Page 1
140 MHz to 1000 MHz
FEATURES
140 MHz to 1000 MHz operating frequency
+2.5 dBm P1dB @ 800 MHz
−155 dBm/Hz noise floor
0.5 degree RMS phase error (IS95)
0.2 dB amplitude balance
Single 2.7 V to 5.5 V supply
Pin-compatible with AD8346 and AD8349
16-lead TSSOP_EP package
APPLICATIONS
Cellular communication systems
W-CDMA/CDMA/GSM/PCS/ISM transceivers
Fixed broadband access systems LMDS/MMDS
Wireless LAN
Wireless local loop
Digital TV/CATV modulators
Single sideband upconverter
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Quadrature Modulator
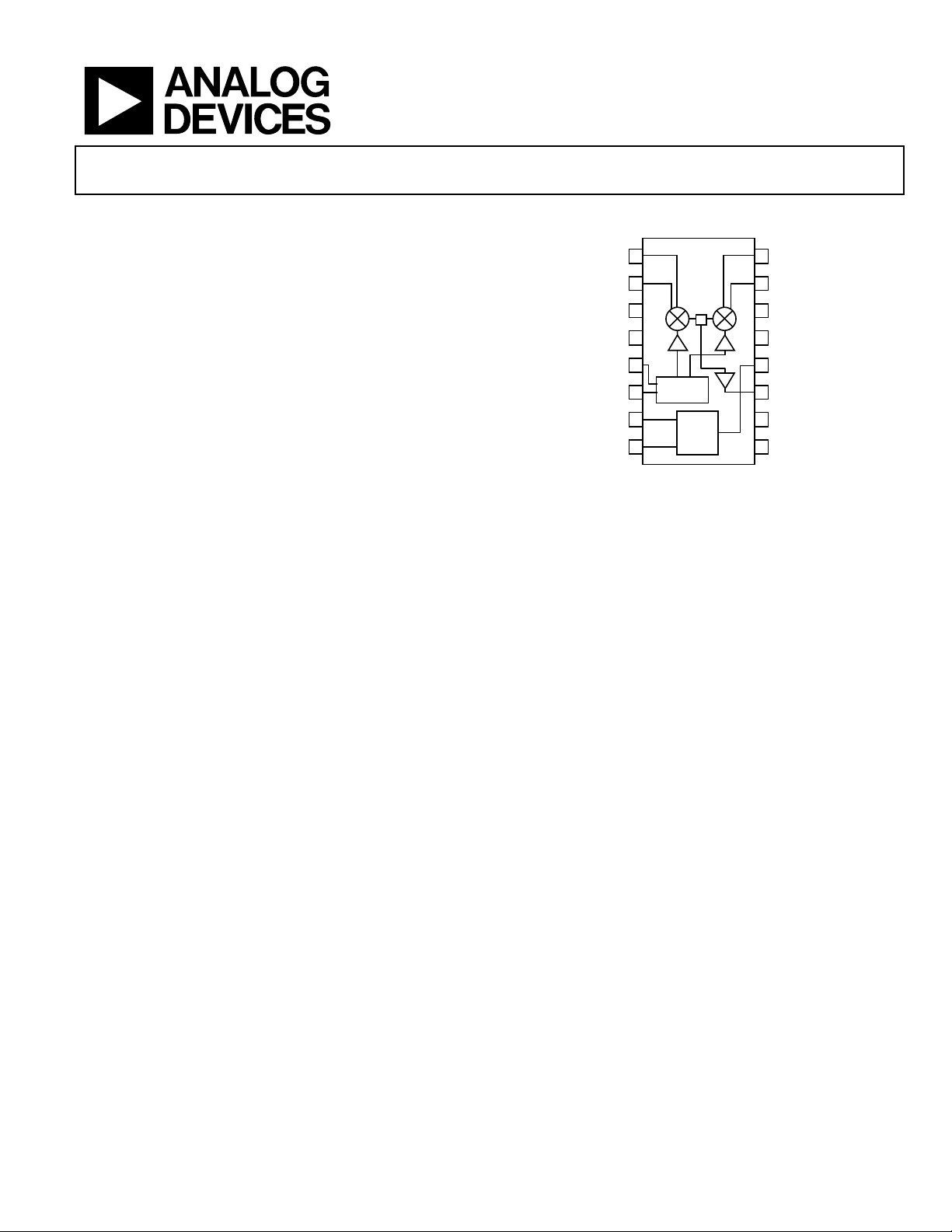
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
IBBP
IBBN
COM3
COM1
LOIN
LOIP
VPS1
ENBL
APPLICATIONS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
AD8345
PHASE
SPLITTER
BIAS
Figure 1.
AD8345
16
QBBP
15
QBBN
14
13
12
11
10
9
COM3
COM3
VPS2
VOUT
COM2
COM3
00932-001
+
The AD8345 is a silicon RFIC quadrature modulator, designed
for use from 140 MHz to 1000 MHz. Its excellent phase
accuracy and amplitude balance enable the high performance
direct modulation of an IF carrier.
The AD8345 accurately splits the external LO signal into two
quadrature components through the polyphase phase splitter
network. The I and Q LO components are mixed with the
baseband I and Q differential input signals. Finally, the outputs
of the two mixers are combined in the output stage to provide a
single-ended 50 Ω drive at VOUT.
The AD8345 modulator can be used as the IF transmit
modulator in digital communication systems such as GSM and
PCS transceivers. It can also directly modulate an LO signal to
produce QPSK and various QAM formats for 900 MHz
communication systems as well as digital TV and CATV
systems.
Additionally, this quadrature modulator can be used with direct
digital synthesizers in hybrid phase-locked loops to generate
signals over a wide frequency range with millihertz resolution.
The AD8345 modulator is supplied in a 16-lead TSSOP_EP
package. Its performance is specified over a −40°C to +85°C
temperature range. This device is fabricated on Analog Devices’
advanced silicon bipolar process.
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 © 2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

