ANALOG DEVICES AD7653 Service Manual
16-Bit 1 MSPS PulSAR
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TM
FEATURES
Throughput:
1 MSPS (Warp mode)
800 kSPS (Normal mode)
666 kSPS (Impulse mode)
16-bit resolution
Analog input voltage range: 0 V to 2.5 V
No pipeline delay
Parallel and serial 5 V/3 V interface
®/QSPI
TM
/MICROWIRETM/DSP compatible
SPI
Single 5 V supply operation
Power dissipation
92 mW typ @ 666 kSPS, 138 µW @ 1 kSPS without REF
128 mW typ @ 1 MSPS with REF
48-lead LQFP and 48-lead LFCSP packages
Pin-to-pin compatible with PulSAR ADCs
APPLICATIONS
Data acquisition
Instrumentation
Digital signal processing
Spectrum analysis
Medical instruments
Battery-powered systems
Process control
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7653* is a 16-bit, 1 MSPS, charge redistribution SAR
analog-to-digital converter that operates from a single 5 V
power supply. The part contains a high speed 16-bit sampling
ADC, internal conversion clock, internal reference, error
correction circuits, and both serial and parallel system interface
ports. It features a very high sampling rate mode (Warp), a fast
mode (Normal) for asynchronous conversion rate applications,
and a reduced power mode (Impulse) for low power applications where power is scaled with the throughput. The AD7653 is
fabricated using Analog Devices’ high performance, 0.6 micron
CMOS process, with correspondingly low cost. It is available in
a 48-lead LQFP and a tiny 48-lead LFCSP with operation
specified from –40°C to +85°C.
*
Patent Pending.
Unipolar ADC with Reference
AD7653
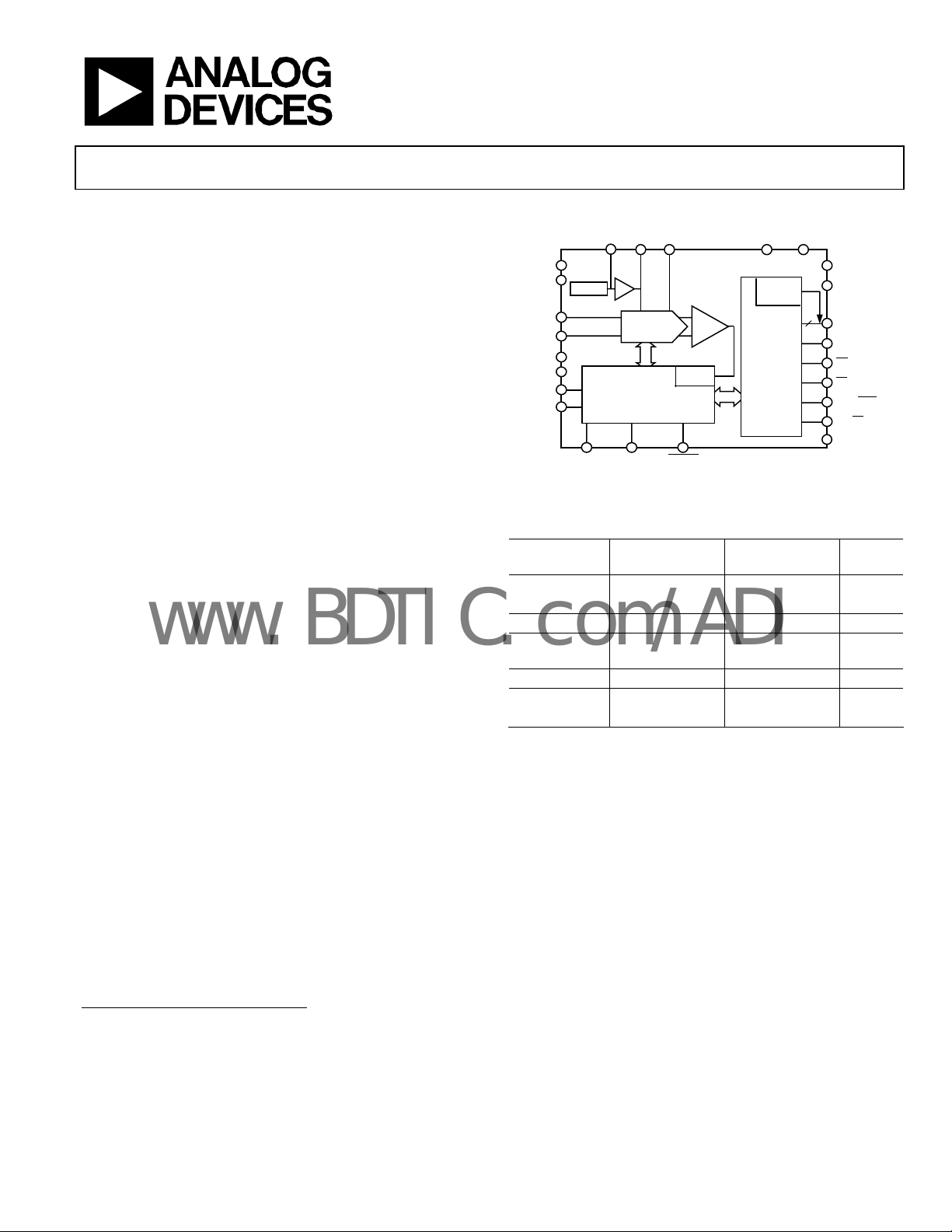
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
REFBUFIN
AGND
AVDD
INGND
PDREF
PDBUF
RESET
REF
IN
PD
Table 1. PulSAR Selection
Type/kSPS 100–250 500–570
PseudoDifferential
True Bipolar AD7663 AD7665 AD7671
True
Differential
18-Bit AD7678 AD7679 AD7674
Multichannel/
Simultaneous
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Fast Throughput.
