
2 ADC, 8 DAC,
a
FEATURES
5 V Stereo Audio System with 3.3 V Tolerant
Digital Interface
Supports up to 96 kHz Sample Rates
192 kHz Sample Rate Available on 1 DAC
Supports 16-, 20-, 24-Bit Word Lengths
Multibit - Modulators with
Perfect Differential Linearity Restoration for
Reduced Idle Tones and Noise Floor
Data Directed Scrambling DACs—Least
Sensitive to Jitter
Single-Ended Outputs
ADCs: –95 dB THD + N, 105 dB SNR and
Dynamic Range
DACs: –92 dB THD + N, 108 dB SNR and
Dynamic Range
On-Chip Volume Controls per Channel with
1024-Step Linear Scale
DAC and ADC Software Controllable Clickless Mutes
Digital De-emphasis Processing
Supports 256 f
Mode Clocks
Power-Down Mode Plus Soft Power-Down Mode
Flexible Serial Data Port with Right-Justified, Left-
Justified, I
Modes
TDM Interface Mode Supports 8 In/8 Out Using a
Single SHARC
52-Lead MQFP Plastic Package
, 512 fS, and 768 fS Master
S
2
S Compatible, and DSP Serial Port
®
SPORT
96 kHz, 24-Bit - Codec
AD1837A
APPLICATIONS
DVD Video and Audio Players
Home Theater Systems
Automotive Audio Systems
Audio/Visual Receivers
Digital Audio Effects Processors
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD1837A is a high performance single-chip codec featuring
four stereo DACs and one stereo ADC. Each DAC comprises a
high performance digital interpolation filter, a multibit -
modulator featuring Analog Devices’ patented technology, and a
continuous-time voltage out analog section. Each DAC has independent volume control and clickless mute functions. The ADC
comprises two 24-bit conversion channels with multibit S-D
modulators and decimation filters.
The AD1837A also contains an on-chip reference with a nominal
value of 2.25 V.
The AD1837A contains a flexible serial interface that allows for
glueless connection to a variety of DSP chips, AES/EBU receivers,
and sample rate converters. The AD1837A can be configured in
left-justified, right-justified, I
Control of the AD1837A is achieved by means of an SPI compatible serial port. While the AD1837A can be operated from a single
5 V supply, it also features a separate supply pin for its digital interface, which allows the device to be interfaced to other devices using
3.3 V power supplies.
The AD1837A is available in a 52-lead MQFP package and is specified for the industrial temperature range of –40ºC to +85ºC.
2
S, or DSP compatible serial modes.
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DVDD
-
ADC
-
ADC
AD1837A
ODVDD
DIGITAL
FILTER
DIGITAL
FILTER
SERIAL DATA
I/O PORT
DGND
DGND
AGN D
DVD D
DLRCLK
DBCLK
DSDATA1
DSDATA2
DSDATA3
DSDATA4
ADCLP
ADCLN
ADCRP
ADCRN
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
AGND
MCLKASDATAABCLKALRCLK
CLOCK
DIGITAL
FILTER
DIGITAL
FILTER
DIGITAL
FILTER
DIGITAL
FILTER
PD/RST M/S
V
-
DAC
-
DAC
-
DAC
-
DAC
REF
AV DD
AV DD
OUTL1
OUTR1
OUTL2
OUTR2
OUTL3
OUTR3
OUTL4
OUTR4
FILTD
FILTR
CINCLATCHCCLK COUT
CONTROL PORT
VOLUME
VOLUME
VOLUME
VOLUME
VOLUME
VOLUME
VOLUME
VOLUME
AGN D
AGN D
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
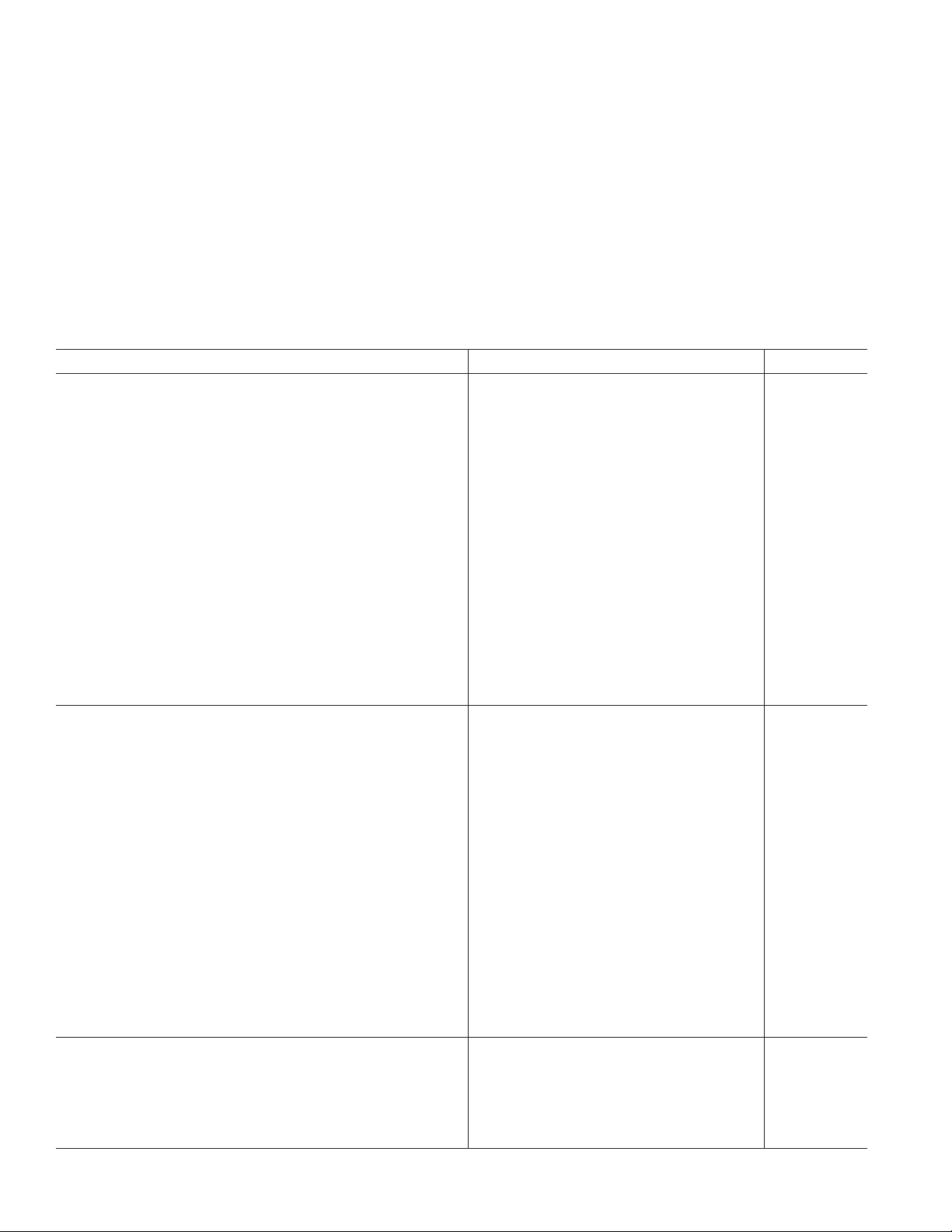
AD1837A–SPECIFICATIONS
TEST CONDITIONS
Supply Voltages (AVDD, DVDD) 5.0 V
Ambient Temperature 25∞C
Input Clock 12.288 MHz, (256 f
ADC Input Signal 1.0078125 kHz, –1 dBFS (Full Scale)
DAC Input Signal 1.0078125 kHz, 0 dBFS (Full Scale)
Input Sample Rate (f
) 48 kHz
S
Measurement Bandwidth 20 Hz to 20 kHz
Word Width 24 Bits
Load Capacitance 100 pF
Load Impedance 47 kW
Performance of all channels is identical (exclusive of the Interchannel Gain Mismatch and Interchannel Phase Deviation
specifications).
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
ADC Resolution 24 Bits
Dynamic Range (20 Hz to 20 kHz, –60 dB Input)
No Filter 103 dB
With A-Weighted (48 kHz and 96 kHz) 100 105 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (THD + N)
= 48 kHz –95 –88.5 dB
f
S
= 96 kHz –95 –87.5 dB
f
S
Interchannel Isolation 100 dB
Interchannel Gain Mismatch 0.025 dB
Analog Inputs
Differential Input Range (± Full Scale) –2.828 +2.828 V
Common-Mode Input Voltage 2.25 V
Input Impedance 4 kW
Input Capacitance 15 pF
V
REF
DC Accuracy
Gain Error ± 5%
Gain Drift 35 ppm/ºC
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
DAC Resolution 24 Bits
Dynamic Range (20 Hz to 20 kHz, –60 dBFS Input)
No Filter 103 105 dB
With A-Weighted Filter (48 kHz and 96 kHz) 105 108 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise (48 kHz and 96 kHz) –92 dB
Interchannel Isolation 100 dB
DC Accuracy
Gain Error ± 4%
Interchannel Gain Mismatch 0.025 dB
Gain Drift 200 ppm/∞C
Interchannel Phase Deviation ± 0.1 Degrees
Volume Control Step Size (1023 Linear Steps) 0.098 %
Volume Control Range (Maximum Attenuation) 60 dB
Mute Attenuation –100 dB
De-emphasis Gain Error ± 0.1 dB
Full-Scale Output Voltage at Each Pin (Single-Ended) 1.0 (2.8) V rms (V p-p)
Output Resistance at Each Pin 180 W
Common-Mode Output Voltage 2.25 V
ADC DECIMATION FILTER, 48 kHz*
Pass Band 21.77 kHz
Pass-Band Ripple ± 0.01 dB
Stop Band 26.23 kHz
Stop-Band Attenuation 120 dB
Group Delay 910 ms
Mode)
S
2.25 V
–2–
REV. A
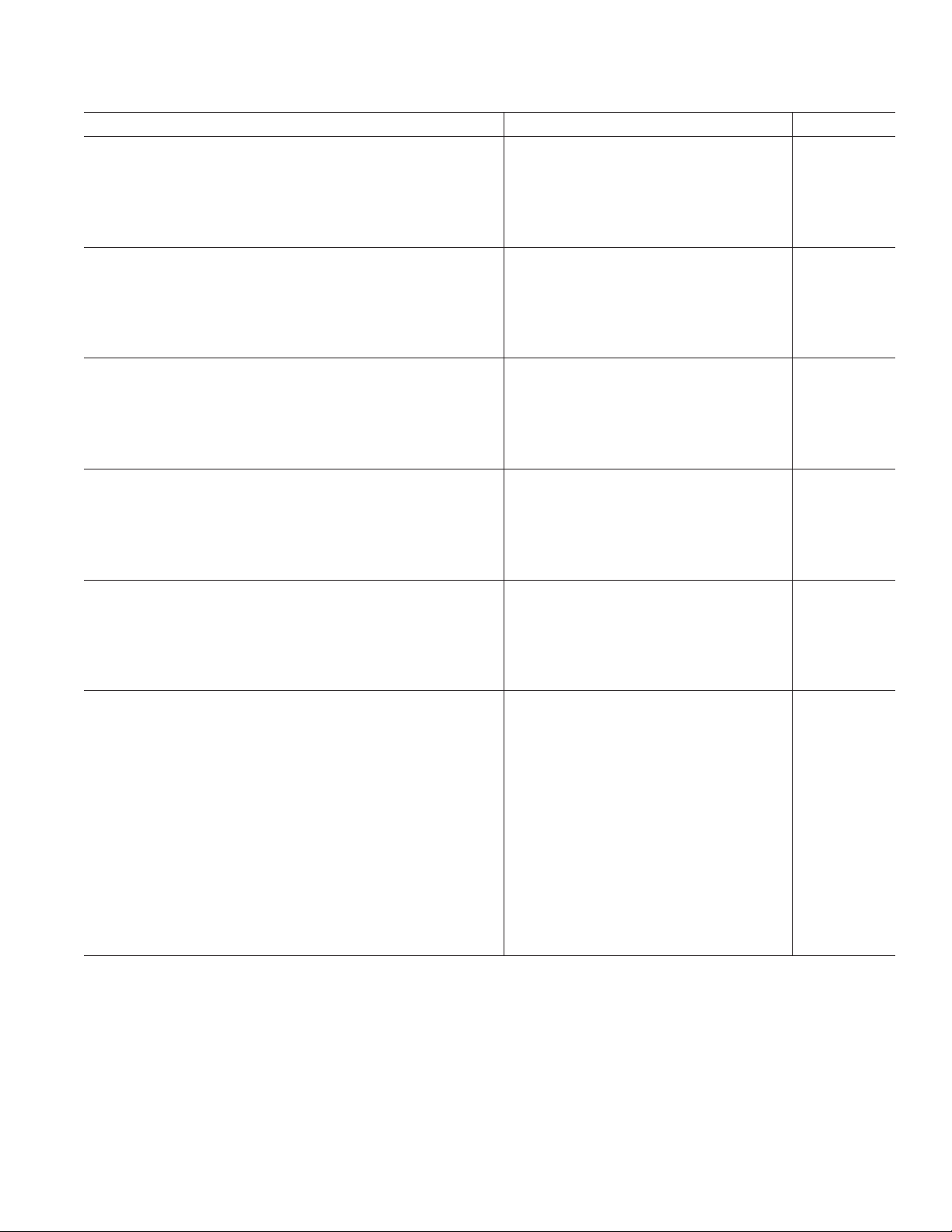
AD1837A
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
ADC DECIMATION FILTER, 96 kHz*
Pass Band 43.54 kHz
Pass-Band Ripple ± 0.01 dB
Stop Band 52.46 kHz
Stop-Band Attenuation 120 dB
Group Delay 460 ms
DAC INTERPOLATION FILTER, 48 kHz*
Pass Band 21.77 kHz
Pass-Band Ripple ± 0.06 dB
Stop Band 28 kHz
Stop-Band Attenuation 55 dB
Group Delay 340 ms
DAC INTERPOLATION FILTER, 96 kHz*
Pass Band 43.54 kHz
Pass-Band Ripple ± 0.06 dB
Stop Band 52 kHz
Stop-Band Attenuation 55 dB
Group Delay 160 ms
DAC INTERPOLATION FILTER, 192 kHz*
Pass Band 81.2 kHz
Pass-Band Ripple ± 0.06 dB
Stop Band 97 kHz
Stop-Band Attenuation 80 dB
Group Delay 110 ms
DIGITAL I/O
Input Voltage High 2.4 V
Input Voltage Low 0.8 V
Output Voltage High ODVDD – 0.4 V
Output Voltage Low 0.4 V
Leakage Current ± 10 mA
POWER SUPPLIES
Supply Voltage (AVDD and DVDD) 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
Supply Voltage (ODVDD) 3.0 DVDD V
Supply Current I
Supply Current I
Supply Current I
Supply Current I
ANALOG
ANALOG,
DIGITAL
DIGITAL,
Power-Down 55 67 mA
Power-Down 1 4.5 mA
Dissipation
Operation, Both Supplies 740 mW
Operation, Analog Supply 420 mW
Operation, Digital Supply 320 mW
Power-Down, Both Supplies 280 mW
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
1 kHz, 300 mV p-p Signal at Analog Supply Pins –70 dB
20 kHz, 300 mV p-p Signal at Analog Supply Pins –75 dB
*Guaranteed by design.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
84 95 mA
64 74 mA
REV. A
–3–
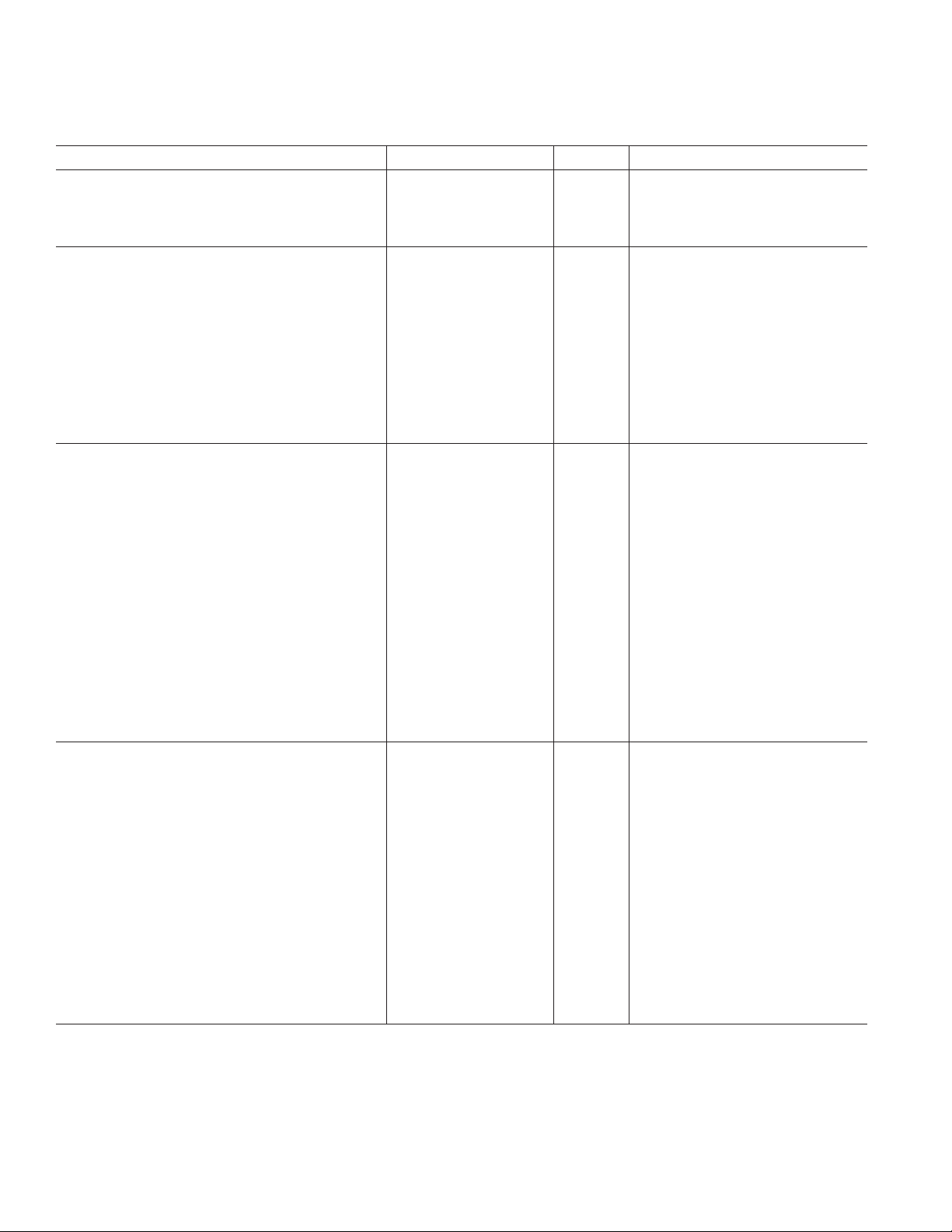
AD1837A
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Parameter Min Max Unit Comments
MASTER CLOCK AND RESET
t
MH
t
ML
t
PDR
®
PORT
SPI
t
CCH
t
CCL
t
CCP
t
CDS
t
CDH
t
CLS
t
CLH
t
COE
t
COD
t
COTS
DAC SERIAL PORT (48 kHz and 96 kHz)
Normal Mode (Slave)
t
DBH
t
DBL
f
DB
t
DLS
t
DLH
t
DDS
t
DDH
Packed 128/256 Modes (Slave)
t
DBH
t
DBL
f
DB
t
DLS
t
DLH
t
DDS
t
DDH
ADC SERIAL PORT (48 kHz and 96 kHz)
Normal Mode (Master)
