Low Cost, 4-Channel, 16-Bit
FEATURES
4-channel, 16-bit resolution ADC
2 track-and-hold amplifiers
Throughput:
1 MSPS (Normal mode)
888 kSPS (Impulse mode)
Analog input voltage range: 0 V to 5 V
No pipeline delay
Parallel and serial 5 V/3 V interface
SPI®/QSPI™/MICROWIRE™/DSP-compatible
Single 5 V supply operation
Power dissipation:
120 mW typical
2.6 mW @ 10 kSPS
Package: 48-lead quad flatpack (LQFP)
or 48-lead frame chip scale package (LFCSP)
Pin-to-pin compatible with the AD7654
Low cost
APPLICATIONS
AC motor control
3-phase power control
4-channel data acquisition
Uninterrupted power supplies
Communications
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD76551 is a low cost, simultaneous sampling, dualchannel, 16-bit, charge redistribution SAR, analog-to-digital
converter that operates from a single 5 V power supply. It
contains two low noise, wide bandwidth, track-and-hold
amplifiers that allow simultaneous sampling, a high speed
16-bit sampling ADC, an internal conversion clock, error
correction circuits, and both serial and parallel system interface
ports. Each track-and-hold has a multiplexer in front to provide
a 4-channel input ADC. The A0 multiplexer control input
allows the choice of simultaneously sampling input pairs
INA1/INB1 (A0 = High) or INA2/INB2 (A0 = Low). The part
features a very high sampling rate mode (Normal) and, for low
power applications, a reduced power mode (Impulse) where the
power is scaled with the throughput. Operation is specified
from −40°C to +85°C.
1 MSPS PulSAR
®
ADC
AD7655
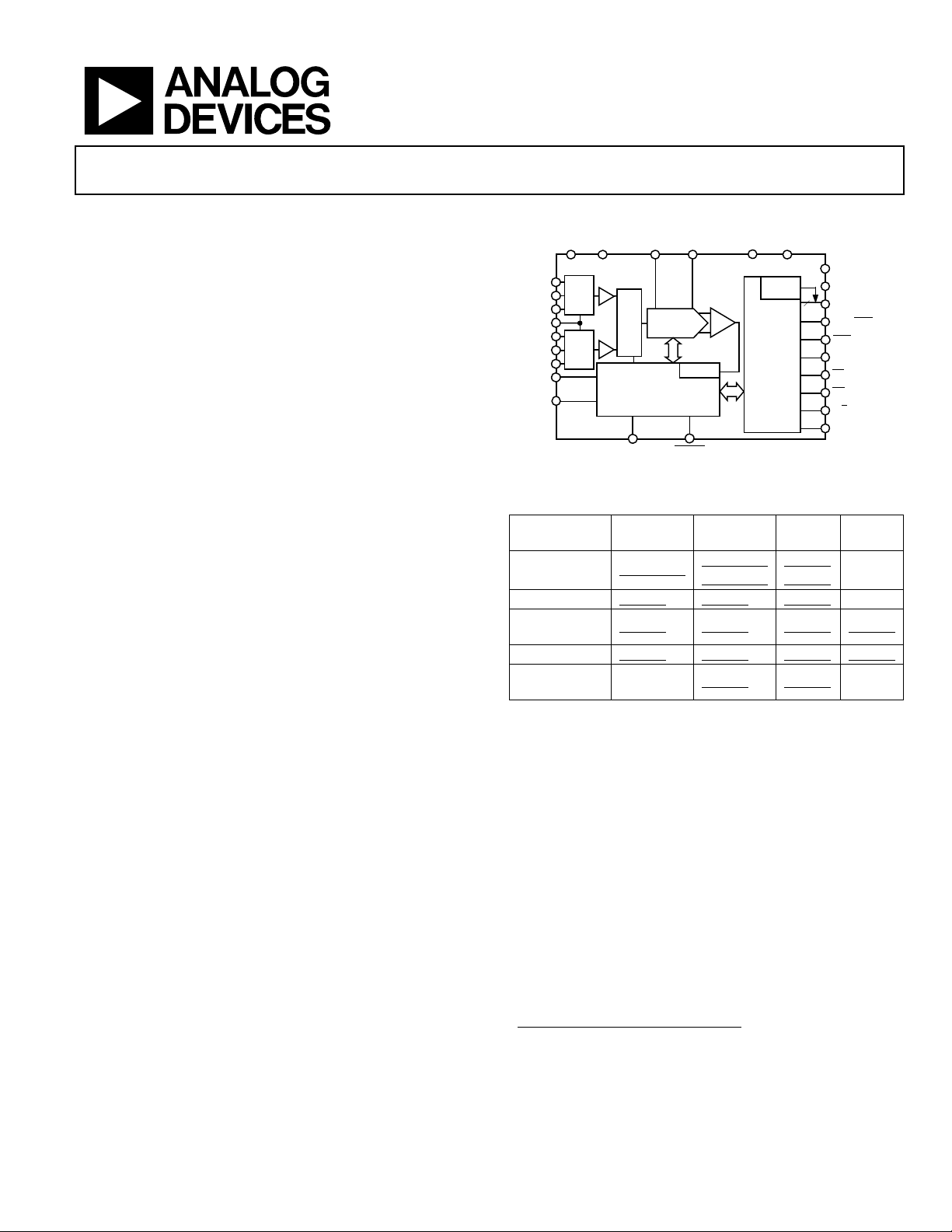
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AVDD AGND REFxREFGND
TRACK/HOLD
INA1
INAN
INA2
A0
INB1
INBN
INB2
PD
RESET
×2
MUX
MUX
MUX
CONTROL LOGIC AND
CALIBRATION CIRCUITRY
AD7655
IMPULSE
SWITCHED
CAP DAC
CLOCK
CNVST
Figure 1.
Table 1. PulSAR® Selection
Type / kSPS 100 - 250 500 - 570
Pseudo
Differential
AD7660/61
AD7650/52
AD7664/66
True Bipolar AD7663 AD7665 AD7671
True
Differential
AD7675 AD7676 AD7677 AD7621
18 Bit AD7678 AD7679 AD7674 AD7641
Multichannel/
Simultaneous
AD7654 AD7655
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Multichannel ADC.
The AD7655 features 4-channel inputs with two sampleand-hold circuits that allow simultaneous sampling.
2. Fast throughput.
The AD7655 is a 1 MSPS, charge redistribution, 16-bit SAR
ADC with internal error correction circuitry.
3. Single-supply operation.
The AD7655 operates from a single 5 V supply. In Impulse
mode, its power dissipation decreases with throughput.
4. Serial or parallel interface.
Versatile parallel or 2-wire serial interface arrangement is
compatible with both 3 V and 5 V logic.
1
Patent pending.
DGNDDVDD
SERIAL
PORT
PARALLEL
INTERFACE
16
800 1000
AD7653
AD7667
OVDD
OGND
D[15:0]
SER/PAR
EOC
BUSY
CS
RD
A/B
BYTESWAP
>1000
03536-001
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

