CMOS Single Supply
SDA
SDB
5
6
V–
+IN B
4
7
OUT A
–IN A
+IN A
V+
OUT B
1
2
3
10
9
8
–IN B
AD8592
(Not to Scale)
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
NC = NO CONNECT
OUT A
2IN A
V1
1IN A
1IN B
2IN B
OUT B
NC
OUT D
2IN D
1IN D
V2
1IN C
2IN C
OUT C
SD
AD8594
Rail-to-Rail Input/Output
a
FEATURES
Single Supply Operation: +2.5 V to +6 V
High Output Current: ⴞ250 mA
Extremely Low Shutdown Supply Current: 100 nA
Low Supply Current: 750 A/Amp
Wide Bandwidth: 3 MHz
Slew Rate: 5 V/s
No Phase Reversal
Very Low Input Bias Current
High Impedance Outputs When in Shutdown Mode
Unity Gain Stable
APPLICATIONS
Mobile Communication Handset Audio
PC Audio
PCMCIA/Modem Line Driving
Battery Powered Instrumentation
Data Acquisition
ASIC Input or Output Amplifier
LCD Display Reference Level Driver
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD8591, AD8592 and AD8594 are single, dual and quad
rail-to-rail input and output single supply amplifiers featuring
250 mA output drive current and a power saving shutdown
mode. The AD8592 includes an independent shutdown function for each amplifier. When both amplifiers are in shutdown
mode the total supply current is reduced to less than 1 µA. The
AD8591 and AD8594 include a single master shutdown func-
tion that reduces total supply current to less than 1 µA. All
amplifier outputs are in a high impedance state when in shutdown mode.
These amplifiers have very low input bias currents, making them
suitable for integrators and diode amplification. Outputs are
stable with virtually any capacitive load. Supply current is less
