16-Bit, 4-Channel,
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
250 kSPS PulSAR® ADC
Preliminary Technical Data
FEATURES
16-bit resolution with no missing codes
4-channel multiplexer with:
Unipolar single ended or
Differential (GND sense)/pseudo-bipolar inputs
Throughput: 250 kSPS
INL/DNL: ±0.6 LSB typical
Dynamic range: 93.5 dB
SINAD: 92.5 dB @ 20 kHz
THD: −100 dB @ 20 kHz
Analog input range:
0 V to V
with V
REF
up to VDD
REF
Reference:
Internal selectable 2.5 V/4.096 V or
External buffered (up to 4.096 V)
External (up to VDD)
Internal temperature sensor
Channel sequencer, selectable 1-pole filter, BUSY indicator
No pipeline delay, SAR architecture
Single-supply 2.7V – 5.5 V operation with
1.8 V to 5 V logic interface
Serial interface SPI®/QSPI™/MICROWIRE™/DSP compatible
Power dissipation:
6 mW @ 5 V/100 kSPS
Standby current: 1 nA
20-lead 4 mm × 4 mm LFCSP package
APPLICATIONS
Battery-powered equipment
Medical instruments
Mobile communications
Personal digital assitants
Data acquisition
Seismic data acquisition systems
Instrumentation
Process Control
IN0
IN1
IN2
IN3
COM
Table 1. Multichannel14-/16-Bit PulSAR ADC
Type Channels
14-Bit 8 AD7949 ADA4841-x
16-Bit 4 AD7682 ADA4841-x
16-Bit 8 AD7689 AD7699 ADA4841-x
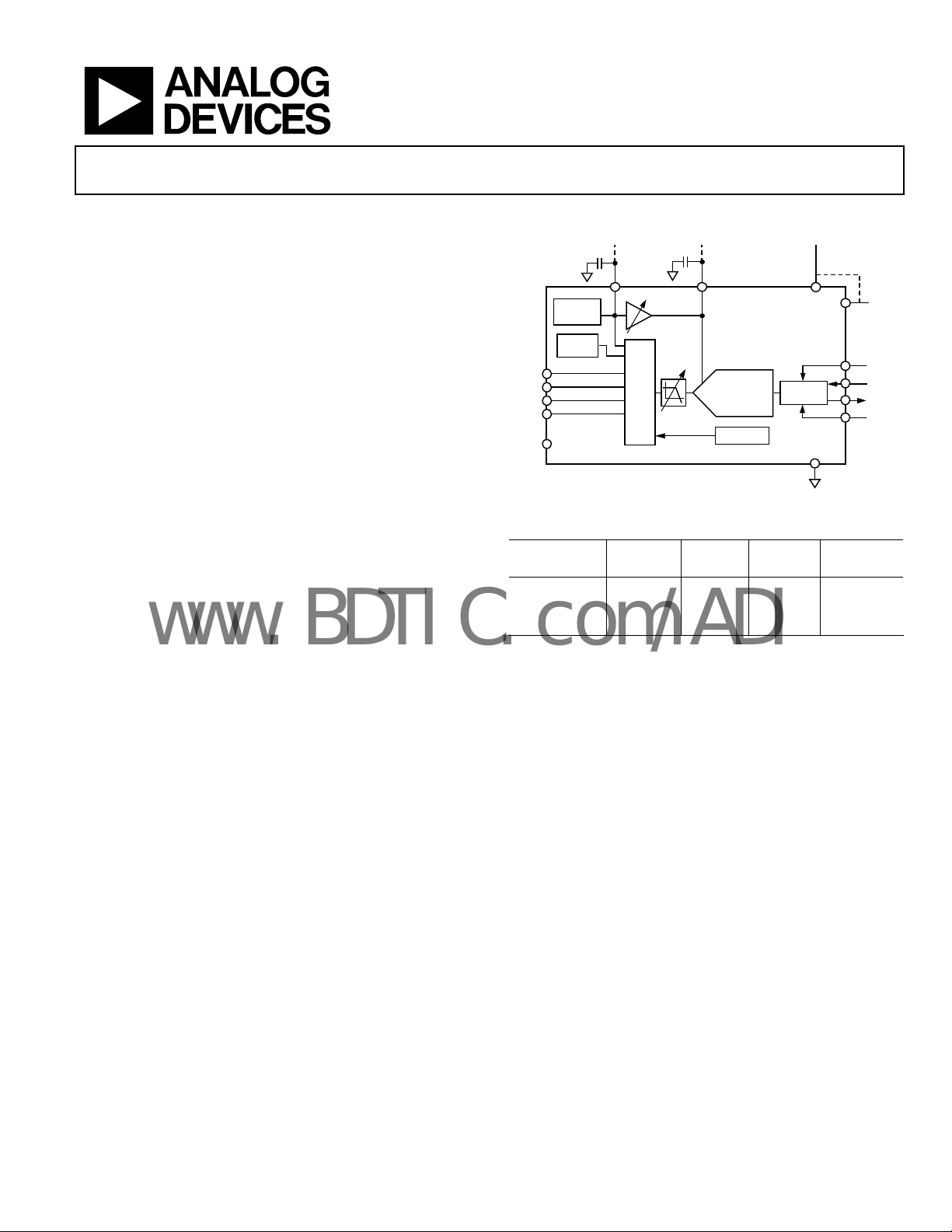
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7682 is a 4-channel 16-bit, charge redistribution successive
approximation register (SAR), analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
that operates from a single power supply, VDD.
The AD7682 contains all of the components for use in a multichannel, low power, data acquisition system including: a true 16-bit
SAR ADC with no missing codes; a 4-channel, low crosstalk
multiplexer useful for configuring the inputs as single ended (with
or without ground sense), differential or bipolar; an internal low
drift reference (selectable 2.5V or 4.096V) and buffer; a
temperature sensor; a selectable 1-pole filter; and a sequencer
useful when channels are continuously scanned in order.
The AD7682 uses a simple SPI interface for writing to the
configuration register and receiving conversion results. The SPI
interface uses a separate supply, VIO, which is set to the host logic
level.
Power dissipation scales with throughput.
The AD7682 is housed in a tiny 20-lead LFCSP with operation
specified from −40°C to +85°C.
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
0.5V to 4.096V
Band Gap
REF
Temp
Sensor
0.1μF
REFIN
MUX
0.5V to VDD
10μF
1-Pole
LPF
REF