AD8345
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Basic Connections .......................................................................... 12
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Product Description......................................................................... 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 4
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 4
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 5
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 6
Equivalent Circuits......................................................................... 10
Circuit Description......................................................................... 11
Overview...................................................................................... 11
LO Interface................................................................................. 11
Differential Voltage-to-Current Converter............................. 11
LO Drive...................................................................................... 12
LO Frequency Range ................................................................. 12
Baseband I and Q Channel Drive ............................................ 13
Reduction of LO Leakage.......................................................... 13
Single-Ended I and Q Drive...................................................... 13
RF Output.................................................................................... 14
Application with TxDAC®......................................................... 14
Soldering Information............................................................... 15
Evaluation Board........................................................................ 15
Characterization Setups................................................................. 17
SSB Setup..................................................................................... 17
Modulated Waveform Setup ..................................................... 18
CDMA IS95................................................................................. 18
WCDMA 3GPP.......................................................................... 18
GSM ............................................................................................. 18
Mixers .......................................................................................... 11
Differential-to-Single-Ended Converter ................................. 11
Bias ............................................................................................... 11
REVISION HISTORY
12/05—Rev. A to Rev. B
Updated Format..................................................................Universal
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 19
4/05—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Updated Format..................................................................Universal
Change to Part Name .........................................................Universal
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 19
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 19
7/01—Revision 0: Initial Version
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 19
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 19
Rev. B | Page 2 of 20
Page 3
AD8345
SPECIFICATIONS
VS = 5 V; LO = −2 dBm @ 800 MHz; 50 Ω source and load impedances; I and Q inputs 0.7 V ±0.3 V on each side for a 1.2 V p-p
differential input, I and Q inputs driven in quadrature @ 1 MHz baseband frequency. T
Table 1.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
RF OUTPUT
Operating Frequency
1
140 1000 MHz
Output Power 0.5 dBm 140 MHz
0.5 dBm 220 MHz
−3 −1 +2 dBm 800 MHz
Output P1dB 2.5 dBm
Noise Floor −155 dBm/Hz 20 MHz offset from LO, all BB inputs at 0.7 V
Quadrature Error 0.5 Degree rms CDMA IS95 setup (see Figure 38)
I/Q Amplitude Balance 0.2 dB CDMA IS95 setup (see Figure 38)
LO Leakage −41 dBm 140 MHz
−40 dBm 220 MHz
−42 −33 dBm 800 MHz
Sideband Rejection −33 dBc 140 MHz
−48 −40 dBc 220 MHz
−42 −34 dBc 800 MHz
Third Order Distortion −52 dBc
Second Order Distortion −60 dBc
Equivalent Output IP3 25 dBm
Equivalent Output IP2 59 dBm
Output Return Loss (S22) −20 dB
RESPONSE TO CDMA IS95 See Figure 38
BASEBAND SIGNALS
ACPR −72 dBc
EVM 1.3 %
Rho 0.9995
LO INPUT
LO Drive level −10 −2 0 dBm
LOIP Input Return Loss (S11)
2
−5 dB No termination on LOIP, LOIN at ac ground
−9 dB 50 Ω terminating resistor, differential drive via balun
BASEBAND INPUTS
Input Bias Current 10 μA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
DC Common Level 0.6 0.7 0.8 V
Bandwidth (3 dB) 80 MHz Full power (0.7 V ±0.3 V on each input, see Figure 4)
ENABLE
Turn-On 2.5 μs Enable high to output within 0.5 dB of final value
Turn-Off 1.5 μs Enable low to supply current dropping below 2 mA
ENBL High Threshold (Logic 1) +VS/2 V
ENBL Low Threshold (Logic 0) +VS/2 V
POWER SUPPLIES
Voltage 2.7 5.5 V
Current Active 50 65 78 mA
Current Standby 70 μA
1
For information on operation below 140 MHz, see Figure 29.
2
See the LO Interface section for more details on input matching.
= 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
A
Rev. B | Page 3 of 20
Page 4
AD8345
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage VPS1, VPS2 5.5 V
Input Power LOIP, LOIN (re 50 Ω) 10 dBm
IBBP, IBBN, QBBP, QBBN 0 V, 2.5 V
Internal Power Dissipation 500 mW
θJA (Exposed Paddle Soldered Down) 30°C/W
θJA (Exposed Paddle not Soldered Down) 95°C/W
Maximum Junction Temperature 150°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) 300°C
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
Rev. B | Page 4 of 20
Page 5
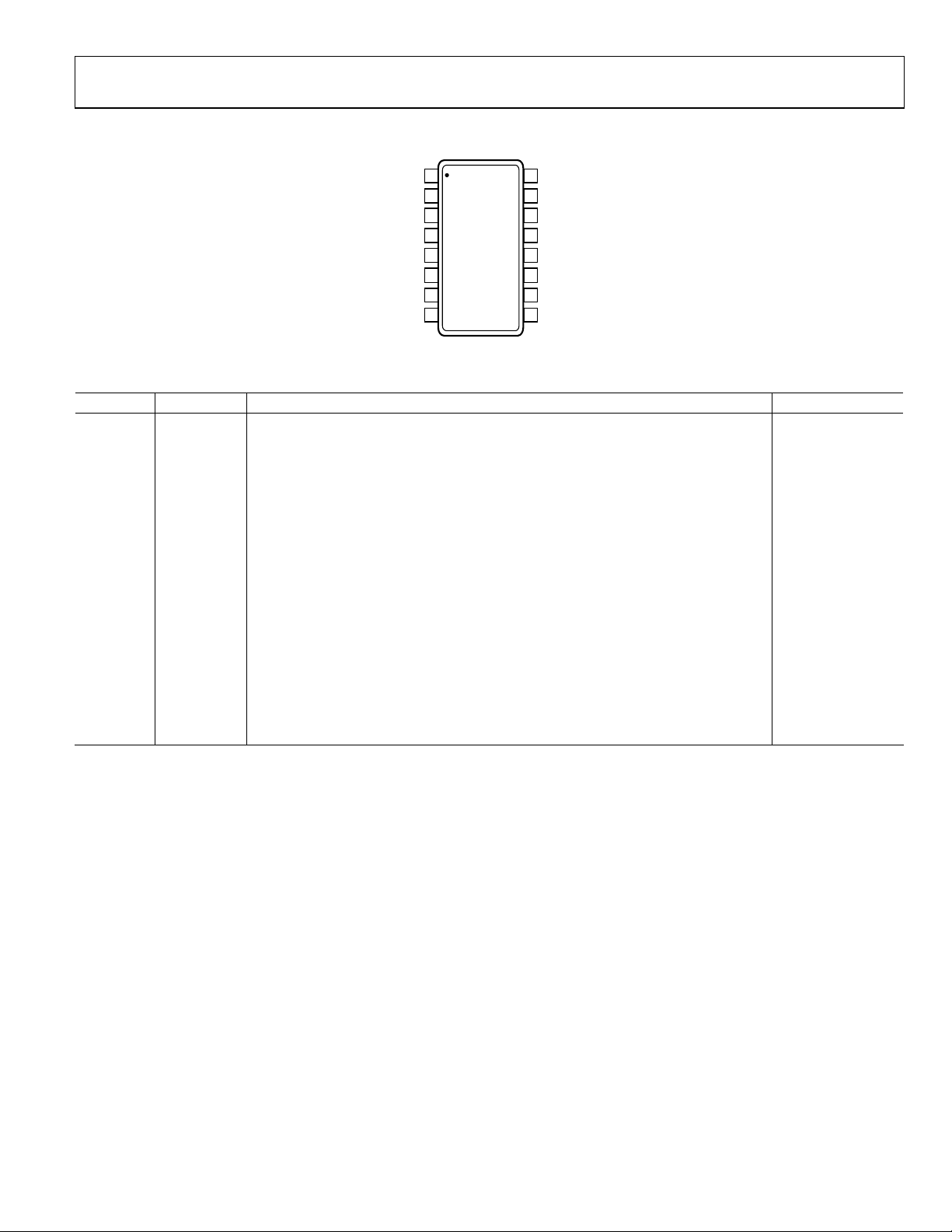
AD8345
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
1
IBBP
2
IBBN
3
COM3
COM1
LOIN
LOIP
VPS1
ENBL COM3
AD8345
4
TOP VIEW
(Not t o Scal e)
5
6
7
8
16
QBBP
15
QBBN
14
COM3
13
COM3
12
VPS2
11
VOUT
10
COM2
9
00932-002
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
Table 3. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description Equivalent Circuit
1, 2 IBBP, IBBN
I Channel Baseband Differential Input Pins. These high impedance inputs should be
Circuit A
dc-biased to approximately 0.7 V. Nominal characterized ac swing is 0.6 V p-p on each
pin (0.4 V to 1 V). This gives a differential drive of 1.2 V p-p. Inputs are not self-biasing, so
external biasing circuitry must be used in ac-coupled applications.
3, 9, 13, 14 COM3 Ground Pin for Input V-to-I Converters and Mixer Core.
4 COM1 Ground Pin for the LO Phase Splitter and LO Buffers.
5, 6 LOIN, LOIP
Differential LO Drive Pins. Internal dc bias (approximately 1.8 V @ V
= 5 V) is supplied.
S
Circuit B
Pins must be ac-coupled. Single-ended or differential drive is permissible.
7 VPS1
Power Supply Pin for the Bias Cell and LO Buffers. This pin should be decoupled using
local 1000 pF and 0.01 μF capacitors.
8 ENBL Enable Pin. A high level enables the device; a low level puts the device in sleep mode. Circuit C
10 COM2 Ground Pin for the Output Stage of Output Amplifier.
11 VOUT 50 Ω DC-Coupled RF Output. Pin should be ac-coupled. Circuit D
12 VPS2
Power Supply Pin for Baseband Input Voltage to Current Converters and Mixer Core.
This pin should be decoupled using local 1000 pF and 0.01 μF capacitors.
15, 16 QBBN, QBBP
Q Channel Baseband Differential Input Pins. Inputs should be dc-biased to approxi-
Circuit A
mately 0.7 V. Nominal characterized ac swing is 0.6 V p-p on each pin (0.4 V to 1 V). This
gives a differential drive level of 1.2 V p-p. Inputs are not self-biasing, so external biasing
circuitry must be used in ac-coupled applications.
Rev. B | Page 5 of 20
Page 6
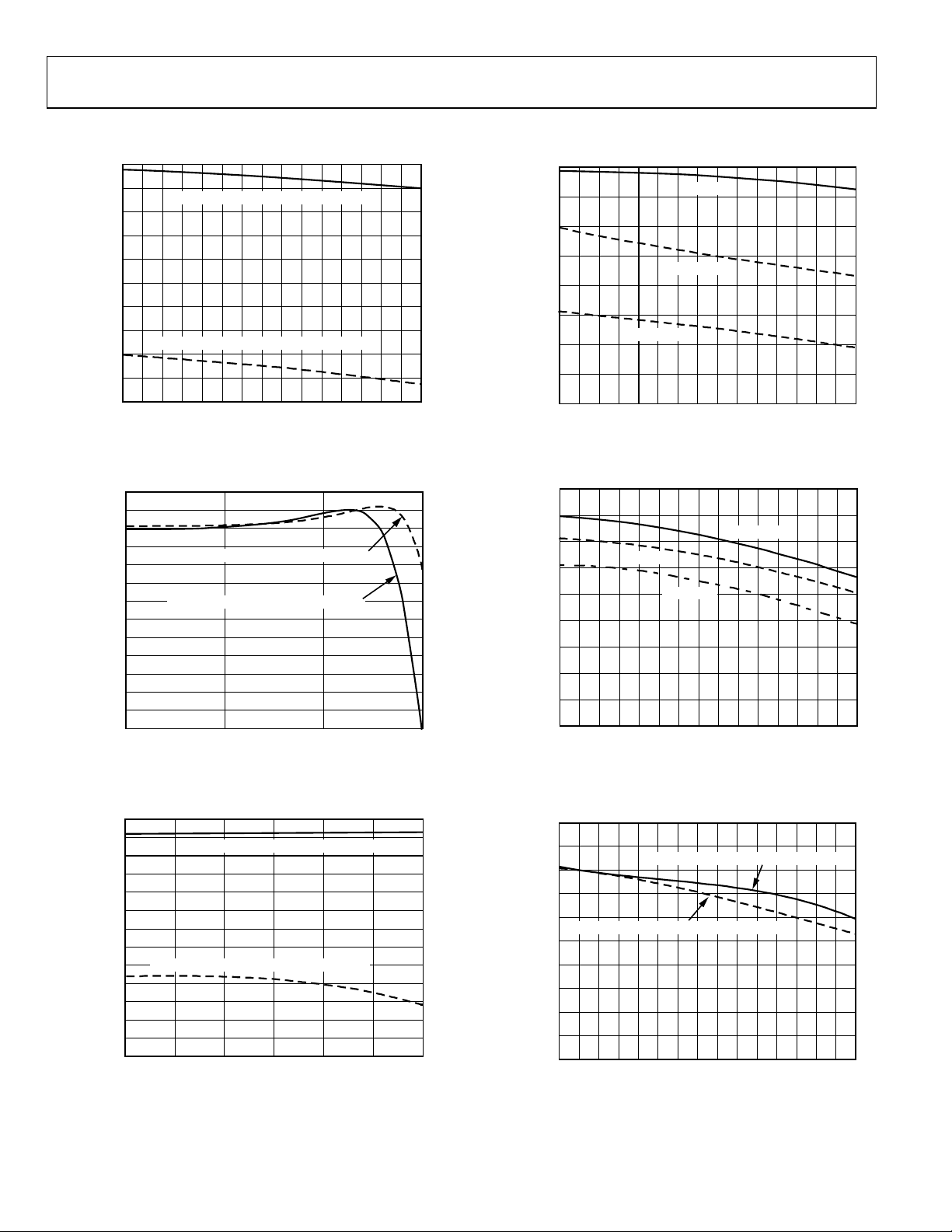
AD8345
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
0
–2
–4
–6
–8
–10
–12
SSB POWER (dBm)
–14
–16
–18
–20
250
Figure 3. Single Sideband (SSB) Output Power (P
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTI AL INPUT = 200mV p-p
V
S
300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800 850 900 9501000
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
) vs. LO Frequency (FLO)
OUT
(I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature at Baseband Frequency (F
= 25°C)
T
A
1.0
0.5
0.0
–0.5
VS = 2.7V, 5V DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
–1.0
–1.5
OUTPUT P OWER VARIATION ( d B)
–2.0
–2.5
–3.0
–3.5
–4.0
–4.5
–5.0
–5.5
0.1
V
= 5V DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
S
110
BASEBAND FREQ UENC Y ( M Hz )
Figure 4. I and Q Input Bandwidth
= 25°C, FLO = 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm,
(T
A
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature)
0
–2
–4
–6
–8
–10
–12
–14
–16
SSB POWER (dBm)
–18
–20
–22
–24
–26
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
V
S
–40
–20 20 60
= 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm, FBB = 1 MHz,
(F
LO
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
040
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 5. SSB P
vs. Temperature
OUT
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature)
00932-007
) = 1 MHz;
BB
00932-008
100
00932-009
80
0
TA = –40°C
TA = +25°C
= +85°C
A
500 800
LO FRE QUENCY (MHz)
SSB OUTPUT P 1d B ( dBm)
–10
–12
–14
–16
–2
–4
–6
–8
T
250
350 650 950300 400 450 550 600 700 750 850 900 1000
Figure 6. SSB Output 1 dB Compression Point (OP1dB) vs. F
= 2.7 V, LO Level = −2 dBm,
(V
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature, F
S
4.0
3.5
SSB OUTPUT P1dB (dBm)
–0.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
250
T
= +25°C
A
350 650 950300 400 450 550 600 700 750 850 900 1000
500 800
LO FREQUENCY (MHz )
T
= –40°C
A
= +85°C
T
A
= 1 MHz)
BB
Figure 7. SSB Output 1 dB Compression Point (OP1dB) vs. F
(VS = 5 V, LO Level = −2 dBm,
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature, F
–40
–41
–42
–43
–44
VS = 2.7V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
–45
–46
–47
–48
CARRIER FEEDT HROUGH (dBm)
–49
–50
250
350 650 950300 400 450 550 600 700 750 850 900 1000
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
500 800
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 8. Carrier Feedthrough vs. F
= 1 MHz)
BB
LO
(LO Level = −2 dBm, TA = 25°C)
LO
LO
00932-010
00932-011
00932-012
Rev. B | Page 6 of 20
Page 7

