AMD Advanced Micro Devices AM28F020A-200JCB, AM28F020A-200FIB, AM28F020A-200FI, AM28F020A-200FEB, AM28F020A-200FE Datasheet
...
FINAL
Am28F020A
2 Megabit (256 K x 8-Bit)
CMOS 12.0 Volt, Bulk Erase Flash Memory with Embedded Algorithms
■
DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS
■
High performance
— Access times as fast as 70 ns
■
CMOS low power consumption
— 30 mA max imum active current
— 100 µA maximum standby current
— No data retention power consumption
■
Compatible with JEDEC-standard byte-wide
32-pin EPROM pinouts
— 32-pin PDIP
— 32-pin PLCC
— 32-pin TSOP
■
100,000 write/erase cycles minimum
■
Write and erase voltage 12.0 V ±5%
Latch-up protected to 100 mA from
–1 V to V
■
Embedded Erase Electrical Bulk Chip Erase
— Five seconds typical chip erase, including
pre-programming
■
Embedded Program
— 14 µs typical byte program, including time-out
— 4 seconds typical chip program
■
Command regist er architecture for
microprocessor/microcontroller compatible
write interface
■
On-chi p add r es s and dat a latches
■
Advanced CMOS flash memory technology
— Low cost single transistor memory cell
■
Embed ded al gori thms f or com plet ely self -ti med
write /er as e op er a tio n s
CC
+1 V
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Am 28F02 0A is a 2 Mega bit F lash me mor y orga nize d as 25 6 Kb y tes of 8 bit s ea ch. AM D’s Flash memories offer the most cost-effective and reliable read/
write non-volat ile random access memory. The
Am28F020A is packaged in 32-pin PDIP, PLCC, and
TSOP v ers ions . It i s des ign ed to be repr ogr amme d and
erased in-system or in standard EPROM programmers.
The Am28F020A is erased when shipped from
the factory.
The standard Am28F020A offers access times of as
fast as 70 ns, allow ing h igh s peed m icr oproc esso rs to
operate without wait states. To eliminate bus contention, the device has separate chip enable (CE#) and
output enable (OE#) controls.
AMD’s Flash memories augment EPROM funct ionality
with i n-circuit elec trical e rasure and programming. The
Am28F020A uses a command register to manage this
functionality. The command register allows for 100%
TTL level control inputs and fixed power supply levels
during erase and programming, while maintaining
maximum EPROM compatibility.
The Am28F020A is compatible with the AMD
Am28F256A, Am28F512A, and Am28F010A Flash
memor ies. A ll devices in the Am28Fx xx family follow
the JEDEC 32-pin pinout standard. In addition, all
devices within this family that offer Embedded Algorithms use the same command set. This offers
designers the flexibility to retain the same device footprint and command set, at any density between
256 Kbits and 2 Mbits.
AMD’s Flash technology reliably stores memory contents even after 100,000 erase and program cycles.
The AMD cell is designed to optimize the erase and
programming mechanisms. In addition, the combination of advanced tunnel oxide processing and low
internal ele ctric fiel ds f or er ase an d prog ra mming operations produce s reliab le cyc ling. The Am28F0 20A uses
a 12.0±5% VPP supply in put to p erfor m the e rase an d
programming functions.
The highest degree of latch-up protection is achieved
with AMD’s prop r ietary non -e pi pr oc e ss. Lat ch- up pro tection is provided for stresses up to 100 mA on
address and data pins from –1 V to VCC +1 V.
AMD’s Flash technology combines years of EPROM
and EEPROM experience to produce the highest levels
of quality, reliability, and cost effectiveness. Th e
Am28F0 20A elec trica lly era ses a ll bits simult ane ously
using Fowler-Nordheim t unneling. The bytes are
programmed one byte at a time using the EPROM
programming mechanism of hot electron injection.
Publication#
Issu e Date:
Rev: DAmendment/
17502
January 1998
+1
Embedded Program
The Am28F020A is byte programmable using the
Embedde d P ro gram algorithm, whi c h do es no t req uir e
the system to tim e- out o r verif y th e da ta progra mmed .
The typi cal r oom te mper at ure pr og ram ming time of this
device is four seconds.
Comparing Embedded Algorithms with Flasherase and Flashrite Algorithms
Embedded Erase
The entire device is bulk erased using the Embedded
Erase al gorithm , which au tomaticall y program s the
entire array prior to electrical erase. The timing and verification of electrical erase are controlled internal to the
devi ce . Typical er asu re tim e at ro om te mper at ure is fiv e
seconds, including preprogramming.
Embedded
Programming
Algorithm vs.
Flashrite
Programming
Algorithm
Embedded Erase
Algorithm vs.
Flasherase Erase
Algorithm
Am28F020A with
Embedded Algorithms
AMD’s Embedded Programming algorithm
requires the user to only write a program
set-up command and a program command
(program data and address). The device
automatically times the programming
pulse width, verifies the programming, and
counts the number of sequences. A status
bit, Data# Polling, provides the user with
the programming operation status.
AMD’s Embedded Erase algorithm
requires the user to only write an erase setup command and erase command. The
device automatically pre-programs and
verifies the entire array. The device then
automatically times the erase pulse width,
verifies the erase operation, and counts
the number of sequences. A status bit,
Data# Polling, provides the user with the
erase operation status.
Am28F020 using AMD Flashrite
and Flasherase Algorithms
The Flashrite Programming algorithm requires the
user to write a program set-up command, a program
command, (program data and address), and a
program verify command, followed by a read and
compare operation. The user is required to time the
programming pulse width in order to issue the
program verify command. An integrated stop timer
prevents any possibility of overprogramming.
Upon completion of this sequence, the data is read
back from the device and compared by the user with
the data intended to be written; if there is not a
match, the sequence is repeated until there is a
match or the sequence has been repeated 25 times.
The Flasherase Erase algorithm requires the device
to be completely programmed prior to executing an
erase command.
To invoke the erase operation, the user writes an
erase set-up command, an erase command, and an
erase verify command. The user is required to time
the erase pulse width in order to issue the erase
verify command. An integrated stop timer prevents
any possibility of overerasure.
Upon completion of this sequence, the data is read
back from the device and compared by the user with
erased data. If there is not a match, the sequence is
repeated until there is a match or the sequence has
been repeated 1,000 times.
