Single-Supply
a
FEATURES
Single 5 V Power Supply
Single-Ended Dual-Channel Analog Inputs
92 dB (Typ) Dynamic Range
90 dB (Typ) S/(THD + N)
0.006 dB Decimator Pass-Band Ripple
Fourth Order, 64ⴛ Oversampling ⌺-⌬ Modulator
Three-Stage, Linear-Phase Decimator
256 ⴛ f
Less than 100 W (Typ) Power-Down Mode
Input Overrange Indication
On-Chip Voltage Reference
Flexible Serial Output Interface
28-Lead SOIC Package
APPLICATIONS
Consumer Digital Audio Receivers
Digital Audio Recorders, Including Portables
Multimedia and Consumer Electronics Equipment
Sampling Music Synthesizers
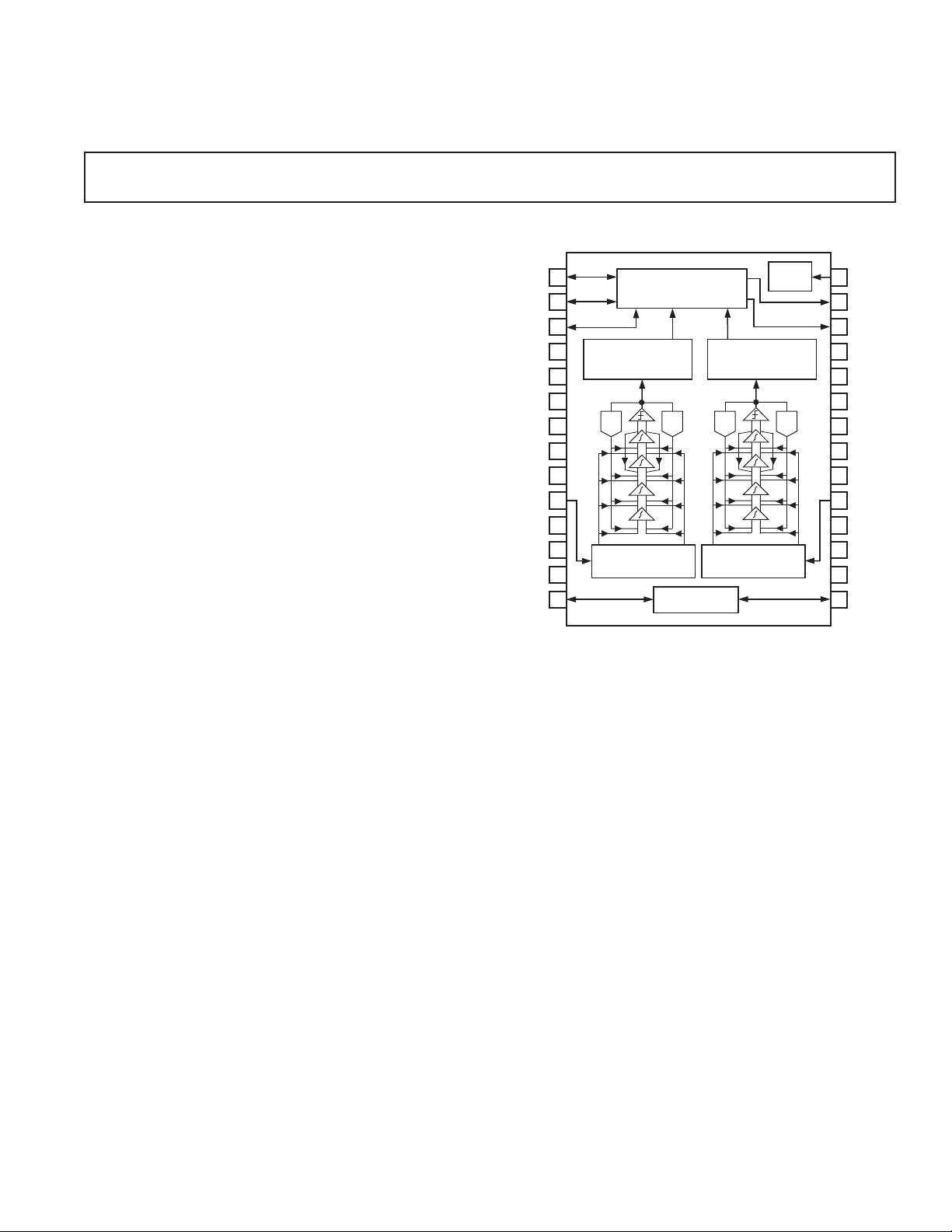
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The AD1870 is a stereo, 16-bit oversampling ADC based on
sigma-delta (⌺-⌬) technology intended primarily for digital
audio bandwidth applications requiring a single 5 V power supply.
Each single-ended channel consists of a fourth order one-bit
noise shaping modulator and a digital decimation filter. An on-chip
voltage reference, stable over temperature and time, defines the
full-scale range for both channels. Digital output data from both
channels are time multiplexed to a single, flexible serial interface. The AD1870 accepts a 256 × f
(f
is the sampling frequency) and operates in both serial port
S
Master and Slave Modes. In Slave Mode, all clocks must be externally derived from a common source.
Input signals are sampled at 64 × f
switched capacitors, eliminating external sample-and-hold amplifiers and minimizing the requirements for antialias filtering at the
input. With simplified antialiasing, linear phase can be preserved
across the pass band. The on-chip single-ended-to-differential signal converters save the board designer from having to provide
them externally. The AD1870’s internal differential architecture
provides increased dynamic range and excellent power supply
rejection characteristics. The AD1870’s proprietary fourth order
differential switched-capacitor ⌺-⌬ modulator architecture
*Protected by U.S. Patent Numbers 5055843, 5126653; others pend ing.
or 384 ⴛ fS Input Clock
S
CD-R, DCC, MD, and DAT
or a 384 × fS input clock
S
onto internally buffered
S
16-Bit ⌺-⌬ Stereo ADC
AD1870
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
LRCK
WCLK
BCLK
DV
DD
DGND1
RDEDGE
S/M
384/256
AV
VINL
CAPL1
CAPL2
AGNDL
V
REF
1
2
3
THREE-STAGE FIR
4
1
5
6
7
8
9
DD
10
11
12
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT
13
14
L
SERIAL OUTPUT
DECIMATION
FILTER
DAC
SINGLE-TO-
CONVERTER
INTERFACE
THREE-STAGE FIR
DAC DAC DAC
SINGLE-TO-
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT
CONVERTER
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
shapes the one-bit comparator’s quantization noise out of the
audio pass band. The high order of the modulator randomizes the
modulator output, reducing idle tones in the AD1870 to very
low levels. Because its modulator is single bit, the AD1870 is
inherently monotonic and has no mechanism for producing
differential linearity errors.
The input section of the AD1870 uses autocalibration to correct
any dc offset voltage present in the circuit, provided that the inputs
are ac-coupled. The single-ended dc input voltage can swing
between 0.7 V and 3.8 V typically. The AD1870 antialias input
circuit requires four external 470 pF NPO ceramic chip filter
capacitors, two for each channel. No active electronics are needed.
Decoupling capacitors for the supply and reference pins are
also required.
The dual-digital decimation filters are triple-stage, finite impulse
response filters for effectively removing the modulator’s high
frequency quantization noise and reducing the 64 × f
output data rate to an f
word rate. They provide linear phase
S
and a narrow transition band that properly digitizes 20 kHz signals
at a 44.1 kHz sampling frequency. Pass-band ripple is less than
0.006 dB, and stop-band attenuation exceeds 90 dB.
