16-Channel, 1 MSPS, 12-Bit ADC
V
FEATURES
Fast throughput rate: 1 MSPS
Specified for V
Low power at maximum throughput rates
5.4 mW maximum at 870 kSPS with 3 V supplies
12.5 mW maximum at 1 MSPS with 5 V supplies
16 (single-ended) inputs with sequencer
Wide input bandwidth
69.5 dB SNR at 50 kHz input frequency
Flexible power/serial clock speed management
No pipeline delays
High speed serial interface, SPI/QSPI™/MICROWIRE™/
DSP compatible
Full shutdown mode: 0.5 μA maximum
28-lead TSSOP and 32-lead LFCSP packages
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7490 is a 12-bit high speed, low power, 16-channel,
successive approximation ADC. The part operates from a single
2.7 V to 5.25 V power supply and features throughput rates up
to 1 MSPS. The part contains a low noise, wide bandwidth
track-and-hold amplifier that can handle input frequencies in
excess of 1 MHz.
The conversion process and data acquisition are controlled
CS
using
easily interface with microprocessors or DSPs. The input signal
is sampled on the falling edge of
initiated at this point. There are no pipeline delays associated
with the part.
The AD7490 uses advanced design techniques to achieve very
low power dissipation at high throughput rates. For maximum
throughput rates, the AD7490 consumes just 1.8 mA with 3 V
supplies, and 2.5 mA with 5 V supplies.
By setting the relevant bits in the control register, the analog
input range for the part can be selected to be a 0 V to REF
input or a 0 V to 2 × REF
or twos complement output coding. The AD7490 features 16
single-ended analog inputs with a channel sequencer to allow a
preprogrammed selection of channels to be converted sequentially. The conversion time is determined by the SCLK
and the serial clock signal, allowing the device to
of 2.7 V to 5.25 V
DD
input, with either straight binary
IN
CS
, and conversion is also
IN
with Sequencer in 28-Lead TSSOP
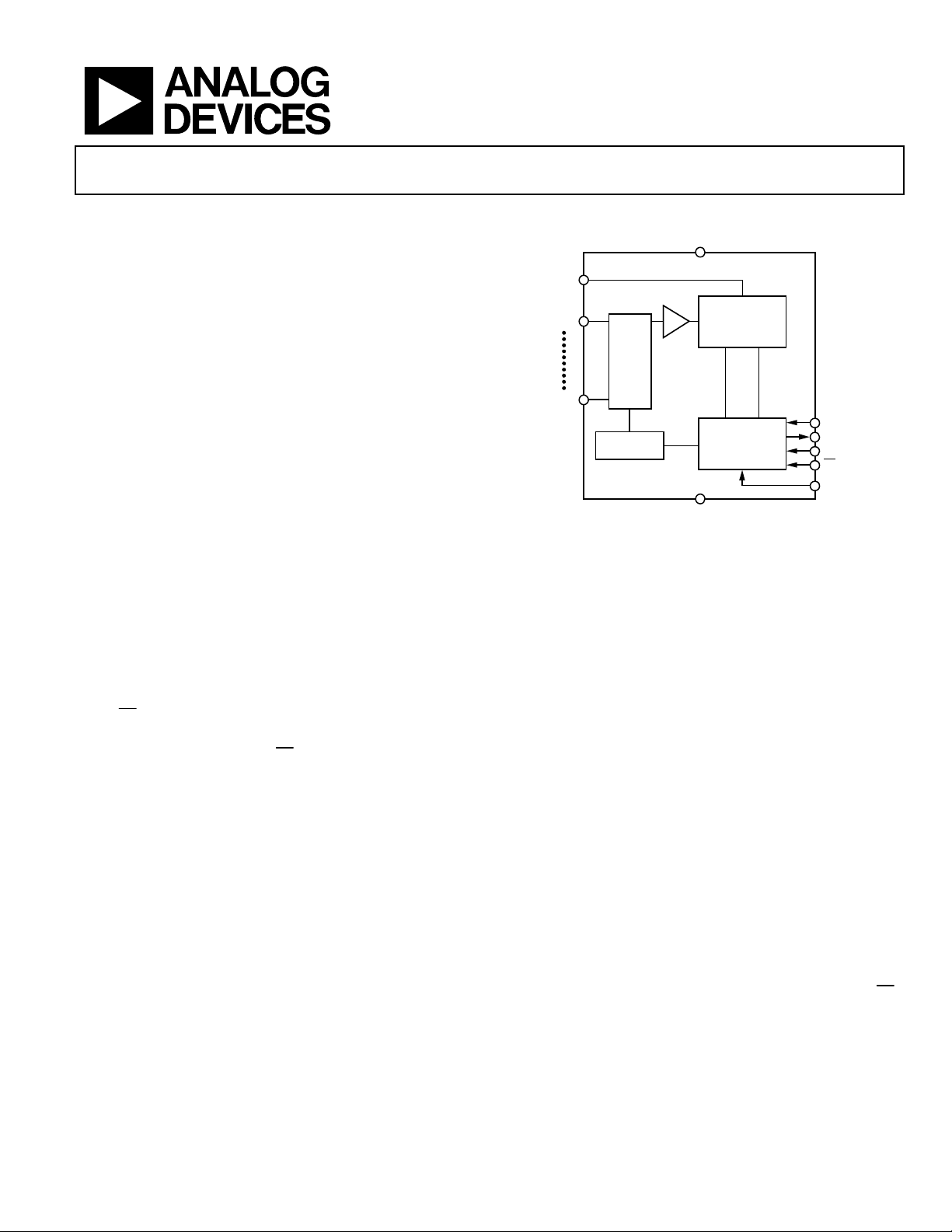
AD7490
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DD
REF
IN
VIN0
VIN15
frequency because this is also used as the master clock to
control the conversion.
The AD7490 is available in a 32-lead LFCSP and a 28-lead
TSSOP package.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The AD7490 offers up to 1 MSPS throughput rates. At
maximum throughput with 3 V supplies, the AD7490
dissipates just 5.4 mW of power.
2. A sequence of channels can be selected, through which the
AD7490 cycles and converts.
3. The AD7490 operates from a single 2.7 V to 5.25 V supply.
The V
directly to either 3 V or 5 V processor systems independent
of V
4. The conversion rate is determined by the serial clock,
allowing the conversion time to be reduced through the
serial clock speed increase. The part also features various
shutdown modes to maximize power efficiency at lower
throughput rates. Power consumption is 0.5 µA, maximum,
when in full shutdown.
5. The part features a standard successive approximation
ADC with accurate control of the sampling instant via a
input and once off conversion control.
AD7490
12-BIT
T/H
INPUT
MUX
SEQUENCER
function allows the serial interface to connect
DRIVE
.
DD
SUCCESSIVE
APPROXIMATION
ADC
CONTROL
LOGIC
AGND
Figure 1.
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
CS
V
DRIVE
02691-001
CS
Rev. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2002–2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD7490
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Product Highlights ........................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 6
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 6
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ........................... 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 8
Terminology .................................................................................... 10
Internal Register Structure ............................................................ 12
Control Register .......................................................................... 12
Shadow Register ......................................................................... 14
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 16
Circuit Information .................................................................... 16
Converter Operation .................................................................. 16
ADC Transfer Function ............................................................. 17
Typical Connection Diagram ................................................... 18
Modes of Operation ................................................................... 19
Serial Interface ............................................................................ 22
Power vs. Throughput Rate ....................................................... 23
Microprocessor Interfacing ....................................................... 24
Application Hints ....................................................................... 25
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 26
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 27
REVISION HISTORY
6/09—Rev. B to Rev. C
Change to I
5/08—Rev. A to Rev. B
Updated Format .................................................................. Universal
Changes to Table 1 ............................................................................ 3
Changes to Figure 12 and Figure 13 ............................................. 14
Changes to Figure 14 ...................................................................... 15
Changes to Reference Section ....................................................... 19
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 26
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 27
Auto Standby Mode Parameter, Table 1 ............... 4
DD
10/02—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Addition to General Description..................................................... 1
Changes to Timing Specification Notes ......................................... 4
Change to Absolute Maximum Ratings ......................................... 5
Addition to Ordering Guide ............................................................ 5
Changes to Typical Performance Characteristics .......................... 8
Added new Figure 9 .......................................................................... 8
Changes to Figure 12 and Figure 14............................................. 11
Changes to Figure 20 ...................................................................... 13
Changes to Figure 20 to Figure 26 ................................................ 14
Addition to Analog Input section ................................................ 14
Change to Figure 29 caption ......................................................... 18
Change to Figure 30 to Figure 32 ................................................. 18
Added Application Hints section ................................................. 20
1/02—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. C | Page 2 of 28
AD7490
SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = V
= 2.7 V to 5.25 V, REFIN = 2.5 V, f
DRIVE
−40°C to +85°C.
Table 1.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE fIN = 50 kHz sine wave, f
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) (SINAD)
2
V
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)2 69.5 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
2
V
V
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise (SFDR)
2
V
V
Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)
2
fa = 40.1 kHz, fb = 41.5 kHz
Second-Order Terms −85 dB
Third-Order Terms −85 dB
Aperture Delay 10 ns
Aperture Jitter 50 ps
Channel-to-Channel Isolation
2
f
Full Power Bandwidth 3 dB 8.2 MHz
0.1 dB 1.6 MHz
DC ACCURACY
2
Resolution 12 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity ±1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity Guaranteed no missed codes to 12 bits −0.95/+1.5 LSB
0 V to REF
Input Range Straight binary output coding
IN
Offset Error ±0.6 ±8 LSB
Offset Error Match ±0.5 LSB
Gain Error ±2 LSB
Gain Error Match ±0.6 LSB
0 V to 2 × REFIN Input Range
Positive Gain Error ±2 LSB
Positive Gain Error Match ±0.5 LSB
Zero Code Error ±0.6 ±8 LSB
Zero Code Error Match ±0.5 LSB
Negative Gain Error ±1 LSB
Negative Gain Error Match ±0.5 LSB
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Range RANGE bit set to 1 0 REFIN V
DC Leakage Current ±1 μA
Input Capacitance 20 pF
REFERENCE INPUT
REFIN Input Voltage ±1% specified performance 2.5 V
DC Leakage Current ±1 μA
REFIN Input Impedance f
1
= 20 MHz, TA = T
SCLK
to T
MIN
= 20 MHz
SCLK
, unless otherwise noted. Temperature range (B Version):
MAX
VDD = 5 V 69 70.5 dB
= 3 V 68 69.5 dB
DD
= 5 V −84 −74 dB
DD
= 3 V −77 −71 dB
DD
= 5 V −86 −75 dB
DD
= 3 V −80 −73 dB
DD
= 400 kHz −82 dB
IN
to +REFIN biased about REFIN
−REF
IN
with twos complement output coding
offset
RANGE bit set to 0, V
for 0 V to 2 × REF
= 1 MSPS 36 kΩ
SAMPLE
= 4.75 V to 5.25 V
DD
IN
0 2 × REF
V
IN
Rev. C | Page 3 of 28
AD7490
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current, IIN VIN = 0 V or V
Input Capacitance, CIN+
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, VOH I
Output Low Voltage, VOL I
Floating State Leakage Current
Floating State Output Capacitance
Output Coding Coding bit set to 1 Straight (Natural) Binary
Coding bit set to 0 Twos Complement
CONVERSION RATE
Conversion Time 16 SCLK cycles, SCLK = 20 MHz 800 ns
Track-and-Hold Acquisition Time
Full-scale step input 300 ns
Throughput Rate
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VDD 2.7 5.25 V
V
2.7 5.25 V
DRIVE
4
I
DD
Normal Mode (Static) VDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, SCLK on or off 600 μA
Normal Mode (Operational) VDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V, f
(fS = Maximum Throughput) VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V, f
Auto Standby Mode f
Static 100 μA
Auto Shutdown Mode f
Static 0.5 μA
Full Shutdown Mode SCLK on or off 0.02 0.5 μA
Power Dissipation
Normal Mode (Operational) VDD = 5 V, f
V
Auto Standby Mode (Static) VDD = 5 V 460 μW
V
Auto Shutdown Mode (Static) VDD = 5 V 2.5 μW
V
Full Shutdown Mode VDD = 5 V 2.5 μW
V
1
Specifications apply for f
2
See the Terminology section.
3
Guaranteed by characterization.
4
See the Power vs. Throughput Rate section.
0.7 × V
INH
0.3 × V
INL
±0.01 ±1 μA
3
10 pF
SOURCE
= 200 μA 0.4 V
SINK
WEAK/TRI
3
2
Sine wave input 300 ns
WEAK/TRI bit set to 0
= 5 V (see the Serial Interface
V
DD
DRIVE
= 200 μA; VDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V V
bit set to 0
DRIVE
±10 μA
10 pF
1 MSPS
V
DRIVE
V
DRIVE
− 0.2 V
section)
Digital inputs = 0 V or V
= 500 kSPS 1.55 mA
SAMPLE
= 250 kSPS 960 μA
SAMPLE
4
= 20 MHz 12.5 mW
SCLK
= 3 V, f
DD
= 3 V 276 μW
DD
= 3 V 1.5 μW
DD
= 3 V 1.5 μW
DD
up to 20 MHz. However, for serial interfacing requirements, see the Timing Specifications section.
SCLK
= 20 MHz 5.4 mW
SCLK
DRIVE
= 20 MHz 2.5 mA
SCLK
= 20 MHz 1.8 mA
SCLK
Rev. C | Page 4 of 28
AD7490
T
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, V
Table 2. Timing Specifications
Limit at T
Parameter VDD = 3 V VDD = 5 V Unit Description
2
f
SCLK
10 10 kHz min
16 20 MHz max
t
16 × t
CONVER T
t
50 50 ns min Minimum quiet time required between bus relinquish and start of next conversion
QUIET
SCLK
t2 12 10 ns min
3
t
3
20 14 ns max
t3b4 30 20 ns max
3
t
60 40 ns max Data access time after SCLK falling edge
4
t5 0.4 × t
t6 0.4 × t
SCLK
SCLK
t7 15 15 ns min SCLK to DOUT valid hold time
5
t
15/50 15/50 ns min/max SCLK falling edge to DOUT high impedance
8
t9 20 20 ns min DIN setup time prior to SCLK falling edge
t10 5 5 ns min DIN hold time after SCLK falling edge
t11 20 20 ns min
t12 1 1 μs max Power-up time from full power-down/auto shutdown/auto standby modes
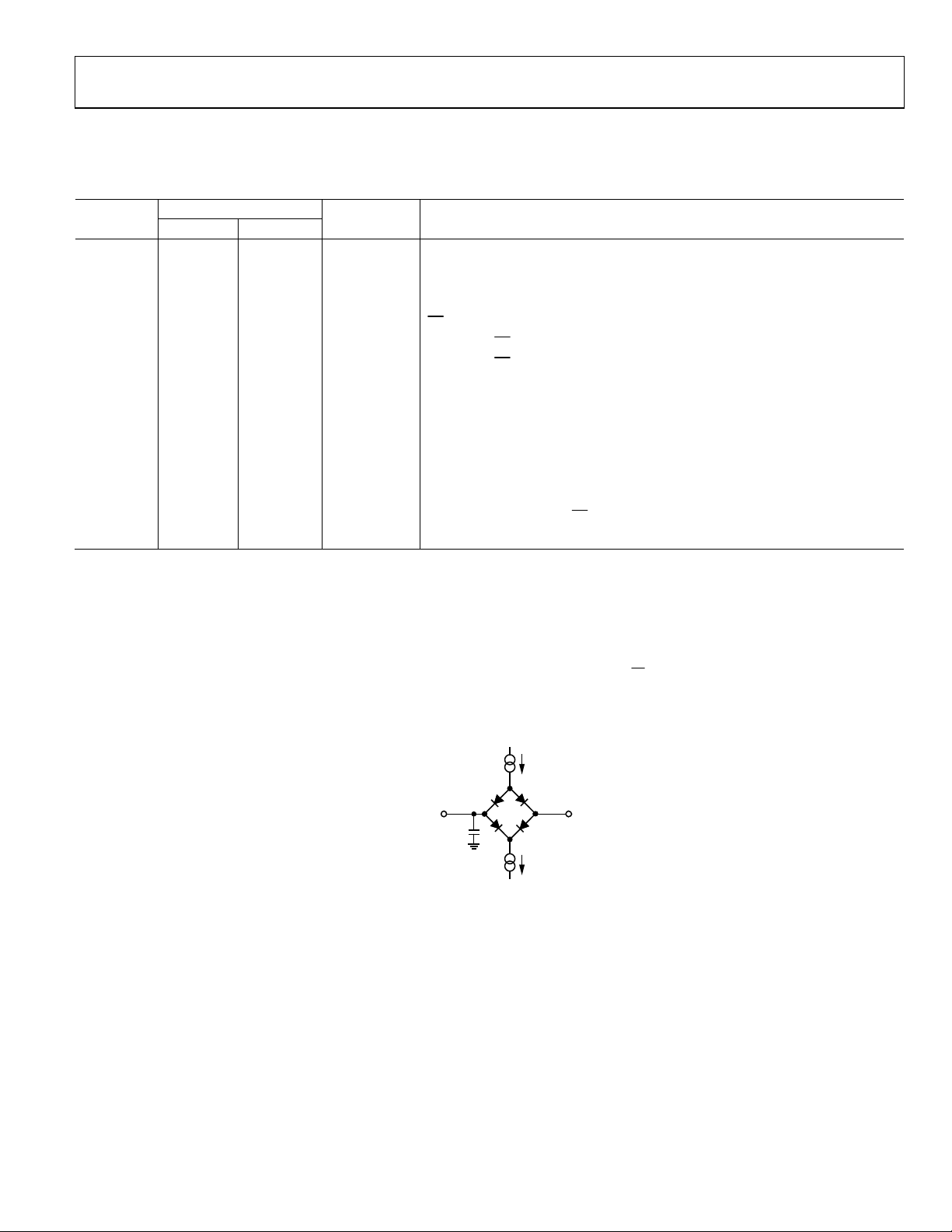
1
Guaranteed by characterization. All input signals are specified with tR = tF = 5 ns (10% to 90% of VDD) and timed from a voltage level of 1.6 V (see Figure 2). The 3 V
operating range spans from 2.7 V to 3.6 V. The 5 V operating range spans from 4.75 V to 5.25 V.
2
The mark/space ratio for the SCLK input is 40/60 to 60/40. The maximum SCLK frequency is 16 MHz with VDD = 3 V to give a throughput of 870 kSPS. Care must be
taken when interfacing to account for data access time, t4, and the setup time required for the user’s processor. These two times determine the maximum SCLK
frequency with which the user’s system can operate (see the Serial Interface section).
3
Measured with the load circuit of Figure 2 and defined as the time required for the output to cross 0.4 V or 0.7 V
4
t3b represents a worst-case figure for having ADD3 available on the DOUT line, that is, if the AD7490 goes back into three-state at the end of a conversion and some
other device takes control of the bus between conversions, the user has to wait a maximum time of t3b before having ADD3 valid on the DOUT line. If the DOUT line is
weakly driven to ADD3 between conversions, the user typically has to wait 17 ns at 3 V and 12 ns at 5 V after the CS falling edge before seeing ADD3 valid on DOUT.
5
t8 is derived from the measured time taken by the data outputs to change 0.5 V when loaded with the circuit of Figure 2. The measured number is then extrapolated
back to remove the effects of charging or discharging the 25 pF capacitor. This means that the time, t8, quoted in the timing characteristics, is the true bus relinquish
time of the part and is independent of the bus loading.
≤ VDD, REFIN = 2.5 V; TA = T
DRIVE
1
, T
MIN
MAX
16 × t
0.4 × t
0.4 × t
SCLK
ns min SCLK low pulse width
SCLK
ns min SCLK high pulse width
SCLK
to T
MIN
CS
Delay from CS
Delay from CS
16
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
to SCLK setup time
until DOUT three-state disabled
to DOUT valid
th
SCLK falling edge to CS high
DRIVE
.
O OUTPUT
PIN
25pF
C
200µA I
L
200µA I
OL
1.6V
OH
02691-002
Figure 2. Load Circuit for Digital Output Timing Specifications
Rev. C | Page 5 of 28

