1.25 MSPS, 16 mW Internal REF and CLK,
A
V
FEATURES
Specified for VDD of 2.7 V to 5.25 V
Throughput rate of 1 MSPS (AD7492)
Throughput rate of 1.25 MSPS (AD7492-5)
Throughput rate of 400 kSPS (AD7492-4)
Low power
4 mW typ at 1 MSPS with 3 V supplies
11 mW typ at 1 MSPS with 5 V supplies
Wide input bandwidth
70 dB typ SNR at 100 kHz input frequency
2.5 V internal reference
On-chip CLK oscillator
Flexible power/throughput rate management
No pipeline delays
High speed parallel interface
Sleep mode: 50
24-lead SOIC and TSSOP packages
nA typ
V
CONVST
12-Bit Parallel ADC
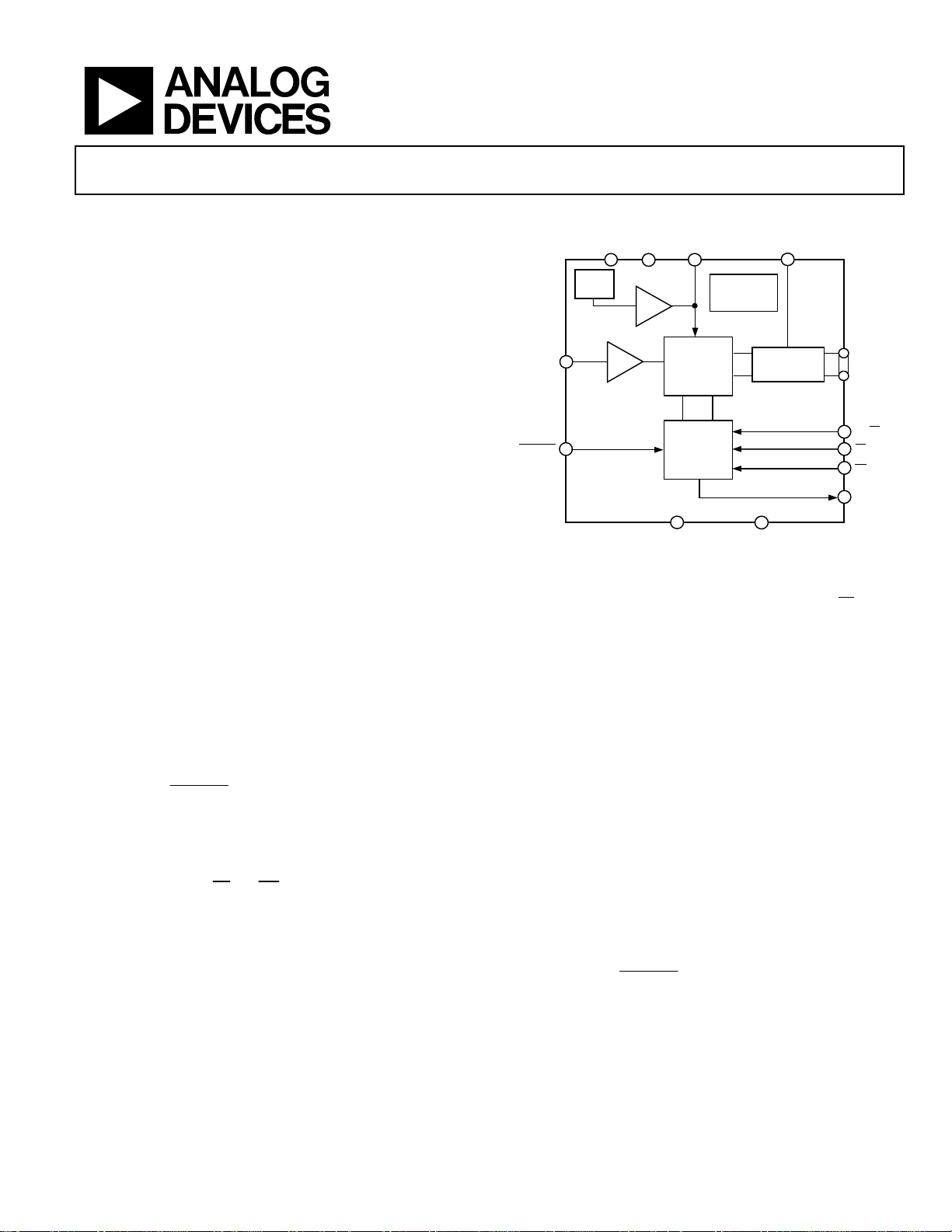
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
V
DV
DD
DD
4
2.5V
REF
6
IN
10
T/H
AD7492
REF OUT
20 5
CLOCK
BUF
AGND DGND
OSCILLAT OR
12-BIT SAR
ADC
CONTROL
LOGIC
719
Figure 1.
AD7492
DRIVE
21
OUTPUT
DRIVERS
11
12
8
9
DB11
DB0
PS/FS
CS
RD
BUSY
01128-001
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7492, AD7492-4, and AD7492-5 are 12-bit high speed,
low power, successive approximation ADCs. The parts operate
from a single 2.7 V to 5.25 V power supply and feature
throughput rates up to 1.25 MSPS. They contain a low noise,
wide bandwidth track/hold amplifier that can handle
bandwidths up to 10 MHz.
The conversion process and data acquisition are controlled
using standard control inputs allowing for easy interface to
microprocessors or DSPs. The input signal is sampled on the
falling edge of
point. The BUSY pin goes high at the start of conversion and
goes low 880 ns (AD7492/AD7492-4) or 680 ns (AD7492-5)
later to indicate that the conversion is complete. There are no
pipeline delays associated with the part. The conversion result is
accessed via standard
parallel interface.
The AD7492 uses advanced design techniques to achieve very
low power dissipation at high throughput rates. With 5 V
supplies and 1.25 MSPS, the average current consumption
AD7492-5 is typically 2.75 mA. The part also offers flexible
power/throughput rate management.
It is also possible to operate the part in a full sleep mode and a
partial sleep mode, where the part wakes up to do a conversion
and automatically enters a sleep mode at the end of conversion.
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
CONVST
CS
and conversion is also initiated at this
and RD signals over a high speed
FS
The type of sleep mode is hardware selected by the PS/
pin.
Using these sleep modes allows very low power dissipation
numbers at lower throughput rates.
The analog input range for the part is 0 V to REFIN. The
2.5 V reference is supplied internally and is available for
external referencing. The conversion rate is determined by the
internal clock.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. High Throughput with Low Power Consumption. The
AD7492-5 offers 1.25 MSPS throughput with 16 mW
power consumption.
2. Flexible Power/Throughput Rate Management. The
conversion time is determined by an internal clock. The
part also features two sleep modes, partial and full, to
maximize power efficiency at lower throughput rates.
3. No Pipeline Delay. The part features a standard successive
approximation ADC with accurate control of the sampling
instant via a
control.
4. Flexible Digital Interface. The V
voltage levels on the I/O digital pins.
5. Fewer Peripheral Components. The AD7492 optimizes
PCB space by using an internal reference and internal CLK.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
CONVST
input and once-off conversion
feature controls the
DRIVE

