Page 1

WRG-N15
IEEE802.11n Wireless Router
User Guide
November 2007
Page 2

Contents
EFORE YOU START
B
.....................................................................................................................
Installation Overview ................................................................................................................ iv
ACKING LIST ...............................................................................................................................IV
P
Installation Notes ....................................................................................................................... v
Installation Information ............................................................................................................. vi
INTRODUCTION..............................................................................................................................1
OUTER DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
R
RONT VIEW
F
..................................................................................................................................2
........................................................................................1
LED Display ...............................................................................................................................3
EAR PANEL CONNECTIONS ..........................................................................................................4
R
ONNECTING DEVICES TO THE ROUTER ........................................................................................5
C
Connect Router to Ethernet.......................................................................................................5
Connecting through 802.11 Wireless ........................................................................................5
General Guide to Setting Up a Wireless Network.....................................................................5
Installation Considerations for Wireless LAN............................................................................7
POWER ON WIRELESS BROADBAND ROUTER.........................................................................8
Factory Reset Button.................................................................................................................8
CONFIGURATION ...........................................................................................................................9
IV
IP SETTINGS ON YOUR COMPUTER................................................................................................9
CCESS THE CONFIGURATION MANAGER
A
.......................................................................................9
Login to Home Page ................................................................................................................10
EBMANAGER
W
ASIC CONFIGURATION
B
ETUP WIZARD
S
ASIC WIRELESS SETUP
B
...........................................................................................................................11
OME DIRECTORY MENUS
– H
...................................................................12
............................................................................................................................13
..............................................................................................................27
Wireless Security .....................................................................................................................28
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)..................................................................................................29
WAN C
ONFIGURATION ................................................................................................................34
Static IP Address Connection..................................................................................................35
Dynamic IP Connection ...........................................................................................................37
PPPoE Connection..................................................................................................................39
Bridge Connection ...................................................................................................................41
PPTP Connection ....................................................................................................................42
L2TP Connection .....................................................................................................................44
LAN ............................................................................................................................................46
Page 3

DHCP .........................................................................................................................................47
DVANCED DIRECTORY MENUS
A
...................................................................................................49
Virtual Server ...........................................................................................................................50
Applications .............................................................................................................................51
Firewall.....................................................................................................................................52
DMZ .........................................................................................................................................53
IP Filters...................................................................................................................................54
MAC Filters ..............................................................................................................................55
URL Blocking ...........................................................................................................................56
Domain Blocking......................................................................................................................57
Wireless Performance .............................................................................................................58
Dynamic DNS ..........................................................................................................................59
QoS..........................................................................................................................................60
OOLS
.........................................................................................................................................63
T
Change System Password ......................................................................................................63
Remote Web Access ...............................................................................................................63
Time .........................................................................................................................................64
YSTEM.......................................................................................................................................65
S
Save or Load Configuration File..............................................................................................65
Reset to Factory Default Settings ...........................................................................................65
Firmware ..................................................................................................................................66
Miscellaneous ..........................................................................................................................67
TATUS
S
.......................................................................................................................................68
Log ...........................................................................................................................................69
Wireless Clients .......................................................................................................................69
Statistics...................................................................................................................................69
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS....................................................................................................70
ONFIGURING
C
ETTINGS ON YOUR COMPUTER
IP S
.......................................................................72
Page 4
Before You Start
Please read and make sure you understand all the prerequisites for proper installation of your
new Wireless Broadband Router. Have all the necessary information and equipment on hand
before beginning the installation.
Installation Overview
NOTE: You must have an account setup with an ISP (Internet Service Provider)
in order to use this device for Internet access. Contact your preferred
broadband Internet service provider to set up an account.
The procedure to install the Wireless Broadband Router can be described in general terms in the
following steps:
1. Gather information and equipment needed to install the device. Before you begin the
actual installation make sure you have all the necessary information and equipment.
2. Install the hardware, connect the cables to the device and connect the power adapter.
3. Check the IP settings on your computer and change them if necessary so the computer
can access the web-based management software built into the Wireless Broadband
Router.
4. Use the web-based management software to configure the device to suit the
requirements of your Internet service.
Packing List
Open the shipping carton and carefully remove all items. Make sure that you have the items
listed here.
x One LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router
x
One CD-ROM containing the User’s Guide and Quick Installation Guide
x Ethernet cable
x
One power adapter
suitable for your electric
service
x
One Quick Installation
Guide
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
iv
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
CAUTION: The Wireless Broadband Router must be
used with the power adapter included with
the device. Using a power supply with a
different voltage rating will damage and
void the warranty for this product
Page 5