The AD7653 is a 1 MSPS, charge redistribution, 16-bit SAR
ADC with internal error correction circuitry.
2. Internal Reference.
The AD7653 has an internal reference with a typical
temperature drift of 7 ppm/°C.
3. Single-Supply Operation.
The AD7653 operates from a single 5 V supply. In Impulse
mode, its power dissipation decreases with the throughput.
4. Serial or Parallel Interface.
Versatile parallel or 2-wire serial interface arrangement is
compatible with both 3 V and 5 V logic.
REF REFGND
AD7653
SWITCHED
CAP DAC
CLOCK
CONTROL LOGIC AND
CALIBRATION CIRCUITRY
CNVSTWARP IMPULSE
Figure 1.
AD7651
AD7660/AD7661
AD7650/AD7652
AD7664/AD7666
SERIAL
PORT
PARALLEL
INTERFACE
DGNDDVDD
16
AD7675 AD7676 AD7677
AD7654
AD7655
OVDD
OGND
DATA[15:0]
BUSY
RD
CS
SER/PAR
OB/2C
BYTESWAP
02966-0-001
800–
1000
AD7653
AD7667
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

AD7653
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Timing Specifications....................................................................... 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 7
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 8
Definitions of Specifications ......................................................... 11
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 12
Circuit Information........................................................................ 15
Converter Operation.................................................................. 15
Typical Connection Diagram.................................................... 17
Power Dissipation vs. Throughput........................................... 19
Conversion Control.................................................................... 19
Digital Interface.......................................................................... 20
Parallel Interface......................................................................... 20
Serial Interface............................................................................ 20
Master Serial Interface............................................................... 21
Slave Serial Interface.................................................................. 22
Microprocessor Interfacing....................................................... 24
Application Hints............................................................................ 25
Bipolar and Wider Input Ranges.............................................. 25
