Page 1
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, Stratix IV
GT Edition Reference Manual
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
101 Innovation Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
www.altera.com
MNL-01052-1.1
Subscribe
Page 2

© 2011 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos
are trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance of its
semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and
services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service
described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying
on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 3
Contents
Chapter 1. Overview
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Development Board Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–4
Handling the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–5
Chapter 2. Board Components
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Board Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Featured Device: Stratix IV GT Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–5
I/O Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–6
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–9
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–9
Embedded USB-Blaster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–9
Fast Passive Parallel Download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–10
JTAG Programming Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–11
Status and Setup Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–11
Status LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–11
Board Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–12
Clocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–14
General User Input/Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–16
Push Buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–16
User LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–17
LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–17
DIP Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
Flash Memory Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
Components and Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–20
Temperature Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–20
Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–22
Ethernet Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–23
Transceiver Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–24
Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–25
Power Distribution System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–26
Banana Jacks and Fuses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–27
Appendix A. Board Revision History
Single-Die Flash Version Differences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1
Additional Information
Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
How to Contact Altera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
Typographic Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 4

iv Contents
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 5
Introduction
The Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, Stratix® IV GT Edition allows you
to evaluate the performance the Stratix IV GT transceivers and the low power benefits
of the device itself. This document provides the detailed pin-out and component
reference information required to create FPGA designs for implementation on the
development board.
f For information about setting up the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity
development board, and using the included software, refer to the Transceiver Signal
Integrity Development Kit, Stratix IV GT Edition User Guide.
General Description
The Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity development board provides a
hardware platform for evaluating the performance and signal integrity features of the
®
Altera
blocks:
1. Overview
Stratix IV GT devices. The board features the following major component
■ EP4S100G2F40I1N FPGA
■ 0.95-V core
■ 1517-pin Fineline BGA (FBGA)
■ FPGA Configuration
■ MAX
■ Flash storage for two configuration images (factory and user)
■ On-Board USB-Blaster
■ JTAG header for external USB-Blaster with the Quartus II Programmer
■ On-Board Memory
■ 64-MB synchronous flash
®
II+Flash Fast Passive Parallel (FPP) configuration
TM
using the Quartus® II Programmer
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 6

1–2 Chapter 1: Overview
General Description
■ Status and Setup Elements
■ System reset push button
■ CPU reset push button
■ 4-position spread spectrum clock selection DIP switch
■ Three configuration status LEDs (factory, user, configuration error)
■ USB-Blaster activity LED
■ Ethernet link 10 LED
■ Ethernet link 100 LED
■ Ethernet link 1000 LED
■ Ethernet full duplex LED
■ Ethernet TX activity LED
■ Ethernet RX activity LED
■ Over-Temperature warning LED
■ Power LED
■ FPGA Clock Sources
■ FPGA core clock sources
■ 25-MHz/100-MHz/125-MHz/200-MHz selectable spread spectrum clock
oscillator
■ 50-MHz clock oscillator
■ SMA connectors for external differential clock input
■ FPGA transceiver clock sources
■ 100-MHz clock oscillator
■ 644.53-MHz clock oscillator
■ 706.25-MHz clock oscillator
■ SMA connectors for external differential clock input
■ Clock Outputs and Triggers
■ Two FPGA I/O clock outputs to SMA connectors
■ 100-MHz clock trigger output to SMA connector
■ 644.53-MHz clock trigger output to SMA connector
■ 706.25-MHz clock trigger output to SMA connector
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 7

Chapter 1: Overview 1–3
General Description
■ General User Input/Output
■ 8-position user DIP switch
■ Six user push buttons
■ Hex rotary switch
■ Eight user LEDs
■ 16 character × 2 line LCD
■ Components and Interfaces
■ 10/100/1000 Ethernet PHY and RJ-45 jack
■ Transceiver channels
■ Six full-duplex transceiver channels from GXB0 transceiver block brought
out to the backplane connectors
■ Four full-duplex transceiver channels from GXB1 transceiver block brought
out to the SMA connectors
■ Two channels from GXB2 transceiver block brought out to the SMA
connectors. One channel is routed with 15 inches of board trace length on
transmit and 5 inches board trace length on receive to simulate the
degradation associated with long trace PCB routing
■ Power
■ 14-V – 20-V DC input
■ 2.5-mm Barrel Jack for DC power input
■ On/Off slide power switch
■ On-Board power measurement circuitry
■ Heat Sink and Fan
■ 40-mm heat sink and 5-V DC fan combo
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 8
1–4 Chapter 1: Overview
GT
LCD
Power
Measure
24-bit
ADC
Dual Temp
Sensor
Temp
Measure
TDIODES
5-V FAN
USB-Blaster
USB
Type-B
Conn
USB
PHY
MAX
7064A
CPLD
10/100/1000
Ethernet
RJ45
Magnetics
SMSC
8700
Ethernet
PHY
FPP
Configuration
Clock
Circuitry
512-Mbit
Flash
Configuration
Status
LEDs
MAX
7256A
CPLD
PGMSEL
Jumper
2 Reset
Buttons
Buttons
Switches
Displays
Rotary
Switch
16 Char × 2 Line LCD
8 User DIP
6 User
Buttons
8 User
LEDs
Transceivers
Flash
FPP Config
2-wire Ch1
Power
Circuitry
2-wire Ch8
EP4S100G2F40I2N
Backplane
Connectors
ADC
Header
Pwrgood
TEMP
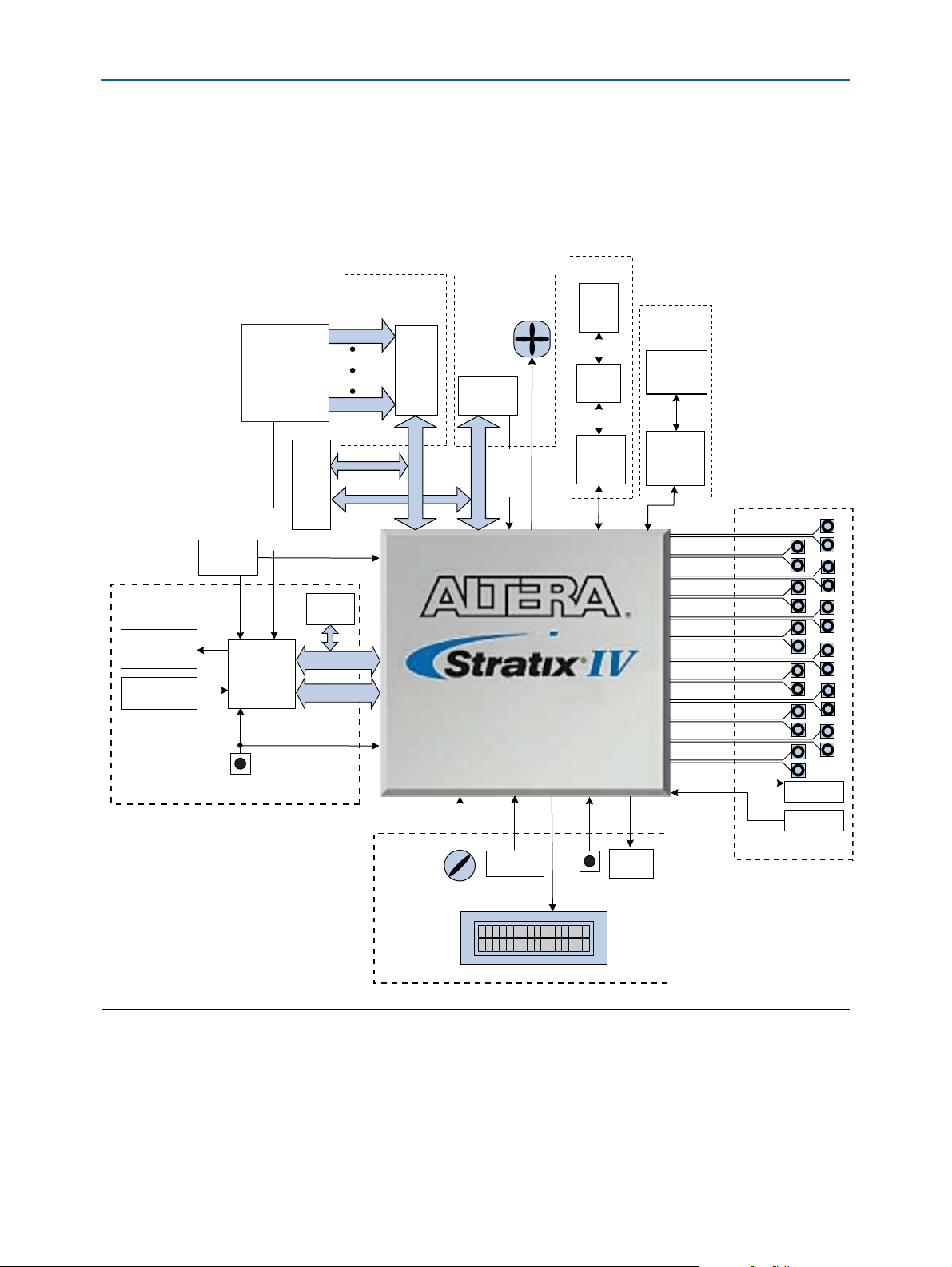
Development Board Block Diagram
Development Board Block Diagram
Figure 1–1 shows the block diagram of the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity
board.
Figure 1–1. Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Board Block Diagram
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 9

Chapter 1: Overview 1–5
Handling the Board
Handling the Board
When handling the board, it is important to observe the following static discharge
precaution:
c Without proper anti-static handling, the board can be damaged. Therefore, use
anti-static handling precautions when touching the board.
The Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity board must be stored between –40º C
and 100º C. The recommended operating temperature is between 0º C and 55º C.
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 10

1–6 Chapter 1: Overview
Handling the Board
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 11