Commands are written to the c ommand reg ister u si ng
standard microprocessor write timings. Register contents serve as input to an internal state-machine,
which controls the erase and programming cir cuitry.
During write cycles, the command register internally
latches addresses and data needed for the programming and erase operations. For system design
simplification, the Am28F010A is designed to support
either WE# or CE# controlled writes. During a system
write cycle, addresses are latched on the falling edge
of WE# or CE#, whichever occurs last. Data is latched
on the rising edge of WE# or CE#, whichever occurs
first. To simplify the following discussion, the WE# pin
is used as the write cycle control pin throughout the
rest of this text. All setup and hold times are with
respect to the WE# signal.
2 Am28F020A
PRODUCT SELECTOR GUIDE
g
g
Family Part Number
Speed Options (V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 10%)
-70 -90 -120 -150 -200
Am28F020A
Max Access Time (ns) 70 90 120 150 200
CE# (E#) Access (ns) 70 90 120 150 200
OE# (G#) Access (ns) 35 35 50 55 55
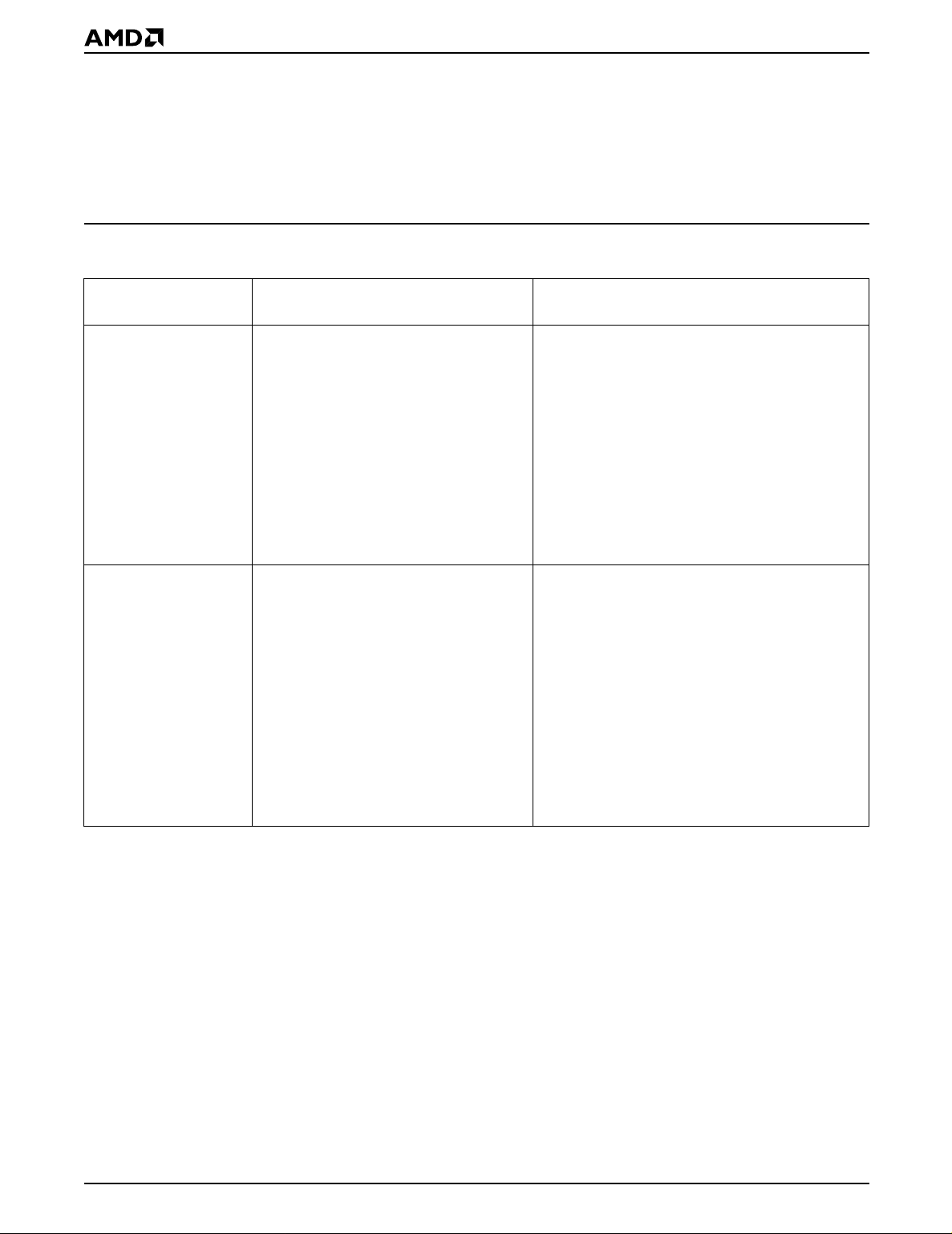
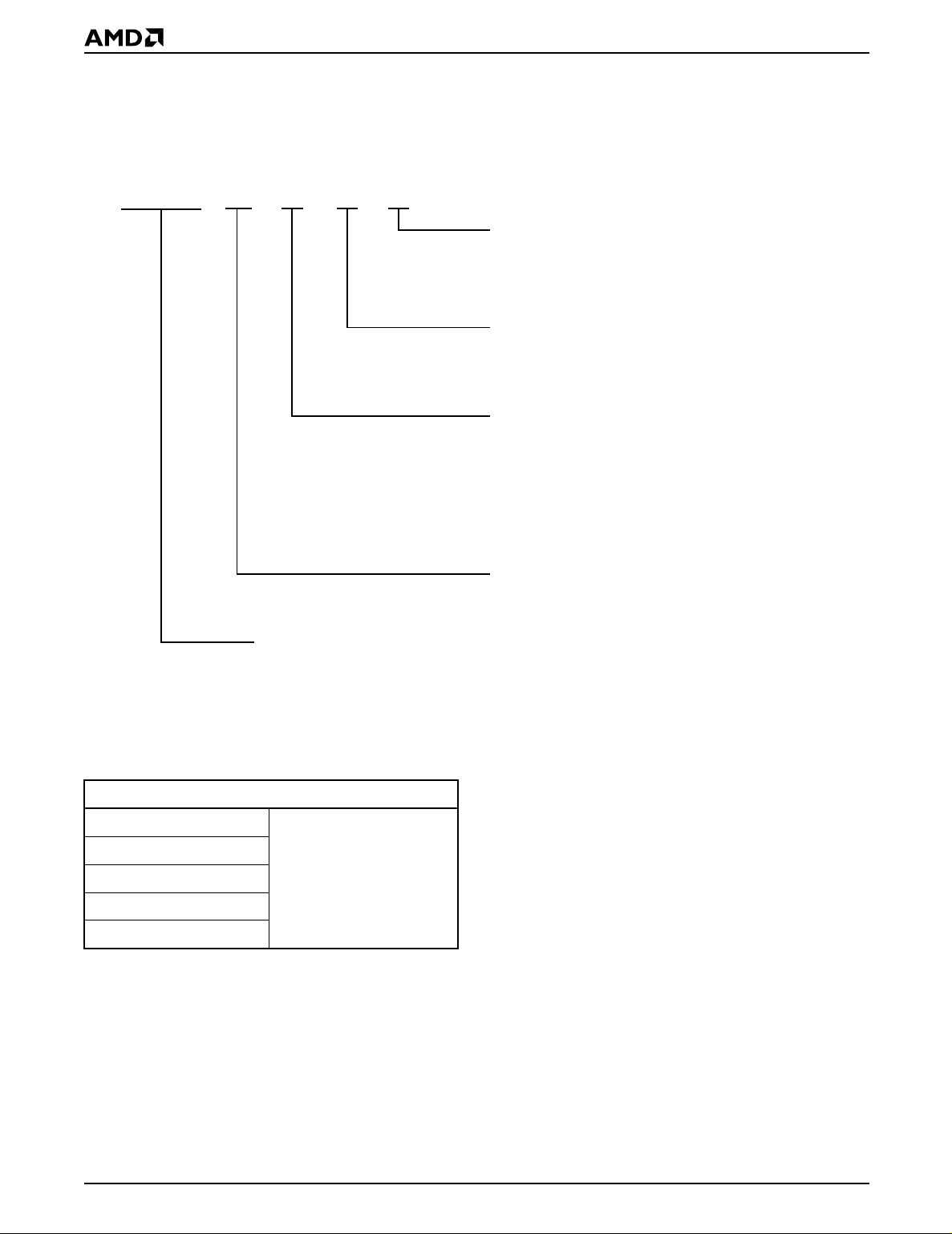
BLOCK DIAGRAM
DQ0–DQ7
V
CC
V
SS
V
PP
WE#
CE#
OE#
State
Control
Command
Re
ister
Program
Volta
Switch
Erase
Voltage
Switch
Input/Output
Buffers
To Array
e
Chip Enable
Output Enable
Logic
A0–A17
Low VCC
Detector
Embedded
Algorithms
Program/Erase
Pulse Timer
Address Latch
Y-Decoder
X-Decoder
Data Latch
Y-Gating
2,097,152
Bit
Cell Matrix
17502D-1
Am28F020A 3
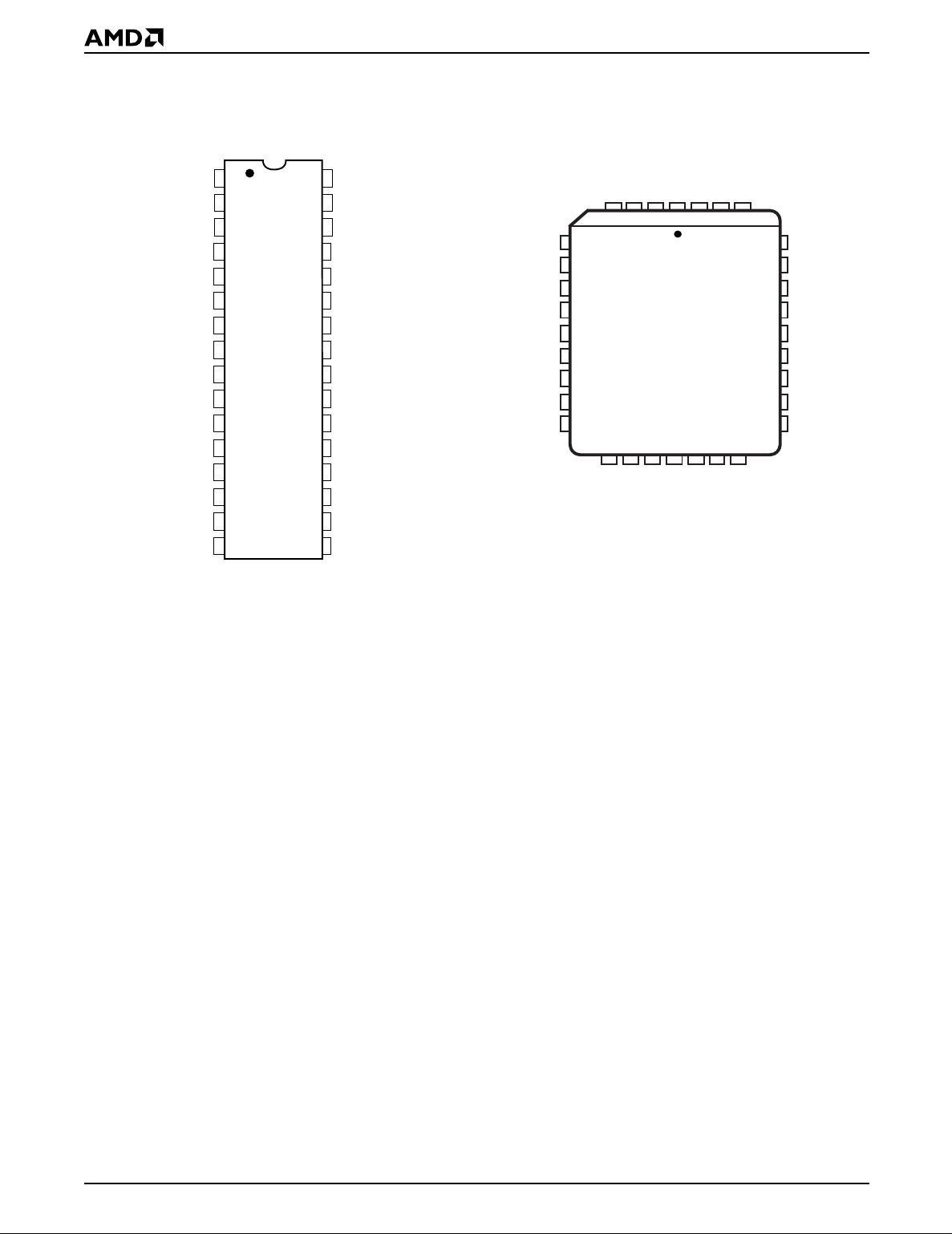
