American Megatrends MegaRAID Express 500 User Manual

MegaRAID®Express 500
Hardware Guide
Preliminary Draft
MAN-475
4/14/2000
© Copyright 2000 American Megatrends, Inc.
All rights reserved.
American Megatrends, Inc.
6145F Northbelt Parkway
Norcross, GA 30071
This publication contains proprietary information whichis protected by copyright.Nopart of this publication can be
reproduced, transcribed, stored in a retrievalsystem, translatedintoanylanguage or computerlanguage, or transmittedin
any form whatsoever withouttheprior written consentofthepublisher, AmericanMegatrends, Inc. American Megatrends,
Inc. acknowledges the following trademarks:
Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation
Sytos 300 is a registered trademark of Sytron Corporation.
MS-DOS, and Microsoft are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Windows 95, Microsoft Windows and
Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
SCO, UnixWare, and Unix are registered trademarks of the Santa Cruz Operation. Inc.
Novell NetWare is a registered trademark of Novell Corporation.
IBM, AT,VGA, PS/2, and OS/2 are registered trademarks and XT and CGAare trademarks of InternationalBusiness
Machines Corporation.
NEC is a registered trademark of Nippon ElectricCorporation.
Sony is a registered trademark of SonyCorporation.
Toshiba is a registered trademark of ToshibaAmerica Corporation.
Archive and Python are registered trademarks of ArchiveCorporation.
Quantum is a registeredtrademark of Quantum Corporation.
Seagate is a registered trademark of SeagateCorporation.
SyQuest is a trademarkofSyQuest Corporation.
Panasonic is a registered trademark of Panasonic Corporation.
Hewlett-Packard is a registered trademark of Hewlett-Packard Corporation.
Amphenolis a trademark of Amphenol Corporation.
Siemens is a registered trademark of Siemens Corporation.
AMP is a trademark of AMPCorporation.
.
Revision History
4/14/00 Initial release.
MegaRAID Express500 Hardware Guide
ii

Table of Contents
1 Overview ...................................................1
Single Ended and Differential SCSI Buses .......................2
Maximum Cable Length for SCSI Standards ....................2
Documentation..................................................................3
MegaRAID Express 500 Block Diagram..........................4
2 Introduction to RAID................................5
RAID Benefits...................................................................5
In This Chapter..................................................................6
MegaRAID Express 500 – Host-Based RAID Solution....7
RAID Overview................................................................8
Consistency Check............................................................8
Fault Tolerance .................................................................8
Disk Striping .....................................................................9
Disk Spanning.................................................................10
Disk Mirroring ................................................................11
Parity...............................................................................12
Hot Spares.......................................................................13
Disk Rebuild ...................................................................14
Logical Drive ..................................................................15
Hot Swap.........................................................................15
SCSI Drive States............................................................15
Logical Drive States........................................................15
Disk Array Types............................................................16
Enclosure Management...................................................16
3 RAID Levels............................................17
Selecting a RAID Level ..................................................18
RAID 0............................................................................19
RAID 1............................................................................20
RAID 3............................................................................21
RAID 5............................................................................23
RAID 10..........................................................................24
RAID 30..........................................................................25
RAID 50..........................................................................26
Preface
iii

Table of Contents,
Continued
4 Features..................................................27
Hardware Requirements..................................................28
Configuration Features....................................................28
Hardware Architecture Features......................................29
Array Performance Features............................................29
RAID Management Features...........................................30
Fault Tolerance Features.................................................30
Software Utilities ............................................................31
Operating System Software Drivers................................31
MegaRAID Express 500 Specifications..........................32
PCI Bridge/CPU..............................................................33
Cache Memory................................................................33
MegaRAID BIOS ............................................................34
Onboard Speaker.............................................................34
Serial Port .......................................................................34
SCSI Bus.........................................................................34
SCSI Connectors.............................................................35
SCSI Termination............................................................35
SCSI Firmware................................................................35
RAID Management.........................................................36
Fault-Tolerance Features.................................................37
Compatibility...................................................................38
Summary.........................................................................38
5 Configuring MegaRAID Express 500....39
Configuring SCSI Physical Drives..................................39
Current Configuration.....................................................40
Logical Drive Configuration...........................................40
Physical Device Layout...................................................42
Configuring Arrays..........................................................44
Configuration Strategies..................................................45
AssigningRAID Levels ..................................................47
Configuring Logical Drives.............................................47
Optimizing Data Storage.................................................48
Planning the Array Configuration ...................................49
Array Configuration Planner...........................................50
MegaRAID Express500 Hardware Guide
iv

Table of Contents,
Continued
6 Hardware Installation ............................51
Installation Steps.............................................................52
Step 1 Unpack.................................................................53
Step 2 Power Down.........................................................53
Step 3 Configure Motherboard........................................53
Step 4 Install Cache Memory..........................................54
Step 5 Set Jumpers..........................................................56
MegaRAID Express 500 Card Layout ............................56
Step 6 Set Termination....................................................59
SCSI Termination............................................................60
Step 7 Install MegaRAID Express 500 ...........................63
Step 8 Connect SCSI Cables...........................................64
Step 9 Set Target IDs......................................................65
Device Identification on MegaRAID Express 500..........66
Step 10 Power Up ...........................................................67
Step 11 Run MegaRAID BIOS Setup.............................67
Step 12 Install the Operating System Driver...................68
7 Troubleshooting ....................................71
BIOS Boot Error Messages.............................................73
Other BIOS Error Messages............................................75
DOS ASPI Driver Error Messages..................................76
Other Potential Problems ................................................77
A SCSI Cables and Connectors ...............79
SCSI Connectors.............................................................79
68-Pin High Density SCSI Internal Connector................79
High-Density 68-Pin SCSI Connector Pinout .................85
68-Pin Connector Pinout for LVD SCSI.........................87
B Audible Warnings .........................................89
Glossary............................................................91
Index................................................................101
Preface
v

Preface
The MegaRAID Express 500 PCI RAID Controller supports all single ended and lowvoltage differential (LVD) SCSI devices on a 160M Ultra and Wide SCSI channel with
data transfer rates up to 160 MB/s (Megabytesper second). This manual describes
MegaRAID Express500.
Limited Warranty The buyer agrees if this product proves to be defective, that American Megatrends is only
obligated to repair or replace this product at American Megatrends’ discretion according
to the terms and conditions of the warranty registration card that accompanies this
product. American Megatrends shall not be liable in tort or contract for any loss or
damage, direct, incidental or consequential resulting from the use of this product. Please
see the Warranty Registration Card shipped with this product for full warranty details.
Limitationsof Liability American Megatrends, Inc. shall in no event be held liable for any loss, expenses, or
damages of any kind whatsoever, whether direct, indirect, incidental, or consequential
(whether arising from the design or use of this product or the support materials provided
with the product). No action or proceeding against American Megatrends may be
commencedmore than two years after the delivery of product to Licensee of Licensed
Software.
Licensee agrees to defend and indemnify American Megatrends from any and all claims,
suits, and liabilities (including attorney’s fees) arising out of or resulting from any actual
or alleged act or omission on the part of Licensee, its authorized third parties, employees,
or agents, in connection with the distribution of Licensed Software to end-users,
including, without limitation, claims, suits, and liability for bodily or other injuries to
end-users resulting from use of Licensee’s product not caused solely by faults in
Licensed Software as provided by American Megatrends to Licensee.
Cont’d
MegaRAID Express500 Hardware Guide
vi

