Amphony RB1 Installation Guide
User and Installation
Guide
2.4 GHz RangeBooster
Transmitter
RR
User and Installation Guide
Unpacking: Check that this package contains:
One 2.4 GHz RangeBooster transmitter, one AC adapter.
How to use the RangeBooster transmitter
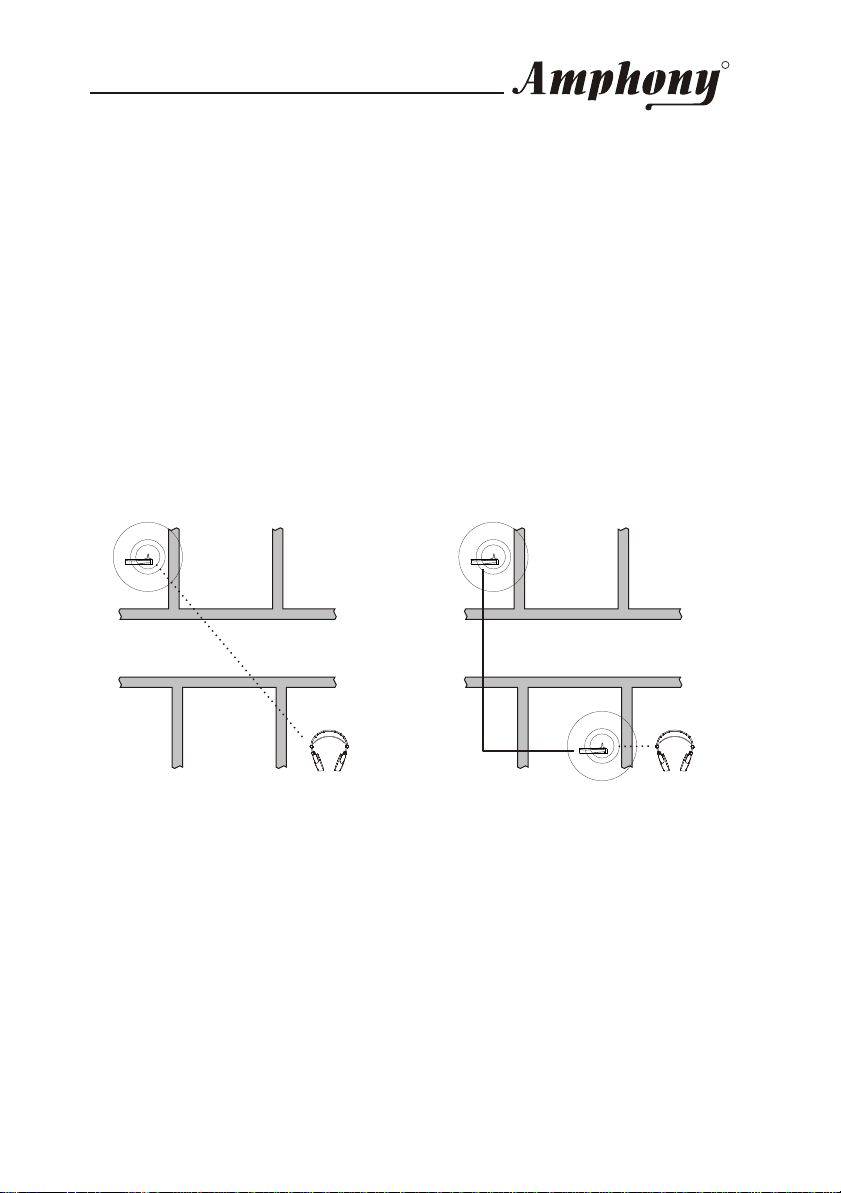
The RangeBooster transmitter can be used in situations where sufficient
coverage cannot be achieved by the primary transmitter and works as a
repeater in conjunction with the primary transmitter. In the example below, a
pair of 2.4 GHz Digital Wireless Headphones is operated such that there are 4
walls between the transmitter and headphones. In this case, the signal
reaching the headphones may be too weak for proper reception. By adding a
RangeBooster transmitter as shown in the example, coverage can be
improved for the area in which the signal of the primary transmitter was too
weak without the RangeBooster transmitter or in cases where there may be
interference from other 2.4 GHz devices. Since the audio signal is transmitted
digitally to the RangeBooster transmitter, no audio degradation will occur.
RR
Primary
transmitter
Example 1: Headphones
without RangeBooster
Primary
transmitter
Data cable
connection
RangeBooster
Example 2: Headphones
using RangeBooster,
reception is improved
The RangeBooster transmitter will reproduce the signal from the primary
transmitter and create a secondary coverage area. The RangeBooster
transmitter will receive a data signal from the primary transmitter via a data
cable connection. The size of the coverage area of the RangeBooster
transmitter will be approximately the same as the coverage area of the
primary transmitter.
Page 1
User and Installation Guide
RR
Step 1
The RangeBooster transmitter requires a data connection with the primary
transmitter. This data connection should be established by using a shielded
coaxial cable which is fitted with two RCA connectors.
This cable is not provided with this set and is available from your local video or
satellite equipment dealer.
Suitable cables are video and satellite cables with a cable impedance between
50 and 75 Ohms. Examples of suitable cable types are: RG-174, RG-58 and
RG-6. Cables with low signal attenuation may improve reception. The cable
diameter itself does not influence reception. Unshielded cables may be
susceptible to interference and deteriorate the data connection. Data network
cables may not provide the correct cable impedance and not guarantee
reliable reception.
Since the data connection will transfer high-speed serial audio data, it is
important to select a cable with the correct cable impedance. If a cable with a
cable impedance outside of the range of 50 to 75 Ohms is used, it may be
necessary to use appropriate adapters that will convert the cable impedance
to 50 to 75 Ohms at each end of the cable in order to avoid a cable impedance
mismatch at the transmitter side.
Preparing the Data cable
RCA connector RCA connector
50 to 75 Ohms shielded coaxial cable
Data cable
Step 2
The location of the RangeBooster transmitter should be chosen such that:
the number of walls and obstacles between the RangeBooster transmitter
and the headphones / receiver is minimized anywhere in the desired
coverage area to improve reception;
the cable length of the data cable will be as short as possible (preferably
less than 30 to 50 ft) to minimize data signal degradation; and
there is sufficient RF signal attenuation between the primary transmitter
and the RangeBooster transmitter (no line of sight) to minimize RF signal
competition between both transmitters.
Elevation as well as the presence of reflecting walls will influence the coverage
area of the RangeBooster transmitter. It is suggested to experiment in order to
find the best location for the RangeBooster transmitter.
Locating the RangeBooster transmitter
Page 2
 Loading...
Loading...