Page 1
Quad, 8-Bit, 100 MSPS
A
V
W
FEATURES
4 ADCs integrated into 1 package
133 mW ADC power per channel at 100 MSPS
SNR = 49 dB (to Nyquist)
ENOB = 7.85 bits
SFDR = 65 dBc (to Nyquist)
Excellent linearity
DNL = ±0.2 LSB (typical)
INL = ±0.2 LSB (typical)
Serial LVDS (AN SI-644, default)
Low power, reduced signal option (similar to IEEE 1596.3)
Data and frame clock outputs
295 MHz full-power analog bandwidth
2 V p-p input voltage range
1.8 V supply operation
Serial port control
Full-chip and individual-channel power-down modes
Flexible bit orientation
Built-in and custom digital test pattern generation
Programmable clock and data alignment
Programmable output resolution
Standby mode
APPLICATIONS
Medical imaging and nondestructive ultrasound
Portable ultrasound and digital beam-forming systems
Quadrature radio receivers
Diversity radio receivers
Tap e dr ive s
Optical networking
Test equipment
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9287 is a quad, 8-bit, 100 MSPS analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an on-chip sample-and-hold circuit designed
for low cost, low power, small size, and ease of use. The product
operates at a conversion rate of up to 100 MSPS and is optimized
for outstanding dynamic performance and low power in
applications where a small package size is critical.
The ADC requires a single 1.8 V power supply and LVPECL-/
CMOS-/LVDS-compatible sample rate clock for full performance
operation. No external reference or driver components are
required for many applications.
The ADC automatically multiplies the sample rate clock for the
appropriate LVDS serial data rate. A data clock output (DCO) for
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Serial LVDS 1.8 V A/D Converter
AD9287
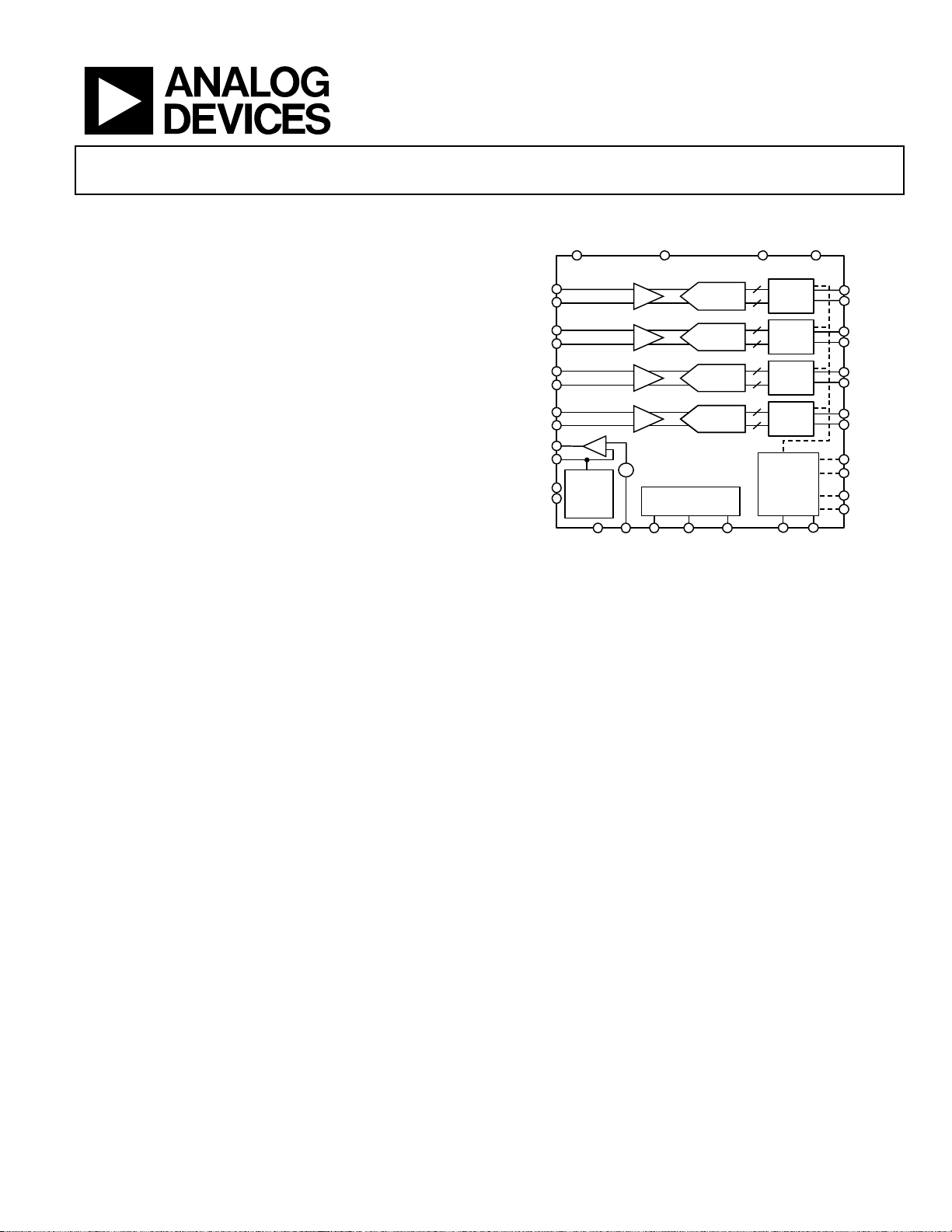
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DD
VIN + A
VIN – A
VIN + B
VIN – B
VIN + C
VIN – C
VIN + D
VIN – D
VREF
SENSE
REFT
REFB
SELECT
REF
+
–
AGND
capturing data on the output and a frame clock output (FCO)
for signaling a new output byte are provided. Individual-channel
power-down is supported and typically consumes less than
2 mW when all channels are disabled.
The ADC contains several features designed to maximize
flexibility and minimize system cost, such as programmable
clock and data alignment and programmable digital test pattern
generation. The available digital test patterns include built-in
deterministic and pseudorandom patterns, along with custom userdefined test patterns entered via the serial port interface (SPI).
The AD9287 is available in a RoHS compliant, 48-lead LFCSP. It is
specified over the industrial temperature range of −40°C to +85°C.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Small Footprint. Four ADCs are contained in a small, space-
saving package.
2. Low power of 133 mW/channel at 100 MSPS.
3. Ease of Use. A data clock output (DCO) is provided that
operates at frequencies of up to 400 MHz and supports
double data rate (DDR) operation.
4. User Flexibility. SPI control offers a wide range of flexible
features to meet specific system requirements.
5. Pin-Compatible Family. This includes the AD9219 (10-bit),
AD9228 (12-bit), and AD9259 (14-bit).
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2006–2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
PD
AD9287
T/H
T/H
T/H
T/H
0.5V
SERIAL PORT
INTERFACE
CSB
SDIO/ODMRBIAS
N
Figure 1.
PIPELINE
ADC
PIPELINE
ADC
PIPELINE
ADC
PIPELINE
ADC
SCLK/DTP
DRVDD
8
SERIAL
8
SERIAL
8
SERIAL
8
SERIAL
DATA RATE
MULTIPLIER
CLK+
DRGND
LVDS
LVDS
LVDS
LVDS
CLK–
D + A
D – A
D + B
D – B
D + C
D – C
D + D
D – D
FCO+
FCO–
DCO+
DCO–
05966-001
Page 2