Preface,
Continued
Package Contents You should have received:
• a MegaRAID Express 500 PCI RAID Controller
• a CD with drivers, utilities, and documentation
• a MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide (on CD)
• a MegaRAID Configuration Software Guide (on CD)
• a MegaRAID Operating System Drivers Guide (on CD)
• software license agreement (on CD)
• a warranty registration card (on CD)
Technical Support If you need help installing, configuring, or running the MegaRAID Express
500 P CI RAID Controller, call your American Megatrends OEM Technical
Support representative. Before you call, please complete the MegaRAID
Problem Report form on the next page.
Web Site We invite you to access the American Megatrends world wide web site at:
http://www.ami.com.
FTP Site The address of the American Megatrends FTP site is:
ftp://ftp.megatrends.com
Preface
vii
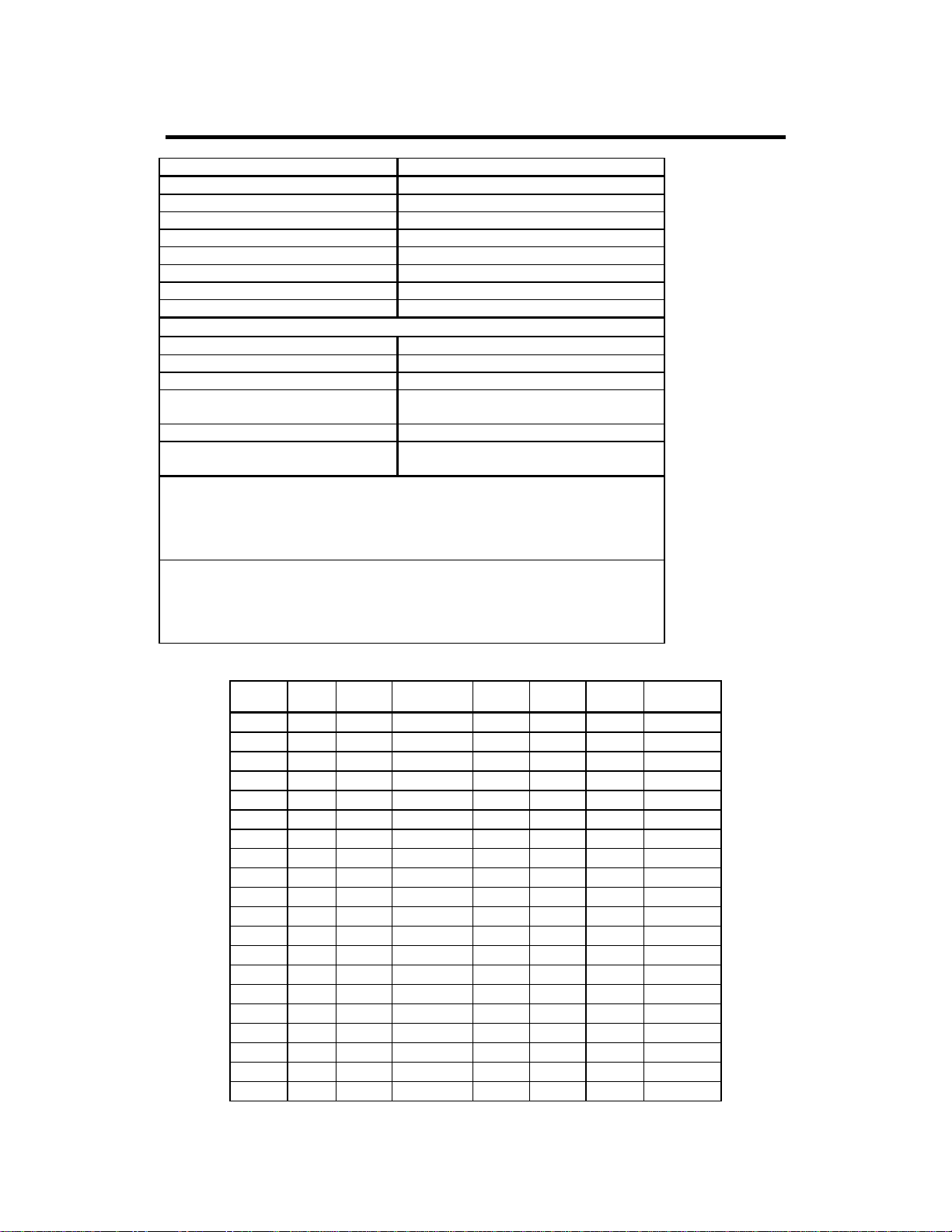
MegaRAID Problem Report Form
Customer Information MegaRAID Information
Name Today’s Date
Company Date of Purchase
Address Invoice Number
City/State Serial Number
Country
email address Cache Memory
Phone FirmwareVersion
Fax BIOS Version
System Information
Motherboard: BIOS manufacturer:
Operating System: BIOS Date:
Op. Sys. Ver.: Video Adapter:
MegaRAID
Driver Ver.:
Network Card: System Memory:
Other disk controllers
installed:
Description of problem:
Steps necessary to re-create problem:
1.
2.
3.
4.
CPU Type/Speed:
Other adapter cards
installed:
Logical Drive Configuration
Logical
Drive
RAID
Level
LD1
LD2
LD3
LD4
LD5
LD6
LD7
LD8
LD9
LD10
LD11
LD12
LD13
LD14
LD15
LD16
LD17
LD18
LD19
LD20
Stripe
Size
Logical Drive
Size
Cache
Policy
Read
Policy
Write
Policy
#ofPhysical
Drives
MegaRAID Express500 Hardware Guide
viii
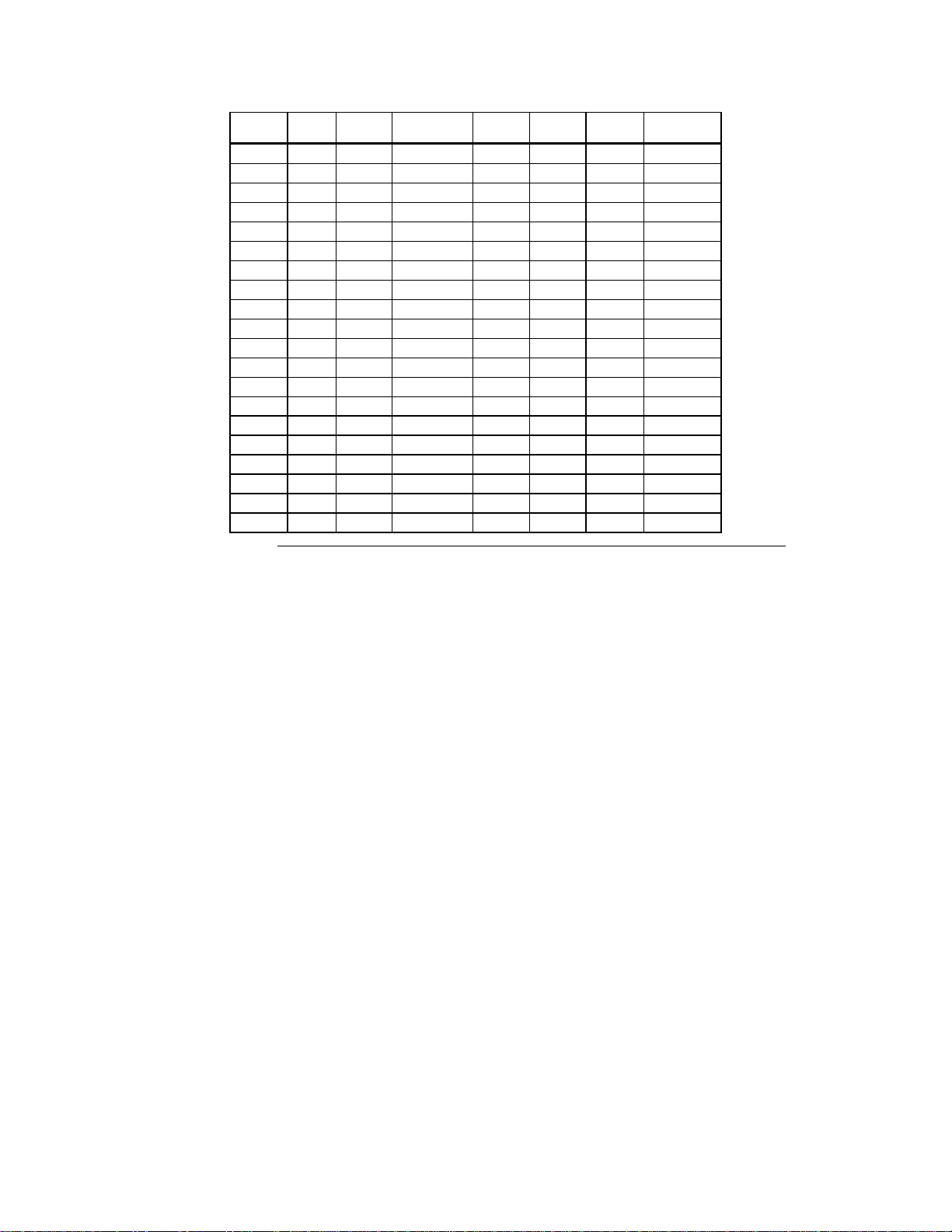
Logical
Drive
LD21
LD22
LD23
LD24
LD25
LD26
LD27
LD28
LD29
LD30
LD31
LD32
LD33
LD34
LD35
LD36
LD37
LD38
LD39
LD40
RAID
Level
Stripe
Size
Logical Drive
Size
Cache
Policy
Read
Policy
Write
Policy
#ofPhysical
Drives
Preface
ix
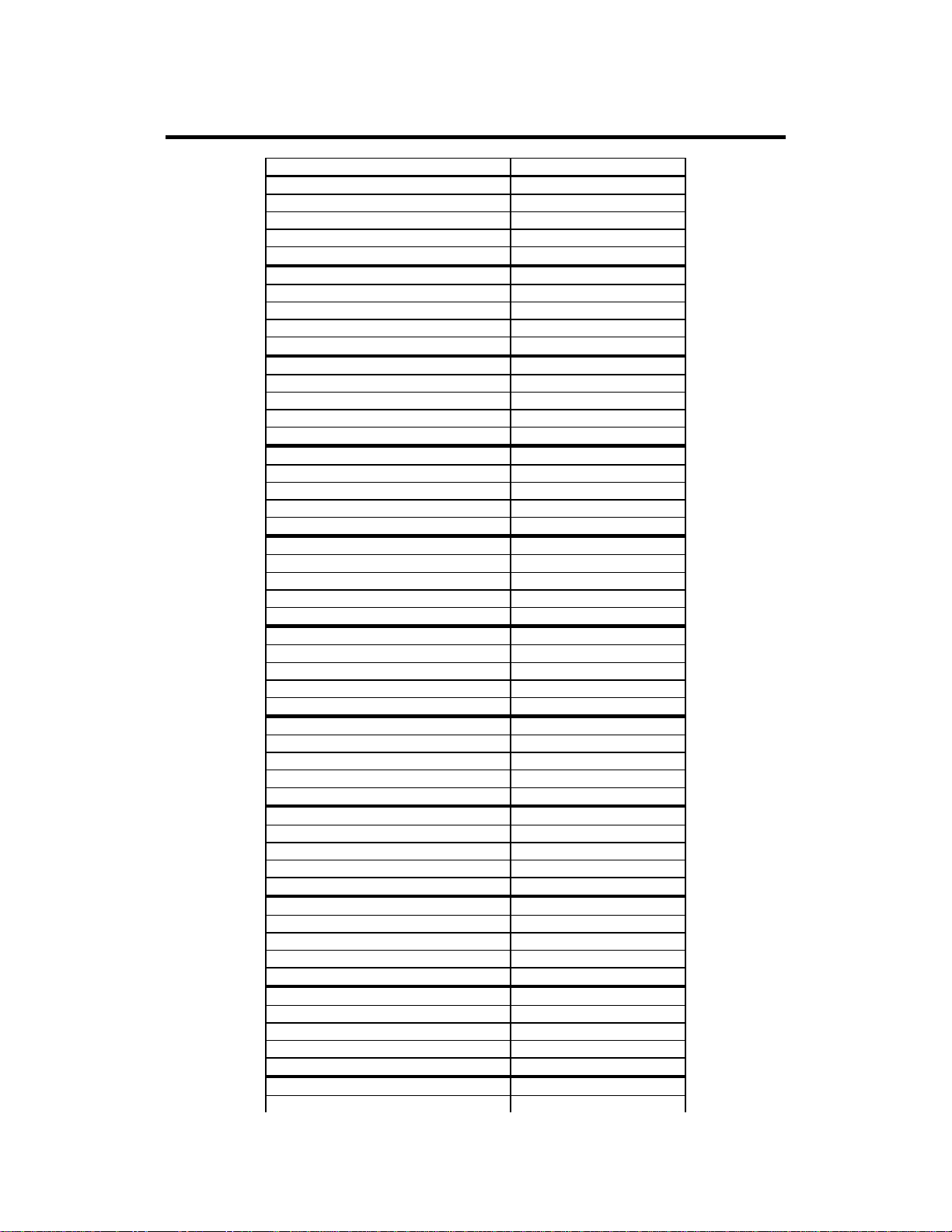
Physical Device Layout
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Channel 1
MegaRAID Express500 Hardware Guide
x
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
LogicalDrive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Channel 1
Preface
xi