Installation Notes
In order to establish a connection to the Internet it will be necessary to provide information to the
router that will be stored in its memory. For some users, only their account information (User
Name and Password) is required. For others, various parameters that control and define the
Internet connection will be required.
Internet Connection
The WL11N is intended for use with a broadband device such as an ADSL, xDSL or cable
(CATV) modem. The physical connection to the Internet must first be established through a
broadband device, typically this should be set up as an invisible bridge.
Operating Systems
The WL11N uses an HTML-based web interface for setup and management. The web
configuration manager may be accessed using any operating system capable of running web
browser software, including Microsoft Windows® operating systems.
Web Browser
Any common web browser can be used to configure the router using the web configuration
management software. The program is designed to work best with more recently released
browsers. The web browser must have JavaScript enabled. JavaScript is enabled by default on
many browsers. Make sure JavaScript has not been disabled by other software (such as virus
protection, firewall software or Internet security packages) that may be running on your computer.
Ethernet or Wireless Adapter
Any computer that uses the router must be able to connect to it through an Ethernet port or
through the wireless 802.11n/g/b connection. The computer therefore must have either an
Ethernet adapter or 802.11n/g/b adapter installed. Network adapters are standard for most
computers sold presently.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
v
Page 6
Installation Information
Print this page and record the listed information here in case you have to re-configure your WAN
(Internet) connection in the future or reset the device configuration settings.
Information you will need from your Internet service provider:
Username
This is the Username that is used to log on to
your Internet service provider’s network. It is
commonly in the form user@isp.com.
Password
This is the Password that is used, in
conjunction with the Username above, to log
on to your Internet provider’s network.
Internet Connection Type
This is the method that your ISP uses to send
and receive data between the Internet and
your computer.
Information you will need about your WL11N Wireless Broadband Router:
Username
This is the Username you will be prompted to
enter when you access the WL11N
configuration screens using a Web browser.
admin
.
Password
The default Username is
This is the Password you will be prompted to
enter when you access the WL11N’s
configuration windows using a Web browser.
admin
.
LAN IP address
The default Password is
This is the IP address you will enter into the
Address field of your Web browser to access
the router’s configuration windows using a
Web Browser. The default IP address is
LAN Subnet Mask
192.168.1.1
This is the subnet mask used by the WL11N,
.
and will be used throughout your LAN. The
default subnet mask is
255.255.255.0
.
Information you will need about your LAN or computer:
DHCP Client status
Your Wireless Broadband Router is
configured, by default, to be a DHCP server.
This means that it can assign an IP address,
subnet mask, and a default gateway address
to computers on your LAN. The range of IP
addresses the will assign are from
192.168.1.100
192.168.1.199
to
using the
default DHCP server settings. Computers
must to be configured to Obtain an IP address
automatically (as DHCP clients) to use the
DHCP server.
Record your
info here.
Record your info
here.
Record your info
here.
vi
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 7
Information about your Wireless LAN:
SSID
Channel
Authentication
WEP (Hex/ASCII) Key 1:
Key 2:
Key 3:
Key 4:
WPA (802.1x)
RADIUS IP Address:
Port:
Secret:
WPA-PSK Pass phrase:
Record your
info here.
Record your info
here.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
vii
Page 8

Page 9

Introduction
This section provides a brief description of the router, its associated technologies, and a list of
router features.
Router Description and Operation
The LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router is designed to provide connectivity for your
private Ethernet and 802.11g/802.11b/802.11n wireless network to the Internet via ADSL, xDSL,
cable modem or other common broadband connection.
The router is easy to install and use. The four standard Ethernet ports are used to connect
computers or other Ethernet devices to the wired LAN (Local Area Network); the embedded
wireless access point is used for connecting 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n wireless devices.
Router Features
The LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router provides the following features:
x 802.11n Wireless LAN
workstations and devices.
x Wi-Fi Protected Status – Quick, effective and simple wireless security implementation for
WPS devices.
x Broadband Connection Sharing
DSL) modem to share the Internet connection.
x Ethernet Switch -
devices.
x VPN Supported -
sessions, so multiple users behind the WL11N can access corporate networks through
various VPN clients more securely.
x Advanced Firewall, MAC Filtering, and WebSite Filtering Features -
user interface displays a number of advanced network management features including:
x Port Forwarding Supported -
your LAN to be accessible to Internet users.
x Special Application Supported -
Internet gaming, video conferencing, Internet telephony and so on. The WL11N can sense
the application type and open a multi-port tunnel for it.
x DMZ Host Supported -
This function is used when the Special Application feature is insufficient to allow an
application to function correctly.
– Wireless connectivity for IEEE 802.11n/802.11g/802.11b
- Connects multiple computers to a Broadband (Cable or
Allows sharing of an Internet connection with multiple computers and
Supports multiple and concurrent IPsec and PPTP pass-through
The Web-based
Enables you to expose WWW, FTP and other services on
Special applications requiring multiple connections, like
Allows a networked computer to be fully exposed to the Internet.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
1
Page 10

Front View
The LED indicators on the Wireless Broadband Router are located on the front panel the device.
Front of Wireless Broadband Router
Place the router in a location where it is not exposed to heat and where the LED indicators are
visible.
2
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 11