t
ABD
t
ALD
t
ABDD
Normal Mode (Slave)
t
ABH
t
ABL
f
AB
t
ALS
t
ALH
t
ABDD
Packed 128/256 Mode (Master)
t
PABD
t
PALD
t
PABDD
MCLK High 15 ns
MCLK Low 15 ns
PD/RST Low 20 ns
CCLK High 40 ns
CCLK Low 40 ns
CCLK Period 80 ns
CDATA Setup 10 ns To CCLK Rising Edge
CDATA Hold 10 ns From CCLK Rising Edge
CLATCH Setup 10 ns To CCLK Rising Edge
CLATCH Hold 10 ns From CCLK Rising Edge
COUT Enable 15 ns From CLATCH Falling Edge
COUT Delay 20 ns From CCLK Falling Edge
COUT Three-State 25 ns From CLATCH Rising Edge
DBCLK High 60 ns
DBCLK Low 60 ns
DBCLK Frequency 64 f
S
DLRCLK Setup 10 ns To DBCLK Rising Edge
DLRCLK Hold 10 ns From DBCLK Rising Edge
DSDATA Setup 10 ns To DBCLK Rising Edge
DSDATA Hold 10 ns From DBCLK Rising Edge
DBCLK High 15 ns
DBCLK Low 15 ns
DBCLK Frequency 256 f
S
DLRCLK Setup 10 ns To DBCLK Rising Edge
DLRCLK Hold 10 ns From DBCLK Rising Edge
DSDATA Setup 10 ns To DBCLK Rising Edge
DSDATA Hold 10 ns From DBCLK Rising Edge
ABCLK Delay 25 ns From MCLK Rising Edge
ALRCLK Delay 5 ns From ABCLK Falling Edge
ASDATA Delay 10 ns From ABCLK Falling Edge
ABCLK High 60 ns
ABCLK Low 60 ns
ABCLK Frequency 64 f
S
ALRCLK Setup 5 ns To ABCLK Rising Edge
ALRCLK Hold 15 ns From ABCLK Rising Edge
ASDATA Delay 15 ns From ABCLK Falling Edge
ABCLK Delay 40 ns From MCLK Rising Edge
LRCLK Delay 5 ns From ABCLK Falling Edge
ASDATA Delay 10 ns From ABCLK Falling Edge
–4–
REV. A
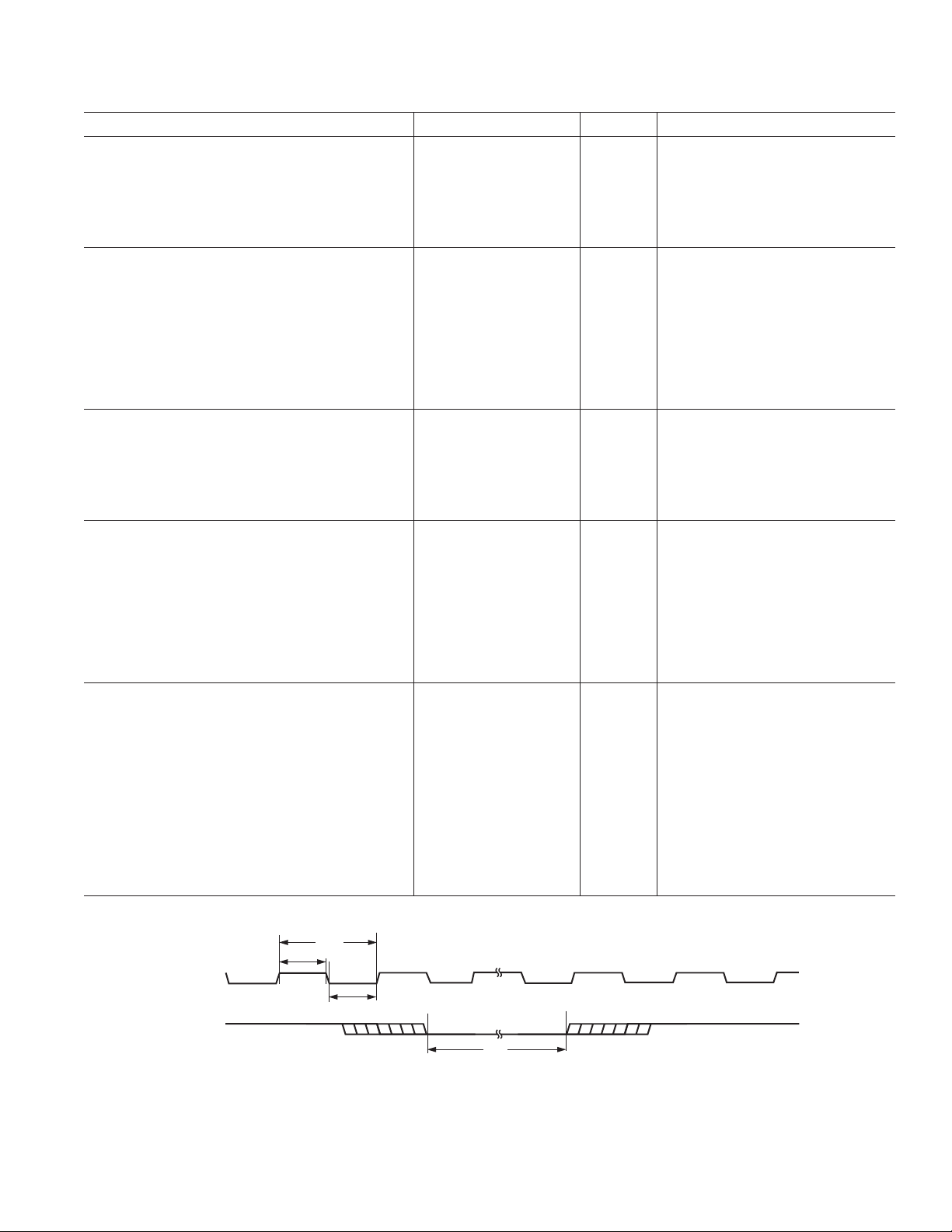
Parameter Min Max Unit Comments
P
TDM256 MODE (Master, 48 kHz and 96 kHz)
t
TBD
t
FSD
t
TABDD
t
TDDS
t
TDDH
BCLK Delay 40 ns From MCLK Rising Edge
FSTDM Delay 5 ns From BCLK Rising Edge
ASDATA Delay 10 ns From BCLK Rising Edge
DSDATA1 Setup 15 ns To BCLK Falling Edge
DSDATA1 Hold 15 ns From BCLK Falling Edge
TDM256 MODE (Slave, 48 kHz and 96 kHz)
f
AB
t
TBCH
t
TBCL
t
TFS
t
TFH
t
TBDD
t
TDDS
t
TDDH
BCLK Frequency 256 f
S
BCLK High 17 ns
BCLK Low 17 ns
FSTDM Setup 10 ns To BCLK Falling Edge
FSTDM Hold 10 ns From BCLK Falling Edge
ASDATA Delay 15 ns From BCLK Rising Edge
DSDATA1 Setup 15 ns To BCLK Falling Edge
DSDATA1 Hold 15 ns From BCLK Falling Edge
TDM512 MODE (Master, 48 kHz)
t
TBD
t
FSD
t
TABDD
t
TDDS
t
TDDH
BCLK Delay 40 ns From MCLK Rising Edge
FSTDM Delay 5 ns From BCLK Rising Edge
ASDATA Delay 10 ns From BCLK Rising Edge
DSDATA1 Setup 15 ns To BCLK Falling Edge
DSDATA1 Hold 15 ns From BCLK Falling Edge
TDM512 MODE (Slave, 48 kHz)
f
AB
t
TBCH
t
TBCL
t
TFS
t
TFH
t
TBDD
t
TDDS
t
TDDH
BCLK Frequency 512 f
S
BCLK High 17 ns
BCLK Low 17 ns
FSTDM Setup 10 ns To BCLK Falling Edge
FSTDM Hold 10 ns From BCLK Falling Edge
ASDATA Delay 15 ns From BCLK Rising Edge
DSDATA1 Setup 15 ns To BCLK Falling Edge
DSDATA1 Hold 15 ns From BCLK Falling Edge
AUXILIARY INTERFACE (48 kHz and 96 kHz)
t
AXDS
t
AXDH
f
ABP
AAUXDATA Setup 10 ns To AUXBCLK Rising Edge
AAUXDATA Hold 10 ns From AUXBCLK Rising Edge
AUXBCLK Frequency 64 f
S
Slave Mode
t
AXBH
t
AXBL
t
AXLS
t
AXLH
AUXBCLK High 15 ns
AUXBCLK Low 15 ns
AUXLRCLK Setup 10 ns To AUXBCLK Rising Edge
AUXLRCLK Hold 10 ns From AUXBCLK Rising Edge
Master Mode
t
AUXLRCLK
t
AUXBCLK
Specifications subject to change without notice.
AUXLRCLK Delay 15 ns From AUXBCLK Falling Edge
AUXBCLK Delay 20 ns From MCLK Rising Edge
AD1837A
t
MCLK
t
MH
MCLK
t
ML
D/RST
t
PDR
Figure 1. MCLK and PD/
REV. A
–5–
RST
Timing
AD1837A
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
(TA = 25∞C, unless otherwise noted.)
AVDD, DVDD, ODVDD to AGND, DGND
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +6 V
AGND to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +0.3 V
Digital I/O Voltage to DGND . . . –0.3 V to ODVDD + 0.3 V
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Specifications Guaranteed 25 ∞C
Functionality Guaranteed –40 +85 ∞C
Storage –65 +150 ∞C
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Analog I/O Voltage to AGND . . . . . –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial (A Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40∞C to +85∞C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD1837AAS –40
AD1837AAS-REEL –40
AD1837AASZ* –40
AD1837AASZ-REEL* –40
o
C to +85oC 52-Lead MQFP S-52-1
o
C to +85oC 52-Lead MQFP S-52-1
o
C to +85oC 52-Lead MQFP S-52-1
o
C to +85oC 52-Lead MQFP S-52-1
EVAL-AD1837AEB Evaluation Board
*Z = Pb free part.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD1837A features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–6–
REV. A
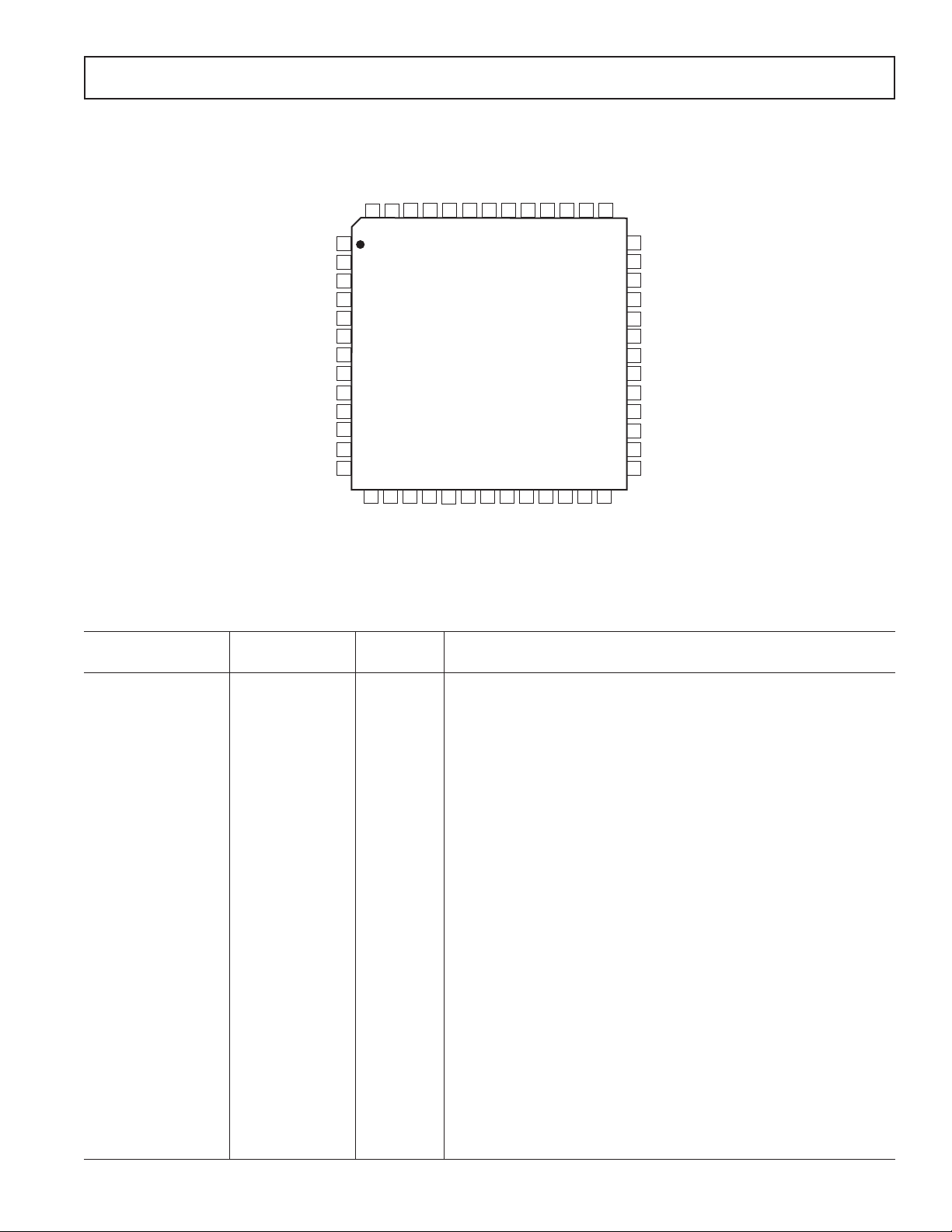
PIN CONFIGURATION
AD1837A
DSDATA2
DSDATA1
NC
AGND
DGND
OUTL3
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
DVDD
DBCLK
DLRCLK
M/S
AGND
OUTR4
NC
OUTL4
NC
AGND
AVDD
OUTR3
NC
1
DVDD
CLATCH
2
3
CIN
4
PD/RST
5
AGND
NC
6
OUTL1
7
NC
8
OUTR1
9
AGND
10
AVDD
11
NC
12
OUTL2
13
NC = NO CONNECT
DGND
CCLK
COUT
ASDATA
ODVDD
MCLK
ALRCLK
ABCLK
DSDATA4
ADCLP
DSDATA3
ADCRP
ADCRN
50 494847 46 45 44 43 42 41 40
51
52
AD1837A
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
NC
AGND
OUTR2
FILTD
FILTR
AVDD
ADCLN
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Input/
Pin Number Mnemonic Output Description
1, 39 DVDD Digital Power Supply. Connect to digital 5 V supply.
2CLATCH I Latch Input for Control Data.
3 CIN I Serial Control Input.
4 PD/RST I Power-Down/Reset.
5, 10, 16, 24, 30, 35 AGND Analog Ground.
6, 12, 25, 31 NC Not Connected.
7, 13, 26, 32 OUTLx O DACx Left Channel Output.
8, 14, 27, 33 NC Not Connected.
9, 15, 28, 34 OUTRx O DACx Right Channel Output.
11, 19, 29 AVDD Analog Power Supply. Connect to analog 5 V supply.
17 FILTD Filter Capacitor Connection. Recommended 10 mF/100 nF.
18 FILTR Reference Filter Capacitor Connection. Recommended 10 mF/100 nF.
20 ADCLN I ADC Left Channel Negative Input.
21 ADCLP I ADC Left Channel Positive Input.
22 ADCRN I ADC Right Channel Negative Input.
23 ADCRP I ADC Right Channel Positive Input.
36 M/S I ADC Master/Slave Select.
37 DLRCLK I/O DAC LR Clock.
38 DBCLK I/O DAC Bit Clock.
40, 52 DGND Digital Ground.
41 to 44 DSDATAx I DACx Input Data (Left and Right Channels).
45 ABCLK I/O ADC Bit Clock.
46 ALRCLK I/O ADC LR Clock.
47 MCLK I Master Clock Input.
48 ODVDD Digital Output Driver Power Supply.
49 ASDATA O ADC Serial Data Output.
50 COUT O Output for Control Data.
51 CCLK I Control Clock Input for Control Data.
REV. A
–7–
AD1837A
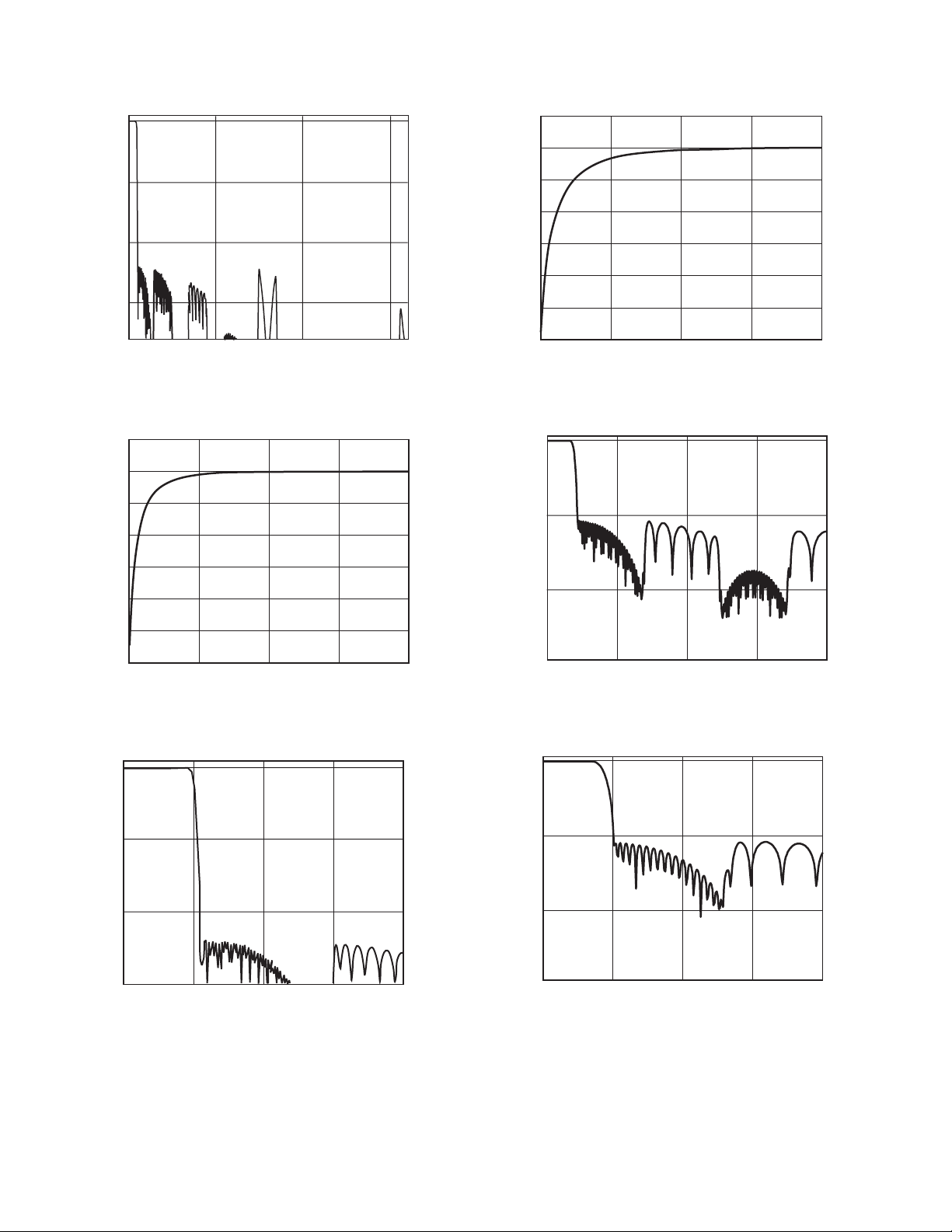
–Typical Performance Characteristics
0
–50
–100
MAGNITUDE – dB
–150
05
FREQUENCY – Normalized to f
10
TPC 1. ADC Composite Filter Response
5
0
–5
–10
–15
MAGNITUDE – dB
–20
5
0
–5
–10
–15
MAGNITUDE – dB
–20
–25
15
S
–30
0205
10 15
FREQUENCY – Hz
TPC 4. ADC High-Pass Filter Response, fS = 96 kHz
0
–50
MAGNITUDE – dB
–100
–25
–30
0205
10 15
FREQUENCY – Hz
TPC 2. ADC High-Pass Filter Response, fS = 48 kHz
0
–50
MAGNITUDE – dB
–100
–150
02.00.5
FREQUENCY – Normalized to f
1.0 1.5
S
TPC 3. ADC Composite Filter Response
(Pass-Band Section)
–150
020050 100 150
FREQUENCY – kHz
TPC 5. DAC Composite Filter Response, fS = 48 kHz
0
–50
MAGNITUDE – dB
–100
–150
020050 100 150
FREQUENCY – kHz
TPC 6. DAC Composite Filter Response, fS = 96 kHz
–8–
REV. A

