a
Stereo, 96 kHz, Multibit ⌺⌬ DAC
AD1855*
FEATURES
5 V Stereo Audio DAC System
Accepts 16-/18-/20-/24-Bit Data
Supports 24 Bits and 96 kHz Sample Rate
Multibit Sigma-Delta Modulator with “Perfect Differen-
tial Linearity Restoration” for Reduced Idle Tones
and Noise Floor
Data Directed Scrambling DAC—Least Sensitive to
Jitter
Differential Output for Optimum Performance
113 dB Signal-to-Noise and Dynamic
Range at 48 kHz
Sample Rate
110 dB Signal-to-Noise and Dynamic Range at 96 kHz
Sample Rate
–97 dB THD+N
On-Chip Volume Control with 1024 Steps
Hardware and Software Controllable Clickless Mute
Zero Input Flag Outputs for Left and Right Channels
Digital De-Emphasis Processing
Supports 128, 256, 384, and 512 ⴛ F
Master Mode
S
Clock
Switchable Clock Doubler
Power-Down Mode Plus Soft Power-Down Mode
Flexible Serial Data Port with Right-Justified, Left-
Justified, I
2
S-Compatible and DSP Serial Port Modes
28-Lead SSOP Plastic Package
APPLICATIONS
DVD, CD, Set-Top Boxes, Home Theater Systems, Auto-
motive Audio Systems, Computer Multimedia Prod-
ucts, Sampling Musical Keyboards, Digital Mixing
Consoles, Digital Audio Effects Processors
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The AD1855 is a high performance, single-chip stereo, audio
DAC delivering 113 dB Dynamic Range and SNR (A-weighted—
not muted) at 48 kHz sample rate. It is comprised of a multibit
sigma-delta modulator with dither, continuous time analog
filters and analog output drive circuitry. Other features include
an on-chip stereo attenuator and mute, programmed through an
SPI-compatible serial control port. The AD1855 is fully compatible with current DVD formats, including 96 kHz sample
frequency and 24 bits. It is also backwards compatible by supporting 50 µs/15 µs digital de-emphasis intended for “redbook”
44.1 kHz sample frequency playback from compact discs.
The AD1855 has a very simple but very flexible serial data input
port that allows for glueless interconnection to a variety of ADCs,
DSP chips, AES/EBU receivers and sample rate converters.
The AD1855 can be configured in left-justified, I
2
S, rightjustified, or DSP serial port compatible modes. The AD1855
accepts 16-/18-/20-/24-bit serial audio data in MSB first, twoscomplement format. A power-down mode is offered to minimize power consumption when the device is inactive. The
AD1855 operates from a single +5 V power supply. It is fabricated on a single monolithic integrated circuit and housed in a
28-lead SSOP package for operation over the temperature range
0°C to +70°C.
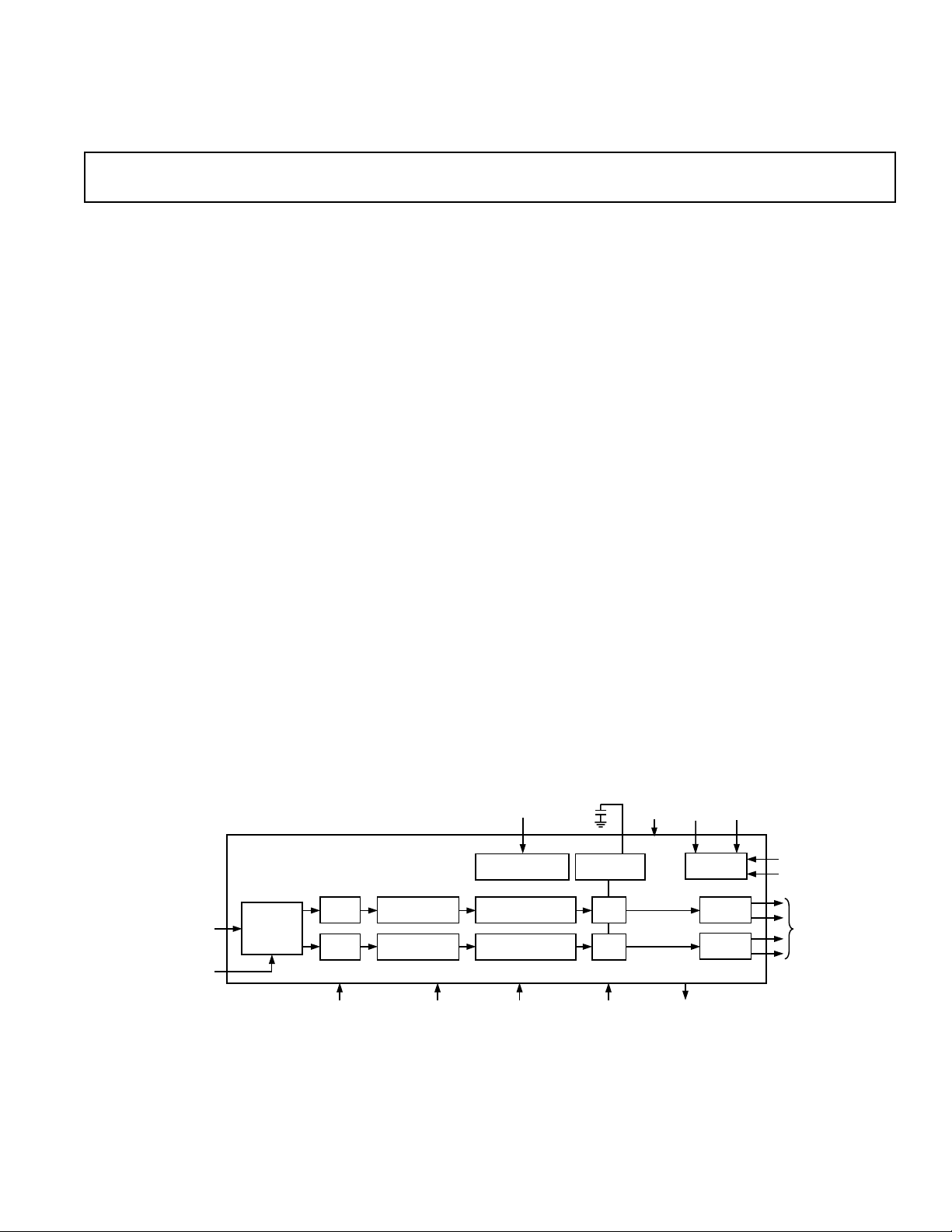