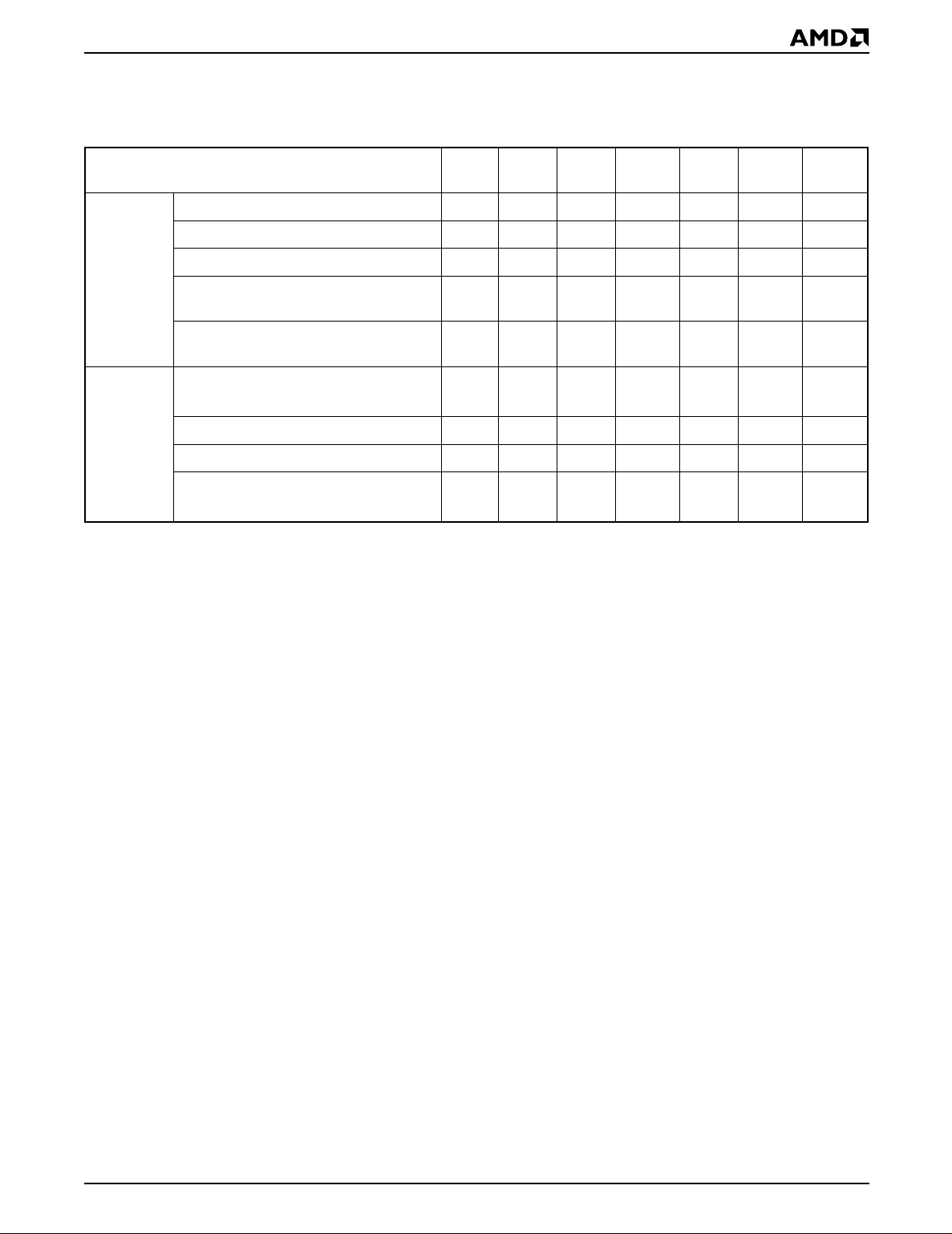
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
V
PP
A16
A15
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
V
SS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
PDIP
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
V
CC
WE# (W#)
A17
A14
A13
A8
A9
A11
OE# (G#)
A10
CE# (E#)
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
17502D-2
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
DQ0
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A12
4
DQ1
3
15
DQ2
PLCC
A16
A15
2
17
VSS
1
DQ3
VPP
32
18
DQ4
WE# (W#)
VCC
31 30
19 2016
DQ5
A17
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
DQ6
A14
A13
A8
A9
A11
OE# (G#)
A10
CE# (E#)
DQ7
17502D-3
Note: Pin 1 is marked for orientation.