Preface,
Disclaimer This manual describes the operation of the American Megatrends MegaRAID Express
Continued
500 Disk Array Controller. Although efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of the
information contained here, American Megatrends expressly disclaims liability for any
error in this information, and for damages, whether direct, indirect, special, exemplary,
consequential or otherwise, that may result from such error, including but not limited to
the loss of profits resulting from the use or misuse o f the manual or information
contained therein (even if American Megatrends has been advised of the possibility of
such damages). Any questions or comments regarding this document or its contents
should be addressed to American Megatrends at the address shown on the cover.
American Megatrends provides this publication “as is” without warranty of any kind,
either expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantabilityor fitness for a specific purpose.
Some states do not allow disclaimer of express or implied warranties or the limitation or
exclusion of liability for indirect, special, exemplary, incidental or consequential
damages in certain transactions; therefore, this statement may not apply to you. Also, you
may have other rights which vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
This publication could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes
are periodically made to the information herein; these changes will be incorporated in
new editions of the publication. American Megatrends maymake improvements and/or
revisions in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this publication at any
time.
Requests for technical information about American Megatrends products should be made
to your American Megatrends authorized reseller or marketing representative.
MegaRAID Express500 Hardware Guide
xii
FCC Regulatory Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.Operation is subject to the followingtwo conditions: (1) this device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept anyinterference received,including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
Warning: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Note:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits fora Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15
of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonableprotection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. Thisequipment generates,uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installedand used in
accordance with the instructions, maycause harmful interference to radio communications.However, there is no guarantee
that interferencewill not occur in a specific installation. Ifthisequipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment offand on, tryto correct the interferenceby one or
more of the following measures:
1) Reorientorrelocate the receiving antenna.
2) Increase the separation between the equipment and
3)
4) Consult the dealer or an experiencedradio/TV technician
Shielded interface cables must be used with this product to ensure compliance with the Class B
FCC limits.
American Megatrends MegaRAID Express 500 PCI RAID Controller
the receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiveris connected.
for help.
Model Number: Series 475
FCCIDNumber: IUESER475
AMI certifies only that this product will work correctly when this
product is used with the same jumper settings, the same system
configuration, the same memory module parts, and the same
peripherals that were tested by AMI with this product. The complete
list of tested jumper settings, system configurations, peripheral
devices, and memory modules are documented in the AMI
Compatibility Report for this product. Call your AMI sales
representative for a copy of the Compatibility Report for this product.
Disclaimer
Preface
xiii