CLOCK
DIVIDER
DECIMATION
FILTER
AD1870
(Continued on Page 7)
*
CLKIN
28
27
TAG
26
SOUT
DV
25
DD
24
DGND2
23
RESET
22
MSBDLY
21
RLJUST
20
AGND
R
V
19
IN
CAPR1
18
17
CAPR2
AGNDR
16
V
15
REF
single-bit
S
2
R
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
AD1870–SPECIFICATIONS
TEST CONDITIONS UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED
Supply Voltages 5.0 V
Ambient Temperature 25 °C
Input Clock (f
Input Signal 991.768 Hz
Measurement Bandwidth 23.2 Hz to 19.998 kHz
Load Capacitance on Digital Outputs 50 pF
Input Voltage HI (V
Input Voltage LO (V
Master Mode, Data I
Device Under Test (DUT) bypassed and decoupled as shown in Figure 3.
DUT is antialiased and ac-coupled as shown in Figure 2. DUT is calibrated.
Values in bold typeface are tested; all others are guaranteed but not tested.
ANALOG PERFORMANCE
Resolution 16 Bits
Dynamic Range (20 Hz to 20 kHz, –60 dB Input)
Without A-Weight Filter 89 93 dB
With A-Weight Filter 92 96 dB
Signal to (THD + Noise) 86.5 90.5 dB
Signal to THD 94 dB
Analog Inputs
Single-Ended Input Range (± Full Scale)* V
Input Impedance at Each Input Pin 32 kΩ
V
REF
DC Accuracy
Gain Error ±0.5 ⴞ2.5 %
Interchannel Gain Mismatch 0.05 dB
Gain Drift 115 ppm/°C
Midscale Offset Error (After Calibration) ±3 ⴞ20 LSBs
Midscale Drift –0.2 LSB/°C
Crosstalk (EIAJ Method) –110 –100 dB
*VIN p-p = V
REF
) [256 × fS] 12.288 MHz
CLKIN
–0.5 dB Full Scale
) 2.4 V
IH
) 0.8 V
IL
2
S-Justified (Refer to Figure 14).
× 1.326.
Min Typ Max Unit
± 1.49 V
REF
2.05 2.25 2.55 V
Minimum Input V
Maximum Input V
–
=
REF
=+
REF
×
2
×
2
..1 326
1 326
–2–
REV. A
V
REF
V
REF
AD1870
DIGITAL I/O
Min Typ Max Unit
Input Voltage HI (V
Input Voltage LO (V
Input Leakage (I
Input Leakage (I
Output Voltage HI (V
Output Voltage LO (V
Input Capacitance 15 pF
DIGITAL TIMING (Guaranteed over –40°C to +85°C, DVDD = AVDD = 5 V ± 5%. Refer to Figures 17–19.)
t
CLKIN
f
CLKIN
t
CPWL
t
CPWH
t
RPWL
t
BPWL
t
BPWH
t
DLYCKB
t
DLYBLR
t
DLYBWR
t
DLYBWF
t
DLYDT
t
SETLRBS
t
DLYLRDT
t
SETWBS
t
DLYBDT
) 2.4 V
IH
) 0.8 V
IL
@ VIH = 5 V) 10 µA
IH
@ VIL = 0 V) 10 µA
IL
@ IOH = –2 mA) 2.4 V
OH
@ IOL = 2 mA) 0.4 V
OL
Min Typ Max Unit
CLKIN Period 48 81 780 ns
CLKIN Frequency (1/t
) 1.28 12.288 20.48 MHz
CLKIN
CLKIN LO Pulsewidth 15 ns
CLKIN HI Pulsewidth 15 ns
RESET LO Pulsewidth 50 ns
BCLK LO Pulsewidth 15 ns
BCLK HI Pulsewidth 15 ns
CLKIN Rise to BCLK Xmit (Master Mode) 15 ns
BCLK Xmit to LRCK Transition (Master Mode) 15 ns
BCLK Xmit to WCLK Rise 10 ns
BCLK Xmit to WCLK Fall 10 ns
BCLK Xmit to DATA/TAG Valid (Master Mode) 10 ns
LRCK Setup to BCLK Sample (Slave Mode) 10 ns
LRCK Transition to DATA/TAG Valid (Slave Mode)
No MSB Delay Mode (for MSB Only) 40 ns
WCLK Setup to BCLK Sample (Slave Mode)
Data Position Controlled by WCLK Input Mode 10 ns
BCLK Xmit to DATA/TAG Valid (Slave Mode)
All Bits Except MSB in No MSB Delay Mode
All Bits in MSB Delay Mode 40 ns
POWER
Min Typ Max Unit
Supplies
Voltage, Analog and Digital 4.75 5 5.25 V
Analog Current 43 52 mA
Analog Current–Power-Down (CLKIN Running) 25 µA
Digital Current 9.3 12 mA
Digital Current–Power-Down (CLKIN Running) 50 µA
Dissipation
Operation–Both Supplies 263 315 mW
Operation–Analog Supply 216 260 mW
Operation–Digital Supply 47 55 mW
Power-Down–Both Supplies (CLKIN Running) 375 µW
Power-Down–Both Supplies (CLKIN Not Running) 375 µW
Power Supply Rejection (See TPC 5)
1 kHz 300 mV p-p Signal at Analog Supply Pins 90 dB
20 kHz 300 mV p-p Signal at Analog Supply Pins 68 dB
Stop Band (>0.55 × fS)—any 300 mV p-p Signal 110 dB
REV. A
–3–
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
AD1870
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Min Typ Max Unit
Specifications Guaranteed +25 °C
Functionality Guaranteed –40 +85 °C
Storage –60 +100 °C
DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS
Min Typ Max Unit
Decimation Factor 64
Pass-Band Ripple 0.006 dB
Stop-Band* Attenuation 90 dB
48 kHz f
44.1 kHz f
32 kHz f
Other f
Group Delay 36/f
Group Delay Variation 0 µs
*Stop band repeats itself at multiples of 64 × fS, where fS is the output word rate. Thus the digital filter will attenuate to 0 dB across the frequency spectrum except
for a range ± 0.55 × fS wide at multiples of 64 × fS.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
(at Recommended Crystal Frequencies)
S
Pass Band 0 21.6 kHz
Stop Band 26.4 kHz
(at Recommended Crystal Frequencies)
S
Pass Band 0 20 kHz
Stop Band 24.25 kHz
(at Recommended Crystal Frequencies)
S
Pass Band 0 14.4 kHz
Stop Band 17.6 kHz
S
Pass Band 0 0.45 f
Stop Band 0.55 f
S
S
S
s
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Min Typ Max Unit
1 to DGND1 and DVDD2 to DGND2 0 +6 V
DV
DD
to AGND/AGNDL/AGNDR 0 +6 V
AV
DD
Digital Inputs DGND – 0.3 DV
Analog Inputs AGND – 0.3 AV
+ 0.3 V
DD
+ 0.3 V
DD
AGND to DGND –0.3 +0.3 V
Reference Voltage Indefinite Short Circuit to Ground
Soldering (10 sec) +300 °C
ORDERING GUIDE
Package Package
Model Temperature Description Option
AD1870AR –40°C to +85°C SOIC R-28
AD1870AR–REEL –40°C to +85°C SOIC R-28 in 13” Reel (1000 pcs.)