than 750 µA per amplifier in active mode.
Applications for these amplifiers include audio amplification for
portable computers, portable phone headsets, sound ports, sound
cards and set-top boxes. The AD859x family is capable of driving
heavy capacitive loads such as LCD panel reference levels.
The ability to swing rail-to-rail at both the input and output
enables designers to buffer CMOS DACs, ASICs and other
wide output swing devices in single supply systems.
The AD8591, AD8592 and AD8594 are specified over the indus-
trial (–40°C to +85°C) temperature range. The AD8591, single,
is available in the tiny 6-lead SOT package. The AD8592, dual, is
available in the 10-lead µSOIC surface mount package. The
AD8594, quad, is available in 16-lead narrow SOIC and 16-lead
TSSOP packages.
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Operational Amplifiers with Shutdown
AD8591/AD8592/AD8594
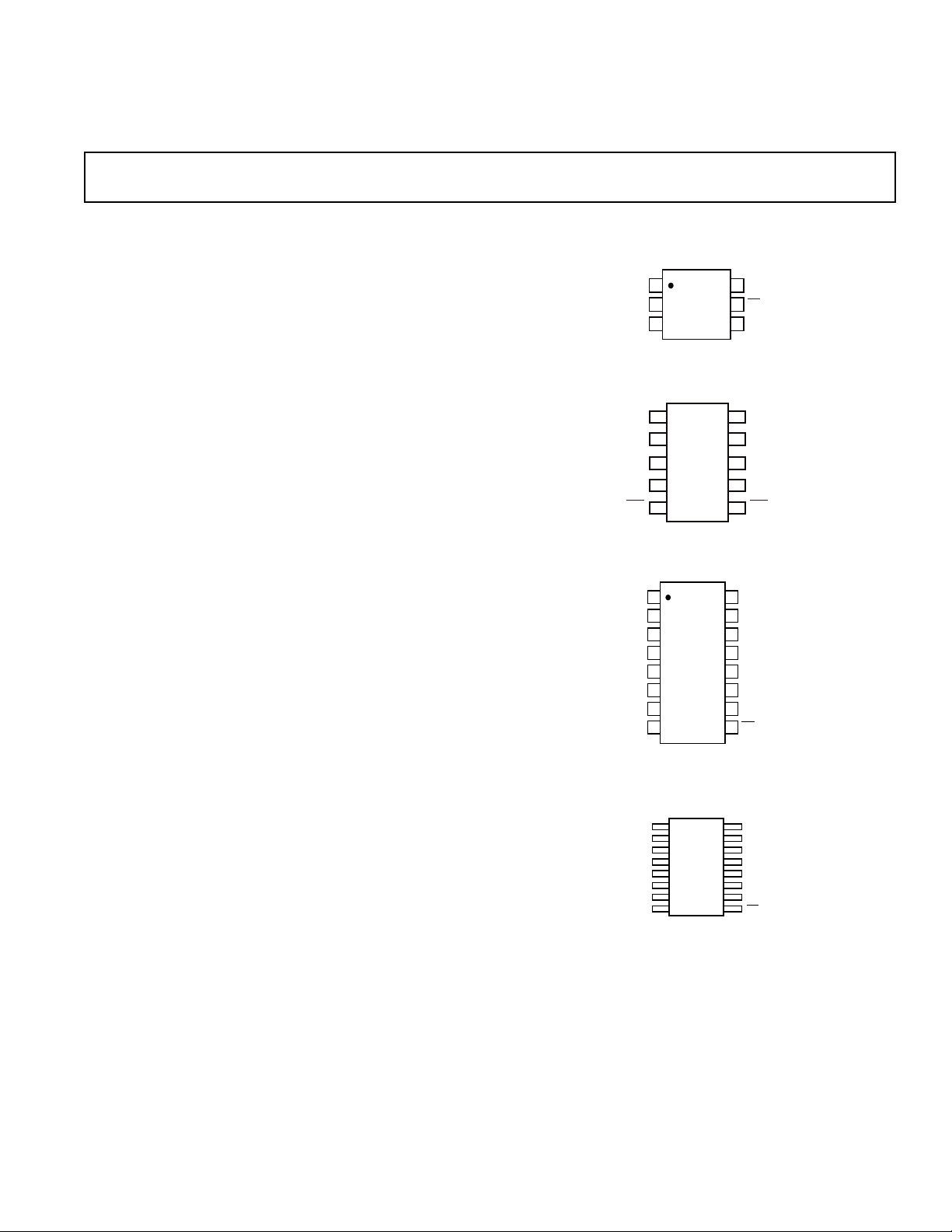
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
6-Lead SOT
(RT Suffix)
1
OUT A
2
V2
AD8591
3
1IN A
10-Lead SOIC
(RM Suffix)
16-Lead Narrow SOIC
(R Suffix)
16-Lead TSSOP
(RU Suffix)
1
OUT A
2IN A
1IN A
1IN B
2IN B
OUT B
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1999
1
V1
AD8594
89
NC
NC = NO CONNECT
6
V1
5
SD
2IN A
4
OUT D
16
2IN D
1IN D
V2
+IN C
2IN C
OUT C
SD
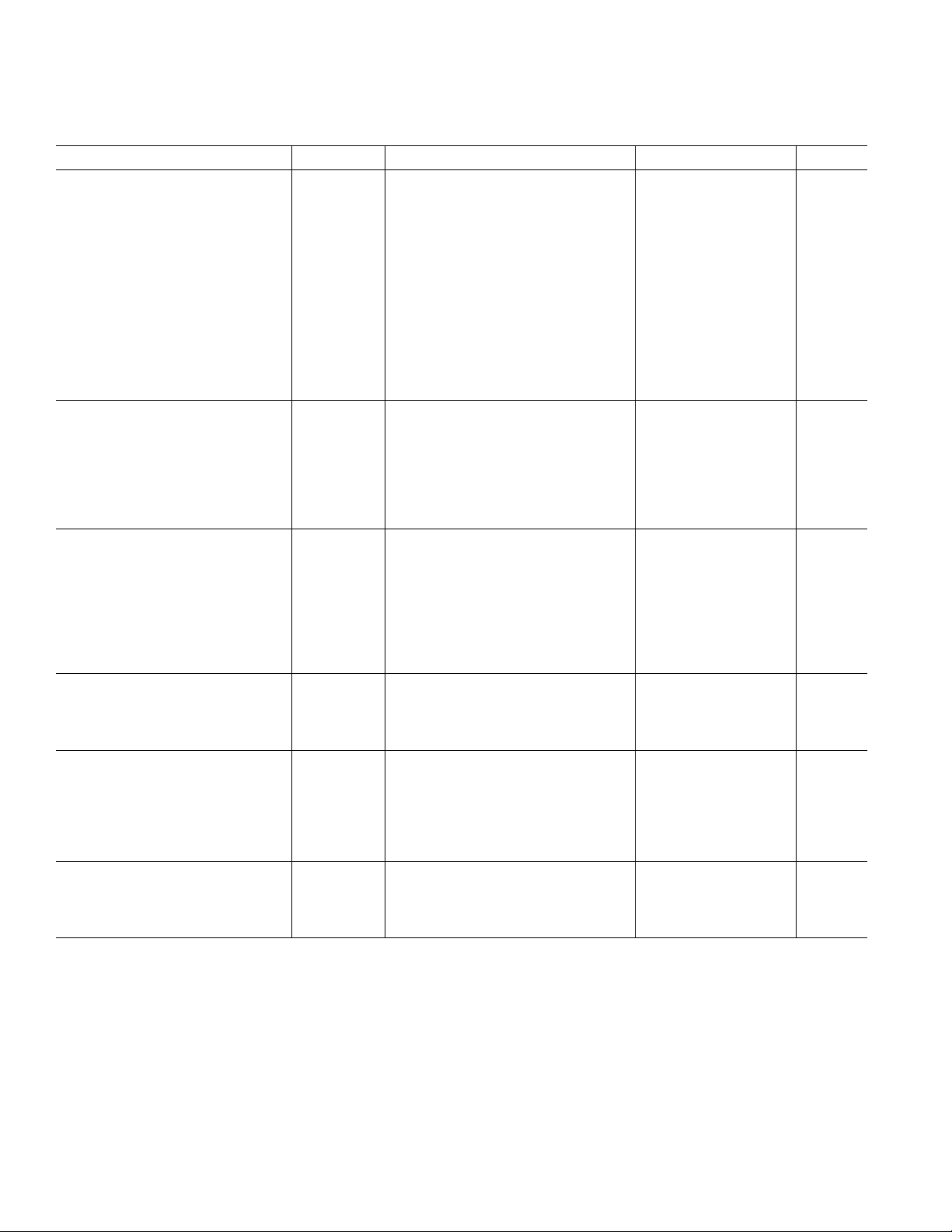
AD8591/AD8592/AD8594–SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VS = +2.7 V, VCM = +1.35 V, TA = +25ⴗC unless otherwise noted)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS␣
Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current I
