Page 1
16 V, 250 μA, Dual Precision, CMOS,
FEATURES
Lower power at high voltage: 180 μA typical
Low offset voltage: 100 μV
Voltage noise
21 nV/√Hz at 10 kHz
23 nV/√Hz at 1 kHz
Low input bias current: 300 fA
Single-supply operation: 5 V to 16 V
Dual-supply operation: ±2.5 V to ±8 V
Output drive: 10 mA
Unity gain stable
APPLICATIONS
Medical equipment
Physiological measurement
Precision references
Buffer/level shifting
Portable operated systems
High density power budget systems
Multipole filters
Sensors
Photodiode amplification
ADC drivers
Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifier
AD8667
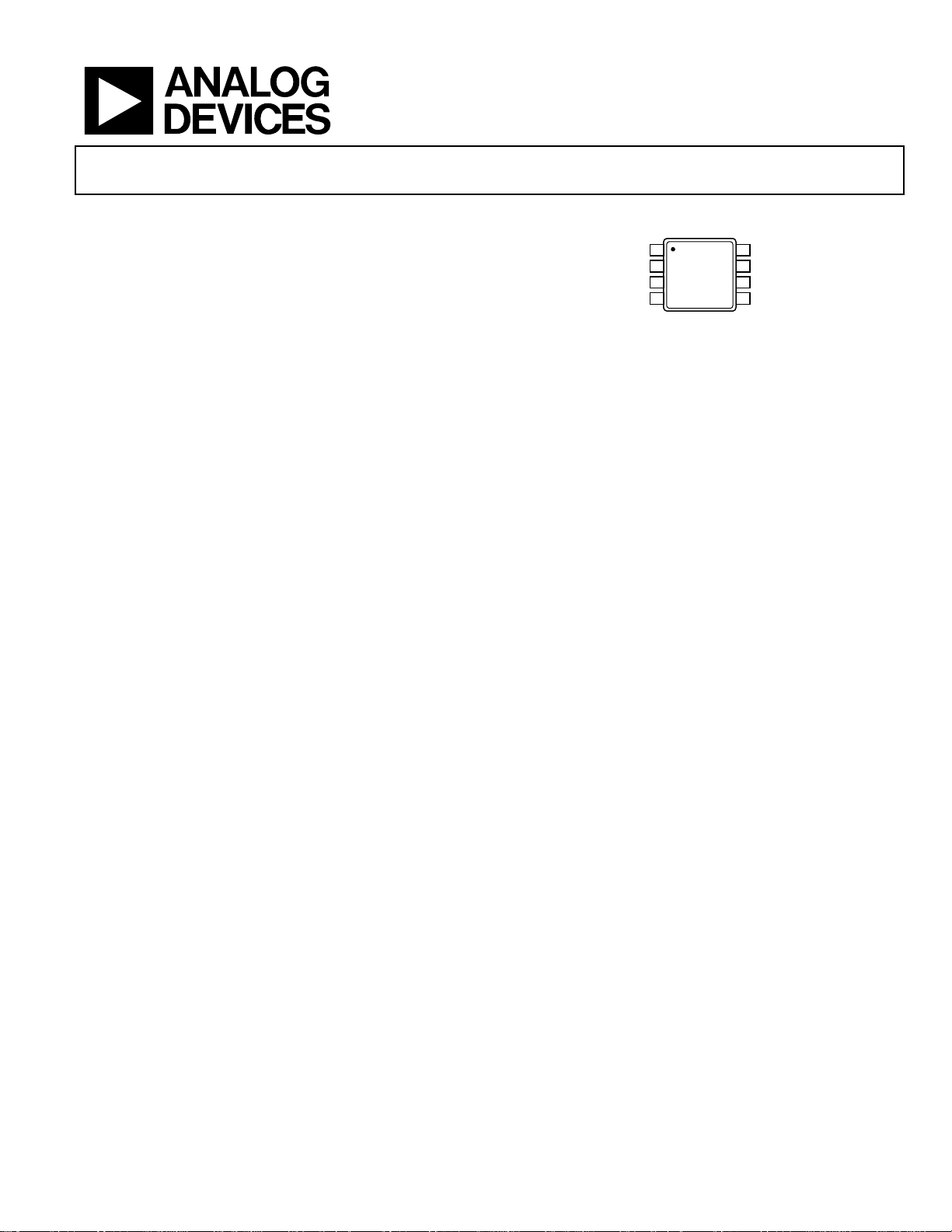
PIN CONFIGURATION
OUT A
1
AD8667
2
–IN A
+IN A
Figure 1. 8-Lead MSOP, 8-Lead SOIC
V–
TOP VIEW
3
(Not to Scale)
4
8
7
6
5
V+
OUT B
–IN B
+IN B
06276-001
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD8667 is a dual, rail-to-rail output, single-supply/dual-supply
amplifier that uses Analog Devices, Inc. patented DigiTrim®
trimming technique to achieve low offset voltage, 300 μV over
the common-mode range. The AD8667 features an extended
operating range with supply voltages up to 16 V for low power
operation with an I
The device is designed for low noise at higher voltages: 21 nV/√Hz
at 10 kHz and 23 nV/√Hz at 1 kHz. It also features a low input
bias current of 300 fA and a 10 mA output drive.
The combination of low supply currents, low offsets, very low
input bias currents, and wide supply range makes the AD8667
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
of <325 μA per amplifier over temperature.
SY
ideal for a wide variety of low power applications. Systems
utilizing dc-to-low frequency measurements or high impedance
sensors, such as photodiodes, benefit from the low input bias
current, low noise, low offset, and low drive current. The wide
operating voltage range matches today’s high performance
ADCs and DACs. Medical monitoring equipment can take
advantage of the low voltage noise, high input impedance, low
voltage, and low current noise.
The AD8667 is specified over the extended industrial
temperature range of −40°C to +125°C.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