AD1837A
0.2
0.1
–0.2
05010 20 30 40
0
–0.1
FREQUENCY – kHz
MAGNITUDE – dB
0.10
0.05
–0.10
010020 40 60 80
0
–0.05
FREQUENCY – kHz
MAGNITUDE – dB
0
–50
–100
MAGNITUDE – dB
–150
020050 100 150
FREQUENCY – kHz
TPC 7. DAC Composite Filter Response, fS = 192 kHz
0.10
0.05
0
MAGNITUDE – dB
–0.05
–0.10
02051015
FREQUENCY – kHz
TPC 8. DAC Composite Filter Response, fS = 48 kHz
(Pass-Band Section)
TPC 9. DAC Composite Filter Response, fS = 96 kHz
(Pass-Band Section)
TPC 10. DAC Composite Filter Response, fS = 192 kHz
(Pass-Band Section)
REV. A
–9–

AD1837A
TERMINOLOGY
Dynamic Range
The ratio of a full-scale input signal to the integrated input noise
in the pass band (20 Hz to 20 kHz), expressed in decibels (dB).
Dynamic range is measured with a –60 dB input signal and is
equal to (S/[THD + N]) + 60 dB. Note that spurious harmonics
are below the noise with a –60 dB input, so the noise level
establishes the dynamic range. The dynamic range is specified
with and without an A-weight filter applied.
Signal-to-(Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise)
[S/(THD + N)]
The ratio of the root-mean-square (rms) value of the fundamental input signal to the rms sum of all other spectral components in the pass band, expressed in decibels (dB).
Pass Band
The region of the frequency spectrum unaffected by the attenuation of the digital decimator’s filter.
Pass-Band Ripple
The peak-to-peak variation in amplitude response from equalamplitude input signal frequencies within the pass band, expressed
in decibels.
Stop Band
The region of the frequency spectrum attenuated by the
digital decimator’s filter to the degree specified by stop-band
attenuation.
Gain Error
With a near full-scale input, the ratio of actual output to expected
output, expressed as a percentage.
Interchannel Gain Mismatch
With identical near full-scale inputs, the ratio of outputs of the
two stereo channels, expressed in decibels.
Gain Drift
Change in response to a near full-scale input with a change in
temperature, expressed as parts-per-million (ppm) per ∞C.
Crosstalk (EIAJ Method)
Ratio of response on one channel with a grounded input to a
full-scale 1 kHz sine wave input on the other channel, expressed
in decibels.
Power Supply Rejection
With no analog input, signal present at the output when a
300 mV p-p signal is applied to power supply pins, expressed
in decibels of full scale.
Group Delay
Intuitively, the time interval required for an input pulse to
appear at the converter’s output, expressed in microseconds
(ms). More precisely, the derivative of radian phase with
respect to radian frequency at a given frequency.
Group Delay Variation
The difference in group delays at different input frequencies.
Specified as the difference between largest and the smallest
group delays in the pass band, expressed in microseconds (ms).
ACRONYMS
ADC—Analog-to-Digital Converter.
DAC—Digital-to-Analog Converter.
DSP—Digital Signal Processor.
IMCLK—Internal Master Clock Signal used to clock the ADC
and DAC engines.
MCLK—External Master Clock Signal applied to the AD1837A.
–10–
REV. A

