V
Touch Screen Digitizer
FEATURES
4-wire touch screen interface
Specified throughput rate of 125 kSPS
Low power consumption:
1.37 mW max at 125 kSPS with V
Single supply, V
of 2.2 V to 5.25 V
CC
Ratiometric conversion
High speed serial interface
Programmable 8-bit or 12-bit resolution
2 auxiliary analog inputs
Shutdown mode: 1 µA max
16-lead QSOP and TSSOP packages
APPLICATIONS
Personal digital assistants
Smart hand-held devices
Touch screen monitors
Point-of-sales terminals
Pagers
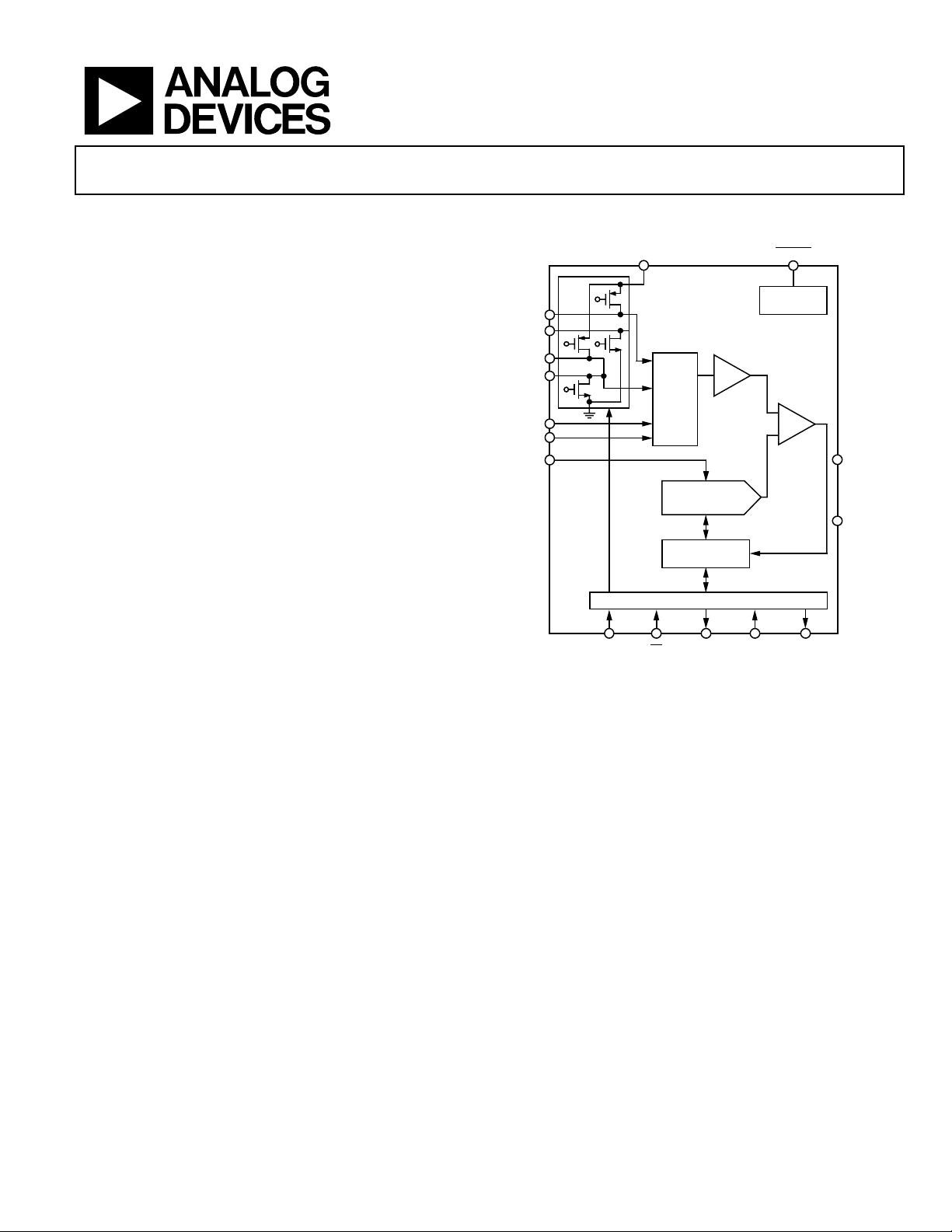
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7843 is a 12-bit successive approximation ADC with a
synchronous serial interface and low on resistance switches for
driving touch screens. The part operates from a single 2.2 V to
5.25 V power supply and features throughput rates greater than
125 kSPS.
The external reference applied to the AD7843 can be varied
from 1 V to +V
The device includes a shutdown mode that reduces the
V
REF.
current consumption to less than 1 µA.
The AD7843 features on-board switches. This, coupled with low
power and high speed operation, make this device ideal for
battery-powered systems such as personal digital assistants with
resistive touch screens, and other portable equipment. The part
is available in a 16-lead 0.15" quarter size outline package
(QSOP) and a 16-lead thin shrink small outline package
(TSSOP).
, while the analog input range is from 0 V to
CC
= 3.6 V
CC
AD7843
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
+V
CC
X+
X–
Y+
Y–
IN3
IN4
REF
DIN CS DOUT DCLK BUSY
AD7843
4-TO-1
I/P
MUX
REDISTRIBUTION
CONTROL LOGIC
T/H
CHARGE
DAC
SAR + ADC
SPORT
Figure 1.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Ratiometric conversion mode available eliminating errors
due to on-board switch resistances.
2. Maximum current consumption of 380 µA while operating
at 125 kSPS.
3. Power-down options available.
4. Analog input range from 0 V to V
5. Versatile serial I/O port.
REF
.
PENIRQ
PEN
INTERRUPT
COMP
GND
+V
CC
02144-B-001
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD7843
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Analog Input............................................................................... 12
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 4
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 5
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 6
Terminology ...................................................................................... 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 8
Circuit Information........................................................................ 11
ADC Transfer Function............................................................. 11
Typical Connection Diagram ................................................... 11
REVISION HISTORY
3/04—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. A to Rev. B
Updated Format..................................................................Universal
Changes to Absolute Maximum Ratings ....................................... 5
Addition to the PD0 and PD1 Section......................................... 14
Additions to Ordering Guide........................................................ 20
Control Register ......................................................................... 14
Power vs. Throughput Rate....................................................... 15
Serial Interface............................................................................ 16
Detailed Serial Interface Timing .............................................. 17
Pen Interrupt Request................................................................ 19
Grounding and Layout .............................................................. 19
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 20
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 20
3/03—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 16
Rev. B | Page 2 of 20
AD7843
SPECIFICATIONS
VCC = 2.7 V to 3.6 V, V
Table 1.