AD7655
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Power Supply............................................................................... 17
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 7
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 7
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 8
Definitions of Specifications ......................................................... 11
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 12
Application Information................................................................ 14
Circuit Information.................................................................... 14
Modes of Operation ................................................................... 14
Transfer Functions......................................................................14
Typical Connection Diagram ................................................... 16
Analog Inputs.............................................................................. 16
Input Channel Multiplexer........................................................ 16
Driver Amplifier Choice............................................................ 16
Voltage Reference Input............................................................. 17
REVISION HISTORY
12/04—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Figure 17...................................................................... 15
Changes to Figure 18...................................................................... 16
Changes to Voltage Reference Input section............................... 17
Power Dissipation....................................................................... 17
Conversion Control ................................................................... 18
Digital Interface.......................................................................... 18
Parallel Interface......................................................................... 18
Serial Interface............................................................................ 19
Master Serial Interface............................................................... 20
Slave Serial Interface.................................................................. 21
Microprocessor Interfacing....................................................... 23
SPI Interface (ADSP-219x) ....................................................... 23
Application Hints ........................................................................... 24
Layout .......................................................................................... 24
Evaluating the AD7655’s Performance.................................... 24
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 25
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 25
Changes to Conversion Control section ..................................... 18
Changes to Digital Interface section............................................ 18
Updated Outline Dimensions...................................................... 25
11/02—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 28
AD7655
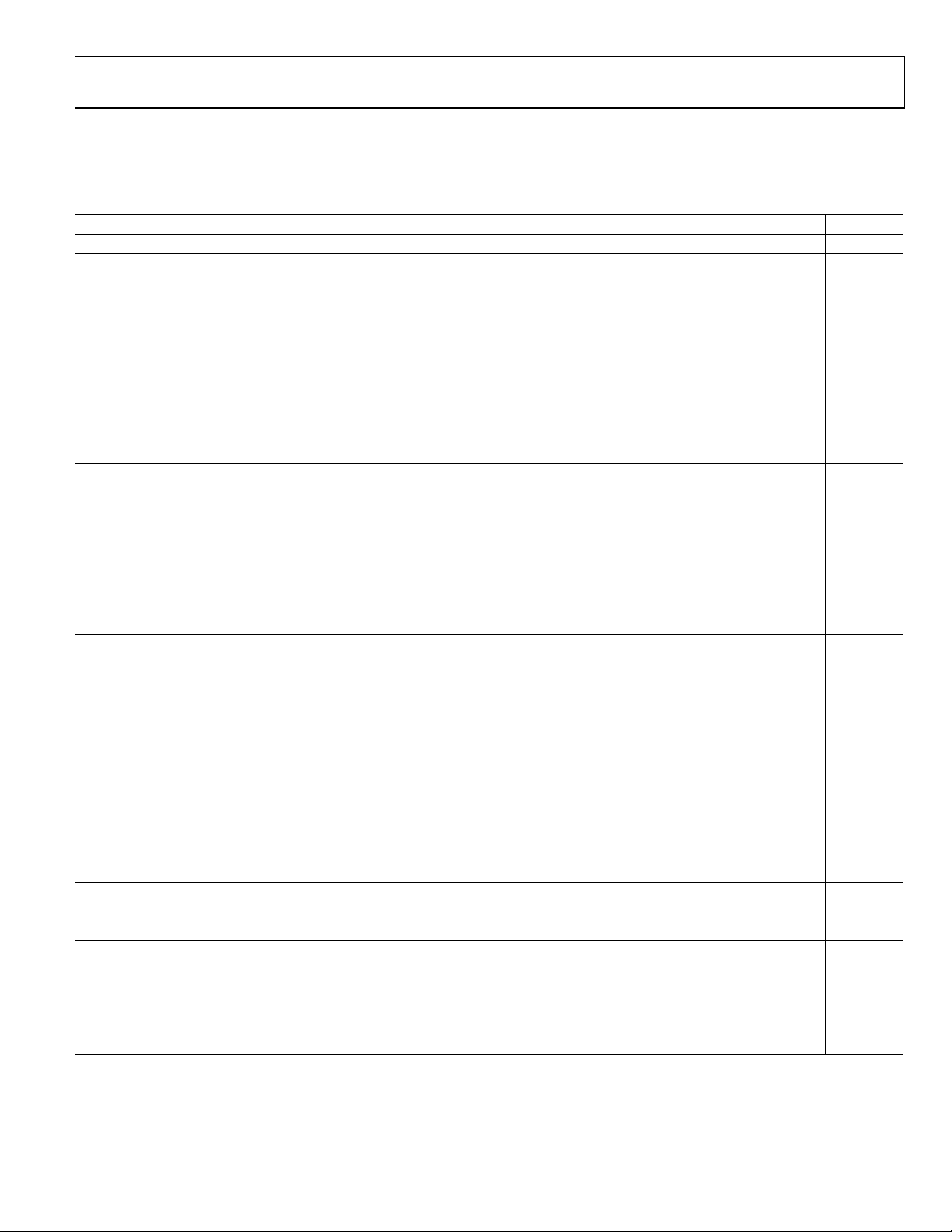
SPECIFICATIONS
−40°C to +85°C, V
Table 2.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 16 Bits
ANALOG INPUT
Voltage Range V
Common-Mode Input Voltage V
Analog Input CMRR fIN = 100 kHz 55 dB
Input Current 500 kSPS throughput 45 µA
Input Impedance1
THROUGHPUT SPEED
Complete Cycle (2 Channels) In Normal mode 2 µs
Throughput Rate In Normal mode 0 1 MSPS
Complete Cycle (2 Channels) In Impulse mode 2.25 µs
Throughput Rate In Impulse mode 0 888 kSPS
DC ACCURACY
Integral Linearity Error −6 +6 LSB2
No Missing Codes 15 Bits
Transition Noise 0.8 LSB
Full-Scale Error3 T
Full-Scale Error Drift3 ±2 ppm/°C
Unipolar Zero Error3 T
Unipolar Zero Error Drift3 ±0.8 ppm/°C
Power Supply Sensitivity AVDD = 5 V ±5% ±0.8 LSB
AC ACCURACY
Signal-to-Noise fIN = 100 kHz 86 dB4
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range fIN = 100 kHz 98 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion fIN = 100 kHz −96 dB
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) fIN = 100 kHz 86 dB
f
Channel-to-Channel Isolation fIN = 100 kHz −92 dB
−3 dB Input Bandwidth 10 MHz
SAMPLING DYNAMICS
Aperture Delay5 2 ns
Aperture Delay Matching5 30 ps
Aperture Jitter5 5 ps rms
Transient Response Full-scale step 250 ns
REFERENCE
External Reference Voltage Range 2.3 2.5 AVDD/2 V
External Reference Current Drain 500 kSPS throughput 180 µA
DIGITAL INPUTS
Logic Levels
VIL −0.3 +0.8 V
VIH +2.0 OVDD + 0.3 V
IIL −1 +1 µA
IIH −1 +1 µA
= 2.5 V, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, OVDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, unless otherwise noted.
REF
– V
INx
INxN
MIN
MIN
IN
0 2 V
INxN
−0.1 +0.5 V
to T
±0.25 ±0.5 % of FSR
MAX
to T
±0.25 % of FSR
MAX
= 100 kHz, −60 dB Input 30 dB
V
REF
Rev. A | Page 3 of 28
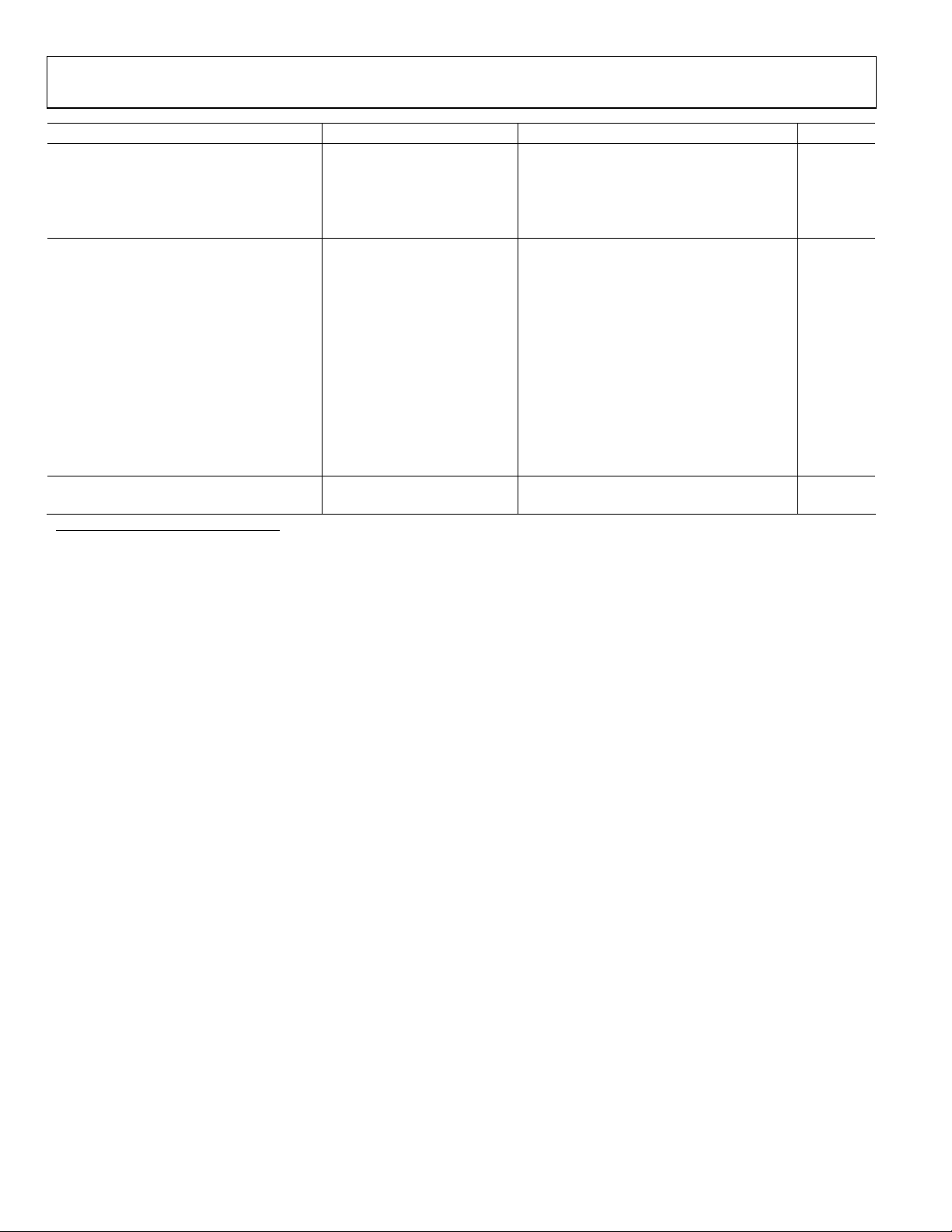
AD7655
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Data Format6
Pipeline Delay7
VOL I
VOH I
POWER SUPPLIES
Specified Performance
AVDD 4.75 5 5.25 V
DVDD
OVDD 2.7 5.258 V
Operating Current9 1 MSPS throughput
AVDD 15.5 mA
DVDD 8.5 mA
OVDD 100 µA
Power Dissipation 1 MSPS throughput9 120 135 mW
20 kSPS throughput10 2.6 mW
888 kSPS throughput10 114 125 mW
TEMPERATURE RANGE11
Specified Performance T
1
See Analog Inputs section.
2
LSB means least significant bit. Within the 0 V to 5 V input range, one LSB is 76.294 V.
3
See Definition of Specifications section. These specifications do not include the error contribution from the external reference.
4
All specifications in dB are referred to as full-scale input FS; tested with an input signal at 0.5 dB below full scale unless otherwise specified.
5
Sample tested during initial release.
6
Parallel or serial 16-bit.
7
Conversion results are available immediately after completed conversion.
8
The maximum should be the minimum of 5.25 V and DVDD + 0.3 V.
9
In Normal mode; tested in parallel reading mode.
10
In Impulse mode; tested in parallel reading mode.
11
Consult sales for extended temperature range.
= 1.6 mA 0.4 V
SINK
= −500 µA OVDD − 0.2 V
SOURCE
4.75 5 5.25 V
to T
MIN
−40 +85 °C
MAX
Rev. A | Page 4 of 28
AD7655
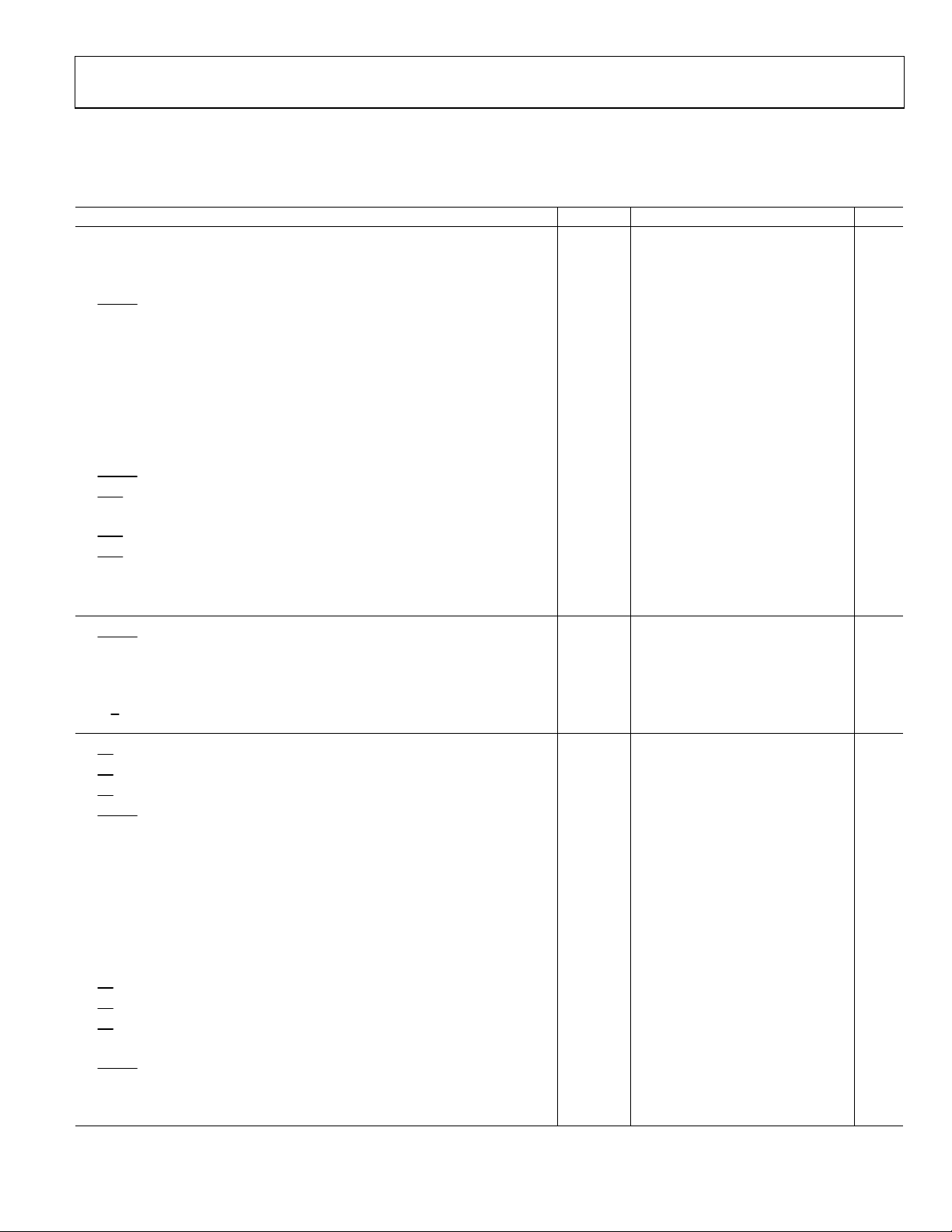
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
−40°C to +85°C, V
Table 3.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Refer to Figure 21 and Figure 22
Convert Pulse Width t1 5 ns
Time between Conversions
(Normal Mode/Impulse Mode) t2 2/2.25 µs
CNVST
Low to BUSY High Delay
BUSY High All Modes Except in Master Serial Read after Convert Mode
(Normal Mode/Impulse Mode) t4 1.75/2 µs
Aperture Delay t5 2 ns
End of Conversions to BUSY Low Delay t6 10 ns
Conversion Time
(Normal Mode/Impulse Mode) t7 1.75/2 µs
Acquisition Time t8 250 ns
RESET Pulse Width t9 10 ns
CNVST Low to High Delay
EOC High for Channel A Conversion
(Normal Mode/Impulse Mode) t
EOC Low after Channel A Conversion
EOC High for Channel B Conversion
Channel Selection Setup Time t
Channel Selection Hold Time t
Refer to Figure 23 to Figure 27 (Parallel Interface Modes)
CNVST
Low to DATA Valid Delay
DATA Valid to BUSY Low Delay t
Bus Access Request to DATA Valid t18 40 ns
Bus Relinquish Time t
A/B Low to Data Valid Delay
Refer to and (Master Serial Interface Modes)