MegaRAID Express500 Hardware Guide
xiv

1Overview
The MegaRAID® Express 500 PCI RAID controller is a high performance
intelligent PCI-to-SCSI host adapter with RAID control capabilities. The
MegaRAID Express 500 provides reliability, high performance, and faulttolerant disk subsystem management. The MegaRAID Express 500 is part of the
American Megatrends Intel i960RM/RS-based MegaRAID controller family.
The MegaRAID Express 500 is an entry level-to mid-range RAID controller
solution. MegaRAID Express 500 offers a cost-effective way to implement
RAID in a server. The MegaRAID Express 500 has a 160 M Ultra and Wide
SCSI channel supporting data transfer rates up to 160 Megabytes per second
(MB/s) per channel. The SCSI channel supports up to fifteen non-Ultra SCSI
devices. MegaRAID Express 500 includes MegaRAID features and
performance.
Features MegaRAID Express 500 features include:
• provides a high performance I/O migration path while preserving existing P CI-SCSI
software
• Performs SCSI data transfers up to 160 MB/s
• performs synchronous operation on a wide LVD SCSI bus
• allows up to 15 LVD SCSI devices on the wide bus
• includes an Intel® i960RM that performs RAID calculationsand routing
• supports 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 MB of SDRAM cache memory in a DIMM socket
used for read and write-back caching and RAID 5 parity generation
SCSI Channel The MegaRAID Express 500 upgrade card includes one Ultra3 SCSI channel.
The channel is powered by a Q-Logic ISP10160A 160M SCSI processor.
NVRAM and Flash ROM A 32 KB x 8 NVRAM stores RAID system configuration information.
The MegaRAID Express 500 firmware is stored in flash ROM for easy upgrade.
SCSI Connectors MegaRAID Express 500 has one ultra high density 68-pin external connector
for external storage subsystem and one high density 68-pin internal connector.
Chapter 1 Overview
1

Single Ended and Differential SCSI Buses
The SCSI standard defines two electrical buses:
• a single ended bus
• low-voltage differential bus
Maximum Cable Length for SCSI Standards
Standard Single ended LVD Maximum Number of
SCSI I 6 m 12 m 7
Fast SCSI 6 m 12 m 7
Fast Wide SCSI 6 m 12 m 15
Ultra SCSI 1.5 m 12 m 7
Ultra SCSI 3 m 12 m 3
Wide Ultra SCSI 12 m 15
Wide Ultra SCSI 1.5 m 12 m 7
Wide Ultra SCSI 3 m 12 m 3
Ultra 2 SCSI 25 m 1
Ultra 2 SCSI 12 m 7
Wide Ultra 2 SCSI 25 m 1
Wide Ultra 2 SCSI 12 m 15
Ultra3 SCSI 25m 1
Ultra3 SCSI 12m 7
Wide Ultra3 SCSI 25m 1
Wide Ultra3 SCSI 12m 15
Drives
SCSI Bus Widths and Maximum Throughput
SCSI Standard SCSI Bus Width SCSI Throughput
SCSI I 8 bits 5 MB/s
Fast SCSI 8 bits 10 MB/s
Fast Wide SCSI 16 bits 20 MB/s
Ultra SCSI 8 bits 20 MB/s
Wide Ultra SCSI 16 bits 40 MB/s
Ultra 2 SCSI 8 bits 40 MB/s
Wide Ultra 2 SCSI 16 bits 80 MB/s
Ultra3 SCSI 8 bits 80 MB/s
Wide Ultra3 SCSI 16 bits 160 MB/s
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
2

Documentation
The MegaRAID Express 500 documentation set includes:
MegaRAID Configuration Hardware Guide This manual contains the RAID overview, RAID
planning, and RAID system configuration information you will need first. Read
the MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide first.
MegaRAID Configuration Software Guide This manual describes the software configuration
utilities that configure and modify RAID systems.
MegaRAID Operating System Drivers Guide This manual provides detailed information about
installing the MegaRAID Express 500 operating system drivers.
Chapter 1 Overview
3
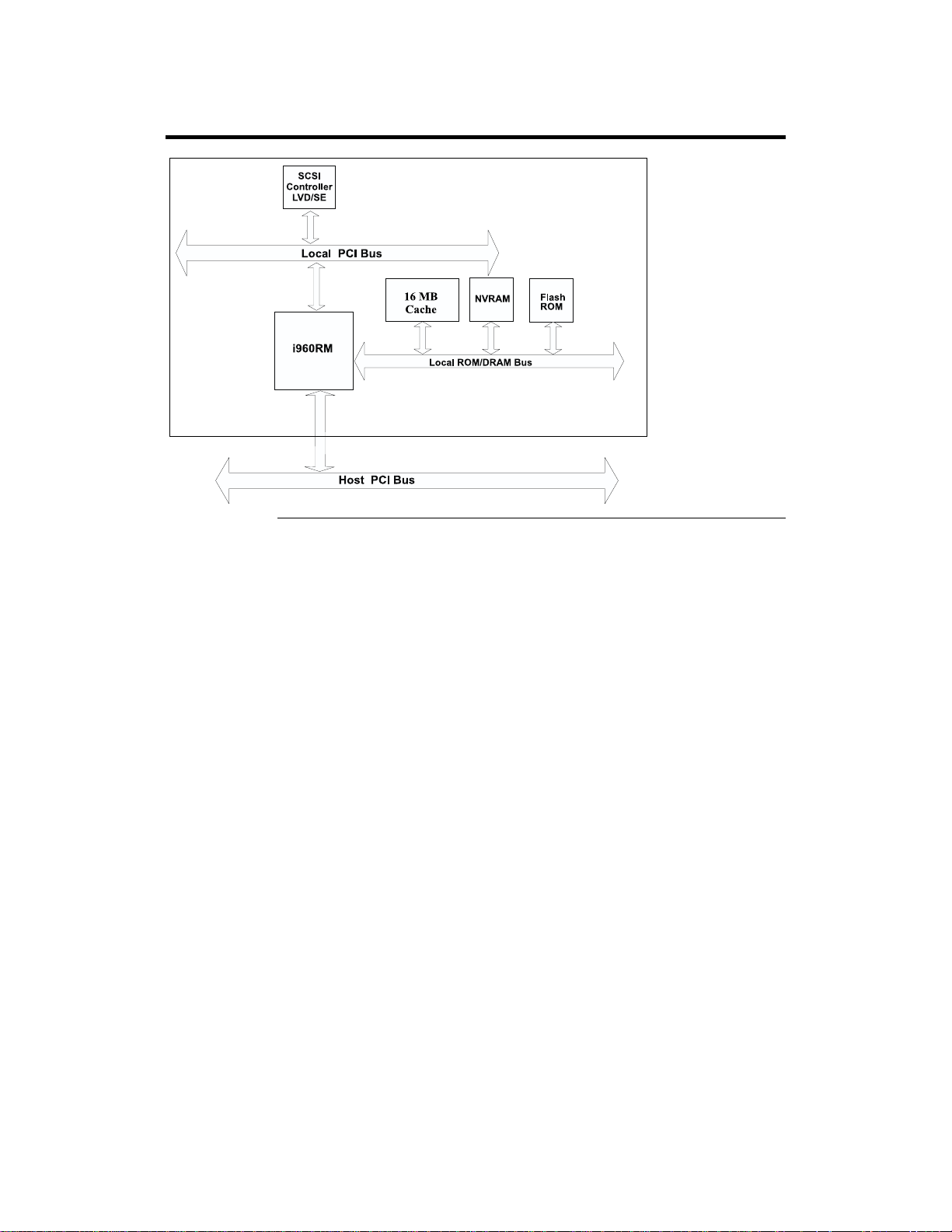
MegaRAID Express 500 Block Diagram
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
4