LED Display
Place the router in a location that permits an easy view of the LED indicators on the front of the
device.
The LED indicators include the
WLAN
and Ethernet indicators monitor link status and activity (Link/Act).
WPS,LAN, WLAN, WAN, Status
and
Power
indicators. The
WPS
LAN (1-4)
WLAN
WAN
Status
Power
Blinks blue for 120 seconds while searching for WPS enabled station. See Wi-Fi
Protected Setup (WPS) for more information.
A solid green light indicates a valid link on startup. This light blinks when there is
activity currently passing through the Ethernet ports.
Steady green light indicates a wireless connection. A blinking green light indicates
activity on the WLAN interface
Lights steady green during power on self-test (POST). Once the connection status
has been settled, the light will blink green. If the indicator lights steady green after
the POST, the system has failed and the device should be rebooted.
Blinks green when system function is normal.
Steady green light indicates the unit is powered on. When the device is powered off
this remains dark.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
3
Page 12
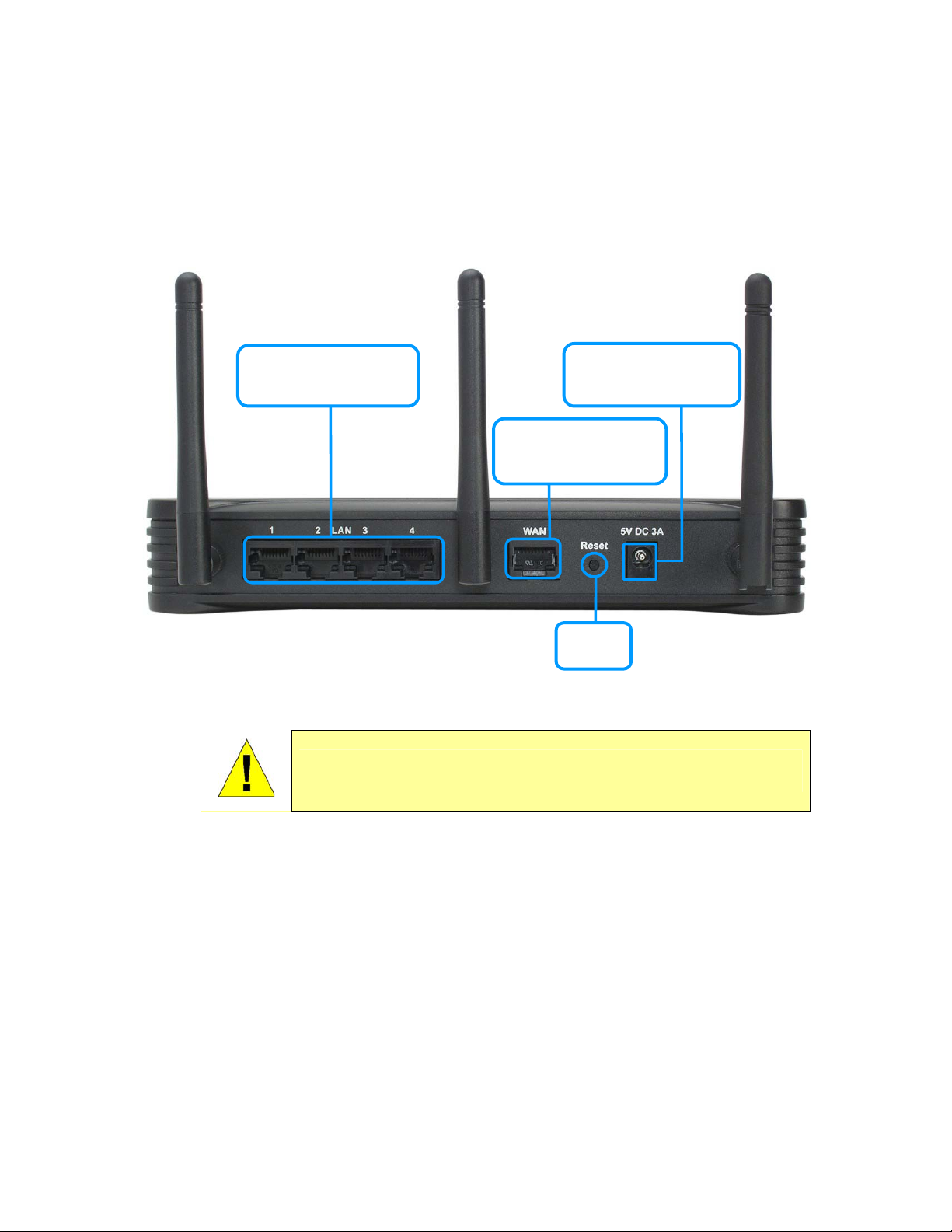
Rear Panel Connections
All cable connections to the router and the power adapter connect at the rear panel. Use the
Reset button to restore the settings to the factory default values. See the next section for
instructions to connect the power adapter and power on the router.
Ethernet Ports
Connect to computers
and Ethernet LAN
Rear Panel View of Wireless Broadband Router
CAUTION: Using a power supply with a different voltage rating will damage the
device and void the warranty of this product.
Power Input
Connect to AC Power
Adapter
WAN Port
Connect to broadband
Internet device
Reset
button
4
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 13

Connecting Devices to the Router
The Wireless Broadband Router connects three separate networks, a private Ethernet LAN,
Wireless LAN and the public Internet (WAN). Choose a location for the router where Ethernet
devices can be connected to the LAN ports and the WAN port can be easily connected to the
cable modem or DSL modem that provides the broadband Internet connection. Typically the
broadband device is configured as a bridge, however some devices allow for more complex
options. Consult the user manual of the broadband device for more information on how best to
configure the broadband Internet connection.
The router should be protected from dust, water, moisture and heat. Make sure network cables,
power adapters and power cords are placed safely out of the way so they do not create a
tripping hazard. As with any electrical appliance, observe common sense safety procedures.
Place the router on a shelf, desktop, or other secure stable platform. Ideally you should be able
to view the LED indicators on the front panel.
Connect Router to Ethernet
The router can be connected to computers or other Ethernet devices using the four Ethernet
LAN ports on the rear panel. Any connection to an Ethernet concentrating device such as a
switch or hub must operate at a speed of 10/100 Mbps only. When connecting the router to any
Ethernet device capable of operating at speeds between 10~100Mbps, be sure that the device
has auto-negotiation (NWay) enabled for the connecting port. Use standard CAT5 or better
Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors. The Ethernet LAN ports are auto MDI-II/MDI-X so you
can use straight-through or crossover Ethernet cabling.
The rules governing Ethernet cable lengths apply to the LAN to router connection. Be sure the
Ethernet cables connected to the LAN ports do not exceed 100 meters in length.
Connecting through 802.11 Wireless
The default wireless settings of the access point allow roaming 802.11g and 802.11b wireless
clients to associate with it. The first time you set up the router however, use the Ethernet
connection to configure the channel and SSID. For wireless client-to-Internet connection through
the router, first configure the Internet connection through the Ethernet. When the Internet
connection has been established, make sure the wireless clients are configured as DHCP clients
if you are using the router’s DHCP server. Otherwise, make certain the wireless clients have IP
settings that allow them to use the router as a gateway to the Internet.
General Guide to Setting Up a Wireless Network
In order to get the best performance from the wireless component of the router, you should have
some basic understanding of how wireless networks operate. Wireless networking is a relatively
new technology and there are more factors to consider when setting up or designing a wireless
network than designing a wired network. If you are setting up a wireless network, especially if
you are using multiple access points and/or covering a large area, good planning from the outset
can ensure the best possible reliability, performance, coverage and effective security.
Radio
Wireless local network (as called WI-FI) devices such as notebook computers and wireless
access points use electromagnetic waves within a broad, unlicensed range of the radio spectrum
(between 2.4GHz and 2.5GHz) to transmit and receive radio signals. A wireless access point
(AP) becomes a base station for the wireless nodes (notebook computer for example) in its
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
5
Page 14

