Analog Devices AD9432 Datasheet
12-Bit, 80 MSPS/105 MSPS
a
FEATURES
On-Chip Reference and Track/Hold
On-Chip Input Buffer
850 mW Typical Power Dissipation at 105 MSPS
500 MHz Analog Bandwidth
SNR = 67 dB @ 49 MHz AIN at 105 MSPS
SFDR = 80 dB @ 49 MHz AIN at 105 MSPS
2.0 V p-p Differential Analog Input Range
Single +5.0 V Supply Operation
+3.3 V CMOS/TTL Outputs
Two’s Complement Output Format
APPLICATIONS
Communications
Basestations and ‘Zero-IF’ Subsystems
Wireless Local Loop (WLL)
Local Multipoint Distribution Service (LMDS)
HDTV Broadcast Cameras and Film Scanners
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
The AD9432 is a 12-bit monolithic sampling analog-to-digital
converter with an on-chip track-and-hold circuit and is optimized
for high-speed conversion and ease of use. The product operates
at a 105 MSPS conversion rate with outstanding dynamic performance over its full operating range.
The ADC requires only a single 5.0 V power supply and a
105 MHz encode clock for full-performance operation. No
external reference or driver components are required for many
applications. The digital outputs are TTL/CMOS compatible
and a separate output power supply pin supports interfacing
with 3.3 V logic. The encode input supports either differential
or single-ended and is TTL/CMOS-compatible.
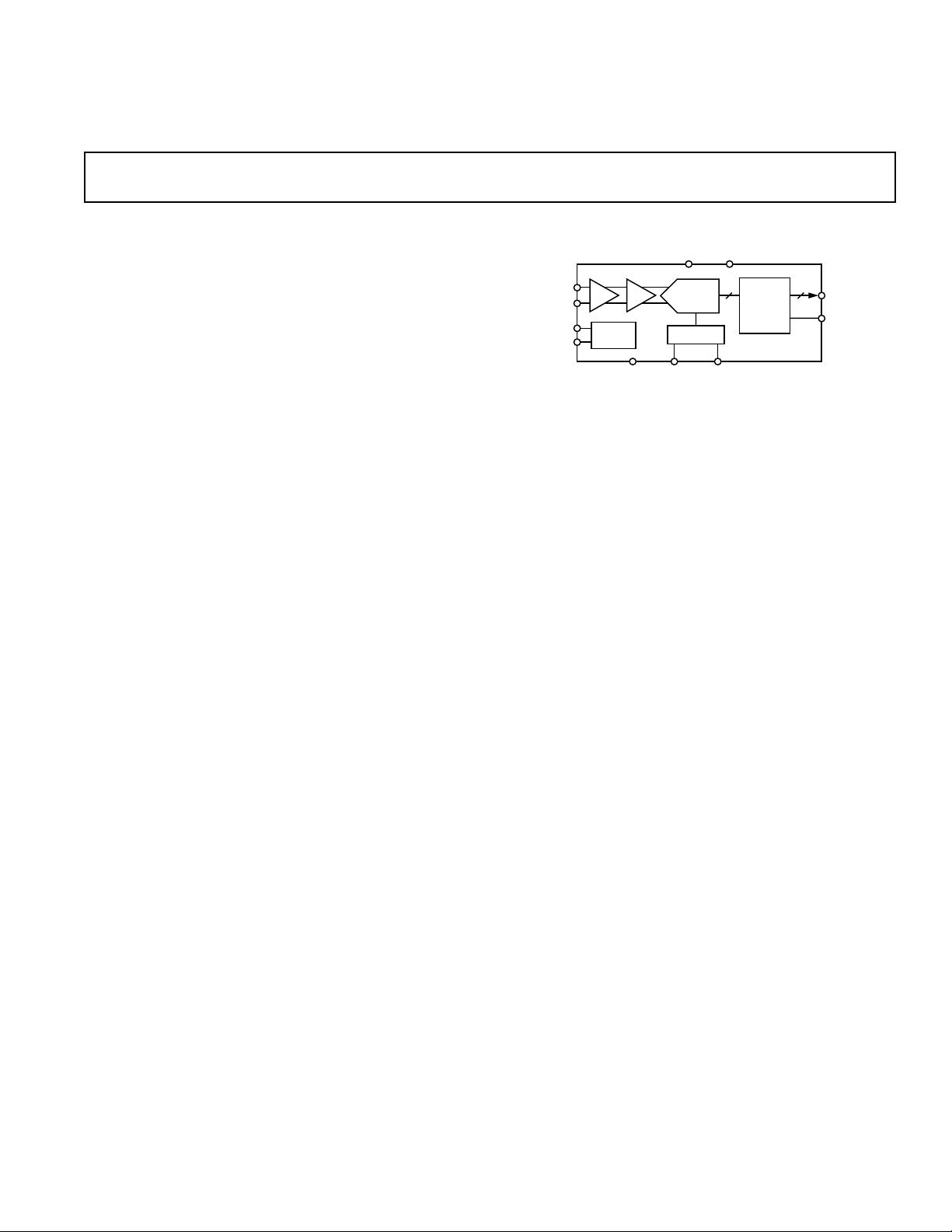
A/D Converter
AD9432
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
V
V
CC
DD
AD9432
12
D11–D0
OR
AIN
AIN
ENCODE
ENCODE
BUF T/H
TIMING
GND VREFOUT
PIPELINE
ADC
REF
VREFIN
12
OUTPUT
STAGING
Fabricated on an advanced BiCMOS process, the AD9432 is
available in a 52-lead plastic quad flatpack package (LQFP)
specified over the industrial temperature range (–40°C to
+85°C).
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2000
(VDD = 3.3 V, VCC = 5.0 V; external reference; differential encode input, unless
AD9432–SPECIFICATIONS
otherwise noted)
Test AD9432BST-80 AD9432BST-105
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 12 12 Bits
DC ACCURACY
Differential Nonlinearity +25°C I –0.75 ± 0.25 +0.75 –0.75 ± 0.25 +0.75 LSB
Full VI –1.0 ± 0.5 +1.0 –1.0 ± 0.5 +1.0 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity +25°C I –1.0 ± 0.5 +1.0 –1.0 ± 0.5 +1.0 LSB