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
VOLUME
MUTE
AD1855
16-/18-/20-/24-BIT
DATA INPUT
*Patents Pending.
DIGITAL
SERIAL
MODE
3
2
SERIAL
DATA
INTERFACE
ATTEN/
MUTE
ATTEN/
MUTE
PD/RST
8ⴛ
INTERPOLATOR
8ⴛ
INTERPOLATOR
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
96/48F
CONTROL DATA
INPUT
3
SERIAL CONTROL
INTERFACE
MULTIBIT SIGMA-
DELTA MODULATOR
MULTIBIT SIGMA-
DELTA MODULATOR
DE-EMPHASISMUTE
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2000
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
DAC
DAC
ANALOG
SUPPLY
DIGITAL
SUPPLY
2
CLOCK
ZERO
FLAG
IN
CLOCK
CIRCUIT
22
CLOCK
OUTPUT
BUFFER
OUTPUT
BUFFER
S
384/256
X2MCLK
ANALOG
OUTPUTS
AD1855–SPECIFICATIONS
TEST CONDITIONS UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED
Supply Voltages (AVDD, DVDD) +5.0 V
Ambient Temperature +25°C
Input Clock 24.576 MHz (512 × F
Input Signal 1.0013 kHz
–0.5 dB Full Scale
Input Sample Rate 48 kHz
Measurement Bandwidth 20 Hz to 20 kHz
Word Width 20 Bits
Load Impedance 6 kΩ
Input Voltage HI 4.0 V
Input Voltage LO 0.8 V
Performance of right and left channels are identical (exclusive of the Interchannel Gain Mismatch and Interchannel Phase Deviation specifications).
ANALOG PERFORMANCE
Resolution 20 Bits
Dynamic Range (20 Hz to 20 kHz, –60 dB Input)
No Filter 110 dB
With A-Weighted Filter 108 113 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise –97 –91 dB
Analog Outputs
Differential Output Range (±Full Scale) 5.6 V p-p
Output Impedance at Each Output Pin 200 Ω
Output Capacitance at Each Output Pin 20 pF
CMOUT 2.5 V
Gain Error –5.0 ± 3.0 +5.0 %
Interchannel Gain Mismatch –0.15 +0.15 dB
Gain Drift 150 300 ppm/°C
Interchannel Crosstalk (EIAJ Method) –120 dB
Interchannel Phase Deviation ± 0.1 Degrees
Mute Attenuation –120 dB
De-Emphasis Gain Error ± 0.1 dB
Mode)
S
Min Typ Max Units
0.0014 %
DIGITAL TIMING (Guaranteed over 0ⴗC to +70ⴗC, AV
t
DMP
t
DMP
t
DMP
t
DML
t
DMH
t
DBH
t
DBL
t
DBP
t
DLS
t
DLH
t
DDS
t
DDH
t
PDRP
MCLK Period (512 FS Mode) 35 ns
MCLK Period (384 FS Mode) 48 ns
MCLK Period (256 FS Mode) 70 ns
MCLK LO Pulsewidth (All Mode) 0.4 × t
MCLK HI Pulsewidth (All Mode) 0.4 × t
BCLK HI Pulsewidth 20 ns
BCLK LO Pulsewidth 20 ns
BCLK Period 140 ns
LRCLK Setup 20 ns
LRCLK Hold (DSP Serial Port Mode Only) 5 ns
SDATA Setup 5 ns
SDATA Hold 10 ns
PD/RST LO Pulsewidth 4 MCLK Periods ns
= DVDD = +5.0 V ⴞ 10%)
DD
Min Max Units
DMP
DMP
ns
ns
–2–
REV. B
AD1855
DIGITAL I/O (0ⴗC to +70ⴗC)
Min Typ Max Units
Input Voltage HI (V
Input Voltage LO (V
High Level Output Voltage (V
Low Level Output Voltage (V
Input Leakage (I
Input Leakage (I
Input Capacitance 10 pF
