Alpha XM2-300HP Technical Manual

AlphaNet IDH4 for XM2 and XM2-300HP Series DOCSIS® Status Monitor
Technical Manual
Effective: January, 2014
Alpha Technologies
Power
®
AlphaNet IDH4 Series for XM2 and XM2-300HP
DOCSIS® Status Monitor
Technical Manual
745-257-B2-001, Rev. B
Effective Date: January, 2014
Copyright 2014
Alpha Technologies, Inc.
NOTE:
Alpha denies responsibility for any damage or injury involving its enclosures, power supplies, generators,
batteries or other hardware, manufactured by Alpha or members of the Alpha Group, when used for an
unintended purpose, installed or operated in an unapproved manner, or improperly maintained.
NOTE:
Photographs and drawings in this manual are for illustrative purposes only and might not exactly match your
installation.
NOTE:
Review this manual before proceeding. If there are questions regarding the safe installation or operation of
this product, please contact Alpha Technologies or your nearest Alpha representative.
Contacting Alpha Technologies: www.alpha.com
or
For general product information and customer service (7 AM to 5 PM, Pacic Time), call
1-800-863-3930
For complete technical support, call
1-800-863-3364
7 AM to 5 PM, Pacic Time or 24/7 emergency support
To report errors in this document, send email to:Techpubs@alpha.com

Table of Contents
Safety Notes .......................................................................................................................................................................7
1.0 Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................................8
2.0 Overview.....................................................................................................................................................................10
2.1 System Diagram ............................................................................................................................................10
2.2 Network Connectivity .....................................................................................................................................11
2.3 System Conguration and Installation ........................................................................................................... 11
2.4 IDH4 Series Start-up and Reboot Routine ....................................................................................................12
3.0 Network Conguration ................................................................................................................................................13
3.1 Provisioning the DHCP Server with the MAC addresses ..............................................................................13
3.2 The DOCSIS Conguration File ....................................................................................................................14
3.2.1 Setting Modem Community Strings..................................................................................................14
3.2.2 Setting SNMP Trap Destination Addresses ......................................................................................15
3.2.3 Sample DOCSIS Conguration File Entries .....................................................................................16
3.2.4 Proprietary Conguration File ‘idhdoc04.cfg’ ...................................................................................17
3.2.5 Changing Default idhdoc04.cfg Download Settings .........................................................................17
3.3 Setting Communication Options ....................................................................................................................18
4.0 Web Interface .............................................................................................................................................................19
Overview ..............................................................................................................................................................19
4.1 Local Web Server Access ..............................................................................................................................19
4.2 Remote Web Server Access ..........................................................................................................................22
4.3 Navigating the Web Page ..............................................................................................................................23
4.3 Navigating the Web Page ..............................................................................................................................24
4.3.1 Web Interface Security Levels .........................................................................................................24
4.4 Verifying Communication Parameters ...........................................................................................................24
4.4 Verifying Communication Parameters ...........................................................................................................25
4.5 Verifying Power Supply and Battery Parameters ...........................................................................................26
4.6 Remote Self Tests via the Web Page ............................................................................................................27
4.7 Viewing HMS Alarm Status via the Web Page ..............................................................................................28
4.8 Setting the I/O Controller via the Web Page ..................................................................................................29
4.9 Viewing Power Supply Settings via the Web Page .......................................................................................30
4.10 Viewing and Conguring Generator Settings via the Web Page .................................................................31
4.11 Viewing the Modem Event Log via the Web Page .......................................................................................32
4.12 QAM Constellation .......................................................................................................................................33
4.13 Controls .......................................................................................................................................................33
4.14 Downstream Data ........................................................................................................................................33
4.15 Interpreting QAM Constellation Data by Visual Inspection ..........................................................................34
4.16 Interpreting QAM Constellation Data by Visual Inspection ..........................................................................35
4.16 Interpreting QAM Constellation Data by Visual Inspection ..........................................................................36
4.16 Interpreting QAM Constellation Data by Visual Inspection ..........................................................................37
4.16 Interpreting QAM Constellation Data by Visual Inspection ..........................................................................38
4.17 Microreections ...........................................................................................................................................39
5.0 Upgrading Firmware ...................................................................................................................................................40
5.1 Upgrading IDH4 Series Modem Firmware .....................................................................................................40