4 Am28F020A
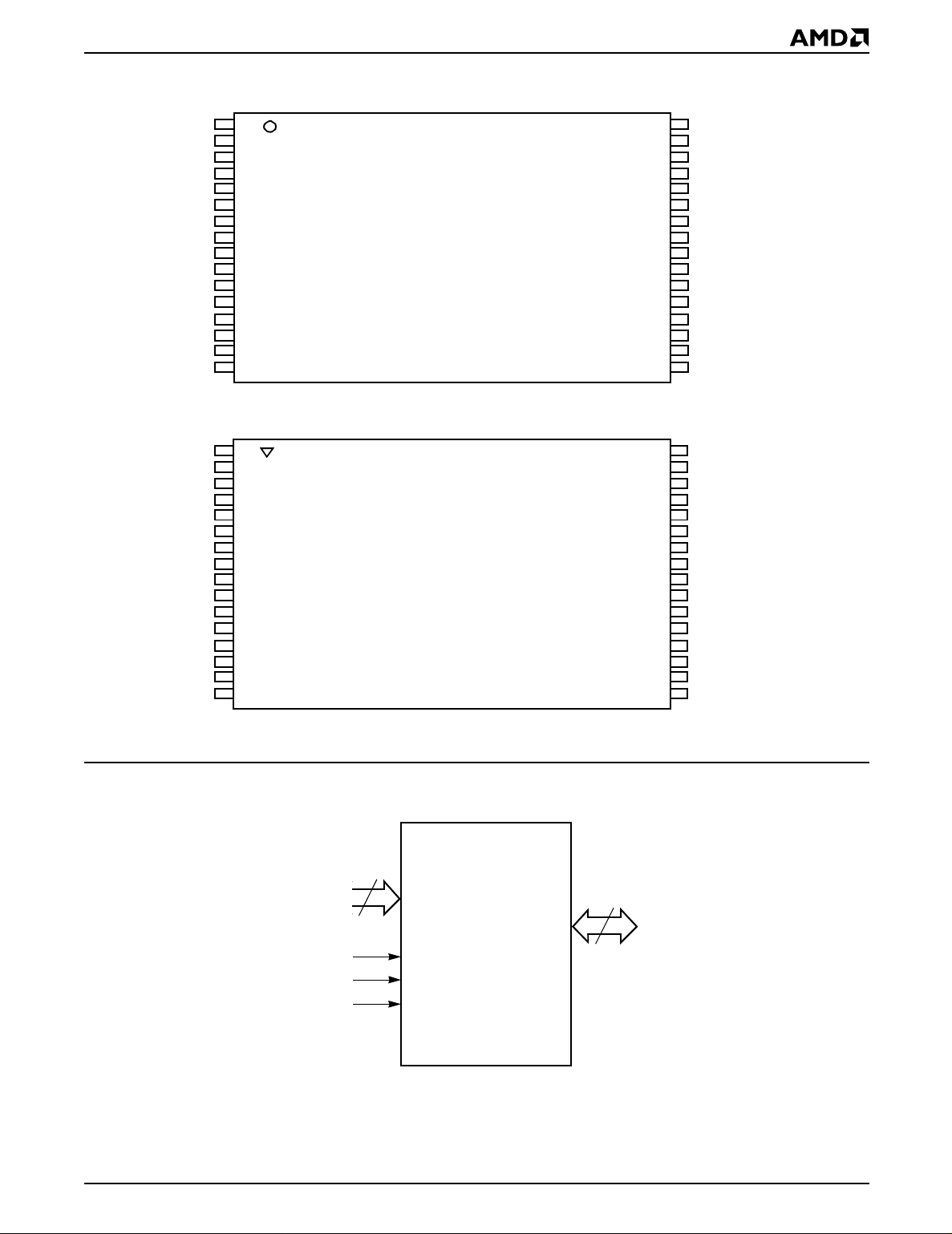
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS (Contin ued)
A11
A9
A8
A13
A14
A17
WE#
V
CC
V
PP
A16
A15
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
OE#
A10
CE#
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
V
SS
D2
D1
D0
A0
A1
A2
A3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
32-Pin TSOP—Standard Pinout
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
OE#
A10
CE#
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
V
SS
D2
D1
D0
A0
A1
A2
A3
A11
A9
A8
A13
A14
A17
WE#
V
CC
V
PP
A16
A15
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
LOGIC SYMBOL
32-Pin TSOP—Reverse Pinout
18
A0–A17
DQ0–DQ7
CE# (E#)
OE# (G#)
WE# (W#)
17502D-4
8
17502D-5
Am28F020A 5
ORDERIN G IN FOR MATION
Standard Products
AMD standard pro ducts are avail able in several packages and operating rang es. The order ing number (Va lid Combinatio n) is
formed by a combination of the following:
AM28F020A -70 J C
DEVICE NUMBER/DESCRIPTION
Am28F020A
2 Megabit (256 K x 8-Bit) CMOS Flash Memory with Embedded Algorithms
B
OPTIONAL PROCESSING
Blank = Standard Processing
B = Burn-In
Contact an AMD representative for more information.
TEMPERATURE RANGE
C = Commercial (0°C to +70°C)
I = Industrial (–40°C to +85°C)
E = Extended (–55°C to +125°C)
PACKAGE TYPE
P = 32-Pin Plastic DIP (PD 032)
J = 32-Pin Rectangular Plastic Leaded Chip
Carrier (PL 032)
E = 32-Pin Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP)
Standard Pinout (TS 032)
F = 32-Pin Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP)
Reverse Pinout (TSR032)
SPEED OPTION
See Product Selector Guide and Valid Combinations
Valid Combinations
AM28F020A-70
AM28F020A-90
AM28F020A-120
AM28F020A-150
AM28F020A-200
PC, PI, PE,
JC, JI, JE,
EC, EI, EE,
FC, FI, FE
Valid Combinations list configurations planned to be supported in volume for this device. Consult the local AMD sales office to confirm availab ility of specific val id combination s and
to check on newly released combinations.
6 Am28F020A
Valid Combinations

PIN DESCRIPTION
A0–A17
Address In puts for memor y lo cations. Inte rnal la tches
hold addresses during write cycles.
CE# (E#)
Chip Enable active low input activates the chip’s control
logic and input buffers. Chip Enable high will deselect
the device and operates the chip in stand-by mode.
DQ0–DQ7
Data Inputs during memory write cycles. Internal
latches hold data during write cycles. Data Outputs
during memory read cycles.
NC
No Conn ect- corre spond ing pin i s no t conn ec ted in ternally to the die.
OE# (G#)
Output Enable active low input gates the outputs of
the device th rough the da ta buffers during me mor y
read cycles. Output Enable is high during command
sequencing and program/erase operations.
V
PP
Program voltage input. VPP must be at hi gh voltag e in
order to write to the command register. The command
register controls all functions required to alter the memory array contents. Memory contents cannot be altered
when VPP ≤ VCC +2 V.
V
CC
Po w er supp ly for de vi ce oper at ion . (5.0 V ± 5% or 10%)
V
SS
Ground.
WE# (W#)
Write Enable active low input controls the write function
of the command register to the memory array. The target address is latched on the falling edge of the Write
Enable pulse and the appropriate data is latched on the
rising edg e of t he pul se. Writ e E nabl e h igh i nhi bit s wri ting to the device.
Am28F020A 7

BASIC PRINCIPLES
The Am28FxxxA family uses 100% TTL-level control
inputs to manage the command regi ster. Erase and
reprogramming op erations use a fixed 12.0 V ± 5%
high voltage input.
Read Only Memory
Without high VPP voltage, the device functions as a
read only memory and operates like a standard
EPROM. Th e control inpu ts still ma nage traditi onal
read, standby, output disable, and Auto select modes.
Command Register
The command register is enabled only when high voltage is applied to the VPP pin. The erase and reprogramming operations are only accessed via the
register. In addition, two-cycle commands are required
for erase and reprogramming op erations. The traditional read, standby, output disable, and Auto select
modes are available via the register.