CS Low to SYNC Valid Delay
CS Low to Internal SCLK Valid Delay1
CS Low to SDOUT Delay
CNVST
Low to SYNC Delay (Read during Convert)
(Normal Mode/Impulse Mode) t
SYNC Asserted to SCLK First Edge Delay t25 3 ns
Internal SCK Period2 t
Internal SCLK High2 t
Internal SCLK Low2 t
SDOUT Valid Setup Time2 t
SDOUT Valid Hold Time2 t
SCLK Last Edge to SYNC Delay2 t
CS
High to SYNC HI-Z
CS
High to Internal SCLK HI-Z
CS
High to SDOUT HI-Z
BUSY High in Master Serial Read after Convert2 t
CNVST
Low to SYNC Asserted Delay
(Normal Mode/Impulse Mode) t
SYNC Deasserted to BUSY Low Delay t
= 2.5 V, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, OVDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, unless otherwise noted.
REF
32 ns
t
3
t
30 ns
10
1/1.25 µs
11
t
45 ns
12
t
0.75 µs
13
250 ns
14
30 ns
15
1.75/2 µs
t
16
14 ns
17
5 15 ns
19
t
40 ns
20
t
10 ns
21
t
10 ns
22
t
10 ns
23
250/500 ns
24
23 40 ns
26
12 ns
27
7 ns
28
4 ns
29
2 ns
30
1 ns
31
10 ns
t
32
t
10 ns
33
10 ns
t
34
See Table 4
35
0.75/1 µs
36
25 ns
37
Rev. A | Page 5 of 28
AD7655
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Refer to Figure 31 and Figure 32 (Slave Serial Interface Modes)
External SCLK Setup Time t38 5 ns
External SCLK Active Edge to SDOUT Delay t39 3 18 ns
SDIN Setup Time t40 5 ns
SDIN Hold Time t41 5 ns
External SCLK Period t42 25 ns
External SCLK High t43 10 ns
External SCLK Low t44 10 ns
1
In serial interface modes, the SYNC, SCLK, and ADOUT timings are defined with a maximum load CL of 10 pF; otherwise CL is 60 pF maximum.
2
In serial master read during convert mode. See for serial master read after convert mode. Table 4
Table 4. Serial Clock Timings in Master Read after Convert
DIVSCLK[1]
DIVSCLK[0] Symbol 0 1 0 1 Unit
SYNC to SCLK First Edge Delay Minimum
Internal SCLK Period Minimum t26 25 50 100 200 ns
Internal SCLK Period Typical t26 40 70 140 280 ns
Internal SCLK High Minimum t27 12 22 50 100 ns
Internal SCLK Low Minimum t28 7 21 49 99 ns
SDOUT Valid Setup Time Minimum t29 4 18 18 18 ns
SDOUT Valid Hold Time Minimum t30 2 4 30 80 ns
SCLK Last Edge to SYNC Delay Minimum t31 1 3 30 80 ns
Busy High Width Maximum (Normal) t35 3.25 4.25 6.25 10.75 µs
Busy High Width Maximum (Impulse) t35 3.5 4.5 6.5 11 µs
0 0 1 1
3 17 17 17 ns
t
25
Rev. A | Page 6 of 28
AD7655
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5.
Parameter Values
Analog Input
INAx1, INBx1, REFx, INxN, REFGND
AVDD +0.3 V to
AGND −0.3 V
Ground Voltage Differences
AGND, DGND, OGND ±0.3 V
Supply Voltages
AVDD, DVDD, OVDD –0.3 V to +7 V
AVDD to DVDD, AVDD to OVDD ±7 V
DVDD to OVDD –0.3 V to +7 V
Digital Inputs –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Internal Power Dissipation2 700 mW
Internal Power Dissipation3 2.5 W
Junction Temperature 150°C
Storage Temperature Range –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range
(Soldering 10 sec) 300°C
1
See Analog Inputs section.
2
Specification is for device in free air:
48-lead LQFP: θ
3
Specification is for device in free air: 48-lead LFCSP: θJA = 26°C/W.
= 91°C/W, θJC = 30°C/W.
JA
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
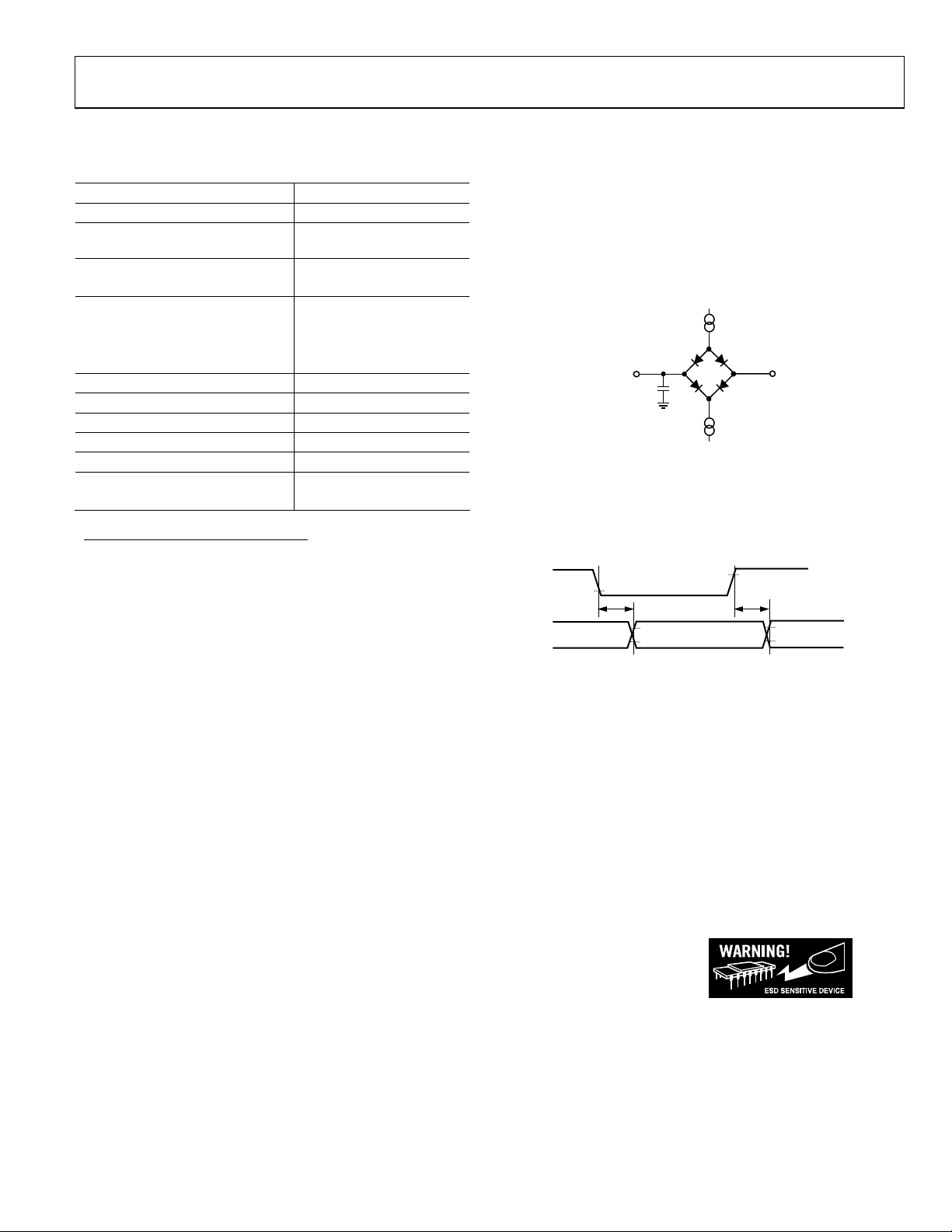
I
1.6mA
TO OUTPUT
PIN
C
L
60pF*
500µA
*IN SERIAL INTERFACE MODES, THE SYNC, SCLK, AND
SDOUT TIMINGS ARE DEFINED WITH A MAXIMUM LOAD
C
OF 10pF; OTHERWISE, THE LOAD IS 60pF MAXIMUM.
L
OL
1.4V
I
OH
03536-002
Figure 2. Load Circuit for Digital Interface Timing.
SDOUT, SYNC, SCLK Outputs, CL = 10 pF
0.8V
t
DELAY
2V
0.8V
Figure 3. Voltage Reference Levels for Timing
2V
t
DELAY
2V
0.8V
03536-003
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate
on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product
features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to
high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid
performance degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. A | Page 7 of 28
AD7655
D
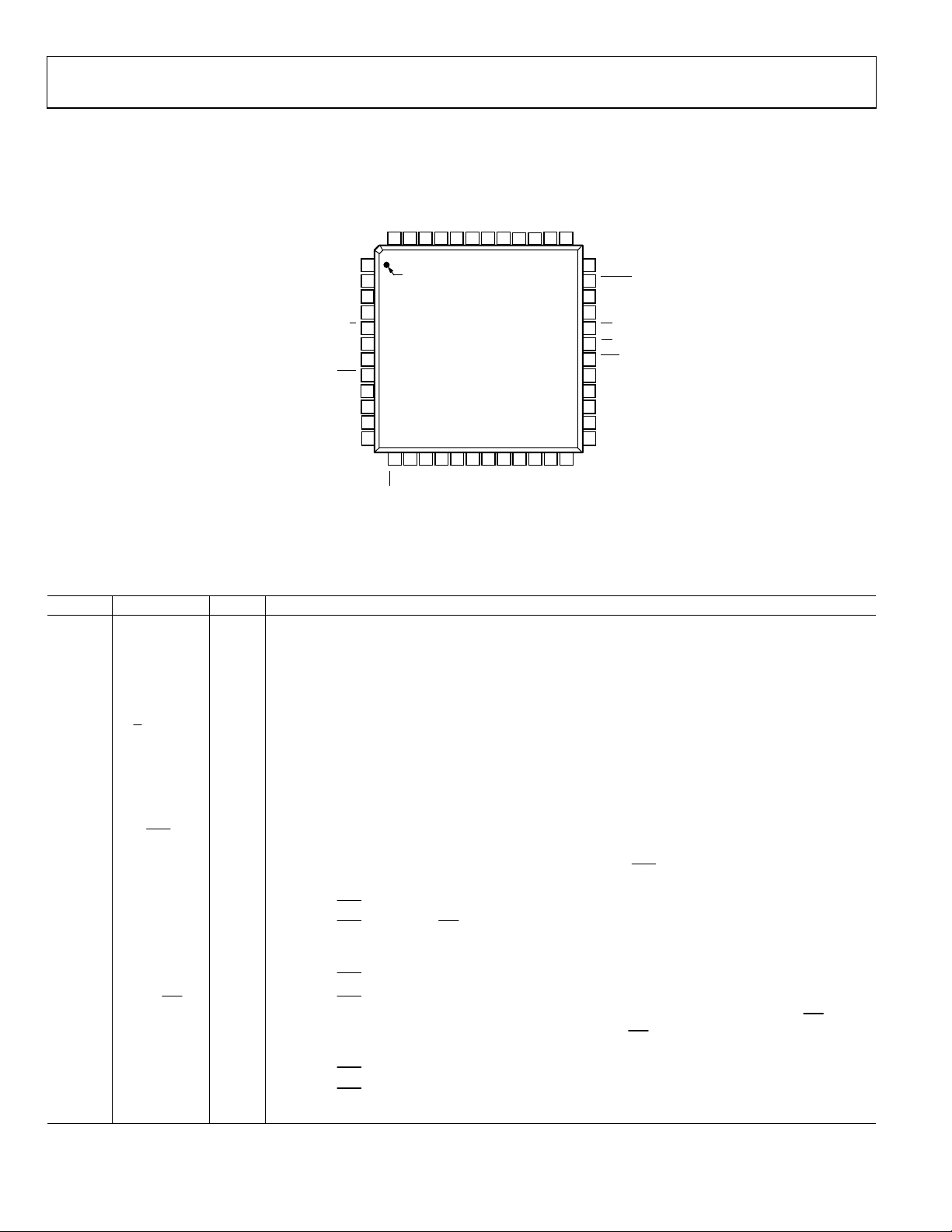
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
AGND47AGND46INA145INAN44INA243REFA42REFB41INB240INBN39INB138REFGN
48
1
AGND
AVDD
A0
BYTESWAP
A/B
DGND
IMPULSE
SER/PAR
D0
D1
D2/DIVSCLK[0]
D3/DIVSCLK[1]
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
PIN 1
13
14
D4/EXT/INT
D5/INVSYNC
AD7655
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
15
16
17
D6/INVSCLK
D7/RDC/SDIN
18
OVDD
OGND
19
DVDD
Figure 4. 48-Lead LQFP (ST-48) and 48-Lead LFCSP (CP-48)
Table 6. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Type1 Description
1, 47, 48 AGND P Analog Power Ground Pin.
2 AVDD P Input Analog Power Pin. Nominally 5 V.
3 A0 DI
Multiplexer Select. When LOW, the analog inputs INA1 and INB1 are sampled simultaneously, then
converted. When HIGH, the analog inputs INA2 and INB2 are sampled simultaneously, then converted.
4 BYTESWAP DI
Parallel Mode Selection (8 bit, 16 bit). When LOW, the LSB is output on D[7:0] and the MSB is output
on D[15:8]. When HIGH, the LSB is output on D[15:8] and the MSB is output on D[7:0].
5
A/
B
DI
Data Channel Selection. In parallel mode, when LOW, the data from Channel B is read. When HIGH, the
data from Channel A is read. In serial mode, when HIGH, Channel A is output first followed by Channel
B. When LOW, Channel B is output first followed by Channel A.
6, 20 DGND P Digital Power Ground.
7 IMPULSE DI
Mode Selection. When HIGH, this input selects a reduced power mode. In this mode, the power
dissipation is approximately proportional to the sampling rate.
8
SER/
PAR
DI
Serial/Parallel Selection Input. When LOW, the parallel port is selected; when HIGH, the serial interface
mode is selected and some bits of the DATA bus are used as a serial port.
9, 10 D[0:1] DO
Bit 0 and Bit 1 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus. When SER/
impedance.
11, 12 D[2:3] or DI/O
DIVSCLK[0:1]
When SER/
When SER/
PAR is LOW, these outputs are used as Bit 2 and Bit 3 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
PAR is HIGH, EXT/INT is LOW, and RDC/SDIN is LOW, which is the serial master read after
convert mode; these inputs, part of the serial port, are used to slow down if desired the internal serial
clock that clocks the data output. In the other serial modes, these inputs are not used.
13 D[4] DI/O
or EXT/
INT
When SER/
When SER/PAR is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used as a digital select input for choosing
PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 4 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
the internal or an external data clock, called respectively, master and slave mode. With EXT/
LOW, the internal clock is selected on SCLK output. With EXT/
synchronized to an external clock signal connected to the SCLK input.
14 D[5] DI/O
or INVSYNC
When SER/
When SER/
PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 5 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
PAR is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used to select the active state of the SYNC
signal in Master modes. When LOW, SYNC is active HIGH. When HIGH, SYNC is active LOW.
20
DGND
21
22
D8/SDOUT
D9/SCLK
REF
37
36
DVDD
35
CNVST
34
PD
33
RESET
32
CS
31
RD
30
EOC
29
BUSY
28
D15
27
D14
26
D13
25
D12
23
24
D10/SYNC
D11/RDERROR
03536-004
PAR is HIGH, these outputs are in high
INT tied
INT set to a logic HIGH, output data is
Rev. A | Page 8 of 28