5.1.1 Identifying the Modem and Obtaining Firmware Files ......................................................................40
5.1.2 Modem Firmware Upgrade SNMP Parameters ...............................................................................40
5.1.3 Upgrading Manually by Setting SNMP Parameters .........................................................................41
5.1.4 Upgrading via the DOCSIS Conguration File .................................................................................41
4 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)

Contents
6.0 Data Management ......................................................................................................................................................42
6.1 SCTE-HMS MIBs ..........................................................................................................................................42
6.2 SCTE-HMS MIB Alarms ................................................................................................................................43
6.2.1 SCTE-HMS Congurable Alarms .....................................................................................................43
6.2.2 SNMP Traps .....................................................................................................................................46
6.2.3 General Power Supply Alarms .........................................................................................................48
6.3 The Alpha MIBs .............................................................................................................................................49
6.3 The Alpha MIBs ............................................................................................................................................51
6.3.1 The Alpha MIB Structure ..................................................................................................................51
7.0 Installation ..................................................................................................................................................................52
7.1 Verifying Power Supply Device Address .......................................................................................................52
7.2 Installation / Replacement Procedure in XM2 Power Supplies .....................................................................53
7.3 IDH4L Installation / Replacement Procedure in XM2-300HP Power Supplies ..............................................55
7.4 IDH4X LEDs and Connections ......................................................................................................................57
7.5 IDH4L Connections .......................................................................................................................................58
7.6 Connecting the RF Drop ................................................................................................................................59
7.7 Front Panel Connections ...............................................................................................................................59
7.8 Environmental Connections ...........................................................................................................................60
7.8.1 Connecting the Battery Heater Mat Controller .................................................................................60
7.9 Environmental Control MIBs .........................................................................................................................61
7.10 Conguring the Battery Heater Mat Controller ............................................................................................63
8.0 Battery Sense Wire Kits..............................................................................................................................................64
8.1 36V Single and Dual Strings ..........................................................................................................................64
8.2 48V Single and Dual Strings ..........................................................................................................................65
9.0 Start Up and Verication .............................................................................................................................................66
9.1 Initial Startup and Local Verication ..............................................................................................................66
9.1.1 To Verify Network Connectivity:........................................................................................................66
9.2 Verifying Correct Hardware Interconnection ..................................................................................................67
9.3 System Status Indicators and Reset button ..................................................................................................68
9.3.1 Detailed LED Descriptions ...............................................................................................................68
9.3.2 Resetting the Transponder ...............................................................................................................70
9.4 Verifying Communications via the Headend ..................................................................................................70
10.0 Alpha MIB Parameters..............................................................................................................................................71
10.1 Denitions and Settings ...............................................................................................................................71
11.0 Dual IP Mode ........................................................................................................................................................... 76
11.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................................... 76
11.2 Web Comparison, Single IP Mode/Dual IP Mode ....................................................................................... 77
11.3 Conguring Dual IP Mode .......................................................................................................................... 78
11.3.1 atidoc03.cfg in Dual IP Mode ..........................................................................................................80
11.3.2 Changing Default atidoc03.cfg Download Settings in Dual IP Mode ..............................................80
11.3.3 Specifying atidoc03.cfg Name and Location via DHCP Tags ..........................................................81
11.4 Dual IP SNMP Community Strings .............................................................................................................82
11.5 Security in Dual IP Mode ............................................................................................................................82
12.0 Specications ...........................................................................................................................................................83
13.0 Glossary ...................................................................................................................................................................85
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
5

Figures
Fig. 1-1, AlphaNet IDH4X Series.................................................................................................................................................................8