AD8345
–30
–32
–34
–36
–38
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
V
S
–20 20 40 60 80
0
TEMPERATURE (°C)
00932-013
CARRIER FEEDTHROUGH (d Bm)
–40
–42
–44
–46
–48
–50
–40
Figure 9. Carrier Feedthrough vs. Temperature
= 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm)
(F
LO
30
28
26
24
22
20
18
16
14
12
PERCENTAGE
10
T = +85
T = –40
8
6
4
2
0
–82 –78 –74 –70 –66 –62 –58 –54 –5 0
–86
CARRIER FEEDTHRO UGH (dBm)
Figure 10. Carrier Feedthrough Distribution at Temperature Extremes After
SIDEBAND SUPPRE S S ION (dBc)
Feedthrough Nulled to <−65 dBm at T
= 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm)
(F
LO
–30
–32
–34
–36
–38
–40
–42
–44
–46
–48
–50
V
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
S
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 11. Sideband Suppression vs. F
= 25°C, LO Level = −2 dBm, FBB = 1 MHz,
(T
A
= 25°C
A
LO
00932-015
950900850800750700650600550500450400350300250
1000
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature)
00932-014
–26
–28
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
–30
–32
–34
–36
–38
–40
SIDEBAND SUPPRESSIO N (dBc)
–42
V
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTI AL INPUT = 200mV p-p
S
–44
BASEBAND FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 12. Sideband Suppression vs. F
(TA = 25°C, FLO = 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm,
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature)
–35
–36
SIDEBAND SUPPRESSION (dBc)
–37
–38
–39
–40
–41
–42
–43
–44
–45
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
V
S
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 13. Sideband Suppression vs. Temperature
(F
= 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm, FBB = 1 MHz,
LO
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature)
–20
–25
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
–30
–35
–40
–45
THIRD ORD E R DISTORTION (dBc)
–50
–55
–60
–65
0
V
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
S
5 101 52 02 53 03 54 04 55 0
BASEBAND FREQUENC Y (MHz)
Figure 14. Third Order Distortion vs. F
= 25°C, FLO = 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm,
(T
A
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature)
454035302520151050
50
BB
6040200–20–40
BB
80
00932-016
00932-017
00932-018
Rev. B | Page 7 of 20
Page 8

