American Fibertek ET42202XM-S-PD User Manual

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
ET42202XM-S-PD
100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX or

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
About This Manual
Copyright
.
Purpose
Audience
CONVENTIONS
WARRANTY
Disclaimer
FCC Warning
Copyright © 2015 Manufacture Technology Corp. All rights reserved.
The products and programs described in this User’s Manual are licensed
products of Manufacture Technology, This User’s Manual contains proprietary
information protected by copyright, and this User’s Manual and all
accompanying hardware, software and documentation are copyrighted. No
parts of this User’s manual may be copied, photocopied, reproduced,
translated or reduced to any electronic medium or machine-readable from by
any means by electronic or mechanical. Including photocopying, recording, or
information storage and retrieval systems, for any purpose other than the
purchaser’s personal use, and without the prior express written permission of
Manufacture Technology.
This manual gives specific information on how to operate and use the
management functions of the ET42202XM-S-PD
The Manual is intended for use by network administrators who are
responsible for operating and maintaining network equipment;
consequently, it assumes a basic working knowledge of general
switch functions, the Internet Protocol (IP), and Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP).
The following conventions are used throughout this manual to show
information.
See the Customer Support/ Warranty booklet included with the
product. A copy of the specific warranty terms applicable to your
Manufacture products and replacement parts can be obtained from
your Manufacture Sales and Service Office authorized dealer.
Manufacture Technology does not warrant that the hardware will
work properly in all environments and applications, and marks no
warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with
respect to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a
particular purpose. Manufacture disclaims liability for any
inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred. Information in
this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not
represent a commitment on the part of Manufacture. Manufacture
assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be
contained in this User’s Manual. Manufacture makes no commitment
to update or keep current the information in this User’s Manual, and
reserves the righter to make improvements to this User’s Manual
and /or to the products described in this User’s Manual, at any time
without notice.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
ET42202XM-S-PD
Emph
asizes important
inform
ation or calls y
our
Alerts
you to a potential
hazard
that
could
cause
Alert
s you to a potential hazar
d that
coul
d cause
loss
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
accordance with the Instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications.
FCC Caution
CE mark
Warning
To assure continued compliance (example-use only shielded
interface cables when connection to computer or peripheral devices).
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate
the equipment. This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the Following two conditions: (1) This device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This is a Class B device, In a domestic environment, this product may
may cause radio interference, in which case the user may be
required to take adequate measures.
N
OTE
:
attention to related features or instructions.
W
ARNING
personal injury.
C
AUTION
of data, or damage the system or equipment.
:
:

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
Table of Contents
Revision History .............................................................................................................................................. viii
INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................ 1
CHAPTER 1 OPERATION OF WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT .............................. 2
CHAPTER 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION ...................................................... 6
2-1 System ....................................................................................................................................................... 6
2-1.1 Information ............................................................................................................................................... 6
2-1.2 IP ............................................................................................................................................................. 11
2-1.3 NTP ......................................................................................................................................................... 14
2-1.4 Time ........................................................................................................................................................ 15
2-1.5 Log .......................................................................................................................................................... 18
2-2 Green Ethernet ........................................................................................................................................ 19
2-3 Ports Configuration .................................................................................................................................. 18
2-3.1 Ports ........................................................................................................................................................ 18
2-3.2 Ports Description .................................................................................................................................... 20
2-4DHCP ........................................................................................................................................................ 21
2-4.1 Server ...................................................................................................................................................... 21
2-4.1.1 Mode ............................................................................................................................................. 21
2-4.1.2 Excluded IP .................................................................................................................................. 23
2-4.1.3 Pool ............................................................................................................................................... 24
2-4.2 Snooping ................................................................................................................................................. 26
2-4.3 Relay ....................................................................................................................................................... 27
2-5 Security .................................................................................................................................................... 28
2-5.1 Switch ..................................................................................................................................................... 28
2-5.1.1 Users ............................................................................................................................................. 28
2-5.1.2 Privilege Level ............................................................................................................................. 30
2-5.1.3 Authentication Method ................................................................................................................ 31
2-5.1.4 SSH ............................................................................................................................................... 32
2-5.1.5 HTTPs ........................................................................................................................................... 33
2-5.1.6 Access Management .................................................................................................................. 34
2-5.1.7 SNMP............................................................................................................................................ 35
2-5.2 Network .................................................................................................................................................. 57
2-5.2.1 Limit Control ................................................................................................................................. 57
2-5.2.2 NAS ............................................................................................................................................... 60
2-5.2.3 ACL ............................................................................................................................................... 68
2-5.2.4 IP Source Guard ......................................................................................................................... 75
2-5.2.5 ARP Inspection ............................................................................................................................ 79
2-5.3 AAA ......................................................................................................................................................... 87
2-5.3.1 RADIUS ........................................................................................................................................ 87
2-5.3.2 TACACS+ ..................................................................................................................................... 90
2-6 Aggregation ............................................................................................................................................. 92
2-6.1 Static ....................................................................................................................................................... 92
2-6.2 LACP ........................................................................................................................................................ 94
2-7 Loop Protection ....................................................................................................................................... 96
2-8 Spanning Tree .......................................................................................................................................... 98
2-8.1 Bridge Setting .......................................................................................................................................... 98

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
2-8.2 MSTI Mapping ....................................................................................................................................... 101
2-8.3 MSTI Priorities ....................................................................................................................................... 103
2-8.4 CIST Ports .............................................................................................................................................. 104
2-8.5 MSTI Ports ............................................................................................................................................. 106
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-9 IPMC Profile ........................................................................................................................................... 108
2-9.1 Profile Table .......................................................................................................................................... 108
2-9.1.1 IPMC Profile Rule Settings Table ........................................................................................... 109
2-9.2 Address Entry ........................................................................................................................................ 111
2-10MVR ...................................................................................................................................................... 113
2-11 IPMC .................................................................................................................................................... 116
2-11.1 IGMP Snooping ................................................................................................................................... 116
2-11.1.1 Basic Configuration ................................................................................................................. 116
2-11.1.2 VLAN Configuration ................................................................................................................ 118
2-11.1.3 Port Filtering Profile ................................................................................................................ 120
2-11.2 MLD Snooping ..................................................................................................................................... 122
2-11.2.1 Basic Configuration ................................................................................................................. 122
2-11.2.2 VLAN Configuration ................................................................................................................ 125
2-11.2.3 Port Group Filtering ................................................................................................................ 127
2-12 LLDP ..................................................................................................................................................... 128
2-12.1 LLDP Configuration ............................................................................................................................. 128
2-12.2 LLDP-MED Configuration .................................................................................................................... 131
2-13 MAC Table ............................................................................................................................................ 137
2-14 VLANs .................................................................................................................................................. 139
2-15 Private VLANs ...................................................................................................................................... 143
2-15.1 VLAN Membership .............................................................................................................................. 143
2-15.2 Port Isolation....................................................................................................................................... 145
2-16 VCL ....................................................................................................................................................... 146
2-16.1 MAC-based VLAN ................................................................................................................................ 146
2-16.2 Protocol -based VLAN ......................................................................................................................... 148
2-16.2.1 Protocol to Group .................................................................................................................... 148
2-16.2.2 Group to VLAN ........................................................................................................................ 150
2-16.3 IP Subnet-based VLAN ........................................................................................................................ 151
2-17 VOICE VLAN ......................................................................................................................................... 153
2-17.1 Configuration ...................................................................................................................................... 153
2-17.2 OUI ...................................................................................................................................................... 155
2-18 QoS ...................................................................................................................................................... 156
2-18.1 Port Classification ............................................................................................................................... 156
2-18.2 Port Policing ........................................................................................................................................ 159
2-18.4 Port Schedulers ................................................................................................................................... 160
2-18.5 Port Shaping ........................................................................................................................................ 163
2-18.6 Port Tag Remarking ............................................................................................................................. 166
2-18.7 Port DSCP ............................................................................................................................................ 169
2-18.8 DSCP-Based QoS ................................................................................................................................. 171
2-18.9 DSCP Translation ................................................................................................................................. 173
2-18.10 DSCP Classification ............................................................................................................................ 175
2-18.11 QoS Control List Configuration ......................................................................................................... 176
2-18.12 Storm Control ................................................................................................................................... 180
2-18.13 WRED ................................................................................................................................................ 182
2-19 Mirror .................................................................................................................................................. 184

