16-Bit, 80 MSPS/105 MSPS/125 MSPS, 1.8 V Dual
S
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES
SNR = 78.2 dBFS @ 70 MHz and 125 MSPS
SFDR = 88 dBc @ 70 MHz and 125 MSPS
Low power: 750 mW @ 125 MSPS
1.8 V analog supply operation
1.8 V CMOS or LVDS output supply
Integer 1-to-8 input clock divider
IF sampling frequencies to 300 MHz
−153.6 dBm/Hz small-signal input noise with 200 Ω input
impedance @ 70 MHz and 125 MSPS
Optional on-chip dither
Programmable internal ADC voltage reference
Integrated ADC sample-and-hold inputs
Flexible analog input range: 1 V p-p to 2 V p-p
Differential analog inputs with 650 MHz bandwidth
ADC clock duty cycle stabilizer
95 dB channel isolation/crosstalk
Serial port control
User-configurable, built-in self-test (BIST) capability
Energy-saving power-down modes
APPLICATIONS
Communications
Diversity radio systems
Multimode digital receivers (3G)
GSM, EDGE, W-CDMA, LTE,
CDMA2000, WiMAX, TD-SCDMA
I/Q demodulation systems
Smart antenna systems
General-purpose software radios
Broadband data applications
Ultrasound equipment
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
AD9268
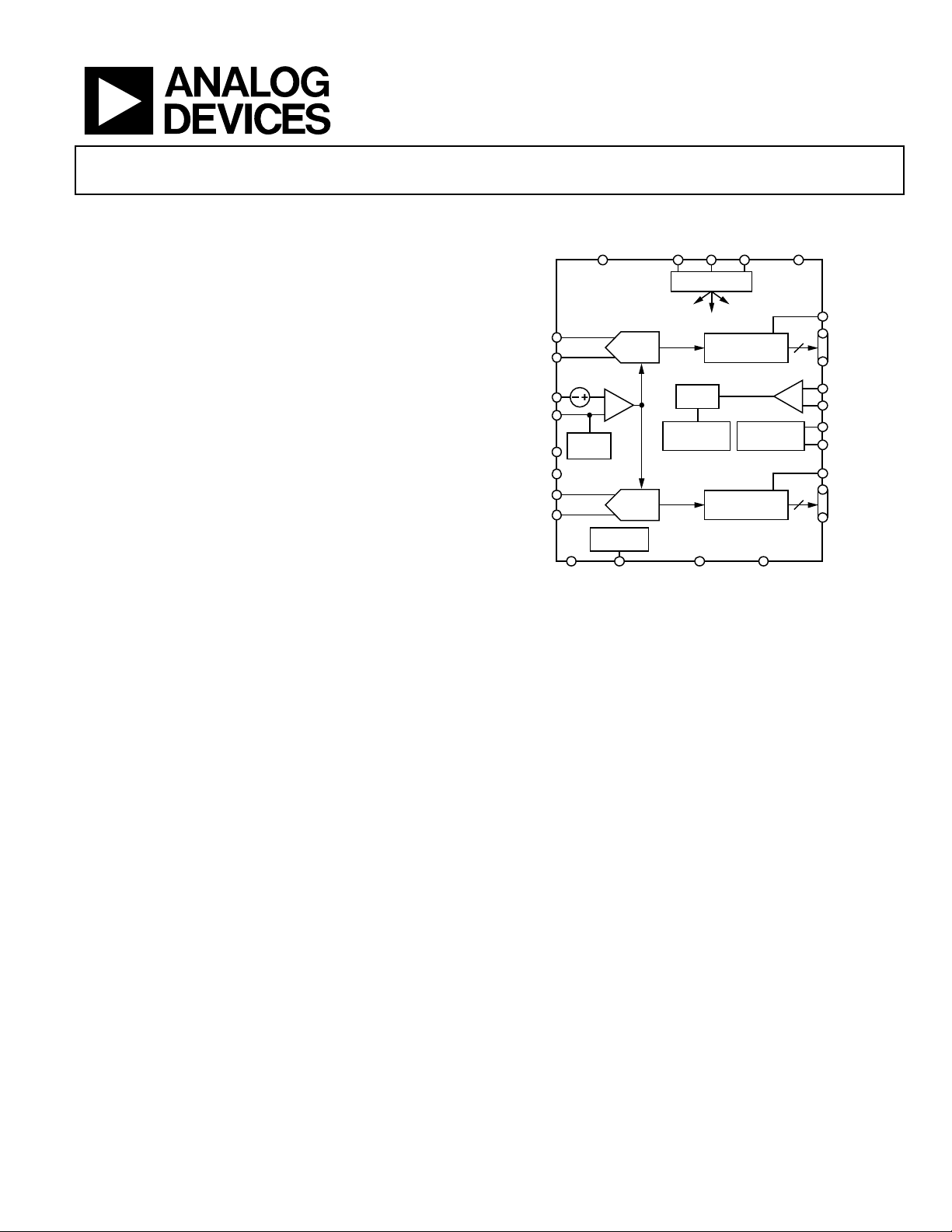
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
SDIO/
SCLK/
DCS
DFS
AD9268
VIN+A
VIN–A
VREF
ENSE
SELECT
VCM
RBIAS
VIN–B
VIN+B
NOTES
1. PIN NAMES ARE FOR THE CMOS PIN CONFIGURATION ONLY;
SEE FIGURE 7 FORLVDS PIN NAMES.
REF
MULTICHIP
ADC
ADC
SYNC
SYNCAGND
SPI
PROGRAMMI NG DATA
CMOS/LVDS
OUTPUT BUFFER
DIVIDE 1
TO 8
DUTY CYCLE
STABILIZER
CMOS/LVDS
OUTPUT BUFFER
PDWN OEB
Figure 1.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. On-chip dither option for improved SFDR performance
with low power analog input.
2. Proprietary differential input that maintains excellent SNR
performance for input frequencies up to 300 MHz.
3. Operation from a single 1.8 V supply and a separate digital
output driver supply accommodating 1.8 V CMOS or
LVDS outputs .
4. Standard serial port interface (SPI) that supports various
product features and functions, such as data formatting
(offset binary, twos complement, or gray coding), enabling
the clock DCS, power-down, test modes, and voltage
reference mode.
5. Pin compatibility with the AD9258, allowing a simple
migration from 16 bits to 14 bits. The AD9268 is also pin
compatible with the AD9251, AD9231, and AD9204 family
of products for lower sample rate, low power applications.
DRVDDCSBAVDD
DCO
GENERATION
ORA
D15A (MSB)
16
TO
D0A (LSB)
CLK+
CLK–
DCOA
DCOB
ORB
D15B (MSB)
16
TO
D0B (LSB)
08123-001
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Product Highlights ........................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
General Description ......................................................................... 3
Specifications ..................................................................................... 4
ADC DC Specifications ............................................................... 4
ADC AC Specifications ................................................................. 6
Digital Specifications ................................................................... 7
Switching Specifications ................................................................ 9
Timing Specifications ................................................................ 10
Absolute Maximum Ratings .......................................................... 12
Thermal Characteristics ............................................................ 12
ESD Caution ................................................................................ 12
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ......................... 13
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 17
Equivalent Circuits ......................................................................... 25
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 26
ADC Architecture ...................................................................... 26
Analog Input Considerations .................................................... 26
Voltage Reference ....................................................................... 29
Clock Input Considerations ...................................................... 30
Channel/Chip Synchronization ................................................ 31
Power Dissipation and Standby Mode .................................... 32
Digital Outputs ........................................................................... 32
Timing ......................................................................................... 33
Built-In Self-Test (BIST) and Output Test .................................. 34
Built-In Self-Test (BIST) ............................................................ 34
Output Test Modes ..................................................................... 34
Serial Port Interface (SPI) .............................................................. 35
Configuration Using the SPI ..................................................... 35
Hardware Interface ..................................................................... 36
Configuration Without the SPI ................................................ 36
SPI Accessible Features .............................................................. 36
Memory Map .................................................................................. 37
Reading the Memory Map Register Table ............................... 37
Memory Map Register Table ..................................................... 38
Memory Map Register Descriptions ........................................ 40
Applications Information .............................................................. 41
Design Guidelines ...................................................................... 41
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 42
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 42
REVISION HISTORY
9/09—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Features List .................................................................. 1
Changes to Specifications Section .................................................. 4
Changes to Table 5 .......................................................................... 10
Changes to Typical Performance Characteristics Section ......... 17
5/09—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9268 is a dual, 16-bit, 80 MSPS/105 MSPS/125 MSPS
analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The AD9268 is designed to
support communications applications where high performance,
combined with low cost, small size, and versatility, is desired.
The dual ADC core features a multistage, differential pipelined
architecture with integrated output error correction logic. Each
ADC features wide bandwidth, differential sample-and-hold
analog input amplifiers that support a variety of user-selectable
input ranges. An integrated voltage reference eases design considerations. A duty cycle stabilizer is provided to compensate for
variations in the ADC clock duty cycle, allowing the converters
to maintain excellent performance.
The ADC output data can be routed directly to the two external
16-bit output ports. These outputs can be set to either 1.8 V
CMOS or LVDS.
Flexible power-down options allow significant power savings,
when desired.
Programming for setup and control is accomplished using a 3-wire
SPI-compatible serial interface.
The AD9268 is available in a 64-lead LFCSP and is specified over
the industrial temperature range of −40°C to +85°C.
Rev. A | Page 3 of 44
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
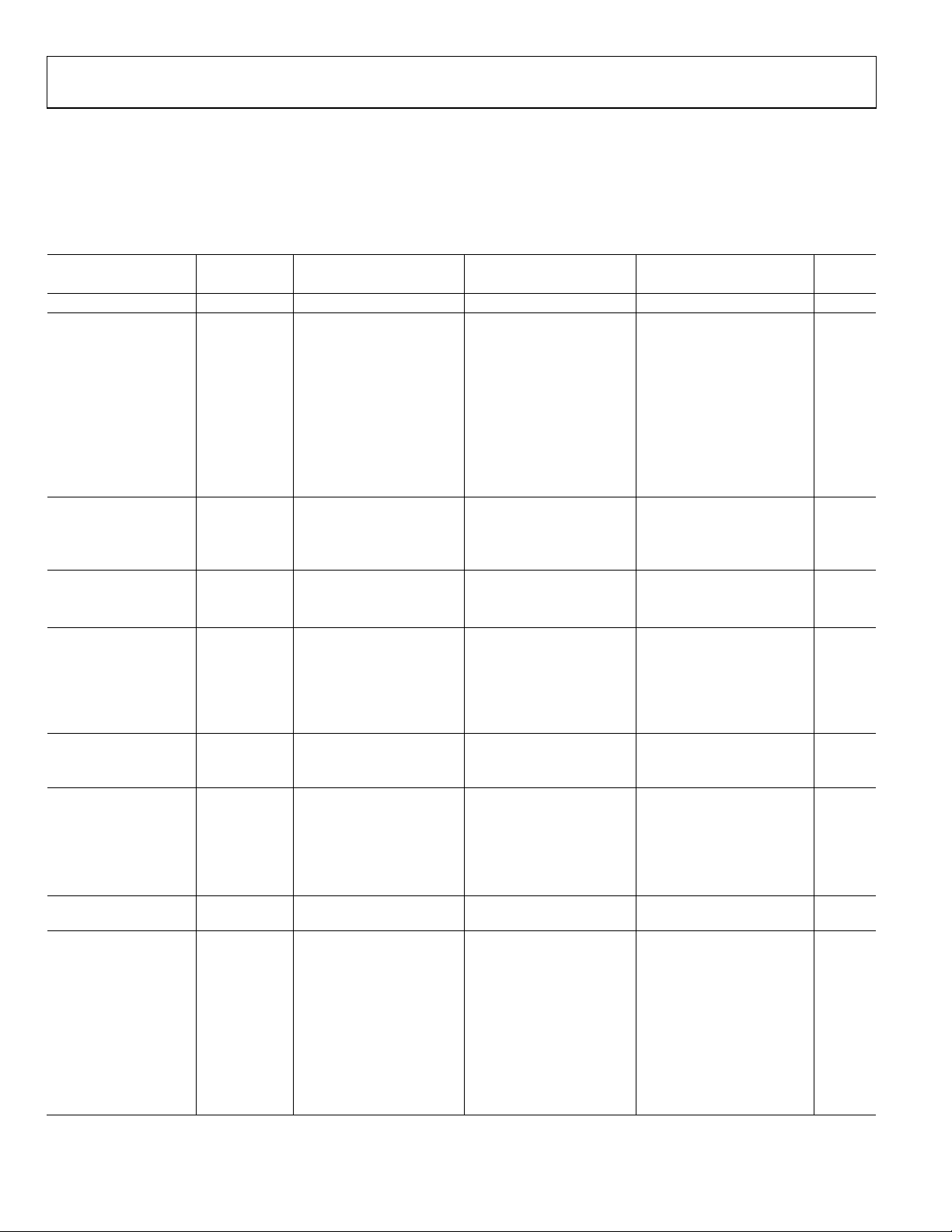
SPECIFICATIONS
ADC DC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, DCS enabled, unless
otherwise noted.
Table 1.