broadcast range. Often a wireless access point such as the AP embedded in the LinkTek
WL11N, will also provide a connection to a wired network - usually Ethernet - and ultimately an
Internet connection. The IEEE 802.11 standard precisely defines the encoding techniques used
to digitally used for data transmission. The embedded wireless access point can be used by
IEEE 802.11g, 802.11b and 802.11n devices. These standards are compatible but use different
algorithms for data transmission.
802.11g uses a method called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for
transmitting data at higher data rates. OFDM is a more efficient encoding method than Direct
Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) transmission, the method used by 802.11b devices.
However, in order to support different data transmission rates while also be compatible with
802.11b, 802.11g uses a combination of OFDM and DSSS when 802.11b devices are present.
Range
An access point will send and receive signals within a limited range. Also, be aware that the
radio signals are emitted in all directions giving the access point a spherical operating range.
The physical environment in which the AP is operating can have a huge impact on its
effectiveness. If you experience low signal strength or slow throughput, consider positioning the
router in a different location. See the discussion below concerning the wireless environment and
location of the AP (LinkTek WL11N).
SSID and Channel
Wireless networks use an SSID (Service Set Identifier) as means of identifying a group of
wireless devices, similar to a domain or subnet. This allows wireless devices to roam from one
AP to another and remain connected. Wireless devices that wish to communicate with each
other must use the same SSID. Several access points can be set up using the same SSID so
that wireless stations can move from one location to another without losing connection to the
wireless network.
The embedded wireless access point of the router operates in Infrastructure mode. It controls
network access on the wireless interface in its broadcast area. It will allow access to the wireless
network to devices using the correct SSID after a negotiation process takes place. By default,
the LinkTek WL11N broadcasts its SSID so that any wireless station in range can learn the SSID
and ask permission to associate with it. Many wireless adapters are able to survey or scan the
wireless environment for access points. An access point in Infrastructure mode allows wireless
devices to survey that network and select an access point with which to associate. You may
disable SSID broadcasting in the web manager’s wireless menu.
In addition, the AP can use different channels (frequency bands) to avoid unwanted overlap or
interfere between control zones of separate APs. Wireless nodes must use the same SSID and
the same channel as the AP with which it wishes to associate. However, because of the nature
of the CSMA/CA (carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance) protocol, using the
same channel on two different APs can contribute significantly to wireless congestion. If you are
using multiple APs on your network and are experiencing low throughput or significant
transmission delay, carefully consider how channels are assigned to the different APs.
Wireless Security
Various security options are available on the LinkTek WL11N including open or WEP and WPA
(including WPA-PSK). Authentication may use an open system or a shared key. Read below for
more information on configuring security for the wireless interface.
6
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 15

Installation Considerations for Wireless LAN
Many physical environmental factors can impact wireless networks. Radio waves are used to
carry the encoded data between devices. These radio transmissions can become degraded due
to signal attenuation, multi-path distortion and interference or noise. Attenuation simply means
that the strength of the signal weakens with the distance it travels, even if the transmission path
is unobstructed. Multi-path distortion occurs when radio signals bounce off objects like walls,
ceilings, metal appliances, etc. This may cause a signal to be duplicated, with each separate yet
identical signal arriving at a receiver at different times. Interference and noise from electrical
devices such as microwave ovens, fluorescent lights, automobile engines and other radio
emitting devices can cause signal degradation. With all of this in mind, choose a location for all
access points on the wireless LAN.
Wireless networking lets you access your network from nearly anywhere you want. However, the
number of walls, ceilings, or other objects that the wireless signals must pass through can limit
signal range. Typical ranges vary depending on the types of materials and background RF noise
in your home or business. To maximize range and signal strength, use these basic guidelines:
x
Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the access point and other network
devices to a minimum - each wall or ceiling can reduce your wireless device’s range from
3-90 feet (1-30 meters.) Position wireless devices so that the number of walls or ceilings
is minimized.
x
Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet thick (.5
meters), at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree
angle it looks over 42 feet (14 meters) thick! Position devices so that the signal will travel
straight through a wall or ceiling (instead of at an angle) for better reception.
x Materials can impede the wireless signal - a solid metal door or aluminum studs may
have a negative effect on range. Try to position wireless devices and computers with
wireless adapters so that the signal passes through drywall or open doorways and not
dense, especially metallic, materials. Also, note that metal filing cabinets and appliances
can reflect radio signals. When these metal objects are moved around, your wireless
network may be affected.
x
Keep your access point away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical devices or
appliances that generate extreme RF noise such as microwave ovens, CRT monitors,
motors, etc.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
7
Page 16

Power on Wireless Broadband Router
CAUTION: The Wireless Broadband Router must be used with the power adapter included
with the device. Using a power supply with a different voltage rating will damage and void
the warranty for this product
To power on the Wireless Broadband Router:
1. Insert the AC Power Adapter cord into the power receptacle located on the rear panel of the
Wireless Broadband Router and plug the adapter into a suitable nearby power source. See
the back panel illustration above to view the power receptacle.
2. The Power LED indicator will immediately light green and remain lit. The Status LED should
light steady green initially and begin to blink after a few seconds.
3. If an Ethernet port is connected to a computer or other device, look at the Ethernet Link/Act
LED indicators to make sure they have valid connections. The Wireless Broadband Router
will attempt to establish the WAN connection, if the WAN line is connected and the
connection is properly configured the WAN LED indicator will light up after several seconds.
Factory Reset Button
The Wireless Broadband Router may be reset to the original factory default settings by
depressing the reset button for a few seconds while the device is powered on. Use a ballpoint or
paperclip to gently push down the reset button. Remember that this will wipe out any settings
stored in flash memory including user account information and LAN IP settings. The device
settings will be restored to the factory default IP address
255.255.255.0
The router may also be reset to factory default configuration settings through the web
management interface.
, the default management Username is
192.168.1.1
admin
and the default Password is
and the subnet mask is
admin
.
8
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 17