AD1837A
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
ADCs
There are two ADC channels in the AD1837A, configured as a
stereo pair. Each ADC has fully differential inputs. The ADC
section can operate at a sample rate of up to 96 kHz. The ADCs
include on-board digital decimation filters with 120 dB stop-band
attenuation and linear phase response, operating at an oversampling ratio of 128 (for 48 kHz operation) or 64 (for 96 kHz
operation).
ADC peak level information for each ADC may be read from the
ADC Peak 0 and ADC Peak 1 registers. The data is supplied as
a 6-bit word with a maximum range of 0 dB to –63 dB and a
resolution of 1 dB. The registers will hold peak information until
read; after reading, the registers are reset so that new peak
information can be acquired. Refer to the register description
for details on the format. The two ADC channels have a common serial bit clock and a left-right framing clock. The clock
signals are all synchronous with the sample rate.
The ADC digital pins, ABCLK and ALRCLK, can be set to
operate as inputs or outputs by connecting the M/S pin to
ODVDD or DGND, respectively. When the pins are set as
outputs, the AD1837A will generate the timing signals. When
the pins are set as inputs, the timing must be generated by
the external audio controller.
DACs
The AD1837A has eight DAC channels arranged as four independent stereo pairs, with eight single-ended analog outputs for
improved noise and distortion performance. Each channel has
its own independently programmable attenuator, adjustable in
1024 linear steps. Digital inputs are supplied through four serial
data input pins (one for each stereo pair) and a common frame
(DLRCLK) and bit (DBLCK) clock. Alternatively, one of the
packed data modes may be used to access all eight channels on a
single TDM data pin. A stereo replicate feature is included where
the DAC data sent to the first DAC pair is also sent to the
other DACs in the part. The AD1837A can accept DAC data at
a sample rate of 192 kHz on DAC 1 only. The stereo replicate feature can then be used to copy the audio data to the
other DACs.
Each of the output pins sits at a dc level of V
± 1.4 V for a 0 dB digital input signal. A single op amp thirdorder external low-pass filter is recommended to remove high
frequency noise present on the output pins. Note that the use of
op amps with low slew rate or low bandwidth may cause high
frequency noise and tones to fold down into the audio band;
care should be exercised in selecting these components.
The FILTD pin should be connected to an external grounded
capacitor. This pin is used to reduce the noise of the internal
DAC bias circuitry, thereby reducing the DAC output noise. In
some cases, this capacitor may be eliminated with little affect
on performance.
DAC and ADC Coding
The DAC and ADC output data stream is in a twos complement encoded format. The word width can be selected from
16 bit, 20 bit, or 24 bit. The coding scheme is detailed
in Table I.
and swings
REF
Table I. Coding Scheme
Code Level
0111 . . . . 11111 +FS
0000 . . . . 00000 0 (Ref Level)
1000 . . . . 00000 –FS
AD1837A CLOCKING SCHEME
By default, the AD1837A requires an MCLK signal that is
256 times the required sample frequency up to a maximum of
12.288 MHz. The AD1837A uses a clock scaler to double the
clock frequency for internal use. The default setting of the clock
scaler is multiply by two. The clock scaler can also be set to
multiply by 1 (bypass) or multiply by 2/3. The internal MCLK
signal, IMCLK, should not exceed 24.576 MHz in order to
ensure correct operation.
The MCLK of the AD1837A should remain constant during
normal operation of the DAC and ADC. If it is required to
change the MCLK rate, the AD1837A should be reset. Additionally, if MCLK scaler needs to be modified so that the IMCLK
does not exceed 24.576 MHz, this should be done during the
internal reset phase of the AD1837A by programming the bits in
the first 3072 MCLK periods following the reset.
Selecting DAC Sampling Rate
The AD1837A DAC engine has a programmable interpolator
that allows the user to select different interpolation rates
based on the required sample rate and MCLK value available. Table II shows the settings required for sample rates
based on a fixed MCLK of 12.288 MHz.
Table II. DAC Sample Rate Settings
Sample Rate Interpolator Rate DAC Control 1 Register
48 kHz 8x 000000xxxxxxxx00
96 kHz 4x 000000xxxxxxxx01
192 kHz 2x 000000xxxxxxxx10
Selecting an ADC Sample Rate
The AD1837A ADC engine has a programmable decimator
that allows the user to select the sample rate based on the
MCLK value. By default, the output sample rate is IMCLK/
512. To achieve a sample rate of IMCLK/256, the sample
rate bit in the ADC Control 1 register should be set as shown
in Table III.
Table III. ADC Sample Rate Settings
Sample Rate ADC Control 1 Register
IMCLK/512 1100000xx0xxxxxx (48 kHz)
IMCLK/256 1100000xx1xxxxxx (96 kHz)
To maintain the highest performance possible, it is recommended
that the clock jitter of the master clock signal be limited to less
than 300 ps rms, measured using the edge-to-edge technique.
Even at these levels, extra noise or tones may appear in the
REV. A
–11–