Full VI –1.5 ± 1.0 +1.5 –1.5 ± 1.0 +1.5 LSB
No Missing Codes Full VI Guaranteed Guaranteed
Gain Error
Gain Tempco
1
1
+25°C I –3 +2 +7 –3 +2 +7 % FS
Full V 150 150 ppm/°C
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Range (AIN–AIN) Full V ± 1.0 ± 1.0 V
Common-Mode Voltage Full V 3.0 3.0 V
Input Offset Voltage Full VI –5 ± 0+5 –5 ± 0+5 mV
Input Resistance Full VI 2 3 4 2 3 4 kΩ
Input Capacitance +25°CV 4 4 pF
Analog Bandwidth, Full Power +25°C V 500 500 MHz
ANALOG REFERENCE
Output Voltage Full VI 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.4 2.5 2.6 V
Tempco Full V 50 50 ppm/°C
Input Bias Current Full VI 15 50 15 50 µΑ
SWITCHING PERFORMANCE
Maximum Conversion Rate Full VI 80 105 MSPS
Minimum Conversion Rate Full IV 1 1 MSPS
Encode Pulsewidth High (t
Encode Pulsewidth Low (t
Aperture Delay (t
) +25°C V 2.0 2.0 ns
A
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) +25°C V 0.25 0.25 ps rms
Output Valid Time (t
V
Output Propagation Delay (t
Output Rise Time (t
Output Fall Time (t
)
R
) Full V 1.9 1.9 ns
F
) +25°C IV 4.0 6.2 4.0 4.8 ns
EH
) +25°C IV 4.0 6.2 4.0 4.8 ns
EL
2
)
2
PD
2
)
Full VI 3.0 5.3 3.0 5.3 ns
Full VI 5.5 8.0 5.5 8.0 ns
Full V 2.1 2.1 ns
Out-of-Range Recovery Time +25°CV 2 2 ns
Transient Response Time +25°CV 2 2 ns
Latency Full IV 10 10 Cycles
DIGITAL INPUTS
Encode Input Common Mode Full V 1.6 1.6 V
Differential Input (ENC–ENC) Full V 750 750 mV
Single-Ended
Logic “1” Voltage Full IV 2.0 2.0 V
Logic “0” Voltage Full IV 0.8 0.8 V
Input Resistance Full VI 3 5 8 3 5 8 kΩ
Input Capacitance +25°C V 4.5 4.5 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Logic “1” Voltage (VDD = +3.3 V) Full VI VDD – 0.05 VDD – 0.05 V
Logic “0” Voltage (V
= +3.3 V) Full VI 0.05 0.05 V
DD
Output Coding Two’s Complement Two’s Complement
POWER SUPPLY
Power Dissipation
3
Full VI 790 1000 850 1100 mW
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR) +25°C I –5 0.5 +5 –5 0.5 +5 mV/V
I
VCC
I
VDD
Full VI 158 200 170 220 mA
Full VI 9.5 12.2 12.5 16 mA
–2–
REV. B
AD9432
Test AD9432BST-80 AD9432BST-105
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
(Without Harmonics)
f
= 10.3 MHz +25°C I 65.5 67.5 65.5 67.5 dB
IN
= 40 MHz +25°C I 65 67.2 67.2 dB
f
IN
f