Input Offset Current I
B
OS
OS
–40°C < T
–40°C < T
–40°C < T
< +85°C30mV
A
< +85°C60pA
A
< +85°C30pA
A
25 mV
550 pA
125 pA
Input Voltage Range 0 +2.7 V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR V
Large Signal Voltage Gain A
Offset Voltage Drift ∆V
Bias Current Drift ∆I
VO
/∆T20µV/°C
OS
/∆T 50 fA/°C
B
= 0 V to +2.7 V 38 45 dB
CM
R
= 2 kΩ , V
L
= +0.3 V to +2.4 V 25 V/mV
O
Offset Current Drift ∆IOS/∆T 20 fA/°C
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High V
OH
IL = 10 mA +2.55 +2.61 V
–40°C to +85°C +2.5 V
Output Voltage Low V
OL
IL = 10 mA 60 100 mV
–40°C to +85°C 125 mV
Output Current I
Open-Loop Impedance Z
OUT
OUT
f = 1 MHz, A
= 1 60 Ω
V
±250 mA
POWER SUPPLY␣
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR VS = +2.5 V to +6 V 45 55 dB
Supply Current/Amplifier I
Supply Current Shutdown Mode I
I
I
SY
SD
SD1
SD2
VO = 0 V 1 mA
–40°C < T
< +85°C 1.25 mA
A
All Amplifiers Shut Down 0.1 1 µA
–40°C < T
< +85°C1µA
A
Amplifier 1 Shut Down (AD8592) 1.4 mA
Amplifier 2 Shut Down (AD8592) 1.4 mA
SHUTDOWN INPUTS
Logic High Voltage V
Logic Low Voltage V
Logic Input Current I
INH
INL
IN
–40°C < TA < +85°C +1.6 V
–40°C < TA < +85°C +0.5 V
–40°C < TA < +85°C1µA
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE␣
Slew Rate SR R
Settling Time t
S
= 2 kΩ 3.5 V/µs
L
To 0.01% 1.4 µs
Gain Bandwidth Product GBP 2.2 MHz
Phase Margin Φo 67 Degrees
Channel Separation CS f = 1 kHz, R
= 2 kΩ 65 dB
L
NOISE PERFORMANCE␣
Voltage Noise Density e
n
f = 1 kHz 45 nV/√Hz
f = 10 kHz 30 nV/√Hz
Current Noise Density i
Specifications subject to change without notice.