Introduction
1 A complete set of schematics, a physical layout database, and GERBER files for the
f For information about powering up the board and installing the development kit
2. Board Components
This chapter introduces all the important components on the Stratix IV GT transceiver
signal integrity development board. Figure 2–1 illustrates major component locations
and Table 2–1 provides a brief description of all features of the board.
development board reside in the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity
development kit installation directory.
software, refer to the Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, Stratix IV GT Edition
User Guide.
This chapter consists of the following sections:
■ “Board Overview”
■ “Featured Device: Stratix IV GT Device” on page 2–5
■ “Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements” on page 2–9
■ “General User Input/Output” on page 2–16
■ “Flash Memory Device” on page 2–18
■ “Components and Interfaces” on page 2–20
■ “Power” on page 2–25
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 12
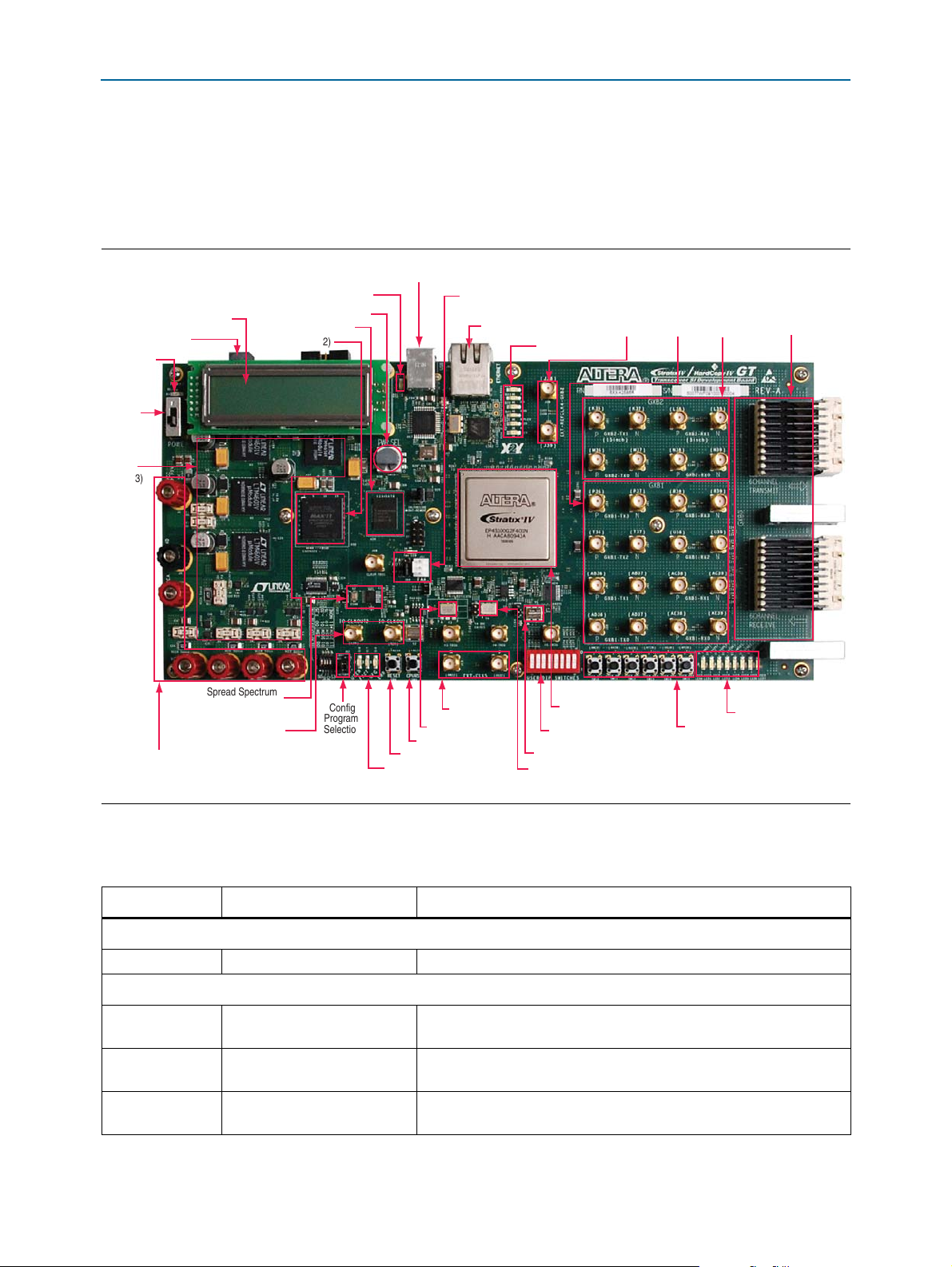
2–2 Chapter 2: Board Components
Powe r
Switch
(SW1)
DC Power Jack (J1)
Power LED
(D3)
LCD Display (J24)
Powe r
Circuit
(U1-U13)
MAX II CPLD (U32)
Flash Memory (U39)
Power Select Switch (SW16)
Spread Spectrum
Clock (X2, U21)
IO CLK OUT from
FPGA to SMA (J16, J17)
Config
Program
Selection
Jumper
(J62)
User DIP Switches (SW7)
706.25 MHz Osc (Y5)
External Clock
SMA to FPGA
(J14, J15)
100 MHz Osc (Y4)
644.53 MHz Osc (Y3)
CPU Reset (SW9)
Board Reset (SW8)
Config Status LEDs
(D16-D18)
Fan Connector (J12)
Fan Jumper (J64)
Fan LED (D6)
Embedded USB-Blaster Activity LED (D7)
GXB2
TX/RX
SMAs
(J30-J37)
GXB1
TX/RX
SMAs
(J38-J45,
J54-J61)
Ethernet Status
LEDs (D19-D24)
Embedded USB-Blaster (CN1)
Stratix IV GT FPGA (U33)
10/100 /1000 Ethernet (J68)
User Push-Buttons
(SW10-SW15)
User LEDs (D8-D15)
External Power
Input Banana Jacks
(J2-J4, J7-J10)
GXB0 TX/RX
to Backplane
Connector
(J70-J71)
External
Refclk
SMAs
(J19, J20)
Board Overview
Board Overview
This section provides an overview of the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity
development board, including an annotated board image and component
descriptions. Figure 2–1 provides an overview of the board features.
Figure 2–1. Overview of the Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Board Features
Tab le 2– 1 describes the components and lists their corresponding board references.
Table 2–1. Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Board Components (Part 1 of 4)
Board Reference Type Description
Featured Devices
U33 EP4S100G2F40I1N Stratix IV GT device in a 1517-pin FBGA package.
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
J28 JTAG programming header
J26
J63
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
MAX II JTAG configuration
jumper
JTAG for embedded
USB-Blaster MAX II CPLD
JTAG programming header for connecting an Altera USB-Blaster
dongle to program the FPGA and MAX II CPLD devices.
Jumper to bypass the MAX II CPLD from the JTAG programming
chain.
JTAG for embedded USB-Blaster MAX II CPLD device programming.
Page 13
Chapter 2: Board Components 2–3
Board Overview
Table 2–1. Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Board Components (Part 2 of 4)
Board Reference Type Description
U32 MAX II CPLD
D6 Fan LED
Altera EPM1270256C3N, MAX II 256-pin CPLD for MAX II+FPP
configuration.
Indicates an FPGA over-temperature condition exists and a fan should
be attached to the FPGA and running.
D16–D18 Configuration status LEDs LEDs to indicate the status of FPP configuration.
J62
Configuration program select
jumper
Jumper to select the flash configuration image to load upon power-on
or reset.
J65 Y3 OSC enable/disable jumper Jumper to enable or disable the Y3 OSC.
J66 Y4 OSC enable/disable jumper Jumper to enable or disable the Y4 OSC.
J67 Y5 OSC enable/disable jumper Jumper to enable or disable the Y5 OSC.
D3 Power LED Blue LED to indicate board power status.
D7 USB-Blaster LED Green activity status LED for the embedded USB-Blaster.
D19–D24
SW16
SW2
Bank of Ethernet LINK and
Status LEDs
Power measurement rotary
switch
Spread spectrum
configuration DIP switch
Ethernet Link, Speed, Full Duplex, Transmit and Receive activity LEDs.
This switch selects 1 of 6 measured FPGA power rails to display on the
LCD.
DIP switch to set the spread spectrum output clock frequency and
down-spread percentages.
J18 Spread spectrum clock trigger Spread spectrum clock source routed to SMA for triggering purposes.
J21 Y3 OSC clock trigger Y3 oscillator clock source routed to SMA for triggering purposes.
J22 Y4 OSC clock trigger Y4 oscillator clock source routed to SMA for triggering purposes.
J23 Y5 OSC clock trigger Y5 oscillator clock source routed to SMA for triggering purposes.
J14, J15
J19, J20
J16, J17
Differential SMA clock input to
FPGA core
Differential SMA clock input to
FPGA transceiver
Differential SMA clock output
from FPGA core
SMA for receiving a differential external clock input to the FPGA core.
SMA for receiving a differential external clock input to the FPGA
transceiver.
SMA for sending a differential clock output from the FPGA core.
Clock Circuitry
Y2, U20 50-MHz OSC and clock buffer 50-MHz clock to the FPGA and MAX II CPLD.
Y3, U22
Y4, U23
Y5, U24
644.53-MHz OSC and clock
buffer
100-MHz OSC and clock
buffer
706.25-MHz OSC and clock
buffer
644.53-MHz clock to the FPGA transceivers.
100-MHz clock to the FPGA transceivers.
706.25-MHz clock to the FPGA transceivers.
X1 6-MHz XTAL XTAL for FTDI USB PHY device.
Y1 24-MHz OSC 24-MHz oscillator for embedded USB-Blaster MAX II CPLD.
X3 25-MHz OSC 25-MHz oscillator for Marvell 88E1111 Ethernet PHY device.
X2, U21
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
25-MHz OSC and spread
spectrum clock buffer
25-MHz oscillator and spread spectrum clock buffer circuitry.
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 14