AD9287
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Product Highlights........................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
AC Specifications.......................................................................... 4
Digital Specifications ................................................................... 5
Switching Specifications .............................................................. 6
Timing Diagrams.............................................................................. 7
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 9
Thermal Impedance..................................................................... 9
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 9
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 10
Analog Input Considerations ................................................... 18
Clock Input Considerations...................................................... 20
Serial Port Interface (SPI).............................................................. 28
Hardware Interface..................................................................... 28
Memory Map .................................................................................. 30
Reading the Memory Map Table.............................................. 30
Reserved Locations .................................................................... 30
Default Values............................................................................. 30
Logic Levels................................................................................. 30
Evaluation Board ............................................................................ 34
Power Supplies ............................................................................ 34
Input Signals................................................................................ 34
Output Signals ............................................................................ 34
Default Operation and Jumper Selection Settings................. 35
Alternative Analog Input Drive Configuration...................... 36
Equivalent Circuits......................................................................... 12
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 14
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 18
REVISION HISTORY
5/07—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Logic Output (SDIO/ODM)....................................... 5
Change to Pipeline Latency............................................................. 6
Added Endnote 2 to Table 4 ............................................................ 6
Changes to Figure 2 to Figure 4...................................................... 7
Changes to Figure 10...................................................................... 12
Change to Figure 15 Caption........................................................ 14
Changes to Figure 29...................................................................... 16
Changes to Figure 41...................................................................... 19
Changes to Clock Duty Cycle Considerations Section.............. 20
Changes to Power Dissipation and Power-Down Mode Section ...21
Changes to Figure 50 to Figure 52 Captions............................... 23
Change to Table 8 ........................................................................... 23
Changes to Table 9 Endnote.......................................................... 24
Changes to Digital Outputs and Timing Section ....................... 25
Added Table 10 ............................................................................... 25
Changes to RBIAS Pin Section ..................................................... 26
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 50
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 50
Deleted Figure 53 and Figure 54 .................................................. 26
Changes to Figure 56...................................................................... 27
Changes to Hardware Interface Section ...................................... 28
Added Figure 57 ............................................................................. 29
Changes to Table 15 ....................................................................... 29
Changes to Reading the Memory Map Table Section ............... 30
Changes to Output Signals Section.............................................. 34
Changes to Figure 60...................................................................... 34
Changes to Default Operation and
Jumper Selection Settings Section........................................... 35
Changes to Alternative Analog Input Drive
Configuration Section............................................................... 36
Changes to Figure 63...................................................................... 38
Changes to Table 17 ....................................................................... 46
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 50
7/06—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 52
Page 3
AD9287
SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, AIN = −0.5 dBFS, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter
1
Temp Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 8 Bits
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes Full Guaranteed
Offset Error Full ±5 ±23.4 mV
Offset Matching Full ±5 ±23.4 mV
Gain Error Full ±6 % FS
Gain Matching Full ±0.5 ±2 % FS
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) Full ±0.2 ±0.8 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity (INL) Full ±0.2 ±0.65 LSB
TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset Error Full ±2 ppm/°C
Gain Error Full ±17 ppm/°C
Reference Voltage (1 V Mode) Full ±21 ppm/°C
REFERENCE
Output Voltage Error (V
Load Regulation at 1.0 mA (V
= 1 V) Full ±5 ±30 mV
REF
= 1 V) Full 3 mV
REF
Input Resistance Full 6 kΩ
ANALOG INPUTS
Differential Input Voltage (V
= 1 V) Full 2 V p-p
REF
Common-Mode Voltage Full AVDD/2 V
Differential Input Capacitance Full 7 pF
Analog Bandwidth, Full Power Full 295 MHz
POWER SUPPLY
AVDD Full 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
DRVDD Full 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
I
AVDD
I
DRVDD
Full 260 274 mA
Full 34.5 38 mA
Total Power Dissipation (Including Output Drivers) Full 530 562 mW
Power-Down Dissipation Full 2 4 mW
Standby Dissipation
2
Full 72 mW
CROSSTALK Full −100 dB
CROSSTALK (Overrange Condition)
1
See the AN-835 Application Note, Understanding High Speed ADC Testing and Evaluation, for definitions and for details on how these tests were completed.
2
Can be controlled via the SPI.
3
Overrange condition is specific with 6 dB of the full-scale input range.
3
Full −100 dB
Rev. A | Page 3 of 52
Page 4
AD9287
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, AIN = −0.5 dBFS, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter
1
Temp Min Typ Max Unit
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO (SNR)
fIN = 2.4 MHz Full 49.2 dB
fIN = 49.7 MHz Full 46.5 49.0 dB
fIN = 70 MHz Full 49.0 dB
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE AND DISTORTION RATIO (SINAD)
fIN = 2.4 MHz Full 49.0 dB
fIN = 49.7 MHz Full 46.0 48.5 dB
fIN = 70 MHz Full 48.5 dB
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS (ENOB)
fIN = 2.4 MHz Full 7.88 Bits
fIN = 49.7 MHz Full 7.43 7.85 Bits
fIN = 70 MHz Full 7.85 Bits
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
fIN = 2.4 MHz Full 70.0 dBc
fIN = 49.7 MHz Full 54.0 65.0 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz Full 62.0 dBc
WORST HARMONIC (Second or Third)
fIN = 2.4 MHz Full −70.0 dBc
fIN = 49.7 MHz Full −65.0 −54.0 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz Full −62.0 dBc
WORST OTHER (Excluding Second or Third)
fIN = 2.4 MHz Full −77.0 dBc
fIN = 49.7 MHz Full −74.0 −58.5 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz Full −71.0 dBc
TWO-TONE INTERMODULATION DISTORTION (IMD)—
AIN1 AND AIN2 = −7.0 dBFS
f
= 15 MHz,
IN1
f
= 16 MHz
IN2
f
= 70 MHz,
IN1
= 71 MHz
f
IN2
1
See the AN-835 Application Note, Understanding High Speed ADC Testing and Evaluation, for definitions and for details on how these tests were completed.
25°C 70.0 dBc
25°C 68.5 dBc
Rev. A | Page 4 of 52
Page 5
AD9287
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, AIN = −0.5 dBFS, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter
1
Temp Min Typ Max Unit
CLOCK INPUTS (CLK+, CLK−)
Logic Compliance CMOS/LVDS/LVPECL
Differential Input Voltage
2
Full 250 mV p-p
Input Common-Mode Voltage Full 1.2 V
Input Resistance (Differential) 25°C 20 kΩ
Input Capacitance 25°C 1.5 pF
LOGIC INPUTS (PDWN, SCLK/DTP)
Logic 1 Voltage Full 1.2 3.6 V
Logic 0 Voltage Full 0.3 V
Input Resistance 25°C 30 kΩ
Input Capacitance 25°C 0.5 pF
LOGIC INPUT (CSB)
Logic 1 Voltage Full 1.2 3.6 V
Logic 0 Voltage Full 0.3 V
Input Resistance 25°C 70 kΩ
Input Capacitance 25°C 0.5 pF
LOGIC INPUT (SDIO/ODM)
Logic 1 Voltage Full 1.2 DRVDD + 0.3 V
Logic 0 Voltage Full 0 0.3 V
Input Resistance 25°C 30 kΩ
Input Capacitance 25°C 2 pF
LOGIC OUTPUT (SDIO/ODM)
3
Logic 1 Voltage (IOH = 800 μA) Full 1.79 V
Logic 0 Voltage (IOL = 50 μA) Full 0.05 V
DIGITAL OUTPUTS (D + x, D − x), (ANSI-644)
Logic Compliance LVDS
Differential Output Voltage (VOD) Full 247 454 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS) Full 1.125 1.375 V
Output Coding (Default) Offset binary
DIGITAL OUTPUTS (D + x, D − x),
(Low Power, Reduced Signal Option)
Logic Compliance LVDS
Differential Output Voltage (VOD) Full 150 250 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS) Full 1.10 1.30 V
Output Coding (Default) Offset binary
1
See the AN-835 Application Note, Understanding High Speed ADC Testing and Evaluation, for definitions and for details on how these tests were completed.
2
This is specified for LVDS and LVPECL only.
3
This is specified for 13 SDIO pins sharing the same connection.
Rev. A | Page 5 of 52
Page 6
AD9287
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, AIN = −0.5 dBFS, unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
Parameter
CLOCK
1, 2
3
Temp Min Typ Max Unit
Maximum Clock Rate Full 100 MSPS
Minimum Clock Rate Full 10 MSPS
Clock Pulse Width High (tEH) Full 5 ns
Clock Pulse Width Low (tEL) Full 5 ns
OUTPUT PARAMETERS
3
Propagation Delay (tPD) Full 2.0 2.7 3.5 ns
Rise Time (tR) (20% to 80%) Full 300 ps
Fall Time (tF) (20% to 80%) Full 300 ps
FCO Propagation Delay (t
DCO Propagation Delay (t
DCO to Data Delay (t
DATA
DCO to FCO Delay (t
Data to Data Skew
(t
DATA-MAX
− t
DATA-MIN
)
) Full 2.0 2.7 3.5 ns
FCO
4
FRAME
)
CPD
4
)
4
)
Full
Full (t
Full (t
SAMPLE
SAMPLE
/16) − 300 (t
/16) − 300 (t
+
t
FCO
(t
/16)
SAMPLE
/16) (t
SAMPLE
/16) (t
SAMPLE
ns
/16) + 300 ps