AD8667
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................5
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Pin Configuration............................................................................. 1
General Description......................................................................... 1
Revision History ...............................................................................2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Electrical Characteristics............................................................. 3
REVISION HISTORY
5/07—Revision 0: Initial Version
Thermal Resistance.......................................................................5
ESD Caution...................................................................................5
Typical Performance Characteristics..............................................6
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 13
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 13
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 16
Page 3
AD8667
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VS = 5.0 V, VCM = VS/2, TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage VOS V
−40°C < TA < +125°C 350 μV
V
−40°C < TA < +85°C 100 450 μV
V
Input Bias Current IB 0.3 pA
−40°C < TA < +85°C 20 pA
−40°C < TA < +125°C 150 pA
Input Offset Current IOS 0.2 pA
−40°C < TA < +85°C 15 pA
−40°C < TA < +125°C 50 pA
Input Voltage Range IVR −40°C < TA < +85°C 0 3.5 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C 0.2 3.5 V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR VCM = 0 V to 3.5 V 80 90 dB
V
Large Signal Voltage Gain AVO R
Offset Voltage Drift ΔVOS/ΔT −40°C < TA < +125°C 1.3 5 μV/°C
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High VOH I
−40°C < TA < +125°C 4.6 4.7 V
Output Voltage Low VOL I
−40°C < TA < +125°C 200 250 mV
Short-Circuit Current ISC ±6 mA
Closed-Loop Output Impedance Z
f = 100 kHz, AV = 1 120 Ω
OUT
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR VS = 5 V to 16 V 95 105 dB
Supply Current/Amplifier ISY 180 275 μA
−40°C < TA < +125°C 325 μA
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Slew Rate SR RL = 2 kΩ 0.2 V/μs
Settling Time tS To 0.1%, 0 V to 2 V step, AV = 10 12 μs
Gain Bandwidth Product GBP 600 kHz
Phase Margin ΦM 60 Degrees
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Peak-to-Peak Noise e
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 3 μV p-p
n p-p
Voltage Noise Density en f = 10 kHz 21 nV/√Hz
f = 1 kHz 23 nV/√Hz
Current Noise Density in f = 1 kHz 0.05 pA/√Hz
= 2.5 V 100 μV
CM
= 0 V to 3.5 V 70 300 μV
CM
= 0.2 V to 3.5 V, −40°C < TA < +125°C 100 450 μV
CM
= 0.2 V to 3.5 V, −40°C < TA < +125°C 80 90 dB
CM
= 2 kΩ, VO = 0.5 V to 4.5 V 106 115 dB
L
= 1 mA 4.65 4.8 V
L
= 1 mA 150 200 mV
L
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 16
Page 4
AD8667
VS = 16 V, VCM = VS/2, TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage VOS V
−40°C < TA < +125°C 350 μV
V
−40°C < TA < +85°C 450 μV
V
Input Bias Current IB 0.3 pA
−40°C < TA < +85°C 30 pA
−40°C < TA < +125°C 250 pA
Input Offset Current IOS 0.2 pA
−40°C < TA < +85°C 25 pA
−40°C < TA < +125°C 150 pA
Input Voltage Range IVR −40°C < TA < +85°C 0 14.5 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C 0.2 14.5 V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR VCM = 0 V to 14.5 V 90 100 dB
V
Large Signal Voltage Gain AVO R
Offset Voltage Drift ΔVOS/ΔT 1.2 5 μV/°C
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High VOH I
I
I
Output Voltage Low VOL I
I
I
Short-Circuit Current ISC ±50 mA
Closed-Loop Output Impedance Z
f = 100 kHz, AV = 1 100 Ω
OUT
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR VS = 5 V to 16 V, −40°C < TA < +125°C 95 105 dB
Supply Current/Amplifier ISY 230 285 μA
−40°C < TA < +125°C 325 μA
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Slew Rate SR RL = 2 kΩ 0.3 V/μs
Settling Time tS To 0.1%, 0 V to 2 V step 12 μs
Gain Bandwidth Product GBP 600 kHz
Phase Margin ΦM 60 Degrees
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Peak-to-Peak Noise e
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 3 μV p-p
n p-p
Voltage Noise Density en f = 1 kHz 23 nV/√Hz
f = 10 kHz 21 nV/√Hz
Current Noise Density in f = 1 kHz 0.05 pA/√Hz
= 8 V 40 300 μV
CM
= 0 V to 14.5 V 70 300 μV
CM
= 0.2 V to 14.5 V, −40°C < TA < +125°C 450 μV
CM
= 0.2 V to 14.5 V, −40°C < TA < +125°C 90 100 dB
CM
= 2 kΩ, VO = 0.5 V to 15.5 V 112 124 dB
L
= 1 mA 15.8 15.9 V
L
= 10 mA 14.8 15.1 V
L
= 10 mA, −40°C < TA < +125°C 14.65 14.8 V
L
= 1 mA 80 100 mV
L
= 10 mA 600 720 mV
L
= 10 mA, −40°C < TA < +125°C 800 900 mV
L
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 16
Page 5