2–4 Chapter 2: Board Components
Board Overview
Table 2–1. Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Board Components (Part 3 of 4)
Board Reference Type Description
General User Input and Output
SW7 Bank of 8 user DIP switches User DIP switches.
SW10–SW15 Bank of 6 user push buttons User push buttons switches.
D8–D15 Bank of 8 user LEDs User LEDs.
J25
General purpose user I/O
header field
Four user I/Os brought out to a 0.1 inch header field.
J24 LCD interface header Header for interfacing a 16 character × 2 line LCD.
Memory Devices
U39 Flash memory Numonyx 48F4400P0VB00, 512-Mb flash memory.
Components and Interfaces
CN1 USB Type-B connector USB interface for embedded USB-Blaster.
U17 MAX II CPLD
Altera EPM7064AETC44 MAX II CPLD device for embedded
USB-Blaster circuitry.
J68 Ethernet RJ45 jack Halo HFJ11-1G02E RJ45 Ethernet jack with integrated magnetic.
U40 10/100/1000 Ethernet PHY Marvell 88E1111 triple speed Ethernet PHY.
J70 GXB0 transmit channel 0-5
J71 GXB0 receive channel 0-5
Transceiver GXB0 transmit channel 0-5 connected to a backplane
connector.
Transceiver GXB0 receive channel 0-5 connected to a backplane
connector.
J39, J41 GXB1 transmit channel 0 Transceiver GXB1 transmit channel 0 connected to SMA.
J43, J45 GXB1 transmit channel 1 Transceiver GXB1 transmit channel 1 connected to SMA.
J55, J57 GXB1 transmit channel 2 Transceiver GXB1 transmit channel 2 connected to SMA.
J59, J61 GXB1 transmit channel 3 Transceiver GXB1 transmit channel 3 connected to SMA.
J38, J40 GXB1 receive channel 0 Transceiver GXB1 receive channel 0 connected to SMA.
J42, J44 GXB1 receive channel 1 Transceiver GXB1 receive channel 1 connected to SMA.
J54, J56 GXB1 receive channel 2 Transceiver GXB1 receive channel 2 connected to SMA.
J58, J60 GXB1 receive channel 3 Transceiver GXB1 receive channel 3 connected to SMA.
J34, J36 GXB2 transmit channel 0 Transceiver GXB2 transmit channel 0 connected to SMA.
J30, J32 GXB2 receive channel 0 Transceiver GXB2 receive channel 0 connected to SMA.
J31, J33 GXB2 transmit channel 1 Transceiver GXB2 transmit channel 1 connected to SMA.
J35, J37 GXB2 receive channel 1 Transceiver GXB2 receive channel 1 connected to SMA.
J12 Fan power connector Power connector for 5-V DC fan sink.
J64 Fan control jumper
Jumper to select whether the fan is always on or automatically
controlled by the FPGA.
SW8 Reset push button Board reset push button.
SW9 CPU reset push button CPU reset push button.
Power
J1 Power Input Jack
14-V – 20-V DC female input power jack. Accepts 2.5-mm male
center-positive barrel from supplied 16-V DC power supply.
SW1 Power switch Switch to power on/off the board.
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 15

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–5
Featured Device: Stratix IV GT Device
Table 2–1. Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Board Components (Part 4 of 4)
Board Reference Type Description
J2 0.95-V banana jack
Banana jack for supplying external 0.95-V V
Fuses F1 and F2 must be removed prior to supplying external power to
power to the FPGA.
CC
this banana jack.
J3 VCCA banana jack
J7 VCCR banana jack
J8 VCCT banana jack
J9 VCCH banana jack
J10 VCCL banana jack
Banana jack for supplying external V
must be removed prior to supplying external power to this banana jack.
Banana jack for supplying external V
must be removed prior to supplying external power to this banana jack.
Banana jack for supplying external V
must be removed prior to supplying external power to this banana jack.
Banana jack for supplying external V
must be removed prior to supplying external power to this banana jack.
Banana jack for supplying external V
must be removed prior to supplying external power to this banana jack.
power to the FPGA. Fuse F3
CCA
power to the FPGA. Fuse F4
CCR
power to the FPGA. Fuse F5
CCT
power to the FPGA. Fuse F6
CCH
power to the FPGA. Fuse F7
CCL
J4 GND banana jack Banana jack connected to GND of the board.
F1, F2 10A fuse
F3 2A fuse
F6 5A fuse
F7 2A fuse
F4 2A fuse
F5 2A fuse
U14 Power measurement ADC
Fuses for 0.95-V V
when an external power is applied to this banana jack.
Fuse for V
CCA
external power is applied to this banana jack.
Fuse for V
CCH
external power is applied to this banana jack.
Fuse for V
CCL
external power is applied to this banana jack.
Fuse for V
CCR
external power is applied to this banana jack.
Fuse for V
CCT
external power is applied to this banana jack.
Linear Technology LTC2418CGN 24-bit delta-sigma analog to digital
converter (ADC).
R3 0.001-Ω Rsense Sense resistor for measuring FPGA V
R11 0.009-Ω Rsense Sense resistor for measuring FPGA V
R24 0.009-Ω Rsense Sense resistor for measuring FPGA V
R25 0.009-Ω Rsense Sense resistor for measuring FPGA V
R20 0.009-Ω Rsense Sense resistor for measuring FPGA V
R21 0.009-Ω Rsense Sense resistor for measuring FPGA V
core of the FPGA. These fuses must be removed
CC
power of the FPGA. This fuse must be removed when an
power of the FPGA. This fuse must be removed when an
power of the FPGA. This fuse must be removed when an
power of the FPGA. This fuse must be removed when an
power of the FPGA. This fuse must be removed when an
core power.
CC
power.
CCA
power.
CCH
power.
CCL
power.
CCR
power.
CCT
Featured Device: Stratix IV GT Device
The Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity development board features the
EP4S100G2F40I1N Stratix IV FPGA device (U33) in a 1517-pin FBGA package.
f For more information about the Stratix IV GT devices, refer to the Stratix IV Device
Handbook.
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 16

2–6 Chapter 2: Board Components
Bank 8B 24
Bank 7A 40
Bank 7B 24
Bank 7C 32
22 Bank 1C
23 Bank 2C
24 Bank 3B
40 Bank 4A
24 Bank 4B
32 Bank 4C
Bank 6C 23
Bank 5C 23
46 Bank 2A
Bank 8C 32
Bank 8A 40
32 Bank 3C
40 Bank 3A
Bank 5A 46
Bank 6A 44
Bank
Name
Number
of I/Os
Bank
Name
Number
of I/Os
43 Bank 1A
Bank
GXBL2
Bank
GXBL1
Bank
GXBL0
4 (1)
Bank
GXBR2
Bank
GXBR1
Bank
GXBR0
4 (1)
4 (1)
4 (1)
4 (1)
4 (1)
EP4S40G2
EP4S40G5
EP4S100G2
EP4S100G5
Featured Device: Stratix IV GT Device
Tab le 2– 2 lists the features of the Stratix IV GT EP4S100G2F40I1N device.
Table 2–2. Stratix IV GT Device EP4S100G2F40I1N Features
ALMs
Equivalent
LEs
M9K
RAM
Blocks
M144K
Blocks
Total
RAM
bits
DSP
Blocks
18-bit × 18-bit
Multipliers
PLLs
Maximum
User I/O pins
91,200 228,000 1,235 22 17,133 161 1,288 8 636
Tab le 2– 3 lists the Stratix IV GT component reference and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–3. Stratix IV GT Device Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
U33 Stratix IV GT Altera
Corporation EP4S100G2F40I1N www.altera.com
Manufacturing
Part Number
I/O Resources
Figure 2–2 shows the bank organization and I/O count for the EP4S100G2F40I1N
device in the 1517-pin FBGA package.
Figure 2–2. Stratix IV GT Device I/O Bank Diagram
(1)
Package
Type
1517-pin
FBGA
Manufacturer
Website
Note to Figure 2–2:
(1) There are two additional PMA-only transceiver channels in each transceiver bank.
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 17

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–7
Featured Device: Stratix IV GT Device
Tab le 2– 4 summarizes the FPGA I/O usage by function on the Stratix IV GT
transceiver signal integrity development board. I/O direction is with respect to the
FPGA.
Table 2–4. Stratix IV GT I/O Usage Summary (Part 1 of 3)
Function I/O Type I/O Count Description
FPGA Transceiver Clocks
100-MHz Diff Clock LVDS input 2 Diff REFCLK Input
644.25-MHz Diff Clock LVDS input 2 Diff REFCLK Input
706.53-MHz Diff Clock LVDS input 2 Diff REFCLK Input
SMA Diff Clock Inputs LVDS input 2 Diff REFCLK Input
FPGA Global Clocks
50-MHz Clock 2.5-V CMOS input 1 Global Clock Input
Spread Spectrum Clock LVDS input 2 Diff Global Clock
SMA Diff Clock Input LVDS input 2 Diff Global Clock
SMA Diff I/O or Clock Output — 2 Diff Global I/O or Clock Output
Temperature Monitor
Temp Sense Diodes Analog 2 Stratix IV GT Internal Sense Diode
Power Measure
ADC Interface 2.5-V CMOS 5 8 Diff Channel 24-bit A/D Converter
Temp Measure
MAX1619 Interface 2.5-V CMOS 4 Die Temp Sense
EEPROM
EEP_CSn 2.5-V CMOS output 1 EEPROM Chip Select
Fan
FAN_On 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Fan Control
FAN_LED 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Fan LED
USB-Blaster
JTAG USB-Blaster or JTAG
header
2.5-V CMOS 4
Built-in USB-Blaster or JTAG 0.1-mm header for
Debug
FPP Configuration
FPGA Dclk 2.5-V CMOS input 1 FPP Dclk
FPGA D[7:0] 2.5-V CMOS input 8 FPP Data
MSEL [2:0] 2.5-V CMOS input 3 Dedicated Configuration Pins
NCONFIG 2.5-V CMOS input 1 Dedicated Configuration Pins
NSTATUS 2.5-V CMOS inout 1 Dedicated Configuration Pins
NCE 2.5-V CMOS input 1 Dedicated Configuration Pins
CONFIG_DONE 2.5-V CMOS inout 1 Dedicated Configuration Pins
INIT_DONE 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Dedicated Configuration Pins
PGM[2:0] 2.5-V CMOS output 3 Configuration Program Select Pins
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 18