AD7490
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
VDD to GND −0.3 V to +7 V
V
to GND −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
DRIVE
Analog Input Voltage to GND −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
Digital Input Voltage to GND −0.3 V to +7 V
Digital Output Voltage to GND −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
REFIN to GND −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
Input Current to Any Pin Except Supplies1±10 mA
Operating Temperature Ranges
Commercial (B Version) −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
LFCSP, TSSOP Package, Power Dissipation 450 mW
θJA Thermal Impedance 108.2°C/W (LFCSP)
97.9°C/W (TSSOP)
θJC Thermal Impedance 32.71°C/W (LFCSP)
14°C/W (TSSOP)
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) 220°C
ESD 1 kV
1
Transient currents of up to 100 mA do not cause SCR latch-up.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. C | Page 6 of 28
AD7490
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
9
10
11
12
13
14
IN
IN
IN
V
V
V
28
27
26NC25
24
VIN15
NC
23
AGND
22
REF
21
IN
20
V
DD
AGND
19
CS
18
DIN
17
13
14
15NC16
DRIVE
SCLK
DOUT
V
02691-032
or 0 V to 2 × REFIN as selected
IN
V
11
1
IN
VIN10
2
VIN9
3
NC
4
VIN8
5
VIN7
VIN6
VIN5
VIN4
VIN3
VIN2
VIN1
VIN0
AGND
NC = NO CONNECT
ALL NC PINS SHOULD BE
CONNECTED STRAI GHT TO AGND
AD7490
6
TOP VIEW
7
(Not to Scale)
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
VIN12
28
VIN13
27
VIN14
26
VIN15
25
AGND
24
REF
23
V
22
DD
AGND
21
CS
20
DIN
19
NC
18
V
17
DRIVE
SCLK
16
DOUT
15
Figure 3. 28-Lead TSSOP Pin Configuration
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No.
Mnemonic Description TSSOP LFCSP
20 18
Chip Select. Active low logic input. This input provides the dual function of initiating
CS
23 21 REFIN
22 20 V
DD
14, 21, 24 12, 19, 22 AGND
V
13 to 5,
3 to 1,
28 to 25
11 to 9,
7 to 2,
31 to 26,
0 to VIN15
IN
24
19 17 DIN
15 13 DOUT
16 14 SCLK
17 15 V
DRIVE
IN
IN
V
31
30
AD7490
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
10
11
1
0
IN
IN
V
V
IN
V
29
12
ANGD
NC32V
1
NC
VIN8
2
VIN7
IN
02691-003
3
VIN6
4
5
VIN5
VIN4
6
VIN3
7
NC
8
9
2
IN
V
NC = NO CONNECT
ALL NC PINS SHOUL D BE
CONNECTED STRAI GHT TO AGND
Figure 4. 32-Lead LFCSP Pin Configuration
conversions on the AD7490 and also frames the serial data transfer.
Reference Input for the AD7490. An external reference must be applied to this input. The
voltage range for the external reference is 2.5 V ± 1% for specified performance.
Power Supply Input. The V
range, V
should be from 4.75 V to 5.25 V.
DD
range for the AD7490 is from 2.7 V to 5.25 V. For the 0 V to 2 × REFIN
DD
Analog Ground. Ground reference point for all circuitry on the AD7490. All analog/digital input
signals and any external reference signal should be referred to this AGND voltage. All AGND pins
should be connected together.
Analog Input 0 through Analog Input 15. Sixteen single-ended analog input channels that are
multiplexed into the on chip track-and-hold. The analog input channel to be converted is
selected by using the address bits ADD3 through ADD0 of the control register. The address bits,
in conjunction with the SEQ and SHADOW bits, allow the sequence register to be programmed.
The input range for all input channels can extend from 0 V to REF
via the RANGE bit in the control register. Any unused input channels should be connected to
AGND to avoid noise pickup.
Data In. Logic input. Data to be written to the control register of the AD7490 is provided on this
input and is clocked into the register on the falling edge of SCLK (see the Control Register
section).
Data Out. Logic output. The conversion result from the AD7490 is provided on this output as a
serial data stream. The bits are clocked out on the falling edge of the SCLK input. The data
stream consists of four address bits indicating which channel the conversion result corresponds
to, followed by the 12 bits of conversion data, which is provided by MSB first. The output coding
can be selected as straight binary or twos complement via the CODING bit in the control
register.
Serial Clock. Logic input. SCLK provides the serial clock for accessing data from the part. This
clock input is also used as the clock source for the conversion process of the AD7490.
Logic Power Supply Input. The voltage supplied at this pin determines at what voltage the serial
interface of the AD7490 operates.
Rev. C | Page 7 of 28
AD7490
–
–
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
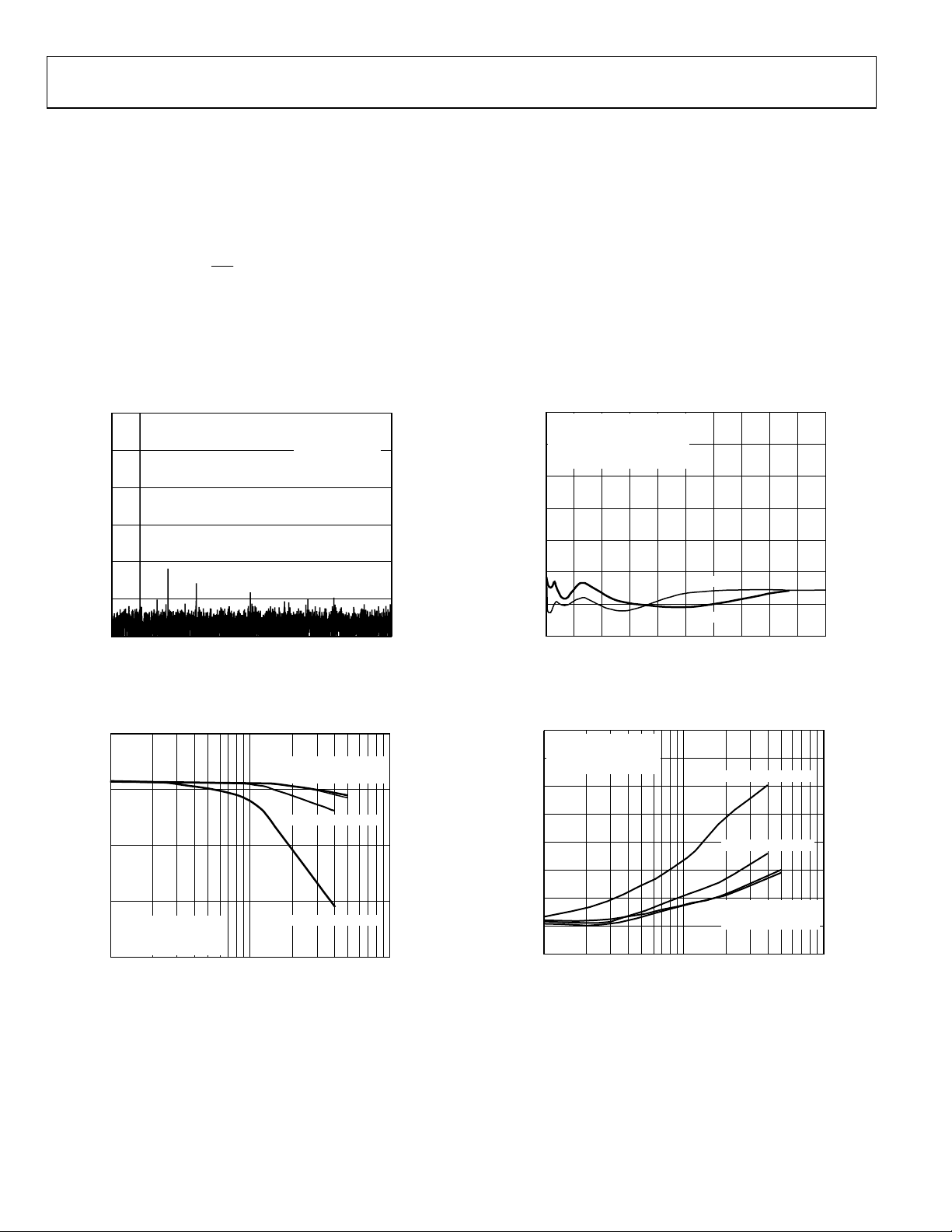
Figure 5 shows a typical FFT plot for the AD7490 at 1 MSPS sample rate and 50 kHz input frequency.
Figure 7 shows the power supply rejection ratio vs. supply ripple frequency for the AD7490. The power supply rejection ratio is defined as
the ratio of the power in the ADC output at full-scale frequency f, to the power of a 200 mV p-p sine wave applied to the ADC V
of frequency f
PSRR log10dB
.
S
()
⎛
⎞
Pf
⎜
×=
⎟
⎜
⎟
Pf
s
⎝
⎠
where:
Pf is equal to the power at frequency f in ADC output.
Pf
is equal to power at frequency fS coupled onto the ADC VDD supply input.
S
Here, a 200 mV p-p sine wave is coupled onto the V
was used on the REF
5
–15
–35
–55
SNR (dB)
–75
–95
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 500450
pin.
IN
8192 POINT FFT
f
SAMPLE
f
= 50kHZ
IN
SINAD = 70.697dB
THD = –79.171dB
SFDR = –79.93dB
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Figure 5. Dynamic Performance at 1 MSPS
supply. 10 nF decoupling was used on the supply, and a 1 µF decoupling capacitor
DD
20
V
= 3V/5V, 10nF CAP
= 1MSPS
02691-004
DD
200mV p-p SINE WAVE ON V
–30
REFIN = 2.5V, 1µF CAP
T
= 25°C
A
–40
–50
–60
PSRR (dB)
–70
–80
–90
0 100k 200k 300k 400k 500k 600k 700k 800k 900k 1M
DD
VDD = 5V
V
= 3V
DD
INPUT FREQ UENCY (Hz)
Figure 7. PSRR vs. Supply Ripple Frequency
supply
DD
02691-006
75
VDD = V
70
65
SINAD (dB)
60
f
= MAX THROUGHPUT
S
T
= 25°C
A
RANGE = 0V TO REF
55
10 100 1000
IN
INPUT F REQUE NCY (kHz)
V
V
DD
V
DD
= 5.25V
DRIVE
= V
DD
DRIVE
= V
= 3.6V
DRIVE
= V
= 2.7V
DRIVE
Figure 6. SINAD vs. Analog Input Frequency
for Various Supply Voltages at 1 MSPS
= 4.75V
02691-005
Rev. C | Page 8 of 28
50
f
= MAX THROUGHPUT
S
= 25°C
T
A
–55
RANGE = 0V TO REF
–60
–65
–70
THD (dB)
–75
–80
–85
–90
10 100 1000
IN
INPUT F REQUE NCY (kHz)
VDD = V
V
V
V
= 2.7V
DRIVE
= V
= V
= V
DRIVE
DRIVE
DRIVE
= 3.6V
= 4.75V
= 5.25V
DD
DD
DD
Figure 8. THD vs. Analog Input Frequency
for Various Supply Voltages at 1 MSPS
02691-007
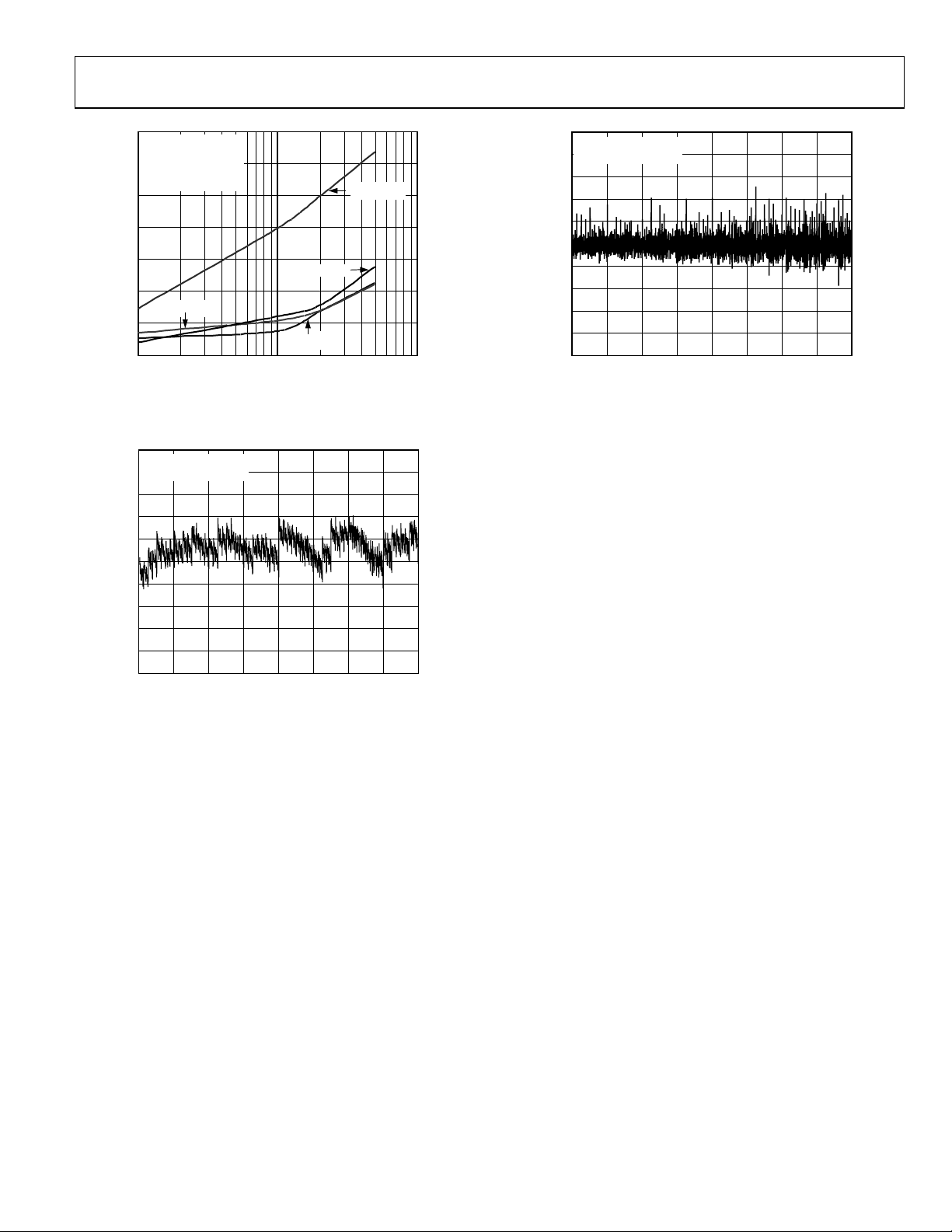
AD7490
–
50
f
= 1MSPS
S
T
= 25°C
A
–55
V
= 5.25V
DD
RANGE = 0V TO REF
–60
–65
–70
THD (dB)
–75
= 5Ω
R
–80
–85
IN
10 100 1000
IN
= 100Ω
R
IN
R
= 10Ω
IN
INPUT FREQ UENCY (Hz)
RIN = 1000Ω
Figure 9. THD vs. Analog Input Frequency
for Various Analog Source Impedances
1.0
VDD = V
0.8
TEMPERATURE = 25°C
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
INL ERROR (LSB)
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0 512 1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096
DRIVE
= 5V
CODE
Figure 10. Typical INL
02691-008
02691-009
1.0
VDD = V
0.8
TEMPERATURE = 25°C
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
DNL ERROR (LSB)
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
0 512 1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096
DRIVE
= 5V
CODE
Figure 11. Typical DNL
02691-010
Rev. C | Page 9 of 28