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
2-20 UPnP .................................................................................................................................................... 186
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-21. GVRP ................................................................................................................................................... 188
2-21.1 Global Config ...................................................................................................................................... 188
2-21.2 Port Config .......................................................................................................................................... 190
2-22. sFlow .................................................................................................................................................. 191
CHAPTER 3. MONITOR ........................................................................... 194
3-1 System ................................................................................................................................................... 194
3-1.1 Information ........................................................................................................................................... 194
3-1.3 IP Status ................................................................................................................................................ 196
3-1.4 Log ........................................................................................................................................................ 198
3-1.5 Detailed Log .......................................................................................................................................... 200
3-2 Green Ethernet ...................................................................................................................................... 201
3-2.1 Port Power Savings ............................................................................................................................... 201
3-3 Ports ...................................................................................................................................................... 202
3-3.1 Traffic Overview .................................................................................................................................... 202
3-3.2 Qos Statistics ......................................................................................................................................... 204
3-3.3 QCL Status ............................................................................................................................................. 205
3-3.4 Detailed Statistics.................................................................................................................................. 207
3-4 DHCP ...................................................................................................................................................... 211
3-4.1 Server .................................................................................................................................................... 211
3-4.1.1 Statistics ..................................................................................................................................... 211
3-4.1.2 Binding ........................................................................................................................................ 212
3-4.1.3 Declined IP ................................................................................................................................. 213
3-4.2 Snooping Table ...................................................................................................................................... 214
3-4.3 Relay Statistics ...................................................................................................................................... 215
3-4.4 Detailed Statistics.................................................................................................................................. 217
3-5 Security .................................................................................................................................................. 219
3-5.1 Access Management Statistics .............................................................................................................. 219
3-5.2 Network ................................................................................................................................................ 220
3-5.2.1 Port Security .............................................................................................................................. 220
3-5.2.2 NAS ............................................................................................................................................. 224
3-5.2.3 ARP Inspection .......................................................................................................................... 231
3-5.2.4 IP Source Guard ....................................................................................................................... 232
3-5.3 AAA ....................................................................................................................................................... 234
3-5.3.1 RADIUS Overview .................................................................................................................... 234
3-5.3.2 RADIUS Details ......................................................................................................................... 236
3-5.4 Switch ................................................................................................................................................... 241
3-5.4.1 RMON ......................................................................................................................................... 241
3-6 LACP ...................................................................................................................................................... 250
3-6.1 System Status ........................................................................................................................................ 250
3-6.3 Port Statistics ........................................................................................................................................ 252
3-7 Loop Protection ..................................................................................................................................... 254
3-8 Spanning Tree ........................................................................................................................................ 255
3-8.1 Bridge Status ......................................................................................................................................... 255
3-8.2 Port Status ............................................................................................................................................ 257
3-8.3 Port Statistics ........................................................................................................................................ 258
3-9 MVR ....................................................................................................................................................... 259

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
3-9.1 Statistics ................................................................................................................................................ 259
3-9.2 MVR Channels Groups .......................................................................................................................... 260
3-9.3 MVR SFM Information .......................................................................................................................... 262
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
3-10 IPMC .................................................................................................................................................... 264
3-10.1 IGMP Snooping ................................................................................................................................... 264
3-10.1.1 Status ........................................................................................................................................ 264
3-10.1.2 Group Information ................................................................................................................... 266
3-10.1.3 IPv4 SFM Information ............................................................................................................ 268
3-10.2 MLD Snooping ..................................................................................................................................... 270
3-10.2.1 Status ........................................................................................................................................ 270
3-10.2.2 Group Information ................................................................................................................... 272
3-10.2.3 IPv6 SFM Information ............................................................................................................ 274
3-11 LLDP ..................................................................................................................................................... 276
3-11.1 Neighbour ........................................................................................................................................... 276
3-12 MAC Table ............................................................................................................................................ 285
3-13 VLANs .................................................................................................................................................. 287
3-13.1 VLAN Membership .............................................................................................................................. 287
3-13.2 VLAN Port ........................................................................................................................................... 289
3-14 VCL ....................................................................................................................................................... 291
3-14.1 MAC-based VLAN ................................................................................................................................ 291
3-14.2 Protocol-based VLAN .......................................................................................................................... 292
3-14.2.1 Protocol to Group .................................................................................................................... 292
3-14.2.2 Group to VLAN ........................................................................................................................ 294
3-14.3 IP Subnet-based VLAN ........................................................................................................................ 295
3-15 sFlow ................................................................................................................................................... 296
CHAPTER 4. DIAGNOSTICS ..................................................................... 298
4-1 Ping ........................................................................................................................................................ 298
4-2 Ping6 ...................................................................................................................................................... 300
4-3 VeriPHY .................................................................................................................................................. 302
4-4 Traceroute.............................................................................................................................................. 303
CHAPTER 5. MAINTENANCE ................................................... 304
5-1 Restart Device ........................................................................................................................................ 304
5-2 Factory Defaults ..................................................................................................................................... 305
5-3 Firmware ............................................................................................................................................... 306
5-3.1 Firmware upgrade ................................................................................................................................ 306
5-3.2 Firmware Selection ............................................................................................................................... 307
5-4 Configuration ......................................................................................................................................... 308
5-4.1 Save startup-config ............................................................................................................................... 308
5-4.2 Upload ................................................................................................................................................... 309
5-4.3 Download .............................................................................................................................................. 310
5-4.5 Delete.................................................................................................................................................... 312

ET42202XM-S-PD
Release
Date
Revision
V
1.0 05/10/2016 A1
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
Revision History

