) for
offset binary format.
Set Pin for LVDS Output Current.
Place 3.7 kΩ resistor terminated to
DRGND.
Reference Mode Selection.
Connect to AGND for internal 1 V
reference, and connect to AVDD2
for external reference.
1.0 V Reference I/O—Function
Dependent on SENSE. Decouple
to ground with 0.1 µF and 10 µF
capacitors.
Analog Ground. The exposed
heat sink on the bottom of the
package must be connected to
AGND.
Differential Reference Output.
Decoupled to ground with 0.1 µF
capacitor and to REFB (Pin 14) with
0.1 µF and 10 µF capacitors.
Differential Reference Output.
Decoupled to ground with a 0.1 µF
capacitor and to REFT (Pin 13) with
0.1 µF and 10 µF capacitors.
Internal Bypass Node. Connect a
0.1 µF capacitor from this pin
to AGND.
D0 Complement Output Bit
(LVDS Levels).
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
44 D0+ D0 True Output Bit.
45 D1− D1 Complement Output Bit.
46 D1+ D1 True Output Bit.
47, 54, 62,
75, 83
48, 53, 61,
67, 74, 82
49 D2− D2 Complement Output Bit.
50 D2+ D2 True Output Bit.
51 D3− D3 Complement Output Bit.
52 D3+ D3 True Output Bit.
55 D4− D4 Complement Output Bit.
56 D4+ D4 True Output Bit.
57 D5− D5 Complement Output Bit.
58 D5+ D5 True Output Bit.
59 D6− D6 Complement Output Bit.
60 D6+ D6 True Output Bit.
63 DCO− Data Clock Output—Complement.
64 DCO+ Data Clock Output—True.
65 D7− D7 Complement Output Bit.
66 D7+ D7 True Output Bit.
68 D8− D8 Complement Output Bit.
69 D8+ D8 True Output Bit.
70 D9− D9 Complement Output Bit.
71 D9+ D9 True Output Bit.
72 D10− D10 Complement Output Bit.
73 D10+ D10 True Output Bit.
76 D11− D11 Complement Output Bit.
77 D11+ D11 True Output Bit.
78 D12− D12 Complement Output Bit.
79 D12+ D12 True Output Bit.
80 D13− D13 Complement Output.
81 D13+ (MSB) D13 True Output Bit.
84 OR−
85 OR+ Out-of-Range True Output Bit.
100 DCS MODE
DRVDD
DRGND Digital Ground.
3.3 V Digital Output Supply
(3.0 V to 3.6 V).
Out-of-Range Complement
Output Bit.
Clock Duty Cycle Stabilizer (DCS)
Control Pin, CMOS-Compatible.
DCS = low (AGND) to enable DCS
(recommended). DCS = high
(AVDD1) to disable DCS.
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 40
Page 12
AD9444
AVDD1
DNC
DNC
DNC
OUTPUT MODE
DFS
DNC
AVDD1
AVDD1
SENSE
VREF
AGND
REFT
REFB
AGND
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD2
AGND
VIN+
VIN–
AGND
AVDD1
AVDD1
DCS MODE
AGND
AVDD1
AGND
AGND
99989796959493
100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
929190
AVDD1
AVDD1
AGND
89
88
AD9444
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
AVDD1
AGNDORD13 (MSB)
8786858483
DRVDD
DRGND
D12
81
82
D11
80
D10D9D8
797877
D7
76
75
DRVDD
74
DRGND
73
D6
72
D5
71
D4
70
D3
69
D2
68
D1
67
DRGND
66
D0 (LSB)
65
DNC
64
DCO+
63
DCO–
62
DRVDD
61
DRGND
60
DNC
59
DNC
58
DNC
57
DNC
56
DNC
DNC
55
54
DRVDD
53
DRGND
52
DNC
51
DNC
2627282930
AVDD1
AVDD1
DNC = DO NOT CONNECT
Figure 5. 100-Lead TQFP/EP Pin Configuration in CMOS Mode
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD2
31
AVDD2
32
AGND
33
C1
343536
AVDD1
AVDD1
CLK+
37
CLK–
38
AVDD1
39
AVDD2
40
AVDD2
414243
AVDD1
AVDD1
4445464748
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DRVDD
49
DNC
DRGND
50
DNC
05089-005
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 40
Page 13

AD9444
Table 8. Pin Function Descriptions—100-Lead TQFP/EP in CMOS Mode
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1, 8 to 9, 16 to 18,
24 to 27, 34 to 35,
38, 41 to 42, 87,
89 to 95, 98
2 to 4, 7,
43 to 46, 49 to 52,
55 to 60, 65
5
6 DFS
10 SENSE
11 VREF
12, 15, 20, 23,
32, 86, 88, 96 to
97, 99, Exposed
Heat Sink
13 REFT
14 REFB
19, 28 to 31,
39 to 40
21 VIN+ Analog Input—True.
22 VIN− Analog Input—Complement.
AVDD1 3.3 V (±5%) Analog Supply.
DNC
OUTPUT
MODE
AGND
AVDD2 5.0 V Analog Supply (±5%).
Do Not Connect. These
pins should float.
CMOS Compatible Output
Logic Mode Control Pin.
OUTPUT MODE = 0 for CMOS
mode, and OUTPUT MODE =
1 (AVDD1) for LVDS outputs.
Data Format Select Pin.
CMOS control pin that determines the format of the
output data. DFS = high
(AVDD1) for twos complement, DFS = low (ground) for
offset binary format.
Reference Mode Selection.
Connect to AGND for internal
1 V reference, and connect to
AVDD2 for external reference.
1.0 V Reference I/O—
Function Dependent on
SENSE. Decouple to ground
with 0.1 µF and 10 µF
capacitors.
Analog Ground. The exposed
heat sink on the bottom of
the package must be
connected to AGND.
Differential Reference Output. Decoupled to ground
with 0.1 µF capacitor and to
REFB (Pin 14) with 0.1 µF and
10 µF capacitors.
Differential Reference Output. Decoupled to ground
with a 0.1 µF capacitor and to
REFT (Pin 13) with 0.1 µF and
10 µF capacitors.
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
33 C1
36 CLK+ Clock Input—True.
37 CLK− Clock Input—Complement.
47, 54, 62,
75, 83
48, 53, 61,
67, 74, 82
63 DCO−
64 DCO+
66 D0 (LSB)
68 D1 D1 Output Bit.
69 D2 D2 Output Bit.
70 D3 D3 Output Bit.
71 D4 D4 Output Bit.
72 D5 D5 Output Bit.
73 D6 D6 Output Bit.
76 D7 D7 Output Bit.
77 D8 D8 Output Bit.
78 D9 D9 Output Bit.
79 D10 D10 Output Bit.
80 D11 D11 Output Bit.
81 D12 D12 Output Bit.
84 D13 (MSB) D13 Output Bit.
85 OR Out-of-Range Output.
100 DCS MODE
DRVDD
DRGND Digital Ground.
Internal Bypass Node.
Connect a 0.1 µF capacitor
from this pin to AGND.
3.3 V Digital Output
Supply (2.5V to 3.6 V).
Data Clock Output—
Complement (CMOS Levels).
Data Clock Output—
True.
D0 Output Bit (LSB)
(CMOS Levels).
Clock Duty Cycle Stabilizer
(DCS) Control Pin, CMOSCompatible. DCS = low
(AGND) to enable DCS
(recommended). DCS =
high (AVDD1) to disable DCS.
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 40
Page 14

AD9444
EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS
AVDD2
VIN+
AVDD2
2.5pF
3.5V
X1
DRVDD
1k
Ω
DX
SHA
1k
AVDD2
VIN–
2.5pF
Ω
Figure 6. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
DRVDD DRVDD
I
LVDSOUT
K
1.2V
LVDSBIAS
3.74k
Ω
Figure 7. Equivalent LVDS BIAS Circuit
DRVDD
V
DX– DX+
V
V
V
05089-008
Figure 8. Equivalent LVDS Digital Output Circuit
05089-006
05089-007
05089-009
Figure 9. Equivalent CMOS Digital Output Circuit
VDD
DCS MODE,
OUTPUT MODE,
DFS
30k
Ω
05089-010
Figure 10. Equivalent Digital Input Circuit,
DFS, DCS MODE, OUTPUT MODE
AVDD2
Ω
CLK+
10k
12k
150
Ω
Ω
12k
150
Ω
Ω
10k
Ω
CLK–
05089-011
Figure 11. Equivalent Sample Clock Input Circuit
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 40
Page 15

