High Speed Oversampling CMOS ADC with
16-Bit Resolution at a 2.5 MHz Output Word Rate
FEATURES
Monolithic 16-bit, oversampled A/D converter
8× oversampling mode, 20 MSPS clock
2.5 MHz output word rate
1.01 MHz signal passband with 0.004 dB ripple
Signal-to-noise ratio: 88.5 dB
Total harmonic distortion: –96 dB
Spurious-free dynamic range: 100 dB
Input referred noise: 0.6 LSB
Selectable oversampling ratio: 1×, 2×, 4×, 8×
Selectable power dissipation: 150 mW to 585 mW
85 dB stop-band attenuation
0.004 dB pass-band ripple
Linear phase
Single 5 V analog supply, 5 V/3 V digital supply
Synchronize capability for parallel ADC interface
Twos complement output data
44-lead MQFP
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD9260 is a 16-bit, high-speed oversampled analog-todigital converter (ADC) that offers exceptional dynamic range
over a wide bandwidth. The AD9260 is manufactured on an
advanced CMOS process. High dynamic range is achieved with
an oversampling ratio of 8× through the use of a proprietary
technique that combines the advantages of sigma-delta and
pipeline converter technologies. The AD9260 is a switchedcapacitor ADC with a nominal full-scale input range of 4 V. It
offers a differential input with 60 dB of common-mode rejection of common-mode signals. The signal range of each differential input is ±1 V centered on a 2.0 V common-mode level.
The on-chip decimation filter is configured for maximum
performance and flexibility. A series of three half-band FIR
filter stages provide 8× decimation filtering with 85 dB of stopband attenuation and 0.004 dB of pass-band ripple. An onboard
digital multiplexer allows the user to access data from the
various stages of the decimation filter. The on-chip
programmable reference and reference buffer amplifier are
configured for maximum accuracy and flexibility. An external
reference can also be chosen to suit the user’s specific dc
accuracy and drift requirements.
The AD9260 operates on a single +5 V supply, typically
consuming 585 mW of power. A power scaling circuit is
provided allowing the AD9260 to operate at power consump-
AD9260
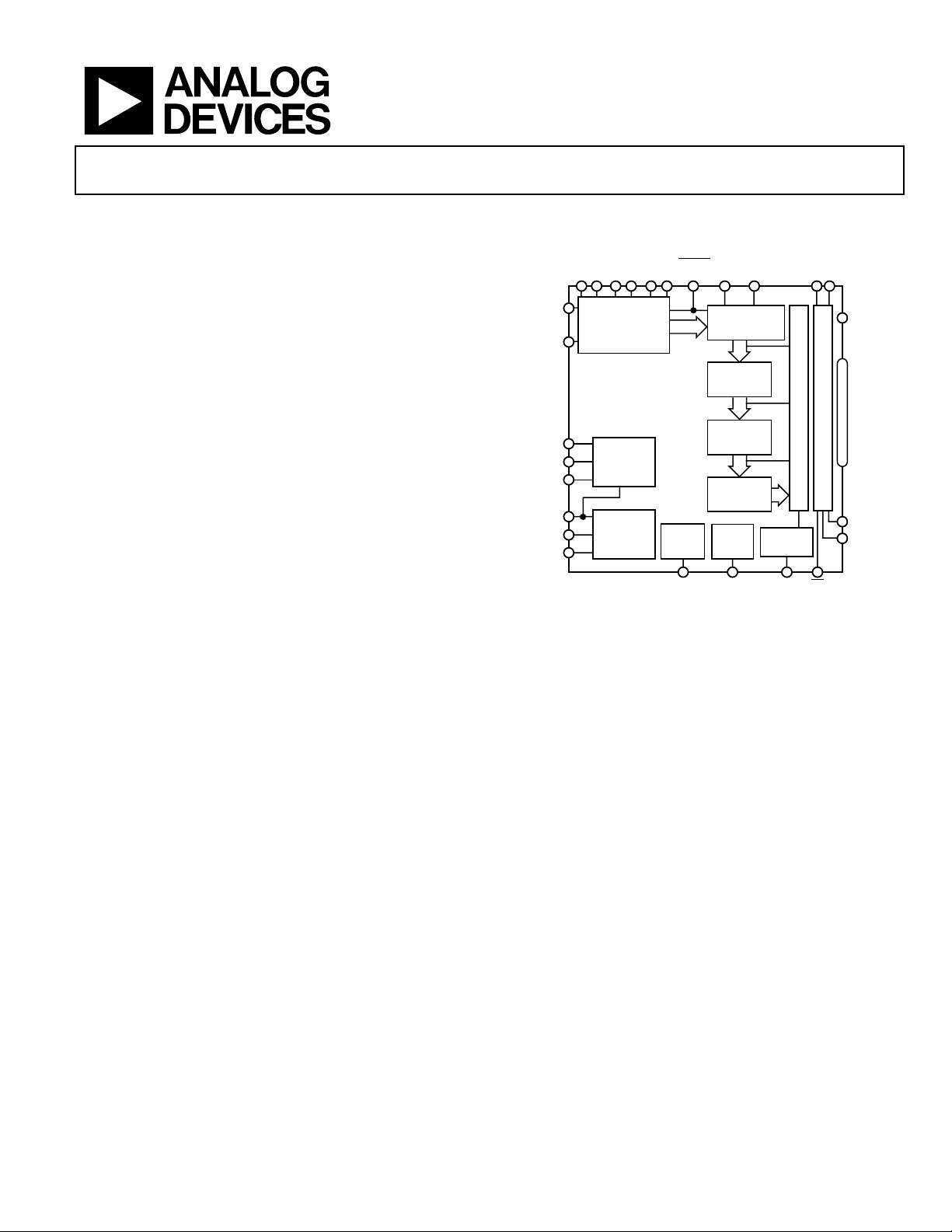
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AVSS
AVDD
CIRCUIT
RESET/
AVSS
SYNC
12-BIT:
20MHz
16-BIT:
10MHz
16-BIT:
5MHz
16-BIT:
2.5MHz
BIAS
DVSS DVDD
DIGITAL
DEMODULATOR
STAGE 1:2X
DECIMATION
FILTER
STAGE 2:2X
DECIMATION
FILTER
STAGE 3:2X
DECIMATION
FILTER
CLOCK
BUFFER
Figure 1.
MODE
REGISTER
MODECLKBIAS ADJUST
VINA
VINB
REF TOP
REF
BOTTOM
COMMON
MODE
VREF
SENSE
REFCOM
AVSS
AVDD
AVDD
MULTIBIT
SIGMA-DELTA
MODULATOR
AD9260
REFERENCE
BUFFER
BANDGAP
REFERENCE
tion levels as low as 150 mW at reduced clock and data rates.
The AD9260 is available in a 44-lead MQFP package and is
specified to operate over the industrial temperature range.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
The AD9260 is fabricated on a very cost effective CMOS
process. High speed, precision, mixed-signal analog circuits are
combined with high density digital filter circuits. The AD9260
offers a complete single-chip 16-bit sampling ADC with a 2.5
MHz output data rate in a 44-lead MQFP.
Selectable Internal Decimation Filtering—The AD9260
provides a high performance decimation filter with 0.004 dB
pass-band ripple and 85 dB of stop-band attenuation. The filter
is configurable with options for 1×, 2×, 4×, and 8× decimation.
Power Scaling—The AD9260 consumes a low 585 mW of
power at 16-bit resolution and 2.5 MHz output data rate. Its
power can be scaled down to as low as 150 mW at reduced
clock rates.
Single Supply—Both the analog and digital portions of the
AD9260 can operate off of a single +5 V supply, simplifying
system power supply design. The digital logic will also
accommodate a single +3 V supply for reduced power.
