Monolithic Synchronous
FEATURES
Full-scale frequency (up to 2 MHz) set by external system
clock
Extremely low linearity error (0.005% max at 1 MHz FS,
0.02% max at 2 MHz FS)
No critical external components required
Accurate 5 V reference voltage
Low drift (25 ppm/°C max)
Dual- or single-supply operation
Voltage or current input
MIL-STD-883 compliant versions available
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD652 synchronous voltage-to-frequency converter
(SVFC) is a powerful building block for precision analog-todigital conversion, offering typical nonlinearity of 0.002%
(0.005% maximum) at a 100 kHz output frequency. The inherent monotonicity of the transfer function and wide range of
clock frequencies allow the conversion time and resolution to
be optimized for specific applications.
The AD652 uses a variation of the charge-balancing technique
to perform the conversion function. The AD652 uses an
external clock to define the full-scale output frequency, rather
than relying on the stability of an external capacitor. The result
is a more stable, more linear transfer function, with significant
application benefits in both single- and multichannel systems.
Gain drift is minimized using a precision low drift reference
and low TC, on-chip, thin-film scaling resistors. Furthermore,
initial gain error is reduced to less than 0.5% by the use of laserwafer-trimming.
The analog and digital sections of the AD652 have been
designed to allow operation from a single-ended power source,
simplifying its use with isolated power supplies.
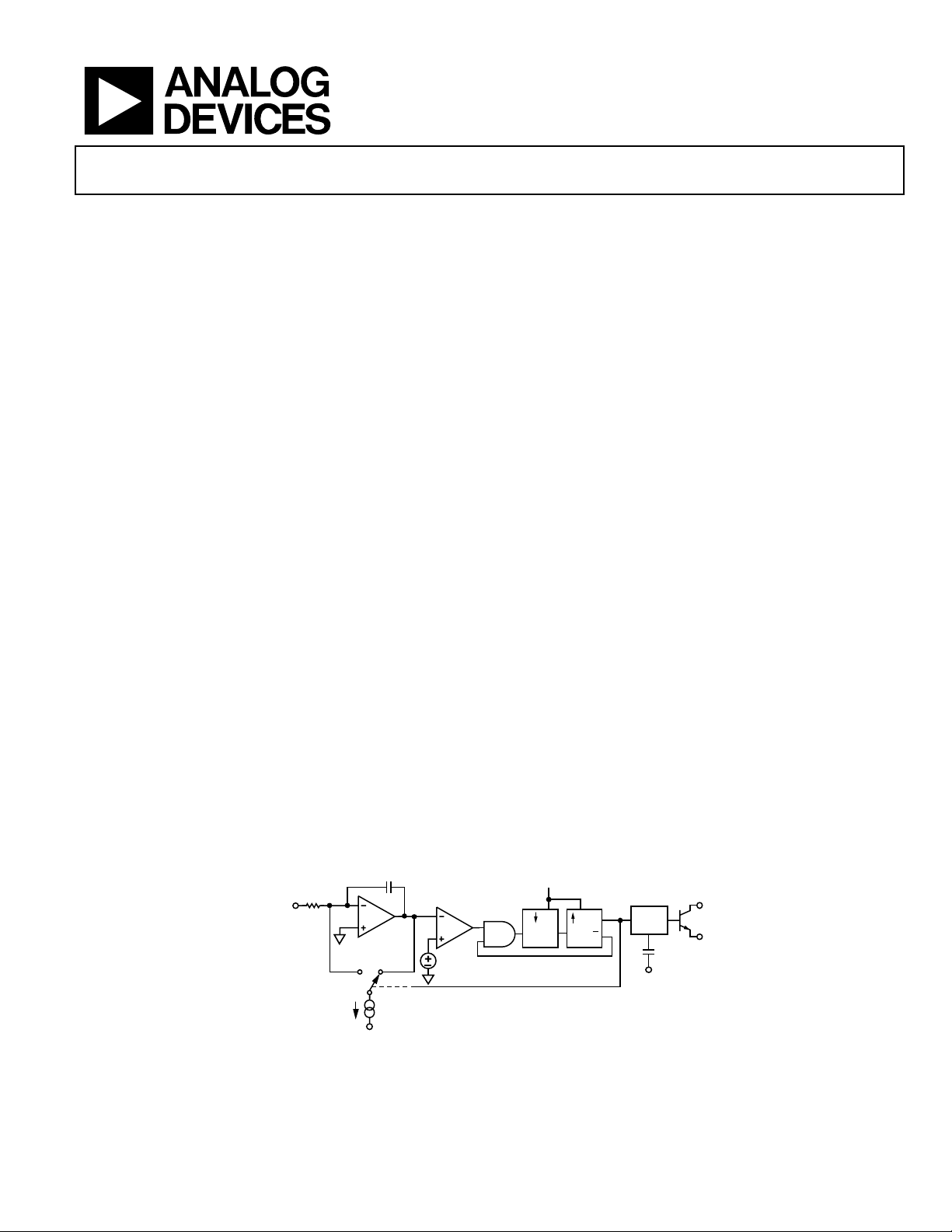
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
R
IN
V
IN
INTEGRATOR
HL
C
INT
COMPARATOR
5V
Voltage-to-Frequency Converter
AD652
The AD652 is available in five performance grades. The 20-lead
PLCC-packaged JP and KP grades are specified for operation
over the 0°C to +70°C commercial temperature range. The
16-lead CERDIP-packaged AQ and BQ grades are specified for
operation over the −40°C to +85°C industrial temperature
range. The AD652SQ is available for operation over the full
−55°C to +125°C extended temperature range.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The use of an external clock to set the full-scale frequency
allows the AD652 to achieve linearity and stability far
superior to other monolithic VFCs. By using the same clock
to drive the AD652 and set the counting period (through a
suitable divider), conversion accuracy is maintained
independent of variations in clock frequency.
2. The AD652 synchronous VFC requires only one external
component (a noncritical integrator capacitor) for
operation.
3. The AD652 includes a buffered, accurate 5 V reference.
4. The AD652’s clock input is TTL and CMOS compatible and
can also be driven by sources referred to the negative power
supply. The flexible open-collector output stage provides
sufficient current sinking capability for TTL and CMOS
logic, as well as for optical couplers and pulse transformers.
A capacitor-programmable one-shot is provided for selection of optimum output pulse width for power reduction.
5. The AD652 can also be configured for use as a synchronous
F/V converter for isolated analog signal transmission.
6. The AD652 is available in versions compliant with
MILSTD-883. Refer to the Analog Devices Military
Products Databook or current AD652/883B data sheet for
detailed specifications.
CLOCK IN
D FLOP LATCH
CKQDG
AND
Q
D
Q
ONE
SHOT
C
OS
1mA
–V
S
Rev. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Figure 1.
00798-001
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