Parameter AD7843A1 Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 12 Bits
No Missing Codes 11 Bits min
Integral Nonlinearity2 ±2 LSB max
Offset Error2 ±6 LSB max VCC = 2.7 V
Offset Error Match3 1 LSB max
0.1 LSB typ
Gain Error2 ±4 LSB max
Gain Error Match3 1 LSB max
0.1 LSB typ
Power Supply Rejection 70 dB typ
SWITCH DRIVERS
On-Resistance2
Y+, X+ 5 Ω typ
Y−, X− 6 Ω typ
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Ranges 0 to V
DC Leakage Current ±0.1 µA typ
Input Capacitance 37 pF typ
REFERENCE INPUT
V
Input Voltage Range 1.0/+VCC V min/max
REF
DC Leakage Current ±1 µA max
V
Input Impedance 5 GΩ typ
REF
V
Input Current3 20 µA max 8 µA typ
REF
1 µA typ f
1 µA max
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current, IIN ±1 µA max Typically 10 nA, VIN = 0 V or +VCC
Input Capacitance, C
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, VOH VCC − 0.2 V min I
Output Low Voltage, VOL 0.4 V max I
PENIRQ Output Low Voltage, VOL
Floating-State Leakage Current ±10 µA max
Floating-State Output Capacitance4 10 pF max
Output Coding Straight (Natural) Binary
CONVERSION RATE
Conversion Time 12 DCLK Cycles max
Track-and-Hold Acquisition Time 3 DCLK Cycles min
Throughput Rate 125 kSPS max
Footnotes on next page.
= 2.5 V, f
REF
2.4 V min
INH
0.4 V max
INL
4
10 pF max
IN
= 2 MHz, TA = −40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted.
SCLK
V
REF
0.4 V max I
= GND or +VCC
CS
= 12.5 kHz
SAMPLE
= +VCC; 0.001 µA typ
CS
= 250 µA; VCC = 2.2 V to 5.25 V
SOURCE
= 250 µA
SINK
= 250 µA; 100 kW pull-up
SINK
Rev. B | Page 3 of 20
AD7843
Parameter AD7843A1 Unit Test Conditions/Comments
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VCC (Specified Performance) 2.7/3.6 V min/max Functional from 2.2 V to 5.25 V
5
I
Digital I/Ps = 0 V or VCC
CC
Normal Mode (f
Normal Mode (f
Normal Mode (Static) 150 µA typ VCC = 3.6 V
Shutdown Mode (Static) 1 µA max
Power Dissipation5
Normal Mode (f
Shutdown 3.6 µW max VCC = 3.6 V
1
Temperature range as follows: A Version: −40°C to +85°C.
2
See the Terminology section.
3
Guaranteed by design.
4
Sample tested @ 25°C to ensure compliance.
5
See the Power vs. Throughput Rate section.
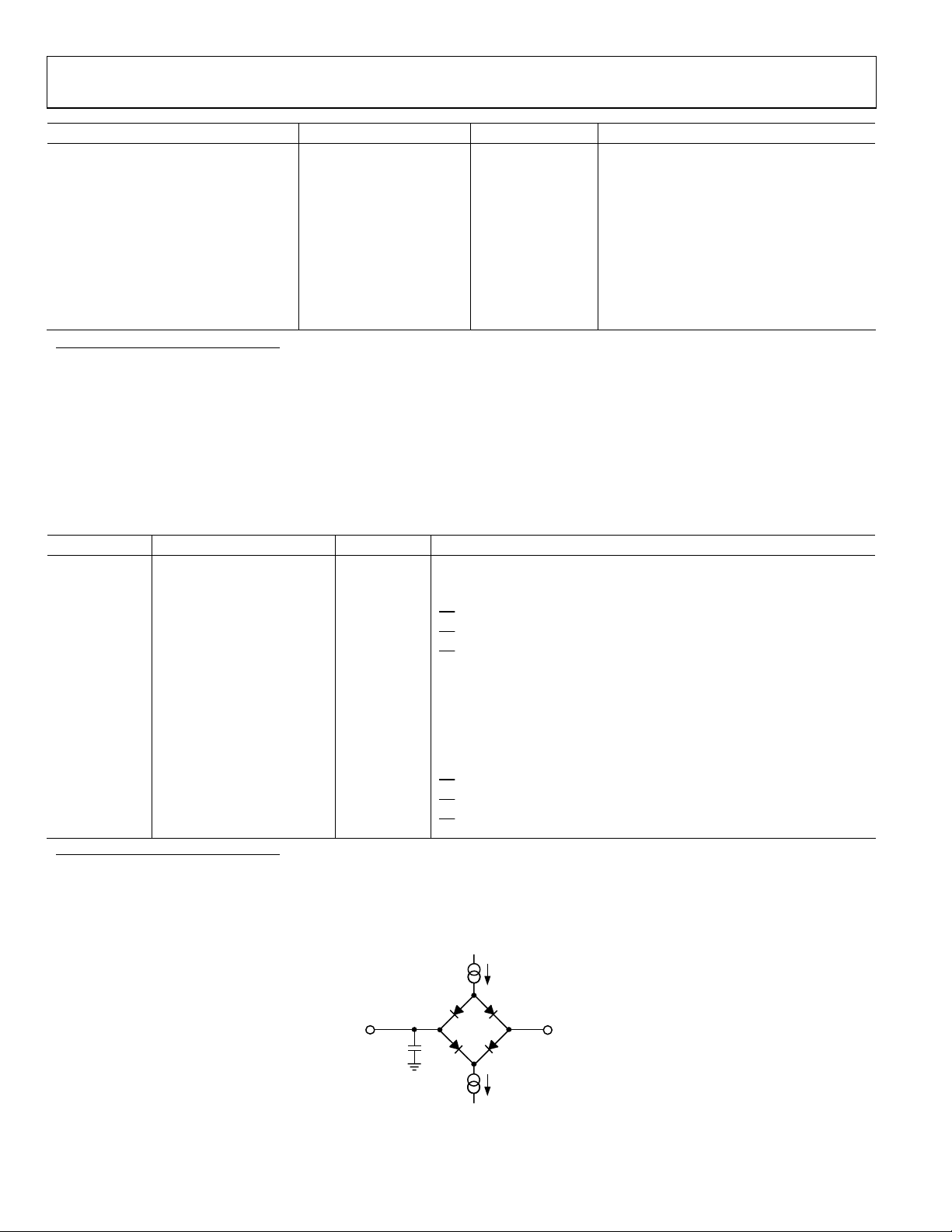
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
TA = T
Table 2. Timing Specifications
Parameter Limit at T
f
DCLK
2 MHz max
t
ACQ
t1 10 ns min
t2 60 ns max
t3 60 ns max
t4 200 ns min DCLK high pulse width
t5 200 ns min DCLK low pulse width
t6 60 ns max DCLK falling edge to BUSY rising edge
t7 10 ns min Data setup time prior to DCLK rising edge
t8 10 ns min Data valid to DCLK hold time
3
t
9
t10 0 ns min
t11 200 ns max
t
12
1
Sample tested at 25°C to ensure compliance. All input signals are specified with tr = tf = 5 ns (10% to 90% of VCC) and are timed from a voltage level of 1.6 V.
2
Mark/space ratio for the SCLK input is 40/60 to 60/40.
3
Measured with the load circuit in Figure 2 and defined as the time required for the output to cross 0.4 V or 2.0 V.
