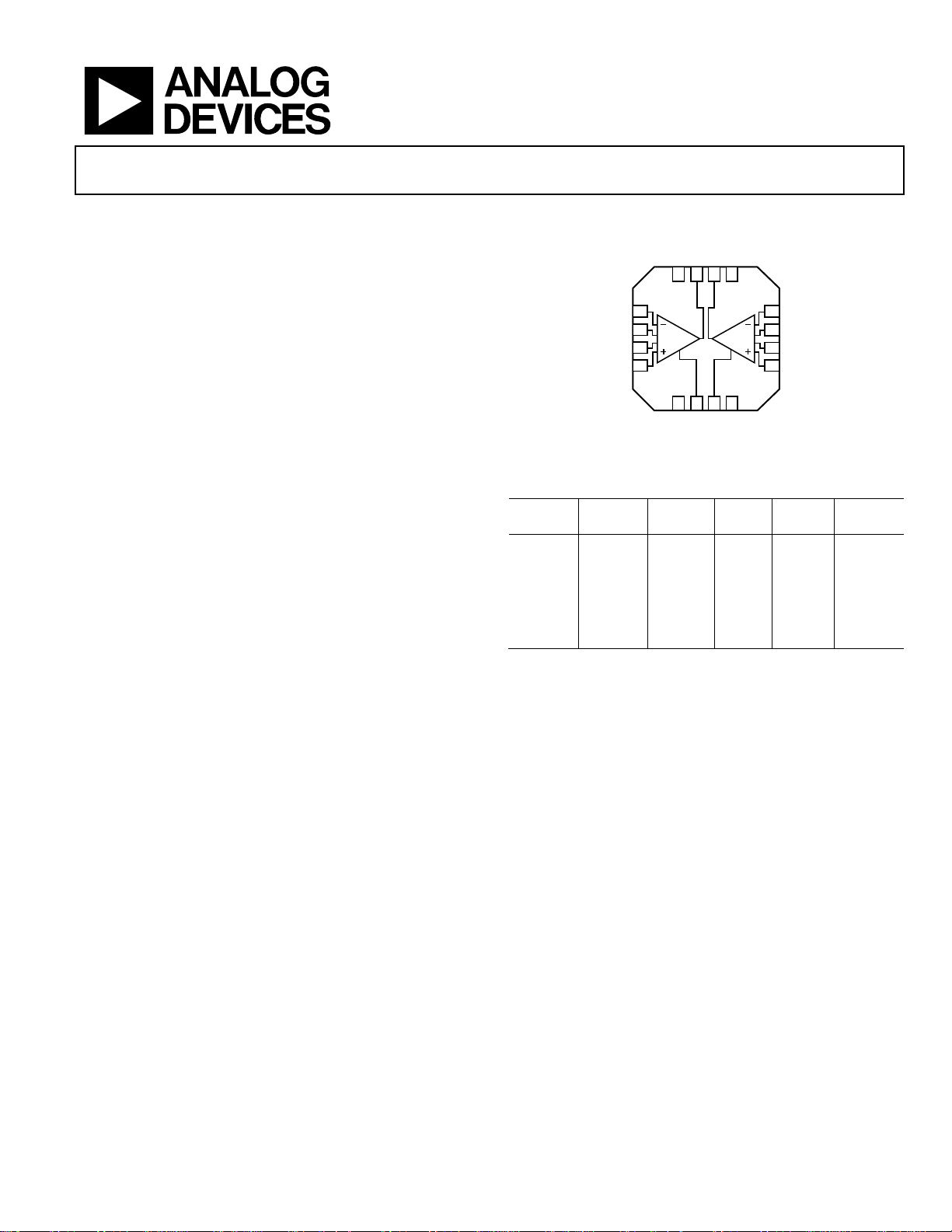
Precision, Dual-Channel, JFET Input,
FEATURES
Two channels in a small 4 mm × 4 mm LFCSP
Custom LFCSP package with hidden paddle
Permits routing and vias underneath package
Allows full bias current performance
Low input currents
10 pA maximum input bias current (B Grade)
0.6 pA maximum input offset current (B Grade)
High CMRR
100 dB CMRR (minimum), G = 10 (B Grade)
90 dB CMRR (minimum) to 10 kHz, G = 10 (B Grade)
Excellent ac specifications and low power
1.5 MHz bandwidth (G = 1)
14 nV/√Hz input noise (1 kHz)
Slew rate: 2 V/μs
750 μA quiescent current per amplifier
Versatility
Rail-to-rail output
Input voltage range to below negative supply rail
4 kV ESD protection
4.5 V to 36 V single supply
±2.25 V to ±18 V dual supply
Gain set with single resistor (G = 1 to 1000)
APPLICATIONS
Medical instrumentation
Precision data acquisition
Transducer interfaces
Differential drives for high resolution input ADCs
Remote sensors
Rail-to-Rail Instrumentation Amplifier
AD8224
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
REF1
S
OUT2
–V
13141516
S
–V
REF2
Mil
Grade
12
11
10
9
Low
Power
–IN2
R
G2
R
G2
+IN2
06286-001
Digital
Gain
+VSOUT1
AD8224
1
–IN1
2
R
G1
3
R
G1
4
+IN1
5678
S
+V
Figure 1.
