Page 1

SM10P
-Port 10/100/1000Base-T +
2 RJ-45/100/1000 SFP Combo Port
Managed Switch
User Guide
Rev.A1
19-Mar-12
Page 2

Regulatory Approval
- FCC Class A
- CE
Safety Compliance
- LVD
Warranty
© Copyright 2012 Transition Networks
Lifetime
To Contac t Transitio n Networks
For prompt response when calling for service information, have the following information ready:
-
Product serial number and revision
-
Date of purchase
-
Vendor or place of purchase
You can reach Transition Networks technical support at:
E-mail: techsupport@transition.com
Transition Networks
10900 Red Circle Drive
Minnetonka, MN 55344
United States of America
Telephone: +1.800.526.9267
Fax: +1.952.941.2322
http://www.transition.com
info@ Transition.com
Revision A1
Page 3

Purpose
Audience
About This Manual
This manual gives specific information on how to operate and use the
management functions of the SM10P
The Manual is intended for use by network administrators who are
responsible for operating and maintaining network equipment;
consequently, it assumes a basic working knowledge of general
switch functions, the Internet Protocol (IP), and Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP).
ii
i
Publication date: Feb., 2012
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 4

Table of Contents
Revision History......................................................... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ... ...viii
INTRODUCTION ............................... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ...1
CHAPTER 1 OPERATION OF WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT ........................................ ..... ........ ......2
CONNECTING NETWORK DEVICES...................................... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ...2
TWISTED-PAIR DEVICES..................... ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ..... ... ... ...2
CABLING GUIDELINEST
PINOUT CONFIGURATION, SO YOU CAN USE STANDARD STRAIGHT-THROUGH TWISTED-PAIR CABLES TO
CONNECT TO ANY OTHER NETWORK DEVICE (PCS, SERVERS, SWITCHES, ROUTERS, OR HUBS)...............2
CHAPTER 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION ........................... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ...4
YSTEM INFORMATION...................................... ....... ...... .......... ....... ...... ....... ......... ....... ...... .......... ....... ...... ....... .......4
2-1 S
2-1.1 Information................ ... ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ...... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ...4
2-1.2 Configuration................................... ................................................. ....................................................... ...7
2-1.3 CPU Load....................................................................................................................... .........................8
2-2 T
IME............................ ... ...... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... . ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ...9
2-2.1 Manual............................................................................................................ ............................................9
2-2.2 NTP ........................................................................ ................................................. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. .....11
2-3 A
CCOUNT....................................... ......................................................................................... . ......................12
2-3.1 Users...................................... .... ... .. ..... .. .. ..... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .... ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. ..... .. ...................................12
2-3.2 Privitege Level.......................................................................................................................................14
2-4 IP................................. ................... ..................... ................... ..................... ................... ................................17
2-4.1 IPV4 .................................... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... .17
2-4.2 IPV6 .................................... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... .19
2-5 S
YSLOG........................................................... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ..... ... ... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... .21
2-5.1 Configuration..................................................................................................................................... .. ... .21
2-5.2 Log........................................................................................................................................................22
2-5.3 Detailed Log.........................................................................................................................................23
2-6 SNMP....................................................... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... .24
2-6.1 System ....................................................................................................................... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ....24
2-6.2 Communities..................................................... ........................................................................................26
2-6.3 Users...................................... .... ... .. ..... .. .. ..... ... .. .. ..... .. ... .... ... .. ..... .. .. ... .... ... .. ..... .. ...................................27
2-6.4 Groups......................................................................................................................................... ...... .......... ..29
2-6.5 Views ................................ ................ ................ ..................... ................ ................ ............ ............ ................ ....30
2-6.6 Access....................................................... ......... ........ ........ ........... ........ ........ ........... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ....32
2-6.7 Tarp......................................................... ........................... ..................... ..................... ........................... ...............34
CHAPTER 3. CONFIGURATION .......................... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... .36
3-1 P
ORT.............................................................................. ............. ............ ................ ............ ................ ............ ............36
3-1.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ....................................................... .36
3-1.2 Port Description...... ................................................. .................................................... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... .38
3-1.3 Traffic Overview....................................................... ........ ........ ........ ......... ........ ........ .............. .. ... ..... ... ... .39
3-1.4 Detailed Statistics............................................................... .... ... ... ....... ... ... ... ....... ... ... .... ......... ....... ...... ....... ..40
3-1.5 Qos Statistics ...................................... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... .42
3-1.6 SFP Information...... .. ...... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... ..... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ....43
3-1.7 EEE ........................................................................ ................................................. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... .45
3-2 ACL................................................................................................ ...............................................................47
3-2.1 Ports............................................ ....................................................................................................... ... ....47
3-2.2 Rate Limiters....................................... ................................................. .....................................................49
3-2.3 Access Control List..................................... ......... ....... ....... .......... ....... ......... ....... ...................................50
3-2.4 ACL Status.............................................................. .......... .......... .......... ............. ............. ...... ....... ......... ....... ..53
3-3 A
GGREGATION................................................................................... ............ ............ ................ ............ ................ ....55
3-3.1 Static Trunk ............................................. ......... .... .... ........ .... .... .... ........ .... .... ........ .... ............ ................ ............55
3-3.1.1 Static Trunk..............................................................................................................................................................55
3-3.2 LACP.........................................................................................................................................................57
3-3.2.1 Configuration...................................................................................................................................... ........ ....... ..57
3-3.2.2 System Status ...................................................................................................... ........ ............... ........ ........ .........59
3-3.2.3 Port Status............................................................................................. ........ ....... ........ ............... ........ ........ ....... ..60
3-3.2.4 Port Statistics..................................................................................................................................................... ..61
3-4 SPANNING TREE.............................................. .. ...... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... .62
HE RJ-45 PORTS ON THE SWITCH SUPPORT AUTOMATIC MDI/MDI-X
Revision A1
Page 5

3-4.1 Bridge Settings ......................................................................................................................................62
2-4.2 MSTI Mapping..................................................................................... .....................................................65
3-4.3 MSTI Priorities......................................................... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ... .67
3-4.4 CIST Ports............................................................................................................................. ... .. ... ..... ... ... .68
3-4.5 MSTI Ports............................... ........................................................................................................ .. ...... .70
3-4.6 Bridge Status....................................................... ........................................................... ...... .......... ...... ....... ..72
3-4.7 Port Status.............................................. .......................................................................................................73
3-4.8 Port Statistics............................................................................................................. ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... .74
3-5 IGMP S
NOOPING............................................................ ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ... ... ..... ... .76
3-5.1 Basic Configuration ............................................................................ .....................................................76
3-5.2 VLAN Configuration ........................................................ ........ ........ ......... ........ ........ ........ ...... .. ... ... ..... ... .78
3-5.3 Port Group Filtering ....................... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... .80
3-5.4 Status ................................................................ ... ....... ... ... ... ....... ... ... .... ... ...... .... ... .......... ...... ....... ...... .......... ..82
3-5.5 Group Infermation........................................................................................................................ ...... .. ... .84
3-5.6 IPv4 SSM information........ .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ....85
3-6 MLD S
NOOPING.......................................................... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... .. ...... .87
3-6.1 Basic Configuration ............................................................................ .....................................................87
3-6.2 VLAN Configuration ........................................................ ........ ........ ......... ........ ........ ........ ...... .. ... ... ..... ... .89
3-6.3 Port Group Filtering ....................... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... .91
3-6.4 Status ................................................................ ... ....... ... ... ... ....... ... ... .... ... ...... .... ... .......... ...... ....... ...... .......... ..92
3-6.5 Group Infermation........................................................................................................................ ...... .. ... .94
3-6.6 IPv6 SSM Information........................................ ... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ... .96
3-7 MVR.............................................. ............................................ ....................................................................97
3-7.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ....................................................... .97
3-7.2 Groups Information....................................................... .............. ......................... ............. ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... .99
3-7.3 Statistics.. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ........ ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ..100
3-8 LLDP............................................. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ..101
3-8.1 LLDP Configuration ..............................................................................................................................101
3-8.2 LLDP Neighbours................................................................................................................................. ..104
3-8.3 LLDP-MED Configuration....................................................................................................... ... ... ..... ..106
3-8.4 LLDP-MED Neighbours....................................................... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ..112
3-8.5 EEE ........................................................................ ................................................. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ....115
3-8.6 Port Statistics............................................................................................................. ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ..117
3- 9 F
ILTERING DATA BASE........................................ ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. .....119
3- 9.1 Configuration................................ .. ...... .. ... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ..119
3- 9.2 Dynamic MAC Table.................................................................. ........ .... .... .... ........ .... .... ........ ................ ......121
3-10 VLAN..................................................... ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. .....123
3-10.1 VLAN Membership ................... ........ ........ ........ ......... ........ ........ ........ ........... ........ ........ ........... ... ... ..... ..123
3-10.2 Ports....................................................................................................................................... .. ... ... ..... ..125
3-10.3 Switch Status........................................... ....... ... ... .... ... ...... .... ... ... ....... ... ... ... ....... ... .. ..... ...... ....... ...... .......... 128
3-10.4 Po rt Status.......................................................................................................................... ....... ......... ....... 129
3-10.5 Private VLANs...................................................................................................................................131
3-10.5.1 Private VLANs Membership.......................... ........ ....... ................ ........ ....... ........ ................ ....... ........ .......131
3-10.5.2 Port Isolation ............................................ ........ ........ ............... ........ ........ ............... ........ ....... ............... ........132
3-10.6 MAC-based VLAN................................................................................................................................133
3-10.6.1 Configuration.................................................................................................. ........ ........ ............... ....... ........133
3-10.6.2 Status ......................................................................................................................................................................135
3-10.7 PROTOCOL -BASED VLAN............................................. ............................................. ............................136
3-10.7.1 Protocol to Group........................................................................................................................................136
3-10.7.2 Group to VLAN ................................. ....... ........ ................ ....... ........ ....... ................ ........ ....... ................ .......138
3-11 VOICE VLAN ...................... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ..... ... ... ... .. ... ..... ... ..140
3-11.1 Configuration........................................................................................................................................140
3-11.2 OUI............................................ ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ....142
3-12 GARP.............................................................. ..................... ...................... ...................... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ..143
3-12.1 Configuration .......................................................................................................................................143
3-12.2 Statistics................................................................................................................................................145
3-13 GVRP.............................................................. ..................... ...................... ...................... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ..146
3-13.1 Configuration .......................................................................................................................................146
3-13.2 Statistics................................................................................................................................................148
3-14 Q
OS ..................................... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ...... .. ... ... .... . ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. .....149
3-14.1 Port Classification............................ ....................................................... .. ...... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ..149
3-14.2 Port Policing ...................................................................................................................................... ..151
3-14.3 Port Scheduler......................................................................................................................................152
3-14.4 Port Shaping.........................................................................................................................................155
3-14.5 Port Tag Remarking ....................................................................... ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ..... ... ..158
v
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 6

3-14.6 Port DSCP............................................................................................................................. ............159
3-14.7 DSCP-Based QoS..............................................................................................................................161
3-14.8 DSCP Translation.....................................................................................................................................163
3-14.9 DSCP Classification.............................................................................................................................165
3-14.10 QoS Control List Configuration ........................................................................................................166
3-14.11 QCL Status............ .......................................................... ........................................................... ...... ....... 170
3-14.12 Storm Control ................................. ........................................................................................................172
3-15 T
HERMAL PROTECTION................................................ ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ..173
3-15.1 Configuration .......................................................................................................................................173
3-15.2 Status .........................................................................................................................................................175
3-16
S-FLOW AGENT.......................................................... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... .. .....176
3-16.1 Collector .......................................................................................................................... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ..176
3-16.2 Sampler........................................................ ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ....178
3-17 L
OOP PROTECTION.....................................................................................................................................180
3-17.1 Configuration .......................................................................................................................................180
3-17.2 Status .........................................................................................................................................................182
3-18 S
INGLE IP.................................................................................................................. .................................183
3-19 E
ASY PORT...................................................................................... ............ ............ ................ ............ ................ ..186
3-20 M
IRRORING ............................................... ... ... ..... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ..188
3-21 TRAP EVENT SEVERITY...................................................... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ..190
3-22 SMTP C
3-23 UP
ONFIGURATION ........ ............ ................ ............ ............. ................ ............ ............ ................ ............ ......192
NP........ ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ..... ... ... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ..193
CHAPTER 4. SECURITY............................... ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ..195
4-1 IP S
OURCE GUARD.......................................................................................................................................195
4-1.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ......................................................195
4-1.2 Static Table .................................................. ..... ........... ..... ..... ...... .......... ..... ...... ...... ......... ...................... .............197
4-1.3 Dynamic Table............ .... .... .... ........ .... .... ........ ..... .... ........ .... .... ........ .... .... .... ........ .... ........ ................ ............ ..198
4-2 ARP I
NSPRCTION .................................... ........................................................................................... ..........199
4-2.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ......................................................199
4-2.2 Static Table .................................................. ..... ........... ..... ..... ...... .......... ..... ...... ...... ......... ...................... .............200
4-2.3 Dynamic Table............ .... .... .... ........ .... .... ........ ..... .... ........ .... .... ........ .... .... .... ........ .... ........ ................ ............ ..202
4-3 DHCP S
NOOPING .................. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... ... ....203
4-3.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ......................................................203
4-3.2 Statistics.. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ........ ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ..204
4-4 DHCP R
ELAY....................................................................................................... ..................... ..................... .............206
4-4.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ......................................................206
4-4.2 Statistics.. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ........ ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ..208
4-5 NAS.......................................... ........................ ...................... ...................... ................... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ....210
4-5.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ......................................................210
4-5.2 Switch Status....................................................... ... ... .... ...... .... ... ... ....... ... ... ... .... ...... . .. .......... ....... ...... ....... ...218
4-5.3 Port Status.............................................. .....................................................................................................220
4-6 AAA ................................... ............................................ ............................................ ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ....223
4-6.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ......................................................223
4-6.2 Radius Overview................................................................................................ .....................................227
4-6.3 Radius Details............................. ..................................................................................................... ... ....229
4-7 P
ORT SECURITY.............................................. .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ... .. .....230
4-7.1 Limit Control........................................................................................................................ .......... ...... ....... 230
4-7.2 Switch Status....................................................... ... ... .... ...... .... ... ... ....... ... ... ... .... ...... . .. .......... ....... ...... ....... ...233
4-7.3 Port Status.............................................. .....................................................................................................235
4-8 A
CCESS MANAGEMENT.......................................................... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ..236
4-8.1 Configuration................................... ................................................. ......................................................236
4-8.2 Statistics.. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ........ ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ..238
4-9 SSH........................................... ...................... ...................... ..................... ...................... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ..239
4-10 HTTP
4-11 A
S.............................. ...... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... . .... ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ..240
UTH METHOD.......................................... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ...... ..................241
CHAPTER 5. MAINTENANCE .......................................................................................................242
5-1 R
ESTART DEVICE......................................... ... ... ..... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .... . ...... .. ... ..242
5-2 F
IRMWARE........................................................................ ............. ................ ............ ............ ................ ............ ......243
5-2.1 Firmware Upgrade............................................................................................................ ... ... ..... ... ... ....243
5-2.2 Firmware Selection ................................................................................................................................244
5-3 S
AVE / RESTORE ............................... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ... ..... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... .. .....246
vi
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 7