INTRODUCTION
Overview
In this user’s manual, it will not only tell you how to install and connect your network
system but configure and monitor the ET42202XM-S-PD through the web by (RJ-45) serial
interface and Ethernet ports step-by-step. Many explanations in detail of hardware and
software functions are shown as well as the examples of the operation for web-based
interface.
The ET42202XM-S-PD series, the next generation Web managed switches from
Manufacture, is a portfolio of affordable managed switches that provides a reliable
infrastructure for your business network. These switches deliver more intelligent features
you need to improve the availability of your critical business applications, protect your
sensitive information, and optimize your network bandwidth to deliver information and
applications more effectively. It provides the ideal combination of affordability and
capabilities for entry level networking includes small business or enterprise application
and helps you create a more efficient, better-connected workforce.
ET42202XM-S-PD Web Managed Switches provide 24 ports in a single device; the
specification is highlighted as follows.
L2+ features provide better manageability, security, QoS, and performance.
Support IPv4/IPv6 dual stack management
Support SSH/SSL secured management
Support SNMP v1/v2c/v3
Support RMON groups 1,2,3,9
Support sFlow
Support IGMP v1/v2/v3 Snooping
Support MLD v1/v2 Snooping
Support RADIUS and TACACS+ authentication
Support IP Source Guard
Support DHCP Relay (Option 82)
Support DHCP Snooping
Support ACL and QCL for traffic filtering
Support 802.1d(STP), 802.1w(RSTP) and 802.1s(MSTP)
Support LACP and static link aggregation
Support Q-in-Q double tag VLAN
Support GVRP dynamic VLAN
Overview of this user’s manual
Chapter 1 “Operation of Web-based Management”
Chapter 2 “System Configuration”
Chapter 3 “Configuration”
Chapter 4 “Security”
Chapter 5 “Maintenance”
1
Publication date: Jan., 2016
Revision A2
Default
N
:
Chapter 1
Management
Initial
Configuration
This chapter instructs you how to configure and manage the
ET42202XM-S-PD
can easily access and monitor through any one port of the switch all the
status of the switch, including MIBs status, each port activity, Spanning tree
status, port aggregation status, multicast traffic, VLAN and priority status,
even illegal access record and so on.
T
he default values of the ET42202XM-S-PD are listed in the table below:
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Username
Password
After the ET42202XM-S-PD has been finished configuration the it interface,
you can browse it. For instance, type http://192.168.2.1 in the address
row in a browser, it will show the following screen and ask you inputting
username and password in order to login and access authentication.
Operation of Web-based
through the web user interface. With this facility, you
192.168.2.1
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.254
admin
system
The default username is “admin” and password is system. For the first
time to use, please enter the default username and password, and then click
the <Login> button. The login process now is completed. In this login menu,
you have to input the complete username and password respectively, the
ET42202XM-S-PD will not give you a shortcut to username automatically.
This looks inconvenient,
In the ET42202XM-S-PD, allowed two or more users using administrator’s
identity to manage this switch, which administrator to do the last setting, it
will be an available configuration to effect the system.
OTE
When you login the Switch WEB/CLI to manager. You must first type
the Username of the admin. Password was blank, so when you
type after the end Username, please press enter. Management page
to enter WEB/CLI.
When you login ET42202XM-S-PD series switch Web UI
management, you can use both ipv4 ipv6 login to manage
To optimize the display effect, we recommend you use Microsoft IE
6.0 above, Netscape V7.1 above or FireFox V1.00 above and have
the resolution 1024x768. The switch supported neutral web browser
interface
but safer.
2
Publication date: Jan., 2016
Revision A2

N
:
OTE
Figure 1 The login page
AS ET42202XM-S-PD the function enable dhcp, so If you do not
have DHCP server to provide ip addresses to the switch, the Switch
default ip 192.168.2.1
5
Publication date: Jan., 2016
Revision A2

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
Chapter 2
This chapter describes the entire basic configuration tasks which includes the System
Information and any manage of the Switch (e.g. Time, Account, IP, Syslog and NTP.)
2-1
System
2-1.1 Information
Web interface
You can identify the system by configuring the contact information, name, and location of the
switch.
The switch system’s contact information is provided here.
To configure System Information in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, System, and Information.
2. Write System Contact, System Name, System Location information in this page.
System Configuration
3. Click Apply
Figure 2-1.1: System Information
Parameter description:
System Contact:
The textual identification of the contact person for this managed node, together
with information on how to contact this person. The allowed string length is 0 to
128, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 32 to 126.
System name:
An administratively assigned name for this managed node. By convention, this is
the node's fully-qualified domain name. A domain name is a text string drawn
from the alphabet (A-Za-z), digits (0-9), minus sign (-). No space characters are
permitted as part of a name. The first character must be an alpha character. And
the first or last character must not be a minus sign. The allowed string length is 0
to 128.
System Location:
The physical location of this node(e.g., telephone closet, 3rd floor). The allowed

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
string length is 0 to 128, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 32
to 126.
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-1.2 IP
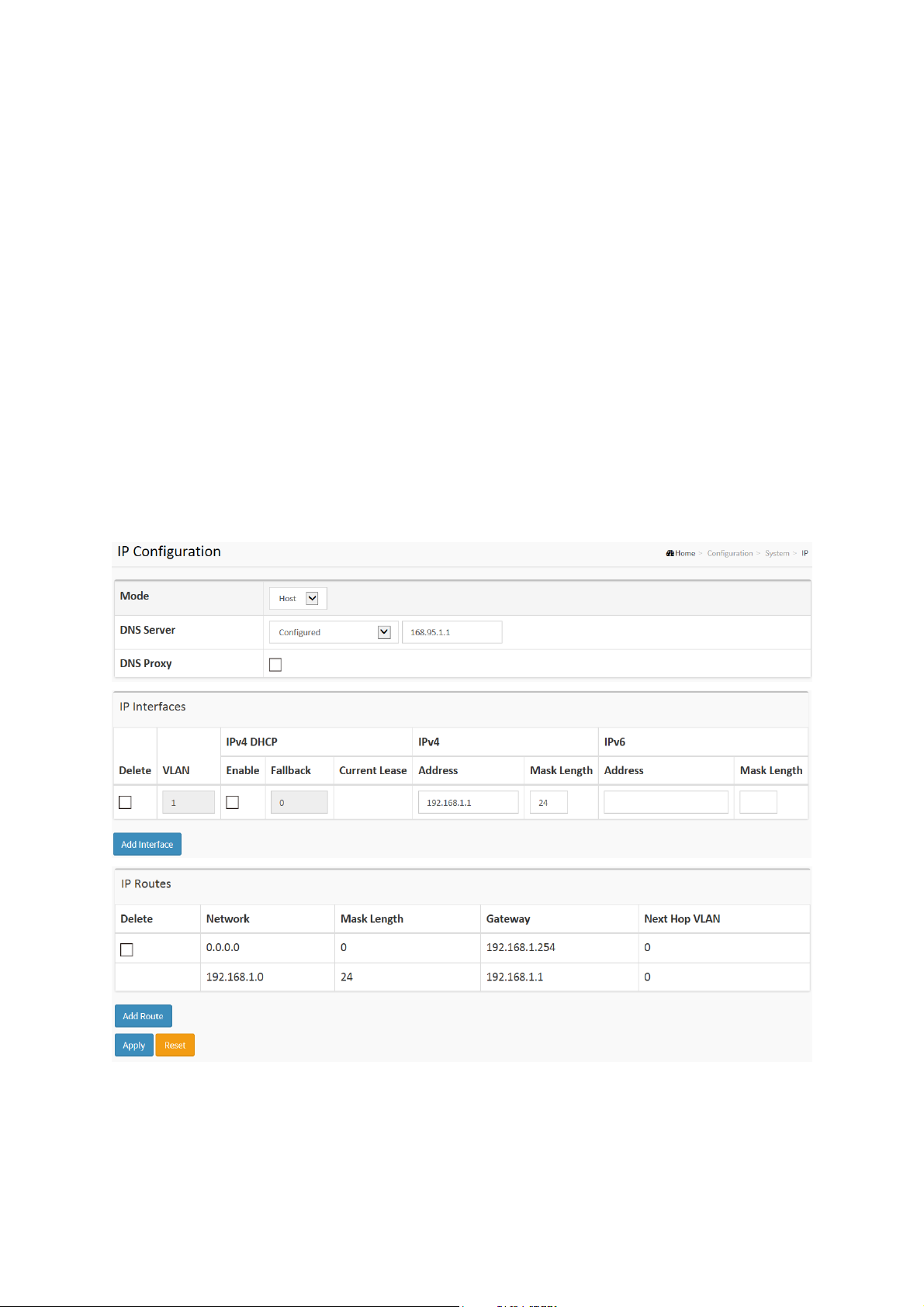
The IPv4 address for the switch could be obtained via DHCP Server for VLAN 1. To manually
configure an address, you need to change the switch's default settings to values that are
compatible with your network. You may also need to establish a default gateway between the
switch and management stations that exist on another network segment.
Configure the switch-managed IP information on this page
Configure IP basic settings, control IP interfaces and IP routes.
The maximum number of interfaces supported is 8 and the maximum number of routes is 32.
Web Interface
To configure an IP address in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, System, IP.
2. Click Add Interface then you can create new Interface on the switch.
3. Click Add Route then you can create new Route on the switch
4. Click Apply
Figure2-1.2: The IP configuration
Parameter description:
IP Configuration
Mode:
Configure whether the IP stack should act as a Host or a Router. In Host mode, IP traffic
between interfaces will not be routed. In Router mode traffic is routed between all
11
Publication date: Jan., 2016
Revision A2