AD7490
TERMINOLOGY
Integral Nonlinearity
This is the maximum deviation from a straight line passing
through the endpoints of the ADC transfer function. The endpoints of the transfer function are zero scale, a point 1 LSB
below the first code transition, and full scale, a point 1 LSB
above the last code transition.
Differential Nonlinearity
This is the difference between the measured and the ideal 1 LSB
change between any two adjacent codes in the ADC.
Offset Error
This is the deviation of the first code transition (00 … 000) to
(00 … 001) from the ideal, that is, AGND + 1 LSB.
Offset Error Match
This is the difference in offset error between any two channels.
Gain Error
This is the deviation of the last code transition (111 … 110) to
(111 … 111) from the ideal (that is, REF
− 1 LSB) after the
IN
offset error has been adjusted out.
Gain Error Match
This is the difference in gain error between any two channels.
Zero Code Error
This applies when using the twos complement output coding
option, in particular to the 2 × REF
to +REF
biased about the REFIN point. It is the deviation of the
IN
midscale transition (all 0s to all 1s) from the ideal V
that is, REF
− 1 LSB.
IN
input range with −REFIN
IN
voltage,
IN
Zero Code Error Match
This is the difference in zero code error between any two
channels.
Positive Gain Error
This applies when using the twos complement output coding
option, in particular the 2 × REF
+REF
biased about the REFIN point. It is the deviation of the
IN
input range with −REFIN to
IN
last code transition (011 … 110) to (011 … 111) from the ideal
(that is, +REF
− 1 LSB) after the zero code error has been
IN
adjusted out.
Positive Gain Error Match
This is the difference in positive gain error between any two
channels.
Negative Gain Error
This applies when using the twos complement output coding
option, in particular to the 2 × REF
to +REF
biased about the REFIN point. It is the deviation of the
IN
input range with −REFIN
IN
first code transition (100 … 000) to (100 … 001) from the ideal
(that is, −REF
+ 1 LSB) after the zero code error has been
IN
adjusted out.
Negative Gain Error Match
This is the difference in negative gain error between any two
channels.
Channel-to-Channel Isolation
Channel-to-channel isolation is a measure of the level of
crosstalk between channels. It is measured by applying a fullscale 400 kHz sine wave signal to all 15 nonselected input
channels and determining how much that signal is attenuated in
the selected channel with a 50 kHz signal. This specification is
the worst case across all 16 channels for the AD7490.
PSR (Power Supply Rejection)
Variations in power supply affect the full scale transition, but
not the converter linearity. Power supply rejection is the
maximum change in the full-scale transition point due to a
change in power supply voltage from the nominal value. (see
the Typical Performance Characteristics section).
Track-and-Hold Acquisition Time
The track-and-hold amplifier returns into track on the 14th
SCLK falling edge. Track-and-hold acquisition time is the
minimum time required for the track-and-hold amplifier to
remain in track mode for its output to reach and settle to within
±1 LSB of the applied input signal, given a step change to the
input signal.
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) Ratio
This is the measured ratio of signal to (noise + distortion) at the
output of the analog-to-digital converter. The signal is the rms
amplitude of the fundamental. Noise is the sum of all nonfundamental signals up to half the sampling frequency (f
/2), excluding
S
dc. The ratio is dependent on the number of quantization levels
in the digitization process; the more levels, the smaller the quantization noise. The theoretical signal-to-(noise + distortion) ratio
for an ideal N-bit converter with a sine wave input is given by
Signal-to-(Noise + Distortion) (dB) = 6.02N + 1.76
Thus for a 12-bit converter, this is 74 dB.
Total Harmonic Distortion
Total harmonic distortion (THD) is the ratio of the rms sum of
harmonics to the fundamental. For the AD7490, it is defined as
22222
VVVVV
++++
()
THD
where V
V
is the rms amplitude of the fundamental and V2, V3,
1
, V5, and V6 are the rms amplitudes of the second through the
4
log20dB
×=
V
1
65432
sixth harmonics.
Rev. C | Page 10 of 28