5-3.1 Factory Defaults................................................................................................................................ .....246
5-3.2 Save Start................................................. ..... .... ........ .... .... .... ........ .... .... .... ........ .... .... ............ ............ ..............246
5-3.3 Save User......... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... .....................................247
5-3.4 Restore User.............. ............................................. .............................................................................247
XPORT / IMPORT................................................. ................. ............ ............ ................ ............ ............ ................ ..248
5-4 E
5-4.1 Export Config .........................................................................................................................................248
5-4.2 Import Config ................................................... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... ..... ... ... ... ..... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ..249
5-5 D
IAGMOSTICS......................................... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... .. ... ...... .. ... ... ..... ... ... .. ...... ... .. ... ... ... ..... ... ... .. ..250
5-5.1 Ping.................................................................................................................................................. ... ....250
5-5.2 Ping6..................................................................................................................................................... ..251
5-5.3 VeriPHY.................................................................................... ............ ................ ................ ............ ............ ..252
A. GLOSSARY OF WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT........................................................................................253
A ................................................................................................................................................................... .....253
C........................................ .................................................................................................................................254
D ................................................................................................................................................................... .....254
E.......................................................................................................................... ...............................................256
F.........................................................................................................................................................................256
H ................................................................................................................................................................... .....256
I.............................................. ............................................ ................................................................................257
L.......................................................................................................................... ...............................................258
M................................................ .......................................................................................... ..............................258
N ................................................................................................................................................................... .....259
O ................................................................................................................................................................... .....260
P.........................................................................................................................................................................260
Q ................................................................................................................................................................... .....261
R........................................ .................................................................................................................................262
S.........................................................................................................................................................................262
T.......................................................................................................................... ...............................................263
U ................................................................................................................................................................... .....264
V ................................................................................................................................................................... .....264
vii
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 8

Revision History
Date Revision
03/20/2012 A1
viii
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 9

INTRODUCTION
Overview
The SM10P is an affordable managed switch that provides a reliable
infrastructure for your business network. These switches deliver more intelligent
features you need to improve the availability of your critical business applications,
protect your sensitive information, and optimize your network bandwidth to deliver
information and applications more effectively. It provides the ideal combination of
affordability and capabilities for entry level networking includes small business or
enterprise application and helps you create a more efficient, better-connected workforce.
SM10P
specification is hig h lig h te d as follo ws.
L2+ features provide better manageability, security, QoS, and performance.
High port count design with all Gigabit Ethernet ports
Support guest VLAN, voice VLAN, Port based, tag-based and Protocol based
VLANs.
Support 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet standard
Support 8K MAC table
Support IPv6/ IPv4 Dual stack
Support s-Flow
Support Easy-Configuration-Port for easy implement the IP Phone, IP Camera
or Wireless environment.
Overview of this user’s manual
Chapter 1 “Operation of Web-based Management”
Chapter 2 “Maintenance”
Managed Switch
provides
10 ports in
a single device;
the
1
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 10

Chapter 1 Operation of Web-based Management
Initial
Configuration
This chapter instruct s you how to conf igure an d manage the SM10P
through the web user interface. With this facility, you can easily access
and monitor through any one port of the switch all t he stat us of the swit ch,
including MIBs status, each port activity, Spanning tree status, port
aggregation status, mult icast traffic , VLAN and priorit y status, even illegal
access record and so on.
The default values of the SM10P are listed in the table below:
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Username
Password
After the SM10P has been finished configuration the interface, you can
browse it. For instance, type http://192.168.1.77
in a browser, it will show the following screen and ask you inputting
username and password in order to login and access authentication.
The default username is “admin” and password is admin. For the first
time to use, please enter the default username and password, and then
click the <Login> button.
In the SM10P, it supports a simple user management function allowing
only one administrator to configure the system at the same time. If there
are two or more users using administrator’s identity, it will allow the
only one who logins first to configure the system. The rest of users,
even with administrat or’s identity, can only monitor the syst em. For those
who have no administrator’s identity, can only monitor the system. There
are only a maximum of three users able to login simultaneously in the
SM10P.
192.168.1.77
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.254
admin
admin
in the address row
NOTE:
When you login SM10P series switch Web UI management, you
can use both ipv4 ipv6 login to manage
To optimize the display effect, we recommend you use Microsoft
IE 6.0 above, Netscape V7.1 above or FireFox V1.00 above and
have the resolution 1024x768. The switch supported neutral web
browser interface
2 Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 11
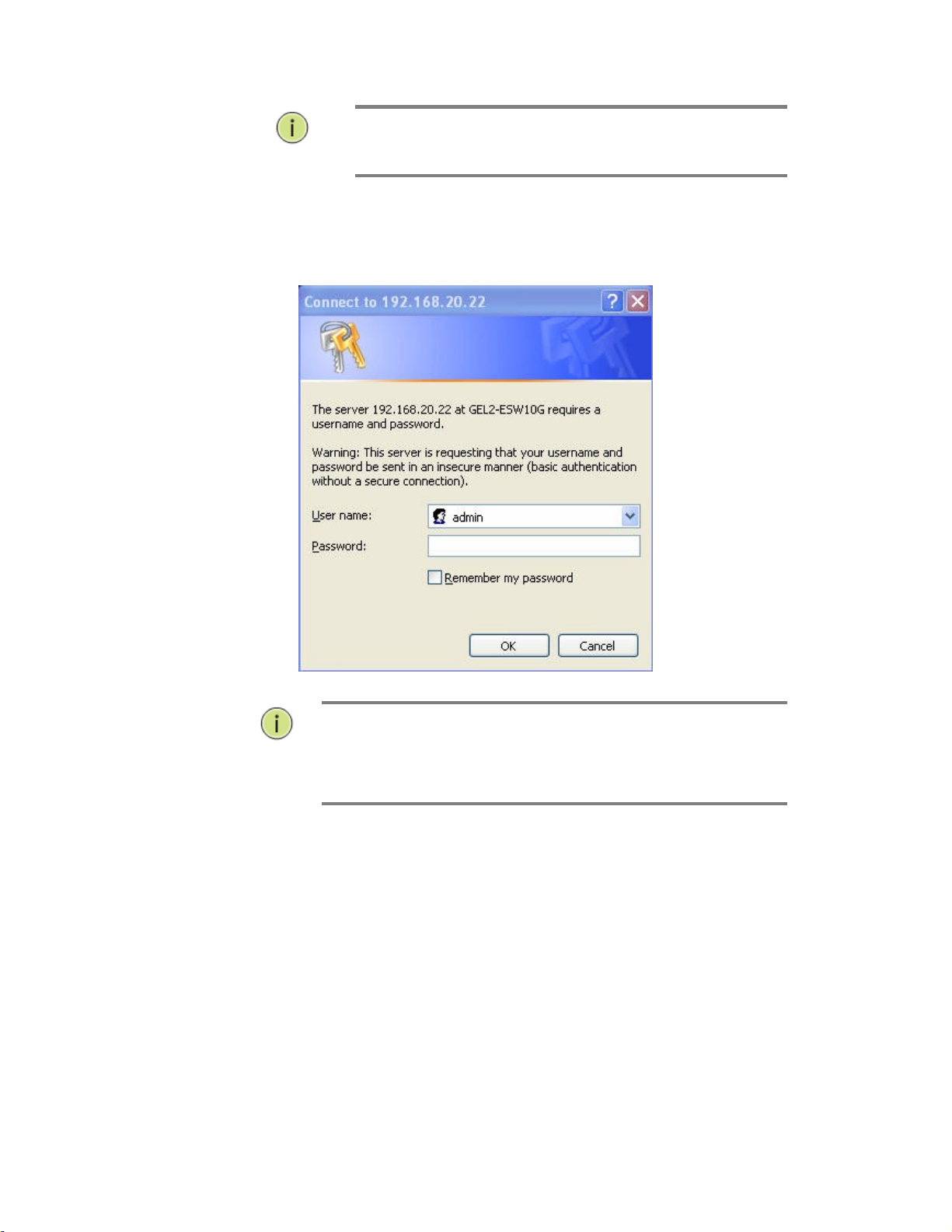
NOTE:
AS SM10P the function enable dhcp, so If you do not have
DHCP server to provide ip addresses to the switch, the
Switch default ip 192.168.1.77
Figure 1 The login page
NOTE: If you need to configuration the function or parameter
then you can refer the detail in the User Guide. Or you could
access to the Switch and click the "help" under the web GUI
and the switch will po p- u p the simple help content to teach
you how to set the parameters.
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 12

SM10P web help function:
CONNECTING
NETWORK
DEVICES
TWISTED-PAIR
The switch is designed to be connected to 10, 100 or
1000Mbps network cards in PCs and serve rs, as well as
to other switches and hubs. It may also be connected
to remote devices using optional SFP transceivers.
DEVICES
Publication date: Mar ., 2012
Revision A1
Page 13

Each device requires
an unshielded twistedpair (UTP) cable with
RJ-45 connectors at
CABLING
GUIDELINES
See Appendix B for further information on cabling.
both ends. Use Category 5, 5e or 6 cable for
1000BASE-T connections, Category 5 or better for
100BASE-TX connections.
The RJ-45 ports on the switch support automatic
MDI/MDI-X pinout configuration, so you can use
standard straight-through twisted-pair cables to
connect to any other network device (PCs, servers,
switches, routers, or hubs).
CAUTION:
port. This will damage the switch. Use only twisted-pair
cables with RJ-45 connectors that conform to FCC
standards.
Do not plug a phone jack connector into an RJ-45
CONNECTING TO PCS, SERVERS, HUBS AND SWITCHES
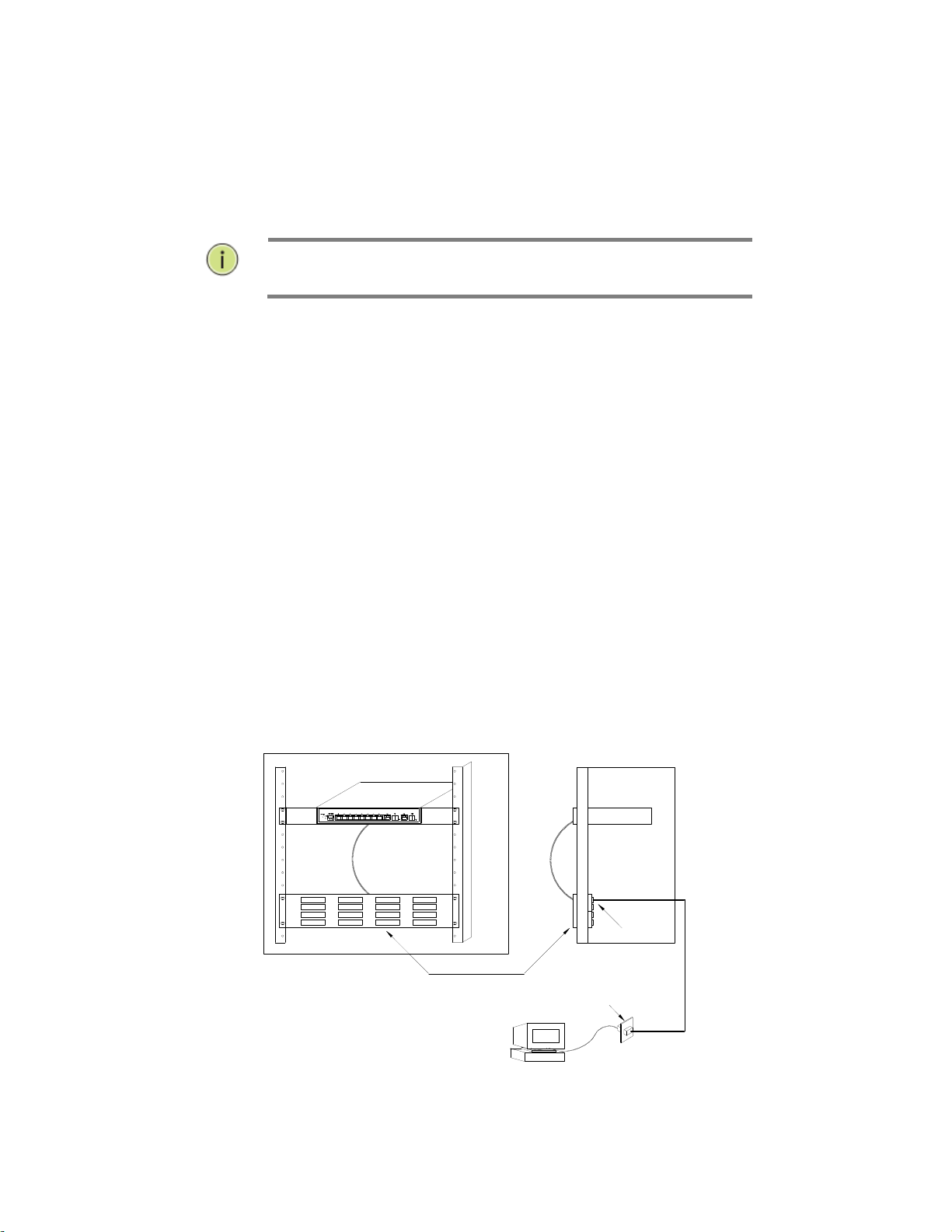
Step1. Attach one end of a twisted-pair cable segment to the device’s RJ-45
connector.
Figure 16: Making Twisted-Pair Connections
2 Publication date: Mar ., 2012
Revision A1
Page 14

Page 15
quip
Step2. If the device is a network card and the switch is in the wiring closet, attach the
other end of the cable segment to a modular wall outlet that is connected to
the wiring closet. (See the section “Network Wiring Connections.”) Otherwise,
attach the other end to an available port on the switch.
Make sure each twisted pair cable does not exceed 100 meters (328 ft) in length.
NOTE: Avoid using flow control on a port connected to a hub
unless it is actually required to solve a problem. Otherwise
back pressure jamming signals may degrade overall
performance for the segment attached to the hub.
Step3. As each connection is made, the Link LED (on the switch) corresponding to
each port will light green (1000 Mbps) or amber (100 Mbps) to indicate that
the connection is valid.
NETWORK WIRING CONNECTIONS
Today, the punch-down block is an integral part of many of the newer equipment racks.
It is actually part of the patch panel. Instructions for making connections in the wiring
closet with this type of equipment follows.
Step1. Attach one end of a patch cable to an available port on the switch , and the
other end to the pat c h p anel.
Step2. If not already in place, attach one end of a cable segment to the back of the
patch panel where the punch-down block is located, and the other end to a
modular wall outlet.
Step3. Label the cables to simplify future troubleshooting. See “Cable Labeling and
Connection Records” on page 29
.
Figure 17: Network Wiring Connections
Switch
ment Rack
E
(side view)
Patch-Down Block
Patch Panel
Wall
3 Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 16

Chapter 2 System Configuration
This chapter describes the entire basic configuration tasks which includes the System
Information and any manage of th e Swit ch (e.g. Ti me, Acco unt , IP, Syslog and SNMP.)
2-1 System Information
After you login, the switch shows you the system information. This page is default and tells
you the basic information of the system, including “Model Name”, “System Description”,
“Contact”, “Device Name”, “System Up Time”, “BIOS Version”, “Firmware Version”,
“Hardware-Mechanical Version”, “Serial Number”, “Host IP Address”, “Host Mac Address”,
“Device Port”, “RAM Size” , “Flash Size” and. With this information, you will know the software
version used, MAC address, serial number, how many ports good and so on. This is helpful
while malfunctioning.
2-1.1 Information
The switch system information is provided here.
Web interface
To configure System Information in the web interface:
1. Click SYSTEM, System, and Information.
2. Specify the contact information for the system administrator as well as the name and
location of the switch. Also indicate the local time zone by configuring the appropriate
offset.
3. Click Refresh
Figure 2-1.1: System
Information
4
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 17