EVAL-AD1870EB Evaluation Board
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD1870 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–4–
REV. A
AD1870
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Input/ Pin
Pin Output Name Description
1 I/O LRCK Left/Right Clock
2 I/O WCLK Word Clock
3 I/O BCLK Bit Clock
4I DV
1 5 V Digital Supply
DD
5 I DGND1 Digital Ground
6 I RDEDGE Read Edge Polarity Select
7I S/M Slave/Master Select
8 I 384/256 Clock Mode
9I AV
10 I V
DD
L Left Channel Input
IN
5 V Analog Supply
11 O CAPL1 Left External Filter Capacitor 1
12 O CAPL2 Left External Filter Capacitor 2
13 I AGNDL Left Analog Ground
14 O V
15 O V
L Left Reference Voltage Output
REF
R Right Reference Voltage Output
REF
16 I AGNDR Right Analog Ground
17 O CAPR2 Right External Filter Capacitor 2
18 O CAPR1 Right External Filter Capacitor 1
19 I V
R Right Channel Input
IN
20 I AGND Analog Ground
21 I RLJUST Right/Left Justify
22 I MSBDLY Delay MSB One BCLK Period
23 I RESET Reset
24 I DGND2 Digital Ground
25 I DV
2 5 V Digital Supply
DD
26 O SOUT Serial Data Output
27 O TAG Serial Overrange Output
28 I CLKIN Master Clock
DEFINITIONS
Dynamic Range
The ratio of a full-scale output signal to the integrated output noise
in the pass band (20 Hz to 20 kHz), expressed in decibels (dB).
Dynamic range is measured with a –60 dB input signal and is equal
to (S/(THD + N)) 60 dB. Note that spurious harmonics are below
the noise with a –60 dB input, so the noise level establishes the
dynamic range. The dynamic range is specified with and without an A-Weight filter applied.
Signal to Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
(S/(THD + N))
The ratio of the root-mean-square (rms) value of the fundamental input signal to the rms sum of all other spectral components
in the pass band, expressed in decibels.
Signal to Total Harmonic Distortion (S/THD)
The ratio of the rms value of the fundamental input signal to the
rms sum of all harmonically related spectral components in the
pass band, expressed in decibels.
Pass Band
The region of the frequency spectrum unaffected by the attenuation of the digital decimator’s filter.
Pass-Band Ripple
The peak-to-peak variation in amplitude response from equalamplitude input signal frequencies within the pass band,
expressed in decibels.
Stop Band
The region of the frequency spectrum attenuated by the digital decimator’s filter to the degree specified by stop-band
attenuation.
Gain Error
With a near full-scale input, the ratio of actual output to
expected output, expressed as a percentage.
Interchannel Gain Mismatch
With identical near full-scale inputs, the ratio of outputs of the
two stereo channels, expressed in decibels.
Gain Drift
Change in response to a near full-scale input with a change in
temperature, expressed as parts-per-million (ppm) per °C.
Midscale Offset Error
Output response to a midscale dc input, expressed in least
significant bits (LSBs).
Midscale Drift
Change in midscale offset error with a change in temperature,
expressed as parts-per-million (ppm) per °C.
Crosstalk (EIAJ Method)
Ratio of response on one channel with a grounded input to a
full-scale 1 kHz sine wave input on the other channel, expressed
in decibels.
Power Supply Rejection
With no analog input, signal present at the output when a
300 mV p-p signal is applied to the power supply pins, expressed in decibels of full scale.
Group Delay
Intuitively, the time interval required for an input pulse to
appear at the converter’s output, expressed in milliseconds
(ms). More precisely, the derivative of radian phase with respect
to radian frequency at a given frequency.
Group Delay Variation
The difference in group delays at different input frequencies.
Specified as the difference between the largest and smallest
group delays in the pass band, expressed in microseconds (µs).
REV. A
–5–
AD1870
–Typical Performance Characteristics
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
dBFS
–100
–120
–140
2022201816141210864
FREQUENCY – kHz
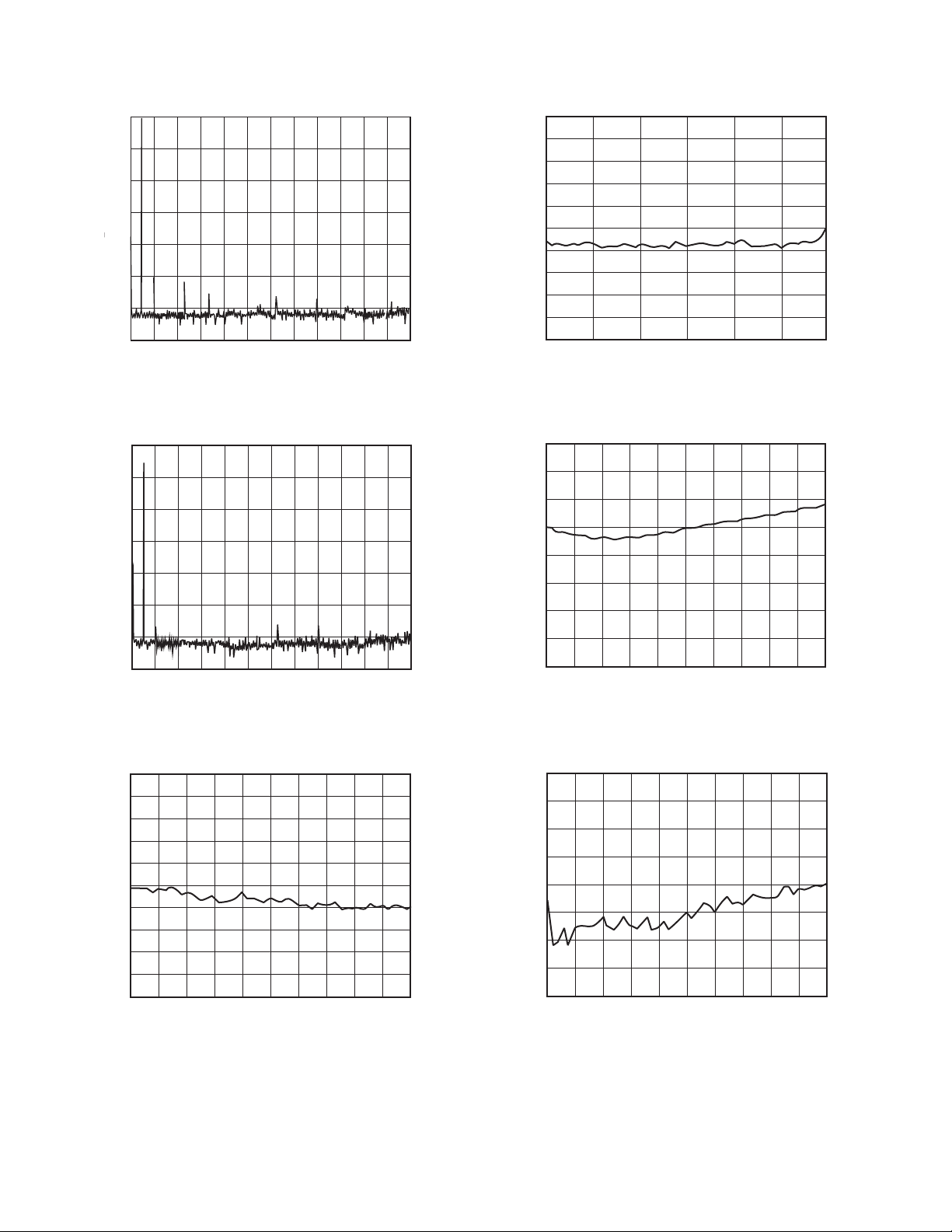
TPC 1. 1 kHz Tone at –0.5 dBFS (16 k-Point FFT)
0
–20
–40
–60
dBFS
–80
–100
–120
–80
–82
–84
–86
–88
–90
dBFS
–92
–94
–96
–98
–100
24
–60
INPUT AMPLITUDE – dBFS
–0.5–50 –40 –30 –20 –10
TPC 4. THD + N vs. Input Amplitude at 1 kHz
–60
–65
–70
–75
–80
dBFS
–85
–90
–95
–140
2
0
FREQUENCY – kHz
TPC 2. 1 kHz Tone at –10 dBFS (16 k-Point FFT)
–80
–82
–84
–86
–88
–90
dBFS
–92
–94
–96
–98
–100
2
0
FREQUENCY – kHz
1816141210864
TPC 3. THD + N vs. Frequency at –0.5 dBFS
22201816141210864
24
–100
20
FREQUENCY – kHz
TPC 5. Power Supply Rejection to 300 mV p-p on AV
–80
–85
–90
–95
–100
dBFS
–105
–110
–115
20
–120
2
0
FREQUENCY – kHz
20
1816141210864
DD
20
1816141210864
TPC 6. Channel Separation vs. Frequency at –0.5 dBFS
–6–
REV. A

AD1870
10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
dBFS
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
0.10.0
NORMALIZED
f
S
TPC 7. Digital Filter Signal Transfer Function to f
(
Continued from Page 1
)
1.0
0.90.80.70.60.50.40.30.2
S
The flexible serial output port produces data in two’s complement,
MSB-first format. The input and output signals are TTL
compatible. The port is configured by pin selections. Each 16-bit
output word of a stereo pair can be formatted within a 32-bit
field of a 64-bit frame as either right-justified, I
2
S compatible,
word clock controlled, or left-justified positions. Both 16-bit
samples can also be packed into a 32-bit frame, in left-justified
2
S compatible positions.