AD7655
Pin No. Mnemonic Type1 Description
15 D[6] DI/O
or INVSCLK
16 D[7] DI/O
or RDC/SDIN
17 OGND P Input/Output Interface Digital Power Ground.
18 OVDD P
19, 36 DVDD P Digital Power. Nominally at 5 V.
21 D[8] DO
or SDOUT
If INVSCLK is LOW, SDOUT is updated on the SCLK rising edge and valid on the next falling edge.
If INVSCLK is HIGH, SDOUT is updated on the SCLK falling edge and valid on the next rising edge.
22 D[9] DI/O
or SCLK
23 D[10] DO
or SYNC
24 D[11] DO
or RDERROR
25 to 28 D[12:15] DO
29 BUSY DO
30
31
32
33 RESET DI
34 PD DI
EOC
RD
CS
DO End of Convert Output. Goes LOW at each channel conversion.
DI
DI
When SER/
When SER/
both Master and Slave modes.
When SER/
When SER/
read mode selection input, depending on the state of EXT/
When EXT/
from two or more ADCs onto a single SDOUT line. The digital data level on SDIN is output on SDOUT
with a delay of 32 SCLK periods after the initiation of the read sequence.
When EXT/
previous data is output on SDOUT during conversion. When RDC/SDIN is LOW, the data can be output
on SDOUT only when the conversion is complete.
Input/Output Interface Digital Power. Nominally at the same supply as the supply of the host interface
(5 V or 3 V).
When SER/
When SER/
to SCLK. Conversion results are stored in a 32-bit on-chip register. The AD7655 provides the two
conversion results, MSB first, from its internal shift register. The order of channel outputs is controlled
by A/B. In serial mode, when EXT/INT is LOW, SDOUT is valid on both edges of SCLK.
In Serial Mode, when EXT/
When SER/
When SER/
dependent upon the logic state of the EXT/
depends on the logic state of the INVSCLK pin.
When SER/
When SER/
synchronization for use with the internal data clock (EXT/
When a read sequence is initiated and INVSYNC is LOW, SYNC is driven HIGH and frames SDOUT. After
the first channel is output, SYNC is pulsed LOW. When a read sequence is initiated and INVSYNC is
HIGH, SYNC is driven LOW and remains LOW while SDOUT output is valid. After the first channel is
output, SYNC is pulsed HIGH.
When SER/
When SER/
incomplete read error flag. In Slave mode, when a data read is started and not complete when the
following conversion is complete, the current data is lost and RDERROR is pulsed HIGH.
Bit 12 to Bit 15 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus. When SER/
impedance.
Busy Output. Transitions HIGH when a conversion is started and remains HIGH until the two
conversions are complete and the data is latched into the on-chip shift register. The falling edge of
BUSY can be used as a data ready clock signal.
Read Data. When
Chip Select. When
also used to gate the external serial clock.
Reset Input. When set to a logic HIGH, reset the AD7655. Current conversion if any is aborted. If not
used, this pin could be tied to DGND.
Power-Down Input. When set to a logic HIGH, power consumption is reduced and conversions are
inhibited after the current one is completed.
PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 6 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
PAR is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used to invert the SCLK signal. It is active in
PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 7 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
PAR is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used as either an external data input or a
INT.
INT is HIGH, RDC/SDIN can be used as a data input to daisy-chain the conversion results
INT is LOW, RDC/SDIN is used to select the read mode. When RDC/SDIN is HIGH, the
PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 8 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
PAR is HIGH, this output, part of the serial port, is used as a serial data output synchronized
INT is HIGH:
PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 9 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
PAR
is HIGH, this pin, part of the serial port, is used as a serial data clock input or output,
INT pin. The active edge where the data SDOUT is updated
PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 10 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
PAR is HIGH, this output, part of the serial port, is used as a digital output frame
INT = Logic LOW).
PAR is LOW, this output is used as Bit 11 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus.
PAR is HIGH and EXT/INT is HIGH, this output, part of the serial port, is used as an
PAR is HIGH, these outputs are in high
CS and RD are both LOW, the interface parallel or serial output bus is enabled.
CS and RD are both LOW, the interface parallel or serial output bus is enabled. CS is
Rev. A | Page 9 of 28