AD9268BCPZ-80 AD9268BCPZ-105 AD9268BCPZ-125
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION Full 16 16 16 Bits
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes Full Guaranteed Guaranteed Guaranteed
Offset Error Full ±0.2 ±0.4 ±0.2 ±0.5 ±0.4 ±0.65 % FSR
Gain Error Full ±0.4 ±2.5 ±0.4 ±2.5 ±0.4 ±2.5 % FSR
Differential
Nonlinearity (DNL)
25°C ±0.65 ±0.7 ±0.7 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity
1
(INL)
25°C ±2.0 ±3.0 ±3.0 LSB
MATCHING
CHARACTERISTIC
Offset Error Full ±0.1 ±0.4 ±0.1 ±0.4 ±0.2 ±0.45 % FSR
Gain Error Full ±0.3 ±1.3 ±0.3 ±1.3 ±0.3 ±1.3 % FSR
TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset Error Full ±2 ±2 ±2 ppm/°C
Gain Error Full ±15 ±15 ±15 ppm/°C
INTERNAL VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
Output Voltage Error
(1 V Mode)
Load Regulation @
1.0 mA
INPUT REFERRED NOISE
VREF = 1.0 V 25°C 2.17 2.23 2.27
ANALOG INPUT
Input Span, VREF =
1.0 V
Input Capacitance
Input Common-
Mode Voltage
REFERENCE INPUT
RESISTANCE
POWER SUPPLIES
Supply Voltage
AVDD Full 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
DRVDD Full 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
Supply Current
1
IAVDD
Full 234 240 293 300 390 400 mA
IDRVDD1 (1.8 V
CMOS)
IDRVDD1 (1.8 V
LVD S)
Full −1.0 +1.4 −1.0 +1.3 −1.0 +1.2 LSB
1
Full ±4.5 ±5.1 ±5.5 LSB
Full ±5 ±12 ±5 ±12 ±5 ±12 mV
Full 5 5 5 mV
LSB
rms
Full 2 2 2 V p-p
2
Full 8 8 8 pF
Full 0.9 0.9 0.9 V
Full 6 6 6 kΩ
Full 35 45 55 mA
Full 89 89 94 mA
Rev. A | Page 4 of 44
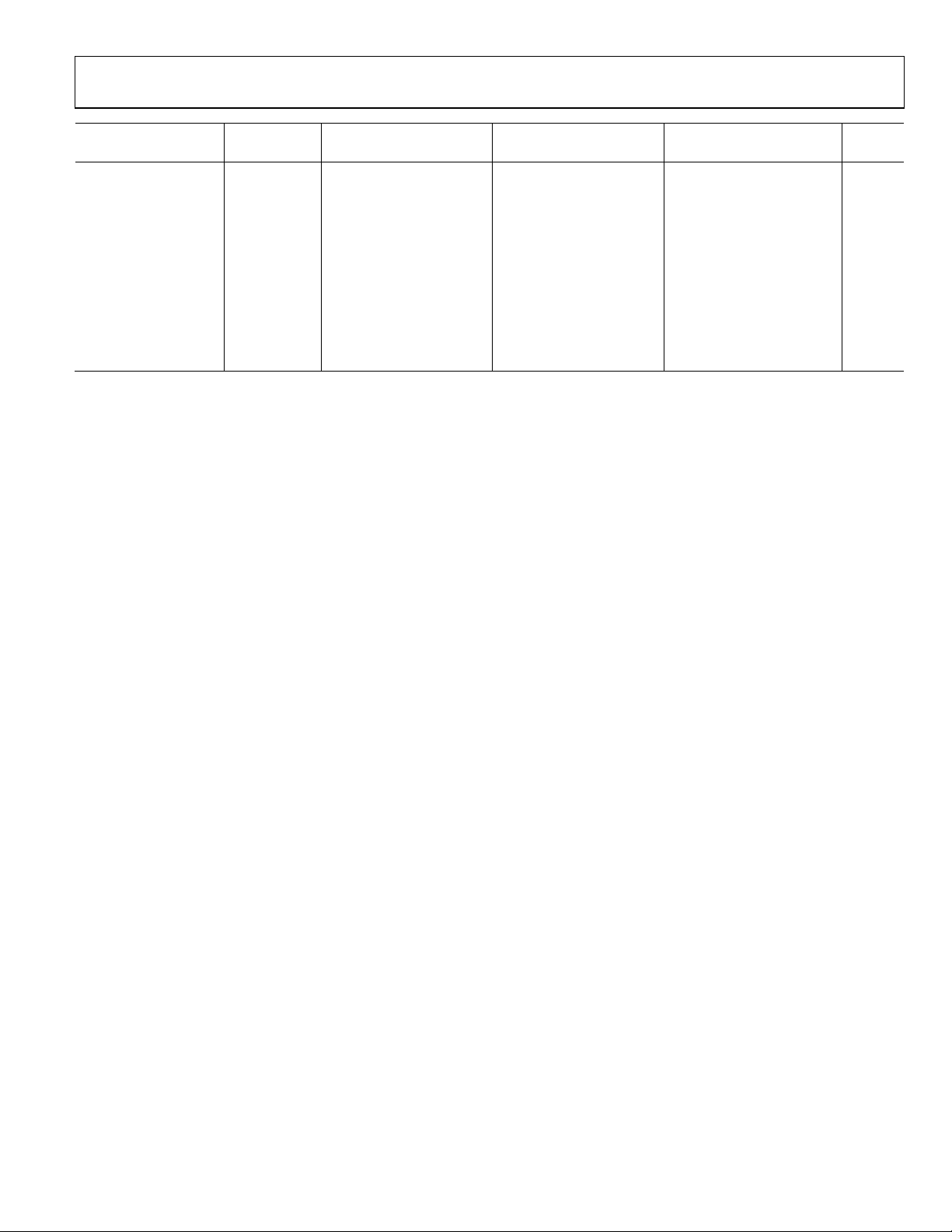
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
AD9268BCPZ-80 AD9268BCPZ-105 AD9268BCPZ-125
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
POWER CONSUMPTION
DC Input Full 420 450 565 590 750 777 mW
Sine Wave Input1
(DRVDD = 1.8 V
CMOS Output
Mode)
Sine Wave Input1
(DRVDD = 1.8 V
LVDS Output
Mode)
Standby Power
Power-Down Power Full 0.5 2.5 0.5 2.5 0.5 2.5 mW
1
Measured with a low input frequency, full-scale sine wave, with approximately 5 pF loading on each output bit.
2
Input capacitance refers to the effective capacitance between one differential input pin and AGND.
3
Standby power is measured with a dc input and with the CLK pins inactive (set to AVDD or AGND).
Full 485 608 800 mW
Full 582 685 870 mW
3
Full 45 45 45 mW
Rev. A | Page 5 of 44
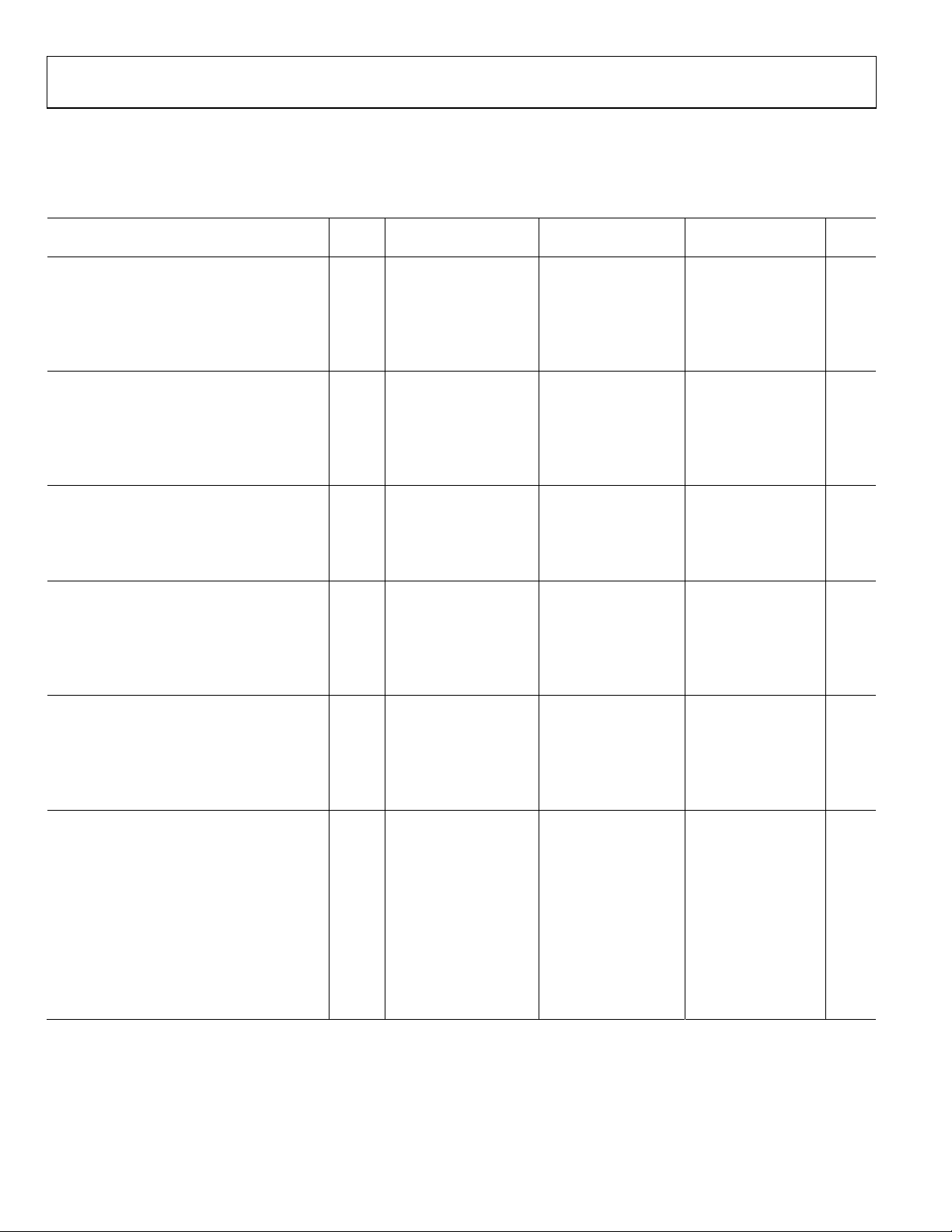
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ADC AC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, DCS enabled, unless
otherwise noted.
Table 2.
AD9268BCPZ-80 AD9268BCPZ-105 AD9268BCPZ-125
Parameter
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO (SNR)
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C 79.7 78.9 78.8 dBFS
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 78.3 79.0 77.2 78.8 77.2 78.2 dBFS
Full 78.0 77.1 76.5 dBFS
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 77.4 76.9 77.1 dBFS
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 75.5 75.0 75.5 dBFS
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE-AND-DISTORTION (SINAD)
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C 79.4 78.3 78.3 dBFS
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 78.1 78.5 77.1 78.6 76.8 77.7 dBFS
Full 77.7 76.8 76.2 dBFS
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 75.4 75.9 75.8 dBFS
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 74.3 72.2 74.0 dBFS
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS (ENOB)
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C 12.9 12.7 12.7 Bits
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 12.8 12.7 12.6 Bits
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 12.2 12.3 12.3 Bits
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 12.0 11.7 12.0 Bits
WORST SECOND OR THIRD HARMONIC
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C −92 −87 −90 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C −91 −88 −93 −87 −88 −85 dBc
Full −87 −87 −84 dBc
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C −80 −84 −83 dBc
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C −82 −77 −79 dBc
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C 92 87 90 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 88 91 87 93 85 88 dBc
Full 87 87 84 dBc
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 80 84 83 dBc
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 82 77 79 dBc
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
Without Dither (AIN@ −23 dBFS)
With On-Chip Dither (AIN @ −23 dBFS)
1
Temp Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C 93 100 88 dBFS
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 95 96 89 dBFS
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 98 96 90 dBFS
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 102 100 89 dBFS
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C 107 106 106 dBFS
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 107 109 106 dBFS
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C 106 104 104 dBFS
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 104 108 105 dBFS
Rev. A | Page 6 of 44
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
AD9268BCPZ-80 AD9268BCPZ-105 AD9268BCPZ-125
Parameter
WORST OTHER (HARMONIC OR SPUR)
Without Dither
With On-Chip Dither
TWO-TONE SFDR, WITHOUT DITHER
fIN = 29 MHz (−7 dBFS ), 32 MHz (−7 dBFS) 25°C 93 92 90 dBc
fIN = 169 MHz (−7 dBFS ), 172 MHz (−7 dBFS) 25°C 81 80 82 dBc
CROSSTALK
ANALOG INPUT BANDWIDTH 25°C 650 650 650 MHz
1
See the AN-835 Application Note, Understanding High Speed ADC Testing and Evaluation, for a complete set of definitions.
2
Crosstalk is measured at 100 MHz with −1 dBFS on one channel and no input on the alternate channel.
1
Temp Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C −99 −100 −100 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C −100 −96 −99 −94 −100 −94 dBc
Full −96 −94 −94 dBc
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C −98 −98 −98 dBc
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C −96 −94 −96 dBc
fIN = 2.4 MHz 25°C −108 −107 −108 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C −106 −96 −107 −95 −106 −95 dBc
Full −96 −95 −95 dBc
fIN = 140 MHz 25°C −105 −104 −103 dBc
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C −102 −102 −99 dBc
2
Full −95 −95 −95 dB
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, and DCS enabled, unless
otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
DIFFERENTIAL CLOCK INPUTS (CLK+, CLK−)
Logic Compliance CMOS/LVDS/LVPECL
Internal Common-Mode Bias Full 0.9 V
Differential Input Voltage Full 0.3 3.6 V p-p
Input Voltage Range Full AGND AVDD V
Input Common-Mode Range Full 0.9 1.4 V
High Level Input Current Full −100 +100 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −100 +100 μA
Input Capacitance Full 4 pF
Input Resistance Full 8 10 12 kΩ
SYNC INPUT
Logic Compliance CMOS
Internal Bias Full 0.9 V
Input Voltage Range Full AGND AVDD V
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.2 AVDD V
Low Level Input Voltage Full AGND 0.6 V
High Level Input Current Full −100 +100 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −100 +100 μA
Input Capacitance Full 1 pF
Input Resistance Full 12 16 20 kΩ
Rev. A | Page 7 of 44
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Unit
LOGIC INPUT (CSB)1
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 2.1 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full 40 132 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 2 pF
LOGIC INPUT (SCLK/DFS)2
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 2.1 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current (VIN = 1.8 V) Full −92 −135 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 2 pF
LOGIC INPUT/OUTPUT (SDIO/DCS)
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 2.1 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full 38 128 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 5 pF
LOGIC INPUTS (OEB, PDWN)
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.22 2.1 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.6 V
High Level Input Current (VIN = 1.8 V) Full −90 −134 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 5 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
CMOS Mode—DRVDD = 1.8 V
High Level Output Voltage
IOH = 50 μA Full 1.79 V
IOH = 0.5 mA Full 1.75 V
Low Level Output Voltage
IOL = 1.6 mA Full 0.2 V
IOL = 50 μA Full 0.05 V
LVDS Mode—DRVDD = 1.8 V
Differential Output Voltage (VOD), ANSI Mode Full 290 345 400 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS), ANSI Mode Full 1.15 1.25 1.35 V
Differential Output Voltage (VOD), Reduced Swing Mode Full 160 200 230 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS), Reduced Swing Mode Full 1.15 1.25 1.35 V
1
Pull up.
2
Pull down.
1
2
Rev. A | Page 8 of 44
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, VIN = −1.0 dBFS differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, and DCS enabled,
unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
AD9268BCPZ-80 AD9268BCPZ-105 AD9268BCPZ-125
Parameter Temperature Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
CLOCK INPUT PARAMETERS
Input Clock Rate Full 625 625 625 MHz
Conversion Rate1
DCS Enabled Full 20 80 20 105 20 125 MSPS
DCS Disabled Full 10 80 10 105 10 125 MSPS
CLK Period—Divide-by-1 Mode (t
CLK Pulse Width High (tCH)
Divide-by-1 Mode, DCS Enabled Full
Divide-by-1 Mode, DCS Disabled Full
Divide-by-2 Mode Through Divide-
by-8 Mode
Aperture Delay (tA) Full 1.0 1.0 1.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter, tJ) Full 0.07 0.07 0.07
DATA OUTPUT PARAMETERS
CMOS Mode
Data Propagation Delay (tPD) Full
DCO Propagation Delay (t
DCO to Data Skew (t
SKEW
LVDS Mode
Data Propagation Delay (tPD) Full 2.9 3.7 4.5 2.9 3.7 4.5 2.9 3.7 4.5 ns
DCO Propagation Delay (t
DCO to Data Skew (t
SKEW
CMOS Mode Pipeline Delay
(Latency)
LVDS Mode Pipeline Delay (Latency)
Channel A/Channel B
Wake-Up Time3 Full 500 500 500 μs
Out-of-Range Recovery Time Full 2 2 2 Cycles
1
Conversion rate is the clock rate after the divider.