AD1837A
MCLK
12.288MHz
DAC INPUT
CLOCK SCALING
1
2
2/3
ADC OUTPUT
48kHz/96kHz/192kHz
48kHz/96kHz
INTERPOLATION
FILTER
IMCLK = 24.576MHz
OPTIONAL
HPF
Figure 2. Modulator Clocking Scheme
DAC ENGINE
S-D
MODULATOR
ADC ENGINE
DECIMATO R/
FILTER
DAC
S-D
MODULATOR
ANALOG
OUTPUT
ANALOG
INPU T
t
CLATCH
CCLK
CIN
COUT
t
COE
CLS
t
CCP
D15 D14
t
COD
t
CCHtCCL
D9
D9
t
t
CDH
CDS
D8
D8 D0
Figure 3. Format of SPI Timing
DAC outputs if the jitter spectrum contains large spectral peaks.
It is highly recommended that the master clock be generated by
an independent crystal oscillator. In addition, it is especially
important that the clock signal not be passed through an FPGA
or other large digital chip before being applied to the AD1837A.
In most cases, this will induce clock jitter due to the fact that
the clock signal is sharing common power and ground connections with other unrelated digital output signals.
Power-Down and RESET
PD/RST powers down the chip and sets the control registers to
their default settings. After PD/RST is de-asserted, an initialization
routine runs inside the AD1837A to clear all memories to zero.
This initialization lasts for approximately 20 LRCLK intervals.
During this time, it is recommended that no SPI writes occur.
Power Supply and Voltage Reference
The AD1837A is designed for 5 V supplies. Separate power
supply pins are provided for the analog and digital sections.
These pins should be bypassed with 100 nF ceramic chip capacitors, as close to the pins as possible, to minimize noise pickup. A
bulk aluminum electrolytic capacitor of at least 22 mF should also
provided on the same PC board as the codec. For critical appli-
be
cations, improved performance will be obtained with separate supplies for the analog and digital sections. If this is not possible, it is
recommended that the analog and digital supplies be isolated by
t
CLH
t
COTS
D0
means of two ferrite beads in series with the bypass capacitor of
each supply. It is important that the analog supply be as clean
as possible.
The internal voltage reference is brought out on the FILTR pin
and should be bypassed as close as possible to the chip, with a
parallel combination of 10 mF and 100 nF. The reference voltage
may be used to bias external op amps to the common-mode
voltage of the analog input and output signal pins. The current
drawn from the V
pin should be limited to less than 50 mA.
REF
Serial Control Port
The AD1837A has an SPI compatible control port to permit
programming the internal control registers for the ADCs and
DACs and for reading the ADC signal levels from the internal
peak detectors. The SPI control port is a 4-wire serial control port.
The format is similar to the Motorola SPI format except the
input data-word is 16 bits wide. The maximum serial bit clock
frequency is 12.5 MHz and may be completely asynchronous to
the sample rate of the ADCs and DACs. Figure 3 shows the
format of the SPI signal.
Serial Data Ports—Data Format
The ADC serial data output mode defaults to the popular I2S
format, where the data is delayed by one BCLK interval from
the edge of the LRCLK. By changing Bits 6 to 8 in ADC
–12–
REV. A