DRVSS
DRVDD
OUTPUT REGISTER
OUTPUT MODE MULTIPLEXER
CS
OTR
BIT1–
BIT16
DAV
READ
00581-C-001
Rev. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

AD9260
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 23
Clock Input Frequency Range .................................................... 3
DC Specifications ......................................................................... 3
AC Specifications.......................................................................... 4
Digital Filter Characteristics ....................................................... 6
Digital Filter Characteristics ....................................................... 7
Digital Specifications ................................................................... 9
Switching Specifications ............................................................ 10
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 11
Thermal Characteristics ............................................................ 11
ESD Caution................................................................................ 11
Te r mi n ol o g y .................................................................................... 12
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 13
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 14
Typical AC Characterization Curves
vs. Decimation Mode
Typical AC Characterization Curves for 8× Mode................ 16
Typical AC Characterization Curves for 4× Mode................ 17
Typical AC Characterization Curves for 2× Mode................ 18
Typical AC Characterization Curves for 1× Mode................ 19
Typical AC Characterization Curves ....................................... 20
Additional AC Characterization Curves .................................21
................................................................. 15
Analog Input and Reference Overview ....................................... 24
Input Span ................................................................................... 24
Input Compliance Range........................................................... 24
Analog Input Operation............................................................ 24
Driving the Input........................................................................ 25
Reference Operation ...................................................................... 28
Digital Inputs and Outputs ........................................................... 30
Digital Outputs........................................................................... 30
Mode Operation ......................................................................... 31
Bias Pin Operation ..................................................................... 32
Power Dissipation Considerations ............................................... 33
Digital Output Driver Considerations (DRVDD)................. 33
Grounding and Decoupling ...................................................... 34
Evaluation Board General Description ....................................... 36
Features and User Controls....................................................... 36
Shipment Configuration............................................................ 37
Quick Setup................................................................................. 37
Application Information ........................................................... 38
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 43
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 43
REVISION HISTORY
7/04—Changed from Rev. B to Rev. C
Changed “trimpot” to “variable resistor” .....................Universal
Updated Format................................................................ Universal
Updated Outline Dimensions......................................................43
Changes to Ordering Guide.........................................................43
5/00—Changed from Rev. A to Rev. B.
1/98—Changed from Rev. 0 to Rev. A.
Rev. C | Page 2 of 44
AD9260
SPECIFICATIONS
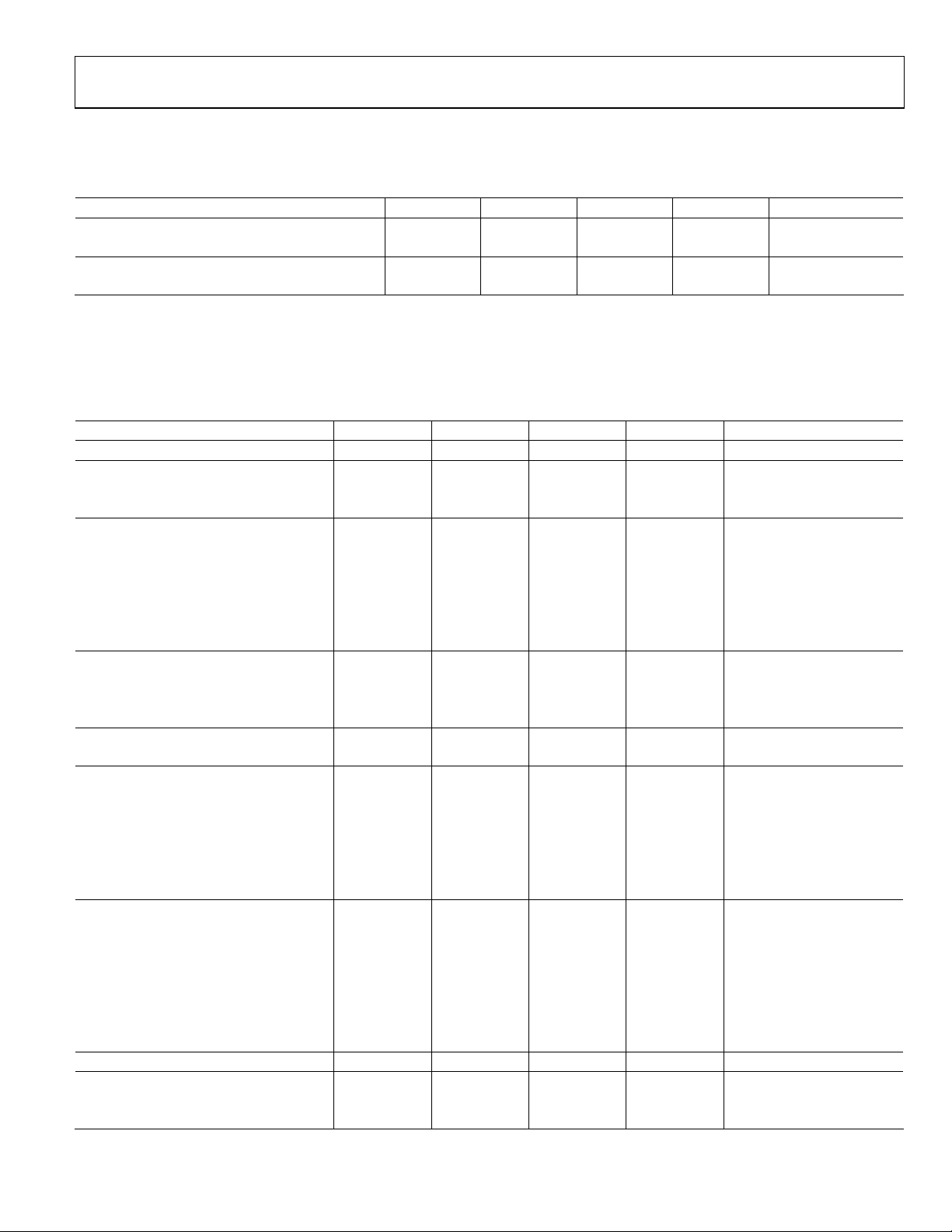
CLOCK INPUT FREQUENCY RANGE
Table 1.
Parameter—Decimation Factor (N) AD9260 (8) AD9260 (4) AD9260 (2) AD9260 (1) Unit
CLOCK INPUT (Modulator Sample Rate, f
20 20 20 20 MHz max
OUTPUT WORD RATE (FS = f
/N) 0.125 0.250 0.500 1 kHz min
CLOCK
2.5 5 10 20 MHz max
DC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = +5 V, DVDD = +3 V, DRVDD = +3 V, f
= 2 kΩ.
R
BIAS
Table 2.