POWER
Supplies
Voltage, Analog and Digital 4.5 5 5.50 V
Analog Current 24 30 35 mA
Analog Current—Power-Down 23 29 33 mA
Digital Current 17 20 24 mA
Digital Current—Power-Down 1 2.5 5 mA
Dissipation
Operation—Both Supplies 250 mW
Operation—Analog Supply 150 mW
Operation—Digital Supply 100 mW
Power-Down—Both Supplies 190 mW
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
1 kHz 300 mV p-p Signal at Analog Supply Pins –60 dB
20 kHz 300 mV p-p Signal at Analog Supply Pins –50 dB
) 2.4 V
IH
) 1.0 V
IL
@ VIH = 5 V) 10 µA
IH
@ V
IL
IL
) IOH = 1 mA 2.0 V
OH
) IOL = 1 mA 0.4 V
OL
= 0 V) 10 µA
Min Typ Max Units
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Min Typ Max Units
Specifications Guaranteed 25 °C
Functionality Guaranteed 0 70 °C
Storage –55 +125 °C
DIGITAL FILTER CHARACTERISTICS
Min Typ Max Units
Passband Ripple ± 0.04 dB
Stopband Attenuation 47 dB
Passband 0.448 F
Stopband 0.552 F
Group Delay
32, 44.1, 48 kHz (8× Interpolation Mode) 106/F
96 kHz (4× Interpolation Mode) 53/F
S
S
sec
sec
Group Delay Variation 0 µs
Specifications subject to change without notice.
S
S
–3–REV. B
AD1855
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Min Max Units
DV
to DGND –0.3 6 V
DD
AV
to AGND –0.3 6 V
DD
Digital Inputs DGND – 0.3 DV
Analog Outputs AGND – 0.3 AV
+ 0.3 V
DD
+ 0.3 V
DD
AGND to DGND –0.3 0.3 V
Reference Voltage (AV
+ 0.3)/2
DD
Soldering +300 °C
10 sec
*Stresses greater than those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation
of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
PACKAGE CHARACTERISTICS
Min Typ Max Units
(Thermal Resistance
θ
JA
[Junction-to-Ambient]) 109 °C/W
(Thermal Resistance
θ
JC
[Junction-to-Case]) 39 °C/W
ORDERING GUIDE
PIN CONFIGURATION
DGND
MCLK
CLATCH
CCLK
CDATA
384/256
X2MCLK
ZEROR
DEEMP
96/48
AGND
OUTR+
OUTR–
FILTR
1
2
3
4
5
6
AD1855
7
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
DVDD
SDATA
BCLK
L/RCLK
PD/RST
MUTE
ZEROL
IDPM0
IDPM1
FILTB
AVDD
OUTL+
OUTL–
AGND
Model Temperature Package Description Package Options
AD1855JRS 0°C to +70°C 28-Lead Shrink Small Outline RS-28
AD1855JRSRL 0°C to +70°C 28-Lead Shrink Small Outline RS-28 on 13″ Reels
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD1855 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–4–
REV. B
AD1855
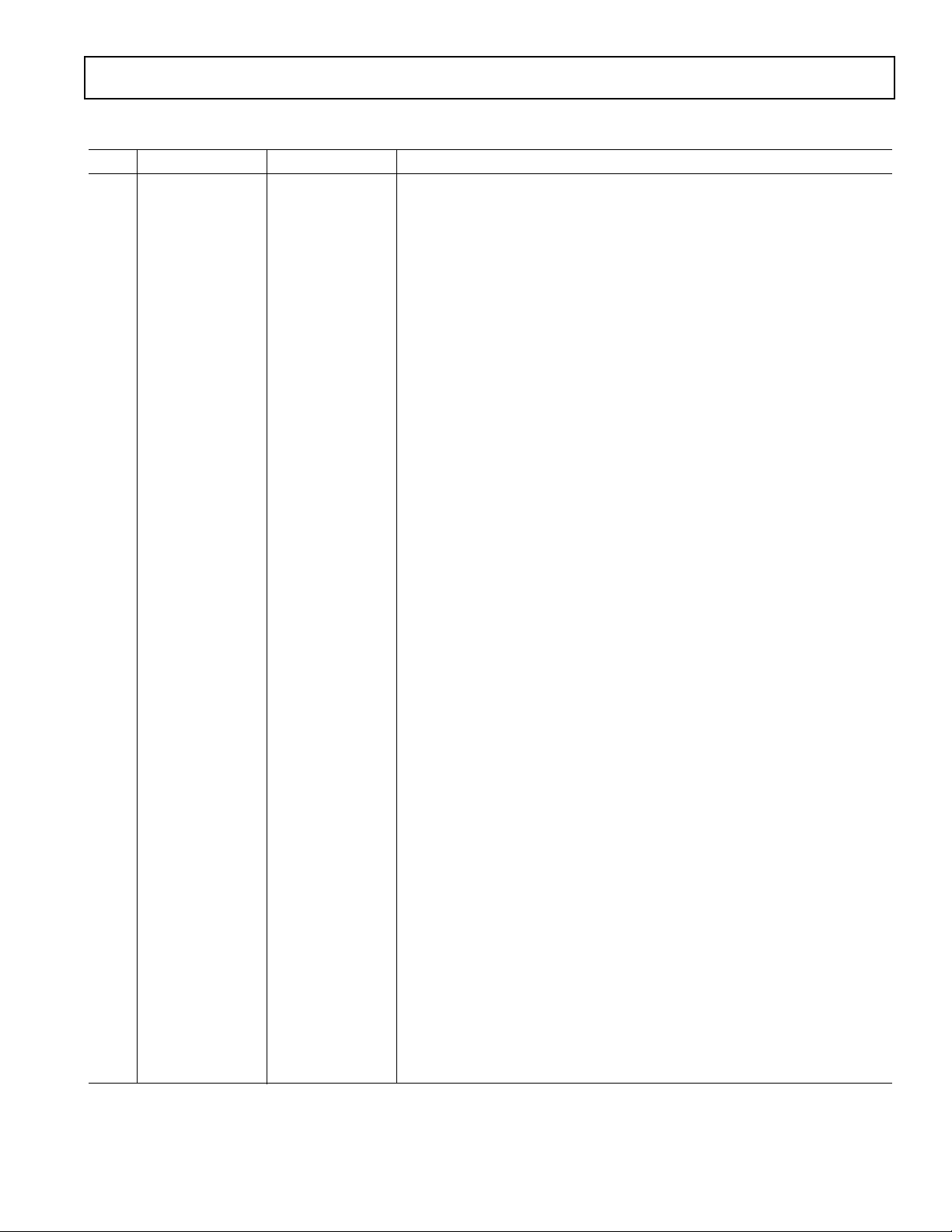
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Input/Output Pin Name Description
1 I DGND Digital Ground.
2 I MCLK Master Clock Input. Connect to an external clock source at either 128, 256,
384 or 512 F
3 I CLATCH Latch input for control data. This input is rising-edge sensitive.