2 Introduction to RAID
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is an array of multiple
independent hard disk drives that provide high performance and fault tolerance.
A RAID disk subsystem improves I/O performance over a computer using only a
single drive. The RAID array appears to the host computer as a single storage
unit or as multiple logical units. I/O is expedited because several disks can be
accessed simultaneously. RAID systems improve data storage reliability and
fault tolerance compared to single-drive computers. Data loss because of a disk
drive failure can be recovered by reconstructing missing data from the remaining
data and parity drives.
RAID Benefits
RAID has gained popularity because it improves I/O performance and increases
storage subsystem reliability. RAID provides data security through fault
tolerance and redundant data storage. The MegaRAID Express 500 management
software configures and monitors RAID disk arrays.
Improved I/O Although disk drive capabilities have improved drastically, actual performance
has been improved only three to four times in the last decade. Computing
performance has been improved over 50 times during the same time period.
Increased Reliability The electromechanical components of a disk subsystem operate more
slowly, require more power, and generate more noise and vibration than
electronic devices. These factors reduce the reliability of data stored on disks.
Chapter 2 IntroductiontoRAID
5
In This Chapter
The following topics are discussed:
Host-based solution page 7
RAID overview page 8
Major Topic Subtopic turn to
Consistency check page 8
Fault tolerance page 8
Disk striping page 9
Disk spanning page 10
Disk mirroring page 11
Parity page 12
Hot spares page 13
Disk rebuilds page 14
Logical drive page 15
Hot swap page 15
SCSI drive states page 15
Logical drive states page 15
Disk array types page 16
Enclosure management page 16
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
6

MegaRAID Express 500 – Host-Based RAID Solution
RAID products are either:
• host-based or
• SCSI-to-SCSI
The MegaRAID Express 500 controller is a host-based RAID solution.
MegaRAID Express 500 is a PCI adapter card that is installed in any available
PCI expansion slot in a host system.
Host-Based A host-based RAID product puts all of the RAID intelligence on an adapter card
that is installed in a network server. A host-based RAID product provides the
best performance. MegaRAID Express 500 is part of the file server, so it can
transmit data directly across the computer’s buses at data transfer speeds up to
132 MB/s.
The available sequential data transfer rate is determined by the following factors:
• the sustained data transfer rate on the motherboard PCI bus
• the sustained data transfer rate on the i960RM PCI to PCI bridge
• the sustained data transfer rate of the SCSI controller
• the sustained data transfer rate of the SCSI devices
• the number of SCSI channels
• the number of SCSI disk drives
Host-based solutions must provide operating system-specific drivers.
SCSI-to-SCSI A SCSI-to-SCSI RAID product puts the RAID intelligence inside the RAID
chassis and uses a plain SCSI Host Adapter installed in the network server. The
data transfer rate is limited to the bandwidth of the SCSI channel. A SCSI-toSCSI RAID product that has two wide SCSI channels operating at speeds up to
160 MB /s must squeeze the data into a single wide SCSI (160 MB/s) channel
back to the host computer.
In SCSI-to-SCSI RAID products, the hard drive subsystemuses only a single
SCSI ID, which allows you to connect multiple drive subsystems to a single
SCSI controller.
Chapter 2 IntroductiontoRAID
7