Layout .......................................................................................... 25
Evaluating the AD7653’s Performance .................................... 25
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 26
Ordering Guide........................................................................... 26
REVISION HISTORY
Location Page
9/03—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Change to Product Highlights .................................................... 1
Changes to Specifications............................................................ 3
Changes to Absolute Maximum Ratings ................................... 7
Changes to Figure 15.................................................................. 13
Changes to Figure 22.................................................................. 16
Changes to Voltage Reference Input section........................... 18
Changes to Figure 31.................................................................. 20
Rev. A | Page 2 of 28
AD7653
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
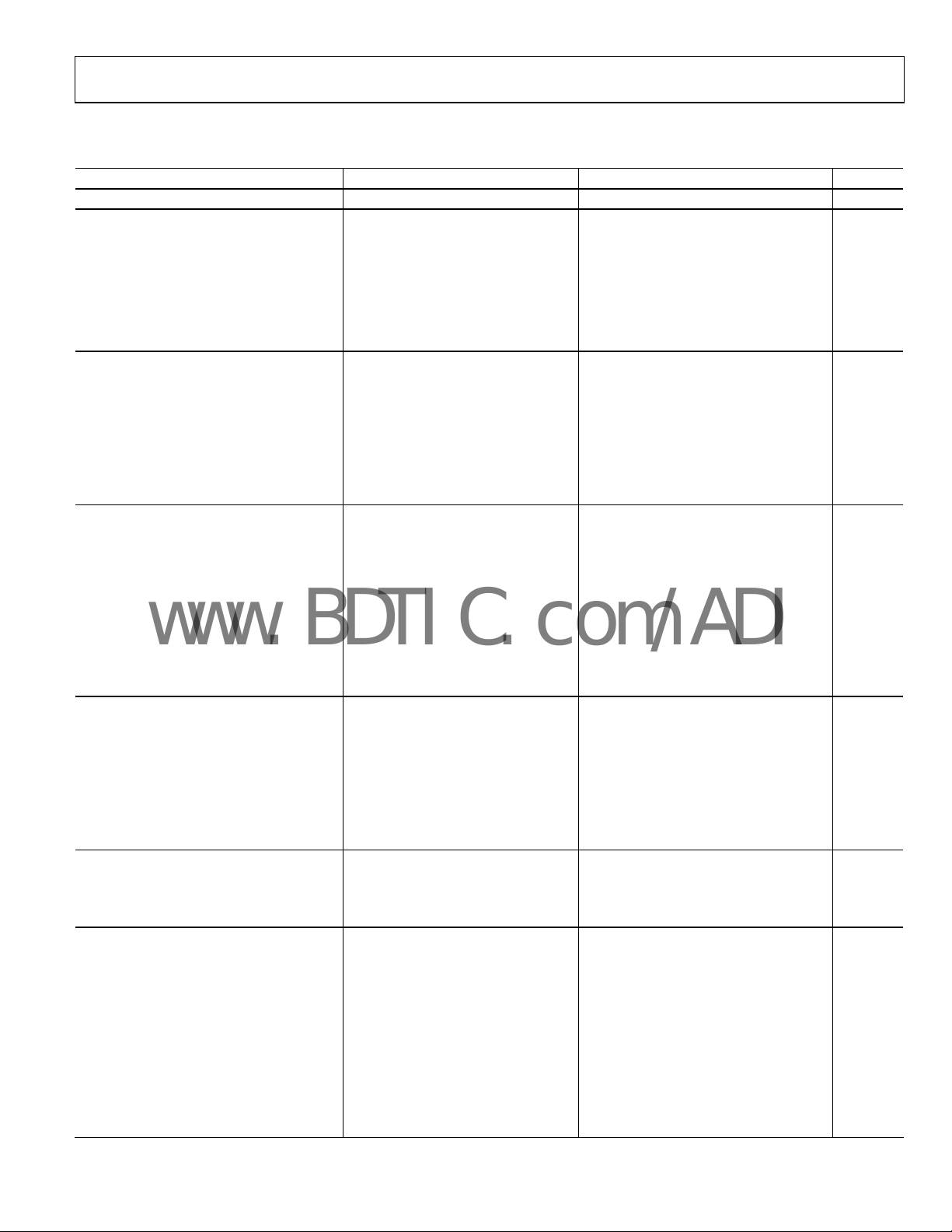
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 2. –40°C to +85°C, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, OVDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, unless otherwise noted
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 16 Bits
ANALOG INPUT
Voltage Range VIN – V
Operating Input Voltage VIN –0.1 +3 V
0 V
INGND
V
REF
V
Analog Input CMRR fIN = 10 kHz 65 dB
Input Current 1 MSPS Throughput 12 µA
Input Impedance1
THROUGHPUT SPEED
Complete Cycle In Warp Mode 1 µs
Throughput Rate In Warp Mode 1 1000 kSPS
Time between Conversions In Warp Mode 1 ms
Complete Cycle In Normal Mode 1.25 µs
Throughput Rate In Normal Mode 0 800 kSPS
Complete Cycle In Impulse Mode 1.5 µs
Throughput Rate In Impulse Mode 0 666 kSPS
DC ACCURACY
Integral Linearity Error –6 +6 LSB2
No Missing Codes 15 Bits
Differential Linearity Error –2 +3 LSB
Transition Noise 0.7 LSB
Unipolar Zero Error, T
Unipolar Zero Error Temperature Drift ±0.2 ppm/°C
Full-Scale Error, T
Full-Scale Error Temperature Drift
Power Supply Sensitivity AVDD = 5 V ± 5%, with REF ±2 LSB
AC ACCURACY
Signal-to-Noise fIN = 100 kHz 86 dB4
Spurious Free Dynamic Range fIN = 100 kHz 98 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion fIN = 45 kHz –98 dB
f