Table 1. In Amps and Difference Amplifiers by Category
High
Perform
Low
Cost
High
Voltage
AD82201 AD85531 AD628 AD620 AD6271 AD82311
AD8221 AD6231 AD629 AD621 AD8250
AD8222 AD524 AD8251
AD526 AD85551
AD624 AD85561
AD85571
1
Rail-to-rail output.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD8224 is the first single-supply, JFET input instrumentation
amplifier available in the space-saving 16-lead, 4 mm × 4 mm
LFCSP. It requires the same board area as a typical single
instrumentation amplifier yet doubles the channel density
and offers a lower cost per channel without compromising
performance.
Designed to meet the needs of high performance, portable
instrumentation, the AD8224 has a minimum common-mode
rejection ratio (CMRR) of 86 dB at dc and a minimum CMRR
of 80 dB at 10 kHz for G = 1. Maximum input bias current is
10 pA and typically remains below 300 pA over the entire
industrial temperature range. Despite the JFET inputs, the
AD8224 typically has a noise corner of only 10 Hz.
With the proliferation of mixed-signal processing, the number
of power supplies required in each system has grown. Designed
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
to alleviate this problem, the AD8224 can operate on a ±18 V
dual supply, as well as on a single +5 V supply. The device’s railto-rail output stage maximizes dynamic range on the low
voltage supplies common in portable applications. Its ability to
run on a single 5 V supply eliminates the need for higher
voltage, dual supplies. The AD8224 draws 750 µA of quiescent
current per amplifier, making it ideal for battery powered
devices.
In addition, the AD8224 can be configured as a single-channel,
differential output, instrumentation amplifier. Differential
outputs provide high noise immunity, which can be useful when
the output signal must travel through a noisy environment, such
as with remote sensors. The configuration can also be used to
drive differential input ADCs. For a single-channel version, use
the AD8220.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2007–2010 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD8224
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Layout .......................................................................................... 21
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 9
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 9
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 9
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ........................... 10
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 11
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 20
Gain Selection ............................................................................. 20
Reference Terminal .................................................................... 21
REVISION HISTORY
5/10—Rev. A to Rev. B
Changes to Features Section............................................................ 1
Added Table 10 ................................................................................. 9
Changes to Figure 3 and Table 11 ................................................. 10