2
Additional DCO delay can be added by writing to Bit 0 through Bit 4 in SPI Register 0x17 (see Table 17).
3
Wake-up time is defined as the time required to return to normal operation from power-down mode.
) Full 12.5 9.5 8 ns
CLK
3.75
6.25
5.95
6.25
Full 0.8
8.75 2.85
6.55 4.5
0.8
4.75
4.75
6.65
2.4 4 5.6 ns
5.0
3.8 4 4.2 ns
0.8
ns
ps
rms
)2 Full
DCO
2.8
3.5
3.1
4.2 2.8
3.5
3.1
4.2
2.8 3.5 4.2 ns
3.1
ns
) Full −0.6 −0.4 0 −0.6 −0.4 0 −0.6 −0.4 0 ns
)2 Full
DCO
3.9
3.9
3.9
ns
) Full −0.1 +0.2 +0.5 −0.1 +0.2 +0.5 −0.1 +0.2 +0.5 ns
Full 12 12 12 Cycles
Full 12/12.5 12/12.5 12/12.5 Cycles
Rev. A | Page 9 of 44
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
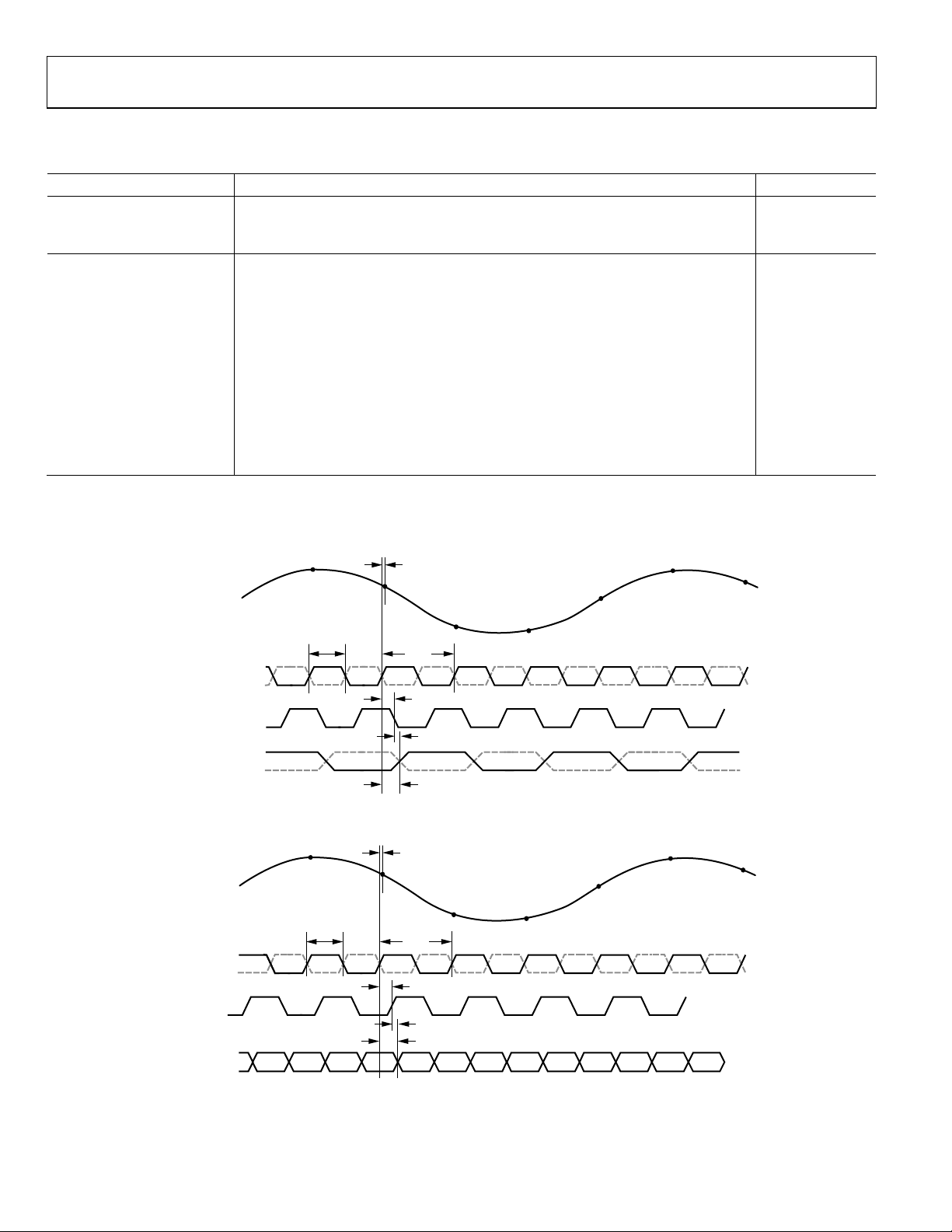
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 5.
Parameter Conditions Limit
SYNC TIMING REQUIREMENTS
t
SYNC to rising edge of CLK+ setup time 0.3 ns typ
SSYNC
t
SYNC to rising edge of CLK+ hold time 0.40 ns typ
HSYNC
SPI TIMING REQUIREMENTS
tDS Setup time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK 2 ns min
tDH Hold time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK 2 ns min
t
Period of the SCLK 40 ns min
CLK
tS Setup time between CSB and SCLK 2 ns min
tH Hold time between CSB and SCLK 2 ns min
t
SCLK pulse width high 10 ns min
HIGH
t
SCLK pulse width low 10 ns min
LOW
t
EN_SDIO
t
DIS_SDIO
Timing Diagrams
CH A/CH B DATA
CH A/CH B DATA
VIN
CLK+
CLK–
DCOA/DCOB
VIN
CLK+
CLK–
DCOA/DCOB
Time required for the SDIO pin to switch from an input to an output relative to the SCLK
falling edge
Time required for the SDIO pin to switch from an output to an input relative to the SCLK
rising edge
N – 1
t
CH
t
A
N
N + 1
t
CLK
t
DCO
t
SKEW
N – 12N – 13
t
PD
N + 2
N – 11 N – 10 N – 9 N – 8
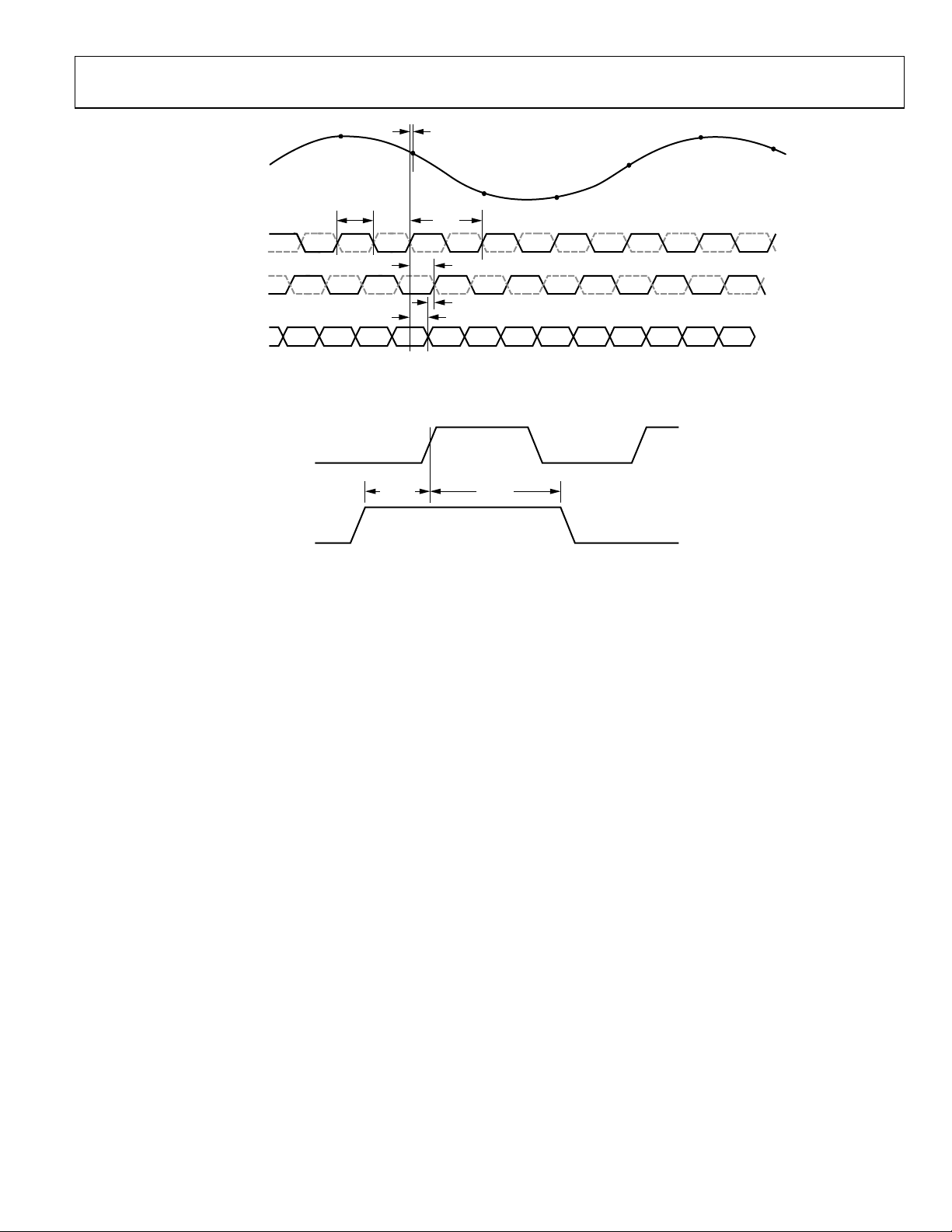
Figure 2. CMOS Default Output Mode Data Output Timing
N – 1
t
CH
t
DCO
t
A
N
N + 1
t
CLK
t
SKEW
t
PD
CH A
CH B
N – 12
N – 12
CH A
N – 11
N + 2
CH B
N – 11
CH A
N – 10
Figure 3. CMOS Interleaved Output Mode Data Output Timing
N + 3
N + 3
CH B
N – 10
CH A
N – 9
N + 4
N + 4
CH B
N – 9
CH A
N – 8
N + 5
N + 5
10 ns min
10 ns min
08123-002
08123-057
Rev. A | Page 10 of 44
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VIN
CLK+
CLK–
DCOA/DCOB
CH A/CH B DATA
N – 1
CH A
N – 9
N + 4
CH B
N – 9
CH A
N – 8
N + 5
08123-003
t
A
N
N + 1
t
CH
t
DCO
t
CLK
t
t
SKEW
PD
CH A
CH B
N – 12
N – 12
CH A
N – 11
N + 2
CH B
N – 11
CH A
N – 10
N + 3
CH B
N – 10
Figure 4. LVDS Mode Data Output Timing
CLK+
t
HSYNC
08123-004
SYNC
t
SSYNC
Figure 5. SYNC Input Timing Requirements
Rev. A | Page 11 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 6.
Parameter Rating
ELECTRICAL1
AVDD to AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
DRVDD to AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
VIN+A/VIN+B, VIN−A/VIN−B to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
CLK+, CLK− to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
SYNC to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
VREF to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
SENSE to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
VCM to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
RBIAS to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
CSB to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.2 V
SCLK/DFS to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.2 V
SDIO/DCS to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.2 V
OEB −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.2 V
PDWN −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.2 V
D0A/D0B through D15A/D15B to
AGND
DCOA/DCOB to AGND
−0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.2 V
−0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.2 V
ENVIRONMENTAL
Operating Temperature Range
−40°C to +85°C
(Ambient)
Maximum Junction Temperature
150°C
Under Bias
Storage Temperature Range
−65°C to +150°C
(Ambient)
1
The inputs and outputs are rated to the supply voltage (AVDD or ARVDD) +
0.2 V but should not exceed 2.1 V.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
The exposed paddle must be soldered to the ground plane for
the LFCSP package. Soldering the exposed paddle to the PCB
increases the reliability of the solder joints and maximizes the
thermal capability of the package.
Typical θ
is specified for a 4-layer PCB with a solid ground
JA
plane. As shown in Ta b l e 7 , airflow improves heat dissipation,
which reduces θ
. In addition, metal in direct contact with the
JA
package leads from metal traces, through holes, ground, and
power planes, reduces θ
.
JA
Table 7. Thermal Resistance
Airflow
Packa ge Type
64-Lead LFCSP
(CP-64-6)
Veloc ity
(m/sec) θ
0 18.5 1.0 °C/W
1.0 16.1 9.2 °C/W
1, 2
JA
1, 3
θ
JC
1, 4
θ
Unit
JB
2.5 14.5 °C/W
1
Per JEDEC 51-7, plus JEDEC 25-5 2S2P test board.
2
Per JEDEC JESD51-2 (still air) or JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air).
3
Per MIL-Std 883, Method 1012.1.
4
Per JEDEC JESD51-8 (still air).
ESD CAUTION
Rev. A | Page 12 of 44
AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
AVDD
AVDD
VIN+B
VIN–B
AVDD
AVDD
RBIAS
VCM
SENSE
VREF
AVDD
AVDD
VIN–A
VIN+A
AVDD
646362616059585756555453525150
AVDD
49
CLK+
CLK–
SYNC
D0B (LSB)
D1B
D2B
D3B
D4B
D5B
DRVDD
10
D6B
11
D7B
12
D8B
13
D9B
14
D10B
15
D11B
16
NOTES
1. THE EXPOSED THERMAL PAD O N THE BOTTOM OF T HE PACKAGE
PROVIDES THE ANALOG G ROUND FOR THE PART. THIS E X P OSED
PAD MUST BE CONNECTED TO GROUND FOR PROPE R OPERATIO N.
PIN 1
1
INDICATOR
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
171819202122232425262728293031
D12B
PARALLEL CMOS
(Not to Scale)
D13B
D14B
DRVDD
D15B (MSB)
AD9268
TOP VIEW
ORB
DCOA
DCOB
D0A (LSB)
D1A
D2A
D3A
D4A
DRVDD
48
PDWN
47
OEB
46
CSB
45
SCLK/DFS
44
SDIO/DCS
43
ORA
42
D15A (MSB)
41
D14A
40
D13A
39
D12A
38
D11A
37
DRVDD
36
D10A
35
D9A
34
D8A
33
D7A
32
D5A
D6A
05
08123-0
Figure 6. LFCSP Parallel CMOS Pin Configuration (Top View)
Table 8. Pin Function Descriptions (Parallel CMOS Mode)
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
ADC Power Supplies
10, 19, 28, 37 DRVDD Supply Digital Output Driver Supply (1.8 V Nominal).