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) fIN = 100 kHz 86 dB
–60 dB Input, fIN = 100 kHz 30 dB
–3 dB Input Bandwidth 12 MHz
SAMPLING DYNAMICS
Aperture Delay 2 ns
Aperture Jitter 5 ps rms
Transient Response Full-Scale Step 250 ns
REFERENCE
Internal Reference Voltage V
Internal Reference Temperature Drift –40°C to +85°C ±7 ppm/°C
Line Regulation
Turn-On Settling Time C
Temperature Pin
Voltage Output @ 25°C 300 mV
Temperature Sensitivity 1 mV/°C
Output Resistance 4.3 kΩ
External Reference Voltage Range 2.3 2.5 AVDD – 1.85 V
External Reference Current Drain 1 MSPS Throughput 300 µA
MIN
MIN
to T
3
to T
MAX
±25 LSB
MAX
3
REF = 2.5 V ±0.12 % of FSR
–0.1 +0.5 V
INGND
±0.4
= 100 kHz –96 dB
IN
@ 25°C 2.48 2.50 2.52 V
REF
AVDD = 5 V ± 5%
= 10 µF 5 ms
REF
±24 ppm/V
ppm/°C
Rev. A | Page 3 of 28
AD7653
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
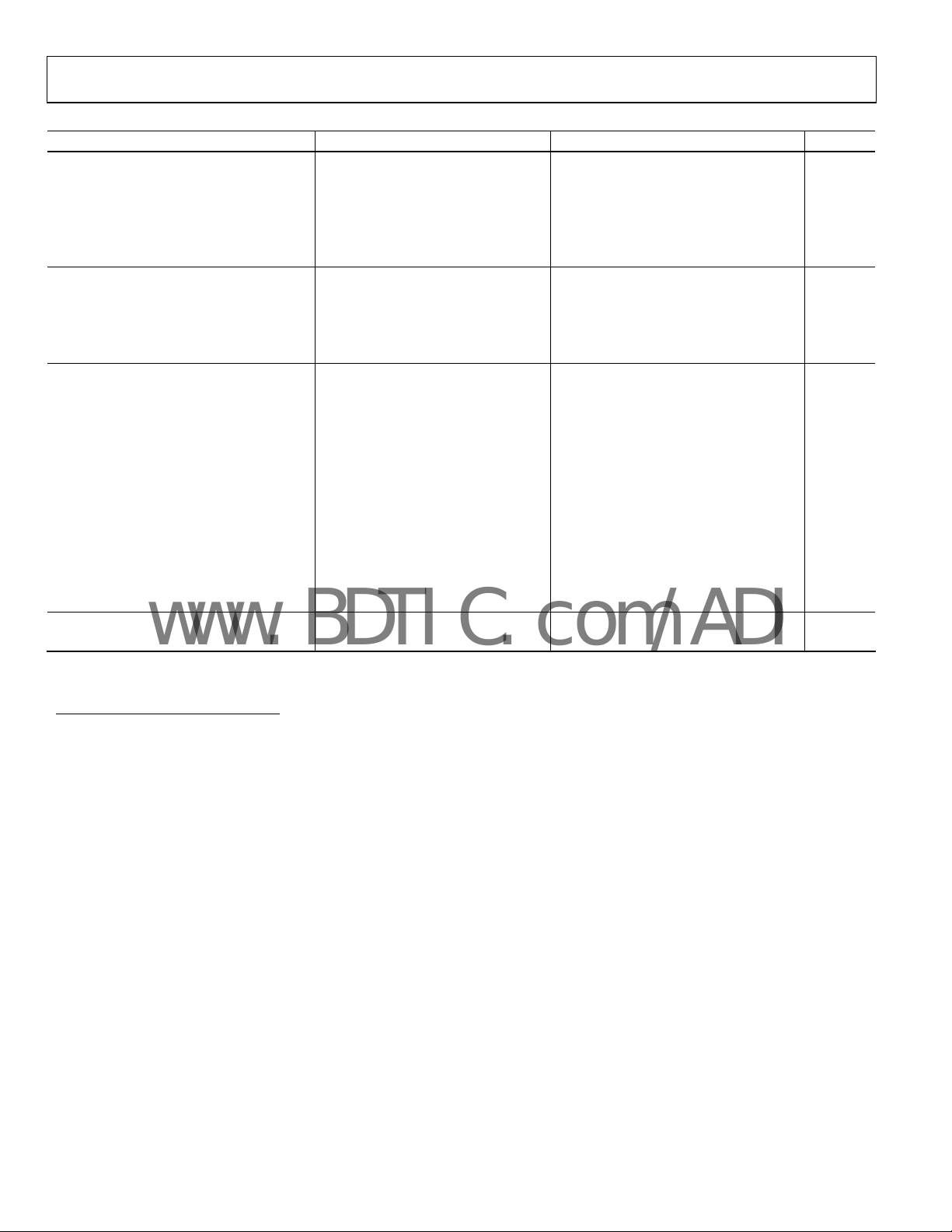
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DIGITAL INPUTS
Logic Levels
VIL –0.3 +0.8 V
VIH 2.0 DVDD + 0.3 V
IIL –1 +1 µA
IIH –1 +1 µA
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Data Format5
Pipeline Delay6
VOL I
VOH I
POWER SUPPLIES
Specified Performance
AVDD 4.75 5 5.25 V
DVDD 4.75 5 5.25 V
OVDD 2.7 5.257 V
Operating Current8 1 MSPS Throughput
AVDD9 With Reference and Buffer 18.7 mA
AVDD10 Reference and Buffer Alone 3 mA
DVDD11 6.7 mA
OVDD11 200 µA
Power Dissipation without REF 666 kSPS Throughput11 92 115 mW
1 kSPS Throughput11 138 µW
Power Dissipation with REF 1 MSPS Throughput8 128 145 mW
TEMPERATURE RANGE12
Specified Performance T
= 1.6 mA 0.4 V
SINK
= –500 µA OVDD – 0.6 V
SOURCE
to T
MIN
–40 +85 °C
MAX
1
See Analog Input section.
2
LSB means least significant bit. With the 0 V to 2.5 V input range, 1 LSB is 38.15 µV.
3
See Definitions of Specifications section. These specifications do not include the error contribution from the external reference.
4
All specifications in dB are referred to a full-scale input FS. Tested with an input signal at 0.5 dB below full-scale, unless otherwise specified.
5
Parallel or serial 16-bit.
6
Conversion results are available immediately after completed conversion.
7
The max should be the minimum of 5.25 V and DVDD + 0.3 V.
8
In Warp mode.
9
With REF, PDREF and PDBUF are LOW; without REF, PDREF and PDBUF are HIGH.
10
With PDREF, PDBUF LOW and PD HIGH.
11
Impulse Mode. Tested in Parallel Reading mode.
12