AD7492
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Converter Operation.................................................................. 13
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Product Highlights....................................................................... 1
Revision History ........................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
AD7492-5 ...................................................................................... 3
AD7492/AD7492-4 ...................................................................... 4
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 6
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 7
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 7
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 8
Typical Peformance Characteristics............................................. 10
Terminology .................................................................................... 12
Circuit Description......................................................................... 13
Typical Connection Diagram ................................................... 13
ADC Transfer Function............................................................. 13
AC Acquisition Time................................................................. 14
DC Acquisition Time................................................................. 14
Analog Input............................................................................... 14
Parallel Interface......................................................................... 14
Operating Modes........................................................................ 14
Power-Up..................................................................................... 16
Grounding and Layout.............................................................. 18
Power Supplies............................................................................ 18
Microprocessor Interfacing....................................................... 18
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 21
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 21
REVISION HISTORY
5/06—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Added AD7492-4................................................................Universal
Changes to Table 4............................................................................ 8
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 22
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 22
1/01—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 24
AD7492
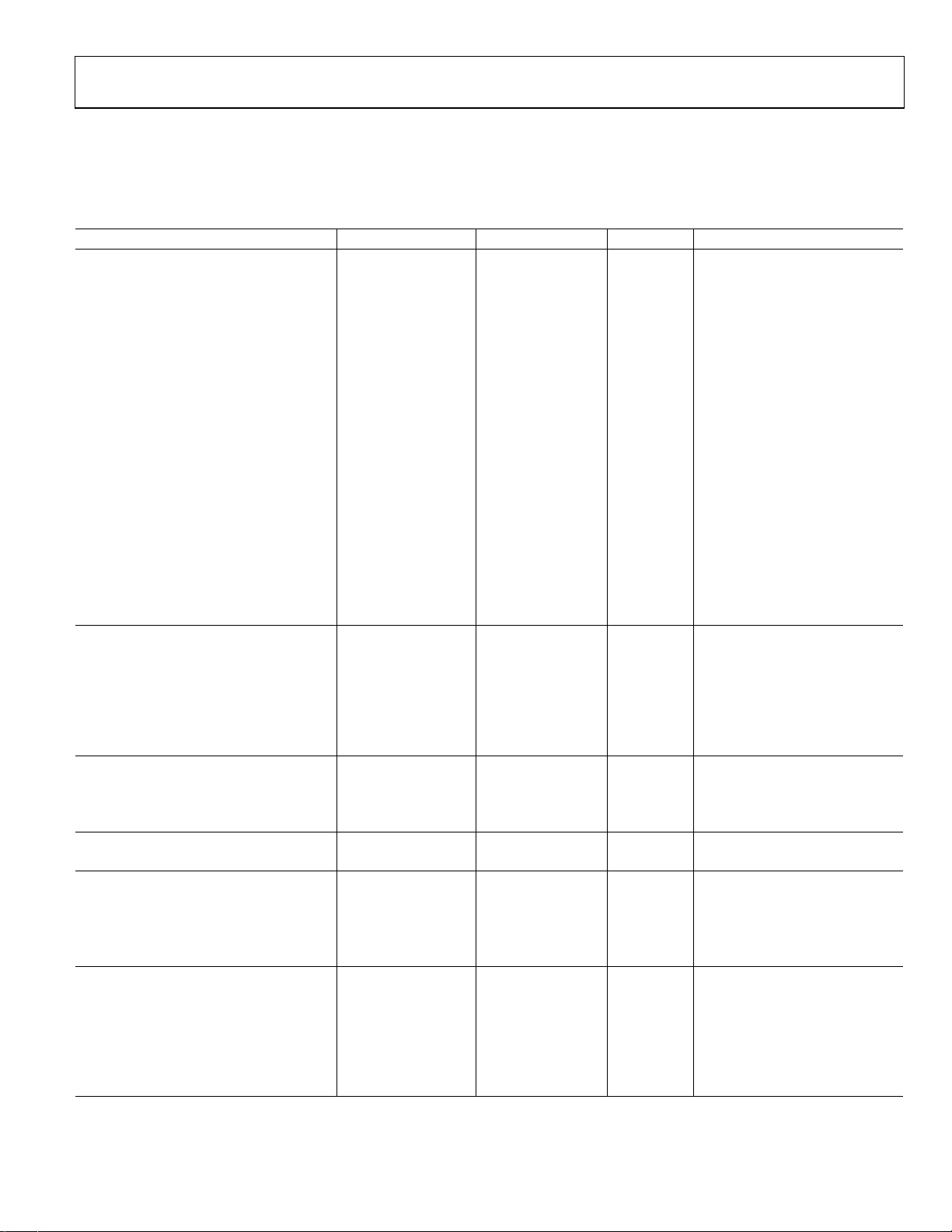
SPECIFICATIONS
AD7492-5
VDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V, TA = T
Table 1.
Parameter A Version1 B Version1 Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE fS = 1.25 MSPS
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion (SINAD) 69 69 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave
68 68 dB min fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) 70 70 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave
68 68 dB min fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) −83 −83 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave
−87 −87 dB typ fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
−75 −75 dB max fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Peak Harmonic or Spurious-Free
Dynamic Noise (SFDR)
−90 −90 dB typ fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
−76 −76 dB max fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)
Second Order Terms −82 −82 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave
−90 −90 dB typ fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Third Order Terms −71 −71 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave
−88 −88 dB typ fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Aperture Delay 5 5 ns typ
Aperture Jitter 15 15 ps typ
Full Power Bandwidth 10 10 MHz typ
DC ACCURACY fS = 1.25 MSPS
Resolution 12 12 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity ±1.5 ±1.25 LSB max
Differential Nonlinearity +1.5/–0.9 +1.5/−0.9 LSB max
Offset Error ±9 ±9 LSB max
Gain Error ±2.5 ±2.5 LSB max
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Ranges 0 to 2.5 0 to 2.5 V
DC Leakage Current ±1 ±1 μA max
Input Capacitance 33 33 pF typ
REFERENCE OUTPUT
REF OUT Output Voltage Range 2.5 2.5 V ±1.5% for specified performance
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
INH
2
INL
Input Current, IIN ±1 ±1 μA max Typically 10 nA, VIN = 0 V or VDD
Input Capacitance, C
3
10 10 pF max
IN
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, VOH V
Output Low Voltage, VOL 0.4 0.4 V max I
Floating-State Leakage Current ±10 ±10 μA max
Floating-State Output Capacitance 10 10 pF max
Output Coding
to T
MIN
2
V
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
V
−83 −83 dB typ f
× 0.7 V
DRIVE
× 0.3 V
DRIVE
− 0.2 V
DRIVE
Straight (natural)
binary
× 0.7 V min VDD = 5 V ± 5%
DRIVE
× 0.3 V max VDD = 5 V ± 5%
DRIVE
− 0.2 V min I
DRIVE
Straight (natural)
binary
= 500 kHz sine wave
IN
Guaranteed no missed codes to
12 bits (A and B versions)
= 200 μA
SOURCE
= 200 μA
SINK
Rev. A | Page 3 of 24
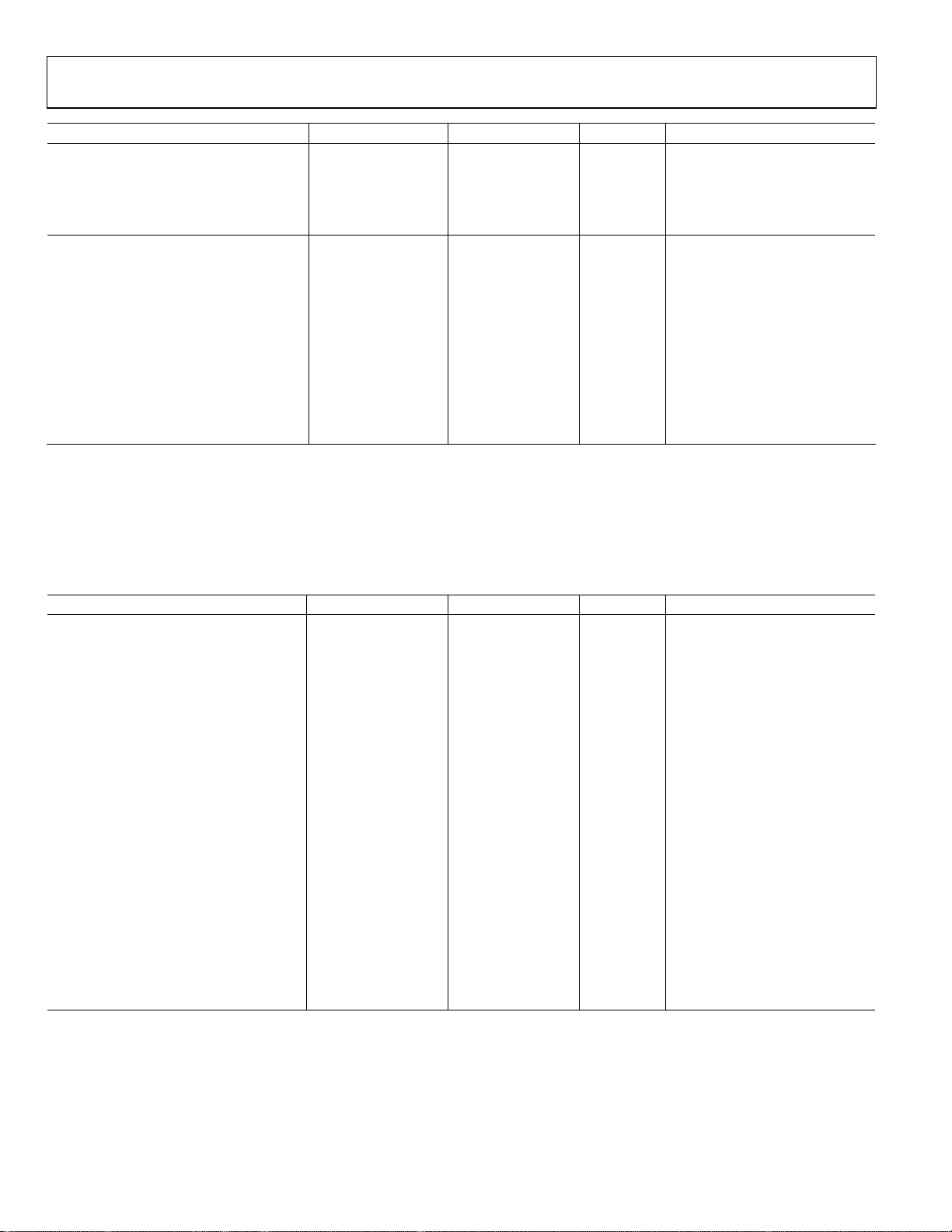
AD7492
Parameter A Version1 B Version1 Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CONVERSION RATE
Conversion Time 680 680 ns max
Track/Hold Acquisition Time 120 120 ns min
Throughput Rate 1.25 1.25 MSPS max
POWER REQUIREMENTS
V
4.75/5.25 4.75/5.25 V min/max
DD
IDD Digital I/Ps = 0 V or DVDD
Normal Mode 3.3 3.3 mA max fS = 1.25 MSPS, typ 2.75 mA
Quiescent Current 1.8 1.8 mA max
Partial Sleep Mode 250 250 μA max Static, typ 190 μA
Full Sleep Mode 1 1 μA max Static, typ 200 nA
Power Dissipation4 Digital I/Ps = 0 V or DVDD
Normal Mode 16.5 16.5 mW max
Partial Sleep Mode 1.25 1.25 mW max
Full Sleep Mode 5 5 μW max
1
Temperature ranges as follows: A and B Versions: −40°C to +85°C.
2
V
and V
INH
3
Sample tested @ 25°C to ensure compliance.
4
See the Power vs. Throughput section.
trigger levels are set by the V
INL
voltage. The logic interface circuitry is powered by V
DRIVE
DRIVE
.
AD7492/AD7492-4
VDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, TA = T
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
Table 2.
Parameter A Version
2
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE fS = 1 MSPS for AD7492
f
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion (SINAD) 69 69 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave
68 68 dB min fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) 70 70 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave3
68 68 dB min fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) −85 −85 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave3
−87 −87 dB typ fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
−75 −75 dB max fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Peak Harmonic or Spurious-Free
−86 −86 dB typ f
Dynamic Noise (SFDR)
−90 −90 dB typ fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
−76 −76 dB max fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)
Second Order Terms −77 −77 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave3
−90 −90 dB typ fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Third Order Terms −69 −69 dB typ fIN = 500 kHz sine wave3
−88 −88 dB typ fIN = 100 kHz sine wave
Aperture Delay 5 5 ns typ
Aperture Jitter 15 15 ps typ
Full Power Bandwidth 10 10 MHz typ
1
B Version2 Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Conversion time + acquisition
time
= 400 kSPS for AD7492-4
S
= 500 kHz sine wave3
IN
3
Rev. A | Page 4 of 24
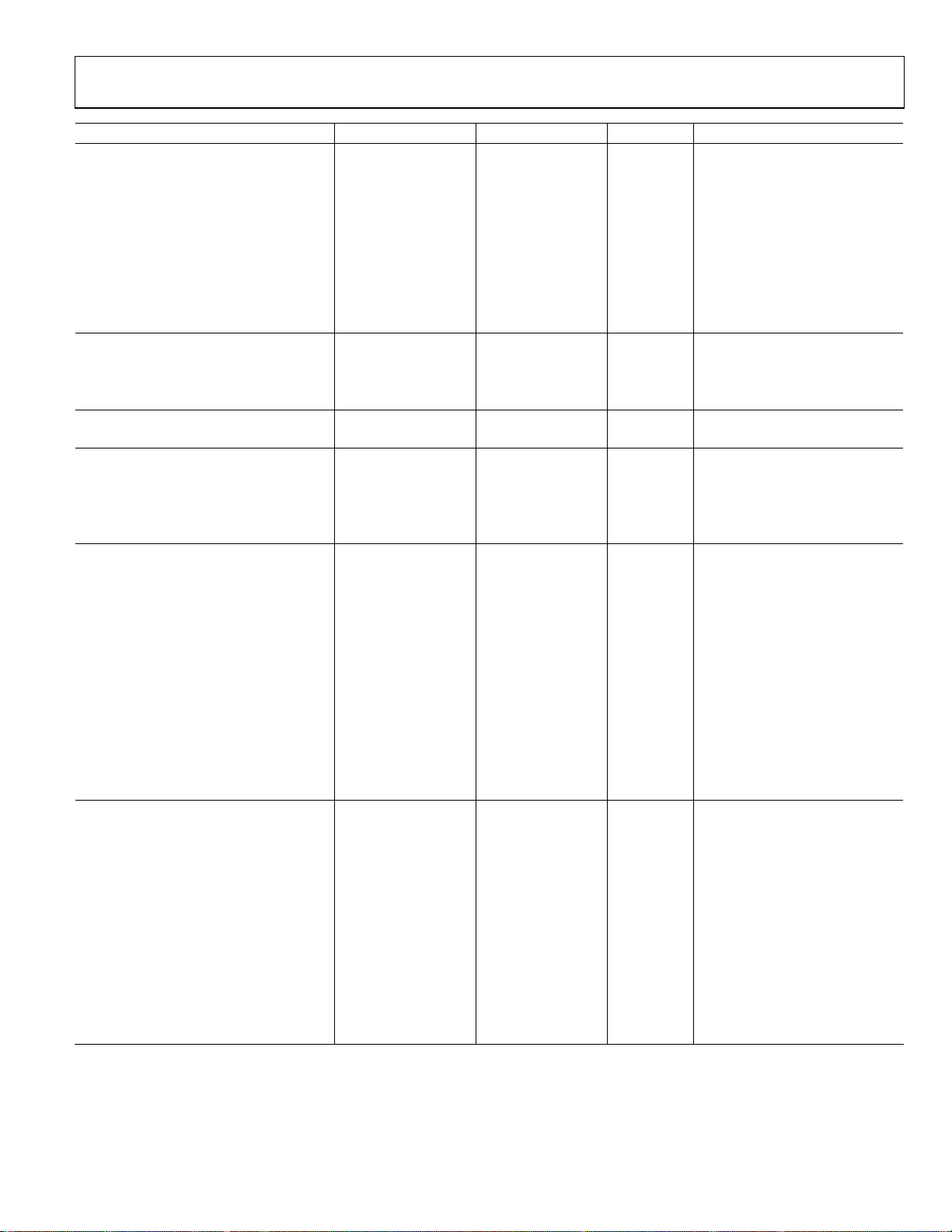
AD7492
Parameter A Version
2
B Version2 Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DC ACCURACY fS = 1 MSPS for AD7492
f
= 400 kSPS for AD7492-4
S
Resolution 12 12 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity ±1.5 LSB max
±0.6 LSB typ VDD = 5 V
±1 LSB max VDD = 3 V
Differential Nonlinearity +1.5/−0.9 +1.5/−0.9 LSB max Guaranteed no missed codes to
12 bits (A and B versions)
Offset Error ±9 ±9 LSB max
Gain Error ±2.5 ±2.5 LSB max
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Ranges 0 to 2.5 0 to 2.5 V
DC Leakage Current ±1 ±1 μA max
Input Capacitance 33 33 pF typ
REFERENCE OUTPUT
REF OUT Output Voltage Range 2.5 2.5 V ±1.5% for specified performance
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
4
V
INH
4
V
INL
× 0.7 V
DRIVE
× 0.3 V
DRIVE
× 0.7 V min VDD = 5 V ± 5%
DRIVE
× 0.3 V max VDD = 5 V ± 5%
DRIVE
Input Current, IIN ±1 ±1 μA max Typically 10 nA, VIN = 0 V or VDD
5
Input Capacitance, C
3,
10 10 pF max
IN
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, VOH V