SAMPLE
/16) + 300 ps
SAMPLE
Full ±50 ±150 ps
Wake-Up Time (Standby) 25°C 600 ns
Wake-Up Time (Power-Down) 25°C 375 μs
Pipeline Latency Full 8 CLK cycles
APERTURE
Aperture Delay (tA) 25°C 500 ps
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) 25°C <1 ps rms
Out-of-Range Recovery Time 25°C 2 CLK cycles
1
See the AN-835 Application Note, Understanding High Speed ADC Testing and Evaluation, for definitions and for details on how these tests were completed.
2
Measured on standard FR-4 material.
3
Can be adjusted via the SPI.
4
t
/16 is based on the number of bits multiplied by 2; delays are based on half duty cycles.
SAMPLE
Rev. A | Page 6 of 52
Page 7
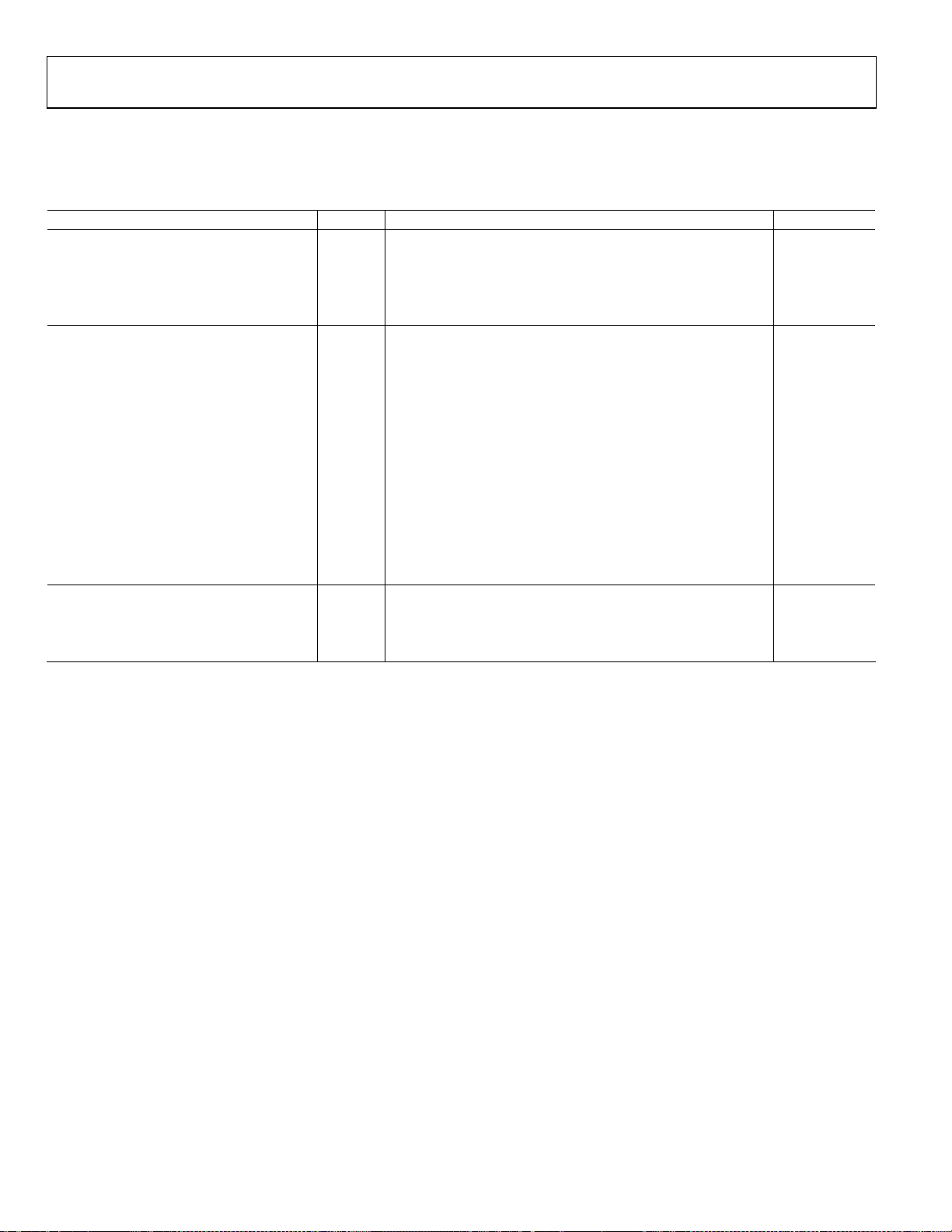
AD9287
TIMING DIAGRAMS
N – 1
AIN
CLK–
CLK+
DCO–
DCO+
FCO–
FCO+
D – x
D + x
t
A
N – 1
N
D4
N – 9
D3
N – 9
t
EL
t
DATA
D2
N – 9
D1
N – 9
D0
N – 9
MSB
N – 8
D6
N – 8
D5
N – 8D4N – 8
D3
N – 8D2N – 8
D1
N – 8
5966-040
t
EH
t
CPD
MSB
N – 9
t
FRAME
D6
N – 9
D5
N – 9
t
FCO
t
PD
Figure 2. 8-Bit Data Serial Stream, MSB First (Default)
AIN
CLK–
CLK+
DCO–
DCO+
FCO–
FCO+
D – x
D + x
t
A
N
t
t
t
FCO
PD
CPD
t
EH
t
FRAME
MSB
D10
N – 9
N – 9D9N – 9D8N – 9D7N – 9D6N – 9D5N – 9D4N – 9D3N – 9
Figure 3. 12-Bit Data Serial Stream, MSB First
t
EL
t
DATA
D2
D1
N – 9
0
D0
N – 9
0
N – 9
0
0
MSB
N – 8
D10
N – 8
5966-039
Rev. A | Page 7 of 52
Page 8
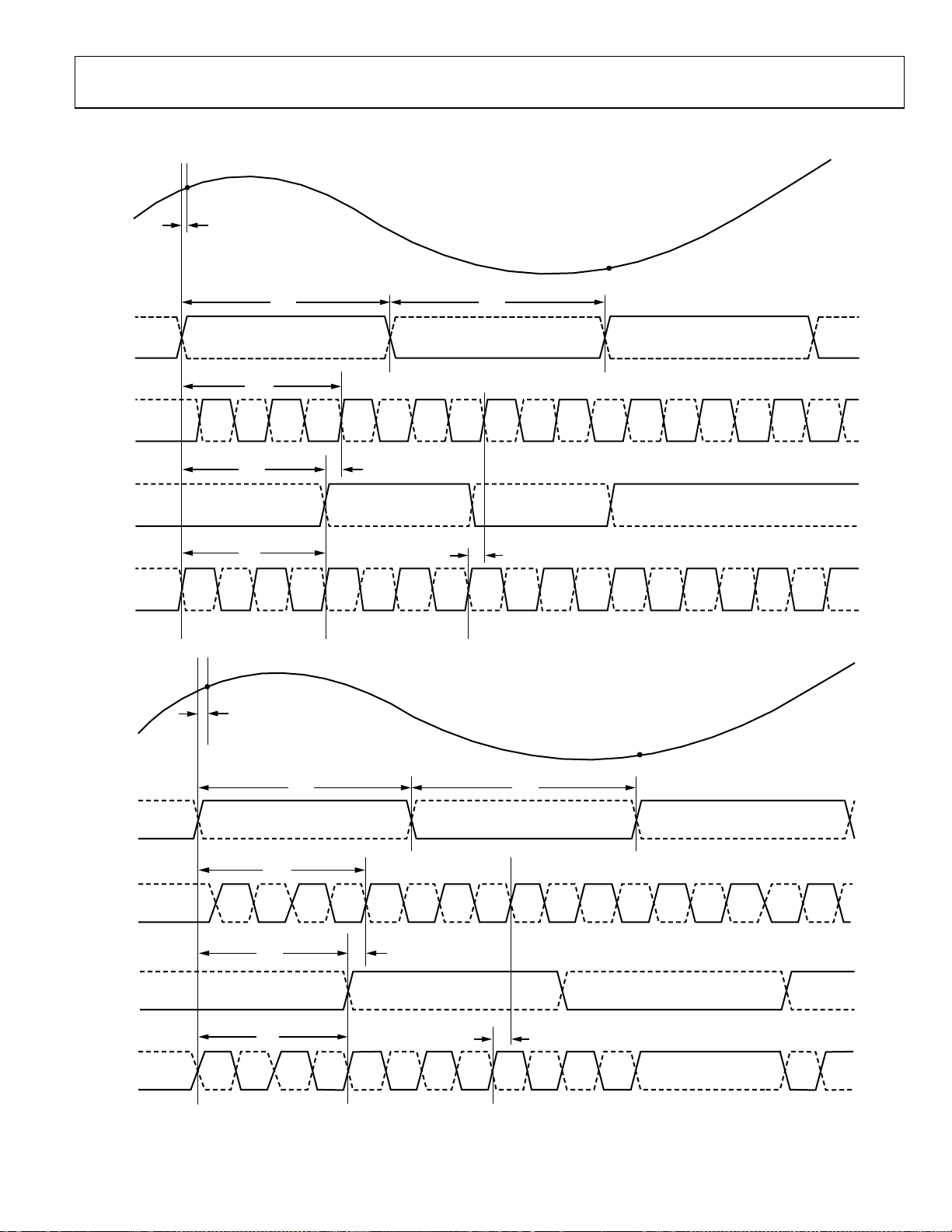
AD9287
N – 1
AIN
t
A
N
CLK–
CLK+
DCO–
DCO+
FCO–
FCO+
D – x
D + x
t
EH
t
CPD
t
FCO
t
PD
t
FRAME
LSB
N – 9D0N – 9D1N – 9D2N – 9D3N – 9D4N – 9D5N – 9D6N – 9
t
EL
t
DATA
LSB
N – 8D0N – 8D1N – 8D2N – 8D3N – 8D4N – 8
05966-041
Figure 4. 8-Bit Data Serial Stream, LSB First
Rev. A | Page 8 of 52
Page 9
AD9287
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5.
With
Parameter
ELECTRICAL
AVDD AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
DRVDD DRGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
AGND DRGND −0.3 V to +0.3 V
AVDD DRVDD −2.0 V to +2.0 V
Digital Outputs
(D + x, D − x, DCO+,
DCO−, FCO+, FCO−)
CLK+, CLK− AGND −0.3 V to +3.9 V
VIN + x, VIN − x AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
SDIO/ODM AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
PDWN, SCLK/DTP, CSB AGND −0.3 V to +3.9 V
REFT, REFB, RBIAS AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
VREF, SENSE AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
ENVIRONMENTAL
Operating Temperature
Range (Ambient)
Maximum Junction
Temperature
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 10 sec)
Storage Temperature
Range (Ambient)
Respect To
DRGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
−40°C to +85°C
150°C
300°C
−65°C to +150°C
Rating
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL IMPEDANCE
Table 6.
Air Flow Velocity (m/sec) θ
0.0 24 °C/W
1.0 21 12.6 1.2 °C/W
2.5 19 °C/W
1
θJA for a 4-layer PCB with solid ground plane (simulated). Exposed pad
soldered to PCB.
1
θ
JA
θ
JB
Unit
JC
ESD CAUTION
Rev. A | Page 9 of 52
Page 10
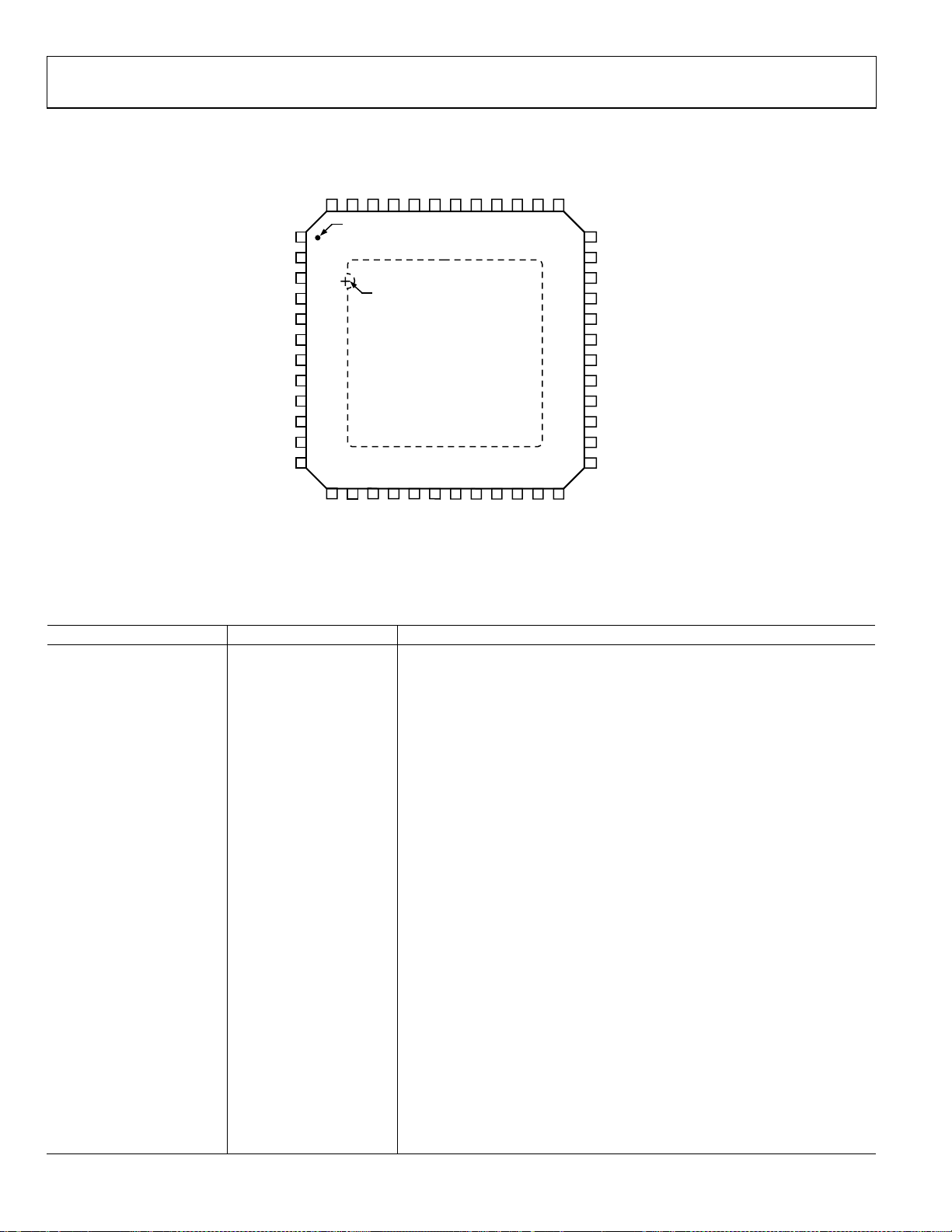
AD9287
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
AVDD
AVDD
VIN – D
VIN + D
AVDD
AVDD
CLK–
CLK+
AVDD
AVDD
DRGND
DRVDD
VIN – C
VIN + C
47
48
PIN 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
INDICATOR
14
13
D – D
D + D
REFT
REFB
43
44
AD9287
TOP VIEW
17
18
D – B
D + B
VREF
42
19
D – A
AVDD
AVDD
45
46
EXPOSED PADDLE, PIN 0
(BOTTO M OF PACKAGE)
16
15
D – C
D + C
SENSE
41
20
D + A
VIN + B
VIN – B
AVDD
RBIAS
37
38
39
40
36
AVDD
35
AVDD
34
VIN – A
33
VIN + A
32
AVDD
31
PDWN
30
CSB
29
SDIO/ODM
28
SCLK/DTP
27
AVDD
26
DRGND
25
DRVDD
222123
24
FCO–
FCO+
DCO–
DCO+
Figure 5. 48-Lead LFCSP Pin Configuration, Top View
Table 7. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
0 AGND Analog Ground (Exposed Paddle)
1, 2, 5, 6, 9, 10, 27, 32,
35, 36, 39, 45, 46
11, 26
12, 25
3
4
7
AVDD 1.8 V Analog Supply
DRGND Digital Output Driver Ground
DRVDD 1.8 V Digital Output Driver Supply
VIN − D ADC D Analog Input Complement
VIN + D ADC D Analog Input True
CLK− Input Clock Complement
8 CLK+ Input Clock True
13
14
15
16
17
18
D − D ADC D Digital Output Complement
D + D ADC D Digital Output True
D − C ADC C Digital Output Complement
D + C ADC C Digital Output True
D − B ADC B Digital Output Complement
D + B ADC B Digital Output True
19 D − A ADC A Digital Output Complement
20 D + A ADC A Digital Output True
21
22
23
24
FCO− Frame Clock Output Complement
FCO+ Frame Clock Output True
DCO− Data Clock Output Complement
DCO+ Data Clock Output True
28 SCLK/DTP Serial Clock/Digital Test Pattern
29
30
SDIO/ODM Serial Data IO/Output Driver Mode
CSB Chip Select Bar
31 PDWN Power-Down
33
34
VIN + A ADC A Analog Input True
VIN − A ADC A Analog Input Complement
Rev. A | Page 10 of 52
05966-003
Page 11
AD9287
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
37
38
40
41
42
43
44
47
48
VIN − B ADC B Analog Input Complement
VIN + B ADC B Analog Input True
RBIAS External resistor sets the internal ADC core bias current
SENSE Reference Mode Selection
VREF Voltage Reference Input/Output
REFB Differential Reference (Negative)
REFT Differential Reference (Positive)
VIN + C ADC C Analog Input True
VIN − C ADC C Analog Input Complement
Rev. A | Page 11 of 52
Page 12
AD9287
V
C
S
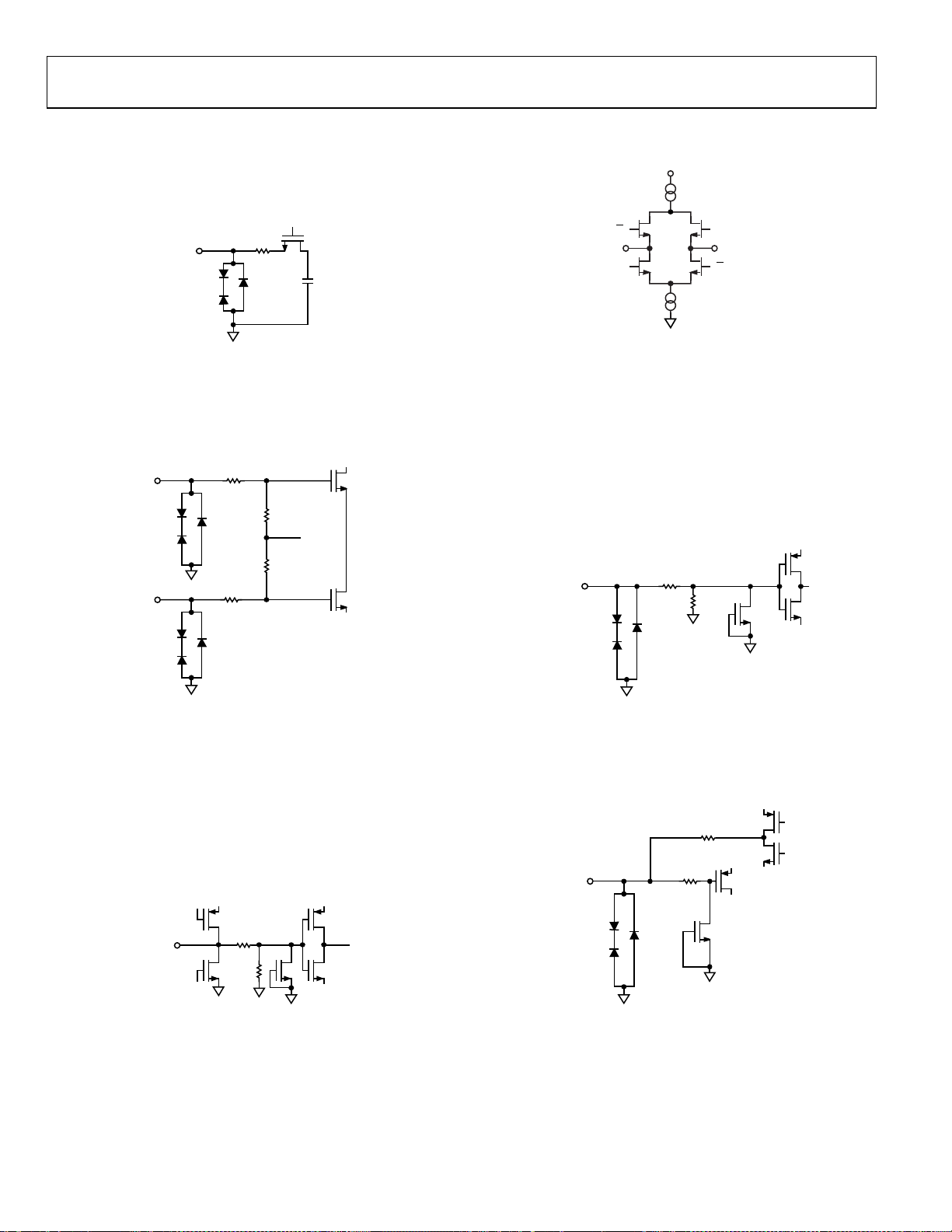
EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS
DRVDD
IN ± x
Figure 6. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
LK+
CLK–
10
10k
10k
10
1.25V
V
D– D+
V
05966-030
DRGND
V
V
5966-005
Figure 9. Equivalent Digital Output Circuit
SCLK/DTP
AND
PDWN
1k
30k
Figure 7. Equivalent Clock Input Circuit
DIO/ODM
350
30k
Figure 8. Equivalent SDIO/ODM Input Circuit
05966-032
05966-033
Figure 10. Equivalent SCLK/DTP and PDWN Input Circuit
RBIAS
05966-035
100
05966-031
Figure 11. Equivalent RBIAS Circuit
Rev. A | Page 12 of 52
Page 13
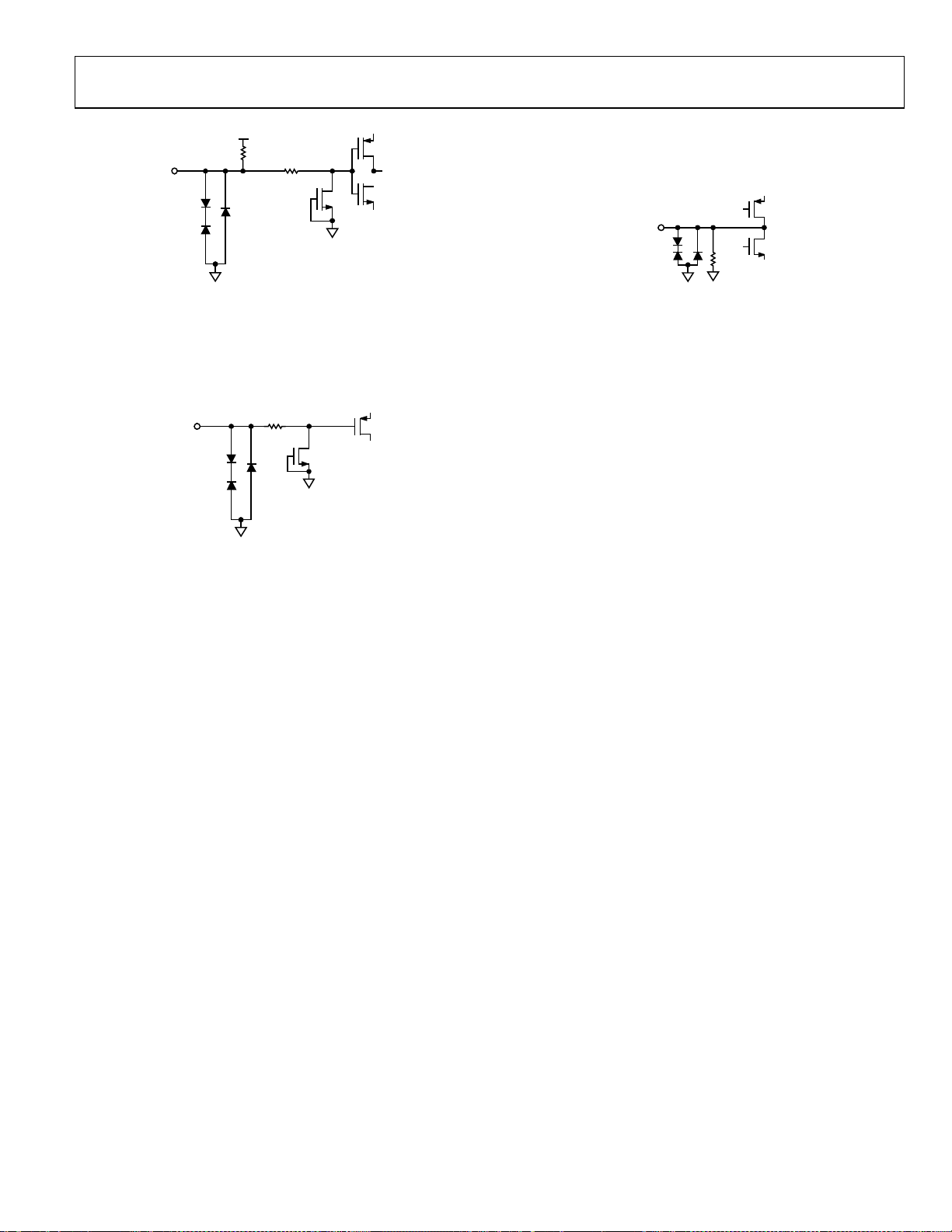
AD9287
A
V
DD
70k
CSB
Figure 12. Equivalent CSB Input Circuit
1k
VREF
6k
05966-034
5966-037
Figure 14. Equivalent VREF Circuit
SENSE
1k
05966-036
Figure 13. Equivalent SENSE Circuit
Rev. A | Page 13 of 52
Page 14
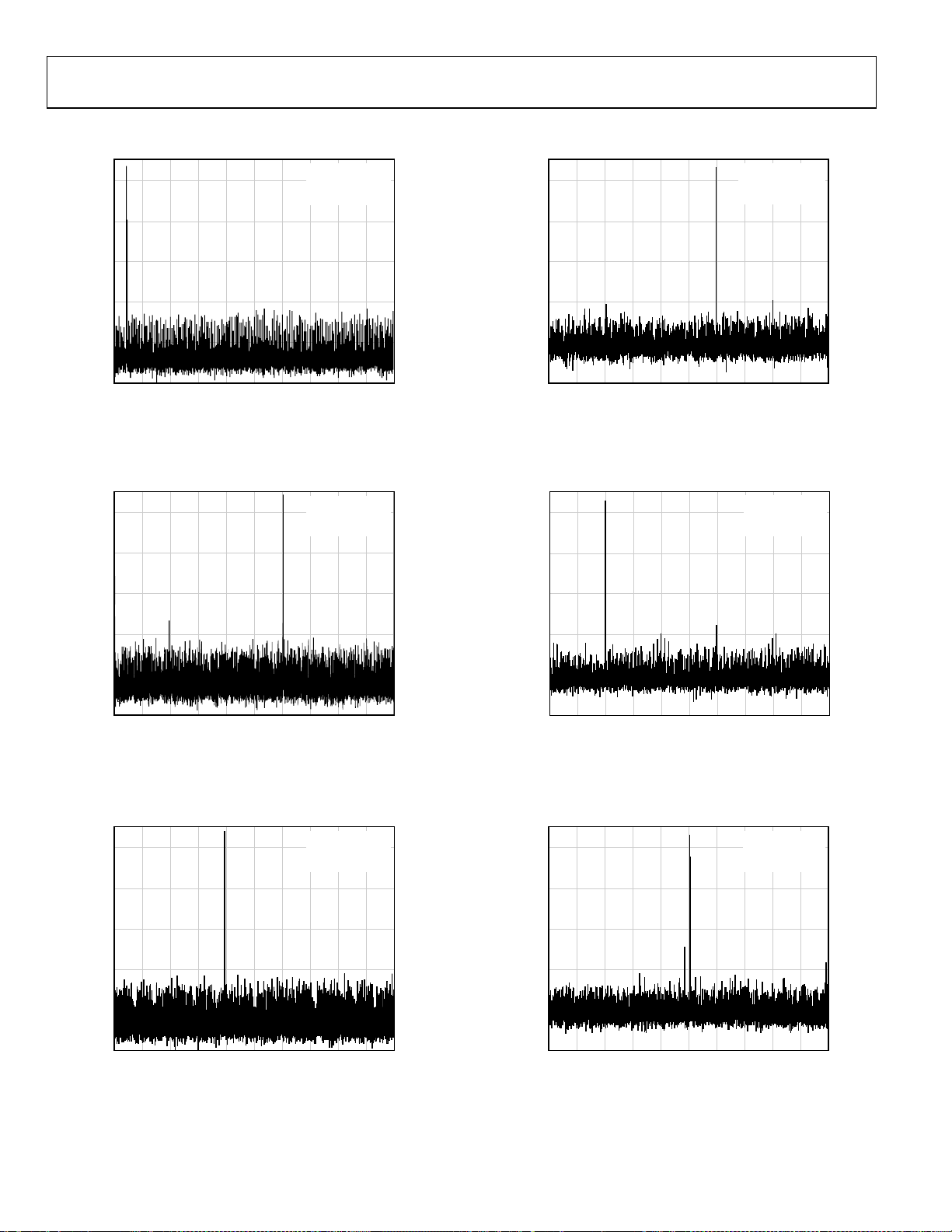
AD9287
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
–10
–30
AIN = –0.5dBF S
SNR = 49.21dB
ENOB = 7.88 BI TS
SFDR = 70.89dBc
–10
–30
AIN = –0.5dBF S
SNR = 48.36dB
ENOB = 7.74 BITS
SFDR = 65.17dBc
–50
–70
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–90
–110
05
5 1015202530354045
FREQUENCY (MHz )
Figure 15. Single-Tone 32k FFT with f
–10
–30
–50
–70
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–90
= 2.4 MHz, f
IN
SAMPLE
AIN = –0.5dBF S
SNR = 49.17dB
ENOB = 7.87 BITS
SFDR = 62.44dBc
0
05966-055
= 100 MSPS
–50
–70
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–90
–110
050
5 1015202530354045
Figure 18. Single-Tone 32k FFT with f
–10
–30
–50
–70
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–90
FREQUENCY (MHz )
= 170 MHz, f
IN
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
AIN = –0.5dBF S
SNR = 48.07dB
ENOB = 7.69 BI TS
SFDR = 61.37dBc
05966-051
–110
05
5 1015202530354045
FREQUENCY (MHz )
Figure 16. Single-Tone 32k FFT with f
–10
–30
–50
–70
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–90
–110
05
5 1015202530354045
FREQUENCY (MHz )
Figure 17. Single-Tone 32k FFT with f
= 70 MHz, f
IN
= 120 MHz, f
IN
SAMPLE
AIN = –0.5dBF S
SNR = 49.16dB
ENOB = 7.87 BITS
SFDR = 70.32dBc
SAMPLE
0
05966-059
= 100 MSPS
0
05966-060
= 100 MSPS
–110
050
5 1015202530354045
Figure 19. Single-Tone 32k FFT with f
–10
–30
–50
–70
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–90
–110
050
5 1015202530354045
Figure 20. Single-Tone 32k FFT with f
FREQUENCY (MHz)
= 190 MHz, f
IN
FREQUENCY (MHz )
= 225 MHz, f
IN
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
AIN = –0.5dBF S
SNR = 48.32dB
ENOB = 7.73 BITS
SFDR = 54.48dBc
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
05966-052
05966-053
Rev. A | Page 14 of 52
Page 15
AD9287
80
80
75
70
2V p-p, SFDR
65
60
55
SNR/SFDR (dB)
50
2V p-p, SNR
45
40
10 100
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
f
(MSPS)
SAMPLE
Figure 21. SNR/SFDR vs. f
80
70
2V p-p, SFDR
60
, fIN = 10.3 MHz, f
SAMPLE
SAMPLE
= 100 MSPS
70
60
50
40
30
SNR/SFDR (dB)
20
10
0
–60 0
–50 –40 –30 –20 –10
05966-061
ANALOG INP UT LEVEL (dBFS)
Figure 24. SNR/SFDR vs. Analog Input Level, f
–10
–30
–50
2V p-p, SFDR
60dB REFERENCE
2V p-p, SNR
= 35 MHz, f
IN
AIN1 AND AIN2 = –7dBF S
SAMPLE
SFDR = 72.90dBc
IMD2 = 70.43dBc
IMD3 = 71.97dBc
05966-058
= 100 MSPS
50
SNR/SFDR (dB)
2V p-p, SNR
40
30
10 100
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
f
(MSPS)
SAMPLE
Figure 22. SNR/SFDR vs. f
80
70
60
50
40
30
SNR/SFDR (dB)
20
10
0
–60 0
–50 –40 –30 –20 –10
ANALOG INP UT LEVEL (dBFS)
, fIN = 35 MHz, f
SAMPLE
2V p-p, SNR
Figure 23. SNR/SFDR vs. Analog Input Level, f
SAMPLE
2V p-p, SFDR
60dB REFERENCE
= 10.3 MHz, f
IN
= 100 MSPS
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
–70
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–90
–110
05
5 1015202530354045
= 16 MHz, f
f
IN2
= 71 MHz, f
f
IN2
FREQUENCY (MHz )
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
FREQUENCY (MHz )
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
= 15 MHz and
IN1
= 70 MHz and
IN1
05966-062
Figure 25. Two-Tone 32k FFT with f
AIN1 AND AIN2 = –7dBF S
SFDR = 71.14dBc
–10
IMD2 = 69.46d Bc
IMD3 = 70.33d Bc
–30
–50
–70
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–90
–110
05
5 1015202530354045
05966-057
Figure 26. Two-Tone 32k FFT with f
0
05966-049
0
05966-050
Rev. A | Page 15 of 52
Page 16
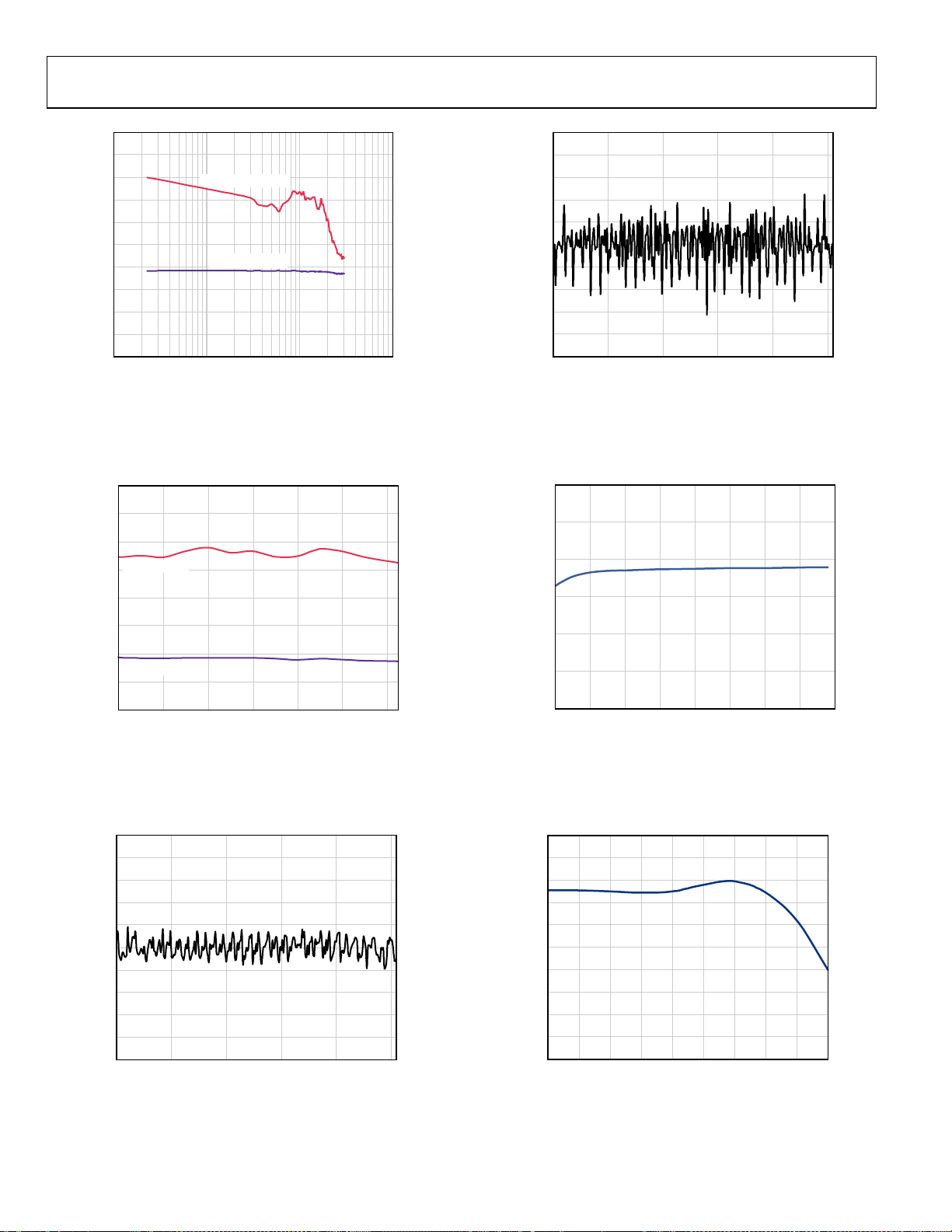
AD9287
–
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
SNR/SFDR (dB)
45
40
35
30
1
2V p-p, SFDR (dBc)
2V p-p, SNR ( dB)
10 100
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 27. SNR/SFDR vs. Analog Input Frequency, f
SAMPLE
1000
= 100 MSPS
05966-063
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
DNL (LSB)
–0.1
–0.2
–0.3
–0.4
–0.5
0
50 100 150 200 250
Figure 30. DNL, f
CODE
= 2.4 MHz, f
IN
SAMPLE
= 100 MSPS
05966-066
80
75
70
2V p-p, SFDR
65
60
55
SNR/SFDR (dB)
50
2V p-p, SNR
45
40
–40
–200 20406080
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 28. SINAD/SFDR vs. Temperature, f
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
INL (LSB)
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0 50 100 150 200 250
CODE
Figure 29. INL, f
= 2.4 MHz, f
IN
= 10.3 MHz, f
IN
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
45.0
–45.5
–46.0
–46.5
CMRR (dB)
–47.0
–47.5
–48.0
10 15 20 25 35 4530 40 50
05966-064
Figure 31. CMRR vs. Analog Input Frequency, f
0
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
–1.2
–1.4
–1.6
INPUT FULL-SCALE AMPL ITUDE (dB)
–1.8
–2.0
10 100
05966-065
Figure 32. Input Full-Scale Amplitude vs. f
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
f
(MSPS)
SAMPLE
SAMPLE
05966-075
05966-048
Rev. A | Page 16 of 52
Page 17