4 I CCLK Control clock input for control data. Control input data must be valid on the
rising edge of CCLK. CCLK may be continuous or gated.
5 I CDATA Serial control input, MSB first, containing 16 bits of unsigned data per
channel. Used for specifying channel specific attenuation and mute.
6 I 384/256 Selects the master clock mode as either 384 times the intended sample fre-
quency (HI) or 256 times the intended sample frequency (LO). The state of
this input should be hardwired to logic HI or logic LO, or may be changed
while the AD1855 is in power-down/reset. It must not be changed while the
AD1855 is operational.
7 I X2MCLK Selects internal clock doubler (LO) or internal clock = MCLK (HI).
8 O ZEROR Right Channel Zero Flag Output. This pin goes HI when Right Channel has
no signal input for more than 1024 LR Clock Cycles.
9 I DEEMP De-Emphasis. Digital de-emphasis is enabled when this input signal is HI.
This is used to impose a 50 µs/15 µs response characteristic on the output
audio spectrum at an assumed 44.1 kHz sample rate.
10 I 96/48 Selects 48 kHz (LO) or 96 kHz Sample Frequency Control.
11, 15 I AGND Analog Ground.
12 O OUTR+ Right Channel Positive line level analog output.
13 O OUTR– Right Channel Negative line level analog output.
14 O FILTR Voltage Reference Filter Capacitor Connection. Bypass and decouple the
voltage reference with parallel 10 µF and 0.1 µF capacitors to the AGND.
16 O OUTL– Left Channel Negative line level analog output.
17 O OUTL+ Left Channel Positive line level analog output.
18 I AVDD Analog Power Supply. Connect to analog +5 V supply.
19 O FILTB Filter Capacitor connection, connect 10 µF capacitor to AGND.
20 I IDPM1 Input serial data port mode control one. With IDPM0, defines one of four
serial modes.
21 I IDPM0 Input serial data port mode control zero. With IDPM1, defines one of four
serial modes.
22 O ZEROL Left Channel Zero Flag output. This pin goes HI when Left Channel has no
signal input for more than 1024 LR Clock Cycles.
23 I MUTE Mute. Assert HI to mute both stereo analog outputs. Deassert LO for nor-
mal operation.
24 I PD/RST Power-Down/Reset. The AD1855 is placed in a low power consumption
mode when this pin is held LO. The AD1855 is reset on the rising edge of
this signal. The serial control port registers are reset to the default values.
Connect HI for normal operation. A reset should always be performed at
power-on.
25 I L/RCLK Left/Right clock input for input data. Must run continuously.
26 I BCLK Bit clock input for input data. Need not run continuously; may be gated or
used in a burst fashion.