The device’ s command register is written using standard
microproce ssor wr ite timin gs. The register c ontrols an
interna l state machine that mana ges all device operations. For system design simplification, the device is designed to support either WE# or CE# control led writes.
During a system write cycle, addresses are latched on
the falling edge of WE# or CE# whichever occurs last.
Data is latched on the rising edge of WE# or CE# whichever occur first. To si mplify the following discussion, the
WE# pin is used as t he write cycle control pin throughout
the rest of this text. All setup and hold times are with respect to the WE# signal.
OVERVIEW OF ERASE/PROGRAM OPERATIONS
Embedded
AMD now makes erasure extremely simple and reliable. The Embedded Erase algorithm requires the user
to only write an erase setup command and erase command. The d evice will autom atically pre-pr ogram and
verify the entir e array. The device automatical ly times
the erase pulse width, provides the erase verify and
counts the number of sequences. A status bit, Data#
Polling, provides feedback to the user as to the status
of the erase operation.
Erase Algorithm
Embedded Programming Algorithm
AMD now makes programming extremely simple and
reliable. The Embedded P rogramming algorith m re-
quires the user to on ly writ e a pr ogr am s etu p comma nd
and a program comm and. The device automatically
times the programm ing puls e width, provi des the p rogram verify and counts the number of sequences. A
status bit, Data# Polling, provides feedback to the user
as to the status of the programming operation.
DATA PROTECTION
The device is designed to offer protection aga inst acci dental erasure or programming ca used by spurious
system level signals that may exist during power transitions . The d evice po wers up in it s r ea d onl y st at e . A ls o,
with its control register architecture, alteration of the
memory contents only occurs after successful completion of specific command sequences.
The device al so i ncor pora tes s everal feat ures t o pre vent inadvertent write cycles resulting from V
power-up and power-down transitions or system noise.
CC
Low VCC Write Inhibit
To avoid initiation of a write cycle during VCC power -up
and power-d own, the d evice locks out wr ite cycl es for
VCC < V
ages). When VCC < V
abled, all internal program/erase circuits are disabled,
and the device resets to the read mode. The device ignores all writes until V
that the control pins are in the correct logic state when
VCC > V
(see DC characteristics section for volt-
LKO
to prevent unintentional writes.
LKO
, the command register is dis-
LKO
> V
CC
. The user m ust ensure
LKO
Write Pulse “Glitch” Protection
Noise pulses of less than 10 ns (typical) on OE#, CE#
or WE# will not initiate a write cycle.
Logical Inhibit
Writing is inhibited by holding any one of OE# = VIL,
CE# = VIH or WE# = VIH. To initiate a wri te cycle CE#
and WE# must be a logical zero while OE# is a logical
one.
Power-Up Write Inhibit
Power-up of th e device with W E# = CE # = VIL and
OE# = VIH will not a ccept comman ds on the r ising
edge of WE#. The internal state ma chine is automatically reset to the read mode on power-up.
8 Am28F020A
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
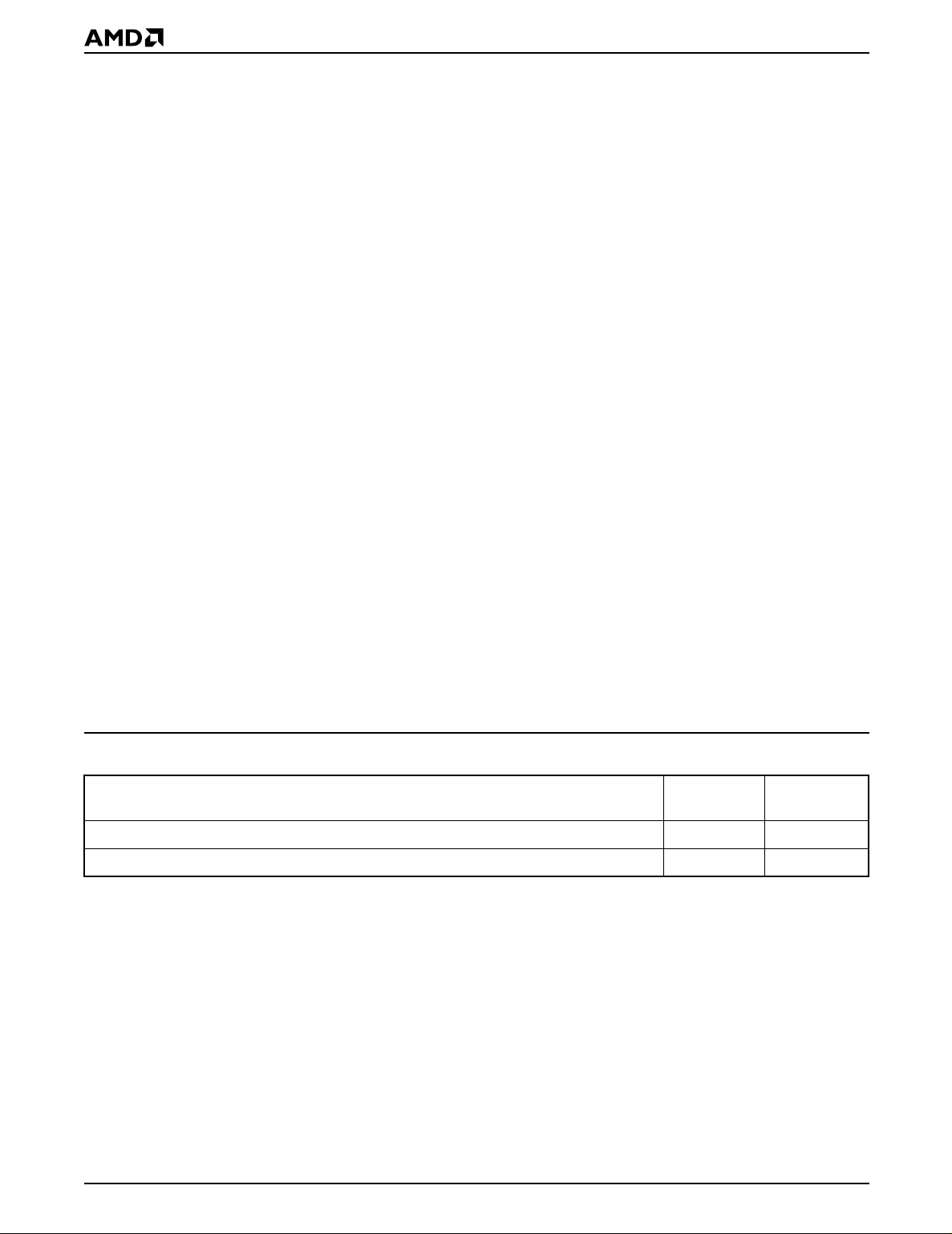
Description Of User Modes
Table 1. Am28F0 20A Device Bus Operations (Notes 7 and 8)
Read-Only
Read/Write
CE
Operation
(E#)
Read V
Standby V
Output Disable V
Auto-select Manufacturer
Code (Note 2)
Auto-select Device
Code (Note 2)
Read V
Standby (Note 5) V
Output Disable V
Write V
V
V
OE
#
(G#)
IL
IH
IL
IL
IL
IL
IH
IL
IL
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
WE
#
(W#)
IL
XV
XXV
V
IH
IL
IL
IL
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
XXV
V
IH
IH
IH
V
IL
V
#
PP
(Note 1) A0 A9 I/O
PPL
PPL
V
PPL
V
PPL
V
PPL
V
PPH
PPH
V
PPH
V
PPH
A0 A9 D
X X HIGH Z
X X HIGH Z
V
V
IL
V
IH
ID
(Note 3)
V
ID
(Note 3)
A0 A9
X X HIGH Z
X X HIGH Z
A0 A9
Legend:
X = Don’t care, where Don’t Care is either V
of V
. 0 V < An < VCC + 2 V, (normal TTL or CMOS input levels, where n = 0 or 9).