AD8667
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage 18 V
Input Voltage −0.1 V to VS
Differential Input Voltage 18 V
Output Short-Circuit Duration to GND Indefinite
Storage Temperature Range −60°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 60 sec) 300°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +125°C
Junction Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device
soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount packages.
Table 4. Thermal Resistance
Package Type θJA θ
8-Lead MSOP 145 45 °C/W
8-Lead SOIC 125 43 °C/W
Unit
JC
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 16
Page 6

AD8667
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Specifications at VSY = ±8 V, unless otherwise noted.
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
VS = ±8V
0V < V
= 25°C
T
A
CM
< 14.5V
100
±8V
10
600
NUMBER OF AMPLI FIERS
400
200
0
0 50 100 150 200 250–50–100–150–200–250
VOS (µV)
Figure 2. Input Offset Voltage Distribution
40
35
30
25
20
15
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
10
5
0
0 0.4 0.8 1.2 1.6 2.0 2.4 2.8 3.2 3.6 4.0 4.4 4.8
TCV
OS
VS = ±8V
–40°C < T
(µV/°C)
Figure 3. Input Offset Voltage Drift Distribution
< +125°C
A
1
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (pA)
±2.5V
0.1
0 25 50 75 100 125
06276-003
TEMPERATURE (° C)
06276-006
Figure 5. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
10000
VS = 5V
= 25°C
T
A
1000
100
10
1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE TO SUPPLY RAIL (mV)
0.1
06276-004
0.001 0. 01 0.1 1 10
SOURCE
SINK
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
06276-007
Figure 6. Output Swing Saturation Voltage vs. Load Current
300
VS = 16V
250
200
150
100
50
(µs)
0
OS
V
–50
–100
–150
–200
–250
–300
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
0V < V
= 25°C
T
A
CM
< 14.5V
(V)
V
CM
Figure 4. Input Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode Voltage
06276-005
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 16
10000
VS = 16V
= 25°C
T
A
1000
100
10
1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE TO SUPPLY RAIL (mV)
0.1
0.001 0.01 0. 1 1 10 100
SOURCE
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
SINK
Figure 7. Output Swing Saturation Voltage vs. Load Current
06276-008
Page 7

AD8667
1200
1100
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
VOL @ 1mA VS = 5V
200
OUTPUT SAT URATION VO LTAGE (mV)
100
0
–40 –25 –10 5 20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
VDD – VOH @ 10mA VS = 16V
VOL @ 10mA VS = 16V
VDD – VOH @ 1mA VS = 16V
VDD – VOH @ 1mA VS = 5V
VOL @ 1mA VS = 16V
TEMPERATURE ( °C)
Figure 8. Output Saturation Voltage vs. Temperature
150
VS = 16V
T
= 125°C
A
100
50
0
(pA)
B
I
–50
06276-009
1200
VSY = ±8V
1000
800
(Ω)
600
OUT
Z
400
AV = 100
200
0
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
AV = 10 AV = 1
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 11. Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency
120
VS = ±8V
100
80
CMRR (dB)
60
06276-012
–100
–150
0246810121416
V
(V)
CM
Figure 9. Input Bias Current vs. Common Mode Voltage at 125°C
90
70
50
30
10
–10
GAIN (dB)
–30
–50
–70
–90
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PHASE
GAIN
VSY = 16V
Figure 10. Open-Loop Gain and Phase Shift vs. Frequency
135
90
45
0
–45
–90
–135
06276-010
PHASE (Degrees)
40
20
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
06276-013
Figure 12. CMRR vs. Frequency
100
PSRR–
90
80
70
60
50
PSRR (dB)
40
30
20
10
0
06276-011
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PSRR+/PSRR– CHA
VS = ±8V
PSRR+
06276-014
Figure 13. PSRR vs. Frequency
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 16
Page 8

AD8667
OVERSHOOT (%)
60
50
40
30
20
10
VSY = ±8V
= 10kΩ
R
L
OS+
OS–
VOLTAGE (50mV/DIV)
VSY = ±8V
A
= 1
V
C
= 200pF
L
R
= 10kΩ
L
0
10 100
CAPACITANCE (pF )
Figure 14. Small Signal Overshoot vs. Load Capacitance
600
500
400
300
(µA)
SY
I
200
100
0
–40 –25 –10 5 20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
16V
5V
TEMPERATURE ( °C)
Figure 15. Supply Current vs. Temperature
2.0
= ±8V
V
SY
1.5
1.0
500
TIME (2µs/DIV)
06276-015
06276-018
Figure 17. Small Signal Transient Response
VSY = ±8V
A
= 1
V
C
= 200pF
L
R
= 2kΩ
L
VOLTAGE (2V/ DIV)
TIME (20µs/DIV)
06276-016
06276-019
Figure 18. Large Signal Transient Response
= –100
27
22
17
0.15
0.10
0.05
INPUT VOLTAGE
VSY = ±8V
A
V
0.5
0
–0.5
VOLTAGE (µV/DIV)
–1.0
–1.5
–2.0
012345678910
TIME (1s/DIV)
Figure 16. 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz Input Voltage Noise
06276-017
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 16
INPUT VOLTAGE (50mV/DIV)
–0.05
–0.10
–0.15
–0.20
–0.25
0
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
TIME (20µs/DIV)
12
7
2
–3
–8
–13
OUTPUT VO LTAGE (5V/DIV)
06276-020
Figure 19. Positive Overload Recovery
Page 9