AD8345
–45
80
–50
–55
= 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
V
S
–60
–65
–70
THIRD ORDER DISTOR TION (dBc)
–75
–80
V
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
S
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 15. Third Order Distortion vs. Temperature
= 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm, FBB = 1 MHz,
(F
LO
I and Q Inputs Driven in Quadrature)
–10
–15
–20
–25
–30
–35
–40
–45
–50
–55
THIRD O R DE R D ISTORTION (dBc)
–60
–65
–70
BASEBAND DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE (V p-p)
SSB P
OUT
THIRD O RDER DISTORTIO N
Figure 16. Third Order Distortion and SSB P
Volta ge (T
= 25°C, FLO = 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm, FBB = 1 MHz, VS = 2.7 V)
A
–5
–10
–15
–20
–25
–30
–35
–40
–45
–50
–55
THIRD O RDE R DISTOR T I ON (dBc)
–60
–65
–70
BASEBAND DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE (V p-p)
SSB P
OUT
THIRD ORDER DISTORT ION
Figure 17. Third Order Distortion and SSB P
Volta ge (T
= 25°C, FLO = 800 MHz, LO Level = −2 dBm, FBB = 1 MHz, VS = 5 V)
A
6040200–20–40
vs. Baseband Differential Input
OUT
vs. Baseband Differential Input
OUT
80
3.02.52.01.51.00.50.0
3.02.52.01.51.00.50.0
–2
–4
–6
–8
–10
–12
–14
–16
–18
–20
–22
–24
–26
4
2
0
–2
–4
–6
–8
–10
–12
–14
–16
–18
–20
–22
75
70
65
60
55
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
50
45
00932-019
40
= 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V p-p
V
S
V
= 2.7V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 200mV p-p
S
–40
–20 20406080
0
TEMPERATURE (°C)
00932-022
Figure 18. Power Supply Current vs. Temperature
1GHz
SMITH CHART
NORMALIZED
WITH 50Ω
SSB OUTPUT P O WER (dBm)
00932-020
WITH 100Ω
1GHz
TO 50Ω
LOIN NO BALUN
OR TERMINATION
250MHz
00932-023
Figure 19. Smith Chart of LOIN Port S11 (LOIP Pin AC-Coupled to Ground);
Curves with Balun and External Termination Resistors Also Shown
= 5 V, TA = 25°C)
(V
S
0
–5
–10
–15
–20
SSB OUTPUT POWER (dBm)
00932-021
RETURN LOSS (dB)
VS = 2.7V
–25
V
= 5V
–30
250
300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800 850 900 9501000
S
FREQUENCY (M Hz )
Figure 20. Return Loss (S22) of VOUT Output ( T
= 25°C)
A
00932-024
Rev. B | Page 8 of 20
Page 9