49, 50, 53, 54, 59,
AVDD Supply Analog Power Supply (1.8 V Nominal).
60, 63, 64
0
AGND,
Exposed Pad
Ground
The exposed thermal pad on the bottom of the package provides the analog
ground for the part. This exposed pad must be connected to ground for proper
operation.
ADC Analog
51 VIN+A Input Differential Analog Input Pin (+) for Channel A.
52 VIN−A Input Differential Analog Input Pin (−) for Channel A.
62 VIN+B Input Differential Analog Input Pin (+) for Channel B.
61 VIN−B Input Differential Analog Input Pin (−) for Channel B.
55 VREF Input/Output Voltage Reference Input/Output.
56 SENSE Input Voltage Reference Mode Select. See Tab le 11 for details.
58 RBIAS Input/Output External Reference Bias Resistor.
57 VCM Output Common-Mode Level Bias Output for Analog Inputs.
1 CLK+ Input ADC Clock Input—True.
2 CLK− Input ADC Clock Input—Complement.
Digital Input
3 SYNC Input Digital Synchronization Pin. Slave mode only.
Digital Outputs
25 D0A (LSB) Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
26 D1A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
27 D2A Output
29 D3A Output
30 D4A Output
31 D5A Output
Channel A CMOS Output Data.
Channel A CMOS Output Data.
Channel A CMOS Output Data.
Channel A CMOS Output Data.
32 D6A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
Rev. A | Page 13 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
33 D7A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
34 D8A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
35 D9A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
36 D10A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
38 D11A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
39 D12A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
40 D13A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
41 D14A Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
42 D15A (MSB) Output Channel A CMOS Output Data.
43 ORA Output Channel A Overrange Output.
4 D0B (LSB) Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
5 D1B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
6 D2B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
7 D3B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
8 D4B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
9 D5B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
11 D6B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
12 D7B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
13 D8B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
14 D9B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
15 D10B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
16 D11B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
17 D12B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
18 D13B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
20 D14B Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
21 D15B (MSB) Output Channel B CMOS Output Data.
22 ORB Output Channel B Overrange Output
24 DCOA Output Channel A Data Clock Output.
23 DCOB Output Channel B Data Clock Output.
SPI Control
45 SCLK/DFS Input SPI Serial Clock/Data Format Select Pin in External Pin Mode.
44 SDIO/DCS Input/Output SPI Serial Data I/O/Duty Cycle Stabilizer Pin in External Pin Mode.
46 CSB Input SPI Chip Select (Active Low).
ADC Configuration
47 OEB Input Output Enable Input (Active Low) in External Pin Mode.
48 PDWN Input
Power-Down Input in External Pin Mode. In SPI mode, this input can be
configured as power-down or standby.
Rev. A | Page 14 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
AVDD
AVDD
VIN+B
VIN–B
AVDD
AVDD
RBIAS
VCM
SENSE
VREF
AVDD
AVDD
VIN–A
VIN+A
AVDD
646362616059585756555453525150
AVDD
49
CLK+
CLK–
SYNC
D0– (LSB)
D0+ (LSB )
D1–
D1+
D2–
D2+
DRVDD
10
D3–
11
D3+
12
D4–
13
D4+
14
D5–
15
D5+
16
NOTES
1. THE EXPOSED THERMAL PAD O N THE BOTTOM OF T HE PACKAGE
PROVIDES THE ANALOG G ROUND FOR THE P ART. THIS EX P OSED
PAD MUST BE CONNECTED TO GROUND FOR PROPE R OPERATIO N.
PIN 1
1
INDICATOR
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
171819202122232425262728293031
D6–
PARALLEL LVDS
D7–
D6+
D7+
DRVDD
AD9268
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
D8–
D8+
DCO–
DCO+
D9–
D9+
D10–
D10+
DRVDD
48
PDWN
47
OEB
46
CSB
45
SCLK/DFS
44
SDIO/DCS
43
OR+
42
OR–
41
D15+ (MSB)
40
D15– (MSB)
39
D14+
38
D14–
37
DRVDD
36
D13+
35
D13–
34
D12+
33
D12–
32
D11–
D11+
08123-006
Figure 7. LFCSP Interleaved Parallel LVDS Pin Configuration (Top View)
Table 9. Pin Function Descriptions (Interleaved Parallel LVDS Mode)
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
ADC Power Supplies
10, 19, 28, 37 DRVDD Supply Digital Output Driver Supply (1.8 V Nominal).
49, 50, 53, 54, 59,
AVDD Supply Analog Power Supply (1.8 V Nominal).
60, 63, 64
0
AGND,
Exposed Pad
Ground
The exposed thermal pad on the bottom of the package provides the analog
ground for the part. This exposed pad must be connected to ground for proper
operation.
ADC Analog
51 VIN+A Input Differential Analog Input Pin (+) for Channel A.
52 VIN−A Input Differential Analog Input Pin (−) for Channel A.
62 VIN+B Input Differential Analog Input Pin (+) for Channel B.
61 VIN−B Input Differential Analog Input Pin (−) for Channel B.
55 VREF Input/Output Voltage Reference Input/Output.
56 SENSE Input Voltage Reference Mode Select. See Tab le 11 for details.
58 RBIAS Input/Output External Reference Bias Resistor.
57 VCM Output Common-Mode Level Bias Output for Analog Inputs.
1 CLK+ Input ADC Clock Input—True.
2 CLK− Input ADC Clock Input—Complement.
Digital Input
3 SYNC Input Digital Synchronization Pin. Slave mode only.
Digital Outputs
5 D0+ (LSB) Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 0—True.
4 D0− (LSB) Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 0—Complement.
7 D1+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 1—True.
6 D1− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 1—Complement.
9 D2+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 2—True.
8 D2− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 2—Complement.
12 D3+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 3—True.
Rev. A | Page 15 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
11 D3− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 3—Complement.
14 D4+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 4—True.
13 D4− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 4—Complement.
16 D5+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 5—True.
15 D5− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 5—Complement.
18 D6+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 6—True.
17 D6− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 6—Complement.
21 D7+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 7—True.
20 D7− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 7—Complement.
23 D8+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 8—True.
22 D8− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 8—Complement.
27 D9+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 9—True.
26 D9− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 9—Complement.
30 D10+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 10—True.
29 D10− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 10—Complement.
32 D11+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 11—True.
31 D11− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 11—Complement.
34 D12+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 12—True.
33 D12− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 12—Complement.
36 D13+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 13—True.
35 D13− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 13—Complement.
39 D14+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 14—True.
38 D14− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 14—Complement.
41 D15+ (MSB) Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 15—True.
40 D15− (MSB) Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 15—Complement.
43 OR+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Overrange Output—True.
42 OR− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Overrange Output—Complement.
25 DCO+ Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Data Clock Output—True.
24 DCO− Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Data Clock Output—Complement.
SPI Control
45 SCLK/DFS Input SPI Serial Clock/Data Format Select Pin in External Pin Mode.
44 SDIO/DCS Input/Output SPI Serial Data I/O/Duty Cycle Stabilizer Pin in External Pin Mode.
46 CSB Input SPI Chip Select (Active Low).
ADC Configuration
47 OEB Input Output Enable Input (Active Low) in External Pin Mode.
48 PDWN Input
Power-Down Input in External Pin Mode. In SPI mode, this input can be
configured as power-down or standby.
Rev. A | Page 16 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, rated sample rate, DCS enabled, 1.0 V internal reference, 2 V p-p differential input, VIN = −1.0 dBFS, and
32k sample, T
–20
–40
= 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
A
0
80MSPS
2.4MHz @ –1dBF S
SNR = 79.0dB (80.0dBFS)
SFDR = 98dBc
0
80MSPS
200.3MHz @ –1dBF S
–20
SNR = 74.3dB (75. 3dBFS)
SFDR = 83dBc
–40
–60
SECOND HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0102030
THIRD HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 8. AD9268-80 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 2.4 MHz
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0102030
SECOND HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
80MSPS
70.1MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 77.5dB (7 8.5dBFS)
SFDR = 89.2dBc
THIRD HARMONIC
Figure 9. AD9268-80 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 70.1 MHz
0
–20
–40
–60
SECOND HARMONIC
0102030
FREQUENCY (MHz)
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–80
–100
–120
–140
80MSPS
140.1MHz @ –1dBF S
SNR = 76.0dB (7 7.0dBFS)
SFDR = 81.1dBc
THIRD HARMONIC
Figure 10. AD9268-80 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 140.1 MHz
40
08123-062
40
08123-063
40
08123-064
–60
SECOND HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
010
FREQUENCY (MHz)
20
THIRD HARMONIC
30 40
Figure 11. AD9268-80 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 200.1 MHz
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0102030
SECOND HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
80MSPS
70.1MHz @ –6dBF S
SNR = 73.0dB (79.0d BFS)
SFDR = 98dBc
THIRD HARMONIC
40
Figure 12. AD9268-80 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 70.1 MHz with Dither
Enabled
120
100
80
60
40
SNR/SFDR (dBc AND dBFS)
20
0
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBF S )
SNR (dBFS)
SFDR (dBc)
SNR (dBc)
SFDR (dBFS)
08123-067
Figure 13. AD9268-80 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (AIN)
= 98.12 MHz
with f
IN
08123-065
08123-066
Rev. A | Page 17 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
120
110
100
SNRFS (DIT HER ON)
SNRFS (DIT HER OFF)
90
SFDRFS (DI THER ON)
SNR/SFDR (dBFS)
SFDRFS (DI THER OFF)
80
70
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
Figure 14. AD9268-80 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (A
= 30 MHz with and without Dither Enabled
f
IN
100
95
90
SNR @ –40°C
SFDR @ –40°C
SNR @ +25°C
SFDR @ +25°C
SNR @ +85°C
SFDR @ +85°C
) with
IN
08123-068
200,000
180,000
160,000
140,000
120,000
100,000
80,000
NUMBER OF HITS
60,000
40,000
20,000
0
N –6
N – 9
N – 8
N – 5
N – 4
N – 11
N – 7
N – 10
N
N – 3
N – 2
N – 1
OUTPUT CO DE
Figure 17. AD9268-80 Grounded Input Histogram
4
2
2.17 LSB rms
N + 1
N + 2
N + 3
N + 4
N + 5
DITHER ENABLED
DITHER DISABLE D
N + 6
N + 7
N + 8
N + 9
N + 10
N + 11
08123-071
85
80
75
SNR/SFDR (dBFS/dBc)
70
65
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
INPUT FREQ UE NCY ( M Hz)
Figure 15. AD9268-80 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (f
with 2 V p-p Full Scale
105
100
95
90
85
SNR/SFDR (dBFS AND dBc)
80
75
25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
SNR, CHANNEL B
SFDR, CHANNEL B
SNR, CHANNEL A
SFDR, CHANNEL A
Figure 16. AD9268-80 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Sample Rate (fS)
with f
= 70.1 MHz
IN
0
INL ERROR (LSB)
–2
–4
0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 50,000 60,000
08123-069
)
IN
DNL ERROR (LSB)
08123-070
Figure 18. AD9268-80 INL with f
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
–0.25
–0.50
–0.75
–1.00
0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 50,000 60,000
OUTPUT CO DE
OUTPUT CODE
= 9.7 MHz
IN
08123-072
08123-073
Figure 19. AD9268-80 DNL with fIN = 9.7 MHz
Rev. A | Page 18 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
0
–20
–40
SECOND HARMONIC
–60
–80
–100
THIRD HARMONIC
105MSPS
2.4MHz @ –6dBFS
SNR = 78.2dB (79.2dBFS)
SFDR = 90dBc
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
0
SECOND
HARMONIC
105MSPS
200.3MHz @ –1dBF S
SNR = 74.0dB (75.0d BFS)
SFDR = 79dBc
THIRD HARMONIC
–120
–140
01020304050
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 20. AD9268-105 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 2.4 MHz
0
105MSPS
70.1MHz @ –1dBFS
–20
SNR = 77.5dB (78.5dBFS)
SFDR = 93.0dBc
–40
–60
THIRD HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
01020304050
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SECOND
HARMONIC
Figure 21. AD9268-105 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 70.1 MHz
0
105MSPS
140.1MHz @ –1dBF S
–20
SNR = 75.7dB (76. 7dBFS)
SFDR = 85.5d Bc
–40
–60
THIRD HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
01020304050
SECOND HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 22. AD9268-105 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 140.1 MHz
–120
–140
01020304050
08123-074
FREQUENCY (MHz)
08123-077
Figure 23. AD9268-105 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 200.3 MHz
0
105MSPS
70.1MHz @ –6dBF S
–20
SNR = 72.7dB (78. 7dBFS)
SFDR = 97.6d Bc
–40
–60
THIRD HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
01020304050
08123-075
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SECOND
HARMONIC
08123-078
Figure 24. AD9268-105 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 70.1 MHz with Dither
Enabled
120
100
80
60
40
SNR/SFDR (dBc AND dBFS)
20
0
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
08123-076
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBF S )
SNR (dBFS)
SFDR (dBc)
SNR (dBc)
SFDR (dBFS)
08123-079
Figure 25. AD9268-105 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (AIN)
= 98.12 MHz
with f
IN
Rev. A | Page 19 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
120
250,000
2.23 LSB rms
110
100
SNRFS (DITHER O N)
SNRFS (DITHER O F F )
90
SFDRFS (DITHER ON)
SNR/SFDR (dBFS)
SFDRFS (DITHER OFF)
80
70
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
Figure 26. AD9268-105 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (A
= 30 MHz with and without Dither Enabled
with f
IN
100
95
90
85
80
75
SNR/SFDR (dBFS AND dBc)
70
SNR @ –40°C
SFDR @ –40°C
SNR @ +25°C
SFDR @ +25°C
SNR @ +85°C
SFDR @ +85°C
200,000
150,000
100,000
NUMBER OF HITS
50,000
0
N – 9
N – 8
N – 7
N – 6
N – 5
08123-080
)
IN
N – 11
N – 10
Figure 29. AD9268-105 Grounded Input Histogram
6
4
2
0
–2
INL ERROR (LSB)
–4
N – 4
N
N – 3
N – 2
N – 1
OUTPUT CO DE
N + 1
N + 2
N + 3
N + 4
N + 5
N + 6
N + 7
DITHER ENABLED
DITHER DISABLE D
N + 8
N + 9
N + 10
N + 11
08123-083
65
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
INPUT FREQ UE NCY ( M Hz)
08123-081