RAID Overview
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a collection of specifications
that describe a system for ensuring the reliability and stability of data stored on
large disk subsystems. A RAID system can be implemented in a number of
different versions (or RAID Levels). The standard RAID levels are 0, 1, 3, and
5. MegaRAID Express 500 supports all standard RAID levels and RAID levels
10, 30, and 50, special RAID versions supported b y MegaRAID Express 500.
Consistency Check
In RAID, check consistency verifies the correctness of redundant data in an
array. For example, in a system with dedicated parity, checking consistency
means computing the parity of the data drives and comparing the results to the
contents of the d edicated parity drive.
Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is achieved through cooling fans, power supplies, and the ability
to hot swap drives. MegaRAID Express 500 provides hot swapping through the
hot spare feature. A hot spare drive is an unused online available drive that
MegaRAID Express 500 instantly plugs into the system when an active drive
fails.
After the hot spare is automatically moved into the RAID subsystem, the failed
drive is automatically rebuilt. The RAID disk array continues to handle request
while the rebuild occurs.
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
8
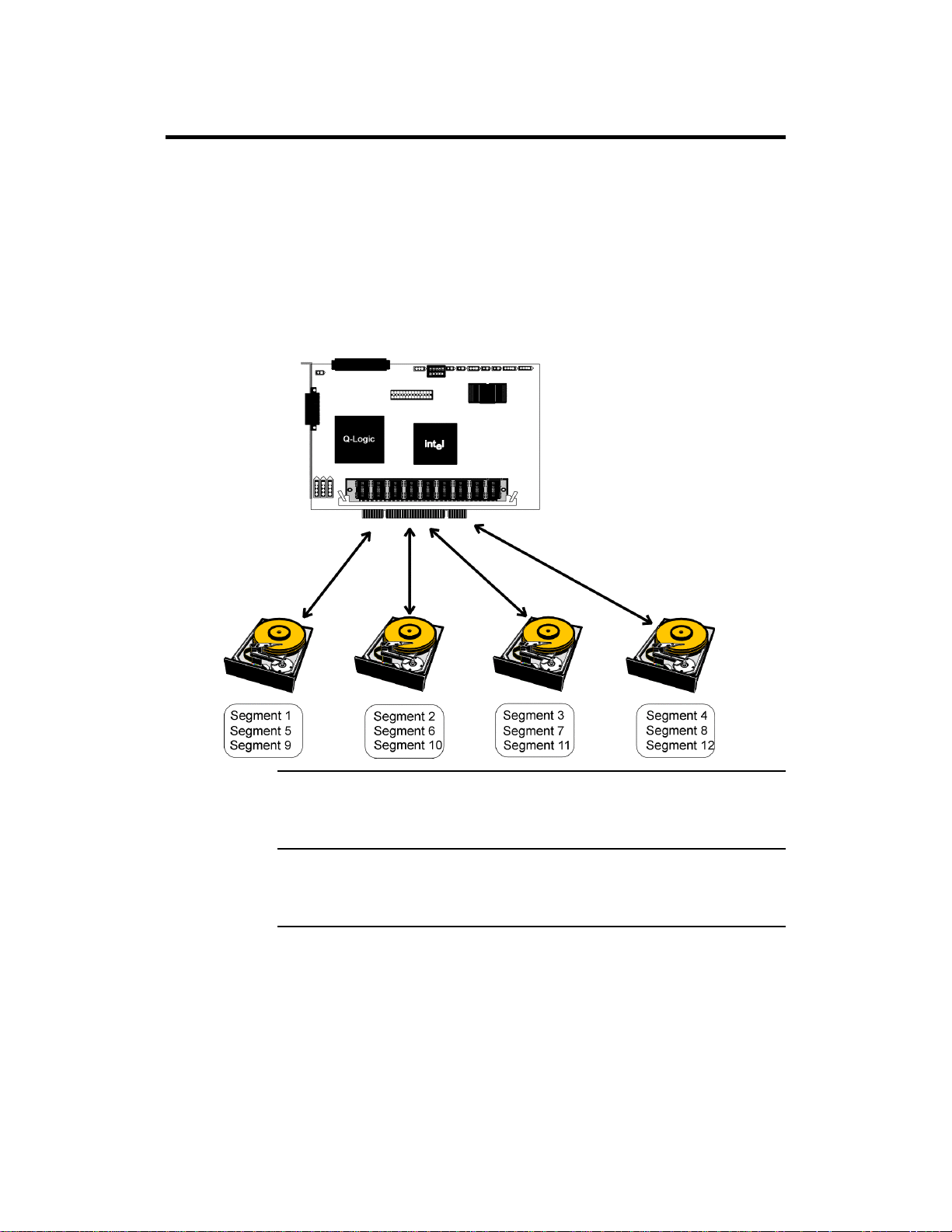
Disk Striping
Disk striping writes data across multiple disk drives instead of just one disk
drive. Disk striping involves partitioning each drive storage space into stripes
that can vary in size from 2 KB to 128 KB. These stripes are interleaved in a
repeated sequential manner. The combined storage space is composed of stripes
from each drive. MegaRAID Express 500 supports stripe sizes of 2 KB, 4 KB, 8
KB, 16 KB, 32 KB, 64 KB, or 128 KB.
For example, in a four-disk system using only disk striping (as in RAID level 0),
segment 1 is written to disk 1, segment 2 is written to disk 2, and so on. Disk
striping enhances performance because multiple drives are accessed
simultaneously; but disk striping does not provide data redundancy.
Stripe Width Stripe width is a measure of the number of disks involved in an array where
striping is implemented. For example, a four-disk array with disk striping has a
stripe width of four.
Stripe Size The stripe size is the length of the interleaved data segments that MegaRAID
Express 500 writes across multiple drives. MegaRAID Express 500 supports
stripe sizes of 2 KB, 4 KB, 8 KB, 16 KB, 32 KB, 64 KB, or 128 KB.
Chapter 2 IntroductiontoRAID
9
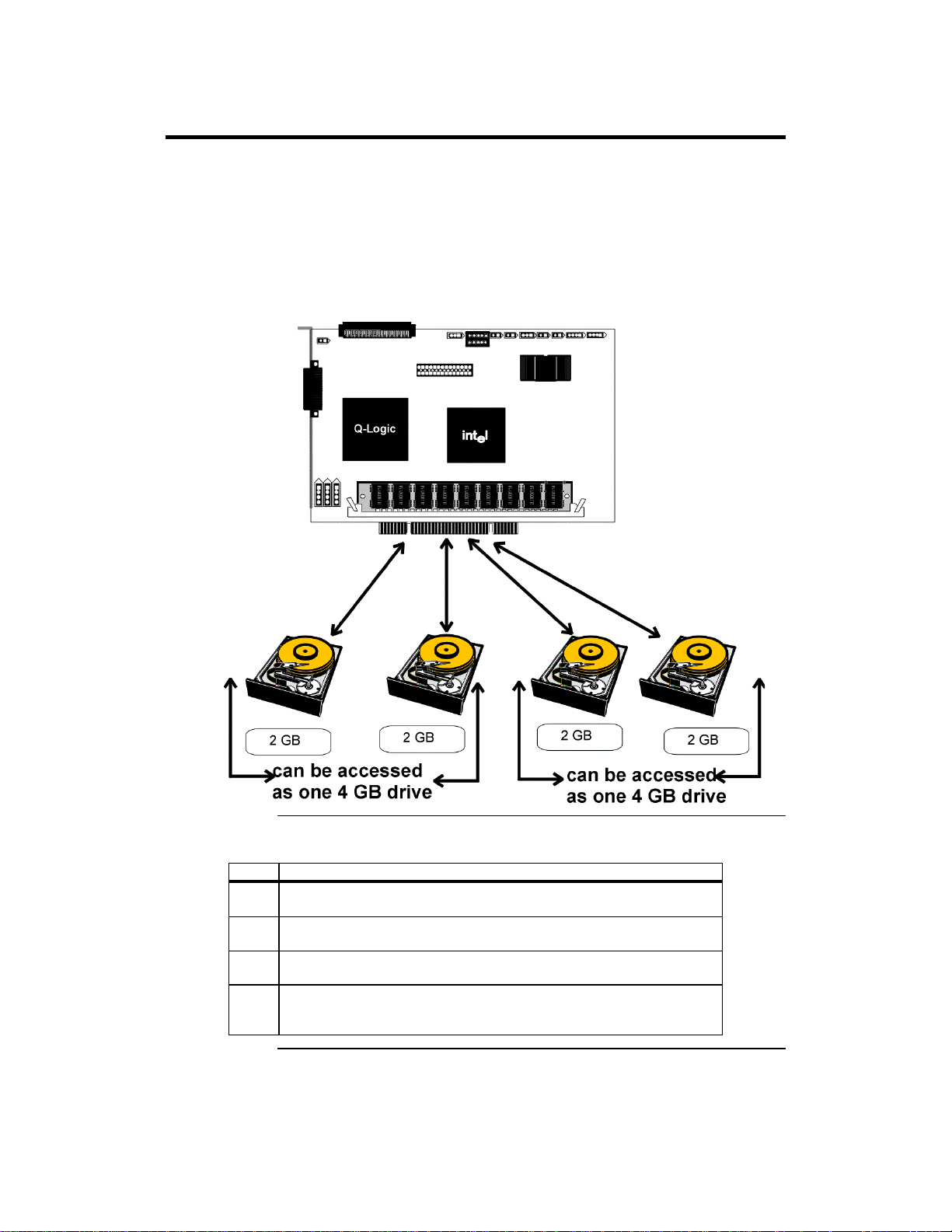
Disk Spanning
Disk spanning allows multiple disk drives to function like one big drive.
Spanning overcomes lack of disk space and simplifies storage management by
combining existing resources or adding relatively inexpensive resources. For
example, four 400 MB disk drives can be combined to appear to the operating