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
interfaces.
DNS Server
This setting controls the DNS name resolution done by the switch. The following modes are
supported:
• From any DHCP interfaces
The first DNS server offered from a DHCP lease to a DHCP-enabled interface will be
used.
• No DNS server
No DNS server will be used.
• Configured
Explicitly provide the IP address of the DNS Server in dotted decimal notation.
• From this DHCP interface
Specify from which DHCP-enabled interface a provided DNS server should be
preferred.
DNS Proxy
When DNS proxy is enabled, system will relay DNS requests to the currently configured
DNS server, and reply as a DNS resolver to the client devices on the network.
IP Interfaces
Delete
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
Select this option to delete an existing IP interface.
VLAN
The VLAN associated with the IP interface. Only ports in this VLAN will be able to access
the IP interface. This field is only available for input when creating an new interface.
IPv4 DHCP Enabled
Enable the DHCP client by checking this box. If this option is enabled, the system will
configure the IPv4 address and mask of the interface using the DHCP protocol. The DHCP
client will announce the configured System Name as hostname to provide DNS lookup.
IPv4 DHCP Fallback Timeout
The number of seconds for trying to obtain a DHCP lease. After this period expires, a
configured IPv4 address will be used as IPv4 interface address. A value of zero disables
the fallback mechanism, such that DHCP will keep retrying until a valid lease is obtained.
Legal values are 0 to 4294967295 seconds.
IPv4 DHCP Current Lease
For DHCP interfaces with an active lease, this column show the current interface address,
as provided by the DHCP server.
IPv4 Address
The IPv4 address of the interface in dotted decimal notation.
If DHCP is enabled, this field is not used. The field may also be left blank if IPv4 operation
on the interface is not desired.
IPv4 Mask
The IPv4 network mask, in number of bits (prefix length). Valid values are between 0 and
30 bits for a IPv4 address.
If DHCP is enabled, this field is not used. The field may also be left blank if IPv4 operation
on the interface is not desired.
IPv6 Address
The IPv6 address of the interface. A IPv6 address is in 128-bit records represented as eight
fields of up to four hexadecimal digits with a colon separating each field (:). For example,
fe80::215:c5ff:fe03:4dc7. The symbol :: is a special syntax that can be used as a shorthand
way of representing multiple 16-bit groups of contiguous zeros; but it can appear only once.
It can also represent a legally valid IPv4 address. For example, ::192.1.2.34.
The field may be left blank if IPv6 operation on the interface is not desired.
IPv6 Mask