4
t12 is derived from the measured time taken by the data outputs to change 0.5 V when loaded with the circuit in Figure 2. The measured number is then extrapolated
back to remove the effects of charging or discharging the 50 pF capacitor. This means that the time, t
time of the part and is independent of the bus loading.
to T
MIN
MAX
2
10 kHz min
1.5 µs min Acquisition time
200 ns max Data access time after DCLK falling edge
4
200 ns max
= 125 kSPS) 380 µA max VCC = 3.6 V, 240 µA typ
SAMPLE
= 12.5 kSPS) 170 µA typ VCC = 2.7 V, f
SAMPLE
= 125 kSPS) 1.368 mW max VCC = 3.6 V
SAMPLE
, unless other wise noted; VCC = 2.7 V to 3.6 V, V
1
, T
MIN
Unit Description
MAX
= 2.5 V.
REF
CS
falling edge to First DCLK rising edge
CS
falling edge to BUSY three-state disabled
CS
falling edge to DOUT three-state disabled
CS
rising edge to DCLK ignored
CS
rising edge to BUSY high impedance
CS
rising edge to DOUT high impedance
, quoted in the timing characteristics is the true bus relinquish
12
= 200 kHz
DCLK
TO
OUTPUT
PIN
50pF
200µA
C
L
200µA
I
OL
1.6V
I
OH
02144-B-002
Figure 2. Load Circuit for Digital Output Timing Specifications
Rev. B | Page 4 of 20
AD7843
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
+VCC to GND −0.3 V to +7 V
Analog Input Voltage to GND −0.3 V to VCC + 0.3 V
Digital Input Voltage to GND −0.3 V to VCC + 0.3 V
Digital Output Voltage to GND −0.3 V to VCC + 0.3 V
V
to GND −0.3 V to VCC + 0.3 V
REF
Input Current to Any Pin Except Supplies1
Operating Temperature Range
Commercial −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
QSOP, TSSOP Package, Power Dissipation 450 mW
θJA Thermal Impedance 149.97°C/W (QSOP)
150.4°C/W (TSSOP)
θJC Thermal Impedance 38.8°C/W (QSOP)
27.6°C/W (TSSOP)
IR Reflow Soldering
Peak Temperture
Time-to-Peak Temperture
Ramp-Down Rate
Pb-free parts only
Peak Temperture 250°C
Time-to-Peak Temperture
Ramp-Up Rate
Ramp-Down Rate
±10 mA
220°C (±5°C)
10 sec to 30 sec
6°C/sec max
20 sec to 40 sec
3°C/sec max
6°C/sec max
________________
1
Transient currents of up to 100 mA do not cause SCR latch-up.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Rating
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those listed in the operational sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. B | Page 5 of 20
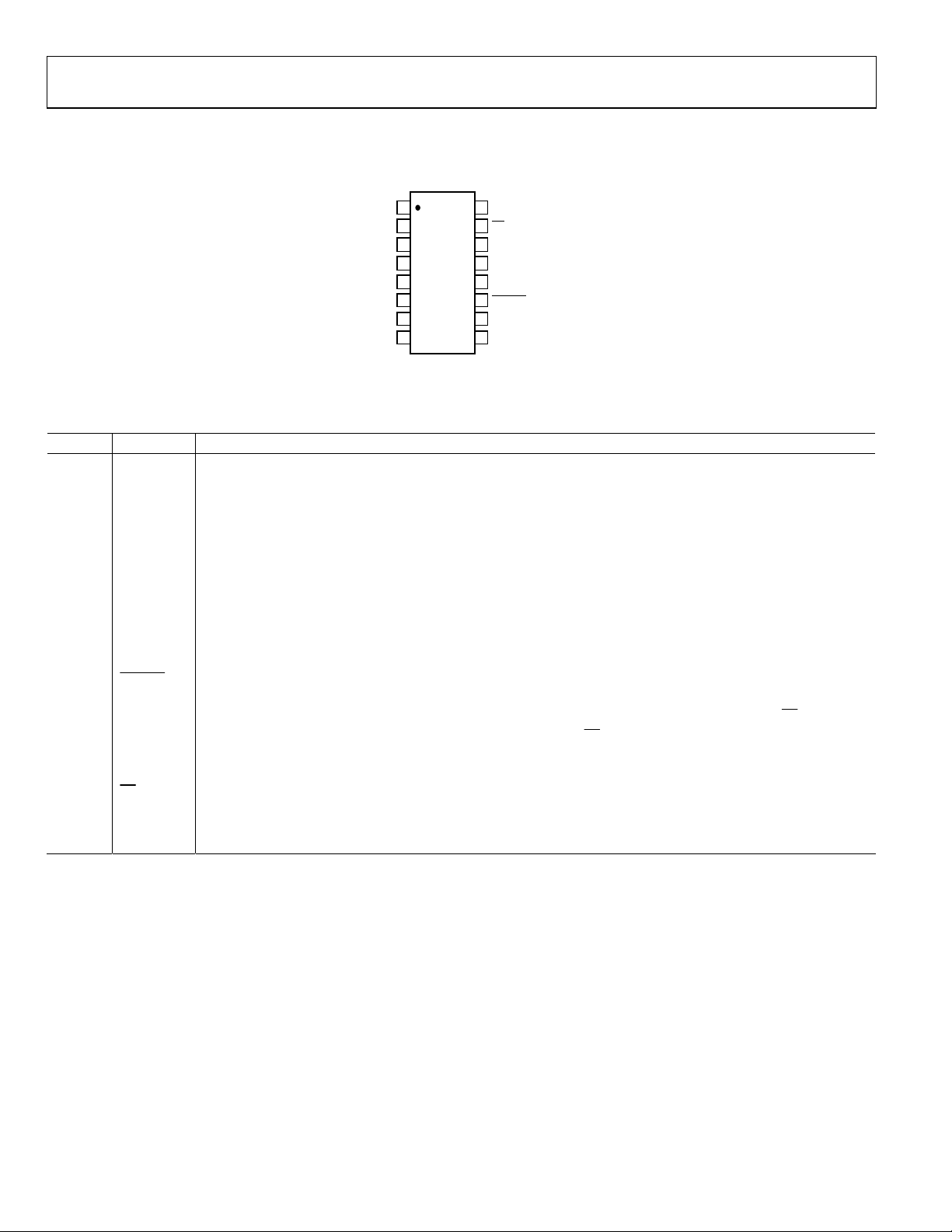
AD7843
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
1
+V
CC
2
X+
3
Y+
AD7843
4
X–
TOP VIEW
5
Y–
(Not to Scale)
6
GND
7
IN3
8
IN4
Figure 3. Pin Configuration QSOP/TSSOP
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Function
1, 10 +VCC
Power Supply Input. The +V
range for the AD7843 is from 2.2 V to 5.25 V. Both +VCC pins should be connected
CC
directly together.
2 X+ X+ Position Input. ADC Input Channel 1.
3 Y+ Y+ Position Input. ADC Input Channel 2.
4 X− X− Position Input.
5 Y− Y− Position Input.
6 GND
Analog Ground. Ground reference point for all circuitry on the AD7843. All analog input signals and any external
reference signal should be referred to this GND voltage.
7 IN3 Auxiliary Input 1. ADC Input Channel 3.
8 IN4 Auxiliary Input 2. ADC Input Channel 4.
9 V
REF
Reference Input for the AD7843. An external reference must be applied to this input. The voltage range for the
external reference is 1.0 V to +VCC. For specified performance, it is 2.5 V.