and I
The AD1870 is fabricated on a single monolithic integrated circuit
using a 0.5 µm CMOS double polysilicon, double metal process
and is offered in a plastic 28-lead SOIC package. Analog and
digital supply connections are separated to isolate the analog
circuitry from the digital supply and reduce digital crosstalk.
The AD1870 operates from a single 5 V power supply over the
temperature range of –40°C to +85°C and typically consumes
less than 260 mW of power.
THEORY OF OPERATION
⌺-⌬ Modulator Noise Shaping
The stereo, internally differential, analog modulator of the
AD1870 employs a proprietary feedforward and feedback architecture that passes input signals in the audio band with a unity
transfer function yet simultaneously shapes the quantization
noise generated by the one-bit comparator out of the audio
band (see Figure 1). Without the ⌺-⌬ architecture, this quantization noise would be spread uniformly from dc to one-half
the oversampling frequency, 64 × f
ⴙV
IN
V
IN
SINGLE-TO-
DIFFERENTIAL
CONVERTER
ⴚV
IN
.
S
DAC
MODULATOR
BITSTREAM
OUTPUT
DAC
Figure 1. Modulator Noise Shaper (One Channel)
⌺-⌬ architectures “shape” the quantization noise-transfer function
in a nonuniform manner. Through careful design, this transfer
function can be specified to high-pass filter the quantization
noise out of the audio band into higher frequency regions. The
AD1870 also incorporates a feedback resonator from the fourth
integrator’s output to the third integrator’s input. This resonator does not affect the signal transfer function but allows the
flexible placement of a zero in the noise transfer function for
more effective noise shaping.
Oversampling by 64 simplifies the implementation of a high
performance audio analog-to-digital conversion system. Antialias
requirements are minimal; a single pole of filtering will usually
suffice to eliminate inputs near f
and its higher multiples.
S
A fourth order architecture was chosen both to strongly shape
the noise out of the audio band and to help break up the idle
tones produced in all ⌺-⌬ architectures. These architectures
have a tendency to generate periodic patterns with a constant dc
input, a response that looks like a tone in the frequency domain.
These idle tones have a direct frequency dependence on the input
dc offset and an indirect dependence on temperature and time
as it affects the dc offset. The AD1870 suppresses idle tones 20
dB or better below the integrated noise floor.
The AD1870’s modulator was designed, simulated, and exhaustively tested to remain stable for any input within a wide
tolerance of its rated input range. The AD1870 is designed to
internally reset itself should it ever be overdriven, to prevent it
from going unstable. It will reset itself within 5 µs at a 48 kHz
sampling frequency after being overdriven. Overdriving the inputs
will produce a waveform “clipped” to plus or minus full scale.
See TPCs 1 through 6 for illustrations of the AD1870’s typical
analog performance as measured by an Audio Precision System
One. Signal-to-(distortion + noise) is shown under a range of
conditions. Note that there is a small variance between the
AD1870 analog performance specifications and some of the
performance plots. This is because the Audio Precision System
One measures THD and noise over a 20 Hz to 24 kHz bandwidth, while the analog performance is specified over a 20 Hz to
20 kHz bandwidth (i.e., the AD1870 performs slightly better
than the plots indicate). The power supply rejection graph (TPC 5)
illustrates the benefits of the AD1870’s internal differential architecture. The excellent channel separation shown in TPC 6 is
the result of careful chip design and layout.
Digital Filter Characteristics
The digital decimator accepts the modulator’s stereo bit stream
and simultaneously performs two operations on it. First, the
decimator low-pass filters the quantization noise that the modulator shaped to high frequencies and filters any other out-ofaudio-band input signals. Second, it reduces the data rate to an
output word rate equal to f
. The high frequency bit stream is
S
decimated to stereo 16-bit words at 48 kHz (or other desired
f
). The out-of-band one-bit quantization noise and other high
S
frequency components of the bit stream are attenuated by at
least 90 dB.
The AD1870 decimator implements a symmetric finite impulse
response (FIR) filter that possesses a linear phase response.
This filter achieves a narrow transition band (0.1 × f
), high
S
stop-band attenuation (>90 dB), and low pass-band ripple
(<0.006 dB). The narrow transition band allows the unattenuated digitization of 20 kHz input signals with f
as low as
S
REV. A
–7–

AD1870
44.1 kHz. The stop-band attenuation is sufficient to eliminate
modulator quantization noise from affecting the output. Low
pass-band ripple prevents the digital filter from coloring the
audio signal. See TPC 7 for the digital filter’s characteristics.
The output from the decimator is available as a single serial
output, multiplexed between left and right channels.
Note that the digital filter itself is operating at 64 × f
. As a
S
consequence, Nyquist images of the pass-band, transition band,
and stop band will be repeated in the frequency spectrum at
multiples of 64 × f
. Thus the digital filter will attenuate to
S
greater than 90 dB across the frequency spectrum, except for a
window ±0.55 × f
wide centered at multiples of 64 × fS. Any in-
S
put signals, clock noise, or digital noise in these frequency
windows will not be attenuated to the full 90 dB. If the high
frequency signals or noise appear within the pass-band images
within these windows, they will not be attenuated at all, and
input antialias filtering should therefore be applied.
Sample Delay
The sample delay or “group delay” of the AD1870 is dominated
by the processing time of the digital decimation filter. FIR filters
convolve a vector representing time samples of the input with
an equal-sized vector of coefficients. After each convolution, the
input vector is updated by adding a new sample at one end of
the “pipeline” and discarding the oldest input sample at the
other. For a FIR filter, the time at which a step input appears at
the output will be when that step input is halfway through
the input sample vector pipeline. The input sample vector
is updated every 64 × f
. The equation that expresses the
S
group delay for the AD1870 is:
Group Delay (sec) = 36/f
(Hz)
S
For the most common sample rates, this can be summarized as:
f
S
Group Delay
48 kHz 750 µs
44.1 kHz 816 µs
32 kHz 1125 µs
Due to the linear phase properties of FIR filters, the group
delay variation, or differences in group delay at different
frequencies, is essentially zero.
OPERATING FEATURES
Voltage Reference and External Filter Capacitors
The AD1870 includes a 2.25 V on-board reference that determines the AD1870’s input range. The left and right reference
pins (Pin 14 and Pin 15) should be bypassed with a 0.1 µF
ceramic chip capacitor in parallel with a 4.7 µF tantalum as
shown in Figure 3. Note that the chip capacitor should be closest to the pin. The internal reference can be overpowered by
applying an external reference voltage at the V
V
R (Pin 15) pins, allowing multiple AD1870s to be calibrated
REF
L (Pin 14) and
REF
to the same gain. It is not possible to overpower the left and
right reference pins individually; the external reference voltage
should be applied to both Pin 14 and Pin 15. Note that the reference pins must still be bypassed as shown in Figure 3.
