Datasheet AM27C2048-200JC, AM27C2048-200DIB, AM27C2048-200DI, AM27C2048-200DEB, AM27C2048-200DE Datasheet (AMD Advanced Micro Devices)
...
FINAL
Publication# 11407 Rev: G Amendment/0
Issue Date: May 1998
Am27C2048
2 Megabit (128 K x 16-Bit) CMOS EPROM
DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS
■ Fast access time
— Speed options as fast as 55 ns
■ Low power consumption
— 100 µA maximum CMOS standby current
■ JEDEC-approved pinout
— Plug-in upgrade of 1 Mbit EPROM
— 40-pin DIP/PDIP
— 44-pin PLCC
■ Single +5 V power supply
■ ±10% power supply tolerance standard
■ 100% Flashrite programming
— Typical programming time of 16 seconds
■ Latch-up protected to 100 mA from –1 V to
V
CC
+ 1 V
■ Versatile features for simple interfacing
— Both CMOS and TTL input/output compatibility
— Two line control functions
■ High noise immunity
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Am27C2048 is a 2 Mbit, ultraviolet erasable programmable read-only memory. It is organiz ed as 128 K
words, operates from a single +5 V supply, has a static
standby mode, and features fast single address location programming. The Am27C2048 is ideal for use in
16-bit microprocessor systems. The device is avai labl e
in windowed ceramic DIP packages, and plastic one
time programmable (OTP) PDIP and PLCC packages.
Data can be typically accessed in less than 55 ns, allowing high-p erformance m icroproces sors to ope rate