PPH
or VIH levels. V
IL
= VPP < VCC + 2 V. See DC Characteristics for voltage levels
PPL
Notes:
1. V
may be grounded, connected with a resistor to ground, or < VCC + 2.0 V. V
PPL
the device. Refer to the DC characteristics. When VPP = V
, memory contents can be read but not written or erased.
PPL
is the programming voltage specified for
PPH
2. Manufacturer and device codes may also be accessed via a command register write sequence. Refer to Table 2.
3. 11.5 < V
4. Read operation with V
5. With V
6. Refer to Table 3 for valid D
7. All inputs are Don’t Care unless otherwise stated, where Don’t Care is either V
addresses except A
8. If V
< 13.0 V. Minimum VID rise time and fall time (between 0 and VID voltages) is 500 ns.
ID
= V
PP
at high voltage, the standby current is ICC + IPP (standby).
PP
and A0 must be held at VIL.
9
1.0 Volt, the voltage difference between VPP and VCC should not exceed 10.0 volts. Also, the Am28F256 has a VPP
≤
CC
may access array data or the Auto select codes.
PPH
during a write operation.
IN
or VIH levels. In the Auto select mode all
IL
rise time and fall time specification of 500 ns minimum.
OUT
CODE
(01h)
CODE
(29h)
D
OUT
(Note 4)
D
IN
(Note 6)
Am28F020A 9
READ-ONLY MODE
When VPP is less than V
is inactive. The device can either read array or autoselect data, or be standby mode.
+ 2 V, the comm and regis ter
CC
Read
The device f unc t ion s as a r ea d o nly m em ory wh en V
< V
+ 2 V . The de v ice ha s tw o con tro l fu ncti ons . Bo th
CC
must be satisfied in order to output data. CE# controls
power to the d evice. This pin sh ould be used for specific device selection. OE# controls the device outputs
and shou ld be used to gate data to the output pin s if a
device is selected.
Address access time t
is equal to the delay from
ACC
stable addresses to valid ou tput data. Th e ch i p en able
access time tCE is the delay from stable addresses and
stable CE# to valid data at the output pins. The output
enable access time is the delay from the falling edge of
OE# to valid dat a at the o utp ut pins (assumi n g th e ad dresses have been stable at least t
ACC
- tOE).
PP
Standby Mode
The device has two standby modes. The CMOS
standby mode (CE# input held at V
sumes less than 100 µA of curren t. TTL standby mode
(CE# is held at VIH) reduces the current requirements
to less than 1 m A . When in the stan dby mo de the outputs are in a high impedance state, independent of the
OE# input.
If the device is deselected during eras ure, programming, or p rogram/erase verificati on, the device will
draw active current until the operation is terminated.
± 0.5 V), con-
CC
Output Dis a ble
Output from the device is disabled when OE# is at a
logic high level. When disabled, output pins are in a
high impedance state.
Auto Select
Flash memories can be programmed in-system or in a
standard PROM programmer. The device may be soldered to the circuit board upon receipt of shipment and
programmed in-system. Alternatively, the device may
initially be programmed in a PROM programmer pr ior
to soldering the device to the board.
The Auto se l e ct m od e allows th e r e ad in g ou t of a bin a ry
code from the device that will identify its manufacturer and
type. This mode is intended for the purpose of automatically matching the device to be programmed with its corresponding pr ogramming algorithm . This mode is
functio nal ove r the entir e temperat ure range of the devi ce.
Programming In A PROM Programmer
To activate thi s mode, the programmin g equipm ent
must force VID (11.5 V to 13.0 V ) on addre ss A9 . Two
identi fie r b yte s ma y th en be seq uence d fr om th e de vi ce
outputs by toggling address A0 from VIL to VIH. All other
address lines must be held at VIL, and VPP must be
less than or equal to VCC + 2.0 V while using this Auto
select mode. Byte 0 (A0 = VIL) repr esen ts th e man uf acturer code and byte 1 (A0 = VIH) the device identifier
code. For the device the two bytes are given in the table
2 of the device data sheet. All identifiers for manufacturer and device codes will exhibit o dd parity with th e
MSB (DQ7) defined as the parity bit.
Table 2. (Am28F020A Auto Select Code
Type A0
Manufacturer Code V
Device Code V
10 Am28F020A
Code
(HEX)
IL
IH
01
29
ERASE, PROGRAM, AND READ MODE
When VPP is equal to 12.0 V ± 5%, the command register is active. All fu nctions ar e available. Tha t is, the
device can program, erase, read array or autoselect
data, or be standby mode.
Write Operations
High voltage must be applied to the VPP pin in orde r to
activate the command register. Data written to the register serves as input to the internal state machine. The
output of the state machine determines the operational
function of the device.