Parameter description:
Model name:
The model name of this device.
System description:
As it is, this tells what this device is. Here, it is “8 port 10/100/1000 Base-T
+ 2-Port 100/1000 SFP/RJ-45 Managed Switch”.
Location:
Basically, it is the location where this switch is put. User-defined.
Contact:
For easily managing and maintaining device, you may write down the contact
person and phone here for getting help soon. You can configure this parame t er
through the device’s user interface or SNMP.
Device nam e:
The name of the switch. User-defin e d .
System Date:
Show the system time of the switch. Its format: day of week, month, day,
hours : minutes : seconds, year.
System up time:
The time accumulated since this switch is powered up. Its format is day, hour, minute,
second.
BIOS version:
The version of the BIOS in this switch.
Firmware version:
The firmware version in this switch.
Hardware-Mechanical version:
The version of Hardware and Mechanical. The figure before the hyphen is the version of
electronic hardware; the one after the hyphen is the version of mechanical.
Serial number:
The serial number is assigned by the Manufacture.
Host IP address:
The IP address of the switch.
Host MAC address:
It is the Ethernet MAC address of the management agent in this switch.
Device Port:
Show all types and numbers of the port in the switch.
RAM size:
The size of the RAM in this switch.
Flash size:
The size of the flash memory in this switch.
Bridge FDB size :
To display the bridge FDB size information.
Transmit Queue :
5 Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 18

To display the device’s transmit hardware prio rity qu eue information .
Maximum Frame size :
To display the device’s maximum frame size information.
6
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 19

2-1.2 Configuration
You can identify the system by configuring the contact information, name, and location of the
switch.
Web interface
To configure System Information in the web interface:
1. Click System, System Information and Configuration.
2. Write System Contact , System Name, System Location information
in this page.
3. Click Save
Figure 2-1.2: System Information configuration
SM10P
Parameter description:
System Contact :
The textual identification of the contact person for this ma naged node , toget her
with information on how to contac t this person. The allowed string length is 0
to 255, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 32 to 126.
System Name :
An administratively assigned name for this managed node. By convention, this
is the node's fully-qualified domain name. A domain name is a text string
drawn from the alphabet (A-Za-z), digits (0-9), minus sign (-). No space
characters are permitted as part of a name. The first character must be an
alpha character. And the first or last character must not be a minus sign. The
allowed string length is 0 to 255.
System Location :
The physical location of this node(e.g., telephone closet, 3rd floor). The allowed
string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from
32 to 126.
7 Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 20
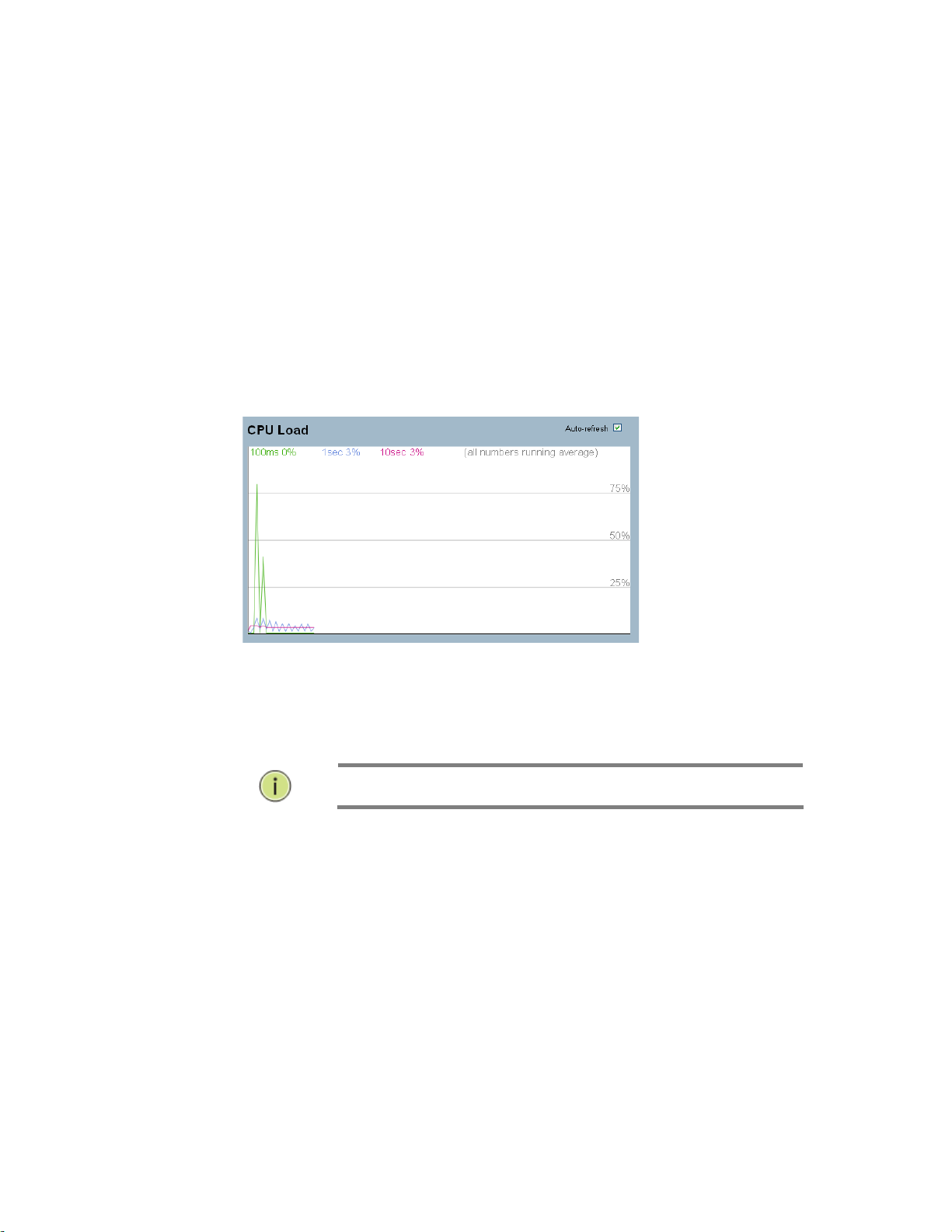
2-1.3 CPU Load
This page displays the CPU load, using an SVG graph. The load is measured as averaged
over the last 100ms, 1sec and 10 seconds intervals. The last 120 samples are graphed, and
the last numbers are displayed as text as well. In order to display the SVG graph, your
browser must support the SVG format. Consult the SVG Wiki for more information on browser
support. Specifically, at the time of writing, Microsoft Internet Explorer will need to have a plug
in installed to support SVG.
Web interface
To configure System Information in the web interface:
1. Click System, System Information, CPU Load .
2. Display the CPU Load on the screen
3. Click Auto-refresh .
Figure 2-1.3: CPU Load
Parameter description:
Auto-refresh
To evoke the auto-refresh icon then the device will refresh the log automatically.
NOTE: The under “from” and “to” was display ed what you set
on the “From” and “To” field info r ma ti on .
8 Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 21

2-2 Time
This page configure the switch Time. Time configure is including Time Configuration and NTP
Configuration
2-2.1 Manual
The switch provides manual and automatic ways to set the system time via NTP. Manual
setting is simple and you just input “Year”, “Month”, “Day”, “Hour”, “Minute” and “Second”
within the valid value range indicated in each item.
Web Interface
To configur e Time in the web in t er f ac e:
1. Click Time , Manual.
2. Specify the Time parameter in manual parameters.
3. Click Save.
Figure 2-2.1: The time configuration
Parameter description:
Clock Source:
To click what clock source for the SM10P. You can select “Use local
Settings” or “Use NTP Server” for SM10P time clock source.
Local Time:
Show the current time of the system.
Time Zone Offset:
Provide the time zone offset relative to UTC/GMT. The offset is given in minutes
east of GMT. The valid range is from -720 to 720 minutes
Daylight Saving:
Daylight saving is adopted in some countries. If set, it will adjust the time lag
or in advance in unit of hours, according to the starting date and the ending
date. For example, if you set the day light saving to be 1 hour. When the time
passes over the starting time, the system time will be increased one hour after
one minute at the time since it passed over. And when the time passes over the
ending time, the system time will be decreased one hour after one minute at
the time since it passed over.
The switch supports valid configurable day light saving time is –5 ~ +5 step
one hour. The zero for this parameter means it need not have to adjust current
9
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 22

time, equivalent to in-act daylight saving. You don’t have to set the
starting/ending date as well. If you set daylight saving to be non-zero, you
have to set the starting/ending date as well; otherwise, the daylight saving
function will not be activated.
Time Set Offset:
Provide the Daylight saving time set offset. The offset is given in minutes east
of GMT. The valid range is from 1 to 1440 minutes. default is 60 mins
Daylight Savings Type:
Provide the Daylight savings type selection. You can select “ By Dates” or
“Recurring” two type for Daylight saving type.
From:
To configure when Daylight saving start date and time, the format is “YYYY-MM-
DD HH:MM”.
To:
To configure when Daylight saving end date and time, the format is “YYYY-MM-
DD HH:MM”.
NOTE: The under “from” and “to” was display ed what you set
on the “From” and “To” field info r ma ti on .
10 Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 23

2-2.2 NTP
Web Interface
NTP is Network Time Protocol and is used to sync the network time based Greenwich Mean
Time (GMT). If use the NTP mode and select a built-in NTP time server or manually specify
an user-defined NTP server as well as Time Zone, the switch will sync the time in a short after
pressing <Apply> button. Though it synchronizes the time automatically, NTP does not update
the time periodically without user’s processing.
Time Zone is an offset time off GMT. You have to select the time zone first and then perform
time sync via NTP because the switch will combine this time zone offset and updated NTP
time to come out the local time, otherwise, you will not able to get the correct time. The switch
supports configurable time zone from –12 to +13 step 1 hour.
Default Time zone: +8 Hrs.
To configur e Time in the web in t er f ac e:
1. Click SYSTEM, NTP.
2. Specify the Time parameter in manual parameters.
3. Click Save.
Figure 2-2.2: The NTP configuration
Parameter description:
Server 1to 5 :
Provide the NTP IPv4 or IPv6 address of this switch. IPv6 address is in 128-bit
records represented as eight fields of up to four hexadecimal digits with a colon
separating each field (:). For example, 'fe80::215:c5ff:fe03:4dc7'. The symbol
'::' is a special syntax that can be used as a shorthand way of representing
multiple 16-b it groups of contiguo us zeros; but it can on ly appear once. It c an
also represent a legally valid IPv4 address. For example, '::192.1.2.34'.
Buttons
These buttons are displayed on the NTP page:
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset - Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
11
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 24
2-3 Account
In this function, only administrator can create, modify or delete the username and password.
Administrator can modify other guest identities’ password without confirming the password but
it is necessary to modify the administrator-equivalent identity. Guest-equivalent identity can
modify his password only. Please note that you must confirm administrator/guest identity in
the field of Authorization in advance before configuring the username and password. Only one
administrator is allowed to exist and unable to be deleted. In addition, up to 4 guest accounts
can be created.
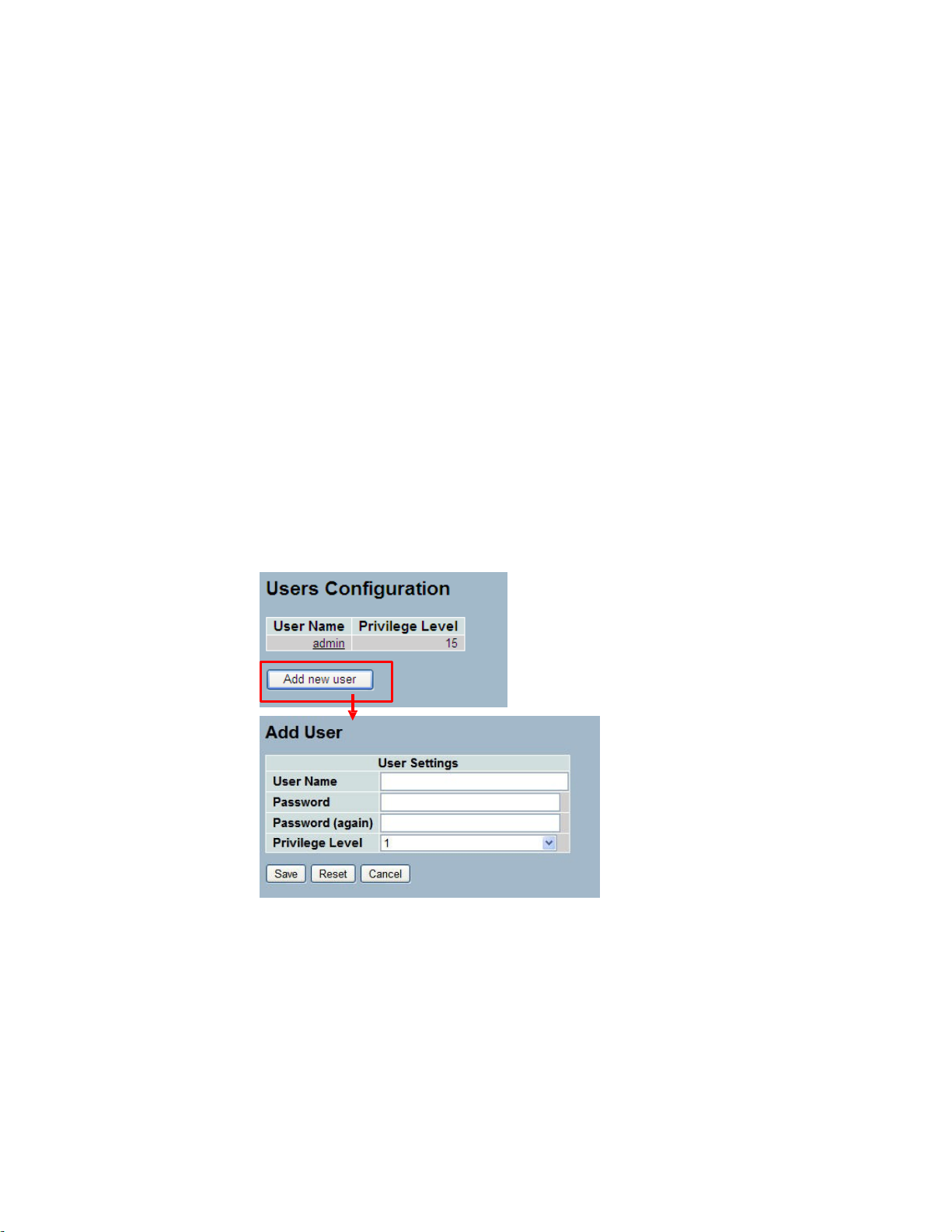
2-3.1 Users
This page provides an overview of the current users. Currently the only way to login as
another user on the web server is to close and reopen the browser
Web Interface
To configure Account in the web interface:
1. Click SYSTEM, Account, Users.
2. Click Add new user
3. Specify the User Name parameter.
4. Click Save.
Figure2- 3. 1: The Users Account configuration
Parameter description:
User Name :
The name identifying the user. This is also a link to Add/Edit User.
Password
To type the password. The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed
content is the ASCII characters from 32 to 126 .
Password (again)
To type the password again. You must type the same password again in the
field.
12 Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 25

Privilege Level :
The privilege level of the user. The allowed range is 1 to 15. If the privilege
level value is 15, it can acces s all g roups, i.e. that is grante d the fully cont rol o f
the device. But others value need to refer to each group privilege level. User's
privilege should be same or greater than the group privilege level to have the
access of that group. By default setting, most groups privilege level 5 has the
read-only access and privilege level 10 has the read-write access. And the
system maintenance (software upload, factory defaults and etc.) need user
privilege level 15. Generally, the privilege level 15 can be used for an
administrator account, privilege level 10 for a standard user account and
privilege level 5 for a guest account.
13
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 26