AD8345
–150
–151
–152
–153
NOISE FLOOR (dBm/Hz)
–154
–155
–156
–157
–158
–159
–160
–9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2
–10
LO LEVEL (dBm)
V
= 5V
S
Figure 21. Noise Floor vs. LO Input Power
= 25°C, FLO = 800 MHz, VS = 5 V, All I and Q Inputs Are DC-Biased to 0.7 V)
(T
A
Noise Measured at 20 MHz Offset from Carrier
00932-025
CARRIER FEEDTHROUGH (dBm)
–36
–38
–40
–42
–44
–46
–48
–50
–10
–9 –8 –7 –6 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2
VS = 5.5V
LO LEVEL (dBm)
Fig ure 2 2. LO Fe edth roug h vs. LO Inp ut Pow er
= 25°C, LO = 800 MHz, VS = 5.5 V)
(T
A
00932-026
Rev. B | Page 9 of 20
Page 10

AD8345
EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS
INPUT
VPS2
BUFFER
CURRENT
MIRROR
Figure 23. Circuit A
TO MIXER
CORE
ENBL
00932-003
VPS2
Figure 25. Circuit C
100kΩ
100kΩ
100kΩ
TO BIAS FOR
STARTUP/
SHUTDOWN
00932-005
VPS2
40Ω
VOUT
40Ω
Figure 26. Circuit D
00932-006
LOIN
LOIP
VPS1
Figure 24. Circuit B
PHASE
SPLITTER
CONTINUES
00932-004
Rev. B | Page 10 of 20
Page 11

AD8345
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
OVERVIEW
The AD8345 can be divided into the following sections: local
oscillator (LO) interface, mixer, differential voltage-to-current
(V-to-I) converter, differential-to-single-ended (D-to-S)
converter, and bias. A block diagram of the part is shown in
Figure 27.
LOIP
LOIN
IBBP
IBBN
QBBP
QBBN
Figure 27. AD8345 Block Diagram
The LO interface generates two LO signals at 90° of phase
difference with each other, to drive two mixers in quadrature.
Baseband signals are converted into current form in the
differential V-to-I converters, feeding into the two mixers. The
outputs of the mixers are combined to feed the differential-tosingle-ended converter, which provides a 50 Ω output interface.
Bias currents to each section are controlled by the enable
(ENBL) signal. A detailed description of each section follows.
PHASE
SPLITTER
Σ
OUT
00932-027
DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE-TO-CURRENT CONVERTER
In this circuit, each baseband input pin is connected to an op amp
driving a transistor connected as an emitter follower. A resistor
between the two emitters maintains a varying current proportional
to the differential input voltage through the transistor. These
currents are fed to the two mixers in differential form.
MIXERS
There are two double-balanced mixers, one for the in-phase
channel (I channel) and one for the quadrature channel
(Q channel). Each mixer uses the Gilbert-cell design with four
cross-connected transistors. The bases of the transistors are
driven by the LO signal of the corresponding channel. The
output currents from the two mixers are summed together in
two load resistors. The signal developed across the load resistors
is sent to the differential-to-single-ended converter.
DIFFERENTIAL-TO-SINGLE-ENDED CONVERTER
The differential-to-single-ended converter consists of two
emitter followers driving a totem-pole output stage whose
output impedance is established by the emitter resistors in the
output transistors. The output of this stage is connected to the
output pin (VOUT).
LO INTERFACE
The LO interface consists of interleaved stages of polyphase
phase splitters and buffer amplifiers. The polyphase phase
splitter contains resistors and capacitors connected in a circular
manner to split the LO signal into I and Q paths in precise
quadrature with each other. The signal on each path goes
through a buffer amplifier to make up for the loss and high
frequency roll-off. The two signals then go through another
polyphase network to enhance the quadrature accuracy. The
broad operating frequency range (140 MHz to 1000 MHz) is
achieved by staggering the RC time constants of each stage of
the phase splitters. The outputs of the second phase splitter are
fed into the driver amplifiers for the mixers’ LO inputs.
BIAS
A band gap reference circuit based on the Δ-VBE principle
generates the proportional-to-absolute temperature (PTAT) as
well as temperature-stable currents used by the different
sections as references. When the band gap reference is disabled
by pulling down the voltage at the ENBL pin, all other sections
are shut off accordingly.
Rev. B | Page 11 of 20
Page 12