Added Hidden Paddle Package Section and Exposed Paddle
Package Section and Figure 58 ...................................................... 21
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 26
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 27
4/07—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Features, General Description, and Figure 1 ............ 1
Changes to Table 2 ............................................................................ 3
Changes to Table 3 and Table 4 ....................................................... 5
Changes to Table 5 ............................................................................ 6
Solder Wash ................................................................................. 22
Input Bias Current Return Path ............................................... 22
Input Protection ......................................................................... 22
RF Interference ........................................................................... 23
Common-Mode Input Voltage Range ..................................... 23
Applications Information .............................................................. 24
Driving an ADC ......................................................................... 24
Differential Output .................................................................... 24
Driving a Differential Input ADC ............................................ 25
Driving Cabling .......................................................................... 25
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 26
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 27
Changes to Table 6 and Table 7 ....................................................... 8
Changes to Figure 2 ........................................................................... 9
Changes to Figure 3 ........................................................................ 10
Inserted Figure 4, Figure 5, and Figure 6; Renumbered
Sequentially ..................................................................................... 11
Changes to Figure 7 ........................................................................ 11
Changes to Figure 20 and Figure 21............................................. 13
Changes to Figure 28 ...................................................................... 15
Changes to Theory of Operation and Figure 55 ........................ 20
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 26
1/07—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. B | Page 2 of 28
AD8224
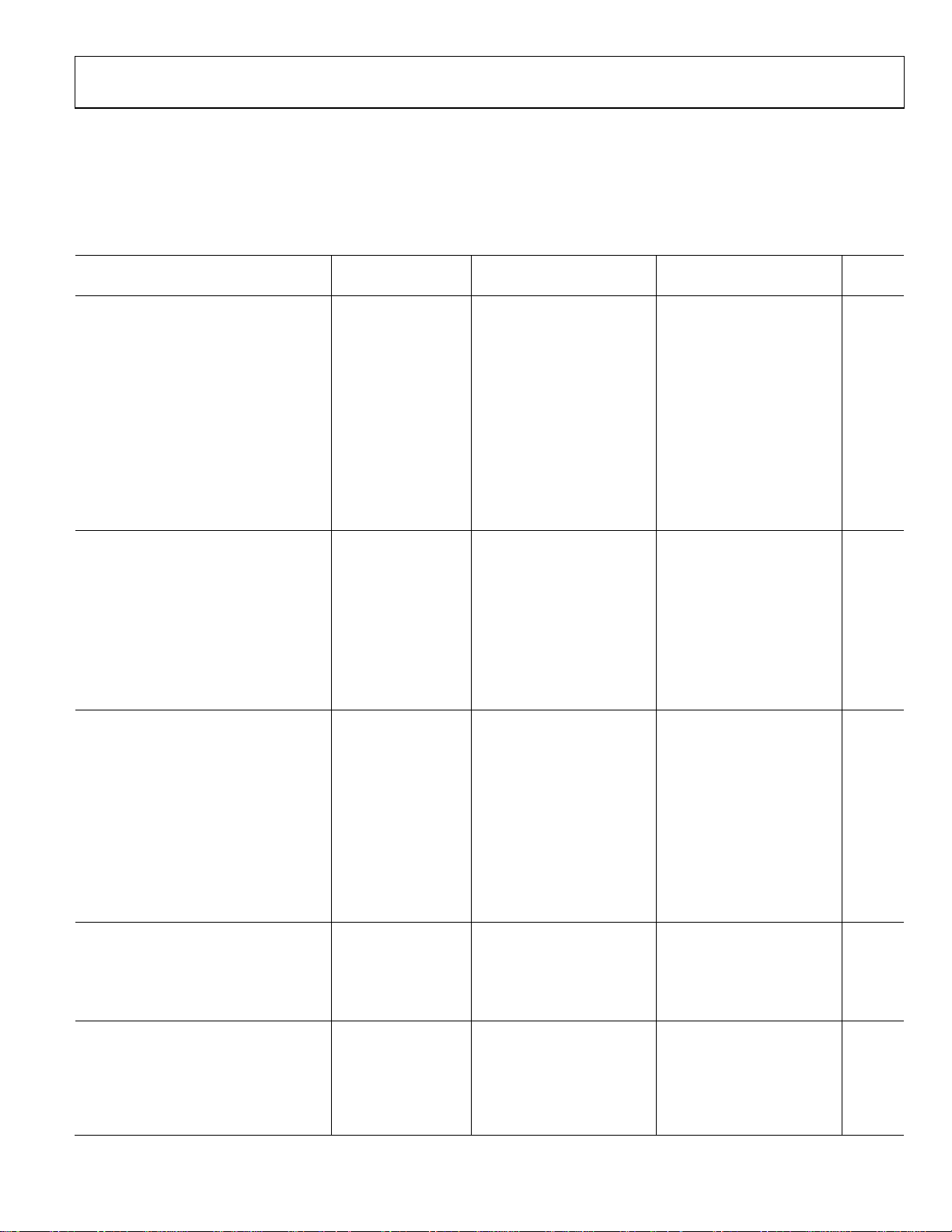
SPECIFICATIONS
VS+ = +15 V, VS− = −15 V, V
individual instrumentation amplifier configured for a single-ended output or dual instrumentation amplifiers configured for differential
outputs as shown in Figure 63.
Table 2. Individual Amplifier in Single-Ended Configuration or Dual Amplifiers in Differential Output Configuration
A Grade B Grade
Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
COMMON-MODE REJECTION RATIO (CMRR)
CMRR DC to 60 Hz with
1 kΩ Source Imbalance
G = 1 78 86 dB
G = 10 94 100 dB
G = 100 94 100 dB