AD7490
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise
Peak harmonic or spurious noise is defined as the ratio of the
rms value of the next largest component in the ADC output
spectrum (up to f
/2 and excluding dc) to the rms value of the
S
fundamental. Normally, the value of this specification is
determined by the largest harmonic in the spectrum, but for
ADCs where the harmonics are buried in the noise floor, it is a
noise peak.
Intermodulation Distortion
With inputs consisting of sine waves at two frequencies, fa
and fb, any active device with nonlinearities creates distortion
products at the sum and difference frequencies of mfa ± nfb,
where m, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. Intermodulation distortion
terms are those for which neither m nor n are equal to zero.
For example, the second order terms include (fa + fb) and
(fa − fb), while the third order terms include (2fa + fb), (2fa − fb),
(fa + 2fb) and (fa − 2fb).
The AD7490 is tested using the CCIF standard where two input
frequencies near the top end of the input bandwidth are used.
In this case, the second order terms are usually distanced in
frequency from the original sine waves, and the third order
terms are usually at a frequency close to the input frequencies.
As a result, the second and third order terms are specified
separately. The calculation of the intermodulation distortion is
per the THD specification, where it is the ratio of the rms sum
of the individual distortion products to the rms amplitude of
the sum of the fundamentals expressed in decibels.
Rev. C | Page 11 of 28

AD7490
INTERNAL REGISTER STRUCTURE
CONTROL REGISTER
The control register on the AD7490 is a 12-bit, write-only
register. Data is loaded from the DIN pin of the AD7490 on the
falling edge of SCLK. The data is transferred on the DIN line at
the same time as the conversion result is read from the part.
The data transferred on the DIN line corresponds to the
Table 5. Control Register
MSB
11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
WRITE SEQ ADD3 ADD2 ADD1 ADD0 PM1 PM0 SHADOW
Table 6. Control Register Bit Functions
Bit Name Description
11 WRITE
10 SEQ
9 to 6
5, 4 PM1, PM0 Power management bits. These two bits decode the mode of operation of the AD7490, as shown in Tab le 8.
3 SHADOW
2
1 RANGE
0 CODING
The value written to this bit of the control register determines whether the following 11 bits are loaded to the
control register or not. If this bit is a 1, the following 11 bits are written to the control register; if it is a 0, the
remaining 11 bits are not loaded to the control register, and it remains unchanged.
The SEQ bit in the control register is used in conjunction with the SHADOW bit to control the use of the sequencer
function and access the Shadow register (see Table 9).
ADD3 to
ADD0
WEAK/TRI
These four address bits are loaded at the end of the present conversion sequence and select which analog input
channel is to be converted on in the next serial transfer, or they may select the final channel in a consecutive
sequence, as described in Table 9. The selected input channel is decoded as shown in Table 7. The next channel to
be converted on is selected by the mux on the 14th SCLK falling edge. The address bits corresponding to the
conversion result are also output on DOUT prior to the 12 bits of data (see the Serial Interface section).
The SHADOW bit in the control register is used in conjunction with the SEQ bit to control the use of the sequencer
function and access the Shadow register (see Table 9).
This bit selects the state of the DOUT line at the end of the current serial transfer. If it is set to 1, the DOUT line is
weakly driven to the ADD3 channel address bit of the ensuing conversion. If this bit is set to 0, DOUT returns to
three-state at the end of the serial transfer. See the Control Register section for more details.
This bit selects the analog input range to be used on the AD7490. If it is set to 0, the analog input range extends
from 0 V to 2 × REFIN. If it is set to 1, the analog input range extends from 0 V to REFIN (for the next conversion).
For 0 V to 2 × REF
This bit selects the type of output coding used by the AD7490 for the conversion result. If this bit is set to 0, the
output coding for the part is twos complement. If this bit is set to 1, the output coding from the part is straight
binary (for the next conversion).
, VDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V.
IN
AD7490 configuration for the next conversion. This requires
16 serial clocks for every data transfer. Only the information
provided on the first 12 falling clock edges (after the
CS
falling
edge) is loaded to the control register. MSB denotes the first bit
in the data stream. The bit functions are outlined in . Table 5
LSB
RANGE CODING
WEAK/TRI
Rev. C | Page 12 of 28

AD7490
Table 7. Channel Selection
ADD3 ADD2 ADD1 ADD0 Analog Input Channel
0 0 0 0 VIN0
0 0 0 1 VIN1
0 0 1 0 VIN2
0 0 1 1 VIN3
0 1 0 0 VIN4
0 1 0 1 VIN5
0 1 1 0 VIN6
0 1 1 1 VIN7
1 0 0 0 VIN8
1 0 0 1 VIN9
1 0 1 0 VIN10
1 0 1 1 VIN11
1 1 0 0 VIN12
1 1 0 1 VIN13
1 1 1 0 VIN14
1 1 1 1 VIN15
Table 8. Power Mode Selection
PM1 PM0 Mode
1 1
1 0
0 1
0 0
Sequencer Operation
The configuration of the SEQ and SHADOW bits in the control register allows the user to select a particular mode of operation of the
sequencer function. Ta ble 9 outlines the four modes of operation of the sequencer.
Normal operation. In this mode, the AD7490 remains in full power mode, regardless of the status of any of the logic inputs.
This mode allows the fastest possible throughput rate from the AD7490.
Full shutdown. In this mode, the AD7490 is in full shutdown mode, with all circuitry on the AD7490 powering down. The
AD7490 retains the information in the control register while in full shutdown. The part remains in full shutdown until these
bits are changed in the control register.
Auto shutdown. In this mode, the AD7490 automatically enters shutdown mode at the end of each conversion when the
control register is updated. Wake-up time from shutdown is 1 μs, and the user should ensure that 1 μs has elapsed before
attempting to perform a valid conversion on the part in this mode.
Auto standby. In this standby mode, portions of the AD7490 are powered down, but the on-chip bias generator remains
powered up. This mode is similar to auto shutdown and allows the part to power up within one dummy cycle, that is, 1 μs
with a 20 MHz SCLK.
Table 9. Sequence Selection
SEQ SHADOW Sequence Type
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
This configuration means the sequence function is not used. The analog input channel selected for each individual
conversion is determined by the contents of the channel address bits ADD0 through ADD3 in each prior write
operation. This mode of operation reflects the normal operation of a multichannel ADC, without the sequencer
function being used, where each write to the AD7490 selects the next channel for conversion (see Figure 12).
This configuration selects the Shadow register for programming. After the write to the control register, the following
write operation loads the contents of the Shadow register. This programs the sequence of channels to be converted on
continuously with each successive valid
selected need not be consecutive.
If the SEQ and SHADOW bits are set in this way, the sequence function is not interrupted upon completion of the write
operation. This allows other bits in the control register to be altered while in a sequence without terminating the cycle.
This configuration is used in conjunction with the ADD3 to ADD0 channel address bits to program continuous
conversions on a consecutive sequence of channels from Channel 0 through to a selected final channel, as determined
by the channel address bits in the control register (see Figure 14).
CS
falling edge (see Shadow register, and ). The channels
Rev. C | Page 13 of 28
Table 10 Figure 13