11
PENIRQ
12 DOUT
Pen Interrupt. CMOS logic open-drain output (requires 10 kΩ to 100 kΩ pull-up register externally).
Data Out. Logic Output. The conversion result from the AD7843 is provided on this output as a serial data stream.
The bits are clocked out on the falling edge of the DCLK input. This output is high impedance when CS
13 BUSY
14 DIN
BUSY Output. Logic Output. This output is high impedance when CS
Data In. Logic input. Data to be written to the AD7843 control register is provided on this input and is clocked into
the register on the rising edge of DCLK (see the Control Register section).
15
Chip Select Input. Active Low Logic Input. This input provides the dual function of initiating conversions on the
CS
AD7843 and also enables the serial input/output register.
16 DCLK
External Clock Input. Logic Input. DCLK provides the serial clock for accessing data from the part. This clock input
is also used as the clock source for the AD7843 conversion process.
16
DCLK
15
CS
14
DIN
13
BUSY
12
DOUT
11
PENIRQ
10
+V
CC
9
V
REF
02144-B-003
is high.
is high.
Rev. B | Page 6 of 20

AD7843
TERMINOLOGY
Integral Nonlinearity
This is the maximum deviation from a straight line passing
through the endpoints of the ADC transfer function. The
endpoints of the transfer function are zero scale, a point 1 LSB
below the first code transition, and full scale, a point 1 LSB
above the last code transition.
Differential Nonlinearity
This is the difference between the measured and the ideal 1 LSB
change between any two adjacent codes in the ADC.
Offset Error
This is the deviation of the first code transition (00…000) to
(00…001) from the ideal, that is, AGND + 1 LSB.
Gain Error
This is the deviation of the last code transition (111…110) to
(111…111) from the ideal (V
has been adjusted out.
− 1 LSB) after the offset error
REF
Track-and-Hold Acquisition Time
The track-and-hold amplifier enters the acquisition phase on
the fifth falling edge of DCLK after the START bit has been
detected. Three DCLK cycles are allowed for the track-and-hold
acquisition time. The input signal is fully acquired to the 12-bit
level within this time even with the maximum specified DCLK
frequency. See the Analog Input section for more details.
On Resistance
This is a measure of the ohmic resistance between the drain and
source of the switch drivers.
Rev. B | Page 7 of 20

AD7843
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
207
206
205
204
203
202
201
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
200
199
198
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
230
220
210
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 4. Supply Current vs. Temperature
f
= 12.5kHz
SAMPLE
= +V
V
REF
CC
02144-B-004
141
140
139
138
137
136
SUPPLY CURRENT (nA)
135
134
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 7. Power-Down Supply Current vs. Temperature
1000
02144-B-007
200
190
180
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
170
160
150
2.2 2.6 3.0 3.4 3.8 4.2 4.6 5.0
+V
(V)
CC
Figure 5. Supply Current vs. +V
CC
0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
0
–0.05
DELTA FROM +25°C (LSB)
–0.10
–0.15
V
= +V
REF
CC
SAMPLE RATE (kSPS)
100
02144-B-005
3.2 3.72.2 2.7 4.2 4.7 5.2
+V
(V)
CC
Figure 8. Maximum Sample Rate vs. +V
02144-B-008
CC
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
DELTA FROM +25°C (LSB)
–0.4
–0.20
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 6. Change in Gain vs. Temperature
02144-B-006
Rev. B | Page 8 of 20
–0.6
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 9. Change in Offset vs. Temperature
02144-B-009

AD7843
7.5
6.5
5.5
4.5
3.5
2.5
REFERENCE CURRENT (µA)
1.5
0.5
705525 4010 85 100 115 130
SAMPLE RATE (kHz)
02144-B-010
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
REFERENCE CURRENT (µA)
4
3
2
020–40 –20 40 60 80
TEMPERATURE (°C)
02144-B-013
Figure 10. Reference Current vs. Sample Rate
10
9
Y+
X+
8
(Ω)
7
ON
R
6
5
4
2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5
X–
Y–
+V
(V)
CC
Figure 11. Switch-On Resistance vs. +V
(X+, Y+: +V
to Pin; X−, Y−: Pin to GND)
CC
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
ERROR (LSB)
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
15 35 55 75 95 115 135 155 175 195
INL: R = 500
Ω
DNL: R = 2k
Ω
DNL: R = 500
SAMPLING RATE (kSPS)
INL: R = 2k
Ω
Figure 12. Maximum Sampling Rate vs. R
Figure 13. Reference Current vs. Temperature
9
8
7
(Ω)
6
ON
R
5
4
3
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
02144-B-011
CC
Figure 14. Switch-On Resistance vs. Temperature
Y–
TEMPERATURE (°C)
(X+, Y+:+V
Y+
X–
to Pin; X−, Y−: Pin to GND)
CC
X+
02144-B-014
0
f
= 125kHz
SAMPLE
f
= 15kHz
= 15 kHz)
INPUT
IN
SNR = 68.34dB
02144-B-015
20
Ω
02144-B-012
IN
40
60
SNR (dB)
80
100
120
30.022.57.5 15.00 37.5 45.0 52.5 60.0
FREQUENCY (kHz)
Figure 15. Auxiliary Channel Dynamic Performance
=125 kHz, f
(f
SAMPLE
Rev. B | Page 9 of 20

AD7843
0
VCC = 3V, V
100mV p-p SINEWAVE ON +V
–20
f
SAMPLE
–40
= 2.5V
REF
= 125kHz, fIN = 20kHz
Figure 16 shows the power supply rejection ratio versus V
CC
supply frequency for the AD7843. The power supply rejection
CC
ratio is defined as the ratio of the power in the ADC output at
full-scale frequency f
applied to the ADC V
to the power of a 100 mV sine wave
S
supply of frequency fS:
CC
–60
PSRR (dB)
–80
–100
–120
0 102030405060708090100
V
RIPPLE FREQUENCY (kHz)
CC
Figure 16. AC PSRR vs. Supply Ripple Frequency
PSRR (dB) = 10 log (Pf/Pfs)
where:
Pf is the power at frequency f in ADC output.
Pfs is the power at frequency f
coupled onto the ADC VCC
S
supply.
02144-B-016
Here a 100 mV p-p sine wave is coupled onto the V
Decoupling capacitors of 10 µF and 0.1 µF were used on the
supply.
CC
supply.
Rev. B | Page 10 of 20

AD7843
CIRCUIT INFORMATION
The AD7843 is a fast, low-power, 12-bit, single-supply, A/D
converter. The AD7843 can be operated from a 2.2 V to 5.25 V
supply. When operated from either a 5 V supply or a 3 V supply,
the AD7843 is capable of throughput rates of 125 kSPS when
provided with a 2 MHz clock.
The AD7843 provides the user with an on-chip track-and-hold,
multiplexer, ADC, and serial interface housed in tiny 16-lead
QSOP or TSSOP packages, which offer the user considerable
space-saving advantages over alternative solutions. The serial
clock input (DCLK) accesses data from the part and also provides
the clock source for the successive approximation ADC. The
analog input range is 0 V to V
V
can be between 1 V and VCC).