n
f = 1 kHz 0.05 pA/√Hz
–2–
REV. A
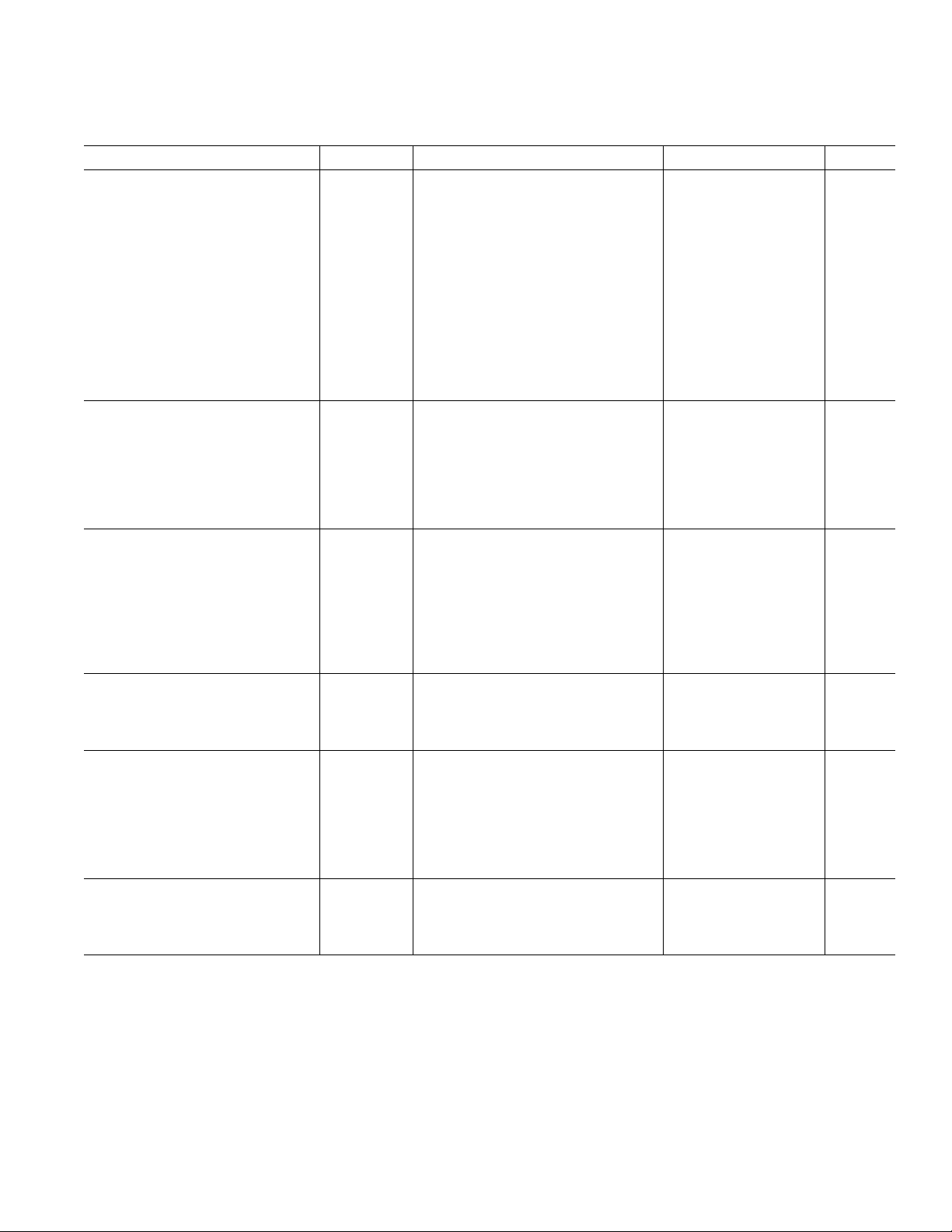
AD8591/AD8592/AD8594
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VS = +5.0 V, VCM = +2.5 V, TA = +25ⴗC unless otherwise noted)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS␣
Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current I
Input Offset Current I
B
OS
OS
–40°C < T
–40°C < T
–40°C < T
< +85°C30mV
A
< +85°C60pA
A
< +85°C30pA
A
225 mV
550 pA
125 pA
Input Voltage Range 0+5V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR V
Large Signal Voltage Gain A
Offset Voltage Drift ∆V
Bias Current Drift ∆I
VO
/∆T –40°C < TA < +85°C20µV/°C
OS
/∆T 50 fA/°C
B
= 0 V to +5 V 38 47 dB
CM
R
= 2 kΩ , V
L
= +0.5 V to +4.5 V 15 30 V/mV
O
Offset Current Drift ∆IOS/∆T 20 fA/°C
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High V
OH
IL = 10 mA +4.9 +4.94 V
–40°C to +85°C +4.85 V
Output Voltage Low V
OL
IL = 10 mA 50 100 mV
–40°C to +85°C 125 mV
Output Current I
Open-Loop Impedance Z
OUT