2-3.2 Privilege Level
This page provides an overview of the privilege levels. The switch provides user set Account,
Aggregation, Diagnostics, EEE, GARP,GVRP,IP, IPMC Snooping LACP LLDP LLDP-MED
MAC Table MRP MVR MVRP Maintenance Mirroring POE Ports Private VLANs QoS SMTP
SNMP Security Spanning Tree System Trap Event VCL VLANs Voice VLAN Privilege Levels
form 1 to 15 .
Web Interface
To configure Privilege Level in the web interface:
1. Click SYSTEM, Account, Privilege Level.
2. Specify the Privilege parameter.
3. Click Save.
Figure2- 3.2: The Privilege Level configuration
14
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 27

Parameter description:
Group Name
The name identifying the privilege group. In most cases, a privilege level group
consists of a single module (e.g. LACP, RSTP or QoS), but a few of them
contains more than one. The following description defines these privilege level
groups in details:
System: Contact, Name, L oc a ti on , Timezone, Log.
Security: Authentication, System Access Management, Port (contains Dot1x
port, MAC based and the MAC Address Limit), ACL, HTTPS, SSH, ARP
Inspection and IP source guard.
IP: Everything except 'ping'.
Port: Everything except 'VeriPHY'.
Diagnostics: 'ping' and 'VeriPHY'.
Maintenance: System Reboot, System Restore Default, System Password,
15
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 28

Configuration Save, Configuration Load and Firmware Load. Web- Users,
Privilege Levels and everything in Maintenance.
Privilege Levels
Every group has an authorization Privilege level for the following sub groups:
configuration read-only, configuration/execute read-write, status/statistics
read-only, status/statistics read-write (e.g. for clearing of statistics). User
Privilege should be same or greater than the authorization Privilege level to
have the access to that group.
16
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 29
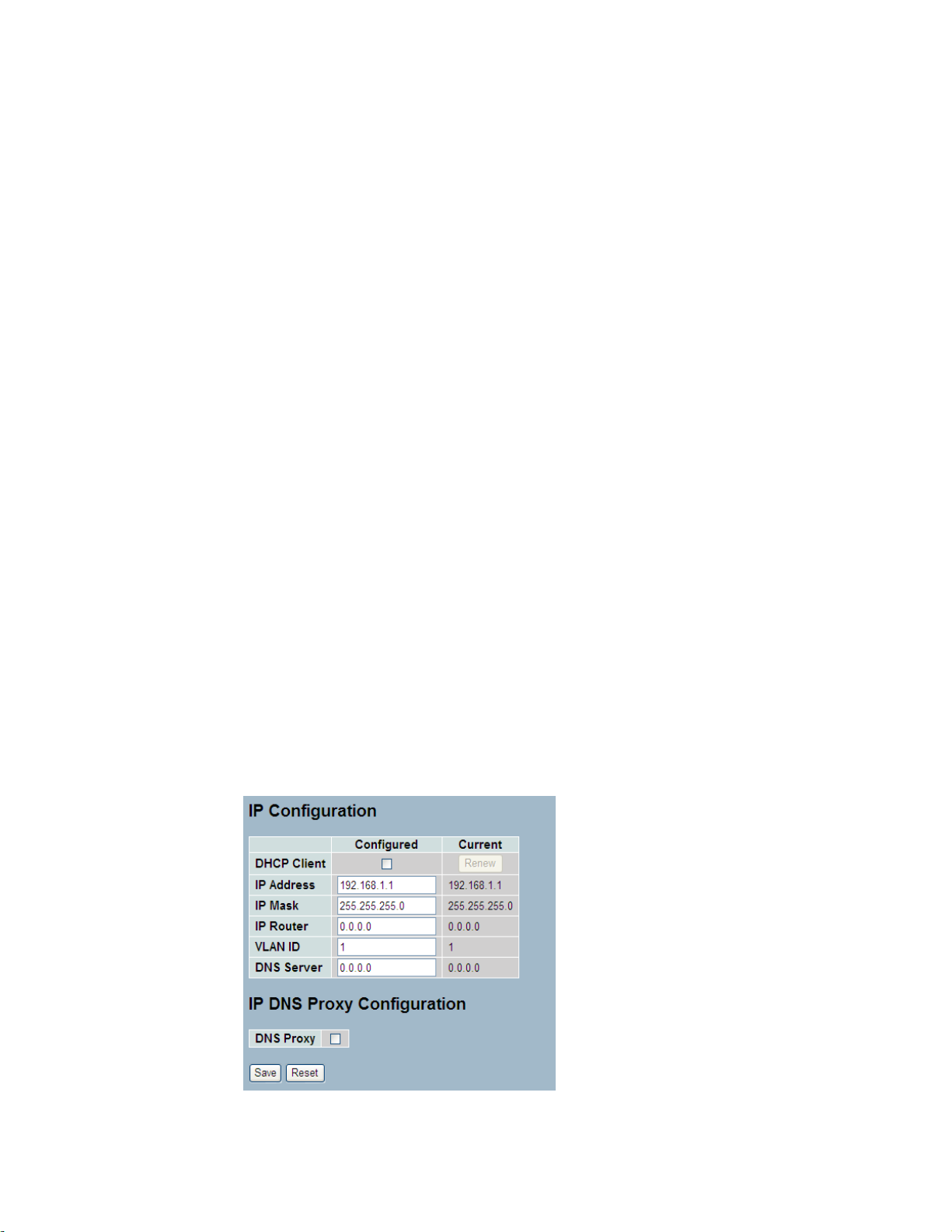
2-4 IP
IP is an acronym for Internet Protocol. It is a protocol used for communicating data across an
internet network.
IP is a "best effort" system, which means that no packet of information sent over is assured to
reach its destination in the same condition it was sent. Each device connected to a Local Area
Network (LAN) or Wide Area Network (WAN) is given an Internet Protocol address, and this
IP address is used to identify the device uniquely among all other devices connected to the
extended network.
The current version of the Internet protocol is IPv4, which has 32-bits Internet Protocol
addresses allowing for in excess of four billion unique addresses. This number is reduced
drastically by the practice of webmasters taking addresses in large blocks, the bulk of which
remain unused. There is a rather substantial movement to adopt a new version of the Internet
Protocol, IPv6, which would have 128-bits Internet Protocol addresses. This number can be
represented roughly by a three with thirty-nine zeroes after it. However, IPv4 is still the
protocol of choice for most of the Internet.
2-4.1 IPV4
The IPv4 address for the switch could be obtained via DHCP Server for VLAN 1. To manually
configure an address, you need to change the switch's default settings to values that are
compatible with your network. You may also need to a establish a default gateway between
the switch and management stations that exist on another network segment.
Configure the switch-managed IP information on this page
The Configured column is used to view or change the IP configuration.
The Current column is used to show the active IP configuration.
Web Interface
To configure an IP address in the web interface:
1. Click System, IP Configuration.
2. Specify the IPv4 settings, and enable DNS proxy service if required.
3. Click Save.
Figure2- 4.1: The IP configuration
Parameter description:
17
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 30

DHCP Client :
Enable the DHCP client by checking this box. If DHCP fails and the configured
IP address is zero, DHCP will retry. If DHCP fails and the configured IP address
is non-zero, DHCP will stop and the configured IP settings will be used. The
DHCP client will announce the configured System Name as hostname to provide
DNS lookup.
IP Address :
Provide the IP address of this switch in dotted decimal notation.
IP Mask :
Provide the IP mask of this switch dotted decimal notation.
IP Router :
Provide the IP address of the router in dotted decimal notation.
SNTP Server :
Provide the IP address of the SNTP Server in dotted decimal notation.
DNS Server :
Provide the IP address of the DNS Server in dotted decimal notation.
VLAN ID :
Provide the managed VLAN ID. The allowed range is 1 to 4095.
DNS Proxy :
When DNS proxy is enabled, DUT will relay DNS requests to the current
configured DNS server on DUT, and reply as a DNS resolver t o the client device
on the network.
18
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 31

2-4.2 IPV6
This section describes how to configure the switch-managed IPv6 information. The
Configured column is used to view or change the IPv6 configuration. And the Current column
is used to show the active IPv6 configuration.
Configure the switch-managed IPv6 information on this page.
The Configured column is used to view or change the IPv6 configuration.
The Current column is used to show the active IPv6 configuration.
Web Interface
To configure Management IPv6 of the switch in the web interface:
1. Click System, IPv6 Configuration.
2. Specify the IPv6 settings, and enable Auto Configuration service
if required.
3. Click Save.
Figure2- 4.2: The IPv6 configuration
Parameter description:
Auto Configuration :
Enable IPv6 auto-configuration by checking this box. If fails, the configured
IPv6 address is zero. The router may delay responding to a router solicitation
for a few seconds, the total time needed to complete auto-configuration can be
significantly longer.
Address :
Provide the IPv6 address of this switch. IPv6 address is in 128-bit records
represented as eight fields of up to four hexadecimal digits with a colon
separating each field (:). For example, 'fe80::215:c5ff:fe03:4dc7'. The symbol
'::' is a special syntax that can be used as a shorthand way of representing
multiple 16-b it groups of contiguo us zeros; but it can on ly appear once. It c an
also represent a legally valid IPv4 address. For example, '::192.1.2.34'.
Prefix :
Provide the IPv6 Prefix of this switch. The allowed range is 1 to 128.
Router
Provide the IPv6 gateway address of this switch. IPv6 address is in 128-bit
records represented as eight fields of up to four hexadecimal digits with a colon
separating each field (:). For example, 'fe80::215:c5ff:fe03:4dc7'. The symbol
'::' is a special syntax that can be used as a shorthand way of representing
multiple 16-b it groups of contiguo us zeros; but it can on ly appear once. It c an
also represent a legally valid IPv4 address. . For example, '::192.1.2.34'.
19
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 32

20
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 33

2-5 Syslog
The Syslog is a standard for logging program messages . It allows separation of the software
that generates messages from the system that stores them and the software that reports and
analyzes them. It can be used as well a generalized informational, analysis and debugging
messages. It is supported by a wide variety of devices and receivers across multiple platforms.
2-5.1 Configuration
This section describes how to configure the system log and provide a wide variety of devices
and receivers across multiple platforms.
Web Interface
To configure Syslog configuration in the web interface:
1. Click SYSTEM, Syslog.
2. Specify the syslog parameters includes IP Address of Syslog server
and Port number.
3. Evoke the Sylog to enable it.
4. Click Save.
Figure2- 5.1: The System Log configuration
Parameter description:
Server Mode :
Indicates the server mode operation. When the mode operation is enabled, the
syslog message will send out to syslog server. The syslog protocol is based on
UDP communication and received on UDP port 514 and the syslog server will
not send acknowledgments back sender since UDP is a connectionless protocol
and it does not provide acknowledgments. The syslog packet will always send
out even if the syslog server does not exist. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable server mode operation.
Disabled: Disable server mode operation.
Server Address 1 and 2 :
Indicates the IPv4 host address of syslog server 1 and server 2 (For
redundancy). If the switch provide DNS feature, it also can be a host name.
Syslog Level :
Indicates what kind of message will send to syslog server. Possible modes are:
Info: Send informations, warnings and errors. Warning: Send warnings and
errors. Error: Send errors.
21
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 34

2-5.2 Log
This section describes that display the system log information of the switch
Web Interface
To display the log configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Syslog, Log.
2. Display the log information.
Figure2- 5.2: The System Log configuration
Parameter description:
Auto-refresh
To evoke the auto-refresh icon then the device will refresh the log automatically.
Level
level of the system log entry. The follo wing level ty pes are supported :
Information level of the system log.
Warning: Warning level of the system log.
Error: Error level of the system log.All: All levels.
ID
ID (>= 1) of the system log entry.
Time
It will display the log record by device time. The time of the system log entry.
Message
It will display the log detail message. The message of the system log entry.
Upper right icon (Refresh, clear,….)
You can click them for refresh the system log or clear them by manual, others
for next/up page or entry.
22
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 35

2-5.3 Detailed Log
This section describes that display the detailed log information of the switch
Web Interface
To display the detailed log configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Syslog, Detailed Log.
2. Display the log information.
Figure2- 5.3: The Detailed System Log Information
Parameter description:
ID
The ID (>= 1) of the system log entry.
Message
The detailed message of the system lo g e ntry.
Upper right icon (Refresh, clear,….)
You can click them for refresh the system log or clear them by manual, others
for next/up page or entry.
23
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 36

2-6 SNMP
Any Network Management System (NMS) running the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP) can manage the Managed devices equipped with SNMP agent, provided that the
Management Information Base (MIB) is installed correctly on the managed devices. The
SNMP is a protocol that is used to govern the transfer of information between SNMP manager
and agent and traverses the Object Identity (OID) of the management Information Base (MIB),
described in the form of SMI syntax. SNMP agent is running on the switch to response the
request issued by SNMP manager.
Basically, it is passive except issuing the trap information. The switch supports a switch to turn
on or off the SNMP agent. If you set the field SNMP “Enable”, SNMP agent will be started up.
All supported MIB OIDs, including RMON MIB, can be accessed via SNMP manager. If the
field SNMP is set “Disable”, SNMP agent will be de-activated, the related Community Name,
Trap Host IP Address, Trap and all MIB counters will be ignored.
2-6.1 System
This section describes how to configure SNMP System on the switch. This function is used
to configure SNMP settings, community name, trap host and public traps as well as the
throttle of SNMP. A SNMP manager must pass the authentication by identifying both
community names, then it can access the MIB information of the target device. So, both
parties must have the same community name. Once completing the setting, click <Apply>
button, the setting takes effect.
Web Interface
To display the configure SNMP System in the web interface:
1. Click SNMP, System.
2. Evoke SNMP State to enable or disable the SNMP function .
3. Specify the Engine ID
4. Click Apply.
Figure2- 6.1: The SNMP System Configuration
Parameter description:
These parameters are displayed on the SNMP System Configuration page:
SNMP State :
The term SNMP here The term SNMP here is used for the activation or deactivation of SNMP.
Enable: Enable SNMP state operation.
Disable: Disable SNMP state operation.
Default: Enable.
Engine ID :
SNMPv3 engine ID. syntax: 0-9,a-f,A-F, min 5 octet, max 32 octet, fifth octet
24
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 37

can't input 00. IF change the Engin e ID tha t will cl ear all origi n al user.
25
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 38

2-6.2 Communities
The function is used to configure SNMPv3 communities. The Community and UserName is
unique. To create a new community account, please check <Add new community> button,
and enter the account information then check <Save>. Max Group Number : 4.
Web Interface
To display the configure SNMP Communities in the web interface:
1. Click SNMP, Communities.
2. Click Add new community.
3. Specify the SNMP communities parameters.
4. Click Save.
5. If you want to modify or clear the setting then click Reset.
Figure2- 6.2: The SNMPv1/v2 Communities Security Configuration
Parameter description:
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Community
Indicates the community access string to permit access to SNMPv3 agent. The
allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is ASCII characters
from 33 to 126. The community string will be treated as security name and
map a SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c community string.
UserName:
The UserName access string to permit acccess to SNMPv3 agent. The length of
“UserName” string is restricted to 1-32.
Source IP
Indicates the SNMP access source address. A particular range of source
addresses can be used to restrict source subnet when combined with source
mask.
Source Mask
Indicates the SNMP access source address mask
26
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 39

2-6.3 Users
The function is used to configure SNMPv3 user. The Entry index key is UserName. To create
a new UserName account, please check <Add new user> button, and enter the user
information then check <Save>. Max Group Number : 10.
Web Interface
To display the configure SNMP Users in the web interface:
1. Click SNMP, Users.
2. Specify the Privilege parameter.
3. Click Save.
Figure 2-6.3: The SNMP Users Configuration
Parameter description:
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
User Name
A string identifying the user name that this entr y should belong to. The allowe d
string length is 1 to 32, and the allowe d content is ASCII characters fr om 33 to
126.
Security Level
Indicates the security model that this entry should belo ng to. Possible secur ity
models are:
NoAuth, NoPriv: No authentication and no privacy.
Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and no privacy.
Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
The value of security level cannot be modified if entry already exists. That
means it must first be ensured that the value is set correctly.
Authentication Protocol
Indicates the authentication protocol that this entry should belong to. Possible
authentication protocols are:
None: No authentication protocol.
27
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 40