without any WAIT states. The device offers separate
Output Enable (OE#) and Chip Enable (CE#) controls,
thus eliminating bus contention in a mul tiple bus microprocessor system.
AMD’s CMOS process technology provides high
speed, low power, and high noise immunity. Typical
power consumption is only 125 mW in active mode,
and 100 µW in standby mode.
All signals are TTL levels, including programming signals. Bit locations may be programmed singly, in
blocks, or at random. The device supports AMD’s
Flashrite programming alg orithm (100 µs pulses), resulting in a typical programming time of 16 seconds.
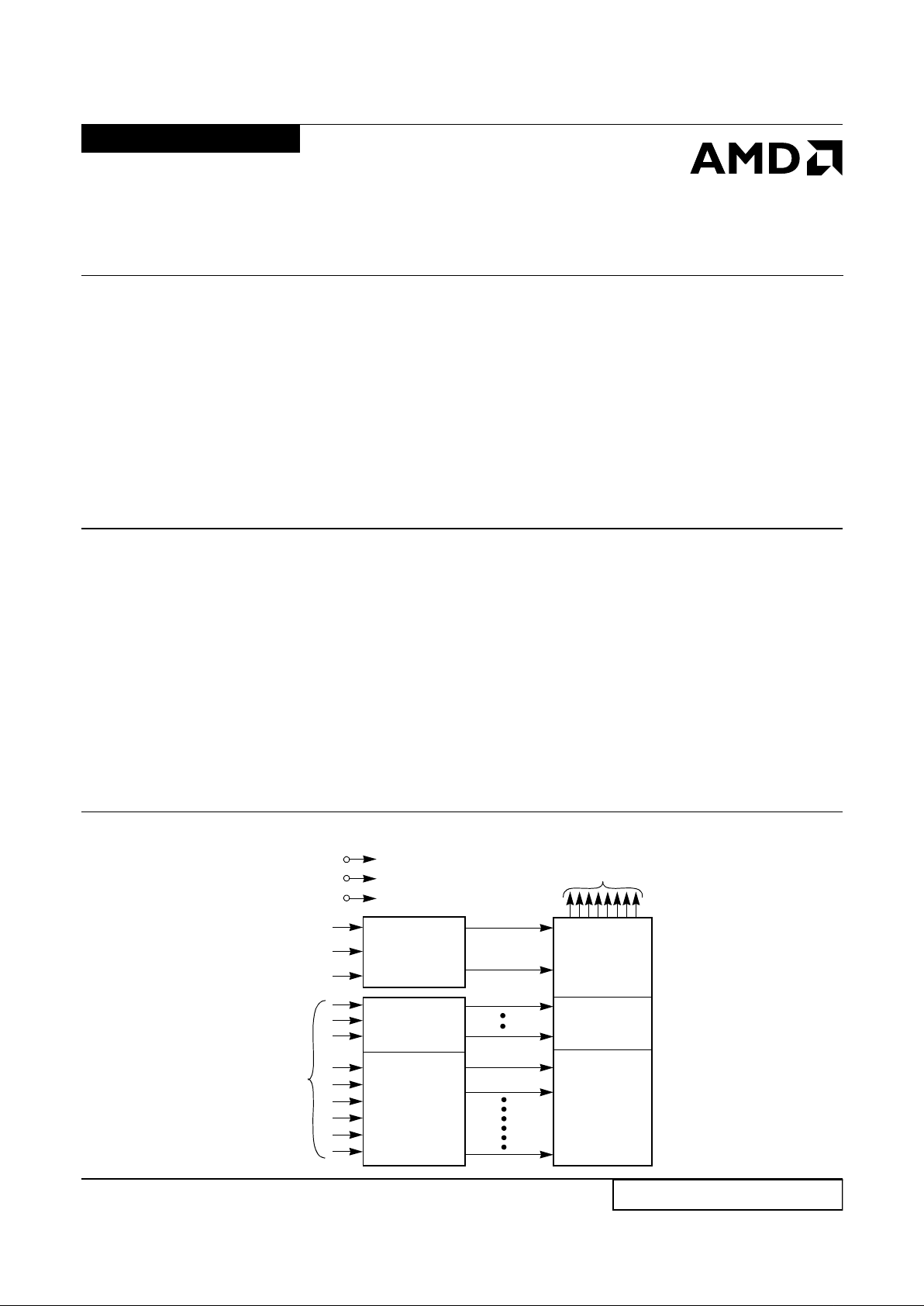
BLOCK DIAGRAM
11407G-1
A0–A16
Address
Inputs
PGM#
CE#
OE#
V
CC
V
SS
V
PP
Data Outputs
DQ0–DQ15
Output
Buffers
Y
Gating
2,097,152
Bit Cell
Matrix
X
Decoder
Y
Decoder
Output Enable
Chip Enable
and
Prog Logic
2 Am27C2048
PRODUCT SELECTOR GUIDE
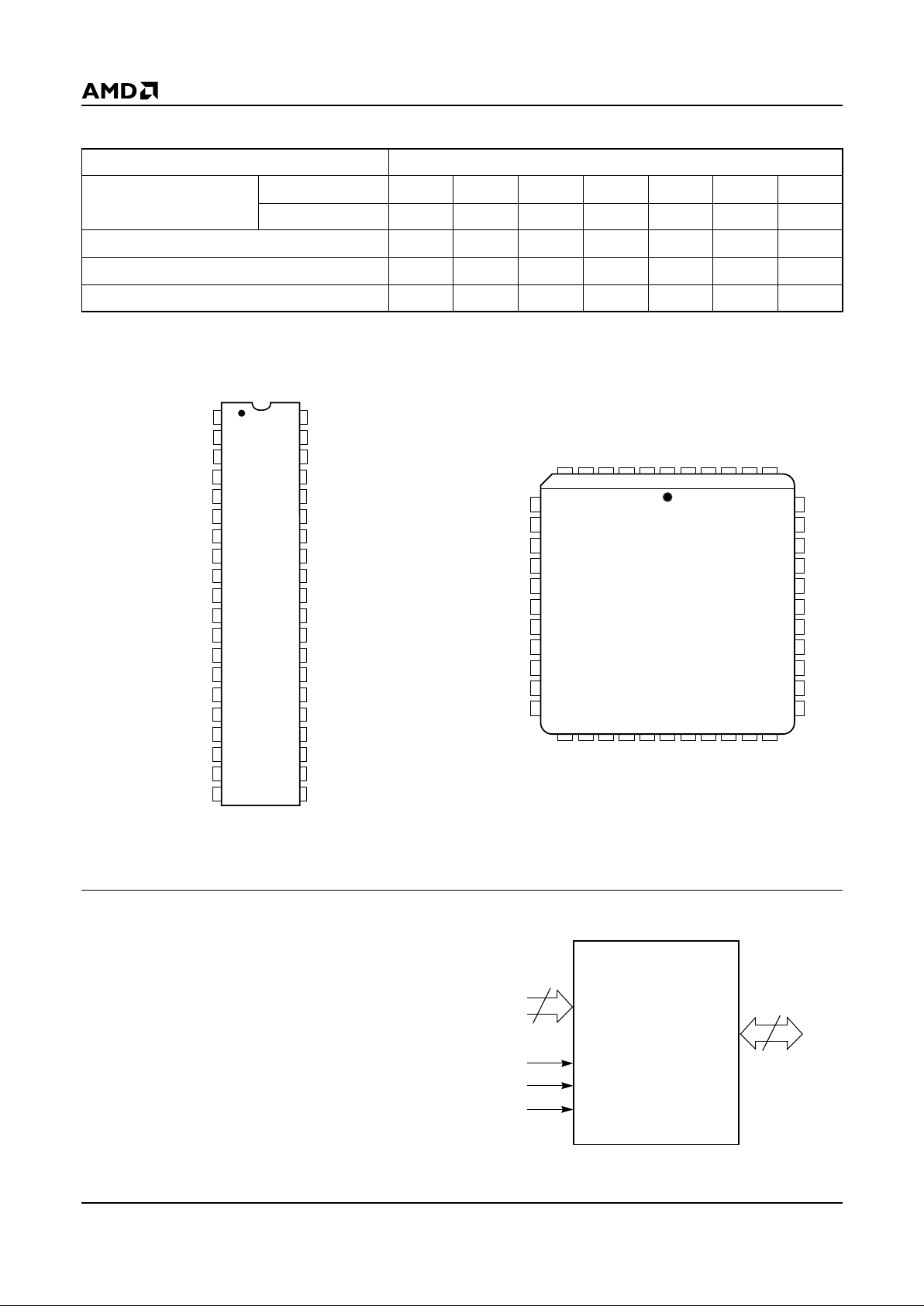
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
Top View
DIP PLCC
Notes:
1. JEDEC nomenclature is in parenthesis.
2. Don’t use (DU) for PLCC.
PIN DESIGNATIONS
A0–A16 = Address Inputs
CE# (E#) = Chip Enable Input
DQ0–DQ15 = Data Input/Outputs
OE# (G#) = Output Enable Input
PGM# (P#) = Program Enable Input
V
CC
=VCC Supply Voltage
V
PP
= Program Voltage Input
V
SS
= Ground
LOGIC SYMBOL
Family Part Number Am27C2048
Speed Options
V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 5% -55 -255