AD9287
NPR = 40.1 2dB
–10
–30
–50
–70
AMPLI TUDE (d B)
–90
–110
05
5 1015202530354045
FREQUENCY (MHz )
Figure 33. Noise Power Ratio (NPR), f
NOTCH = 18MHz
NOTCH WIDTH = 3MHz
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
0
05966-054
0
–1
–2
–3
–4
–5
–6
–7
FUNDAMENTAL L EVEL (dBF S)
–8
–9
–10
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
FREQUENCY (MHz )
Figure 34. Full-Power Bandwidth vs. Frequency, f
–3dB CUTOFF = 295MHz
SAMPLE
05966-077
= 100 MSPS
Rev. A | Page 17 of 52
Page 18

AD9287
THEORY OF OPERATION
The AD9287 architecture consists of a pipelined ADC divided into
three sections: a 4-bit first stage followed by eight 1.5-bit stages and
a final 3-bit flash. Each stage provides sufficient overlap to correct
for flash errors in the preceding stage. The quantized outputs from
each stage are combined into a final 8-bit result in the digital
correction logic. The pipelined architecture permits the first stage
to operate with a new input sample while the remaining stages
operate with preceding samples. Sampling occurs on the rising
edge of the clock.
Each stage of the pipeline, excluding the last, consists of a low
resolution flash ADC connected to a switched-capacitor DAC
and an interstage residue amplifier (for example, a multiplying
digital-to-analog converter (MDAC)). The residue amplifier
magnifies the difference between the reconstructed DAC output
and the flash input for the next stage in the pipeline. One bit of
redundancy is used in each stage to facilitate digital correction of
flash errors. The last stage simply consists of a flash ADC.
The output staging block aligns the data, corrects errors, and
passes the data to the output buffers. The data is then serialized
and aligned to the frame and data clocks.
ANALOG INPUT CONSIDERATIONS
The analog input to the AD9287 is a differential switchedcapacitor circuit designed for processing differential input
signals. The circuit can support a wide common-mode range
while maintaining excellent performance. By using an input
common-mode voltage of midsupply, users can minimize
signal-dependent errors and achieve optimum performance.
H
C
VIN + x
VIN – x
PAR
C
SAMPLE
SS
SS
C
SAMPLE
C
PAR
H
Figure 35. Switched-Capacitor Input Circuit
The clock signal alternately switches the input circuit between
sample mode and hold mode (see
Figure 35). When the input
circuit is switched to sample mode, the signal source must be
capable of charging the sample capacitors and settling within
one-half of a clock cycle. A small resistor in series with each
input can help reduce the peak transient current injected from
the output stage of the driving source. In addition, low-Q inductors
or ferrite beads can be placed on each leg of the input to reduce
high differential capacitance at the analog inputs and therefore
achieve the maximum bandwidth of the ADC. Such use of low-Q
H
H
5966-006
Rev. A | Page 18 of 52
inductors or ferrite beads is required when driving the converter
front end at high IF frequencies. Either a shunt capacitor or two
single-ended capacitors can be placed on the inputs to provide a
matching passive network. This ultimately creates a low-pass
filter at the input to limit unwanted broadband noise. See the
AN-742 Application Note, the AN-827 Application Note, and the
Analog Dialogue article “Transformer-Coupled Front-End for
Wideband A/D Converters” (Volumne 39, April 2005) for more
information on this subject. In general, the precise values
depend on the application.
The analog inputs of the AD9287 are not internally dc-biased.
Therefore, in ac-coupled applications, the user must provide
this bias externally. Setting the device so that V
= AV D D /2 is
CM
recommended for optimum performance, but the device can
function over a wider range with reasonable performance, as
shown in
Figure 36 and Figure 37.
90
f
= 2.4MHz
IN
f
= 100MSPS
SAMPLE
80
70
60
50
40
SNR/SFDR (dB)
30
20
10
0
0.2 1.6
0.4 0.6 0.8 1. 0 1.2 1.4
ANALOG INP UT COMMON- MODE VOL TAGE (V)
Figure 36. SNR/SFDR vs. Common-Mode Voltage,
= 2.4 MHz, f
f
IN
90
f
= 30MHz
IN
f
= 100MSPS
SAMPLE
80
70
60
50
40
SNR/SFDR (dB)
30
20
10
0
0.2 1.6
0.4 0.6 0.8 1. 0 1.2 1.4
ANALOG INP UT COMMON- MODE VOL TAGE (V)
Figure 37. SNR/SFDR vs. Common-Mode Voltage,
= 30 MHz, f
f
IN
SFDR (dBc)
SNR (dB)
SAMPLE
SFDR (dBc)
SNR (dB)
= 100 MSPS
SAMPLE
= 100 MSPS
05966-067
05966-068
Page 19

AD9287
A
A
2
A
V
F
For best dynamic performance, the source impedances driving
VIN + x and VIN − x should be matched such that commonmode settling errors are symmetrical. These errors are reduced
by the common-mode rejection of the ADC. An internal
reference buffer creates the positive and negative reference
voltages, REFT and REFB, respectively, that define the span of
the ADC core. The output common-mode of the reference buffer
is set to midsupply, and the REFT and REFB voltages and span
are defined as
REFT = 1/2 (AVDD + VREF)
REFB = 1/2 (AVDD − VREF)
Span = 2 × (REFT − REFB) = 2 × VREF
It can be seen from these equations that the REFT and REFB
voltages are symmetrical about the midsupply voltage and, by
definition, the input span is twice the value of the VREF voltage.
Maximum SNR performance is achieved by setting the ADC to
the largest span in a differential configuration. In the case of the
AD9287, the largest input span available is 2 V p-p.
Differential Input Configurations
There are several ways to drive the AD9287 either actively or
passively; however, optimum performance is achieved by driving
the analog input differentially. For example, using the
AD8332
differential driver to drive the AD9287 provides excellent performance and a flexible interface to the ADC (see
Figure 41) for
baseband applications. This configuration is commonly used
for medical ultrasound systems.
For applications where SNR is a key parameter, differential
transformer coupling is the recommended input configuration
(see
Figure 38 and Figure 39), because the noise performance of
most amplifiers is not adequate to achieve the true performance
of the AD9287.
Regardless of the configuration, the value of the shunt capacitor,
C, is dependent on the input frequency and may need to be
reduced or removed.
DT1-1WT
2V p-p
1k
1k
1
C
DIFF
1:1 Z RATIO
49.9
AVD D
0.1F
IS OPTIONAL
C
R
1
C
DIFF
R
C
VIN + x
VIN – x
ADC
AD9287
AGND
05966-008
Figure 38. Differential Transformer-Coupled Configuration
for Baseband Applications
2V p-p
16nH
65
0.1F
1k
1k
DT1-1WT
1:1 Z RATIO
AVD D
499
0.1F
16nH
16nH
33
2.2pF 1k
33
VIN + x
ADC
AD9287
VIN – x
Figure 39. Differential Transformer-Coupled Configuration
for IF Applications
Single-Ended Input Configuration
A single-ended input may provide adequate performance in costsensitive applications. In this configuration, SFDR and distortion
performance degrade due to the large input common-mode swing.
If the application requires a single-ended input configuration,
ensure that the source impedances on each input are well matched
in order to achieve the best possible performance. A full-scale
input of 2 V p-p can be applied to the ADC’s VIN + x pin while the
VIN − x pin is terminated.
Figure 40 details a typical single-
ended input configuration.
DD
C
V p-p
49.9
0.1µF
0.1µF
AVD D
1k
1k
1k
25
R
1
C
DIFF
R
C
VIN + x
VIN – x
ADC
AD9287
05966-047
1V p-p
0.1F
0.1
LOP
120nH
0.1F
Figure 41. Differential Input Configuration Using the
22pF
18nF
INH
AD8332
LNA
LMD
LON
274
VIP
VIN
0.1F
1
C
IS OPTIONAL
DIFF
Figure 40. Single-Ended Input Configuration
680nH
187
VOH
VGA
VOL
AD8332 with Two-Pole, 16 MHz Low-Pass Filter
187
68pF
680nH
LPF
10k
33
10k
+
AVDD
10k
33
10k
AVDD
1k
VIN + x
ADC
AD9287
VIN – x
05966-007
05966-009
Rev. A | Page 19 of 52
Page 20

AD9287
A
C
A
CLOCK INPUT CONSIDERATIONS
For optimum performance, the AD9287 sample clock inputs
(CLK+ and CLK−) should be clocked with a differential signal.
This signal is typically ac-coupled to the CLK+ and CLK− pins
via a transformer or capacitors. These pins are biased internally
and require no additional biasing.
Figure 42 shows a preferred method for clocking the AD9287. The
low jitter clock source is converted from a single-ended signal to a
differential signal using an RF transformer. The back-to-back
Schottky diodes across the secondary transformer limit clock
excursions into the AD9287 to approximately 0.8 V p-p differential.
This helps prevent the large voltage swings of the clock from
feeding through to other portions of the AD9287, and it preserves
the fast rise and fall times of the signal, which are critical to low
jitter performance.
XFMR
0.1µF
®
0.1µF0.1µF
0.1µF
SCHOTTKY
DIODES:
HSM2812
0.1µF
100
0.1µF
240240
0.1µF
100
0.1µF
Figure 45). Although the
CLK+
ADC
AD9287
CLK–
CLK+
ADC
AD9287
CLK–
CLK+
ADC
AD9287
CLK–
05966-024
Rev. A | Page 20 of 52
Mini-Circuits
ADT1-1WT, 1:1Z
CLK+
50
100
Figure 42. Transformer-Coupled Differential Clock
If a low jitter clock is available, another option is to ac-couple a
differential PECL signal to the sample clock input pins as shown
in
Figure 43. The AD9510/AD9511/AD9512/AD9513/AD9514/
AD9515 family of clock drivers offers excellent jitter performance.
AD9510/AD9511/
AD9512/AD9513/
AD9514/AD9515
CLK+
CLK–
50
1
0.1µF
CLK
PECL DRIVER
0.1µF
50
CLK
1
1
50 RESISTORS ARE OPT IONAL.
Figure 43. Differential PECL Sample Clock
AD9510/AD9511/
AD9512/AD9513/
AD9514/AD9515
CLK+
CLK–
50
1
50 RESISTORS ARE OPT IONAL.
0.1µF
CLK
LVDS DRIVER
0.1µF
50
CLK
1
1
Figure 44. Differential LVDS Sample Clock
In some applications, it is acceptable to drive the sample clock
inputs with a single-ended CMOS signal. In such applications,
CLK+ should be driven directly from a CMOS gate, and the
CLK− pin should be bypassed to ground with a 0.1 F capacitor
in parallel with a 39 kΩ resistor (see
05966-025
05966-026
CLK+ input circuit supply is AVDD (1.8 V), this input is
designed to withstand input voltages of up to 3.3 V and
therefore offers several selections for the drive logic voltage.
D9510/AD9511/
AD9512/AD9513/
0.1µF
LK+
1
1
50
0.1µF
50 RESISTORS ARE OPTIONAL.
AD9514/AD9515
CLK
CMOS DRIVER
CLK
0.1µF
OPTIONA L
100
39k
0.1µF
CLK+
ADC
AD9287
CLK–
Figure 45. Single-Ended 1.8 V CMOS Sample Clock
D9510/AD9511/
AD9512/AD9513/
CLK+
0.1µF
1
50
0.1µF
1
50 RESISTORS ARE OPTIO NAL.
AD9514/AD9515
CLK
CMOS DRIVER
CLK
OPTION AL
100
0.1µF
0.1µF
CLK+
ADC
AD9287
CLK–
Figure 46. Single-Ended 3.3 V CMOS Sample Clock
Clock Duty Cycle Considerations
Typical high speed ADCs use both clock edges to generate a variety
of internal timing signals. As a result, these ADCs may be sensitive
to the clock duty cycle. Commonly, a 5% tolerance is required on
the clock duty cycle to maintain dynamic performance characteristics. The AD9287 contains a duty cycle stabilizer (DCS) that
retimes the nonsampling edge, providing an internal clock signal
with a nominal 50% duty cycle. This allows a wide range of clock
input duty cycles without affecting the performance of the AD9287.
When the DCS is on, noise and distortion performance are nearly
flat for a wide range of duty cycles. However, some applications
may require the DCS function to be off. If so, keep in mind that
the dynamic range performance can be affected when operated
in this mode. See the
Memory Map section for more details on
using this feature.
Jitter in the rising edge of the input is an important concern and
is not reduced by the internal stabilization circuit. The duty cycle
control loop does not function for clock rates of less than 20 MHz
nominal. The loop has a time constant associated with it that
must be considered in applications where the clock rate can
change dynamically. This requires a wait time of 1.5 µs to 5 µs
after a dynamic clock frequency increase (or decrease) before
the DCS loop is relocked to the input signal. During the period
that the loop is not locked, the DCS loop is bypassed, and the
internal device timing is dependent on the duty cycle of the input
clock signal. In such applications, it may be appropriate to disable
the duty cycle stabilizer. In all other applications, enabling the
DCS circuit is recommended to maximize ac performance.
05966-027
05966-028
Page 21

AD9287
Clock Jitter Considerations
High speed, high resolution ADCs are sensitive to the quality of the
clock input. The degradation in SNR at a given input frequency (f
due only to aperture jitter (t
SNR degradation = 20 × log 10(1/2 × π × f
) can be calculated by
J
A
× tJ)
A
In this equation, the rms aperture jitter represents the root mean
square of all jitter sources, including the clock input, analog input
signal, and ADC aperture jitter. IF undersampling applications
are particularly sensitive to jitter (see
Figure 47).
The clock input should be treated as an analog signal in cases
where aperture jitter may affect the dynamic range of the AD9287.
Power supplies for clock drivers should be separated from the
ADC output driver supplies to avoid modulating the clock signal
with digital noise. Low jitter, crystal-controlled oscillators are the
best clock sources. If the clock is generated from another type of
source (by gating, dividing, or another method), it should be
retimed by the original clock during the last step.
Refer to the AN-501 Application Note and to the AN-756
Application Note for more in-depth information about jitter
performance as it relates to ADCs (visit
130
RMS CLOCK JI TTER REQ UIREMENT
120
110
100
90
80
SNR (dB)
70
10 BITS
60
8 BITS
50
40
30
1 10 10 0 1000
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 47. Ideal SNR vs. Input Frequency and Jitter
0.125ps
0.25ps
www.analog.com).
0.5ps
1.0ps
2.0ps
16 BITS
14 BITS
12 BITS
05966-038
)
Power Dissipation and Power-Down Mode
As shown in Figure 48, the power dissipated by the AD9287 is
proportional to its sample rate. The digital power dissipation
does not vary significantly because it is determined primarily by
the DRVDD supply and bias current of the LVDS output drivers.
300
AVDD CURRENT
250
200
150
CURRENT (mA)
100
50
0
Figure 48. Supply Current vs. f
20 40 60 80 100
01
ENCODE (MSPS)
SAMPLE
TOTAL POWER
DRVDD CURRENT
for fIN = 10.3 MHz, f
SAMPLE
600
550
500
450
POWER (mW)
400
350
300
20
= 100 MSPS
05966-069
Rev. A | Page 21 of 52
Page 22

AD9287
By asserting the PDWN pin high, the AD9287 is placed into
power-down mode. In this state, the ADC typically dissipates
3 mW. During power-down, the LVDS output drivers are placed
into a high impedance state. If any of the SPI features are changed
before the power-down feature is enabled, the chip continues to
function after PDWN is pulled low without requiring a reset. The
AD9287 returns to normal operating mode when the PDWN pin
is pulled low. This pin is both 1.8 V and 3.3 V tolerant.
In power-down mode, low power dissipation is achieved by
shutting down the reference, reference buffer, PLL, and biasing
networks. The decoupling capacitors on REFT and REFB are
discharged when entering power-down mode and must be
recharged when returning to normal operation. As a result, the
wake-up time is related to the time spent in the power-down
mode: shorter cycles result in proportionally shorter wake-up
times. With the recommended 0.1 µF and 2.2 µF decoupling
capacitors on REFT and REFB, approximately 1 sec is required
to discharge the reference buffer decoupling capacitors fully and
approximately 375 µs is required to restore full operation.
There are several other power-down options available when
using the SPI. The user can individually power down each
channel or put the entire device into standby mode. The latter
option allows the user to keep the internal PLL powered when
fast wake-up times (~600 ns) are required. See the
Map
section for more details on using these features.
Memory
Digital Outputs and Timing
The AD9287 differential outputs conform to the ANSI-644 LVDS
standard on default power-up. This can be changed to a low power,
reduced signal option (similar to the IEEE 1596.3 standard) via
the SDIO/ODM pin or SPI. The LVDS standard can reduce the
overall power dissipation of the device by approximately 17 mW.
See the
SDIO/ODM Pin section or Tab le 1 6 in the Memory Map
section for more information. The LVDS driver current is derived
on-chip and sets the output current at each output equal to a
nominal 3.5 mA. A 100 Ω differential termination resistor placed at
the LVDS receiver inputs results in a nominal 350 mV swing at
the receiver.
The AD9287 LVDS outputs facilitate interfacing with LVDS
receivers in custom ASICs and FPGAs for superior switching
performance in noisy environments. Single point-to-point net
topologies are recommended with a 100 Ω termination resistor
placed as close to the receiver as possible. If there is no far-end
receiver termination or there is poor differential trace routing,
timing errors may result. To avoid such timing errors, it is recommended that each trace length is less than 24 inches and that the
differential output traces are close together and at equal lengths.
An example of the FCO and data stream with proper trace length
and position is shown in
CH1 500mV/DIV = F CO
CH2 500mV/DIV = DATA
CH3 500mV/DIV = DCO
Figure 49. LVDS Output Timing Example in ANSI-644 Mode (Default)
Figure 49.
2.5ns/DIV
05966-056
An example of the LVDS output using the ANSI-644 standard
(default) data eye and a time interval error (TIE) jitter histogram
with trace lengths less than 24 inches on standard FR-4 material is
shown in
Figure 50. Figure 51 shows an example of trace lengths
exceeding 24 inches on standard FR-4 material. Notice that the
TIE jitter histogram reflects the decrease of the data eye opening
as the edge deviates from the ideal position. It is the user’s responsibility to determine if the waveforms meet the timing budget of
the design when the trace lengths exceed 24 inches. Additional SPI
options allow the user to further increase the internal termination
(increasing the current) of all four outputs in order to drive longer
trace lengths (see
Figure 52). Even though this produces sharper
rise and fall times on the data edges and is less prone to bit errors,
the power dissipation of the DRVDD supply increases when this
option is used. In addition, notice in
is improved compared with that shown in
Figure 52 that the histogram
Figure 51. See the
Memory Map section for more details.
Rev. A | Page 22 of 52
Page 23