AD652
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 5
Definitions of Specifications....................................................... 5
Theory of Operation ........................................................................ 6
Overrange...................................................................................... 8
SVFC Connection for Dual Supply, Positive Input Voltages .. 9
SVFC Connections for Negative Input Voltages ...................... 9
SVFC Connection for Bipolar Input Voltages ........................ 10
PLCC Connections..................................................................... 11
Gain and Offset Calibration...................................................... 11
Gain Performance ......................................................................12
Reference Noise .......................................................................... 12
Digital Interfacing Considerations........................................... 12
Component Selection ................................................................ 12
Digital Ground............................................................................ 13
Single-Supply Operation........................................................... 14
Frequency-to-Voltage Converter ............................................. 15
Decoupling and Grounding...................................................... 16
Frequency Output Multiplier.................................................... 17
Single-Line Multiplexed Data Transmission .......................... 18
Isolated Front End...................................................................... 22
A-to-D Conversion .................................................................... 22
Delta Modulator......................................................................... 23
Bridge Transducer Interface...................................................... 24
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 25
Ordering Guide............................................................................... 26
REVISION HISTORY
5/04—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. B to Rev. C
Updated Format..............................................................Universal
Changes to Gain and Offset Calibration section.................... 11
Updated Outline Dimensions................................................... 25
Changes to Ordering Guide...................................................... 26
2/00—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. A to Rev. B
Rev. C | Page 2 of 28
AD652
SPECIFICATIONS
Typical @ TA = 25°C, VS = ±15 V, unless otherwise noted. Specifications in boldface are 100% tested at final test and are used to measure
outgoing quality levels.
Table 1.
AD652JP/AQ/SQ AD652KP/BQ
Parameter Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
VOLTAGE-TO-FREQUENCY MODE
Gain Error
f
= 200 kHz ±0.5 ±1 ±0.25 ±0.5 %
CLOCK
f
= 1 MHz ±0.5
CLOCK
f
= 4 MHz ±0.5
CLOCK
±1
±1.5
Gain Temperature Coefficient
f
= 200 kHz ±25 ±50 ±15 ±25 ppm/°C
CLOCK
f
= 1 MHz ±25
CLOCK
±10
f
= 4 MHz ±25
CLOCK
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 0.001
±50
±50
±75
0.01
Linearity Error
f
= 200 kHz ±0.002 ±0.02 ±0.002 ±0.005 %
CLOCK
f
= 1 MHz ±0.002
CLOCK
f
= 2 MHz ±0.01 ±0.02 ±0.002 ±0.005 %
CLOCK
f
= 4 MHz ±0.02
CLOCK
Offset (Transfer Function, RTI) ± 1
Offset Temperature Coefficient ±10
±0.02
±0.05
±3
±50
Response Time One Period of New Output Frequency Plus One Clock Period.
FREQUENCY-TO-VOLTAGE MODE
Gain Error, fIN = 100 kHz FS ±0.5 ±1 ±0.25 ±0.5 %
Linearity Error, fIN = 100 kHz FS ±0.002 ±0.02 ±0.002 ±0.01 %
INPUT RESISTORS
CERDIP (Figure 2)(0 to 10 V FS Range) 19.8 20 20.2 19.8 20 20.2 kΩ
PLCC (Figure 3)
Pin 8 to Pin 7 9.9 10 10.1 9.9 10 10.1 kΩ
Pin 7 to Pin 5 (0 V to 5 V FS Range) 9.9 10 10.1 9.9 10 10.1 kΩ
Pin 8 to Pin 5 (0 V to 10 V FS Range) 19.8 20 20.2 19.8 20 20.2 kΩ
Pin 9 to Pin 5 (0 V to 8 V FS Range) 15.8 16 16.2 15.8 16 16.2 kΩ
Pin 10 to Pin 5 (Auxiliary Input) 19.8 20 20.2 19.8 20 20.2 kΩ
Temperature Coefficient (All) ±50
±100
INTEGRATOR OP AMP
Input Bias Current
Inverting Input (Pin 5) ±5
Noninverting Input (Pin 6) 20
Input Offset Current 20
±20
50
70
Input Offset Current Drift 1 3 1 2 nA/°C
Input Offset Voltage ±1
±3
Input Offset Voltage Drift ±10 ±25 ±10 ±15 µV/°C
Open-Loop Gain 86 86 dB
Common-Mode Input Range –VS + 5 +VS – 5 –VS + 5 +VS – 5 V
CMRR 80 80 dB
Bandwidth 14 95 14 95 MHz
Output Voltage Range
−1
− 4) −1
(+V
S
(Referred to Pin 6, R1 > = 5 kΩ)
±0.25
±0.25
±15
±10
±15
0.001
±0.002
±0.01
±1
±10
±50
±5
20
20
±1
±0.5
±0.75
±25
±30
±50
0.01
±0.005
±0.02
±2
±25
±100
±20
50
70
±2
(+VS − 4)
%
%
ppm/°C
ppm/°C
ppm/°C
%/V
%
%
mV
µV/°C
ppm/°C
nA
nA
nA
mV
V
1
Rev. C | Page 3 of 28
AD652
AD652JP/AQ/SQ AD652KP/BQ
Parameter Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
COMPARATOR
Input Bias Current 0.5 5 0.5 5 µA
Common-Mode Voltage −VS + 4 + VS − 4 −VS + 4 +VS − 4 V
CLOCK INPUT
Maximum Frequency
4
Threshold Voltage (Referred to Pin 12) 1.2 1.2 V
T
to T
MIN
MAX
0.8
Input Current
(−VS < V
< +VS) 5
CLK
Voltage Range −VS +V
Rise Time 2 2 µs
OUTPUT STAGE
VOL (I
= 10 mA)
OUT
I
OL
VOL < 0.8 V
VOL < 0.4 V, T
MIN
to T
MAX
IOH (Off Leakage) 0.01
Delay Time, Positive Clock Edge to Output Pulse
Fall Time (Load = 500 pF and I
= 5 mA) 100 100 ns
SINK
150
Output Capacitance 5 5 pF
OUTPUT ONE-SHOT
Pulse Width, t
COS = 300 pF
OS
1
COS = 1000 pF 4 5 6 4 5 6 µs
REFERENCE OUTPUT
Voltage
4.950
Drift
Output Current
Source T
MIN
to T
MAX
10
Sink 100 500 100 500 µA
Power Supply Rejection
Supply Range = ±12.5 V to ±17.5 V 0.015 0.015 %/V
Output Impedance (Sourcing Current) 0.3
POWER SUPPLY
Rated Voltage ±15 ±15 V
Operating Range
Dual Supply ±6 ±15 ±18 ±6 ±15 ±18 V
Single Supply (−VS = 0) +12 +36 +12 +36 V
Quiescent Current ±11
Digital Common −VS +VS − 4 –V
Analog Common −V
S
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specified Performance
JP, KP Grade 0 +70 0 +70 °C
AQ, BQ Grade −40 +85 −40 +85 °C
SQ Grade −55 +125 °C
1
Referred to internal V
. In PLCC package, tested on 10 V input range only.
REF
5
2.0 0.8
20
S
0.4
15
8
10
200
1.5
5.0
250 150
2
5.050 4.975
100
2
±15
+V
S
4
5
−V
S
0.01
1 1.5
10
0.3
±11
S
−V
S
5 MHz
2.0
20
+V
0.4
15
8
10
200
250
2
5.0
5.025
50
mA
2
±15
+VS − 4 V
+V
V
µA
S
V
V
mA
mA
µA
ns
µs
V
ppm/°C
Ω
mA
S
V
Rev. C | Page 4 of 28
AD652
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Ratings
Total Supply Voltage +VS to −V
Maximum Input Voltage (Figure 6) 36 V
Maximum Output Current
(Open Collector Output)
Amplifier Short-Circuit to Ground Indefinite
Storage Temperature Range: CERDIP −65°C to +150°C
Storage Temperature Range: PLCC −65°C to +150°C
S
36 V
50 mA
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
DEFINITIONS OF SPECIFICATIONS
Gain Error
The gain of a voltage-to-frequency converter is the scale factor
setting that provides the nominal conversion relationship, e.g.,
1 MHz full scale. The gain error is the difference in slope
between the actual and ideal transfer functions for the V-F
converter.
Linearity Error
The linearity error of a V-F is the deviation of the actual
transfer function from a straight line passing through the
endpoints of the transfer function.
Gain Temperature Coefficient
The gain temperature coefficient is the rate of change in fullscale frequency as a function of the temperature from +25°C to
or T
T
MIN
MAX
.
Table 3. Pin Configurations
Pin No. Q-16 Package P-20A Package
1 +V
2 TRIM +V
3 TRIM NC
4 OP AMP OUT OP AMP OUT
5 OP AMP “−“ OP AMP “−“
6 OP AMP “+” OP AMP “+”
7 10 VOLT INPUT 5 VOLT INPUT
8 −V
9 C
10 CLOCK INPUT OPTIONAL 10 V INPUT
11 FREQ OUT −V
12 DIGITAL GND C
13 ANALOG GND CLOCK INPUT
14 COMP “−“ FREQ OUT
15 COMP “+” DIGITAL GND
16 COMP REF ANALOG GND
17 COMP “−“
18 COMP “+”
19 NC
20 COMP REF
S
S
OS
NC
S
10 VOLT INPUT
8 VOLT INPUT
S
OS
Rev. C | Page 5 of 28
AD652
T
THEORY OF OPERATION
A synchronous VFC is similar to other voltage-to-frequency
converters in that an integrator is used to perform a chargebalance of the input signal with an internal reference current.
However, rather than using a one-shot as the primary timing
element, which requires a high quality and low drift capacitor, a
synchronous voltage-to-frequency converter (SVFC) uses an
external clock. This allows the designer to determine the system
stability and drift based upon the external clock selected. A
crystal oscillator may also be used if desired.
The SVFC architecture provides other system advantages
besides low drift. If the output frequency is measured by
counting pulses gated to a signal that is derived from the clock,
the clock stability is unimportant and the device simply
performs as a voltage-controlled frequency divider, producing a
high resolution A/D. If a large number of inputs must be
monitored simultaneously in a system, the controlled timing
relationship between the frequency output pulses and the usersupplied clock greatly simplifies this signal acquisition. Also, if
the clock signal is provided by a VFC, the output frequency of
the SVFC is proportional to the product of the two input
voltages. Therefore, multiplication and A-to-D conversion on
two signals are performed simultaneously.
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
+V
TRIM
TRIM
OP AMP OUT
OP AMP "–"
OP AMP "+"
10 VOLT INPUT
–V
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
S
CONVERTER
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
S
Figure 2. CERDIP Pin Configuration
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
"D"
FLOP
COMP REF
16
COMP "+"
15
14
COMP "–"
13
ANALOG GND
DIGITAL GND
12
FREQ OUT
11
10
CLOCK INPUT
9
C
OS
00798-002
S
OP AMP OU
OP AMP "–"
OP AMP "+"
5V INPUT
10V INPUT
NC3+V
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-FREQUENCY
4
5
6
7
8
CONVERTER
10kΩ
10kΩ
16kΩ
9
8V INPUT
2
1mA
4kΩ
10
10V INPUT
OPTIONAL
NC1COMP REF20NC
5V
REFERENCE
"D"
Q
FLOP
D
AND
Q
CK
ONE
SHOT
11
12
S
OS
–V
C
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
NC = NO CONNECT
INPUT
CLOCK
COMP "+"
COMP "–"
ANALOG GND
DIGITAL GND
FREQ OUT
Figure 3. PLCC Pin Configuration
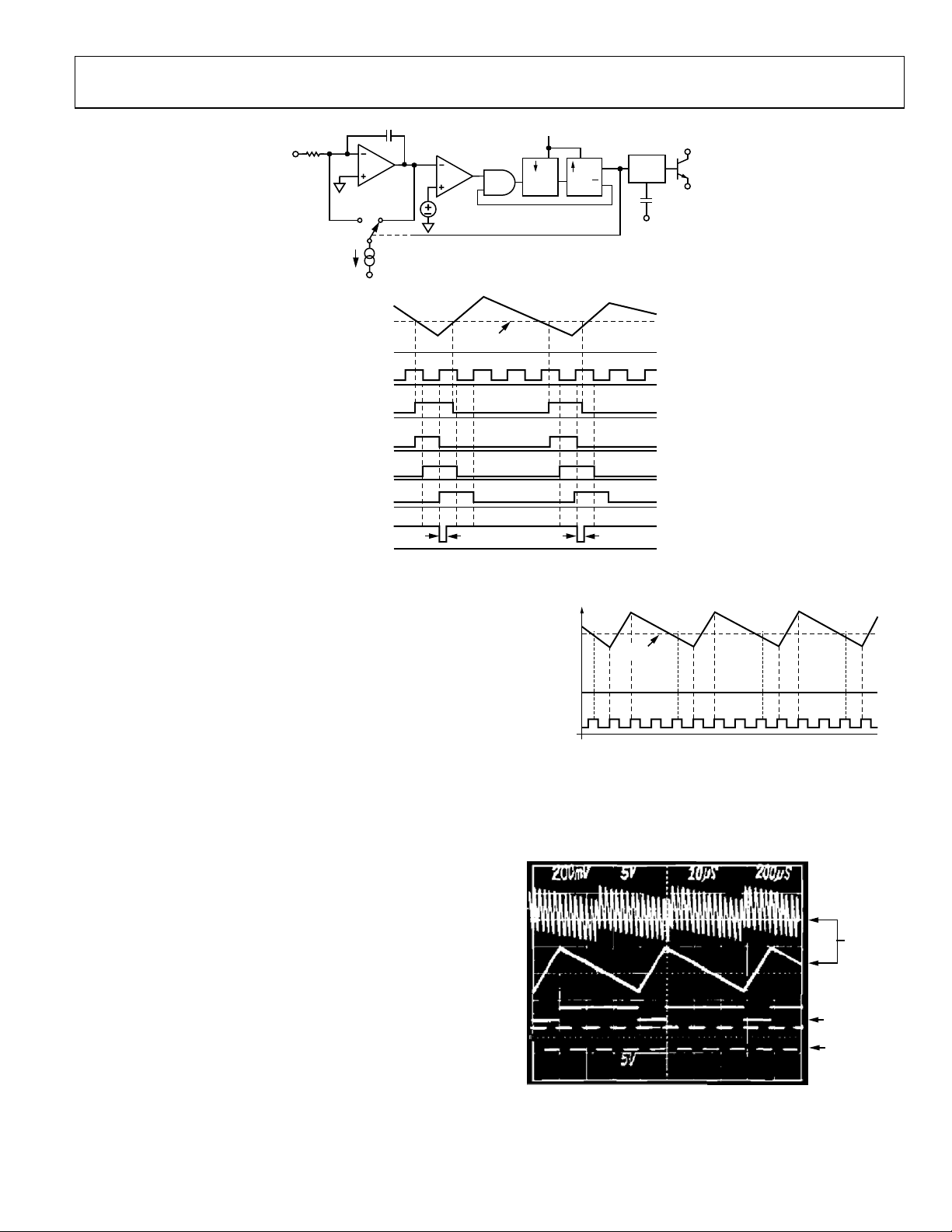
Figure 4 shows the typical up-and-down ramp integrator output
of a charge-balance VFC. After the integrator output has
crossed the comparator threshold and the output of the AND
gate has gone high, nothing happens until a negative edge of the
clock comes along to transfer the information to the output of
the D FLOP. At this point, the clock level is low, so the latch does
not change state. When the clock returns high, the latch output
goes high and drives the switch to reset the integrator; at the
same time, the latch drives the AND gate to a low output state.
On the very next negative edge of the clock, the low output state
of the AND gate is transferred to the output of the D FLOP.
When the clock returns high, the latch output goes low and
drives the switch back into the Integrate mode. At the same
time, the latch drives the AND gate to a mode where it
truthfully relays the information presented to it by the
comparator.
00798-003
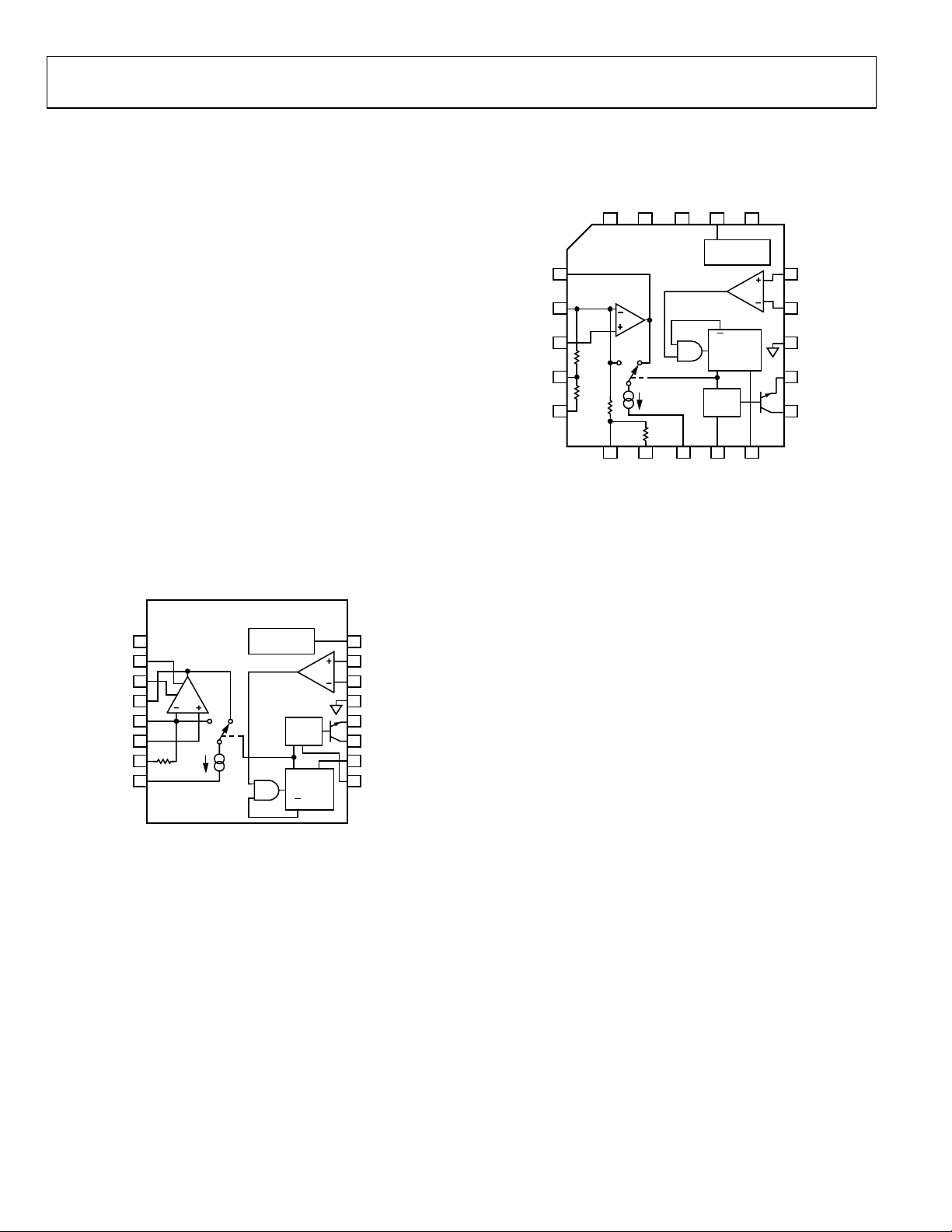
The pinouts of the AD652 SVFC are shown in Figure 2 and
Figure 3. A block diagram of the device configured as an SVFC,
along with various system waveforms, is shown in Figure 4.
Rev. C | Page 6 of 28
Because the reset pulses applied to the integrator are exactly one
clock period long, the only place where drift can occur is in a
variation of the symmetry of the switching speed with
temperature.
Since each reset pulse is identical, the AD652 SVFC produces a
very linear voltage-to-frequency transfer relation. Also, because
all reset pulses are gated by the clock, there are no problems
with dielectric absorption causing the duration of a reset pulse
to be influenced by the length of time since the last reset.
AD652
R
CLOCK IN
D FLOP LATCH
CKQDG
AND
ONE
Q
D
SHOT
Q
t
OS
C
OS
00798-004
V
IN
R
IN
1mA
INTEGRATOR
COMPARATOR
C
INT
INTEGRATOR
HL
–V
S
OUTPUT
CLOCK
OUT
AND
OUT
D FLOP
OUT
LATCH
OUT
FREQ
OUT
COMPARATOR
5V
THRESHOLD
t
OS
Figure 4. Block Diagram and System Waveforms
Figure 4 shows that the period between output pulses is
constrained to be an exact multiple of the clock period.
Consider an input current of exactly one quarter the value of
the reference current. In order to achieve a charge balance, the
output frequency equals the clock frequency divided by four:
one clock period for reset and three clock periods of integrate.
This is shown in Figure 5. If the input current is increased by a
very small amount, the output frequency should also increase
by a very small amount. Initially, however, no output change is
observed for a very small increase in the input current. The
output frequency continues to run at one quarter of the clock,
delivering an average of 250 µA to the summing junction. Since
the input current is slightly larger than this, charge accumulates
in the integrator and the sawtooth signal starts to drift downward. As the integrator sawtooth drifts down, the comparator
threshold is crossed earlier and earlier in each successive cycle,
until finally, a whole cycle is lost. When the cycle is lost, the
integrate phase lasts for two periods of the clock instead of the
usual three periods. Thus, among a long string of divide-byfours, an occasional divide-by-three occurs; the average of the
output frequency is very close to one quarter of the clock, but
the instantaneous frequency can be very different.
INTEGRATO
OUT
THRESHOLD
CLOCK
Figure 5. Integrator Output for I
= 250 µA
IN
Because of this, it is very difficult to observe the waveform on
an oscilloscope. During all of this time, the signal at the output
of the integrator is a sawtooth wave with an envelope that is also
a sawtooth. See Figure 6.
200µs/BOX
C
INT
100µs/BOX
FREQ OUT
10µs/BOX
CLOCK IN
10µs/BOX
00798-006
Figure 6. Integrator Output for I
Slightly Greater than 250 µs
IN
00798-005
Rev. C | Page 7 of 28
AD652
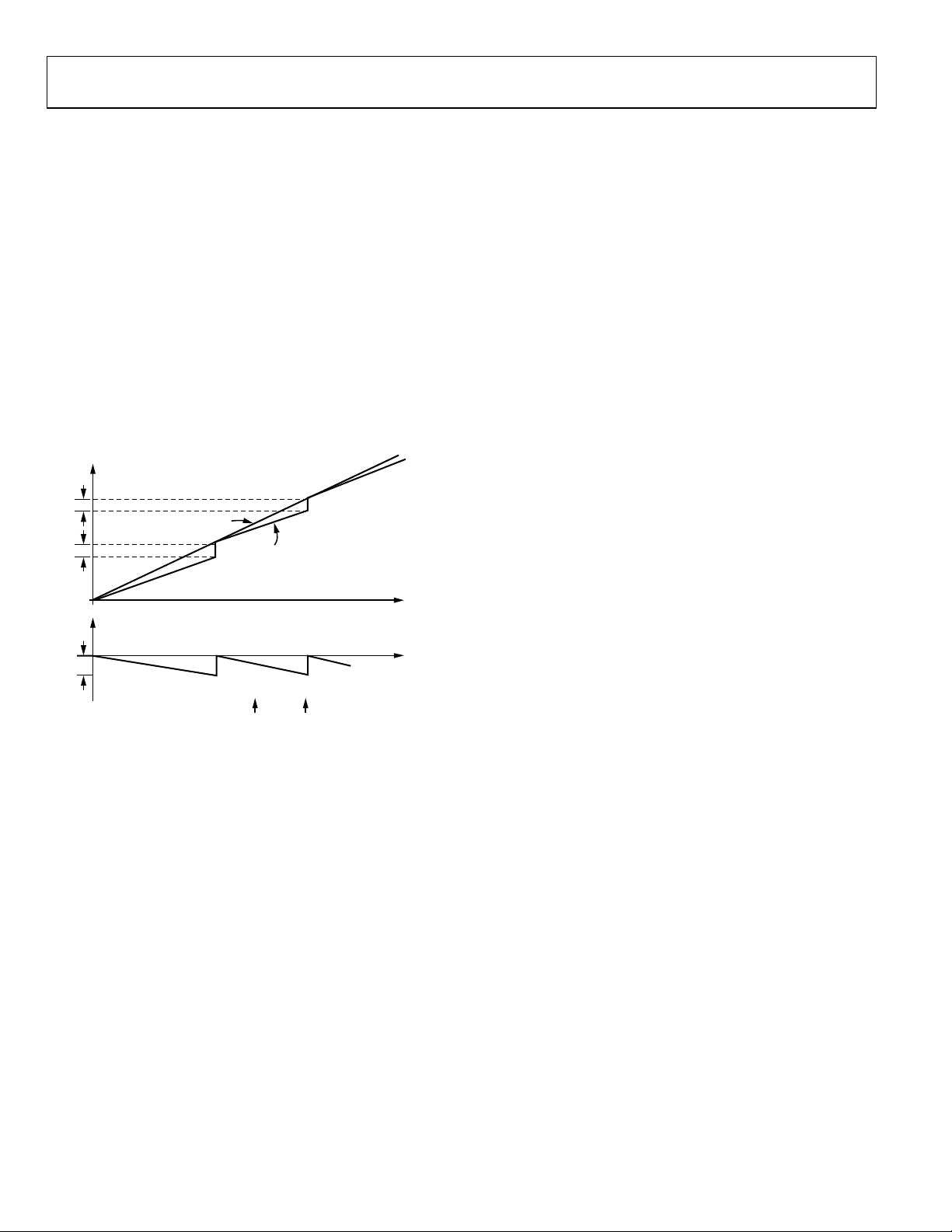
Another way to view this is that the output is a frequency of
approximately one-quarter of the clock that has been phase
modulated. A constant frequency can be thought of as
accumulating phase linearly with time at a rate equal to 2πf
radians per second. Therefore, the average output frequency,
which is slightly in excess of a quarter of the clock, requires
phase accumulation at a certain rate. However, since the SVFC
is running at exactly one-quarter of the clock, it does not
accumulate enough phase (see Figure 7). When the difference
between the required phase (average frequency) and the actual
phase equals 2π, a step-in phase is taken where the deficit is
made up instantaneously. The output frequency is then a steady
carrier that has been phase modulated by a sawtooth signal (see
Figure 7). The period of the sawtooth phase modulation is the
time required to accumulate a 2π difference in phase between
the required average frequency and one quarter of the clock
frequency. The sawtooth phase modulation amplitude is 2π.
PHASE
2
π
2
π
EXPECTED
PHASE
ACTUAL PHASE
The result of this synchronism is that the rate at which data may
be extracted from the series bit stream produced by the SVFC is
limited. The output pulses are typically counted during a fixed
gate interval and the result is interpreted as an average
frequency. The resolution of such a measurement is determined
by the clock frequency and the gate time. For example, if the
clock frequency is 4 MHz and the gate time is 4.096 ms, a
maximum count of 8,192 is produced by a full-scale frequency
of 2 MHz. Thus, the resolution is 13 bits.
OVERRANGE
Since each reset pulse is only one clock period in length, the
full-scale output frequency is equal to one-half the clock
frequency. At full scale, the current steering switch spends half
of the time on the summing junction; thus, an input current of
0.5 mA can be balanced. In the case of an overrange, the output
of the integrator op amp drifts in the negative direction and the
output of the comparator remains high. The logic circuits
simply settle into a divide-by-two of the clock state.
TIME
φ
MOD (t)
2
π
V
(t) = COS (2
OUT
CARRIER FREQUENCY
Figure 7. Phase Modulation
π×f
AVE
AVERAGE
×
t +φMOD (t))
TIME
PHASE
MODULATION
00798-007
Rev. C | Page 8 of 28
AD652
V
C
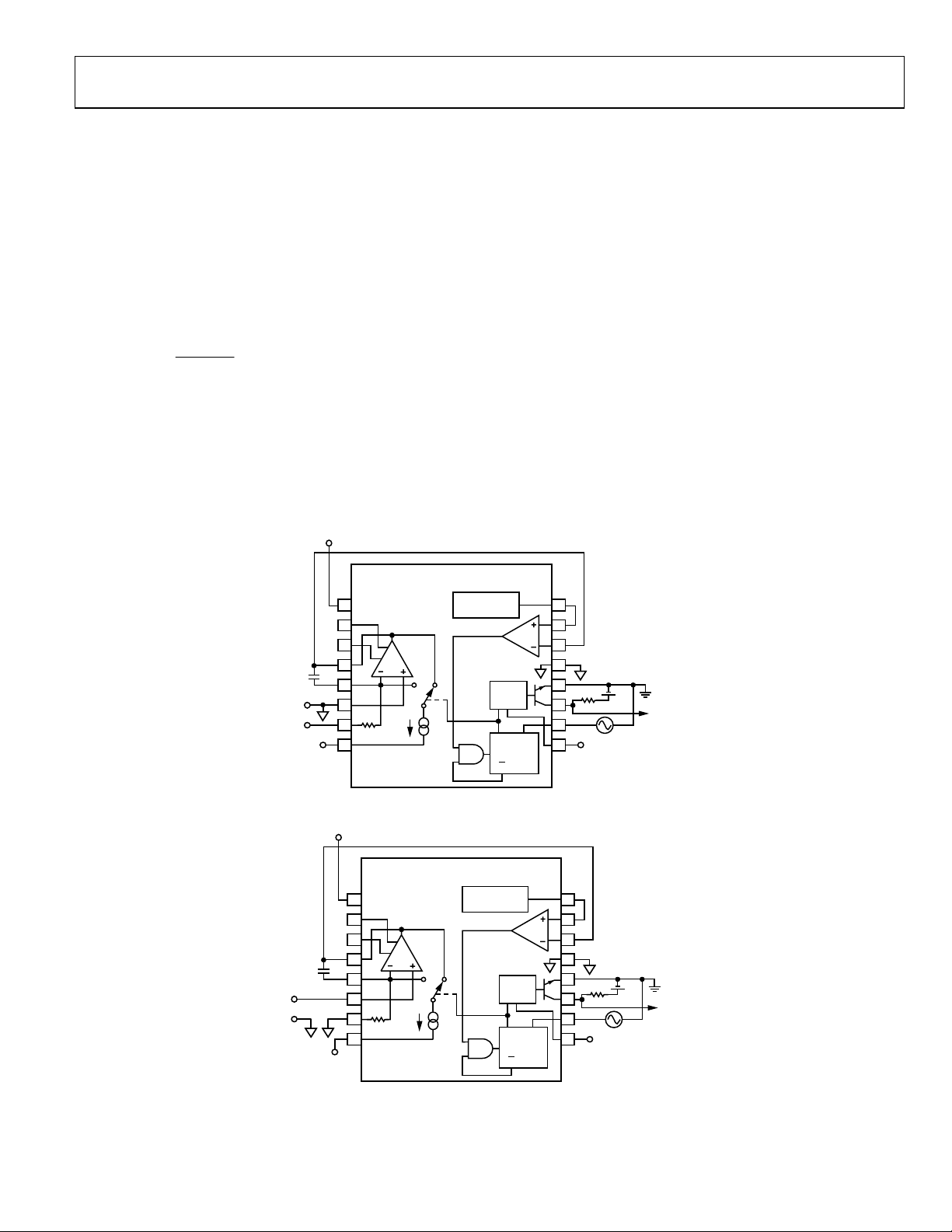
SVFC CONNECTION FOR DUAL SUPPLY, POSITIVE INPUT VOLTAGES
Figure 8 shows the AD652 connection scheme for the
traditional dual supply, positive input mode of operation. The
range is from ±6 V to ±18 V. When +VS is lower than 9.0 V,
±V
S
As shown in Figure 8, three additional connections are required
The first connection is to short Pin 13 to Pin 8 (Analog Ground
) and add a pull-up resistor to +VS (as shown in
to −V
S
Figure 21). The pull-up resistor is determined by the following
equation:
V
V52 −
S
R
PULLUP
=
These connections ensure proper operation of the 5 V reference.
Tie Pin 16 to Pin 6 (as shown in Figure 21) to ensure that the
integrator output ramps down far enough to trip the
comparator.
The CERDIP-packaged AD652 accepts either a 0 V to 10 V or
0 mA to 0.5 mA full-scale input signal. The temperature drift of
µA500
+
S
the AD652 is specified for a 0 V to 10 V input range using the
internal 20 kΩ resistor. If a current input is used, the gain drift is
degraded by a maximum of 100 ppm/°C (the TC of the 20 kΩ
resistor). If an external resistor is connected to Pin 5 to establish
a different input voltage range, drift is induced to the extent that
the external resistor’s TC differs from the TC of the internal
resistor. The external resistor used to establish a different input
voltage range should be selected to provide a full-scale current
of 0.5 mA (i.e., 10 kΩ for 0 V to 5 V).
SVFC CONNECTIONS FOR NEGATIVE INPUT VOLTAGES
Voltages that are negative with respect to ground may be used
as the input to the AD652 SVFC. In this case, Pin 7 is grounded
and the input voltage is applied to Pin 6 (see Figure 9). In this
mode, the input voltage can go as low as 4 V above −V
configuration, the input is a high impedance, and only the
20 nA (typical) input bias current of the op amp must be
supplied by the input signal. This is contrasted with the more
usual positive input voltage configuration, which has a 20 kΩ
input impedance and requires 0.5 mA from the signal source.
. In this
S
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
INT
–
V
+
4
5
6
IN
–V
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
S
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
"D"
FLOP
16
15
14
13
ANALOG
GND
12
R
L
11
10
9
5V
CLOCK
+V
S
Figure 8. Standard V/F Connection for Positive Input Voltage with Dual Supply
+V
S
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
C
INT
–
V
IN
+
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
–V
S
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
"D"
FLOP
16
15
14
13
ANALOG
GND
12
R
L
11
10
9
5V
CLOCK
+V
S
Figure 9. Negative Voltage Input
DIGITAL
GND
FREQ
OUT
DIGITAL
GND
FREQ
OUT
00798-008
00798-009
Rev. C | Page 9 of 28