AD9444
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
AVDD1 = 3.3 V, AVDD2 = 5.0 V, DRVDD = 3.3 V, sample rate = 80 MSPS, LVDS mode, DCS enabled, TA = 25°C, 2 V p-p differential
input, AIN = −0.5 dBFS, internal trimmed reference (nominal VREF = 1.0 V), unless otherwise noted.
–20
–40
0
80MSPS
10.1MHz @ –0.5dBFS
SNR: 73.9dB
ENOB: 12.0BITS
SFDR: 97dBc
–20
–40
0
80MSPS
100.3MHz @ –0.5dBFS
SNR: 72.3dB
ENOB: 11.8BITS
SFDR: 96dBc
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 12. 64K Point Single-Tone FFT/80 MSPS/10.1 MHz
0
80MSPS
30.3MHz @ –0.5dBFS
SNR: 74.0dB
–20
ENOB: 12.1BITS
SFDR: 95dBc
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 13. 64K Point Single-Tone FFT/80 MSPS/30.3 MHz
05089-012
05089-013
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 15. 64K Point Single-Tone FFT/80 MSPS/100 MHz
0
80MSPS
125MHz @ –0.5dBFS
SNR: 71.2dB
–20
ENOB: 11.6BITS
SFDR: 91dBc
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 16. 64K Point Single-Tone FFT/80 MSPS/125 MHz
05089-015
05089-016
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
80MSPS
70.3MHz @ –0.5dBFS
SNR: 73.3dB
ENOB: 11.9BITS
SFDR: 100dBc
Figure 14. 64K Point Single-Tone FFT/80 MSPS/70 MHz
05089-014
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 40
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
80MSPS
151MHz @ –0.5dBFS
SNR: 71.1dB
ENOB: 11.5BITS
SFDR: 87dBc
Figure 17. 64K Point Single-Tone FFT/80 MSPS/151 MHz
05089-017
Page 16

AD9444
75
74
73
72
71
70
(dB)
69
68
67
66
65
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
Figure 18. SNR vs. Analog Input Frequency, 80 MSPS/LVDS Mode
SNR dB @ –40°C
SNR dB @ +25°C
SNR dB @ +85°C
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
05089-018
75
74
73
72
SNR dB @ +25°C
71
70
(dB)
69
68
67
66
65
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
SNR dB @ –40°C
SNR dB @ +85°C
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 21. SNR vs. Analog Input Frequency, 80 MSPS/CMOS Mode
05089-021
105
100
(dB)
SFDR dBc @ +85°C
95
90
85
80
75
70
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
SFDR dBc @ –40°C
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
SFDR dBc @ +25°C
Figure 19. SFDR vs. Analog Input Frequency, 80 MSPS/LVDS Mode
120
110
100
90
80
70
(dB)
60
50
40
30
20
10
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
THIRD –dBFS
SFDR –dBFS
ANALOG INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBc)
SECOND –dBFS
SECOND –dBc
THIRD –dBc
SFDR –dBFS
Figure 20. Single-Tone SFDR/Second/Third vs.
Analog Input Level, 80 MSPS, A
= 30.3 MHz
IN
05089-019
05089-020
105
SFDR dBc @ +85°C
100
95
90
SFDR dBc @ –40°C
(dB)
85
80
75
70
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
SFDR dBc @ +25°C
Figure 22. SFDR vs. Analog Input Frequency, 80 MSPS/CMOS Mode
120
110
100
90
80
70
(dB)
60
50
40
30
20
10
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
SFDR –dBFS
THIRD –dBc
ANALOG INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBc)
SECOND –dBFS
SECOND –dBc
THIRD –dBFS
SFDR –dBFS
Figure 23. Single-Tone SFDR/Second/Third vs.
Analog Input Level 80 MSPS, A
= 70.30 MHz
IN
05089-022
05089-023
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 40
Page 17

AD9444
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SFDR: 102dBFS
Figure 24. 32K Point Two-Tone FFT 80 MSPS/9.8 MHz/10.8 MHz
05089-024
0
–10
–20
–30
SFDR (dBc)
–40
–50
IMD (dBFS)
–100
–110
–120
–60
–70
–80
–90
WORST THIRD-ORDER IMD (dBc)
–110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
90dBFS REFERENCE LINE
SFDR (dBFS)
WORST THIRD-ORDER IMD (dBFS)
ANALOG INPUT LEVEL (dBFS)
Figure 27. Two-Tone SFDR vs. Analog Input Level, A
= 9.8 MHz/10.8 MHz
IN
05089-027
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–90
–100
–110
–120
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SFDR: –100dBFS
Figure 25. 32K Point Two-Tone FFT 80 MSPS/69.3 MHz/70.3 MHz
100
95
90
85
SFDR (dB)
80
05089-025
0
–10
–20
–30
SFDR (dBc)
–40
–50
–60
WORST THIRD-ORDER IMD (dBc)
–70
–80
SFDR AND IMD3 (dB)
–90
–100
–110
–120
–110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
90dBFS REFERENCE LINE
SFDR (dBFS)
WORST THIRD-ORDER IMD (dBFS)
ANALOG INPUT LEVEL (dBFS)
Figure 28. Two-Tone SFDR vs. Analog Input Level, A
100
95
90
85
SFDR (dB)
80
= 69.3 MHz/70.3 MHz
IN
05089-028
75
70
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Figure 26. SFDR vs. Sample Rate, V
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
= 10.3 MHz @ −0.5 dBFS
IN
05089-026
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 40
75
70
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Figure 29. SFDR vs. Sample Rate, V
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
= 70.3 MHz @ −0.5 dBFS
IN
05089-029
Page 18

AD9444
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
0 7.68 15.36 23.04 30.72
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 30. 64K FFT, 61.44 MSPS, 4 @ WCDMA, IF = 46.08 MHz
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 31. NPR, 80 MSPS/18 MHz Notch
61.44MSPS
TOTAL INPUT SIGNAL
POWER: –30dBFS
NPR: 63.1dB
05089-030
05089–031
12000
10000
8000
6000
FREQUENCY
4000
2000
0
8179 8180 8181 8182 8183 8184 8185 8186 8187
B
IN
Figure 33. Ground Input Histogram
80 MSPS, VIN+ = VIN−, 32K Samples
250
230
210
190
170
150
130
CURRENT (mA)
110
90
70
50
DRVDD (3.3V)
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130
Figure 34. I
AVDD1 (3.3V)
AVDD2 (5.0V)
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
vs. Sample Rate, AIN = 10.3 MHz @ −0.5 dBFS
SUPPLY
05089-033
05089-034
105
SFDR - DCS ON (dBFS)
100
95
90
dB
85
80
75
SNR - DCS ON (dB)
70
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
SFDR - DCS OFF (dBFS)
SNR - DCS OFF (dB)
CLOCK DUTY CYCLE (%)
Figure 32. Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Clock Duty Cycle,
= 80 MSPS, 10.3 MHz @ −0.5 dBFS
F
SAMPLE
05089-032
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 40
100
95
90
85
80
(dB)
75
70
65
60
2.5 2.7 2.9 3.1 3.3 3.5 3.7 3.9
SFDR (dBc)
SNR (dB)
V
COMMON-MODE (V)
IN
Figure 35. Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs.
Common-Mode Voltage 80 MSPS/10.3 MHz
V
IN
05089-035
Page 19

AD9444
0.961
0.960
0.959
0.958
0.957
0.956
0.955
0.954
REFERENCE VOLTAGE (V)
0.953
0.952
0.951
–20 0 20 40 60 80
–40
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 36. VREF vs. Temperature
05089-036
GAIN (%FS)
0.2
0.1
–0.1
–0.2
–0.3
–0.4
–0.5
0
–20 0 20 40 60 80
–40
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 38. Gain vs. Temperature
05089-038
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
–0.25
DNL ERROR (LSB)
–0.50
–0.75
–1.00
0 2048 4096 6144 8192 10240 12288 14336 16384
OUTPUT CODE
Figure 37. DNL Error vs. Output Code, 80 MSPS, A
= 15 MHz
IN
05089-037
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
–0.25
INL ERROR (LSB)
–0.50
–0.75
–1.00
0 2048 4096 6144 8192 10240 12288 14336 16384
OUTPUT CODE
Figure 39. INL Error vs. Output Code, 80 MSPS, A
= 15 MHz
IN
05089-039
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 40
Page 20