AD9287
500
EYE: ALL BITS
ULS: 10000/15600
400
200
EYE: ALL BITS
ULS: 9599/15599
0
EYE DIAGRAM VOLTAG E (V)
–500
–1.0ns –0.5ns 0ns 0.5ns 1. 0ns
100
50
TIE JITTER HISTO GRAM (Hits)
0
–100ps 0ps 100ps
5966-043
Figure 50. Data Eye for LVDS Outputs in ANSI-644 Mode with Trace Lengths
Less than 24 Inches on Standard FR-4, External 100 Ω Far Termination Only
EYE: ALL BITS
200
0
EYE DIAG RAM VOLTAG E (V)
–200
–1.0ns –0.5ns 0ns 0.5ns 1.0n s
100
50
TIE JITTER HISTO GRAM (Hits)
ULS: 9600/15600
0
–200
EYE DIAGRA M VOLT AGE (V)
–400
–1.0ns –0.5ns 0ns 0.5ns 1.0n s
100
50
TIE JIT TER HIST OGRAM (Hit s)
0
–150ps –100p s –50ps 0p s 50ps 100ps 150ps
05966-042
Figure 52. Data Eye for LVDS Outputs in ANSI-644 Mode with 100 Ω Internal
Termination on and Trace Lengths Greater than 24 Inches on Standard FR-4,
External 100 Ω Far Termination Only
The format of the output data is offset binary by default. An
example of the output coding format can be found in
Tabl e 8.
To change the output data format to twos complement, see the
Memory Map section.
Table 8. Digital Output Coding
(VIN + x) − (VIN − x),
Input Span = 2 V p-p (V)
Code
255 +1.00 1111 1111
128 0.00 1000 0000
127 −0.007813 0111 1111
0 −1.00 0000 0000
Digital Output Offset Binary
(D7 ... D0)
Data from each ADC is serialized and provided on a separate
channel. The data rate for each serial stream is equal to 8 bits
times the sample clock rate, with a maximum of 800 Mbps
(8 bits × 100 MSPS = 800 Mbps). The lowest typical conversion
rate is 10 MSPS. However, if lower sample rates are required for
a specific application, the PLL can be set up via the SPI to allow
encode rates as low as 5 MSPS. See the
Memory Map section for
details on enabling this feature.
0
–150ps –100p s –50ps 0p s 50ps 100ps 150ps
05966-044
Figure 51. Data Eye for LVDS Outputs in ANSI-644 Mode with Trace Lengths
Greater than 24 Inches on Standard FR-4, External 100 Ω Far Termination
Only
Rev. A | Page 23 of 52
Page 24

AD9287
Two output clocks are provided to assist in capturing data from
the AD9287. The DCO is used to clock the output data and is
equal to four times the sample clock (CLK) rate. Data is clocked
out of the AD9287 and must be captured on the rising and
Table 9. Flexible Output Test Modes
Output Test Mode
Bit Sequence
Pattern Name Digital Output Word 1 Digital Output Word 2
0000 Off (default) N/A N/A N/A
0001 Midscale short
1000 0000 (8-bit)
10 0000 0000 (10-bit)
1000 0000 0000 (12-bit)
10 0000 0000 0000 (14-bit)
0010 +Full-scale short
1111 1111 (8-bit)
11 1111 1111 (10-bit)
1111 1111 1111 (12-bit)
11 1111 1111 1111 (14-bit)
0011 −Full-scale short
0000 0000 (8-bit)
00 0000 0000 (10-bit)
0000 0000 0000 (12-bit)
00 0000 0000 0000 (14-bit)
0100 Checkerboard
1010 1010 (8-bit)
10 1010 1010 (10-bit)
1010 1010 1010 (12-bit)
10 1010 1010 1010 (14-bit)
0101 PN sequence long
0110 PN sequence short
0111 One-/zero-word toggle
1
1
N/A N/A Yes
N/A N/A Yes
1111 1111 (8-bit)
11 1111 1111 (10-bit)
1111 1111 1111 (12-bit)
11 1111 1111 1111 (14-bit)
1000 User input Register 0x19 to Register 0x1A Register 0x1B to Register 0x1C No
1001 1-/0-bit toggle
1010 1010 (8-bit)
10 1010 1010 (10-bit)
1010 1010 1010 (12-bit)
10 1010 1010 1010 (14-bit)
1010 1× sync
0000 1111 (8-bit)
00 0001 1111 (10-bit)
0000 0011 1111 (12-bit)
00 0000 0111 1111 (14-bit)
1011 One bit high
1000 0000 (8-bit)
10 0000 0000 (10-bit)
1000 0000 0000 (12-bit)
10 0000 0000 0000 (14-bit)
1100 Mixed frequency
1010 0011 (8-bit)
10 0110 0011 (10-bit)
1010 0011 0011 (12-bit)
10 1000 0110 0111 (14-bit)
1
All test mode options except PN sequence short and PN sequence long can support 8- to 14-bit word lengths in order to verify data capture to the receiver.
falling edges of the DCO that supports double data rate (DDR)
capturing. The FCO is used to signal the start of a new output
byte and is equal to the sample clock rate. See the timing
diagram shown in
Figure 2 for more information.
Subject to Data
Format Select
Same Yes
Same Yes
Same Yes
0101 0101 (8-bit)
No
01 0101 0101 (10-bit)
0101 0101 0101 (12-bit)
01 0101 0101 0101 (14-bit)
0000 0000 (8-bit)
No
00 0000 0000 (10-bit)
0000 0000 0000 (12-bit)
00 0000 0000 0000 (14-bit)
N/A No
N/A No
N/A No
N/A No
Rev. A | Page 24 of 52
Page 25

AD9287
When the SPI is used, the DCO phase can be adjusted in 60°
increments relative to the data edge. This enables the user to refine
system timing margins if required. The default DCO+ and DCO−
timing, as shown in
Figure 2, is 90° relative to the output data edge.
A 10-, 12-, or 14-bit serial stream can also be initiated from the
SPI. This allows the user to implement and test compatibility with
higher resolution systems. However, when using the 12-bit option,
the data stream stuffs four 0s at the end of the 12-bit serial data
(see
Figure 3).
When the SPI is used, all of the data outputs can also be
inverted from their nominal state. This is not to be confused
with inverting the serial stream to an LSB-first mode. In default
mode, as shown in
Figure 2, the MSB is first in the data output
serial stream. However, this can be inverted so that the LSB is
first in the data output serial stream (see
Figure 4).
There are 12 digital output test pattern options available that
can be initiated through the SPI. This is a useful feature when
validating receiver capture and timing. Refer to
Tabl e 9 for the
output bit sequencing options available. Some test patterns have
two serial sequential words and can be alternated in various ways,
depending on the test pattern chosen. It should be noted that some
patterns do not adhere to the data format select option. In addition,
custom user-defined test patterns can be assigned in the 0x19,
0x1A, 0x1B, and 0x1C register addresses. All test mode options
except PN sequence short and PN sequence long can support
8- to 14-bit word lengths in order to verify data capture to the
receiver.
The PN sequence short pattern produces a pseudorandom bit
9
sequence that repeats itself every 2
− 1 or 511 bits. A description
of the PN sequence and how it is generated can be found in
Section 5.1 of the ITU-T 0.150 (05/96) standard. The only
difference is that the starting value must be a specific value
instead of all 1s (see
Tabl e 10 for the initial values).
Table 10. PN Sequence
Initial
Sequence
PN Sequence Short 0x0df 0xbf, ox93, 0x53
PN Sequence Long 0x029b80 0xf5, 0x91, 0xfd
Value
First Three Output Samples
(MSB First)
Consult the Memory Map section for information on how to
change these additional digital output timing features through
the SPI.
SDIO/ODM Pin
The SDIO/ODM pin is for use in applications that do not require
SPI mode operation. This pin can enable a low power, reduced
signal option (similar to the IEEE 1596.3 reduced range link
output standard) if it and the CSB pin are tied to AVDD during
device power-up. This option should only be used when the
digital output trace lengths are less than 2 inches to the LVDS
receiver. When this option is used, the FCO, DCO, and outputs
function normally, but the LVDS signal swing of all channels is
reduced from 350 mV p-p to 200 mV p-p, allowing the user to
further reduce the power on the DRVDD supply.
For applications where this pin is not used, it should be tied low.
In this case, the device pin can be left open, and the 30 kΩ internal
pull-down resistor pulls this pin low. This pin is only 1.8 V tolerant.
If applications require this pin to be driven from a 3.3 V logic level,
insert a 1 kΩ resistor in series with this pin to limit the current.
Table 11. Output Driver Mode Pin Settings
Resulting
Selected ODM ODM Voltage
Normal
operation
ODM AVDD Low power,
10 kΩ to AGND ANSI-644
Output Standard
(default)
reduced
signal option
Resulting
FCO and DCO
ANSI-644
(default)
Low power,
reduced
signal option
The PN sequence long pattern produces a pseudorandom bit
23
sequence that repeats itself ever y 2
− 1 or 8,388,607 bits. A
description of the PN sequence and how it is generated can be
found in Section 5.6 of the ITU-T 0.150 (05/96) standard. The
only differences are that the starting value must be a specific
value instead of all 1s (see
Tabl e 10 for the initial values) and the
AD9287 inverts the bit stream with relation to the ITU standard.
Rev. A | Page 25 of 52
Page 26

AD9287
SCLK/DTP Pin
The SCLK/DTP pin is for use in applications that do not require
SPI mode operation. This pin can enable a single digital test
pattern if it and the CSB pin are held high during device powerup. When SCLK/DTP is tied to AVDD, the ADC channel
outputs shift out the following pattern: 1000 0000. The FCO
and DCO function normally while all channels shift out the
repeatable test pattern. This pattern allows the user to perform
timing alignment adjustments among the FCO, DCO, and output
data. For normal operation, this pin should be tied to AGND
through a 10 kΩ resistor. This pin is both 1.8 V and 3.3 V
tolerant.
Table 12. Digital Test Pattern Pin Settings
Resulting
Selected DTP DTP Voltage
Normal
operation
DTP AVDD 1000 0000 Normal operation
10 kΩ to AGND Normal
D + x and D − x
operation
Resulting
FCO and DCO
Normal operation
Additional and custom test patterns can also be observed when
commanded from the SPI port. Consult the
Memory Map
section for information about the options available.
CSB Pin
The CSB pin should be tied to AVDD for applications that do
not require SPI mode operation. By tying CSB high, all SCLK
and SDIO information is ignored. This pin is both 1.8 V and
3.3 V tolerant.
RBIAS Pin
To set the internal core bias current of the ADC, place a resistor
(nominally equal to 10.0 kΩ) to ground at the RBIAS pin. The
resistor current is derived on-chip and sets the AVDD current of
the ADC to a nominal 260 mA at 100 MSPS. Therefore, it is
imperative that at least a 1% tolerance on this resistor be used to
achieve consistent performance.
Voltage Reference
A stable, accurate 0.5 V voltage reference is built into the
AD9287. This is gained up internally by a factor of 2, setting
V
to 1.0 V, which results in a full-scale differential input span
REF
of 2 V p-p. The V
is set internally by default; however, the
REF
VREF pin can be driven externally with a 1.0 V reference to
improve accuracy.
When applying the decoupling capacitors to the VREF, REFT,
and REFB pins, use ceramic low ESR capacitors. These capacitors
should be close to the ADC pins and on the same layer of the
PCB as the AD9287. The recommended capacitor values and
configurations for the AD9287 reference pin are shown in
Figure 53.
Table 13. Reference Settings
Resulting
Differential
Selected Mode SENSE Voltage Resulting VREF (V)
External
reference
Internal,
2 V p-p FSR
AVDD N/A 2 × external
AGND to 0.2 V 1.0 2.0
Span (V p-p)
reference
Rev. A | Page 26 of 52
Page 27

AD9287
Internal Reference Operation
A comparator within the AD9287 detects the potential at the
SENSE pin and configures the reference. If SENSE is grounded,
the reference amplifier switch is connected to the internal
resistor divider (see
Figure 53), setting VREF to 1 V.
External Reference Operation
The use of an external reference may be necessary to enhance
the gain accuracy of the ADC or to improve thermal drift
characteristics.
Figure 56 shows the typical drift characteristics
of the internal reference in 1 V mode.
The REFT and REFB pins establish the input span of the ADC
core from the reference configuration. The analog input fullscale range of the ADC equals twice the voltage of the reference
pin for either an internal or an external reference configuration.
If the reference of the AD9287 is used to drive multiple
converters to improve gain matching, the loading of the reference by the other converters must be considered.
Figure 55
depicts how the internal reference voltage is affected by loading.
VIN + x
VIN – x
VREF
1µF 0. 1µF
SENSE
VIN + x
VIN – x
EXTERNAL
REFERENCE
1
1µF
0.1µF
SENSE
ADC
CORE
SELECT
LOGIC
Figure 53. Internal Reference Configuration
ADC
CORE
VREF
1
AVD D
SELECT
LOGIC
0.5V
0.5V
REFT
0.1µF
0.1µF 2.2µF
REFB
0.1µF
REFT
0.1µF
0.1µF 2.2µF
REFB
0.1µF
+
+
When the SENSE pin is tied to AVDD, the internal reference is
disabled, allowing the use of an external reference. The external
reference is loaded with an equivalent 6 kΩ load. An internal
reference buffer generates the positive and negative full-scale
references, REFT and REFB, for the ADC core. Therefore, the
external reference must be limited to a nominal 1.0 V.
5
0
–5
–10
ERROR (%)
–15
REF
V
–20
–25
–30
01.00.5 2. 01.5 3.02.5 3.5
0.02
ERROR (%)
REF
V
–0.02
–0.04
–0.06
–0.08
–0.10
–0.12
–0.14
–0.16
–0.18
0
–40 806040200–20
05966-010
Figure 56. V
CURRENT LOAD (mA)
Figure 55. V
TEMPERATURE ( °C)
Error vs. Temperature
REF
Error vs. Load
REF
05966-083
05966-084
1
OPTIONAL.
Figure 54. External Reference Operation
05966-089
Rev. A | Page 27 of 52
Page 28

AD9287
SERIAL PORT INTERFACE (SPI)
The AD9287 serial port interface allows the user to configure the
converter for specific functions or operations through a structured
register space provided in the ADC. This may provide the user
with additional flexibility and customization depending on the
application. Addresses are accessed via the serial port and can
be written to or read from via the port. Memory is organized
into bytes that can be further divided into fields, as documented
in the
Memory Map section. Detailed operational information
can be found in the Analog Devices, Inc., AN-877 Application
Note, Interfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI.
There are three pins that define the SPI: SCLK, SDIO, and CSB
Tabl e 14 ). The SCLK pin is used to synchronize the read
(see
and write data presented to the ADC. The SDIO pin is a dualpurpose pin that allows data to be sent to and read from the
internal ADC memory map registers. The CSB pin is an active
low control that enables or disables the read and write cycles.
Table 14. Serial Port Pins
Pin Function
SCLK
SDIO
CSB
Serial Clock. The serial shift clock input. SCLK is used to
synchronize serial interface reads and writes.
Serial Data Input/Output. A dual-purpose pin. The typical
role for this pin is as an input or output, depending on
the instruction sent and the relative position in the
timing frame.
Chip Select Bar (Active Low). This control gates the read
and write cycles.
The falling edge of the CSB in conjunction with the rising edge of
the SCLK determines the start of the framing sequence. During an
instruction phase, a 16-bit instruction is transmitted followed by
one or more data bytes, which is determined by Bit Field W0 and
Bit Field W1. An example of the serial timing and its definitions
can be found in
Figure 58 and Tab l e 15 . During normal operation,
CSB is used to signal to the device that SPI commands are to be
received and processed. When CSB is brought low, the device
processes SCLK and SDIO to obtain instructions. Normally,
CSB remains low until the communication cycle is complete.
However, if connected to a slow device, CSB can be brought
high between bytes, allowing older microcontrollers enough
time to transfer data into shift registers. CSB can be stalled
when transferring one, two, or three bytes of data. When W0
and W1 are set to 11, the device enters streaming mode and
continues to process data, either reading or writing, until the
CSB is taken high to end the communication cycle. This allows
complete memory transfers without requiring additional instructions. Regardless of the mode, if CSB is taken high in the middle
of a byte transfer, the SPI state machine is reset and the device
waits for a new instruction.
In addition to the operation modes, the SPI port configuration
influences how the AD9287 operates. For applications that do
not require a control port, the CSB line can be tied and held high.
This places the remainder of the SPI pins into their secondary
modes, as defined in the
SDIO/ODM Pin and SCLK/DTP Pin
section. CSB can also be tied low to enable 2-wire mode. When
CSB is tied low, SCLK and SDIO are the only pins required for
communication. Although the device is synchronized during
power-up, the user should ensure that the serial port remains
synchronized with the CSB line when using this mode. When
operating in 2-wire mode, it is recommended to use a 1-, 2-,
or 3-byte transfer exclusively. Without an active CSB line,
streaming mode can be entered but not exited.
In addition to word length, the instruction phase determines if
the serial frame is a read or write operation, allowing the serial
port to be used to both program the chip and read the contents
of the on-chip memory. If the instruction is a readback operation,
performing a readback causes the SDIO pin to change from an
input to an output at the appropriate point in the serial frame.
Data can be sent in MSB- or LSB-first mode. MSB-first mode
is the default at power-up and can be changed by adjusting the
configuration register. For more information about this and
other features, see the AN-877 Application Note, Inter facing to
High Speed ADCs via SPI.
HARDWARE INTERFACE
The pins described in Ta b l e 14 compose the physical interface
between the user’s programming device and the serial port of
the AD9287. The SCLK and CSB pins function as inputs when
using the SPI. The SDIO pin is bidirectional, functioning as an
input during write phases and as an output during readback.
If multiple SDIO pins share a common connection, care should
be taken to ensure that proper V
same load for each AD9287,
SDIO pins that can be connected together and the resulting V
level. This interface is flexible enough to be controlled by either
serial PROMS or PIC mirocontrollers, providing the user with
an alternative method, other than a full SPI controller, to
program the ADC (see the AN-812 Application Note).
levels are met. Assuming the
OH
Figure 57 shows the number of
OH
Rev. A | Page 28 of 52
Page 29