AD8667
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT VO LTAGE (5V/DIV)
0
10k
VSY = ±8V
1k
(Ω)
100
OUT
Z
10
AV = 100 AV = 10 AV = 1
–0.05
–0.10
–0.15
–0.20
–0.25
INPUT VOLTAGE (50mV/DIV)
–0.30
0.05
0
INPUT VOLTAGE
VSY = ±8V
= –100
A
V
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
–0.35
TIME (20µs/DIV)
Figure 20. Negative Overload Recovery
1000
100
VOLTAGE NOISE DENSITY (n V/ Hz)
10
1 10 100 1000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VSY = ±8V
Figure 21. Voltage Noise Density vs. Frequency
600
550
500
450
400
350
300
(µA)
SY
I
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 2 4 6 8 10121416
VS = 0V TO ±8V, –40°C < TA < +125°C
V
+125°C
+85°C
+25°C
–40°C
(V)
SY
Figure 22. Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
–5
06276-021
1
100 1k 10k 100k 1M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
06276-024
Figure 23. Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
CHANNEL SEPARATI ON (dB)
–140
–160
06276-022
100 1k 10k 100k
20kΩ
2kΩ
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VSY = ±8V
06276-025
Figure 24. Channel Separation vs. Frequency
06276-023
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 16
Page 10

AD8667
Specifications at VSY =±2.5 V, unless otherwise noted.
1600
1400
1200
1000
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
VSY = ±2.5V
V
=+5V
S
800
600
400
200
0
–0.1V < V
T
A
=25°C
CM
< +3.5V
VOS(µV)
Figure 25. Input Offset Voltage Distribution
0 50 100 150 200 250–50–100–150–200–250
06276-026
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
GAIN (dB)
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VSY = ±2.5V
Figure 28. Open-Loop Gain and Phase Shift vs. Frequency
135
90
45
0
–45
–90
–135
PHASE (Degrees)
06276-029
40
35
30
25
20
15
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
10
5
0
0123 45
TCV
OS
(µV)
VSY = ±2.5V
–40°C < T
< 125°C
A
Figure 26. Input Offset Voltage Drift Distribution
150
100
50
0
(µs)
OS
V
–50
VSY = ±2.5V
0V < V
CM
T
= 25°C
A
<+3.5V
60
VSY = ±2.5V
AV = 100
40
AV = 10
20
AV = 1
0
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
–20
–40
06276-027
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
06276-030
Figure 29. Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency
10k
VSY = ±2.5V
1k
(Ω)
100
OUT
Z
AV = 100 AV = 10 AV = 1
–100
–150
–200
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5
VCM (V)
Figure 27. Input Offset Voltage vs. Common-Mode Voltage
06276-028
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 16
10
1
100 1k 10k 100k 1M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 30. Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency
06276-031
Page 11