V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 10% -55 -70 -90 -120 -150 -200
Max Access Time (ns) 55 70 90 120 150 200 250
CE# (E#) Access (ns) 55 70 90 120 150 200 250
OE# (G#) Access (ns) 40 40 40 50 65 75 75
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
V
CC
PGM# (P#)
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
V
SS
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
V
PP
CE# (E#)
DQ15
DQ14
DQ13
DQ12
DQ11
DQ10
DQ9
DQ8
V
SS
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
DQ2
DQ1
DQ0
OE# (G#)
11407G-2
1 444342543264140
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
V
SS
NC
A8
A7
A6
A5
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
CE (E)
VPPDU (Note 2)
VCCPGM# (P#)
A16
A15
A14
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
DQ12
DQ11
DQ10
DQ9
DQ8
V
SS
NC
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
DQ2
DQ1
DQ0
OE# (G#)
DU (Note 2)
A0A1A2A3A4
23 24 25 2619 20 21 2218 27 28
11407G-3
17
16
DQ0–DQ15
A0–A16
CE# (E#)
PMG (P#)
OE# (G#)
11407G-4
Am27C2048 3
ORDERING INFORMATION
UV EPROM Products
AMD standard products are available in several packages and operating ranges. The order number (Valid Combination) is formed
by a combination of the following:
Valid Combinations
Valid Combinations list configurations planned to be supported in volume for this device. Consult the local AMD sales
office to confirm availability of specific valid combinations and
to check on newly released combinations.