AD9287
1.800
1.795
1.790
1.785
1.780
1.775
1.770
1.765
1.760
OH
1.755
V
1.750
1.745
1.740
1.735
1.730
1.725
1.720
1.715
0302010 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
NUMBER OF SDIO PINS CONNECTE D TOGETHER
Figure 57. SDIO Pin Loading
05966-090
If the user chooses not to use the SPI, these dual-function pins
serve their secondary functions when the CSB is strapped to
AVDD during device power-up. See the
Theory of Operation
section for details on which pin-strappable functions are
supported on the SPI pins.
For users who wish to operate the ADC without using the SPI,
remove any connections from the CSB, SCLK/DTP, and SDIO/
ODM pins. By disconnecting these pins from the control bus, the
ADC can function in its most basic operation. Each of these pins
has an internal termination and will float to its respective level.
t
HI
t
t
LO
CSB
SCLK
SDIO
DON’T CARE
t
DS
t
S
R/W W1 W 0 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7
t
DH
Figure 58. Serial Timing Details
Table 15. Serial Timing Definitions
Parameter Timing (Minimum, ns) Description
t
DS
t
DH
t
CLK
t
S
t
H
t
HI
t
LO
t
EN_SDIO
5 Setup time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK
2 Hold time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK
40 Period of the clock
5 Setup time between CSB and SCLK
2 Hold time between CSB and SCLK
16 Minimum period that SCLK should be in a logic high state
16 Minimum period that SCLK should be in a logic low state
10
Minimum time for the SDIO pin to switch from an input to an output relative to the SCLK
falling edge (not shown in
t
DIS_SDIO
10
Minimum time for the SDIO pin to switch from an output to an input relative to the SCLK
rising edge (not shown in
CLK
Figure 58)
Figure 58)
D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
t
H
DON’T CARE
DON’T CAREDON’T CARE
05966-012
Rev. A | Page 29 of 52
Page 30

AD9287
MEMORY MAP
READING THE MEMORY MAP TABLE
Each row in the memory map table has eight address locations. The
memory map is divided into three sections: the chip configuration
register map (Address 0x00 to Address 0x02), the device index
and transfer register map (Address 0x05 and Address 0xFF), and
the ADC functions register map (Address 0x08 to Address 0x22).
The leftmost column of the memory map indicates the register
address number, and the default value is shown in the second
rightmost column. The (MSB) Bit 7 column is the start of the
default hexadecimal value given. For example, Address 0x09, the
clock register, has a default value of 0x01, meaning that Bit 7 = 0,
Bit 6 = 0, Bit 5 = 0, Bit 4 = 0, Bit 3 = 0, Bit 2 = 0, Bit 1 = 0, and
Bit 0 = 1, or 0000 0001 in binary. This setting is the default for
the duty cycle stabilizer in the on condition. By writing a 0 to Bit 6
of this address followed by a 0x01 in Register 0xFF (transfer bit),
the duty cycle stabilizer turns off. It is important to follow each
writing sequence with a transfer bit to update the SPI registers. For
more information on this and other functions, consult the AN-877
Application Note, Interfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI.
RESERVED LOCATIONS
Undefined memory locations should not be written to except
when writing the default values suggested in this data sheet.
Addresses that have values marked as 0 should be considered
reserved and have a 0 written into their registers during power-up.
DEFAULT VALUES
When the AD9287 comes out of a reset, critical registers are
preloaded with default values. These values are indicated in
Tabl e 16 , where an X refers to an undefined feature.
LOGIC LEVELS
An explanation of various registers follows: “Bit is set” is
synonymous with “bit is set to Logic 1” or “writing Logic 1 for
the bit.” Similarly, “clear a bit” is synonymous with “bit is set to
Logic 0” or “writing Logic 0 for the bit.”
Rev. A | Page 30 of 52
Page 31

AD9287
Table 16. Memory Map Register
Default
Addr.
(Hex)
Chip Configuration Registers
00 chip_port_config 0 LSB first
01 chip_id 8-bit Chip ID Bits [7:0]
02 chip_grade X Child ID [6:4]
Device Index and Transfer Registers
05 device_index_A X X Clock
FF device_update X X X X X X X SW
ADC Functions
08 modes X X X X X Internal power-down mode
09 clock X X X X X X X Duty
0D test_io User test mode
Register Name
(MSB)
Bit 7
00 = off (default)
01 = on, single alternate
10 = on, single once
11 = on, alternate once
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
(identify device variants of Chip ID)
011 = 100 MSPS
Soft
reset
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
Channel
DCO
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
Reset
PN long
gen
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
1 1 Soft
(AD9287 = 0x05), (default)
Clock
Channel
FCO
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
Reset
PN short
gen
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
(LSB)
Bit 0
LSB first
reset
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
X X X X Read
Data
Channel
D
1 = on
(default)
0 = off
Output test mode—see
Data
Channel
C
1 = on
(default)
0 = off
000 = chip run (default)
001 = full power-down
010 = standby
011 = reset
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
Data
Channel
B
1 = on
(default)
0 = off
Table 9 in the
0 0x18 The nibbles
Data
Channel
A
1 = on
(default)
0 = off
transfer
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
cycle
stabilizer
1 = on
(default)
0 = off
Digital Outputs and Timing section
0000 = off (default)
0001 = midscale short
0010 = +FS short
0011 = −FS short
0100 = checkerboard output
0101 = PN 23 sequence
0110 = PN 9
0111 = one-/zero-word toggle
1000 = user input
1001 = 1-/0-bit toggle
1010 = 1× sync
1011 = one bit high
1100 = mixed bit frequency
(format determined by output_mode)
Value
(Hex)
0x05 Default is unique
only
0x0F Bits are set to
0x00 Synchronously
0x00 Determines
0x01 Turns the
0x00 When set, the
Default Notes/
Comments
should be
mirrored so that
LSB- or MSB-first
mode is set correctly regardless
of shift mode.
chip ID, different
for each device.
This is a readonly register.
Child ID used to
differentiate
graded devices.
determine which
on-chip device
receives the next
write command.
transfers data
from the master
shift register to
the slave.
various generic
modes of chip
operation.
internal duty
cycle stabilizer
on and off.
test data is
placed on the
output pins in
place of normal
data.
Rev. A | Page 31 of 52
Page 32

AD9287
Default
Addr.
(Hex)
14 output_mode X 0 = LVDS
15 output_adjust X X Output driver
16 output_phase X X X X 0011 = output clock phase adjust
19 user_patt1_lsb B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 0x00 User-defined
1A user_patt1_msb B15 B14 B13 B12 B11 B10 B9 B8 0x00 User-defined
1B user_patt2_lsb B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 0x00 User-defined
1C user_patt2_msb B15 B14 B13 B12 B11 B10 B9 B8 0x00 User-defined
21 serial_control LSB first
22 serial_ch_stat X X X X X X Channel
Register Name
(MSB)
Bit 7
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
ANSI-644
(default)
1 = LVDS
low
power,
(IEEE
1596.3
similar)
X X X <10
X X X Output
X X X X 0x00 Determines
termination
00 = none (default)
01 = 200 Ω
10 = 100 Ω
11 = 100 Ω
(0000 through 1010)
(Default: 180° relative to data edge)
0000 = 0° relative to data edge
0001 = 60° relative to data edge
0010 = 120° relative to data edge
0011 = 180° relative to data edge
0100 = 240° relative to data edge
0101 = 300° relative to data edge
0110 = 360° relative to data edge
0111 = 420° relative to data edge
1000 = 480° relative to data edge
1001 = 540° relative to data edge
1010 = 600° relative to data edge
1011 to 1111 = 660° relative to data edge
MSPS,
low
encode
rate
mode
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
invert
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
000 = 8 bits (default, normal bit
stream)
001 = 8 bits
010 = 10 bits
011 = 12 bits
100 = 14 bits
00 = offset binary
(default)
01 = twos
complement
output
reset
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
(LSB)
Bit 0
Channel
powerdown
1 = on
0 = off
(default)
Value
(Hex)
0x00 Configures the
0x03 On devices that
0x00 Serial stream
0x00 Used to power
Default Notes/
Comments
outputs and the
format of the
data.
LVDS or other
output properties.
Primarily functions to set the
LVDS span and
common-mode
levels in place of
an external
resistor.
utilize global
clock divide,
determines
which phase of
the divider
output is used to
supply the
output clock.
Internal latching
is unaffected.
pattern, 1 LSB.
pattern, 1 MSB.
pattern, 2 LSB.
pattern, 2 MSB.
control. Default
causes MSB first
and the native
bit stream
(global).
down individual
sections of a
converter (local).
Rev. A | Page 32 of 52
Page 33

AD9287
Power and Ground Recommendations Exposed Paddle Thermal Heat Slug Recommendations
When connecting power to the AD9287, it is recommended
that two separate 1.8 V supplies be used: one for analog (AVDD)
and one for digital (DRVDD). If only one supply is available, it
should be routed to the AVDD first and then tapped off and
isolated with a ferrite bead or a filter choke preceded by
decoupling capacitors for the DRVDD. The user can employ
several different decoupling capacitors to cover both high and
low frequencies. These should be located close to the point of
entry at the PC board level and close to the parts, with minimal
trace lengths.
A single PC board ground plane should be sufficient when
using the AD9287. With proper decoupling and smart partitioning of the PC board’s analog, digital, and clock sections,
optimum performance can be easily achieved.
It is required that the exposed paddle on the underside of the
ADC is connected to analog ground (AGND) to achieve the
best electrical and thermal performance of the AD9287. An
exposed continuous copper plane on the PCB should mate to
the AD9287 exposed paddle, Pin 0. The copper plane should
have several vias to achieve the lowest possible resistive thermal
path for heat dissipation to flow through the bottom of the PCB.
These vias should be solder-filled or plugged.
To maximize the coverage and adhesion between the ADC
and PCB, partition the continuous copper plane by overlaying a
silkscreen on the PCB into several uniform sections. This provides
several tie points between the ADC and PCB during the reflow
process, whereas using one continuous plane with no partitions
only guarantees one tie point. See
Figure 59 for a PCB layout
example. For detailed information on packaging and the PCB
layout of chip scale packages, see the AN-772 Application Note,
A Design and Manufacturing Guide for the Lead Frame Chip
Scale Package (LFCSP), at
SILKSCREEN PARTITIO N
PIN 1 INDICATOR
www.analog.com.
05966-013
Figure 59. Typical PCB Layout
Rev. A | Page 33 of 52
Page 34

AD9287
EVALUATION BOARD
The AD9287 evaluation board provides all of the support circuitry required to operate the ADC in its various modes and
configurations. The converter can be driven differentially using a
transformer (default) or an
AD8332 driver. The ADC can also be
driven in a single-ended fashion. Separate power pins are provided
to isolate the DUT from the drive circuitry of the
AD8332. Each
input configuration can be selected by changing the connection
of various jumpers (see
Figure 62 to Figure 66). Figure 60 shows
the typical bench characterization setup used to evaluate the ac
performance of the AD9287. It is critical that the signal sources
used for the analog input and clock have very low phase noise
(<1 ps rms jitter) to realize the optimum performance of the
converter. Proper filtering of the analog input signal to remove
harmonics and lower the integrated or broadband noise at the
input is also necessary to achieve the specified noise performance.
Figure 62 to Figure 70 for the complete schematics and
See
layout diagrams demonstrating the routing and grounding
techniques that should be applied at the system level.
POWER SUPPLIES
This evaluation board has a wall-mountable switching power
supply that provides a 6 V, 2 A maximum output. Connect the
supply to the rated 100 V ac to 240 V ac wall outlet at 47 Hz to
63 Hz. The other end of the supply is a 2.1 mm inner diameter
jack that connects to the PCB at P503. Once on the PC board,
the 6 V supply is fused and conditioned before connecting to
three low dropout linear regulators that supply the proper bias
to each of the various sections on the board.
When operating the evaluation board in a nondefault condition,
L504 to L507 can be removed to disconnect the switching
power supply. This enables the user to bias each section of the
board individually. Use P501 to connect a different supply for
WALL OU TL ET
100V TO 240V AC
47Hz TO 63Hz
6V DC
SWITCHING
POWER
SUPPLY
ROHDE & SCHWARZ,
SMHU,
2V p-p SIGNAL
SYNTHESIZER
ROHDE & SCHWARZ,
SMHU,
2V p-p SIGNAL
SYNTHESIZER
2A MAX
BAND-PASS
FILTER
XFMR
INPUT
CLK
5.0V
–+
GND
1.8V
–+–+
GND
AVD D_5V
AVDD_DUT
AD9287
EVALUATION BOARD
Figure 60. Evaluation Board Connection
1.8V
GND
DRVDD_DUT
–+
CH A TO CH D
each section. At least one 1.8 V supply is needed for AVDD_DUT
and DRVDD_DUT; however, it is recommended that separate
supplies be used for analog and digital signals and that each supply
have a current capability of 1 A. To operate the evaluation board
using the VGA option, a separate 5.0 V analog supply (AVDD_5 V)
is needed. To operate the evaluation board using the SPI and alternate clock options, a separate 3.3 V analog supply (AVDD_3.3 V)
is needed in addition to the other supplies.
INPUT SIGNALS
When connecting the clock and analog sources to the evaluation
board, use clean signal generators with low phase noise, such as
Rohde & Schwarz SMHU or HP8644 signal generators or the
equivalent, as well as a 1 m, shielded, RG-58, 50 Ω coaxial cable.
Enter the desired frequency and amplitude from the ADC specifications tables. Typically, most Analog Devices evaluation boards
can accept approximately 2.8 V p-p or 13 dBm sine wave input
for the clock. When connecting the analog input source, it is
recommended to use a multipole, narrow-band, band-pass filter
with 50 Ω terminations. Good choices of such band-pass filters
are available from TTE, Allen Avionics, and K&L Microwave, Inc.
The filter should be connected directly to the evaluation board
if possible.
OUTPUT SIGNALS
The default setup uses the HSC-ADC-FPGA-4/HSC-ADC-
FPGA-8
digital output data and convert it to parallel CMOS. These two
channels interface directly with the Analog Devices standard
dual-channel FIFO data capture board (
Two of the four channels can then be evaluated at the same time.
For more information on the channel settings and optional
settings of these boards, visit www.analog.com/FIFO.
3.3V
GND
AVDD_3.3V
8-BIT
SERIAL
LVDS
SPI SPISPI SPI
high speed deserialization board to deserialize the
HSC-ADC-EVALB-DC).
3.3V
–+
GND
HSC-ADC-FPGA-4/
HSC-ADC-FPGA-8
DESERIALIZ ATION
1.5V
–+
3.3V_D
HIGH SPEED
BOARD
PARALLEL
CMOS
GND
2 CH
8-BIT
1.5V_FPG A
HSC-ADC-EVALB-DC
3.3V
–+
GND
FIFO DATA
CAPTURE
BOARD
CONNECTION
VCC
USB
PC
RUNNING
ADC
ANALYZER
AND SPI
USER
SOFTWARE
5966-014
Rev. A | Page 34 of 52
Page 35