AD9444
THEORY OF OPERATION
The AD9444 architecture is optimized for high speed and ease
of use. The analog inputs drive an integrated, high bandwidth,
track-and-hold circuit that samples the signal prior to quantization by the 14-bit pipeline ADC core. The device includes an
on-board reference and input logic that accepts TTL, CMOS, or
LVPECL levels. The digital output logic levels are user selectable
as standard 3 V CMOS or LVDS (ANSI-644 compatible) via the
OUTPUT MODE pin.
ANALOG INPUT AND REFERENCE OVERVIEW
A stable and accurate 0.5 V voltage reference is built into the
AD9444. The input range can be adjusted by varying the reference voltage applied to the AD9444, using either the internal
reference or an externally applied reference voltage. The input
span of the ADC tracks reference voltage changes linearly. The
various reference modes are described in the next few sections.
Internal Reference Connection
A comparator within the AD9444 detects the potential at the
SENSE pin and configures the reference into four possible
states, which are summarized in Table 9. If SENSE is grounded,
the reference amplifier switch is connected to the internal resistor divider (see Figure 40), setting VREF to ~1 V. Connecting
the SENSE pin to VREF switches the reference amplifier output
to the SENSE pin, completing the loop and providing a ~0.5 V
reference output. If a resistor divider is connected, as shown in
Figure 41, the switch again sets to the SENSE pin. This puts the
reference amplifier in a noninverting mode with the VREF
output defined as
R2
VREF 10.5
⎛
⎜
⎝
In all reference configurations, REFT and REFB drive the A/D
conversion core and establish its input span. The input range of
the ADC always equals twice the voltage at the reference pin for
either an internal or an external reference.
⎞
+×=
⎟
R1
⎠
Internal Reference Trim
The internal reference voltage is trimmed during the production test to adjust the gain (analog input voltage range) of the
AD9444. Therefore, there is little advantage to the user supplying an external voltage reference to the AD9444. The gain trim
is performed with the AD9444’s input range set to 2 V p-p
nominal (SENSE connected to AGND). Because of this trim,
and because the 2 V p-p analog input range provides maximum
ac performance, there is little benefit to using analog input
ranges < 2 V p-p. Users are cautioned that the differential
nonlinearity of the ADC varies with the reference voltage.
Configurations that use < 2 V p-p may exhibit missing codes
and, therefore, degraded noise and distortion performance.
VIN+
10µF+0.1µF
10µF+0.1µF
VIN–
ADC
CORE
VREF
SELECT
LOGIC
SENSE
0.5V
AD9444
Figure 40. Internal Reference Configuration
VIN+
VIN–
VREF
R2
SENSE
SELECT
LOGIC
ADC
CORE
REFT
0.1µF
0.1µF 10µF
REFB
0.1µF
REFT
0.1µF
0.1µF 10µF
REFB
0.1µF
+
+
05089-043
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 40
R1
Figure 41. Programmable Reference Configuration
0.5V
AD9444
05089-042
Page 21

AD9444
Table 9. Reference Configuration Summary
Selected Mode SENSE Voltage Resulting VREF (V) Resulting Differential Span (V p-p)
External Reference AVDD N/A 2 × External Reference
Internal Fixed Reference VREF 0.5 1.0
Programmable Reference 0.2 V to VREF
R2
⎛
⎜
⎝
⎞
(See Figure 41)
+×
10.5
⎟
R1
⎠
Internal Fixed Reference AGND to 0.2 V 1.0 2.0
External Reference Operation
The AD9444’s internal reference is trimmed to enhance the gain
accuracy of the ADC. An external reference may be more stable
over temperature, but the gain of the ADC is not likely to be
VIN+
improved. Figure 36 shows the typical drift characteristics of the
internal reference in both 1 V and 0.5 V modes.
When the SENSE pin is tied to AVDD, the internal reference is
disabled, allowing the use of an external reference. An internal
reference buffer loads the external reference with an equivalent
7 kΩ load. The internal buffer still generates the positive and
1Vp-p
VIN–
DIGITAL OUT = ALL 1s DIGITAL OUT = ALL 0s
negative full-scale references, REFT and REFB, for the ADC
core. The input span is always twice the value of the reference
voltage; therefore, the external reference must be limited to a
maximum of 1 V.
Analog Inputs
As with most new high speed, high dynamic range ADCs, the
analog input to the AD9444 is differential. Differential inputs
improve on-chip performance as signals are processed through
attenuation and gain stages. Most of the improvement is a result
of differential analog stages having high rejection of even-order
harmonics. There are also benefits at the PCB level. First,
differential inputs have high common-mode rejection of stray
signals, such as ground and power noise. Second, they provide
good rejection of common-mode signals, such as local oscillator
feedthrough. The specified noise and distortion of the AD9444
cannot be realized with a single-ended analog input, so such
configurations are discouraged. Contact ADI for recommendations of other 14-bit ADCs that support single-ended analog
input configurations.
With the 1 V reference (nominal value, see the Internal Reference Trim section), the differential input range of the AD9444’s
analog input is nominally 2 V p-p or 1 V p-p on each input
(VIN+ or VIN−).
The AD9444 analog input voltage range is offset from ground
by 3.5 V. Each analog input connects through a 1 kΩ resistor to
the 3.5 V bias voltage and to the input of a differential buffer.
The internal bias network on the input properly biases the
buffer for maximum linearity and range (see the Equivalent
Circuits section). Therefore, the analog source driving the
AD9444 should be ac-coupled to the input pins. The recommended method for driving the analog input of the AD9444 is
to use an RF transformer to convert single-ended signals to
differential (see Figure 44). Series resistors between the output
of the transformer and the AD9444 analog inputs help isolate
the analog input source from switching transients caused by the
internal sample-and-hold circuit. The series resistors, along with
the 1 kΩ resisters connected to the internal 3.5 V bias, must be
considered in impedance matching the transformers input. For
example, if R
with a 1:1 impedance ratio transformer, the input would match
a 50 Ω source with a full-scale drive of 10.0 dBm. The 50 Ω
impedance matching can also be incorporated on the secondary
side of the transformer, as shown in the evaluation board schematic (see Figure 47 and Figure 59).
Figure 42. Differential Analog Input Range for VREF = 1 V
ANALOG
INPUT
SIGNAL
Figure 43. Transformer-Coupled Analog Input Circuit
2 × VREF
3.5V
were set to 51 Ω and RS were set to 33 Ω, along
T
0.1
R
S
AIN
AD9444
R
S
µF
AIN
05089-046
R
T
ADT1–1WT
05089-045
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 40
Page 22