AD7490
CSC
C
SHADOW REGISTER
The Shadow register on the AD7490 is a 16-bit, write-only
register. Data is loaded from the DIN pin of the AD7490 on the
falling edge of SCLK. The data is transferred on the DIN line at
the same time that a conversion result is read from the part.
This requires 16 serial falling edges for the data transfer. The
information is clocked into the Shadow register, provided the
SEQ and SHADOW bits are set to 0, 1, respectively, in the
previous write to the control register. MSB denotes the first bit
in the data stream. Each bit represents an analog input from
Channel 0 through Channel 15. A sequence of channels can be
selected through which the AD7490 cycles with each consecutive
CS
falling edge after the write to the Shadow register. To select a
sequence of channels, the associated channel bit must be set for
each analog input. The AD7490 continuously cycles through
the selected channels in ascending order, beginning with the
lowest channel, until a write operation occurs (that is, the WRITE
bit is set to 1), with the SEQ and SHADOW bits configured in
any way except 1, 0 (see ). The bit functions are outlined
in .
Tabl e 10
Figure 12 reflects the normal operation of a multichannel ADC,
where each serial transfer selects the next channel for conversion.
In this mode of operation, the sequencer function is not used.
DIN: WRITE TO CONTROL RE GISTER,
WRITE BIT = 1,
SELECT CODING, RANGE, AND POWE R MODE
SELECT CH ANNEL ADD3 TO ADD0 FOR
CONVERSI ON,
SEQ = SHADOW = 0
Tabl e 9
POWER ON
DUMMY CONVERSIONS
DIN = ALL 1s
Figure 13 shows how to program the AD7490 to continuously
convert on a particular sequence of channels using the Shadow
register. To exit this mode of operation and revert back to the
normal mode of operation of a multichannel ADC (as outlined
in Figure 12), ensure that WRITE = 1 and SEQ = SHADOW = 0
on the next serial transfer.
POWER ON
DUMMY CONVERSI ONS
DIN = ALL 1s
DIN: WRITE TO CO NTROL REGIST ER,
WRITE BIT = 1,
SELECT CODI NG, RANGE, AND POWER M ODE
SELECT CHANNE L ADD3 TO ADD0 FOR
CONVERSION,
SEQ = 0 SHADOW = 1
DOUT: CONVERSION RESULT FROM
PREVIOUSLY SELECTE D CHANNEL ADD3 TO
ADD0
DIN: WRITE TO SHADO W REGISTER,
SELECTING WHICH CHANNELS TO CONVERT
ON; CHANNELS SEL ECTED NEED NOT BE
CONSECUTIVE
WRITE BIT = 0
CONTINUOUS LY
CONVERTS ON T HE
SELECTED SE QUENCE
OF CHANNELS
WRITE BIT = 0
WRITE BIT = 1,
SEQ = 1, SHADOW = 0
CONTINUOUS LY
CONVERTS ON THE
SELECTED SEQUENCE
OF CHANNELS BUT
ALLOWS RANG E,
CODING, AND SO ON,
TO CHANGE IN THE
CONTROL REGI STER
WITHOUT
INTERRUPTING THE
SEQUENCE PROVIDED,
SEQ = 1 SHADOW = 0
S
WRITE
BIT = 0
CS
CS
WRITE BIT = 1,
DOUT: CONVERSION RESULT F ROM
PREVIOUSLY SELECTED CHANNEL ADD3 TO
S
ADD0
DIN: WRITE TO CONTROL RE GISTER,
WRITE BIT = 1,
SELECT CODING, RANGE,AN D POWER M ODE
SELECT ADD3 TO ADD0 FO R CONVERS ION,
SEQ = SHADOW = 0
WRITE BIT = 1,
SEQ = SHADOW = 0
02691-011
Figure 13. SEQ Bit = 0, SHADOW Bit = 1 Flowchart
SEQ = 1,
SHADOW = 0
02691-012
Figure 12. SEQ Bit = 0, SHADOW Bit = 0 Flowchart
Table 10. Shadow Register
MSB
LSB
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VIN0 VIN1 VIN2 VIN3 VIN4 VIN5 VIN6 VIN7 VIN8 VIN9 VIN10 VIN11 VIN12 VIN13 VIN14 VIN15
Rev. C | Page 14 of 28

AD7490
Figure 14 shows how a sequence of consecutive channels can be
converted on without having to program the Shadow register or
write to the part on each serial transfer. Again, to exit this mode
of operation and revert back to the normal mode of operation
POWER ON
DUMMY CONVERSI ONS
DIN = ALL 1s
DIN: WRITE TO CONTROL REGIST ER,
CS
CS
CS
WRITE BIT = 1,
SELECT CODI NG, RANGE, AND POWER MODE
SELECT CHANNE L ADD3 TO ADD0 FOR
CONVERSION,
SEQ = 1 SHADOW = 1
DOUT: CONVERSION RESULT FROM
CHANNEL 0
CONTINUOUS LY CONVERTS ON A
CONSECUTIVE SEQUENCE OF CHANNELS
FROM CHANNEL 0 UP TO AND INCLUDING
THE PREVIO USLY SELECTED ADD3 TO ADD0
IN THE CONTROL REGISTER
CONTINUOUS LY CONVERTS ON THE
SELECTED SE QUENCE OF CHANNEL S BUT
WILL ALLOW RANGE, CODING, AND SO ON,
TO CHANGE IN THE CONTROL REGISTER
WITHOUT INTERRUPTI NG THE SEQ UENCE
PROVIDED, SEQ = 1, SHADOW = 0
Figure 14. SEQ Bit = 1, SHADOW Bit = 1 Flowchart
of a multichannel ADC (as outlined in Figure 12), ensure that
the WRITE = 1 and SEQ = SHADOW = 0 on the next serial
transfer.
WRITE
BIT = 0
WRITE BIT = 1,
SEQ = 1,
SHADOW = 0
WRITE BIT = 1,
SEQ = 1,
SHADOW = 0
02691-013
Rev. C | Page 15 of 28

AD7490
A
V
V
THEORY OF OPERATION
CIRCUIT INFORMATION
The AD7490 is a fast, 16-channel, 12-bit, single-supply, analogto-digital converter. The parts can be operated from a 2.7 V to
5.25 V supply. When operated from a 5 V supply and provided
with a 20 MHz clock, the AD7490 is capable of throughput rates
of up to 1 MSPS.
The AD7490 provides the user with an on-chip, track-and-hold
ADC and a serial interface housed in either a 28-lead TSSOP or
32-lead LFCSP package. The AD7490 has 16 single-ended input
channels with a channel sequencer, allowing the user to select a
sequence of channels through which the ADC can cycle with each
consecutive
CS
falling edge. The serial clock input accesses data
from the part, controls the transfer of data written to the ADC,
and provides the clock source for the successive approximation
ADC. The analog input range for the AD74790 is 0 V to REF
or 0 V to 2 × REF
control register. For the 0 V to 2 × REF
, depending on the status of Bit 1 in the
IN
range, the part must be
IN
IN
operated from a 4.75 V to 5.25 V supply.
The AD7490 provides flexible power management options to
allow the user to achieve the best power performance for a
given throughput rate. These options are selected by programming the power management bits in the control register.
CONVERTER OPERATION
The AD7490 is a 12-bit successive approximation ADC based
around a capacitive DAC. The AD7490 can convert analog
input signals in the range 0 V to REF
Figure 15 and Figure 16 show simplified schematics of the
ADC. The ADC comprises control logic, SAR, and a capacitive
DAC, which are used to add and subtract fixed amounts of
charge from the sampling capacitor to bring the comparator
back into a balanced condition. Figure 15 shows the ADC
during its acquisition phase. SW2 is closed and SW1 is in
Position A. The comparator is held in a balanced condition,
and the sampling capacitor acquires the signal on the selected
channel.
V
IN
When the ADC starts a conversion (see Figure 16), SW2 opens
and SW1 moves to Position B, causing the comparator to become
unbalanced. The control logic and the capacitive DAC are used
to add and subtract fixed amounts of charge from the sampling
capacitor to bring the comparator back into a balanced condition. When the comparator is rebalanced, the conversion is
complete. The control logic generates the ADC output code.
Figure 18 shows the ADC transfer function.
or 0 V to 2 × REFIN.
IN
VIN0
VIN15
AGND
A
SW1
Figure 15. ADC Acquisition Phase
4kΩ
B
SW2
COMPARATOR
VIN0
VIN15
GND
A
SW1
Figure 16. ADC Conversion Phase
4kΩ
B
SW2
COMPARATOR
Analog Input
Figure 17 shows an equivalent circuit of the analog input structure of the AD7490. The two diodes, D1 and D2, provide ESD
protection for the analog inputs. Care must be taken to ensure
that the analog input signal never exceeds the supply rails by
more than 200 mV. This causes these diodes to become forward
biased and to start conducting current into the substrate. The
maximum current these diodes can conduct without causing
irreversible damage to the part is 10 mA. Capacitor C1 in Figure 17
is typically about 4 pF and can primarily be attributed to pin
capacitance. Resistor R1 is a lumped component made up of the
on resistance of a track-and-hold switch and includes the on
resistance of the input multiplexer. The total resistance is typically
about 400 Ω. Capacitor C2 is the ADC sampling capacitor and
typically has a capacitance of 30 pF.
DD
D1
IN
C1
D2
4pF
CONVERSION PHASE—SWITCH OPEN
TRACK PHASE—SWITCH CL OSED
Figure 17. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
R1
For ac applications, removing high frequency components from
the analog input signal is recommended by use of an RC lowpass filter on the relevant analog input pin. In applications where
harmonic distortion and signal-to-noise ratio are critical, the
analog input should be driven from a low impedance source.
Large source impedances significantly affect the ac performance
of the ADC. This may necessitate the use of an input buffer
amplifier. The choice of the op amp is a function of the particular
application.
C2
30pF
CAPACITIVE
DAC
CONTROL
LOGIC
CAPACITIVE
DAC
CONTRO L
LOGIC
02691-016
02691-014
02691-015
Rev. C | Page 16 of 28

AD7490
V
When no amplifier is used to drive the analog input, the source
impedance should be limited to low values. The maximum
source impedance depends on the amount of total harmonic
distortion (THD) that can be tolerated. The THD increases as
the source impedance increases, and performance degrades (see
Figure 9).
ADC TRANSFER FUNCTION
The output coding of the AD7490 is either straight binary or
twos complement depending on the status of the LSB
(CODING bit) in the control register. The designed code
transitions occur midway between successive LSB values (that
is, 1 LSB, 2 LSBs, and so on). The LSB size is equal to
REF
/4096. The ideal transfer characteristic for the AD7490
IN
when straight binary coding is selected is shown in Figure 18.
111.. .111
111. ..110
111...000
REF
REF
/4096
– 1LSB
02691-017
011...111
000...010
000...001
000...000
V
REF
1LSB +V
0V
IS EITHER REFIN OR 2 × REF
1LSB = V
ANALOG INPUT
IN
Figure 18. Straight Binary Transfer Characteristic
Handling Bipolar Input Signals
Figure 20 shows how useful the combination of the 2 × REFIN
input range and the twos complement output coding scheme is
for handling bipolar input signals. If the bipolar input signal is
biased about REF
selected, REF
full scale, and +REF
dynamic range of 2 × REF
011. ..111
011...110
000...001
000...000
111.. .111
ADC CODE
100...010
100...001
100...000
Figure 19. Twos Complement Transfer Characteristic
and twos complement output coding is
IN
becomes the zero code point, −REFIN is negative
IN
becomes positive full scale, with a
IN
.
IN
REF
/4096
REF
– 1LSB–V
02691-018
V
DD
+ 1LSB
REF
with REF
1LSB = 2 × V
+V
– 1LSB
V
REF
ANALOG INPUT
± REFIN Input Range
IN
V
V
REF
0.1µF
V
0
R3
R2
V
R1 = R2 = R3 = R4
R4
R1
REF
VIN0
VIN15
DD
IN
V
AD7490
DRIVE
DOUT
TWOS
COMPLEMENT
DSP/µP
+REF
(= 2 × REFIN)
REF
–REF
(= 0V)
IN
IN
IN
011...111
000...000
100...000
02691-019
Figure 20. Handling Bipolar Signals
Rev. C | Page 17 of 28