DEVICE NUMBER/DESCRIPTION
Am27C2048
2 Megabit (128 K x 16-Bit) CMOS UV EPROM
AM27C2048 -55 D C
OPTIONAL PROCESSING
Blank = Standard Processing
B = Burn-In
VOLTAGE TOLERANCE
5=V
CC
± 5%, 55 ns only
See Product Selector Guide and Valid Combinations
TEMPERATURE RANGE
C = Commercial (0°C to +70
°C)
I=Industrial (–40
°C to +85°C)
E = Extended (–55°C to +125°C)
PACKAGE TYPE
D = 40-Pin Ceramic DIP (CDV040)
SPEED OPTION
See Product Selector Guide and
Valid Combinations
B
5
Valid Combinations
AM27C2048-55
V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 5%
DC5, DC5B, DI5, DI5B
AM27C2048-55
V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 10%
DC, DCB, DI, DIB
AM27C2048-70
AM27C2048-90
AM27C2048-120
DC, DCB, DE, DEB, DI, DIBAM27C2048-150
AM27C2048-200
AM27C2048-255
V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 5%
DC, DCB, DI, DIB
4 Am27C2048
ORDERING INFORMATION
OTP EPROM Products
AMD standard products are available in several packages and operating ranges. The order number (Valid Combination) is formed
by a combination of the following:
Valid Combinations
Valid Combinations list configurations planned to be supported in volume for this device. Consult the local AMD sales
office to confirm availability of specific valid combinations and
to check on newly released combinations.
DEVICE NUMBER/DES CR IP TIO N
Am27C2048
2 Megabit (128 K x 16-Bit) CMOS OTP EPROM
AM27C2048 -55 J C
OPTIONAL PROCESSING
Blank = Standard Processing
VOLTAGE TOLERANCE
5=V
CC
± 5%, -55 ns only
See Product Selector Guide and
Valid Combinations
TEMPERATURE RANGE
C = Commercial (0
°C to +70°C)
I=Industrial (–40
°C to +85°C)
PACKAGE TYPE
P = 40-Pin Plastic DIP (PD 040)
J = 44-Pin Square Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PL 044)
SPEED OPTION
See Product Selector Guide and
Valid Combinations
5
Valid Combinations
AM27C2048-55
V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 5%
PC5, PI5, JC5, JI5
AM27C2048-55
V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 10%
PC, PI, JC, JI
AM27C2048-70
AM27C2048-90
AM27C2048-120
AM27C2048-150
AM27C2048-200
AM27C2048-255
V
CC
= 5.0 V ± 5%

Am27C2048 5
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Device Erasure
In order to clear all locations of their programmed contents, the device m ust be exp osed to an ultra violet light
source. A dosage of 15 W seconds/cm
2
is required to
completely erase the device. This dosage can be ob-
tained by exposure to an ultraviolet lamp—wavelength
of 2537 Å—with intensity of 12,000 µW/cm
2
for 15 to 20
minutes. The device shoul d be directly under and about
one inch from the source, and all filters should be removed from the UV light source prior to erasure.
Note that all UV erasable devices will erase with light
sources having wav elengths shorter than 4000 Å, such
as fluorescent light and sunlight. Although the erasure
process happens over a much longer time period, exposure to any light source should be prevented for
maximum system reliability. Simply cover the package
window with an opaque label or substance.
Device Programming
Upon delivery, or after each erasure, the device has
all of its bits in t he “ONE”, or HIGH s tate . “ZER Os” are
loaded into the device through the programming procedure.
The device enters the programming mode when 12.75
V ± 0.25 V is applied to the V
PP
pin, and CE# and
PGM# are at V
IL
.
For programming, the data to be programmed is applied 16 bits in parallel to the data pins.
The flowchart in the Programming section (Section 5,
Figure 5-1) shows AMD’s Flashrite algorithm. The
Flashrite algorithm reduces pro gramming time by using
a 100 µs programming pulse and by giving each address
only as many pulses to reliably program the data. After
each pulse is applied to a given address, the data in that
address is verified. If the data does not verify, additional
pulses are given until it verifies or the maximum pulses
allowed is reached. This process i s repeated while sequencing through each address of the device. This part
of the algorithm is done at V
CC
= 6.25 V to assure that
each EPROM bit is programmed to a sufficiently high
threshold voltage. After the final address is completed,
the entire EPROM memory is verified at V
CC
= VPP =
5.25 V.
Please refer to Section 5 f or additional progr amming in-
formation and specifications.
Program Inhibit
Programming different data to multiple devices in parallel is easily accomplished. Except for CE#, all like inputs of the devices may be common. A TTL low-level
program pulse applied to one device’s CE# input with
V
PP
= 12.75 V ± 0.25 V and PGM# LOW will program
that particular device. A high-level CE# input inhibits
the other devices from being programmed.
Program Verify
A verification should be performed on the programmed
bits to determine that they were correctly progr ammed.
The verify should be performed with OE# and CE#, at
V
IL
, PGM# at VIH, and VPP between 12.5 V and 13.0 V.