AD9287
DEFAULT OPERATION AND JUMPER SELECTION SETTINGS
The following is a list of the default and optional settings or
modes allowed on the AD9287 Rev. A evaluation board.
• POWER: Connect the switching power supply that is
provided with the evaluation kit between a rated 100 V ac
to 240 V ac wall outlet at 47 Hz to 63 Hz and P503.
• AIN: The evaluation board is set up for a transformer-
coupled analog input with an optimum 50 Ω impedance
match of 190 MHz of bandwidth (see
bandwidth response, the differential capacitor across the
analog inputs can be changed or removed. The common
mode of the analog inputs is developed from the center tap
of the transformer or AVDD_DUT/2.
0
–2
–4
–6
–8
–10
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–12
–14
–16
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
0
Figure 61. Evaluation Board Full-Power Bandwidth
–3dB CUTOFF = 190MHz
FREQUENCY (MHz)
• VREF: VREF is set to 1.0 V by tying the SENSE pin to ground,
R237. This causes the ADC to operate in 2.0 V p-p full-scale
range. A separate external reference option using the ADR510
or ADR520 is also included on the evaluation board. Populate
R231 and R235 and remove C214. Proper use of the VREF
options is noted in the
Volt a ge R e fe r e nc e section.
• RBIAS: RBIAS has a default setting of 10 kΩ (R201) to
ground and is used to set the ADC core bias current.
• CLOCK: The default clock input circuitry is derived from a
simple transformer-coupled circuit using a high bandwidth
1:1 impedance ratio transformer (T201) that adds a very
low amount of jitter to the clock path. The clock input is
50 Ω terminated and ac-coupled to handle single-ended
sine wave types of inputs. The transformer converts the
single-ended input to a differential signal that is clipped
before entering the ADC clock inputs.
Figure 61). For more
05966-088
A differential LVPECL clock can also be used to clock the
ADC input using the AD9515 (U202). Populate R225 and
R227 with 0 Ω resistors and remove R217 and R218 to
disconnect the default clock path inputs. In addition, populate
C207 and C208 with a 0.1 F capacitor and remove C210 and
C211 to disconnect the default clock path outputs. The
AD9515 has many pin-strappable options that are set to a
default mode of operation. Consult the AD9515 data sheet
for more information about these and other options.
In addition, an on-board oscillator is available on the OSC201
and can act as the primary clock source. The setup is quick
and involves installing R212 with a 0 Ω resistor and setting
the enable jumper (J205) to the on position. If the user wishes
to employ a different oscillator, two oscillator footprint options
are available (OSC201) to check the ADC performance.
• PDWN: To enable the power-down feature, short J201 to
AVDD on the PDWN pin.
• SCLK/DTP: To enable the digital test patterns on the digital
outputs of the ADC, use J204. If J204 is tied to AVDD during
device power-up, Test Pattern 1000 0000 is enabled. See the
SCLK/DTP Pin section for details.
• SDIO/ODM: To enable the low power, reduced signal option
(similar to the IEEE 1595.3 reduced range link LVDS output
standard), use J203. If J203 is tied to AVDD during device
power-up, it enables the LVDS outputs in a low power,
reduced signal option from the default ANSI-644 standard.
This option changes the signal swing from 350 mV p-p to
200 mV p-p, reducing the power of the DRVDD supply. See
the
SDIO/ODM Pin section for more details.
• CSB: To enable processing of the SPI information on the SDIO
and SCLK pins, tie J202 low in the always enable mode. To
ignore the SDIO and SCLK information, tie J202 to AVDD.
• Non-SPI Mode: For users who wish to operate the DUT
without using SPI, remove Jumpers J202, J203, and J204.
This disconnects the CSB, SCLK/DTP, and SDIO/ODM pins
from the control bus, allowing the DUT to operate in its
simplest mode. Each of these pins has internal termination
and will float to its respective level.
• D + x, D − x: If an alternative data capture method to the setup
described in
Figure 60 is used, optional receiver terminations,
R206 to R211, can be installed next to the high speed backplane connector.
Rev. A | Page 35 of 52
Page 36

AD9287
ALTERNATIVE ANALOG INPUT DRIVE CONFIGURATION
The following is a brief description of the alternative analog input
drive configuration using the
option is in use, some components may need to be populated, in
which case all the necessary components are listed in
more details on the
and its optional pin settings, consult the
To configure the analog input to drive the VGA instead of the
default transformer option, the following components need to
be removed and/or changed.
• Remove R102, R115, R128, R141, R161, R162, R163, R164,
T101, T102, T103, and T104 in the default analog input path.
AD8332 dual VGA, including how it works
AD8332 dual VGA. If this drive
Tabl e 17 . For
AD8332 data sheet.
• Populate R101, R114, R127, and R140 with 0 Ω resistors in
the analog input path.
• Populate R105, R113, R118, R124, R131, R137, R151, and
R160 with 0 Ω resistors in the analog input path to connect
the
AD8332.
• Populate R152, R153, R154, R155, R156, R157, R158, R159,
C103, C105, C110, C112, C117, C119, C124, and C126
with 10 kΩ resistors to provide an input common-mode
level to the ADC analog inputs.
• Remove R305, R306, R313, R314, R405, R406, R412, and
R424 to configure the
In this configuration, L301 to L308 and L401 to L408 are
populated with 0 Ω resistors to allow signal connection and use
of a filter if additional requirements are necessary.
AD8332.
Rev. A | Page 36 of 52
Page 37

AD9287
R105
DNP
CH_A
VGA INPUT CO NNECTION
CHANNEL A
P101
INH1
AIN
R101
DNP
R102
64.9
P102
DNP
AIN
AVDD_DUT
R103
0
R104
0
FB101
10
C102
0.1µF
R111
1k
C101
0.1µF
E101
CM1
CH_A
R112
1k
CM1
1
2
3
T101
R113
DNP
6
5
4
C107
0.1µF
CM1
R107
DNP
C106
DNP
R106
DNP
FB102
10
R161
499
FB103
10
R108
33
C103
DNP
R110
33
AVDD_DUT
C104
2.2pF
C105
DNP
AVDD_DUT
R152
DNP
R109
1k
R156
DNP
VIN_A
VIN_A
AVDD_DUT
CH_B
CM2
CH_B
R126
1k
R132
DNP
6
5
4
C128
0.1µF
CM2
T102
1
2
3
R124
FB108
FB109
CM4
R118
DNP
DNP
10
R163
499
10
R145
DNP
C127
DNP
6
5
4
C114
0.1µF
R134
33
C117
DNP
R136
33
R144
DNP
CM2
R120
DNP
C113
DNP
FB111
10
R164
499
FB112
10
R119
DNP
AVDD_DUT
C118
2.2pF
C119
DNP
AVDD_DUT
R146
33
C124
DNP
R147
33
FB105
10
R162
499
FB106
10
R154
DNP
R135
1k
R158
DNP
R121
33
C110
DNP
R122
33
VIN_C
VIN_C
AVDD_DUT
C125
2.2pF
C126
DNP
AVDD_DUT
R155
DNP
R148
1k
R159
DNP
C111
2.2pF
C112
DNP
R153
DNP
R123
1k
R157
DNP
AVDD_DUT
VIN_D
VIN_D
VIN_B
VIN_B
05966-015
VGA INPUT CO NNECTION
CHANNEL C
P105
INH3
AIN
VGA INPUT CO NNECTION
CHANNEL D
P107
AIN
DNP: DO NOT PO PULATE
VGA INP UT CONN ECTIO N
CHANNEL B
P103
INH2
AIN
P106
DNP
R130
0
AIN
R127
DNP
FB107
R129
0
AVDD_DUT
10
R138
1k
R128
64.9
INH4
R140
DNP
R141
64.9
P108
DNP
AIN
R142
AVDD_DUT
R114
DNP
R115
64.9
C116
0.1µF
E103
0
P104
DNP
AIN
C115
0.1µF
R139
R117
AVDD_DUT
CH_C
CM3
CH_C
CM3
1k
FB110
10
R143
0
0
1
2
3
R149
1k
R131
DNP
T103
R137
DNP
C122
0.1µF
C123
0.1µF
E104
FB104
10
R116
0
6
5
4
C121
0.1µF
CM4
R150
1k
CH_D
CH_D
R125
1k
CM3
R133
CM4
C108
0.1µF
C109
0.1µF
E102
DNP
C120
DNP
T104
1
2
3
R160
DNP
R151
DNP
Figure 62. Evaluation Board Schematic, DUT Analog Inputs
Rev. A | Page 37 of 52
Page 38

AD9287
R206
DNP
R207
FCO
DCO
50
D9
D10
GNDCD9
GNDCD10
C10
P202
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
T
U
D
_
E
S
V
N
5
.
E
0
S
=
V
F
E
R
V
T
P
C
N
E
D
L
E
S
4
F
P
3
E
N
2
R
D
R
V
T
I
U
C
R
I
C
E
C
N
E
R
E
F
E
R
T
U
D
_
F
E
R
V
1
P
3
2
N
R
D
k
9
T
9
2
9
U
2
.
D
R
4
_
D
+
D
V
V
A
0
2
/
0
1
L
V
5
1
A
F
N
E
O
R
I
T
T
P
X
O
E
C
R
N
/
D
A
M
3
I
0
R
2
T
U
REFERENCE
DECOUPLI NG
C204
0.1µF
C9
40
60
59
FCO
DCO
)
L
3
A
3
N
2
R
R
/
E
2
T
3
X
2
E
R
+
=
1
(
F
V
E
5
.
R
0
V
=
F
E
R
V
P
P
N
N
D
D
5
6
P
P
3
3
N
N
2
2
D
D
R
R
AVDD_DUT
4
2
P
1
3
F
N
2
2
µ
D
C
1
R
P
N
D
0
3
k
2
0
R
1
2
F
1
µ
2
1
.
C
0
–
V
8
k
2
0
2
7
R
4
1
0
k
2
0
R
1
C203
0.1µF
C202
2.2µF
DNP
49
GNDCD8
39
3
1
2
C
C201
CW
R209
R208
DNP
CHB
CHA
48
D8
D7
GNDCD7
C8
C7
38
57
58
CHB
CHA
V
1
=
F
E
R
V
F
E
R
V
L
A
N
R
E
T
X
7
E
3
2
0
G
R
N
I
S
U
N
E
H
3
P
3
W
N
2
D
4
R
1
2
F
C
µ
E
1
.
V
0
O
M
E
R
T
U
D
_
D
D
V
A
VIN_B
VIN_B
AVDD_DUT
VSENSE_DUT
VREF_DUT
AVDD_DUT
AVDD_DUT
VIN_C
VIN_C
0.1µF
47
GNDCD6
37
DNP
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
U201
R211
DNP
R210
DNP
CHD
CHC
46
45
44
43
42
41
20
19
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
B10
GNDCD1
GNDCD2
GNDCD3
GNDCD4
GNDCD5
C6
C5
C4
C3
C2
32
33
34
35
36
54
55
56
CHD
CHC
52
53
0
R257
DNP
R256
AVDD_3.3V
0
0
R247
R245
DNP
DNP
R244
R246
I
P
S
E
L
AVDD_3.3V
E
L
B
A
N
E
N
D
W
P
3
2
J201
J202
1
1
R202
100k
100k - DNP
R267
100k - DNP
R266
T
T
T
U
D
_
D
D
V
A
36
AVDD
AVDD
1
T
U
D
_
D
D
V
A
U
U
D
D
_
_
D
A
A
D
_
_
D
D
N
N
V
V
I
I
A
V
V
A
33
34
32
35
AVDD
AVDD
VIN – A
VIN + A
VIN – B
VIN + B
AVDD
RBIAS
SENSE
VREF
REFB
REFT
AVDD
AVDD
VIN + C
VIN – C
VIN + D
VIN – D
AVDD
AVDD
5
4
3
2
T
T
D
D
_
_
U
U
N
N
D
D
I
I
_
_
V
V
D
D
D
D
V
V
A
A
AVDD_3.3V
B
A
N
E
S
Y
A
W
L
ODM ENABLE
A
3
3
3
4
0
0
2
2
2
2
J
J
1
1
CSB_DUT
SDIO_ODM
28
29
31
27
CSB
PDWN
SCLK/DTP
SDIO/ODM
AD9287 LFCSP
CLK+
CLK–
AVDD
AVDD
8
730
6
9
10
T
T
K
L
U
U
CLK
C
D
D
_
_
D
D
D
D
V
V
A
A
GNDAB9
GNDAB10
C1
C10
31
10
30
51
0
R259
R261
DNP
R258
R260
S6
S7
AVDD_3.3V
0
R249
R251
DNP
R248
R250
S2
S1
AVDD_3.3V
E
L
B
A
N
E
P
T
D
3
2
P
T
D
_
K
10k
L
R205
C
S
100k
R204
100k
R203
T
T
U
U
D
_
D
_
D
D
D
D
V
D
N
V
R
A
G
D
25
26
AVDD
DRVDD
DRGND
DCO+
DCO–
FCO+
FCO–
D + A
D – A
D + B
D – B
D + C
D – C
D + D
D – D
DRVDD
DRGND
AVDD
11
12
T
T
D
U
U
N
D
D
G
_
_
D
D
D
D
V
V
A
R
D
18
B9
B8
B7
GNDAB7
GNDAB8
A7
A8
A9
9
8
29
28
27
0
0
0
R263
R265
DNP
DNP
DNP
R262
R264
S9
S8
AVDD_3.3V
AVDD_3.3V
0
0
0
R253
R255
DNP
DNP
DNP
R252
R254
S4S0S5
S3
AVDD_3.3V
AVDD_3.3V
DCO
24
DCO
23
FCO
22
FCO
21
CHA
20
CHA
19
CHB
18
CHB
17
CHC
16
CHC
15
CHD
14
13
AVDD_3.3V
CHD
SCLK_CHA
17
16
B6
B5
GNDAB5
GNDAB6
A5
A6
6
7
25
26
SCLK_CHB
S10
AVDD_3.3V
AVDD_3.3V
OPTI ONAL CLO CK DRIVE CIRC UIT
ENABLE
R214
10k
C224
0.1µF
OSCILLATOR
OPTI ONAL CLO CK
CSB1_CHA
SDI_CHA
15
14
B4
B3
GNDAB3
GNDAB4
A3
A4
4
5
24
SDI_CHB
CSB3_CHB
CLK
DNP
C207
0.1µF
AVDD_3.3V
2
2
k
2
2
R
0
.
4
R221
10k
AVDD_3.3V
DNP
R220
DNP
R219
J205
DISABLE
R215
10k
1
2
5
OE
OE'
OSC201
VCC'
VCC
14
12
10
AVDD_3.3V
GNDAB2
13
GND'
OUT'
C208
33
31
1
32
U202
OPT_CLK
ENCODE
R242
7813
SDO_CHA
CSB2_CHA
12
11
B2
B1
GNDAB1
A1
A2
HEADER 6469 169-1
1
2233
21
22
LVPECL OUTPUT
T
C
E
R205 TO R211
N
N
O
C
O
SDO_CHB
N
CSB4_CHB
=
C
N
CLK
E202
1
DNP
0.1µF
100
23
22
OUT0
GND_PAD
GND
VS
RSET
CLK
3
2
6
2
9
.
2
9
R
4
5
2
2
0
R
OUT0B
CLKB
P
N
D
AD9515
P
N
D
R241
R240
SIGNAL = AV DD_3.3V;4,17, 20,21,24,26,29, 30
5
C209
243
243
18
19
S0
OUT1
OUT1B
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
S8
SIGNAL = DNC;27,28
S9
S10
VREF
SYNCB
9
3
k
2
0
R
1
8
P
3
2
N
R
D
7
P
2
N
2
0
D
R
0.1µF
R243
9
8
7
6
C223
0.1µF
C222
0.1µF
C221
0.1µF
TERMINATIONS
OPTIONAL OUTPUT
C220
0.1µF
C219
0.1µF
C218
0.1µF
AVDD_3.3V
C217
0.1µF
E203
)
LVDS OUTPUT
DNP
100
25
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
T
L
1
U
A
F
E
D
(
T
U
O
DNP
C215
0.1µF
E
N
I
S
P
I
L
CLK
C
C210
0.1µF
S0S1S2S3S4S5S6S7S8S9S10
3
CR201
HSMS2812
1
E201
3
2
2
0
R
43
T201
7
1
2
0
R
OPT_CLK
OPT_CLK
OPT_CLK
C205
GNDOUT
0.1µF
VFAC3H-L
R213
P201
49.9k
P203
ENC
ENC
DNP
R2120DNP
INPUT
CLOCK CI RCUIT
5
2
C216
R216
05966-016
CLK
C211
0.1µF
E
1
T
A
L
U
P
2
O
P
T
O
N
O
D
:
P
N
D
4
2
2
0
R
F
6
µ
0
1
2
.
C
0
6
1
8
1
2
0
R
0.1µF
0
Figure 63. Evaluation Board Schematic, DUT, VREF, Clock Inputs, and Digital Output Interface
Rev. A | Page 38 of 52
Page 39

AD9287
POPULATE L301 TO L308 WITH
0 RESISTORS OR DESIGN
YOUR OWN FI LTER.
POWER DOW N ENABLE
C311
0.1µF
C312
0.1µF
R312
10k
(0V TO 1V = DISABLE POW ER)
R313
10k
DNP
AVDD_5V
AVDD_5V
VPSV
LMD1
5
0
L307
0
C307
0.1µF
2023182219
NC
LMD2
CH_C
C302
DNP
C304
DNP
R304
DNP
R306
374
R309
187
VOL2
INH2
7
VOH2
VPS2
17
COMM
LON2
8
R302
DNP
L304
0
L308
0
C308
0.1µF
1000pF
R310
187
RCLMP
GAIN
MODE
VCM2
VIN2
VIP2
COM2
LOP2
CH_C
EXTERNAL VARIABL E GAIN DRIVE
VARIABLE GAIN CIRCUIT
(0V TO 1.0V DC)
C309
AVDD_5V
C310
0.1µF
16
VG
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
C313
0.1µF
C314
0.1µF
R320
39k
R311
10k
DNP
CW
AVDD_5V
VG
R319
10k
R314
10k
DNP
VG
1
JP301
2
GND
RCLAMP P IN
HILO PIN = LO = ±50mV
HILO PIN = H = ±75mV
24
LON1
2
C301
DNP
C303
DNP
R303
DNP
R305
374
R308
187
VOH1
COMM
VPS1
364
INH1
CH_D
L3020L303
L306
0
C306
0.1µF
21
VOL1
AD8332
CH_D
R301
DNP
L301
0
L305
0
C305
0.1µF
R307
187
U301
25
ENBV
26
ENBL
27
HILO
28
VCM1
29
VIN1
30
VIP1
31
COM1
32
LOP1
1
HILO PIN
HI GAIN RANGE = 2.25V TO 5.0V
LO GAI N RANGE = 0V TO 1.0V
OPTIONAL VGA DRIVE CI RCUIT FOR CHANNEL C AND CHANNEL D
R315
10k
DNP: DO NOT POPULATE
C315
10µF
C316
0.1µF
R316
274
C317
0.018µF
C320
0.1µF
AVDD_5V
C318
22pF
L309
120nH
C319
0.1µF
INH4 INH3
C321
0.1µF
AVDD_5V
C323
22pF
L310
120nH
C324
0.1µF
R317
274
C322
0.018µF
C325
0.1µF
Figure 64. Evaluation Board Schematic, Optional DUT Analog Input Drive and SPI Interface Circuit
C326
10µF
R318
10k
MODE PIN
POSITIVE GAIN SLOPE = 0V TO 1.0V
NEGATIVE GAIN SLOPE = 2.25V TO 5.0V
05966-017
Rev. A | Page 39 of 52
Page 40