Output Low Voltage, VOL 0.4 0.4 V max I
− 0.2 V
DRIVE
− 0.2 V min I
DRIVE
= 200 μA
SOURCE
= 200 μA
SINK
Floating-State Leakage Current ±10 ±10 μA max
Floating-State Output Capacitance 10 10 pF max
Output Coding
Straight (Natural)
Binary
Straight (Natural)
Binary
CONVERSION RATE
Conversion Time 880 880 ns max
Track/Hold Acquisition Time 120 120 ns min
Throughput Rate 1
400
1 MSPS max
kSPS max
Conversion time + acquisition
time for AD7492
Conversion time + acquisition
time for AD7492-4
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VDD 2.7/5.25 2.7/5.25 V min/max
IDD Digital I/Ps = 0 V or DVDD.
Normal Mode 3 3 mA max fS = 1 MSPS, typ 2.2 mA
f
= 400 kSPS, Typ 2.2 mA
S
(AD7492-4)
Quiescent Current 1.8 1.8 mA max
Partial Sleep Mode 250 250 μA max Static, typ 190 μA
Full Sleep Mode 1 1 μA max Static, typ 200 nA
Power Dissipation
4, 6
Digital I/Ps = 0 V or DVDD
Normal Mode 15 15 mW max VDD = 5 V
Partial Sleep Mode 1.25 1.25 mW max VDD = 5 V
Full Sleep Mode 5 5 μW max VDD = 5 V
1
Only A version specification applies to the AD7492-4.
2
Temperature ranges as follows: A and B versions: −40°C to +85°C.
3
500 kHz sine wave specifications do not apply for the AD7492-4.
4
V
and V
INH
5
Sample tested @ 25°C to ensure compliance.
6
See the Power vs. Throughput section.
trigger levels are set by the V
INL
voltage. The logic interface circuitry is powered by V
DRIVE
DRIVE
.
Rev. A | Page 5 of 24
AD7492
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, TA = T
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
Table 3.
Limit at T
MIN
, T
MAX
Parameter AD7492/AD7492-4 AD7492-52 Unit Description
t
880 680 ns max
CONVER T
t
203 203 μs max Partial Sleep Wake-Up Time
WAKE UP
500 500 μs max Full Sleep Wake-Up Time
t1 10 10 ns min
t2 10 10 ns max
40 N/A ns max
t3 0 0 ns max
4
t
0 0 ns max
4
t5 20 20 ns min
4
t
15 15 ns min
6
5
t
8 8 ns max
7
t8 0 0 ns max
t9 120 120 ns min Acquisition Time
t10 100 100 ns min Quiet Time
1
Sample tested @ 25°C to ensure compliance. All input signals are specified with tR = tF = 5 ns (10% to 90% of VDD) and timed from a voltage level of 1.6 V (see Figure 2).
2
The AD7492-5 is specified with VDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V.
3
This is the time needed for the part to settle within 0.5 LSB of its stable value. Conversion can be initiated earlier than 20 μs, but there is no guarantee that the part
samples within 0.5 LSB of the true analog input value. Therefore, the user should not start conversion until after the specified time.
4
Measured with the load circuit of Figure 2 and defined as the time required for the output to cross 0.8 V or 2.0 V
5
t7 is derived from the measured time taken by the data outputs to change 0.5 V when loaded with the circuit of Figure 2. The measured number is then extrapolated
back to remove the effects of charging or discharging the 50 pF capacitor. This means that the time, t7, quoted in the timing characteristics is the true bus relinquish
time of the part and is independent of the bus loading.
1
CONVST Pulse Width
CONVST to BUSY Delay, VDD = 5 V
CONVST to BUSY Delay, VDD = 3 V
BUSY to
CS Setup Time
CS to RD Setup Time
RD Pulse Width
Data Access Time after Falling Edge of
Bus Relinquish Time after Rising Edge of
RD
RD
CS to RD Hold Time
TO OUTPUT
PIN
50pF
200µA
C
L
200µA
I
OL
1.6V
I
OH
1128-002
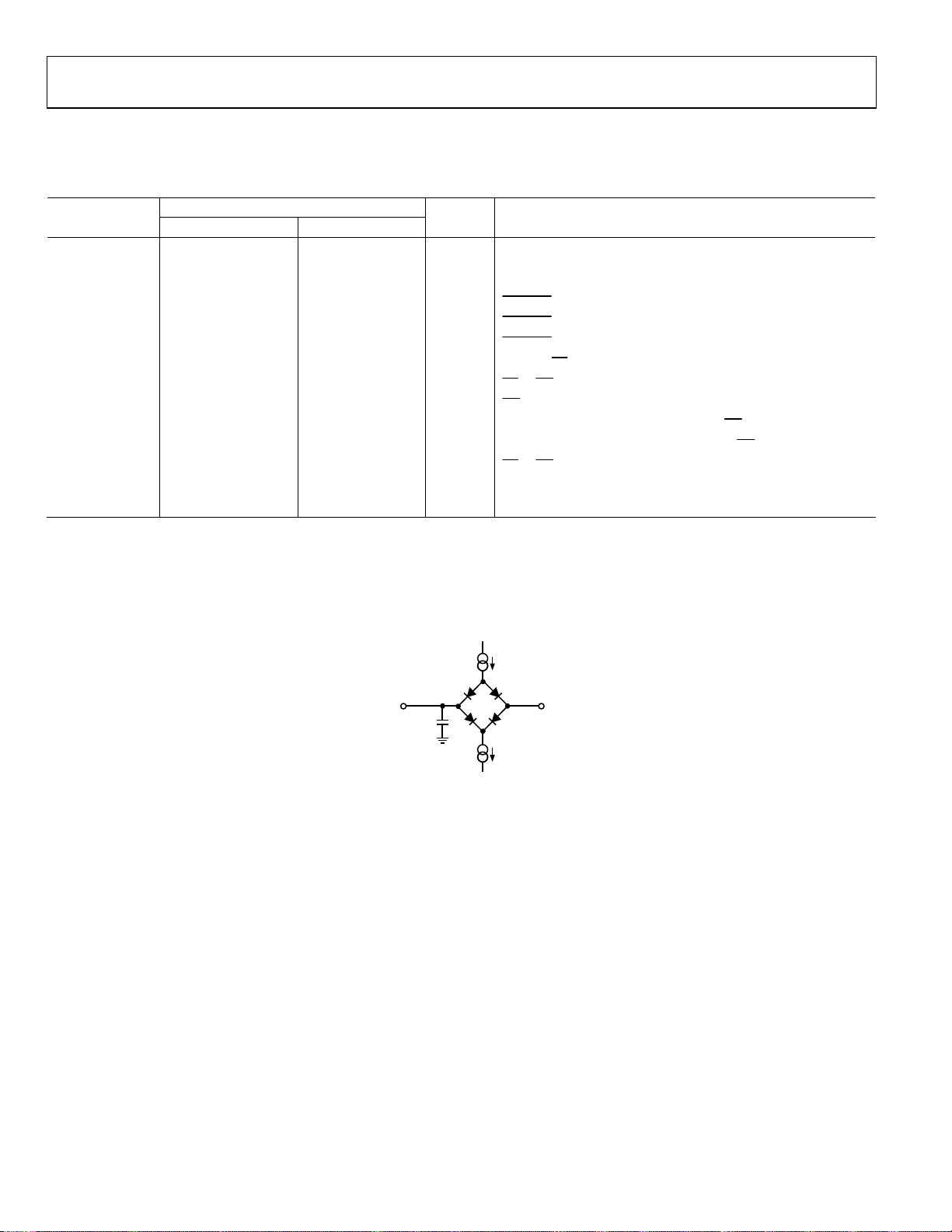
Figure 2. Load Circuit for Digital Output Timing Specifications
Rev. A | Page 6 of 24
AD7492
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
Parameter Ratings
AV
to AGND/DGND −0.3 V to +7 V
DD
DV
to AGND/DGND −0.3 V to +7 V
DD
V
to AGND/DGND −0.3 V to +7 V
DRIVE
AVDD to DV
V
DRIVE
−0.3 V to +0.3 V
DD
to DV
−0.3 V to DV
DD
+ 0.3 V
DD
AGND to DGND −0.3 V to +0.3 V
Analog Input Voltage to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Digital Input Voltage to DGND −0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Input Current to Any Pin Except
Supplies
1
Operating Temperature Range
±10 mA
Commercial (A and B Versions) −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
SOIC, TSSOP Package Dissipation 450 mW
θ
Thermal Impedance 75°C/W (SOIC)
JA
θ
Thermal Impedance 25°C/W (SOIC)
JC
Lead Temperature, Soldering
115°C/W (TSSOP)
35°C/W (TSSOP)
Vapor Phase (60 sec) 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) 220°C
1
Transient currents of up to 100 mA do not cause SCR latch-up.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
Rev. A | Page 7 of 24
AD7492
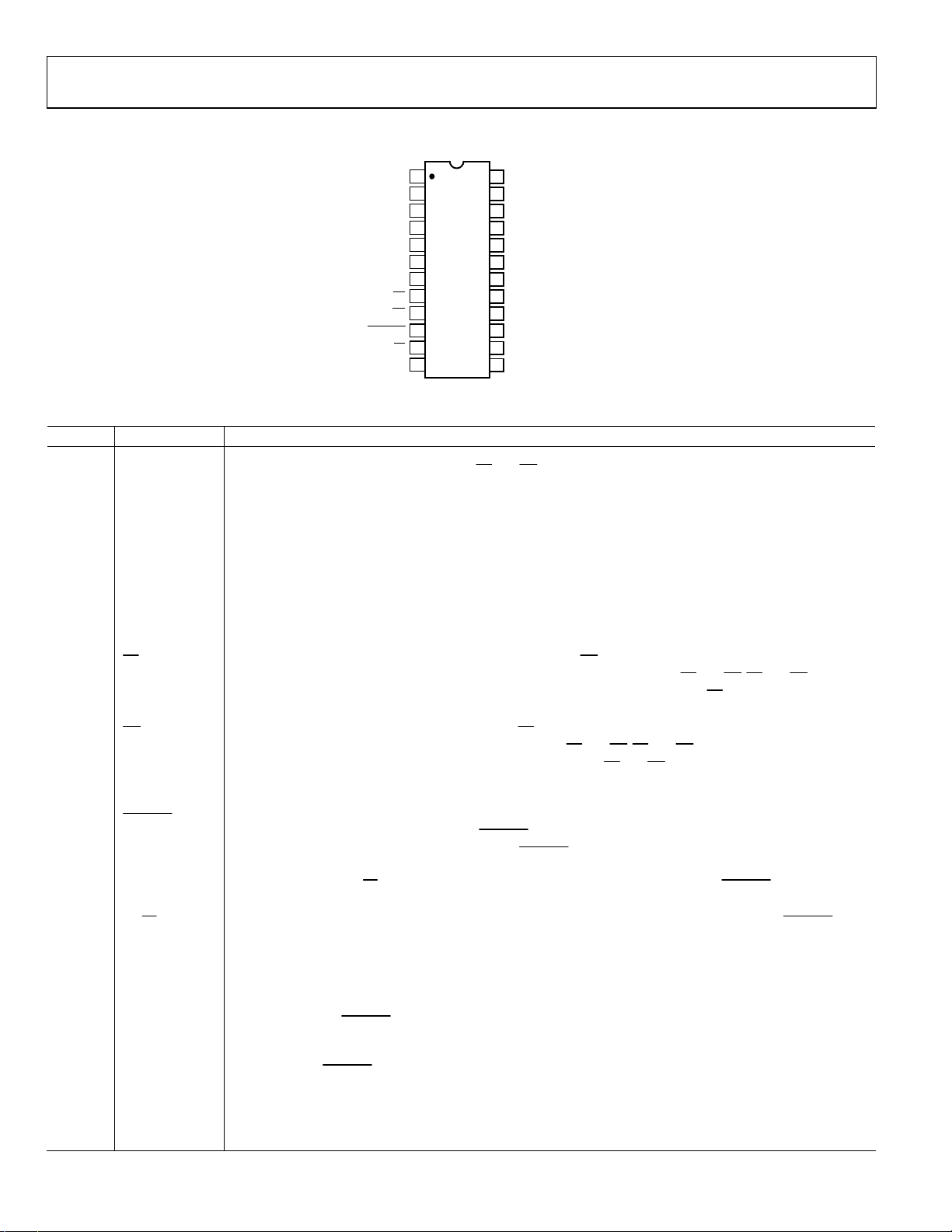
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
DB9
DB10
(MSB) DB11
AV
REF OUT
V
AGND
CS
RD
CONVST
PS/FS
BUSY
DD
IN
1
2
3
4
5
AD7492
6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
DB8
DB7
DB6
V
DRIVE
DV
DD
DGND
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0 (LSB)
01128-003
Figure 3. Pin Configuration
Table 5. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin Mnemonic Function
1 to 3,
13 to 18,
22 to 24
4 AVDD
DB11 to DB0
Data Bit 11 to Data Bit 0. Parallel digital outputs that provide the conversion result for the part. These are
three-state outputs that are controlled by
determined by the V
DRIVE
input.
CS and RD. The output high voltage level for these outputs is
Analog Supply Voltage, 2.7 V to 5.25 V. This is the only supply voltage for all analog circuitry on the AD7492.
The AV
and DVDD voltages should ideally be at the same potential and must not be more than 0.3 V apart,
DD
even on a transient basis. This supply should be decoupled to AGND.
5 REF OUT Reference Out. The output voltage from this pin is 2.5 V ± 1%.
6 VIN
Analog Input. Single-ended analog input channel. The input range is 0 V to REFIN. The analog input presents
a high dc input impedance.
7 AGND
Analog Ground. Ground reference point for all analog circuitry on the AD7492. All analog input signals
should be referred to this AGND voltage. The AGND and DGND voltages should ideally be at the same
potential and must not be more than 0.3 V apart, even on a transient basis.
8
CS Chip Select. Active low logic input used in conjunction with RD to access the conversion result. The
conversion result is placed on the data bus following the falling edge of both
connected to the same AND gate on the input so the signals are interchangeable.
permanently low.
9
RD Read Input. Logic input used in conjunction with CS to access the conversion result. The conversion result is
placed on the data bus following the falling edge of both
CS and RD. CS and RD are both connected to the
same AND gate on the input so the signals are interchangeable.
low, in which case the data bus is always active and the result of the new conversion is clocked out slightly
before to the BUSY line going low.
10
CONVST Conversion Start Input. Logic input used to initiate conversion. The input track/hold amplifier goes from track
mode to hold mode on the falling edge of
conversion input can be as narrow as 10 ns. If the
CONVST and the conversion process is initiated at this point. The
CONVST input is kept low for the duration of conversion
and is still low at the end of conversion, the part automatically enters a sleep mode. The type of sleep mode is
determined by the PS/
FS pin. If the part enters a sleep mode, the next rising edge of CONVST wakes up the
part. Wake-up time depends on the type of sleep mode.
11
FS Partial Sleep/Full Sleep Mode. This pin determines the type of sleep mode the part enters if the CONVST pin is
PS/
kept low for the duration of the conversion and is still low at the end of conversion. In partial sleep mode the
internal reference circuit and oscillator circuit are not powered down and draws 250 μA maximum. In full
sleep mode all of the analog circuitry are powered down and the current drawn is negligible. This pin is
12 BUSY
hardwired either high (DV
BUSY Output. Logic output indicating the status of the conversion process. The BUSY signal goes high after
the falling edge of
CONVST and stays high for the duration of the conversion. Once the conversion is
) or low (GND).
DD
complete and the conversion result is in the output register, the BUSY line returns low. The track/hold returns
to track mode just prior to the falling edge of BUSY and the acquisition time for the part begins when BUSY
goes low. If the
CONVST input is still low when BUSY goes low, the part automatically enters its sleep mode
on the falling edge of BUSY.
19 DGND
Digital Ground. This is the ground reference point for all digital circuitry on the AD7492. The DGND and AGND
voltages should ideally be at the same potential and must not be more than 0.3 V apart, even on a transient
basis.
CS and RD. CS and RD are both
CS can be hardwired
CS and RD can be hardwired permanently
Rev. A | Page 8 of 24