= 49 MHz +25°C I 67.0 64 67.0 dB
IN
f
= 70 MHz +25°C V 66.1 66.1 dB
IN
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SINAD)
(With Harmonics)
= 10.3 MHz +25°C I 65 67.2 65 67.2 dB
f
IN
= 40 MHz +25°C I 64.5 66.9 66.9 dB
f
IN
f
= 49 MHz +25°C I 66.7 63 66.7 dB
IN
f
= 70 MHz +25°C V 65.8 65.8 dB
IN
Effective Number of Bits
= 10 MHz +25°C V 11.0 11.0 Bits
f
IN
f
= 40 MHz +25°C V 10.9 10.9 Bits
IN
= 49 MHz +25°C V 10.9 10.9 Bits
f
IN
f
= 70 MHz +25°C V 10.7 10.7 Bits
IN
Second and Third Harmonic Distortion
= 10 MHz +25°C I –75 –85 –75 –85 dBc
f
IN
f
= 40 MHz +25°C I –73 –85 –83 dBc
IN
f
= 49 MHz +25°C I –83 –72 –80 dBc
IN
= 70 MHz +25°C V –80 –78 dBc
f
IN
Worst Harmonic or Spur
(Excluding Second and Third)
= 10 MHz +25°C I –80 –90 –80 –90 dBc
f
IN
f
= 40 MHz +25°C I –80 –90 –90 dBc
IN
f
= 49 MHz +25°C I –90 –80 –90 dBc
IN
= 70 MHz +25°C V –90 –90 dBc
f
IN
Two-Tone Intermod Distortion (IMD)
f
= 29.3 MHz; f
IN1
f
= 70.3 MHz; f
IN1
NOTES
1
Gain error and gain temperature coefficients are based on the ADC only (with a fixed 2.5 V external reference and a 2 V p-p differential analog input).
2
tV and tPD are measured from the transition points of the ENCODE input to the 50%/50% levels of the digital outputs swing. The digital output load during test is
not to exceed an ac load of 10 pF or a dc current of ± 40 µA. Rise and fall times measured from 10% to 90%.
3
Power dissipation measured with encode at rated speed and a dc analog input. (Outputs Static, I
4
SNR/harmonics based on an analog input voltage of –0.5 dBFS referenced to a 2 V full-scale input range.
Typical θJA for LQFP package = 50°C/W.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
IN2
IN2
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +6 V
V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +6 V
CC
Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to V
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to V
VREFIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to V
Digital Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 mA
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +175°C
Maximum Case Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +150°C
4
= 30.3 MHz +25°C V –75 –75 dBc
= 71.3 MHz +25°C V –66 –66 dBc
= 0.)