AD652
V
V
IN
±5V
20kΩ
C
INT
+V
S
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
–V
S
REFERENCE
AND
Figure 10. Bipolar Offset
SVFC CONNECTION FOR BIPOLAR INPUT VOLTAGES
A bipolar input voltage of ±5 V can be accommodated by
injecting a 250 µA current into Pin 5 (see Figure 10). A −5 V
signal provides a zero sum current at the integrator summing
junction, which results in a zero-output frequency; a +5 V signal
provides a 0.5 mA (full-scale) sum current, which results in the
full-scale output frequency.
Using an external resistor to inject the offset current has some
effect on the bipolar offset temperature coefficient. The ideal
transfer curve with bipolar inputs is shown in Figure 11. The
user actually has four options to use in injecting the bipolar
offset current into the inverting input of the op amp:
1. Use an external resistor for R
resistor for R
(as shown in Figure 10).
IN
2. Use the internal 20 kΩ resistor as R
3. Use two external resistors.
4. Use two internal resistors for R
PLCC version only).
Option 4 provides the closest to the ideal transfer function as
diagrammed in Figure 11. Figure 12 shows the effects of the
transfer relation on the other three options. In the first case, the
slope of the transfer function is unchanged with temperature.
However, V
frequency of 0 Hz) and F
= 0 V) changes as the transfer function is displaced parallel
V
IN
(the input voltage required to produce an output
ZERO
ZERO
to the voltage axis with temperature. In the second case, F
remains constant, but V
rotates about F
with temperature changes. In the third case,
ZERO
changes as the transfer function
ZERO
with two external resistors, the V
while the slope and offset of the transfer function change with
temperature. If selecting this third option, the user should select
low drift, matched resistors.
and the internal 20 kΩ
OS
and an external RIN.
OS
and ROS (available on
IN
(the output frequency when
point remains invariant
ZERO
ZERO
5V
D
ONE
SHOT
QCK
"D"
FLOP
Q
CASE 1
R
R
CASE 2
R
R
CASE 3
R
R
16
15
14
13
ANALOG
GND
12
R
L
11
10
9
V
REF
R
R
IN
IN
5V
CLOCK
C
OS
OS
DIGITAL
GND
FREQ
OUT
00798-010
IDEAL
TRANSFER
RELATION
–5V +5V
V
ZERO
F
OUT
Figure 11. Ideal Bipolar Input Transfer Curve over Temperature
F
OUT
∼
INTERNAL
IN
∼
OS
∼
EXTERNAL
IN
∼
OS
∼
EXTERNAL
IN
∼
OS
EXTERNAL
INTERNAL
V
ZERO
EXTERNAL
–5V
–5V
–5V
IDEAL
IDEAL
V
ZERO
V
ZERO
F
OUT
IDEAL
F
OUT
F
F
F
ZERO
ZERO
ZERO
TEMPERATURE
PERTURBED
TRANSFER
TEMPERATURE
PERTURBED
TEMPERATURE
PERTURBED
Figure 12. Actual Bipolar Input Transfer over Temperature
F
ZERO
V
IN
00798-011
V
IN
V
IN
V
IN
00798-012
Rev. C | Page 10 of 28