Consult factory for extended temperature range.
Rev. A | Page 4 of 28
AD7653
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
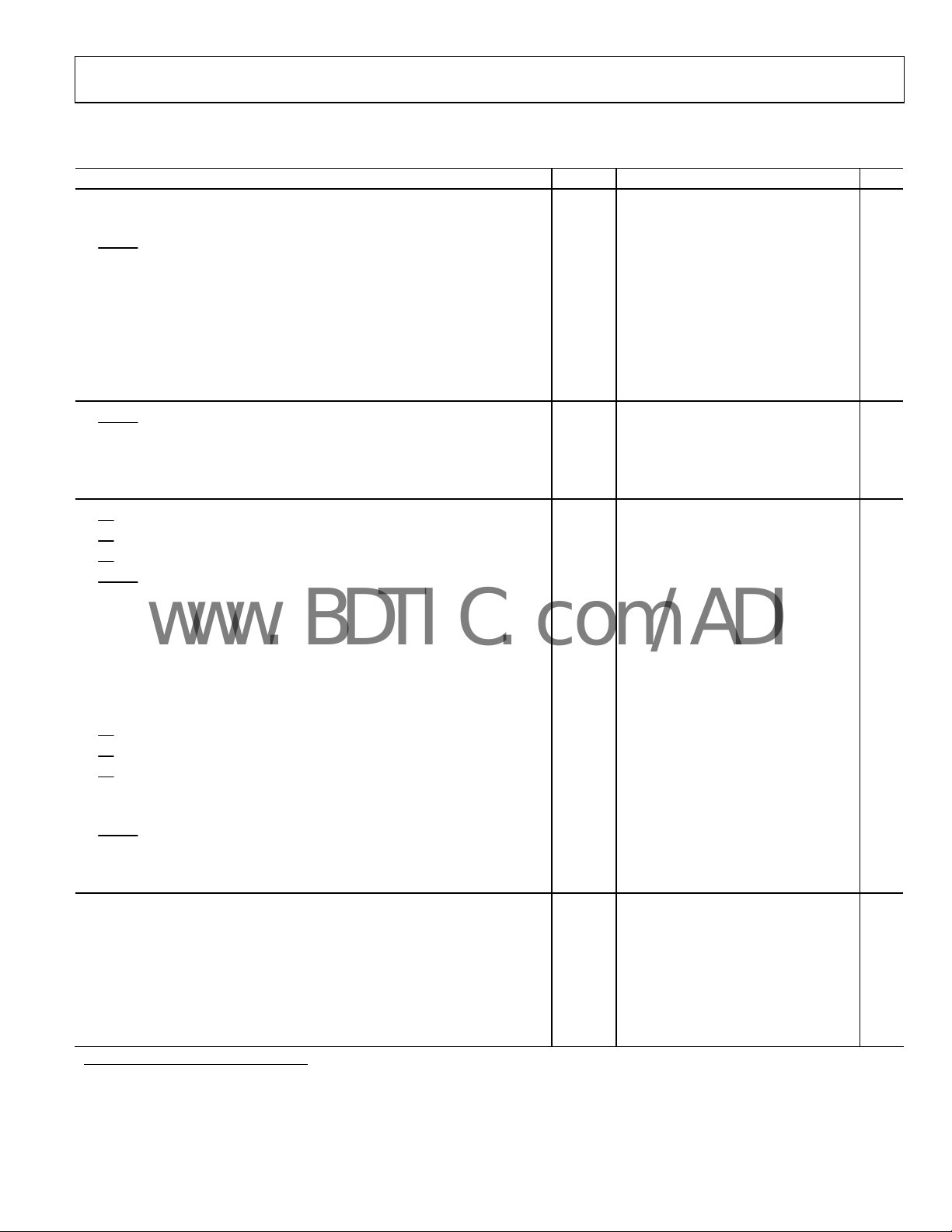
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3. –40°C to +85°C, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, OVDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, unless otherwise noted
Parameter
Refer to Figure 26 and Figure 27
Convert Pulse Width
Time between Conversions (Warp Mode/Normal Mode/Impulse Mode)1
CNVST
LOW to BUSY HIGH Delay t3
BUSY HIGH All Modes Except Master Serial Read after Convert
(Warp Mode/Normal Mode/Impulse Mode)
Aperture Delay
End of Conversion to BUSY LOW Delay
Conversion Time (Warp Mode/Normal Mode/Impulse Mode)
Acquisition Time
RESET Pulse Width
Refer to Figure 28, Figure 29, and (Parallel Interface Modes)
CNVST
LOW to DATA Valid Delay (Warp Mode/Normal Mode/Impulse Mode) t10
Figure 30
DATA Valid to BUSY LOW Delay
Bus Access Request to DATA Valid
Bus Relinquish Time
Refer to Figure 32 and Figure 33 (Master Serial Interface Modes)2
CS
LOW to SYNC Valid Delay t14
CS
LOW to Internal SCLK Valid Delay2
CS
LOW to SDOUT Delay t16
CNVST
LOW to SYNC Delay (Warp Mode/Normal Mode/Impulse Mode) t17
SYNC Asserted to SCLK First Edge Delay
Internal SCLK Period3
Internal SCLK HIGH3
Internal SCLK LOW3
SDOUT Valid Setup Time3
SDOUT Valid Hold Time3
SCLK Last Edge to SYNC Delay3
CS
HIGH to SYNC HI-Z t25
CS
HIGH to Internal SCLK HI-Z t26
CS
HIGH to SDOUT HI-Z t27
BUSY HIGH in Master Serial Read after Convert3
(Warp Mode/Normal Mode/Impulse Mode)
CNVST
LOW to SYNC Asserted Delay
(Warp Mode/Normal Mode/Impulse Mode)
SYNC Deasserted to BUSY LOW Delay
Refer to and (Slave Serial Interface Modes) 2
Figure 34 Figure 35
External SCLK Setup Time
External SCLK Active Edge to SDOUT Delay
SDIN Setup Time
SDIN Hold Time
External SCLK Period
External SCLK HIGH
External SCLK LOW
1In Warp mode only, the maximum time between conversions is 1 ms; otherwise, there is no required maximum time.
2
In serial interface modes, the SYNC, SCLK, and SDOUT timings are defined with a maximum load CL of 10 pF; otherwise, the load is 60 pF maximum.
3
In Serial Master Read during Convert Mode. See for Serial Master Read after Convert mode. Table 4
Symbol
t
1
t
2
t
4
t
5
t
6
t
7
t
8
t
9
t
11
t
12
t
13
t
15
t
18
t
19
t
20
t
21
t
22
t
23
t
24
t
28
t
29
t
30
t
31
t
32
t
33
t
34
t
35
t
36
t
37
Min Typ Max Unit
10 ns
1/1.25/1.5 µs