Configuration
All device configuration for the router is done through the web-based management software.
Use a standard web browser with JavaScript enabled to connect to the web manager. Make
sure the proxy settings for the browser do not require use of a proxy server.
IP Settings on Your Computer
In order to configure your system to receive IP settings from the router it must first have the
TCP/IP protocol installed. If you have an Ethernet port on your computer, it probably already has
TCP/IP protocol installed. The DHCP server will automatically enable your computer to use a
browser to manage the router. Configuring IP Settings on Your Computer on page 72 describes
how to change the IP configuration for a computer running a Windows operating system to be a
DHCP client. If you are running another operating system, make sure your computer is
configured as a DHCP client so it can automatically obtain IP settings from the router. Some
operating systems will automatically select the best IP settings. Consult the user manual for the
operating system (OS) if you are unsure.
For computers using manually configured IP settings, make sure the IP address is on the same
subnet as the router. The computer should use an IP address in the range 192.168.1.2 to
192.168.1.254 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
NOTE: If you are not sure how to configure your Windows computer to be a DHCP client, see
Configuring IP Settings on Your Computer in Configuring IP Settings on Your Computer.
Access the Configuration Manager
In order to make sure your computer’s IP settings allow it to communicate with the router, it is
advisable to configure your system be a DHCP client – that is, it will get IP settings from the
router. Configuring IP Settings on Your Computer on page 72 describes how to configure
different Windows operating systems to “Obtain IP settings automatically”.
Be sure that the web browser on your computer is not configured to use a proxy server in the
Internet settings. In Windows Internet Explorer, you can check if a proxy server is enabled using
the following procedure:
1. In Windows, click on the
2. In the
3. In the
4. In the
5. Verify that the “Use a proxy server for your LAN (These settings will not apply to dial-up
Alternatively, you can access this Internet Options menu using the Tools pull-down menu in
Internet Explorer.
Control Panel
Network and Internet Connections
Internet Properties
Settings
or VPN connections).” option is NOT checked. If it is checked, click in the checked box to
deselect the option and click OK.
button
Start
button and choose
window, click on the
window, click on the
Network and Internet Options
Control Panel
window, click the
Connections
.
icon.
Internet Options
tab and click on the
icon.
LAN
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
9
Page 18

Login to Home Page
To use the web-based management software, launch a suitable web browser and direct it to the
IP address of the router. Type in
address bar of the browser. The URL in the address bar should read:
the default User Name admin and the default Password admin then click the
access the web-based manager.
http://
followed by the default IP address,
192.168.1.1
http://192.168.1.1
Submit
button to
in the
. Type in
Enter Password
It is recommended to change the web-based manager access user name and password once
you have verified that a connection can be established. The user name and password allows
any PC within the same subnet as the router to access the web-based manger.
10
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 19

Web Manager
When you successfully connect to the web manager, the
Status
menu directory is displayed. For quick configuration of the Internet connection, launch
Device Information
display in the
the Setup Wizard in the Home directory.
Click on parent
directory links to see
available configuration
menus. Clink on menu
links to see menu.
Web Manager – First Time Log On
All configuration and management of the router is done using the web-based management
interface. To view the menus contained in each menu directory, click the + symbol to expand the
menu tree.
Parent Directory Configuration and Read-only menus
Click the Home link to access the Setup Wizard and the menus used to configure the
Home
Advanced
Tools
Status
basic router settings. The Home directory menus are Wizard, Wireless, WAN, LAN and
DHCP.
Click the Advanced link to access the Virtual Server, Applications, Firewall, DMZ, IP
Filters, MAC Filters, URL Blocking, Domain Blocking, Wireless Performance, DDNS and
QoS menus.
Click the Tools link to access the Administrator (used to set the system password),
Time, System, Firmware and Miscellaneous menus.
Click the Status link to view the DHCP Clients, View Log, Wireless Clients and Statistics
displays.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
11
Page 20

Basic Configuration – Home Directory Menus
The first time you setup the router it is recommended that you configure the WAN connection
using a single computer making sure that both the computer and the router are not connected to
the Ethernet LAN or other Ethernet devices. Once the Internet connection is configured and
working, go ahead and connect other Ethernet and wireless devices.
Home Directory Menus
The Setup Wizard page is the first page to appear when clicking on the Home directory link.
12
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 21

Setup Wizard
To use the Setup Wizard, click the
in the Home directory and follow the instructions in the pop-up window that appears.
Run Wizard
Click the Run Wizard button
button in the first browser window that appears
to launch the Setup Wizard
Launch Setup Wizard
Follow the instruction below to the type of connection used for your broadband Internet
connection.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
13
Page 22

Using the Setup Wizard
The initial window summarizes the setup process. Click the Next button to proceed. You may
stop using the Setup Wizard at any time by clicking the
return to the
process.
Setup Wizard
window without saving any of the settings changed during the
Exit
button. If you exit the wizard you will
The first pop-up window of the Setup Wizard lists the basic steps in the process. These steps
are as follows:
1. Set the system password
2. Set the system time.
3. Configure the connection to the Internet.
4. Set the wireless configuration.
5. Save the new configuration settings and reboot the system.
14
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 23

Using the Setup Wizard- Set System Password
Change the password used for management access of the router. Type the new Password and
Confirm
it in the spaces provided. Click the
Next
button to proceed.
NOTE: The System user name “admin” cannot be changed.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
15
Page 24

Using the Setup Wizard - Choose Time Zone
Choose the time zone you are in from the pull-down menu and click Next. This sets the system
time used for the router. If you wish to return to the previous window during the setup process,
click the
Back
button.
Select the
Wizard
16
window. Follow the instructions below for the type of connection you have selected.
Connection Type
specific to your service and click
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Next
to go to the next
Setup
Page 25

Using the Setup Wizard - Choose Connection Type
Now select the Connection Type used for the Internet connection. Your ISP has given this
information to you. The connection types available for are
L2tP
and
Wizard
. Each connection type has different settings that are configured in the next
window.
Static IP,Dynamic IP,PPPoE,PPtP
Setup
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
17
Page 26