AD7655
Pin No. Mnemonic Type1 Description
35
37 REF AI This input pin is used to provide a reference to the converter.
38 REFGND AI Reference Input Analog Ground.
39, 41 INB1, INB2 AI Channel B Analog Inputs.
40, 45 INBN, INAN AI Analog Inputs Ground Senses. Allow to sense each channel ground independently.
42, 43 REFB, REFA AI These inputs are the references applied to Channel A and Channel B, respectively.
44, 46 INA2, INA1 AI Channel A Analog Inputs.
CNVST
1
Al input; DI/O = bidirectional digital; DO = digital output; P = power.
DI
Start Conversion. A falling edge on CNVST puts the internal sample-and-hold into the hold state and
initiates a conversion. In impulse mode (IMPULSE = HIGH), if
phase (t8) is complete, the internal sample-and-hold is put into the hold state and a conversion is
immediately started.
CNVST is held LOW when the acquisition
Rev. A | Page 10 of 28

AD7655
DEFINITIONS OF SPECIFICATIONS
Integral Nonlinearity Error (INL)
Linearity error refers to the deviation of each individual code
from a line drawn from negative full scale through positive full
scale. The point used as negative full scale occurs 1/2 LSB
before the first code transition. Positive full scale is defined as a
level 1 1/2 LSB beyond the last code transition. The deviation is
measured from the middle of each code to the true straight line.
Differential Nonlinearity Error (DNL)
In an ideal ADC, code transitions are 1 LSB apart. Differential
nonlinearity is the maximum deviation from this ideal value. It
is often specified in terms of resolution for which no missing
codes are guaranteed.
Full-Scale Error
The last transition (from 111. . .10 to 111. . .11) should occur for
an analog voltage 1 1/2 LSB below the nominal full scale
(4.999886 V for the 0 V to 5 V range). The full-scale error is the
deviation of the actual level of the last transition from the ideal
level.
Unipolar Zero Error
In unipolar mode, the first transition should occur at a level
1/2 LSB above analog ground. The unipolar zero error is the
deviation of the actual transition from that point.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
The difference, in decibels, between the rms amplitude of the
input signal and the peak spurious signal.
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
THD is the ratio of the rms sum of the first five harmonic
components to the rms value of a full-scale input signal and is
expressed in decibels.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
SNR is the ratio of the rms value of the actual input signal to the
rms sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, excluding harmonics and dc. The value for SNR is
expressed in decibels.
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) Ratio (SINAD)
SINAD is the ratio of the rms value of the actual input signal to
the rms sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, including harmonics but excluding dc. The value for
SINAD is expressed in decibels.
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
ENOB is a measurement of the resolution with a sine wave
input. It is related to SINAD by the following formula:
ENOB = ((SINAD
and is expressed in bits.
Aperture Delay
Aperture delay is a measure of acquisition performance and is
measured from the falling edge of the
the input signals are held for a conversion.
Transi en t Resp on se
The time required for the AD7655 to achieve its rated accuracy
after a full-scale step function is applied to its input.
− 1.76) / 6.02)
dB
CNVST
input to when
Rev. A | Page 11 of 28

AD7655
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
5
4
3
2
1
0
INL (LSB)
–1
–2
–3
–4
–5
0 32768
16384
CODE
49152
65536
03536-005
3
2
1
0
DNL (LSB)
–1
–2
–3
163840
32768
CODE
49152
65536
03536-008
Figure 5. Integral Nonlinearity vs. Code
8000
7059
7000
6000
5000
4000
COUNTS
3000
2000
1000
1094
0
0
0
101
77
103 104 105 106 107 108 109 10A
102
6894
1230
29
CODE IN HEX
Figure 6. Histogram of 16,384 Conversions of a DC Input at the
Code Transition
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
AMPLITUDE (dB of Full Scale)
–140
–160
–180
0
50
25
100
75
FREQUENCY (kHz)
125
8192 POINT FFT
= 500kHz
f
S
f
= 100kHz, –0.5dB
IN
SNR = 85.8dB
THD = –91.4dB
SFDR = 93.6dB
SINAD = 84.5dB
150
175
200
Figure 8. Differential Nonlinearity vs. Code
9000
8000
7000
6000
5000
4000
COUNTS
3000
2000
1000
0
0
03536-006
0
0
102
220
5
103 104 105 106 107 108 109 10A
8480
3505
CODE IN HEX
3396
739
39
0
03536-009
Figure 9. Histogram of 16,384 Conversions of a DC Input at the
Code Center
–90
–94
–98
–102
–106
THD (dB)
03536-010
225
250
03536-007
SNR (dB)
96
93
90
87
84
–55
THD
SNR
–15 5 25 45 65 85 105 125
–35
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 7. FFT Plot
Figure 10. SNR, THD vs. Temperature
Rev. A | Page 12 of 28

AD7655
100
95
90
85
80
SNR AND SINAD (dB)
75
SNR
ENOB
SINAD
16.0
15.5
15.0
14.5
ENOB (Bits)
14.0
13.5
OPERATING CURRENTS (mA)
100
10
1
0.1
0.01
0.001
NORMAL DVDD
IMPULSE AVDD
OVDD 2.7V
NORMAL AVDD
IMPULSE DVDD
70
1
10 100
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Figure 11. SNR, SINAD, and ENOB vs. Frequency
–75
THD, HARMONICS (dB)
–80
–85
–90
–95
–100
–105
–110
SFDR
CROSSTALK B TO A
CROSSTALK A TO B
THIRD HARMONIC
1
THD
SECOND HARMONIC
10 100
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Figure 12. SNR and SINAD vs. Input Level (Referred to Full Scale)
5
4
3
FULL SCALE
2
1
0
LSB
–1
–2
–3
–4
–5
–55 5 65 125
25–35 –15 45 85 105
TEMPERATURE (
OFFSET DRIFT
°
C)
Figure 13. THD, Harmonics, Crosstalk, and SFDR vs. Frequency
1000
1000
13.0
03536-011
03536-012
03536-013
0.0001
1
10
SAMPLING RATE (kSPS)
100
Figure 14. Full Scale and Zero Error vs. Temperature
50
40
30
DELAY (ns)
12
20
t
10
0
0 50 100 1000
OVDD = 2.7V @ 25°C
OVDD = 5V @ 25°C
CL (pF)
OVDD = 2.7V @ 85°C
OVDD = 5V @ 85°C
Figure 15. Operating Currents vs. Sample Rate
150
1000
03536-014
03536-015
Rev. A | Page 13 of 28
AD7655
APPLICATION INFORMATION
CIRCUIT INFORMATION
The AD7655 is a very fast, low power, single-supply, precise
simultaneous sampling 16-bit analog-to-digital converter
(ADC).
The AD7655 provides the user with two on-chip track-andhold, successive approximation ADCs that do not exhibit any
pipeline or latency, making it ideal for multiple multiplexed
channel applications. The AD7655 can also be used as a
4-channel ADC with two pairs simultaneously sampled.
The AD7655 can be operated from a single 5 V supply and be
interfaced to either 5 V or 3 V digital logic. It is housed in
48-lead LQFP or tiny, 48-lead LFCSP packages that combine
space savings and allow flexible configurations as either a serial
or parallel interface. The AD7655 is pin-to-pin compatible with
PulSAR ADCs.
MODES OF OPERATION
The AD7655 features two modes of operation, Normal and
Impulse. Each of these modes is more suitable for specific
applications.
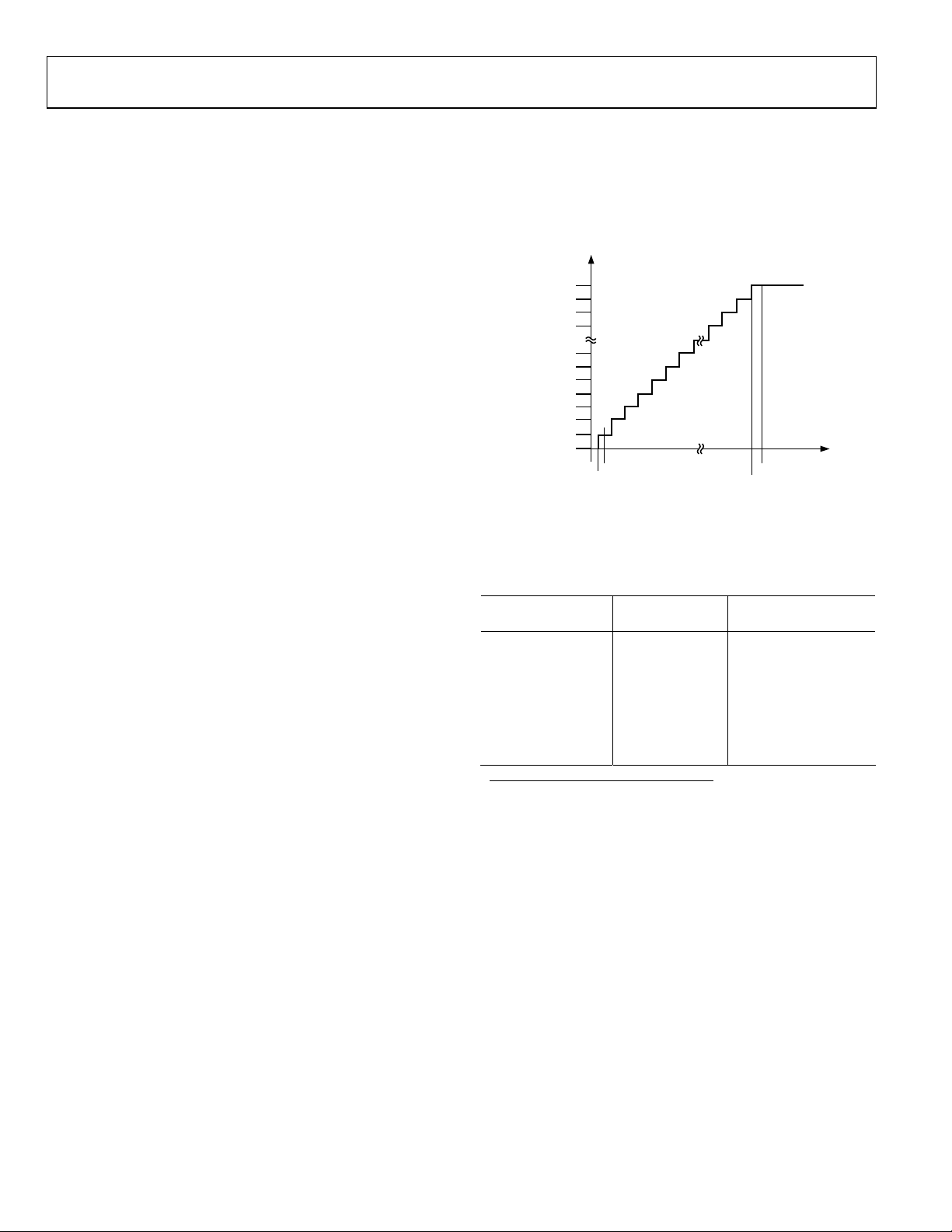
TRANSFER FUNCTIONS
The AD7655 data format is straight binary. The ideal transfer
characteristic for the AD7655 is shown in Figure 16 and Table 7.
The LSB size is 2*V
111...111
111...110
111...101
ADC CODE (Straight Binary)
000...010
000...001
000...000
–FS + 0.5 LSB
/65536, which is about 76.3 µV.
REF
–FS + 1 LSB–FS
ANALOG INPUT
Figure 16. ADC Ideal Transfer Function
+FS – 1.5 LSB
+FS – 1 LSB
03536-016
The Normal mode is the fastest mode (500 kSPS). Except when
it is powered down (PD = HIGH), the power dissipation is
almost independent of the sampling rate.
The Impulse mode, the lowest power dissipation mode, allows
power saving between conversions. The maximum throughput
in this mode is 444 kSPS. When operating at 10 kSPS, for
example, it typically consumes only 2.6 mW. This feature makes
the AD7655 ideal for battery-powered applications.
Table 7. Output Codes and Ideal Input Voltages
Analog Input
Description
V
= 2.5 V Digital Output Code
REF
FSR − 1 LSB 4.999924 V 0xFFFF1
FSR − 2 LSB 4.999847 V 0xFFFE
Midscale + 1 LSB 2.500076 V 0x8001
Midscale 2.5 V 0x8000
Midscale − 1 LSB 2.499924 V 0x7FFF
−FSR + 1 LSB −76.29 µV 0x0001
−FSR 0 V 0x00002
1
This is also the code for overrange analog input
(V
– V
above 2 × (V
INx
INxN
2
This is also the code for underrange analog input (V
– V
REFGND
)).
below V
INx
REF
INxN
).
Rev. A | Page 14 of 28