MD5: An optional flag to indicate that this user uses MD5 authentication
protocol.
SHA: An optional flag to indicate that this user uses SHA authentication
protocol.
The value of security level cannot be modified if entry already exists. That
means must first ensure that the value is set correctly.
Authentication Password
A string identifying the authentication password phrase. For MD5 authentication
protocol, the allowed string length is 8 to 32. For SHA authentication protocol,
the allowed string length is 8 to 40. The allowed content is ASCII characters
from 33 to 126.
Privacy Protocol
Indicates the privacy protocol that this entry should belong to. Possible privacy
protocols are:
None: No privacy protocol.
DES: An optional flag to indicate that this user uses DES authentication
protocol.
Privacy Passw ord
A string identifying the privacy password phrase. The allowed string length is 8
to 32, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
28
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 41

2-6.4 Groups
The function is used to configure SNMPv3 group. The Entry index key are Security Model and
Security Name. To create a new group account, please check <Add new group> button, and
enter the group information then check <Save>. Max Group Number : v1: 2, v2: 2, v3:10.
Web Interface
To display the configure SNMP Groups in the web interface:
1. Click SNMP, Groups.
2. Specify the Privilege parameter.
3. Click Save.
Figure 2-6.4: The SNMP Groups Configuration
Parameter description:
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Security Model
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possible security
models are:
v1: Reserved fo r SNMPv1.
v2c: Reserved for SNMPv2c.
usm: User-based Security Model (USM).
Security Name
A string identifying the security name that this entry should belong to. The
allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is ASCII characters
from 33 to 126.
Group Name
A string identifying the group name that this entry should belong to. The
allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is ASCII characters
from 33 to 126.
29
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 42

2-6.5 Views
The function is used to configure SNMPv3 view. The Entry index key are OID Subtree and
View Name. To create a new view account, please check <Add new view> button, and enter
the view information then check <Save>. Max Group Number : 28.
Configure SNMPv3 view table on this page. The entry index keys are View Name and OID
Subtree.
Web Interface
1. Click SNMP, Views.
2. Click Add new View.
3. Specify the SNMP View parameters.
4. Click Save.
5. If you want to modify or clear the setting then click Reset.
Figure 2-6.5: The SNMP Views Configuration
Parameter description:
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
View Name
A string identifying the view name that this entry should belong to. The allowed
string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to
126.
View Type
Indicates the view type that this entry should belong to. Possible view types
are:
included: An optiona l flag t o indicat e that this view subtree should be included.
excluded: An optional flag to indicate that this view subtree should be
excluded.
In general, if a view entry's view type is 'excluded', there should be another
30
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 43

view entry existing with view type as 'included' and it's OID subtree should
overstep the 'excluded' view entry.
OID Subtree
The OID defining the root of the subtree to add to the named view. The allowed
OID length is 1 to 128. The allowed string content is digital number or
asterisk(*).
Save
To click the Save icon to save the configuration to ROM.
31
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 44

2-6.6 Access
The function is used to configure SNMPv3 accesses. The Entry index key are Group Name,
Security Model and Security level. To create a new access account, please check <Add new
access> button, and enter the access information then check <Save>. Max Group Number :
14
Web Interface
To display the configure SNMP Access in the web interface:
1. Click SNMP, Accesses.
2. Click Add new Access.
3. Specify the SNMP Access parameters.
4. Click Save.
5. If you want to modify or clear the setting then click Reset.
.
Figure 2-6.6: The SNMP Accesses Configuration
Parameter description:
Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Group Name
A string identifying the group name that this entry should belong to. The
allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is ASCII characters
from 33 to 126.
Security Model
Indicates the security model that this entry should belo ng to. Possible secur ity
models are:
any: Any security model accepted(v1| v2 c| usm).
v1: Reserved for SNMPv1.
v2c: Reserved for SNMPv2c.
usm: User-based Security Model (USM).
Security Level
32
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 45

Indicates the security model that this entry sho uld belong to. Possible se curity
models are:
NoAuth, NoPriv: No authentication and no privacy.
Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and no privacy.
Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
Read View Name
The name of the MIB view defining the MIB objects for which this request may
request the current values. The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the
allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126. Wri te Vi ew Name
The name of the MIB view defining the MIB objects for which this request may
potentially set new values. The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed
content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
33
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 46

2-6.7 Tar p
The function is used to configure SNMP trap. To create a new trap account, please check <No
number> button, and enter the trap information then check <Apply>. Max Group Number : 6.
Web Interface
To configure SNMP Trap setting:
1. Click SNMP, Trap .
2. Display the SNMP Trap Hosts information table.
3. Choice a entry to display and modify the detail parameters or click
delete button to delete the trap hosts entry.
Figure 2-6.7: The SNMP Trap Host Configuration
Parameters description:
Delete:
Check <Delete> entry then check <Save> button, the entry will be delete.
Trap Version:
You may choose v1, v2c or v3 trap.
Server IP:
To assign the SNMP Host IP address.
UDP Port:
To assign Port number. Default: 162
34
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 47

Community / Security Name:
The length of “Community / Security Name” string is restricted to 1-32.
Security Level:
Indicates what kind of message will send to Security Level.
Possible modes are:
Info: Send informations, warnings and errors.
Warning: Send warnings and errors.
Error: Send errors.
Security Level:
There are three kinds of choices.
NoAuth, NoPriv: No authentication and no privacy.
Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and no privacy.
Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
Authentication Protocol:
You can choose MD5 or SHA for authentication.
Authentication Password:
The length of 'MD5 Authentication Password' is restricted to 8 – 32.
The length of 'SHA Authentication Password' is res tricted to 8 – 40.
Privacy Protocol:
You can set DES encryption for UserName.
Privacy Passw ord:
The length of ' Privacy Password ' is restricted to 8 – 32.
35
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 48

Chapter 3. Configuration
This chapter describes all of the basic network configuration tasks which includes the
Ports, Layer 2 network protocol (e.g. VLANs, QoS, IGMP, ACLs and PoE etc.) and
any setting of the Switch.
3-1 Port
The section describes to configure the Port detail parameters of the switch. Others you could
using the Port configure to enable or disable the Port of the switch. Monitor the ports content
or status in the function.
3-1.1 Configuration
This chapter describes how to view the current port configuration and how to configure ports to
non-default settings, including
Linkup/Linkdown
Speed (Current and configured)
Flow Control (Current Rx, Current Tx and Configured)
Maximum Frame Size
Excessive Collision Mode
Power Control.
Web Interface
To configure an Current Port Configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Port, then Configuration
2. Specify the Speed Configured, Flow Control , Maximum Frame size ,
Excessive Collision mode and Power Control.
3. Click Save.
Figure 3-1.1: The Port Configuration
36
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 49

Parameter description:
Port :
This is the logical port number for this row.
Link :
The current link state is displayed graphically. Green indicates the link is up and
red that it is down.
Current Link Speed :
Provides the current link speed of the port.
Configured Link Speed :
Select any available link speed for the given switch port.
Auto Speed selects the highest speed that is compatible with a link partner.
Disabled disabl es the switch port operation.
Flow Control :
When Auto Speed is selected on a port, this section indicates the flow control
capability that is advertised to the link partner. When a fixed-speed setting is
selected, that is what is used. The Current Rx column indicates whether pause
frames on the port are obeyed, and the Current Tx column indicates whether
pause frames on the port are transmitted. The Rx and Tx settings are
determined by the r esu lt of the la s t Auto-Negotiation.
Check the co nfigured column to use flow c ontrol. This setting is rel ated to the
setting for Configured Link Speed.
Maximum Frame Size :
Enter the maximum frame size allowed for the switch port, includi ng FCS .
Excessive Collision Mode :
Configure port transmit collision behavior.
Discard: Discard frame after 16 collisions (default).
Restart: Restart backoff algorithm after 16 collisions.
Power Control :
The Usage column shows the current percentage of the power consumption per
port. The Configured column allows for changing the power savings mode
parameters per port.
Disabled: All power savings mechanisms disabled.
ActiPHY: Link down power savings enabled.
PerfectReach: Link up power savings enabled.
Enabled: Both link up and link down power savings enabled.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
Upper right icon (Refresh)
You can click them for refresh the Port link Status by manual
37
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 50

3-1.2 Port Description
The section describes to configure the Port’s alias or any descriptions for the Port Identity. It
provides user to write down an alphanumeric string describing the full name and version
identification for the system’s hardware type, software version, and networking application
Web Interface
To configure an Port Description in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Port, then Port Description
2. Specify the detail Port alias or description an alphanumeric string
describing the full name and version identification for the system’s
hardware type, software version, and networking application.
3. Click Save.
Figure 3-1.2: The Port Configuration
Parameter description:
Port :
This is the logical port number for this row.
Description :
Description of device ports can not include “ # % & ‘ + \.
Buttons
Apply – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
38
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 51

3-1.3 Traffic Overview
The section describes to the Port statistics information and provides overview of general traffic
statistics for all switch ports.
Web Interface
To Display the Port Statistics Overview in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Port, then Traffic Overview
2. If you want to auto-refresh then you need to evoke the “Auto-refresh” .
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the port statistics or clear all information
when you click “ Clear”.
Figure 3-1.3: The Port Statistics Overview
Parameter description:
Port :
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
Packets :
The number of received and transmitted packets per port.
Bytes :
The number of received and transmitted bytes per port.
Errors
The number of frames received in error and the number of incomplete
transmissions per port.
Drops
The number of frames discarded due to ingress or egress congestion.
Filtered
The number of received frames filtered by the forwarding
Auto-refresh :
To evoke the auto-refresh icon then the device will refresh the information automatically.
Upper right icon (Refresh, Clear):
You can click them for refresh the Port Statistics information by manual. Others click Clear
to clean up all Port Statistics.
39
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 52

3-1.4 Detailed Statisti cs
The section describes how to provide detailed traffic statistics for a specific switch port. Use the
port select box to select which switch port details to display.
The displayed counters are the totals for receive and transmit, the size counters for receive and
transmit, and the error counters for receive and transmit.
Web Interface
To Display the per Port Port detailed Statistics Overview in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Port, then Detailed Port Statistics
2. Scroll the Port Index to select which port you want to show the detailed
Port statistica overview” .
3. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
4. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the port detailed statistics or clear all
information when you click “ Clear”.
Figure 3-1.4: The Port Detail Statisitcs Overview
Parameter description:
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the
automatically.
Upper left scroll bar:
To scroll which port to display the Port statistics with “Port-0”, “Po r t- 1 ...
ReceiveTotalandTransmitTotal
Rx and Tx Packets :
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) packets.
Rx and Tx Octets :
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) bytes. Includes FCS,
but excludes framing bits.
Rx and Tx Unicast
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) unicast packets.
auto-refresh to
40
refresh the Port Statistics information
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 53

Rx and Tx Multicast :
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) multicast packets.
Rx and Tx Broadcast :
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) broadcast packet s.
Rx and Tx Pause :
A count of the MAC Control frames received or transmitted on this port that
have an opcode indicating a PAUSE operation.
ReceiveandTransmitSizeCounters
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) packets split into categories based on
their respective frame sizes.
ReceiveandTransmitQueueCounters
The number of received and transmitted packets per input and output queue.
ReceiveErrorCounters
Rx Drops :
The number of frames dropped due to lack of receive buffers or egress
congestion.
Rx CRC/Alignment :
The number of frames received with CRC or alignment errors.
Rx Undersize :
The number of short 1 frames received with valid CRC.
Rx Oversize :
The number of long 2 frames received with valid CRC.
Rx Fragments :
The number of short 1 frames received with invalid CRC.
Rx Jabber :
The number of long 2 frames received with invalid CRC.
Rx Filtered :
The number of received frames filtered by th e forwarding process.
Short frames are frames that are smaller than 64 bytes.
Long frames are frames that are longer than the configured maximum frame
length for this port.
TransmitErrorCounters
Tx Drops :
The number of frames dropped du e to output bu ffer c ongestion .
Tx Late/Exc. Coll. :
The number of frames dropped due to excessive or late collisions.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the Queuing Counters a utomaticall y .
Upper right icon (Refresh, clear)
You can click them for refresh the Port Detail Statistics or clear them by manual.
41
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 54

3-1.5 Qos Statistics
The section describes that switch could display the QoS detailed Queuing counters for a
specific switch port. for the different queues for all switch ports.
Web Interface
To Display the Queuing Counters in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Port, then QoS Statistics
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the Queuing Counters or clear all information
when you click “ Clear”.
Figure 3-1.5: The Queuing Counters Overview
Parameter description:
Port :
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
Qn :
Qn is the Queue number, QoS queues per port. Q0 is the lowest priority queue.
Rx/Tx :
The number of received and transmitted pack ets per queue.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the Queuing Counters a utomaticall y .
Upper right icon (Refresh, clear)
You can click them for refresh the Qu eu ing Counters or clear them by manual.
42
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 55

3-1.6 SFP Information
The section describes that switch could display the SFP module detail information which you
connect it to the switch. The information includes: Connector type, Fiber type, wavelength,
banud rate and Vendor OUI etc.
Web Interface
To Display the SFP information in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Port, then SFP Information
2. To display the SFP Information.
Figure 3-1.6: The SFP Information Overview
Parameter description:
Connector Type:
Display the connector type, for instance, UTP, SC, ST, LC and so on.
Fiber Type:
Display the fiber mode, for instance, Multi-Mode, Single-Mode.
Tx Central Wavelength:
Display the fiber optical transmitting central wavelength, for instance, 850nm,
1310nm, 1550nm and so on.
Baud Rate:
Display the maximum baud rate of the fiber module supported, for instance,
10M, 100M, 1G and so on.
Vendor OUI:
Display the Manufacturer's OUI code which is assigned by IEEE.
Vendor Name:
Display the comp any name of the module manufactu r er.
Vendor P/N:
Display the product name of the naming by module manufacturer.
43
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 56

Vendor Rev (Revision):
Display the module revision.
Vendor SN (Serial Number):
Show the serial number assigned by the manufacturer .
Date Cod e:
Show the date this SFP module was made.
Temperature:
Show the current temperature of SFP module.
Vcc:
Show the working DC voltage of SFP module.
Mon1(Bias) mA:
Show the Bias current of SFP mod u le .
Mon2(TX PWR):
Show the transmit power of SFP module.
Mon3(RX PWR):
Show the receiver power of SFP module.
44
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 57

3-1.7 EEE
The section which allows the user to inspect and configure the current EEE port settings.
EEE is a power saving option that reduces the power usage when there is very low traffic
utilization (or no traffic).
EEE works by powering down circuits when there is no traffic. When a port gets data to be
transmitted all circuits are powered up. The time it takes to power up the circuits is named
wakeup time. The default wakeup time is 17 us for 1Gbit links and 30 us for other link speeds.
EEE devices must agree upon the value of the wakeup time in order to make sure that both
the receiving and transmitting device has all circuits powered up when traffic is transmitted.
The devices can exchange information about the devices wakeup time using the LLDP
protocol.
For maximizing the power saving, the circuit isn't started at once transmit data are ready for a
port, but is instead queued until 3000 bytes of data are ready to be transmitted. For not
introducing a large delay in case that data less then 3000 bytes shall be transmitted, data are
always transmitted after 48 us, giving a maximum latency of 48 us + the wakeup time.
If desired it is possible to minimize the latency for specific frames, by mapping the frames to a
specific queue (done with QOS), and then mark the queue as an urgent queue. When an
urgent queue gets data to be transmitted, the circuits will be powered up at once and the
latency will be reduced to the wakeup time.
Web Interface
To configure the EEE Configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Port, then EEE
2. To evoke which port wants to enable the EEE function. To evolke which
3. EEE Urgent Queues level and the range from 1 to 8. the queue will
postponethe transmsion until 3000 bytes are ready to be transmitted.
4. Click the save to save the setting
5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values.
.
Figure 3-1.7: The EEE Configuration
45
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 58