AD8345
BASIC CONNECTIONS
IP
IN
C6
1000pF
T1
C4
0.01μF
1
2
34
C7
1000pF
C3
1000pF
+V
LO
5
R1
ETC1-1-13
50Ω
S
Figure 28. Basic Connections
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
IBBP
IBBN
COM3
COM1
LOIN
LOIP
VPS1
ENBL
AD8345
QBBP
QBBN
COM3
COM3
VPS2
VOUT
COM2
COM3
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
C1
1000pF
1000pF
C2
0.01μF
C5
QP
QN
+V
VOUT
S
00932-028
The basic connections for operating the AD8345 are shown in
Figure 28. A single power supply of between 2.7 V and 5.5 V is
applied to the VPS1 pin and the VPS2 pin. A pair of ESD
protection diodes is connected internally between the VPS1 pin
and the VPS2 pin so these must be tied to the same potential.
Both pins should be individually decoupled using 1000 pF and
0.01 μF capacitors, located as close as possible to the device. For
normal operation, the enable pin (ENBL) must be pulled high.
The turn-on threshold for ENBL is V
/2. COM1 to COM3
S
should all be tied to the same low impedance ground plane.
LO DRIVE
In Figure 28, a 50 Ω resistor to ground combines with the
device’s high input impedance to provide an overall input
impedance of approximately 50 Ω (see
LO port input impedance). For maximum LO suppression at
the output, a differential LO drive is recommended. In
Figure 28, this is achieved using a balun (M/A-COM part
number ETC1-1-13).
The outputs of the balun are ac-coupled to the LO inputs, which
have a bias level of approximately 1.8 V dc. An LO drive level of
−2 dBm is recommended for lowest output noise. Higher levels
degrade linearity while lower levels tend to increase the noise
floor slightly. For example, reducing the LO power from −2 dBm
to −10 dBm increases the noise floor by approximately 0.3 dB
(see
Figure 21).
The LO input pins can be driven single-ended at the expense of
slightly higher LO leakage. LOIN is ac-coupled to ground using
a capacitor and LOIP is driven through a coupling capacitor
from a (single-ended) 50 Ω source. (This scheme could also be
reversed with the drive signal being applied to LOIN.)
Figure 19 for a plot of
LO FREQUENCY RANGE
The frequency range on the LO input is limited by the internal
quadrature phase splitter. The phase splitter generates drive
signals for the internal mixers which are 90° out of phase
relative to one another.
Outside of the specified LO frequency range of 140 MHz to 1 GHz,
this quadrature accuracy degrades, resulting in decreased sideband
suppression. See
LO frequency from 250 MHz to 1 GHz.
sideband suppression of a typical device from 70 MHz to 300 MHz.
0
–5
–10
–15
–20
–25
–30
–35
–40
SIDEBAND SUPPRE S S ION (dBc)
–45
–50
Figure 29. Typical Lower Frequency Sideband Suppression Performance
Figure 11 for a plot of sideband suppression vs.
Figure 29 shows the
VS = 5V, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT = 1.2V
60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 280 300
40
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
00932-029
Rev. B | Page 12 of 20
Page 13

AD8345
BASEBAND I AND Q CHANNEL DRIVE
The I channel and Q channel baseband inputs should be driven
differentially. This is convenient as most modern high-speed
DACs have differential outputs. For optimal performance at
V
= 5 V, the drive signal should be a 1.2 V p-p differential
S
signal with a bias level of 0.7 V; that is, each input should swing
from 0.4 V to 1 V. If the AD8345 is being run on a lower supply
voltage, then the peak-to-peak voltage on the I and Q channel
inputs must be reduced to avoid input clipping. For example, at
a supply voltage of 2.7 V, a 200 mV p-p differential drive is
recommended. This results in a corresponding reduction in
output power (see
Figure 3). The I and Q inputs have a large
input bandwidth of approximately 80 MHz. At lower baseband
input levels, the input bandwidth increases (see
Figure 4).
If the baseband signal has a high peak-to-average ratio (such as
CDMA or WCDMA), then the rms signal strength must be
backed off from this peak level in order to prevent clipping of
the signal peaks.
Clipping of signal peaks tends to increase signal leakage into
adjacent channels. Backing off the I and Q signal strength, in
the manner recommended, reduces the output power by a
corresponding amount. This also applies to multicarrier
applications where the per-carrier output power is lower by
3 dB for each doubling of the number of output carriers.
The I and Q inputs have high input impedances because they
connect directly to the bases of PNP transistors. If a dc-coupled
filter is being used between a DAC and the modulator inputs,
then the filter must be terminated with the appropriate
resistance. If the filter is differential, then the termination
resistor should be connected across the I and Q differential
inputs.
REDUCTION OF LO LEAKAGE
Because the I and Q signals are being effectively multiplied with
the LO, any internal offset voltages on these inputs result in
leakage of the LO. The nominal LO leakage of −42 dBm, which
results from these internal offset voltages, can be reduced further
by applying offset compensation voltages on the I and Q inputs.
(Note that LO feedthrough is reduced by varying the differential
offset voltages on the I and Q inputs, not by varying the nominal
bias level of 0.7 V.) The reduction is easily accomplished by
programming (and then storing) the appropriate DAC offset
code. This does, however, require dc coupling the path from the
DAC to the I and Q inputs. (DC coupling is also advantageous
from the perspective of I and Q input biasing if the DAC is
capable of delivering a bias level of 0.7 V.)
The procedure for reducing the LO feedthrough is simple. In
order to isolate the LO in the output spectrum, a single
sideband configuration is recommended (set I and Q signals to
sine and cosine waves at, for example, 100 kHz; set LO to
F
− 100 kHz). An offset voltage is applied from the I DAC
RF
until the LO leakage reaches a trough. With this offset level
held, an offset voltage is applied to the Q DAC until a (lower)
trough is reached.
LO leakage compensation holds up well over temperature.
Figure 10 shows the effect of temperature on LO leakage after
compensation at ambient.
Compensated LO leakage degrades somewhat as the frequency
is moved away from the frequency at which the compensation
was performed. This is due to the effects of LO to RF output
leakage, which is not a result of offsets on the I and Q inputs.
SINGLE-ENDED I AND Q DRIVE
Where only single-ended I and Q signals are available, a
differential amplifier such as the AD8132 or AD8138 can be
used to generate the required differential drive signal for the
AD8345.
Although most DACs have differential outputs, using a singleended, low-pass filter between the dual DAC and the I and Q
inputs can be more desirable from the perspective of
component count and cost. As a result, the output signal from
the filter must be converted back to differential mode and
possibly be rebiased to 0.7 V common mode.
Figure 30 shows a circuit that converts a ground-referenced,
single-ended signal to a differential signal and adds the required
0.7 V bias voltage. Two AD8132 differential op amps configured
for unity gain are used. With a 50 Ω input impedance, this
circuit is configured to accept a signal from a 50 Ω source (for
example, a low-pass filter). The input impedance can be easily
changed by replacing the 49.9 Ω shunt resistor (and the
corresponding 24.9 Ω resistor on the inverting input) with the
appropriate value. The required dc-bias level is conveniently
added to the signal by applying 0.7 V to the V
differential amplifiers.
Differential amplifiers, such as the AD8132 and AD8138, can
also be used to implement active filters. For more information
on this topic, refer to the data sheets of these devices.
pins of the
OCM
Rev. B | Page 13 of 20
Page 14