Figure 27. AD9268-105 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (fIN)
with 2 V p-p Full Scale
105
100
SNR/SFDR (dBFS AND dBc)
SNR, CHANNEL B
SFDR, CHANNEL B
SNR, CHANNEL A
SFDR, CHANNEL A
95
90
85
80
75
25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
08123-082
Figure 28. AD9268-105 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Sample Rate (fS)
= 70.1 MHz
with f
IN
–6
0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 50,000 60,000
OUTPUT CO DE
Figure 30. AD9268-105 INL with fIN = 9.7 MHz
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
–0.25
DNL ERROR (LSB)
–0.50
–0.75
–1.00
0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 50,000 60,000
OUTPUT CODE
Figure 31. AD9268-105 DNL with fIN = 9.7 MHz
08123-084
08123-073
Rev. A | Page 20 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
0
–20
–40
AMPLITUDE ( d BF S)
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
SECOND HARMONIC
THIRD HARMONIC
0 102030405060
FREQUENCY (MHz)
125MSPS
2.4MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 77.7dB (7 8.7dBFS)
SFDR = 90dBc
Figure 32. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 2.4 MHz
0
125MSPS
30.3MHz @ –1dBF S
–20
SNR = 77.4dB ( 78.4dBFS)
SFDR = 91.2d Bc
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( d BF S)
–100
–120
–140
0 102030405060
FREQUENCY (MHz)
THIRD HARMONI C
Figure 33. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 30.3 MHz
0
125MSPS
70.1MHz @ –1dBF S
–20
SNR = 77.2dB (7 8.2dBFS)
SFDR = 87.8dBc
–40
–60
SECOND HARMONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0 102030405060
THIRD HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 34. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with f
SECOND HARMONIC
= 70.1 MHz
IN
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0 102030405060
08123-016
SECOND HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
125MSPS
140.1MHz @ –1dBFS
SNR = 76.0dB (77.0d BFS)
SFDR = 84.0dBc
THIRD HARMONIC
08123-019
Figure 35. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 140.1 MHz
0
125MSPS
200.3MHz @ –1dBF S
–20
SNR = 74.7dB ( 75.7dBFS)
SFDR = 80dBc
–40
–60
THIRD HAR M ONIC
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0 102030405060
08123-017
08123-018
Figure 36. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 200.3 MHz
0
125MSPS
220.1MHz @ –1dBF S
–20
SNR = 74.3dB ( 75.3dBFS)
SFDR = 78.5d Bc
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0 102030405060
THIRD HARMONI C
Figure 37. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with f
SECOND HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SECOND HARMONIC
= 220.1 MHz
IN
08123-020
08123-021
Rev. A | Page 21 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
0
125MSPS
70.1MHz @ –6dBF S
–20
SNR = 72.2dB ( 78.2dBFS)
SFDR = 97dBc
–40
–60
–80
SECOND HARMONIC
AMPLITUDE ( d BF S)
–100
–120
–140
0 102030405060
THIRD HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 38. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 70.1 MHz @ −6 dBFS
with Dither Enabled
0
125MSPS
–15
70.1MHz @ –23dBF S
SNR = 56.8dB (7 9.8dBFS)
SFDR = 67.7dBc
–30
–45
–60
–75
SECOND HARMONIC
–90
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–105
–120
–135
–150
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60
THIRD HARMONIC
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 39. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 70.1 MHz @ −23 dBFS
with Dither Disabled, 1M Sample
0
125MSPS
–15
70.1MHz @ –23dBF S
SNR = 56.2dB (5 7.2dBFS)
SFDR = 86.6dBc
–30
–45
–60
–75
SECOND HARMONIC THIRD HARMONIC
–90
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–105
–120
–135
–150
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 40. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with fIN = 70.1 MHz @ −23 dBFS
with Dither Enabled, 1M Sample
120
100
80
60
40
SNR/SFDR (dBc AND dBFS)
20
0
08123-022
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
SFDR (dBc)
SFDR (dBFS )
SNR (dBFS)
SNR (dBc)
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBF S )
08123-023
Figure 41. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (AIN)
= 2.4 MHz
with f
IN
120
100
80
60
40
SNR/SFDR (dBc AND dBFS)
20
0
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
08123-088
Figure 42. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (AIN)
SNR (dBFS)
SFDR (dBc)
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBF S )
with f
120
110
100
90
SNR/SFDR (dBFS)
80
70
–100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0
08123-089
Figure 43. AD9268-125 Single Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (AIN)
SNR (DITHER OFF)
SNR (DITHER ON)
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
SFDR (dBFS)
SNR (dBc)
= 98.12 MHz
IN
SFDR (DITHER ON)
SFDR (DITHER OFF)
08123-024
08123-061
with fIN = 30 MHz with and without Dither Enabled
Rev. A | Page 22 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
100
95
90
85
80
75
SNR/SFDR (dBFS AND dBc)
70
65
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
INPUT FREQ UE NCY ( M Hz )
SNR @ –40°C
SFDR @ –40°C
SNR @ +25°C
SFDR @ +25°C
SNR @ +85°C
SFDR @ +85°C
Figure 44. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (f
with 2 V p-p Full Scale
08123-025
)
IN
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
SFDR/IMD3 ( dBc AND dBFS)
–100
IMD3 (dBFS)
–120
–90 –78 –66 –54 –42 –30 –18 –6
SFDR (dBc)
IMD3 (dBc)
SFDR (dBFS )
INPUT AMPL ITUDE (dBFS )
Figure 47. AD9268-125 Two-Tone SFDR/IMD3 vs. Input Amplitude (A
with f
= 169.1 MHz, f
IN1
= 172.1 MHz, fS = 125 MSPS
IN2
08123-028
)
IN
95
90
85
80
75
70
SNR/SFDR (d BFS/dBc)
65
60
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
INPUT FREQ UE NCY ( M Hz )
SFDR (dBc)
SNR (dBFS)
08123-026
Figure 45. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (fIN)
with 1 V p-p Full Scale
0
–20
SFDR (dBc)
–40
IMD3 (dBc)
–60
–80
SFDR/IMD3 ( dBc AND dBFS)
–100
–120
–90 –78 –66 –54 –42 –30 –18 –6
SFDR (dBFS)
IMD3 (dBFS )
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
08123-027
0
125MSPS
29.1MHz @ –7dBF S
–20
32.1MHz @ –7dBF S
SFDR = 89dBc (96dBFS)
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE ( dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0 102030405060
Figure 48. AD9268-125 Two-Tone FFT with f
0
125MSPS
169.1MHz @ –7dBF S
–20
172.1MHz @ –7dBF S
SFDR = 81.8dBc (88.8dBF S )
–40
–60
–80
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
–140
0 102030405060
FREQUENCY (MHz)
= 29.1 MHz and f
IN1
FREQUENCY (MHz)
= 32.1 MHz
IN2
08123-029
08123-030
Figure 46. AD9268-125 Two-Tone SFDR/IMD3 vs. Input Amplitude (A
with f
= 29.1 MHz, f
IN1
= 32.1 MHz, fS = 125 MSPS
IN2
)
IN
Rev. A | Page 23 of 44
Figure 49. AD9268-125 Two-Tone FFT with f
f
= 172.1 MHz
IN2
= 169.1 MHz and
IN1

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
100
SFDR (dBc), CHANNEL B
95
1.00
0.75
0.50
90
85
SNR/SFDR (dBFS/d B c)
SNR (dBFS), CHANNEL B
80
SNR (dBFS), CHANNEL A
75
25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
SFDR (dBc), CHANNEL A
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
Figure 50. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Sample Rate (fS)
= 70.1 MHz
with f
IN
NUMBER OF HITS
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
N – 9
N – 8
N – 7
N – 6
N – 5
N – 10
N – 4
N
N – 3
N – 2
N – 1
N + 1
OUTPUT CODE
N + 2
N + 3
N + 4
N + 5
2.27LSB rms
N + 6
N + 7
N + 8
N + 9
N + 10
0.25
0
–0.25
DNL ERROR (LSB)
–0.50
–0.75
–1.00
0 16,384 32,768 49,152 65,536
08123-031
OUTPUT CODE
08123-033
Figure 53. AD9268-125 DNL with fIN = 9.7 MHz
100
90
80
70
60
50
SNR/SFDR (dBFS/dBc)
40
30
0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 1.05 1.10 1.15 1.20
08123-059
INPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (V)
SFDR (dBc)
SNR (dBFS)
08123-053
Figure 51. AD9268-125 Grounded Input Histogram
4
2
0
INL ERROR (LSB)
–2
–4
0 16,384 32,768 49,152 65,536
OUTPUT CODE
DITHER ENABLED
DITHER DISABL E D
Figure 52. AD9268-125 INL with fIN = 9.7 MHz
08123-032
Rev. A | Page 24 of 44
Figure 54. SNR/SFDR vs. Input Common Mode (VCM)
= 30 MHz
with f
IN

AD9268
V
S
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS
AVDD
IN
ENSE
350Ω
CLK+
08123-007
Figure 55. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
AVDD
0.9V
10kΩ 10kΩ
Figure 56. Equivalent Clock Input Circuit
DRVDD
PAD
Figure 57. Digital Output
08123-012
Figure 60. Equivalent SENSE Circuit
DRVDD
26kΩ
CLK–
CSB
8123-008
350Ω
08123-013
Figure 61. Equivalent CSB Input Circuit
AVDD
VREF
6kΩ
08123-009
08123-014
Figure 62. Equivalent VREF Circuit
SDIO/DCS
DRVDD
350Ω
Figure 58. Equivalent SDIO/DCS Circuit
DRVDD
SCLK/DFS
OR OEB
350Ω
26kΩ
Figure 59. Equivalent SCLK/DFS or OEB Input Circuit
26kΩ
08123-010
08123-011
Rev. A | Page 25 of 44
PDWN
350Ω
26kΩ
08123-015
Figure 63. Equivalent PDWN Input Circuit

AD9268
V
V
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
THEORY OF OPERATION
The AD9268 dual-core analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
design can be used for diversity reception of signals, in which the
ADCs are operating identically on the same carrier but from two
separate antennae. The ADCs can also be operated with independent analog inputs. The user can sample any f
/2 frequency
S
segment from dc to 200 MHz, using appropriate low-pass or
band-pass filtering at the ADC inputs with little loss in ADC
performance. Operation to 300 MHz analog input is permitted,
but it occurs at the expense of increased ADC noise and distortion.
In nondiversity applications, the AD9268 can be used as a baseband or direct downconversion receiver, in which one ADC is
used for I input data, and the other is used for Q input data.
Synchronization capability is provided to allow synchronized
timing between multiple devices.
Programming and control of the AD9268 are accomplished
using a 3-wire SPI-compatible serial interface.
ADC ARCHITECTURE
The AD9268 architecture consists of a dual front-end sampleand-hold circuit, followed by a pipelined, switched-capacitor
ADC. The quantized outputs from each stage are combined into
a final 16-bit result in the digital correction logic. The pipelined
architecture permits the first stage to operate on a new input
sample and the remaining stages to operate on the preceding
samples. Sampling occurs on the rising edge of the clock.
Each stage of the pipeline, excluding the last, consists of a low
resolution flash ADC connected to a switched-capacitor digitalto-analog converter (DAC) and an interstage residue amplifier
(MDAC). The MDAC magnifies the difference between the
reconstructed DAC output and the flash input for the next stage
in the pipeline. One bit of redundancy is used in each stage to
facilitate digital correction of flash errors. The last stage simply
consists of a flash ADC.
The input stage of each channel contains a differential sampling
circuit that can be ac- or dc-coupled in differential or singleended modes. The output staging block aligns the data, corrects
errors, and passes the data to the output buffers. The output buffers
are powered from a separate supply, allowing digital output noise to
be separated from the analog core. During power-down, the output
buffers go into a high impedance state.
ANALOG INPUT CONSIDERATIONS
The analog input to the AD9268 is a differential switchedcapacitor circuit that has been designed for optimum performance
while processing a differential input signal.
The clock signal alternatively switches the input between sample
mode and hold mode (see Figure 64). When the input is switched
into sample mode, the signal source must be capable of charging
the sample capacitors and settling within ½ of a clock cycle.
A small resistor in series with each input can help reduce the
peak transient current required from the output stage of the
driving source. A shunt capacitor can be placed across the inputs
to provide dynamic charging currents. This passive network
creates a low-pass filter at the ADC input; therefore, the precise
values are dependent on the application.
In intermediate frequency (IF) undersampling applications, any
shunt capacitors should be reduced. In combination with the
driving source impedance, the shunt capacitors limit the input
bandwidth. Refer to the AN-742 Application Note, Frequency
Domain Response of Switched-Capacitor ADCs; the AN-827
Application Note, A Resonant Approach to Interfacing Amplifiers to
Switched-Capacitor ADCs; and the Analog Dialogue article,
“Transformer-Coupled Front-End for Wideband A/D Converters,”
for more information on this subject (refer to www.analog.com).
BIAS
IN+
IN–
C
C
PAR1
PAR1
S
C
S
C
PAR2
H
C
S
C
PAR2
S
Figure 64. Switched-Capacitor Input
BIAS
S
C
FB
S
C
S
FB
S
08123-034
For best dynamic performance, the source impedances driving
VIN+ and VIN− should be matched, and the inputs should be
differentially balanced.
An internal differential reference buffer creates positive and
negative reference voltages that define the input span of the ADC
core. The span of the ADC core is set by this buffer to 2 × VREF.
Input Common Mode
The analog inputs of the AD9268 are not internally dc biased.
In ac-coupled applications, the user must provide this bias externally. Setting the device so that VCM = 0.5 × AVDD (or 0.9 V) is
recommended for optimum performance, but the device
functions over a wider range with reasonable performance
(see Figure 54). An on-board common-mode voltage reference
is included in the design and is available from the VCM pin.
Optimum performance is achieved when the common-mode
voltage of the analog input is set by the VCM pin voltage
(typically 0.5 × AVDD). The VCM pin must be decoupled to
ground by a 0.1 µF capacitor, as described in the Applications
Information section.
Rev. A | Page 26 of 44

AD9268
V
F
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Common-Mode Voltage Servo
In applications where there may be a voltage loss between the VCM
output of the AD9268 and the analog inputs, the common-mode
voltage servo can be enabled. When the inputs are ac-coupled and
a resistance of >100 Ω is placed between the VCM output and the
analog inputs, a significant voltage drop can occur and the
common-mode voltage servo should be enabled. Setting Bit 0 in
Register 0x0F to a logic high enables the VCM servo mode. In
this mode, the AD9268 monitors the common-mode input level
at the analog inputs and adjusts the VCM output level to keep the
common-mode input voltage at an optimal level. If both channels
are operational, Channel A is monitored. However, if Channel A
is in power-down or standby mode, then the Channel B input is
monitored.
Dither
The AD9268 has an optional dither mode that can be selected
for one or both channels. Dithering is the act of injecting a known
but random amount of white noise, commonly referred to as
dither, into the input of the ADC. Dithering has the effect of
improving the local linearity at various points along the ADC
transfer function. Dithering can significantly improve the SFDR
when quantizing small-signal inputs, typically when the input
level is below −6 dBFS.
As shown in Figure 65, the dither that is added to the input of
the ADC through the dither DAC is precisely subtracted out
digitally to minimize SNR degradation. When dithering is
enabled, the dither DAC is driven by a pseudorandom number
generator (PN gen). In the AD9268, the dither DAC is precisely
calibrated to result in only a very small degradation in SNR and
SINAD. The typical SNR and SINAD degradation values, with
dithering enabled, are only 1 dB and 0.8 dB, respectively.