Parameter description:
EEE Port Configuration:
The EEE port settings relate to the currently selected, as reflected by the page
header.
Port :
The switch port number of the logical EEE port.
EEE Enabled :
Controls whether EEE is enabled for this switch port.
EEE Urgent Queues :
Queues set will activate transition of frames as soon as any data is available.
Otherwise the queue will postpone the transmission until 3000 bytes are ready
to be transmitted.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
46
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 59

3-2 ACL
The SM10P switch access control list (ACL) is probably the most commonly used object in
the IOS. It is used for packet filtering but also for selecting types of traffic to be analyzed,
forwarded, or influenced in some way. The ACLs are divided into EtherTypes. IPv4, ARP
protocol, MAC and VLAN parameters etc. Here we will just go over the standard and
extended access lists for TCP/IP. As you create ACEs for ingress classification, you can
assign a policy for each port, the policy number is 1-8, however, each policy can be applied to
any port. This makes it very easy to determine what type of ACL policy you will be working
with.
3-2.1 Ports
The section describes how to configure the ACL parameters (ACE) of the each switch port.
These parameters will affect frames received on a port unless the frame matches a specific
ACE
Web Interface
To configure the ACL Ports Configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, ACL, then Ports
2. To scroll the specific parameter value to select the correct value for port
ACL setting.
3. Click the save to save the setting
4. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button. It
will revert to previously saved values.
5. After you configure complete then you could see the Counter of the port .
then you could click refresh to update the counter or Clear the information.
Figure 3-2.1: The ACL Ports Configuration
Parameter description:
Port :
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
Policy ID :
Select the policy to apply to this port. The allowed values are 1 through 8. The
47
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 60

default value is 1.
Action :
Select whether forwarding is permitted ("Permit") or denied ("Deny"). The
default value is "Permit".
Rate Limiter ID :
Select which rate limiter to apply on this port. The allowed values are Disabled
or the values 1 through 16. The default value is "Disabled".
Port Copy :
Select which port frames are copied on. The allowed values are Disabled or a
specific port number. The default value is "Disabled".
Mirror :
Specify the mirror operation of this port. The allowed values are:
Enabled: Frames received on the port are mirrored.
Disabled: Frames received on the port are not mirrored.
The default value is "Disabled".
Logging :
Specify the logging operation of this port. The allowed values are:
Enabled: Frames received on the port are stored in the Syste m L og.
Disabled: Frames received on the port are not logged.
The default value is "Disabled". Please note that the Syste m Log memory size
and logging rate is limited.
Shutdown :
Specify the port shut down operation of this port. The allowed val u es are:
Enabled: If a frame is received on the port, the port will be disabled.
Disabled: Port shut down is disabled.
The default value is "Disabled".
Counter :
Counts the number of frames that match this ACE.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
Upper right icon (Refresh, clear)
You can click them for refresh the ACL Port Configuration or clear them by
manual.
48
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 61

3-2.2 Rate Limiters
The section describes how to configure the switch’s ACL Rate Limiter parameters. The Rate
Limiter Level from 1 to 16 that allow user to set rate limiter value and units with pps or kbps.
Web Interface
To configure ACL Rate Limiter in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, ACL, then Rate Limiter
2. To specific the Rate field and the range from 0 to 3276700.
3. To scroll the Unit with pps or kbps
4 . Click the save to save the setting
5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values.
Figure 3-2.2: The ACL Rate Limiter Configuration
Parameter description:
Rate Limiter ID :
The rate limiter ID for the settings contained in the same row.
Rate
The allowed values are: 0-3276700 in pps or 0, 100, 200, 300, ..., 1000000 in
kbps.
Unit :
Specify the rate unit. The allowed values are:
pps: packets per second.
kbps: Kbits per second.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
49
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 62

3-2.3 Access Control List
The section describes how to configure Access Control List rule. An Access Control List (ACL)
is a sequential list of permit or deny conditions that apply to IP addresses, MAC addresses, or
other more specific criteria. This switch tests ingress packets against the conditions in an ACL
one by one. A packet will be accepted as soon as it matches a permit rule, or dropped as
soon as it matches a deny rule. If no rules match, the frame is accepted. Other actions can
also be invoked when a matching packet is found, including rate limiting, copying matching
packets to another port or to the system log, or shutting down a port.
This page shows the Access Control List (ACL), which is made up of the ACEs defined on
this switch. Each row describes the ACE that is defined. The maximum number of ACEs is
256 on each switch. Click on the lowest plus sign to add a new ACE to the list. The reserved
ACEs used for internal protocol, cannot be edited or deleted, the order sequence cannot be
changed an the priority is highest
Web Interface
To configure Access Control List in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, ACL, then Configuration
2. Click the
button to add a new ACL, or use the other ACL
modification buttons to specify the editing action (i.e., edit, delete, or
moving the relative position of entry in the list)
3. To specific the parameter of the ACE
4. Click the save to save the setting
5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values.
6. When editing an entry on the ACE Configuration page, note that the
Items displayed depend on various selections, such as Frame Type and IP Protocol Type.
Specify the relevant criteria to be matched for this rule,
and set the actions to take when a rule is matched (such as Rate Limiter,
Port Copy, Logging, and Shutdown).
Figure 3-2.3: The ACL Rate Limiter Configuration
50
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 63

Parameter description:
Ingress Port :
Indicates the ingress port of the ACE. Possible values are:
Any: The ACE will match any ingress port.
Policy: The ACE will match ingress ports with a specific po licy.
Port: The ACE will match a specific ingress port.
Frame Type :
Indicates the frame type of the ACE. Possible valu es are:
Any: The ACE will match any frame type.
Ethernet ype: The ACE will match Ethernet Type frames. Note that an
Ethernet Type based ACE will not get matched by IP and ARP frames.
ARP: The ACE will match ARP/RARP frames.
IPv4: The ACE will match all IPv4 frames.
Action :
Indicates the forwarding action of the ACE.
Permit: Frames matching the ACE may be forwarded and learned.
Deny: Frames matching the ACE are dropped.
Rate Limiter :
Indicates the rate limiter number of the ACE. The allowed range is 1 to 16.
When Disabled is displayed, the rate limiter operation is disabled.
Port Copy :
Indicates the port copy operation of the ACE. Frames matching the ACE are
copied to the port number. The allowed values are Disabled or a specific port
number. When Disabled is displayed, the port copy operation is disabled.
Mirror :
Specify the mirror operation of this port. The allowed values are:
Enabled: Frames received on the port are mirrored.
Disabled: Frames received on the port are not mirrored.
The default value is "Disabled".
Logging :
Indicates the logging operation of the ACE. Possible values are:
Enabled: Frames matching the ACE are stored in the System Log.
Disabled: Frames matching the ACE are not logged.
Please note that the System Log memory size and logging rate is limited.
Shutdown :
Indicates the port shut down operation of the ACE. Possible values are:
Counter :
Enabled: If a frame matches the ACE, the ingress port will be disabled.
Disabled: Port shut down is disabled for the ACE.
The counter indicates the number of times the ACE was hit by a frame.
Modification Buttons
51
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 64

You can modify each ACE (Access Control Entry) in the table using the following
buttons:
: Inserts a new ACE before the current row.
: Edits the ACE row.
: Moves the ACE up the list.
: Moves the ACE down the list.
: Deletes the ACE.
: The lowest plus sign adds a new entry at the bottom of the ACE listings.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the information au t o matically.
Upper right icon (Refresh, clear, Remove All)
You can click them for refresh the ACL configuration or clear them by manual.
Others remove all to clean up all ACL configurations on the table.
52
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 65

3-2.4 ACL Status
The section describes how to shows the ACL status by different ACL users. Each row
describes the ACE that is defined. It is a conflict if a specific ACE is not applied to the
hardware due to hardware limitations. The maximum number of ACEs is 256 on each switch.
Web Interface
To display the ACL status in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, ACL, then ACL status
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the ACL Status
Figure 3-2.4: The ACL Rate Limiter Configuration
Parameter description:
User :
Indicates the ACL user.
Ingress Port :
Indicates the ingress port of the ACE. Possible values are:
Any: The ACE will match any ingress port.
Policy: The ACE will match ingress ports with a specific po licy.
Port: The ACE will match a specific ingress port.
Frame Type :
Indicates the frame type of the ACE. Possible valu es are:
Any: The ACE will match any frame type.
EType: The ACE will match Et hernet Type frames. Note that an Ethernet Type
based ACE will not get matched by IP and ARP frames.
ARP: The ACE will match ARP/RARP frames.
IPv4: The ACE will match all IPv4 frames.
Action :
Indicates the forwarding action of the ACE.
Permit: Frames matching the ACE may be forwarded and learned.
Deny: Frames matching the ACE are dropped.
Rate Limiter :
Indicates the rate limiter number of the ACE. The allowed range is 1 to 16.
When Disabled is displayed, the rate limiter operation is disabled.
Port Copy :
Indicates the port copy operation of the ACE. Frames matching the ACE are
53
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 66

copied to the port number. The allowed values are Disabled or a specific p ort
number. When Disabled is displayed, the port copy operation is disabled.
Mirror :
Specify the mirror operation of this port. The allowed values are:
Enabled: Frames received on the port are mirrored.
Disabled: Frames received on the port are not mirrored.
The default value is "Disabled".
CPU :
Forward packet that matched the specif ic ACE to CPU.
CPU Once :
Forward first packet that matched the specific ACE to CPU.
Counter :
The counter indicates the number of times the ACE was hit by a frame.
Conflict :
Indicates the hardware status of the specific ACE. The specific ACE is not
applied to the hardware due to hardware limitations.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the information au t o matically.
Upper right icon (Refresh)
You can click them for refresh the ACL status information by manual.
54
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 67

3-3 Aggregation
The Aggregation is used to configure the settings of Link Aggregation. You can bundle more
than one port with the same speed, full duplex and the same MAC to be a single logical port,
thus the logical port aggregates the bandwidth of these ports. This means you can apply your
current Ethernet equipment’s to build the bandwidth aggregation. For example, if there are
three Fast Ethernet ports aggregated in a logical port, then this logical port has bandwidth
three times as high as a single Fast Ethernet port has.
3-3.1 Static T run k
The Aggregation Configuration is used to configure the settings of Link Aggregation. You can
bundle more than one port with the same speed, full duplex and the same MAC to be a single
logical port, thus the logical port aggregates the bandwidth of these ports. This means you
can apply your current Ethernet equipment’s to build the bandwidth aggregation.
3-3.1.1 Static Trunk
Ports using Static Trunk as their trunk method can choose their unique Static GroupID to form
a logic “trunked port”. The benefit of using Static Trunk method is that a port can immediately
become a member of a trunk group without any handshaking with its peer port. This is also a
disadvantage because the peer ports of your static trunk group may not know that they should
be aggregate together to form a “logic trunked port”. Using Static Trunk on both end of a link
is strongly recommended. Please also note that low speed links will stay in “not ready” state
when using static trunk to aggregate with high speed links.
Web Interface
To configure the Trunk Aggregation Hash mode and Aggregation Group in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Static Trunk, and then Aggregation Mode Configuration.
2. Evoke to enable or disable the aggregation mode function.
Evoke Aggregation Group ID and Port members
3. Click the save to save the setting
4. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button. It
will revert to previously saved values.
Figure 3-3.1.1: The Aggregation Mode Configuration
55
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 68

Parameter description:
Hash Code Contributors
Source MAC Address :
The Source MAC address can be used to calculate the destination port for the
frame. Check to enable the use of the Source MAC address, or uncheck to
disable. By default, Source MAC Address is enabled.
Destination MAC Address :
The Destination MAC Address can be used to calculate the destination port for
the frame. Check to enable the use of the Destination MAC Address, or uncheck
to disable. By default, Destination MAC Address is disabled.
IP Address :
The IP address can be used to calculate the destination port for the frame.
Check to enable the use of the IP Address, or uncheck to disable. By default, IP
Address is enabled.
TCP/UDP Port Number :
The TCP/UDP port number can be used to calculate the destination port for the
frame. Check to enable the use of the TCP/UDP Port Number, or uncheck to
disable. By default, TCP/UDP Port Number is enabled.
Aggregation Group Configuration
Locality :
Indicates the aggregation group type. This field is only valid for switches.
Global: The group mem bers may reside on different units. The device supports
two 8-port global aggregations.
Local: The group members reside on the same unit. Each local aggregation
may consist of up to 16 members.
Group ID :
Indicates the group ID for the settings contained in the same row. Group ID
"Normal" indicates there is no aggregation. Only one group ID is valid per port.
Port Members :
Each switch port is listed for each group ID. Select a radio button to include a
port in an aggregation, or clear the radio button to remove the port from the
aggregation. By default, no ports belong to any aggregation group. Only full
duplex ports can join an aggregation and ports must be in the same speed in
each group.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
56
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 69

3-3.2 LACP
Ports using Link Aggregation Control Protocol (according to IEEE 802.3ad specification) as their
trunking method can choose their unique LACP GroupID to form a logic “trunked port”. The
benefit of using LACP is that a port makes an agreement with its peer port before it becomes a
ready member of a “trunk group” (also called aggregator). LACP is safer than the other trunking
method - static trunk.
3-3.2.1 Configuration
This page allows the user to inspect the current LACP port configurations, and possibly
change them as well An LACP trunk group with more than one ready member-ports is a “real
trunked” group. An LACP trunk group with only one or less than one ready member-ports is
not a “real trunked” group.
Web Interface
To configure the Trunk Aggregation LACP parameters in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, LACP, Configuration
2. Evoke to enable or disable the LACP on the port of the switch.
Scroll the Key parameter with Auto or Specific Default is Auto.
3. Scroll the Role with Active or Passive. Default is Active
4. Click the save to save the setting
5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-3.2.1: The LACP Port Configuration
Parameter description:
Port :
The switch port number.
57
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 70

LACP Enabled :
Controls whether LACP is enabled on this switch port. LACP will form an
aggregation when 2 or more ports are connected to the same partner. LACP
can form max 12 LLAGs per switch and 2 GLAGs.
Key :
The Key value incurred by the port, range 1-65535 . The Auto setting will set
the key as appropriate by the physical link speed, 10Mb = 1, 100Mb = 2, 1Gb
= 3. Using the Specific setting, a user-defined value can be entered. Ports with
the same Key value can participate in the same aggregation group, while ports
with different keys cannot.
Role :
The Role shows the LACP activity status. The Active will transmit LACP packets
each second, while Passive will wait for a LACP packet from a partner (speak if
spoken to).
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
58
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 71

3-3.2.2 System Status
This section describes that when you complete to set LACP function on the switch then it
provides a status overview for all LACP instances
Web Interface
To display the LACP System status in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, LACP, System Status
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the LACP System Status.
Figure 3-3.2.2: The LACP System Status
Parameter description:
Aggr ID :
The Aggregation ID associated with this aggregation instance. For LLAG the id
is shown as 'isid:aggr-id' and for GLAGs as 'aggr-id'
Partner System ID :
The system ID (MAC address) of the aggregation partner.
Partner Key :
The Key that the partner has assigned to this aggregation ID.
Last changed :
The time since this aggregation changed.
Local Ports :
Shows which ports are a part of this aggregation for this switch. The format is:
"Switch ID:Port".
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the information automatically.
Upper right icon (Refresh)
You can click them for refresh the LACP System status information by manual.
59
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 72