Parameter—Decimation Factor (N) AD9260 (8) AD9260 (4) AD9260 (2) AD9260 (1) Unit
RESOLUTION 16 16 16 12 Bits min
INPUT REFERRED NOISE (TYP)
1.0 V Reference 1.40 2.4 6.0 1.3 LSB rms typ
2.5 V Reference1 0.68 (90.6) 1.2 (86) 3.7 (76) 1.0 (63.2) LSB rms typ (dB typ)
ACCURACY
Integral Nonlinearity (INL) ± 0.75 ± 0.75 ± 0.75 ± 0.3 LSB typ
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) ± 0.50 ± 0.50 ± 0.50 ± 0.25 LSB typ
No Missing Codes 16 16 16 12 Bits Guaranteed
Offset Error 0.9 (0.5) (0.5) (0.5) (0.5) % FSR max (typ @ +25°C)
Gain Error
Gain Error3 1.35 (0.7) (0.7) (0.7) (0.7) % FSR max (typ @ +25°C)
TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset Error 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 ppm/°C typ
Gain Error2 22 22 22 22 ppm/°C typ
Gain Error3 7.0 7.0 7.0 7.0 ppm/°C typ
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION
AVDD, DVDD, DRVDD (+5 V ±0.25 V) 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 % FSR max
ANALOG INPUT
Input Span
Input (VINA or VINB) Range +0.5 +0.5 +0.5 +0.5 V min
+AVDD –0.5 +AVDD –0.5 +AVDD –0.5 +AVDD –0.5 V max
Input Capacitance 10.2 10.2 10.2 10.2 pF typ
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Output Voltage (1 V Mode) 1 1 1 1 V typ
Output Voltage Error (1 V Mode) ± 14 ± 14 ± 14 ± 14 mV max
Output Voltage (2.5 V Mode) 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 V typ
Output Voltage Error (2.5 V Mode) ± 35 ± 35 ± 35 ± 35 mV max
Load Regulation4
REFERENCE INPUT RESISTANCE 8 8 8 8 kΩ
POWER SUPPLIES
Supply Voltages
2
V
= 1.0 V 1.6 1.6 1.6 1.6 V p p Diff. max
REF
V
= 2.5 V 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 V p p Diff. max
REF
1 V REF 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 mV max
2.5 V REF 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 mV max
AVDD +5 +5 +5 +5 V (± 5%)
) 1 1 1 1 kHz min
CLOCK
= 20 MSPS, V
CLOCK
= +2.5 V, Input CML = 2.0 V T
REF
MIN
to T
unless otherwise noted,
MAX
2.75 (0.66) (0.66) (0.66) (0.66) % FSR max (typ @ +25°C)
Rev. C | Page 3 of 44
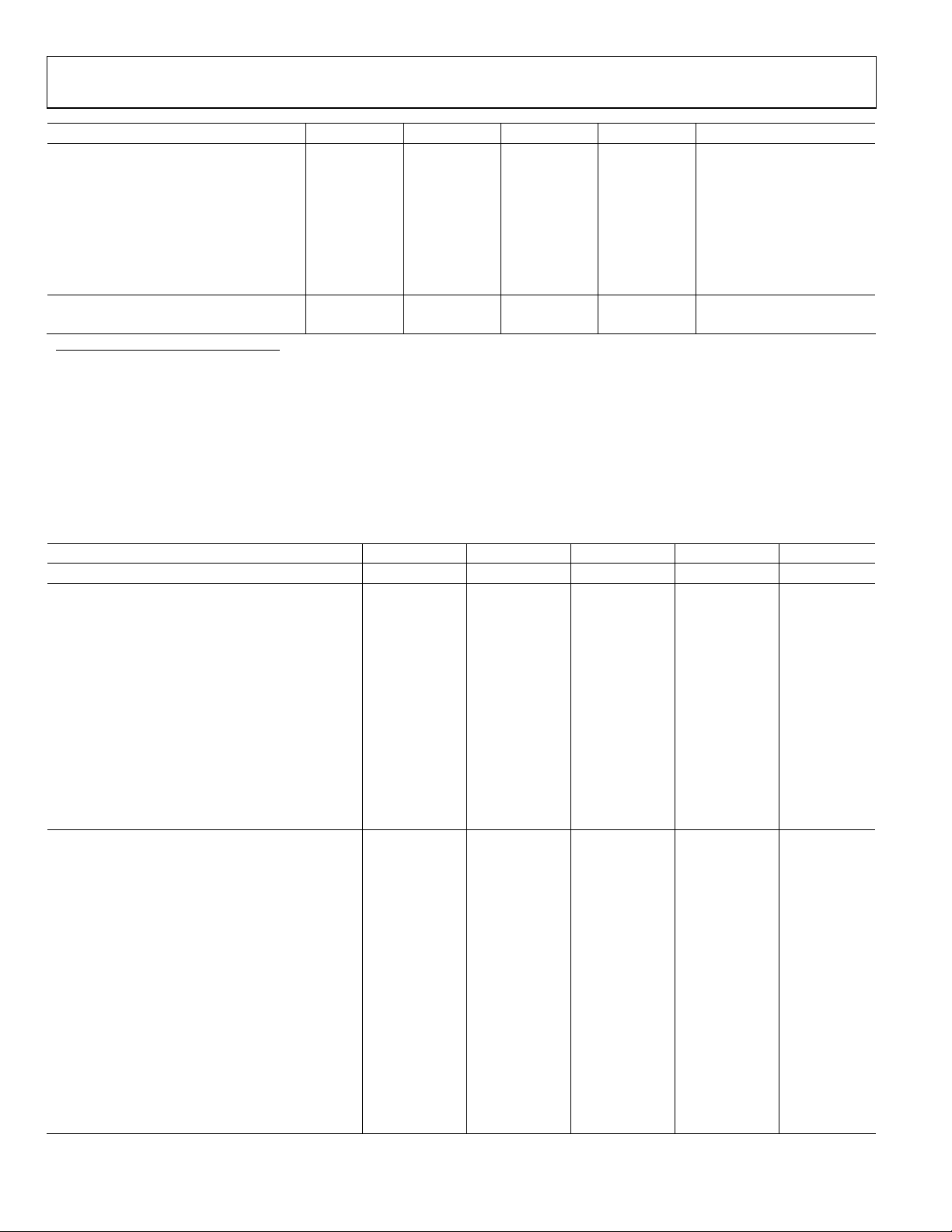
AD9260
Parameter—Decimation Factor (N) AD9260 (8) AD9260 (4) AD9260 (2) AD9260 (1) Unit
DVDD and DRVDD +5.5 +5.5 +5.5 +5.5 V max
+2.7 +2.7 +2.7 +2.7 V min
Supply Current
IAVDD 115 115 115 115 mA typ
134 mA max
IDVDD 12.5 10.3 6.5 2.4 mA typ
3.5 mA max
IDRVDD 0.450 0.850 1.7 2.6 mA typ
POWER CONSUMPTION 613 608 600 585 mW typ
630 mW max
1
VINA and VINB connect to DUT CML.
2
Including Internal 2.5 V reference.
3
Excluding Internal 2.5 V reference.
4
Load regulation with 1 mA load current (in addition to that required by AD9260).
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = +5 V, DVDD = +3 V, DRVDD = +3 V, f
= 2 kΩ.
R
BIAS
Table 3.