AD652
5
6
10kΩ
7
NC
10kΩ
8
+
V
IN
–
A. PLCC 0V TO 10V INPUT
5
6
10kΩ
+
–
7
V
IN
10kΩ
8
NC
C. PLCC 0V TO 5V INPUT
16kΩ
9 10
NC NC
16kΩ
9 10
NC NC
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
4kΩ
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
4kΩ
PLCC CONNECTIONS
The PLCC packaged AD652 offers additional input resistors not
found on the CERDIP-packaged device. These resistors provide
the user with additional input voltage ranges. Besides the 10 V
range available using the on-chip resistor in the CERDIP the
PLCC also offers 8 V and 5 V ranges. Figure 13A to Figure 13C
show the proper connections for these ranges with positive
input voltages. For negative input voltages, the appropriate
resistor should be tied to analog ground and the input voltage
should be applied to Pin 6, the + input of the op amp.
Bipolar input voltages can be accommodated by injecting
250 µA into Pin 5 with the use of the 5 V reference and the
input resistors. For the ±5 V or ±2.5 V range, the reference
output, Pin 20, should be tied to Pin 10. The input signal should
then be applied to Pin 8 for a ±5 V signal and to Pin 7 for a
±2.5 V signal. The input connections for a ±5 V range are
shown in Figure 13D. For a ±4 V range, the input signal should
be applied to Pin 9, and Pin 20 should be connected to Pin 8.
GAIN AND OFFSET CALIBRATION
The gain error of the AD652 is laser trimmed to within ±0.5%.
If higher accuracy is required, the internal 20 kΩ resistor must
be shunted with a 2 MΩ resistor to produce a parallel equivalent
that is 1% lower in value than the nominal 20 kΩ. Full-scale
adjustment is then accomplished using a 500 Ω series trimmer.
See Figure 14 and Figure 15. When negative input voltages are
used, this 500 Ω trimmer is tied to ground and Pin 6 is the
input pin.
Figure 13.
5
6
10kΩ
7
NC
10kΩ
8
NC
+
V
–
B. PLCC 0V TO 8V INPUT
5
6
10kΩ
7
NC
10kΩ
8
V
IN
±
5V
±
3.5mV
OFFSET
TRIM
V
NC
D. PLCC±5V INPUT
+V
250kΩ
0.02µF
2MΩ
500Ω
V
IN
500Ω
500Ω
IN
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
16kΩ
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
4kΩ
9 10
NC
IN
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
16kΩ
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
5V REF
4kΩ
9 10
NC = NO CONNECT
S
20kΩ
20
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
8
1mA
00798-013
Figure 14. CERDIP Gain and Offset Trim
20kΩ
0.02µF
2MΩ
350kΩ
4
5
6
7
8
3 2 1 20 19
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
10kΩ
10kΩ
16kΩ
1mA
9 10 11 12 13
Figure 15. PLCC Gain and Offset Trim
5V
REFERENCE
D
AND
AND
4kΩ
ONE
SHOT
QCK
"D"
FLOP
Q
REFERENCE
Q
D
Q
ONE
SHOT
5V
"D"
FLOP
CK
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
00798-014
18
17
16
15
14
00798-015
Rev. C | Page 11 of 28