G = 1000 94 100 dB
CMRR at 10 kHz VCM = ±10 V
G = 1 74 80 dB
G = 10 84 90 dB
G = 100 84 90 dB
G = 1000 84 90 dB
NOISE
Voltage Noise, 1 kHz
Input Voltage Noise, eni V
Output Voltage Noise, eno V
RTI, 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
G = 1 5 5 μV p-p
G = 1000 0.8 0.8 μV p-p
Current Noise f = 1 kHz 1 1 fA/√Hz
VOLTAGE OFFSET
Input Offset, V
300 175 μV
OSI
Average TC T = −40°C to +85°C 10 5 μV/°C
Output Offset, V
1200 800 μV
OSO
Average TC T = −40°C to +85°C 10 5 μV/°C
Offset RTI vs. Supply (PSR) VS = ±5 V to ±15 V
G = 1 86 86 dB
G = 10 96 100 dB
G = 100 96 100 dB
G = 1000 96 100 dB
INPUT CURRENT (PER CHANNEL)
Input Bias Current 25 10 pA
Over Temperature3 T = −40°C to +85°C 300 300 pA
Input Offset Current 2 0.6 pA
Over Temperature3 T = −40°C to +85°C 5 5 pA
REFERENCE INPUT
RIN 40 40 kΩ
IIN V
Voltage Range −VS +VS −VS +VS V
Gain to Output
= 0 V, TA = 25°C, G = 1, RL = 2 k1, unless otherwise noted. Ta bl e 2 displays the specifications for an
REF
2
, VS = ±15 V
= ±10 V
V
CM
RTI noise =
2
√(e
+ (eno/G)2)
ni
+, VIN− = 0 V 14 14 17 nV/√Hz
IN
+, VIN− = 0 V 90 90 100 nV/√Hz
IN
=
RTI V
OS
) + (V
(V
OSI
+, VIN− = 0 V 70 70 μA
IN
OSO
/G)
1 ±
0.0001
1 ±
V/V
0.0001
Rev. B | Page 3 of 28
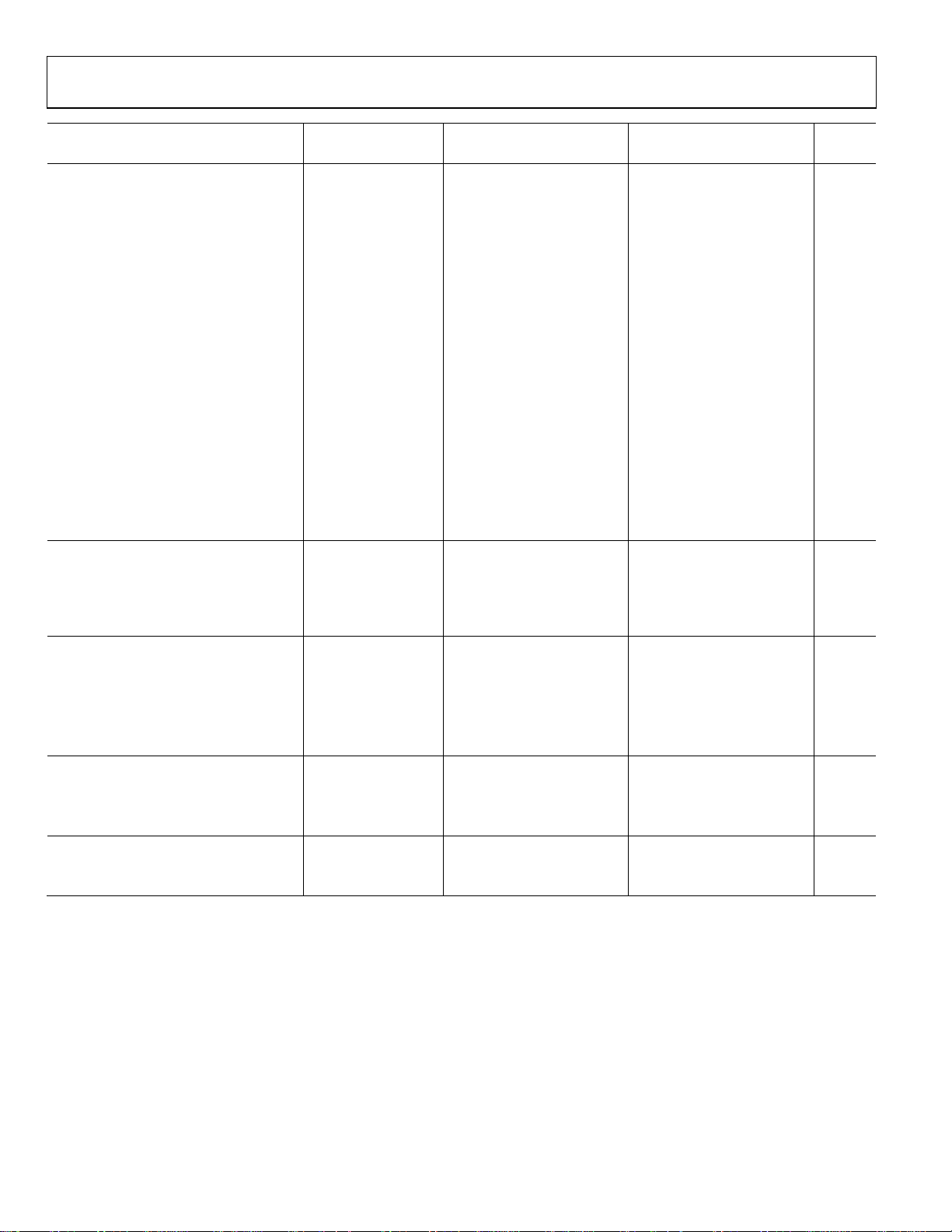
AD8224
A Grade B Grade
Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
GAIN G = 1 + (49.4 kΩ/RG)
Gain Range 1 1000 1 1000 V/V
Gain Error V
G = 1 0.06 0.04 %
G = 10 0.3 0.2 %
G = 100 0.3 0.2 %
G = 1000 0.3 0.2 %
Gain Nonlinearity V
G = 1 RL = 10 kΩ 8 15 8 15 ppm
G = 10 RL = 10 kΩ 5 10 5 10 ppm
G = 100 RL = 10 kΩ 15 25 15 25 ppm
G = 1000 RL = 10 kΩ 100 150 100 150 ppm
G = 1 RL = 2 kΩ 15 20 15 20 ppm
G = 10 RL = 2 kΩ 12 20 12 20 ppm
G = 100 RL = 2 kΩ 35 50 35 50 ppm
G=1000 RL = 2 kΩ 180 250 180 250 ppm
Gain vs. Temperature
G = 1 3 10 2 5 ppm/°C
G > 10 −50 −50 ppm/°C
INPUT
Impedance (Pin to Ground)4 104||5 104||5 GΩ||pF
Input Operating Voltage Range5
Over Temperature T = −40°C to +85°C −VS − 0.1 +VS − 2.1 −VS − 0.1 +VS − 2.1 V
OUTPUT
Output Swing RL = 2 kΩ −14.25 +14.25 −14.25 +14.25 V
Over Temperature T = −40°C to +85°C −14.3 +14.1 −14.3 +14.1 V
Output Swing RL = 10 kΩ −14.7 +14.7 −14.7 +14.7 V
Over Temperature T = −40°C to +85°C −14.6 +14.6 −14.6 +14.6 V
Short-Circuit Current 15 15 mA
POWER SUPPLY (PER AMPLIFIER)
Operating Range ±2.256 ±18 ±2.256 ±18 V
Quiescent Current 750 800 750 800 μA
Over Temperature T = −40°C to +85°C 850 900 850 900 μA
TEMPERATURE RANGE
For Specified Performance −40 +85 −40 +85 °C
Operational7 −40 +125 −40 +125 °C
1
When the output sinks more than 4 mA, use a 47 pF capacitor in parallel with the load to prevent ringing. Otherwise, use a larger load, such as 10 kΩ.
2
Refers to the differential configuration shown in . Figure 63
3
Refer to and for the relationship between input current and temperature. Figure 14 Figure 15
4
Differential and common-mode input impedance can be calculated from the pin impedance: Z
5
The AD8224 can operate up to a diode drop below the negative supply; however, the bias current increases sharply. The input voltage range reflects the maximum
allowable voltage where the input bias current is within the specification.