AD7492
Pin Mnemonic Function
20 DVDD
21 V
DRIVE
Digital Supply Voltage, 2.7 V to 5.25 V. This is the supply voltage for all digital circuitry on the AD7492 apart
from the output drivers and input circuitry. The DV
and AVDD voltages should ideally be at the same
DD
potential and must not be more than 0.3 V apart even on a transient basis. This supply should be decoupled
to DGND.
Supply Voltage for the Output Drivers and Digital Input Circuitry, 2.7 V to 5.25 V. This voltage determines the
output high voltage for the data output pins and the trigger levels for the digital inputs. It allows the AV
and DV
to operate at 5 V (and maximize the dynamic performance of the ADC) while the digital input and
DD
DD
output pins can interface to 3 V logic.
Rev. A | Page 9 of 24

AD7492
TYPICAL PEFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
SNR+D (dB)
64
63
62
61
60
0
500 1000 1500 2000 2500
INPUT FREQUENCY (kHz)
5V
3V
Figure 4. Typical SNR + D vs. Input Tone
95
90
85
80
75
70
THD (dB)
65
60
55
50
100 200 350 500 1000 2000
INPUT FREQUENCY (kHz)
3V
Figure 5. Typical THD vs. Input Tone
70.60
70.4
70.2
70.0
69.8
SNR (dB)
69.6
69.4
69.2
69.0
–55°C
2.50 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5
+125°C
–40°C
SUPPLY (Volts)
5V
+25°C
+85°C
01128-004
1128-005
1128-006
0
–20
–40
–60
(dB)
–80
–100
–120
0 10 0000 200000 300000 400000 500000 600000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 7. Typical SNR @ 500 kHz Input Tone
0
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
(dB)
–2.0
–2.5
–3.0
–3.5
1 10 100 1000 10000 100000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
5V
Figure 8. Typical Bandwidth
0
VCC = 5V
100mV p-p SINEWAVE ON V
–20
f
= 1MHz,
SAMPLE
–40
–60
PSSR (dB)
–80
–100
–120
0 5 10 16 20 26 31 36 41 46 51 57 61 67 72 77 82 88 92 97
3 8 13 18 23 28 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 69 74 80 84 89 94 100
f
RIPPLE FREQUENCY (kHz)
V
CC
= 100kHz
IN
CC
01128-007
1128-008
01128-009
Figure 6. Typical SNR vs. Supply
Figure 9. Typical Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
Rev. A | Page 10 of 24