AD8667
VOLTAGE (µV/DIV)
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
V
= ±2.5V
SY
0
CMRR (dB)
140
VSY = ±2.5V
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 31. CMRR vs. Frequency
100
90
80
70
60
50
PSRR (dB)
40
30
20
10
0
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VSY = ±2.5V
PSRR+
PSRR–
Figure 32. PSRR vs. Frequency
80
VSY = ±2.5V
70
R
= 10kΩ
L
60
50
40
30
OVERSHOOT (%)
20
OS–
10
OS+
0
10 100 500
CAPACITANCE (pF )
Figure 33. Small Signal Overshoot vs. Load Capacitance
–2.0
012345678910
06276-032
TIME (1s/DIV)
06276-035
Figure 34. 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz Input Voltage Noise
VSY = ±2.5V
A
= 1
V
C
= 200pF
L
R
= 10kΩ
L
VOLTAGE (50mV/DIV)
TIME (2µs/DIV)
06276-033
06276-036
Figure 35. Small Signal Transient Response
VSY = ±2.5V
A
= 1
V
C
= 200pF
L
R
= 2kΩ
L
VOLTAGE (20mV/DIV)
TIME (10µs/DIV)
06276-034
06276-037
Figure 36. Large Signal Transient Response
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 16
Page 12

AD8667
1000
100
10
VOLTAGE NOISE DENSITY (n V/ Hz)
0
1 10 100 1k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VSY = ±2.5V
Figure 39. Voltage Noise Density vs. Frequency
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
CHANNEL SEPARATI ON (dB)
–140
–160
100 1k 10k 100k
20kΩ
2kΩ
FREQUENCY (Hz)
VSY = ±2.5V
Figure 40. Channel Separation vs. Frequency
06276-040
06276-041
–0.05
–0.10
–0.15
INPUT VOLTAGE (50mV/DIV)
–0.20
–0.25
INPUT VOLTAGE (50mV/DIV)
0.15
0.10
0.05
0.05
–0.05
–0.10
–0.15
–0.20
–0.25
–0.30
–0.35
4.5
VSY = ±2.5V
= –100
A
INPUT VOLTAGE
0
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
TIME (20µ s/DIV)
V
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
–2.0
–2.5
–3.0
–3.5
OUTPUT VO LTAGE (1V/DIV)
06276-038
Figure 37. Positive Overload Recovery
7.0
0
INPUT VOLTAGE
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
TIME (20µ s/DIV)
VSY = ±2.5V
= –100
A
V
6.5
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
–0.5
–1.0
OUTPUT VO LTAGE (1V/DIV)
06276-039
Figure 38. Negative Overload Recovery
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 16
Page 13

AD8667
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
3.20
3.00
2.80
3.20
3.00
2.80
PIN 1
0.95
0.85
0.75
0.15
0.00
COPLANARITY
8
1
0.38
0.22
0.10
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-187-AA
0.65 BSC
5
5.15
4.90
4.65
4
SEATING
PLANE
1.10 MAX
0.23
0.08
8°
0°
0.80
0.60
0.40
Figure 41. 8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP]
(RM-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
5.00 (0.1968)
4.80 (0.1890)
4.00 (0.1574)
3.80 (0.1497)
85
1
6.20 (0.2441)
5.80 (0.2284)
4
1.27 (0.0500)
BSC
0.25 (0.0098)
0.10 (0.0040)
COPLANARITY
0.10
SEATING
PLANE
CONTROLL ING DIMENSI ONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DI MENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRI ATE FOR USE IN DES IGN.
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-012-A A
1.75 (0.0688)
1.35 (0.0532)
0.51 (0.0201)
0.31 (0.0122)
8°
0°
0.25 (0.0098)
0.17 (0.0067)
0.50 (0.0196)
0.25 (0.0099)
1.27 (0.0500)
0.40 (0.0157)
45°
012407-A
Figure 42. 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
Narrow Body
(R-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option Branding
AD8667ARMZ-R2
AD8667ARMZ-REEL
AD8667ARZ
AD8667ARZ-REEL
AD8667ARZ-REEL7
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
1
−40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP] RM-8 A1E
1
1
−40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP] RM-8 A1E
−40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N] R-8
1
−40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N] R-8
1
−40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N] R-8
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 16
Page 14

AD8667
NOTES
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 16
Page 15

AD8667
NOTES
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 16
Page 16

AD8667
NOTES
©2007 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D06276-0-5/07(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 16
 Loading...
Loading...