OUT
f = 1 MHz, A
= 1 40 Ω
V
±250 mA
POWER SUPPLY␣
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR VS = +2.5 V to +6 V 45 55 dB
Supply Current/Amplifier I
Supply Current-Shutdown Mode I
I
I
SY
SD
SD1
SD2
VO = 0 V 1.25 mA
–40°C < T
< +85°C 1.75 mA
A
All Amplifiers Shut Down 0.1 1 µA
–40°C < T
< +85°C1µA
A
Amplifier 1 Shut Down (AD8592) 1.6 mA
Amplifier 2 Shut Down (AD8592) 1.6 mA
SHUTDOWN INPUTS
Logic High Voltage V
Logic Low Voltage V
Logic Input Current I
INH
INL
IN
–40°C < TA < +85°C +2.4 V
–40°C < TA < +85°C +0.8 V
–40°C < TA < +85°C1µA
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE␣
Slew Rate SR R
Full-Power Bandwidth BW
Settling Time t
P
S
= 2 kΩ 5V/µs
L
1% Distortion 325 kHz
To 0.01% 1.6 µs
Gain Bandwidth Product GBP 3 MHz
Phase Margin Φo 70 Degrees
Channel Separation CS f = 1 kHz, R
= 10 kΩ 65 dB
L
NOISE PERFORMANCE␣
Voltage Noise Density e
n
f = 1 kHz 45 nV/√Hz
f = 10 kHz 30 nV/√Hz
Current Noise Density i
Specifications subject to change without notice.