27 I SDATA Serial input, MSB first, containing two channels of 16, 18, 20, and 24 bits of
twos complement data per channel.
28 I DVDD Digital Power Supply Connect to digital +5 V supply.
, based on sample rate and clock doubler mode.
S
–5–REV. B

AD1855
OPERATING FEATURES
Serial Data Input Port
The AD1855’s flexible serial data input port accepts data in
twos-complement, MSB-first format. The left channel data field
always precedes the right channel data field. The input data
consists of either 16, 18, 20 or 24 bits, as established by the
mode select pins (IDPM0 Pin 21 and IDPM1 Pin 20) or the
mode select bits (Data 15 and 14) in the control register
through the SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) control port. Neither the pins nor the SPI controls has preference; to ensure
proper control the selection not being used should be tied LO.
Therefore, when the SPI bits are used to control Serial Data
Input Format, Pins 20 and 21 should be tied LO. Similarly,
when the Pins are to be used to select the Data Format, the SPI
bits should be set to Zeros. When the SPI Control Port is not
being used, the SPI Pins (3, 4 and 5) should be tied LO.
Serial Data Input Mode
The AD1855 uses two multiplexed input pins to control the
mode configuration of the input data port mode as follows:
Table I. Serial Data Input Modes
IDPM1 IDPM0
(Pin 20) (Pin 21) Serial Data Input Format
0 0 Right Justified (16 Bits Only)
01 I
2
S-Compatible
1 0 Left Justified
1 1 DSP
Figure 1 shows the right-justified mode. L/RCLK is HI for the
left channel, LO for the right channel. Data is valid on the
rising edge of BCLK. The MSB is delayed 16 bit clock periods
from an L/RCLK transition, so that when there are 64 BCLK
periods per L/RCLK period, the LSB of the data will be right
justified to the next L/RCLK transition. The right-justified
mode can only be used with 16-bit inputs.
2
Figure 2 shows the I
S-justified mode. L/RCLK is LO for the
left channel and HI for the right channel. Data is valid on the
rising edge of BCLK. The MSB is left justified to an L/RCLK
transition but with a single BCLK period delay. The I
2
S-justified
mode can be used with 16-/18-/20- or 24-bit inputs.
Figure 3 shows the left-justified mode. L/RCLK is HI for the
left channel, and LO for the right channel. Data is valid on the
rising edge of BLCK. The MSB is left justified to an L/RCLK
transition, with no MSB delay. The left-justified mode can be
used with 16-/18-/20- or 24-bit inputs.
Figure 4 shows the left-justified DSP serial port style mode.
L/RCLK must pulse HI for at least one bit clock period before
the MSB of the left channel is valid, and L/RCLK must pulse
HI again for at least one bit clock period before the MSB of the
right channel is valid. Data is valid on the falling edge of BCLK.
The left-justified DSP serial port style mode can be used with
16-/18-/20- or 24-bit inputs.
Note that in this mode, it is the responsibility of the DSP to
ensure that the left data is transmitted with the first L/RCLK
pulse, and that synchronism is maintained from that point
forward.
The AD1855 is capable of a 32 × F
BCLK frequency “packed
S
mode” where the MSB is left justified to an L/RCLK transition,
and the LSB is right justified to an L/RCLK transition. L/RCLK
is HI for the left channel and LO for the right channel. Data is
valid on the rising edge of BLCK. Packed mode can be used
when the AD1855 is programmed in right- or left-justified
mode. Packed mode is shown is Figure 5.
Table II. Frequency Mode Settings
F
S
96/48 MCLK X2MCLK 384/256 Note
8× Interpolation Mode
Normal, 32 kHz–48 kHz 0 256 × F
0 384 × F
0 512 × F
0 1 1 Not Allowed
4× Interpolation Mode
Double FS (96 kHz) 1 128 × F
1 (384/2) × F
1 256 × F
1 1 1 Not Allowed
S
S
S
S
S
–6–
00
01
10
00
S
01
10
REV. B

AD1855
L/RCLK
INPUT
LEFT CHANNEL
RIGHT CHANNEL
BCLK
INPUT
SDATA
INPUT
LSB MSB–1MSB–2 LSB+2 LSB+1 LSB MSB MSB–1 MSB–2 LSB+2 LSB+1 LSB MSB MSB–1MSB
L/RCLK
INPUT
BCLK
INPUT
SDATA
INPUT
L/RCLK
INPUT
BCLK
INPUT
SDATA
INPUT
L/RCLK
INPUT
BCLK
INPUT
MSB
MSB
LEFT CHANNEL
LSBMSB–2MSB–1 LSB+2 LSB+1
MSB
MSB–2MSB–1
RIGHT CHANNEL
LSB+2 LSB+1
LSB
Figure 1. Right-Justified Mode
LEFT CHANNEL
MSB–2MSB–1 LSB+2 LSB+1 LSB MSB–2MSB–1MSB LSB+2 LSB+1 LSB MSB
RIGHT CHANNEL
Figure 2. I2S-Justified Mode
LEFT CHANNEL
RIGHT CHANNEL
MSB
SDATA
INPUT
L/RCLK
INPUT
BCLK
INPUT
SDATA
INPUT
MSB
MSB–2MSB–1 LSB+2 LSB+1 LSB MSB–2MSB–1MSB LSB+2 LSB+1 LSB MSB–1MSB
Figure 3. Left-Justified Mode
LEFT CHANNEL
MSB–1 LSB+2 LSB+1 LSB MSB–1 LSB+2 LSB+1 LSBMSB MSB–1MSB
MSB
RIGHT CHANNEL
Figure 4. Left-Justified DSP Mode
Figure 5. 32 × FS Packed Mode
–7–REV. B

AD1855
Serial Control Port
The AD1855 serial control port is SPI compatible. SPI (Serial
Peripheral Interface) is an industry standard serial port protocol.