AD8345
+5V
10kΩ
1.5kΩ
348Ω
+
0.1μF10μF
0.01μF
1000pF
1000pF
0.01μF
49.9Ω
24.9Ω
49.9Ω
24.9Ω
348Ω
348Ω
348Ω
0.1μF
348Ω
0.1μF
I
IN
Q
IN
8
2
1
348Ω
348Ω
8
2
1
348Ω
3
AD8132
6
–5V
+5V
3
AD8132
6
–5V
5
4
0.1μF
+
+
0.1μF10μF
5
4
+
10μF0.1μF
10μF
VPS1 VPS2
IBBP
IBBN
QBBP
QBBN
COM1 COM2 COM3
PHASE
SPLITTER
Σ
AD8345
VOUT
LOIP
LOIN
00932-030
Figure 30. Single-Ended 1Q Drive Circuit
Note that this circuit assumes that the single-ended I and Q
signals are ground-referenced. Any differential dc-offsets result
in increased LO leakage at the output of the AD8345.
It is possible to drive the baseband inputs with a single-ended
signal biased to 0.7 V, with the unused inputs being biased to a
dc level of 0.7 V. However, this mode of operation is not recommended because any dc level difference between the bias level
of the drive signal and the dc level on the unused input
(including the effect of temperature drift) results in increased
LO leakage. In addition, the maximum output power is reduced
by 6 dB.
RF OUTPUT
The RF output is designed to drive a 50 Ω load but should be ac
coupled as shown in
in quadrature by 1.2 V p-p signals, then the resulting output
power is approximately −1 dBm (see
impedance is very close to 50 Ω. As a result, no additional
matching circuitry is required if the output is driving a 50 Ω
load.
Figure 28. If the I and Q inputs are driven
Figure 3). The RF output
APPLICATION WITH TxDAC®
Figure 31 shows the AD8345 driven by the AD9761 TxDAC.
(Any of the devices in the Analog Devices’ TxDAC family can
also be used in this application.)
The I and Q DACs generate differential output currents of 0 mA
to 10 mA and 10 mA to 0 mA, respectively. The combination of
140 Ω resistors shunted to ground off each DAC output, along
with 210 Ω resistors shunted between each differential DAC
pair, produces a baseband signal into the AD8345 I and Q
inputs that has a differential peak-to-peak swing of 1.2 V with a
dc common-mode bias of 700 mV.
Rev. B | Page 14 of 20
Page 15

AD8345
AVDDDVDD DCOM
"I"
DAC
"Q"
DAC
REFIOFS ADJ
0.1μF
DAC
DATA
INPUTS
SELECT
WRITE
CLOCK
MUX
CONTROL
LATCH
"I"
LATCH
"Q"
SLEEP
2⋅
AD9761
2⋅
R
2kΩ
SET
Figure 31. AD8345/TxDAC Interface
SOLDERING INFORMATION
The AD8345 is packaged in a 16-lead TSSOP_EP package. For
optimum thermal conductivity, the exposed pad can be
soldered to the exposed metal of a ground plane. This results in
a junction-to-air thermal impedance (θ
) of 30°C/W. However,
JA
soldering is not necessary for safe operation. If the exposed pad
is not soldered down, then the θ
is equal to 95°C/W.
JA
EVALUATION BOARD
Figure 32 shows the schematic of the AD8345 evaluation board.
Note that uninstalled components are marked as open. This is a
4-layer board, with the two center layers used as ground plane,
and top and bottom layers used as signal and power planes.
IOUTA
IOUTB
QOUTA
QOUTB
IBBP
210Ω
140Ω140Ω
210Ω
140Ω140Ω
IBBN
QBBP
QBBN
The board is powered by a single supply (V
VPS1 VPS2
Σ
PHASE
SPLITTER
AD8345
) in the range 2.7 V
S
VOUT
LOIP
LOIN
00932-031
to 5.5 V. The power supply is decoupled by 0.01 μF and 1000 pF
capacitors. The circuit closely follows the basic connection
schematic with SW1 in Position B. If SW1 is in Position A, the
enable pin (ENBL) is pulled to ground by a 10 kΩ resistor, and
the device is in its power-down mode.
All connectors are SMA-type. The I and Q inputs are dc-coupled to
allow a direct connection to a dual DAC with differential outputs.
Resistor pads are provided in case termination at the I and Q inputs
is required. The local oscillator input (LO) is terminated to approximately 50 Ω with an external 50 Ω resistor to ground. A 1:1 wideband transformer (ETC1-1-13) provides a differential drive to the
AD8345’s differential LO input.
LO
VPOS
R6
50Ω
C3
0.01μF
ENBL
IP
IN
5
T1
ETC1-1-13
R7
0Ω
R8
10kΩ
(OPEN)
1
2
34
C4
1000pF
A
B
VPOS
R1
(OPEN)
R2
C1
1000pF
C2
1000pF
SW1
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
AD8345
IBBP
IBBN
COM3
COM1
LOIN
LOIP
VPS1
ENBL
Figure 32. Evaluation Board Schematic
Rev. B | Page 15 of 20
QBBP
QBBN
COM3
COM3
VPS2
VOUT
COM2
COM3
R9
(OPEN)
16
15
R10
(OPEN)
14
C5
1000pF
R14
(OPEN)
R11
0Ω
R12
0Ω
13
12
11
C7
1000pF
107
9
R15
(OPEN)
QP
QN
C6
0.01μF
VPOS
VOUT
00932-032
Page 16