REF
(where the externally-applied
REF
The analog input to the ADC is provided via an on-chip
multiplexer. This analog input can be any one of the X and Y
panel coordinates. The multiplexer is configured with low
resistance switches that allow an unselected ADC input channel
to provide power and an accompanying pin to provide ground
for an external device. For some measurements, the on resistance
of the switches could present a source of error. However, with a
differential input to the converter and a differential reference
architecture, this error can be negated.
ADC TRANSFER FUNCTION
The output coding of the AD7843 is straight binary. The
designed code transitions occur at successive integer LSB values
(that is, 1 LSB, 2 LSBs, and so forth.). The LSB size equals
/4096. The ideal transfer characteristic for the AD7843 is
V
REF
shown in Figure 17.
111...111
111...110
111...000
011...111
ADC CODE
000...010
000...001
000...000
1LSB = V
1LSB
0V
ANALOG INPUT
/4096
REF
–1LSB
+V
REF
02144-B-017
Figure 17. AD7843 Transfer Characteristic
TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Figure 18 shows a typical connection diagram for the AD7843
in a touch screen control application. The AD7843 requires an
external reference and an external clock. The external reference
can be any voltage between 1 V and V
reference voltage sets the input range of the converter. The
conversion result is output MSB first, followed by the remaining
11 bits and three trailing zeroes, depending on the number of
clocks used per conversion. (See the Serial Interface section.)
For applications where power consumption is a concern, the
power management option should be used to improve power
performance. See Table 7 for the available power management
options.
. The value of the
CC
2.2V TO 5V
TOUCH
SCREEN
1µF TO 10µF
(OPTIONAL)
AUXILIARY INPUTS
0.1µF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
+V
CC
X+
AD7843
Y+
X–
Y–
GND
IN3
IN4
DCLK
CS
DIN
BUSY
DOUT
PENIRQ
+V
V
REF
CC
Figure 18. Typical Application Circuit
Rev. B | Page 11 of 20
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
0.1µF
SERIAL/CONVERSION CLOCK
CHIP SELECT
SERIAL DATA IN
CONVERTER STATUS
SERIAL DATA OUT
PEN INTERRUPT
100kΩ
(OPTIONAL)
02144-B-018

AD7843
(
Ω+×
=
ANALOG INPUT
Figure 19 shows an equivalent circuit of the analog input
structure of the AD7843, which contains a block diagram of the
input multiplexer, the differential input of the ADC, and the
differential reference.
Table 5 shows the multiplexer address corresponding to each
DFR
analog input, both for the SER/
set high and low. The control bits are provided serially to the
device via the DIN pin. For more information on the control
register, see the Control Register section.
bit in the control register
Acquisition Time
The track-and-hold amplifier enters tracking mode on the
falling edge of the fifth DCLK after the START bit us detected
(see Figure 24). The time required for the track-and-hold
amplifier to acquire an input signal depends on how quickly the
37 pF input capacitance is charged. With zero source impedance
on the analog input, three DCLK cycles are always sufficient to
acquire the signal to the 12-bit level. With a source impedance
on the analog input, the actual acquisition time required is
R
IN
calculated using the formula:
When the converter enters hold mode, the voltage difference
between the +IN and −IN inputs (see Figure 19) is captured on
the internal capacitor array. The input current on the analog
inputs depends on the conversion rate of the device. During the
sample period, the source must charge the internal sampling
capacitor (typically 37 pF). Once the capacitor is fully charged,
there is no further input current. The rate of charge transfer
from the analog source to the converter is a function of
conversion rate.
V
CC
X+
X–
Y+
Y–
ON-CHIP SWITCHES
X+
Y+
IN3
IN4
4-TO-1
MUX
where R
and 37 pF is the input RC value. Depending on the frequency of
DCLK used, three DCLK cycles may or may not be sufficient to
acquire the analog input signal with various source impedance
values.
REF
X+ Y+
EXT
3-TO-1
MUX
IN+
REF+
ADC CORE DATA OUT
IN+
IN– REF–
3-TO-1
MUX
)
Rt
INACQ
is the source impedance of the input signal and 100 Ω
IN
pF371004.8 ×
X– Y– GND
Figure 19. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
02144-B-019
Table 5. Analog Input, Reference, and Touch Screen Control
A21 A11 A01
SER/
0 0 1 1 X+ OFF ON V
0 1 0 1 IN3 OFF OFF V
1 0 1 1 Y+ ON OFF V
1 1 0 1 IN4 OFF OFF V
DFR
Analog Input X Switches Y Switches +REF2 –REF2
GND
REF
GND
REF
GND
REF
GND
REF
0 0 1 0 X+ OFF ON Y+ Y−
1 0 1 0 Y+ ON OFF X+ X−
1 1 0 0 Outputs Identity Code, 1000 0000 0000
1
All remaining configurations are invalid addresses.
2
Internal node − not directly accessible by the user.
Rev. B | Page 12 of 20

AD7843
Touch Screen Settling
In some applications, external capacitors could be required
across the touch screen to filter noise associated with it, for
example, noise generated by the LCD panel or backlight
circuitry. The value of these capacitors causes a settling time
requirement when the panel is touched. The settling time
typically appears as a gain error. There are several methods for
minimizing or eliminating this issue. The problem could be that
the input signal, reference, or both have not settled to their final
value before the sampling instant of the ADC. Additionally, the
reference voltage could still be changing during the conversion
cycle. One option is to stop, or slow down the DCLK for the
required touch screen settling time. This allows the input and
reference to stabilize for the acquisition time, which resolves the
issue for both single-ended and differential modes.
The other option is to operate the AD7843 in differential mode
only for the touch screen and to program the AD7843 to keep
the touch screen drivers on and not go into power-down (PD0
= PD1 = 1). Several conversions might be required, depending
on the settling time required and the AD7843 data rate. Once
the required number of conversions are made, the AD7843 can
then be placed into a power-down state on the last
measurement. The last method is to use the 15 DCLK cycle
mode, which maintains the touch screen drivers on until it is
commanded to stop by the processor.
Reference Input
The voltage difference between +REF and −REF (see Figure 19)
sets the analog input range. The AD7843 operates with a reference input in the range of 1 V to V
. The voltage into the V
CC
REF
input is not buffered and directly drives the capacitor DAC
portion of the AD7843. Figure 20 shows the reference input
circuitry. Typically, the input current is 8 µA with V
and f
= 125 kHz. This value varies by a few microamps,
SAMPLE
= 2.5 V
REF
depending on the result of the conversion. The reference current
diminishes directly with both conversion rate and reference
voltage. As the current from the reference is drawn on each bit
decision, clocking the converter more quickly during a given
conversion period does not reduce the overall current drain
from the reference.
X+
Y+
V
REF
Figure 20. Reference Input Circuitry
3-TO-1
MUX
ADC
02144-B-020
switches that supply the external touch screen can be turned off
once the acquisition is complete, resulting in a power saving.
However, the on resistance of the Y drivers affects the input
voltage that can be acquired. The full touch screen resistance
may be in the order of 200 Ω to 900 Ω, depending on the manufacturer. Therefore if the on resistance of the switches is
approximately 6 Ω, true full-scale and zero-scale voltages cannot
be acquired regardless of where the pen/stylus is on the touch
screen. Note that the minimum touch screen resistance
recommended for use with the AD7843 is approximately 70 Ω.