Parameter—Decimation Factor (N) AD9260(8) AD9260(4) AD9260(2) AD9260(1) Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
INPUT TEST FREQUENCY: 100 kHz (typ)
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 88.5 82 74 63 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 82.5 78 68 58 dB typ
SNR and Distortion (SINAD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 87.5 82 74 63 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 82 77.5 69 58 dB typ
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS –96 –96 –97 –98 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS –93 –98 –96 –98 dB typ
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 100 98 98 88 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 94 100 94 84 dB typ
INPUT TEST FREQUENCY: 500 kHz
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 86.5 82 74 63 dB typ
80.5 dB min
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 82.5 77 68 58 dB typ
SNR and Distortion (SINAD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 86.0 81 74 63 dB typ
80.0 dB min
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 82.0 77 68 58 dB typ
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS –97.0 –92 –89 –86 dB typ
–90.0 dB max
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS –95.5 –96 –89 –86 dB typ
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 99.0 92 91 88 dB typ
90.0 dB max
= 20 MSPS, V
CLOCK
= +2.5 V, Input CML = 2.0 V T
REF
MIN
to T
unless otherwise noted,
MAX
Rev. C | Page 4 of 44

AD9260
Parameter—Decimation Factor (N) AD9260(8) AD9260(4) AD9260(2) AD9260(1) Unit
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 98 100 91 82 dB typ
INPUT TEST FREQUENCY: 1.0 MHz (typ)
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 85 82 74 63 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 80 76 68 58 dB typ
SNR and Distortion (SINAD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 84.5 81 74 63 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 80 76 69 58 dB typ
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS –102 –96 –82 –79 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS –96 –94 –84 –77 dB typ
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 105 98 83 80 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 98 96 87 80 dB typ
INPUT TEST FREQUENCY: 2.0 MHz (typ)
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 82 74 63 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 76 68 58 dB typ
SNR and Distortion (SINAD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 81 73 62 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 76 69 58 dB typ
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS –101 –80 –75 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS –95 –80 –76 dB typ
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 104 80 78 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 100 83 79 dB typ
INPUT TEST FREQUENCY: 5.0 MHz (typ)
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 59 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 57 dB typ
SNR and Distortion (SINAD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 58 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 57 dB typ
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS –58 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS –67 dB typ
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
Input Amplitude = –0.5 dBFS 59 dB typ
Input Amplitude = –6.0 dBFS 70 dB typ
INTERMODULATION DISTORTION
fIN1 = 475 kHz, fIN2 = 525 kHz –93 –91 –91 –83 dBFS typ
fIN1 = 950 kHz, fIN2 = 1.050 MHz –95 –86 –85 –83 dBFS typ
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Full Power Bandwidth 75 75 75 75 MHz typ
Small Signal Bandwidth (AIN = –20 dBFS) 75 75 75 75 MHz typ
Aperture Jitter 2 2 2 2 ps rms typ
Rev. C | Page 5 of 44
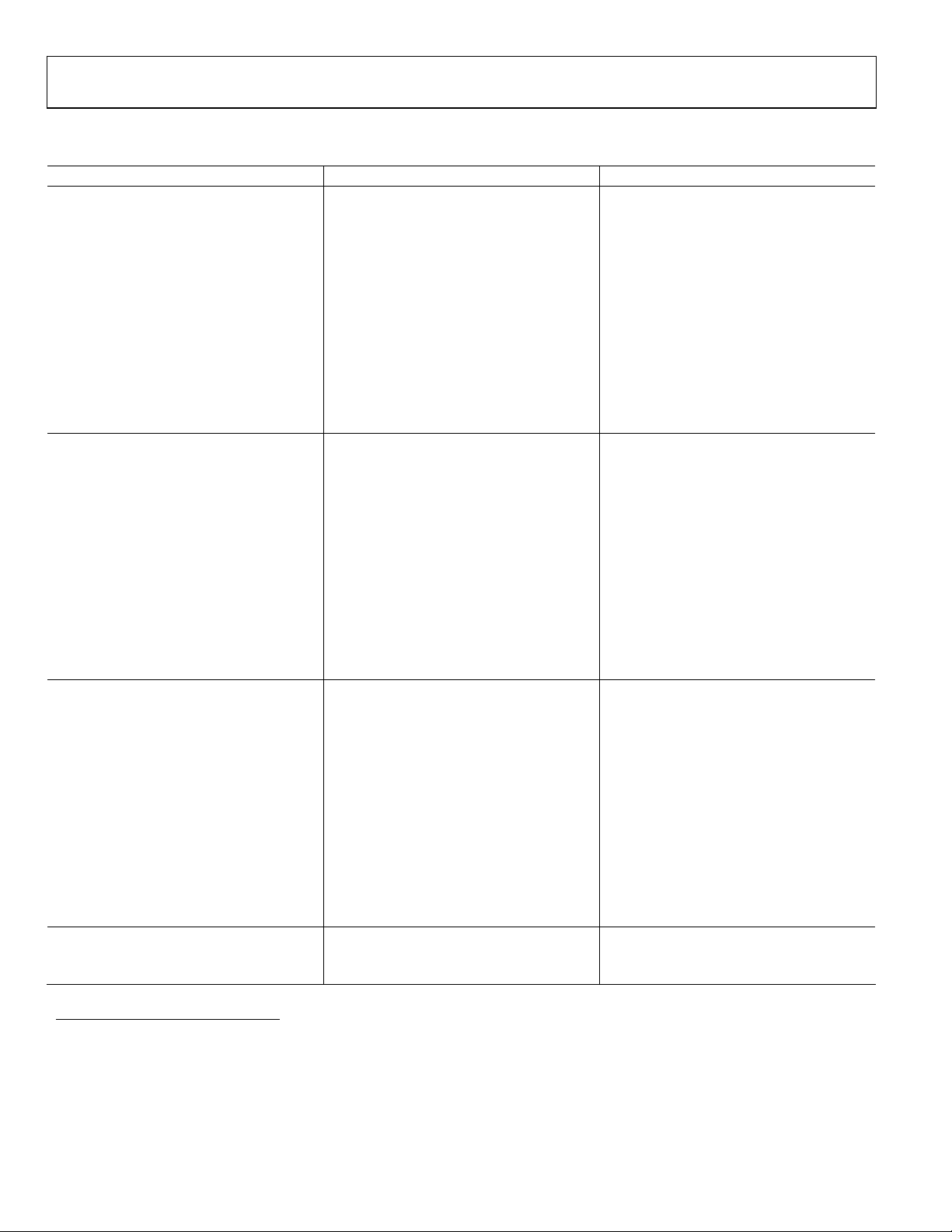
AD9260
DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS
Table 4.
Parameter AD9260 Unit
8× DECIMATION (N = 8)
Pass-Band Ripple 0.00125 dB max
Stop-Band Attenuation 82.5 dB min
Pass-Band 0 MHz min
0.605 × (f
Stop-Band 1.870 × (f
18.130 × (f
Pass-Band/Transition Band Frequency
(–0.1 dB Point) 0.807 × (f
(–3.0 dB Point) 1.136 × (f
Absolute Group Delay1 13.55 × (20 MHz/f
Group Delay Variation 0 µs max
Settling Time (to ± 0.0007%)1 24.2 × (20 MHz/f
4× DECIMATION (N = 4)
Pass-Band Ripple 0.001 dB max
Stop-Band Attenuation 82.5 dB min
Pass-Band 0 MHz min
1.24 × (f
Stop-Band 3.75 × (f
16.25 × (f
Pass-Band/Transition Band Frequency
(–0.1 dB Point) 1.61 × (f
(–3.0 dB Point) 2.272 × (f
Absolute Group Delay1 2.90 × (20 MHz/f
Group Delay Variation 0 µs max
Settling Time (to ± 0.0007%)1 5.05 × (20 MHz/f
2× DECIMATION (N = 2)
Pass-Band Ripple 0.0005 dB max
Stop-Band Attenuation 85.5 dB min
Pass-Band 0 MHz min
2.491 × (f
Stop-Band 7.519 × (f
12.481 × (f
Pass-Band/Transition Band Frequency
(–0.1 dB Point) 3.231 × (f
(–3.0 dB Point) 4.535 × (f
Absolute Group Delay1 0.80 × (20 MHz/f
Group Delay Variation 0 µs max
Settling Time (to ± 0.0007%)1 1.40 × (20 MHz/f
1× DECIMATION (N = 1)
Propagation Delay: t
13 ns max
PROP
Absolute Group Delay (225 × (20 MHz/f
1
To determine overall Absolute Group Delay and/or Settling Time inclusive of delay from the sigma-delta modulator, add Absolute Group Delay and/or Settling Time
pertaining to specific decimation mode to the Absolute Group Delay specified in 1 ×decimation.