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
The IPv6 network mask, in number of bits (prefix length). Valid values are between 1 and
128 bits for a IPv6 address.
The field may be left blank if IPv6 operation on the interface is not desired.
IP Routes
Delete
Select this option to delete an existing IP route.
Network
The destination IP network or host address of this route. Valid format is dotted decimal
notationor a valid IPv6 notation. A default route can use the value 0.0.0.0or IPv6 :: notation.
Mask Length
The destination IP network or host mask, in number of bits (prefix length). It defines how
much of a network address that must match, in order to qualify for this route. Valid values
are between 0 and 32 bits respectively 128 for IPv6 routes. Only a default route will have a
mask length of 0 (as it will match anything).
Gateway
The IP address of the IP gateway. Valid format is dotted decimal notationor a valid IPv6
notation. Gateway and Network must be of the same type.
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
Next Hop VLAN (Only for IPv6)
The VLAN ID (VID) of the specific IPv6 interface associated with the gateway.
The given VID ranges from 1 to 4094 and will be effective only when the corresponding
IPv6 interface is valid.
If the IPv6 gateway address is link-local, it must specify the next hop VLAN for the gateway.
If the IPv6 gateway address is not link-local, system ignores the next hop VLAN for the
gateway.
Buttons
Add Interface:
Click to add a new IP interface. A maximum of 8 interfaces is supported.
Add Route:
Click to add a new IP route. A maximum of 32 routes is supported.
Apply:
Click to save changes.
Reset:
Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values.
ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-1.3 NTP
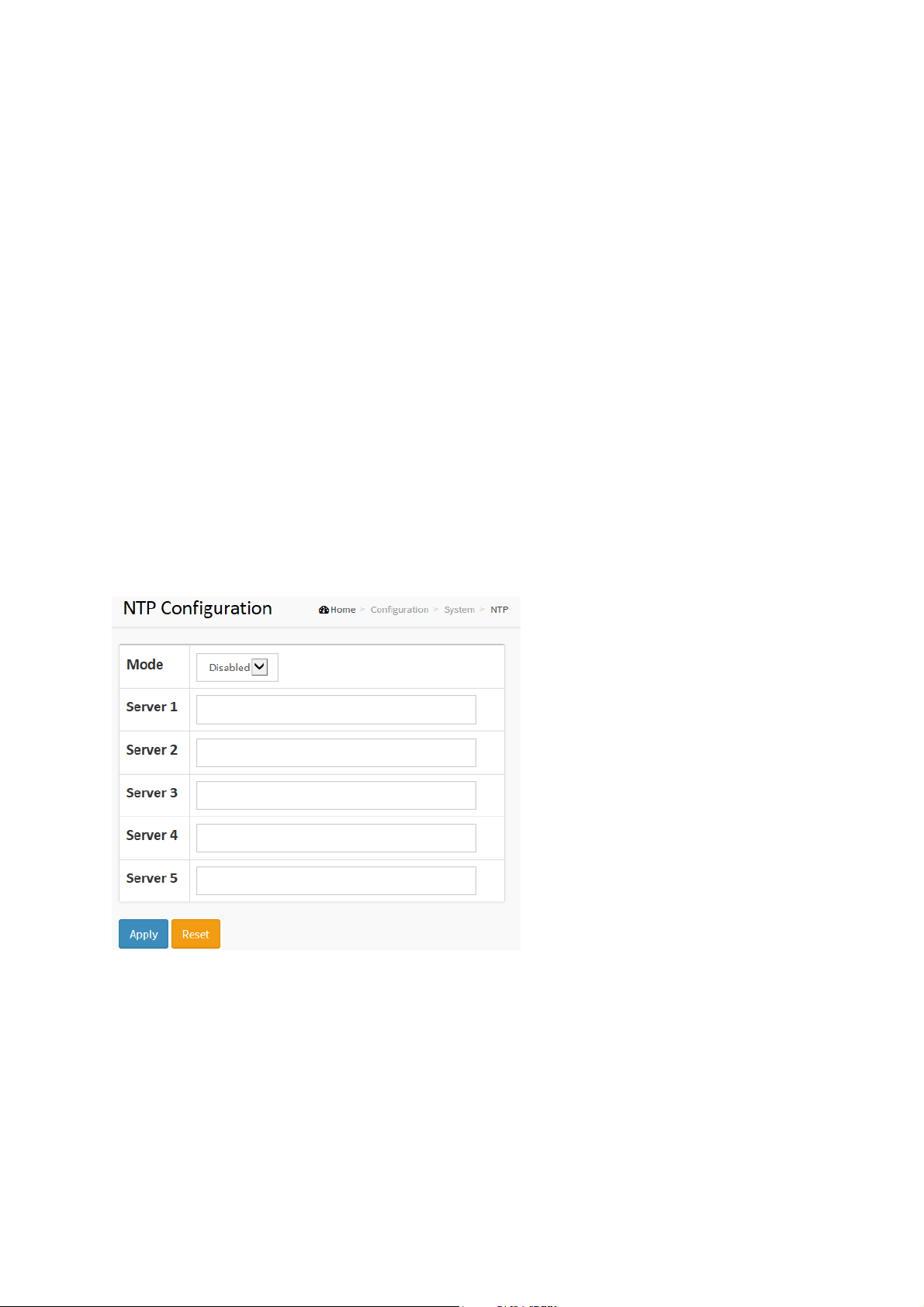
NTP is Network Time Protocol and is used to sync the network time based Greenwich Mean
Time (GMT). If use the NTP mode and select a built-in NTP time server or manually specify an
user-defined NTP server as well as Time Zone, the switch will sync the time in a short after
pressing <Apply> button. Though it synchronizes the time automatically, NTP does not update
the time periodically without user’s processing.
Time Zone is an offset time off GMT. You have to select the time zone first and then perform
time sync via NTP because the switch will combine this time zone offset and updated NTP time
to come out the local time, otherwise, you will not able to get the correct time. The switch
supports configurable time zone from –12 to +13 step 1 hour.
Default Time zone: +8 Hrs.
Web Interface
To configure NTP in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, System, NTP.
2. Specify the Time parameter in manual parameters.
3. Click Apply.
Figure 2-1.3: The NTP configuration
Parameter description:
Mode :
Indicates the NTP mode operation. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable NTP client mode operation.
Disabled: Disable NTP client mode operation.
Server 1 to 5 :
Provide the NTP IPv4 or IPv6 address of this switch. IPv6 address is in 128-bit
records represented as eight fields of up to four hexadecimal digits with a colon
separating each field (:). For example, 'fe80::215:c5ff:fe03:4dc7'. The symbol
'::' is a special syntax that can be used as a shorthand way of representing
multiple 16-bit groups of contiguous zeros; but it can only appear once. It can
also represent a legally valid IPv4 address. For example, '::192.1.2.34'.
ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
Buttons
These buttons are displayed on the NTP page:
Apply – Click to save changes.
Reset - Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
values.
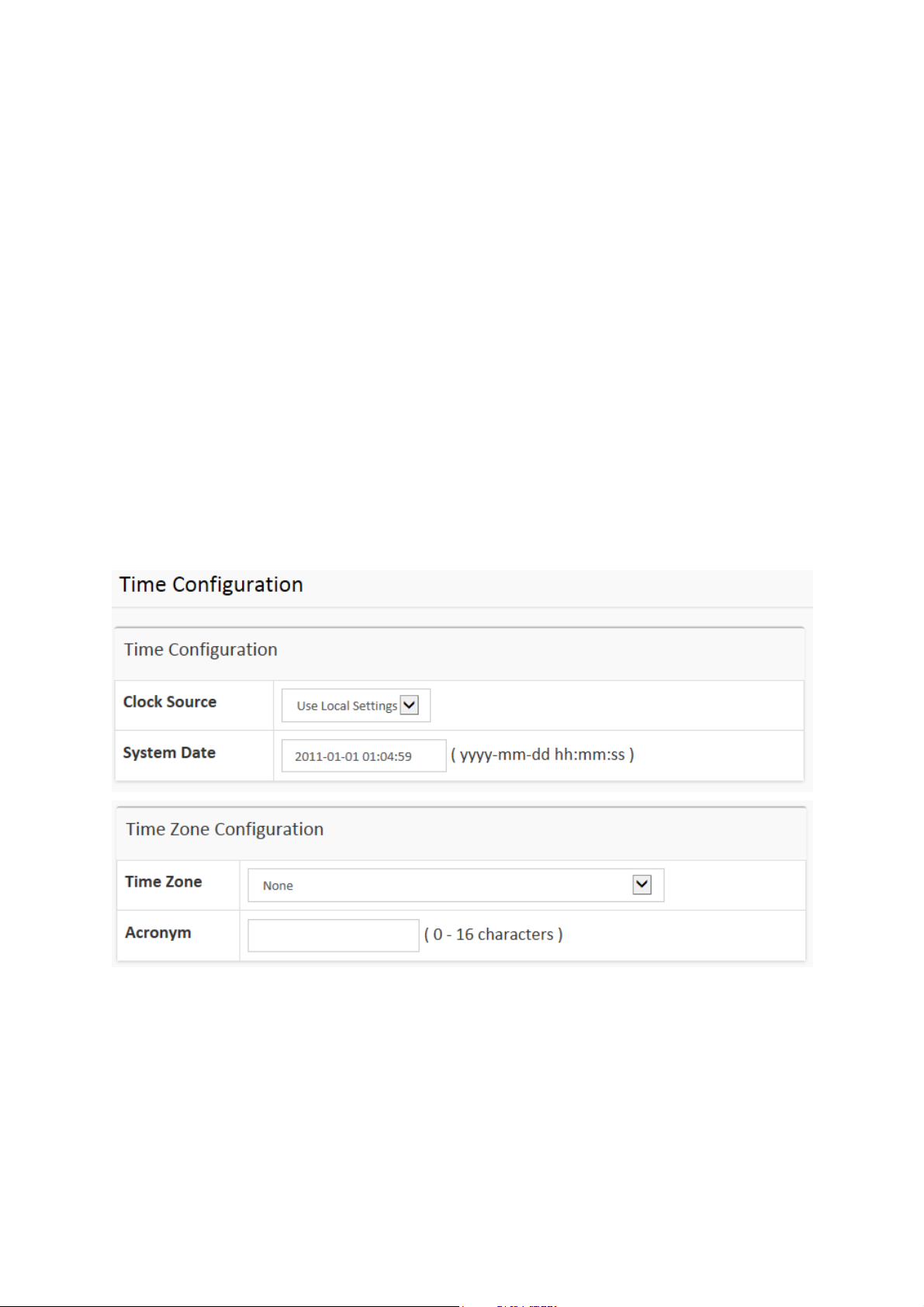
2-1.4 Time
The switch provides manual and automatic ways to set the system time via NTP. Manual
setting is simple and you just input “Year”, “Month”, “Day”, “Hour” and “Minute” within the valid
value range indicated in each item.
Web Interface
To configure Time in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, System and Time
2. Specify the Time parameter.
3. Click Apply.
Figure 2-1.4: The time configuration
ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
Parameter description:
Time Configuration
Clock Source:
There are two modes for configuring how the Clock Source from. Select "Use
Local Settings" : Clock Source from Local Time. Select "Use NTP Server" : Clock
Source from NTP Server.
System Date:
Show the current time of the system. The year of system date limits between
2011 and 2037.
Time Zone Configuration
Time Zone:
Lists various Time Zones world wide. Select appropriate Time Zone from the drop
down and click Apply to set.
Acronym:
User can set the acronym of the time zone. This is a User configurable acronym to
identify the time zone. ( Range : Up to 16 characters )
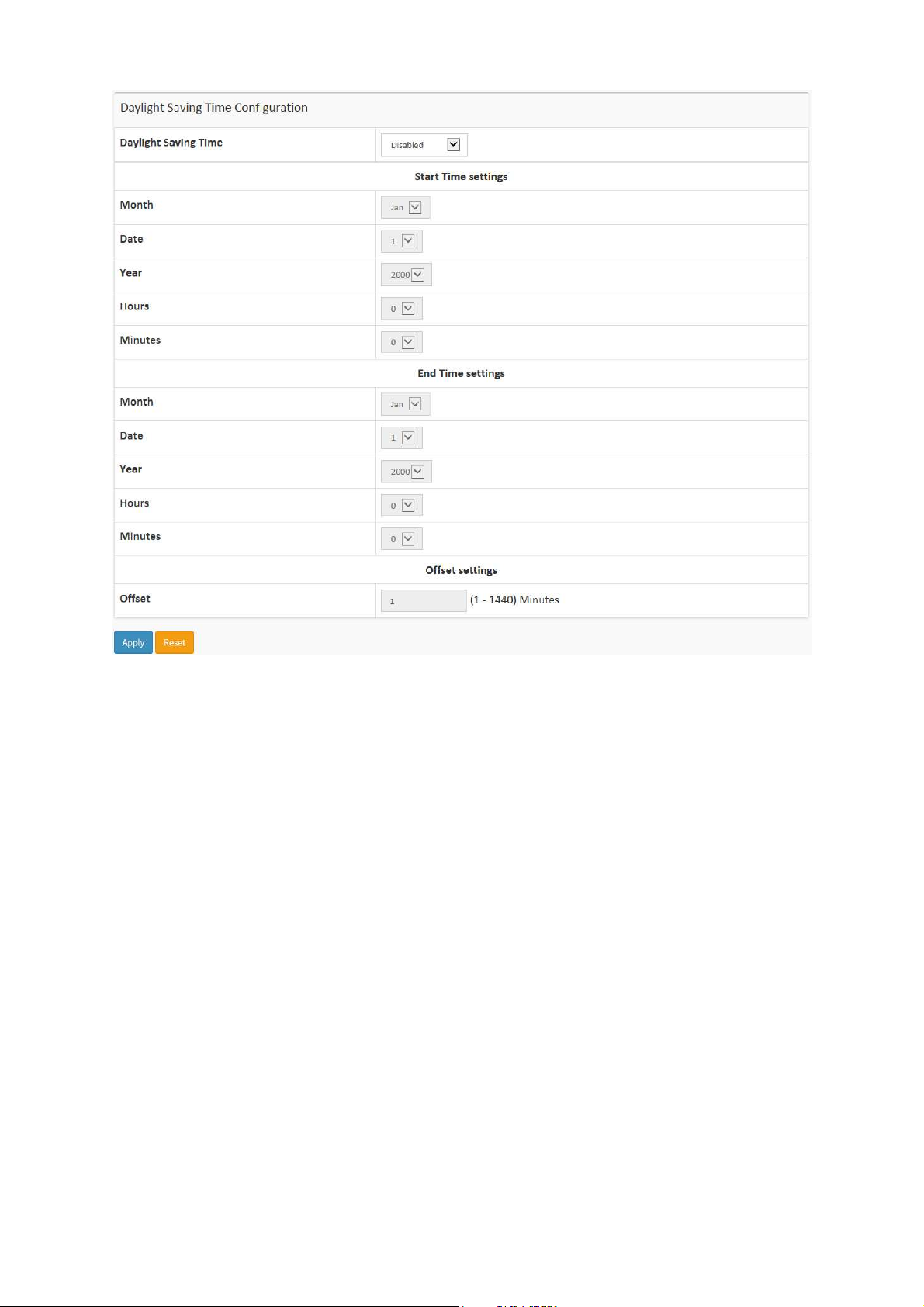
Daylight Saving Time Configuration
Daylight Saving Time:
This is used to set the clock forward or backward according to the configurations
set below for a defined Daylight Saving Time duration. Select 'Disable' to disable
the Daylight Saving Time configuration. Select 'Recurring' and configure the
Daylight Saving Time duration to repeat the configuration every year. Select
'Non-Recurring' and configure the Daylight Saving Time duration for single time
configuration. ( Default : Disabled ).