n
f = 1 kHz 0.05 pA/√Hz
–3–REV. A
AD8591/AD8592/AD8594
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +6 V
Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . GND to V
Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±6 V
Output Short Circuit
Duration to GND
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . Observe Derating Curves
Storage Temperature Range
R, RT, RM, RU Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range
AD8591/AD8592/AD8594 . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Junction Temperature Range
R, RT, RM, RU Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering, 60 sec) . . . . . . . +300°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
For supplies less than ±5 V the differential input voltage is limited to the supplies.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD8591/AD8592/AD8594 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage
may occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
1
Package Type
6-Lead SOT-23 (RT) 230 92 °C/W
S
10-Lead µSOIC (RM) 200 44 °C/W
16-Lead SOIC (R) 120 36 °C/W
16-Lead TSSOP (RU) 180 35 °C/W
NOTE
1
θJA is specified for worst case conditions, i.e., θ
for surface mount packages.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Description Option
AD8591ART –40°C to +85°C 6-Lead SOT-23 RT-6
AD8592ARM –40°C to +85°C 10-Lead µSOIC RM-10
AD8594AR –40°C to +85°C 16-Lead SOIC R-16A
AD8594ARU –40°C to +85°C 16-Lead TSSOP RU-16
1
JA
JC
is specified for device in socket
JA
Units
Typical Performance Characteristics
1k
VS = +2.7V
= +258C
T
A
100
10
1
∆OUTPUT VOLTAGE – mV
0.1
SOURCE
0.1 1 10
LOAD CURRENT – mA
SINK
100
1k0.01
Figure 1. Output Voltage to Supply
Rail vs. Load Current
10k
VS = +5V
= +258C
T
A
1k
100
10
∆OUTPUT VOLTAGE – mV
1
0.1
Figure 2. Output Voltage to Supply
Rail vs. Load Current
SOURCE
0.1 1 10
LOAD CURRENT – mA
SINK
100
0.90
0.85
0.80
0.75
0.70
0.65
0.60
0.55
SUPPLY CURRENT/AMPLIFIER – mA
1k0.01
0.50
240 220
0 20406080
TEMPERATURE – 8C