6
At this supply voltage, ensure that the input common-mode voltage is within the input voltage range specification.
7
The AD8224 is characterized from −40°C to +125°C. See the section for expected operation in this temperature range. Typical Performance Characteristics
= ±10 V
OUT
= −10 V to +10 V
OUT
−V
= ±2.25 V to ±18 V
V
S
− 0.1 +VS − 2 −VS − 0.1 +VS − 2 V
S
for dual supplies
= 2(Z
DIFF
); ZCM = Z
PIN
/2.
PIN
Rev. B | Page 4 of 28
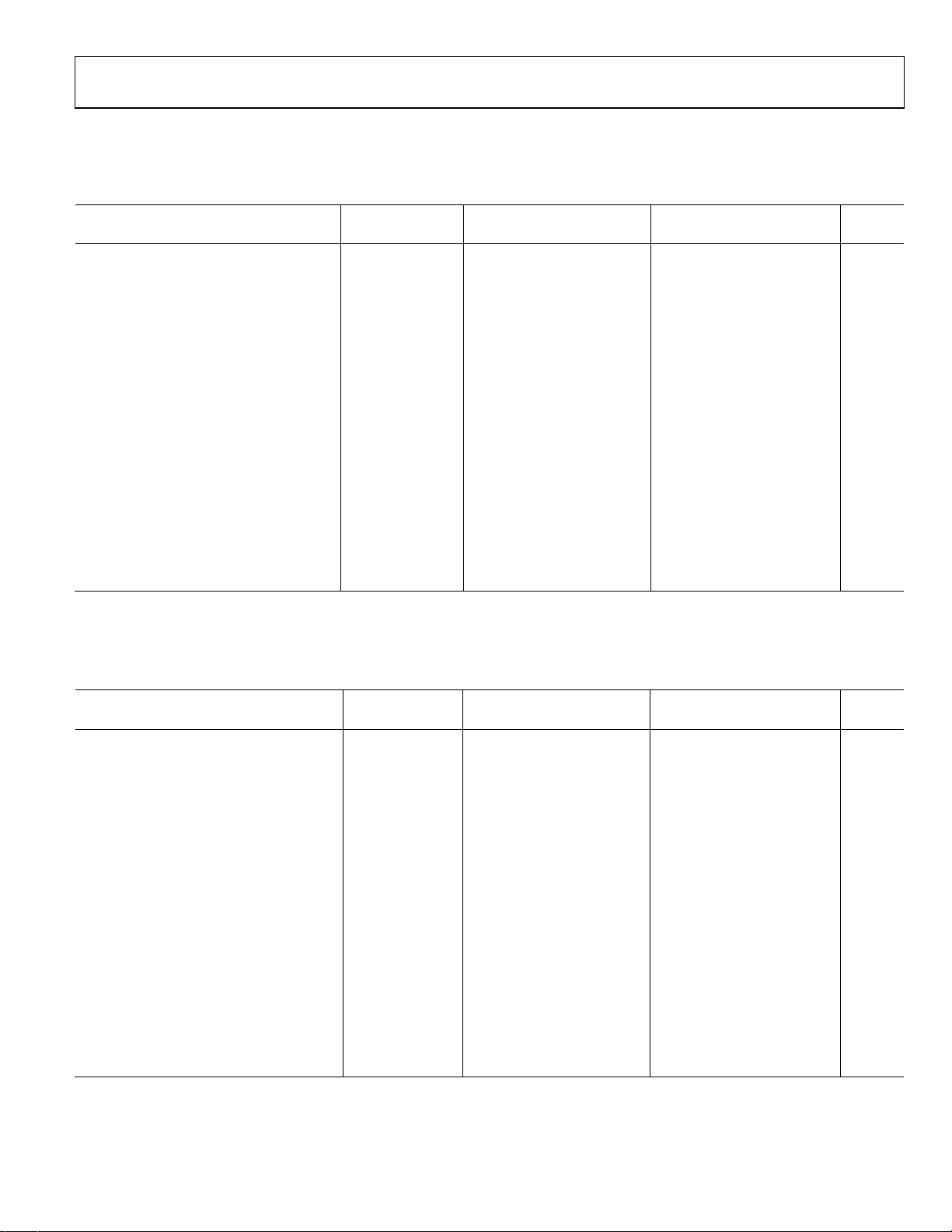
AD8224
VS+ = +15 V, VS− = −15 V, V
dynamic performance of each individual instrumentation amplifier.
= 0 V, TA = 25°C, G = 1, RL = 2 k1, unless otherwise noted. Ta bl e 3 displays the specifications for the
REF
Table 3. Dynamic Performance of Each Individual Amplifier—Single-Ended Output Configuration, V
= ±15 V
S
A Grade B Grade
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC RESPONSE
Small Signal Bandwidth −3 dB
G = 1 1500 1500 kHz
G = 10 800 800 kHz
G = 100 120 120 kHz
G =1000 14 14 kHz
Settling Time 0.01% ΔVO = ±10 V step
G = 1 5 5 μs
G = 10 4.3 4.3 μs
G = 100 8.1 8.1 μs
G =1000 58 58 μs
Settling Time 0.001% ΔVO = ±10 V step
G = 1 6 6 μs
G = 10 4.6 4.6 μs
G = 100 9.6 9.6 μs
G =1000 74 74 μs
Slew Rate
G = 1 to 100 2 2 V/μs
1
When the output sinks more than 4 mA, use a 47 pF capacitor in parallel with the load to prevent ringing. Otherwise, use a larger load, such as 10 kΩ.