Fig. 1-2, AlphaNet IDH4L ............................................................................................................................................................................ 8
Fig. 1-3, Side view, AlphaNet IDH4 Series .................................................................................................................................................. 9
Fig. 2-1, Representative System Arrangement .........................................................................................................................................10
Fig. 3-1, Locations of MAC Address labels ...............................................................................................................................................13
Fig. 3-2, Sample DOCSIS Conguration File ............................................................................................................................................ 16
Fig. 4-1, IDH4 Series Web Page ............................................................................................................................................................... 19
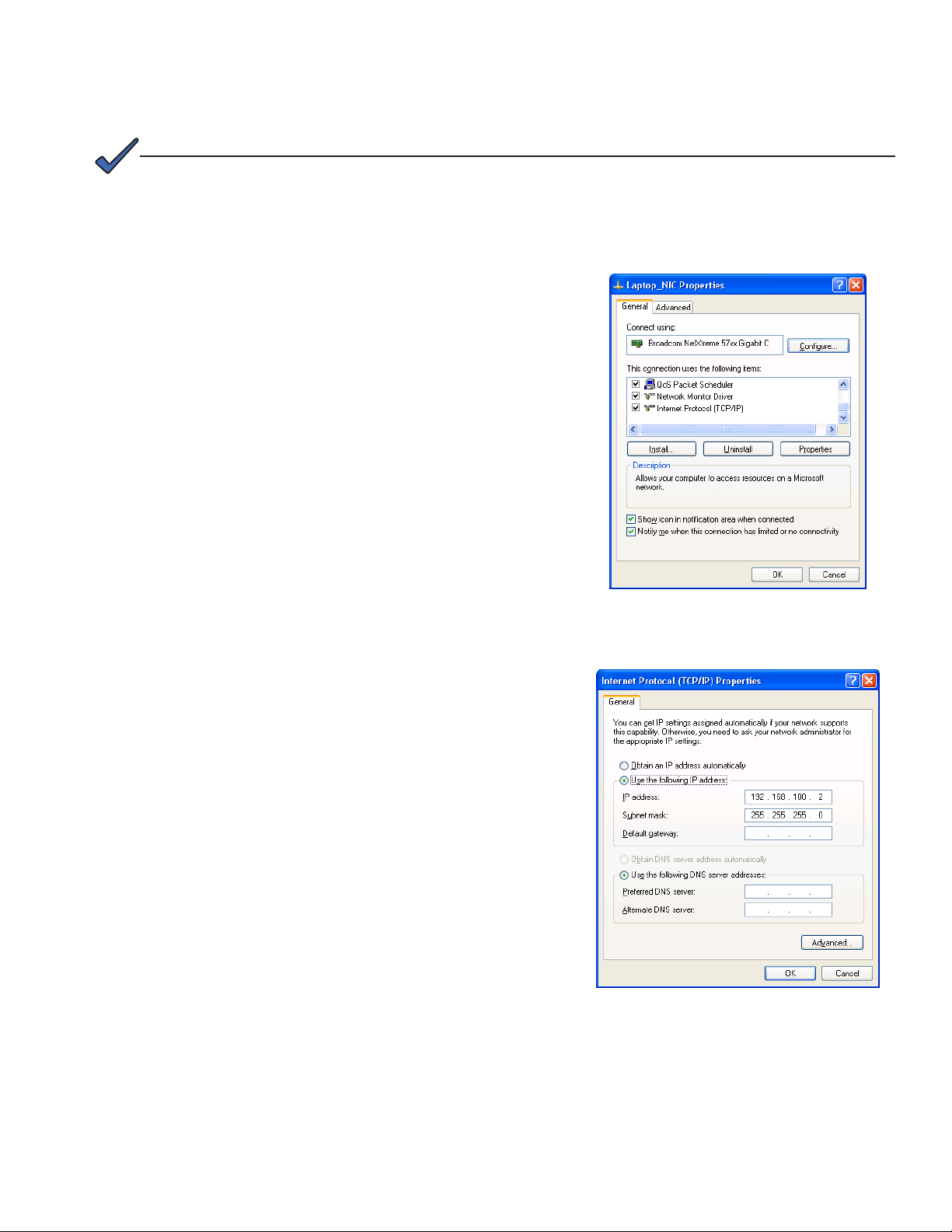
Fig. 4-2, Local Area Connection Properties Screen .................................................................................................................................. 20
Fig. 4-3, Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Screen ............................................................................................................................. 20
Fig. 4-4, Local Area Connection Properties Screen, Windows 7 ..............................................................................................................21
Fig. 4-5, Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Screen, Windows 7 ......................................................................................................... 21
Fig. 4-6, Web Server Home Page ............................................................................................................................................................. 22
Fig. 4-7, IDH4 Series Navigation Bar Items .............................................................................................................................................. 23
Fig. 4-9, Communication Parameters ....................................................................................................................................................... 24
Fig. 4-8, IDH4 Series Transponder Security Levels .................................................................................................................................. 24
Fig. 4-10, Communication Parameters ..................................................................................................................................................... 25
Fig. 4-11, Power Supply and Battery Parameters .....................................................................................................................................26
Fig. 4-13, Location of Start Button for Self Test ........................................................................................................................................ 27
Fig. 4-14, HMS Alarm Conguration .........................................................................................................................................................28
Fig. 4-15, Advanced I/O Controller Status Screen ....................................................................................................................................29
Fig. 4-16, Advanced Power Supply Settings Screen ................................................................................................................................30
Fig. 4-18, Advanced Generator Status Screen ........................................................................................................................................31
Fig. 4-19, Event Log Screen ..................................................................................................................................................................... 32
Fig. 4-20, IDH4 Constellation Page........................................................................................................................................................... 33
Fig. 4-21, IDH4 Constellation Page........................................................................................................................................................... 34
Fig. 4-22, Sample QAM Constellation—Normal Centered Dots (Good Quality) ....................................................................................... 35
Fig. 4-23, Sample QAM Constellation—Fuzzy (Low CNR and/or Low MER) ........................................................................................... 35
Fig. 4-24, Sample QAM Constellation—"Doughnuts" (Coherent Interference) ......................................................................................... 36
Fig. 4-25, Sample QAM Constellation—Gaussian Noise .......................................................................................................................... 36
Fig. 4-26, Sample QAM Constellation—Circular Smear (Phase Noise) ................................................................................................... 37
Fig. 4-27, Sample QAM Constellation—Corners Squeezed to Center (Gain Compression) .................................................................... 37
Fig. 4-28, Sample QAM Constellation—Rectangular vs. Square (I-Q Imbalance).................................................................................... 38
Fig. 4-29, Sample QAM Constellation—Twisted or Skewed (Quadrature Distortion) ............................................................................... 38
Fig. 4-30, IDH4 Constellation Page........................................................................................................................................................... 39
Fig. 6-1, Sample Raw SNMP Alarm Trap .................................................................................................................................................. 46
Fig. 6-2, Sample Translated SNMP Alarm Trap ........................................................................................................................................46
Fig. 7-1, Removing the Inverter Module from the Power Supply ............................................................................................................. 53
Fig. 7-4, Connecting the Transponder to the Inverter Module...................................................................................................................54
Fig. 7-2, The 18-pin jumper ....................................................................................................................................................................... 54
Fig. 7-3, The 18-pin jumper installed .........................................................................................................................................................54
Fig. 7-5, Removing the Inverter Module from the Power Supply ............................................................................................................. 55
Fig. 7-6, Removing the IDH4L sheet metal from the Inverter Module ....................................................................................................... 55
Fig. 7-7, The 18-pin jumper installed .........................................................................................................................................................56