AD7490
V
TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Figure 21 shows a typical connection diagram for the AD7490.
In this setup, the AGND pin is connected to the analog ground
plane of the system. In Figure 21, REF
decoupled 2.5 V supply from a reference source, the AD780, to
provide an analog input range of 0 V to 2.5 V (if the RANGE bit
is 1) or 0 V to 5 V (if the RANGE bit is 0). Although the AD7490
is connected to a V
a 3 V microprocessor. The V
of 5 V, the serial interface is connected to
DD
DRIVE
to the same 3 V supply of the microprocessor to allow a 3 V
logic interface (see the Digital Input section). The conversion
result is output in a 16-bit word. This 16-bit data stream
consists of four address bits, indicating which channel the
conversion result corresponds to, followed by the 12 bits of
conversion data. For applications where power consumption is
of concern, the power-down modes should be used between
conversions or bursts of several conversions to improve power
performance (see the Modes of Operation section).
0.1µF 10µF
V
DD
V
0
0V TO REF
IN
IN
VIN15
AGND
0.1µF
Figure 21. Typical Connection Diagram
REF
AD7490
IN
2.5V
AD780
Analog Input Channels
Any one of 16 analog input channels can be selected for conversion by programming the multiplexer with the ADD3 to ADD0
address bits in the control register. The channel configurations
are shown in Ta bl e 7 . The AD7490 can also be configured to
automatically cycle through a number of channels, as selected.
The sequencer feature is accessed via the SEQ and SHADOW
bits in the control register (see Tab le 9 ). The AD7490 can be
programmed to continuously convert on a selection of channels
in ascending order. The sequence of analog input channels to be
converted on is selected through programming the relevant bits
in the Shadow register (see Tab le 1 0 ). The next serial transfer
then acts on the sequence programmed by executing a conversion on the lowest channel in the selection.
The next serial transfer results in a conversion on the next
highest channel in the sequence, and so on. It is not necessary
to write to the control register once a sequencer operation has
been initiated. The WRITE bit must be set to 0 or the DIN line
is connected to a
IN
pin of the AD7490 is connected
5
V
DRIVE
SUPPLY
SCLK
DOUT
CS
DIN
0.1µF
SERIAL
INTERFACE
10µF
µCONTROLLER/
3V
SUPPLY
µPROCESSOR
02691-020
tied low to ensure the control register is not accidentally overwritten or the sequence operation interrupted. If the control
register is written to at any time during the sequence, it must be
ensured that the SEQ and SHADOW bits are set to 1, 0 to avoid
interrupting the automatic conversion sequence. This pattern
continues until such time as the AD7490 is written to and the
SEQ and SHADOW bits are configured with any bit combination
except 1, 0. On completion of the sequence, the AD7490 sequencer
returns to the first selected channel in the Shadow register and
commences the sequence again, if uninterrupted.
Rather than selecting a particular sequence of channels, a number
of consecutive channels beginning with Channel 0 can also be
programmed via the control register alone without needing to
write to the Shadow register. This is possible if the SEQ and
SHADOW bits are set to 1, 1. The ADD3 through ADD0 channel
address bits then determine the final channel in the consecutive
sequence. The next conversion is on Channel 0, then Channel 1,
and so on until the channel selected via the ADD3 through
ADD0 address bits is reached. The cycle begins again on the
next serial transfer, provided the WRITE bit is set to low; or, if
high, that the SEQ and SHADOW bits are set to 1, 0, then the
ADC continues its preprogrammed automatic sequence uninterrupted. Regardless of which channel selection method is used,
the 16-bit word output from the AD7490 during each conversion
always contains the channel address that the conversion result
corresponds to, followed by the 12-bit conversion result (see the
Serial Interface section).
Digital Input
The digital inputs applied to the AD7490 are not limited by the
maximum ratings that limit the analog inputs. Instead, the
digital inputs applied can go to 7 V and are not restricted by the
+ 0.3 V limit as on the analog inputs.
V
DD
CS
Another advantage of SCLK, DIN, and
by the V
issues are avoided. If
+ 0.3 V limit is the fact that power supply sequencing
DD
CS
, DIN, or SCLK is applied before VDD,
not being restricted
there is no risk of latch-up as there would be on the analog
inputs if a signal greater than 0.3 V were applied prior to V
V
DRIVE
The AD7490 also has the V
voltage at which the serial interface operates. V
DRIVE
feature. V
controls the
DRIVE
DRIVE
allows the
DD
.
ADC to easily interface to both 3 V and 5 V processors. For
example, if the AD7490 is operated with a V
of 5 V, the V
DD
DRIVE
pin can be powered from a 3 V supply. The AD7490 has better
dynamic performance with a V
of 5 V, while still being able
DD
to interface to 3 V processors. Care should be taken to ensure
that V
does not exceed VDD by more than 0.3 V (see the
DRIVE
Absolute Maximum Ratings section).
Rev. C | Page 18 of 28

AD7490
Reference Section
An external reference source should be used to supply the 2.5 V
reference to the AD7490. Errors in the reference source result
in gain errors in the AD7490 transfer function and add to the
specified full-scale errors of the part. A capacitor of at least 0.1 µF
should be placed on the REF
pin. Suitable reference sources
IN
for the AD7490 include the AD780, REF192, AD1582, ADR03,
ADR381, ADR391, and ADR421.
If 2.5 V is applied to the REF
pin, the analog input range can
IN
either be 0 V to 2.5 V or 0 V to 5 V, depending on the RANGE
bit in the control register.
MODES OF OPERATION
The AD7490 has a number of different modes of operation.
These modes are designed to provide flexible power management options. These options can be chosen to optimize the
power dissipation/throughput rate ratio for differing application
requirements. The mode of operation of the AD7490 is controlled
by the power management bits, PM1 and PM0, in the control
register, as detailed in Ta b le 7 . When power supplies are first
applied to the AD7490, care should be taken to ensure that the
part is placed in the required mode of operation (see the
Powering Up the AD7490 section).
Normal Mode (PM1 = PM0 = 1)
This mode is intended for the fastest throughput rate performance
because the user does not have to worry about any power-up
times with the AD7490 remaining fully powered at all times.
Figure 22 shows the general diagram of the operation of the
AD7490 in this mode.
CS
112
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
NOTES
1. CONTROL REG ISTER DATA IS LOADED ON FIRST 12 SCLK CYCLE S
2. SHADOW REG ISTER DATA IS LOADED ON FIRST 16 SCLK CYCL ES
CHANNE L IDENTI FIER BI TS + CONV ERSION RE SULT
DATA IN TO CO NTROL/SHADOW REGI STER
Figure 22. Normal Mode Operation
PART IS IN FULL
SHUTDOWN
CS
116114 1614
SCLK
16
02691-021
PART BEGINS TO POWER UP ON CS
RISING EDGE AS PM1 = 1, PM0 = 1
The conversion is initiated on the falling edge of CS, and the
track-and-hold enters hold mode, as described in the
Interface
section. The data presented to the AD7490 on the
Serial
DIN line during the first 12 clock cycles of the data transfer is
loaded
to the control register (provided the WRITE bit is 1). If data is
to be written to the Shadow register (SEQ = 0, SHADOW = 1
on previous write), data presented on the DIN line during the
first 16 SCLK cycles is loaded into the Shadow register. The part
remains fully powered up in normal mode at the end of the
conversion as long as PM1 and PM0 are set to 1 in the write
transfer during that conversion. To ensure continued operation
in normal mode, PM1 and PM0 are both loaded with 1 on every
data transfer. Sixteen serial clock cycles are required to complete
the conversion and access the conversion result. The track-andhold goes back into track on the 14
th
SCLK falling edge. CS may
then idle high until the next conversion or may idle low until
sometime prior to the next conversion, (effectively idling
CS
low).
Once a data transfer is complete (DOUT has returned to threestate WEAK/
after the quiet time, t
TRI
bit = 0), another conversion can be initiated
, has elapsed by bringing CS low again.
QUIET
Full Shutdown (PM1 = 1, PM0 = 0)
In this mode, all internal circuitry on the AD7490 is powered
down. The part retains information in the control register
during full shutdown. The AD7490 remains in full shutdown
until the power management bits in the control register, PM1
and PM0, are changed.
If a write to the control register occurs while the part is in
full shutdown, with the power management bits changed to
PM0 = PM1 = 1 (normal mode), the part begins to power up
CS
on the
rising edge. The track-and-hold that was in hold
while the part was in full shutdown returns to track on the 14
SCLK falling edge.
To ensure that the part is fully powered up, t
CS
elapse before the next
falling edge. shows the
Figure 23
POWER UP (t12
) should
general diagram for this mode.
PART IS FULLY POWERED UP
t
POWER UP
HAS ELAPSED
ONCE
t
12
th
DOUT
DIN
DATA IN TO CO NTROL REGIST ER
CONTROL REGI STER IS L OADED ON THE
FIRST 12 CL OCKS, PM1 = 1, PM0 = 1
Figure 23. Full Shutdown Mode Operation
Rev. C | Page 19 of 28
CHANNE L IDENTI FIER BI TS + CONV ERSION RE SULT
DATA I N TO CONTROL/SHADOW REGI STER
TO KEEP PART IN NORMAL MODE, LOAD
PM1 = 1, PM0 = 1 IN CONTROL REG ISTER
02691-B-022

AD7490
A
A
Auto Shutdown (PM1 = 0, PM0 = 1)
In this mode, the AD7490 automatically enters shutdown at the
end of each conversion when the control register is updated.
When the part is in shutdown, the track-and-hold is in hold
mode. Figure 24 shows the general diagram of the operation of
the AD7490 in this mode.
In shutdown mode, all internal circuitry on the AD7490 is
powered down. The part retains information in the control
register during shutdown. The AD7490 remains in shutdown
CS
until the next
falling edge it receives. On this CS falling edge,
the track-and-hold that was on hold while the part was in shutdown mode returns to track-and-hold. Wake-up time from auto
shutdown is 1 µs, and the user should ensure that 1 µs elapses
before attempting a valid conversion. When running the AD7490
with a 20 MHz clock, one dummy cycle of 16 × SCLK should be
sufficient to ensure the part is fully powered up. During this
dummy cycle, the contents of the control register should remain
unchanged; therefore, the WRITE bit should be 0 on the DIN
line. This dummy cycle effectively halves the throughput rate of
the part, with every other conversion result being valid. In this
mode, the power consumption of the part is greatly reduced
with the part entering shutdown at the end of each conversion.
When the control register is programmed to move into auto
shutdown, it does so at the end of the conversion. The user can
move the ADC in and out of the low power state by controlling
CS
the
signal.
PAR T E NTE RS
SHUTDOWN ON CS
RISING EDGE AS
PM1 = 0, PM0 = 1
PART BEGINS
TO POW ER
UP ON CS
FALLING EDGE
Auto Standby (PM1 = PM0 = 0)
In this mode, the AD7490 automatically enters standby mode at
the end of each conversion when the control register is updated.
Figure 25 shows the general diagram of the operation of the
AD7490 in this mode. When the part is in standby, portions of
the AD7490 are powered-down, but the on-chip bias generator
remains powered up. The part retains information in the control
register during standby. The AD7490 remains in standby until it
receives the next
CS
falling edge. On this CS falling edge, the
track-and-hold that was on hold while the part was in standby
returns to track. Wake-up time from standby is 1 µs; the user
should ensure that 1 µs elapses before attempting a valid conversion on the part in this mode. When running the AD7490 with
a 20 MHz clock, one dummy cycle of 16 × SCLK should be
sufficient to ensure the part is fully powered up. During this
dummy cycle, the contents of the control register should remain
unchanged; therefore, the WRITE bit should be set to 0 on the
DIN line. This dummy cycle effectively halves the throughput
rate of the part with every other conversion result being valid.
In this mode, the power consumption of the part is greatly
reduced with the part entering standby at the end of each conversion. When the control register is programmed to move into
auto standby, it does so at the end of the conversion. The user
can move the ADC in and out of the low power state by
controlling the
CS
signal.
PART IS FULLY
POWERED UP
RT ENTERS
P
SHUTDOWN ON CS
RISING EDGE AS
PM1 = 0, PM0 = 1
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
CS
11611611
CHANNEL I DENTIFIER BITS + CONVERSION RESU LT
DATA IN TO CONTRO L/SHADOW REG ISTER
CONTROL REGIS TER IS LOADE D ON THE
FIRST 12 CLOCKS, PM1 = 0, PM0 = 1
CONTROL REGIST ER CONTENTS SHO ULD
NOT CHANGE, W RITE BIT = 0
DUMMY CONVERSION
INVALID DATA
6
CHANNEL I DENTIFIER BITS + CONVERSION RESU LT
DATA IN TO CONTRO L/S HADOW REGIST ER
TO KEEP PART IN THIS MODE, LOAD PM1 = 0, PM0 = 1
IN CONTROL REGISTE R OR SET WRI TE BIT = 0
02691-023
Figure 24. Auto Shutdown Mode Operation
PART ENTERS
STANDBY ON CS
RISING EDGE AS
PM1 = 0, PM0 = 0
CS
112161121611216
CHANNEL I DENTIFIER BITS + CONVERSION RESU LT
DATA IN TO CONTRO L/S HADOW REGIST ER
CONTROL REGIST ER IS LOADED ON THE
FIRST 12 CLOCKS, PM1 = 0, PM0 = 0
PART BEGINS
TO POW ER
UP ON CS
FALLING EDGE
DUMMY CONVERSION
INVALID DATA
CONTROL REGISTE R CONTENTS SHOUL D
REMAIN UNCHANGED, WRIT E BIT = 0
PART IS FULLY
POWERED UP
CHANNEL I DENTIFIER BITS + CONVERSION RESU LT
DATA IN TO CONTROL/SHADOW REG ISTER
TO KEEP PART IN THIS MODE, LOAD PM1 = 0,
PM0 = 0 IN CONTROL REGISTER
RT ENTERS
P
STANDBY ON CS
RISING EDGE AS
PM1 = 0, PM0 = 0
02691-024
Figure 25. Auto Standby Mode Operation
Rev. C | Page 20 of 28