AD7492
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
(INL)
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0
512
CODE
Figure 10. Typical INL for 2.75 V @ 25°C
4089
357830672556204515341023
01128-010
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
(DNL)
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0
512
CODE
Figure 11. Typical DNL for 2.75 V @ 25°C
4089
357830672556204515341023
01128-011
Rev. A | Page 11 of 24

AD7492
(
)
TERMINOLOGY
Integral Nonlinearity
This is the maximum deviation from a straight line passing
through the endpoints of the ADC transfer function. The
endpoints of the transfer function are zero scale, a point
1/2 LSB below the first code transition, and full scale, a point
1/2 LSB above the last code transition.
Differential Nonlinearity
This is the difference between the measured and the ideal 1 LSB
change between any two adjacent codes in the ADC.
Offset Error
This is the deviation of the first code transition (00 . . . 000) to
(00 . . . 001) from the ideal, that is, AGND + 1 LSB.
Gain Error
The last transition should occur at the analog value 1 1/2 LSB
below the nominal full scale. The first transition is a 1/2 LSB
above the low end of the scale (zero in the case of AD7492). The
gain error is the deviation of the actual difference between the
first and last code transitions from the ideal difference between
the first and last code transitions with offset errors removed.
Trac k / Hold Ac q u isiti o n Ti me
The track/hold amplifier returns into track mode after the end
of the conversion. Track/Hold acquisition time is the time
required for the output of the track/hold amplifier to reach its
final value, within ±0.5 LSB, after the end of conversion.
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio
This is the measured ratio of signal-to-noise and distortion at
the output of the A/D converter. The signal is the rms
amplitude of the fundamental. Noise is the sum of all
nonfundamental signals up to half the sampling frequency
(f
/2), excluding dc. The ratio is dependent on the number of
S
quantization levels in the digitization process; the more levels,
the smaller the quantization noise. The theoretical signal to
(noise + distortion) ratio for an ideal N-bit converter with a sine
wave input is given by:
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion = (6.02 N + 1.76) dB
Thus for a 12-bit converter, this is 74 dB and for a 10-bit
converter is 62 dB.
Total Harmonic Distortion
Total harmonic distortion (THD) is the ratio of the rms sum of
harmonics to the fundamental. For the AD7492 it is defined as:
2
2
2
2
2
2
dBTHD
log20)(
=
4
3
V
1
VVVVV
++++
6
5
where:
V
is the rms amplitude of the fundamental.
1
V
, V3, V4, V5, and V6 are the rms amplitudes of the second
2
through the sixth harmonics.
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise
Peak harmonic or spurious noise is defined as the ratio of the
rms value of the next largest component in the ADC output
spectrum (up to f
/2 and excluding dc) to the rms value of the
S
fundamental. Normally, the value of this specification is
determined by the largest harmonic in the spectrum, but for
ADCs where the harmonics are buried in the noise floor, it is a
noise peak.
Intermodulation Distortion
With inputs consisting of sine waves at two frequencies, fa and
fb, any active device with nonlinearities creates distortion
products at sum and difference frequencies of mfa ± nfb where
m, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, etc. Intermodulation distortion terms are those
for which neither m nor n is equal to zero. For example, the
second order terms include (fa + fb) and (fa − fb), while the
third order terms include (2fa + fb), (2fa − fb), (fa + 2fb), and
(fa − 2fb).
The AD7492 is tested using the CCIF standard where two input
frequencies near the top end of the input bandwidth are used.
In this case, the second order terms are usually distanced in
frequency from the original sine waves while the third order
terms are usually at a frequency close to the input frequencies.
As a result, the second and third order terms are specified
separately. The calculation of the intermodulation distortion is
as per the THD specification where it is the ratio of the rms
sum of the individual distortion products to the rms amplitude
of the sum of the fundamentals expressed in dBs.
Aperture Delay
In a sample/hold, the time required after the hold command for
the switch to open fully is the aperture delay. The sample is, in
effect, delayed by this interval, and the hold command would
have to be advanced by this amount for precise timing.
Aperture Jitter
Aperture jitter is the range of variation in the aperture delay. In
other words, it is the uncertainty about when the sample is
taken. Jitter is the result of noise that modulates the phase of the
hold command. This specification establishes the ultimate
timing error, hence the maximum sampling frequency for a
given resolution. This error increases as the input dV/dt
increases.
Rev. A | Page 12 of 24