Fig. 7-9, IDH4L attached to sheet metal ...................................................................................................................................................56
Fig. 7-10, IDH4L / IM connection ..............................................................................................................................................................56
Fig. 7-11, Completed assembly .................................................................................................................................................................56
Fig. 7-8, IDH4L 18-pin header ................................................................................................................................................................... 56
Fig. 7-12, IDH4X LEDs and Connectors ................................................................................................................................................... 57
Fig. 7-15, Connecting the RF Drop ........................................................................................................................................................... 59
Fig. 7-16, System Interconnection Diagram .............................................................................................................................................. 59
Fig. 8-1, 36V System, Single String .......................................................................................................................................................... 64
Fig. 8-2, 36V System, Dual String ............................................................................................................................................................. 64
Fig. 8-3, 48V, Single String ....................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Fig.8-4, 48V, Dual String ........................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Fig. 9-1, Initial Web Page .......................................................................................................................................................................... 66
Fig. 9-2, HMS Tab Screen ......................................................................................................................................................................... 67
Fig. 9-3, LED Functionality and Indications............................................................................................................................................... 68
Fig. 11-1, Simplied Block Diagram Single IP Mode ................................................................................................................................. 76
Fig. 11-2, Simplied Block DiagramDual IP Mode .................................................................................................................................... 76
Fig. 11-3, Single IP IDH4 Series Web Page .............................................................................................................................................. 77
Fig. 11-4, Dual IP IDH4 Series Web Page ................................................................................................................................................ 77
Fig. 11-5, Dual IP Conguration Settings for Transponder Web Server Communications Page ..............................................................79
Fig. 11-6, Dual IP Parameters for Transponder Web Server General Page .............................................................................................79
6 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)

Tables
Table 2-1, LEDs and Indications ....................................................................................................................................................12
Table 3-1, Modem Community String Parameters .........................................................................................................................14
Table 3-2, Trap Destination Addresses ..........................................................................................................................................15
Table 3-3, Changing Default idhdoc04.cfg Download Settings ......................................................................................................17
Table 3-4, Transponder Communications Parameters ...................................................................................................................18
Table 5-1, Modem Firmware Upgrade SNMP Parameters .............................................................................................................40
Table 6-1, SCTE-HMS MIB Files ....................................................................................................................................................42
Table 6-2, Binary to Hex Conversions for Alarm Settings ..............................................................................................................43
Table 6-3, Recommended Settings for IDH4 Series Analog Alarms .............................................................................................44
Table 6-4, Recommended Settings for IDH4L Analog Alarms .......................................................................................................44
Table 6-5, Recommended Settings for Discrete Alarms ................................................................................................................45
Table 6-6, SNMP Alarm Trap Varbinds and Explanations ..............................................................................................................47
Table 6-7, XM2 Major and Minor Alarms ........................................................................................................................................48
Table 6-8, Alpha MIB Hierarchy ......................................................................................................................................................50
Table 7-1, Environmental Control MIBs ..........................................................................................................................................61
Table 7-1, Environmental Control MIBs, continued ........................................................................................................................62
Table 7-2, OID Values for Battery Heater Mat Controller ...............................................................................................................63
Table 7-3, SNMP MIB Points for Battery Heater Mat Controller .....................................................................................................63
Table 11-1, Single IP Mode versus Dual IP Mode .................................................................................................................76
Table 11-2, Enabling Dual IP mode ......................................................................................................................................78
Table 11-3, CPE Communications Module IP Settings ........................................................................................................78
Table 11-4, Download Options .............................................................................................................................................80
Safety Notes
Review the drawings and illustrations contained in this manual before proceeding. If there are any questions regarding
the safe installation or operation of the system, contact Alpha Technologies or the nearest Alpha representative. Save this
document for future reference.