The command register does not occupy an addressable memory locat ion. The re giste r is a latch t hat stor es
the com mand , along with th e addr ess and data in formation needed to execute the command. The register
is written by bringing WE# and CE# to VIL, while OE#
is at VIH. Addresses are latched on the falling edge of
WE#, while data is latched on the rising edge of the
WE# pulse. Standard microprocessor write timings are
used.
The device requires the OE# pin to be VIH for write operations. This condition eliminates the possibility for
bus contention during programming operations. In
order to write, OE# must be VIH, and CE# and WE#
must be VIL. If any pin is not in the correct state a write
command will not be executed.
Refer to AC Write Characteristics and the Erase/Programming Waveforms for specific timing parameters.
Command Definitions
The contents of the command register default to 00h
(Read Mode) in the absence of high v oltage appl ied to
the VPP pin. The d evice op erates as a read only
memory. High voltage on the VPP pin enables the
command register. Device operations are selected by
writing specific dat a code s into t he command regi st er .
Table 3 in the de vice d ata sheet defi nes thes e regi ster
commands.
Read Command
Memor y conte nts can be acces sed via th e read com mand when VPP is high. To read from the device, write
00h into the command register. Standard microprocessor read cycles access data from the memory. The device will remain in the read mode until the command
register contents are altered.
The comma nd register defaults to 00h (r ead mode)
upon VPP power -up . The 00h (Rea d Mode ) regis ter default helps ensure that inadvertent alteration of the
memory contents does not occur during the VPP power
transition. Refer to the AC Read Characteristics and
Waveform s for the spec ifi c timi n g para m ete rs.
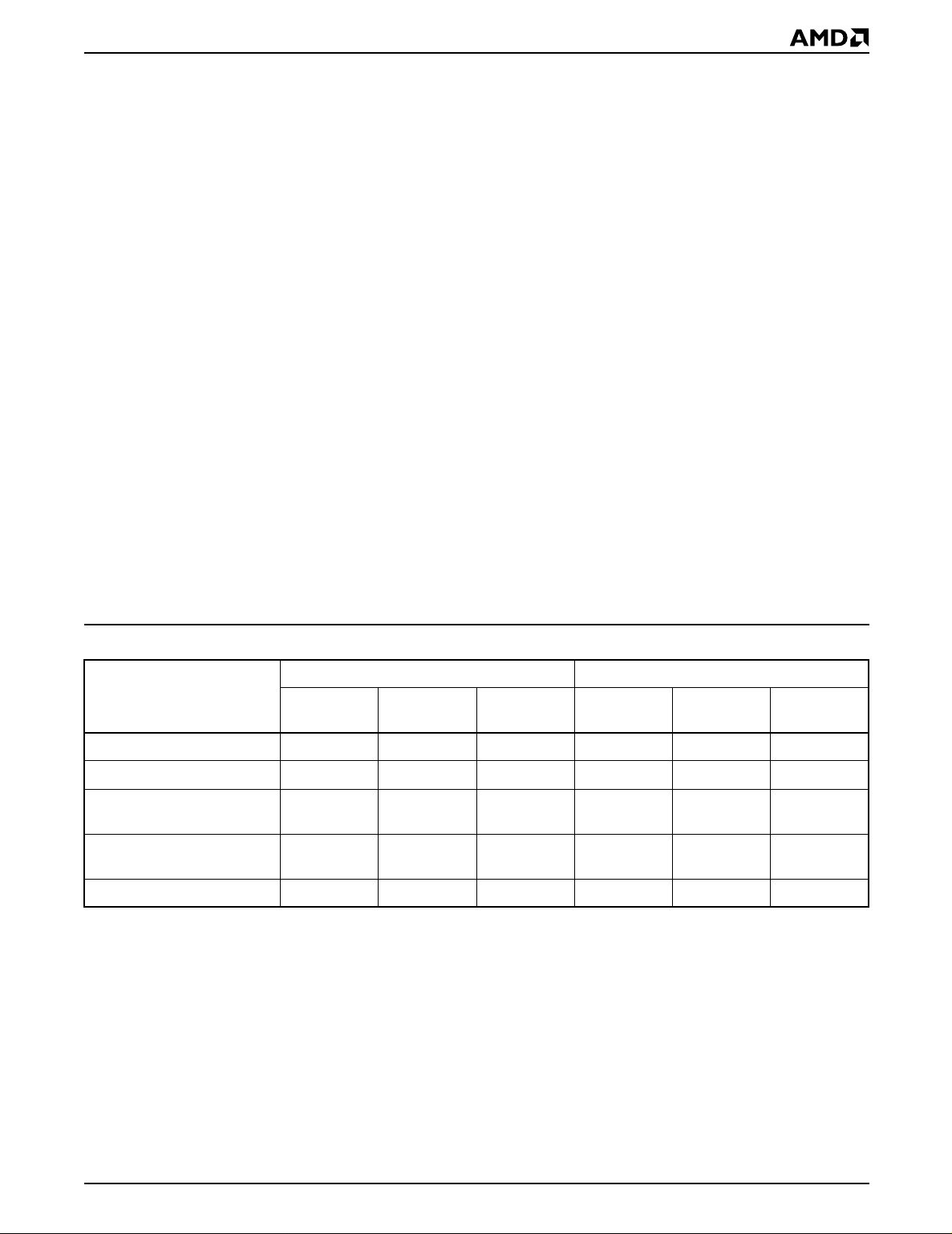
Table 3. Am28F020A Command Definitions
First Bus Cycle Second Bus Cycle
Operation
Command
Read Memory (Note 4) Write X 00h/FFh Read RA RD
Read Auto select Write X 80h or 90h Read 00h/01h 01h/29h
Embedded Erase Set-up/
Embedded Erase
Embedded Program Set-up/
Embedded Program
Reset (Note 4) Write X 00h/FFh Write X 00h/FFh
Notes:
1. Bus operations are defined in Table 1.
2. RA = Address of the memory location to be read.
PA = Address of the memory location to be programmed.
Addresses are latched on the falling edge of the WE
X = Don’t care.
3. RD = Data read from location RA during read operation.
PD = Data to be programmed at location PA. Data latched on the rising edge of WE
4. Please reference Reset Command section.
(Note 1)
Write X 30h Write X 30h
Write X 10h or 50h Write PA PD
Address
(Note 2)
pulse.
#
Data
(Note 3)
Operation
(Note 1)
.
#
Address
Note 2)
Data
(Note 3)
Am28F020A 11
 Loading...
Loading...