2–8 Chapter 2: Board Components
Featured Device: Stratix IV GT Device
Table 2–4. Stratix IV GT I/O Usage Summary (Part 2 of 3)
Function I/O Type I/O Count Description
Flash Memory
ADDR[25:0] 2.5-V CMOS output 26 Flash Address Bus
DATA[15:0] 2.5-V CMOS inout 16 Flash Data Bus
FLASH_CEn 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Flash Chip Enable
FLASH_OEn 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Flash Read Strobe
FLASH_WEn 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Flash Write Strobe
FLASH_BSYn 2.5-V CMOS input 1 Flash Busy
FLASH_CLK 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Flash Clock
FLASH_RSTn 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Flash Reset
FLASH_ADVn 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Flash Address Valid
FLASH_WPn 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Flash Write Protect
Resets
CPU_RESETn 2.5-V CMOS input 1 Nios
®
II CPU Reset
S4GT_RESETn 2.5-V CMOS input 1 S4GT General FPGA Reset
Switches, Buttons, LEDS
User Push Buttons 2.5-V CMOS input 6 6 User Push buttons
User DIP Switches 2.5-V CMOS input 8 8 User DIP Switches
User LEDS 2.5-V CMOS output 8 8 User LEDs (Green)
HEX Rotary Switch 2.5-V CMOS input 4 16 Position Rotary Switch
User I/Os 2.5-V CMOS inout 4 4 User I/O pins to header field
LCD
16 Character × 2 Line LCD 2.5-V CMOS 11 LCD
Ethernet
TXD[3:0] 2.5-V CMOS output 4 Ethernet Transmit RGMII Data Bus
TXEN 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Ethernet Transmit Enable
GTXCLK 2.5-V CMOS output 1 Ethernet Transmit Clock
RXD[3:0] 2.5-V CMOS input 4 Ethernet Receive RGMII Data Bus
RXDV 2.5-V CMOS input 1 Receive Data Valid
RXCLK 2.5-V CMOS input 1 Receive Clock
MDC 2.5-V CMOS input 1 Ethernet MII Clock
MDIO 2.5-V CMOS inout 1 Ethernet MII Data
ENET_SGMII_TXP/N LVDS output 2 Ethernet SGMII Transmit Data Positive/Negative
ENET_SGMII_RXP/N LVDS input 2 Ethernet SGMII Receive Data Positive/Negative
Transceivers
GXB0 Transmit Channel Transceiver channel 12
GXB0 Receive Channel Transceiver channel 12
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Six matched length GXB0 transmit channels
routed to a backplane connector J70.
Six matched length GXB0 receive channels routed
to a backplane connector J71.
Page 19

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–9
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
Table 2–4. Stratix IV GT I/O Usage Summary (Part 3 of 3)
Function I/O Type I/O Count Description
GXB2 Short Transmit Channel Transceiver channel 2 Short transmit trace length (11.3G)
GXB2 Short Receive Channel Transceiver channel 2 Short receive trace length (11.3G)
GXB2 Long Transmit Channel Transceiver channel 2 15 inches trace length (11.3G)
GXB2 Long Receive Channel Transceiver channel 2 5 inches trace length (11.3G)
GXB1 Four Full-Duplex
Transceiver Channels
(One entire block, excluding
two clock multiplier unit
(CMU) channels)
Spares
Spare[7:0] 2.5-V CMOS inout 8 Spare signals to the MAX II CPLD
Total Device I/O: 220
Available Stratix IV GT I/O: 636
Transceiver channel 16
Four full-duplex channels from one entire
transceiver block (excluding two CMU channels)
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
This section describes the board’s configuration, status, and setup elements.
Configuration
The Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity development board supports three
configuration methods:
■ Embedded USB-Blaster is the default method for configuring the FPGA at any
time using the Quartus II Programmer in JTAG mode with the supplied USB cable.
■ MAX II+Flash FPP download for configuring the FPGA using stored images from
flash on either power-up or pressing the reset (SW8) push button.
■ JTAG programming header (J28) for configuring the FPGA using an external
USB-Blaster (not supplied) and the Quartus II Programmer.
The following sections describe each of these methods.
Embedded USB-Blaster
The embedded USB-Blaster is implemented using a Type-B USB connector (CN1), a
Future Technologies FT245BL USB PHY device (U16), and an Altera EPM7064 MAX II
CPLD (U17). This allows the configuration of the FPGA using a USB cable directly
connected between the USB port on the board (CN1) and a USB port of a PC running
the Quartus II software.
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 20

2–10 Chapter 2: Board Components
USB Type-B
Connector
(CN1)
FTDI
FT245BL
USB PHY
(U16)
USB FIFO BUS
EPM7064
MAX II
CPLD
(U17)
JTAG
JTAG
JTAG Programming
Header (J28)
USB
Stratix IV GT
FPGA (U33)
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
A green USB-Blaster LED (D7) is also provided to indicate USB-Blaster activity. The
embedded USB-Blaster is automatically disabled when an external USB-Blaster
connects to the JTAG chain at header J28. Figure 2–3 shows the block diagram for the
embedded USB-Blaster.
Figure 2–3. Embedded USB-Blaster
Fast Passive Parallel Download
Figure 2–4 shows the block diagram for the MAX II+Flash FPP configuration. This
method is used for automatic configuration of the FPGA with the configuration
programming image stored in the flash memory. The FPP download controller is
implemented within an Altera EPM1270F256C3N MAX II CPLD (U32). This
controller, together with the Numonyx PC28F512P30BF 512-Mb CFI NOR-type flash
memory (U39), performs the FPP configuration upon board power-up or reset. The
CPLD shares the flash interface with the FPGA. The configuration program select
jumper, PGMSEL, (J62) selects between two Programmer Object Files (.pof)—factory
.pof or user .pof file stored in the flash. The FPP controller uses the Altera Parallel
Flash Loader (PFL) megafunction to configure the FPGA by reading data from the
flash and converting it to FPP format. This data is written to the FPGA’s dedicated
configuration pins during configuration. The configuration mode select signals,
MSEL[2:0]
green configuration status LEDs (D16–D18) indicate the status of the FPP
configuration.
, are pulled to
[0,0,0]
on the board for FPP mode configuration. Three
Figure 2–4. MAX II+Flash FPP Configuration
RESET
Push-Button
(SW8)
PGMSEL
Jumper (J62)
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
MAX II CPLD
FACTORY LED
(U32)
(D17)
USER LED
(D18)
FPP Configuration
(D16)
ERROR LED
Flash
Flash
Flash
(U39)
Stratix IV GT
FPGA
(U33)
Page 21

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–11
J28
U33
Stratix IV GT
Stratix IV GT
and MAX II
External
USB-Blaster
Header
Remove Jumper to
Remove MAX_FPP Device
from JTAG Header
J26
TDI
TMS
TCK
LAST_TDO
S4GT_TDI
S4GT_TDO
JTAG_TMS
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TMS
JTAG_TCK
MAX_FPP_TDI
MAX_FPP_TDO
U32
MAX II CPLD
9
5
1
3
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
JTAG Programming Header
Figure 2–5 shows the schematic connections for the dedicated JTAG programming
header (J28). This header provides another method for configuring the FPGA (U33)
using an Altera USB-Blaster with the Quartus II Programmer running on a PC. The
MAX II JTAG configuration jumper (J26) allows the MAX II CPLD device to be
removed from the JTAG chain so that the FPGA is the only device on the JTAG chain.
Figure 2–5. JTAG Programming Header
Status and Setup Elements
The development board includes board-specific status LEDs, jumpers, and switches
for enabling and configuring various features on the board, as well as a
16 character × 2 line LCD for displaying board power and temperature
measurements. This section describes the status and setup elements.
Status LEDs
Tab le 2– 5 lists the LED board references, names, and functional descriptions.
Table 2–5. Board-Specific LEDs (Part 1 of 2)
Board
Reference
D3 POWER
D6 FAN
D7 BLASTER Green LED. Blinks to indicate the embedded USB-Blaster activity.
D16 ERROR Red LED. Illuminates when a configuration error has occurred.
D17 FACTORY
D18 USER
D19 TX Green LED. Blinks to indicate Ethernet transmit activity.
D20 RX Green LED. Blinks to indicate Ethernet receive activity.
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
LED Name Description
Blue LED. Illuminates when the board power switch (SW1) is on.
(Requires 14–20 V input to DC input jack J1)
Amber LED. Illuminates to indicate an FPGA over-temperature condition. A fan sink
must be attached to the FPGA and running to prevent overheating.
Green LED. Illuminates when the factory POF image is successfully programmed into
the FPGA.
Green LED. Illuminates when the user POF image is successfully programmed into the
FPGA.
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 22

2–12 Chapter 2: Board Components
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
Table 2–5. Board-Specific LEDs (Part 2 of 2)
Board
Reference
LED Name Description
D21 DUPLEX Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet full duplex status.
D22 1000 Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 1000 Mbps.
D23 100 Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 100 Mbps.
D24 10 Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 10 Mbps.
Tab le 2– 6 shows the surface mount LEDs which indicate various status of the board.
Table 2–6. Status LEDs
Board
Reference
Description
D3 Power LED
D17 FACTORY LED
D18 USER LED
D16 ERROR LED
D19 Ethernet transmit activity LED
D20 Ethernet receive activity LED
D21 Ethernet Full-Duplex LED
D22 Ethernet 1000-MB Link LED
D23 Ethernet 100-MB Link LED
D24 Ethernet 100-MB Link LED
D6 Over-Temperature LED
D7 USB-Blaster activity LED
Schematic
Signal Name
5V
FACTORY_IMAGE
USER_IMAGE
CONFIG_ERR
ENET_LED_TX
ENET_LED_RX
ENET_LED_DUPLEX
ENET_LED_LINK1000
ENET_LED_LINK100
ENET_LED_LINK10
FAN_LED
USB_LED
I/O Standard
———
2.5-V CMOS
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin F14 —
3.3-V CMOS — U17 pin 8
Stratix IV GT
Pin Number
Device
Other
Connections
— U32 pin R8
— U32 pin R7
— U32 pin R9
— U40 pin 68
— U40 pin 69
— U40 pin 70
— U40 pin 73
— U40 pin 74
— U40 pin 76
Board Jumpers
Tab le 2– 7 lists the board jumper references, names, and functional descriptions.
Table 2–7. Board Jumpers (Part 1 of 2)
Board
Reference
J26
J62 PGMSEL
J64 FAN
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Jumper Name Description
When a jumper is installed, the MAX II CPLD device (U32) is included in the JTAG
MAXII
BYPASS
programming chain.
When a jumper is removed, the MAX II CPLD device (U32) is removed from the JTAG
programming chain.
When a jumper is installed on pins 1-2, FPP configuration loads the user POF image
from flash.
When a jumper is installed on pins 2-3, FPP configuration loads the factory POF
image from flash.
When a jumper is installed on pins 1-2, the fan is automatically controlled by the
FPGA.
When a jumper is installed on pins 2-3, the fan is always on.
Page 23