To reduce the risk of injury or death and to ensure the continued safe operation of this product, the following symbols have
been placed throughout this manual. Where these symbols appear, use extra care and attention.
WARNING!
WARNING presents safety information to PREVENT INJURY OR DEATH to the technician
or user.
CAUTION!
The use of CAUTION indicates safety information intended to PREVENT DAMAGE to material or
equipment.
NOTE:
A NOTE provides additional information to help complete a specic task or procedure.
ATTENTION:
The use of ATTENTION indicates specic regulatory/code requirements that may affect the placement of
equipment and /or installation procedures.
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
7
1.0 Introduction
The AlphaNet IDH4 Series Embedded DOCSIS Transponder allows monitoring of Alpha power supplies through
existing cable network infrastructure. Advanced networking services provide quick reporting and access to critical
powering information.
The IDH4 Series utilizes Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and standard Management Information
Bases (MIBs) to provide network status monitoring and diagnostics. A Web interface enables authorized
personnel direct access to advanced diagnostics using a common Web browser. No custom software is required.
This manual addresses the three models of the IDH4 Series. The table below compares the differences between
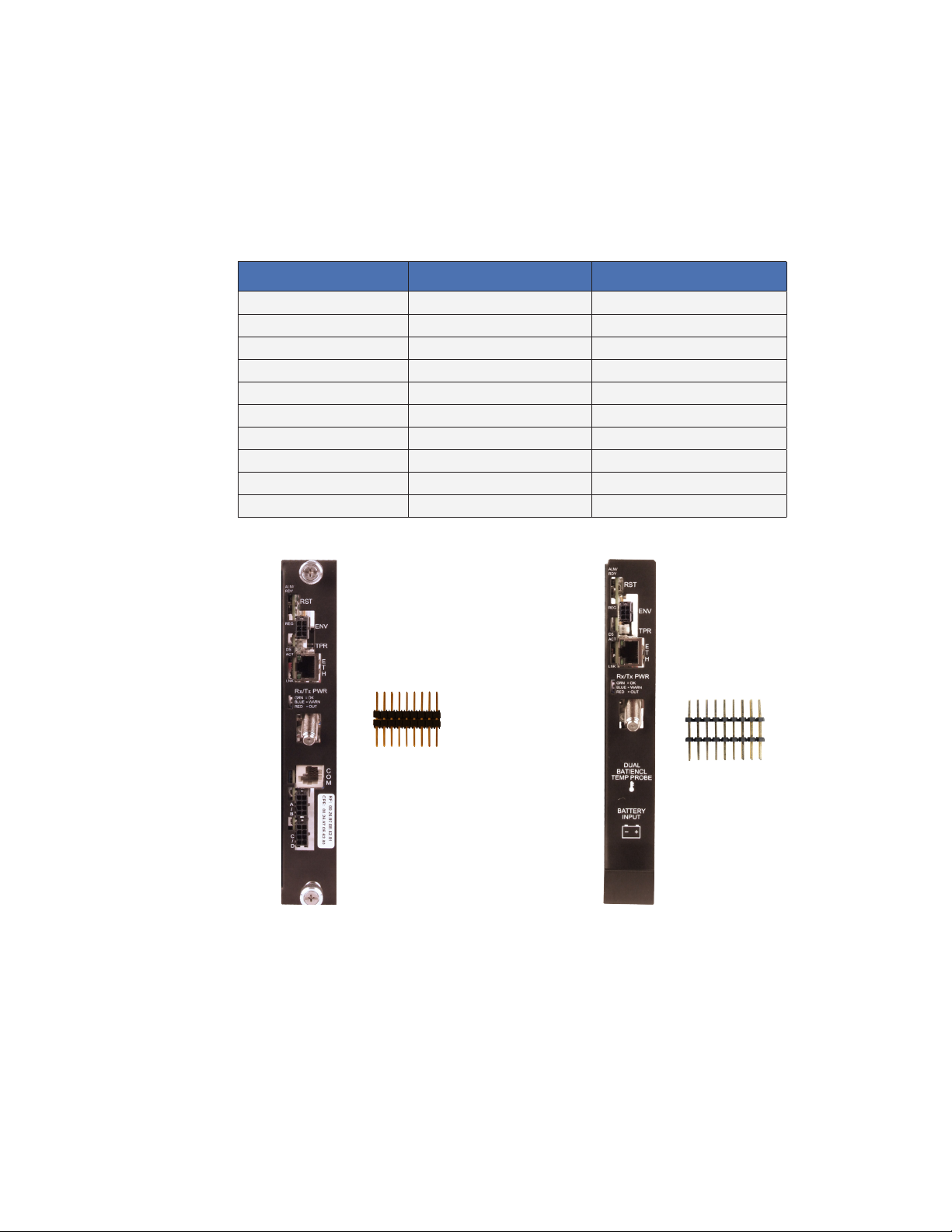
the transponder models.