AD652
This gain trim should be done with an input voltage of 9 V, and
the output frequency should be adjusted to exactly 45% of the
clock frequency. Since the device settles into a divide-by-2 mode
for an input overrange condition, adjusting the gain with a 10 V
input is impractical; the output frequency is exactly one-half the
clock frequency if the gain is too high and does not change with
adjustment until the exact proper scale factor was achieved.
Thus, the gain adjustment should be done with a 9 V input.
The offset of the op amp may be trimmed to zero with the trim
scheme shown in Figure 14 for the CERDIP package and
Figure 15 for the PLCC package. One way of trimming the
offset is by grounding Pin 7 (8) of the CERDIP (PLCC) device
and observing the waveform at Pin 4. If the offset voltage of the
op amp is positive, the integrator has saturated and the voltage
is at the positive rail. If the offset voltage is negative, there is a
small effective input current that causes the AD652 to oscillate;
a sawtooth waveform is observed at Pin 4. The potentiometer
should be adjusted until the downward slope of this sawtooth
becomes very slow, down to a frequency of 1 Hz or less. In an
analog-to-digital conversion application, an easier way to trim
the offset is to apply a small input voltage, such as 0.01% of the
full-scale voltage, and adjust the potentiometer until the correct
digital output is reached.
GAIN PERFORMANCE
The AD652 gain error is specified as the difference in slope
between the actual and the ideal transfer function over the fullscale frequency range. Figure 16 shows a plot of the typical gain
error changes versus the clock input frequency, normalized to
100 kHz. Figure 16 shows the typical gain changes normalized
to the original 100 kHz gain if, after using the AD652 with a
full-scale clock frequency of 100 kHz, the necessary gating time
is reduced by increasing the clock frequency.
5
4
3
2
3
10
1
×
0
–1
ERROR (ppm)
–2
–3
–4
–5
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 4500 5000
CLOCK FREQUENCY (kHz)
Figure 16. Gain vs. Clock Input
00798-016
REFERENCE NOISE
The AD652 has an on-board, precision buffered 5 V reference
available to the user. Besides being used to offset the noninverting comparator input in the voltage-to-frequency mode, this
reference can be used for other applications such as offsetting
the input to handle bipolar signals and providing bridge excitation. It can source 10 mA and sink 100 µA, and is short-circuit
protected. Heavy loading of the reference does not change the
gain of the VFC, though it does affect the external reference
voltage. For example, a 10 mA load interacting with a 0.3 Ω typical output impedance changes the reference voltage by 0.06%.
DIGITAL INTERFACING CONSIDERATIONS
The AD652 clock input has a high impedance input with a
threshold voltage of two diode voltages with respect to Digital
Ground at Pin 12 (approximately 1.2 V at room temperature).
When the clock input is low, 5 µA to 10 µA flows out of this pin.
When the clock input is high, no current flows.
The frequency output is an open collector pull-down capable of
sinking 10 mA with a maximum voltage of 0.4 V. This drives
6 standard TTL inputs. The open collector pull-up voltage can
be as high as 36 V above digital ground.
COMPONENT SELECTION
The AD652 integrating capacitor should be 0.02 µF. If a large
amount of normal mode interference is expected (more than
0.1 V) and the clock frequency is less than 500 kHz, an
integrating capacitor of 0.1 µF should be used. Mylar,
polypropylene, or polystyrene capacitors should be used.
The open collector pull-up resistor should be chosen to give
adequately fast rise times. At low clock frequencies (100 kHz),
larger resistor values (several kΩ) and slower rise times may be
tolerated. However, at higher clock frequencies (1 MHz), a lower
value resistor should be used. The loading of the logic input that
is being driven must also be taken into consideration.
For example, if two standard TTL loads are to be driven, a
3.2 mA current must be sunk, leaving 6.8 mA for the pull-up
resistor if the maximum low level voltage is to be maintained at
0.4 V. A 680 Ω resistor would therefore be selected
((5 V – 0.4 V)/6.8 mA) = 680 Ω.
Rev. C | Page 12 of 28

AD652
The one-shot capacitor controls the pulse width of the
frequency output. The pulse is initiated by the rising edge of the
clock signal. The delay time between the rising edge of the clock
and the falling edge of the frequency output is typically 200 ns.
The width of the pulse is 5 ns/pF, and the minimum width is
about 200 ns with Pin 9 floating. If the one-shot period is
accidentally chosen longer than the clock period, the width of
the pulse defaults to equal the clock period. The one-shot can be
disabled by connecting Pin 9 to +V
(Figure 17); the output
S
pulse width is then equal to the clock period. The one-shot is
activated (Figure 18) by connecting a capacitor from Pin 9 to
, −VS, or Digital Ground (+VS is preferred).
+V
S
+V
S
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
Figure 17. One-Shot Disabled
5V
REFERENCE
AND
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
FLOP
Q
"D"
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
00798-017
DIGITAL GROUND
Digital Ground can be at any potential between −VS and
– 4 V). This can be very useful in systems with derived
(+V
S
grounds rather than stiff supplies. For example, in a small
isolated power circuit, often only a single supply is generated
and the ground is set by a divider tap. Such a ground cannot
handle the large currents associated with digital signals. With
the AD652 SVFC, it is possible to connect the Digital Ground to
for a solid logic reference, as shown in Figure 19.
–V
S
+V
S
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
C
INT
–
V
+
4
5
6
IN
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
–V
S
Figure 19. Digital GND at −V
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
"D"
FLOP
16
15
14
13
12
R
L
CLOCK
C
OS
5V
11
10
9
S
FREQ
OUT
00798-019
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
1
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
8
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
1mA
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
(+V
"D"
FLOP
Q
,–VS, OR DIGITAL GND)
S
ANY AC GND
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
C
OS
00798-018
Figure 18. One-Shot Enabled
Rev. C | Page 13 of 28

AD652
SINGLE-SUPPLY OPERATION
In addition to the Digital Ground being connected to –VS, it is
also possible to connect Analog Ground to –V
Thus, the device is truly operating from a single-supply voltage
that can range from 12 V to 36 V. This is shown in Figure 21 for
a positive voltage input, and in Figure 20 for a negative voltage
input.
In Figure 21, the comparator reference is used as a derived
ground; the input voltage is referred to this point as well as to
the op amp common mode (Pin 6 is tied to Pin 16). Since the
input signal source must drive 0.5 mA of full-scale signal
current into Pin 7, it must also draw the exact same current
from the input reference potential. This current is therefore
provided by the 5 V reference.
In single-supply operation, an external resistor, R
necessary between the power supply, +V
of the AD652.
S
, is
PULLUP
, and the 5 V reference
S
+V
S
R
PULLUP
output. This resistor should be selected such that a current of
approximately 500 µA flows during operation. For example,
with a power supply voltage of +15 V, a 20 kΩ resistor is selected
((15 V–5 V)/500 µA = 20 kΩ).
Figure 20 shows the negative voltage input configuration for
using the AD652 in single-supply mode. In this mode, the signal
source is driving the + input of the op amp, which requires only
20 nA (typical) compared to the 0.5 mA required in the positive
input voltage configuration. The voltage at Pin 6 may go as low
as 4 V above ground (−V
Pin 8). Since the input reference is 5.0
S
V above ground, this leaves a 1 V window for the input signal.
To drive the integrating capacitor with a 0.5 mA full-scale
current, it is necessary to provide an external 2 kΩ resistor. This
results in a 2 kΩ resistor and a 1 V input range. The external
2 kΩ resistor should be a low TC metal-film type for lowest
drift degradation.
INPUT
REFERENCE
SIGNAL
SOURCE
1V FULL SCALE
INPUT
REFERENCE
–
+
SIGNAL
SOURCE
+
2kΩ
–
I
SIGNAL
I
SIGNAL
0.5mA
FULL SCALE
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
INT
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
C
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
Figure 20. Single-Supply Mode Negative Voltage Input
+V
S
R
PULLUP
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
INT
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
C
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
FLOP
"D"
FLOP
"D"
16
15
14
13
ANALOG
GND
12
11
10
9
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
R
L
ANALOG
GND
R
L
CLOCK
5V
CLOCK
C
OS
5V
DIGITAL
GND
00798-021
DIGITAL
GND
FREQ
OUT
C
OS
ANALOG
GND
Figure 21. Single-Supply Mode Positive Voltage Input
00798-020
Rev. C | Page 14 of 28