AD1837A
Control Register 2, the serial mode can be changed to rightjustified (RJ), left-justified DSP (DSP), or left-justified (LJ).
In the RJ mode, it is necessary to set Bits 4 and 5 to define the
width of the data-word.
The DAC serial data input mode defaults to I
2
S. By changing
Bits 5, 6, and 7 in DAC Control Register 1, the mode can be
changed to RJ, DSP, LJ, Packed Mode 1, or Packed Mode 2. The
word width defaults to 24 bits but can be changed by reprogramming Bits 3 and 4 in DAC Control Register 1.
Packed Modes
The AD1837A packed mode allows a DSP or other controller to
write to all DACs and read all ADCs using one input data pin
and one output data pin. Packed Mode 256 refers to the number
of BCLKs in each frame. The LRCLK is low while data from a
left channel DAC or ADC is on the data pin and high while data
from a right channel DAC or ADC is on the data pin. DAC data is
applied on the DSDATA1 pin, and ADC data is available on the
ASDATA pin. Figures 7 to 10 show the timing
for the packed
mode. Packed mode is available for 48 kHz and 96 kHz.
LRCLK
BCLK
LEFT CHANNEL RIGHT CHANNEL
Auxiliary (TDM) Mode
A special auxiliary mode is provided to allow three external stereo
ADCs to be interfaced to the AD1837A to provide 8-in/8-out
operation. In addition, this mode supports glueless interface to a
single SHARC
®
DSP serial port, allowing a SHARC DSP to
access all eight channels of analog I/O. In this special mode,
many pins are redefined; see Table IV for a list of redefined pins.
The auxiliary and the TDM interfaces are independently
configurable to operate as masters or slaves. When the auxiliary
interface is set as a master, by programming the Auxiliary Mode
bit in ADC Control Register 2, AUXLRCLK and AUXBCLK are
generated by the AD1837A. When the auxiliary interface is set
as a slave, AUXLRCLK and AUXBCLK need to be generated
by an external ADC, as shown in Figure 13.
The TDM interface can be set to operate as a master or slave by
connecting the M/S pin to DGND or ODVDD, respectively. In
master mode, the FSTDM and BCLK signals are outputs generated by the AD1837A. In slave mode, FSTDM and BCLK are
inputs and should be generated by the SHARC. Both 48 kHz
and 96 kHz operations are available (based on a 12.288 MHz or
24.576 MHz MCLK) in this mode.
SDATA
LRCLK
BCLK
SDATA
LRCLK
BCLK
SDATA
LRCLK
BCLK
SDATA
MSB
LEFT CHANNEL
MSB MSB
LEFT CHANNEL RIGHT CHANNEL
MSB MSB
MSB MSB
NOTES
1. DSP MODE DOES NOT IDENTIFY CHANNEL.
2. LRCLK NORMALLY OPERATES AT fS EXCEPT FOR DSP MODE, WHICH IS 2 f
3. BCLK FREQUENCY IS NORMALLY 64 LRCLK BUT MAY BE OPERATED IN BURST MODE.
LSB
LEFT-JUSTIFIED MODE—16 BITS TO 24 BITS PER CHANNEL
LSB LSB
I2S MODE—16 BITS TO 24 BITS PER CHANNEL
RIGHT-JUSTIFIED MODE—SELECT NUMBER OF BITS PER CHANNEL
LSB LSB
DSP MODE— 16 BITS TO 24 BITS PER CHANNEL
MSB
LSB LSB
1/f
S
.
S
LSB
RIGHT CHANNEL
REV. A
Figure 4. Stereo Serial Modes
–13–

AD1837A
ASDATA
LEFT-JUSTIFIED
ASDATA
2
S COMPATIBLE
I
ASDATA
RIGH T-JUSTIFIED
ABCLK
ALRCLK
MODE
MODE
MODE
DBCLK
DLRCLK
t
DBH
t
t
t
t
ABL
ALS
DBL
DLS
MSB
t
ABDD
MSB-1
MSB
Figure 5. ADC Serial Mode Timing
MSB
LSB
t
ALH
t
DLH
DSDATA
LEFT-JUSTIFIED
MODE
DSDATA
2
I
S COMPATIBLE
MODE
DSDATA
RIGH T-JUSTIFIED
MODE
t
DDS
MSB
t
DDH
MSB-1
t
DDS
MSB
t
DDH
t
DDS
MSB
Figure 6. DAC Serial Mode Timing
t
DDH
t
DDS
LSB
t
DDH
–14–
REV. A

LRCLK
BCLK
ADC DATA
LRCLK
BCLK
ADC DATA
128 BCLKs
16 BCLKs
SLOT 1
LEFT
SLOT 3 SLOT 4 SLOT 7 SLOT 8
SLOT 2
MSB MSB – 1 MSB – 2
SLOT 5
RIGHT
Figure 7a. ADC Packed Mode 128
256 BCLKs
32 BCLKs
SLOT 1
LEFT
SLOT 3 SLOT 4 SLOT 7 SLOT 8
SLOT 2
MSB MSB – 1 MSB – 2
SLOT 5
RIGHT
AD1837A
SLOT 6
SLOT 6
LRCLK
BCLK
DAC DATA
LRCLK
BCLK
DAC DATA
Figure 7b. ADC Packed Mode 256
128 BCLKs
16 BCLKs
SLOT 2
SLOT 3
SLOT 1
LEFT 1
LEFT 2
MSB MSB – 1 MSB – 2
LEFT 3
SLOT 4
LEFT 4
SLOT 5
RIGHT 1
Figure 8a. DAC Packed Mode 128
256 BCLKs
32 BCLKs
SLOT 2
SLOT 3
SLOT 1
LEFT 1
LEFT 2
MSB MSB – 1 MSB – 2
LEFT 3
SLOT 4
LEFT 4
SLOT 5
RIGHT 1
SLOT 6
RIGHT 2
SLOT 6
RIGHT 2
SLOT 7
RIGHT 3
SLOT 7
RIGHT 3
SLOT 8
RIGHT 4
SLOT 8
RIGHT 4
REV. A
Figure 8b. DAC Packed Mode 256
–15–