Using the Setup Wizard - For Dynamic IP Address connections:
1. Select the specific Connection Type from the drop-down menu. The available Dynamic
IP Address connection and encapsulation types are 1483 Bridged IP LLC and 1483
Bridged IP VC-Mux.
2. If you are instructed to change the
available entry fields. Most users will not need to change these settings. The Internet
connection cannot function if these values are incorrect.
3. You may want to copy the MAC address of your Ethernet adapter to the router. Some
ISPs record the unique MAC address of your computer’s Ethernet adapter when you first
access their network. This can prevent the router (which has a different MAC address)
from being allowed access to the ISPs network (and the Internet). To clone the MAC
address of your computer’s Ethernet adapter, type in the MAC address in the Cloned
MAC Address field and click the
information to a file used by the router to present to the ISP’s server used for DHCP.
4. Click
Next
to go to the
Set Wireless LAN Connection
VPI
Clone MAC Address
or
VCI
number, type in the correct setting in the
button. This will copy the
pop-up window.
18
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 27

Using the Setup Wizard - For Static IP Address connections:
1. Select the specific Connection Type from the drop-down menu. The available Static IP
Address connection and encapsulation types are 1483 Bridged IP LLC, 1483 Bridged IP
VC-Mux, 1483 Routed IP LLC, 1483 Routed IP VC-Mux and IPoA.
2. Change the
Secondary DNS
and
connections it may also be necessary to change the
connection users who have not been given this information should leave the field blank.
3. If you are instructed to change the
available entry fields. Most users will not need to change these settings. The Internet
connection cannot function if these values are incorrect.
4. Click
IP Address,Subnet Mask,ISP Gateway Address, Primary DNS Address
Address
VPI
or
as instructed by your ISP. For IPoA
ARP Server Address
VCI
number, type in the correct setting in the
pop-up window.
Next
to go to the
Server IP
Set Wireless LAN Connection
. IPoA
,
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
19
Page 28

Using the Setup Wizard - For PPPoE connections:
1. Type in the Username and Password used to identify and verify your account to the ISP.
Retype
2. Click Next to go to the Set Wireless LAN Connection pop-up window.
the password to make sure it is correct.
20
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 29

Using the Setup Wizard – For PPTP Client connections:
1. Enter the appropriate PPTP Client information including PPTP Server IP, PPTP
Account
2. Click
Configuration
name, and the
Next
when you are ready to continue to the
window.
PPTP Password
twice.
Set 802.11g Wireless LAN
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
21
Page 30

Using the Setup Wizard – For L2TP Client connections:
1. Enter the appropriate L2TP Client information including L2TP Server IP, L2TP Account
name, and the
2. Click
Next
Configuration
L2TP Password
when you are ready to continue to the
window.
twice.
Set 802.11g Wireless LAN
22
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 31

Using the Setup Wizard - Wireless LAN connection:
1. The SSID identifies members of the Service Set. Accept the default name or change it
to something else. If the default SSID is changed, all other devices on the wireless
network must use the same SSID.
2. The wireless
What channels are available for use by the access point depends on the local
regulatory environment. Remember that all devices communicating with the device
must use the same channel (and use the same SSID). Use the drop-down menu to
select the channel used for your 802.11 Wireless LAN.
3. Click Next to go to the next window.
Channel
number is available from your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
23
Page 32

Using the Setup Wizard - Wireless LAN security:
Wireless LAN security supported includes WEP and WPA versions 1 and 2. Select the preferred
method from the list and click on the
which case choose the Disabled option. If you choose to leave security disabled at this time, the
next menu will be the Save and Take Effect wizard menu.
Next
button. You can choose to setup security later, in
24
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 33

Using the Setup Wizard – WEP Configuration
The Setup Wizard wireless LAN security configuration is limited to WEP; for WPA or WPA2
security, use the web-based manager Wireless Settings menu. To configure WEP in the Setup
Wizard, select Open, Shared or Both for Authentication Type, use the Cipher: pull down menu to
select the level of encryption or cipher rate, 64 bits or 128 bits and type in an encryption key of
appropriate length. For 64-bit encryption, type a key ten hexadecimal digit (0~9,A~F) key, for
128-bit encryption type a 26 hexadecimal digit key.
Using the Setup Wizard – WPA2 Auto Configuration
If you are configuring WPA security, select
used for authentication. Click Next to continue to the final menu.
Security
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
type WPA2 Auto, enter the
Passphrase
25
Page 34

Using the Setup Wizard - Finish and Restart
Finally you can confirm that the setup process is completed. If you are satisfied that you have
entered all the necessary information correctly, click the
configuration settings and restart the router. If you need to change settings from a previous
window, click the
Back
button.
CAUTION: Do not turn the router off while it is restarting. After the router is finished
restarting, you are now ready to continue to configure the router as desired. You may want
to test the WAN connection by accessing the Internet with your browser.
Restart
button to save the new
26
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 35

Basic Wireless Setup
To configure the router’s basic wireless and wired network configuration settings without running
the Setup Wizard, you can access the windows used to configure Wireless, WAN, LAN and
DHCP settings directly from the Home directory. To access the Wireless Settings window, click
Wireless
on the
access the web manager.
link on the left side of the first window that appears when you successfully
Wireless Settings menu – default settings
By default the wireless AP is enabled for use by 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n workstations.
Set Wireless Mode
The
only, 11n only, a mix of 11b and 11g, or a mix of all three standards. To turn off all wireless
function, select the Disable option.
SSID
The
something else. All other devices on the wireless network using the Wireless Broadband Router
must use the same SSID.
What channels are available for use by the access point depends on the local regulatory
environment. Remember that all devices communicating with the device must use the same
channel (and use the same SSID). Use the drop-down menu to select the
your 802.11 Wireless LAN. The wireless channel number is available from your Internet Service
Provider (ISP).
If network
Wi-Fi Protected Function is enabled by default. See below for more information on Wi-Fi
Protected Status or WPS.
identifies members of the Service Set. Accept the default name or change it to
Security
NOTE: For wireless stations that support WPS push button method, the easiest way to establish a
secure connection is to simultaneously press the WPS button on the wireless workstation and the
WPS button on the front of the Wireless Broadband Router. See below for more information on WPS.
options are used to configure the access point to use 11b only, 11g
Channel
is not used, click None, then click
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Apply
.
used for
27
Page 36