35 ns
0.75/1/1.25 µs
2 ns
10 ns
0.75/1/1.25 µs
250 ns
10 ns
0.75/1/1.25 µs
12 ns
45 ns
5 15 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
25/275/525 ns
3 ns
25 40 ns
12 ns
7 ns
4 ns
2 ns
3 ns
10 ns
10 ns
10 ns
See Table 4
0.75/1/1.25 µs
25 ns
5 ns
3 18 ns
5 ns
5 ns
25 ns
10 ns
10 ns
Rev. A | Page 5 of 28
AD7653
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Table 4. Serial Clock Timings in Master Read after Convert
DIVSCLK[1] 0 0 1 1
DIVSCLK[0] Symbol 0 1 0 1 Unit
SYNC to SCLK First Edge Delay Minimum t18 3 17 17 17 ns
Internal SCLK Period Minimum t19 25 50 100 200 ns
Internal SCLK Period Maximum t19 40 70 140 280 ns
Internal SCLK HIGH Minimum t20 12 22 50 100 ns
Internal SCLK LOW Minimum t21 7 21 49 99 ns
SDOUT Valid Setup Time Minimum t22 4 18 18 18 ns
SDOUT Valid Hold Time Minimum t23 2 4 30 80 ns
SCLK Last Edge to SYNC Delay Minimum t24 3 55 130 290 ns
BUSY HIGH Width Maximum (Warp) t28 1.5 2 3 5.25 µs
BUSY HIGH Width Maximum (Normal) t28 1.75 2.25 3.25 5.55 µs
BUSY HIGH Width Maximum (Impulse) t28 2 2.5 3.5 5.75 µs
Rev. A | Page 6 of 28
AD7653
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5. AD7653 Absolute Maximum Ratings1
Parameter Rating
IN2, TEMP2,REF, REFBUFIN,
INGND, REFGND to AGND
AVDD + 0.3 V to
AGND – 0.3 V
Ground Voltage Differences
AGND, DGND, OGND ±0.3 V
Supply Voltages
AVDD, DVDD, OVDD –0.3 V to +7 V
AVDD to DVDD, AVDD to OVDD ±7 V
TO OUTPUT
PIN
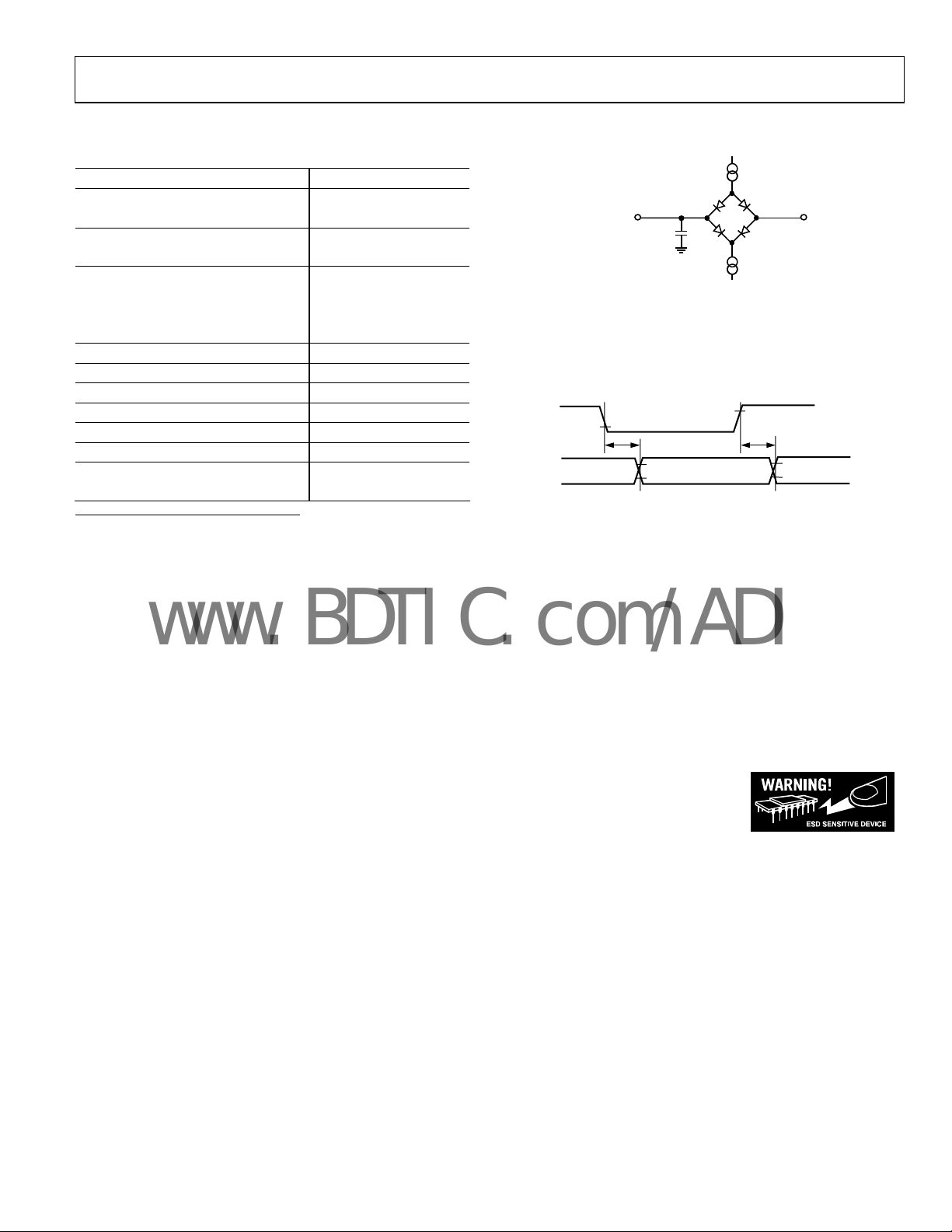
60pF*
* IN SERIAL INTERFACE MODES, THE SYNC, SCLK, AND
SDOUT TIMINGS ARE DEFINED WITH A MAXIMUM LOAD
OF 10pF; OTHERWISE,THE LOAD IS 60pF MAXIMUM.
C
L
1.6mA
C
L
500µA
DVDD to OVDD –0.3 V to +7 V
Digital Inputs –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
PDREF, PDBUF3 ±20 mA
Internal Power Dissipation4 700 mW
Figure 2. Load Circuit for Digital Interface Timing,
SDOUT, SYNC, SCLK Outputs C
Internal Power Dissipation5 2.5 W
Junction Temperature 150°C
Storage Temperature Range –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range
300°C
0.8V
t
DELAY
2V
0.8V
(Soldering 10 sec)
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those listed
in the operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
2
See section.
Analog Input
3
See Voltage Reference Input section.
4
Specification is for the device in free air:
48-Lead LQFP; θJA = 91°C/W, θJC = 30°C/W
5
Specification is for the device in free air:
48-Lead LFCSP; θJA = 26°C/W.