AD8345
00932-033
Figure 33. Evaluation Board Silkscreen
00932-034
Figure 34. Layout of Evaluation Board, Top Layer
00932-035
Figure 35. Layout of Evaluation Board, Bottom Layer
Rev. B | Page 16 of 20
Page 17

AD8345
CHARACTERIZATION SETUPS
SSB SETUP
Essentially, two primary setups are used to characterize the
AD8345. These setups are shown in
Figure 37 shows the setup used to evaluate the product as a
single sideband modulator. The interface board converts the
single-ended I and Q inputs from the arbitrary function
generator to differential inputs with a dc bias of approximately
0.7 V. The interface board also provides connections for power
supply routing. The HP34970A and its associated plug-in 34901
are used to monitor power supply currents and voltages being
supplied to the AD8345 characterization board. Two HP34907
plug-ins are used to provide additional miscellaneous dc and
control signals to the interface board. The LO inputs are driven
directly by an RF signal generator, and the output is measured
directly with a spectrum analyzer. With the I channel driven
with a sine wave and the Q channel driven with a cosine wave,
the lower sideband is the single sideband output. The typical
SSB output spectrum is shown in
Figure 37 and Figure 38.
Figure 36.
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
AMPLI TUDE (dBm )
–70
–80
–90
–100
CENTER = 900MHz SPAN = 1MHz
Figure 36. Typical SSB Output Spectrum
00932-037
IEEE
HP34970A
D1 D2 D3
34901 34907 34907
D1 D2 D3
TEKAFG2020
OUTPUT_1
OUTPUT_2
ARB FUNCTIO N G EN
HP8593E
RF I/P
SWEEP OUT
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
IEEE
28V
IEEE
00932-036
IEEE
HP3631
HP8648C
+15V MAX
+25V MAX
–25V MAX
RFOUTIEEE
IEEE
PC CONTROLLER
COM
VPS1
INTERFACE
BOARD
VN
GND
VP
P1 IN IP QP QN
IP QP
IN
LO
ENBL
AD8345
CHARACTERIZATION
BOARD
P1
I_IN
Q_IN
QN
VOUT
Figure 37. Characterization Board SSB Test Setup
Rev. B | Page 17 of 20
Page 18

AD8345
MODULATED WAVEFORM SETUP
To evaluate the AD8345 with modulated waveforms, the setup
shown in
Figure 38 is used. A Rohde & Schwarz AMIQ signal
generator with differential outputs is used to generate the
baseband signals. For all measurements, the input level on each
baseband input pin is 0.7 V ±0.3 V peak. The output is
measured with a Rohde & Schwarz FSIQ spectrum/vector
analyzer.
PC CONTROL
IN IP QP QN
IEEE
PC CONTRO LLER
HP3631
IN
LO
ENBL
+15V MAX
+25V MAX
–25V MAX
IEEE
HP8648C
RFOUT
IEEE
Figure 38. Test Setup for Evaluating AD8345 with Modulated Waveforms
AMIQ
IP QP
AD8345
CHARACTERIZATION
BOARD
COM
VOUT
P1
QN
FSIQ
RF I/P
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
IEEE
CDMA IS95
To measure ACPR, the I and Q input signals used are generated
with Pilot channel (Walsh Code 00), Sync channel (WC 32), Paging
channel (WC 01), and six Traffic (WC 08, 09, 10, 11, 12, 13)
channels active.
this configuration.
To perform EVM, Rho, phase, and amplitude balance
measurements, the I and Q input signals used are generated
with only the Pilot channel (Walsh Code 00) active.
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
AMPLITUDE (d Bm)
–80
–90
–100
–110
Figure 39 shows the typical output spectrum for
CH PWR = –12.41dBm
ACP UP = –72.9dB
ACP LOW = –72.9dB
CENTER = 880MHz SPAN = 7.5MHz
Figure 39. Typical IS95 Output Spectrum
00932-039
00932-038
WCDMA 3GPP
To evaluate the AD8345 for WCDMA, the 3GPP standard is
used with a chip rate of 3.84 MHz. The plot in
Figure 40 is an
ACPR plot of the AD8345 using Test Model 1 from the 3GPP
specification with 64 channels active.
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
AMPLI TUDE (dBm )
–80
–90
–100
–110
CENTER = 380MHz SPAN = 14.7MHz
Figure 40. Typical AD8345 WCDMA 3GPP Output Spectrum
CH PWR = –10.95dBm
ACP UP = –52.51dB
ACP LOW = –52. 41dB
00932-040
GSM
To compare the AD8345 output to the GSM transmit mask, I
and Q signals are generated using MSK modulation, GSM
differential coding, a Gaussian filter, and a symbol rate of
270.833 kHz. The transmit mask is manually generated on the
FSIQ using the GSM BTS specification for reference. The plot in
Figure 41 shows that the AD8345 meets the GSM transmit
mask requirements.
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
AMPLITUDE (d Bm)
–70
–80
–90
–100
CENTER = 900MHz SPAN = 1MHz
Figure 41. Typical AD8345 GSM Output Spectrum
00932-041
Rev. B | Page 18 of 20
Page 19

AD8345
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
5.10
5.00
4.90
BOTTOM
VIEW
0.15
0.00
16
TOP
VIEW
1.20 MAX
SEATING
PLANE
0.65
BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-153-ABT
0.30
0.19
9
4.50
6.40
4.40
BSC
4.30
81
1.05
1.00
0.80
0.20
0.09
8°
0°
EXPOSED
PAD
(Pins Up)
0.75
0.60
0.45
3.00
SQ
Figure 42. 16-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline with Exposed Pad (TSSOP_EP)
(RE-16-2)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD8345ARE −40°C to +85°C 16-Lead TSSOP with Exposed Pad, Tube RE-16-2
AD8345ARE-REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 16-Lead TSSOP with Exposed Pad, 7" Tape and Reel RE-16-2
AD8345AREZ
AD8345AREZ-RL7
AD8345-EVAL Evaluation Board
1
Z = Pb-free part.
1
1
−40°C to +85°C 16-Lead TSSOP with Exposed Pad, Tube RE-16-2
−40°C to +85°C 16-Lead TSSOP with Exposed Pad, 7" Tape and Reel RE-16-2
Rev. B | Page 19 of 20
Page 20

AD8345
NOTES
© 2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
C00932-0-12/05(B)
Rev. B | Page 20 of 20
 Loading...
Loading...