The write-only serial control port gives the user access to: select
input mode, soft power-down control, soft de-emphasis, channelspecific attenuation and mute (both channels at once). The
AD1855 serial control port consists of three signals, control
clock CCLK (Pin 4), control data CDATA (Pin 5), and control
latch CLATCH (Pin 3). The control data input must be valid
on the control clock rising edge, and the control clock must
make a LO to HI transition when there is valid data. The control latch must make a LO to HI transition after the LSB has
been clocked into the AD1855, while the control clock is inactive. The timing relation between these signals is shown in Figure 6. The control bits are assigned as in Table III.
Digital Timing
Min Unit
CCLK HI Pulsewidth 40 (Burst Mode) ns
t
CCH
t
CCLK LO Pulsewidth 40 (Burst Mode) ns
CD
t
CCLK Period 80 (Burst Mode) ns
CCP
CCLK Setup Time 100 ns
t
CCSU
t
CDATA Setup Time 10 ns
CSU
t
CDATA Hold Time 10 ns
CHD
CLATCH LO Pulsewidth 10 ns
t
CLL
t
CLATCH HI Pulsewidth 130 ns
CLH
t
CLATCH HI Setup 130 ns
CLSU
The serial control port is byte oriented. The data is MSB first,
and is unsigned. There is one control register for the left channel or the right channel, as distinguished by bit Data 10. For
power-up and reset, the default settings are: Data 11 the Mute
control bit, reset default state is LO, which is the normal
(nonmuted) setting. Data 10 is LO, the Volume 9 through Volume 0 control bits have a reset default value of 11 1111 1111,
which is an attenuation of 0.0 dB (i.e., full scale, no attenuation). The intent with these reset defaults is to enable AD1855
applications without requiring the use of the serial control port.
For those users who do not use the serial control port, it is still
possible to mute the AD1855 output by using the MUTE (Pin
23) signal.
Note that the serial control port timing is asynchronous to the
serial data port timing. Changes made to the attenuator level
will be updated on the next edge of the L/RCLK after the
CLATCH write pulse as shown in Figure 7.
Mute
The AD1855 offers two methods of muting the analog output.
By asserting the MUTE (Pin 23) signal HI, both the left and
right channel are muted. As an alternative, the user can assert
the mute bit in the serial control register (Data 11) HI. The
AD1855 has been designed to minimize pops and clicks when
muting and unmuting the device.
t
t
D14
CSU
CHD
D0
t
CLH
t
CLL
t
t
CCSU
CLSU
CDATA
CCLK
CLATCH
t
CCP
D15
t
CCL
t
CCH
Figure 6. Serial Control Port Timing
Table III. Serial Control Bit Definitions
MSB LSB
Data 15 Data 14 Data 13 Data 12 Data 11 Data 10 Data 9 Data 8 Data 7 Data 6 Data 5 Data 4 Data 3 Data 2 Data 1 Data 0
IDPM1 IDPM0 Soft Soft 1/Mute 1/Right Volume Volume Volume Volume Volume Volume Volume Volume Volume Volume
Input Input Power- De- 0/Normal 0/Left Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control Control
Mode1 Mode0 Down Emphasis (Nonmute) Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data
Select Select
–8–
REV. B

AD1855
CLATCH
CCLK
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
CDATA
>130ns
TIME – ns
SPI Port Modes
The SPI port can be used in either of two modes, Burst Mode,
or Continuous CCLK Mode, as described below:
Continuous CCLK Mode
In this mode, the maximum CCLK frequency is 3 MHz. The
CCLK can run continuously between transactions. Please note
that the Low-to-Hi transition of the CLATCH with respect to
the rising edge of CCLK must be at least 130 ns, as shown in
Figure 7.
Figure 7. SPI Port Continuous CCLK Mode
Burst Mode
To operate with SPI CCLK frequencies up to 12.288 MHz, the
SPI port can be operated in Burst Mode. This means that when
CLATCH is high, CCLK cannot be HI, as shown in Figure 8.