AD9444
CLOCK INPUT CONSIDERATIONS
Any high speed ADC is extremely sensitive to the quality of the
sampling clock provided by the user. A track-and-hold circuit is
essentially a mixer, and any noise, distortion, or timing jitter on
the clock is combined with the desired signal at the A/D output.
For that reason, considerable care was taken in the design of the
clock inputs of the AD9444, and the user is advised to give
careful thought to the clock source.
Typical high speed ADCs use both clock edges to generate a
variety of internal timing signals and, as a result, may be
sensitive to the clock duty cycle. Commonly a 5% tolerance is
required on the clock duty cycle to maintain dynamic performance characteristics. The AD9444 contains a clock duty cycle
stabilizer (DCS) that retimes the nonsampling edge, providing
an internal clock signal with a nominal 50% duty cycle. As
shown in Figure 32, noise and distortion performance are nearly
flat for a 30% to 70% duty cycle with the DCS enabled. The DCS
circuit locks to the rising edge of CLK+ and optimizes timing
internally. This allows for a wide range of input duty cycles at
the input without degrading performance. Jitter in the rising
edge of the input is still of paramount concern and is not reduced by the internal stabilization circuit. The duty cycle control loop does not function for clock rates less than 30 MHz
nominally. The loop has a time constant associated with it that
needs to be considered in applications where the clock rate can
change dynamically, which requires a wait time of 1.5 µs to 5 µs
after a dynamic clock frequency increase (or decrease) before
the DCS loop is relocked to the input signal. During the time
period the loop is not locked, the DCS loop is bypassed, and the
internal device timing is dependant on the duty cycle of the
input clock signal. In such an application, it may appropriate to
disable the duty cycle stabilizer. In all other applications,
enabling the DCS circuit is recommended to maximize ac
performance.
the CLK+ and CLK− pins via a transformer or capacitors.
Figure 44 shows one preferred method for clocking the AD9444.
The clock source (low jitter) is converted from single-ended-todifferential using an RF transformer. The back-to-back Schottky
diodes across the transformer secondary limit clock excursions
into the AD9444 to approximately 0.8 V p-p differential. This
helps prevent the large voltage swings of the clock from feeding
through to other portions of the AD9444 and limits the noise
presented to the sample clock inputs.
If a low jitter clock is available, another option is to ac couple a
differential ECL/PECL signal to the encode input pins, as shown
in Figure 46.
CLOCK
SOURCE
Figure 44. Crystal Clock Oscillator, Differential Encode
ECL/
PECL
ADT1–1WT
0.1
µF
HSMS2812
DIODES
VT
0.1
µF
0.1µF
VT
Figure 45. Differential ECL for Encode
CLK+
AD9444
CLK–
ENCODE
AD9444
ENCODE
05089-048
05089-047
Jitter Considerations
High speed, high resolution ADCs are sensitive to the quality
of the clock input. The degradation in SNR at a given input
frequency (
(
t
) can be calculated using the following equation.
J
f
) and rms amplitude due only to aperture jitter
INPUT
SNR = 20 log[2πf
INPUT
× tJ]
The DCS circuit is controlled by the DCS MODE pin; a CMOS
logic low (AGND) on DCS MODE enables the duty cycle stabilizer, and logic high (AVDD1 = 3.3 V) disables the controller.
The AD9444 input sample clock signal must be a high quality,
extremely low phase noise source to prevent degradation of
performance. Maintaining 14-bit accuracy places a premium on
the encode clock phase noise. SNR performance can easily
degrade by 3 dB to 4 dB with 70 MHz analog input signals
when using a high jitter clock source. (See
AN-501, Aperture
Uncertainty and ADC System Performance, for complete
details.) For optimum performance, the AD9444 must be
clocked differentially. The sample clock inputs are internally
biased to ~2.2 V, and the input signal is usually ac-coupled into
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 40
In the equation, the rms aperture jitter represents the root-mean
square of all jitter sources, which includes the clock input,
analog input signal, and ADC aperture jitter specification. IF
undersampling applications are particularly sensitive to jitter,
see Figure 46.
The clock input should be treated as an analog signal in cases
where aperture jitter may affect the dynamic range of the
AD9444. Power supplies for clock drivers should be separated
from the ADC output driver supplies to avoid modulating the
clock signal with digital noise. Low jitter, crystal-controlled
oscillators make the best clock sources. If the clock is generated
from another type of source (by gating, dividing, or other methods), it should be retimed by the original clock at the last step.
Page 23

AD9444
75
70
65
60
55
SNR (dBc)
50
45
40
1
Figure 46. SNR vs. Input Frequency and Jitter
INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
0.2ps
0.5ps
1.0ps
1.5ps
2.0ps
2.5ps
3.0ps
100010010
05089-049
POWER CONSIDERATIONS
Care should be taken when selecting a power source. The use of
linear dc supplies is highly recommended. Switching supplies
tend to have radiated components that may be received by the
AD9444. Each of the power supply pins should be decoupled as
closely to the package as possible using 0.1 µF chip capacitors.
The AD9444 has separate digital and analog power supply
pins. The analog supplies are denoted AVDD1 (3.3 V) and
AVDD2 (5 V) and the digital supply pins are denoted DRVDD.
Although the AVDD1 and DRVDD supplies may be tied
together, best performance is achieved when the supplies are
separate. This is because the fast digital output swings can
couple switching current back into the analog supplies. Note
that both AVDD1 and AVDD2 must be held within 5% of the
specified voltage.
The DRVDD supply of the AD9444 is a dedicated supply for the
digital outputs, in either LVDS or CMOS output modes. When
in LVDS mode, the DRVDD should be set to 3.3 V. In CMOS
mode, the DRVDD supply may be connected from 2.5 V to
3.6 V to be compatible with the receiving logic.
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
LVDS Mode
The off-chip drivers on the chip can be configured to provide
LVDS-compatible output levels via Pin 5 (OUTPUT MODE).
LVDS outputs are available when OUTPUT MODE is CMOS
logic high (or AVDD1 for convenience) and a 3.74 kΩ R
resistor is placed at Pin 7 (LVDSBIAS) to ground. Dynamic
performance, including both SFDR and SNR, is maximized
when the AD9444 is used in LVDS mode, and designers are
encouraged to take advantage of this mode. The AD9444 outputs include complimentary LVDS outputs for each data bit
(DX+/DX−), the overrange output (OR+/OR−), and the output
data clock output (DCO+/DCO−). The R
resistor current is
SET
ratioed on-chip, setting the output current at each output equal
). A 100 Ω differential termina-
to a nominal 3.5 mA (11 ×
I
R
SET
SET
tion resistor placed at the LVDS receiver inputs results in a
nominal 350 mV swing at the receiver. LVDS mode facilitates
interfacing with LVDS receivers in custom ASICs and FPGAs
that have LVDS capability for superior switching performance
in noisy environments. Single point-to-point net topologies are
recommended with a 100 Ω termination resistor as close to the
receiver as possible. It is recommended to keep the trace length
less than 1 inch to 2 inches and to keep differential output trace
lengths as equal as possible.
CMOS Mode
In applications that can tolerate a slight degradation in dynamic
performance, the AD9444 output drivers can be configured to
interface with 2.5 V or 3.3 V logic families by matching DRVDD
to the digital supply of the interfaced logic. CMOS outputs are
available when OUTPUT MODE is CMOS logic low (or AGND
for convenience). In this mode, the output data bits are singleended CMOS, DX, as is the overrange output, OR. The output
clock is provided as a differential CMOS signal, DCO+/DCO−.
Lower supply voltages are recommended to avoid coupling
switching transients back to the sensitive analog sections of the
ADC. The capacitive load to the CMOS outputs should be
minimized, and each output should be connected to a single
gate through a series resistor (220 Ω) to minimize switching
transients caused by the capacitive loading.
TIMING
The AD9444 provides latched data outputs with a pipeline delay
of 12 clock cycles. Data outputs are available one propagation
delay (t
) after the rising edge of CLK+. Refer to Figure 2 and
PD
Figure 3 for detailed timing diagrams.
OPERATIONAL MODE SELECTION
Data Format Select
The data format select (DFS) pin of the AD9444 determines
the coding format of the output data. This pin is 3.3 V CMOS
compatible, with logic high (or AVDD1, 3.3 V) selecting twos
complement, and DFS logic low (AGND) selecting offset binary
format. Table 10 summarizes the output coding.
Output Mode Select
The OUPUT MODE pin controls the logic compatibility,
as well as the pinout of the digital outputs. This pin is a CMOS
compatible input. With OUTPUT MODE = 0 (AGND), the
AD9444 outputs are CMOS-compatible and the pin assignment
for the device is defined in Table 8. With OUTPUT MODE = 1
(AVDD1, 3.3 V), the AD9444 outputs are LVDS-compatible and
the pin assignment for the device is defined in Table 7.
Duty Cycle Stabilizer
The DCS circuit is controlled by the DCS MODE pin; a CMOS
logic low (AGND) on DCS MODE enables the DCS, and logic
high (AVDD1, 3.3 V) disables the controller.
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 40
Page 24

AD9444
Table 10. Digital Output Coding
VIN+ − VIN−
Code
16383 1.000 0.500 11 1111 1111 1111 01 1111 1111 1111
8192 0 0 10 0000 0000 0000 00 0000 0000 0000
8191 −0.000122 −0.000061 01 1111 1111 1111 11 1111 1111 1111
0 −1.00 −0.5000 00 0000 0000 0000 10 0000 0000 0000
Input Span = 2 V p-p (V)
VIN+ − VIN−
Input Span = 1 V p-p (V)
Digital Output
Offset Binary (D9••••••D0)
Digital Output
Twos Complement (D9••••••D0)
EVALUATION BOARD
Evaluation boards are offered to configure the AD9444 in
either CMOS or LVDS mode. Each represents a recommended
configuration for using the device over a wide range of sample
rates and analog input frequencies. These evaluation boards
provide all the support circuitry required to operate the ADC in
its various modes and configurations. Complete schematics and
layout plots follow and demonstrate the proper routing and
grounding techniques that should be applied at the system level.
It is critical that signal sources with very low phase noise
(< 1 ps rms jitter) be used to realize the ultimate performance
of the converter. Proper filtering of the input signal, to remove
harmonics and lower the integrated noise at the input, is also
necessary to achieve the specified noise performance.
The evaluation boards are shipped with an ac to 6 V dc power
supply. The evaluation boards include low dropout regulators to
generate the various dc supplies required by the AD9444 and its
support circuitry. Separate power supplies are provided to isolate the DUT from the support circuitry. Each input configuration can be selected by proper connection of various jumpers
(see Figure 47 to Figure 50 and Figure 59 to Figure 61).
Both the LVDS and CMOS versions of the evaluation board are
compatible with the high speed ADC FIFO evaluation kit (part
number HSC-ADC-EVALA-SC). The kit includes a high speed
data capture board that provides a hardware solution for capturing up to 32Ksamples of high speed ADC output data in a FIFO
memory chip (user upgradeable to 256K samples). Software is
provided to enable the user to download the captured data to a
PC via the USB port. This software also includes a behavioral
model of the AD9444 and many other high speed ADCs.
Behavioral modeling of the AD9444 is also available at
www.analog.com/ADIsimADC. The ADIsimA DC™ software
supports virtual ADC evaluation using ADI proprietary
behavioral modeling technology. This allows rapid comparison
between the AD9444 and other high speed ADCs, with or
without hardware evaluation boards.
The AD9444 LVDS evaluation board includes an on-board,
LVDS-to-CMOS translator, but the user may choose to remove
the translator and terminations to access the LVDS outputs
directly.
The CMOS evaluation board includes a buffer for the output
data and the DCO output clock of the AD9444.
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 40
Page 25