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–13
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
Table 2–7. Board Jumpers (Part 2 of 2)
Board
Reference
J65
J66
J67
Jumper Name Description
Y3 OSC
EN/DIS
Y4 OSC
EN/DIS
Y5 OSC
EN/DIS
When a jumper is installed, Y3 oscillator is disabled.
When a jumper is removed, Y3 oscillator is enabled and running.
When a jumper is installed, Y4 oscillator is disabled.
When a jumper is removed, Y4 oscillator is enabled and running.
When a jumper is installed, Y5 oscillator is disabled.
When a jumper is removed, Y5 oscillator is enabled and running.
There is a spread spectrum configuration DIP switch (SW2) for configuring the spread
spectrum clock device (U21). Tab le 2– 8 lists the connection of the spread spectrum
configuration DIP switch (SW2).
Table 2–8. Spread Spectrum Configuration DIP Switch Pin-Out (SW2)
Board
Reference
Description
SW2 pin 1 (S0) Spread spectrum clock
SW2 pin 2 (S1)
SW2 pin 3 (S2)
configuration DIP switch.
When the switch is in the
open position, a logic 1 is
Schematic
Signal Name
S0
S1
SS0
selected. When the switch is
SW2 pin 4 (S3)
in the closed position, a logic
SS1
0 is selected.
I/O Standard
2.5-V CMOS
Stratix IV GT
Device
Pin Name
— U21 pin 1
— U21 pin 2
— U21 pin 3
— U21 pin 8
Other
Connections
Tab le 2– 9 summarizes the functionality of the spread spectrum configuration DIP
switch (SW2).
Table 2–9. Spread Spectrum Configuration DIP Switch (SW2) Configuration
S1 S0 Clock Frequency S3 S2 Spread Spectrum %
0 0 25 MHz 0 0 Center ±25
0 1 100 MHz 0 1 Down –0.50
1 0 125 MHz 1 0 Down –0.75
1 1 200 MHz 1 1 No spread spectrum
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 24

2–14 Chapter 2: Board Components
50-MHz
OSC (Y2)
ICS8304
CLKBUF
(U20)
MAX II CPLD
(U32)
CLKIN SMA
(J14, J15)
Trigger
SMA (J18)
Trigger
SMA (J21)
25-MHz
XTAL (Y2)
Trigger
SMA (J22)
Trigger
SMA (J23)
CLKIN SMA
(J19, J20)
ICS557
Spread
Spectrum
CLKBUF
(U21)
DIPSW
(SW2)
Stratix IV GT
FPGA
(U33)
CLKOUT SMA
(J16, J17)
644.25-MHz
OSC
(Y3)
ICS8543
CLKBUF
(U22)
EN JMP
(J66)
100-MHz
OSC
(Y4)
ICS85411
CLKBUF
(U23)
ICS8543
CLKBUF
(U24)
EN JMP
(J67)
706.53-MHz
OSC
(Y5)
EN JMP
(J65)
Clocks
Clocks
Clocking for the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity board is provided
separately for both the FPGA core and transceivers. The core clocks include a
dedicated 50-MHz clock, a spread spectrum clock capable of producing either
25-MHz, 100-MHz, 125-MHz, or 200-MHz clock, and a pair of SMA connectors to
receive a differential external clock. The dedicated transceiver clocks include a
100-MHz, 644.25-MHz, and a 706.53-MHz clock oscillator source. The 706.53-MHz
clock oscillator is an I
provides any custom frequency to the transceivers. Additionally, for further flexibility,
the transceivers can receive a differential clock from an external source through a pair
of SMA connectors.
Figure 2–6 shows the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity development board
clocking diagram.
Figure 2–6. Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Board Clocking Diagram
2
C programmable clock oscillator device from Silicon Labs that
Tab le 2– 10 shows the clock distribution for the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal
integrity development board.
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 25

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–15
Clocks
Table 2–10. Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Board Clock Distribution
Frequency Signal Name Signal Originates From
50 MHz
User Input
User Defined
User Defined
25 MHz, 100 MHz, 125 MHz, 200 MHz
(Y2)
(Frequencies set by switch SW2)
User Input
644.53 MHz
(Y3)
706.25 MHz
(Y5)
100 MHz
(Y4)
25 MHz, 100 MHz, 125 MHz, 200 MHz
644.53 MHz
(Y3)
100 MHz
(Y4)
706.25 MHz
(Y5)
MAXII_50M_CLK
S4GT_50M_CLK4P
S4GT_EXT_CLK5P
S4GT_EXT_CLK5N
IO_CLKOUT1
IO_CLKOUT2
S4GT_CLK1P
S4GT_CLK1N
EXT_REFCLK4P_GXB2
EXT_REFCLK4N_GXB2
644.53M_REFCLK2P_GXB1
644.53M_REFCLK2N_GXB1
706.25M_REFCLK3P_GXB1
706.25M_REFCLK3N_GXB1
100M_REFCLK5P_GXB2
100M_REFCLK5N_GXB2
X2 Trigger
Y3 Trigger
Y4 Trigger
Y5 Trigger
Signal
Propagates To
U20 pin 8
U20 pin 7
SMA J14
SMA J15
U32 pin H5
U33 pin AR22
U33 pin AV22
U33 pin AW22
U33 pin M20 SMA J16
U33 pin L20 SMA J17
U21 pin 15
U21 pin 14
SMA J19
SMA J20
U22 pin 20
U22 pin 19
U24 pin 1
U24 pin 2
U23 pin 1
U23 pin 2
U33 pin K34
U33 pin J34
U33 pin J38
U33 pin J39
U33 pin AA38
U33 pin AA39
U33 pin W38
U33 pin W39
U33 pin G38
U33 pin G39
U21 pin 11 SMA J18
U22 pin 12 SMA J21
U23 pin 3 SMA J22
U24 pin 3 SMA J23
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 26

2–16 Chapter 2: Board Components
General User Input/Output
General User Input/Output
This section describes the user I/O interface to the FPGA including the push buttons,
user and status LEDs, LCD, and user DIP, rotary, and slide switches. Table 2–11 lists
the component references and the manufacturing information.
Table 2–11. Component Reference Input and Ouput Devices
Board Reference
SW8–SW15 Push buttons Panasonic Corporation EVQPAC07K www.panasonic.com
D7–D15,
D17–D24
D16 Red LED Lumex Inc. SML-LX1206IC-TR www.lumex.com
D6 Amber LED Lite-on Technology Corporation LTST-C150KYKT www.liteon.com
D3 Blue LED Lumex Inc. SML-LX1206USBC-TR www.lumex.com
LCD LCD Lumex Inc. LCM-S01602DSR/C www.lumex.com
SW7 DIP switch Grayhill Corporation 76SB08ST www.grayhill.com
SW2 Mini-DIP switch
SW16 Rotary switch Grayhill Corporation 94HCB16WT www.grayhill.com
SW1 Slide switch E-switch Inc. EG2201A www.e-switch.com
Device
Description
Green LEDs Lumex Inc. SML-LX1206GC-TR www.lumex.com
C&K Components /
ITT Industries
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Part Number
TDA04H0SB1 www.ittcannon.com
Manufacturer
Website
Push Buttons
The board has eight push buttons for user-defined logic input. Each push-button
when pressed drives logic low and when released returns to driving logic high.
Tab le 2– 12 summarizes the push buttons signal name and function.
Table 2–12. Push Button Signal Names and Functions
Board
Reference
SW10
SW11
SW12
SW13
SW14
SW15
SW8
SW9
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
General purpose user push-button
switches. These switches are not
debounced.
Board reset. This switch is not
debounced.
CPU reset. This switch is not
debounced.
Description
Schematic
Signal Name
USR_PB0
USR_PB1
USR_PB2
USR_PB3
USR_PB4
USR_PB5
RESETn
CPURSTn
I/O Standard
2.5-V CMOS
Stratix IV GT
Device
Pin Number
U33 pin AW28
U33 pin AV28
U33 pin AU28
U33 pin AT28
U33 pin AR28
U33 pin AP28
— U32 pin T2
U33 pin AW18
Other
Connections
10-kΩ pull-up
resistor to 2.5 V
10-kΩ pull-up
resistor to 2.5 V
Page 27

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–17
General User Input/Output
User LEDs
A bank of eight green, surface mount LEDs (SM1206 type) are provided for general
purpose use. The cathodes of these LEDs each connects to an FPGA I/O pin while the
anodes are pulled to 2.5 V through a current limiting resistor. Driving the
corresponding FPGA I/O pin low illuminates the LED. Driving the pin high turns the
LED off. Table 2–13 lists the assignment for each user LED.
Table 2–13. User LED Pin-Out (Green)
Board
Reference
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
General purpose green
surface mount (type 1206)
User LEDs.
Driving a logic 0 on the I/O
port turns the LED ON.
Driving a logic 1 on the I/O
port turns the LED OFF.
Description
LCD
The development board includes a 16 character × 2 line LCD. The display connects
directly to the FPGA device. Table 2–14 lists the LCD pin assignments.
Table 2–14. Seven-Segment Display Pin-Out
Board
Reference
LCD LCD DATA 0
LCD LCD DATA 1
LCD LCD DATA 2
LCD LCD DATA 3
LCD LCD DATA 4
LCD LCD DATA 5
LCD LCD DATA 6
LCD LCD DATA 7
LCD LCD enable signal
LCD LCD data/control signal
LCD LCD write enable strobe
Description
Schematic
Signal Name
USR_LED0
USR_LED1
USR_LED2
USR_LED3
USR_LED4
USR_LED5
USR_LED6
USR_LED7
Schematic
Signal Name
LCD_DATA0
LCD_DATA1
LCD_DATA2
LCD_DATA3
LCD_DATA4
LCD_DATA5
LCD_DATA6
LCD_DATA7
LCD_EN
LCD_D_Cn
LCD_Wen
I/O Standard
2.5-V CMOS
I/O Standard
2.5-V CMOS
Stratix IV GT
Device
Pin Number
U33 pin AW29 160 Ω to 2.5 V
U33 pin AV29 160 Ω to 2.5 V
U33 pin AU29 160 Ω to 2.5 V
U33 pin AT29 160 Ω to 2.5 V
U33 pin AW30 160 Ω to 2.5 V
U33 pin AT30 160 Ω to 2.5 V
U33 pin AP30 160 Ω to 2.5 V
U33 pin AN30 160 Ω to 2.5 V
Stratix IV GT
Device
Pin Name
U33 pin B17 J24 pin 7
U33 pin B19 J24 pin 8
U33 pin D21 J24 pin 9
U33 pin D22 J24 pin 10
U33 pin D23 J24 pin 11
U33 pin E22 J24 pin 12
U33 pin E23 J24 pin 13
U33 pin F23 J24 pin 14
U33 pin C22 J24 pin 6
U33 pin A18 J24 pin 4
U33 pin A17 J24 pin 5
Other
Connections
Other
Connections
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 28