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz min
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
) µs max
CLOCK
) µs max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz min
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
) µs max
CLOCK
) µs max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz min
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
/20 MHz) MHz max
CLOCK
) µs max
CLOCK
) µs max
CLOCK
)) + t
CLOCK
ns max
PROP
Rev. C | Page 6 of 44
AD9260
DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS
0
1.0
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–100
–120
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–100
–20
–40
–60
–80
–20
–40
–60
–80
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
NORMALIZED OUTPUT RESPONSE
–0.2
0.4 0.60 0.2 0.8 1.0 1.2
FREQUENCY (NORMALIZED TO π)
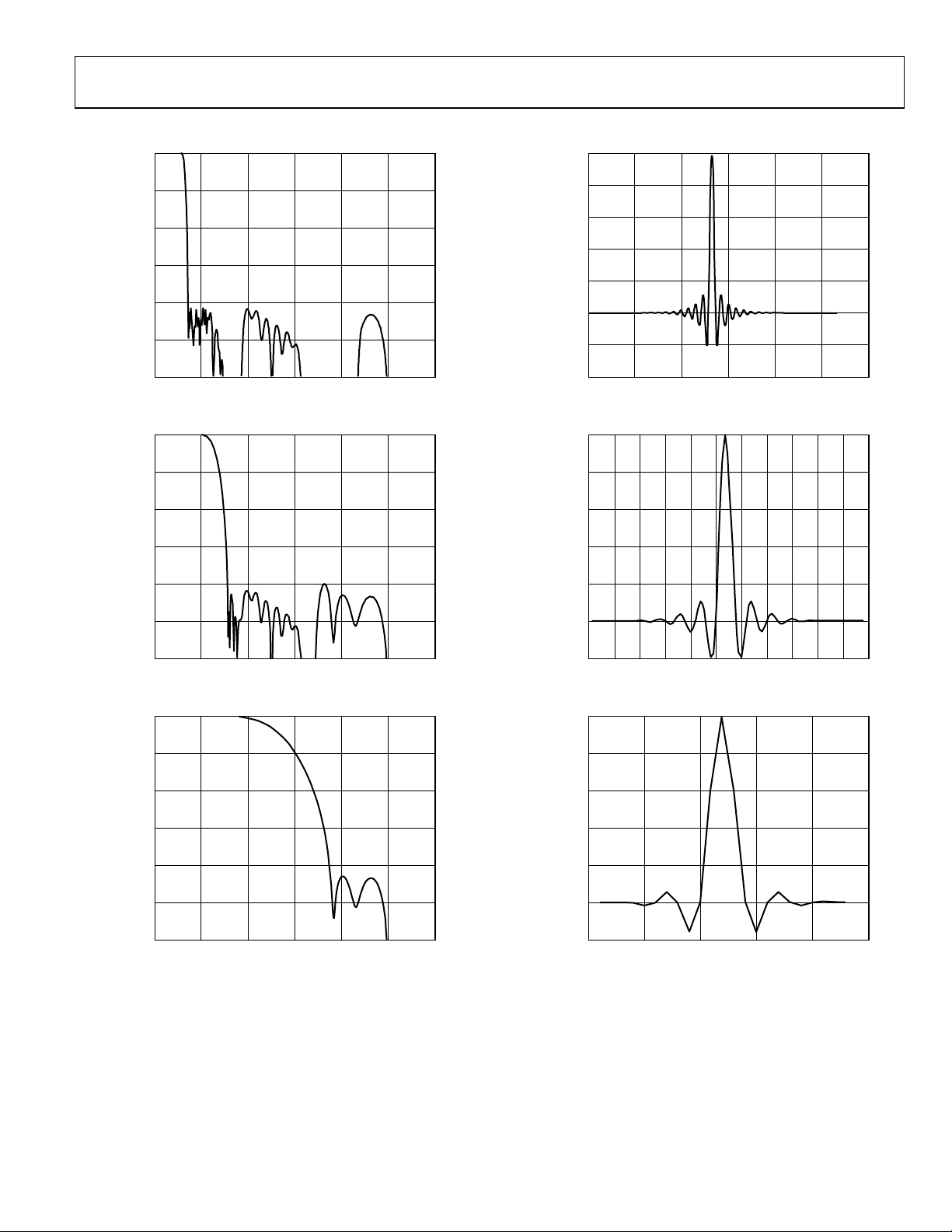
Figure 2. 8x FIR Filter Frequency Response
0
00581-C-002
–0.4
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
NORMALIZED OUTPUT RESPONSE
200 3000 100 400 500 600
CLOCK PERIODS (RELATIVE TO CLK)
Figure 5. 8x FIR Filter Impulse Response
00581-C-005
–120
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–100
–120
–20
–40
–60
–80
0.4 0.60 0.2 0.8 1.0 1.2
FREQUENCY (NORMALIZED TO π)
Figure 3. 4x FIR Filter Frequency Response
0
0.4 0.60 0.2 0.8 1.0 1.2
FREQUENCY (NORMALIZED TO π)
Figure 4. 2x FIR Filter Frequency Response
00581-C-003
00581-C-004
–0.2
0 102030405060708090100110
CLOCK PERIODS (RELATIVE TO CLK)
Figure 6. 4x FIR Filter Impulse Response
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
NORMALIZED OUTPUT RESPONSE
–0.2
0 5 10 15 20 25
CLOCK PERIODS (RELATIVE TO CLK)
Figure 7. 2x FIR Filter Impulse Response
00581-C-006
00581-C-007
Rev. C | Page 7 of 44
AD9260
Table 5. Integer Filter Coefficients for First Stage
Decimation Filter (23-Tap Half-Band FIR Filter)
Lower Coefficient Upper Coefficient Integer Value
H(1) H(23) –1
H(2) H(22) 0
H(3) H(21) 13
H(4) H(20) 0
H(5) H(19) –66
H(6) H(18) 0
H(7) H(17) 224
H(8) H(16) 0
H(9) H(15) –642
H(10) H(14) 0
H(11) H(13) 2496
H(12) 4048
Table 6. Integer Filter Coefficients for Second Stage
Decimation Filter (43-Tap Half-Band FIR Filter)
Lower Coefficient Upper Coefficient Integer Value
H(1) H(43) 3
H(2) H(42) 0
H(3) H(41) –12
H(4) H(40) 0
H(5) H(39) 35
H(6) H(38) 0
H(7) H(37) –83
H(8) H(36) 0
H(9) H(35) 172
H(10) H(34) 0
H(11) H(33) –324
H(12) H(32) 0
H(13) H(31) 572
H(14) H(30) 0
H(15) H(29) –976
H(16) H(28) 0
H(17) H(27) 1680
H(18) H(26) 0
H(19) H(25) –3204
H(20) H(24) 0
H(21) H(23) 10274
H(22) 16274
NOTE: The composite filter undecimated coefficients (i.e.,
impulse response) in the 4× decimation mode can be
determined by convolving the first stage filter taps with a
“zero stuffed” version of the second stage filter taps (i.e., insert
one zero between samples). Similarly, the composite filter
coefficients in the 8× decimation mode can be determined by
convolving the taps of the composite 4× decimation mode (as
previously determined) with a “zero stuffed” version of the third
stage filter taps (i.e., insert three zeros between samples).
Table 7. Integer Filter Coefficients for Third Stage
Decimation Filter (107-Tap Half-Band FIR Filter)
Lower Coefficient Upper Coefficient Integer Value
H(1) H(107) –1
H(2) H(106) 0
H(3) H(105) 2
H(4) H(104) 0
H(5) H(103) –2
H(6) H(102) 0
H(7) H(101) 3
H(8) H(100) 0
H(9) H(99) –3
H(10) H(98) 0
H(11) H(97) 1
H(12) H(96) 0
H(13) H(95) 3
H(14) H(94) 0
H(15) H(93) –12
H(16) H(92) 0
H(17) H(91) 27
H(18) H(90) 0
H(19) H(89) –50
H(20) H(88) 0
H(21) H(87) 85
H(22) H(86) 0
H(23) H(85) –135
H(24) H(84) 0
H(25) H(83) 204
H(26) H(82) 0
H(27) H(81) –297
H(28) H(80) 0
H(29) H(79) 420
H(30) H(78) 0
H(31) H(77) –579
H(32) H(76) 0
H(33) H(75) 784
H(34) H(74) 0
H(35) H(73) –1044
H(36) H(72) 0
H(37) H(71) 1376
H(38) H(70) 0
H(39) H(69) –1797
H(40) H(68) 0
H(41) H(67) 2344
H(42) H(66) 0
H(43) H(65) –3072
H(44) H(64) 0
H(45) H(63) 4089
H(46) H(62) 0
H(47) H(61) –5624
H(48) H(60) 0
H(49) H(59) 8280
H(50) H(58) 0
H(51) H(57) –14268
H(52) H(56) 0
H(53) H(55) 43520
H(54) 68508
Rev. C | Page 8 of 44

AD9260
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = +5 V, DVDD = +5 V, T
Table 8.