CLATCH
CCLK
CDATA
200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
TIME – ns
Figure 8. SPI Port Burst Mode
–9–REV. B

AD1855
Timing Diagrams
The serial data port timing is shown in Figures 9 and 10. The
minimum bit clock HI pulsewidth is t
clock LO pulsewidth is t
t
. The left/right clock minimum setup time is t
DBP
. The minimum bit clock period is
DBL
left/right clock minimum hold time is t
t
DBH
BCLK
t
DBL
t
DLS
L/RCLK
t
SDATA
LEFT-JUSTIFIED
MODE
SDATA
2
I
S-JUSTIFIED
MODE
RIGHT-JUSTIFIED
SDATA
MODE
DDS
MSB
and the minimum bit
DBH
and the
t
DDS
MSB-1
MSB
DLS
t
DDH
. The serial data
DLH
t
DBP
t
DDH
minimum setup time is t
time is t
DDH
.
and the minimum serial data hold
DDS
The power-down/reset timing is shown in Figure 11. The minimum reset LO pulse width is t
(four MCLK periods) to
PDRP
accomplish a successful AD1855 reset operation.
t
DDS
MSB
t
DDH
t
DDS
LSB
t
DDH
Figure 9. Serial Data Port Timing
BCLK
L/RCLK
SDATA
LEFT-JUSTIFIED
DSP SERIAL
PORT STYLE MODE
t
DBH
t
DLS
t
DLH
t
DDS
MSB
t
DDH
t
DBP
t
DBL
MSB-1
Figure 10. Serial Data Port Timing–DSP Serial Port Style Mode
t
DMH
t
DML
t
PDRP
Power-Down/Reset
Timing
MCLK
PD/RST
t
DMP
Figure 11.
–10–
REV. B

AD1855
0202 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
0
–10
–90
–50
–60
–70
–80
–30
–40
–20
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
dB
FREQUENCY – kHz
–150
–160
0
–10
–90
–50
–60
–70
–80
–30
–40
–20
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
dB
–150
–160
–120 0–110 –100 –90 –80 –70 –60 –50 –40 –30
0
–60
–80
–40
–20
–100
–120
dBr – A
AMPLITUDE – dBFS
–20 –10
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
dBr – B
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE
Figures 12 through 15 illustrate the typical analog performance
of the AD1855, at F
= 48 kHz, as measured by an Audio Preci-
S
sion System Two. Signal-to-Noise and THD+N performance
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
dB
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
–160
02024681012141618
FREQUENCY – kHz
Figure 12. 1 kHz Tone at –0.5 dBFS (8K-Point FFT)
–40
–45
–50
–55
–60
–65
–70
–75
dBr – A
–80
–85
–90
–95
–100
–105
–110
0202468
10 12 14 16 18
FREQUENCY – kHz
22
–40
–45
–50
–55
–60
–65
–70
–75
–80
–85
–90
–95
–100
–105
–110
dBr – B
Figure 13. THD+N vs. Frequency at –0.5 dBFS
are shown under a range of conditions. Figure 16 shows the
power supply rejection performance of the AD1855. Figure 17
shows the noise floor of the AD1855. The digital filter transfer
function is shown in Figure 18. The two-tone test in Figure 19
is per the SMPTE Standard for Measuring Intermodulation
Distortion.
Figure 14. Dynamic Range: 1 kHz at –60 dB
Figure 15. THD+N vs. Amplitude at 1 kHz
–11–REV. B

AD1855
0
–5
–10
–15
–20
–25
–30
–35
–40
dBr – A
–45
–50
–55
–60
–65
–70
–75
–80
20 50 100 200 500
FREQUENCY – Hz
1k
2k 5k 10k 20k
0
–5
–10
–15
–20
–25
–30
–35
–40
–45
–50
–55
–60
–65
–70
–75
–80
dBr – B
Figure 16. Power Supply Rejection to 300 mV p-p on AV
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
dBr – A
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
0202 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
FREQUENCY – kHz
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
dBr – B
Figure 17. Noise Floor
DD
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
MAGNITUDE RESPONSE – dB
–80
–90
–100
0
20 60 80 100 120 140
FREQUENCY – kHz
Figure 18. Digital Filter Response
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
dBr – A
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
0202 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
FREQUENCY – kHz
Figure 19. Two-Tone Test
16040
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
–80
dBr – B
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
–12–
REV. B

AD1855
Smooth Volume Control with Auto Ramp Up/Down
The AD1855 incorporates ADI’s 1024 step “Smooth Volume
Control” with auto ramp up/down. Once per L/RCLK cycle,
the AD1855 compares current volume level register to the volume level request register Data 9 through Data 0. If different,
volume is adjusted 1 step/sample. Therefore a change from
max to min volume takes 1024 samples or about 20 ms as
shown in Figure 20.
LEVEL – dB
0
–60
0
–60
20ms
VOLUME REQUEST REGISTER
ACTUAL VOLUME REGISTER
TIME
Figure 20. Smooth Volume Control
Output Drive, Buffering and Loading
The AD1855 analog output stage is able to drive a 1 kΩ (in
series with 2 nF) load.
Power-Down/Reset
The AD1855 offers two methods for power-down and reset.