While it is possible to bypass each reference pin (V
V
R) with a capacitor larger than the suggested 4.7 µF, it
REF
REF
L and
is not recommended. A larger capacitor will have a longer
charge-up time, which may extend into the autocalibration period,
yielding incorrect results.
The AD1870 requires four external filter capacitors on Pins 11,
12, 17, and 18. These capacitors are used to filter the single-todifferential converter outputs and are too large for practical
integration onto the die. They should be 470 pF NPO ceramic
chip type capacitors, as shown in Figure 3, placed as close to
the AD1870 package as possible.
Sample Clock
An external master clock supplied to CLKIN (Pin 28) drives
the AD1870 modulator, decimator, and digital interface. As
with any analog-to-digital conversion system, the sampling clock
must be low jitter to prevent conversion errors. If a crystal oscillator is used as the clock source, it should be bypassed with a
0.1 µF capacitor, as shown below in Figure 3.
For the AD1870, the input clock operates at either 256 × f
384 × f
as selected by the 384/256 pin. When 384/256 is HI,
S
S
or
the 384 Mode is selected; when 384/256 is LO, the 256
Mode is selected. In both cases, the clock is divided down to
obtain the 64 × f
word rate itself will be at f
clock required for the modulator. The output
S
. This relationship is illustrated for
S
popular sample rates below:
256 Mode 384 Mode Modulator Output Word
CLKIN CLKIN Sample Rate Rate
12.288 MHz 18.432 MHz 3.072 MHz 48 kHz
11.2896 MHz 16.9344 MHz 2.822 MHz 44.1 kHz
8.192 MHz 12.288 MHz 2.048 MHz 32 kHz
The AD1870 serial interface will support both Master and Slave
Modes. Note that in Slave Mode it is required that the serial
interface clocks be externally derived from a common source.
In Master Mode, the serial interface clock outputs are internally
derived from CLKIN.
Reset, Autocalibration, and Power-Down
The active LO RESET pin (Pin 23) initializes the digital decimation filter and clears the output data buffer. While in the reset
state, all digital pins defined as outputs of the AD1870 are
driven to ground (except for BCLK, which is driven to the state
defined by RDEDGE (Pin 6)). Analog Devices recommends
resetting the AD1870 on initial power-up so that the device is
properly calibrated. The reset signal must remain LO for the
minimum period specified in the Specifications section. The reset
pulse is asynchronous with respect to the master clock, CLKIN.
If, however, multiple AD1870s are used in a system, and it is
desired that they leave the reset state at the same time, the
common reset pulse should be made synchronous to CLKIN
(i.e., RESET should be brought HI on a CLKIN falling edge).
Multiple AD1870s can be synchronized to each other by using
a single master clock and a single reset signal to initialize all
devices. On coming out of reset, all AD1870s will begin sampling at the same time. Note that in Slave Mode, the AD1870
is inactive (and all outputs are static, including WCLK) until
the first rising edge of LRCK after the first falling edge of
LRCK. This initial low going then high going edge of LRCK can
be used to “skew” the sampling start-up time of one AD1870
relative to other AD1870s in a system. In the data position controlled by the WCLK Input Mode, WCLK must be HI with
LRCK HI, then WCLK HI with LRCK LO, then WCLK HI
with LRCK HI before the AD1870 starts sampling.
–8–
REV. A

AD1870
The AD1870 achieves its specified performance without the
need for user trims or adjustments. This is accomplished through
the use of on-chip automatic offset calibration that takes place
immediately following reset. This procedure nulls out any offsets in the single-to-differential converter, the analog modulator,
and the decimation filter. Autocalibration completes in approximately 8192 × (1/(F
) seconds and need only be performed
LRCK
once at power-up in most applications. (In Slave Mode, the 8192
cycles required for autocalibration do not start until after the
first rising edge of LRCK following the first falling edge of
LRCK.) The autocalibration scheme assumes that the inputs
are ac-coupled. DC-coupled inputs will work with the AD1870,
but the autocalibration algorithm will yield an incorrect offset
compensation.
The AD1870 also features a Power-Down Mode. It is enabled
by the active LO RESET Pin 23 (i.e., the AD1870 is in PowerDown Mode while RESET is held LO). The power savings are
specified in the Specifications section. The converter is shut
down in the power-down state and will not perform conversions.
The AD1870 will be reset upon leaving the power-down state, and
autocalibration will commence after the RESET pin goes HI.
Power consumption can be further reduced by slowing down the
master clock input (at the expense of input pass band width).
Note that a minimum clock frequency, f
, is specified for
CLKIN
the AD1870.
TAG Overrange Output
The AD1870 includes a TAG serial output (Pin 27) that is provided to indicate status on the level of the input voltage. The
TAG output is at TTL compatible logic levels. A pair of unsigned
binary bits are output, synchronous with LRCK (MSB then
LSB), that indicate whether the current signal being converted
is: more than 1 dB under full scale, within 1 dB under full scale,
within 1 dB over full scale, or more than 1 dB over full scale.
The timing for the TAG output is shown in Figures 7–16. Note
that the TAG Bits are not “sticky”; i.e., they are not peak reading, but rather change with every sample. Decoding of these two
bits is as follows:
APPLICATION ISSUES
Recommended Input Structure
The AD1870 input structure is single-ended to allow the board
designer to achieve a high level of functional integration. The
very simple recommended input circuit is shown in Figure 2. Note
the 1 µF ac-coupling capacitor, which allows input level shifting
for 5 V only operation and for autocalibration to properly null
offsets. The 3 dB point of the single-pole antialias RC filter is
240 kHz, which results in essentially no attenuation at 20 kHz.
Attenuation at 3 MHz is approximately 22 dB, which is adequate
to suppress f
noise modulation. If the analog inputs are exter-
S
nally ac-coupled, the 1 µF ac-coupling capacitors shown in
Figure 2 are not required.
2.2nF
NPO
2.2nF
NPO
1F
1F
VINR
AD1870
V
L
IN
RIGHT
INPUT
LEFT
INPUT
300⍀
300⍀
Figure 2. Recommended Input Structure for Externally
DC-Coupled Inputs
Analog Input Voltage Swing
The single-ended input range of the analog inputs is specified in
relative terms in the Specifications section. The input level at
which clipping occurs linearly tracks the voltage reference
level; i.e., if the reference is high relative to the typical 2.25
V, the allowable input range without clipping is correspondingly
wider, and if the reference is low relative to the typical 2.25 V,
the allowable input range is correspondingly narrower.
Thus the maximum input voltage swing can be computed using
the following ratio:
225
.( )
V Nominal Reference Voltage
2 983
.( )
V p p Nominal Voltage Swing
=
()
X V Measured Referenc Voltage
()
Y V Maximum Swing Without Clipping−
e
TAG Bits
MSB LSB Meaning
0 0 More than 1 dB under Full Scale
0 1 Within 1 dB under Full Scale
1 0 Within 1 dB over Full Scale
1 1 More Than 1 dB over Full Scale
REV. A
–9–

AD1870
Layout and Decoupling Considerations
Obtaining the best possible performance from the AD1870
requires close attention to board layout. Adhering to the following principles will produce typical values of 92 dB dynamic range
and 90 dB S/(THD + N) in target systems. Schematics and layout artwork of the AD1870 Evaluation Board, which implement
these recommendations, are available from Analog Devices.
The principles and their rationales are listed below. The first
two pertain to bypassing and are illustrated in Figure 3.