AD7490
V
A
Powering Up the AD7490
When supplies are first applied to the AD7490, the ADC may
power up in any of the operating modes of the part. To ensure
that the part is placed into the required operating mode, the
user should perform a dummy cycle operation, as outlined in
Figure 26.
The three dummy conversion operations outlined in Figure 26
must be performed to place the part into either of the auto modes.
The first two conversions of this dummy cycle operation are
performed with the DIN line tied high, and for the third conversion of the dummy cycle operation, the user should write the
desired control register configuration to the AD7490 to place
the part into the required auto mode. On the third
CS
rising
edge after the supplies are applied, the control register contains
the correct information and valid data results from the next
conversion.
Therefore, to ensure the part is placed into the correct operating
mode when supplies are first applied to the AD7490, the user
must first issue two serial write operations with the DIN line
tied high. On the third conversion cycle, the user can then write
to the control register to place the part into any of the operating
modes. The user should not write to the Shadow register until
the fourth conversion cycle after the supplies are applied to
the ADC to guarantee that the control register contains the
correct data.
If the user wishes to place the part into either normal mode or
full shutdown mode, the second dummy cycle with DIN tied
high can be omitted from the three dummy conversion
operation outlined in Figure 26.
CORRECT
REGISTER VALID DATA F ROM
NEXT CONVERSIO N USER CAN
WRITE TO SHADOW REGISTER
LUE IN CONTROL
IN NEXT CONVERSI ON
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
CS
1 12 16 1 12 16 1 12 16
INVALID DATA INVALID DATA INVALID DATA
KEEP DIN L INE TI ED HIGH FOR FI RST TW O DUMMY CONVERSIO NS
Figure 26. Placing into the Required Operating Mode After Supplies Are Applied
DUMMY CONVERSIONDUMMY CONVERSION
DATA IN TO CONTROL
CONTROL REGIST ER IS LOADED O N THE
FIRST 12 CLOCK EDG ES
02691-025
Rev. C | Page 21 of 28

AD7490
SERIAL INTERFACE
Figure 27 shows the detailed timing diagram for serial interfacing
to the AD7490. The serial clock provides the conversion clock
and also controls the transfer of information to and from the
AD7490 during each conversion.
CS
signal initiates the data transfer and conversion process.
The
The falling edge of
and takes the bus out of three-state. The analog input is sampled
at this point. The conversion is also initiated at this point and
requires 16 SCLK cycles to complete. The track-and-hold goes
back into track on the 14
Figure 27
at point B, except when the write is to the Shadow
register, in which case the track-and-hold does not return to
track until the rising edge of
On the 16
th
three-state (assuming the WEAK/
serial clock cycles are required to perform the conversion
process and to access data from the AD7490. The 12 bits of
conversion data are preceded by the four channel address bits,
CS
puts the track-and-hold into hold mode
th
SCLK falling edge, as shown in
CS
, that is, Point C in .
Figure 28
SCLK falling edge, the DOUT line goes back into
TRI
bit is set to 0). Sixteen
ADD3 to ADD0, identifying which channel the conversion
CS
result corresponds to.
going low allows the ADD3 address
bit to be read in by the microprocessor or DSP. The remaining
address bits and data bits are then clocked out by subsequent
SCLK falling edges, beginning with the second address bit,
ADD2. Thus, the first SCLK falling edge on the serial clock has
the ADD3 address bit provided and also clocks out address bit
ADD2. The final bit in the data transfer is valid on the 16
falling edge, having being clocked out on the previous (15
th
th
)
falling edge.
Writing information to the control register takes place on the
first 12 falling edges of SCLK in a data transfer, assuming the
MSB, that is, the WRITE bit, has been set to 1. If the control
register is programmed to use the Shadow register, writing
information to the Shadow register takes place on all 16 SCLK
falling edges in the next serial transfer (see Figure 28). The
CS
Shadow register is updated upon the rising edge of
, and the
track-and-hold begins to track the first channel selected in the
sequence.
CS
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
t
3
THREE-
STATE
t
t
2
1 2 3 4 5 6 13 14 15 16
t
b
3
ADD2 ADD1 ADD0 DB11 DB10 DB2 DB1 DB0
t
ADD3
WRITE SEQ ADD3 ADD2 ADD1 ADD0 DONTC DONTC DONTC
FOUR IDENTIFICATION BITS
9
t
4
t
6
CONVERT
t
10
t
7
B
t
5
t
11
t
8
t
QUIET
THREE-
STATE
02691-026
Figure 27. Serial Interface Timing Diagram
C
CS
t
CONVERT
t
6
t
7
t
10
4VIN5V
IN
t
5
13 VIN14 VIN15
IN
t
11
t
8
THREE-
STATE
02691-027
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
THREE-
STATE
t
2
1 2 3 4 5 6 13 14 15 16
t
3
ADD3
ADD2 ADD1 ADD0 DB11 DB10 DB2 DB1 DB0
t
9
VIN0VIN1V
t
4
FOUR IDENTIFICATION BITS
2VIN3V
IN
Figure 28. Writing to Shadow Register Timing Diagram
Rev. C | Page 22 of 28

AD7490
If the WEAK/
returning to true three-state on the 16
TRI
bit in the control register is set to 1, instead of
th
SCLK falling edge, the
DOUT line is pulled weakly to the logic level corresponding to
ADD3 of the next serial transfer. This is done to ensure that the
MSB of the next serial transfer is set up in time for the first
SCLK falling edge after the
CS
falling edge. If the WEAK/
TRI
bit
is set to 0 and the DOUT line has been in true three-state
between conversions, the ADD3 address bit may not be set up
in time for the DSP/microcontroller to clock it in successfully,
depending on the particular DSP or microcontroller interfacing
to the AD7490. In this case, ADD3 would only be driven from
the falling edge of
CS
and must then be clocked in by the DSP
on the following falling edge of SCLK. However, if the WEAK/
TRI
bit is set to 1, although DOUT is driven with the ADD3
address bit since the last conversion, it is nevertheless so weakly
driven that another device may still take control of the bus. It
does not lead to a bus contention (for example, a 10 kΩ pull-up
or pull-down resistor is sufficient to overdrive the logic level of
ADD3 between conversions), and all 16 channels may be
identified. If this does happen and another device takes control
of the bus, it is not guaranteed that DOUT will be fully driven
to ADD3 again in time for the read operation when control of
the bus is taken back.
This is especially useful if using an automatic sequence mode to
identify to which channel each result corresponds. If only the
first eight channels are in use, Address Bit ADD3 does not need
to be decoded, and whether it is successfully clocked in as a 1
or 0 does not matter as long as it is still counted by the DSP/
microcontroller as the MSB of the 16-bit serial transfer.
POWER vs. THROUGHPUT RATE
By operating the AD7490 in auto shutdown or auto standby
mode, the average power consumption of the ADC decreases at
lower throughput rates. Figure 29 shows that as the throughput
rate is reduced, the part remains in shutdown state longer and
the average power consumption drops accordingly over time.
For example, if the AD7490 is operated in a continuous
sampling mode with a throughput rate of 100 kSPS and an
SCLK of 20 MHz (V
is, the device is in auto shutdown mode), the power
consumption is calculated as shown in Equation 1.
The maximum power dissipation during normal operation is
12.5 mW (V
= 5 V). If the power-up time from auto shut-
DD
down is one dummy cycle, that is, 1 µs, and the remaining
conversion time is another cycle, that is, 1 µs, then the AD7490
can be said to dissipate 12.5 mW for 2 µs during each conversion cycle. For the remainder of the conversion cycle, 8 µs, the
= 5 V), with PM1 = 0 and PM0 = 1 (that
DD
part remains in shutdown mode. The AD7490 can be said to
dissipate 2.5 µW for the remaining 8 µs of the conversion cycle.
If the throughput rate is 100 kSPS, the cycle time is 10 µs and
the average power dissipated during each cycle is
2
10
8
mW5.12
10
=×+×
(1)
mW502.2W5.2
When operating the AD7490 in auto standby mode (PM1 =
PM0 = 0 at 5 V, 100 kSPS), the AD7490 power dissipation is
calculated as shown in Equation 2.
The maximum power dissipation is 12.5 mW at 5 V during normal operation. Again the power-up time from auto standby is
one dummy cycle, 1 µs, and the remaining conversion time is
another dummy cycle, 1 µs. The AD7490 dissipates 12.5 mW
for 2 µs during each conversion cycle. For the remainder of the
conversion cycle, 8 µs, the part remains in standby mode,
dissipating 460 µW for 8 µs. If the throughput rate is 100 kSPS,
the cycle time is 10 µs and the average power dissipated during
each conversion cycle is
2
10
8
mW5.12
10
=×+×
(2)
mW868.2W460
Figure 29 shows the power vs. throughput rate when using both
the auto shutdown mode and auto standby mode with 5 V
supplies. At the lower throughput rates, power consumption for
the auto shutdown mode is lower than that for the auto standby
mode, with the AD7490 dissipating less power when in shutdown compared to standby. As the throughput rate is increased,
however, the part spends less time in power-down states; hence,
the difference in power dissipated is negligible between modes.
For 3 V supplies, the power consumption of the AD7490
decreases. Similar power calculations can be done at 3 V.
10
VDD = 5V
AUTO STANDBY
AUTO SHUTDOW N
1
POWER (mV)
0.1
0.01
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350
Figure 29. Power vs. Throughput Rate in Auto Shutdown
THROUG HPUT ( kSPS)
and Auto Standby Mode
02691-028
Rev. C | Page 23 of 28