VDD
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions outside of those indicated in the operation
+ 0.5 V
CC
+ 0.5 V
DD
+ 0.5 V
CC
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum
ratings for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Ranges Descriptions Option
AD9432BST
-80, -105 –40°C to +85°C 52-Lead Plastic Quad ST-52
Flatpack (LQFP)
AD9432/PCB +25°C Evaluation Board
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD9432 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. B –3–
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
AD9432
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
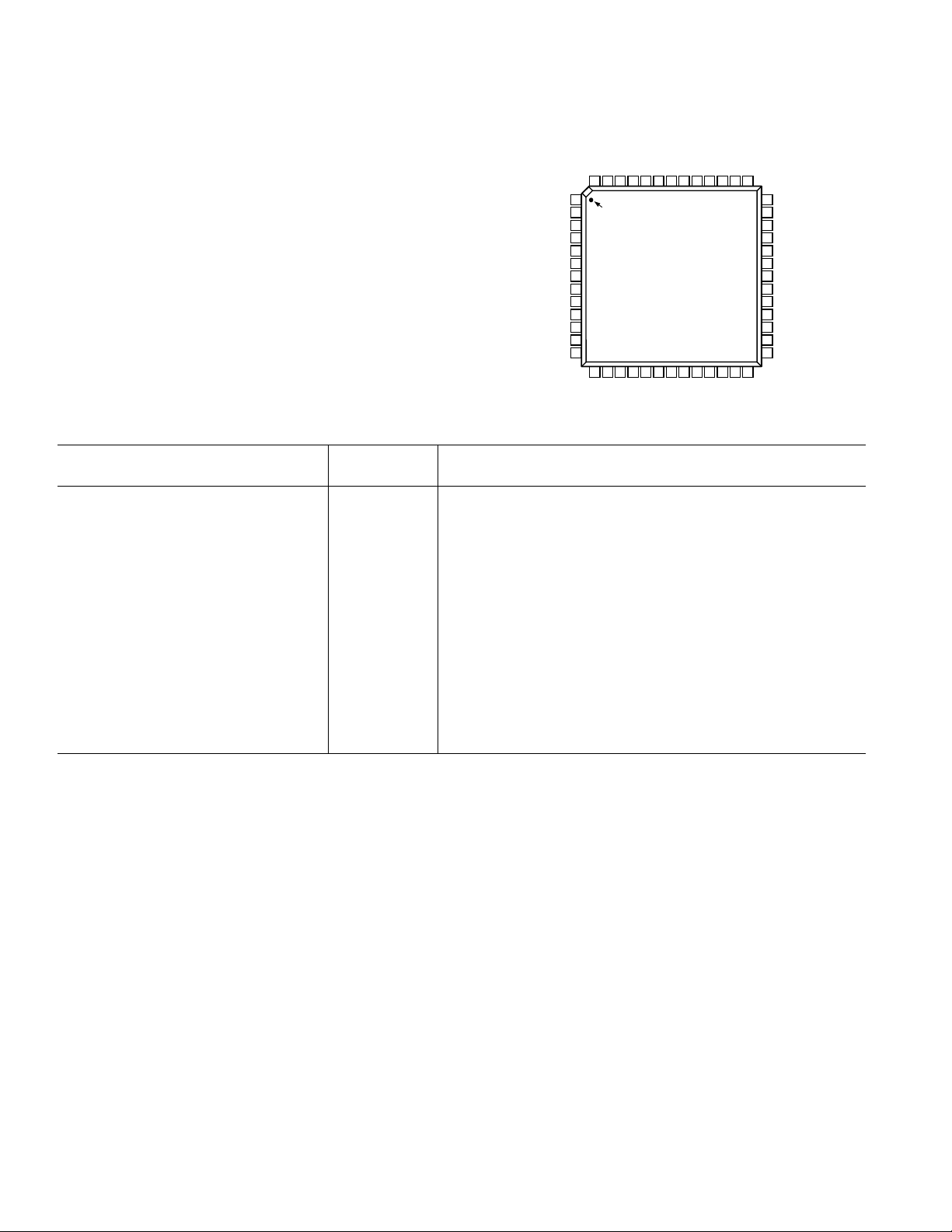
PIN CONFIGURATION
Test Level
I 100% production tested.
II 100% production tested at +25°C and sample tested at
specified temperatures.
III Sample tested only.
IV Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization
testing.
V Parameter is a typical value only.
VI 100% production tested at +25°C; guaranteed by design
and characterization testing for industrial temperature
range.