Parameter AD9260 Unit
CLOCK1 AND LOGIC INPUTS
High Level Input Voltage
(DVDD = +5 V) +3.5 V min
(DVDD = +3 V) +2.1 V max
Low Level Input Voltage
(DVDD = +5 V) +1.0 V min
(DVDD = +3 V) +0.9 V max
High Level Input Current (VIN = DVDD) ± 10 µA max
Low Level Input Current (VIN = 0 V) ± 10 µA max
Input Capacitance 5 pF typ
LOGIC OUTPUTS (with DRVDD = 5 V)
High Level Output Voltage (IOH = 50 µA) +4.5 V min
High Level Output Voltage (IOH = 0.5 mA) +2.4 V min
Low Level Output Voltage2 (IOL = 0.3 mA) +0.4 V max
Low Level Output Voltage (IOL = 50 µA) +0.1 V max
Output Capacitance 5 pF typ
LOGIC OUTPUTS (with DRVDD = 3 V)
High Level Output Voltage (IOH = 50 µA) +2.4 V min
Low Level Output Voltage (IOL = 50 µA) +0.7 V max
1
Since CLK is referenced to AVDD, +5 V logic input levels only apply.
2
The AD9260 is not guaranteed to meet VOL = 0.4 V max for standard TTL load of IOL = 1.6 mA.
ANALOG INPUT
INPUT CLOCK
DATA OUTPUT
DAV
to T
MIN
S1
t
CH
t
H
unless otherwise noted.
MAX
S2
t
C
t
CL
t
DI
t
DS
t
OE
t
DAV
t
OD
READ
CS
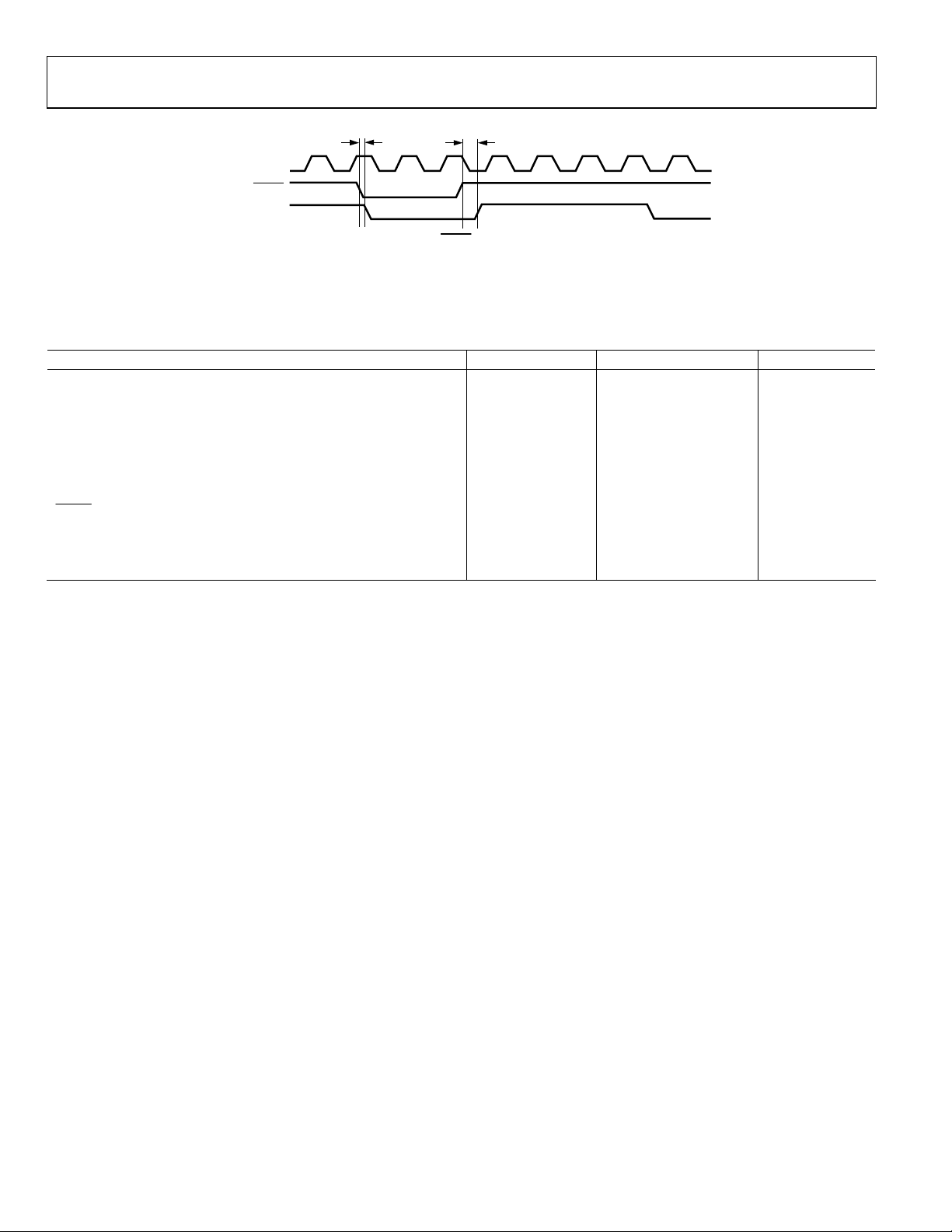
Figure 8. Timing Diagram
Rev. C | Page 9 of 44
00581-C-008
AD9260
INPUT CLOCK
RESET
DAV
t
RES-DAV
Figure 9.
t
CLK-DAV
RESET
Timing Diagram
00581-C-009
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = +5 V, DVDD = +5 V, CL = 20 pF, T
Table 9.
Parameters Symbol AD9260 Unit
Clock Period tC 50 ns min
Data Available (DAV) Period t
Data Invalid tDI 40% t
Data Set-Up Time tDS t
Clock Pulse-Width High tCH 22.5 ns min
Clock Pulse-Width Low tCL 22.5 ns min
Data Hold Time tH 3.5 ns min
RESET
to DAV Delay
CLOCK to DAV Delay t
Three-State Output Disable Time tOD 8 ns typ
Three-State Output Enable Time tOE 45 ns typ
MIN
to T
unless otherwise noted.
MAX
tC ×Mode ns min
DAV
ns max
DAV
–tH –tDI ns min
DAV
t
10 ns typ
RES–DAV
15 ns typ
CLK–DAV
Rev. C | Page 10 of 44

AD9260
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 10.
Parameter Rating
AVDD to AVSS –0.3 V to +6.5 V
DVDD to DVSS –0.3 V to +6.5 V
AVSS to DVSS –0.3 V to +0.3 V
AVDD to DVDD –6.5 V to +6.5 V
DRVDD to DRVSS –0.3 V to +6.5 V
DRVSS to AVSS –0.3 V to +0.3 V
REFCOM to AVSS –0.3 V to +0.3 V
CLK, MODE, READ, CS, and
DVSS
Digital Outputs to DRVSS –0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
VINA, VINB, CML, and BIAS to AVSS –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
VREF to AVSS –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
SENSE to AVSS –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
CAPB and CAPT to AVSS –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Junction Temperature 150°C
Storage Temperature –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (10 s) 300°C
RESET
–0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
to
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum ratings for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Thermal Resistance
44-Lead MQFP
= 53.2°C/W
θ
JA
= 19°C/W
θ
JC
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the
human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. C | Page 11 of 44

AD9260
TERMINOLOGY
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
INL refers to the deviation of each individual code from a line
drawn from “negative full scale” through “positive full scale.”