AD9268
VIN
ADC CORE
DITHER
DAC
PN GEN
Figure 65. Dither Block Diagram
DITHER ENABLE
DOUT
08123-058
Large-Signal FFT
In most cases, dithering does not improve SFDR for large-signal
inputs close to full scale, for example, with a −1 dBFS input. For
large-signal inputs, the SFDR is typically limited by front-end
sampling distortion, which dithering cannot improve. However,
even for such large-signal inputs, dithering may be useful for
certain applications because it makes the noise floor whiter.
As is common in pipeline ADCs, the AD9268 contains small
DNL errors caused by random component mismatches that
produce spurs or tones that make the noise floor somewhat
randomly colored part-to-part. Although these tones are
Rev. A | Page 27 of 44
typically at very low levels and do not limit SFDR when the
ADC is quantizing large-signal inputs, dithering converts these
tones to noise and produces a whiter noise floor.
Small-Signal FFT
For small-signal inputs, the front-end sampling circuit typically
contributes very little distortion, and, therefore, the SFDR is likely
to be limited by tones caused by DNL errors due to random component mismatches. Therefore, for small-signal inputs (typically,
those below −6 dBFS), dithering can significantly improve
SFDR by converting these DNL tones to white noise.
Static Linearity
Dithering also removes sharp local discontinuities in the INL
transfer function of the ADC and reduces the overall peak-topeak INL.
In receiver applications, utilizing dither helps to reduce DNL errors
that cause small-signal gain errors. Often this issue is overcome
by setting the input noise 5 dB to 10 dB above the converter
noise. By utilizing dither within the converter to correct the
DNL errors, the input noise requirement can be reduced.
Differential Input Configurations
Optimum performance is achieved while driving the AD9268
in a differential input configuration. For baseband applications,
the AD8138, ADA4937-2, and ADA4938-2 differential drivers
provide excellent performance and a flexible interface to the
ADC.
The output common-mode voltage of the ADA4938-2 is easily
set with the VCM pin of the AD9268 (see Figure 66), and the
driver can be configured in a Sallen-Key filter topology to
provide band limiting of the input signal.
15p
200Ω
33Ω
33Ω
5pF
15pF
15Ω
15Ω
VIN–
AD9268
VIN+
AVDD
VCM
76.8Ω
IN
0.1µF
Figure 66. Differential Input Configuration Using the ADA4938-2
90Ω
ADA4938-2
120Ω
200Ω
For baseband applications in which SNR is a key parameter,
differential transformer coupling is the recommended input
configuration. An example is shown in Figure 67. To bias the
analog input, the VCM voltage can be connected to the center
tap of the secondary winding of the transformer.
C2
R2
R1
2V p-p
49.9Ω
0.1µF
Figure 67. Differential Transformer-Coupled Configuration
C1
R1
C2
VIN+
AD9268
R2
VIN–
VCM
08123-035
08123-036

AD9268
2
p
V
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
The signal characteristics must be considered when selecting
a transformer. Most RF transformers saturate at frequencies
below a few megahertz (MHz). Excessive signal power can also
cause core saturation, which leads to distortion.
At input frequencies in the second Nyquist zone and above, the
noise performance of most amplifiers is not adequate to achieve
the true SNR performance of the AD9268. For applications in
which SNR is a key parameter, differential double balun coupling
is the recommended input configuration (see Figure 68). In this
configuration, the input is ac-coupled, and the CML is provided
to each input through a 33 Ω resistor. These resistors compensate
for losses in the input baluns to provide a 50 Ω impedance to
the driver.
In the double balun and transformer configurations, the value of
the input capacitors and resistors is dependent on the input frequency and source impedance and may need to be reduced or
removed. Ta b l e 1 0 displays recommended values to set the RC
network. At higher input frequencies, good performance can be
V p-
0.1µF
SP
A
S
0.1µF
P
0.1µF
achieved by using a ferrite bead in series with a resistor and
removing the capacitors. However, these values are dependent
on the input signal and should be used only as a starting guide.
Table 10. Example RC Network
Frequency
Range
(MHz)
R1 Series
(Ω Each)
C1 Differential
(pF)
R2 Series
(Ω Each)
C2 Shunt
(pF Each)
0 to 100 33 5 15 15
100 to 200 10 5 10 10
100 to 300 101 Remove 66 Remove
1
In this configuration, R1 is a ferrite bead with a value of 10 Ω @ 100 MHz.
An alternative to using a transformer-coupled input at frequencies in the second Nyquist zone is to use the AD8352
differential driver. An example is shown in Figure 69. See the
AD8352 data sheet for more information.
C2
33Ω
33Ω
0.1µF
R1
C1
R1R2R2
VIN+
AD9268
VIN–
VCM
C2
08123-038
Figure 68. Differential Double Balun Input Configuration
CC
0.1µF
ANALOG INPUT
ANALOG INPUT
0Ω
16
1
2
R
R
0.1µF
G
D
3
4
5
0Ω
C
D
8, 13
AD8352
14
10
0.1µF
0.1µF
11
0.1µF
200Ω
200Ω
0.1µF
R
R
0.1µF
VIN+
C
AD9268
VIN–
VCM
08123-039
Figure 69. Differential Input Configuration Using the AD8352
Rev. A | Page 28 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
A stable and accurate voltage reference is built into the AD9268.
The input range can be adjusted by varying the reference voltage
applied to the AD9268, using either the internal reference or an
externally applied reference voltage. The input span of the ADC
tracks reference voltage changes linearly. The various reference
modes are summarized in the sections that follow. The Reference
Decoupling section describes the best practices PCB layout of
the reference.
Internal Reference Connection
A comparator within the AD9268 detects the potential at the
SENSE pin and configures the reference into four possible modes,
which are summarized in Tabl e 11 . If SENSE is grounded, the
reference amplifier switch is connected to the internal resistor
divider (see Figure 70), setting VREF to 1.0 V for a 2.0 V p-p fullscale input. In this mode, with SENSE grounded, the full scale can
also be adjusted through the SPI port by adjusting Bit 6 and Bit 7 of
Register 0x18. These bits can be used to change the full scale to
1.25 V p-p, 1.5 V p-p, 1.75 V p-p, or to the default of 2.0 V p-p,
as shown in Tab l e 1 7 .
Connecting the SENSE pin to the VREF pin switches the reference
amplifier output to the SENSE pin, completing the loop and
providing a 0.5 V reference output for a 1 V p-p full-scale input.
VIN+A/VIN+B
VIN–A/VIN–B
ADC
CORE
VREF
0.1µF1.0µF
SENSE
SELECT
LOGIC
0.5V
If a resistor divider is connected external to the chip, as shown
in Figure 71, the switch again sets to the SENSE pin. This puts
the reference amplifier in a noninverting mode with the VREF
output, defined as follows:
R2
⎞
⎛
VREF 15.0
+×=
⎟
⎜
R1
⎠
⎝
The input range of the ADC always equals twice the voltage at
the reference pin (VREF) for either an internal or an external
reference.
VIN+A/VIN+B
VIN–A/VIN–B
ADC
CORE
VREF
0.1µF1.0µF
Figure 71. Programmable Reference Configuration
R2
SENSE
R1
SELECT
LOGIC
0.5V
AD9268
08123-041
If the internal reference of the AD9268 is used to drive multiple
converters to improve gain matching, the loading of the reference
by the other converters must be considered. Figure 72 shows
how the internal reference voltage is affected by loading.
0
–0.5
VREF = 0.5V
–1.0
VREF = 1V
–1.5
AD9268
Figure 70. Internal Reference Configuration
Table 11. Reference Configuration Summary
Selected Mode SENSE Voltage Resulting VREF (V) Resulting Differential Span (V p-p)
External Reference AVDD N/A 2 × external reference
Internal Fixed Reference VREF 0.5 1.0
Programmable Reference 0.2 V to VREF
Internal Fixed Reference AGND to 0.2 V 1.0 2.0
08123-040
⎛
⎜
⎝
Rev. A | Page 29 of 44
–2.0
–2.5
REFERENCE VOLTAGE ERRO R ( %)
–3.0
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
Figure 72. Reference Voltage Accuracy vs. Load Current
R2
⎞
(see Figure 71)
+×
10.5
⎟
R1
⎠
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
2 × VREF
08123-054

AD9268
K
C
C
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
External Reference Operation
The use of an external reference may be necessary to enhance
the gain accuracy of the ADC or improve thermal drift characteristics. Figure 73 shows the typical drift characteristics of the
internal reference in 1.0 V mode.
When the SENSE pin is tied to AVDD, the internal reference is
disabled, allowing the use of an external reference. An internal
reference buffer loads the external reference with an equivalent
6 kΩ load (see Figure 62). The internal buffer generates the positive
and negative full-scale references for the ADC core. Therefore,
the external reference must be limited to a maximum of 1.0 V.
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
–0.5
–1.0
REFERENCE VOLTAGE ERRO R ( mV)
–1.5
–2.0
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80
VREF = 1. 0V
TEMPERATURE ( °C)
08123-055
Figure 73. Typical VREF Drift
CLOCK INPUT CONSIDERATIONS
For optimum performance, the AD9268 sample clock inputs,
CLK+ and CLK−, should be clocked with a differential signal.
The signal is typically ac-coupled into the CLK+ and CLK− pins
via a transformer or capacitors. These pins are biased internally
(see Figure 74) and require no external bias. If the inputs are
floated, the CLK− pin is pulled low to prevent spurious clocking.
AVDD
0.9V
CLK+
Figure 74. Equivalent Clock Input Circuit
Clock Input Options
The AD9268 has a very flexible clock input structure. Clock input
can be a CMOS, LVDS, LVPECL, or sine wave signal. Regardless of
the type of signal being used, clock source jitter is of the most
concern, as described in the Jitter Considerations section.
Figure 75 and Figure 76 show two preferred methods for clocking
the AD9268 (at clock rates up to 625 MHz). A low jitter clock
source is converted from a single-ended signal to a differential
signal using either an RF balun or an RF transformer.
CLK–
4pF4pF
8123-044
The RF balun configuration is recommended for clock frequencies
between 125 MHz and 625 MHz, and the RF transformer is recommended for clock frequencies from 10 MHz to 200 MHz. The
back-to-back Schottky diodes across the transformer/balun
secondary limit clock excursions into the AD9268 to approximately 0.8 V p-p differential.
This limit helps prevent the large voltage swings of the clock
from feeding through to other portions of the AD9268 while
preserving the fast rise and fall times of the signal that are critical
to a low jitter performance.
XFMR
0.1µF
®
0.1µF0.1µF
0.1µF
0.1µF1nF
0.1µF
SCHOTTKY
DIODES:
HSMS2822
SCHOTTKY
DIODES:
HSMS2822
AD9268
CLK+
CLK–
ADC
AD9268
CLK+
CLK–
ADC
08123-046
Mini-Circuits
ADT1-1WT, 1:1Z
CLOC
INPUT
50Ω
100Ω
Figure 75. Transformer-Coupled Differential Clock (Up to 200 MHz)
CLOCK
INPUT
50Ω
1nF
Figure 76. Balun-Coupled Differential Clock (Up to 625 MHz)
If a low jitter clock source is not available, another option is to
ac couple a differential PECL signal to the sample clock input
pins, as shown in Figure 77. The AD9510/AD9511/AD9512/
AD9513/AD9514/AD9515/AD9516/AD9517/AD9518 clock
drivers offer excellent jitter performance.
CLOCK
INPUT
CLOCK
INPUT
0.1µF
AD951x
PECL DRI V ER
0.1µF
50kΩ 50kΩ
Figure 77. Differential PECL Sample Clock (Up to 625 MHz)
0.1µF
CLK+
100Ω
0.1µF
240Ω240Ω
ADC
AD9268
CLK–
A third option is to ac couple a differential LVDS signal to the
sample clock input pins, as shown in Figure 78. The AD9510/
AD9511/AD9512/AD9513/AD9514/AD9515/AD9516/AD9517/
AD9518 clock drivers offer excellent jitter performance.
LOCK
INPUT
LOCK
INPUT
50kΩ 50kΩ
0.1µF
0.1µF
AD951x
LVDS DRIVER
Figure 78. Differential LVDS Sample Clock (Up to 625 MHz)
0.1µF
100Ω
0.1µF
CLK+
ADC
AD9268
CLK–
08123-045
08123-047
08123-048
Rev. A | Page 30 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
In some applications, it may be acceptable to drive the sample
clock inputs with a single-ended CMOS signal. In such applications, the CLK+ pin should be driven directly from a CMOS gate,
and the CLK− pin should be bypassed to ground with a 0.1 F
capacitor (see Figure 79).
V
CC
0.1µF
1kΩ
1kΩ
AD951x
CMOS DRIVER
CLOCK
INPUT
1
50Ω RESISTOR IS OPTIONAL.
1
50Ω
Figure 79. Single-Ended 1.8 V CMOS Input Clock (Up to 200 MHz)
OPTIONAL
100Ω
0.1µF
0.1µF
CLK+
ADC
AD9268
CLK–
Input Clock Divider
The AD9268 contains an input clock divider with the ability to
divide the input clock by integer values between 1 and 8. For
divide ratios of 1, 2, or 4, the duty cycle stabilizer (DCS) is
optional. For other divide ratios, divide by 3, 5, 6, 7, and 8, the
duty cycle stabilizer must be enabled for proper part operation.
The AD9268 clock divider can be synchronized using the external
SYNC input. Bit 1 and Bit 2 of Register 0x100 allow the clock
divider to be resynchronized on every SYNC signal or only on
the first SYNC signal after the register is written. A valid SYNC
causes the clock divider to reset to its initial state. This synchronization feature allows multiple parts to have their clock dividers
aligned to guarantee simultaneous input sampling.
Clock Duty Cycle
Typical high speed ADCs use both clock edges to generate a variety
of internal timing signals and, as a result, may be sensitive to clock
duty cycle. The AD9268 requires a tight tolerance on the clock duty
cycle to maintain dynamic performance characteristics.
The AD9268 contains a duty cycle stabilizer (DCS) that retimes
the nonsampling (falling) edge, providing an internal clock signal
with a nominal 50% duty cycle. This allows the user to provide
a wide range of clock input duty cycles without affecting the
perfor-mance of the AD9268. Noise and distortion performance
are nearly flat for a wide range of duty cycles with the DCS
enabled.
Jitter in the rising edge of the input is still of paramount concern
and is not easily reduced by the internal stabilization circuit. The
duty cycle control loop does not function for clock rates of less
than 20 MHz, nominally. The loop has a time constant associated
with it that must be considered in applications in which the clock
rate can change dynamically. A wait time of 1.5 µs to 5 µs is
required after a dynamic clock frequency increase or decrease
before the DCS loop is relocked to the input signal. During the
time period that the loop is not locked, the DCS loop is bypassed,
and internal device timing is dependent on the duty cycle of the
input clock signal. In such applications, it may be appropriate to
disable the duty cycle stabilizer. In all other applications, enabling
the DCS circuit is recommended to maximize ac performance.