Wireless Security
Wireless Settings
In the
will change to present the settings specific to the method being configured. The Wireless
Broadband Router’s wireless security options include three levels of WEP encryption, WPA for
IEEE 802.1x network authentication, and WPA with a user-configured Pre Shared Key (PSK) or
RADIUS authentication. The Wireless Broadband Router supports Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
for quickly establishing a secure link to stations that support WPS. Enabling WEP or WPA
security will automatically disable WPS function.
window, select the type of security you want to configure. The window
Wireless Settings window – WEP
Wireless bandwidth, Short Guard Interval and SSID Broadcast options are available for
configuration for all security methods including WPS.
NOTE:
Enabling WEP or WPA security will automatically disable WPS function.
28
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 37

Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
WPS provides an easy way to configure a secure connection to your wireless LAN. This option
can be used on wireless stations that support Wi-Fi Protected Setup or WPS. The Wireless
Broadband Router supports push button and PIN methods of WPS. WPS cannot be used with
WPA or WPA2.
The WPS menu is located at the bottom of the Wireless menu. To use WPS click to select the
Enabled
radio button for
Wi-Fi Protected Function
.
NOTE:
Router’s own PIN. This is used when the router needs to connect to other
WPS enabled access points.
Wireless Settings menu
To add a wireless station using WPS, enter the PIN number of the WPS enabled wireless device
and click on the
Connect
Generate New PIN
The
button.
button is for the Wireless Broadband
WPS station PIN entry / Virtual Push Button menu
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
29
Page 38

The router will attempt to establish the WPS secure connection for 120 seconds. Now start the
WPS connection process on the device attempting to make the connection.
While the router is searching for the wireless station with the PIN just entered, a message
informs you to start the WPS device.
WPS start PIN device message
Alternatively, for wireless stations that support the push button WPS method, click on the
Virtual
Push Button or press the red WPS button on the front panel of the router to begin the WPS
connection process.
WPS push button on WPS device message
The router will attempt to establish the WPS secure connection for 120 seconds. Press the
button on the device trying to connect.
30
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 39

WEP Encryption
Use WEP encryption for basic wireless data encryption. Use WPA if wireless LANs that require a
higher level of security. WEP (Wireless Encryption Protocol) encryption can be enabled for
security and privacy. WEP encrypts the data portion of each frame transmitted from the wireless
adapter using one of the predefined keys. The router offers 64 or 128-bit encryption with four
keys available. Select the WEP option from the Security: pull-down menu to configure WEP
encryption.
Wireless Settings menu – WEP encryption
Enter the appropriate parameters for the type of security selected from this menu. WEP security
requires the following:
x Authentication Type:
Encryption Length:
x
x Key Type:
x Key: Type up to four keys of appropriate length, 10 characters for 64-bit Hex or 26
characters for 128-bit Hex.
ASCII or Hexidecimal.
NOTE: If encryption of any kind, at any level is applied to the Wireless Broadband Router, all
wireless devices using the router on the network must comply with all security measures.
Open Key or Shared Key.
The IP address of the RADIUS server.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
31
Page 40

WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
Wi-Fi Protected Access was designed to provide improved data encryption, perceived as weak
in WEP, and to provide user authentication, largely nonexistent in WEP.
Wireless Settings menu – WPA2 EAP
Enter the appropriate parameters for the type of security selected from this menu. For EAP
authentication using WPA or WPA2, enter the following:
Cypher Type:
x
x RADIUS Server:
RADIUS Port:
x
x Shared Key:
x Key Renewal: The time (in seconds) after which the Shared Key is changed
automatically.
32
Choose TKIP, AES or TKIP/AES.
The IP address of the RADIUS server.
The port number used for 802.1x.
The password or character string used for wireless station authentication.
NOTE: If encryption of any kind, at any level is applied to the Wireless Broadband
Router, all wireless devices using the router on the network must comply with all security
measures.
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 41

Select the PSK authentication option to view the WPA passkey configuration menu.
Wireless Settings menu – WPA-PSK
Enter the appropriate parameters for the type of security from this menu. For PSK authentication
using WPA or WPA2, enter the following:
x Cypher Type: Choose TKIP, AES or TKIP/AES.
Key Type:
x
x Passphrase:
Key Renewal:
x
automatically.
Choose ASCII or Hexidecimal.
The password or character string used for wireless station authentication.
The time (in seconds) after which the Shared Key is changed
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
33
Page 42

WAN Configuration
To configure the router’s WAN configuration settings without running the Setup Wizard, you can
access the windows used to configure WAN, LAN, DHCP, and DNS settings directly from the
Home directory. To access the WAN Settings window, click on the WAN menu link on the left
side of the first window that appears when you successfully access the web manager.
Select Internet Connection Type
The default Internet Connection menu displays the Dynamic IP (DHCP) Internet Connection
Type menu. To select another connection type, use the pull-down
menu to select the connection type you wish to configure. The menu configuration parameters in
the display will change according to the connection option you choose. The available Internet
connection types are:
Static IP Address
Dynamic IP Address (DHCP)
PPPoE (Username / Password)
Bridge Connection
PPTP (Username / Password)
L2TP (Username / Password)
Each connection type is discussed in its own section below.
My Internet Connection is:
34
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 43

Static IP Address Connection
When the router is configured to use Static IP Address assignment for the WAN connection, you
must manually assign a global IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway IP Address used for the
WAN connection.
WAN Settings menu - Static IP Address
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
35
Page 44

Configure the Static IP address connection and click the
Apply
button to put the new settings
into effect. See the table below for a description of the parameters configured for the connection.
Static IP Parameters Description
IP Address
Subnet Mask
ISP Gateway Address
MAC Address/Clone MAC
Address
DNS (Primary/
Secondary)
MTU
This is the permanent global IP address for your account. This is the address
that is visible outside your private network. Get this from your ISP.
This is the Subnet mask for the WAN interface. Get this from your ISP.
This is the IP address of your ISP’s Gateway router. It provides the connection
to the router for IP routed traffic that is outside your ISP’s network. That is,
this will be the primary connection from the router to most of the Internet. Get
this IP address from your ISP.
This field will instruct the user to enter the Media Access Control (MAC)
address of the Ethernet Card of your computer, if instructed to do so by your
ISP. To quickly accomplish this, click the Clone MAC Address button, which
will automatically copy the MAC address of your Ethernet card and enter it into
the space provided, which will replace the MAC address of the router.
These are the IP addresses of your primary and backup domain name server,
which should also be provided to you by your ISP. The router will first try the
Primary DNS Address to resolve a website’s URL IP address. If this IP
address fails, the router will then try the Secondary DNS Address.
The Maximum Transmission Unit size may be changed if you want to optimize
efficiency for uploading data through the WAN interface. The default setting
(1492 bytes) should be suitable for most users. Some user may want to adjust
the setting to optimize performance for wireless traffic or when low latency is
desired (such as with Internet gaming). It is highly recommended that the user
research how adjusting the MTU may affect network traffic throughput.
36
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 45