16-Bit SAR
Sequencer
Figure 1.
250
kSPS
ADC
AD7682
2.7V to 5V
VDD
AD7682
SPI Serial
Interface
GND
500
kSPS
VIO
ADC
Driver
1.8V to
VDD
CNV
SCK
SDO
DIN
Rev. PrA
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2008 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD7682 Preliminary Technical Data
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Timing Specifications....................................................................... 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 7
ESD Caution...................................................................................7
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions............................8
Typical Performance Characteristics..............................................9
Terminology.................................................................................... 10
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 11
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 11
Rev. PrA | Page 2 of 11

Preliminary Technical Data AD7682
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = 2.5 V to 5.5 V, VIO = 2.3 V to VDD, V
Table 2.
Parameter Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 16 Bits
ANALOG INPUT
Voltage Range Unipolar mode 0 +V
Bipolar mode −V
Absolute Input Voltage
Analog Input CMRR fIN = 250 kHz TBD dB
Leakage Current at 25°C Acquisition phase 1 nA
Input Impedance
THROUGHPUT
Conversion Rate VDD = 4.096V to 5.5 0 250 kSPS
VDD = 2.5V to 4.096V 1 200
Transient Response Full-scale step 1.8
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes 16 Bits
Integral Linearity Error -2 ±0.6 +2 LSB1
Differential Linearity Error −1 ±0.25 +1.5 LSB
Transition Noise REF = VDD = 5 V 0.5 LSB
Gain Error2 −30 ±0.5 +30 LSB
Gain Error Match TBD LSB
Gain Error Temperature Drift ±0.3 ppm/°C
Offset Error2 −5 ±0.5 +5 LSB
Offset Error Match TBD LSB
Offset Error Temperature Drift ±0.3 ppm/°C
Power Supply Sensitivity
AC ACCURACY3
Dynamic Range 93.5 dB4
Signal-to-Noise fIN = 20 kHz, VREF = 5V 92.5 dB
f
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) fIN = 20 kHz, VREF = 5V 92.5 dB
f
Total Harmonic Distortion fIN = 20 kHz −100 dB
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range fIN = 20 kHz 110 dB
Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk
Intermodulation Distortion5 115 dB
SAMPLING DYNAMICS
−3 dB Input Bandwidth Selectable 0.425 1.7 MHz
Aperture Delay VDD = 5V 2.5 ns
1
LSB means least significant bit. With the 5 V input range, one LSB is 76.3 µV.