ET42202XM-S-PD
The under
“Start Time
S
ettings”
and
“End Time
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
Recurring Configuration
Start time settings:
Week - Select the starting week number.
Day - Select the starting day.
Month - Select the starting month.
Hours - Select the starting hour.
Minutes - Select the starting minute.
End time settings:
Week - Select the ending week number.
Day - Select the ending day.
Month - Select the ending month.
Hours - Select the ending hour.
Minutes - Select the ending minute.
Offset settings:
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
Offset - Enter the number of minutes to add during Daylight Saving Time. ( Range:
1 to 1440 )
Buttons
These buttons are displayed on the NTP page:
Apply – Click to save changes.
Reset - Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
N
OTE
:
Settings” was displayed what you set on the “Start Time
Settings” and “End Time Settings” field information.

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-1.5 Log
The log is a standard for logging program messages . It allows separation of the software that
generates messages from the system that stores them and the software that reports and
analyzes them. It can be used as well a generalized informational, analysis and debugging
messages. It is supported by a wide variety of devices and receivers across multiple platforms.
Web Interface
To configure log configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, System and log.
2. Specify the syslog parameters include IP Address of Syslog server and Port number.
3. Evoke the Syslog to enable it.
4. Click Apply.
Figure2-1.5: The System Log configuration
Parameter description:
Server Mode :
Indicate the server mode operation. When the mode operation is enabled, the
syslog message will send out to syslog server. The syslog protocol is based on
UDP communication and received on UDP port 514 and the syslog server will not
send acknowledgments back sender since UDP is a connectionless protocol and it
does not provide acknowledgments. The syslog packet will always send out even
if the syslog server does not exist. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable server mode operation.
Disabled: Disable server mode operation.
Server Address :
Indicates the IPv4 hosts address of syslog server. If the switch provide DNS
feature, it also can be a host name.
Syslog Level :
Indicates what kind of message will send to syslog server. Possible modes are:
Info: Send information, warnings and errors.
Warning: Send warnings and errors.
Error: Send errors.
Buttons
These buttons are displayed on the NTP page:
Apply – Click to save changes.
Reset - Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
values.
2-2 Green Ethernet
EEE is a power saving option that reduces the power usage when there is low or no traffic
utilization.
EEE works by powering down circuits when there is no traffic. When a port gets data to be
transmitted all circuits are powered up. The time it takes to power up the circuits is named
wakeup time. The default wakeup time is 17 us for 1Gbit links and 30 us for other link speeds.
EEE devices must agree upon the value of the wakeup time in order to make sure that both the
receiving and transmitting device has all circuits powered up when traffic is transmitted. The
devices can exchange wakeup time information using the LLDP protocol.
EEE works for ports in auto-negotiation mode, where the port is negotiated to either 1G or 100
Mbit full duplex mode.
For ports that are not EEE-capable the corresponding EEE checkboxes are grayed out and
thus impossible to enable EEE for.
When a port is powered down for saving power, outgoing traffic is stored in a buffer until the
port is powered up again. Because there are some overhead in turning the port down and up,
more power can be saved if the traffic can be buffered up until a large burst of traffic can be
transmitted. Buffering traffic will give some latency in the traffic.
Web Interface
To configure a Port Power Saving Configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Green Ethernet
2. Evoke to enable or disable the ActiPHY, PerfectReach, EEE and EEE Urgent Queues .
3. Click Apply.
Figure 2-2.1: The Port Power Saving Configuration
Parameter description:
Optimize EEE for
The switch can be set to optimize EEE for either best power saving or least traffic