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
AIN
D10
AIN
D9D8D7
CC
VREFOUT
V
GND
AD9432
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
D6
CC
GND
V
52 51 50 49 48 43 42 41 4047 46 45 44
1
GND GND
V
GND
GND
V
V
ENCODE
ENCODE
GND
V
GND
DGND
V
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
2
CC
3
4
5
CC
6
CC
7
8
9
10
CC
11
12
13
DD
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
OR
(MSB) D11
CC
VREFIN
V
DDVDD
V
DGND
GND
CC
V
DGND
DNC
D5
GND
D4
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
GND
V
CC
V
CC
GND
GND
GND
V
DD
DGND
D0 (LSB)
D1
D2
D3
Pin Number
AD9432BST Name Function
1, 3, 4, 9, 11, 33, 34, 35, 38, 39, 40, 43, 48, 51 GND Analog Ground.
2, 5, 6, 10, 36, 37, 42, 44, 47, 52 V
CC
Analog Supply (+5 V).
7 ENCODE Encode Clock for ADC–Complementary.
8 ENCODE Encode Clock for ADC–True (ADC samples on rising edge of ENCODE).
14 OR Out of Range Output.
15–20, 25–30 D11–D6, D5–D0 Digital Output.
12, 21, 24, 31 DGND Digital Output Ground.
13, 22, 23, 32 V
DD
Digital Output Power Supply (2.7 V to 3.6 V).
41 DNC Do Not Connect.
45 VREFIN Reference Input for ADC (2.5 V Typical); Bypass with 0.1 µF to Ground.
46 VREFOUT Internal Reference Output (2.5 V Typical).
49 AIN Analog Input–True.
50 AIN Analog Input–Complementary.
DEFINITION OF SPECIFICATIONS
Analog Bandwidth (Small Signal)
The analog input frequency at which the spectral power of the
fundamental frequency (as determined by the FFT analysis) is
reduced by 3 dB.
Aperture Delay
The delay between a differential crossing of ENCODE and
ENCODE and the instant at which the analog input is sampled.
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter)
The sample-to-sample variation in aperture delay.
Differential Nonlinearity
The deviation of any code from an ideal 1 LSB step.
Encode Pulsewidth/Duty Cycle
Pulsewidth high is the minimum amount of time that the
ENCODE pulse should be left in Logic “1” state to achieve
rated performance; pulsewidth low is the minimum time
ENCODE pulse should be left in low state. At a given clock
rate, these specs define an acceptable Encode duty cycle.
Integral Nonlinearity
The deviation of the transfer function from a reference line
measured in fractions of 1 LSB using a “best straight line”
determined by a least square curve fit.
–4–
Minimum Conversion Rate
The encode rate at which the SNR of the lowest analog signal
frequency drops by no more than 3 dB below the guaranteed
limit.
Maximum Conversion Rate
The encode rate at which parametric testing is performed.
Output Propagation Delay
The delay between a differential crossing of ENCODE and
ENCODE and the time when all output data bits are within
valid logic levels.
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
The ratio of a change in input offset voltage to a change in
power supply voltage.
Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion (SINAD)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set at 1 dB below full
scale) to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components, including harmonics but excluding dc.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set at 1 dB below full
scale) to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components, excluding the first five harmonics and dc.
REV. B
AD9432
V
CC
17k⍀
8k⍀
100⍀
100⍀
17k⍀
8k⍀
ENCODE ENCODE
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the
peak spurious spectral component. The peak spurious component may or may not be a harmonic. May be reported in dBc
(i.e., degrades as signal level is lowered), or in dBFS (always
related back to converter full scale).
Two-Tone Intermodulation Distortion Rejection
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value
of the worst third order intermodulation product; reported in dBc.