Figure 3. Voltage Reference Levels for Timing
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the
human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
I
OL
1.4V
I
OH
02966-0-006
= 10 pF
L
2V
t
DELAY
2V
0.8V
02966-0-007
Rev. A | Page 7 of 28
AD7653
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
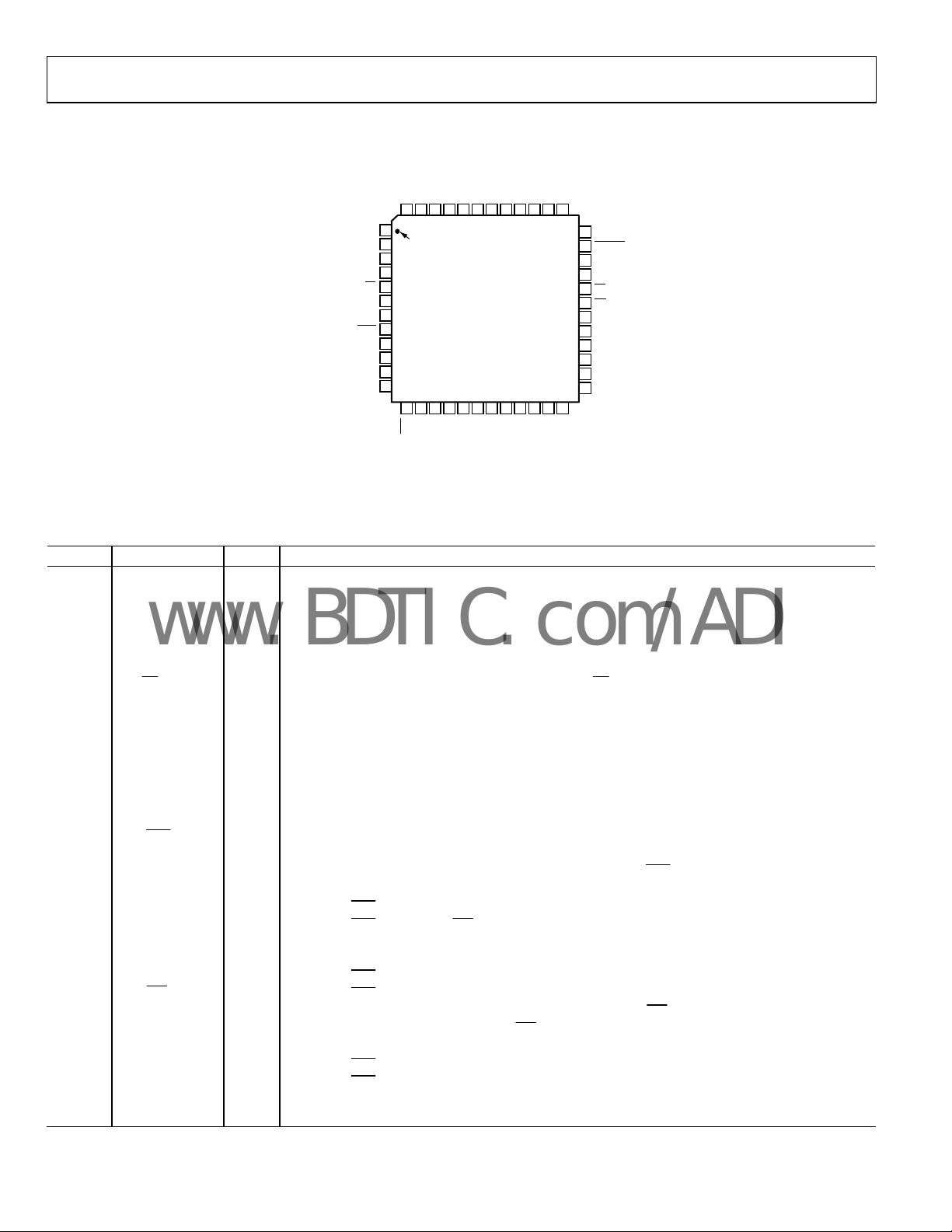
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
PDBUF
PDREF
REFBUFIN
TEMP
AVDDINAGND
AGNDNCINGND
REFGND
48
47 46 45 44 39 38 3743 42 41 40
1
AGND
AVDD
NC
BYTESWAP
OB/2C
WARP
IMPULSE
SER/PAR
D0
D1
D2/DIVSCLK0
D3/DIVSCLK1
NC = NO CONNECT
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14
D4/EXT/INT
AD7653
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
DVDD
OVDD
DGND
OGND
D6/INVSCLK
D5/INVSYNC
D7/RDC/SDIN
Figure 4. 48-Lead LQFP (ST-48) and 48-Lead LFCSP (CP-48)
Table 6. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Type1 Description
1, 36,
AGND P Analog Power Ground Pin.
41, 42
2, 44 AVDD P Input Analog Power Pin. Nominally 5 V.
3, 40 NC No Connect.
4 BYTESWAP DI Parallel Mode Selection (8-/16-bit). When LOW, the LSB is output on D[7:0] and the MSB is output on
D[15:8]. When HIGH, the LSB is output on D[15:8] and the MSB is output on D[7:0].
5
OB/2C
DI
Straight Binary/Binary Twos Complement. When OB/2C is HIGH, the digital output is straight binary;
when LOW, the MSB is inverted, resulting in a twos complement output from its internal shift
register.
6 WARP DI Mode Selection. When this pin is HIGH and the IMPULSE pin is LOW, this input selects the fastest
mode, the maximum throughput is achievable, and a minimum conversion rate must be applied in
order to guarantee full specified accuracy. When LOW, full accuracy is maintained independent of
the minimum conversion rate.
7 IMPULSE DI Mode Selection. When IMPULSE is HIGH and WARP is LOW, this input selects a reduced power
mode. In this mode, the power dissipation is approximately proportional to the sampling rate.
8
SER/PAR
DI Serial/Parallel Selection Input. When LOW, the parallel port is selected; when HIGH, the serial
interface mode is selected and some bits of the DATA bus are used as a serial port.
9, 10 D[0:1] DO
Bit 0 and Bit 1 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus. When SER/PAR
impedance.
11, 12 D[2:3]or
DIVSCLK[0:1]
DI/O
When SER/PAR
When SER/PAR
is LOW, these outputs are used as Bit 2 and Bit 3 of the parallel port data output bus.
is HIGH, EXT/INT is LOW, and RDC/SDIN is LOW (serial master read after convert),
these inputs, part of the serial port, are used to slow down, if desired, the internal serial clock that
clocks the data output. In other serial modes, these pins are not used.