470pF
NPO
4.7F
0.1F
470pF
NPO
AGNDL V
REFLVREF
CAPL2
CAPL1
AGND AVDDDVDD1 DGND1
0.1F
4.7F
0.1F
R
AGNDR
AD1870
10nF
470pF
NPO
CAPR2 CAPR1
CLKIN
DGND2 DV
DD
10nF
470pF
NPO
2
5V
DIGITAL
0.1F
OSCILLATOR
LRCK
WCLK
BCLK
DV
DD
DGND1
RDEDGE
S/M
384/256
AV
VINL
CAPL1
CAPL2
AGNDL
V
REF
1
2
3
4
1
DD
L
DIGITAL GROUND PLANE
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
ANALOG GROUND PLANE
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
CLKIN
TAG
SOUT
DV
DD
DGND2
RESET
MSBDLY
RLJUST
AGND
R
V
IN
CAPR1
CAPR2
AGNDR
V
REF
2
R
1F
5V
ANALOG5VDIGITAL
1F
1F
DIGITAL
5V
Figure 3. Recommended Bypassing and Oscillator Circuits
There are two pairs of digital supply pins on opposite sides of
the part (Pins 4 and 5 and Pins 24 and 25). The user should tie
a bypass chip capacitor (10 nF ceramic) in parallel with a decoupling capacitor (1 µF tantalum) on each pair of supply pins as
close to the pins as possible. The traces between these package
pins and the capacitors should be as short and as wide as possible. This will prevent digital supply current transients from
being inductively transmitted to the inputs of the part.
Use a 0.1 µF chip analog capacitor in parallel with a 1.0 µF
tantalum capacitor from the analog supply (Pin 9) to the analog
ground plane. The trace between this package pin and the
capacitor should be as short and as wide as possible.
The AD1870 should be placed on a split ground plane. The
digital ground plane should be placed under the top end of the
package, and the analog ground plane should be placed under
the bottom end of the package as shown in Figure 4. The split
should be between Pins 8 and 9 and between Pins 20 and 21.
The ground planes should be tied together at one spot underneath the center of the package with an approximately 3 mm
trace. This ground plane technique also minimizes RF transmission and reception.
Figure 4. Recommended Ground Plane
Each reference pin (Pin 14 and Pin 15) should be bypassed with
a 0.1 µF ceramic chip capacitor in parallel with a 4.7 µF tantalum
capacitor. The 0.1 µF chip cap should be placed as close to the
package pin as possible, and the trace to it from the reference
pin should be as short and as wide as possible. Keep this trace
away from any analog traces (Pins 10, 11, 12, 17, 18, 19). Coupling between input and reference traces will cause even order
harmonic distortion. If the reference is needed somewhere else
on the printed circuit board, it should be shielded from any signal
dependent traces to prevent distortion.
Wherever possible, minimize the capacitive load on the digital
outputs of the part. This will reduce the digital spike currents
drawn from the digital supply pins and help keep the IC substrate quiet.
How to Extend SNR
A cost-effective method of improving the dynamic range and
SNR of an analog-to-digital conversion system is to use multiple
AD1870 channels in parallel with a common analog input. This
technique makes use of the fact that the noise in independent
modulator channels is uncorrelated. Thus every doubling of the
number of AD1870 channels used will improve the system dynamic range by 3 dB. The digital outputs from the corresponding deci-mator channels must be arithmetically averaged to
obtain the improved results in the correct data format. A microprocessor, either general purpose or DSP, can easily perform
the averaging operation.
–10–
REV. A

AD1870
Figure 5 shows a circuit for obtaining a 3 dB improvement in
dynamic range by using both channels of a single AD1870 with a
mono input. A stereo implementation would require using
two AD1870s and using the recommended input structure
shown in Figure 2. Note that a single microprocessor would likely
be able to handle the averaging requirements for both left and
right channels.
DIGITAL INTERFACE
Modes of Operation
The AD1870’s flexible serial output port produces data in
two’s-complement, MSB-first format. The input and output
signals are TTL logic-level compatible. Time multiplexed serial
data is output on SOUT (Pin 26), left channel then right channel, as determined by the left/right clock signal LRCK (Pin 1).
Note that there is no method for forcing the right channel to
SINGLE
CHANNEL
INPUT
AD1870
RECOMMENDED
INPUT BUFFER
VINR
AD1870
L
V
IN
DIGITAL
AVERAGER
Figure 5. Increasing Dynamic Range By Using Two
AD1870 Channels
SINGLE
CHANNEL
OUTPUT
precede the left channel. The port is configured by pin selections.
The AD1870 can operate in either Master or Slave Mode, with
the data in right-justified, I
2
S compatible, word clock controlled,
or left-justified positions.
The various mode options are pin programmed with the S/M
(Slave/Master) Pin (7), the Right/Left Justify Pin (21), and the
MSBDLY Pin (22). The function of these pins is summarized
below.
S/M RLJUST MSBDLY WCLK BCLK LRCK Serial Port Operation Mode
1 1 1 Output Input Input Slave Mode. WCLK frames the data. The MSB is output on the
17th BCLK cycle. Provides right-justified data in slave mode
with a 64 × fS BCLK frequency. See Figure 7.
1 1 0 Input Input Input Slave Mode. The MSB is output in the BCLK cycle after
WCLK is detected HI. WCLK is sampled on the BCLK active
edge, with the MSB valid on the next BCLK active edge. Tying
WCLK HI results in I2S-justified data. See Figure 8.
1 0 1 Output Input Input Slave Mode. Data left-justified with WCLK framing the data.
WCLK rises immediately after an LRCK transition. The MSB is
valid on the first BCLK active edge. See Figure 9.
2
1 0 0 Output Input Input Slave Mode. Data I
S-justified with WCLK framing the data.
WCLK rises in the second BCLK cycle after an LRCK transition. The MSB is valid on the second BCLK active edge. See
Figure 10.
0 1 1 Output Output Output Master Mode. Data right-justified. WCLK frames the data,
going HI in the 17th BCLK cycle. BCLK frequency = 64 × fS.
See Figure 11.
0 1 0 Output Output Output Master Mode. Data right-justified + 1. WCLK is pulsed in the
17th BCLK cycle, staying HI for only 1 BCLK cycle. BCLK
frequency = 64 × fS. See Figure 12.
0 0 1 Output Output Output Master Mode. Data left-justified. WCLK frames the data.
BCLK frequency = 64 × fS. See Figure 13.
0 0 0 Output Output Output Master Mode. Data I
2
S-justified. WCLK frames the data.
BCLK frequency = 64 × fS. See Figure 14.
REV. A
–11–

AD1870
Serial Port Data Timing Sequences
The RDEDGE input (Pin 6) selects the bit clock (BCLK) polarity.
RDEDGE HI causes data to be transmitted on the BCLK falling
edge and valid on the BCLK rising edge; RDEDGE LO causes
data to be transmitted on the BCLK rising edge and valid on
the BCLK falling edge. This is shown in the serial data output
timing diagrams. The term “sampling” is used generically to
denote the BCLK edge (rising or falling) on which the serial data is
valid. The term “transmitting” is used to denote the other BCLK
edge. The S/M input (Pin 7) selects Slave Mode (S/M HI) or
Master Mode (S/M LO). Note that in Slave Mode, BCLK may be
continuous or gated, i.e., a stream of pulses during the data phase
followed by periods of inactivity between channels.
In the Master Modes, the bit clock (BCLK), the left/right clock
(LRCK), and the word clock (WCLK) are always outputs, generated internally in the AD1870 from the master clock (CLKIN)
input. In Master Mode, a LRCK cycle defines a 64-bit “frame.”
LRCK is HI for a 32-bit “field” and LRCK is LO for a 32bit “field.”