system as one single 1600 MB drive.
Spanning alone does not provide reliability or performance enhancements.
Spanned logical drives must have the same stripe size and must be contiguous. In
the following graphic, RAID 1 array is turned into a RAID 10 array.
Spanning for RAID 10, RAID 30, or RAID 50
Level Description
10 Configure RAID 10 by spanning two contiguous RAID 1 logical drives.
The RAID 1 logical drives must have the same stripe size.
30 Configure RAID 30 by spanning two contiguous RAID 3 logical drives.
The RAID 3 logical drives must have the same stripe size.
50 Configure RAID 50 by spanning two contiguous RAID 5 logical drives.
The RAID 5 logical drives must have the same stripe size.
Note:
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
10
Spanning two contiguous RAID 0 logical drives does not produce a new
RAID level or add fault tolerance. It does increase the size of the logical
volume and improves performance by doubling the number of spindles.
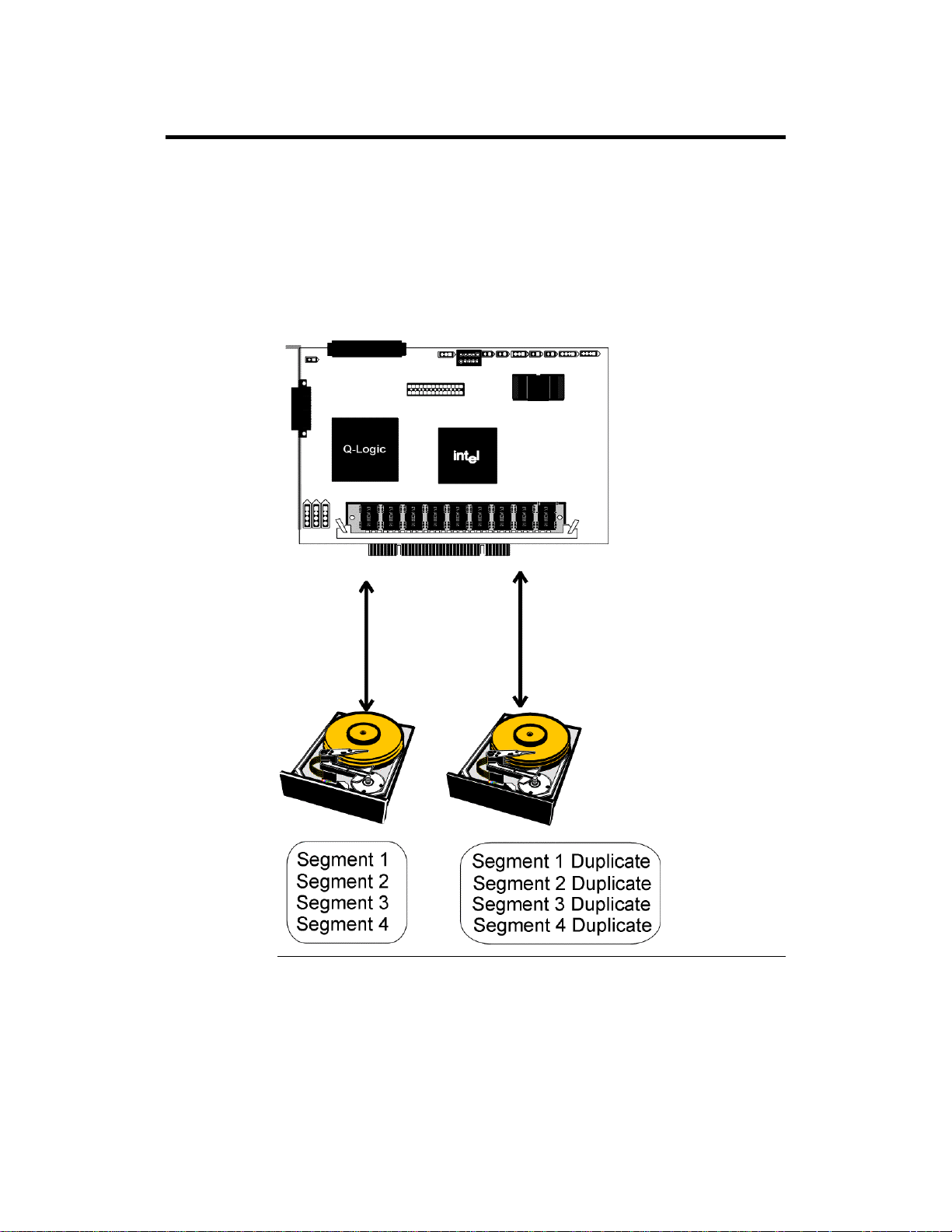
Disk Mirroring
With mirroring (used in RAID 1), data written to one disk drive is
simultaneously written to another disk drive. If one disk drive fails, the contents
of the other disk drive can be used to run the system and reconstruct the failed
drive. The primary advantage of disk mirroring is that it provides 100% data
redundancy. Since the contents of the disk drive are completely written to a
second drive, it does not matter if one of the drives fails. Both drives contain the
same data at all times. Either drive can act as the operational drive.
Disk mirroring provides 100% redundancy, but is expensive because each drive
in the system must be duplicated.
Chapter 2 IntroductiontoRAID
11
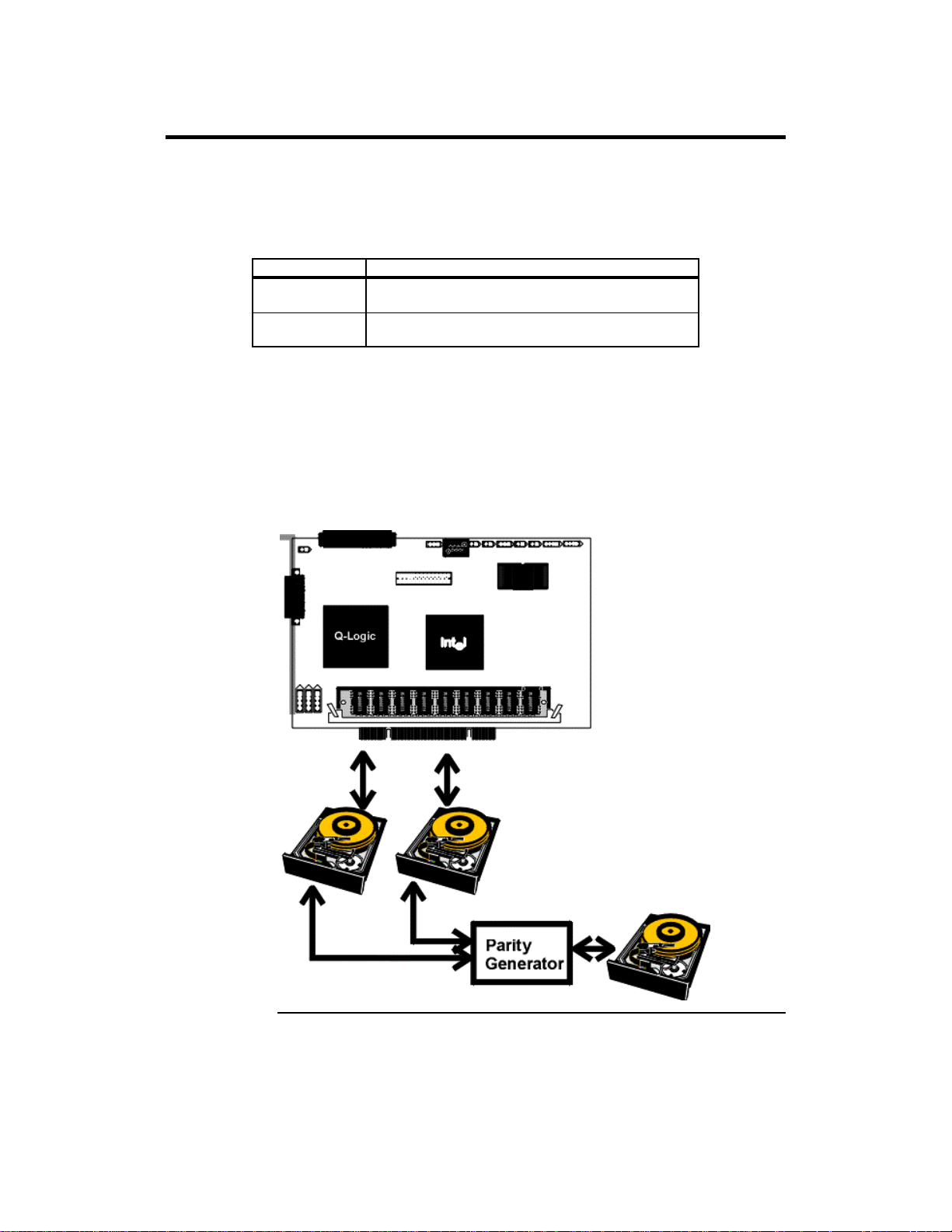
Parity
Parity generates a set of redundancy data from two or more parent data sets. The
redundancy data can be used to reconstruct one of the parent data sets. Parity
data does not fully duplicate the parent data sets. In RAID, this method is
applied to entire drives or stripes across all disk drives in an array. The types of
parity are:
Type Description
Dedicated Parity The parity of the data on two or more disk drives is
stored on an additional disk.
Distributed
Parity
The parity data is distributed across all drives in the
system.
If a single disk drive fails, it can be rebuilt from the parity and the data on the
remaining drives.
RAID level 3 combines dedicated parity with disk striping. The parity disk in
RAID 3 is the last logical drive in a RAID set.
RAID level 5 combines distributed parity with disk striping. Parity provides
redundancy for one drive failure without duplicating the contents of entire disk
drives, but parity generation can slow the write process. A dedicated parity
scheme during normal read/write operations is shown below:
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
12

