Page 1

MiniPCI WLAN Card
OEM installation Manual
Version 0.1
0-Introduction
The Intersil ISL38000M WLAN NIC is a complete wireless high speed Network
Interface Card (NIC) utilizing the Intersil PRISM GT ® chip set. It conforms to the IEEE
802.11g protocol and operates in the 2.45 GHz ISM frequency bands.
It provides a complete reference design evaluation platform of hardware and software to
system providers or integrators requiring wireless data communications capability and is
ideal for integration into computer platforms.
• Fully compliant with the IEEE 802.11g WLAN standards
• FCC Certified Under Part 15 (pending) to Operate in the 2.45 Bands
• Support for 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, and 6 Mbps OFDM, 11 and 5.5 Mbps CCK and
legacy 2 and 1 Mbps data rates
• Driver Supports Microsoft Windows ® 98/SE, ME, XP and 2000 (SR1)
1-OEM Installation procedure
1.1 Installing the miniPCI card into the host PC Notebook
a-open miniPCI slot cover of host PC Notebook housing
b-insert miniPCI card into miniPCI slot
c-connect the host PC notebook antennas to the miniPCI card antenna connectors (Hirose
type UFL connector)
d-close miniPCI slot cover of host PC Notebook housing
1.2 Installing the software drivers
a-Start windows
b-When windows detects new hardware and asks for drivers, point to directory where the
Intersil driver is located (for example floppy drive, cdrom , harddisk) to install.
c-after drivers are installed, restart windows
d-the Intersil WLAN icon will appear in system tray on the bottom right of the screen
(see yellow arrow in fig. 01)
fig, 01: Intersil WLAN icon
Page 2
e-double click the Intersil WLAN icon to open the WLAN settings, the following
window will appear (see fig.02)
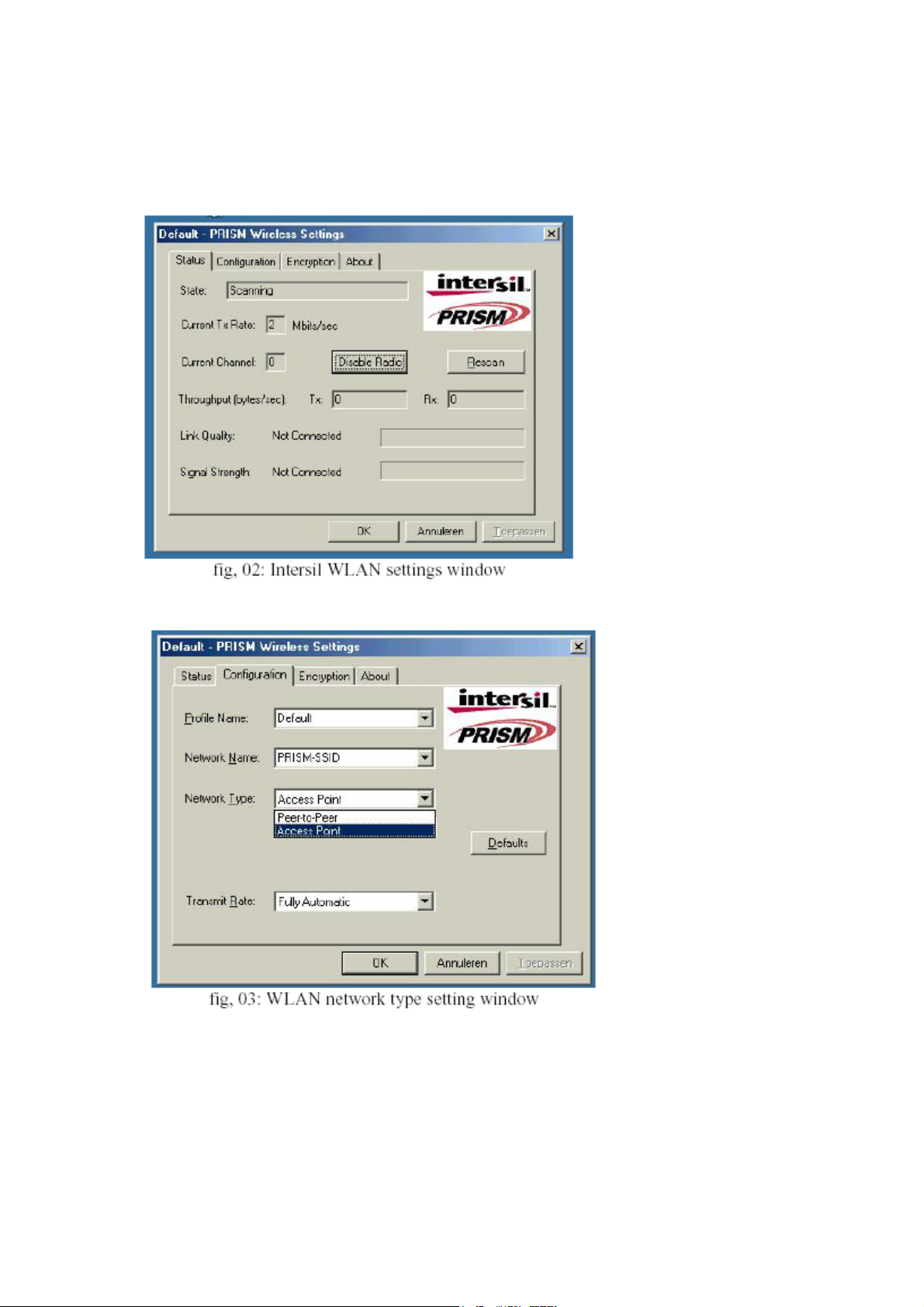
f-click on configuration tab and select which type of network is required (access point or
Peer-to-peer mode), see fig. 03.
g-select what TX rate is required (default setting is fully automatic) see fig. 04.
Page 3
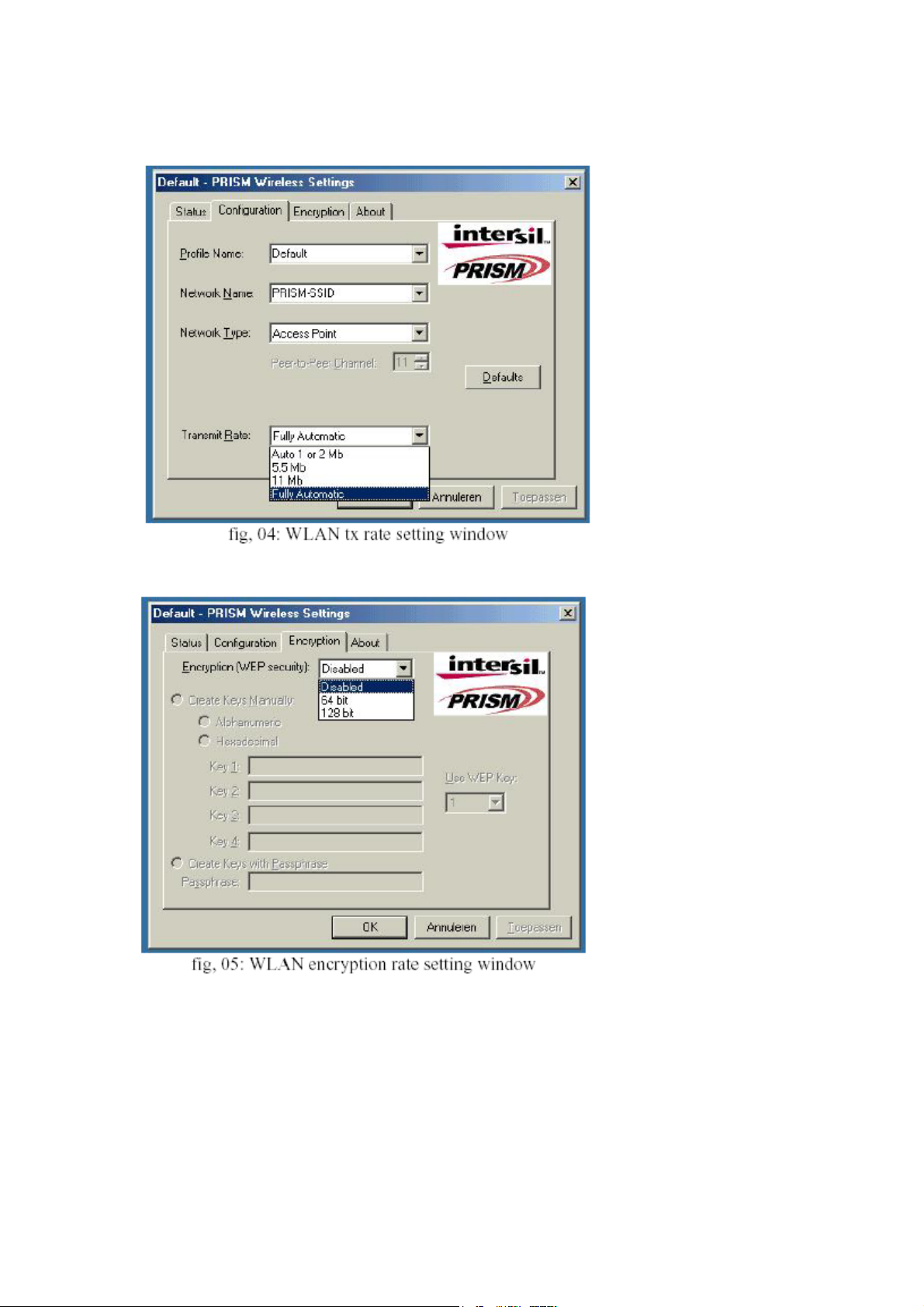
h-select what encryption type is required, 64 or 128 bit WEP (default setting is disabled)
see fig. 05.
i-click on the status tab to see the connection status (fig.06).
Page 4