Autoselect Mode
The autosel ect mode provides ma nufacturer and device identification through iden tifier codes on DQ0–
DQ7. This mode is primarily intended for programming
equipment to automatically match a device to be programmed with its correspo nding programming algorithm. This mode is functional in the 25°C ± 5°C
ambient temperature range that is required when programming the device.
To activate this mode, the programming equipment
must force V
H
on address line A9. Two identifier bytes
may then be sequenced from the de vice outputs b y toggling address line A0 from V
IL
to V
IH
(that is, changing
the address from 00h to 01h). All other address lines
must be held at V
IL
during the autoselect mode.
Byte 0 (A0 = VIL) represents the manufacturer code,
and Byte 1 (A0 = V
IH
), the device identifier code. Both
codes have odd parity, with DQ7 as the parity bit.
Read Mode
T o obtain dat a at the device o utputs, Chip Enable ( CE#)
and Output Enable (OE#) must be driven lo w . CE# controls the power to the de vice and is typically used t o select the device . OE# ena b l es the device to output data,
independent of device selection. Addresses must be
stable for at least t
ACC–tOE.
Refer to the Switching
Waveforms section for the timing diagr am.
Standby Mode
The device enters the CMOS standby mode when CE#
is at V
CC
± 0.3 V. Maximum V
CC
current is reduced to
100 µA. The device enters the TTL-standby mode
when CE# is at V
IH
. Maximum V
CC
current is reduced
to 1.0 mA. When in either standby mode, the device
places its outputs in a high-impedance state, independent of the OE# input.
Output OR-Tieing
To accommodate multiple memor y connections, a
two-line control function provides:
■ low memory power dissipation, and
■ assurance that output bus contention will not occur .
CE# should be decoded and used as the primary device-selecting function, while OE# be made a common
connection to all devices in the array and connected to

6 Am27C2048
the READ line from the system control bus. This assures that all deselected memory devices are in their
low-power standby mode and that the output pins are
only active when data is desired from a particular memory device.
System Applications
During the switch between a ctive and standby conditions, transient current peaks are produced on the rising and falling edges of Chip Enab le. The magnitude of
these transient current peaks is dependent on the out-
put capacitance loading of the de vi ce. At a minim um, a
0.1 µF ceramic capacitor (high frequency, low inherent
inductance) sho uld be used on each device between
V
CC
and VSS to minimize transient effec ts. In addition,
to overcome the voltage drop caused by the inductive
effects of the printed circuit boar d traces on EPROM arrays, a 4.7 µF bul k electrolytic capacitor should be used
between V
CC
and VSS for each eight de vices. The location of the capacitor should be close to where the
power supply is connected to the array.
MODE SELECT TABLE
Notes:
1. V
H
= 12.0 V ± 0.5 V.
2. X = Either V
IH
or VIL.
3. A1–A8 and A10–16 = V
IL
.
4. See DC Programming Characteristics for V
PP
voltage during programming.
Mode CE# OE# PGM# A0 A9 V
PP
Outputs
Read V
IL
V
IL
XXXXD
OUT
Output Disable V
IL
V
IH
X X X X High Z
Standby (TTL) V
IH
X X X X X High Z
Standby (CMOS) V
CC
± 0.3 V X X X X X High Z
Program V
IL
XVILXXVPPD
IN
Program Verify V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
XXVPPD
OUT
Program Inhibit V
IH
XXXXVPPHigh Z
Autoselect
(Note 3)
Manufacturer Code V
IL
V
IL
XVILV
H
X01h
Device Code V
IL
V
IL
XVIHV
H
X98h

Am27C2048 7
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Storage Temperature
OTP Products. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +125°C
All Other Products . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Ambient Temperature
with Power Applied. . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
Voltage with Respect to V
SS
All pins except A9, VPP, VCC . . –0.6 V to VCC + 0.6 V
A9 and VPP (Note 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . .–0.6 V to 13.5 V
V
CC
(Note 1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–0.6 V to 7.0 V
Notes:
1. Minimum DC voltage on inpu t or I/O pins – 0.5 V. During
voltage transitions, the input may overshoot V
SS
to –2.0 V
for periods of up to 20 ns. Max imum DC voltage o n inp ut
and I/O pins is V
CC
+ 5 V . During voltage transitions, input
and I/O pins may overshoot to V
CC
+ 2.0 V for periods up
to 20 ns.