3-3.2.3 Port Status
This section describes that when you complete to set LACP function on the switch then it
provides a Port Status overview for all LACP instances
Web Interface
To display the LACP Port status in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, LACP, Port Status
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the LACP Port Status.
Figure 3-3.2.3: The LACP Status
Parameter description:
Port :
The switch port number.
LACP :
'Yes' means that LACP is enabled and the port link is up. 'No' means that LACP
is not enabled or that the port link is down. 'Backup' means that the po rt could
not join the aggregation group but will join if other port leaves. Meanwhile it's
LACP status is disabled.
Key :
The key assigned to this port. Only ports with the same key can aggregate
together.
Aggr ID :
The Aggregation ID assigned to this aggregation group. IDs 1 and 2 are GLAGs
while IDs 3-14 are LLAGs.
Partner System ID :
The partner's System ID (MAC address).
Partner Port :
The partner's port number connected to this port.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the information automatically.
Upper right icon (Refresh) :
You can click them for refresh the LACP port status information by manual.
60
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 73

3-3.2.4 Port Statistics
This section describes that when you complete to set LACP function on the switch then it
provides a Port Statistics overview for all LACP instances
Web Interface
To display the LACP Port status in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, LACP, Port Statistics
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the LACP Statistics.
Figure 3-3.2.4: The LACP Statistics
Parameter description:
Port :
The switch port number.
LACP Received :
Shows how many LACP frames have been received at each port.
LACP Transmitted :
Shows how many LACP frames have been sent from each port.
Discarded :
Shows how many unknown or illegal LACP frames have been discarded at each
port.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the information au t o matically.
Upper right icon (Refresh, Clear)
You can click them for refresh the LACP port statistics information or clear by
manual.
61
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 74

3-4 Spanning Tree
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) can be used to detect and disable network loops, and to
provide backup links between switches, bridges or routers. This allows the switch to interact
with other bridging devices (that is, an STP-compliant switch, bridge or router) in your network
to ensure that only one route exists between any two stations on the network, and provide
backup links which automatically take over when a primary link goes down.
STP - STP uses a distributed algorithm to select a bridging device (STP- compliant switch,
bridge or router) that serves as the root of the spanning tree network. It selects a root port on
each bridging device (except for the root device) which incurs the lowest path cost when
forwarding a packet from that device to the root device. Then it selects a designated bridging
device from each LAN which incurs the lowest path cost when forwarding a packet from that
LAN to the root device. All ports connected to designated bridging devices are assigned as
designated ports. After determining the lowest cost spanning tree, it enables all root ports and
designated ports, and disables all other ports. Network packets are therefore only forwarded
between root ports and designated ports, eliminating any possible network loops.
Once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for Hello BPDUs
(Bridge Protocol Data Units) transmitted from the Root Bridge. If a bridge does not get a Hello
BPDU after a predefined interval (Maximum Age), the bridge assumes that the link to the Root
Bridge is down. This bridge will then initiate negotiations with other bridges to reconfigure the
network to reestablish a valid network topology.
3-4.1 Bridge Settings
The section describes that how to configure the Spanning Tree Bridge and STP System
settings. It allows you to configure STP System settings are used by all STP Bridge instance
in the Swtich.
Web Interface
To configure the Spanning Tree Bridge Settings parameters in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Spanning Tree, Bridge Settings
2. Scoll to select the parameters and write down available value of
parameters in blank field in Basic Settings
3. Evoke to enable or disable the parameters and write down available
value of parameters in blank field in Advanced settings
4. Click the save to save the setting
5 .If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
62
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 75

Figure 3-4.1: The STP Bridge Configuration
Parameter description:
Basic Settings
Protocol Version :
The STP protocol version setting. Valid values are STP, RSTP and MSTP.
Bridge Priority :
Controls the bridge priority. Lower numeric values have better priority. The
bridge priority plus the MSTI instance number, concatenated with the 6-byte
MAC address of the switch forms a Bridge Ident ifier. For MSTP operation, this is
the priority of the CI ST. Otherwise, this is the p r io ri t y of the S TP/ R S TP b ri dge.
Forward Delay :
The delay used by STP Bridges to transit Root and Designated Ports to
Forwarding (used in STP compatible mode). Valid values are in the range 4 to
30 seconds.
Max Age :
The maximum age of the information transmitted by the Br idge when it is the
Root Bridge. Valid values are in the range 6 to 40 seconds, and MaxAge must
be <= (FwdDelay-1)*2.
Maximum Hop Count :
This defines t he initial value o f remaining Hop s for MSTI informatio n generated
at the boundary of an MSTI region. It defines how many bridges a root bridge
can distribute its BPDU information to. Valid values are in the range 6 to 40
hops.
Transmit Ho ld Coun t :
The number of BPDU's a bridge port can send per second. When exceeded,
transmission of t he next BPDU will be delayed. Valid values are in the range 1
to 10 BPDU's per second.
Advanced Settings
Edge Port BPDU Filtering :
Control whether a port explicitly configured as Edge will transmit and receive
BPDUs.
63
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 76

Edge Port BPDU Guard :
Control whether a port explicitly configured as Edge will disable itself upon
reception of a BPDU. The port will enter the error-disabled state, and will be
removed from the active topolo g y .
Port Error Recovery :
Control whether a port in the error-disabled state automatically will be enabled
after a certain time. If recovery is not enabled, ports have to be disabled and
re-enabled for normal STP operation. The condition is also cleared by a system
reboot.
Port Error Recovery Timeout :
The time to pass before a port in the error-disabled state can be enabled. Valid
values are between 30 and 86400 seconds (24 hours).
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
64
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 77

2-4.2 MSTI Mapping
When you implement an Spanning Tree protocol on the switch that the bridge instance. The
CIST is not available for explicit mapping, as it will receive the VLANs not explicitly mapped.
Due to the reason that you need to set the list of VLANs mapped to the MSTI. The VLANs
must be separated with comma and/or space. A VLAN can only be mapped to one MSTI. An
unused MSTI should just be left empty. (I.e. not having any VLANs mapped to it.)
This section describes it allows the user to inspect the current STP MSTI bridge instance
priority configurations, and possibly change them as well.
Web Interface
To configure the Spanning Tree MSTI Mapping parameters in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Spanning Tree, MSTI Mapping
2. Specify the configuration identification parameters in the field
Specify the VLANs Mapped blank field.
3. Click the save to save the setting
4. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button. It
will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-4.2: The MSTI Configuration
Parameter description:
Configuration Identification
Configuration Name :
The name identifying the VLAN to MSTI mapping. Bridges must share the name
and revision (see below), as well as the VLAN-to-MSTI mapping configuration
in order to share spanning trees for MSTI's (Intra-region). The name is at most
32 characters.
Configuration Revision :
The revision of the MSTI configuration named above. This must be an integer
between 0 and 65535.
65
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 78

MSTI Mapping
MSTI :
The bridge instance. The CIST is not available for explicit mapping, as it will
receive the VL AN s n ot expl ic i tl y map pe d.
VLANs Mapped :
The list of VLANs mapped to the MSTI. The VLANs must be separated with
comma and/or space. A VLAN can only be mapped to one MSTI. An unused
MSTI should just be left empty. (I.e. not having any VLANs
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
66
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 79

3-4.3 MSTI Priorities
When you implement an Spanning Tree protocol on the switch that the bridge instance. The
CIST is the default instance which is always active. For controls the bridge priority. Lower
numeric values have better priority. The bridge priority plus the MSTI instance number,
concatenated with the 6-byte MAC address of the switch forms a Bridege Identifier
The section describes it allows the user to inspect the current STP MSTI bridge instance
priority configurations, and possibly change them as well.
Web Interface
To configure the Spanning Tree MSTI Priorities parameters in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Spanning Tree, MSTI Priorities
2. Scroll the Priority maximum is 240. Default is 128.
3. Click the save to save the setting
4. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-4.3: The MSTI Configuration
Parameter description:
MSTI :
The bridge instance. The CIST is the default instance, which is always active.
Priority :
Controls the bridge priority. Lower numeric values have better priority. The
bridge priority plus the MSTI instance number, concatenated with the 6-byte
MAC address of the swi tc h f or m s a Br i dge Identifier.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
67
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 80

3-4.4 CIST Ports
When you implement an Spanning Tree protocol on the switch that the bridge instance. You
need to configure the CIST Ports. The section describes it allows the user to inspect the to
inspect the current STP CIST port configurations, and possibly change them as well.
Web Interface
To configure the Spanning Tree CIST Ports parameters in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Spanning Tree, CIST Ports
2. Scroll and evoke to set all parameters of CIST Aggregated Port
Configuration.
3. Evoke to enable or disable the STP, then scoll and evoke to set all
parameters of the CIST normal Port configuration.
4. Click the save to save the setting
5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-4.4: The STP CIST Port Configuration
Parameter description:
Port :
The switch port number of the logical STP port.
STP Enabled :
Controls whether STP is enabled on this switch port.
Path Cost :
Controls the path cost incurred by the port. The Auto setting will set the path
cost as appropriate by the physical link speed, using the 802.1D recommended
values. Using the Specific setting, a user-defined value can be entered. The
path cost is used when establishing the active topology of the network. Lower
path cost ports are chosen as forwarding ports in favour of higher path cost
ports. Valid values are in the range 1 to 200000000.
Priority :
Controls the port priority. This can be used to c ontrol priority of ports having
identical port cost. (See above).
68
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 81

operEdge (state flag) :
Operational flag describing whether the port is connecting directly to edge
devices. (No Bridges attached). Transition to the forwarding state is faster for
edge ports (having operEdge true) than for other ports. The value of this flag is
based on AdminEdge and AutoEdge fields. This flag is displayed as Edge in
Monitor->Spanning Tree -> STP Detailed Bridge Status.
AdminEdge :
Controls whether the operEdge flag should start as set or cleared. (The initial
operEdge state when a port is initialized).
AutoEdge :
Controls whether the bridge should enable automatic edge detection on the
bridge port. This allows operEdge to be derived from whether BPDU's are
received on the port or not.
Restricted Role :
If enabled, causes the port not to be selected as Root Port for the CIST or any
MSTI, even if it has the best spanning tree priority v ector. Such a port will be
selected as an Alternate Port after the Root Port has been selected. If set, it
can cause lack of spanning tree connectivity. It can be set by a network
administrator to prevent bridges external to a core region of the network
influence the spanning tree active topology, possibly because those bridges are
not under the full control of the administrator. This feature is also known as
Root Guard.
Restricted TCN :
If enabled, causes the port not to propagate received topology change
notifications and topology changes to other ports. If set it can cause temporary
loss of connectivity after changes in a spanning tree's active topology as a
result of persis tently incorrect learne d station location informat ion. It is set by
a network administrator to prevent bridges external to a core region of the
network, causing address flushing in that region, possibly because those
bridges are not under the full control of the administrator or the physical link
state of the attached LANs transits fr equently.
BPDU Guard :
If enabled, causes the port to disable itself upon receiving valid BPDU's.
Contrary to the similar bridge setting, the port Edge status does not affect this
setting. A port entering error-disabled state due to this setting is subject to the
bridge Port Error Recovery setting as well.
Point to Point
Controls whether the port connects to a point-to-point LAN rather than to a
shared medium. This can be automatically determined, or forced either true or
false. Transition to the forwarding state is faster for point-to-point LANs than
for shared media.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
69
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 82

3-4.5 MSTI Ports
The section describes it allows the user to inspect the current STP MSTI port configurations,
and possibly change them as well.
An MSTI port is a virtual port, which is instantiated separately for each active CIST (physical)
port for each MSTI instance configured on and applicable to the port. The MSTI instance must
be selected before displaying actual MSTI port configuration options. It contains MSTI port
settings for physical and aggregated ports.
Web Interface
To configure the Spanning Tree MSTI Port Configuration parameters in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Spanning Tree, MSTI Ports
2. Scroll to select the MST1 or other MSTI Port
3. Click Get to set the detail parameters of the MSTI Ports.
4. Scroll to set all parameters of the MSTI Port configuration.
5. Click the save to save the setting
6. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-4.5: The MSTI Port Configuration
Parameter description:
Port :
The switch port number of the corresponding STP CIST (and MSTI) port.
Path Cost :
Controls the path cost incurred by the port. The Auto setting will set t he path
cost as appropriate by the physical link speed, using the 802.1D recommended
70
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 83

values. Using the Specific setting, a user-defined value can be entered. The
path cost is used when establishing the active topology of the network. Lower
path cost ports are chosen as forwarding ports in favour of higher path cost
ports. Valid values are in the range 1 to 200000000.
Priority :
Controls the port priority. This can be used to control priority of ports having
identical port cost. (See above).
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
71
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 84

3-4.6 Bridge Status
After you complete the MSTI Port configuration the you could to ask the switch display the
Bridge Status. The Section provides a status overview of all STP bridge instances. The
displayed table contains a row for each STP bridge instance, where the column displays the
following information:
Web Interface
To display the STP Bridges status in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Spanning Tree, STP Bridges
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the STP Bridges.
Figure 3-4.6: The STP Bridges status
Parameter description:
MSTI :
The Bridge Instance. This is also a link to the STP Detailed Bridge Status.
Bridge ID :
The Bridge ID of this Bridge instance.
Root ID :
The Bridge ID of the currently elected root bri dge.
Root Port :
The switch port currently assigned the root port role.
Root Cost :
Root Path Cost. For the Root Bridge it is zero. For all other Bridges, it is the sum of the
Port Path Costs on the least cost path to the Root Bridge.
Topology Flag :
The current state of the Topology Change Flag of this Bridge instance.
Topology Change Last :
The time since last Topology Change occurred.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the information au t o matically.
Upper right icon (Refresh)
You can click them for refresh the STP Bridges status information by manual.
72
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 85

3-4.7 Port Status
After you complete the STP configuration then you could to ask the switch display the STP
Port Status. The Section provides you to ask switch to display the STP CIST port status for
physical ports of the currently selected switch.:
Web Interface
To display the STP Port status in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Spanning Tree, STP Port Status
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the STP Bridges.
Figure 3-4.7: The STP Port status
Parameter description:
Port :
The switch port number of the logical STP port.
CIST Role :
The current STP port role of the CIST port. The port role can be one of the following values:
AlternatePort, Backup Port, RootPort, DesignatedPort Disabled.
CIST State :
The current STP port state of the CIST port. The port state can be one of the following
values: Blocking Learning Forwarding.
Uptime
The time since the bridge port was last initialized.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the information au t o matically.
Upper right icon (Refresh)
You can click them for refresh the STP Port status information by manual.
73
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 86

3-4.8 Port Statistics
After you complete the STP configuration then you could to let the switch display the STP
Statistics. The Section provides you to ask switch to display the STP Statistics detail counters
of bridge ports in the currently selected switch.
Web Interface
To display the STP Port status in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Spanning Tree, Port Statistics
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the STP Bridges.
Figure 3-4.8: The STP Statistics
Parameter description:
Port :
The switch port number of the logical STP port.
MSTP :
The number of MSTP Configuration BPDU's received/transmitted on the port.
RSTP :
The number of RSTP Configuration BPDU's received/transmitted on the port.
STP :
The number of legacy STP Configuration BPDU's received/transmitted on the port.
TCN :
The number of (legacy) Topology Change Notification BPDU's received/transmitted on the
port.
Discarded Unknown :
The number of unknown Spanning Tree BPDU's received (and discarded) on the port.
Discarded Illegal :
The number of illegal Spanning Tree BPDU's received (and discarded) on the port.
Auto-refresh:
To evoke the auto-refresh to refresh the information automatically.
Upper right icon (Refresh, Clear)
You can click them for refresh the STP Statistics information or clear by manual.
74
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 87