Model IDH4X IDH4L
Part Number 746-257-20 746-257-22
Supported Power Supplies XM2, XM2-HP, XM2-VP XM2-300HP
Capacity 5 power supplies (plus generator) 1 power supply
1 & 2 Battery Strings Yes 1 battery (2 for added runtime)
3 & 4 Battery Strings Yes No
Tamper Switch Yes Yes
Environmental Control Yes Yes
COM Port (AlphaBus) Yes No
Ethernet Port Yes Yes
2 x 9 Interconnection Header Alpha p/n 540-286-19 Alpha p/n 540-581-19
IDH4X 2 x 9 header
(Alpha p/n 540-286-19)
IDH4L 2 x 9 header
(Alpha p/n 540-581-19)
Fig. 1-1, AlphaNet IDH4X Series Fig. 1-2, AlphaNet IDH4L
Primary Features:
• 10/100 Mbps auto-negotiating standard Ethernet interface
• Supports SNMPv1, v2c
• Extensive power supply diagnostic MIBs
• Embedded Web server for direct diagnostics
• Environmentally hardened DOCSIS cable modem and transponder
• Local Ethernet port provides technician on-site access to extensive power supply diagnostics*
• Angled RF port reduces cable bend radius
• Diagnostic LEDs
* Ethernet port also available for connecting external CPE devices
8 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