AD7490
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACING
The serial interface on the AD7490 allows the part to be directly
connected to a range of many different microprocessors. This
section explains how to interface the AD7490 with some of the
more common microcontroller and DSP serial interface
protocols.
AD7490 to TMS320C541
The serial interface on the TMS320C541 uses a continuous serial
clock and frame synchronization signals to synchronize the data
transfer operations with peripheral devices like the AD7490.
CS
input allows easy interfacing between the TMS320C541
The
and the AD7490 without any glue logic required. The serial port
of the TMS320C541 is set up to operate in burst mode with
internal CLKX0 (TX serial clock on Serial Port 0) and FSX0
(TX frame sync from Serial Port 0). The serial port control
register (SPC) must have the following setup: FO = 0, FSM = 1,
MCM = 1, and TXM = 1. The connection diagram is shown in
Figure 30
imperative that the frame synchronization signal from the
TMS320C541 provide equidistant sampling. The V
of the AD7490 takes the same supply voltage as that of the
TMS320C541. This allows the ADC to operate at a higher
voltage than the serial interface, that is, TMS320C541, if
necessary.
AD7490 to ADSP-21xx
The ADSP-21xx family of DSPs is interfaced directly to the
AD7490 without any glue logic required. The V
AD7490 takes the same supply voltage as that of the ADSP218x.This allows the ADC to operate at a higher voltage than
the serial interface, that is, ADSP-218x, if necessary.
The SPORT0 control register should be set up as follows:
• TFSW = RFSW = 1, alternate framing
• INVRFS = INVTFS = 1, active low frame signal
• DTYPE = 00, right justify data
• SLEN = 1111, 16-bit data-words
• ISCLK = 1, internal serial clock
• TFSR = RFSR = 1, frame every word
• IRFS = 0
• ITFS = 1
. Note that for signal processing applications, it is
pin
DRIVE
AD7490
SCLK CLKX
DOUT
DIN
CS
V
DRIVE
*ADDITIONAL PINS REMOVED FOR CLARITY
Figure 30. Interfacing to the TMS320C541
TMS320C541*
CLKR
DR
DT
FSX
FSR
V
DD
DRIVE
02691-029
pin of the
The connection diagram is shown in Figure 31. The ADSP-218x
has the TFS and RFS of the SPORT tied together, with TFS set
as an output and RFS set as an input. The DSP operates in
alternate framing mode, and the SPORT control register is set
up as described. The frame synchronization signal generated on
CS
the TFS is tied to
, and, as with all signal processing
applications, equidistant sampling is necessary. In this example,
however, the timer interrupt is used to control the sampling rate
of the ADC, and under certain conditions, equidistant sampling
may not be achieved.
The timer register, for example, is loaded with a value that
provides an interrupt at the required sample interval. When an
interrupt is received, a value is transmitted with TFS/DT (ADC
control word). The TFS is used to control the RFS and, thus, the
reading of data. The frequency of the serial clock is set in the
SCLKDIV register. When the instruction to transmit with TFS
is given (that is, AX0 = TX0), the state of the SCLK is checked.
The DSP waits until the SCLK has gone high, low, and high
before transmission starts. If the timer and SCLK values are
chosen such that the instruction to transmit occurs on or near
the rising edge of SCLK, the data may be transmitted or it may
wait until the next clock edge.
For example, if the ADSP-2189 with a 20 MHz crystal has an
overall master clock frequency of 40 MHz, then the master
cycle time is 25 ns. If the SCLKDIV register is loaded with a
value of 3, an SCLK of 5 MHz is obtained, and eight master
clock periods elapse for every 1 SCLK period. Depending on
the throughput rate selected, if the timer registers are loaded
with the value 803, 100.5 SCLKs occur between interrupts and
subsequently between transmit instructions. This situation
results in nonequidistant sampling because the transmit instruction occurs on a SCLK edge. If the number of SCLKs between
interrupts is a figure of N, equidistant sampling is implemented
by the DSP.
AD7490
SCLK SCLK
DOUT
CS
DIN
V
DRIVE
*ADDITIONAL PINS REMOVED FOR CLARITY
Figure 31. Interfacing to the ADSP-218x
ADSP-218x*
DR
RFS
TFS
DT
V
DD
02691-030
AD7490 to DSP563xx
The connection diagram in Figure 32 shows how the AD7490
can be connected to the ESSI (synchronous serial interface) of
the DSP563xx family of DSPs from Motorola. Each ESSI (two
on board) is operated in synchronous mode (the SYN bit in
CRB = 1) with internally generated word length frame sync for
both Tx and Rx (FSL1 = 0 and FSL0 = 0 in CRB). Normal
operation of the ESSI is selected by making MOD = 0 in the CRB.
Rev. C | Page 24 of 28

AD7490
Set the word length to 16 by setting WL1 = 1 and WL0 = 0 in
CRA. The FSP bit in the CRB should be set to 1 so the frame
sync is negative. Note that for signal processing applications, it
is imperative that the frame synchronization signal from the
DSP563xx provide equidistant sampling.
AD7490
SCLK SCK
V
DRIVE
*ADDITIONAL PINS REMOVED FOR CLARITY
Figure 32. Interfacing to the DSP563xx
DSP563xx*
SRDDOUT
STDCS
SC2DIN
V
DD
02691-031
In the example shown in Figure 32, the serial clock is taken
from the ESSI so the SCK0 pin must be set as an output, SCKD
= 1. The AD7490 V
pin takes the same supply voltage as
DRIVE
that of the DSP563xx. This allows the ADC to operate at a
higher voltage than the serial interface, that is, DSP563xx, if
necessary.
APPLICATION HINTS
Grounding and Layout
The AD7490 has very good immunity to noise on the power
supplies shown in the PSRR vs. Supply Ripple Frequency plot,
Figure 7. Care should still be taken, however, with regard to
grounding and layout.
The printed circuit board that houses the AD7490 should be
designed such that the analog and digital sections are separated
and confined to certain areas of the board. This facilitates the
use of ground planes that can be separated easily. A minimum
etch technique is generally best for ground planes because it
gives the best shielding. All three AGND pins of the AD7490
should be sunk in the AGND plane. Digital and analog ground
planes should be joined at only one place. If the AD7490 is in a
system where multiple devices require an AGND to DGND
connection, the connection should still be made at one point
only, a star ground point that should be established as close as
possible to the AD7490.
Avoid running digital lines under the device because these
couple noise onto the die. The analog ground plane should be
allowed to run under the AD7490 to avoid noise coupling. The
power supply lines to the AD7490 should use as large a trace as
possible to provide low impedance paths and reduce the effects
of glitches on the power supply line. Fast switching signals like
clocks should be shielded with digital ground to avoid radiating
noise to other sections of the board, and clock signals should
never be run near the analog inputs. Avoid crossover of digital
and analog signals. Traces on opposite sides of the board should
run at right angles to each other. This reduces the effects of
feedthrough through the board. A microstrip technique is by far
the best but is not always possible with a double-sided board. In
this technique, the component side of the board is dedicated to
ground planes, and signals are placed on the solder side.
Good decoupling is also important. All analog supplies should
be decoupled with 10 µF tantalum in parallel with 0.1 µF capacitors to AGND. To achieve the best from these decoupling
components, they must be placed as close as possible to the
device, ideally right up against the device. The 0.1 µF capacitors
should have low effective series resistance (ESR) and effective
series inductance (ESI), such as the common ceramic types or
surface mount types, which provide a low impedance path to
ground at high frequencies to handle transient currents due to
internal logic switching.
PCB Design Guidelines for Chip Scale Package
The lands on the chip scale package (CP-32) are rectangular.
The printed circuit board pad for these should be 0.1 mm
longer than the package land length and 0.05 mm wider than
the package land width. The land should be centered on the
pad. This ensures that the solder joint size is maximized. The
bottom of the chip scale package has a central thermal pad. The
thermal pad on the printed circuit board should be at least as
large as this exposed pad. On the printed circuit board, there
should be a clearance of at least 0.25 mm between the thermal
pad and the inner edges of the pad pattern. This ensures that
shorting is avoided. Thermal vias can be used on the printed
circuit board thermal pad to improve thermal performance of
the package. If vias are used, they should be incorporated in the
thermal pad at 1.2 mm pitch grid. The via diameter should be
between 0.3 mm and 0.33 mm, and the via barrel should be
plated with 1 oz. copper to plug the via. The user should
connect the printed circuit board thermal pad to AGND.
Evaluating the AD7490 Performance
The recommended layout for the AD7490 is outlined in the
evaluation board for the AD7490. The evaluation board package
includes a fully assembled and tested evaluation board, documentation, and software for controlling the board from the PC via
the EVAL-CONTROL BRD2. The EVAL-CONTROL BRD2 can
be used in conjunction with the AD7490 evaluation board, as
well as many other Analog Devices, Inc., evaluation boards
ending in the CB designator, to demonstrate and evaluate the ac
and dc performance of the AD7490.
The software allows the user to perform ac (fast Fourier
transform) and dc (histogram of codes) tests on the AD7490.
The software and documentation are on a CD shipped with the
evaluation board.
Rev. C | Page 25 of 28

AD7490
C
Y
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
9.80
9.70
9.60
PIN 1
0.15
0.05
OPLANARIT
0.10
28
0.65
BSC
0.30
0.19
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-153-AE
1.20 MAX
SEATING
PLANE
15
4.50
4.40
4.30
0.20
0.09
6.40 BSC
8°
0°
0.75
0.60
0.45
141
Figure 33. 28-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP]
(RU-28)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
0.08
0.60 MAX
25
24
EXPOSED
PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
17
16
32
1
8
9
3.50 REF
PIN 1
INDICATOR
3.25
3.10 SQ
2.95
0.25 MIN
PIN 1
INDICATOR
1.00
0.85
0.80
12° MAX
SEATING
PLANE
5.00
BSC SQ
TOP
VIEW
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.30
0.23
0.18
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VHHD-2
4.75
BSC SQ
0.20 REF
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.60 MAX
0.50
BSC
0.50
0.40
0.30
COPLANARITY
Figure 34. 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
5 mm × 5 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-32-2)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
Rev. C | Page 26 of 28

AD7490
ORDERING GUIDE
Integral
Model
Temperature
Range
Linearity
Error (LSB)
Package Description
AD7490BCP −40°C to +85°C ±1 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-32-2
AD7490BCP-REEL −40°C to +85°C ±1 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-32-2
AD7490BCP-REEL7 −40°C to +85°C ±1 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-32-2
AD7490BCPZ
AD7490BCPZ-REEL7
1
−40°C to +85°C ±1 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-32-2
1
−40°C to +85°C ±1 32-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-32-2
AD7490BRU −40°C to +85°C ±1 28-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP] RU-28
AD7490BRU-REEL −40°C to +85°C ±1 28-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP] RU-28
AD7490BRU-REEL7 −40°C to +85°C ±1 28-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP] RU-28
AD7490BRUZ
AD7490BRUZ-REEL
AD7490BRUZ-REEL7
EVAL-AD7490CBZ
1
−40°C to +85°C ±1 28-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP] RU-28
1
−40°C to +85°C ±1 28-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP] RU-28
1
−40°C to +85°C ±1 28-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP] RU-28
1, 2
Evaluation Board
EVAL-CONTROL BRD23 Controller Board
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
2
This can be used as a standalone evaluation board or in conjunction with the evaluation controller board for evaluation/demonstration purposes.
3
This board is a complete unit allowing a PC to control and communicate with all Analog Devices evaluation boards ending in a CB designator. To order a complete
evaluation kit, you need to order the particular ADC evaluation board (for example, EVAL-AD7490CBZ), the EVAL-CONTROL-BRD2, and a 12 V ac transformer. See the
relevant evaluation board data sheet for more information.
Package
Option
Rev. C | Page 27 of 28

AD7490
NOTES
©2002–2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D02691-0-6/09(C)
Rev. C | Page 28 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...