+V
CC
Y+
X+ IN+
Y–
GND
Figure 21. Single-Ended Reference Mode (SER/
IN+
V
REF
REF+
ADC CORE
REF–
IN–
DFR
02144-B-021
= 1)
In this mode of operation, therefore, some voltage is likely to be
lost across the internal switches and, in addition to this, it is
unlikely that the internal switch resistance will track the resistance of the touch screen over temperature and supply, providing
an additional source of error.
DFR
The alternative to this situation is to set the SER/
bit low. If
one again considers making a Y-coordinate measurement, but
now the +REF and −REF nodes of the ADC are connected
directly to the Y+ and Y− pins, this means the analog-to-digital
conversion is ratiometric. The result of the conversion is always
a percentage of the external resistance, independent of how it
could change with respect to the on resistance of the internal
switches. Figure 22 shows the configuration for a ratiometric Ycoordinate measurement. It should be noted that the differential
reference mode can be used only with +V
the +REF voltage and cannot be used with V
since the source of
CC
.
REF
The disadvantage of this mode of operation is that during both
the acquisition phase and conversion process, the external touch
screen must remain powered. This results in additional supply
current for the duration of the conversion.
+V
CC
When making touch screen measurements, conversions can be
made in the differential (ratiometric) mode or the single-ended
mode. If the SER/
DFR
bit is set to 1 in the control register, a
single-ended conversion is performed. Figure 21 shows the
configuration for a single-ended Y-coordinate measurement.
The X+ input is connected to the analog to digital converter, the
Y+ and Y− drivers are turned on, and the voltage on X+ is
digitized. The conversion is performed with the ADC referenced
from GND to V
. The advantage of this mode is that the
REF
Rev. B | Page 13 of 20
Y+
X+ IN+
Y–
GND
Figure 22. Differential Reference Mode (SER/
IN+
REF+
ADC CORE
REF–
IN–
DFR
02144-B-022
= 0)

AD7843
CONTROL REGISTER
The control word provided to the ADC via the DIN pin is
shown in Table 6. This provides the conversion start, channel
addressing, ADC conversion resolution, configuration, and
power-down of the AD7843.
Table 6 provides detailed information on the order and
description of these control bits within the control word.
Initiate START
The first bit, the S bit, must always be set to 1 to initiate the start
of the control word. The AD7843 ignores any inputs on the DIN
line until the START bit is detected.
Channel Addressing
The next three bits in the control register, A2, A1, and A0, select
the active input channel(s) of the input multiplexer (see Table 5
and Figure 19), touch screen drivers, and the reference inputs.
MODE
The MODE bit sets the resolution of the analog to digital
converter. With 0 in this bit, the following conversion has 12 bits
of resolution. With 1 in this bit, the following conversion has 8
bits of resolution.
DFR
SER/
The SER/
DFR
bit controls the reference mode, which can be
either single-ended or differential if 1 or 0 is written to this bit,
respectively. The differential mode is also referred to as the
ratiometric conversion mode. This mode is optimum for
X-position and Y-position measurements. The reference is
Table 6. Control Register Bit Function Description
MSB LSB
S A2 A1 A0 MODE
derived from the voltage at the switch drivers, which is almost
the same as the voltage to the touch screen. In this case, a
separate reference voltage is not needed because the reference
voltage to the ADC is the voltage across the touch screen. In
single-ended mode, the reference voltage to the converter is
always the difference between the V
and GND pins. See
REF
Table 5 and Figure 19 through Figure 22 for further
information.
Because the supply current required by the device is so low, a
precision reference can be used as the supply source to the
AD7843. It may also be necessary to power the touch screen
from the reference, which could require 5 mA to 10 mA. A
REF19x voltage reference can source up to 30 mA and, as such,
could supply both the ADC and the touch screen. Care must be
taken, however, to ensure that the input voltage applied to the
ADC does not exceed the reference voltage and therefore the
supply voltage. See the Absolute Maximum Ratings section.
Note that the differential mode can only be used for X-position
and Y-Position measurements. All other measurements require
single-ended mode.
PD0 and PD1
The power management options are selected by programming
the power management bits, PD0 and PD1, in the control
register. Table 7 summarizes the available options. On power-up,
PD0 defaults to 0, while PD1 defaults to 1..
SER/DFR
PD1 PD0
Bit Mnemonic Comment
7 S
6–4 A2–A0
3 MODE
2
SER/DFR
1, 0 PD1, PD0 Power Management Bits. These two bits decode the power-down mode of the AD7843, as shown in Table 7.
Start Bit. The control word starts with the first high bit on DIN. A new control word can start every 15th DCLK cycle
when in the 12-bit conversion mode, or every 11th DCLK cycle when in 8-bit conversion mode.
Channel Select Bits. These three address bits, along with the SER/DFR
switches, and reference inputs, as described in Table 5.
12-Bit/8-Bit Conversion Select Bit. This bit controls the resolution of the following conversion. With 0 in this bit, the
conversion has a 12-bit resolution, or with 1 in this bit, the conversion has a 8-bit resolution.
Single-Ended/Differential Reference Select Bit. Along with Bits A2–A0, this bit controls the setting of the multiplexer
input, switches, and reference inputs, as described in Table 5.
bit, control the setting of the multiplexer input,
Rev. B | Page 14 of 20

AD7843
POWER VS. THROUGHPUT RATE
By using the power-down options on the AD7843 when not
converting, the average power consumption of the device
decreases at lower throughput rates. Figure 23 shows how, as the
throughput rate is reduced while maintaining the DCLK
frequency at 2 MHz, the device remains in its power-down state
longer and the average current consumption over time drops
accordingly.
For example, if the AD7843 is operated in a 24 DCLK
continuous sampling mode, with a throughput rate of 10 kSPS
and a SCLK of 2 MHz, and the device is placed in the powerdown mode between conversions, (PD0, PD1 = 0, 0), the current
consumption is calculated as follows. The power dissipation
during normal operation is typically 210 µA (V
= 2.7 V). The
CC
power-up time of the ADC is instantaneous, so when the part is
converting, it consumes 210 µA. In this mode of operation, the
part powers up on the fourth falling edge of DCLK after the
start bit is recognized. It goes back into power-down at the end
of conversion on the 20th falling edge of DCLK. This means the
part consumes 210 µA for 16 DCLK cycles only, 8 µs, during
each conversion cycle. With a throughput rate of 10 kSPS, the
cycle time is 100 µs and the average power dissipated during
each cycle is (8/100) × (210 µA) = 16.8 µA.
1000
f
= 16 × f
DCLK
100
f
10
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
1
DCLK
0 120
Figure 23. Supply Current vs. Throughput (µA)
SAMPLE
= 2MHz
V
T
40 600 20 80 100
THROUGHPUT (kSPS)
= 2.7V
CC
= –40°C TO +95°C
A
02144-B-023
Table 7. Power Management Options
PD1 PD0
PENIRQ
0 0 Enabled
Description
This configuration results in power-down of the device between conversions. The AD7843 only powers down
between conversions. Once PD1 and PD0 are set to 0, 0, the conversion is performed first, and the AD7843
powers down upon completion of that conversion. At the start of the next conversion, the ADC instantly powers
up to full power. This means there is no need for additional delays to ensure full operation, and the very first
conversion is valid. The Y− switch is on while in power-down.