VS+ = +15 V, VS− = −15 V, V
= 0 V, TA = 25°C, G = 1, RL = 2 k1, unless otherwise noted. Ta bl e 4 displays the specifications for the
REF
dynamic performance of both amplifiers when used in the differential output configuration shown in Figure 63.
Table 4. Dynamic Performance of Both Amplifiers—Differential Output Configuration
2
, VS = ±15 V
A Grade B Grade
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC RESPONSE
Small Signal Bandwidth −3 dB
G = 1 1500 1500 kHz
G = 10 800 800 kHz
G = 100 120 120 kHz
G =1000 14 14 kHz
Settling Time 0.01% ΔVO = ±10 V step
G = 1 5 5 μs
G = 10 4.3 4.3 μs
G = 100 8.1 8.1 μs
G =1000 58 58 μs
Settling Time 0.001% ΔVO = ±10 V step
G = 1 6 6 μs
G = 10 4.6 4.6 μs
G = 100 9.6 9.6 μs
G =1000 74 74 μs
Slew Rate
G = 1 to 100 2 2 V/μs
1
When the output sinks more than 4 mA, use a 47 pF capacitor in parallel with the load to prevent ringing. Otherwise, use a larger load, such as 10 kΩ.
2
Refers to the differential configuration shown in . Figure 63
Rev. B | Page 5 of 28
AD8224
VS + = 5 V, VS− = 0 V, V
individual instrumentation amplifier configured for a single-ended output or dual instrumentation amplifiers configured for differential
outputs as shown in Figure 63.
Table 5. Individual Amplifier in Single-Ended Configuration or Dual Amplifiers in Differential Output Configuration
A Grade B Grade
Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
COMMON-MODE REJECTION RATIO (CMRR)
CMRR DC to 60 Hz with
1 kΩ Source Imbalance
G = 1 78 86 dB
G = 10 94 100 dB
G = 100 94 100 dB
G = 1000 94 100 dB
CMRR at 10 kHz
G = 1 74 80 dB
G = 10 84 90 dB
G = 100 84 90 dB
G = 1000 84 90 dB
NOISE RTI noise = √(e
Voltage Noise, 1 kHz VS = ±2.5 V
Input Voltage Noise, eni V
Output Voltage Noise, eno V
RTI, 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
G = 1 5 5 μV p-p
G = 1000 0.8 0.8 μV p-p
Current Noise f = 1 kHz 1 1 fA/√Hz
VOLTAGE OFFSET RTI VOS = (V
Input Offset, V
OSI
Average TC T = −40°C to +85°C 10 5 μV/°C
Output Offset, V
OSO
Average TC T = −40°C to +85°C 10 5 μV/°C
Offset RTI vs. Supply (PSR)
G = 1 86 86 dB
G = 10 96 100 dB
G = 100 96 100 dB
G = 1000 96 100 dB
INPUT CURRENT (PER CHANNEL)
Input Bias Current 25 10 pA
Over Temperature3 T = −40°C to +85°C 300 300 pA
Input Offset Current 2 0.6 pA
Over Temperature3 T = −40°C to +85°C 5 5 pA
REFERENCE INPUT
RIN 40 40 kΩ
IIN V
Voltage Range −VS +VS −VS +VS V
Gain to Output
= 2.5 V, TA = 25°C, G = 1, RL = 2 k1, unless otherwise noted. Ta b le 5 displays the specifications for an
REF
2
, VS =+5 V
= 0 to 2.5 V
V
CM
2
+ (eno/G)2)
ni
+, VIN− = 0 V, V
IN
+, VIN− = 0 V, V
IN
= 0 V 14 14 17 nV/√Hz
REF
= 0 V 90 90 100 nV/√Hz
REF
) + (V
OSI
/G)
OSO
300 250 μV
1200 800 μV
+, VIN− = 0 V 70 70 μA
IN
1 ±
0.0001
1 ±
0.0001
V/V
Rev. B | Page 6 of 28
AD8224
A Grade B Grade
Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
GAIN G = 1 + (49.4 kΩ/RG)
Gain Range 1 1000 1 1000 V/V
Gain Error
G = 1 V
G = 10 V
G = 100 V
G = 1000 V
Nonlinearity V
V
G = 1 RL = 10 kΩ 35 50 35 50 ppm
G = 10 RL = 10 kΩ 35 50 35 50 ppm
G = 100 RL = 10 kΩ 50 75 50 75 ppm
G = 1000 RL = 10 kΩ 90 115 90 115 ppm
G = 1 RL = 2 kΩ 35 50 35 50 ppm
G = 10 RL = 2 kΩ 35 50 35 50 ppm
G = 100 RL = 2 kΩ 50 75 50 75 ppm
G = 1000 RL = 2 kΩ 175 200 175 200 ppm
Gain vs. Temperature
G = 1 3 10 2 5 ppm/°C
G > 10 −50 −50 ppm/°C
INPUT
Impedance (Pin to Ground)4 104||6 104||6 GΩ||pF
Input Voltage Range5 −0.1 +VS − 2 −0.1 +VS − 2 V
Over Temperature T = −40°C to +85°C −0.1 +VS − 2.1 −0.1 +VS − 2.1 V
OUTPUT
Output Swing RL = 2 kΩ 0.25 4.75 0.25 4.75 V
Over Temperature T = −40°C to +85°C 0.3 4.70 0.3 4.70 V
Output Swing RL = 10 kΩ 0.15 4.85 0.15 4.85 V
Over Temperature T = −40°C to +85°C 0.2 4.80 0.2 4.80 V
Short-Circuit Current 15 15 mA
POWER SUPPLY (PER AMPLIFIER)
Operating Range 4.5 36 4.5 36 V
Quiescent Current 750 800 750 800 μA
Over Temperature T = −40°C to +85°C 850 900 850 900 μA
TEMPERATURE RANGE
For Specified Performance −40 +85 −40 +85 °C
Operational6 −40 +125 −40 +125 °C
1
When the output sinks more than 4 mA, use a 47 pF capacitor in parallel with the load to prevent ringing. Otherwise, use a larger load, such as 10 kΩ.