2. Minimum DC input voltage on A9 is –0.5 V . During voltage
transitions, A9 and V
PP
may overshoot V
SS
to –2.0 V for
periods of up to 20 ns. A9 and V
PP
must not exceed+13.5
V at any time.
Stresses above those listed under “Abso lute Maximum Ratings” may cause per mane nt dam age to the device. This is a
stress rating only; fun ctio nal ope ration of t he d evice at these
or any other condition s above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure of
the device to absolute maximum ratings for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
OPERATING RANGES
Commercial (C) Devices
Ambient Temperature (T
A
) . . . . . . . . . . .0°C to +70°C
Industrial (I) Devices
Ambient Temperature (T
A
) . . . . . . . . .–40°C to +85°C
Extended (E) Devices
Ambient Temperature (T
A
) . . . . . . . .–55°C to +125°C
Supply Read Voltages
V
CC
for ± 5% devices . . . . . . . . . . +4.75 V to +5.25 V
V
CC
for ± 10% devices . . . . . . . . . +4.50 V to +5.50 V
Operating ranges define those limits between which the functionality of the device is guaranteed.

8 Am27C2048
DC CHARACTERISTICS OVER OPERATING RANGE
(unless otherwise specified)
Caution: The device must not be removed from (or inserted into) a socket when VCC or VPP is applied.
Notes:
1. V
CC
must be applied simultaneously or before VPP, and removed simultaneously or after VPP..
2. I
CC
1 is tested with OE# = V
IH
to simulate open outputs.
3. Minimum DC Input Voltage is –0.5 V. During transitions, the inputs may overshoot to –2.0 V for periods less than 20 ns.
Maximum DC Voltage on output pins is V
CC
+ 0.5 V, which may overshoot to VCC + 2.0 V for periods less than 20 ns.
Figure 1. Typical Supply Current vs. Frequency
V
CC
= 5.5 V, T = 25°C
Figure 2. Typical Supply Current vs. Temperature
V
CC
= 5.5 V, f = 5 MHz
Parameter
Symbol Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Max Unit
V
OH
Output HIGH Voltage IOH = –400 µA 2.4 V
V
OL
Output LOW Voltage IOL = 2.1 mA 0.45 V
V
IH
Input HIGH Voltage 2.0 VCC + 0.5 V
V
IL
Input LOW Voltage –0.5 +0.8 V
I
LI
Input Load Current VIN = 0 V to V
CC
C/I Devices 1.0 µA
E Devices 5.0
I
LO
Output Leakage Current V
OUT
= 0 V to V
CC
5.0 µA
I
CC1
VCC Active Current (Note 2)
CE# = V
IL
, f = 5 MHz,
I
OUT
= 0 mA
C/I Devices 50
mA
E Devices 60
I
CC2
VCC TTL Standby Current CE# = V
IH
1.0 mA
I
CC3
VCC CMOS Standby Current CE# = VCC ± 0.3 V 100 µA
I
PP1
VPP Supply Current (Read) CE# = OE# = VIL, VPP = V
CC
100 µA
11407G-5
12345678910
35
30
25
20
15
Frequency in MHz
Supply Current
in mA
11407G-6
–75 –50 –55 0 25 50 75 100 125 150
35
30
25
20
15
Temperature in °C
Supply Current
in mA

Am27C2048 9
TEST CONDITIONS
Table 1. Test Specifications
SWITCHING TEST WAVEFORM
KEY TO SWITCHING WAVEFORMS
2.7 kΩ
C
L
6.2 kΩ
5.0 V
Device
Under
Test
11407G-7
Figure 3. Test Setup
Note:
Diodes are IN3064 or equivalents.
Test Condition -55
All
others Unit
Output Load 1 TTL gate
Output Load Capacitance, C
L
(including jig capacitance)
30 100 pF
Input Rise and Fall Times ≤ 20 ns
Input Pulse Levels 0.0–3.0 0.45–2.4 V
Input timing measurement
reference levels
1.5 0.8, 2.0 V
Output timing measurement
reference levels
1.5 0.8, 2.0 V
2.4 V
0.45 V
Input
Output
Test Points
2.0 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
0.8 V
11407G-8
3 V
0 V
Input
Output
1.5 V
1.5 V
Test Points
Note: For CL = 100 pF.Note: For CL = 30 pF.