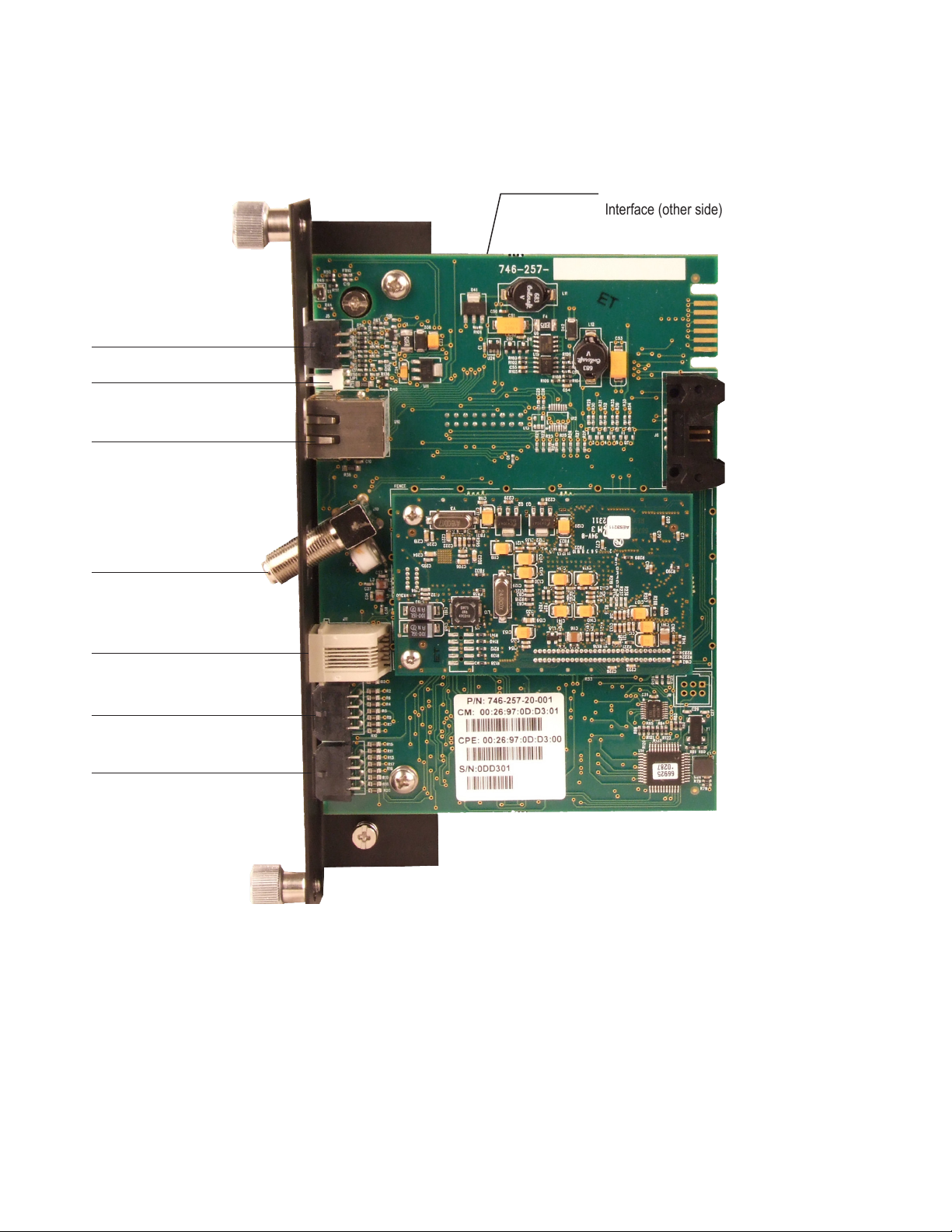
1.0 Introduction
Environmental IO Connector
Tamper Connector
Ethernet Port for Local Diagnostics
Intelligent CableUPS
Interface (other side)
RF Connector
COM Port (IDH4X only)
Battery Monitoring Connection A/B
(IDH4 and IDH4X only)
Battery Monitoring Connection C/D
(IDH4X only)
Fig. 1-3, Side view, AlphaNet IDH4 Series
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
9
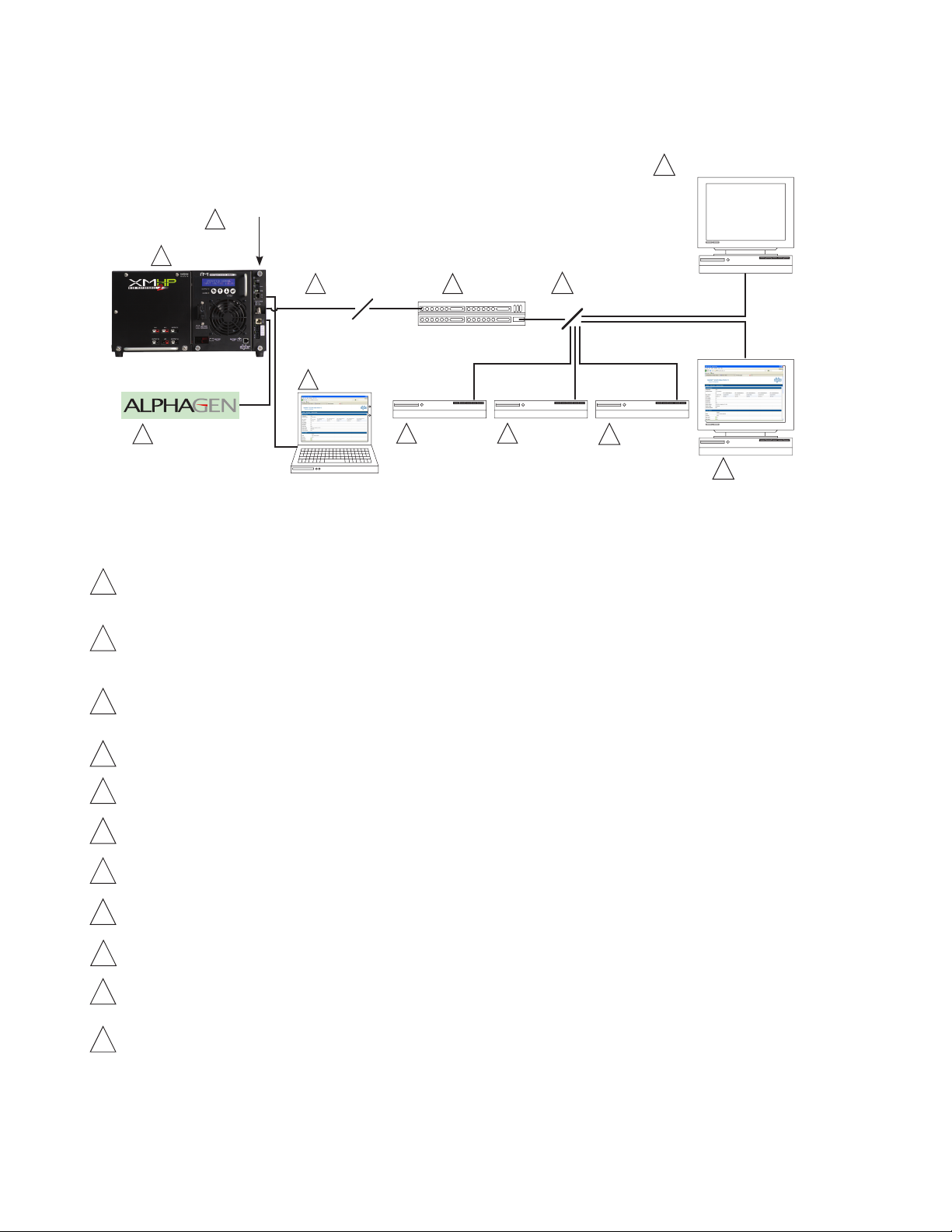
2.0 Overview
2.1 System Diagram
Power Supply
1
SNMP-based Network Management System
10
IDH4
2
Series
Coax/HFC Network
5
Local Computer
4
CMTS
6
TCP/IP Network
7
External Generator
3
DHCP Server
7
TFTP Server TOD Server
8
9
Web Browser
11
Fig. 2-1, Representative System Arrangement
All power supply data is stored in the power supply inverter module's class information base (CIB) tables in the power supply.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
This data is accessible directly via the power supply’s smart display (see the power supply’s technical manual for details).