When the PD/RST input (Pin 24) is asserted LO, the AD1855
is reset. As an alternative, the user can assert the soft powerdown bit (Data 13) HI. All the registers in the AD1855 digital
engine (serial data port, interpolation filter and modulator) are
zeroed. The two 8-bit registers in the serial control port are
initialized back to their default values. The user should wait
100 ms after bringing PD/RST HI before using the serial data
input port and the serial control input. The AD1855 is designed
to minimize pops and clicks when entering and exiting the powerdown state. A reset should always be performed at power-on.
De-Emphasis
The AD1855 offers digital de-emphasis, supporting 50 µs/
15 µs digital de-emphasis intended for “redbook” 44.1 kHz
sample frequency playback from Compact Discs. The AD1855
offers control of de-emphasis by asserting the DEEMP input
(Pin 9) HI or by asserting the de-emphasis register bit (Data 12)
HI. The AD1855’s de-emphasis is optimized for 44.1 kHz but
will scale to the other sample frequencies.
Control Signals
The IDPM0, IDPM1, and DEEMP control inputs are normally
connected HI or LO to establish the operating state of the
AD1855. They can be changed dynamically (and asynchronously to L/RCLK and the master clock) as long as they are
stable before the first serial data input bit (i.e., MSB) is presented to the AD1855.
–13–REV. B

AD1855
MCLK/SR
SEL
JP1
AUDIO
DATA
I/F MODE IDPM1 IDPM0
RJ, 16-BIT 0 0
2
S 0 1
I
LJ 1 0
DSP WCLK 1 1
I/F
MODE
JP2
CONTROL
PORT
NOTE:
R3
10k⍀
SDATA
LRCLK
SCLK
MCLK
DVDD
R4
10k⍀
DE-EMPHASIS
MUTE
RST
DGND
CDATA
CCLK
CLATCH
= DGND
= AGND
DVDD
R2
10k⍀
R5
10k⍀
R1
10k⍀
CLATCH
CDATA
SELECT RATE
SPDIF
DIRECT
DIRECT
MCLK/SR SELECT
44.1
48.0
96.0
AD1855 STEREO DAC
DVDD
C3
100nF
DVDD AVDD
96/48
384/256
X2MCLK
SDATA
L/RCLK
BCLK
MCLK
IDPM0
IDPM1
DEEMP
MUTE
ZR
ZL
ZL
12
ZR
34
CLATCH
CCLK
CDATA
ZEROR
ZEROL
PD/RST
DGND
100nF
U2A
HC04
U2B
HC04
FB1
600Z
C4
CCLK
X2MCLK
0
0
0
OUTL+
OUTL–
U1
AD1855JRS
OUTR+
AGND
R6
221⍀
384/256 96/48
0
0
0
AVDD
C2
100nF
OUTR–
FILTR
FITLB
AGND
DVDD
CR1
ZERO LEFT
0
0
1
1.96k⍀
R
100nF
+
C8
10F
–
MCLK
11.2896
12.2880
12.2880
OUTPUT BUFFERS AND LP FILTERS
R16
R
OPT
R18
1.96k⍀
*
OPT
C1
R7
221⍀
R9
2.15k⍀
C14
1nF, NP0
C13
1nF, NP0
R17
1.96k⍀
R11
*
2.15k⍀
R13
2.15k⍀
C17
1nF, NP0
C16
1nF, NP0
R19
1.96k⍀
R15
2.15k⍀
+
C7
10F
–
CR2
ZERO RIGHT
C9
R8
390pF
953⍀
NP0
U3B
R10
953⍀
C10
390pF
NP0
+AV
C11
390pF
R12
NP0
953⍀
U3A
R14
953⍀
C12
390pF
NP0
–AV
: OPTIONAL. TRIM FOR BEST THD.
*R
OPT
IMPROVES THD UP TO 6dB OVER DATA
SHEET.
R20
549⍀
C15
2.2nF
R21
549⍀
NP0
~2.8s
C18
2.2nF
NP0
SSM2135
3RD ORDER LP BESSEL FILTER
CORNER FREQUENCY: 92kHz
GROUP DELAY:
CC
C5
100nF
SSM2135
C6
100nF
EE
53.6k⍀
53.6k⍀
J1
1
LEFT
OUT
J2
1
RIGHT
OUT
Figure 21. Evaluation Board Circuit
–14–
REV. B

OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
28-Lead Shrink Small Outline Package (SSOP)
(RS-28)
0.41 (10.50)
0.39 (9.90)
28 15
AD1855
0.32 (8.20)
0.29 (7.40)
0.079 (2.0)
MAX
0.002 (0.05)
MIN
PIN 1
0.026
(0.65)
BSC
0.015 (0.38)
0.010 (0.22)
SEATING
PLANE
0.22 (5.60)
0.20 (5.00)
141
0.073 (1.85)
0.065 (1.65)
0.01 (0.25)
0.004 (0.09)
C3274b–1.5–5/00 (rev. B) 00740
8ⴗ
0ⴗ
0.037 (0.95)
0.022 (0.55)
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
–15–REV. B
 Loading...
Loading...