The point used as “negative full scale” occurs 1/2 LSB before the
first code transition. “Positive full scale” is defined as a level 1
1/2 LSB beyond the last code transition. The deviation is
measured from the middle of each particular code to the true
straight line.
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL, No Missing Codes)
An ideal ADC exhibits code transitions that are exactly 1 LSB
apart. DNL is the deviation from this ideal value. Guaranteed
no missing codes to 14-bit resolution indicates that all 16384
codes, respectively, must be present over all operating ranges.
NOTE: Conventional INL and DNL measurements don’t really
apply to ∑∆ converters: the DNL looks continually better if
longer data records are taken. For the AD9260, INL and DNL
numbers are given as representative.
Zero Error
The major carry transition should occur for an analog value 1/2
LSB below VINA = VINB. Zero error is defined as the deviation
of the actual transition from that point.
Gain Error
The first code transition should occur at an analog value 1/2
LSB above negative full scale. The last transition should occur at
an analog value 1 1/2 LSB below the nominal full scale. Gain
error is the deviation of the actual difference and the ideal
difference between first and last code transitions.
Temp er at u re D ri ft
The temperature drift for zero error and gain error specifies the
maximum change from the initial (+25°C) value to the value at
or T
T
MIN
Power Supply Rejection
The specification shows the maximum change in full scale from
the value with the supply at the minimum limit to the value
with the supply at its maximum limit.
MAX
.
Aperture Jitter
Aperture jitter is the variation in aperture delay for successive
samples and is manifested as noise on the input to the A/D.
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion (S/N+D, SINAD) Ratio
S/N+D is the ratio of the rms value of the measured input signal
to the rms sum of all other spectral components below the
Nyquist frequency, including harmonics but excluding dc. The
value for S/N+D is expressed in decibels.
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
For a sine wave, SINAD can be expressed in terms of the
number of bits. Using the following formula, it is possible to get
a measure of performance expressed as N, the effective number
of bits:
N = (SINAD − 1.76)/6.02
Thus, effective number of bits for a device for sine wave inputs
at a given input frequency can be calculated directly from its
measured SINAD.
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
THD is the ratio of the rms sum of the first six harmonic
components to the rms value of the measured input signal and
is expressed as a percentage or in decibels.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
SNR is the ratio of the rms value of the measured input signal to
the rms sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, excluding the first six harmonics and dc. The value
for SNR is expressed in decibels.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
SFDR is the difference in dB between the rms amplitude of the
input signal and the peak spurious signal.
Two -Tone SFDR
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value
of the peak spurious component. The peak spurious component
may or may not be an IMD product. May be reported in dBc
(i.e., degrades as signal level is lowered), or in dBFS (always
related back to converter full scale).
Rev. C | Page 12 of 44
AD9260
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
VINB
42
BIT11
NC
VINA
CML
40 39 3841
AD9260
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
BIT8
BIT9
BIT10
AVSS
BIT7
CAPT
BIT6
CAPB
BIT5
BIAS
BIT4
MODE
BIT3
33
REFCOM
32
VREF
31
SENSE
30
RESET
29
AVSS
28
AVDD
27
CS
26
DAV
25
OTR
24
BIT1 (MSB)
23
BIT2
DVSS
AVSS
DVDD
AVDD
DRVSS
DRVDD
CLK
READ
(LSB) BIT16
BIT15
BIT14
NC
AVDD
4344 36 35 3437
1
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
BIT12
BIT13
NC = NO CONNECT
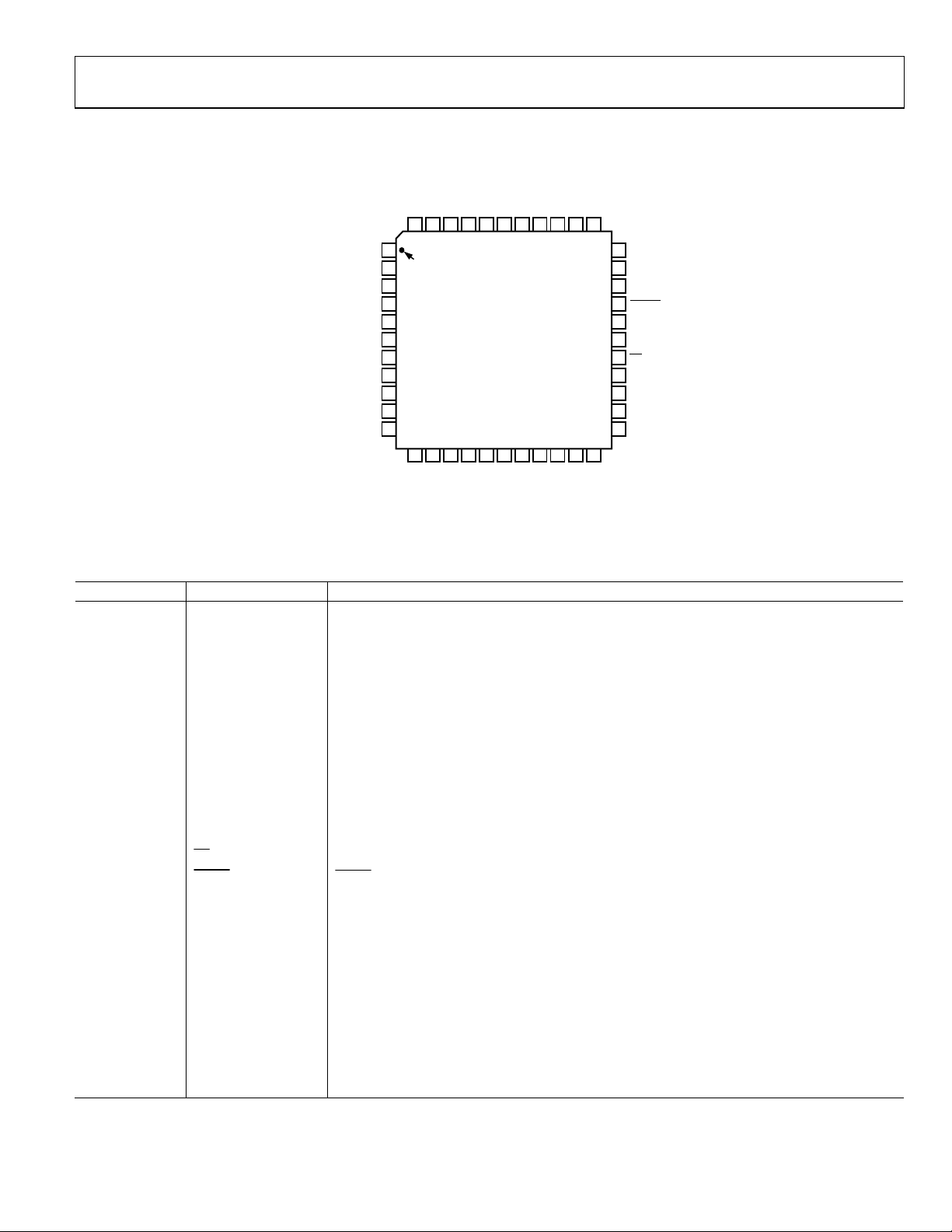
Figure 10. Pin Configuration
Table 11. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 DVSS Digital Ground.