0 1 Disabled
This configuration results in the same behavior as when PD1 and PD0 have been programmed with 0, 0, except
that PENIRQ
1 0 Enabled
1 1 Disabled
This configuration results in keeping the AD7843 permanently powered up with PENIRQ
This configuration results in keeping the AD7843 always powered up with PENIRQ
is disabled. The Y− switch is off while in power-down.
enabled.
disabled.
Rev. B | Page 15 of 20

AD7843
X
SERIAL INTERFACE
Figure 24 shows the typical operation of the serial interface of
the AD7843. The serial clock provides the conversion clock and
also controls the transfer of information to and from the
AD7843. One complete conversion can be achieved with 24
DCLK cycles.
CS
signal initiates the data transfer and conversion process.
The
CS
The falling edge of
out of three-state. The first eight DCLK cycles are used to write
to the control register via the DIN pin. The control register is
updated in stages as each bit is clocked in. Once the converter
has enough information about the following conversion to set
the input multiplexer and switches appropriately, the converter
enters acquisition mode and, if required, the internal switches
are turned on. During the acquisition mode, the reference input
data is updated. After the three DCLK cycles of acquisition, the
takes the BUSY output and the serial bus
control word is complete (the power management bits are now
updated) and the converter enters conversion mode. At this
point, track-and-hold goes into hold mode, the input signal is
sampled, and the BUSY output goes high (BUSY returns low on
the next falling edge of DCLK). The internal switches may also
turn off at this point if in single-ended mode.
The next 12 DCLK cycles are used to perform the conversion
and to clock out the conversion result. If the conversion is
DFR
ratiometric (SER/
set low), the internal switches are on
during the conversion. A 13th DCLK cycle is needed to allow
the DSP/microcontroller to clock in the LSB. Three more DCLK
cycles clock out the three trailing zeroes and complete the 24
DCLK transfer. The 24 DCLK cycles can be provided from a
DSP or via three bursts of 8 clock cycles from a microcontroller.
CS
DCLK
DIN
THREE-STATE
BUSY
THREE-STATE
DOUT
X/Y SWITCHES
(SER/DFR HIGH)
/Y SWITCHES
(SER/DFR LOW)
1
1,2
NOTES
1
Y DRIVERS ARE ON WHEN X+ IS SELECTED INPUT CHANNEL (A2–A0 = 001); X DRIVERS ARE ON WHEN Y+ IS SELECTED INPUT CHANNEL (A2–A0 = 101).
1
WHEN PD1, PD0 = 10 OR 00, Y– WILL TURN ON AT THE END OF THE CONVERSION.
2
DRIVERS WILL REMAIN ON IF POWER-DOWN MODE IS 11 (NO POWER-DOWN) UNTIL SELECTED INPUT CHANNEL, REFERENCE MODE,
1
OR POWER-DOWN MODE IS CHANGED.
18 8 8
S A2 PD1 PD0A1 A0
(START)
IDLE
OFF OFF
OFF OFF
MODE
t
ACQ
11
SER/
DFR
ACQUIRE CONVERSION IDLE
11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
(MSB) (LSB)
ON
ON
Figure 24. Conversion Timing, 24 DCLKS per Conversion Cycle, 8-Bit Bus Interface. No DCLK delay required with dedicated serial por t.
THREE-STATE
THREE-STATE
ZERO FILLED
02144-B-024
Rev. B | Page 16 of 20

AD7843
DETAILED SERIAL INTERFACE TIMING
Figure 25 shows the detailed timing diagram for serial
interfacing to the AD7843. Writing information to the control
register takes place on the first eight rising edges of DCLK in a
data transfer. The control register is written to only if a START
bit is detected (see the Control Register section) on DIN. The
initiation of the following conversion also depends on the
presence of the START bit. Throughout the eight DCLK cycles
when data is being written to the part, the DOUT line is driven
low. The MSB of the conversion result is clocked out on the
falling edge of the ninth DCLK cycle and is valid on the rising
edge of the tenth DCLK cycle; therefore, nine leading zeros can
be clocked out prior to the MSB. This means the data seen on
the DOUT line in the 24 DCLK conversion cycle is presented in
the form of nine leading zeros, twelve bits of data, and three
trailing zeros.
CS
The rising edge of
puts the bus and the BUSY output back
into three-state, the DIN line is ignored, and, if a conversion is
in progress at the time, this is also aborted. However, if
CS
is not
brought high after the completion of the conversion cycle, then
the part waits for the next START bit to initiate the next
conversion. This means that each conversion does not
necessarily need to be framed by
CS
, because once CS goes low,
the part detects each START bit and clocks in the control word
after it on DIN. When the AD7843 is in the 12-bit conversion
mode, a second START bit is not detected until seven DCLK
pulses have elapsed after a control word is clocked in on DIN,
that is, another START bit can be clocked in on the eighth
DCLK rising edge after a control word is written to the device
(see the Fifteen Clocks per Cycle section). If the device is in the
8-bit conversion mode, a second START bit is not recognized
until three DCLK pulses elapse after the control word is clocked
in, that is, another START bit can be clocked in on the fourth
DCLK rising edge after a control word is written to the device.
Because a START bit can be recognized during a conversion, the
control word for the next conversion can be clocked in during
the current conversion, enabling the AD7843 to complete a
conversion cycle in less than 24 DCLKs.
CS
t
DCLK
DIN
BUSY
DOUT
t
1
t
2
t
3
4
t
5
t
8
t
7
t
6
PD0
Figure 25. Detailed Timing Diagram
t
6
DB11
t
9
DB10
t
10
t
11
t
12
02144-B-025
Rev. B | Page 17 of 20

AD7843
Sixteen Clocks per Cycle
The control bits for the next conversion can be overlapped with
the current conversion to allow for a conversion every 16 DCLK
cycles, as shown in Figure 26. This timing diagram also allows
for the possibility of communication with other serial peripherals
between each (eight DCLK) byte transfer between the processor
and the converter. However, the conversion must be completed
within a short enough time frame to avoid capacitive droop
effects that could distort the conversion result. It should also be
noted that the AD7843 is fully powered while other serial
communications are taking place between byte transfers.
Fifteen Clocks per Cycle
Figure 27 shows the fastest way to clock the AD7843. This
scheme does not work with most microcontrollers or DSPs
because, in general, they are not capable of generating a
15-clock-cycle-per-serial transfer. However, some DSPs allow
the number of clocks per cycle to be programmed; this method
could also be used with FPGAs (field programmable gate
arrays) or ASICs (application specific integrated circuits). As in
the 16-clocks-per-cycle case, the control bits for the next
conversion are overlapped with the current conversion to allow
a conversion every 15 DCLK cycles, using 12 DCLKs to
perform the conversion and three DCLKs to acquire the analog
input. This effectively increases the throughput rate of the
AD7843 beyond that used for the specifications that are tested
using 16 DCLKs per cycle, and DCLK = 2 MHz.