AD9444
LVDS EVALUATION BOARD SCHEMATICS
GND
8
7
6
5
P5
4
3
2
1
ENC
ENCODE
GND
R39
XX
GND
50Ω
R7
XTALINPUT
C92
0.1µF
C93
0.1µF
C44
10µF
+
VXTAL
5V
OPTIONAL ENCODE CIRCUITS
E47
E52
VDL
GND
DRVDD
GND
VCC
GND
5V
T3
C36
0.1µF
CR2
GND
ADT1-1WT
C42
6
123
GND
R36
XX
1
2
0.1µF
4
5
NC
C26
0.1µF
J1
ENCODE
GND
R37
XX
VXTAL
U6
ECLOSC
3
J5
VCC
E46
GND
SEC
PRI
GND
ENCB
50Ω
R8
XTALOUTB
8
OUTVCC
14
VXTAL
GND
XTALINPUTB
GND
R38
XX
R40
GND
R27
XX
R20
XX
XTALOUT
VXTAL
1
VEE ~OUT
7
GND
GND
H4
MTHOLE6
H3
MTHOLE6
H2
MTHOLE6
H1
MTHOLE6
D11_C/D7_YN
D11_T/D8_YN
D12_C/D9_YN
D12_T/D10_YN
D13_C/D11_YN
GND
DRVDD
DOR_C/D13_YN
DOR_T/DOR_YN
GND
VCC
GND
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
GND
GND
R9
R12
1kΩ
1kΩ
VCC
GND
E39
VCC
XX
XTALINPUTB
XTALINPUT
VXTAL
VCC
JN00158
FOR VECTRON XTAL
XX
R17
E38
XTALOUTB
OUTPUTB
D3_CN
D3_TN
D4_CN
D4_TN
D5_CN
D5_TN
D6_CN
64
12
E24
R3
E20
DRN
DCO+
U1
AGND
GND
EXTREF
63
PIN DEFINITIONS
13
C3
0.1µF
EXTREF
DRVDD
DRBN
62
DCO–
DRVDD
LVDS/CMOS
REFT
REFB
14
0.1µF
10µF
C24
0.1µF
GND
3.8kΩ
C51
D6_TN
GND
60
61
D6–
D6+
DRGND
AGND
AVDD1
AVDD1
15
16
17
VCC
VCC
GND
C2
C9
0.1µF
GND
+
C39
10µF
GND
R2
GND
18
GND
D5+
AVDD1
VCC
DRVDD
GND
51
52
5556575859
53
54
D5–
D4–
VIN+
21
R28
33Ω
TOUT
ADT1-1WT
GND
DRVDD
VIN–
22
624
153
D3+
DRGND
D2+
D2–
DRGND
DRVDD
D1+
D1–
D0+
(LSB) D0–
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD1
CLK–
CLK+
AVDD1
AVDD1
AGND
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD1
AVDD1
AGND
AVDD1
23
24
25
VCC
GND
R4
36Ω
GND
C12
0.1µF
NC
R5
GND
D3–
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
C1
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
AVDD1
VCC
C13
20pF
OPTIONAL
R13
xx
TOUTB
TINB
C5
L1
100Ω
xx
J4
C91
0.1µF
R6
E15
0.1µF
D2_TN
D2_CN
GND
DRVDD
D1_TN
D1_CND13_T/D12_YN
D0_TN
D0_CN
VCC
VCC
C40
0.1µF
5V
33Ω
R35
5V
GND
VCC
ENCB
ENC
VCC
VCC
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
36Ω
ANALOG
GND
D4+
AVDD2
AGND
20
19
5V
GND
T5
GND
72
73
74
75
D10–
D10+
DRVDD
76
D11–
77
D11+
78
D12–
79
D12+
80
D13–
81
D13+ (MSB)
82
DRGND
83
DRVDD
84
OR–
85
OR+
86
AGND
87
AVDD1
88
AGND
89
AVDD1
90
AVDD1
91
AVDD1
92
AVDD1
93
AVDD1
94
AVDD1
95
AVDD1
96
AGND
97
AGND
98
AVDD1
99
AGND
100
DCS MOD
EPAD
101
GND
E40
GND
XTALOUT
456
OUTPUT
U2
GNDNCE/D
321
R19
XX
GND
GND
XX
R18
DRGND
AVDD1
DNC
DNC
DNC
234
1
1kΩ
R15
VCC
E3
E1
VCC
GND
65
66
686970
71
67
D9–
D8–
D9+
D7–
D8+
D7+
DRGND
AD9444
OUTPUT MODE
DFS
LVDSBIAS/DNC
AVDD1
AVDD1
SENSE
VREF
7
9
5
8
6
10
11
VCC
VCC
1kΩ
R14
GND
C86
0.1µF
GND
GND
E25
E27
E26
E41
VCC
R1
GND
3.8kΩ
E2
GND
3.8kΩ
D7_CN
D7_T/D0_YN
D8_C/D1_YN
D8_T/D2_YN
D9_C/D3_YN
D9_T/D4_YN
D10_C/D5_YN
D10_T/D6_YN
DRVDD
VXTAL
FOR VF XTAL
05089-050
Figure 47. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Schematic
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 40
Page 26

AD9444
POWER OPTIONS
VDL
DRVDD
ADP3338
U4
3.3V
4
OUT
+
C57
10µF
GND
+
C88
10µF
4
ADP3338
OUT
U3
3.3V
GND
OUT1
GND
OUT1
1
GND
2
3
IN
1
2
3
IN
VDL
VCC
VIN
+
C1
10µF
GND
GND
DRVDD
VIN
+
C34
10µF
+
C87
10µF
GND
5V
+
C89
10µF
4
4
OUT
OUT
ADP3338
U15
3.3V
ADP3338
U14
5V
GND
OUT1
GND
OUT1
P4
1
GND
2
VCC
3
IN
+
1
2
3
IN
+
C6
10µF
GND
GND
C4
10µF
VIN
5V
VIN
PJ-102A
2
2
GND
3
3
1
1
+
C33
10µF
GND
VIN
GND
DRVDD
GND
5V
GND
VCC
GND
VCC
GND
05089-051
GND
GND
GND
Figure 48. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Schematic (Continued)
+
+
C65
10µF
+
C56
10µF
C64
10µF
C10
XX
C43
0.1µF
C47
0.1µF
C85
0.1µF
C11
XX
C23
0.1µF
C53
0.1µF
C35
0.1µF
C14
XX
C22
0.1µF
C52
0.1µF
C32
0.1µF
C17
XX
C21
0.1µF
C58
0.1µF
C30
0.1µF
C16
XX
C20
0.1µF
GND
5V
C28
0.1µF
C15
XX
C27
0.1µF
C31
XX
DRVDD
GND
C71XXC72XXC73XXC62
C50
C48
0.1µF
0.1µF
C38
C37
XX
XX
C69XXC70XXC45XXC49XXC59
C60
0.1µF
C29
XX
XX
C61
0.1µF
C19
XX
EXTREF
GND
C46
0.1µF
C18
XX
C75
0.1µF
C90
XX
XX
+
C55
10µF
P19
GND
05089-052
Figure 49. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Schematic (Continued)
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 40
Page 27