2
Refers to the differential configuration shown in . Figure 63
3
Refer to and for the relationship between input current and temperature. Figure 14 Figure 15
4
Differential and common-mode impedance can be calculated from the pin impedance: Z
5
The AD8224 can operate up to a diode drop below the negative supply, but the bias current increases sharply. The input voltage range reflects the maximum
allowable voltage where the input bias current is within the specification.
6
The AD8224 is characterized from −40°C to +125°C. See the section for expected operation in that temperature range. Typical Performance Characteristics
= 0.3 V to 2.9 V 0.06 0.04 %
OUT
= 0.3 V to 3.8 V 0.3 0.2 %
OUT
= 0.3 V to 3.8 V 0.3 0.2 %
OUT
= 0.3 V to 3.8 V 0.3 0.2 %
OUT
= 0.3 V to 2.9 V for G = 1
OUT
= 0.3 V to 3.8 V for G > 1
OUT
= 2(Z
DIFF
); ZCM = Z
PIN
/2.
PIN
Rev. B | Page 7 of 28
AD8224
VS + = 5 V, VS− = 0 V, V
dynamic performance of each individual instrumentation amplifier.
= 2.5 V, TA = 25°C, G = 1, RL = 2 k1, unless otherwise noted. Ta b le 6 displays the specifications for the
REF
Table 6. Dynamic Performance of Each Individual Amplifier—Single-Ended Output Configuration, V
= +5 V
S
A Grade B Grade
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC RESPONSE
Small Signal Bandwidth −3 dB
G = 1 1500 1500 kHz
G = 10 800 800 kHz
G = 100 120 120 kHz
G =1000 14 14 kHz
Settling Time 0.01%
G = 1 ΔVO = 3 V step 2.5 2.5 μs
G = 10 ΔVO = 4 V step 2.5 2.5 μs
G = 100 ΔVO = 4 V step 7.5 7.5 μs
G =1000 ΔVO = 4 V step 60 60 μs
Settling Time 0.001%
G = 1 ΔVO = 3 V step 3.5 3.5 μs
G = 10 ΔVO = 4 V step 3.5 3.5 μs
G = 100 ΔVO = 4 V step 8.5 8.5 μs
G =1000 ΔVO = 4 V step 75 75 μs
Slew Rate
G = 1 to 100 2 2 V/μs
1
When the output sinks more than 4 mA, use a 47 pF capacitor in parallel with the load to prevent ringing. Otherwise, use a larger load, such as 10 kΩ.
V
+ = 5 V, VS− = 0 V, V
S
= 2.5 V, TA = 25°C, G = 1, RL = 2 k1 unless otherwise noted. Ta b le 7 displays the specifications for the
REF
dynamic performance of both amplifiers when used in the differential output configuration shown in Figure 63.
Table 7. Dynamic Performance of Both Amplifiers—Differential Output Configuration
2
, VS = +5 V
A Grade B Grade
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC RESPONSE
Small Signal Bandwidth −3 dB
G = 1 1500 1500 kHz
G = 10 800 800 kHz
G = 100 120 120 kHz
G =1000 14 14 kHz
Settling Time 0.01%
G = 1 ΔVO = 3 V step 2.5 2.5 μs
G = 10 ΔVO = 4 V step 2.5 2.5 μs
G = 100 ΔVO = 4 V step 7.5 7.5 μs
G =1000 ΔVO = 4 V step 60 60 μs
Settling Time 0.001%
G = 1 ΔVO = 3 V step 3.5 3.5 μs
G = 10 ΔVO = 4 V step 3.5 3.5 μs
G = 100 ΔVO = 4 V step 8.5 8.5 μs
G =1000 ΔVO = 4 V step 75 75 μs
Slew Rate
G = 1 to 100 2 2 V/μs
1
When the output sinks more than 4 mA, use a 47 pF capacitor in parallel with the load to prevent ringing. Otherwise, use a larger load, such as 10 kΩ.
2
Refers to the differential configuration shown in . Figure 63
Rev. B | Page 8 of 28
AD8224
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 8.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage ±18 V
Power Dissipation See Figure 2
Output Short-Circuit Current Indefinite1
Input Voltage (Common Mode) ±VS
Differential Input Voltage ±VS
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +130°C
Operating Temperature Range2 −40°C to +125°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) 300°C
Junction Temperature 130°C
Package Glass Transition Temperature 130°C
ESD (Human Body Model) 4 kV
ESD (Charge Device Model) 1 kV
ESD (Machine Model) 0.4 kV
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
1
Assumes the load is referenced to midsupply.