AD652
V
FREQUENCY-TO-VOLTAGE CONVERTER
The AD652 SVFC also works as a frequency-to-voltage
converter. Figure 22 shows the connection diagram for F/V
conversion. In this case, the negative input of the comparator is
fed the input pulses. Either comparator input may be used so
that an input pulse of either polarity may be applied to the F/V.
In Figure 22, the + input is tied to a 1.2 V reference and lowlevel TTL pulses are used as the frequency input. The pulse
must be low on the falling edge of the clock. On the subsequent
rising edge, the 1 mA current source is switched to the
integrator summing junction and ramps up the voltage at Pin 4.
Due to the action of the AND gate, the 1 mA current is switched
off after only one clock period. The average current delivered to
the summing junction varies from 0 mA to 0.5 mA; using the
internal 20 kΩ resistor, this results in a full-scale output voltage
of 10 V at Pin 4.
The frequency response of the circuit is determined by the
capacitor; the −3 dB frequency is simply the RC time constant.
A tradeoff exists between ripple and response. If low ripple is
desired, a large value capacitor must be used (1 µF); if fast
response is needed, a small capacitor is used (1 nF minimum).
The op amp can drive a 5 kΩ resistor load to 10 V, using a 15 V
positive power supply. If a large load capacitance (0.01 µF) must
be driven, it is necessary to isolate the load with a 50 Ω resistor
+V
S
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
4
C
5
6
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
–V
S
OUT
+
5kΩ
–
50Ω
0.01µF
as shown. Because the 50 Ω resistor is 0.25% of the full scale,
and the specified gain error with the 20 kΩ resistor is 0.5%, this
extra resistor only increases the total gain error to 0.75% max.
The circuit shown is unipolar and only a 0 V to +10 V output is
allowed. The integrator op amp is not a general-purpose op
amp. Instead, it has been optimized for simplicity and high
speed. The most significant difference between this amplifier
and a general-purpose op amp is the lack of an integrator (or
level shift) stage.
Consequently, the voltage on the output (Pin 4) must always be
more positive than 1 V below the inputs (Pins 6 and 7). For
example, in the F-to-V conversion mode, the noninverting input
of the op amp (Pin 6) is grounded, which means the output
(Pin 4) cannot go below −1 V. Normal operation of the circuit as
shown never calls for a negative voltage at the output.
A second difference between this op amp and a general-purpose
amplifier is that the output only sinks 1.5 mA to the negative
supply. The only pull-down other than the 1 mA current used
for voltage-to-frequency conversion is a 0.5 mA source. The op
amp sources a great deal of current from the positive supply,
and is internally protected by current limiting. The op amp
output may be driven to within 4 V of the positive supply when
not sourcing external current. When sourcing 10 mA, the output voltage may be driven to within 6 V of the positive supply.
FREQ
5V
IN
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
"D"
FLOP
16
15
14
13
12
11
NC
10
9
NC
5kΩ
1N4148
CLOCK
DIGITAL
GND
CLOCK
FREQ
IN
VOLTS
OUT
LOADS ON FALLING EDGE OF CK
SHIFTS OUT ON RISING EDGE OF CL
FREQUENCY TO VOLTS CONVERTER
00798-022
Figure 22. Frequency-to-Voltage Converter
Rev. C | Page 15 of 28

AD652
DECOUPLING AND GROUNDING
It is good engineering practice to use bypass capacitors on the
supply-voltage pins, and to insert small valued resistors (10 Ω to
100 Ω) in the supply lines to provide a measure of decoupling
between the various circuits in a system. Ceramic capacitors of
0.1 µF to 1.0 µF should be applied between the supply voltage
pins and analog signal ground for proper bypassing on the
AD652.
Additionally, a larger board-level decoupling capacitor of 1 µF
to 10 µF should be located relatively close to the AD652 on each
power supply line. Such precautions are imperative in high
resolution data acquisition applications where one expects to
exploit the full linearity and dynamic range of the AD652.
Separate digital and analog grounds are provided on the AD652.
Only the emitter of the open-collector frequency output
transistor and the clock input threshold are returned to the
digital ground. Only the 5 V reference is connected to analog
ground. The purpose of the two separate grounds is to allow
isolation between the high precision analog signals and the
digital section of the circuitry. Much noise can be tolerated on
the digital ground without affecting the accuracy of the VFC.
Such ground noise is inevitable when switching the large
currents associated with the frequency output signal.
At high full-scale frequencies, it is necessary to use a pull-up
resistor of about 500 Ω in order to get the rise time fast enough
to provide well-defined output pulses. This means that from a
5 V logic supply, for example, the open collector output draws
10 mA. This much current being switched causes ringing on
long ground runs due to the self-inductance of the wires. For
instance, 20-gauge wire has an inductance of about 20 nH per
inch; a current of 10 mA being switched in 50 ns at the end of
12 inches of 20-gauge wire produces a voltage spike of 50 mV.
The separate digital ground of the AD652 easily handles these
types of switching transients.
A problem remains from interference caused by radiation of
electromagnetic energy from these fast transients. Typically, a
voltage spike is produced by inductive switching transients;
these spikes can capacitively couple into other sections of the
circuit. Another problem is ringing of ground lines and power
supply lines due to the distributed capacitance and inductance
of the wires. Such ringing can also couple interference into
sensitive analog circuits. The best solution to these problems is
proper bypassing of the logic supply at the AD652 package. A
1 µF to 10 µF tantalum capacitor should be connected directly
to the supply side of the pull-up resistor and to the digital
ground, Pin 12. The pull-up resistor should be connected
directly to the frequency output, Pin 11. The lead lengths on the
bypass capacitor and the pull-up resistor should be as short as
possible. The capacitor supplies (or absorbs) the current
transients, and large ac signals flow in a physically small loop
through the capacitor, pull-up resistor, and frequency output
transistor. It is important that the loop be physically small for
two reasons: first, there is less inductance if the wires are short,
and second, the loop does not radiate RFI efficiently.
The digital ground (Pin 12) should be separately connected to
the power supply ground. Note that the leads to the digital
power supply are only carrying dc current. There may be a dc
ground drop due to the difference in currents returned on the
analog and digital grounds. This does not cause a problem;
these features greatly ease power distribution and ground
manage-ment in large systems. The proper technique for
grounding requires separate digital and analog ground returns
to the power supply. Also, the signal ground must be referred
directly to the analog ground (Pin 6) at the package. More
information on proper grounding and reduction of interference
can be found in
, by H.W. Ort, (John Wiley, 1976).
Systems
Noise Reduction Techniques in Electronic
Rev. C | Page 16 of 28

AD652
+5V
R
PU
2.87kΩ
1
2
500pF
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
1kΩ
C1
9
A
B
74LS86
+5V
C
f
C
f
OUT
V1
0V–10V
0V–10V
8.06kΩ
V2
–
+
R1
+15V
0.02µF
R2
2kΩ
4
R3
1kΩ
3
R
T
1kΩ
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
8
AD654
AD652
1mA
8
OSC/DRIVER
65
C
T
200pF
5V
REFERENCE
AND
7
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
FLOP
Q
"D"
–15V
+15V
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
V
OUT
400pF
–15V
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
1mA
8
Figure 23. Frequency Output Multip lier
FREQUENCY OUTPUT MULTIPLIER
The AD652 can serve as a frequency output multiplier when
used in conjunction with a standard voltage-to-frequency
converter. Figure 23 shows the low cost AD654 VFC being used
as the clock input to the AD652. Also shown is a second AD652
in the F/V mode. The AD654 is set up to produce an output
frequency of 0 kHz to 500 kHz for an input voltage (V
of 0 V to 10 V. The use of R4, C1, and the XOR gate doubles this
output frequency from 0 kHz–500 kHz to 0 MHz–1 MHz.
) range
1
200pF
+5V
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
"D"
FLOP
2kΩ
16
15
14
13
12
11
1MHz
10
CLOCK
INPUT
9
00798-023
This 1 MHz full-scale frequency is then used as the clock input
to the AD652 SVFC. Because the AD652 full-scale output
frequency is one-half the clock frequency, the 1 MHz FS clock
frequency establishes a 500 kHz maximum output frequency for
the AD652 when its input voltage (V
) is 10 V. The user there-
2
fore has an output frequency range from 0 kHz to 500 kHz,
which is proportional to the product of V
and V2.
1
Rev. C | Page 17 of 28

AD652
This can be shown in equation form, where fC is the AD654
f
output frequency and
C
OUT
OUT
f
= V1 × V2 × 5 kHz/V
OUT
V10
⎛
⎜
⎜
=
Vf
2
⎜
⎜
⎝
=
VVf
21
MHz1
Vf =
1
The scope photo in Figure 24 shows V1 and V2 (top two traces)
and the output of the F-V (bottom trace).
SINGLE-LINE MULTIPLEXED DATA TRANSMISSION
It is often necessary to measure several different signals and
relay the information to some remote location using a minimum amount of cable. Multiple AD652 SVFC devices may be
used with a multiphase clock to combine these measurements
for serial transmission and demultiplexing. Figure 25 shows a
block diagram of a single-line multiplexed data transmission
is the AD652 output frequency:
OUT
f
⎞
C
⎟
2
⎟
⎟
V10
⎟
⎠
⎛
MHz1
⎜
⎜
()()
⎝
Figure 24. Multiplier Waveforms
φ1φ2φ3φ
⎞
⎟
⎟
V10V102
⎠
2
CLK
GENERATOR
4
SVFC MULTIPLEXER
(SEE FIGURE 26)
V
V
V
1
2
OUT
00798-024
system with high noise immunity. Figure 26, Figure 27, and
Figure 30 show the SVFC multiplexer, a representative means of
data transmission, and an SVFC demultiplexer respectively.
Multiplexer
Figure 30 shows the SVFC multiplexer. The clock inputs for the
several SVFC channels are generated by a TIM9904A 4-phase
clock driver, and the frequency outputs are combined by
strapping all the frequency output pins together (a wire OR
connection). The one-shot in the AD652 sets the pulse width of
the frequency output pulses to be slightly shorter than one
quarter of the clock period. Synchronization is achieved by
applying one of the four available phases to a fixed TTL oneshot (’121) and combining the output with external transistor.
The width of this sync pulse is shorter than the width of the
frequency output pulses to facilitate decoding the signal. The
RC lag network on the input of the one-shot provides a slight
delay between the rising edge of the clock and the sync pulse in
order to match the 150 ns delay of the AD652 between the
rising edge of the clock and the output pulse.
Transmitter
The multiplex signal can be transmitted in any manner suitable
to the task at hand. A pulse transformer or an opto-isolator can
provide galvanic isolation; extremely high voltage isolation or
transmission through severe RF environments can be accomplished with a fiber optic link; telemetry can be achieved with a
radio link. The circuit shown in Figure 27 uses an EIA RS-422
standard for digital data transmission over a balanced line.
Figure 24 shows the waveforms of the four clock phases and the
multiplex output signal. Note that the sync pulse is present
every clock cycle, but the data pulses are no more frequent than
every other clock cycle since the maximum output frequency
from the SVFC is half the clock frequency. The clock frequency
used in this circuit is 819.2 kHz, which provides more than
16 bits of resolution if 100 ms gate time is allowed for counting
pulses of the decoded output frequencies.
f1
SVFC
DEMUX
SVFC DEMULTIPLEXER
f2
(SEE FIGURE 30)
f3
ONE
SHOT
AD652
V
IN1
AD652
V
IN2
Figure 25. Single-Line Multiplexed Data Transmission Block Diagram
AD652
V
IN3
TRANSMISSION
LINK
TRANSMISSION
LINK
(SEE FIGURE 27)
Rev. C | Page 18 of 28
φ
2
AD652
V
DEMULTIPLEXER FREQUENCY TO
VOLTAGE CONVERSION
(SEE FIGURE 31)
OUT1
φ
3
AD652
V
OUT2
φ
4
AD652
V
OUT3
00798-025