AD9444
GND
GND
DOR_C/D13_YN
D13_C/D11_YN
D12_C/D9_YN
D11_C/D7_YN
D10_C/D5_YN
D9_C/D3_YN
D8_C/D1_YN
D7_CN
DRBN
D6_CN
D5_CN
D4_CN
D3_CN
D2_CN
D1_CN
D0_CN
GND
U7
SN75LVDS386
DOR_T/DOR_YN
P6
C40MS
39
P39
37
P37
35
P35
33
P33
31
P31
29
P29
27
P27
25
P25
23
P23
21
P21
19
P19
17
P17
15
P15
13
P13
11
P11
9
P9
7
P7
5
P5
3
P3
1
P1
P40
P38
P36
P34
P32
P30
P28
P26
P24
P22
P20
P18
P16
P14
P12
P10
40
GND
38
36
GND
34
DOR_T/DOR_YN
32
D13_T/D12_YN
30
D12_T/D10_YN
28
D11_T/D8_YN
26
D10_T/D6_YN
24
D9_T/D4_YN
22
D8_T/D2_YN
20
D7_T/D0_YN
18
DRN
16
D6_TN
14
D5_TN
12
D4_TN
10
D3_TN
8
P8
P6
P4
P2
D2_TN
6
D1_TN
4
D0_TN
2
GND
DOR_C/D13_YN
D13_T/D12_YN
D13_C/D11_YN
D12_T/D10_YN
D12_C/D9_YN
D11_T/D8_YN
D11_C/D7_YN
D10_T/D6_YN
D10_C/D5_YN
D9_T/D4_YN
D9_C/D3_YN
D8_T/D2_YN
D8_C/D1_YN
D7_T/D0_YN
D7_CN
DRN
DRBN
D6_TN
D6_CN
D5_TN
D5_CN
D4_TN
D4_CN
D3_TN
D3_CN
D2_TN
D2_CN
D1_TN
D1_CN
D0_TN
D0_CN
1
A1A
2
A1B
3
A2A
4
A2B
5
A3A
6
A3B
7
A4A
8
A4B
9
B1A
10
B1B
11
B2A
12
B2B
13
B3A
14
B3B
15
B4A
16
B4B
17
C1A
18
C1B
19
C2A
20
C2B
21
C3A
22
C3B
23
C4A
24
C4B
25
D1A
26
D1B
27
D2A
28
D2B
29
D3A
30
D3B
31
D4A
32
D4B
GND
VCC1
VCC2
GND1
ENA
A1Y
A2Y
A3Y
A4Y
ENB
B1Y
B2Y
B3Y
B4Y
GND2
VCC3
VCC4
GND3
C1Y
C2Y
C3Y
C4Y
ENC
D1Y
D2Y
D3Y
D4Y
END
GND4
VCC5
VCC6
GND5
64
GND
63
VDL
62
VDL
61
GND
60
VDL
59
58
57
56
55
VDL
54
53
52
51
50
GND
49
VDL
48
VDL
47
GND
46
DRP
45
44
43
42
VDL
41
40
39
38
37
VDL
36
GND
35
VDL
34
VDL
33
GND
RZ5
RSO16ISO
R1
1
R2
2
R3
3
R4
4
R5
5
R6
6
R7
7
R8
8
RSO16ISO
R1
1
R2
2
R3
3
R4
4
R5
5
R6
6
R7
7
R8
8
RZ4
220
220
16
ORO
15
D13O
14
D12O
13
D11O
12
D10O
11
D9O
10
D8O
9
D7O
16
D6O
15
D5O
14
D4O
13
D3O
12
D2O
11
D1O
10
D0O
9
GND
40
P40
38
P38
36
P36
34
P34
32
P32
30
P30
28
P28
26
P26
24
P24
22
P22
20
P20
18
P18
16
P16
14
P14
12
P12
10
P10
8
P8
6
P6
4
P4
2
P2
C40MS
39
P39
P37
P35
P33
P31
P29
P27
P25
P23
P21
P19
P17
P15
P13
P11
P9
P7
P5
P3
P1
P3
GND
37
DRO
35
GND
33
D13O
31
D12O
29
D11O
27
D10O
25
D9O
23
D8O
21
D7O
19
D6O
17
D5O
15
D4O
13
D3O
11
D2O
9
D1O
7
D0O
5
ORO
3
1
GND
VDL
GND
E32
E43
E34
VDL
GND
GND
GND
00
R53
XORN
+
C76
10µF
74VCX86
1
1A
2
1B
4
2A
5
2B
9
3A
10
3B
12
4A
13
4B
U10
C97
0.1µF
1Y
2Y
3Y
4Y
C82
0.1µF
3
6
00
8
R52
11
PWR
14
7
GND
C80
0.1µF810.1µF
DRO
VDL
GND
05089-053
Figure 50. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Schematic (Continued)
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 40
Page 28

AD9444
Figure 51. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Primary Side
Figure 52. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Secondary Side
05089-057
05089-058
Figure 54. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Ground Plane 2
Figure 55. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Power Plane 1
05089-060
05089-061
Figure 53. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Ground Plane 1
05089-059
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 40
Figure 56. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Power Plane 2
05089-062
Page 29

AD9444
05089-064
Figure 57. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Primary Silkscreen
05089-063
Figure 58. LVDS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Secondary Silkscreen
Rev. 0 | Page 29 of 40
Page 30

AD9444
LVDS MODE EVALUATION BOARD BILL OF MATERIALS (BOM)
Table 11.
Item Qty. REFDES Description Manufacturer MFG_PART_NO
1 1 AD9444PCB PCB, AD9444 LVDS Engineering Evaluation Board PCSM AD9444LVDSCUSTREVC
2 16
3 38
4 1 C51 Capacitor, Ceramic 10 µF 6.3 V X5R 0805 KEMET C0805C106K9PACTU
5 1 CR2 Diode, Dual Schottky HSMS2812, SOT-23, 30 V, 20 mA Panasonic MA716-(TX)
6 17
7 2 J1, J4 Connector, Gold, Male, Coaxial, SMA, Vertical Johnston Comp. 142-0701-201
8 1 L1 10 nH Inductor Coilcraft 0603CJ-10NXGBU
9 1 P3 Header, 40-Pin, Male, 40-Pin Right Angle Samtec TSW-120-08-T-D-RA
10 1 P4 Power Jack Swithcraft RAPC722
11 1 R3 Resistor, 3.6 kΩ 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2GEJ362X
12 2 R4, R6 Resistor, 36 Ω 1/16 W 5% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2GEJ360X
13 1 R8 Resistor, 49.9 Ω 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2RKF49R9X
14 4
15 2 R28, R35 Resistor, 33 Ω 1/16 W 5% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2GEJ330X
16 3
17 2 RZ4, RZ5 22 Ω Resistor Array, 16 Term CTS Corp. 742163220JTR
18 2 T3, T5 Transformer, ADT1-1WT, CD542, ADT1-1WT Mini-Circuits ADT1-1WT
19 1 U1 14-Bit, 80 MSPS ADC ADI AD9444BSVZ-80
20 3 U3, U4, U15 3.3 V Voltage Regulator ADI ADP3338-3.3 V
21 1 U14 5 V Voltage Regulator ADI ADP3338-5.0 V
22 1 U6 Clock Oscillator, 80 MHz CTS Reeves MX045-80
23 1 U7 LVDS-to-CMOS Translator with 100 Term Texas Instruments SN75LVDT386DGG
24 1 U10 2 Input XOR Gate Fairchild 74VCX86M
25 4 U6 Pin Sockets, Closed End AMP 5-330808-3
C1, C4, C6,
C33, C34,
C39, C44,
C55 to C57,
C64, C65,
C76, C87 to
C89
C2, C3, C5,
C9, C12, C20
to C24, C26
to C28, C30,
C32, C35,
C40, C42,
C43, C46 to
C48, C50,
C52, C53,
C58, C60,
C61, C75,
C80 to C82,
C85, C86,
C91 to C93,
C97
E1 to E3, E24,
to E27, E32,
E34, E38,
E39, E40,
E41, E43,
E46, E47, E52
R9, R12, R14,
R15
R39, R52,
R53
Capacitors, Tantalum, SMT BCAPTAJC, 10 µF, 16 V, 10% KEMET T491C106K016AS
Capacitors, 0.1 µF 10 V Ceramic X5R 0402 Panasonic ECJ-0EB1A104K
40-Pin Breakable Header 3M 2340-611TN
Resistor, 1.00 kΩ 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2RKF1001X
Resistor, 0 Ω 1/16 W 5% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2GE0R00X
Rev. 0 | Page 30 of 40
Page 31