AD1837A
t
ABH
ABCLK
t
ABL
t
ALS
ALRCLK
t
ALH
ASDATA
MSB
Figure 9. ADC Packed Mode Timing
MSB – 1
t
ABDD
t
DBH
DBCLK
t
DBL
t
DLS
DLRCLK
t
DLH
t
DSDATA
DDS
MSB
t
MSB – 1
DDH
Figure 10. DAC Packed Mode Timing
–16–
REV. A

AD1837A
Table IV. Pin Function Changes in Auxiliary Mode
Pin Name I2S Mode Auxiliary Mode
MSB TDM
1ST
CH
2
S Data Out, Internal ADC TDM Data Out to SHARC.
2
S Data In, Internal DAC1 TDM Data In from SHARC.
2
S Data In, Internal DAC2 AUX-I2S Data In 1 (from External ADC).
2
S Data In, Internal DAC4 AUX-I2S Data In 3 (from External ADC).
ADC in slave mode. In master mode, driven by
MCLK/512.
in slave mode. In master mode, driven by MCLK/8.
MSB TDM
8TH
CH
ASDATA (O) I
DSDATA1 (I) I
DSDATA2 (I)/AAUXDATA1 (I) I
DSDATA3 (I)/AAUXDATA2 (I) I2S Data In, Internal DAC3 AUX-I2S Data In 2 (from External ADC).
DSDATA4 (I)/AAUXDATA3 (I) I
ALRCLK (O) LRCLK for ADC TDM Frame Sync Out to SHARC (FSTDM).
ABCLK (O) BCLK for ADC TDM BCLK Out to SHARC.
DLRCLK (I)/AUXLRCLK (I/O) LRCLK In/Out Internal DACs AUX LRCLK In/Out. Driven by external LRCLK from
DBCLK (I)/AUXBCLK (I/O) BCLK In/Out Internal DACs AUX BCLK In/Out. Driven by external BCLK from ADC
FSTDM
BCLK
TDM
ASDATA1
TDM (OUT)
ASDATA
TDM INTERFACE
(FROM AUX ADC NO. 1)
(FROM AUX ADC NO. 1)
(FROM AUX ADC NO. 1)
S INTERFACE
2
(FROM AUX ADC NO. 2)
AUX – I
(FROM AUX ADC NO. 3)
DSDATA1
TDM (IN)
DSDATA1
LRCLK I
BCLK I
AAUXDATA1 (IN)
AAUXDATA2 (IN)
AAUXDATA3 (IN)
INTERNAL
ADC L1
MSB TDM
1ST
CH
INTERNAL
DAC L1
AUX
2
S
AUX
2
S
AUX BCLK FREQUENCY IS 64 FRAME RATE; TDM BCLK FREQUENCY IS 256 FRAME RATE.
AUX_ADC L2
32
INTERNAL
DAC L2
32
AUX_ADC L3
INTERNAL
DAC L3
LEFT
AUX_ADC L4
INTERNAL
DAC L4
INTERNAL
ADC R1
INTERNAL
DAC R1
Figure 11. Auxiliary Mode Timing
AUX_ADC R2
INTERNAL
DAC R2
AUX_ADC R3
INTERNAL
DAC R3
RIGHT
2
S – MSB RIGHTI2S – MSB LEFT
I
I2S – MSB RIGHTI2S – MSB LEFT
2
I
S – MSB RIGHTI2S – MSB LEFT
AUX_ADC R4
MSB TDM
8TH
CH
INTERNAL
DAC R4
REV. A
–17–

AD1837A
ADC
NO. 1
SLAVE
ADC
NO. 2
SLAVE
ADC
NO. 3
SLAVE
LRCLK
BCLK
DATA
MCLK
LRCLK
BCLK
DATA
MCLK
LRCLK
BCLK
DATA
MCLK
30MHz
12.288MHz
FSYNC-TDM (RFS)
DBCLK/AUXBCLK
DLRCLK/AUXLRCLK
DSDATA2/AAUXDATA1
DSDATA3/AAUXDATA2
DSDATA4/AAUXDATA3
MCLK
SHARC
RxDATA
RxCLK
ASDATA FSTDM BCLK DSDATA1
TFS (NC)
TxCLK
AD1837A
MASTER
Figure 12. Auxiliary Mode Connection (Master Mode) to SHARC
30MHz
SHARC
SHARC IS ALWAYS
RUNNING IN SLAVE MODE
(INTERRUPT DRIVEN).
TxDATA
SHARC IS ALWAYS
RUNNING IN SLAVE MODE
(INTERRUPT DRIVEN).
ADC
NO. 1
MASTER
ADC
NO. 2
SLAVE
ADC
NO. 3
SLAVE
12.288MHz
LRCLK
BCLK
DATA
MCLK
LRCLK
BCLK
DATA
MCLK
LRCLK
BCLK
DATA
MCLK
FSYNC-TDM (RFS)
RxDATA
RxCLK
ASDATA FSTDM BCLK DSDATA1
DBCLK/AUXBCLK
DLRCLK/AUXLRCLK
DSDATA2/AAUXDATA1
DSDATA3/AAUXDATA2
DSDATA4/AAUXDATA3
MCLK
TFS (NC)
TxCLK
AD1837A
SLAVE
TxDATA
Figure 13. Auxiliary Mode Connection (Slave Mode) to SHARC
–18–
REV. A

AD1837A
CONTROL/STATUS REGISTERS
The AD1837A has 15 control registers, 13 of which are used to
set the operating mode of the part. The other two registers,
ADC Peak 0 and ADC Peak 1, are read-only and should not be
programmed. Each of the registers is 10 bits wide with the
exception of the ADC peak reading registers which are six bits
wide. Writing to a control register requires a 16-bit data frame
to be transmitted. Bits 15 to 12 are the address bits of the
required register. Bit 11 is a read/write bit. Bit 10 is reserved
and should always be programmed to 0. Bits 9 to 0 contain the
10-bit value that is to be written to the register or, in the case of
a read operation, the 10-bit register contents. Figure 3 shows
the format of the SPI read and write operation.
DAC CONTROL REGISTERS
The AD1837A register map has 10 registers that control the
functionality of the DAC section of the part. The function of the
bits in these registers is discussed in the following sections.
Sample Rate
These bits control the sample rate of the DACs. Based on a
24.576 MHz IMCLK, sample rates of 48 kHz, 96 kHz, and
192 kHz are available. The MCLK scaling bits in ADC Control 3
should be programmed appropriately, based on the master
clock frequency.
Power-Down/Reset
This bit controls the power-down status of the DAC section.
By default, normal mode is selected, but by setting this bit, the
digital section of the DAC stage can be put into a low power
mode, thus reducing the digital current. The analog output
section of the DAC stage is not powered down.
DAC Data-Word Width
These two bits set the word width of the DAC data. Compact
disc (CD) compatibility may require 16 bits, but many modern
digital audio formats require 24-bit sample resolution.
DAC Data Format
The AD1837A serial data interface can be configured to be
compatible with a choice of popular interface formats including
2
S, LJ, RJ, or DSP modes. Details of these interface modes
I
are given in the Serial Data Port section of this data sheet.
De-emphasis
The AD1837A provides built-in de-emphasis filtering for the
three standard sample rates of 32.0 kHz, 44.1 kHz, and 48 kHz.
Mute DAC
Each of the eight DACs in the AD1837A has its own independent
mute control. Setting the appropriate bit mutes the DAC output. The AD1837A uses a clickless mute function that attenuates
the output to approximately –100 dB over a number of cycles.
Stereo Replicate
Setting this bit copies the digital data sent to the stereo pair DAC1
to the three other stereo DACs in the system. This allows all
four stereo DACs to be driven by one digital data stream. Note
that in this mode, DAC data sent to the other DACs is ignored.
DAC Volume Control
Each DAC in the AD1837A has its own independent volume
control. The volume of each DAC can be adjusted in 1024
linear steps by programming the appropriate register. The
default value for this register is 1023, which provides no attenuation, i.e., full volume.
ADC CONTROL REGISTERS
The AD1837A register map has five registers that are used to
control the functionality and read the status of the ADCs. The
function of the bits in each of these registers is discussed in the
following sections.
ADC Peak Level
These two registers store the peak ADC result from each channel
when the ADC peak readback function is enabled. The peak result
is stored as a 6-bit number from 0 dB to –63 dB in 1 dB steps.
The value contained in the register is reset once it has been read,
allowing for continuous level adjustment as required. Note that
the ADC peak level registers use the 6 MSB in the register to
store the results.
Sample Rate
This bit controls the sample rate of the ADCs. Based on a
24.576 MHz IMCLK, sample rates of 48 kHz and 96 kHz are
available. The MCLK scaling bits in ADC Control Register 3
should be programmed appropriately based on the master clock
frequency.
ADC Power-Down
This bit controls the power-down status of the ADC section and
operates in a similar manner to the DAC power-down.
High-Pass Filter
The ADC signal path has a digital high-pass filter. Enabling this
filter removes the effect of any dc offset in the analog input
signal from the digital output codes.
ADC Data-Word Width
These two bits set the word width of the ADC data.
ADC Data Format
The AD1837A serial data interface can be configured to be
compatible with a choice of popular interface formats, including
2
S, LJ, RJ, or DSP modes.
I
Master/Slave Auxiliary Mode
When the AD1837A is operating in the auxiliary mode, the
auxiliary ADC control pins, AUXBCLK and AUXLRCLK, that
connect to the external ADCs, can be set to operate as a master
or slave. If the pins are set in slave mode, one of the external
ADCs should provide the LRCLK and BCLK signals.
ADC Peak Readback
Setting this bit enables ADC peak reading. See the ADCs section
for more information.
REV. A
–19–