In the Slave Modes, the bit clock (BCLK) and the left/right clock
(LRCK) are user-supplied inputs. The word clock (WCLK) is an
internally generated output, except when S/M is HI, RLJUST is
HI, and MSBDLY is LO when it is a user-supplied input that
controls the data position. Note that the AD1870 does not support asynchronous operation in Slave Mode; the clocks
(CLKIN, LRCK, BCLK, and WCLK) must be externally
derived from a common source. In general, CLKIN should be
divided down externally to create LRCK, BCLK, and WCLK.
In the Slave Modes, the relationship between LRCK and BCLK
is not fixed to the extent that there can be an arbitrary number
of BCLK cycles between the end of the data transmission and
the next LRCK transition. The Slave Mode timing diagrams are
therefore simplified as they show precise 32-bit fields and
64-bit frames.
In two Slave Modes, it is possible to pack two 16-bit samples in
a single 32-bit frame, as shown in Figures 15 and 16. BCLK,
LRCK, DATA, and TAG operate at one-half the frequency
(twice the period) as in the 64-bit frame modes. This 32-Bit
Frame Mode is enabled by pulsing the LRCK HI for a minimum of one BCLK period to a maximum of 16 BCLK periods.
The LRCK HI for one BCLK period case is shown in Figures 15
and 16. With a one or two BCLK period HI pulse on LRCK,
note that both the left and right TAG Bits are output immediately, back to back. With a three-to-sixteen BCLK period HI pulse
on LRCK, the left TAG Bits are followed by one to fourteen
“dead” cycles, i.e., zeros, followed by the right TAG Bits. Also
note that WCLK stays HI continuously when the AD1870 is
in the 32-Bit Frame Mode. Figure 15 illustrates the left-justified
case, while Figure 16 illustrates the I
2
S-justified case.
In all modes, the left and right channel data is updated with the
next sample within the last 1/8 of the current conversion cycle, i.e.,
within the last four BCLK cycles in 32-Bit Frame Mode, and
within the last eight BCLK cycles in 64-Bit Frame Mode. The
user must constrain the output timing such that the MSB of the
right channel is read before the final 1/8 of the current conversion period.
Two modes deserve special discussion. The first special mode,
Slave Mode, Data Position Controlled by WCLK Input
(S/M = HI, RLJUST = HI, MSBDLY = LO), shown in
Figure 8, is the only mode in which WCLK is an input. The
16-bit output data-words can be placed at user-defined locations within 32-bit fields. The MSB will appear in the BCLK
period after WCLK is detected HI by the BCLK sampling edge.
If WCLK is HI during the first BCLK of the 32-bit field, i.e, if
WCLK is tied HI, then the MSB of the output word will be
valid on the sampling edge of the second BCLK. The effect is to
delay the MSB for one bit clock cycle into the field, making the
output data compatible at the data format level with the I
2
S data
format. Note that the relative placement of the WCLK input
can vary from 32-bit field to 32-bit field, even within the
same 64-bit frame. For example, within a single 64-bit frame,
the left word could be right-justified (by pulsing WCLK HI on
the 16th BCLK) and the right word could be in an I
2
S compatible data format (by having WCLK HI at the beginning of the second field).
In the second special mode, Master Mode, Right-Justified
with MSB Delay, WCLK Pulsed in 17th BCLK Cycle (S/M
= LO, RLJUST = HI, MSBDLY = LO), shown in Figure 12,
WCLK is an output and is pulsed for one cycle by the AD1870.
The MSB is valid on the 18th BCLK sampling edge, and the
LSB extends into the first BCLK period of the next 32-bit field.
–12–
REV. A

AD1870
Timing Parameters
For master modes, a BCLK transmitting edge (labeled “XMIT”)
will be delayed from a CLKIN rising edge by t
DLYCKB
, as shown
in Figure 17. A LRCK transition will be delayed from a BCLK
transmitting edge by t
delayed from a BCLK transmitting edge by t
. A WCLK rising edge will be
DLYBLR
DLYBWR
, and a WCLK
falling edge will be delayed from a BCLK transmitting edge by
. The DATA and TAG outputs will be delayed from a
t
DLYBWF
transmitting edge of BCLK by t
DLYDT
.
For slave modes, an LRCK transition must be set up to a BCLK
sampling edge (labeled “SAMPLE”) by t
SETLRBS
(see Figure 18).
The DATA and TAG outputs will be delayed from an LRCK
transition by t
DLYLRDT
delayed from BCLK transmitting edge by t
, and DATA and TAG outputs will be
. For Slave
DLYBDT
Mode, Data Position Controlled by WCLK Input, WCLK must
be set up to a BCLK sampling edge by t
SETWBS
.
For both Master and Slave Modes, BCLK must have a minimum LO pulsewidth of t
t
.
BPWH
and a minimum HI pulsewidth of
BPWL
The AD1870 CLKIN and RESET timing is shown in Figure 19.
CLKIN must have a minimum LO pulsewidth of t
minimum HI pulsewidth of t
CLKIN is given by t
pulsewidth of t
RPWL
. RESET must have a minimum LO
CLKIN
. Note that there are no setup or hold time
. The minimum period of
CPWH
CPWL
and a
requirements for RESET.
Master Clock (CLKIN) Considerations
It is recommended that the BCLK and LRCK are derived from
CLKIN to ensure correct phase relationships. The modulator
of the AD1870 runs at 64 × f
obtained when the BCLK rate equals 64 × f
. Therefore, best performance is
S
or 32 × fS. BCLK
S
rates such as 48 × f
may result in an increased spectral noise
S
floor, depending on the phase relationship of BCLK to CLKIN.
Synchronizing Multiple AD1870s
Multiple AD1870s can be synchronized by making all the
AD1870s serial port slaves. This option is illustrated in Figure 6.
See the Reset, Autocalibration, and Power-Down section for
additional information.