2–18 Chapter 2: Board Components
Flash Memory Device
DIP Switches
The user DIP switch is for reference design functions and general purpose use. This
switch connects to the FPGA device I/O pins. Table 2–15 summarizes the function
and connections of the user DIP switch (SW7).
Table 2–15. User DIP Switch Pin-Out (SW7)
Board Reference Description
SW7 pin 1
SW7 pin 2
SW7 pin 3
SW7 pin 4
SW7 pin 5
SW7 pin 6
SW7 pin 7
SW7 pin 8
User DIP switch
connected to FPGA
device. When the switch
is in the open position, a
logic 1 is selected.
When the switch is in the
closed position, a logic 0
is selected.
Flash Memory Device
The board features a Numonyx PC28F512P30BF 512-Mb CFI-compliant NOR-type
flash memory device. This device stores configuration files for the FPGA. Both the
MAX II CPLD (U32) and FPGA (U33) devices can access the flash. The MAX II access
the flash for FPP configuration of the FPGA using the PFL Megafunction. The FPGA
access to the flash’s user space for embedded NIOS applications. Tab le 2– 16 lists the
pin-out information of the flash memory interface to the FPGA. The signal direction is
with respect to the FPGA device.
Schematic
Signal Name
USR_DIP0
USR_DIP1
USR_DIP2
USR_DIP3
USR_DIP4
USR_DIP5
USR_DIP6
USR_DIP7
I/O Standard
2.5-V CMOS
Stratix IV GT
Device
Pin Name
U33 pin AW27
U33 pin AU27
U33 pin AT27
U33 pin AP27
U33 pin AN27
U33 pin AP26
U33 pin AN26
U33 pin AM26
Other
Connections
10-kΩ pull-up
resistor to 2.5 V
Table 2–16. Flash Memory Pin-Out (U39) (Part 1 of 2)
Board
Reference
U39 pin A1 Flash Address bus bit 1
U39 pin B1 Flash Address bus bit 2
U39 pin C1 Flash Address bus bit 3
U39 pin D1 Flash Address bus bit 4
U39 pin D2 Flash Address bus bit 5
U39 pin A2 Flash Address bus bit 6
U39 pin C2 Flash Address bus bit 7
U39 pin A3 Flash Address bus bit 8
U39 pin B3 Flash Address bus bit 9
U39 pin C3 Flash Address bus bit 10
U39 pin D3 Flash Address bus bit 11
U39 pin C4 Flash Address bus bit 12
U39 pin A5 Flash Address bus bit 13
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Description
Schematic
Signal Name
F_AD1
F_AD2
F_AD3
F_AD4
F_AD5
F_AD6
F_AD7
F_AD8
F_AD9
F_AD10
F_AD11
F_AD12
F_AD13
I/O Standard
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AN15 U32 pin M16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AM14 U32 pin M15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AN14 U32 pin M14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AP15 U32 pin N16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AP14 U32 pin N15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AL15 U32 pin J16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AP13 U32 pin N13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AN13 U32 pin N14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin J15 U32 pin C14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin H13 U32 pin B12
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin M13 U32 pin F15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin M14 U32 pin F16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin K15 U32 pin D16
Stratix IV GT
Device
Pin Name
Other
Connections
Page 29

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–19
Flash Memory Device
Table 2–16. Flash Memory Pin-Out (U39) (Part 2 of 2)
Board
Reference
Description
U39 pin B5 Flash Address bus bit 14
U39 pin C5 Flash Address bus bit 15
U39 pin D7 Flash Address bus bit 16
U39 pin D8 Flash Address bus bit 17
U39 pin A7 Flash Address bus bit 18
U39 pin B7 Flash Address bus bit 19
U39 pin C7 Flash Address bus bit 20
U39 pin C8 Flash Address bus bit 21
U39 pin A8 Flash Address bus bit 22
U39 pin G1 Flash Address bus bit 23
U39 pin H8 Flash Address bus bit 24
U39 pin B6 Flash Address bus bit 25
U39 pin F2 Flash Data bus bit 0
U39 pin E2 Flash Data bus bit 1
U39 pin G3 Flash Data bus bit 2
U39 pin E4 Flash Data bus bit 3
U39 pin E5 Flash Data bus bit 4
U39 pin G5 Flash Data bus bit 5
U39 pin G6 Flash Data bus bit 6
U39 pin H7 Flash Data bus bit 7
U39 pin E1 Flash Data bus bit 8
U39 pin E3 Flash Data bus bit 9
U39 pin F3 Flash Data bus bit 10
U39 pin F4 Flash Data bus bit 11
U39 pin F5 Flash Data bus bit 12
U39 pin H5 Flash Data bus bit 13
U39 pin G7 Flash Data bus bit 14
U39 pin E7 Flash Data bus bit 15
U39 pin E6 Flash Clock
U39 pin D4 Flash Reset
U39 pin B4 Flash Chip Enable
U39 pin F8 Flash Output Enable
U39 pin G8 Flash Write Enable
U39 pin F6 Flash Adress Valid
U39 pin C6 Flash Write Protect
U39 pin F7 Flash Busy
Schematic
Signal Name
F_AD14
F_AD15
F_AD16
F_AD17
F_AD18
F_AD19
F_AD20
F_AD21
F_AD22
F_AD23
F_AD24
F_AD25
F_D0
F_D1
F_D2
F_D3
F_D4
F_D5
F_D6
F_D7
F_D8
F_D9
F_D10
F_D11
F_D12
F_D13
F_D14
F_D15
F_CLK
F_RSTn
F_CEn
F_OEn
F_Wen
F_ADVn
F_WPn
F_BSYn
I/O Standard
Stratix IV GT
Device
Pin Name
Other
Connections
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin G13 U32 pin A11
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin G14 U32 pin A12
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin J12 U32 pin B13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin L13 U32 pin E15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AM13 U32 pin L14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AL14 U32 pin J15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin K13 U32 pin D14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AL13 U32 pin K14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin K14 U32 pin D15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin H14 U32 pin A13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin J13 U32 pin B14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin K12 U32 pin C13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AK13 U32 pin L15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AK14 U32 pin L16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AJ13 U32 pin K15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AJ14 U32 pin K16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AH14 U32 pin H16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AH13 U32 pin H15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AG15 U32 pin G16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AG14 U32 pin G15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AE15 U32 pin M13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AD15 U32 pin L13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AF16 U32 pin J13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AE16 U32 pin H13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AG18 U32 pin G13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AE18 U32 pin F13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AG19 U32 pin F14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AF19 U32 pin E14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AU14 U32 pin R16
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin N15 U32 pin H14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AR13 U32 pin P14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AR14 U32 pin P15
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin N13 U32 pin G14
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AT13 U32 pin P13
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin AT14 U32 pin T12
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin R14 U32 pin J14
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 30

2–20 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Interfaces
Tab le 2– 17 lists the flash memory map storage for two FPGA bitstreams (factory and
user) as well as 40 MB of reserved user space for storage of PFL configuration settings,
software binaries, and other data relevant to the targeted FPGA design (Nios II
applications). For the EP4S100G2F40I1N FPGA device, each FPGA bitstream can be a
maximum of 94.54 Mb (less than 12 MB). Hence, the factory and user POF space is set
at 12 MB.
Table 2–17. Flash Memory Map
Name Size (MB) Address
Reserved 40
USER 12
FACTORY 12
0x0180.0000 – 0x03FF.FFFF
0x00C0.0000 – 0x017F.FFFF
0x0000.0000 – 0x00BF.FFFF
Tab le 2– 18 lists the flash memory device component reference and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–18. Flash Memory Device
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
U39 512-Mb NOR-type flash Numonyx PC28F512P30BF www.numonyx.com
Components and Interfaces
This section describes the temperature measurement and power measurement
circuitries and the board’s communication ports.
Temperature Measurement
Figure 2–7 shows the block diagram for the temperature measurement circuitry.
Figure 2–7. Temperature Measurement
TEMPDIODE_P
MAX1619
(U15)
TEMPDIODE_N
OVERTEMPn
ALERTn
SMBDATA
SMBCLK
Stratix IV GT
FPGA
(U33)
Temperature monitoring for the Stratix IV die is achieved by using a MAX1619
temperature sense device. The MAX1619 connects to the FPGA by a 2-wire SMBus
interface. The
OVERTEMPn
and
ALERTn
signals from the MAX1619 connect to the FPGA
to allow it to immediately sense a temperature fault condition and turn on the
attached fan. The FPGA controls the fan based on the
OVERTEMPn
signal from the
MAX1619, or the fan can be set to always ON.
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 31

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–21
Components and Interfaces
Tab le 2– 19 lists the fan control jumper (J64) which configures the fan.
Table 2–19. Fan Control Jumper (J64)
Board Reference Jumper Name Description
J64 FAN
When jumper is installed on pins 1-2, the fan is auto-controlled by the FPGA.
When jumper is installed on pins 2-3, the fan is always on.
An over-temperature orange warning LED (D6) also connects to the FPGA to indicate
that an over-temperature condition exists and that a fan should be attached and
running. Tab le 2 –2 0 lists the pin-out of the temperature sense interface to the FPGA.
Table 2–20. Temperature Sensor Pin-Out
Board
Reference
Description
U15 pin 3 Analog sense DIODE P pin
U15 pin 4 Analog sense DIODE N pin
U15 pin 12 SMBus Data pin
U15 pin 14 SMBus Clock pin
U15 pin 9 Over Temperature signal
U15 pin 11 Alert signal
Tab le 2– 21 lists the temperature
Schematic Signal
Name
TEMPDIODE_P
TEMPDIODE_N
S4_SMBDATA
S4_SMBCLK
OVERTEMPn
ALERTn
sensor component reference and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–21. Temperature Sensor Component Reference
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
U15
Dual temperature sensor with
SMBus interface
Maxim Integrated
Products, Inc.
Stratix IV GT
I/O Standard
Device Pin
Other Connections
Number
Analog U33 pin A9 —
Analog U33 pin E11 —
U33 pin B14
U33 pin A14
2.5-V CMOS
U33 pin C14
U33 pin D14
Manufacturing
Part Number
10-kΩ pull-up
resistor to 2.5 V
10-kΩ pull-up
resistor to 2.5 V
10-kΩ pull-up
resistor to 2.5 V
10-kΩ pull-up
resistor to 2.5 V
Manufacturer
Website
MAX1619MEE+T www.maxim-ic.com
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 32