Rev. A | Page 31 of 44
08123-049
Jitter Considerations
High speed, high resolution ADCs are sensitive to the quality
of the clock input. For inputs near full scale, the degradation in
SNR from the low frequency SNR (SNR
frequency (f
SNR
) due to jitter (t
INPUT
= −10 log[(2π × f
HF
JRMS
INPUT
) at a given input
LF
) can be calculated by
× t
)2 + 10 ]
JRMS
)10/(LFSNR−
In the equation, the rms aperture jitter represents the clock input
jitter specification. IF undersampling applications are particularly
sensitive to jitter, as illustrated in Figure 80. The measured curve in
Figure 80 was taken using an ADC clock source with approximately 65 fs of jitter, which combines with the 70 fs of jitter
inherent in the AD9268 to produce the results shown.
80
75
MEASURED
70
65
SNR (dBc)
60
55
50
1 10 100 1k
Figure 80. SNR vs. Input Frequency and Jitter
INPUT FREQ UE NCY ( M Hz)
0.05ps
0.20ps
0.50ps
1.00ps
1.50ps
08123-050
The clock input should be treated as an analog signal in cases in
which aperture jitter may affect the dynamic range of the AD9268.
Power supplies for clock drivers should be separated from the
ADC output driver supplies to avoid modulating the clock signal
with digital noise. Low jitter, crystal-controlled oscillators make
the best clock sources. If the clock is generated from another type of
source (by gating, dividing, or another method), it should be
retimed by the original clock at the last step.
Refer to the AN-501 Application Note and the AN-756 Application
Note (see www.analog.com) for more information about jitter
performance as it relates to ADCs.
CHANNEL/CHIP SYNCHRONIZATION
The AD9268 has a SYNC input that offers the user flexible
synchronization options for synchronizing the clock divider.
The clock divider sync feature is useful for guaranteeing synchronized sample clocks across multiple ADCs. The input clock
divider can be enabled to synchronize on a single occurrence of
the SYNC signal or on every occurrence.
The SYNC input is internally synchronized to the sample clock;
however, to ensure that there is no timing uncertainty between
multiple parts, the SYNC input signal should be externally synchronized to the input clock signal, meeting the setup and hold
times shown in Tabl e 5. The SYNC input should be driven using
a single-ended CMOS-type signal.

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
POWER DISSIPATION AND STANDBY MODE
As shown in Figure 81, the power dissipated by the AD9268
varies with its sample rate. In CMOS output mode, the digital
power dissipation is determined primarily by the strength of the
digital drivers and the load on each output bit.
The maximum DRVDD current (IDRVDD) can be calculated as
× f
I
DRVDD
CLK
× N
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
SUPPLY CURRENT (A)
08123-056
SUPPLY CURRENT ( A)
08123-086
IDRVDD = VDRVDD × C
LOAD
where N is the number of output bits (32 plus two DCO
outputs, in the case of the AD9268).
This maximum current occurs when every output bit switches on
every clock cycle, that is, a full-scale square wave at the Nyquist
frequency of f
/2. In practice, the DRVDD current is estab-
CLK
lished by the average number of output bits switching, which is
determined by the sample rate and the characteristics of the
analog input signal.
Reducing the capacitive load presented to the output drivers
reduces digital power consumption. The data in Figure 81 was
taken in LVDS output mode, using the same operating conditions
as those used for the Ty p i c al Perform anc e C harac t e r istic s .
1.25
1.00
IAVDD
0.75
0.50
TOTAL POWER (W)
0.25
0
25 50
Figure 81. AD9268-125 Power and Current vs. Encode Frequency (LVDS
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
TOTAL POWER (W)
0.2
0
25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105
Figure 82. AD9268-105 Power and Current vs. Encode Frequency (LVDS
TOTAL POWER
IDRVDD
ENCODE FREQUE NCY ( M Hz )
75 100 125
Output Mode)
TOTAL POWER
I
AVDD
ENCODE FREQUENCY (MSPS)
Output Mode)
1.0
I
AVDD
0.8
0.6
0.4
TOTAL POWER (W)
0.2
0
25 35 45 55 65 75
TOTAL POWER
I
DRVDD
ENCODE FREQUENCY (MSPS)
Figure 83. AD9268-80 Power and Current vs. Encode Frequency (LVDS
0.25
0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
0
SUPPLY CURRENT ( A)
08123-087
Output Mode)
By asserting PDWN (either through the SPI port or by asserting
the PDWN pin high), the AD9268 is placed in power-down
mode. In this state, the ADC typically dissipates 3.3 mW.
During power-down, the output drivers are placed in a high
impedance state. Asserting the PDWN pin low returns the
AD9268 to its normal operating mode.
Low power dissipation in power-down mode is achieved by
shutting down the reference, reference buffer, biasing networks,
and clock. Internal capacitors are discharged when entering powerdown mode and then must be recharged when returning to normal
operation.
When using the SPI port interface, the user can place the ADC
in power-down mode or standby mode. Standby mode allows
the user to keep the internal reference circuitry powered when
faster wake-up times are required.
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
The AD9268 output drivers can be configured to interface with
1.8 V CMOS logic families. The AD9268 can also be configured
for LVDS outputs (standard ANSI or reduced output swing mode)
using a DRVDD supply voltage of 1.8 V.
In CMOS output mode, the output drivers are sized to provide
sufficient output current to drive a wide variety of logic families.
However, large drive currents tend to cause current glitches on
the supplies that may affect converter performance.
Applications requiring the ADC to drive large capacitive loads
or large fanouts may require external buffers or latches.
The default output mode is CMOS, with each channel output
on separate busses as shown in Figure 2. The output can also be
configured for interleaved CMOS via the SPI port. In interleaved
CMOS mode, the data for both channels is output through the
Channel A output bits, and the Channel B output is placed into
high impedance mode. The timing diagram for interleaved
CMOS output mode is shown in Figure 3.
The output data format can be selected for either offset binary
or twos complement by setting the SCLK/DFS pin when operating
in the external pin mode (see Tab l e 1 2 ).
Rev. A | Page 32 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
As detailed in the AN-877 Application Note, Interfacing to High
Speed ADCs via SPI, the data format can be selected for offset
binary, twos complement, or gray code when using the SPI control.
Table 12. SCLK/DFS Mode Selection (External Pin Mode)
Voltage at Pin SCLK/DFS SDIO/DCS
AGND Offset binary (default) DCS disabled
AVDD Twos complement
DCS enabled
(default)
Digital Output Enable Function (OEB)
The AD9268 has a flexible three-state ability for the digital output
pins. The three-state mode is enabled using the OEB pin or
through the SPI. If the OEB pin is low, the output data drivers and
DCOs are enabled. If the OEB pin is high, the output data drivers
and DCOs are placed in a high impedance state. This OEB
function is not intended for rapid access to the data bus. Note
that OEB is referenced to the digital output driver supply
(DRVDD) and should not exceed that supply voltage.
When using the SPI, the data outputs and DCO of each channel
can be independently three-stated by using the output enable
bar bit (Bit 4) in Register 0x14.
TIMING
The AD9268 provides latched data with a pipeline delay of
12 clock cycles. Data outputs are available one propagation
delay (t
The length of the output data lines and loads placed on them
should be minimized to reduce transients within the AD9268.
These transients can degrade converter dynamic performance.
The lowest typical conversion rate of the AD9268 is 10 MSPS.
At clock rates below 10 MSPS, dynamic performance can degrade.
Data Clock Output (DCO)
The AD9268 provides two data clock output (DCO) signals
intended for capturing the data in an external register. In CMOS
output mode, the data outputs are valid on the rising edge of DCO,
unless the DCO clock polarity has been changed via the SPI. In
LVDS output mode, the DCO and data output switching edges
are closely aligned. Additional delay can be added to the DCO
output using SPI Register 0x17 to increase the data setup time.
In this case, the Channel A output data is valid on the rising
edge of DCO, and the Channel B output data is valid on the
falling edge of DCO. See Figure 2, Figure 3, and Figure 4 for a
graphical timing description of the output modes.
) after the rising edge of the clock signal.
PD
Table 13. Output Data Format
Input (V) Condition (V) Offset Binary Output Mode Twos Complement Mode OR
VIN+ − VIN− < −VREF − 0.5 LSB 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000 0000 0000 1
VIN+ − VIN− = −VREF 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000 0000 0000 0000 0
VIN+ − VIN− = 0 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0
VIN+ − VIN− = +VREF − 1.0 LSB 1111 1111 1111 1111 0111 1111 1111 1111 0
VIN+ − VIN− > +VREF − 0.5 LSB 1111 1111 1111 1111 0111 1111 1111 1111 1
Rev. A | Page 33 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
BUILT-IN SELF-TEST (BIST) AND OUTPUT TEST
The AD9268 includes built-in test features designed to enable
verification of the integrity of each channel as well as facilitate
board level debugging. A BIST (built-in self-test) feature is included
that verifies the integrity of the digital datapath of the AD9268.
Various output test options are also provided to place predictable
values on the outputs of the AD9268.
BUILT-IN SELF-TEST (BIST)
The BIST is a thorough test of the digital portion of the selected
AD9268 signal path. When enabled, the test runs from an internal
pseudorandom noise (PN) source through the digital datapath
starting at the ADC block output. The BIST sequence runs for
512 cycles and stops. The BIST signature value for Channel A or
Channel B is placed in Register 0x24 and Register 0x25. If one
channel is chosen, its BIST signature is written to the two registers.
If both channels are chosen, the results from Channel A are placed
in the BIST signature registers.
The outputs are not disconnected during this test, so the PN
sequence can be observed as it runs. The PN sequence can be
continued from its last value or reset from the beginning, based
on the value programmed in Register 0x0E, Bit 2. The BIST
signature result varies based on the channel configuration.
OUTPUT TEST MODES
The output test options are shown in Tab l e 1 7 . When an output
test mode is enabled, the analog section of the ADC is disconnected from the digital back end blocks and the test pattern is run
through the output formatting block. Some of the test patterns are
subject to output formatting, and some are not. The seed value for
the PN sequence tests can be forced if the PN reset bits are used
to hold the generator in reset mode by setting Bit 4 or Bit 5 of
Register 0x0D. These tests can be performed with or without
an analog signal (if present, the analog signal is ignored), but
they do require an encode clock. For more information, see the
AN-877 Application Note, Interfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI.
Rev. A | Page 34 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SERIAL PORT INTERFACE (SPI)
The AD9268 serial port interface (SPI) allows the user to configure
the converter for specific functions or operations through a
structured register space provided inside the ADC. The SPI
gives the user added flexibility and customization, depending on
the application. Addresses are accessed via the serial port and
can be written to or read from via the port. Memory is organized
into bytes that can be further divided into fields, which are documented in the Memory Map section. For detailed operational
information, see the AN-877 Application Note, Interfacing to
High Speed ADCs via SPI.
CONFIGURATION USING THE SPI
Three pins define the SPI of this ADC: the SCLK/DFS pin, the
SDIO/DCS pin, and the CSB pin (see Tabl e 1 4 ). The SCLK/DFS
(a serial clock) is used to synchronize the read and write data
presented from and to the ADC. The SDIO/DCS (serial data
input/output) is a dual-purpose pin that allows data to be sent
to and read from the internal ADC memory map registers. The
CSB (chip select bar) is an active-low control that enables or
disables the read and write cycles.
Table 14. Serial Port Interface Pins
Pin Function
SCLK
SDIO
CSB
Serial Clock. The serial shift clock input, which is used to
synchronize serial interface reads and writes.
Serial Data Input/Output. A dual-purpose pin that
typically serves as an input or an output, depending on
the instruction being sent and the relative position in the
timing frame.
Chip Select Bar. An active-low control that gates the read
and write cycles.
The falling edge of the CSB, in conjunction with the rising edge
of the SCLK, determines the start of the framing. An example of
the serial timing and its definitions can be found in Figure 84
and Tabl e 5.
Other modes involving the CSB are available. When the CSB is
held low indefinitely, which permanently enables the device,
this is called streaming. The CSB can stall high between bytes to
allow for additional external timing. When CSB is tied high, SPI
functions are placed in high impedance mode. This mode turns
on any SPI pin secondary functions.
During an instruction phase, a 16-bit instruction is transmitted.
Data follows the instruction phase, and its length is determined
by the W0 and W1 bits.
In addition to word length, the instruction phase determines
whether the serial frame is a read or write operation, allowing
the serial port to be used both to program the chip and to read
the contents of the on-chip memory. The first bit of the first byte in
a multibyte serial data transfer frame indicates whether a read
command or a write command is issued. If the instruction is a
readback operation, performing a readback causes the serial
data input/output (SDIO) pin to change direction from an input to
an output at the appropriate point in the serial frame.
All data is composed of 8-bit words. Data can be sent in MSB-first
mode or in LSB-first mode. MSB first is the default on power-up
and can be changed via the SPI port configuration register. For
more information about this and other features, see the AN-877
Application Note, Interfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI.
CSB
SCLK
SDIO
DON’T CARE
t
t
DS
t
S
R/W W1 W0 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7
t
DH
HIGH
t
LOW
Figure 84. Serial Port Interface Timing Diagram
t
CLK
Rev. A | Page 35 of 44
D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
t
H
DON’T CARE
DON’T CAREDON’T CARE
08123-052

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
HARDWARE INTERFACE
The pins described in Ta b l e 1 4 comprise the physical interface
between the user programming device and the serial port of the
AD9268. The SCLK pin and the CSB pin function as inputs
when using the SPI. The SDIO pin is bidirectional, functioning
as an input during write phases and as an output during
readback.
The SPI is flexible enough to be controlled by either FPGAs or
microcontrollers. One method for SPI configuration is
described in detail in the AN-812 Application Note, Micro-
controller-Based Serial Port Interface (SPI) Boot Circuit.
The SPI port should not be active during periods when the full
dynamic performance of the converter is required. Because the
SCLK signal, the CSB signal, and the SDIO signal are typically
asynchronous to the ADC clock, noise from these signals can
degrade converter performance. If the on-board SPI bus is used for
other devices, it may be necessary to provide buffers between
this bus and the AD9268 to prevent these signals from transitioning at the converter inputs during critical sampling periods.
Some pins serve a dual function when the SPI is not being used.
When the pins are strapped to AVDD or ground during device
power-on, they are associated with a specific function. The
Digital Outputs section describes the strappable functions
supported on the AD9268.
CONFIGURATION WITHOUT THE SPI
In applications that do not interface to the SPI control registers,
the SDIO/DCS pin, the SCLK/DFS pin, the OEB pin, and the
PDWN pin serve as standalone CMOS-compatible control pins.
When the device is powered up, it is assumed that the user
intends to use the pins as static control lines for the duty cycle
stabilizer, output data format, output enable, and power-down
feature control. In this mode, the CSB chip select bar should be
connected to AVDD, which disables the serial port interface.