VS = +5V
VS = +2.7V
100
Figure 3. Supply Current per
Amplifier vs. Temperature
–4–
REV. A
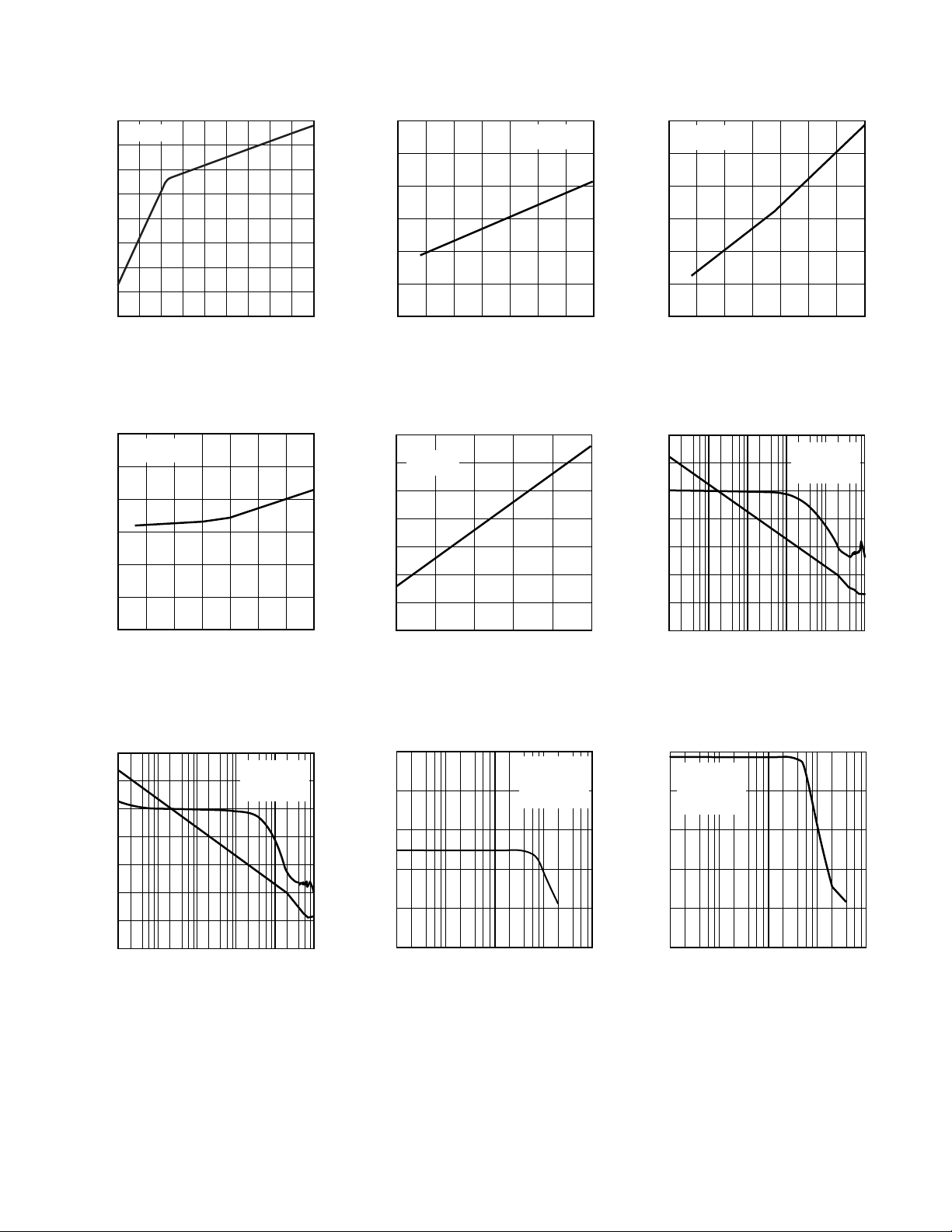
AD8591/AD8592/AD8594
g
0.8
TA = +258C
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
SUPPLY CURRENT/AMPLIFIER – mA
0
0.75 1.25 3
1.75 2.25 2.75
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – 6Volts
Figure 4. Supply Current per
Amplifier vs. Supply Voltage
4
VS = +2.7V, +5V
V
= VS/2
CM
3
2
1
0
21
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT – pA
22
23
24
25
26
27
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE – mV
28
250 235
215
5254565
TEMPERATURE – 8C
VS = +5V
V
= +2.5V
CM
Figure 5. Input Offset Voltage vs.
Temperature
8
VS = +5V
7
T
= +258C
A
6
5
4
3
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
2
8
VS = +2.7V, +5V
V
= VS/2
CM
7
6
5
4
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
3
2
85
250 235
215
5254565
TEMPERATURE – 8C
85
Figure 6. Input Bias Current vs.
Temperature
80
60
40
20
0
GAIN – dB
VS = +2.7V
R
= NO LOAD
L
T
= +258C
A
45
90
135
180
PHASE SHIFT – Degrees
22
250 235
215
5254565
TEMPERATURE – 8C
85
Figure 7. Input Offset Current vs.
Temperature
80
60
40
20
0
GAIN – dB
1k 10k 100M
100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY – Hz
VS = +5V
R
= NO LOAD
L
T
= +258C
A
Figure 10. Open-Loop Gain and
Phase vs. Frequency
45
90
rees
135
180
PHASE SHIFT – De
1
01 5
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE – Volts
234
Figure 8. Input Bias Current vs.
Common-Mode Voltage
5
4
3
2
OUTPUT SWING – V p-p
1
0
1k 10k 10M
FREQUENCY – Hz
VS = +2.7V
R
= 2kV
L
T
= +258C
A
V
= 2.5V p-p
IN
100k 1M
Figure 11. Closed-Loop Output
Voltage Swing vs. Frequency
1k 10k 100M
100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY – Hz
Figure 9. Open-Loop Gain and Phase
vs. Frequency
5
VS = +5V
R
= 2kV
L
4
T
= +258C
A
V
= 4.9V p-p
IN
3
2
OUTPUT SWING – V p-p
1
0
1k 10k 10M
100k 1M
FREQUENCY – Hz
Figure 12. Closed-Loop Output
Voltage Swing vs. Frequency
–5–REV. A
 Loading...
Loading...