Hot Spares
A hot spare is an extra, unused disk drive that is part of the disk subsystem. It is
usually in standby mode, ready for service if a drive fails. Hot spares permit you
to replace failed drives without system shutdown or user intervention.
MegaRAID Express 500 implements automatic and transparent rebuilds using
hot spare drives, providing a high degree of fault tolerance and zero downtime.
The MegaRAID Express 500 RAID Management software allows you to specify
physical drives as hot spares. When a hot spare is needed, the MegaRAID
Express 500 controller assigns the hot spare that has a capacity closest to and at
least as great as that of the failed drive to take the place of the failed drive.
Important
Hot spares are employed only in arrays with redundancy, for
example, RAID levels 1, 3, 5, 10, 30, and 50.
A hot spare connected to a specific MegaRAID Express 500
controller can be used only to rebuild a drive that is
connected to the same controller.
Chapter 2 IntroductiontoRAID
13

Disk Rebuild
You rebuild a disk drive by recreating the data that had been stored on the drive
before the drive failed.
Rebuilding can be done only in arrays with data redundancy such as RAID level
1, 3, 5, 10, 30, and 50.
Standby (warm spare) rebuild is employed in a mirrored (RAID 1) system. If a
disk drive fails, an identical drive is immediately available. The primary data
source disk drive is the original disk drive.
A hot spare can be used to rebuild disk drives in RAID 1, 3, 5, 10, 30, or 50
systems. If a hot spare is not available, the failed disk drive must be replaced
with a new disk drive so that the data on the failed drive can be rebuilt.
The MegaRAID Express 500 controller automatically and transparently rebuilds
failed drives with user-definable rebuild rates. If a hot spare is available, the
rebuild starts automatically when a drive fails. MegaRAID Express 500
automatically restarts the system and the rebuild if the system goes down during
a rebuild.
Rebuild Rate The rebuild rate is the fraction of the compute cycles dedicated to rebuilding
failed drives. A rebuild rate of 100 percent means the system is totally dedicated
to rebuilding the failed drive.
The MegaRAID Express 500 rebuild rate can be configured between 0% and
100%. At 0%, the rebuild is only done if the system is not doing anything else.
At 100%, the rebuild has a higher priority than any other system activity.
Physical Array A RAID array is a collection of physical disk drives governed by the RAID
management software. A RAID array appears to the host computer as one or
more logical drives.
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
14

Logical Drive
A logical drive is a partition in a physical array of disks that is made up of
contiguous data segments on the physical disks. A logical drive can consist of:
• an entire physical array
• more than one entire physical array
• a part of an array
•
parts of more than one array, or
•
a combination of any two of the above conditions
Hot Swap
A hot swap is the manual replacement of a defective physical disk unit while the
computer is still running. When a new drive has been installed, you must issue a
command to rebuild the drive.
SCSI Drive States
A SCSI disk drive can be in one of these states:
State Description
Online
(ONLIN)
Ready
(READY)
Hot Spare
(HOTSP)
Fail
(FAIL )
Rebuild
(REB)
The drive is functioningnormally and is a part of a configured logical
drive.
The drive is functioningnormally but is not part of a configured logical
drive and is not designated as a hot spare.
Thedriveispoweredupandreadyforuseasaspareincaseanonline
drive fails.
A fault has occurred in the driveplacing it out of service.
The drive is beingrebuilt with data from a failed drive.
Logical Drive States
State Description
Optimal The drive operating condition is good. All configured drives are online
Degraded The drive operating condition is not optimal. One of the configured drives
Failed The drive has failed.
Offline The drive is not available to MegaRAID Express 500.
hasfailedorisoffline.
Chapter 2 IntroductiontoRAID
15

Disk Array Types
The RAID disk array types are listed in the following table:
Type Description
Software-
Based
SCSI to SCSI The array controller resides outside of the host computer and
Bus-Based The array controller resides on the bus (for example, a PCI or
The array is managed by software running in a host computer using
the host CP U bandwidth. The disadvantages associated with this
method are the load on the host CPU and the need for different
software for each operating system.
communicates with the host through a SCSI adapter in the host.
The array management software runs in the controller. It is
transparent to the host and independent of the host operating
system. The disadvantage is the limited data transfer rate of the
SCSI channel between the SCSI adapter and the array controller.
EISA bus) in the host computer and has its own CP U to generate
the parity and handle other RAID functions. A bus-based controller
can transfer data at the speed of the host bus (PCI, ISA, EISA, VLBus) but is limited to the bus it is designed for. MegaRAID
Express 500 resides on a PCI bus, which can handle data transfer
at up to 132 MB/s. With MegaRAID Express 500, the channel can
handle data transfer rates up to 160 MB/s per SCSI channel.
Enclosure Management
Enclosure management is the intelligent monitoring of the disk subsystem by
software and/or hardware.
The disk subsystem can be part of the host computer or separate from it.
Enclosure management helps you stay informed of events in the disk subsystem,
such as a drive or power supply failure. Enclosure management increases the
fault tolerance of the disk subsystem.
MegaRAID Express 500 Hardware Guide
16
 Loading...
Loading...