AD9444
Item Qty. REFDES Description Manufacturer MFG_PART_NO
26 24
C10, C11,
C13, to C19,
C29, C31,
C36 to C38,
C45, C49,
C59, C62,
C69, C70 to
C73, C90
27 1 J51 Connector, Gold, Male, Coaxial, SMA, Vertical Johnston Comp. 142-0701-201
28 2 P5, P61 Power Connectors Weiland
29 1
30 1
R1, R2, R5,
1
R7, R13
R17 to R20,
R27, R36 to
R38, R40
31 5 U21 XO Select Vectron
1
Parts not placed.
Capacitors, Select 10 V Ceramic X5R 0402 Panasonic
1
Resistors, Select 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic
Resistors, Select 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic
1
Rev. 0 | Page 31 of 40
Page 32

AD9444
CMOS EVALUATION BOARD SCHEMATICS
GND
8
VDL
7
GND
6
DRVDD
5
GND
P5
4
VCC
3
GND
2
1
5V
H4
MTHOLE6
H3
MTHOLE6
H2
MTHOLE6
H1
R39
MTHOLE6
ENC
3
CR2
C42
6
T3
123
5
ADT1-1WT
NC
XX
C36
0.1µF
XTALINPUT
J5
GND
C96
0.1µF
C92
0.1µF
C93
0.1µF
C44
10µF
+
VXTAL
5V
VCC
GND
ENCODE
GND
GND
50Ω
R7
OPTIONAL ENCODE CIRCUITS
E52
E47
E46
ENCB
1
2
GND
0.1µF
4
SEC
PRI
C26
0.1µF
50Ω
R8
J1
GND
GND
R37
XX
R36
XX
XTALOUTB
VXTAL
8
OUTVCC
U6
ECLOSC
GND
14
VXTAL
D11C/D7YN
D11T/D8YN
D12C/D9YN
D12T/D10YN
D13C/D11YN
D13T/D12YN
GND
DRVDD
DORC/D13Y
DORT/DORY
GND
VCC
GND
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
GND
GND
R9
R12
1kΩ
1kΩ
VCC
GND
GND
GND
XTALINPUTB
XTALOUT
1
VEE ~OUT
7
GND
E39
E40
E38
VCC
GND
R38
XX
R40
XX
XTALINPUTB
GND
VXTAL
GND
R27
XX
R20
XX
XTALINPUT
XTALOUT
XTALOUTB
VXTAL
456
VCC
OUTPUT
OUTPUTB
JN00158
GNDNCE/D
321
GND
FOR VECTRON XTAL
XX
R17
COUTB
DRVDD
GND
73
74
75
DRVDD
R21
1
AVDD1
234
1kΩ
VCC
DRGND
DNC
76
D7
77
D8
78
D9
79
D10
80
D11
81
D12
82
DRGND
83
DRVDD
84
(MSB) D13
85
OR
86
AGND
87
DRVDD
88
AGND
89
AVDD1
90
AVDD1
91
AVDD1
92
AVDD1
93
AVDD1
94
AVDD1
95
AVDD1
96
AGND
97
AGND
98
AVDD1
99
AGND
100
DCS MODE
EPAD
101
U2
R19
XX
GND
XX
R18
D9C/D3Y
D9T/D4Y
D10C/D5YN
D10T/D6YN
72
71
D6D5D4D3D2
DNC
DNC
OUTPUT MODE
DFS
5
6
R15
1kΩ
GND
E3
E2
E1
VCC
GND
D8T/D2Y
LVDSBIAS
7
COUT
66
10
E25
D7T/D0Y
65
D0 (LSB)
SENSE
11
E27
E41
3.8kΩ
REFERENCE
64
63
DNC
DCO+
U1
AD9444
VREF
AGND
13
12
GND
C3
0.1µF
GND
E24
EXTREF
GND
R1
R3
3.8kΩ
EXTREF
INPUT
E20
DRVDD
GND
60
61
62
DNC
DNC
DRVDD
REFB
C78
0.1µF
C51
10µF
C2
+
C39
R2
3.8kΩ
15
DRGND
AGND
GND
0.1µF
GND
GND
DNC
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD1
16
18
17
VCC
VCC
VCC
C9
GND
GND
10µF
DCO–
LVDS/CMOS
PIN DEFINITIONS
REFT
14
0.1µF
19
DNC
AVDD2
5V
GND
DRVDD
51
52
5556575859
53
54
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DRVDD
DRGND
50
DNC
49
DNC
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
C13
20pF
R13
xx
TOUTB
TINB
L110NH
C5
C91
0.1µF
R6
E15
0.1µF
GND
DRVDD
VCC
VCC
C40
0.1µF
5V
33Ω
R35
5V
GND
05089-054
VCC
ENCB
ENC
VCC
VCC
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
36Ω
ANALOG
GND
DRGND
DRVDD
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
AVDD1
AVDD1
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD1
CLK–
CLK+
AVDD1
AVDD1
C1
AGND
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD2
AVDD1
AVDD1
AGND
VIN+
VIN–
AGND
AVDD1
AVDD1
20
23
21
22
24
25
VCC
VCC
GND
GND
OPTIONAL
R28
33Ω
R4
36Ω
GND
C12
0.1µF
TOUT
CT
624
T5
153
PRI SEC
ADT1-1WT
NC
GND
100Ω
xx
R5
J4
GND
GND
D8C/D1Y
686970
67
D1
DRGND
AVDD1
AVDD1
9
8
VCC
VCC
E26
VCC
GND
EXTERNAL
VXTAL
FOR VF XTAL
Figure 59. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Schematic
Rev. 0 | Page 32 of 40
Page 33

AD9444
VDL
DRVDD
+
+
C57
10µF
GND
C88
10µF
4
4
OUT
OUT
ADP3338
U8
3.3V
ADP3338
U3
3.3V
GND
OUT1
GND
OUT1
1
GND
2
VDL
3
IN
C1
+
10µF
GND
1
GND
2
DRVDD
3
IN
C34
+
10µF
VIN
VIN
VCC
C87
+
10µF
GND
5V
C89
+
10µF
4
4
OUT
OUT
ADP3338
U15
3.3V
ADP3338
U14
5V
GND
OUT1
GND
OUT1
P4
1
GND
2
VCC
3
IN
C6
+
10µF
GND
1
GND
2
5V
3
IN
C4
+
10µF
PJ-102A
VIN
VIN
2
2
GND
3
3
1
1
+
C33
10µF
GND
VIN
GND
GND
GND
GND
Figure 60. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Schematic (Continued)
05089-055
Rev. 0 | Page 33 of 40
Page 34

AD9444
DORT/DORY
DORC/D13Y
D13T/D12Y
D13C/D11Y
D12T/D10Y
D12C/D9Y
D11T/D8Y
D11C/D7Y
D10T/D6Y
D10C/D5Y
D9T/D4Y
D9C/D3Y
D8T/D2Y
D8C/D1Y
D7T/D0Y
RZ1
RSO16ISO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
RSO16ISO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
COUTB
COUT
VDL
GND
VDL
GND
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
R7
R8
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
R7
R8
RZ4
220
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
220RZ2
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
NOT PLACED
E42
E31
E49
E45
E32
E30
00
R50
00
R16
XOR2IN
XOR2IN
GND
GATE2
GND
VDL
GND
GND
VDL
GND
XORZIN
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
1
2
4
5
9
10
12
13
U5
SN74LVCH16373A
Q = OUTPUT
D = INPUT
LE2
2D8
2D7
GND GND
2D6
2D5
VCC
2D4
2D3
GND
2D2
2D1
1D8
1D7
GND
1D6
1D5
VCC
1D4
1D3
GND
1D2
1D1
LE1
74VCX86
1A
1B
2A
2B
3A
3B
4A
4B
OE2
2Q8
2Q7
2Q6
2Q5
VCC
2Q4
2Q3
GND
2Q2
2Q1
1Q8
1Q7
GND
1Q6
1Q5
VCC
1Q4
1Q3
GND
1Q2
1Q1
OE1
U4
1Y
2Y
3Y
4Y
P3
C40MS
P39
P37
P35
P33
P31
P29
P27
P25
P23
P21
P19
P17
P15
P13
P11
39
GND
37
DRM
35
GND
33
D13M
31
D12M
29
D11M
27
D10M
25
D9M
23
D8M
21
D7M
19
D6M
17
D5M
15
D4M
13
D3M
11
D2M
9
P9
P7
P5
P3
P1
D1M
7
D0M
5
ORM
3
1
40
220
RZ5
RSO16ISO
R1
1
24
GND
23
22
21
GND
20
19
18
VDL
17
16
15
GND
14
13
12
11
10
GND
9
8
7
VDL
6
5
4
GND
3
2
1
GND
3
6
8
11
PWR
14
GND
7
VDL
GND
00
R42
DRM
R41
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
RSO16ISO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
00
GATE
R14
00
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
R7
R8
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
R7
R8
RZ4
16
ORM
15
D13M
14
D12M
13
D11M
12
D10M
11
D9M
10
D8M
9
D7M
220RZ5
16
D6M
15
D5M
14
D4M
13
D3M
12
D2M
11
D1M
10
D0M
9
GND GND
DRM
P40
38
P38
36
P36
34
P34
32
P32
30
P30
28
P28
26
P26
24
P24
22
P22
20
P20
18
P18
16
P16
14
P14
12
P12
10
P10
8
P8
6
P6
4
P4
2
P2
VDL
GND
U10
+
C66
C25
C41
10µF
0.1µF
0.1µF
C24
0.1µF
C68
0.1µF
C67
0.1µF630.01µF
Figure 61. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Schematic (Continued)
Rev. 0 | Page 34 of 40
05089-056
Page 35