j-click on the about tab to see the software drivers versions and MAC address (fig.07).
1.3 Wireless LAN installation guide lines and Authorization for use
Installation and use of this Wireless LAN device must be in strict accordance with the
instructions included in the user documentation provided with the product. Any changes
or modifications made to this device that are not expressly approved by Intersil may void
the user’s authority to operate the equipment. Intersil is not responsible for any radio or
television interference caused by unauthorized modification of this device, or the
Page 5

substitution or attachment of connecting cables and equipment other than specified. It is
the responsibility of the user to correct any interference caused by such unauthorized
modification, substitution or attachment. Intersil and its authorized resellers or
distributors will assume no liability for any damage or violation of government
regulations arising from failing to comply with these guidelines.
The use of Wireless LAN devices may be restricted in some situations or environments
for example:
* On board of airplanes, or
* In an explosive environment, or
* In case the interference risk to other devices or services is perceived or identified as
harmful.
In case the policy regarding the use of Wireless LAN devices in specific organizations or
environments (e.g. airports, hospitals, chemical/oil/gas industrial plants, private buildings
etc.) is not clear, please first verify authorization to use these devices prior to operating
the equipment.
2-Technical Specifications
Radio Technology
Operating Frequency 2400-2497MHz ISM band
Modulation Schemes DQPSK, DBPSK, CCK, 16 QAM, 64 QAM
RF Channel Availability
13 channels for Europe (2412 MHz to 2472 MHz)
13 channels for Japan (2412 MHz to 2472 MHz), channel 14 only
available in DSSS mode (11 Mbps max)
Data Rate Support for 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, and 6 Mbps OFDM, 11 and
5.5 Mbps CCK and legacy 2 and 1 Mbps data rates
Media Access Protocol CSMA/CA with ACK
Transmitter RF Output Power < 18.0 dBm EIRP (typical) including antenna gain
Antenna Type Internal diversity antennas with 1 dBi rated gain
Operating Voltage 3.3 VDC via PC host miniPCI slot
Interface miniPCI formfactor 3A
Device driver Support Microsoft® Windows® NT, 2000, ME, and XP
3-Regulatory information
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. This Class B digital apparatus complies
with Canada ICES-003. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However,
there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one of the following measures:
IEEE 802.11g Turbo (DSSS and OFDM)
11 channels for United States (2412 MHz to 2462 MHz)
Page 6

- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, (example - use only shielded interface
cables when connecting to computer or peripheral devices) any changes or modifications
not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's
authority to operate this equipment.
"Alpha Networks Inc. declare that WMP-G03 (IEEE 802.11g Mini PCI Card) is limited
in CH1~CH11 by specified firmware controlled in USA."
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules and Canadian Standard RSS-210.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Statement Needed to be Shown on End Product
Since this module is installed inside the end product, the end product should be affixed a
label on visible area showing that this product contain a RF module, and also its FCC ID.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance
20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
This device is intended only for OEM integrators under the following conditions:
1) The antenna must be installed such that 20 cm is maintained between the antenna and
users, and
2) The transmitter module may not be co-located with any other transmitter or antenna.
As long as the 2 conditions above are met, further transmitter testing will not be required.
However, the OEM integrator is still responsible for testing their end-product for any
additional compliance requirements required with this module installed (for example,
digital device emissions, PC peripheral requirements, etc.).
IMPORTANT NOTE:
certain laptop configurations or co-location with another transmitter), then the FCC
authorization is no longer considered valid and the FCC ID can not be used on the final
product. In these circumstances, the OEM integrator will be responsible for re-evaluating
the end product (including the transmitter) and Obtaining a separate FCC authorization.
End Product Labelling
In the event that these conditions can not be met (for example
Page 7

This transmitter module is authorized only for use in devices where the antenna may be
installed such that 20 cm may be maintained between the antenna and users (for example
access points, routers, wireless ASDL modems, and similar equipment). The final end
product must be labeled in a visible area with the following: “ Contains TX FCC ID:
RRK2003120027-1 ”.
Manual Information That Must be Included
The users manual for end users must include the following information in a prominent
location “
IMPORTANT NOTE: To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, the
antenna used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at
least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.”
 Loading...
Loading...