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
latency.
Port:
The switch port number of the logical port.
ActiPHY :
Link down power savings enabled.
ActiPHY works by lowering the power for a port when there is no link. The port is
power up for short moment in order to determine if cable is inserted.
PerfectReach :
Cable length power savings enabled.
PerfectReach works by determining the cable length and lowering the power for
ports with short cables.
EEE :
Controls whether EEE is enabled for this switch port.
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
For maximizing power savings, the circuit isn't started at once transmit data is
ready for a port, but is instead queued until a burst of data is ready to be
transmitted. This will give some traffic latency.
If desired it is possible to minimize the latency for specific frames, by mapping the
frames to a specific queue (done with QOS), and then mark the queue as an
urgent queue. When an urgent queue gets data to be transmitted, the circuits will
be powered up at once and the latency will be reduced to the wakeup time.
2-3 Ports Configuration
The section describes to configure the Port detail parameters of the switch. Others you could
using the Port configure to enable or disable the Port of the switch. Monitor the ports content or
status in the function.
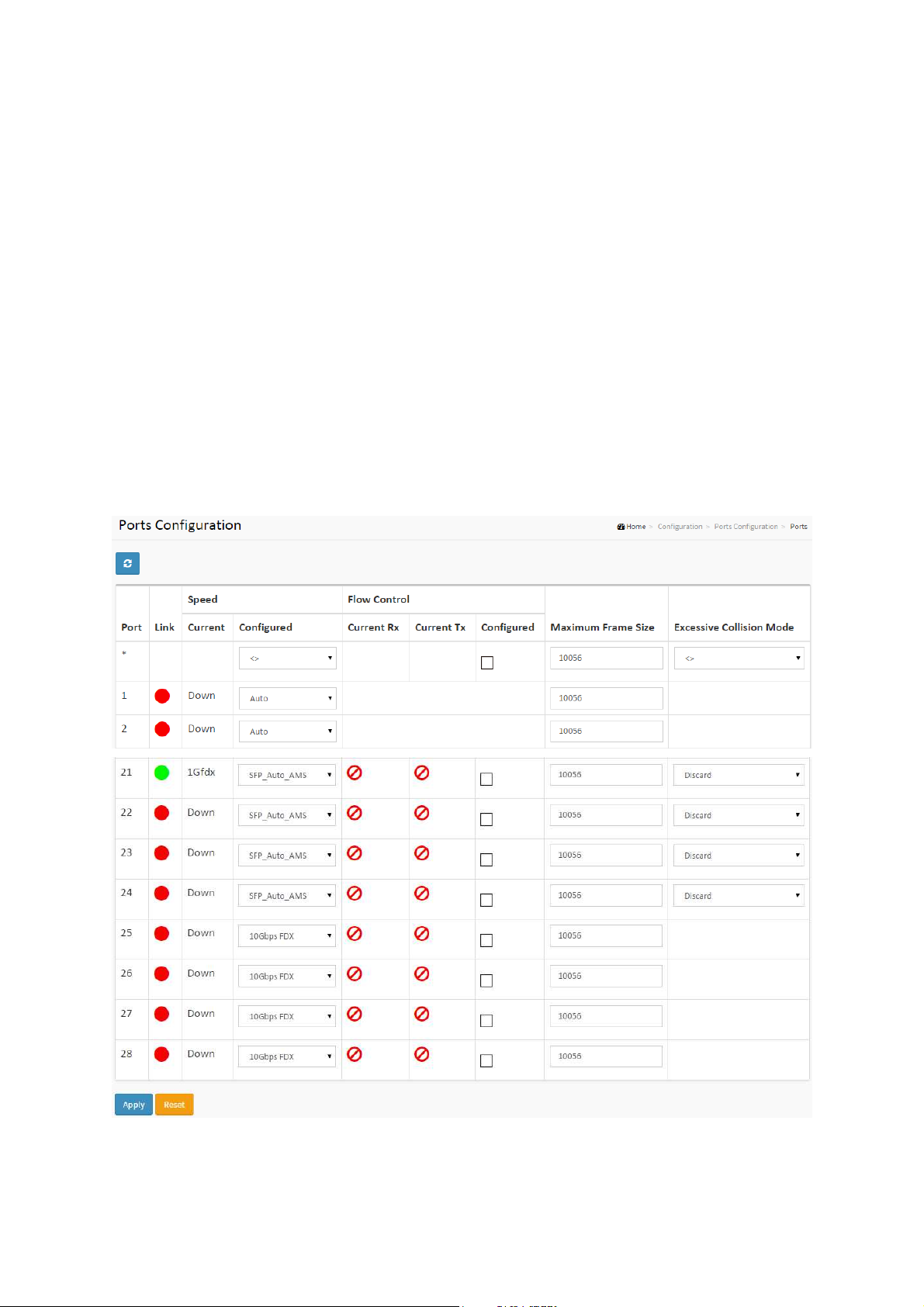
2-3.1 Ports
This page displays current port configurations. Ports can also be configured here.
Web Interface
To configure a Current Port Configuration in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Ports Configuration, and Ports
2. Specify the Speed Configured, Flow Control, Maximum Frame size, Excessive Collision
mode and Power Control.
3. Click Apply.
Figure 2-3.1: The Port Configuration
Parameter description:
Port :
This is the logical port number for this row.