AD1837A
Table V. Control Register Map
Register Address Register Name Description Type Width Reset Setting (Hex)
0000 DACCTRL1 DAC Control 1 R/W 10 000
0001 DACCTRL2 DAC Control 2 R/W 10 000
0010 DACVOL1 DAC Volume—Left 1 R/W 10 3FF
0011 DACVOL2 DAC Volume—Right 1 R/W 10 3FF
0100 DACVOL3 DAC Volume—Left 2 R/W 10 3FF
0101 DACVOL4 DAC Volume—Right 2 R/W 10 3FF
0110 DACVOL5 DAC Volume—Left 3 R/W 10 3FF
0111 DACVOL6 DAC Volume—Right 3 R/W 10 3FF
1000 DACVOL7 DAC Volume—Left 4 R/W 10 3FF
1001 DACVOL8 DAC Volume—Right 4 R/W 10 3FF
1010 ADCPeak0 ADC Left Peak R 6 000
1011 ADCPeak1 ADC Right Peak R 6 000
1100 ADCCTRL1 ADC Control 1 R/W 10 000
1101 ADCCTRL2 ADC Control 2 R/W 10 000
1110 ADCCTRL3 ADC Control 3 R/W 10 000
1111 Reserved Reserved R/W 10 Reserved
Table VI. DAC Control 1
Function
DAC Data- Power-Down
Address R/
15, 14, 13, 12 11 10 9, 8 7, 6, 5 4, 3 2 1, 0
0000 0 0 00 = None 000 = I2S 00 = 24 Bits 0 = Normal
WW
W RES De-emphasis DAC Data Format Word Width Reset Sample Rate
WW
00 = 48 kHz
01 = 44.1 kHz 001 = RJ 01 = 20 Bits 1 = Power-Down
10 = 32.0 kHz 010 = DSP 10 = 16 Bits
11 = 48.0 kHz 011 = LJ 11 = Reserved
01 = 96 kHz
10 = 192 kHz
11 = 48 kHz
100 = Packed 256
101 = Packed 128
110 = Reserved
111 = Reserved
Table VII. DAC Control 2
Function
MUTE DAC
OUTL1
Address R/
Stereo
WW
W RES RES Replicate OUTR4 OUTL4 OUTR3 OUTL3 OUTR2 OUTL2 OUTR1
WW
15, 14,
13, 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 543210
0001 0 0 0 0 = Off 0 = On 0 = On 0 = On 0 = On 0 = On 0 = On 0 = On 0 = On
1 = Replicate 1 = Mute 1 = Mute 1 = Mute 1 = Mute 1 = Mute 1 = Mute 1 = Mute 1 = Mute
–20–
REV. A

AD1837A
Table VIII. DAC Volume Control
Function
Address R/W RES DAC Volume
15, 14, 13, 12 11 10 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
0010 = DACL1 0 0 0000000000 = Mute
0011 = DACR1 0000000001 = 1/1023
0100 = DACL2 0000000010 = 2/1023
0101 = DACR2 1111111110 = 1022/1023
0110 = DACL3 1111111111 = 1023/1023
0111 = DACR3
1000 = DACL4
1001 = DACR4
Table X. ADC Control 1
Address R/W RES Reserved Filter Power-Down Rate Reserved
15, 14, 13, 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
1100 0 0 0 0 = All Pass 0 = Normal 0 = 48 kHz 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
Address R/W RES Six Data Bits Fixed Bits
15, 14, 13, 12 11 10 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4 3, 2, 1, 0
1010 = Left ADC 1 0 000000 = 0 dBFS 0000
1011 = Right ADC 000001 = –1 dBFS
Function
ADC Sample
1 = High-Pass 1 = Power-Down 1 = 96 kHz 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
Table IX. ADC Peak
Function
Four
000010 = –2 dBFS These
four bits
are always
zero.
111111 = –63 dBFS
Table XI. ADC Control 2
Function
R/W Master/Slave ADC ADC Data- ADC MUTE
Address RES RES Aux Mode Data Format Word Width Reserved Right Left
15, 14, 13, 12 11 10 9 8, 7, 6 5, 4 3, 2 1 0
1101 0 0 0 = Slave 000 = I2S 00 = 24 Bits 0, 0 0 = On 0 = On
1 = Master 001 = RJ 01 = 20 Bits 1 = Mute 1 = Mute
010 = DSP 10 = 16 Bits
011 = LJ 11 = Reserved
100 = Packed 256
101 = Packed 128
110 = Auxiliary 256
111 = Auxiliary 512
Table XII. ADC Control 3
Function
R/W IMCLK ADC DAC ADC
Address RES RES Reserved Clocking Scaling Peak Readback Test Mode Test Mode
15, 14,
13, 12 11 10 9, 8 7, 6 5 4, 3, 2 1, 0
1110 0 0 0, 0 00 = MCLK 20 = Disabled Peak Readback 000 = Normal Mode 00 = Normal Mode
01 = MCLK 1 = Enabled Peak Readback All others reserved All others reserved
10 = MCLK 2/3
11 = MCLK 2
REV. A
–21–

AD1837A
CASCADE MODE
Dual AD1837A Cascade
The AD1837A can be cascaded to an additional AD1837A,
which, in addition to six external stereo ADCs, can be used to
create a 32-channel audio system with 16 inputs and 16 outputs.
The cascade is designed to connect to a SHARC DSP and operates
in a time division multiplexing (TDM) format. Figure 14 shows
the connection diagram for cascade operation. The digital interface for both parts must be set to operate in Auxiliary 512 mode
by programming ADC Control Register 2. AD1837A No. 1 is
set as a master device by connecting the M/S pin to DGND and
AD1837A No.2 is set as a slave device by connecting the M/S to
ODVDD. Both devices should be run from the same MCLK
and PD/RST signals to ensure that they are synchronized.
SHARC
(SLAVE)
DRx
RFSx
RCLKx
TFSx
TCLKx
DTx
AUX ADC
(SLAVE)
BCLK
LRCLK
DOUT
ASDATA
ALRCLK
ABCLK
AUX ADC
(SLAVE)
BCLK
LRCLK
AUXBCLK
AUXLRCLK
DOUT
AD1837A NO. 1
AUXDATA1
AUXDATA2
AUXDATA3
AUX ADC
(SLAVE)
BCLK
LRCLK
(MASTER)
DSDATA
With Device 1 set as a master, it will generate the frame-sync
and bit clock signals. These signals are sent to the SHARC and
Device 2 ensuring that both know when to send and receive data.
The cascade can be thought of as two 256-bit shift registers, one
for each device. At the beginning of a sample interval, the shift
registers contain the ADC results from the previous sample
interval. The first shift register (Device 1) clocks data into the
SHARC and also clocks in data from the second shift register
(Device 2). While this is happening, the SHARC is sending
DAC data to the second shift register. By the end of the sample
interval, all 512 bits of ADC data in the shift registers will have
been clocked into the SHARC and been replaced by DAC data,
which is subsequently written to the DACs. Figure 15 shows the
timing diagram for the cascade operation.
DOUT
AUX ADC
(SLAVE)
BCLK
LRCLK
DOUT
ASDATA
ALRCLK
ABCLK
AUX ADC
(SLAVE)
BCLK
LRCLK
AUXBCLK
AUXLRCLK
DOUT
AD1837A NO. 2
AUXDATA1
AUXDATA2
AUXDATA3
AUX ADC
(SLAVE)
BCLK
LRCLK
(SLAVE)
DSDATA
DOUT
TFSx/
RFSx
DTx
DRx
ABCLK
DTx
DRx
Figure 14. AD1837A Cascade
256 ABCLKs
AD1837A NO. 1 DACs
L1 L2 L3 L4 R1 R2 R3 R4
AD1837A NO. 1 ADCs
L1 L2 L3 L4 R1 R2 R3 R4
MSB MSB – 1
MSB
MSB – 1
LSB
LSB
32 ABCLKs
Figure 15. AD1837A Cascade Timing
256 ABCLKs
AD1837A NO. 2 DACs
L1 L2 L3 L4 R1 R2 R3 R4
AD1837A NO. 2 ADCs
L1 L2 L3 L4 R1 R2 R3 R4
DON’T CARE
–22–
REV. A

AUDIO
INPUT
600Z
47F
5.76k
+
100pF
NPO
V
5.76k 5.76k
750k
V
REF
REF
5.76k
120pF NPO
OP275
OP275
237
237
1nF
NPO
1nF
NPO
100pF
NPO
ADCxN
ADCxP
V
BIAS
(2.25V)
OUTx
11k
5.62k
11k
270pF
NPO
560pF
NPO
5.62k
3.01k
1.5k
68pF
NPO
OP275
150pF
NPO
AD1837A
AUDIO
2.2nF
NPO
OUTPUT
604
Figure 16. Typical ADC Input Filter Circuit
Figure 17. Typical DAC Output Filter Circuit
REV. A
–23–

AD1837A
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
52-Lead Metric Quad Flat Package [MQFP]
(S-52-1)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
13.45
13.20 SQ
12.95
39
TOP VIEW
(PINS DOWN)
PIN 1
1
0.40
0.22
27
26
10.20
10.00 SQ
9.80
14
13
2.20
2.00
1.80
0.25
MAX
10
6
2
1.03
0.88
0.73
SEATING
PLANE
0.23
0.11
VIEW A
7
0
0.13 MIN
COPLANARITY
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-022-AC.
2.45
MAX
7.80
REF
40
52
0.65 BSC
Revision History
Location Page
1/04—Data Sheet changed from REV. 0 to REV. A.
Changes to ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Deleted Clock Signals section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Added AD1835A CLOCKING SCHEME section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Added Table II and Table III and renumbered following tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Changes to Auxiliary (TDM Mode) section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Changes to Figure 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Changes to Figure 6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Added Figures 7a and 8a . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Renumbered Figure 7 and Figure 8 to Figure 7b and Figure 8b . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Changes to Figure 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Changes to Table VIII . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Updated OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
C02733–0–1/04(A)
–24–
REV. A
 Loading...
Loading...