CLOCK
SOURCE
#1 AD1870
SLAVE MODE
RESET
CLKIN
#2 AD1870
SLAVE MODE
RESET
CLKIN
#N AD1870
SLAVE MODE
RESET
CLKIN
DATA
BCLK
WCLK
LRCK
DATA
BCLK
WCLK
LRCK
DATA
BCLK
WCLK
LRCK
Figure 6. Synchronizing Multiple AD1870s
REV. A
–13–

AD1870
RDEDGE = LO
RDEDGE = HI
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
RDEDGE = LO
RDEDGE = HI
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
LRCK
INPUT
BCLK
INPUT
WCLK
31 32 1 2 15 16 17 18 19 32 1 2 15 16 17 18 19 32 1 2
BCLK
SOUT
TAG
PREVIOUS DATA
MSB-14 LSB
ZEROS
LEFT TAG
MSB LSB
LEFT DATA
MSB MSB
MSB-1
MSB-2
LSB
ZEROS
RIGHT TAG
MSB LSB
RIGHT DATA
MSB-1 MSB-2
Figure 7. Serial Data Output Timing: Slave Mode, Right-Justified with No MSB Delay,
S/M = Hl, RLJUST = Hl,
LRCK
INPUT
BCLK
INPUT
BCLK
SOUT
WCLK
INPUT
TAG
ZEROS
1234 17 1234 17
LEFT TAG
MSB
MSB
LSB
MSBDLY
LEFT DATA
MSB-1
MSB-2
= Hl
LSB
ZEROS
RIGHT TAG
MSB
RIGHT DATA
MSB
LSB
MSB-1 MSB-2
LSB
LSB
ZEROS
LEFT TAG
MSB LSB
ZEROS
Figure 8. Serial Data Output Timing: Slave Mode, Data Position Controlled by WCLK Input,
S/
LRCK
INPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = LO
INPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = HI
SOUT
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
TAG
OUTPUT
Figure 9. Serial Data Output Timing: Slave Mode, Left-Justified with No MSB Delay, S/M = Hl,
R
M
= Hl, RLJUST = Hl,
31 32 1 2 3 4 16
LEFT DATA
MSB
MSB-1
LEFT TAG
LSB
MSB
L
JUST = LO,
MSBDLY
MSBDLY
MSB-2
= Hl
= LO
17 18 17 18
LSB
31 32 1 2 3 4 16
ZEROSZEROS
RIGHT DATA
MSB
MSB
MSB-1
RIGHT TAG
LSB
MSB-2
LSB
ZEROS
–14–
REV. A

LRCK
INPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = LO
INPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = HI
SOUT
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
TAG
OUTPUT
32 1 2 3 4 17
MSB
MSB
LSB
LEFT DATA
MSB-1
ZEROS
LEFT TAG
5 5
MSB-2
LSB
31 32 1 2 3 4 17
MSB
RIGHT DATA
MSB
LSB
MSB-1
MSB-2
ZEROS
RIGHT TAG
LSB
AD1870
ZEROS
Figure 10. Serial Data Output Timing: Slave Mode, I2S-Justified, S/M = Hl, RLJUST = LO,
LRCK
OUTPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = LO
OUTPUT
RDEDGE = HI
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
31 32 1 2 15 16 17 18 19 32 1 2 15 16 17 18 19 32 1 2
BCLK
SOUT
TAG
PREVIOUS DATA
MSB-14 LSB
ZEROS ZEROS
LEFT TAG
MSB LSB
LEFT DATA
MSB MSB
MSB-1
MSB-2
LSB
RIGHT TAG
MSB LSB
RIGHT DATA
MSB-1 MSB-2
Figure 11. Serial Data Output Timing: Master Mode, Right-Justified with No MSB Delay, S/M = LO,
R
L
LRCK
OUTPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = LO
OUTPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = HI
SOUT
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
TAG
OUTPUT
JUST = Hl,
PREVIOUS DATA
MSB-14 LSB
MSBDLY
32 1 2 16 17 18 19 1 2 16 17 18 19 20 1 2
LEFT TAG
MSB LSB
= Hl
20
ZEROS ZEROS
LEFT DATA
MSB MSB
MSB-1
MSB-2
LSB
RIGHT TAG
MSB LSB
RIGHT DATA
MSB-1 MSB-2
MSBDLY
LSB
LSB
= LO
ZEROS
LEFT TAG
MSB
ZEROS
LSB
REV. A
Figure 12. Serial Data Output Timing: Master Mode, Right-Justified with MSB Delay,
WCLK Pulsed in 17th BCLK Cycle, S/
M
= LO, RLJUST = Hl,
MSBDLY
= LO
–15–

AD1870
RDEDGE = LO
RDEDGE = HI
RDEDGE = LO
RDEDGE = HI
LRCK
OUTPUT
BCLK
OUTPUT 17 1817 18
BCLK
SOUT
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
TAG
OUTPUT
31 32 1 2 3 16
LEFT DATA
MSB
MSB
MSB-1
LEFT TAG
LSB
MSB-2
LSB
31 32 1 2 3 16
ZEROSZEROS ZEROS
RIGHT DATA
MSB
MSB
MSB-1
RIGHT TAG
LSB
MSB-2
Figure 13. Serial Data Output Timing: Master Mode, Left-Justified with No MSB Delay,
M
LRCK
OUTPUT
BCLK
OUTPUT
BCLK
SOUT
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
TAG
OUTPUT
= LO, RLJUST = LO,
S/
321234 17
LEFT DATA
MSB
MSB-1
LEFT TAG
MSB
LSB
MSB-2
MSBDLY
LSB
= Hl
31 32 1 2 3 4 17
MSB
RIGHT DATA
MSB
LSB
MSB-1
MSB-2
ZEROSZEROS ZEROS
RIGHT TAG
LSB
LSB
Figure 14. Serial Data Output Timing: Master Mode, I2S-Justified, S/M = LO, RLJUST = LO,
MSBDLY
LRCK
INPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = LO
INPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = HI
SOUT
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
TAG
OUTPUT
= LO
31 32 1 2 3 4 16
PREVIOUS DATA
LSB
MSB-14
LEFT DATA
MSB
MSB-1 MSB-2 MSB-3
LEFT TAG
LSB
MSB
RIGHT TAG LEFT TAG
MSB
51718
MSB-4 MSB-3 MSB-4
HI HI
LSB
LSB
MSB
19 20 21 32 1 2
RIGHT DATA
MSB-1 MSB-2
LSB
Figure 15. Serial Data Output Timing: Slave Mode, Left-Justified with No MSB Delay,
M
32-Bit Frame Mode, S/
= Hl, RLJUST = LO,
MSBDLY
= Hl
LEFT DATA
MSB
MSB
MSB-1
LSB
–16–
REV. A

LRCK
INPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = LO
INPUT
BCLK
RDEDGE = HI
SOUT
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
TAG
OUTPUT
Figure 16. Serial Data Output Timing: Slave Mode, I2S-Justified, 32-Bit Frame Mode,
M
S/
CLKIN
INPUT
BCLK OUTPUT (64 x
RDEDGE = LO
BCLK OUTPUT (64 x
RDEDGE = HI
LRCK
OUTPUT
WCLK
OUTPUT
DATA AND TAG
OUTPUTS
32 1 2 3 4 5 17
PREVIOUS DATA
LSB
MSB-14
LEFT TAG
MSB
= Hl, RLJUST = LO,
t
f
)
S
f
)
S
DLYCKB
t
MSB
LSB
XMIT
DLYBLR
LEFT DATA
MSB-1 MSB-2 MSB-3
RIGHT TAG
MSB LSB
MSBDLY
XMIT
= LO
t
DLYBWR
61819
LSB
MSB-4 MSB-3 MSB-4
HI HI
MSB MSB
XMIT XMIT
t
DLYBWF
20 21 22 1 2 3
RIGHT DATA
MSB-1 MSB-2
t
DLYDT
t
BPWL
t
BPWH
LSB
LEFT TAG
MSB
t
BPWH
t
BPWL
LEFT DATA
LSB
AD1870
MSB-1
RIGHT TAG
MSB
CLKIN INPUT
RESET INPUT
BCLK INPUT
RDEDGE = LO
BCLK OUTPUT
RDEDGE = HI
LRCK
INPUT
WCLK
INPUT
DATA AND TAG
OUTPUTS
t
CPWH
Figure 17. Master Mode Clock Timing
XMIT
SAMPLE XMIT SAMPLE
t
SETLRBS
t
SETWBS
t
DLYLRDT
MSB MSB-1
t
DLYBDT
Figure 18. Slave Mode Clock Timing
t
CLKIN
t
CPWL
t
RPWL
Figure 19. CLKIN and
RESET
t
BPWL
t
BPWH
Timing
t
BPWH
t
BPWL
REV. A
–17–

AD1870
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
28-Lead Wide-Body SO
Dimensions shown in inches and (millimeters)
28 15
PIN 1
1
R-28 (S-Suffix)
SOL-28
0.2992 (7.60)
0.2914 (7.40)
14
0.4193 (10.65)
0.3937 (10.00)
0.1043 (2.65)
0.0926 (2.35)
0.0125 (0.32)
0.0091 (0.23)
8
ⴗ
0
ⴗ
0.0291 (0.74)
0.0098 (0.25)
0.0500 (1.27)
0.0157 (0.40)
x 45
°
0.0118 (0.30)
0.0040 (0.10)
0.7125 (18.10)
0.6969 (17.70)
0.0500 (1.27)
BSC
0.0192 (0.49)
0.0138 (0.35)
AD1870–Revision History
Location Page
6/02—Data Sheet changed from REV. 0 to REV. A.
Edit to ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
–18–
REV. A

–19–

C00944–0–6/02(A)
–20–
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...