AD7655
A
2
ANALOG
SUPPLY
AD780
2.5V REF
NOTE 1
ANALOG INPUT A1
ANALOG INPUT A2
(5V)
1MΩ
100nF
NOTE 4
NOTE 4
NOTE 3
-
+
C
-
+
C
50Ω
U1
C
50Ω
U2
C
50kΩ
+
C
+
NOTE 2
15Ω
2.7nF
NOTE 5
15Ω
2.7nF
NOTE 5
REF
10µF
30Ω
100nF
1µF
NOTE 6
AVDD AGND DGND
REF
REF A
NOTE 1
REF B
REFGND
INA1
INA2
INAN
+
10µF
AD7655
100nF
DVDD
DVDD
OVDD OGND
SCLK
SDOUT
BUSY
CNVST
SER/PAR
A/B
CS
RD
BYTESWAP
RESET
PD
A0
100nF
+
50Ω
NOTE 7
10µF
SERIAL PORT
DVDD
DIGITAL SUPPLY
(3.3V OR 5V)
D
CLOCK
µC/µP/
DSP
ANALOG INPUT B1
NALOG INPUT B
NOTE 4
NOTE 4
50Ω
-
U3
+
C
50Ω
-
U4
+
C
15Ω
2.7nF
C
NOTE 5
15Ω
2.7nF
C
NOTE 5
NOTES
1. SEE VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUT SECTION.
2. WITH THE RECOMMENDED VOLTAGE REFERENCES, C
3. OPTIONAL CIRCUITRY FOR HARDWARE GAIN CALIBRATION.
4. THE AD8021 IS RECOMMENDED. SEE DRIVER AMPLIFIER CHOICE SECTION.
5. SEE ANALOG INPUTS SECTION.
6. OPTIONAL, SEE POWER SUPPLY SECTION.
7. OPTIONAL LOW JITTER CNVST. SEE CONVERSION CONTROL SECTION.
INB1
INB2
INBN
IS 47µF. SEE VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUT SECTION.
REF
Figure 17. Typical Connection Diagram (Serial Interface)
03536-017
Rev. A | Page 15 of 28

AD7655
TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Figure 17 shows a typical connection diagram for the AD7655.
Different circuitry shown on this diagram is optional and is
discussed below.
ANALOG INPUTS
Figure 18 shows a simplified analog input section of the
AD7655.
AVDD
INA1
INA2
INAN
INBN
INB1
INB2
AGND
Figure 18. Simplified Analog Input
A0 = L
A0 = H
A0 = L
A0 = H
The diodes shown in Figure 18 provide ESD protection for the
inputs. Care must be taken to ensure that the analog input
signal never exceeds the absolute ratings on these inputs. This
causes these diodes to become forward biased and start
conducting current. These diodes can handle a forward-biased
current of 120 mA maximum. This condition could eventually
occur when the input buffer’s (U1) or (U2) supplies are
different from AVDD. In such case, an input buffer with a
short-circuit current limitation can be used to protect the part.
This analog input structure allows the sampling of the
differential signal between INx and INxN. Unlike other
converters, the INxN is sampled at the same time as the INx
input. By using these differential inputs, small signals common
to both inputs are rejected.
R
A
C
S
C
S
R
B
A0
03536-018
total harmonic distortion. The maximum source impedance
depends on the amount of total harmonic distortion (THD)
that can be tolerated. The THD degrades with increase of the
source impedance.
INPUT CHANNEL MULTIPLEXER
The AD7655 allows the choice of simultaneously sampling the
inputs pairs INA1/INB1 or INA2/INB2 with the A0 multiplexer
input. When A0 is low, the input pairs INA1/INB1 are selected
and when A0 is high the input pairs INA2/INB2 are selected.
Note that INAx is always converted before INBx regardless of
the state of the digital interface channel selection A/
pin. It
B
should be noted that the channel selection control A0 should
not be changed during the acquisition phase of the converter.
DRIVER AMPLIFIER CHOICE
Although the AD7655 is easy to drive, the driver amplifier
needs to meet at least the following requirements:
• The driver amplifier and the AD7655 analog input circuit
together must be able to settle for a full-scale step of the
capacitor array at a 16-bit level (0.0015%). In the amplifier’s
data sheet, the settling at 0.1% or 0.01% is more commonly
specified. It could significantly differ from the settling time
at a 16-bit level and, therefore, it should be verified prior to
the driver selection. The tiny op amp AD8021, which
combines ultralow noise and a high gain bandwidth, meets
this settling time requirement even when used with a high
gain of up to 13.
• The noise generated by the driver amplifier needs to be
kept as low as possible to preserve the SNR and transition
noise performance of the AD7655. The noise coming from
the driver is filtered by the AD7655 analog input circuit
one-pole low-pass filter made by R
, RB, and CS.
A
During the acquisition phase, for ac signals, the AD7655
behaves like a one-pole RC filter consisting of the equivalent
resistance R
, RB, and CS. The resistors RA and RB are typically
A
500 Ω and are a lumped component made up of some serial
resistors and the on resistance of the switches. The capacitor C
is typically 32 pF and is mainly the ADC sampling capacitor.
This one-pole filter with a typical −3 dB cutoff frequency of
10 MHz reduces undesirable aliasing effect and limits the noise
coming from the inputs.
Since the input impedance of the AD7655 is very high, the
AD7655 can be driven directly by a low impedance source
without gain error. To further improve the noise filtering of the
AD7655 analog input circuit, an external, one-pole RC filter
between the amplifier output and the ADC input, as shown in
Figure 17, can be used. However, the source impedance has to
be kept low because it affects the ac performance, especially the
Rev. A | Page 16 of 28
• The driver needs to have a THD performance suitable to
that of the AD7655.
The AD8021 meets these requirements and is usually
S
appropriate for almost all applications. The AD8021 needs an
external compensation capacitor of 10 pF. This capacitor should
have good linearity as an NPO ceramic or mica type. The
AD8022 could be used where a dual version is needed and a
gain of +1 is used.
The AD829 is another alternative where high frequency (above
100 kHz) performance is not required. In a gain of +1, it
requires an 82 pF compensation capacitor.
The AD8610 is another option where low bias current is needed
in low frequency applications.

AD7655
VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUT
The AD7655 requires an external 2.5 V reference. The reference
input should be applied to REF, REFA, and REFB. The voltage
reference input REF of the AD7655 has a dynamic input
impedance; it should therefore be driven by a low impedance
source with an efficient decoupling. This decoupling depends
on the choice of the voltage reference but usually consists of a
1 µF ceramic capacitor and a low ESR tantalum capacitor
connected to the REFA, REFB, and REFGND inputs with
minimum parasitic inductance. 47 µF is an appropriate value
for the tantalum capacitor when using one of the recommended
reference voltages:
• The low noise, low temperature drift AD780 voltage
reference
• The low cost AD1582 voltage reference
For applications using multiple AD7655s with one voltage
reference source, it is recommended that the reference source
drives each ADC in a “star” configuration with individual
decoupling placed as close as possible to the REF/REFGND
inputs. Also, it is recommended that a buffer, such as the
AD8031/32, be used in this configuration.
70
65
60
55
PSRR (dB)
50
45
40
1
10
Figure 19. PSRR v s. Frequency
100 1000 10000
FREQUENCY (kHz)
POWER DISSIPATION
In Impulse mode, the AD7655 automatically reduces its power
consumption at the end of each conversion phase. During the
acquisition phase, the operating currents are very low, which
allows significant power savings when the conversion rate is
reduced, as shown in Figure 20. This feature makes the AD7655
ideal for very low power battery applications.
03536-019
Care should be taken with the reference temperature coefficient
of the voltage reference, which directly affects the full-scale
accuracy if this parameter is applicable. For instance, a
15 ppm/°C tempco of the reference changes the full-scale
accuracy by 1 LSB/°C.
POWER SUPPLY
The AD7655 uses three sets of power supply pins: an analog 5 V
supply AVDD, a digital 5 V core supply DVDD, and a digital
input/output interface supply OVDD. The OVDD supply allows
direct interface with any logic working between 2.7 V and
DVDD + 0.3 V. To reduce the number of supplies needed, the
digital core (DVDD) can be supplied through a simple RC filter
from the analog supply, as shown in Figure 17. The AD7655 is
independent of power supply sequencing, once OVDD does not
exceed DVDD by more than 0.3 V, and thus is free from supply
voltage induced latch-up. Additionally, it is very insensitive to
power supply variations over a wide frequency range, as shown
in Figure 19.
It should be noted that the digital interface remains active even
during the acquisition phase. To reduce the operating digital
supply currents even further, the digital inputs need to be
driven close to the power rails (i.e., DVDD and DGND), and
OVDD should not exceed DVDD by more than 0.3 V.
1000
100
10
1
POWER DISSIPATION (mW)
0.1
Figure 20. Power Dissipation vs. Sample Rate
NORMAL
IMPULSE
101
SAMPLING RATE (kSPS)
100 1000
03536-020
Rev. A | Page 17 of 28