When the device is in SPI mode, the PDWN and OEB pins
remain active. For SPI control of output enable and power-down,
the OEB and PDWN pins should be set to their default states.
Table 15. Mode Selection
External
Pin
SDIO/DCS AVDD (default) Duty cycle stabilizer enabled
SCLK/DFS AVDD Twos complement enabled
OEB AVDD Outputs in high impedance
PDWN AVDD
Voltage Configuration
AGND Duty cycle stabilizer disabled
AGND (default) Offset binary enabled
AGND (default) Outputs enabled
Chip in power-down or
standby
AGND (default) Normal operation
SPI ACCESSIBLE FEATURES
Tabl e 16 provides a brief description of the general features that
are accessible via the SPI. These features are described in detail in
the AN-877 Application Note, Interfacing to High Speed ADCs via
SPI. The AD9268 part-specific features are described in detail
following Tabl e 1 7, the external memory map register table.
Table 16. Features Accessible Using the SPI
Feature Name Description
Mode
Clock
Offset
Tes t I /O
Output Mode
Output Phase Allows the user to set the output clock polarity
Output Delay Allows the user to vary the DCO delay
VREF Allows the user to set the reference voltage
Allows the user to set either power-down mode
or standby mode
Allows the user to access the DCS, set the
clock divider, set the clock divider phase, and
enable the sync
Allows the user to digitally adjust the
converter offset
Allows the user to set test modes to have
known data on output bits
Allows the user to set the output mode,
including LVDS
Rev. A | Page 36 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
MEMORY MAP
READING THE MEMORY MAP REGISTER TABLE
Each row in the memory map register table has eight bit locations.
The memory map is roughly divided into four sections: the chip
configuration registers (Address 0x00 to Address 0x02); the
channel index and transfer registers (Address 0x05 and
Address 0xFF); the ADC functions registers, including setup,
control, and test (Address 0x08 to Address 0x30); and the digital
feature control register (Address 0x100).
The memory map register table (see Tab l e 1 7 ) documents the
default hexadecimal value for each hexadecimal address shown.
The column with the heading Bit 7 (MSB) is the start of the
default hexadecimal value given. For example, Address 0x18,
the VREF select register, has a hexadecimal default value of 0xC0.
This means that Bit 7 = 1, Bit 6 = 1, and the remaining bits are 0s.
This setting is the default reference selection setting. The default
value uses a 2.0 V p-p reference. For more information on this
function and others, see the AN-877 Application Note, Interfacing
to High Speed ADCs via SPI. This application note details the
functions controlled by Register 0x00 to Register 0xFF. The
remaining register, Register 0x100, is documented in the Memory
Map Register Table section.
Open Locations
All address and bit locations that are not included in Tabl e 17
are not currently supported for this device. Unused bits of a
valid address location should be written with 0s. Writing to these
locations is required only when part of an address location is
open (for example, Address 0x18). If the entire address location
is open (for example, Address 0x13), this address location should
not be written.
Default Values
After the AD9268 is reset, critical registers are loaded with
default values. The default values for the registers are given in
the memory map register table, Tab l e 1 7 .
Logic Levels
An explanation of logic level terminology follows:
• “Bit is set” is synonymous with “bit is set to Logic 1” or
“writing Logic 1 for the bit.”
• “Clear a bit” is synonymous with “bit is set to Logic 0” or
“writing Logic 0 for the bit.”
Transfer Register Map
Address 0x08 through Address 0x18 and Address 0x30 are
shadowed. Writes to these addresses do not affect part
operation until a transfer command is issued by writing 0x01 to
Address 0xFF, setting the transfer bit. This allows these registers
to be updated internally and simultaneously when the transfer
bit is set. The internal update takes place when the transfer bit is
set, and the bit autoclears.
Channel-Specific Registers
Some channel setup functions, such as the signal monitor
thresholds, can be programmed differently for each channel. In
these cases, channel address locations are internally duplicated for
each channel. These registers and bits are designated in Tab l e 1 7
as local. These local registers and bits can be accessed by setting
the appropriate Channel A or Channel B bits in Register 0x05.
If both bits are set, the subsequent write affects the registers of
both channels. In a read cycle, only Channel A or Channel B
should be set to read one of the two registers. If both bits are set
during an SPI read cycle, the part returns the value for Channel A.
Registers and bits designated as global in Tab le 1 7 affect the entire
part or the channel features for which independent settings are not
allowed between channels. The settings in Register 0x05 do not
affect the global registers and bits.
Rev. A | Page 37 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
MEMORY MAP REGISTER TABLE
All address and bit locations that are not included in Tabl e 17 are not currently supported for this device.
Table 17. Memory Map Registers
Address
(Hex)
Chip Configuration Registers
0x00
0x01 Chip ID
0x02 Chip grade
Channel Index and Transfer Registers
0x05
0xFF Transfer Open Open Open Open Open Open Open Transfer 0x00
ADC Functions
0x08 Power modes
0x09 Global clock
0x0B Clock divide
0x0D
Register
Name
SPI port
configuration
(global)
(global)
(global)
Channel
index
(local)
(global)
(global)
Test mode
(local)
Bit 7
(MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
0 LSB first Soft reset 1 1 Soft reset LSB first 0 0x18
8-bit Chip ID[7:0]
(AD9268 = 0x32)
(default)
Open Open Speed grade ID
Open Open Open Open Open Open
1 Open
Open Open Open Open Open Open Open
Open Open Open Open Open Clock divide ratio
Open Open
01 = 125 MSPS
10 = 105 MSPS
11 = 80 MSPS
External
powerdown pin
function
(local)
0 = pdwn
1 = stndby
Reset PN
long ge n
Open Open Open
Reset
PN short
gen
Rev. A | Page 38 of 44
Open Open Open Open
Data
Channel
B
(default)
Internal power-down
mode (local)
00 = normal operation
01 = full power-down
10 = standby
11 = normal operation
000 = divide by 1
001 = divide by 2
010 = divide by 3
011 = divide by 4
100 = divide by 5
101 = divide by 6
110 = divide by 7
111 = divide by 8
Open Output test mode
000 = off (default)
001 = midscale short
010 = positive FS
011 = negative FS
100 = alternating checkerboard
101 = PN long sequence
110 = PN short sequence
111 = one/zero word toggle
Bit 0
(LSB)
Data
Channel A
(default)
Duty cycle
stabilizer
(default)
Default
Value
(Hex)
0x32 Read only
0x03
0x80
0x01
0x00
0x00
Default
Notes/
Comments
The nibbles
are mirrored
so LSB-first
mode or MSBfirst mode
registers
correctly,
regardless of
shift mode
Speed grade
ID used to
differentiate
devices; read
only
Bits are set
to determine
which device
on the chip
receives the
next write
command;
applies to local
registers only
Synchronously
transfers data
from the
master shift
register to the
slave
Determines
various generic
modes of chip
operation
Clock divide
values other
than 000
automatically
cause the duty
cycle stabilizer
to become
active
When this
register is set,
the test data
is placed on
the output
pins in place of
normal data

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Address
(Hex)
0x0E BIST enable
0x0F
0x10 Offset adjust
0x14 Output mode
0x16
0x17
0x18 VREF select
0x24
0x25
0x30
Digital Feature Control
0x100 Sync control
Register
Name
(global)
ADC input
(global)
(local)
Clock phase
control
(global)
DCO output
delay (global)
(global)
BIST signature
LSB (local)
BIST signature
MSB (local)
Dither enable
(local)
(global)
Bit 7
(MSB)
Open Open Open Open Open
Open Open Open Open Open Open Open
Drive
strength
0 = ANSI
LVDS;
1 =
reduced
swing
LVDS
(global)
Invert
DCO clock
Open Open Open DCO clock delay
Reference voltage
selection
(default)
Open Open Open
Open Open Open Open Open
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
Output
type
0 = CMOS
1 = LVDS
(global)
Open Open Open Open Input clock divider phase adjust
00 = 1.25 V p-p
01 = 1.5 V p-p
10 = 1.75 V p-p
11 = 2.0 V p-p
Default
Bit 0
(LSB)
Reset BIST
sequence
Offset adjust in LSBs from +127 to −128
(twos complement format)
CMOS
output
interleave
enable
(global)
Open Open Open Open Open Open 0xC0
Output
enable
bar
(local)
BIST signature[7:0] 0x00 Read only
BIST signature[15:8] 0x00 Read only
Dither
enable
Open
(must be
written
low)
Open Open Open Open 0x00
Output
invert
(local)
(delay = 2500 ps × register value/31)
00000 = 0 ps
00001 = 81 ps
00010 = 161 ps
…
11110 = 2419 ps
11111 = 2500 ps
Clock
divider
next sync
only
Open
Output format
00 = offset binary
01 = twos
complement
01 = gray code
11 = offset binary
000 = no delay
001 = 1 input clock cycle
010 = 2 input clock cycles
011 = 3 input clock cycles
100 = 4 input clock cycles
101 = 5 input clock cycles
110 = 6 input clock cycles
111 = 7 input clock cycles
Clock
divider
sync
enable
BIST
enable
Commonmode
servo
enable
(local)
Master
sync
enable
Value
(Hex)
0x04
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
Default
Notes/
Comments
Configures the
outputs and
the format of
the data
Allows
selection of
clock delays
into the input
clock divider
Rev. A | Page 39 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
MEMORY MAP REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
For additional information about functions controlled in
Register 0x00 to Register 0xFF, see the AN-877 Application Note,
Interfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI.
Sync Control (Register 0x100)
Bits[7:3]—Reserved
Bit 2—Clock Divider Next Sync Only
If the master sync enable bit (Address 0x100, Bit 0) and the clock
divider sync enable bit (Address 0x100, Bit 1) are high, Bit 2 allows
the clock divider to sync to the first sync pulse it receives and to
ignore the rest. The clock divider sync enable bit (Address 0x100,
Bit 1) resets after it syncs.
Bit 1—Clock Divider Sync Enable
Bit 1 gates the sync pulse to the clock divider. The sync signal is
enabled when Bit 1 is high and Bit 0 is high. This is continuous
sync mode.
Bit 0—Master Sync Enable
Bit 0 must be high to enable any of the sync functions. If the
sync capability is not used this bit should remain low to
conserve power.
Rev. A | Page 40 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
DESIGN GUIDELINES
Before starting design and layout of the AD9268 as a system,
it is recommended that the designer become familiar with these
guidelines, which discuss the special circuit connections and
layout requirements that are needed for certain pins.
Power and Ground Recommendations
When connecting power to the AD9268, it is recommended that
two separate 1.8 V supplies be used. Use one supply for analog
(AVDD); use a separate supply for the digital outputs (DRVDD).
For both AVDD and DRVDD several different decoupling capacitors should be used to cover both high and low frequencies.
Place these capacitors close to the point of entry at the PCB
level and close to the pins of the part, with minimal trace length.
A single PCB ground plane should be sufficient when using the
AD9268. With proper decoupling and smart partitioning of the
PCB analog, digital, and clock sections, optimum performance
is easily achieved.
LVDS Operation
The AD9268 defaults to CMOS output mode on power-up.
If LVDS operation is desired, this mode must be programmed,
using the SPI configuration registers after power-up. When the
AD9268 powers up in CMOS mode with LVDS termination
resistors (100 Ω) on the outputs, the DRVDD current can be
higher than the typical value until the part is placed in LVDS
mode. This additional DRVDD current does not cause damage
to the AD9268, but it should be taken into account when considering the maximum DRVDD current for the part.
To avoid this additional DRVDD current, the AD9268 outputs
can be disabled at power-up by taking the OEB pin high. After
the part is placed in LVDS mode via the SPI port, the OEB pin
can be taken low to enable the outputs.
Exposed Paddle Thermal Heat Slug Recommendations
It is mandatory that the exposed paddle on the underside of the
ADC be connected to analog ground (AGND) to achieve the
best electrical and thermal performance. A continuous, exposed
(no solder mask) copper plane on the PCB should mate to the
AD9268 exposed paddle, Pin 0.
The copper plane should have several vias to achieve the lowest
possible resistive thermal path for heat dissipation to flow through
the bottom of the PCB. These vias should be filled or plugged to
prevent solder wicking through the vias, which can compromise
the connection.
To maximize the coverage and adhesion between the ADC and
the PCB, a silkscreen should be overlaid to partition the continuous
plane on the PCB into several uniform sections. This provides
several tie points between the ADC and the PCB during the reflow
process. Using one continuous plane with no partitions guarantees
only one tie point between the ADC and the PCB. For detailed
information about packaging and PCB layout of chip scale
packages, see the AN-772 Application Note, A Design and
Manufacturing Guide for the Lead Frame Chip Scale Package
(LFCSP), at www.analog.com.
VCM
The VCM pin should be decoupled to ground with a 0.1 F
capacitor, as shown in Figure 67.
RBIAS
The AD9268 requires that a 10 kΩ resistor be placed between
the RBIAS pin and ground. This resistor sets the master current
reference of the ADC core and should have at least a 1% tolerance.
Reference Decoupling
The VREF pin should be externally decoupled to ground with
a low ESR, 1.0 F capacitor in parallel with a low ESR, 0.1 F
ceramic capacitor.
SPI Port
The SPI port should not be active during periods when the full
dynamic performance of the converter is required. Because the
SCLK, CSB, and SDIO signals are typically asynchronous to the
ADC clock, noise from these signals can degrade converter
performance. If the on-board SPI bus is used for other devices,
it may be necessary to provide buffers between this bus and the
AD9268 to keep these signals from transitioning at the converter
inputs during critical sampling periods.
Rev. A | Page 41 of 44

AD9268
http://www.BDTIC.com/ADI
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
49
48
0.60 MAX
EXPOSED PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
PIN 1
64
INDICATOR
1
7.65
7.50 SQ
7.35
PIN 1
INDICATOR
9.00
BSC SQ
TOP VIEW
8.75
BSC SQ
0.60
MAX
0.50
BSC
1.00
0.85
0.80
SEATING
PLANE
12° MAX
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.30
0.23
0.18
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VMMD-4
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.20 REF
33
32
7.50
REF
16
17
FOR PROPER CONNECTION OF
THE EXPOSED PAD, REFERTO
THE PIN CONFIGURATIONAND
FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET.
0.25 MIN
041509-A
Figure 85. 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
9 mm × 9 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-64-6)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD9268BCPZ-80
AD9268BCPZRL7-80
AD9268BCPZ-1051 −40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-6
AD9268BCPZRL7-105
AD9268BCPZ-125
AD9268BCPZRL7-125
AD9268-80EBZ
AD9268-105EBZ
AD9268-125EBZ
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
1
−40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-6
1
−40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-6
1
−40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-6
1
−40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-6
1
−40°C to +85°C 64-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-64-6
1
Evaluation Board
1
Evaluation Board
1
Evaluation Board
Rev. A | Page 42 of 44
 Loading...
Loading...