AD7492
R
C
A
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
CONVERTER OPERATION
The AD7492 is a 12-bit successive approximation analog-todigital converter based around a capacitive DAC. The AD7492
can convert analog input signals in the range 0 V to V
12
shows a very simplified schematic of the ADC. The control
logic, SAR register, and capacitive DAC are used to add and
subtract fixed amounts of charge from the sampling capacitor to
bring the comparator back into a balanced condition.
COMPARATO
CAPACIT IVE
DAC
V
REF
SWITCHES
V
IN
SAR
ONTROL
INPUTS
CONTROL L OGIC
OUTPUT DATA
12-BIT PARALLEL
Figure 12. Simplified Block Diagram of AD7492
Figure 13 shows the ADC during its acquisition phase. SW2 is
closed and SW1 is in Position A. The comparator is held in a
balanced condition and the sampling capacitor acquires the
signal on V
AGND
.
IN
CAPACITIVE
A
V
IN
SW1
2kΩ
B
SW2
COMPARATOR
CONTROL L OGIC
Figure 13. ADC Acquisition Phase
Figure 14 shows the ADC during conversion. When conversion
starts, SW2 opens and SW1 moves to Position B, causing the
comparator to become unbalanced. The ADC then runs
through its successive approximation routine and brings the
comparator back into a balanced condition. When the
comparator is rebalanced, the conversion result is available in
the SAR register.
CAPACITIVE
V
AGND
IN
SW1AB
2kΩ
SW2
COMPARATOR
Figure 14. ADC Conversion Phase
CONTROL L OGIC
DAC
DAC
. Figure
REF
01128-012
01128-013
01128-014
TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Figure 15 shows a typical connection diagram for the AD7492.
Conversion is initiated by a falling edge on
CONVST
goes low the BUSY signal goes high, and at the end of
CONVST
. Once
the conversion, the falling edge of BUSY is used to activate an
interrupt service routine. The
CS
and RD lines are then activated
in parallel to read the 12 data bits. The internal band gap
reference voltage is 2.5 V, providing an analog input range of 0 V
to 2.5 V, making the AD7492 a unipolar A/D. A capacitor with a
minimum capacitance of 100 nF is needed at the output of the
REF OUT pin as it stabilizes the internal reference value. It is
recommended to perform a dummy conversion after power-up as
the first conversion result could be incorrect. This also ensures
that the part is in the correct mode of operation. The
CONVST
pin should not be floating when power is applied, as a rising edge
CONVST
on
Figure 15 the V
In
logic output voltage values being either 0 V or DV
voltage applied to V
logic signals and the input logic signals. For example, if DV
supplied by a 5 V supply and V
might not wake up the part.
pin is tied to DVDD, which results in
DRIVE
controls the voltage value of the output
DRIVE
by a 3 V supply, the logic
DRIVE
DD
. The
DD
is
output voltage levels would be either 0 V or 3 V. This feature
allows the AD7492 to interface to 3 V parts while still enabling
the A/D to process signals at 5 V supply.
NALOG
µC/µP
++
10µF
V
AV
DRIVE
DD
AD7492
DB0 TO
DB9 (DB11)
DD
PS/FS
2.5V
PARALLELED
INTERF ACE
1nF
100nF
DV
REF OUT
CS
CONVST
RD
BUSY
Figure 15. Typical Connection Diagram
0.1µF 47µF
V
IN
0V TO 2.5V
SUPPLY
2.7V TO 5.25V
ADC TRANSFER FUNCTION
The output coding of the AD7492 is straight binary. The
designed code transitions occur at successive integer LSB values
(that is, 1 LSB, 2 LSB, etc.). The LSB size equals 2.5/4096 for the
AD7492. The ideal transfer characteristic for the AD7492 is
shown in
Figure 16.
1128-015
Rev. A | Page 13 of 24

AD7492
V
V
111...111
111...110
111...000
011...111
ADC CODE
000...010
000...001
000...000
0V 1/2LSB +V
Figure 16. Transfer Characteristic for 12 Bits
1LSB = V
ANALOG INPUT
REF
REF
–1LSB
/4096
01128-016
AC ACQUISITION TIME
In ac applications, it is recommended to always buffer analog
input signals. The source impedance of the drive circuitry must
be kept as low as possible to minimize the acquisition time of
the ADC. Large values of impedance at the V
pin of the ADC
IN
cause the THD to degrade at high input frequencies.
Table 6. Dynamic Performance Specifications
Input
Buffers
SNR
500 kHz
THD
500 kHz
Typical Amplifier Current
Consumption
AD9631 69.5 80 17 mA
AD797 69.6 81.6 8.2 mA
DC ACQUISITION TIME
The ADC starts a new acquisition phase at the end of a
conversion and ends it on the falling edge of the
CONVST
signal. At the end of the conversion, there is a settling time
associated with the sampling circuit. This settling time lasts
120 ns. The analog signal on V
is also acquired during this
IN
settling time; therefore, the minimum acquisition time needed
is 120 ns.
Figure 17 shows the equivalent charging circuit for the sampling
capacitor when the ADC is in its acquisition phase. R3
represents the source impedance of a buffer amplifier or
resistive network, R1 is an internal switch resistance, R2 is for
bandwidth control, and C1 is the sampling capacitor. C2 is
back-plate capacitance and switch parasitic capacitance.
During the acquisition phase the sampling capacitor must be
charged to within 0.5 LSB of its final value.
8pF
C1
22pF
C2
R2
636Ω
V
R3
IN
Figure 17. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
R1
125Ω
1128-017
ANALOG INPUT
Figure 18 shows the equivalent circuit of the analog input
structure of the AD7492. The two diodes, D1 and D2, provide
ESD protection for the analog inputs. The Capacitor C3 is
typically about 4 pF and can be primarily attributed to pin
capacitance. The Resistor R1 is an internal switch resistance.
This resistor is typically about 125 Ω. The Capacitor C1 is the
sampling capacitor while R2 is used for bandwidth control.
DD
IN
C3
4pF
D1
D2
Figure 18. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
R1
125Ω
8pF
C1
R2
22pF
636Ω
C2
01128-018
PARALLEL INTERFACE
The parallel interface of the AD7492 is 12 bits wide. The output
CS
data buffers are activated when both
and RD are logic low. At
this point the contents of the data register are placed onto the data
bus.
Figure 19 shows the timing diagram for the parallel port.
Figure 20 shows the timing diagram for the parallel port when
CS
and RD are tied permanently low. In this setup, once the
BUSY line goes from high to low, the conversion process is
completed. The data is available on the output bus slightly
before the falling edge of BUSY.
Note that the data bus cannot change state while the A/D is
doing a conversion, as this would have a detrimental effect on
the conversion in progress. The data out lines go three-state
RD
again when either the
be tied low permanently, leaving the
conversion result access. Please reference the V
or CS line goes high. Thus the CS can
RD
line to control
section for
DRIVE
output voltage levels.
OPERATING MODES
The AD7492 has two possible modes of operation depending
on the state of the
CONVST
Mode 1 and Mode 2.
Mode 1 (High-Speed Sampling)
In this mode of operation the
before the end of conversion, that is, before BUSY goes low (see
Figure 20). If the
CONVST
while BUSY is high, the conversion is restarted. When
operating in this mode a new conversion should not be initiated
until 140 ns after BUSY goes low. This acquisition time allows
the track/hold circuit to accurately acquire the input signal. As
mentioned earlier, a read should not be done during a
conversion. This mode facilitates the fastest throughput times
for the AD7492.
pulse at the end of a conversion,
CONVST
pulse is brought high
pin is brought from high-to-low
Rev. A | Page 14 of 24

AD7492
CONVST
BUSY
CS
RD
DBx
CONVST
BUSY
DBx
t
CONVERT
t
2
Figure 19. Parallel Port Timing
t
CONVERT
t
2
DATA N DATA N+1
Figure 20. Parallel Port Timing with
Mode 2 (Partial or Full Sleep Mode)
Figure 21 shows the AD7492 in Mode 2 operation where the
ADC goes into either partial or full sleep mode after
conversion. The
CONVST
line is brought low to initiate a
conversion and remains low until after the end of the
conversion. If
CONVST
goes high and low again while BUSY is
high, the conversion is restarted. Once the BUSY line goes from
high-to-low, the
CONVST
line has its status checked and, if low,
the part enters a sleep mode. The type of sleep mode the
AD7492 enters depends on what way the PS/
hardwired. If the PS/
partial sleep mode. If the PS/
FS
pin is tied high, the AD7492 enters
FS
pin is tied low, the AD7492
FS
pin is
enters full sleep mode.
The device wakes up again on the rising edge of the
CONVST
signal. From partial sleep the AD7492 is capable of starting
conversions typically 1 μs after the rising edge of
CONVST
line can go from high-to-low during the wake-up time,
CONVST
. The
but the conversion is still not initiated until after 1 μs. It is
recommended that the conversion should not be initiated until at
least 20 μs of the wake-up time has elapsed. This ensures that the
AD7492 has stabilized to within 0.5 LSB of the analog input value.
t
9
t
10
t
3
t
4
t
t
6
t
5
8
t
7
t
9
CS
and RD Tied Low
01128-019
01128-020
After 1 μs, the AD7492 has only stabilized to within approximately 3 LSB of the input value. From full sleep, this wake-up
time is typically 500 μs. In all cases the BUSY line only goes high
CONVST
once
goes low. Superior power performance can be
achieved in these modes of operation by waking up the AD7492
only to carry out a conversion. The optimum power performance
is obtained when using full sleep mode as the ADC comparator,
reference buffer, and reference circuit are powered down. While
in partial sleep mode, only the ADC comparator is powered
down and the reference buffer is put into a low power mode. The
100 nF capacitor on the REF OUT pin is kept charged up by the
reference buffer in partial sleep mode while in full sleep mode
this capacitor slowly discharges. This explains why the wake-up
time is shorter in partial sleep mode. In both sleep modes the
clock oscillator circuit is powered down.
Rev. A | Page 15 of 24