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
Link :
The current link state is displayed graphically. Green indicates the link is up and
red that it is down.
Current Link Speed :
Provides the current link speed of the port.
Configured Link Speed :
Selects any available link speed for the given switch port. Only speeds supported
by the specific port is shown. Possible speeds are:
Disabled - Disables the switch port operation.
Auto - Port auto negotiating speed with the link partner and selects the highest
speed that is compatible with the link partner.
10Mbps HDX - Forces the cu port in 10Mbps half duplex mode.
10Mbps FDX - Forces the cu port in 10Mbps full duplex mode.
100Mbps HDX - Forces the cu port in 100Mbps half duplex mode.
100Mbps FDX - Forces the cu port in 100Mbps full duplex mode.
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
1Gbps FDX - Forces the port in 1Gbps full duplex
SFP_Auto_AMS - Automatically determines the speed of the SFP. Note: There is
no standardized way to do SFP auto detect, so here it is done by reading the SFP
rom. Due to the missing standardized way of doing SFP auto detect some SFPs
might not be detectable. The port is set in AMS mode. Cu port is set in Auto mode.
100-FX - SFP port in 100-FX speed. Cu port disabled.
100-FX_AMS - Port in AMS mode. SFP port in 100-FX speed. Cu port in Auto
mode.
1000-X - SFP port in 1000-X speed. Cu port disabled.
1000-X_AMS - Port in AMS mode. SFP port in 1000-X speed. Cu port in Auto mode.
Ports in AMS mode with 1000-X speed has Cu port preferred. Ports in AMS mode
with 100-FX speed has fiber port preferred.
Flow Control :
When Auto Speed is selected on a port, this section indicates the flow control
capability that is advertised to the link partner. When a fixed-speed setting is
selected, that is what is used. The Current Rx column indicates whether pause
frames on the port are obeyed, and the Current Tx column indicates whether
pause frames on the port are transmitted. The Rx and Tx settings are determined
by the result of the last Auto-Negotiation.
Check the configured column to use flow control. This setting is related to the
setting for Configured Link Speed.
Maximum Frame Size :
Enter the maximum frame size allowed for the switch port, including FCS.
Excessive Collision Mode :
Configure port transmit collision behavior.
Discard: Discard frame after 16 collisions (default).
Restart: Restart backoff algorithm after 16 collisions.
Buttons
Apply – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
Upper right icon (Refresh)
You can click them for refresh the Port link Status by manual
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-3.2 Ports Description
The section describes to configure the Port’s alias or any descriptions for the Port Identity. It
provides user to write down an alphanumeric string describing the full name and version
identification for the system’s hardware type, software version, and networking application
Web Interface
To configure an Port Description in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, Port, then Port Description
2. Specify the detail Port alias or description an alphanumeric string describing the full name
and version identification for the system’s hardware type, software version, and
networking application.
3. Click Apply.
Figure 2-3.1: The Port Configuration
Parameter description:
Port :
This is the logical port number for this row.
Description :
Enter up to 47 characters to be descriptive name for identifies this port.
Buttons
Apply – Click to save changes.
Reset- Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.
ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-4DHCP
The section describes to configure the DHCP Snooping parameters of the switch. The DHCP
Snooping can prevent attackers from adding their own DHCP servers to the network.
2-4.1 Server
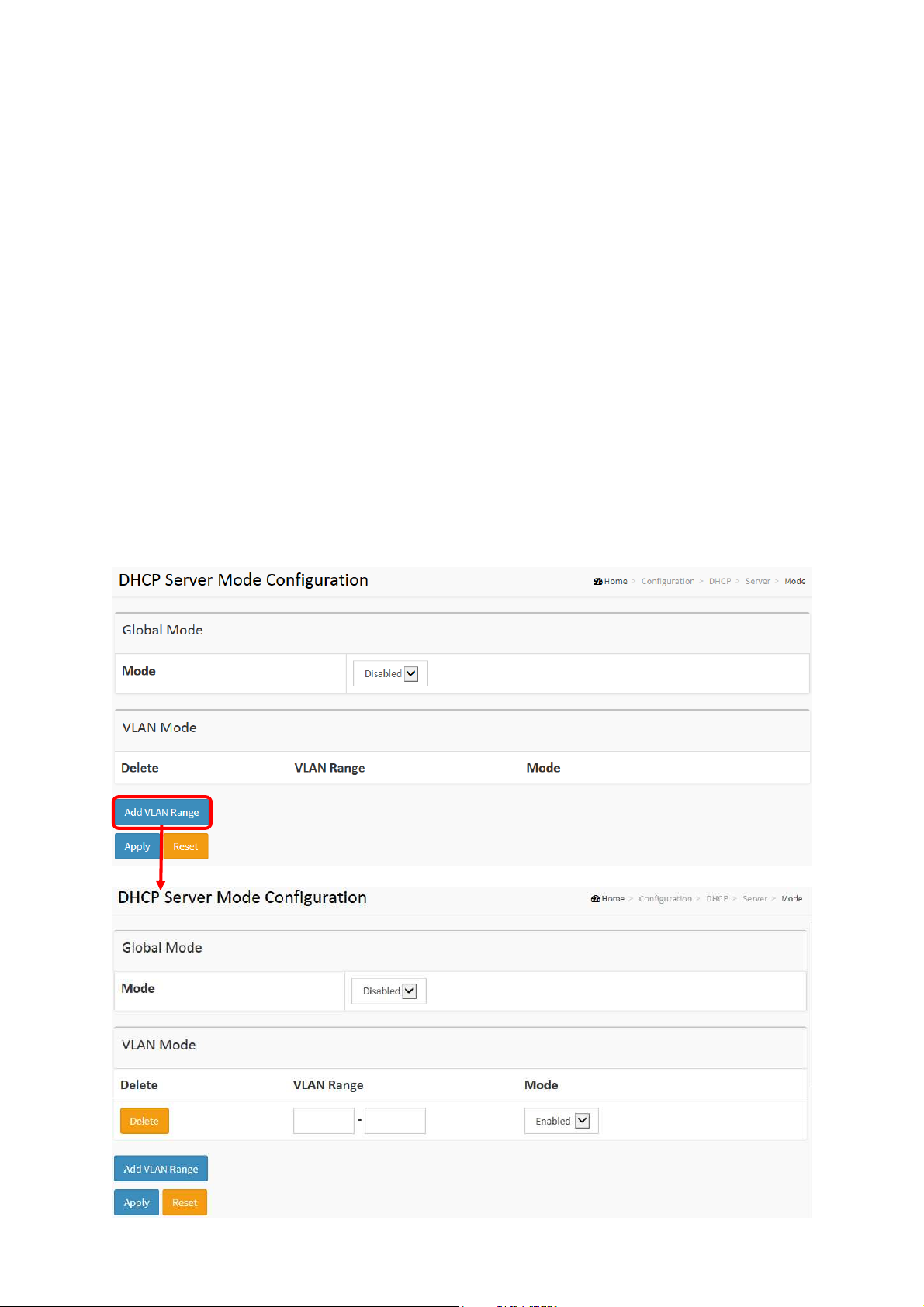
2-4.1.1 Mode
This page configures global mode and VLAN mode to enable/disable DHCP server per system
and per VLAN.
Web Interface
To configure DHCP server mode in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, DHCP, Server, Mode
2. Select “Enabled” in the Global Mode of DHCP Server Mode Configuration.
3. Add Vlan range.
4. Click Apply.
Figure 2-4.1.1: The DHCP server Mode
Parameter description:

ET42202XM-S-PD
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
Mode :
Configure the operation mode per system. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable DHCP server per system.
Disabled: Disable DHCP server pre system.
VLAN Range :
Indicate the VLAN range in which DHCP server is enabled or disabled. The first VLAN ID must be
smaller than or equal to the second VLAN ID. BUT, if the VLAN range contains only 1 VLAN ID, then
you can just input it into either one of the first and second VLAN ID or both.
On the other hand, if you want to disable existed VLAN range, then you can follow the steps.
1. press “ADD VLAN Range” to add a new VLAN range.
2. input the VLAN range that you want to disable.
3. choose Mode to be Disabled.
4. press Apply to apply the change.
Then, you will see the disabled VLAN range is removed from the DHCP Server mode configuration
page.
Mode :
Indicate the the operation mode per VLAN. Possible modes are:
Enabled: Enable DHCP server per VLAN.
Disabled: Disable DHCP server pre VLAN.
Buttons
Add VLAN Range - Click to add a new VLAN range.
Apply – Click to save changes.
Reset - Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-4.1.2 Excluded IP
This page configures excluded IP addresses. DHCP server will not allocate these
excluded IP addresses to DHCP client.
Web Interface
To configure DHCP server excluded IP in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, DHCP, Server, Excluded IP
2. Click Add IP Range then you can create new IP Range on the switch.
3. Click Apply.
Figure 2-4.1.2: The DHCP server excluded IP
Parameter description:
IP Range :
Define the IP range to be excluded IP addresses. The first excluded IP must be smaller than or equal
to the second excluded IP. BUT, if the IP range contains only 1 excluded IP, then you can just input it to
either one of the first and second excluded IP or both.
Buttons
Add IP Range - Click to add a new excluded IP range.
Apply – Click to save changes.
Reset - Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved
values.

ET42202XM-S-PD
or 100/1000Base-FX SFP Combo + 4-port 1000/10GBase-FX SFP Optical Ethernet Switch, AC + DC
power inputs
L2+ Managed 20-port 100/1000Base-FX SFP + 4-port 10/100/1000Base-TX
2-4.1.3 Pool
This page manages DHCP pools. According to the DHCP pool, DHCP server will
allocate IP address and deliver configuration parameters to DHCP client.
Web Interface
To configure DHCP server pool in the web interface:
1. Click Configuration, DHCP, Server, Pool
2. Click Add New Pool then you can create new Pool on the switch.
3. Click Apply.
Figure 2-4.1.1: The DHCP server pool
Parameter description:
Pool Setting
Add or delete pools.
Adding a pool and giving a name is to create a new pool with "default"
configuration. If you want to configure all settings including type, IP subnet mask
and lease time, you can click the pool name to go into the configuration page.
Name :
Configure the pool name that accepts all printable characters, except white space. If you want to
configure the detail settings, you can click the pool name to go into the configuration page.
Type :
Display which type of the pool is.
Network: the pool defines a pool of IP addresses to service more than one DHCP client.
Host: the pool services for a specific DHCP client identified by client identifier or hardware address.
 Loading...
Loading...