KS000010-PAL
WAVEFORM INPUTS OUTPUTS
Steady
Changing from H to L
Changing from L to H
Don’t Care, Any Change Permitted Changing, State Unknown
Does Not Apply Center Line is High Impedance State (High Z)

10 Am27C2048
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Caution: Do not remove the device from (or insert it into) a socket or board that has VPP or V
CC
applied.
Notes:
1. VCC must be applied simultaneously or before VPP, and removed simultaneously or after VPP.
2. This parameter is sampled and not 100% tested.
3. Switching characteristics are over operating range, unless otherwise specified.
4. See Figure 3 and Table 1 for test specifications.
SWITCHING WAVEFORMS
Notes:
1. OE# may be delayed up to t
ACC
– tOE after the falling edge of the addresses without impact on t
ACC
.
2. t
DF
is specified from OE# or CE#, whichever occurs first.
PACKAGE CAPACITANCE
Notes:
1. This parameter is only sampled and not 100% tested.
2. T
A
= +25°C, f = 1 MHz.
Parameter Symbols
Description Test Setup
Am27C2048
UnitJEDEC Standard -55 -70 -90 -120 -150 -200 -255
t
AVQV
t
ACC
Address to Output Delay
CE#,
OE# = V
IL
Max 55 70 90 120 150 200 250 ns
t
ELQV
t
CE
Chip Enable to Output Delay OE# = VILMax 55 70 90 120 150 200 250 ns
t
GLQV
t
OE
Output Enable to Output Delay CE# = VILMax40404050657575ns
t
EHQZ
t
GHQZ
t
DF
(Note 2)
Chip Enable High or Output
Enable High to Output High Z,
Whichever Occurs First
Max25252530304060ns
t
AXQX
t
OH
Output Hold Time from
Addresses, CE# or OE#,
Whichever Occurs First
Min0000000ns
Addresses
CE#
OE#
Output
11407G-9
Addresses Valid
High Z
High Z
t
CE
Valid Output
2.4
0.45
2.0
0.8
2.0
0.8
t
ACC
(Note 1)
t
OE
tDF (Note 2)
t
OH
Parameter
Symbol
Parameter
Description Test Conditions
CDV040 PD 040 PL 044
UnitTyp Max Typ Max Typ Max
C
IN
Input Capacitance VIN = 0 10 12 10 12 7 10 pF
C
OUT
Output Capacitance V
OUT
= 0 12151215 1214pF

Am27C2048 11
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS*
CDV040—40-Pin Ceramic Dual In-Line Package, UV Lens (measured in inches)
* For reference only. BSC is an ANSI standard for Basic Space Centering.
PD 040—40-Pin Plastic Dual In-Line Package (measured in inches)
TOP VIEW
SIDE VIEW
END VIEW
INDEX AND
TERMINAL NO. 1
I.D. AREA
.565
.605
2.035
2.080
.005 MIN
.045
.065
.014
.026
.100 BSC
.015
.060
.160
.220
.125
.200
BASE PLANE
SEATING PLANE
.300 BSC
.600
BSC
.008
.018
94°
105°
.700
MAX
16-000038H-3
CDV040
DF11
3-30-95 ae
DATUM D
CENTER PLANE
DATUM D
CENTER PLANE
1
UV Lens
Pin 1 I.D.
2.040
2.080
.530
.580
.005 MIN
.045
.065
.090
.110
.140
.225
.120
.160
.014
.022
SEATING PLANE
.015
.060
16-038-SC_AF
PD 040
DG76
2-28-95 ae
40
21
20
.630
.700
0°
10°
.600
.625
.008
.015

12 Am27C2048
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
PL 044—44-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (measured in inches)
REVISION SUMMARY FOR AM27C2048
Revision G
Global
Changed formatting to match current data sheets.
Connection Diagrams
Corrected designation for pin 38 on PDIP connection
diagram to A16.
Trademarks
Copyright © 1998 Advanced Micro D evices, Inc. All r ights reserved.
AMD, the AMD logo, and combinations thereof are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Flashrite is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Product names used in this publication are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective companies.
TOP VIEW
SEATING PLANE
.685
.695
.650
.656
Pin 1 I.D.
.685
.695
.650
.656
.026
.032
.050 REF
.042
.056
.062
.083
.013
.021
.590
.630
.500
REF
.009
.015
.165
.180
.090
.120
16-038-SQ
PL 044
EC80
11.3.97 lv
SIDE VIEW
 Loading...
Loading...