AD7492
V
DRIVE
The V
CONVST
BUSY
CS
RD
DBx
pin is used as the voltage supply to the digital output
DRIVE
t
CONVERT
Figure 21. Mode 2 Operation
drivers and the digital input circuitry. It is a separate supply
from AV
and DVDD. The purpose of using a separate supply
DD
for the digital input/output interface is that the user can vary
the output high voltage, V
and V
AV
, from the VDD supply to the AD7492. For example, if
INL
and DVDD are using a 5 V supply, the V
DD
, and the logic input levels, V
OH
pin can be
DRIVE
INH
powered from a 3 V supply. The ADC has better dynamic
performance at 5 V than at 3 V, so operating the part at 5 V,
while still being able to interface to 3 V parts, pushes the
AD7492 to the top bracket of high performance 12-bit ADCs.
Of course, the ADC can have its V
and DVDD pins
DRIVE
connected together and be powered from a 3 V or 5 V supply.
The trigger levels are V
inputs. The pins that are powered from V
CS, RD, CONVST
, and BUSY.
× 0.7 and V
DRIVE
× 0.3 for the digital
DRIVE
are DB11 to DB0,
DRIVE
PS/FS PIN
As previously mentioned, the PS/FS pin is used to control the
type of power-down mode that the AD7492 can enter into if
operated in Mode 2. This pin can be hardwired either high or
low, or even controlled by another device. It is important to
note that toggling the PS/
FS
pin while in power-down mode
does not switch the part between partial sleep and full sleep
modes. To switch from one sleep mode to another, the AD7492
has to be powered up and the polarity of the PS/
FS
pin changed.
It can then be powered down to the required sleep mode.
POWER-UP
It is recommended that the user performs a dummy conversion
after power-up, as the first conversion result could be incorrect.
This also ensures that the part is in the correct mode of
operation. The recommended power-up sequence is as follows:
1. GND
2. VDD
3. V
4. Digital Inputs
5. V
DRIVE
IN
t
WAKEUP
01128-021
Power vs. Throughput
The two modes of operation for the AD7492 produces different
power vs. throughput performances, Mode 1 and Mode 2; see
the
Operating Modes section of the data sheet for more detailed
descriptions of these modes. Mode 2 is the sleep mode
(partial/full) of the part and it achieves the optimum power
performance.
Mode 1
Figure 22 shows the AD7492 conversion sequence in Mode 1
using a throughput rate of 500 kSPS. At 5 V supply, the current
consumption for the part when converting is 3 mA and the
quiescent current is 1.8 mA. The conversion time of 880 ns
contributes 6.6 mW to the overall power dissipation in the
following way:
(880 ns/2 μs) × (5 × 3 mA) = 6.6 mW
The contribution to the total power dissipated by the remaining
1.12 μs of the cycle is 5.04 mW
(1.12 μs/2 μs) × (5 × 1.8 mA) = 5.04 mW
Thus the power dissipated during each cycle is
6.6 mW + 5.04 mW = 11.64 mW
CONVST
2µs
t
QUIESCENT
1.12µs
01128-022
BUSY
t
CONVERT
880ns
Figure 22. Mode 1 Power Dissipation
Rev. A | Page 16 of 24

AD7492
Mode 2 (Full Sleep Mode)
Figure 23 shows the AD7492 conversion sequence in Mode 2,
full sleep mode, using a throughput rate of approximately
100 kSPS. At 5 V supply the current consumption for the part
when converting is 3 mA, while the full sleep current is 1 μA
maximum. The power dissipated during this power-down is
negligible and thus not worth considering in the total power
figure. During the wake-up phase, the AD7492 draws typically
1.8 mA. Overall power dissipated is
Figure 25, Figure 26, and Figure 27 show a typical graphical
representation of power vs. throughput for the AD7492 when in
Mode 1 @ 5 V and 3 V, Mode 2 in full sleep mode @ 5 V and 3
V, and Mode 2 in partial sleep mode @ 5 V and 3 V.
12
10
8
5V
(880 ns/10 ms) × (5 × 3 mA) + (500 μs/10 ms) × (5 × 1.8 mA)
= 451.32 μW
t
CONVERT
880ns
10ms
t
QUIESCENT
9.5ms
CONVST
BUSY
t
WAKEUP
500µs
Figure 23. Full Sleep Power Dissipation
Mode 2 (Partial Sleep Mode)
Figure 24 shows the AD7492 conversion sequence in Mode 2,
partial sleep mode, using a throughput rate of 1 kSPS. At 5 V
supply, the current consumption for the part when converting is
3 mA, while the partial sleep current is 250 μA maximum.
During the wake-up phase, the AD7492 typically draws 1.8 mA.
Power dissipated during wake-up and conversion is
(880 ns/1 ms) × (5 × 3 mA) + (20 μs/1 ms) × (5 × 1.8 mA) =
193.2 mW
Power dissipated during power-down is
(979 μs/1 ms) × (5 × 250 μA) = 1.22 mW
Overall power dissipated is
193.2 μW + 1.22 mW = 1.41 mW
t
CONVERT
880ns
1ms
t
QUIESCENT
979µs
CONVST
BUSY
t
WAKEUP
20µs
Figure 24. Partial Sleep Power Dissipation
6
POWER (mV)
4
2
0
3V
500 600 900 1000
THROUGHPUT (kHz)
700
8004003002001000
01128-025
Figure 25. Power vs. Throughput
01128-023
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
POWER (mV)
1.0
0.5
0
(Mode 1 @ 5 V and 3 V)
5V
3V
50 60 90 100
THROUGHPUT (kHz)
70
80403020100
01128-026
Figure 26. Power vs. Throughput
(Mode 2 in Full Sleep Mode @ 5 V and 3 V)
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
POWER (mV)
01128-024
0.5
5V
3V
Rev. A | Page 17 of 24
0
50 60 90 100
THROUGHPUT (kHz)
Figure 27. Power vs. Throughput
(Mode 2 in Partial Sleep Mode @ 5 V and 3 V)
70
80403020100
01128-027

AD7492
GROUNDING AND LAYOUT
The analog and digital power supplies are independent and
separately pinned out to minimize coupling between analog and
digital sections within the device. To complement the excellent
noise performance of the AD7492, it is imperative that care be
given to the PCB layout.
connection diagram for the AD7492.
All of the AD7492 ground pins should be soldered directly to a
ground plane to minimize series inductance. The AV
pin, and V
DV
DD
analog and digital ground planes. The REF OUT pin should be
decoupled to the analog ground plane with a minimum
capacitor value of 100 nF. This capacitor helps to stabilize the
internal reference circuit. The large value capacitors decouple
low frequency noise to analog ground, the small value
capacitors decouple high frequency noise to digital ground. All
digital circuitry power pins should be decoupled to the digital
ground plane. The use of ground planes can physically separate
sensitive analog components from the noisy digital system. The
two ground planes should be joined in only one place and
should not overlap so as to minimize capacitive coupling
between them. If the AD7492 is in a system where multiple
devices require AGND-to-DGND connections, the connection
should still be made at one point only, a star ground point,
established as close as possible to the AD7492.
+
1nF
10µF
1nF
Figure 28 shows a recommended
pin should be decoupled to both the
DRIVE
47µF0.1µF10µF
AV
DD
DV
DD
AGND
AD7492
DGND
V
DRIVE
+
pin,
DD
ANALOG
SUPPLY
+
5V
• Avoid crossover of digital and analog signals and place
traces that are on opposite sides of the board at right angles
to each other.
Noise to the analog power line can be further reduced by use of
multiple decoupling capacitors as shown in
Figure 28.
Decoupling capacitors should be placed directly at the power
inlet to the PCB and also as close as possible to the power pins
of the AD7492. The same decoupling method should be used
on other ICs on the PCB, with the capacitor leads as short as
possible to minimize lead inductance.
POWER SUPPLIES
Separate power supplies for AVDD and DVDD are desirable, but if
necessary, DV
digital supply (DV
can share its power connection to AVDD. The
DD
) must not exceed the analog supply (AVDD)
DD
by more than 0.3 V in normal operation.
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACING
ADSP-2185 to AD7492 Interface
Figure 29 shows a typical interface between the AD7492 and the
ADSP-2185. The ADSP-2185 processor can be used in one of
two memory modes, full memory mode and host mode. The
Mode C pin determines in which mode the processor works.
The interface in
working in full memory mode, allowing full external addressing
capabilities.
When the AD7492 has finished converting, the BUSY line
requests an interrupt through the
has to be set up in the interrupt control register as edgesensitive. The data memory select (DMS) pin latches in the
address of the ADC into the address decoder. The read
operation is started.
Figure 29 is set up to have the processor
IRQ2
pin. The
IRQ2
OPTIONAL
interrupt
2.5V
100nF
+
REF OUT
Figure 28. Typical Decoupling Circuit
Noise can be minimized by applying the following simple rules
to the PCB layout:
• Analog signals should be kept away from digital signals.
• Fast switching signals like clocks should be shielded with
digital ground to avoid radiating noise to other sections of
the board and clock signals should never be run near the
analog inputs.
• Avoid running digital lines under the device as this couples
noise onto the die.
• The power supply lines to the AD7492 should use as large a
trace as possible to provide a low impedance path and reduce
the effects of glitches on the power supply line.
Rev. A | Page 18 of 24
A0 TO A15
01128-028
ADSP-2185
MODE C
D0 TO D23
ADDRESS BUS
1
DMS
IRQ2
RD
1
Figure 29. ADSP-2185 to AD7492 Interface
ADDRESS
DECODER
100kΩ
DATA BUS
ADDITIONAL PINS OMI TTED FO R CLARITY.
CONVST
AD7492
CS
BUSY
RD
DB0 TO DB9
(DB11)
01128-029