2–22 Chapter 2: Board Components
Stratix IV GT
FPGA
(U33)
SPI Bus
LTC2418
(U14)
0p95V
R3
Reg
(U1)
R20
Reg
(U6, U8)
R25
Reg
(U11)
Reg
(U10, U12)
R24
R11
Reg
(U4)
V
CCR
V
CCL
V
CCH
V
CCA
R21
Reg
(U7, U9)
V
CCT
Components and Interfaces
Power Measurement
Figure 2–8 shows the block diagram for the power measurement circuitry.
Figure 2–8. Power Measurement Circuit
The power measurement is provided for six FPGA power rails (0.95-V VCC core plus
the transceiver power rails—V
CCR
, V
CCT
, V
CCL
, V
CCH
, and V
). The power
CCA
measurement is implemented by a multi-channel differential 24-bit Linear Technology
LT2418 (U14) delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and sense resistors to
measure the small voltage drop across the resistors. This ADC connects to the FPGA
via a serial peripheral interface (SPI) bus. The FPGA handles all power measurement
processing and display to the LCD. A rotary switch (SW16) controls the selection of
specific power rail to be displayed on the LCD. Table 2–22 lists the power rails being
measured along with the value of the sense resistor used for each rail.
Table 2–22. Power Rail Measurements
Power Rail Voltage (V) Board Reference Rsense (Ω)
and V
V
CC
V
CCR
V
CCT
V
CCL
V
CCH
V
CCA
CCHIP
0.95 R3 0.001
1.2 R20 0.009
1.2 R21 0.009
1.2 R25 0.009
1.4 R24 0.009
3.3 R11 0.009
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 33

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–23
Stratix IV GT
FPGA
(U33)
SGMII/RGMII
Marvell 88E1111
(U40)
TX/RX
RJ45 +
Mangetics (J68)
Components and Interfaces
Tab le 2– 23 lists the SPI Bus pin connections to the FPGA for the power measurement
circuitry.
Table 2–23. Power Measurement Pin-Out
Board
Reference
Description
U14 pin 17 Serial data out
U14 pin 20 Serial data in
U14 pin 18 Serial clock
U14 pin 16 Chip select
U14 pin 19 Frequency control
Tab le 2– 24 lists the ADC
Schematic Signal
Name
S4_SPI_MISO
S4_SPI_MOSI
S4_SPI_SCK
S4_ADC_CSn
S4_ADC_Fo
component reference and manufacturing information
I/O Standard
Stratix IV GT Device
Pin Number
Other
Connections
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin C11 —
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin B11 —
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin C12 —
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin C13
10-kΩ pull-up
resistor to 2.5 V
2.5-V CMOS U33 pin A13 —
Table 2–24. ADC Component Reference
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
U14 8-Channel differential 24-bit ADC Linear Technology LTC2418CGN#PBF www.linear.com
Ethernet Port
The Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity development board incorporates a triple
speed 10/100/1000 Base-T Ethernet port. The implementation uses a discrete Ethernet
PHY device and RJ45 connector with integrated magnetics connected to the FPGA.
Figure 2–9 shows the block diagram of the Ethernet port.
Figure 2–9. Ethernet Port
Tab le 2– 25 lists the components used for the Ethernet port and the manufacturing
information.
Table 2–25. Ethernet Component References
Board
Reference
Description Manufacturer
U40 10/100/1000 Base-T Ethernet PHY
Marvell
Semiconductor
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
88E1111-B2-CAA1C000 www.marvell.com
J68 RJ45 with integrated magnetics Halo Electronics HFJ11-1G02ERL www.haloelectronics.com
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 34

2–24 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Interfaces
Tab le 2– 26 lists the SGMII and RGMII interface pin connection to the FPGA for the
Ethernet PHY device.
Table 2–26. Power Measurement Pin-Out
Board
Reference
U40 pin 11 RGMII Transmit Data 0
U40 pin 12 RGMII Transmit Data 1
U40 pin 14 RGMII Transmit Data 2
U40 pin 16 RGMII Transmit Data 3
U40 pin 9 RGMII Transmitter Enable
U40 pin 8 RGMII Transmit Clock
U40 pin 95 RGMII Receive Data 0
U40 pin 92 RGMII Receive Data 1
U40 pin 93 RGMII Receive Data 2
U40 pin 91 RGMII Receive Data 3
U40 pin 94 RGMII Receive Data Valid
U40 pin 2 Receive Clock
U40 pin 82 SGMII Transmit Data P ENET_SGMII_TX_P
U40 pin 81 SGMII Transmit Data N ENET_SGMII_TX_N U33 pin K29 —
U40 pin 77 SGMII Receive Data P ENET_SGMII_RX_P
U40 pin 75 SGMII Receive Data N ENET_SGMII_RX_N U33 pin C31 —
Description
Schematic Signal
Name
TXD0
TXD1
TXD2
TXD3
TXEN
GTXCLK
RXD0
RXD1
RXD2
RXD3
RXDV
RXCLK
I/O Standard
2.5-V CMOS
LVDS output
LVDS input
Stratix IV GT
Device Pin
Number
U33 pin C29 —
U33 pin C30 —
U33 pin A27 —
U33 pin A29 —
U33 pin A31 —
U33 pin B29 —
U33 pin F27 —
U33 pin F26 —
U33 pin E29 —
U33 pin E28 —
U33 pin D28 —
U33 pin D29 —
U33 pin L29 —
U33 pin D31 —
Other
Connections
Transceiver Channels
The Stratix IV GT in the 1517-pin FBGA package incorporates six transceiver blocks
(GXB0 left/right, GXB1 left/right, and GXB2 left/right), with up to six transmit and
six receive channels per GXB block. For evaluation of these channels, this board offers
a total of 12 transceiver channels of the three left GXB blocks to SMA and backplane
connectors. Table 2–27 lists the SMA and backplane connector information.
Table 2–27. SMA Connector Component References
Board
Reference
J30–J61 SMA connector Lighthorse Technology LTI-SASF546-P26-X1 www.maxim-ic.com
J70-J71 FCI Airmax VS connectors FCI 10057041-101LF www.fci.com
Description Manufacturer
In the left GXB0 block, six transmit and six receive channels are sent to the backplane
connectors J70 and J71. In the left GXB1 block, four transmit and four receive channels
are sent to SMA connectors J38-J45 and J54-J61. In the left GXB2 block, two transmit
and two receive channels are sent to SMA connectors J30-J37.
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 35

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–25
Power
Tab le 2– 28 summarizes the transceiver channels available on the Stratix IV GT
transceiver signal integrity development board.
Table 2–28. Transceiver Channel Pin-Out
Board
Reference
J70 TX0 from Left GXB0 Block
J70 TX1 from Left GXB0 Block
J70 TX2 from Left GXB0 Block
J70 TX3 from Left GXB0 Block
J70 TX4 from Left GXB0 Block
J70 TX5 from Left GXB0 Block
J71 RX0 from Left GXB0 Block
J71 RX1 from Left GXB0 Block
J71 RX2 from Left GXB0 Block
J71 RX3 from Left GXB0 Block
J71 RX4 from Left GXB0 Block
J71 RX5 from Left GXB0 Block
J39, J41 TX0 from Left GXB1 Block
J38, J40 RX0 from Left GXB1 Block
J43, J45 TX1 from Left GXB1 Block
J42, J44 RX1 from Left GXB1 Block
J55, J57 TX2 from Left GXB1 Block
J54, J56 RX2 from Left GXB1 Block
J59, J61 TX3 from Left GXB1 Block
J58, J60 RX3 from Left GXB1 Block
J34, J36 TX0 from Left GXB2 Block
J30, J32 RX0 from Left GXB2 Block
J31, J33
J35, J37
15 inches long transmitter TX1
channel from Left GXB2 Block
channel from Left GXB2 Block
Description Schematic Signal Name
5 inches long receiver RX1
GXB0_TX0[p/n]
GXB0_TX1[p/n]
GXB0_TX2[p/n]
GXB0_TX3[p/n]
GXB0_CMU_TX4[p/n]
GXB0_CMU_TX5[p/n]
GXB0_RX0[p/n]
GXB0_RX1[p/n]
GXB0_RX2[p/n]
GXB0_RX3[p/n]
GXB0_CMU_RX4[p/n]
GXB0_CMU_RX5[p/n]
GXB1_TX0[p/n]
GXB1_RX0[p/n]
GXB1_TX1[p/n]
GXB1_RX1[p/n]
GXB1_TX2[p/n]
GXB1_RX2[p/n]
GXB1_TX3[p/n]
GXB1_RX3[p/n]
GXB2_TX0[p/n]
GXB2_RX0[p/n]
GXB2_TX1[p/n]
GXB2_RX1[p/n]
I/O
Standard
— AT36, AT37 J70.F6, J70.E6
— AP36, AP37 J70.E5, J70.D5
— AH36, AH37 J70.L4, J70.K4
— AF36, AF37 J70.K3, J70.J3
— AM36, AM37 J70.F4, J70.E4
— AK36, AK37 J70.E3, J70.D3
— AU38, AU39 J71.F6, J71.E6
— AR38, AR39 J71.E5, J71.D5
— AJ38, AJ39 J71.L4, J71.K4
— AG38, AG39 J71.K3, J71.J3
— AN38, AN39 J71.F4, J71.E4
— AL38, AL39 J71.E3, J71.D3
— AD36, AD37 —
— AE38, AE39 —
— AB36, AB37 —
— AC38, AC39 —
— T36, T37 —
— U38, U39 —
— P36, P37 —
— R38, R39 —
— M36, M37 —
— N38, N39 —
— K36, K37 —
— L38, L39 —
Stratix IV GT
Device Pin
Number
Other
Connections
All receive channels include a 0402 type 0.1-µF DC blocking capacitor in series with
the P and N signals to remove the DC component of the transmitted signal. The
receivers internally regenerate the required DC offset. Blocking capacitors are not
provided for transmit channels.
Power
The board’s power is provided through a laptop style DC power input. The input
voltage must be in the range of 14 V to 20 V. The DC voltage is then stepped down to
the various power rails used by the components on the board. The slide switch (SW1)
is the board power switch.
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 36