AD652
0.02µF
V
IN2
+V
S
1
2
3
AD652
4
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
5
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
φ
2
10
9
0.02µF
V
IN3
+V
S
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
+V
S
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
0.02µF
φ
3
V
IN4
1
2
3
AD652
4
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
5
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
φ
4
10
9
7.4µH
L = 41 TURNS
T50–7 CORE
MICROMETALS
C = 300pF
–V
1 20
2 19
3 18
4 17
5 16
6 15
7 14
φ
3
8 13
φ
4
9 12
10 11
TIM 9904A
TANK 1
TANK 2 XTAL 2
GND 1
FFQ OSCIN
FFD
φ
4 TTL
φ
3 TTL
φ
3V
φ
4
GND 2
FROM
ENCODER
MPX
INPUT
S
XTAL 4
OSCOUT
φ
2
B OUTPUTS
15pF
V
CC
+5V
3.2768MHz
CRYSTAL
1kΩ
+5V
–V
S
φ
1
150Ω
φ
2 TTL
φ
1 TTL
DD
φ
1
+5V
φ
φ
1500pF
1
2
Figure 26. SVFC Multiplexer
QUAD HIGH SPEED DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER
INPUTS A
A OUTPUTS
ENABLE
INPUT B
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
GND
8
500 FEET
BELDEN 9272
78Ω SHIELDED PAIR
AM26LS31
75Ω
MPX OUTPUT
TO DECODER
Figure 27. RS-422 Standard Data Transmission
15pF
ONE SHOT
1 14
2 13
NC
A1
3 12
A2
4 11
5 10
Q
6 9
GND
QQ
7 8
+5V
16
15
INPUTS D
14
D OUTPUTS
13
12
ENABLE
11
C OUTPUTS
10
INPUT C
9
INPUTS A
OUTPUT A
ENABLE
OUTPUT C
INPUTS C
–V
S
'121
V
NC
NC
R
C
R
NC
CC
EXT/CEXT
50pF
EXT
INT
10kΩ
2kΩ
+5V
+5V
500Ω
2N2222
18pF
QUAD DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
AM26LS33
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
15pF
+5V
INPUTS B
OUTPUT B
ENABLE
INPUT D
INPUTS D
00798-027
MULTIPLEX
OUT
00798-026
Rev. C | Page 19 of 28

AD652
X
SVFC Demultiplexer
The demultiplexer needed to separate the combined signals is
shown in Figure 30. A phase-locked loop drives another 4-phase
clock chip to lock onto the reconstructed clock signal. The sync
pulses are distinguished from the data pulses by their shorter
duration. Each falling edge on the multiplex input signal
triggers the one-shot; at the end of this one-shot pulse, the
multiplex input signal is sampled by a D-type flip-flop. If the
signal is high, the pulse was short (a sync pulse) and the
output of the D-flop goes low. The D-flop is cleared a short time
(two gate delays) later, and the clock is reconstructed as a
stream of short, low-going pulses. If the multiplex input is a data
pulse, then the signal will still be low and no pulse will appear at
the reconstructed clock output when the D-flop samples at the
end of the one-shot period. See Figure 29.
If it is desired to recover the individual frequency signals, the
multiplex input is sampled with a D-flop at the appropriate
time, as determined by the rising edge of the various phases
generated by the clock chip. These frequency signals can be
counted as a ratio relative to the reconstructed clock, so it is not
even necessary for the transmitter to be crystal-controlled as
shown in Figure 30.
Q
φ
SYNC
1
φ2φ
DATA
3
Figure 28. Multiplexer Waveforms
φ
1
φ
2
φ
3
φ
4
1MULTIPLE
OUTPUT
00798-029
φ
4
MULTIPLEX
INPUT
ONE SHOT
RECONSTRUCTED
CLOCK
φ
1
(PHASE LOCKED TO
RECONSTRUCTED
CLOCK)
MPX
INPUT
'74 (1/2)
D
CLOCK
Q
1/2 '74
D
CLOCK
Q
1 14
2 13
NC
A1
3 12
A2
4 11
+5V
5 10
6 9
Q
GND
7 8
φ
2
RECONSTRUCTED
CLOCK OUTPUT
Q
CLEAR
'00
'00
ONE SHOT
'121
QQ
'74 (1/2)
D
CLOCK
Q
00798-030
Figure 29. Demultiplexer Waveforms
+5V
14 13 54 10
1
PHASE LOCK LOOP
MC4044
3
4 2 11 8
150Ω
390pF
+5V
130Ω
V
CC
NC
2kΩ
NC
R
EXT/CEXT
50pF
C
EXT
R
INT
NC
'74 (1/2)
D
φ
3
CLOCK
Q
φ
4
1 20
2 19
3 18
4 17
5 16
6 15
7 14
φ
3
8 13
φ
4
9 12
10 11
3.01kΩ
9
719Ω
0.1µF
2
1kΩ
+5V
TIM 9904A
4 PHASE CLOCK
TANK 1
TANK 2 XTAL 2
GND 1
FFQ OSCIN
FFD
φ
4 TTL
φ
3 TTL
φ
3
φ
4
GND 2
V
XTAL 1
OSCOUT
φ
2 TTL
φ
1 TTL
V
+5V
3 16 15 11
VCO
'LS629
6 8 9 7
+5V
CC
DD
φ
1
φ
2
4
50pF
5
φ
1
φ
2
f2
FREQUENCY OUTPUTS
f3
RECONSTRUCTED
f4
NC = NO CONNECT
00798-028
Figure 30. SVFC Demultiplexers
Rev. C | Page 20 of 28

AD652
V
+V
S
1
OLTS
OUT
V
2
0.02µF
–V
S
2
3
AD652
4
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
5
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
6
7
8
1N4148
φ2,φ3,φ
+5V
4kΩ
+V
S
16
VOLTS
15
14
13
12
11
10
OUT
V
φ
2
9
4 ARE PINS 15, 7, 6 OF TIM9904A FROM DEMUX FIGURE 30
3
0.02µF
–V
S
1
2
3
AD652
4
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
5
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
6
7
8
MPX INPUT
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
φ
3
VOLTS
OUT
V
4
0.02µF
–V
+V
S
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
S
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
16
15
14
13
12
11
φ
4
10
9
00798-031
Figure 31. Demultiplexer Frequency-to-Voltage Conversion
10kΩ
V
AD589
1.2V
+5V
1.5kΩ
1 8
2 7
1.2kΩ
3 6
6.8kΩ
4 5
DRIVER
OSC
AD654
200pF
24 TURNS
T50- MICROMETALS
CK
'74
QDQ
2N6659 2N6659
MYLAR
0.01µF
+5V
10µH
12 3
CK
100Ω100Ω
1.65kΩ1.65kΩ
TRANSFORMER
PICO 31080
'74
500Ω
Q
D
5 4
6 3
7 2
8 1
+5V
6N137
OPTO-
ISOLATOR
FREQUENCY
OUTPUT
4567
1N4148
47µF47µF
–15V
7915
REG
LO
V
IN
HI
10kΩ
+15V
7815
REG
47µF47µF
+15V–15V
Figure 32. Isolated Synchronous VFC
Analog Signal Reconstruction
If it is desired to reconstruct the analog voltages from the
multiplex signal, three more AD652 SVFC devices are used as
frequency-to-voltage converters, as shown in Figure 31. The
comparator inputs of all the devices are strapped together, the
“+” inputs are held at a 1.2 V TTL threshold, and the “−” inputs
are driven by the multiplex input. The three clock inputs are
0.02µF
ISOLATION BARRIER
+15V
–15V
driven by the
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
1
CONVERTER
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
8
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
1mA
1nF
ϕ
outputs of the clock chip. Remember that data
AND
QCK
D
Q
"D"
FLOP
16
15
14
13
12
3kΩ
11
10
9
1kΩ
1nF
00798-032
at the comparator input of the SVFC is loaded on the falling
edge of the clock signal and shifted out on the next rising edge.
Note that the frequency signals for each data channel are
available at the frequency output pin of each FVC.
Rev. C | Page 21 of 28

AD652
V
ISOLATED FRONT END
In some applications, it may be necessary to have complete
galvanic isolation between the analog signals being measured
and the digital portions of the circuit. The circuit shown in
Figure 32 runs off a single 5 V power supply and provides a selfcontained, completely isolated analog measurement system. The
power for the AD652 SVFC is provided by a chopper and a
transformer, and is regulated to 15 V.
Both the chopper frequency and the AD652 clock frequency are
125 kHz, with the clock signal being relayed to the SVFC
through the transformer. The frequency output signal is relayed
through an opto-isolator and latched into a D flop. The chopper
frequency is generated from an AD654 VFC, and is frequency
divided by two to develop differential drive for the chopper
transistors, and to ensure an accurate 50% duty cycle. The pullup resistors on the D flop outputs provide a well-defined high
level voltage to the choppers to equalize the drive in each
direction. The 10 µH inductor in the 5 V lead of the transformer
primary is necessary to equalize any residual imbalance in the
drive on each half cycle, and thus prevent saturation of the core.
The capacitor across the primary resonates the system so that
under light loading conditions on the secondary, the wave shape
is sinusoidal and the clock frequency is relayed to the SVFC. To
adjust the chopper frequency, disconnect any load on the
secondary and tune the AD654 for a minimum in the supply
current drawn from the 5 V supply.
A-TO-D CONVERSION
In performing an A-to-D conversion, the output pulses of a
VFC are counted for a fixed-gate interval. To achieve maximum
performance with the AD652, the fixed-gate interval should be
generated using a multiple of the SVFC clock input. Counting
in this manner eliminates any errors due to the clock (whether
it be jitter, drift with time or temperature, and so on) since it is
the ratio of the clock and output frequencies that is being
measured.
Table 4.
Resolution N Clock Conversion or Gate Time (ms) Typical Linearity (%) Comments
12 Bits 4096 81.92 kHz 100 0.002 50 Hz, 60 Hz,400 Hz NMR
12 Bits 4096 2 MHz 4.096 0.01
12 Bits 4096 4 MHz 2.048 0.02
4 Digits 10000 200 kHz 100 0.002 50 Hz, 60 Hz, 400 Hz NMR
14 Bits 16384 327.68 kHz 100 0.002 50 Hz, 60 Hz, 400 Hz NMR
14 Bits 16384 1.966 MHz 16.66 0.01 60 Hz NMR
14 Bits 16384 1.638 MHz 20 0.01 50 Hz NMR
4½ Digits 20000 400 kHz 100 0.002 50 Hz, 60 Hz, 400 Hz NMR
16 Bits 65536 655.36 kHz 200 0.002 50 Hz, 60 Hz, 400 Hz NMR
16 Bits 65536 4 MHz 32.77 0.02
The resolution of the A-to-D conversion measurement is
determined by the clock frequency and the gate time. If, for
instance, a resolution of 12 bits is desired and the clock
frequency is 1 MHz (resulting in an AD652 FS frequency of
500 kHz) the gate time is:
−
−
1–
FreqFS
⎛
⎜
⎜
N
⎝
8192
=
101
×
N is the total number of codes for a given resolution.
Where
⎛
⎞
1
⎜
=
⎟
⎟
⎜
N
2
⎠
⎝
ms192.8sec
=
6
1
FreqClock
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎠
MHz1
⎛
⎜
=
⎜
()
40962
⎝
1
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎠
Figure 33 shows the AD652 SVFC as an A-to-D converter in
block diagram form.
f
INPUT
AD652
IN
CLOCK
Figure 33. Block Diagram of SVFC A-to-D Converter
OUT
COUNTER
GATE
÷
2N
TO µP
To provide the ÷2N block, a single-chip counter such as the
4020B can be used. The 4020B is a 14-stage binary ripple
counter that has a clock and master reset for inputs, and
buffered outputs from the first stage and the last 11 stages. The
output of the first stage is f
of the last stage is f
CLOCK
CLOCK
÷ 214 = f
÷ 21 = f
CLOCK
/2, while the output
CLOCK
/16384. Therefore, using
this single chip counter as the ÷2N block, 13-bit resolution can
be achieved. Higher resolution can be achieved by cascading Dtype flip flops or another 4020B with the counter.
Table 4 shows the relationship between clock frequency and gate
time for various degrees of resolution. Note that if the variables
are chosen such that the gate times are multiples of 50 Hz,
60 Hz, or 400 Hz, normal mode rejection (NMR) of those line
frequencies occur.
00798-033
Rev. C | Page 22 of 28