AD9444
05089-068
Figure 62. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Primar y Side
05089-065
Figure 65. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Ground Plane 2
Figure 63. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Secondary Side
Figure 64. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Ground Plane 1
05089-066
05089-067
Rev. 0 | Page 35 of 40
Figure 66. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Power Plane 1
Figure 67. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Power Plane 2
05089-069
05089-070
Page 36

AD9444
Figure 68. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Primary Silkscreen
05089-071
Figure 69. CMOS Mode Evaluation Board Layout, Secondary Silkscreen
05089-072
Rev. 0 | Page 36 of 40
Page 37

AD9444
CMOS MODE EVALUATION BOARD BILL OF MATERIALS (BOM)
Table 12.
Item Qty. REFDES Description Manufacturer MFG_PART_NO
1 1 AD9444PCB PCB, AD9444 LVDS Evaluation Board PCSM AD9444LVDSCUSTREVC
2 16
C1, C4, C6, C33, C34,
C39, C44, C55 to
C57, C64 to C66,
C87 to C89
Capacitors, Tantalum, SMT BCAPTAJC, 10 µF, 16 V, 10% KEMET T491C106K016AS
3 32
4 5
5 1 C51 Capacitor, Ceramic 10 µF 6.3 V X5R 0805 KEMET C0805C106K9PACTU
6 1 CR2 Diode, Dual Schottky HSMS2812, SOT-23, 30 V, 20 mA Panasonic MA716-(TX)
7 20
8 2 J1, J4 Connector, Gold, Male, Coaxial, SMA, Vertical Johnston Comp. 142-0701-201
9 1 L1 10 nH O402 Inductor Coilcraft 0402CS-10NX_B_
10 1 P3 Header, 40-Pin, Male, 40-Pin Right Angle Samtec TSW-120-08-T-D-RA
11 1 P4 Power Jack Swithcraft RAPC722
12 1 R3 Resistor, 3.6 kΩ 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2GEJ362X
13 2 R4, R6 Resistors, 36 Ω 1/16 W 5% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2GEJ360X
14 1 R8 Resistor, 49.9 Ω 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2RKF49R9X
15 4 R9, R12, R15, R21 Resistors, 1.00 kΩ 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2RKF1001X
16 2 R14, R50 Resistors, 0 Ω 1/10 W 5% 0603 SMD Panasonic ERJ-3GEY0R00V
17 2 R28, R35 Resistors, 33 Ω 1/16 W 5% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2GEJ330X
18 1 R39 Resistor, 0 Ω 1/16 W 5% 0402 SMD Panasonic ERJ-2GE0R00X
19 4 RZ1 to RZ3, RZ6 220 Ω Resistor Array, 16 Term CTS Corp. 742163221JTR
20 2 T3, T5 Transformer, ADT1-1WT, CD542, ADT1-1WT Mini-Circuits ADT1-1WT
21 1 U1 14-Bit, 80 MSPS ADC ADI AD9444BSVZ-80
22 4 U3, U8, U15 3.3 V Voltage Regulator ADI ADP3338-3.3 V
23 1 U14 5 V Voltage Regulator ADI ADP3338-5.0 V
24 1 U5 16-Bit Flip Flop Fairchild 74LVTH162374
25 4 U6 Pin Sockets, Closed End AMP 5-330808-3
C2, C3, C5, C9, C12,
C20 to C23, C26 to
C28, C30, C32, C35,
C40, C42, C43, C46 to
C48, C50, C52, C53,
C58, C60, C61, C75,
C78, C85, C91, C92
C24, C25, C41, C67,
C68
E1 to E3, E24 to E27,
E30 to E32, E38 to
E42, E45 to E47,
E49, E52
Capacitors, 0.1 µF 10 V Ceramic X5R 0402 Panasonic ECJ-0EB1A104K
Capacitors, 0.1 µF 16 V Ceramic X7R 0603 Panasonic ECJ-1VB1C104K
40-Pin Breakable Header 3M 2340-611TN
Rev. 0 | Page 37 of 40
Page 38

AD9444
Item Qty. REFDES Description Manufacturer MFG_PART_NO
26 26
C10, C11, C13, C14 to
C19, C29, C31, C36 to
C37, C38, C45, C49,
C59, C62,C69, C70 to
C73, C90, C93, C96
27 1 J51 Connector, Gold, Male, Coaxial, SMA, Vertical Johnston Comp. 142-0701-201
28 15
R1,R2,R5,R7, R13,
R17 to R20, R27,
R36 to R40
1
29 3 R16, R41, R421 Resistors, Select 1/16 W 5% 0603 SMD Panasonic
30 1 C631 Capacitor, Select 10 V Ceramic X5R 0603 Panasonic
31 1 U41 XOR 74VCX86D Fairchild 74VCX86D
32 2 P5, P61 Power Connectors Weiland
1
Parts not placed.
Capacitors, Select 10 V Ceramic X5R 0402 Panasonic
1
Resistors, Select 1/16 W 1% 0402 SMD Panasonic
Rev. 0 | Page 38 of 40
Page 39

AD9444
2
F
L
E
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
1.20
0.75
MAX
0.60
0.45
SEATING
PLANE
0.20
0.09
NOTES
1. CENTER FIGURES ARE TYPICAL UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED.
. THE PACKAGE HAS A CONDUCTIVE HEAT SLUG TO HELP DISSIPATE HEAT AND ENSURE RELIABLE OPERATION O
THE DEVICE OVER THE FULL INDUSTRIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE. THE SLUG IS EXPOSED ON THE BOTTOM OF
THE PACKAGE AND ELECTRICALLY CONNECTED TO CHIP GROUND. IT IS RECOMMENDED THAT NO PCB SIGNA
TRACES OR VIAS BE LOCATED UNDER THE PACKAGE THAT COULD COME IN CONTACT WITH THE CONDUCTIV
SLUG. ATTACHING THE SLUG TO A GROUND PLANE WILL REDUCE THE JUNCTION TEMPERATURE OF THE
DEVICE WHICH MAY BE BENEFICIAL IN HIGH TEMPERATURE ENVIRONMENTS.
3. THE EXPOSED HEAT SINK SOLDERED TO THE GROUND PLANE IS REQUIRED FOR THE 100-LEAD TQFP/EP.
1
25
26 50
7°
3.5°
0°
Figure 70. 100-Lead Thin Quad Flat Package, Exposed Pad [TQFP_EP]
16.00 SQ
14.00 SQ
76100
75
TOP VIEW
(PINS DOWN)
51
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-026AED-HD
0.27
0.22
0.17
0.15
0.05
75
51
1.05
1.00
0.95
COPLANARITY
0.08
(SV-100-1)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
76 100
BOTTOM VIEW
(PINS UP)
CONDUCTIVE
HEAT SINK
6.50
NOM
1
25
2650
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Outline
AD9444BSVZ-80
AD9444-CMOS/PCB CMOS Mode Evaluation Board
AD9444-LVDS/PCB LVDS Mode Evaluation Board
1
Z = Pb-free part.
1
–40°C to +85°C 100-Lead TQFP_EP SV-100-1
Rev. 0 | Page 39 of 40
Page 40

AD9444
NOTES
© 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D05089–0–10/04(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 40 of 40
 Loading...
Loading...