13 D4 or
INT
EXT/
DI/O
When SER/PAR
When SER/PAR
is LOW, this output is used as Bit 4 of the parallel port data output bus.
is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used as a digital select input for choosing the internal data clock or an external data clock. With EXT/INT
selected on the SCLK output. With EXT/INT
external clock signal connected to the SCLK input.
14 D5 or
INVSYNC
DI/O
When SER/PAR
When SER/PAR
is LOW, this output is used as Bit 5 of the parallel port data output bus.
is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used to select the active state of the
SYNC signal. It is active in both master and slave modes. When LOW, SYNC is active HIGH. When
HIGH, SYNC is active LOW.
REF
36
AGND
35
CNVST
34
PD
33
RESET
32
CS
31
RD
30
DGND
29
BUSY
28
D15
27
D14
26
D13
25
D12
D9/SCLK
D10/SYNC
D8/SDOUT
D11/RDERROR
02966-0-002
is HIGH, these outputs are in high
tied LOW, the internal clock is
set to logic HIGH, output data is synchronized to an
Rev. A | Page 8 of 28
AD7653
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pin No. Mnemonic Type1 Description
15 D6 or
INVSCLK
16 D7 or
RDC/SDIN
17 OGND P Input/Output Interface Digital Power Ground.
18 OVDD P Input/Output Interface Digital Power. Nominally at the same supply as the host interface
19 DVDD P Digital Power. Nominally at 5 V.
20 DGND P Digital Power Ground.
21 D8 or
SDOUT
22 D9 or
SCLK
23 D10 or
SYNC
24 D11 or
RDERROR
25–28 D[12:15] DO Bit 12 to Bit 15 of the Parallel Port Data Output Bus. These pins are always outputs regardless of the
29 BUSY DO Busy Output. Transitions HIGH when a conversion is started and remains HIGH until the conversion
30 DGND P Must Be Tied to Digital Ground.
31
32
33 RESET DI Reset Input. When set to a logic HIGH, this pin resets the AD7653 and the current conversion, if any,
34 PD DI Power-Down Input. When set to logic HIGH, power consumption is reduced and conversions are
35
RD
CS
CNVST
DI/O
DI/O
DO
DI/O
DO
DO
DI
DI
DI
When SER/PAR
When SER/PAR
in both master and slave modes.
When SER/PAR
When SER/PAR
read mode selection input depending on the state of EXT/INT
When EXT/INT
results from two or more ADCs onto a single SDOUT line. The digital data level on SDIN is output on
DATA with a delay of 16 SCLK periods after the initiation of the read sequence.
When EXT/INT is LOW, RDC/SDIN is used to select the read mode. When RDC/SDIN is HIGH, the data
is output on SDOUT during conversion. When RDC/SDIN is LOW, the data can be output on SDOUT
only when the conversion is complete.
(5 V or 3 V).
When SER/PAR
When SER/PAR
nized to SCLK. Conversion results are stored in an on-chip register. The AD7653 provides the
conversion result, MSB first, from its internal shift register. The DATA format is determined by the
logic level of OB/2C
serial mode when EXT/INT
and valid on the next falling edge; if INVSCLK is HIGH, SDOUT is updated on the SCLK falling edge
and valid on the next rising edge.
When SER/PAR
When SER/PAR
depending upon the logic state of the EXT/INT
updated depends upon the logic state of the INVSCLK pin.
When SER/PAR
When SER/PAR
synchronization for use with the internal data clock (EXT/INT
initiated and INVSYNC is LOW, SYNC is driven HIGH and remains HIGH while the SDOUT output is
valid. When a read sequence is initiated and INVSYNC is HIGH, SYNC is driven LOW and remains
LOW while the SDOUT output is valid.
When SER/PAR
SER/PAR
error flag. In slave mode, when a data read is started and not complete when the following
conversion is complete, the current data is lost and RDERROR is pulsed HIGH.
state of SER/PAR
is complete and the data is latched into the on-chip shift register. The falling edge of BUSY could be
used as a data ready clock signal.
Read Data. When CS and RD are both LOW, the interface parallel or serial output bus is enabled.
Chip Select. When CS and RD are both LOW, the interface parallel or serial output bus is enabled. CS
is also used to gate the external clock.
is aborted. If not used, this pin could be tied to DGND.
inhibited after the current one is completed.
Start Conversion. A falling edge on CNVST puts the internal sample/hold into the hold state and
initiates a conversion. In Impulse mode (IMPULSE HIGH, WARP LOW), if CNVST
the acquisition phase (t8) is complete, the internal sample/hold is put into the hold state and a
conversion is immediately started.
is LOW, this output is used as Bit 6 of the parallel port data output bus.
is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used to invert the SCLK signal. It is active
is LOW, this output is used as Bit 7 of the parallel port data output bus.
is HIGH, this input, part of the serial port, is used as either an external data input or a
.
is HIGH, RDC/SDIN could be used as a data input to daisy-chain the conversion
is LOW, this output is used as Bit 8 of the parallel port data output bus.
is HIGH, this output, part of the serial port, is used as a serial data output synchro-
. In serial mode when EXT/INT is LOW, SDOUT is valid on both edges of SCLK. In
is HIGH, if INVSCLK is LOW, SDOUT is updated on the SCLK rising edge
is LOW, this output is used as Bit 9 of the parallel port data or SCLK output bus.
is HIGH, this pin, part of the serial port, is used as a serial data clock input or output,
pin. The active edge where the data SDOUT is
is LOW, this output is used as Bit 10 of the parallel port data output bus.
is HIGH, this output, part of the serial port, is used as a digital output frame
= logic LOW). When a read sequence is
is LOW, this output is used as Bit 11 of the parallel port data output bus. When
and EXT/INT are HIGH, this output, part of the serial port, is used as an incomplete read
.
is held LOW when
Rev. A | Page 9 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...