75
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 88

3-5 IGMP Snooping
The function, is used to establish the multicast groups to forward the multicast packet to the
member ports, and, in nature, avoids wasting the bandwidth while IP multicast packets are
running over the network. This is because a switch that does not support IGMP or IGMP
Snooping can not tell the multicast packet from the broadcast packet, so it can only treat them
all as the broadcast packet. Without IGMP Snooping, the multicast packet forwarding function
is plain and nothing is different from broadcast packet.
A switch supported IGMP Snooping with the functions of query, report and leave, a type of
packet exchanged between IP Multicast Router/Switch and IP Multicast Host, can update the
information of the Multicast table when a member (port) joins or leaves an IP Multicast
Destination Address. With this function, once a switch receives an IP multicast packet, it will
forward the packet to the members who joined in a specified IP multicast group before.
The packets will be discarded by the IGMP Snooping if the user transmits multicast packets to
the multicast group that had not been built up in advance. IGMP mode enables the switch to
issue IGMP function that you enable IGMP proxy or snooping on the switch, which connects
to a router closer to the root of the tree. This interface is the upstream interface. The router on
the upstream interface should be running IGMP.
3-5.1 Basic Configuration
The section describes how to set the basic IGMP snooping on the switch, which connects to a
router closer to the root of the tree. This interface is the upstream interface. The router on the
upstream interface should be running IGMP.
Web Interface
To configure the IGMP Snooping parameters in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, IGMP Snooping, Basic Configuration
2. Evoke to select enable or disable which Global configuration
3. Evoke which port wants to become a Router Port or enable/ disable the Fast Leave
function..
4. Scroll to set the Throtting parameter.
5. Click the save to save the setting
6. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-5.1: The IGMP Snooping Configuration.
76
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 89

Parameter description:
Snooping Enabled:
Enable the Global IGMP Snooping.
Unregistered IPMCv4 Flooding enabled :
Enable unregistered IPMCv4 traffic flooding.
IGMP SSM Range :
SSM (Source-Specific Multicast) Range allows the SSM-aware hosts and routers
run the SSM service model for the groups in the address range. Format: (IP
address/ sub mask)
Proxy Enabled :
Enable IGMP Proxy. This feature can be used to avoid forwarding unnecessary
join and leave messages to the router side.
Port :
It shows the physical Port index of switch.
Router Port :
Specify which ports act as router ports. A router port is a port on the Ethernet
switch that leads towards the Layer 3 multicast device or IGMP querier.
If an aggregation member port is selected as a router port, the whole
aggregation will act as a router port.
Fast Leave :
Enable the fast leave on the port.
Throttling :
Enable to limit the number of multicast groups to which a switch port can
belong.
Buttons
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
77
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 90

3-5.2 VLAN Configuration
The section describes the VLAN configuration setting process integrated with IGMP Snooping
function. For Each setting page shows up to 99 entries from the VLAN table, default being 20,
selected through the "entries per page" input field. When first visited, the web page will show
the first 20 entries from the beginning of the VLAN Table. The first displayed will be the one
with the lowest VLAN ID found in the VLAN Table. The "VLAN" input fields allow the user to
select the starting point in the VLAN Table. Clicking the button will update the displayed table
starting from that or the next closest VLAN Table match.
Web Interface
To configure the IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, IGMP Snooping, VLAN Configuration
2. Evoke to select enable or disable Snooping , IGMP Querier
Specify the parameters in the blank field.
3. Click the refresh to update the data or click << or >> to display previous
entry or next entry.
4. Click the save to save the setting
5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-5.2: The IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration.
Parameter description:
VLAN ID :
It displays the VLAN ID of the entry.
Snooping Enabled :
Enable the per-VLAN IGMP Snooping. Only up to 32 VLANs can be selected. .
IGMP Querier :
A router sends IGMP Query messages onto a particular link. This Router is called the
Querier. Enable the IGMP Querier in the VLAN.
Compatibility :
Compatibility is maintained by hosts and routers taking appropriate actions depending on
the versions of IGMP operating on hosts and routers within a network. The allowed
selection is IGMP-Auto, Forced IGMPv1, Forced IGMPv2, Forced IGMPv3, default
compatibility value is IGMP-Auto.
Rv :
Robustness Variable. The Robustness Variable allows tuning for the expected packet loss
on a network. The allowed range is 1 to 255; default robustness variable value is 2.
QI :
Query Interval. The Query Interval is the interval between General Queries sent by the
78
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 91

Querier. The allowed range is 1 to 31744 seconds; default query interval is 125 seconds.
QRI :
Query Response Interval. The Max Response Time used to calculate the Max Resp Code
inserted into the periodic General Queries. The allowed range is 0 to 31744 in tenths of
seconds; default query response interval is 100 in tenths of seconds (10 seconds).
LLQI (LMQI for IGMP) :
Last Member Query Interval. The Last Member Query Time is the time value represented
by the Last Member Query Interval, multiplied by the Last Member Query Count. The
allowed range is 0 to 31744 in tenths of seconds; default last member query interval is 10
in tenths of seconds (1 second).
URI :
Unsolicited Report Interval. The Unsolicited Report Interval is the time between repetitions
of a host's initial report of membership in a group. The allowed range is 0 to 31744
seconds, default unsolicited report interval is 1 second. .
Buttons :
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
Upper right icon (Refresh, |<<, >>) :
You can click them Refreshes the displayed table starting from the "VLAN" input fields. Or
click “|<<” to update the table starting from the first entry in the VLAN table, i.e. the entry
with the lowest VLAN ID. Others click “>> “ to update the table, starting with the entry after
the last entry currently displayed.
79
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 92

3-5.3 Port Group Filtering
The section describes how to set the IGMP Port Group Filtering? With the IGMP filtering
feature, an user can exert this type of control. In some network Application environments, as
like the metropolitan or multiple-dwelling unit (MDU) installations, a user might want to control
the multicast groups to which a user on a switch port can belong. It allows the user to control
the distribution of multicast services, such as IP/TV, based on some type of subscription or
service plan.
With this feature, you can filter multicast joins on a per-port basis by configuring IP multicast
profiles and associating them with individual switch ports. An IGMP profile can contain one or
more multicast groups and specifies whether access to the group is permitted or denied. If an
IGMP profile denying access to a multicast group is applied to a switch port, the IGMP join
report requesting the stream of IP multicast traffic is dropped, and the port is not allowed to
receive IP multicast traffic from that group. If the filtering action permits access to the
multicast group, the IGMP report from the port is forwarded for normal processing.
IGMP filtering controls only IGMP membership join reports and has no relationship to the
function that directs the forwarding of IP multicast traffic.
Web Interface
To configure the IGMP Snooping Port Group Configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, IGMP Snooping, Port Group Filtering
2. Click Add new Filtering Group
3. Scroll the Port to enable the Port Group Filtering.
Specify the Filtering Groups in the blank field.
4. Click the save to save the setting
5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-5.3: The IGMP Snooping Port Group Filtering Configuration.
Parameter description:
Delete :
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
80
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 93

Port :
To evoke the port enable the IGMP Snooping Port Group Filtering function.
Filtering Grou ps :
The IP Multicast Group that will be filtered.
Buttons:
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
81
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 94

3-5.4 Status
After you complete the IGMP Snooping configuration, then you could to let the switch display
the IGMP Snooping Status. The Section provides you to let switch to display the IGMP
Snooping detail status.
Web Interface
To display the IGMP Snooping status in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, IGMP Snooping, Status
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh the IGMP Snooping Status.
4. Click “ Clear“ to clear the IGMP Snooping Status.
Figure 3-5.4: The IGMP Snooping Status.
Parameter description:
VLAN ID :
The VLAN ID of the entry.
Querier Version :
Working Querier Version currently.
Host Version :
Working Host Version currently.
Querier Status :
Shows the Querier status is "ACTIVE" or "IDLE".
Queries Transmitted :
The number of Transmitted Queries.
Queries Received :
The number of Received Queries.
V1 Reports Received :
The number of Received V1 Reports.
82
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 95

V2 Reports Received :
The number of Received V2 Reports.
V3 Reports Received :
The number of Received V3 Reports.
V2 Leaves Received :
The number of Received V2 Leaves.
Auto-refresh
To evoke the auto-refresh icon then the device will refresh the log automatically.
Upper right icon (Refresh, clear)
You can click them for refresh the Status or clear them by manual.
83
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 96

3-5.5 Group Infermation
After you complete to set the IGMP Snooping function then you could let the switch to display
the IGMP Snooping Group Information. Entries in the IGMP Group Table are shown on this
page. The IGMP Group Table is sorted first by VLAN ID, and then by group. The will use the
last entry of the currently displayed table as a basis for the next lookup. When the end is
reached the text "No more entries" is shown in the displayed table. Use the button to start
over.
Web Interface
To display the IGMP Snooping Group Information in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, IGMP Snooping, Group Information
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh a entry of the IGMP Snooping Groups
Information.
4. Click “<< or >> “ to move to previous or next entry.
Figure 3-5.5: The IGMP Snooping Groups Information.
Parameter description:
Navigating the IGMP Group Tab l e
The "Start from VLAN", and "group" input fields allow the user to select the starting point in
the IGMP Group Table. The will use the last entry of the currently displayed table as a
basis for the next lookup. When the end is reached the text "No more entries" is shown in
the displayed table.
IGMP Group Tabl e Columns
VLAN ID :
VLAN ID of the group.
Groups :
Group address of the group displayed.
Port Members :
Ports under this group.
Auto-refresh
To evoke the auto-refresh icon then the device will refresh the log automatically.
Upper right icon (Refresh, <<, >> )
You can click them for refresh the IGMP Group Status by manual, others for
next/up page or entry..
84
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 97

3-5.6 IPv4 SSM information
Source Specific Multicast (SSM) is a datagram delivery model that best supports one-to-many
applications, also known as broadcast applications. SSM is a core network technology of IP
multicast targeted for audio and video broadcast application environments.
For the SSM delivery mode, an IP multicast receiver host must use IGMP Version 3 (IGMPv3)
to subscribe to channel (S, G). By subscribing to this channel, the receiver host is indicating
that it wants to receive IP multicast traffic sent by source host S to group G. The network will
deliver IP multicast packets from source host S to group G to all hosts in the network that
have subscribed to the channel (S, G).
SSM does not require group address allocation within the network, only within each source
host. Different applications running on the same source host must use different SSM groups.
Different applications running on different source hosts can arbitrarily reuse SSM group
addresses without causing any excess traffic on the network.
Addresses in the range 232.0.0.0/8 (232.0.0.0 to 232.255.255.255) are reserved for SSM by
IANA. In the switch, you can configure SSM for arbitrary IP multicast addresses also.
Web Interface
To display the IGMPv3 IPv4 SSM Information in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, IGMP Snooping, IPv4 SSM Information
2. If you want to auto-refresh the information then you need to evoke the
“Auto-refresh”.
3. Click “ Refresh“ to refresh a entry of the IGMPv3 IPv4 SSM Information.
4. Click “<< or >> “ to move to previous or next entry.
Figure 3-6.6: The IGMPv3 IPv4 SSM Information.
Parameter description:
Navigating the IGMPv3 Information Tabl e
Each page shows up to 99 entries from the IGMPv3 SSM (Source Specific Multicast)
Information table, default being 20, selected through the "entries per page" input field.
When first visited, the web page will show the first 20 entries from the beginning of the
IGMPv3 Information Table.
The "Start from VLAN", and "group" input fields allow the user to select the starting point in
the IGMPv3 Information Table. Clicking the button will update the displayed table starting
from that or the closest next IGMPv3 Information Table match. In addition, the two input
fields will - upon a button click - assume the value of the first displayed entry, allowing for
continuous refresh with the same start address.
The will use the last entry of the currently displayed table as a basis for the next lookup.
When the end is reached the text "No more entries" is shown in the displayed table. Use
the button to start over.
IGMPv3 Information Tab le Columns
85
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 98

VLAN ID :
VLAN ID of the group.
Group :
Group address of the group displayed.
Port :
Switch port number.
Mode :
Indicates the filtering mode maintained per (VLAN ID, port number, Group Address) basis.
It can be either Include or Exclude.
Source Address :
IP Address of the source. Currently, system limits the total number of IP source addresses
for filtering to be 128.
Type :
Indicates the Type. It can be either Allow or Deny.
Auto-refresh
To evoke the auto-refresh icon then the device will refresh the log automatically.
Upper right icon (Refresh, <<, >> )
You can click them for refresh the IGMP Group Status by manual, others for
next/up page or entry..
86
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 99

3-6 MLD Snooping
Curiously enough, a network node that acts as a source of IPv6 multicast traffic is only an
indirect participant in MLD snooping—it just provides multicast traffic, and MLD doesn’t
interact with it. (Note, however, that in an application like desktop conferencing a network
node may act as both a source and an MLD host; but MLD interacts with that node only in its
role as an MLD host.)
A source node creates multicast traffic by sending packets to a multicast address. In IPv6,
addresses with the first eight bits set (that is, “FF” as the first two characters of the address)
are multicast addresses, and any node that listens to such an address will receive the traffic
sent to that address. Application software running on the source and destination systems
cooperates to determine what multicast address to use. (Note that this is a function of the
application software, not of MLD.)
When MLD snooping is enabled on a VLAN, the switch acts to minimize unnecessary
multicast traffic. If the switch receives multicast traffic destined for a given multicast address, it
forwards that traffic only to ports on the VLAN that have MLD hosts for that address. It drops
that traffic for ports on the VLAN that have no MLD hosts
3-6.1 Basic Configuration
The section will let you understand how to configure the MLD Snooping basic configuration
and the parameters .
Web Interface
To configure the MLD Snooping Configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, MLD Snooping, Basic Configuration
2. Evoke to enable or disable the Global configuration parameters
Evoke the port to join Router port and Fast Leave.
3. Scroll to select the Throtting mode with unlimited or 1 to 10
4. Click the save to save the setting
5. If you want to cancel the setting then you need to click the Reset button.
It will revert to previously saved values
Figure 3-6.1: The MLD Snooping Basic Configuration.
87
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
Page 100

Parameter description:
Snooping Enabled :
Enable the Global MLD Snooping.
Unregistered IPMCv6 Flooding enabled :
Enable unregistered IPMCv6 traffic flooding. Please note that disabling unregistered
IPMCv6 traffic flooding may lead to failure of Neighbor Discovery.
MLD SSM Range :
SSM (Source-Specific Multicast) Range allows the SSM-aware hosts and routers run the
SSM service model for the groups in the address (Using IPv6 Address) range.
Proxy Enabled :
Enable MLD Proxy. This feature can be used to avoid forwarding unnecessary join and
leave messages to the router side.
Port:
The Port index what you enable or disable the MLD Snooping function.
Fast Leave :
To evoke to enable the fast leave on the port.
Router Port :
Specify which ports act as router ports. A router port is a port on the Ethernet switch that
leads towards the Layer 3 multicast device or MLD querier. If an aggregation member port
is selected as a router port, the whole aggregation will act as a router port.
Throttling :
Enable to limit the number of multicast groups to which a switch port can belong.
Buttons:
Save – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
88
Publication date: Mar., 2012
Revision A1
 Loading...
Loading...