AD652
)
DELTA MODULATOR
The circuit of Figure 34 shows the AD652 configured as a delta
modulator. A reference voltage is applied to the input of the
integrator (Pin 7), which sets the steady state output frequency
at one-half of the AD652 full-scale frequency (1/4 of the clock
frequency). As a 0 V to 10 V input signal is applied to the
comparator (Pin 15), the output of the integrator attempts to
track this signal. For an input in an idling condition (dc), the
output frequency is one-half full scale. For positive-going
signals, the output frequency is between one-half full scale and
full scale; for negative-going signals, the output frequency is
between zero and one-half full scale. The output frequency
corresponds to the slope of the comparator input signal.
AD652
SYNCHRONOUS
–15V
+15V
360pF
1
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
8
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
1mA
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
"D"
FLOP
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
VIN(0V TO 10V
+5V
0.01µF
CLOCK
1kΩ
F
OUT
The choice of an integrating capacitor is primarily dictated by
the input signal bandwidth. Figure 37 shows this relationship.
Note that as the value of C
is lowered, the ramp size of the
INT
integrator approximation becomes larger. This can be
compensated for by increasing the clock frequency. The effect of
the clock frequency on the ramp size is demonstrated in
Figure 35 and Figure 36.
00798-035
Figure 35. Delta Modulator Input Signal and Ramp-Wise Approximation
0.0047µF
Figure 34. Delta Modulator
Since the output frequency corresponds to the slope of the input
signal, the delta modulator acts as a differentiator. A delta
modulator is thus a direct way of finding the derivative of a
signal. This is useful in systems where, for example, a signal
corresponding to velocity exists, and it is desired to determine
acceleration.
Figure 35 is a scope photo showing a 20 kHz, 0 V to 10 V sine
wave used as the input to the comparator and its ramp-wise
approximation at the integrator output. The clock frequency
used as 2 MHz and the integrating capacitor was 360 pF.
Figure 36 shows the same input signal and its ramp-wise
approximation, along with the output frequency corresponding
to the derivative of the input signal. In this case, the clock
frequency was 50 kHz.
00798-034
Figure 36. Delta Modulator Input Signal Ramp-Wise Approximation and
Output Frequency
10k
(pF)
INT
C
1k
100
100 1k 10k
INPUT SIGNAL BANDWIDTH (Hz)
Figure 37. Maximum Integrating Cap Value vs. Input Signal Bandwidth
00798-036
00798-037
Rev. C | Page 23 of 28

AD652
BRIDGE TRANSDUCER INTERFACE
The circuit of Figure 38 illustrates a simple interface between
the AD652 and a bridge-type transducer. The AD652 is an ideal
choice because its buffered 5 V reference can be used as the
bridge excitation, thereby ratiometrically eliminating the gain
drift related errors. This reference provides a minimum of
10 mA of external current, which is adequate for bridge
resistance of 600 Ω and above. If, for example, the bridge
resistance is 120 Ω or 350 Ω, an external pull-up resistor (
required.
R
and can be calculated using the following formula:
PU
V
V5
−+
R
V5
BRIDGE
S
−
mA10
R
PU
(max)
=
An instrumentation amplifier is used to condition the bridge
signal before presenting it to the SVFC. With its high CMRR,
the AD652 minimizes common-mode errors and can be set to
arbitrary gains between 1 and 10,000 via three resistors,
simplifying the scaling for the part’s calibrated 10 V input range.
R
) is
PU
These resistors should be selected such that the following
equation holds:
V
V10
BRIDGE
where 10 kΩ ≤ R
⎛
⎜
⎜
⎝
≤ 20 kΩ, and V
F
⎞
R
2
F
⎟
1
+=
⎟
R
G
⎠
is the maximum output
BRIDGE
voltage of the bridge.
The bridge output may be unipolar, as is the case for most
pressure transducers, or it may be bipolar as in some strain
measurements. If the signal is unipolar, the reference input of
the AD625 (Pin 7) is simply grounded. If the bridge has a
bipolar output, however, the AD652 reference can be tied to
Pin 7, thereby, converting a 5 V signal (after gain) into a 0 V to
+10 V input for the SVFC.
+15V
R
PU
R
BRIDGE
+–
V
BRIDGE
NOTES
SHOULD BE BETWEEN 10kΩ AND 20kΩ.
1. R
F
NEEDED IF R
2. R
PU
3. S1 IN POSITION 1 FOR UNIPOLAR SIGNALS
AND POSITION 2 FOR BIPOLAR SIGNALS.
BRIDGE
600Ω
1
5
R
F
2
R
G
15
R
F
12
16
+15V
9
AD625
8
–15V
11
10
7
2
1
S1
=V
F
OUT
BRIDGE
C
INT
–15V
2R
F
+ 1
R
G
SYNCHRONOUS
1
2
3
4
5
6
20kΩ
7
8
F
CLOCK
10V
AD652
VOLTAGE-TO-
FREQUENCY
CONVERTER
1mA
2
5V
REFERENCE
ONE
SHOT
QCK
D
AND
Q
"D"
FLOP
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
LOGIC
CLOCK IN
+15V
R
L
FREQ
OUT
00798-038
Figure 38. Bridge Transducer Interface
Rev. C | Page 24 of 28

AD652
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
0.098 (2.49)
16
0.840 (21.34) MAX
MAX
18
0.100
0.070 (1.78)
(2.54)
0.030 (0.76)
BSC
9
0.310 (7.87)
0.220 (5.59)
0.060 (1.52)
0.015 (0.38)
0.150 (3.81)
MIN
SEATING
PLANE
15°
0°
(Q-16)
Dimensions shown in inches and (millimeters)
0.180 (4.57)
0.056 (1.42)
0.042 (1.07)
19
18
0.050
(1.27)
BSC
14
13
SQ
SQ
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-047AA
0.165 (4.19)
0.120 (3.04)
0.090 (2.29)
0.20 (0.51)
MIN
0.021 (0.53)
0.013 (0.33)
0.032 (0.81)
0.026 (0.66)
0.025 (0.64) MIN
0.330 (8.38)
0.290 (7.37)
Figure 40. 20-Lead Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier [PLCC]
(P-20A)
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm)
0.358
(9.09)
MAX
SQ
0.075 (1.91)
0.095 (2.41)
0.075 (1.90)
0.011 (0.28)
0.007 (0.18)
R TYP
0.075 (1.91)
REF
0.055 (1.40)
0.045 (1.14)
REF
19
18
14
13
20
BOTTOM
1
VIEW
0.150 (3.81)
BSC
0.200 (5.08)
REF
0.100 (2.54) REF
0.015 (0.38)
MIN
3
4
0.050 (1.27)
8
BSC
9
45° TYP
Figure 41. 20-Terminal Leadless Chip Carrier [LCC]
(E-20A)
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm)
0.320 (8.13)
0.290 (7.37)
0.015 (0.38)
0.008 (0.20)
0.020 (0.50)
R
0.028 (0.71)
0.022 (0.56)
BOTTOM
VIEW
(PINSUP)
0.048 (1.21)
0.042 (1.07)
0.005
(0.13)
MIN
PIN 1
0.200 (5.08)
MAX
0.200 (5.08)
0.125 (3.18)
0.023 (0.58)
0.014 (0.36)
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES; MILLIMETER DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF INCH EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN
Figure 39. 16-Lead Ceramic Dual In-Line Package [CERDIP]
0.048 (1.21)
0.042 (1.07)
3
4
TOP VIEW
(PINSDOWN)
8
0.020
(0.50)
9
0.356 (9.04)
R
0.350 (8.89)
0.395 (10.02)
0.385 (9.78)
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES; MILLIMETER DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF INCH EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN
0.100 (2.54)
0.064 (1.63)
0.358 (9.09)
0.342 (8.69)
SQ
0.088 (2.24)
0.054 (1.37)
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES; MILLIMETER DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF INCH EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN
Rev. C | Page 25 of 28

AD652
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Gain Drift, 100 kHz 1 MHz Linearity (%) Specified Temperature Range Package Options
AD652JP 50 ppm/°C max 0.02 max 0°C to +70°C PLCC (P-20A)
AD652JP-REEL 50 ppm/°C max 0.02 max 0°C to +70°C PLCC (P-20A)
AD652JP-REEL7 50 ppm/°C max 0.02 max 0°C to +70°C PLCC (P-20A)
AD652KP 25 ppm/°C max 0.005 max 0°C to +70°C PLCC (P-20A)
AD652KP-REEL 25 ppm/°C max 0.005 max 0°C to +70°C PLCC (P-20A)
AD652AQ2
50 ppm/°C max 0.02 max −40°C to +85°C CERDIP (Q-16)
AD652BQ2 25 ppm/°C max 0.005 max −40°C to +85°C CERDIP (Q-16)
AD652SE/883B2 50 ppm/°C max 0.02 max −55°C to +125°C LCC (E-20A)
AD652SQ2 50 ppm/°C max 0.02 max −55°C to +125°C CERDIP (Q-16)
AD652SQ/883B2 50 ppm/°C max 0.02 max −55°C to +125°C CERDIP (Q-16)
1
1
P = Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier; Q = CERDIP, E = Leadless Chip Carrier.
2
For details on grade and package offerings screened in accordance with MILSTD-883, refer to the Analog Devices Military Products Databook or current AD652/883
data sheet.
Rev. C | Page 26 of 28

AD652
NOTES
Rev. C | Page 27 of 28

AD652
NOTES
© 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
C00798–0–5/04(C)
Rev. C | Page 28 of 28
 Loading...
Loading...