AD7655
CONVERSION CONTROL
Figure 21 shows the detailed timing diagrams of the conversion
CNVST
process. The AD7655 is controlled by the signal
initiates conversion. Once initiated, it cannot be restarted or
aborted, even by the power-down input, PD, until the
conversion is complete. The
independently of the
t
1
CNVST
A0
BUSY
t
3
t
10
EOC
t
5
MODE
ACQUIRE
Although
CONVERT A
Figure 21. Basic Conversion Timing
CNVST
is a digital signal, it should be designed with
CNVST
CS
and RD signals.
t
2
t
4
t
11
t
12
CONVERT B
t
7
signal operates
t
t
13
t
6
ACQUIRE
t
14
8
special care with fast, clean edges and levels, and with minimum
overshoot and undershoot or ringing.
For applications where the SNR is critical, the
CNVST
should have very low jitter. Some solutions to achieve this are to
use a dedicated oscillator for
CNVST
generation or, at least, to
clock it with a high frequency low jitter clock, as shown in
Figure 17.
In Impulse mode, conversions can be automatically initiated. If
CNVST
is held low when BUSY is low, the AD7655 controls the
acquisition phase and automatically initiates a new conversion.
By keeping
CNVST
low, the AD7655 keeps the conversion
process running by itself. It should be noted that the analog
input has to be settled when BUSY goes low. Also, at power-up,
CNVST
should be brought low once to initiate the conversion
process. In this mode, the AD7655 could sometimes run
slightly faster than the guaranteed limits in the Impulse mode of
444 kSPS. This feature does not exist in Normal mode.
DIGITAL INTERFACE
The AD7655 has a versatile digital interface; it can be interfaced
with the host system by using either a serial or parallel interface.
The serial interface is multiplexed on the parallel data bus. The
AD7655 digital interface accommodates either 3 V or 5 V logic
by simply connecting the OVDD supply pin of the AD7655 to
the host system interface digital supply.
, which
t
15
CONVERT
signal
03536-021
CS
The two signals
and RD control the interface. When at least
one of these signals is high, the interface outputs are in high
impedance. Usually, CS allows the selection of each AD7655 in
multicircuit applications and is held low in a single AD7655
RD
design.
the data bus. In parallel mode, signal A/
reading either
serial mode, signal A/
is generally used to enable the conversion result on
allows the choice of
B
the output of Channel A or Channel B,
controls which channel is output first.
B
whereas in
Figure 22 details the timing when using the RESET input. Note
the current conversion, if any, is aborted and the data bus is
high impedance while RESET is high.
t
9
RESET
BUSY
DATA
BUS
t
8
CNVST
03536-022
Figure 22. Reset Timing
PARALLEL INTERFACE
The AD7655 is configured to use the parallel interface when
SER/
Master Parallel Interface
Data can be read continuously by tying CS and RD low, thus
requiring minimal microprocessor connections. However, in
this mode the data bus is always driven and cannot be used in
shared bus applications (unless the device is held in RESET).
Figure 23 details the timing for this mode.
CS = RD = 0
CNVST
BUSY
DATA
is held low.
PA R
t
1
t
16
t
t
3
EOC
t
10
PREVIOUS CHANNEL A
BUS
OR B
4
t
PREVIOUS CHANNEL B
OR NEW A
17
NEW A
OR B
Figure 23. Master Parallel Data Timing for Reading (Continuous Read)
03536-023
Rev. A | Page 18 of 28

AD7655
S
Slave Parallel Interface
In Slave Parallel Reading mode, the data can be read either after
each conversion, which is during the next acquisition phase or
during the other channel’s conversion, or during the following
conversion, as shown in Figure 24 and Figure 25, respectively.
When the data is read during the conversion, however, it is
recommended that it is read only during the first half of the
conversion phase. This avoids any potential feedthrough
between voltage transients on the digital interface and the most
critical analog conversion circuitry.
CS
RD
BUSY
DATA BUS
t
18
Figure 24. Slave Parallel Data Timing for Reading (Read after Convert)
CURRENT
CONVERSION
t
19
03536-024
CS
RD
BYTESWAP
PINS D[15:8]
PINS D[7:0]
HI-Z
HI-Z
HIGH BYTE LOW BYTE
t
18
LOW BYTE HIGH BYTE
t
18
HI-Z
t
HI-Z
19
Figure 26. 8-Bit Parallel Interface
Channel A/B Output
The A/B input controls which channel’s conversion results
(INAx or INBx) will
is detailed in Figure 27. When high, the data from
of A/
B
be output on the data bus.
The functionalit
Channel A is available on the data bus. When low, the data from
Channel B is available on the bus. Note that Channel A can be
EOC
read immediately after conversion is done (
), while
Channel B is still in its converting phase.
03536-026
y
CS = 0
t
CNVST, RD
EOC
BUSY
DATA BUS
t
10
t
3
t
18
1
PREVIOUS
CONVERSION
t
12
t
11
t
4
t
19
t
13
Figure 25. Slave Parallel Data Timing for Reading (Read during Convert)
8-Bit Interface (Master or Slave)
The BYTESWAP pin allows a glueless interface to an 8-bit bus.
As shown in Figure 26, the LSB byte is output on D[7:0] and the
MSB is output on D[15:8] when BYTESWAP is low. When
BYTESWAP is high, the LSB and MSB bytes are swapped, the
LSB is output on D[15:8], and the MSB is output on D[7:0]. By
connecting BYTESWAP to an address line, the 16-bit data can
be read in two bytes on either D[15:8] or D[7:0].
03536-025
CS
RD
A/B
DATA BU
HI-Z
CHANNEL A
t
18
Figure 27. A/
CHANNEL B
t
20
B
Channel Reading
HI-Z
SERIAL INTERFACE
The AD7655 is configured to use the serial interface when the
SER/
MSB first, on the SDOUT pin. The order of the channels being
output is also controlled by A/
output first; when low, Channel B is output first. Unlike in
parallel mode, Channel A data is updated only after Channel B
conversion. This data is synchronized with the 32 clock pulses
provided on the SCLK pin.
is held high. The AD7655 outputs 32 bits of data,
PA R
. When high, Channel A is
B
03536-027
Rev. A | Page 19 of 28

AD7655
MASTER SERIAL INTERFACE
Internal Clock
The AD7655 is configured to generate and provide the serial
data clock SCLK when the EXT/
AD7655 also generates a SYNC signal to indicate to the host
when the serial data is valid. The serial clock SCLK and the
SYNC signal can be inverted if desired. The output data is valid
on both the rising and falling edge of the data clock. Depending
on RDC/SDIN input, the data can be read after each conversion
or during the following conversion. Figure 28 and Figure 29
show the detailed timing diagrams of these two modes.
Usually, because the AD7655 is used with a fast throughput, the
Master Read-During-Convert mode is the most recommended
serial mode when it can be used. In this mode, the serial clock
pin is held low. The
INT
and data toggle at appropriate instants, which minimizes
potential feed through between digital activity and the critical
conversion decisions. The SYNC signal goes low after the LSB
of each channel has been output. Note that in this mode, the
SCLK period changes since the LSBs require more time to
settle, and the SCLK is derived from the SAR conversion clock.
In Master Read-After-Convert mode, it should be noted that
unlike in other modes, the signal BUSY returns low after the
32 data bits are pulsed out and not at the end of the conversion
phase, which results in a longer BUSY width. One advantage of
this mode is that it can accommodate slow digital hosts because
the serial clock can be slowed down by using DIVSCLK.
CS, RD
CNVST
BUSY
EOC
SYNC
SCLK
SDOUT
EXT/INT = 0
t
3
t
12
t
13
t
36
t
21
t
22
X
t
23
t
29
RDC/SDIN = 0 INVSCLK = INVSYNC = 0
t
35
t
25
t
26
t
27
t
28
1 2 16 30 31 32
CH A
CH A
D15
D14
t
30
17
CH BD2CH B
t
37
t
31
D1
Figure 28. Master Serial Data Timing for Reading (ReadAfter Convert)
CS, RD
CNVST
BUSY
EOC
SYNC
SCLK
SDOUT
EXT/INT = 0
t
1
t
3
t
10
t
24
t
21
t
22
t
X
t
23
25
t
29
t
26
t
t
28
27
12
CH A
D15
CH A
D14
t
30
t
11
RDC/SDIN = 1
INVSCLK = INVSYNC = 0
t
12
16 1
CH A D0
CH B
D15
CH B
D14
A/B = 1
t
13
t
31
2
Figure 29. Master Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read Previous Conversion During Convert
A/B = 1
CH B D0
16
CH B D0
t
32
t
33
t
34
03536-028
t
32
t
33
t
34
03536-029
Rev. A | Page 20 of 28