2–26 Chapter 2: Board Components
Power
Tab le 2– 29 lists the connection of this power switch.
Table 2–29. Slide Switch Pin-Out (SW1)
Board
Reference
Description
Power switch. Slide switch to ON
SW1
position to power on the board. Slide
switch to OFF position to power off
the board.
Power Distribution System
Figure 2–10 shows the power distribution system on the board.
Figure 2–10. Power Distribution System
14 V - 20 V
DC Input
U1
LTM4601
Switching
LTM4601
Regulator
Switching
Regulator
U2
LTM4601
Switching
Regulator
U3
0.95 V
@ 24 A
5 V @ 12 A
R3
LT3080-1
LDO
U4
LT1761
LDO
U37
3.3 V
@1.1 A
3.3 V
@ 0.1 A
VCC
VCCHIP
LTM4616
Dual Output
Micromodule
R11
U5
Schematic
Signal Name
RUN_SW
3.3 V @ 8 A
2.5 V @ 8 A
VCCA
3.3V_Analog
ADC
LCD, Fan
Bead
I/O
Standard
Stratix IV GT Device
Pin Name
——
VCCD_PLL
3.3 V Devices
VCCIO
VCCPD
VCCREF
VCCPGM
VCCBAT
VCC_CLKIN
2.5 V Devices
LTC3025-1
LDO
LT3080-1
LDO
1.2 V
@ 0.5 A
(U11)
1.4 V
@ 2.2 A
(U10, U12)
R25
R24
Bead
VCCA_PLL
VCCAUX
VCCL_GXB
VCCH_GXB
Other
Connections
DC Input
U1 pin A10
U2 pin A10
U3 pin A10
LDO
LDO
LDO
LT3080-1
LDO
LDO
1.5 V
@ 0.5 A
(U13)
1.2 V
@ 2.2 A
(U7, U9)
1.2 V
@ 2.2 A
(U6, U8)
1.2 V
@ 1.1 A
(U25)
1.8 V
@ 0.5 A
(U38)
R21
R20
VCCIO_1.5 V
VCCPT
VCCT
VCCR
VCC_1.2V
Ethernet
VCC_1.8V
Flash
LEGEND
Stratix IV GT Power
Other Power
LTC3025-1
LT3080-1
LT3080-1
LTC3025-1
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 37

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–27
Power
Tab le 2– 30 lists the power components used on the board.
Table 2–30. Voltage Regulator Component Reference
Reference
Designator
U1, U2, U3
U5
Device Description Manufacturer
µModule Switching
12A
Regulator
Dual 8A/Channel µModule
Switching Regulator
Linear Technology LTM4601EV#PBF www.linear.com
Linear Technology LTM4616EV#PBF www.linear.com
Manufacturer
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
U4, U6, U7,
U8, U9, U10,
1.1A LDO Linear Regulator Linear Technology LT3080EDD-1#PBF www.linear.com
U12, U25
U11, U13, U38 500 mA VLDO Linear Regulator Linear Technology LTC3025EDC-1#PBF www.linear.com
U37
100 mA Low Noise LDO Linear
Regulator
Linear Technology LT1761ES5-SD#PBF www.linear.com
Banana Jacks and Fuses
In addition to the power supplied by the regulators, several power rails can be
directly supplied by an external bench-top power supply through the on-board
banana jacks (J2–J4, J7–J10). Figure 2–11 illustrates how the external power is allowed
in through the banana jacks by first removing the fuses (F1–F7) associated with the
power rail to be externally supplied.
c Failure to remove the associated fuses (F1–F7) or improperly setting the external
supply voltages too high can result in damage to the board.
Figure 2–11. External Power Supplied through Banana Jack
Regulator
Fuse
Tab le 2– 31 summarizes the banana jacks and fuses associated with each power rail
that can be supplied by external power.
Table 2–31. Banana Jack and Fuses Component Reference (Part 1 of 2)
Banana Jack
Board
Reference
J2 F1, F2
Fuse Board
Reference
Device Description Manufacturer
Banana jack and fuse
for supplying external
power to VCC core
Johnson
Components
Littelfuse Inc. 154 010.DR www.littlefuse.com
Banana
Jack
Manufacturer
Part Number
Sense lines to ADC
R
sense
Voltage
Rail
Manufacturer
Website
111-0702-001 www.johnsoncomponents.com
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 38

2–28 Chapter 2: Board Components
Power
Table 2–31. Banana Jack and Fuses Component Reference (Part 2 of 2)
Banana Jack
Board
Reference
Fuse Board
Reference
J3 F3
J9 F6
J10 F7
J7 F84
J8 F5
J4 —
Device Description Manufacturer
Banana jack and fuse
for supplying external
power to VCCA
Banana jack and fuse
for supplying external
power to VCCH
Banana jack and fuse
for supplying external
power to VCCL
Banana jack and fuse
for supplying external
power to VCCR
Banana jack and fuse
for supplying external
power to VCCT
Banana jack
connected to board
GND
Johnson
Components
Littelfuse Inc. 154 002 www.littlefuse.com
Johnson
Components
Littelfuse Inc. 154 005.DR www.littlefuse.com
Johnson
Components
Littelfuse Inc. 154 002 www.littlefuse.com
Johnson
Components
Littelfuse Inc. 154 002 www.littlefuse.com
Johnson
Components
Littelfuse Inc. 154 002 www.littlefuse.com
Johnson
Components
Littelfuse Inc. — www.littlefuse.com
Manufacturer
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
111-0702-001 www.johnsoncomponents.com
111-0702-001 www.johnsoncomponents.com
111-0702-001 www.johnsoncomponents.com
111-0702-001 www.johnsoncomponents.com
111-0702-001 www.johnsoncomponents.com
111-0703-001 www.johnsoncomponents.com
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 39

A. Board Revision History
This appendix catalogs revisions to the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity
development board.
Tab le A– 1 lists the released versions of the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity
development board.
Table A–1. Stratix IV GT Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Board Revision History
Version Release Date Description
Single-die flash November 2011
Production silicon December 2009 Initial release.
Single-Die Flash Version Differences
The single-die flash version of the Stratix IV GT transceiver signal integrity
development board is created to replace the obsolete dual-die flash device with a
single-die flash device. The two flash devices are considered equivalent except for
some software routines used to access them because the single-die device has only
one CFI table whereas the duel-die device has two CFI tables.
Replaced Intel dual-die 512-Mb flash PC48F4400P0VB00 with Numonyx
single-die 512-Mb flash PC28F512P30BF.
To determine which flash your board is using, refer to the device part number
installed at U39. The single-die package is smaller than the dual-die version.
f For more information about the flash change and its application, refer to the
Transceiver Signal Integrity Kit, Stratix IV GT Edition User Guide.
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 40

A–2 Appendix A: Board Revision History
Single-Die Flash Version Differences
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 41

This chapter provides additional information about the document and Altera.
Document Revision History
The following table lists the revision history for this document.
Date Version Changes
■ Added “Single-Die Flash Version Differences” section to document the replacement of
November 2011 1.1
December 2009 1.0 Initial release.
dual-die 512-Mb flash with a single-die 512-Mb flash device.
■ Updated the flash device manufacturing part number in Table 2–16.
■ Converted the document to new frame template and made textual and style changes.
Additional Information
How to Contact Altera
To locate the most up-to-date information about Altera products, refer to the
following table.
Contact
Technical support Website www.altera.com/support
Technical training
Product literature Website www.altera.com/literature
Nontechnical support (general) Email nacomp@altera.com
Note to Table:
(1) You can also contact your local Altera sales office or sales representative.
(1)
(software licensing) Email authorization@altera.com
Contact Method Address
Website www.altera.com/training
Email custrain@altera.com
Typographic Conventions
The following table shows the typographic conventions this document uses.
Visual Cue Meaning
Bold Type with Initial Capital
Letters
bold type
Italic Type with Initial Capital Letters Indicate document titles. For example, Stratix IV Design Guidelines.
Indicate command names, dialog box titles, dialog box options, and other GUI
labels. For example, Save As dialog box. For GUI elements, capitalization matches
the GUI.
Indicates directory names, project names, disk drive names, file names, file name
extensions, software utility names, and GUI labels. For example, \qdesigns
directory, D: drive, and chiptrip.gdf file.
November 2011 Altera Corporation Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit,
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
Page 42

Info–2 Additional Information
Typographic Conventions
Visual Cue Meaning
Indicates variables. For example, n + 1.
italic type
Variable names are enclosed in angle brackets (< >). For example, <file name> and
<project name>.pof file.
Initial Capital Letters
“Subheading Title”
Indicate keyboard keys and menu names. For example, the Delete key and the
Options menu.
Quotation marks indicate references to sections in a document and titles of
Quartus II Help topics. For example, “Typographic Conventions.”
Indicates signal, port, register, bit, block, and primitive names. For example,
tdi
, and
input
. The suffix n denotes an active-low signal. For example,
resetn
data1
.
,
Indicates command line commands and anything that must be typed exactly as it
Courier type
appears. For example,
c:\qdesigns\tutorial\chiptrip.gdf
.
Also indicates sections of an actual file, such as a Report File, references to parts of
files (for example, the AHDL keyword
TRI
example,
).
SUBDESIGN
), and logic function names (for
r An angled arrow instructs you to press the Enter key.
1., 2., 3., and
a., b., c., and so on
■ ■ ■ Bullets indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is not important.
Numbered steps indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is important,
such as the steps listed in a procedure.
1 The hand points to information that requires special attention.
h The question mark directs you to a software help system with related information.
f The feet direct you to another document or website with related information.
m The multimedia icon directs you to a related multimedia presentation.
c
w
A caution calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can damage or
destroy the product or your work.
A warning calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can cause you
injury.
The envelope links to the Email Subscription Management Center page of the Altera
website, where you can sign up to receive update notifications for Altera documents.
Transceiver Signal Integrity Development Kit, November 2011 Altera Corporation
Stratix IV GT Edition Reference Manual
 Loading...
Loading...