2
Temperature for 85°C. For performance
to 125°C, see the section.
specified performance is −40°C to +
Typical Performance Characteristics
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Table 9.
Exposed Paddle Package θJA Unit
CP-16-13: LFCSP Soldered to Board 48 °C/W
CP-16-13: LFCSP Not Soldered to Board 86 °C/W
Table 10.
Hidden Paddle Package θJA Unit
CP-16-19: LFCSP 86 °C/W
The θJA values in Tabl e 9 and Tab l e 10 assume a 4-layer JEDEC
standard board. If the thermal pad is soldered to the board, it is
also assumed it is connected to a plane. θ
4.4°C/W.
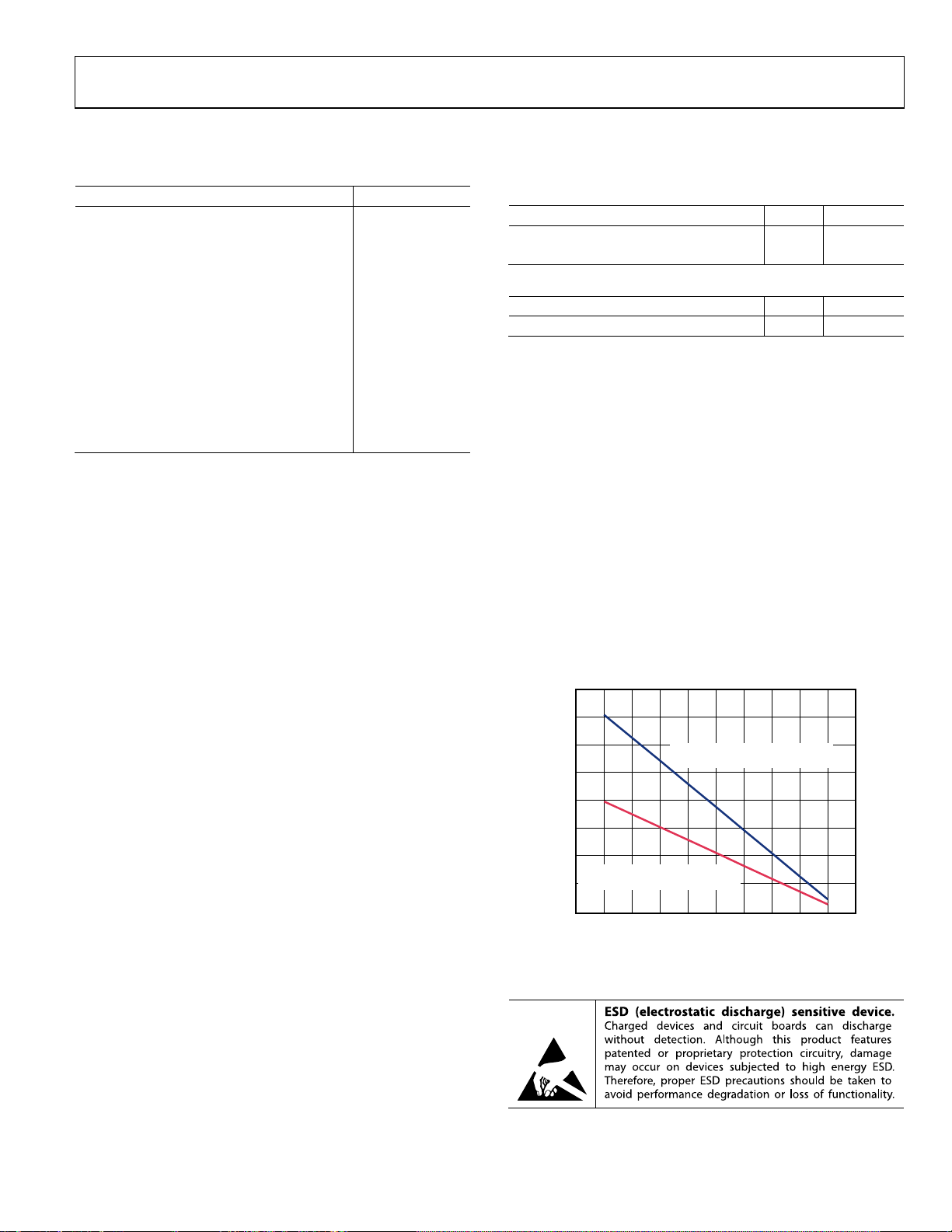
Maximum Power Dissipation
The maximum safe power dissipation for the AD8224 is limited
by the associated rise in junction temperature (T
approximately 130°C, which is the glass transition temperature,
the plastic changes its properties. Even temporarily exceeding
this temperature limit may change the stresses that the package
exerts on the die, permanently shifting the parametric performance
of the amplifiers. Exceeding a temperature of 130°C for an
extended period can result in a loss of functionality. Figure 2
shows the maximum safe power dissipation in the package vs.
the ambient temperature for the LFCSP on a 4-layer JEDEC
standard board.
4.0
at the exposed pad is
JC
) on the die. At
J
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
= 86°C/W WHEN THERMAL PAD
JA
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION (W)
IS NOT SO LDERED TO BO ARD
0.5
0
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Figure 2. Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Ambient Temperature
JA = 48°C/W WHEN THERMAL PAD
IS SOLDERED TO BOARD
AMBIENT TEM PERATURE (°C)
06286-002
ESD CAUTION
Rev. B | Page 9 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...