AD7492
ADSP-21065Lto AD7492 Interface
Figure 30 shows a typical interface between the AD7492 and the
ADSP-21065L SHARC® processor. This interface is an example
MS
of one of three DMA handshake modes. The
X
control line is
actually three memory select lines. Internal ADDR25–24 are
decoded into
DMAR
The
MS
, these lines are then asserted as chip selects.
3-0
(DMA Request 1) is used in this setup as the
1
interrupt to signal end of conversion. The rest of the interface is
standard handshaking operation.
OPTIONAL
ADDR0 TO
ADDR
MS
ADSP-21065L
DMAR
D0 TO 31
ADDRESS BUS
23
ADDRESS
X
1
1
RD
1
ADDITIONAL PINS OMITTED FO R CLARITY.
LATCH
ADDRESS
DECODER
DATA BUS
ADDRESS
BUS
CONVST
AD7492
CS
BUSY
RD
DB0 TO DB9
(DB11)
01128-030
Figure 30. ADSP-21065L to AD7492 Interface
TMS320C25 to AD7492 Interface
Figure 31 shows an interface between the AD7492 and the
TMS320C25. The
CONVST
signal can be applied from the
TMS320C25 or from an external source. The BUSY line
interrupts the digital signal processor when conversion is
completed. The TMS320C25 does not have a separate
output to drive the AD7492
generated from the processor
addition of some glue logic. The
RD
input directly. This has to be
STRB
and R/W outputs with the
RD
signal is OR-gated with the
RD
MSC signal to provide the WAIT state required in the read cycle
for correct interface timing. The following instruction is used to
read the conversion from the AD7492:
IN D,ADC
where:
D is the data memory address.
ADC is the AD7492 address.
OPTIONAL
A0 TO A15
TMS320C25
DMD0 TO DMD15
1
STRB
R/W
READY
MSC
1
ADDITIONAL PINS OMITTED FO R CLARITY.
IS
ADDRESS BUS
ADDRESS
DECODER
DATA BUS
CONVST
AD7492
CS
BUSY
RD
DB0 TO DB9
(DB11)
01128-031
Figure 31. TMS320C25 to AD7492 Interface
PIC17C4x to AD7492 Interface
Figure 32 shows a typical parallel interface between the AD7492
and PIC17C4x. The microcontroller sees the ADC as another
memory device with its own specific memory address on the
memory map. The
CONVST
signal can be controlled by either
the microcontroller or an external source. The BUSY signal
provides an interrupt request to the microcontroller when a
conversion ends. The INT pin on the PIC17C4x must be
configured to be active on the negative edge. Port C and Port D
of the microcontroller are bidirectional and used to address the
AD7492 and to read in the 12-bit data. The
OE
pin on the PIC
can be used to enable the output buffers on the AD7492 and
perform a read operation.
OPTIONAL
PIC17C4x
AD0 TO AD15
1
ADDRESS
ALE
OE
INT
1
ADDITIONAL PINS OMI TTED FO R CLARITY.
LATCH
ADDRESS
DECODER
Figure 32. PIC17C4x to AD7492 Interface
CONVST
DB0 TO DB9
(DB11)
AD7492
CS
RD
BUSY
01128-032
The read operation must not be attempted during conversion.
Rev. A | Page 19 of 24

AD7492
80C186 to AD7492 Interface
Figure 33 shows the AD7492 interfaced to the 80C186
microprocessor. The 80C186 DMA controller provides two
independent high speed DMA channels where data transfer can
occur between memory and I/O spaces. (The AD7492 occupies
one of these I/O spaces.) Each data transfer consumes two bus
cycles, one cycle to fetch data and the other to store data.
After the AD7492 has finished the conversion, the BUSY line
generates a DMA request to Channel 1 (DRQ1). Because of the
interrupt, the processor performs a DMA read operation that
resets the interrupt latch. Sufficient priority must be assigned to
the DMA channel to ensure that the DMA request is serviced
AD0 TO AD15
A16 TO A19
ALE
1
80C186
DRQ1
ADDRESS/DATA BUS
ADDRESS
LATCH
ADDRESS
BUS
ADDRESS
DECODER
RSQ
RD
DATA BUS
1
ADDITIONAL P INS OMITT ED FOR CLARI TY.
Figure 33. 80C186 to AD7492 Interface
OPTIONAL
CONVST
AD7492
CS
BUSY
RD
DB0 TO DB9
(DB11)
01128-033
before the completion of the next conversion. This
configuration can be used with 6 MHz and 8 MHz 80C186
processors.
Rev. A | Page 20 of 24
AD7492
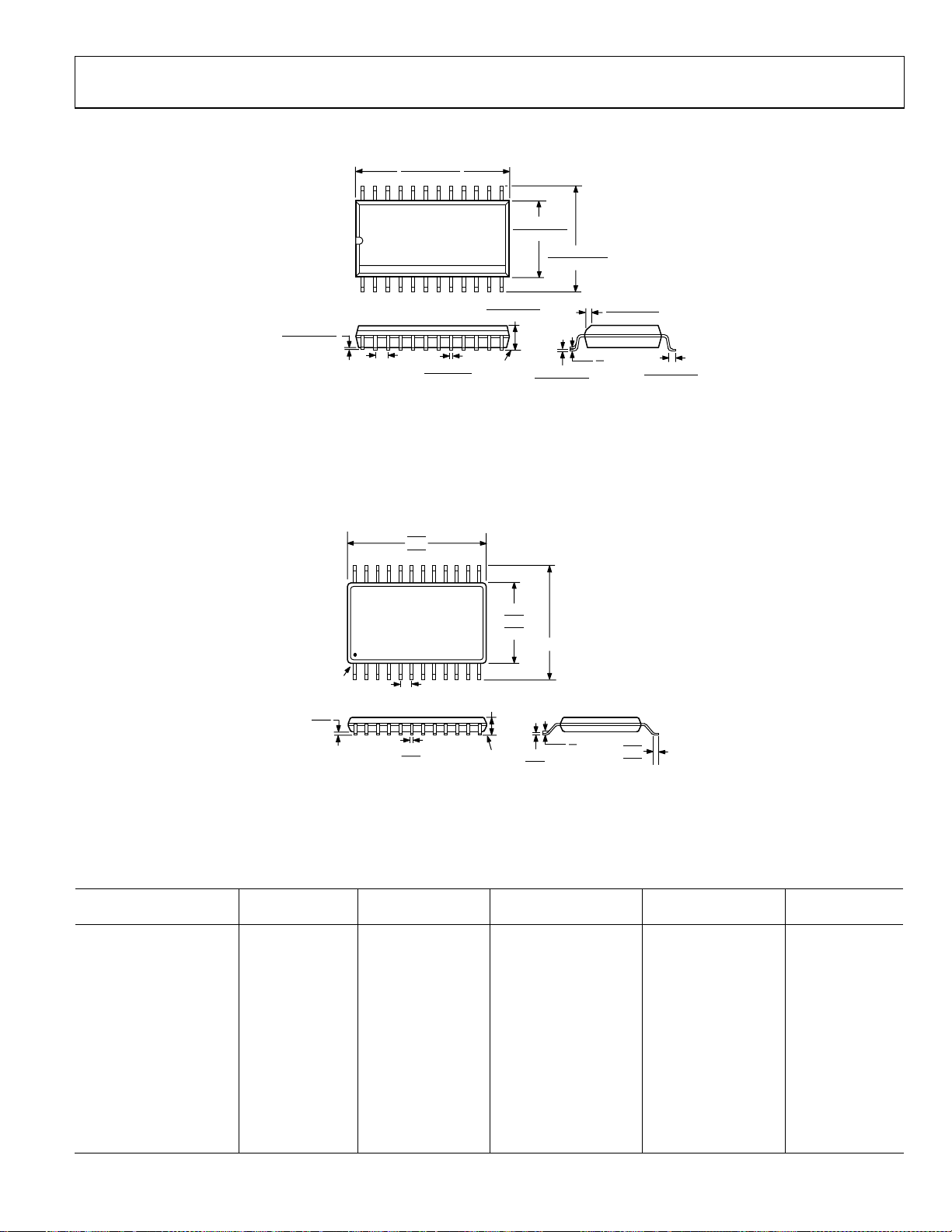
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
15.60 (0.6142)
15.20 (0.5984)
24 13
1
0.30 (0.0118)
0.10 (0.0039)
COPLANARITY
0.10
1.27 (0.0500)
BSC
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN.
0.51 (0.020)
0.31 (0.012)
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-013-AD
7.60 (0.2992)
7.40 (0.2913)
12
2.65 (0.1043)
2.35 (0.0925)
SEATING
PLANE
10.65 (0.4193)
10.00 (0.3937)
0.33 (0.0130)
0.20 (0.0079)
Figure 34. 24-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_W]
Wide Body
(RW-24)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
7.90
7.80
7.70
24
PIN 1
0.15
0.05
0.10 COPLANARITY
0.65
BSC
0.30
0.19
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-153-AD
13
121
1.20
MAX
SEATING
PLANE
4.50
4.40
4.30
6.40 BSC
0.20
0.09
Figure 35. 24-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP]
(RU-24)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
8°
0°
0.75 (0.0295)
0.25 (0.0098)
8°
0°
0.75
0.60
0.45
× 45°
1.27 (0.0500)
0.40 (0.0157)
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature
Model
Range
Resolution (Bits)
AD7492AR −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492AR–REEL −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492AR–REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492ARZ
AD7492ARZ–REEL
AD7492ARZ–REEL7
1
1
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
−40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
−40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492BR −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492BR-REEL −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492BR–REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492BRZ
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492AR-5 −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492AR-5–REEL −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
Rev. A | Page 21 of 24
Throughput Rate
(MSPS)
Package
Description
Package Option

AD7492
Temperature
Model
Range Resolution (Bits)
AD7492AR-5–REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492ARZ-5
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492BR-5 −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492BR-5–REEL −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492BR-5–REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492BRZ-5
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead SOIC_W RW-24
AD7492ARU −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARU–REEL −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARU–REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARUZ
AD7492ARUZ–REEL
AD7492ARUZ–REEL7
1
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
−40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARU-5 −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARU-5–REEL −40°C to +85°C 12 1 .25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARU-5–REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARUZ-5
AD7492ARUZ-5–REEL
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARUZ-5–REEL71−40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492ARUZ-4
AD7492ARUZ-4REEL
AD7492ARUZ-4REEL7
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 0.4 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 0.4 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 0.4 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492BRU −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492BRU–REEL −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492BRU–REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492BRUZ
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492BRU-5 −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492BRU-5–REEL −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492BRU-5–REEL7 −40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
AD7492BRUZ-5
1
−40°C to +85°C 12 1.25 24-Lead TSSOP RU-24
EVAL-AD7492CB2 Evaluation Board
EVAL-CONTROL BRD23 Controller Board
1
Z = Pb–free part.
2
This can be used as a standalone evaluation board or in conjunction with the EVAL-CONTROL BRD2 for evaluation/demonstration purposes.
3
This board is a complete unit allowing a PC to control and communicate with all Analog Devices evaluation boards ending in the CB designators.
Throughput Rate
(MSPS)
Package
Description Package Option
Rev. A | Page 22 of 24

AD7492
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 23 of 24

AD7492
NOTES
©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D01128-0-5/06(A)
Rev. A | Page 24 of 24
 Loading...
Loading...