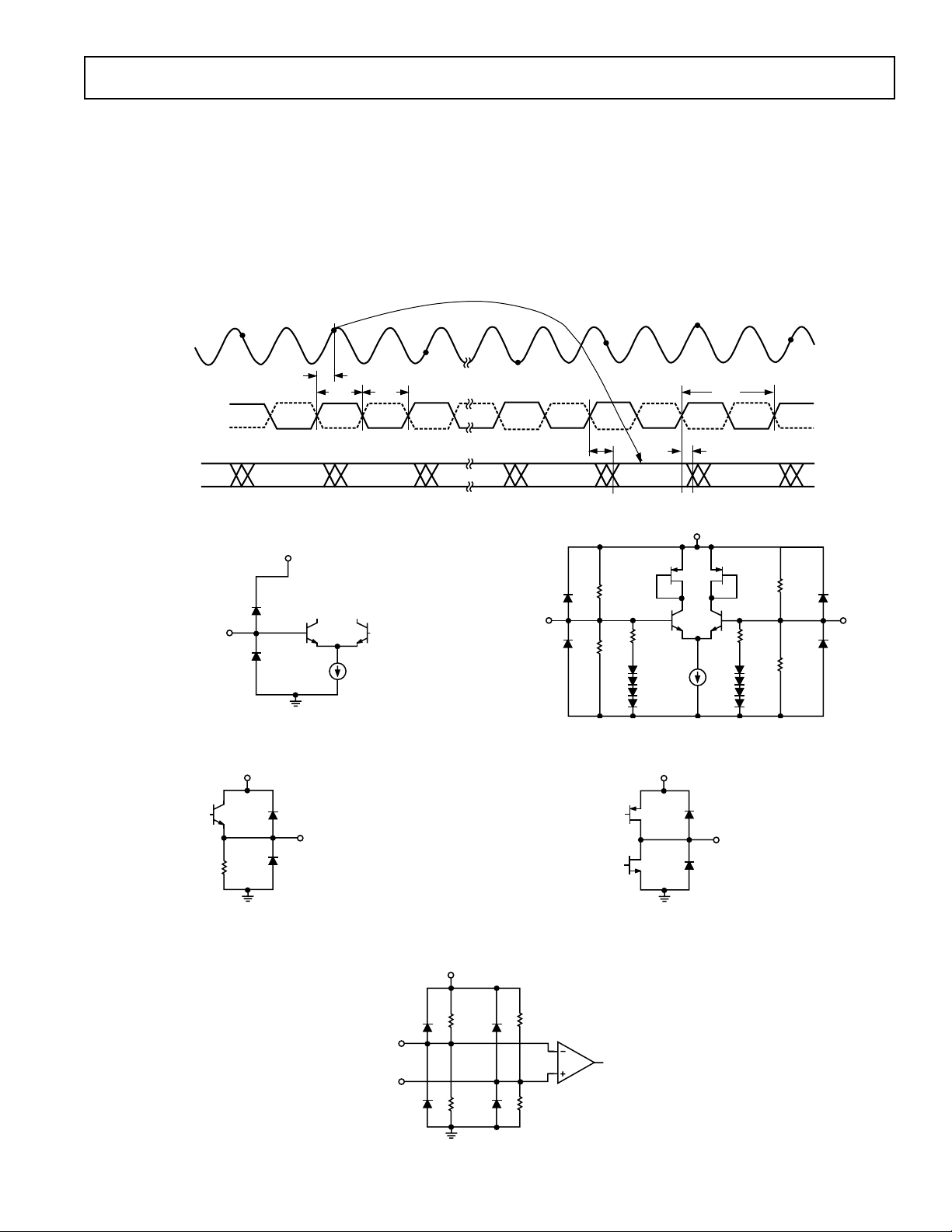
SAMPLE N–1
AIN
ENCODE
ENCODE
D11–D0
SAMPLE N
t
A
t
EH
DATA N–11 DATA N–10 N–9 DATA N–1 DATA N DATA N + 1
SAMPLE N+1
t
EL
N–2
Figure 1. Timing Diagram
V
CC
Two-Tone SFDR
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value
of the peak spurious component. The peak spurious component
may or may not be an IMD product. May be reported in dBc
(i.e., degrades as signal levels is lowered), or in dBFS (always
related back to converter full scale).
Worst Harmonic
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the
worst harmonic component, reported in dBc.
SAMPLE N+10 SAMPLE N+11
SAMPLE N+9
1/f
S
t
PD
t
V
VREFIN
Figure 2. Equivalent Voltage Reference Input Circuit
V
CC
Q1
V
REF
NPN
OUTPUT
VREFOUT
Figure 3. Equivalent Voltage Reference Output Circuit
V
CC
AIN
5k⍀
Figure 4. Equivalent Encode Input Circuit
V
DD
DIGITAL
OUTPUT
DIGITAL OUTPUT
Figure 5. Equivalent Digital Output Circuit
5k⍀
REV. B
AIN
7k⍀
ANALOG INPUT
7k⍀
Figure 6. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
–5–
 Loading...
Loading...