2
See the Terminology section. These specifications include full temperature range variation but not the error contribution from the external reference.
3
With V
= 5 V, unless otherwise noted.
REF
4
All specifications expressed in decibels are referred to a full-scale input FSR and tested with an input signal at 0.5 dB below full scale, unless otherwise specified.
5
f
= 21.4 kHz and f
IN1
= 18.9 kHz, with each tone at −7 dB below full scale.
IN2
= VDD, all specifications T
REF
Positive input, unipolar and
MIN
to T
, unless other wise noted.
MAX
/2 +V
REF
−0.1 V
V
REF
/2
REF
+ 0.1 V
REF
bipolar mode
Negative or COM input, unipolar
−0.1 +0.1
mode
Negative or COM input, bipolar
/2 – 0.1 V
REF
/2 V
REF
/2 + 0.1
REF
V
mode
VDD = 5 V ± 5%
= 20 kHz, VREF = 2.5V 88.5
IN
= 20 kHz, VREF = 2.5V 88.5 dB
IN
= 100 kHz on adjacent
f
IN
±1 ppm
-117 dB
channel(s)
μs
Rev. PrA | Page 3 of 11

AD7682 Preliminary Technical Data
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VDD = 2.5 V to 5.5 V, VIO = 2.3 V to VDD, V
Table 3.
Parameter Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
INTERNAL REFERENCE
Output Voltage For 4.096 V output, @ 25°C 4.086 4.096 4.106
For 2.5 V output, @ 25°C 2.490 2.500 2.510
Temperature Drift –40°C to +85°C ±TBD
Line Regulation VDD = 5 V ± 5% ±TBD
Long-Term Drift 1000 hours 50
Turn-On Settling Time C
EXTERNAL REFERENCE
Voltage Range REF Input 0.5 VDD + 0.3 V
REFIN Input (Buffered) 0.5 VDD – 0.2 V
Current Drain 250 kSPS, REF = 5V 50 µA
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Output Voltage1 @ 25°C 283 mV
Temperature Sensitivity 1 mV/°C
DIGITAL INPUTS
Logic Levels
VIL −0.3 +0.3 × VIO V
VIH 0.7 × VIO VIO + 0.3 V
IIL −1 +1 µA
IIH −1 +1 µA
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Data Format2
Pipeline Delay3
VOL I
VOH I
POWER SUPPLIES
VDD Specified performance 2.3 5.5 V
VIO Specified performance 2.3 VDD + 0.3 V
VIO Range 1.8 VDD + 0.3 V
Standby Current
4, 5
VDD and VIO = 5 V, 25°C 1 50 nA
Power Dissipation VDD = 5V , 100 kSPS throughput 6 mW
VDD = 5V , 250 kSPS throughput 15 mW
Energy per Conversion 50 nJ
TEMPERATURE RANGE6
Specified Performance T
1
The output voltage is internal and present on a dedicated multiplexer input.
2
Unipolar mode: serial 16-bit straight binary
Bipolar mode: serial 16-bit 2’s complement.
3
Conversion results available immediately after completed conversion.
4
With all digital inputs forced to VIO or GND as required.
5
During acquisition phase.
6
Contact an Analog Devices sales representative for the extended temperature range.
= VDD, all specifications T
REF
= 22 µF TBD
REF
= +500 µA 0.4 V
SINK
= −500 µA VIO − 0.3 V
SOURCE
VDD = 5V , 250 kSPS throughput
MIN
to T
, unless other wise noted.
MAX
18.5 mW
internal reference and buffer
enabled
to T
MIN
−40 +85 °C
MAX
V
V
ppm/°C
ppm/V
ppm
ms
Rev. PrA | Page 4 of 11
 Loading...
Loading...