2, 29, 38 AVSS Analog Ground.
3 DVDD +3 V to +5 V Digital Supply.
4, 28, 44 AVDD +5 V Analog Supply.
5 DRVSS Digital Output Driver Ground.
6 DRVDD +3 V to +5 V Digital Output Driver Supply.
7 CLK Clock Input.
8 READ Part of DSP Interface—Pull Low to Disable Output Bits.
9 BIT16 Least Significant Data Bit (LSB).
10–23 BIT15–BIT2 Data Output Bit.
24 BIT1 Most Significant Data Bit (MSB).
25 OTR Out of Range—Set When Converter or Filter Overflows.
26 DAV Data Available.
27
30
CS
RESET
Chip Select (CS): Active LOW.
RESET
: Active LOW.
31 SENSE Reference Amplifier SENSE: Selects REF Level.
32 VREF Input Span Select Reference I/O.
33 REFCOM Reference Common.
34 MODE Mode Select—Selects Decimation Mode.
35 BIAS Power Bias.
36 CAPB Noise Reduction Pin—Decouples Reference Level.
37 CAPT Noise Reduction Pin—Decouples Reference Level.
39 CML Common-Mode Level (AVDD/2.5).
40, 43 NC No Connect (Ground for Shielding Purposes).
41 VINA Analog Input Pin (+).
42 VINB Analog Input Pin (–).
00581-C-010
Rev. C | Page 13 of 44
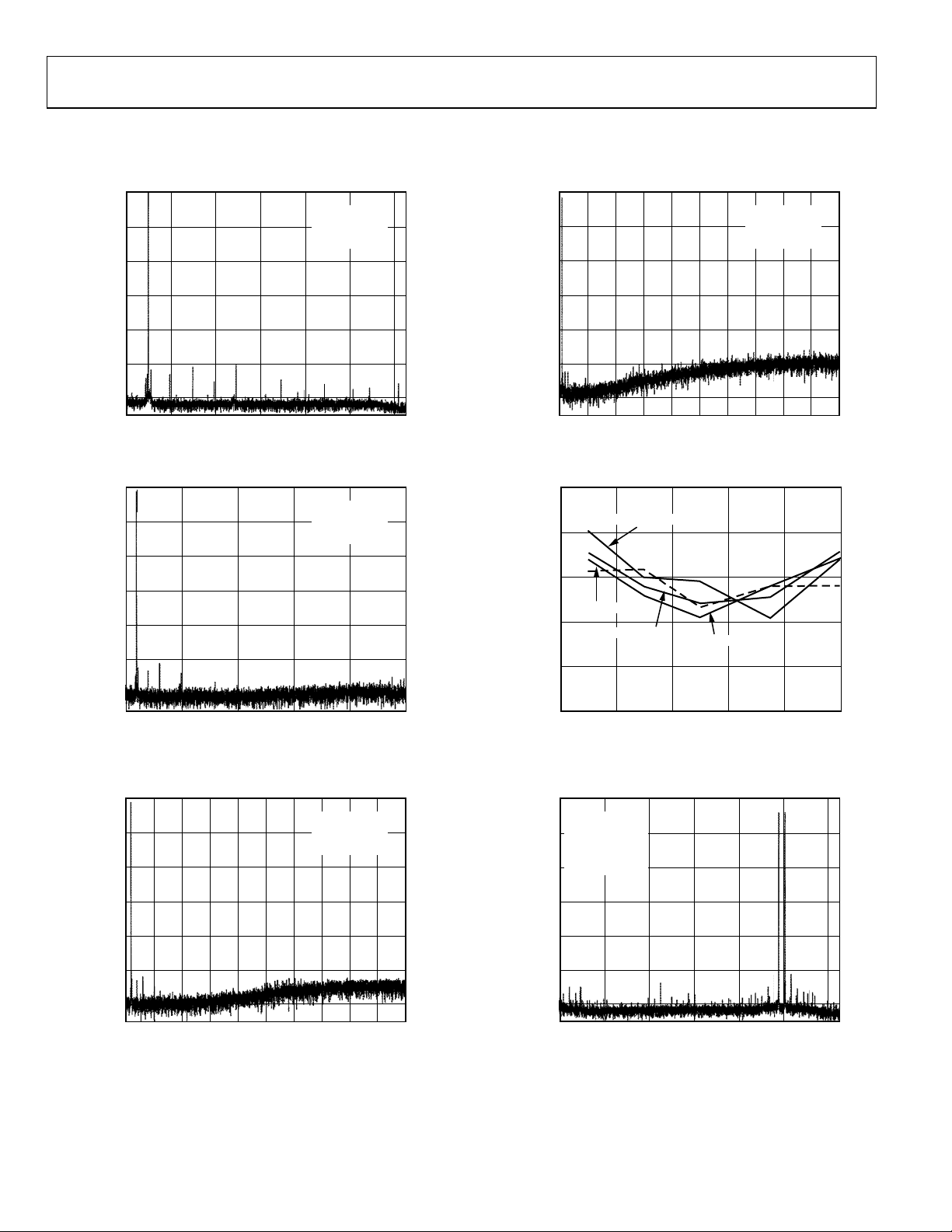
AD9260
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
AVDD = DVDD = DRVDD = +5.0 V, 4 V Input Span, Differential DC Coupled Input with CML = 2.0 V, f
–20
–40
0
100kHz INPUT
20MHz CLOCK
8 × DECIMATION
THD: –96dB
0
–20
–40
= 20 MSPS, Full Bias.
CLOCK
100kHz INPUT
20MHz CLOCK
1 × DECIMATION
THD: –98dB
–60
–80
dB BELOW FULL SCALE
–100
–120
0.4 0.60 0.2 0.8 1.0 1.2
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 11. Spectral Plot of the AD9260 at 100 kHz Input, 20 MHz Clock,
8x OSR (2.5 MHz Output Data Rate)
0
100kHz INPUT
–20
–40
–60
–80
dB BELOW FULL SCALE
–100
–120
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
FREQUENCY (MHz)
20MHz CLOCK
4 × DECIMATION
THD: –98dB
Figure 12. Spectral Plot of the AD9260 at 100 kHz Input, 20 MHz Clock,
4x OSR (5 MHz Output Data Rate)
0
100kHz INPUT
–20
–40
20MHz CLOCK
2 × DECIMATION
THD: –98dB
00581-C-011
00581-C-012
–60
–80
dB BELOW FULL SCALE
–100
–120
012345678910
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 14. Spectral Plot of the AD9260 at 100 kHz Input, 20 MHz Clock,
Undecimated (20 MHz Output Data Rate)
110
106
102
98
WORST CASE SPUR (dBFS)
94
90
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
Figure 15. Dual-Tone SFDR vs. Input Frequency (F
–12dBFS/TONE
–6.5dBFS/TONE
–26dBFS/TONE
–46dBFS/TONE
FREQUENCY (MHz)
= F2, Span = 10% Center
1
Freque ncy, Mode = 8x)
0
DUAL-TONE TEST
f1 = 1.0MHz
–20
f2 = 975kHz
20MHz CLOCK
8 × DECIMATION
–40
IM3: –94dB
00581-C-014
00581-C-015
–60
–80
dB BELOW FULL SCALE
–100
–120
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 13. Spectral Plot of the AD9260 at 100 kHz Input, 20 MHz Clock,
2x OSR (10 MHz Output Data Rate)
Rev. C | Page 14 of 44
00581-C-013
–60
–80
dB BELOW FULL SCALE
–100
–120
0.4 0.60 0.2 0.8 1.0 1.2
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 16. Two-Tone Spectral Performance of the AD9260 Given Inputs at
975 kHz and 1.0 MHz, 20 MHz Clock, 8x Decimation
00581-C-016
 Loading...
Loading...