AD7655
SLAVE SERIAL INTERFACE
External Clock
The AD7655 is configured to accept an externally supplied
INT
serial data clock on the SCLK pin when the EXT/
held high. In this mode, several methods can be used to read
the data. The external serial clock is gated by
RD
are low, the data can be read after each conversion or
and
CS
during the following conversion. The external clock can be
either a continuous or discontinuous clock. A discontinuous
clock can be either normally high or normally low when
inactive. Figure 31 and Figure 32 show the detailed timing
diagrams of these methods.
While the AD7655 is performing a bit decision, it is important
that voltage transients not occur on digital input/output pins or
degradation of the conversion result could occur. This is
particularly important during the second half of the conversion
phase of each channel, because the AD7655 provides error
correction circuitry that can correct for an improper bit
decision made during the first half of the conversion phase. For
this reason, it is recommended that when an external clock is
provided, it is a discontinuous clock that is toggling only when
BUSY is low or, more importantly, that it does not transition
EOC
during the latter half of
high.
External Discontinuous Clock Data Read After Convert
Although the maximum throughput cannot be achieved in this
mode, it is the most recommended of the serial slave modes.
Figure 31 shows the detailed timing diagrams of this method.
After a conversion is complete, indicated by BUSY returning
low, the conversion results can be read while both CS and RD
are low. Data is shifted out from both channels’ MSB first, with
32 clock pulses, and is valid on both rising and falling edges of
the clock.
pin is
. When both CS
An example of the concatenation of two devices is shown in
Figure 30. Simultaneous sampling is possible by using a
common CNVST signal. It should be noted that the RDC/SDIN
input is latched on the edge of SCLK opposite the one used to
shift out the data on SDOUT. Therefore, the MSB of the
upstream converter follows the LSB of the downstream
converter on the next SCLK cycle.
BUSY
OUT
BUSY BUSY
SCLK IN
CS IN
CNVST IN
AD7655
#2 (UPSTREAM)
RDC/SDIN SDOUT
CNVST
CS
SCLK
Figure 30. Two AD7655s in a Daisy-Chain Configuration
AD7655
#1 (DOWNSTREAM)
RDC/SDIN SDOUT
CNVST
CS
SCLK
DATA
OUT
External Clock Data Read (Previous) During Convert
Figure 32 shows the detailed timing diagrams of this method.
CS
During a conversion, while both
and RD are low, the result
of the previous conversion can be read. The data is shifted out,
MSB first, with 32 clock pulses, and is valid on both rising and
falling edges of the clock. The 32 bits have to be read before the
current conversion is completed; otherwise, RDERROR is
pulsed high and can be used to interrupt the host interface to
prevent incomplete data reading. There is no daisy-chain
feature in this mode, and RDC/SDIN input should always be
tied either high or low.
03536-032
Among the advantages of this method is the fact that
conversion performance is not degraded because there are no
voltage transients on the digital interface during the conversion
process. Another advantage is the ability to read the data at any
speed up to 40 MHz, which accommodates both slow digital
host interface and the fastest serial reading.
Finally, in this mode only, the AD7655 provides a daisy-chain
feature using the RDC/SDIN input pin for cascading multiple
converters together. This feature is useful for reducing
component count and wiring connections when it is desired, as
it is for instance, in isolated multiconverters applications.
Rev. A | Page 21 of 28
To reduce performance degradation due to digital activity, a fast
discontinuous clock (at least 32 MHz in Impulse mode and
40 MHz in Normal mode) is recommended to ensure that all of
the bits are read during the first half of each conversion phase
EOC
high, t11, t12).
(
It is also possible to begin to read data after conversion and
continue to read the last bits after a new conversion has been
initiated. This allows the use of a slower clock speed like
26 MHz in Impulse mode and 30 MHz in Normal mode.

AD7655
CS
EOC
BUSY
t
t43t
EXT/INT = 1
42
44
INVSCLK = 0
RD = 0 A/B = 1
SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
t
38
t
23
1 2 3 30313233 34
t
39
D14
D14
CH A
D13
X CH A
D13
X CH B
D1
CH B D0CH B D1
X CH B
D0
X CH A
CH A
CH A
X
D15
t
41
D15
X CH A
X CH A
t
40
D15
Y CH A
D15
X CH A
D14
Y CH A
D14
03536-030
Figure 31. Slave Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read After Convert)
A/B = 1
CS
CNVST
EOC
BUSY
EXT/INT = 1
t
10
t
11
t
3
t
42
t
t
43
44
INVSCLK = 0
t
12
t
RD = 0
13
SCLK
SDOUT
t
23
123 3132
t
38
X
CH A D15
t
39
CH A D14
CH A D13
CH B D1
CH B D0
03536-031
Figure 32. Slave Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read Previous Conversion During Convert)
Rev. A | Page 22 of 28

AD7655
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACING
The AD7655 is ideally suited for traditional dc measurement
applications supporting a microprocessor, and for ac signal
processing applications interfacing to a digital signal processor.
The AD7655 is designed to interface with either a parallel 8-bit
or 16-bit wide interface, a general-purpose serial port, or I/O
ports on a microcontroller. A variety of external buffers can be
used with the AD7655 to prevent digital noise from coupling
into the ADC. The following section illustrates the use of the
AD7655 with an SPI-equipped DSP, the ADSP-219x.
SPI INTERFACE (ADSP-219X)
Figure 33 shows an interface diagram between the AD7655 and
the SPI equipped ADSP-219x. To accommodate the slower
speed of the DSP, the AD7655 acts as a slave device and data
must be read after conversion. This mode also allows the daisychain feature. The convert command can be initiated in
response to an internal timer interrupt. The 32-bit output data
is read with two serial peripheral interface (SPI) 16-bit wide
access. The reading process can be initiated in response to the
end-of-conversion signal (BUSY going low) using an interrupt
line of the DSP. The serial inter-face (SPI) on the ADSP-219x is
configured for master mode—(MSTR) = 1, Clock Polarity bit
(CPOL) = 0, Clock Phase bit (CPHA) = 1, and SPI Interrupt
Enable (TIMOD) = 00—by writing to the SPI control register
(SPICLTx). To meet all timing requirements, the SPI clock
should be limited to 17 Mbps, which allows it to read an ADC
result in less than 1 µs. When a higher sampling rate is desired,
use of one of the parallel interface modes is recommended.
DVDD
AD7655*
SER/PAR
EXT/INT
BUSY
CS
RD
INVSCLK
Figure 33. Interfacing the AD7655 to SPI Interface
SDOUT
SCLK
CNVST
*ADDITIONAL PINS OMITTED FOR CLARITY
ADSP-219x*
PFx
SPIxSEL (PFx)
MISOx
SCKx
PFx or TFSx
03536-033
Rev. A | Page 23 of 28

AD7655
APPLICATION HINTS
LAYOUT
The AD7655 has very good immunity to noise on the power
supplies. However, care should still be taken with regard to
grounding layout.
The printed circuit board that houses the AD7655 should be
designed so the analog and digital sections are separated and
confined to certain areas of the board. This facilitates the use of
ground planes that can be separated easily. Digital and analog
ground planes should be joined in only one place, preferably
underneath the AD7655, or as close as possible to the AD7655.
If the AD7655 is in a system where multiple devices require
analog-to-digital ground connections, the connection should
still be made at one point only, a star ground point that should
be established as close as possible to the AD7655.
Running digital lines under the device should be avoided since
these couple noise onto the die. The analog ground plane
should be allowed to run under the AD7655 to avoid noise
coupling. Fast switching signals like
shielded with digital ground to avoid radiating noise to other
sections of the board, and should never run near analog signal
paths. Crossover of digital and analog signals should be
avoided. Traces on different but close layers of the board should
run at right angles to each other. This reduces the effect of
crosstalk through the board.
The power supply lines to the AD7655 should use as large a
trace as possible to provide low impedance paths and reduce the
effect of glitches on the power supply lines. Good decoupling is
also important to lower the supply’s impedance presented to the
AD7655 and to reduce the magnitude of the supply spikes.
Decoupling ceramic capacitors, typically 100 nF, should be
placed on each power supply pin—AVDD, DVDD, and OVDD
CNVST
or clocks should be
—close to, and ideally right up against these pins and their
corresponding ground pins. Additionally, low ESR 10 µF
capacitors should be located near the ADC to further reduce
low frequency ripple.
The DVDD supply of the AD7655 can be a separate supply or
can come from the analog supply AVDD or the digital interface
supply OVDD. When the system digital supply is noisy or when
fast switching digital signals are present, if no separate supply is
available, the user should connect DVDD to AVDD through an
RC filter (see Figure 17) and the system supply to OVDD and
the remaining digital circuitry. When DVDD is powered from
the system supply, it is useful to insert a bead to further reduce
high frequency spikes.
The AD7655 has five different ground pins: INGND, REFGND,
AGND, DGND, and OGND. INGND is used to sense the
analog input signal. REFGND senses the reference voltage and,
because it carries pulsed currents, should be a low impedance
return to the reference. AGND is the ground to which most
internal ADC analog signals are referenced; it must be
connected with the least resistance to the analog ground plane.
DGND must be tied to the analog or digital ground plane
depending on the configuration. OGND is connected to the
digital system ground.
EVALUATING THE AD7655’S PERFORMANCE
A recommended layout for the AD7655 is outlined in the
documentation of the evaluation board for the
EVAL-AD7655CB. The evaluation board package includes a
fully assembled and tested evaluation board, documentation,
and software for controlling the board from a PC via the
EVAL-CONTROL-BRD2.
Rev. A | Page 24 of 28

AD7655
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
1.45
1.40
1.35
0.15
SEATING
0.05
PLANE
VIEW A
ROTATED 90° CCW
0.75
0.60
0.45
SEATING
0.20
0.09
7°
3.5°
0°
PLANE
10°
6°
2°
0.08 MAX
COPLANARITY
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-026BBC
1.60
MAX
VIEW A
1
12
0.50
BSC
Figure 35. 48-Lead Low Profile Quad Flat Package [LQFP]
(ST-48)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
BSC SQ
PIN 1
INDICATOR
7.00
0.60 MAX
37
36
0.60 MAX
48
13
9.00
BSC SQ
PIN 1
TOP VIEW
(PINS DOWN)
0.30
0.23
0.18
37
36
7.00
BSC SQ
25
24
0.27
0.22
0.17
PIN 1
48
INDICATOR
1
1.00
0.85
0.80
12° MAX
SEATING
PLANE
TOP
VIEW
6.75
BSC SQ
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VKKD-2
0.20 REF
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
25
24
COPLANARITY
0.08
EXPOSED
PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
5.50
REF
5.25
5.10 SQ
4.95
12
13
PADDLE CONNECTED TO AGND.
THIS CONNECTION IS NOT
REQUIRED TO MEET THE
ELECTRICAL PERFORMANCES
0.25 MIN
Figure 36. 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP]
(CP-48)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD7655AST –40°C to +85°C Low Profile Quad Flat Package [LQFP] ST-48
AD7655ASTRL –40°C to +85°C Low Profile Quad Flat Package [LQFP] ST-48
AD7655ASTZ1 –40°C to +85°C Low Profile Quad Flat Package [LQFP] ST-48
AD7655ASTZRL1 –40°C to +85°C Low Profile Quad Flat Package [LQFP] ST-48
AD7655ACP –40°C to +85°C Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP] CP-48
AD7655ACPRL –40°C to +85°C Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP] CP-48
EVAL-AD7655CB2 Evaluation Board
EVAL-CONTROL-BRD23
Controller Board
1
Z = PB-free part.
2
This board can be used as a standalone evaluation board or in conjunction with the EVAL-CONTROL-BRD2 for evaluation/demonstration purposes.
3
This board allows a PC to control and communicate with all Analog Devices evaluation boards ending in CB designators.
Rev. A | Page 25 of 28

AD7655
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 26 of 28

AD7655
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 27 of 28

AD7655
NOTES
© 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
C03536-0-12/04(A)
Rev. A | Page 28 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...