AD9287
R433
1k
AVDD_3.3V
05966-018
AVDD_DUT
SDIO_ODM
REMOVE WHEN USING
OR PROGRAMMING PIC (U402)
SDO_CHA
0
R427
SDI_CHA
0
R420
SCLK_CHA
0
R428
CSB1_CHA
C408
C407
C406
C405
0
R426
R421
0, DNP
VSS
VDD
U402
AVDD_5V
J402
C427
0.1µF
AVDD_3.3V
R413
10k
DNP
C412
0.1µF
C411
R410
187
0.1µF
1000pF
R406
374
0.1µF
0.1µF
R405
0.1µF
17
18
R409
187
19
20
AVDD_5V
21
22
R408
187
23
374
24
R407
187
R423
0, DNP
R422
0, DNP
5
687
GP2
GP0
GP1
PIC12F629
GP4
GP5
MCLR/
GP3
R419
261
4
312
4.75k
R418
3
4
S401
1
2
RESET/REPROGRAM
HILO P IN = H = ± 75mV
HILO PIN = LO = ±50mV
RCLAMP PI N
R424
10k
DNP
AVDD_5V
VG
15
16
GAIN
VCM2
MODE
RCLMP
COMM
VOH2
VOL2
NC
VPSV
VOL1
VOH1
COMM
VCM1
ENBL
ENBV
10k
26
251427
R412
10k
HILO
2813291230
DNP
U401
R411
AVDD_5V
SPI CIRCUITRY F ROM FIFO
+3.3V = NORMAL O PERATION = AVDD_3.3V
+5V = PROGRAMMING = AVDD_5V
YOUR OWN FIL TER.
0 RESISTO RS OR DESIGN
POPULATE L401 TO L408 WITH
CH_A
L404
R402
DNP
DNP
CH_A
CH_B
CH_B
C402
L403
L402
DNP
C401
DNP
L401
R401
0
0
L408
DNP
DNP
C404
R404
0
0
L407
L406
0
0
DNP
R403
DNP
C403
L405
0
0
(0V TO 1V = DISABLE POWER)
POWER DOWN ENABL E
Figure 65. Evaluation Board Schematic, Optional DUT Analog Input Drive and SPI Interface Circuit (Continued)
AVDD_DUT
1k
R431
1k
R432
NC7WZ07
CR401
C423
11
VIP2
VIN2
COM2
AD8332
VIN1
VIP1
COM1
31
C409
C429
0.1µF
5
6
Y1
Y2A2
VCC
GND
A1
1234
OPTIONAL
0.1µF
10
32
0.1µF
U403
R425
10k
E401
C424
0.1µF
9
LOP2
LON2
8
VPS2
7
INH2
6
LMD2
5
LMD1
4
INH1
VPS1
LON1
LOP1
C416
3
2
1
R415
C410
0.1µF
LO GAIN RANGE = 0V TO 1.0V
HI GAIN RANGE = 2. 25V TO 5.0V
HILO PIN
OPTIONAL VGA DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR CHANNEL A AND CHANNEL B
SCLK_DTP
CSB_DUT
AVDD_DUT
C428
0.1µF
5
6
Y1
Y2A2
VCC
NC7WZ16
GND
A11
PICVCC
GP1
GP0
MCLR/GP3
R417
10k
C426
10µF
C425
0.1µF
274
R416
AVDD_5V
C417
0.1µF
0.1µF
AVDD_5V
274
C414
0.1µF
10µF
C413
R414
10k
U404
2
34
R429
10k
R430
10k
J401
2
1
4
3
5
7
9
C415
GP1
GP0
6
8
10
NEGATIVE GAIN SLOPE = 2.25V TO 5.0V
POSITIVE GAIN SLOPE = 0V TO 1.0V
MODE PIN
0.018µF
C420
C421
C418
0.018µF
PICVCC
MCLR/GP3
PIC PROG RAMMI NG HEADER
L410
120nH
22pF
L409
120nH
22pF
DNP: DO NOT POP ULATE
C422
0.1µF
INH2 INH1
C419
0.1µF
Rev. A | Page 40 of 52
Page 41

AD9287
D5023ASHOT_RECT
C531
AVDD_DUT
+1.8V
0.1µF
C530
0.1µF
C529
0.1µF
C528
0.1µF
C527
0.1µF
C526
0.1µF
H3H1
H4
H2
L506
U502
3.3V_AVDD
10µH
C533
1µF
L507
10µH
4
23
OUTPUT1
OUTPUT4
GND
1
ADP33339AKC-3.3
INPUT
1µF
C532
PWR_IN
4
2
OUTPUT1
OUTPUT4
ADP33339AKC-5
INPUT
U504
3
C534
PWR_IN
MOUNTING HOLES
CONNECTED TO GROUND
0.1µF
C517
0.1µF
C525
0.1µF
0.1µF
C524
AVDD_3.3V
+3.3V
C516
DRVDD_DUT
+1.8V
C523
0.1µF
C522
0.1µF
C521
0.1µF
C520
0.1µF
C519
0.1µF
C518
0.1µF
DECOUPLING CAPACITORS
CR501
R501
PWR_IN
DO-214AB
261
AVDD_5V
+5.0V
05966-019
C535
1µF
GND
1
1µF
21
34
FER501
F501
POWER SUPPLY INPUT
6V, 2V MAXIMUM
SMDC110F
1
P503
CHOKE_COIL
D501
S2A_RECT2ADO-214AA
C501
10µF
+
2
3
AVDD_5V
C503
C502
10µF
L503
10µH
DUT_AVDD
5V_AVDD
1234567
P1P2P3P4P5P6P7
P501
OPTIONAL POWER INPUT
AVDD_DUT
L502
3.3V_AVDD
C505
C504
10µH
DUT_DRVDD
0.1µF
AVDD_3.3V
0.1µF
10µF
8
P8
C509
0.1µF
C508
10µF
L508
10µH
L501
DRVDD_DUT
0.1µF
C507
10µF
C506
10µH
DUT_AVDD
L505
10µH
C515
1µF
4
OUTPUT1
OUTPUT4
GND
1
ADP33339AKC-1.8
INPUT
U501
32
1µF
C514
PWR_IN
DUT_DRVDD 5V_AVDD
10µH
L504
U503
C513
1µF
4
OUTPUT4
OUTPUT1
GND
1
ADP33339AKC-1.8
INPUT
32
1µF
C512
DNP: DO NOT POPULATE
PWR_IN
Figure 66. Evaluation Board Schematic, Power Supply Inputs
Rev. A | Page 41 of 52
Page 42

AD9287
05966-020
Figure 67. Evaluation Board Layout, Primary Side
Rev. A | Page 42 of 52
Page 43

AD9287
05966-021
Figure 68. Evaluation Board Layout, Ground Plane
Rev. A | Page 43 of 52
Page 44

AD9287
Figure 69. Evaluation Board Layout, Power Plane
Rev. A | Page 44 of 52
05966-022
Page 45

AD9287
Figure 70. Evaluation Board Layout, Secondary Side (Mirrored Image)
Rev. A | Page 45 of 52
05966-023
Page 46

AD9287
Table 17. Evaluation Board Bill of Materials (BOM)
Item Qty. Reference Designator Device Package Value Manufacturer
1 1 AD9287LFCSP_REVA PCB PCB PCB
2 75
3 4
4 4
5 1 C202 Capacitor 603
6 2 C309, C411 Capacitor 402
7 4
8 4
9 1 C501 Capacitor 1206
10 9
11 8
12 4
13 1 CR201 Diode SOT-23
14 2 CR401, CR501 LED 603
15 1 D502 Diode DO-214AB 3 A, 30 V, SMC
16 1 D501 Diode DO-214AA 2 A, 50 V, SMC
C101, C102, C107,
C108, C109, C114,
C115, C116, C121,
C122, C123, C128,
C201, C203, C204,
C205, C206, C210,
C211, C212, C213,
C216, C217, C218,
C219, C220, C221,
C222, C223, C224,
C310, C311, C312,
C313, C314, C316,
C319, C320, C321,
C324, C325, C409,
C410, C412, C414,
C416, C417, C419,
C422, C423, C424,
C425, C427, C428,
C429, C503, C505,
C507, C509, C516,
C517, C518, C519,
C520, C521, C522,
C523, C524, C525,
C526, C527, C528,
C529, C530, C531
C104, C111, C118,
C125
C315, C326, C413,
C426
C317, C322, C415,
C420
C318, C323, C418,
C421
C214, C512, C513,
C514, C515, C532,
C533, C534, C535
C305, C306, C307,
C308, C405, C406,
C407, C408
C502, C504, C506,
C508
Capacitor 402
Capacitor 402
Capacitor 805
Capacitor 402
Capacitor 402
Capacitor 603
Capacitor 805
Capacitor 603
1
Manufacturer’s
Part Number
0.1 μF, ceramic,
X5R, 10 V, 10% tol
2.2 pF, ceramic,
COG, 0.25 pF tol,
50 V
10 μF, 6.3 V ±10%
ceramic, X5R
2.2 μF, ceramic,
X5R, 6.3 V, 10% tol
1000 pF, ceramic,
X7R, 25 V, 10% tol
0.018 μF, ceramic,
X7R, 16 V, 10% tol
22 pF, ceramic,
NPO, 5% tol, 50 V
10 μF, tantalum,
16 V, 20% tol
1 μF, ceramic, X5R,
6.3 V, 10% tol
0.1 μF, ceramic,
X7R, 50 V, 10% tol
10 μF, ceramic,
X5R, 6.3 V, 20% tol
30 V, 20 mA, dual
Schottky
Green, 4 V, 5 m
candela
Murata GRM155R71C104KA88D
Murata GRM1555C1H2R2GZ01B
Murata GRM219R60J106KE19D
Murata GRM188C70J225KE20D
Murata GRM155R71H102KA01D
AVX 0402YC183KAT2A
Murata GRM1555C1H220JZ01D
Rohm TCA1C106M8R
Murata GRM188R61C105KA93D
Murata GRM21BR71H104KA01L
Murata GRM188R60J106M
Agilent
Technologies
Panasonic LNJ314G8TRA
Micro
Commercial Co.
Micro
Commercial Co.
HSMS2812-TRIG
SK33-TP
S2A-TP
Rev. A | Page 46 of 52
Page 47

AD9287
Manufacturer’s
Item Qty. Reference Designator Device Package Value Manufacturer
17 1 F501 Fuse 1210
18 1 FER501 Choke coil 2020
19 12
20 1 JP301 Connector 2-pin
21 2 J205, J402 Connector 3-pin
22 1 J201 to J204 Connector 12-pin
23 1 J401 Connector 10-pin
24 8
25 4 L309, L310, L409, L410 Inductor 402
26 16
27 1 OSC201 Oscillator SMT
28 5
29 1 P202 Connector Header
30 1 P503 Connector 0.1", PCMT
31 15
32 14
33 4
34 4
FB101, FB102, FB103,
FB104, FB105, FB106,
FB107, FB108, FB109,
FB110, FB111, FB112
L501, L502, L503, L504,
L505, L506, L507, L508
L301, L302, L303, L304,
L305, L306, L307, L308,
L401, L402, L403, L404,
L405, L406, L407, L408
P101, P103, P105,
P107, P201
R201, R205, R214,
R215, R221, R239,
R312, R315, R318,
R411, R414, R417,
R425, R429, R430
R103, R117, R129,
R142, R216, R217,
R218, R223, R224,
R237, R420, R426,
R427, R428
R102, R115, R128,
R141
R104, R116, R130,
R143
Ferrite bead 603
Ferrite bead 1210
Resistor 805 0 Ω, 1/8 W, 5% tol
Connector SMA
Resistor 402
Resistor 402
Resistor 402
Resistor 603
6.0 V, 2.2 A tripcurrent resettable
fuse
10 μH, 5 A, 50 V,
190 Ω @ 100 MHz
10 Ω, test freq
100 MHz, 25% tol,
500 mA
100 mil header
jumper, 2-pin
100 mil header
jumper, 3-pin
100 mil header
male, 4 × 3 triple
row straight
100 mil header,
male, 2 × 5 double
row straight
10 μH, bead core
3.2 × 2.5 × 1.6
SMD, 2 A
120 nH, test freq
100 MHz, 5% tol,
150 mA
Clock oscillator,
100.00 MHz, 3.3 V
Side-mount SMA
for 0.063" board
thickness
1469169-1, right
angle 2-pair,
25 mm, header
assembly
SC1153, power
supply connector
10 kΩ, 1/16 W,
5% tol
0 Ω, 1/16 W,
5% tol
64.9 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
0 Ω, 1/10 W,
5% tol
Tyco/Raychem NANOSMDC110F-2
Murata DLW5BSN191SQ2L
Murata BLM18BA100SN1B
Samtec TSW-102-07-G-S
Samtec TSW-103-07-G-S
Samtec TSW-104-08-G-T
Samtec TSW-105-08-G-D
Murata BLM31PG500SN1L
Murata LQG15HNR12J02B
NIC
Components
Valpey Fisher VFAC3H-L-100MHz
Johnson
Components
Tyco 6469169-1
Switchcraft RAPC722X
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
Part Number
NRC10ZOTRF
142-0710-851
NRC04J103TRF
NRC04Z0TRF
NRC04F64R9TRF
NRC06Z0TRF
Rev. A | Page 47 of 52
Page 48

AD9287
Manufacturer’s
Item Qty. Reference Designator Device Package Value Manufacturer
35 15
36 8
37 4
38 3 R202, R203, R204 Resistor 402
39 1 R222 Resistor 402
40 1 R213 Resistor 402
41 1 R229 Resistor 402
42 2 R230, R319 Potentiometer 3-lead
43 1 R228 Resistor 402
44 1 R320 Resistor 402
45 8
46 4
47 4
48 11
49 1 R418 Resistor 402
50 1 R419 Resistor 402
51 1 R501 Resistor 603
52 2 R240, R241 Resistor 402
53 2 R242, R243 Resistor 402
54 1 S401 Switch SMD
55 5
56 2 U501, U503 IC SOT-223
R109, R111, R112,
R123, R125, R126,
R135, R138, R139,
R148, R149, R150,
R431, R432, R433
R108, R110, R121,
R122, R134, R136,
R146, R147
R161, R162, R163,
R164
R307, R308, R309,
R310, R407, R408,
R409, R410
R305, R306, R405,
R406
R316, R317, R415,
R416
R245, R247, R249,
R251, R253, R255,
R257, R259, R261,
R263, R265
T101, T102, T103, T104,
T201
Resistor 402
Resistor 402
Resistor 402
Resistor 402
Resistor 402
Resistor 402
Resistor 201 0 Ω, 1/20 W, 5% tol Panasonic
Transformer CD542
1 kΩ, 1/16 W,
1% tol
33 Ω, 1/16 W,
5% tol
499 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
100 kΩ, 1/16 W,
1% tol
4.02 kΩ, 1/16 W,
1% tol
49.9 Ω, 1/16 W,
0.5% tol
4.99 kΩ, 1/16 W,
5% tol
10 kΩ, cermet
trimmer
potentiometer,
18-turn top adjust,
10%, 1/2 W
470 kΩ, 1/16 W,
5% tol
39 kΩ, 1/16 W,
5% tol
187 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
374 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
274 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
4.75 kΩ, 1/16 W,
1% tol
261 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
261 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
243 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
100 Ω, 1/16 W,
1% tol
Light touch,
100GE, 5 mm
ADT1-1WT, 1:1
impedance ratio
transformer
ADP33339AKC-1.8,
1.5 A, 1.8 V LDO
regulator
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
Susumu RR0510R-49R9-D
NIC
Components
BC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
NIC
Components
Panasonic EVQ-PLDA15
Mini-Circuits ADT1-1WT+
Analog Devices ADP33339AKCZ-1.8
Part Number
NRC04F1001TRF
NRC04J330TRF
NRC04F4990TRF
NRC04F1003TRF
NRC04F4121TRF
NRC04F4991TRF
CT94EW103
NRC04J474TRF
NRC04J393TRF
NRC04F1870TRF
NRC04F3740TRF
NRC04F2740TRF
ERJ-1GE0R00C
NRC04J472TRF
NRC04F2610TRF
NRC06F2610TRF
NRC04F2430TRF
NRC04F1000TRF
Rev. A | Page 48 of 52
Page 49

AD9287
Manufacturer’s
Item Qty. Reference Designator Device Package Value Manufacturer
57 2 U301, U401 IC
LFCSP,
CP-32
AD8332ACP,
ultralow noise
Analog Devices AD8332ACPZ
precision dual
VGA
58 1 U504 IC SOT-223 ADP3339AKC-5 Analog Devices ADP3339AKCZ-5
59 1 U502 IC SOT-223 ADP3339AKC-3.3 Analog Devices ADP3339AKCZ-3.3
60 1 U201 IC
LFCSP,
CP-48-1
AD9287BCPZ-100,
quad, 8-bit, 100
Analog Devices AD9287BCPZ-100
MSPS serial LVDS
1.8 V ADC
61 1 U203 IC SOT-23
ADR510ARTZ, 1.0 V,
Analog Devices ADR510ARTZ
precision low
noise shunt
voltage reference
62 1 U202 IC
LFCSP
AD9515BCPZ Analog Devices AD9515BCPZ
CP-32-2
63 1 U403 IC
SC70,
NC7WZ07 Fairchild NC7WZ07P6X_NL
MAA06A
64 1 U404 IC
SC70,
NC7WZ16 Fairchild NC7WZ16P6X_NL
MAA06A
65 1 U402 IC 8-SOIC
Flash prog
Microchip PIC12F629-I/SN
mem 1k × 14,
RAM size 64 × 8,
20 MHz speed,
PIC12F controller
series
1
This BOM is RoHS compliant.
Part Number
Rev. A | Page 49 of 52
Page 50

AD9287
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
0.30
0.23
0.18
PIN 1
48
INDICATOR
1
BSC SQ
PIN 1
INDICATOR
7.00
0.60 MAX
37
36
0.60 MAX
1.00
0.85
0.80
12° MAX
SEATING
PLANE
TOP
VIEW
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VKKD-2
6.75
BSC SQ
0.20 REF
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
COPLANARITY
0.08
25
24
EXPOSED
PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
5.50
REF
13
5.25
5.10 SQ
4.95
12
0.25 MIN
Figure 71. 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
7 mm × 7 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-48-1)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD9287BCPZ-100
AD9287BCPZRL7-1001−40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] Tape and Reel CP-48-1
AD9287-100EB Evaluation Board
AD9287-100EBZ
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
1
−40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-48-1
1
Evaluation Board
Rev. A | Page 50 of 52
Page 51

AD9287
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 51 of 52
Page 52

AD9287
NOTES
©2006–2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D05966-0-5/07(A)
Rev. A | Page 52 of 52
 Loading...
Loading...