8-Bit Conversion
By setting the MODE bit to 1 in the control register, the
AD7843 can operate in 8-bit rather than 12-bit mode. This
mode allows a faster throughput rate to be achieved, assuming
8-bit resolution is sufficient. When using the 8-bit mode, a
conversion is complete four clock cycles earlier than in the
12-bit mode. This could be used with serial interfaces that
provide 12 clock transfers, or two conversions could be
completed with three 8-clock transfers. The throughput rate
increases by 25% as a result of the shorter conversion cycle, but
the conversion itself can occur at a faster clock rate because the
internal settling time of the AD7843 is not as critical because
settling to 8 bits is all that is required. The clock rate can be as
much as 50% faster. The faster clock rate and fewer clock cycles
combine to provide double the conversion rate.
DCLK
BUSY
DOUT
DCLK
DIN
BUSY
DOUT
CS
DIN
CS
1
S S
CONTROL BITS CONTROL BITS
111888
11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 11 10 9
Figure 26. Conversion Timing, 16 DCLKS per Cycle, 8-Bit Bus Interface. No DCLK delay required with dedicated serial port.
1
S A2 PD1 PD0A1 A0
MODE
SER/
DFR
11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4
15 1 15 1
SA2 SA2A1 PD1 PD0A0
Figure 27. Conversion Timing, 15 DCLKS per Cycle, Maximum Throughput Rate
MODE
SER/
DFR
02144-B-026
02144-B-027
Rev. B | Page 18 of 20

AD7843
PEN INTERRUPT REQUEST
The pen interrupt equivalent output circuitry is outlined in
Figure 28. By connecting a pull-up resistor (10 kΩ to 100 kΩ)
between V
PENIRQ
and this CMOS logic open-drain output, the
CC
output remains high normally. If
PENIRQ
is enabled
(see Table 7), when the touch screen connected to the AD7843
is touched via a pen or finger, the
PENIRQ
output goes low,
initiating an interrupt to a microprocessor that can then instruct
a control word to be written to the AD7843 to initiate a conversion. This output can also be enabled between conversions
during power-down (see Table 7 ), allowing power-up to be
initiated only when the screen is touched. The result of the first
touch screen coordinate conversion after power-up is valid,
assuming any external reference is settled to the 12- or 8-bit
level as required.
+V
CC
Y+
+V
CC
X+
TOUCH
SCREEN
Figure 28.
Figure 29 assumes that the
Y–
PENIRQ
ENABLE
ON
PENIRQ
Functional Block Diagram
PENIRQ
last write or that the part has just been powered up, so
is enabled by default. Once the screen is touched, the
output goes low a time t
later. This delay is approximately
PEN
EXTERNAL
100kΩ
PULL-UP
PENIRQ
02144-B-028
function is enabled in the
PENIRQ
PENIRQ
5 µs, assuming a 10 nF touch screen capacitance, and varies with
the touch screen resistance actually used.
SCREEN
TOUCHED
PENIRQ
HERE
t
PEN
NO RESPONSE TO TOUCH
Once the START bit is detected, the pen interrupt function is
disabled and the
The
PENIRQ
output remains low until the fourth falling edge
PENIRQ
cannot respond to screen touches.
of DCLK after the START bit has been clocked in, at which
point it returns high as soon as possible, regardless of the touch
screen capacitance. This does not mean that the pen interrupt
function is now enabled again because the power-down bits
have not yet been loaded to the control register. Regardless of
whether
PENIRQ
is to be enabled again or not, the
output normally always idles high. Assuming that the
PENIRQ
PENIRQ
is enabled again as shown in Figure 29, once the conversion is
complete, the
The fact that
PENIRQ
PENIRQ
output responds to a screen touch again.
returns high almost immediately after
the fourth falling edge of DCLK means the user avoids any
spurious interrupts on the microprocessor or DSP, which could
occur if the interrupt request line on the microprocessor/DSP
was unmasked during or toward the end of conversion with the
PENIRQ
the AD7843, the
pin still low. Once the next START bit is detected by
PENIRQ
function is disabled again.
If the control register write operation overlaps with the data
read, a START bit is always detected prior to the end of
conversion. This means that even if the
PENIRQ
function has
been enabled in the control register, it is disabled by the START
bit again before the end of the conversion is reached; therefore
PENIRQ
the
function effectively cannot be used in this mode.
However, as conversions are occurring continuously, the
PENIRQ
function is not necessary and, therefore, redundant.
GROUNDING AND LAYOUT
For information on grounding and layout considerations for the
AD7843, refer to Application Note AN-577, Layout and
Grounding Recommendations for Touch Screen Digitizers.
PD1 = 1, PD0 = 0, PENIRQ
ENABLED AGAIN
INTERRUPT
PROCESSOR
CS
DCLK
SER/
DIN
SA2A1A0 1 0
(START)
Figure 29.
MODE
PENIRQ
DFR
Timing Diagram
Rev. B | Page 19 of 20
81 1 13 16
02144-B-029

AD7843
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
0.193
BSC
9
0.154
BSC
8
0.069
0.053
0.012
SEATING
0.008
PLANE
(RQ-16)
Dimensions shown in inches
0.065
0.049
0.010
0.004
COPLANARITY
16
1
PIN 1
0.025
BSC
0.004
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-137AB
Figure 30. 16-Lead Shrink Small Outline Package [QSOP]
0.236
BSC
0.010
0.006
5.10
5.00
4.90
16
4.50
4.40
4.30
PIN 1
0.15
0.05
8°
0°
0.050
0.016
0.65
BSC
COPLANARITY
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-153AB
0.10
0.30
0.19
9
81
1.20
MAX
SEATING
PLANE
6.40
BSC
0.20
0.09
8°
0°
0.75
0.60
0.45
Figure 31. 16-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP]
(RU-16)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Linearity Error (LSB)1 Package Description Package Option
AD7843ARQ −40°C to +85°C ±2 QSOP RQ-16
AD7843ARQ-REEL −40°C to +85°C ±2 QSOP RQ-16
AD7843ARQ-REEL7 −40°C to +85°C ±2 QSOP RQ-16
AD7843ARQZ2 −40°C to +85°C ±2 QSOP RQ-16
AD7843ARQZ-REEL2 −40°C to +85°C ±2 QSOP RQ-16
AD7843ARQZ-REEL72 −40°C to +85°C ±2 QSOP RQ-16
AD7843ARU −40°C to +85°C ±2 TSSOP RU-16
AD7843ARU-REEL −40°C to +85°C ±2 TSSOP RU-16
AD7843ARU-REEL7 −40°C to +85°C ±2 TSSOP RU-16
EVAL-AD7843CB3 Evaluation Board
EVAL-CONTROL BRD24 Controller Board
1
Linearity error here refers to integral linearity error.
2
Z = Pb-free part. Pb-free parts are branded with a # before the date code.
3
This can be used as a stand-alone evaluation board, or in conjunction with the Evaluation Board Controller for evaluation/demonstration purposes.
4
This Evaluation Board Controller is a complete unit allowing a PC to control and communicate with all Analog Devices evaluation boards ending in the CB designator.
© 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
C02144–0–3/04(B)
Rev. B | Page 20 of 20
 Loading...
Loading...