Dynamic IP Connection
A Dynamic IP Address connection configures the router to automatically obtain its global IP
address from a DHCP server on the ISP’s network. The service provider assigns a global IP
address from a pool of addresses available to the service provider. Typically the IP address
assigned has a long lease time, so it will likely be the same address each time the router
requests an IP address.
WAN Settings window – Dynamic IP Address
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
37
Page 46

Configure the Dynamic IP address connection and click the
Apply
button to put the new settings
into effect. See the table below for a description of the parameters configured for the connection.
Dynamic IP Parameters Description
Host Name
MAC Address/Clone MAC
Address
DNS (Primary/ Secondary)
MTU
Enter the Host Name provided if necessary (optional).
This field will instruct the user to enter the Media Access Control (MAC)
address of the Ethernet Card of your computer, if instructed to do so by
your ISP. To quickly accomplish this, click the Clone MAC Address button,
which will automatically copy the MAC address of your Ethernet card and
enter it into the space provided, which will replace the MAC address of the
router.
These are the IP addresses of your primary and backup domain name
server, which should also be provided to you by your ISP. The router will
first try the Primary DNS Address to resolve a website’s URL IP address.
If this IP address fails, the router will then try the Secondary DNS
Address.
The Maximum Transmission Unit size may be changed if you want to
optimize efficiency for uploading data through the WAN interface. The
default setting (1492 bytes) should be suitable for most users. Some user
may want to adjust the setting to optimize performance for wireless traffic
or when low latency is desired (such as with Internet gaming). It is highly
recommended that the user research how adjusting the MTU may affect
network traffic throughput.
38
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 47

PPPoE Connection
PPP or Point-to-Point protocol is a standard method of establishing a network
connection/session between networked devices. PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet), as described in
RFC 2516, is a method of using PPP through the Ethernet network.
There are two ways to configure the PPoE connection on the router, one is for a
PPPoE
through DHCP, such as the router’s IP address and the default gateway. The other is through a
Static PPPoE connection, in which the user must configure the IP address and the DNS
addresses automatically.
configuration, which means the router will implement some settings automatically
Dynamic
WAN Settings menu – PPPoE connection
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
39
Page 48

Configure the PPPoE connection and click the
Apply
button to put the new settings into effect.
See the table below for a description of the parameters configured for the connection.
PPPoE Parameters Description
User Name
Password
Retype Password
Service Name
IP Address
MAC Address
Primary DNS Address
Secondary DNS Address
Maximum Idle Time
MTU
Connect Mode Select
The user name supplied to you by your ISP.
The password supplied to you by your ISP.
Retype the password entered in the Password feld.
Enter the service name supplied to you by your ISP, if required.
Enter the IP address given to you by your ISP. This field is only to be
completed if the Static PPPoE button is selected.
This field requires the user to enter the Media Access Control (MAC) address of
the Ethernet Card of your computer, if instructed to do so by your ISP. To
quickly accomplish this, click the Clone MAC Address button, which will
automatically copy the MAC address of your Ethernet card and enter it into the
space provided, which will replace the MAC address of the router.
This entry is for the IP address of your primary domain name server, which
should also be provided to you by your ISP. The router will first try the Primary
DNS Address to resolve a website’s URL IP address. If this IP address fails, the
router will then try the Secondary DNS Address. This field is only to be
completed if the Static PPPoE button is selected.
The IP address of the secondary domain name server will be used to resolve a
website’s URL IP address if the Primary DNS Address fails. The information
in this field should also be provided by your ISP and is only to be completed if
the Static PPPoE button is selected.
A value of 0 means that the PPP connection will remain connected. If your
network account is billed according to the amount of time the router is actually
connected to the Internet, enter an appropriate Idle Time value (in seconds).
This will disconnect the router after the WAN connection has been idle for the
amount of time specified. The default value = 5.
This field refers to the Maximum Transfer Unit, which is the maximum size of a
packet, in bytes, that will be accepted by the router. The default setting is 1500
bytes. This field should not be altered unless instructed by your ISP.
This function, with Connect-on-demand selected, will allow the router to
connect any workstation on your LAN to the Internet upon request. If this
function is set at Always-on, no request from the workstation will be needed
to connect to the Internet. If Manual is selected, it will be necessary for the
workstation on the LAN to manually connect to the Internet through this router.
40
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
Page 49

Bridge Connection
A Bridge connection does not require much configuration for the router, however most of the
router functions are not available in bridge mode.
WAN Settings menu – Bridge connection
To configure the WL11N as a bridge for the WAN connection, select the
option and click Apply. Do this immediately change the IP settings status of the device to DHCP
client. Be sure to have a DHCP server running and connected to the network if this option is to
be used. Remember that as a bridge, third party connection software is normally required on
each computer attempting to get Internet access.
Bridge
WAN settings
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
41
Page 50

PPTP Connection
If your ISP is using PPTP to provide your Internet connection, the ISP will give you the
necessary information to configure the router.
There are two ways to enable the router to become a PPTP client, one is through assigning the
router an IP address dynamically, which means that the DHCP protocol will be implemented by
the router to automatically configure the IP settings. The user may input the IP settings manually
by choosing the Static IP option above the configuring area.
PPTP Internet Connection configuration menu
42
LinkTek WL11N Wireless Broadband Router User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...