The CIB tables are the source of the transponder’s data.
The IDH4 Series contains both SCTE-HMS Management Information Base (MIBs) and the proprietary Alpha MIB tables. The
SCTE-HMS MIBs are industry standard MIB tables that store power supply, battery and generator data from the CIB tables
(See Section 6.0, Data Management). The Alpha MIB contains all the data of the SCTE-HMS MIBs plus additional power
supply settings and values as well as IDH4 Series conguration values.
An external generator or additional power supplies may be connected through the COM (AlphaBus) port permitting
monitoring locally through the Ethernet connector or remotely via the Web page or SNMP-based Network Management
System.
Power supply and transponder parameters can be monitored and set locally using a personal computer and a standard
Ethernet cable.
The IDH4 Series transmits data via its cable modem directly over the Coax or Hybrid Fiber Coax network.
The Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) is the bridge between the cable network and the TCP/IP network. The IDH4
Series’ cable modem communicates directly with the CMTS.
The Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server needs to be provisioned with the IDH4’s cable modem RF MAC Address
and the MAC Address needs to be assigned a DOCSIS Conguration File.
8
9
10
11
10 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
The DOCSIS Conguration File and rmware les should be available in the Root Directory of the Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP) Server.
The Time of Day (TOD) Server provides the cable modem with the current date and time via the SNTP protocol.
A Network Management System (NMS) or MIB Browser allows remote monitoring of parameter values and changing of
settings in SNMP MIB tables. SCTE-HMS and Alpha MIBs must be installed in the browser. Alarms and traps can be set and
monitored.
The power supply and generator may be accessed remotely through the transponder's Web page by placing its IP address
into a standard Internet Web browser.

2.0 Overview
2.2 Network Connectivity
The IDH4 Series cable modem must be recognized by the CMTS as a valid device to be assigned an IP
address from the DHCP server, to locate the TFTP and TOD servers and to communicate with the SNMP
management server (trap receiver).
Data from both the cable modem and power supply are accessed and managed through the modem’s
IP address on the secure private modem network. The transponder is not accessible from the public
Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) network. Consequently, the Network Management System (NMS)
that monitors the power supplies must have access to the same private modem network.
CMTS and system vendors use different security methods to insure network integrity, but common
considerations are:
• MAC ltering may have to be modied to allow RF MAC registration of addresses starting with
• For SNMP access, UDP ports 161 and 162 must not be blocked.
• For TFTP access, port 69 must not be blocked.
• For HTTP access, port 80 must not be blocked.
• For SNTP access, port 37 must not be blocked.
00:26:97.
• Firewalls must allow TFTP, DHCP, SNMP and TOD communication to the cable modem.
• If the address of the TFTP or TOD server is different than the DHCP server, the response from the
DHCP server must contain the TFTP and TOD addresses.
2.3 System Conguration and Installation
NOTE:
Before installation, read all of the “System Overview” Sections.
IDH4 Series installation and setup is comprised of three basic steps:
1. Conguring the Network: Provisioning the DHCP Server with the transponder’s MAC Address and
assigning it a DOCSIS Conguration File.
2. Setting Options: The IDH4 Series is designed for out-of-the-box, "plug and play" operation, but
non-default settings such as SNMP trap destination addresses may be required for the Network
Management System (NMS). SNMP trap addresses can be set automatically via the DOCSIS
Conguration File per RFC 4639, while IDH4 Series proprietary options may be set through type-11
TLV entries. The SCTE-HMS and Alpha MIBs may need to be compiled into a MIB browser before it
can be used to monitor or set transponder and power supply parameters.
3. Field Installation of the IDH4 Series into the power supply, connecting the battery sense wire
harnesses and verifying operation.
These steps can be performed independently of one another. However, conguring the network prior
to eld installation will allow the installation to be veried while personnel are still on-site. Performing
eld installation before network conguration and before the installation can be veried, might result in
additional eld service calls to correct mistakes.
Carefully read the following section in order to understand the dependencies within the system before
performing system conguration or hardware installation.
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
11
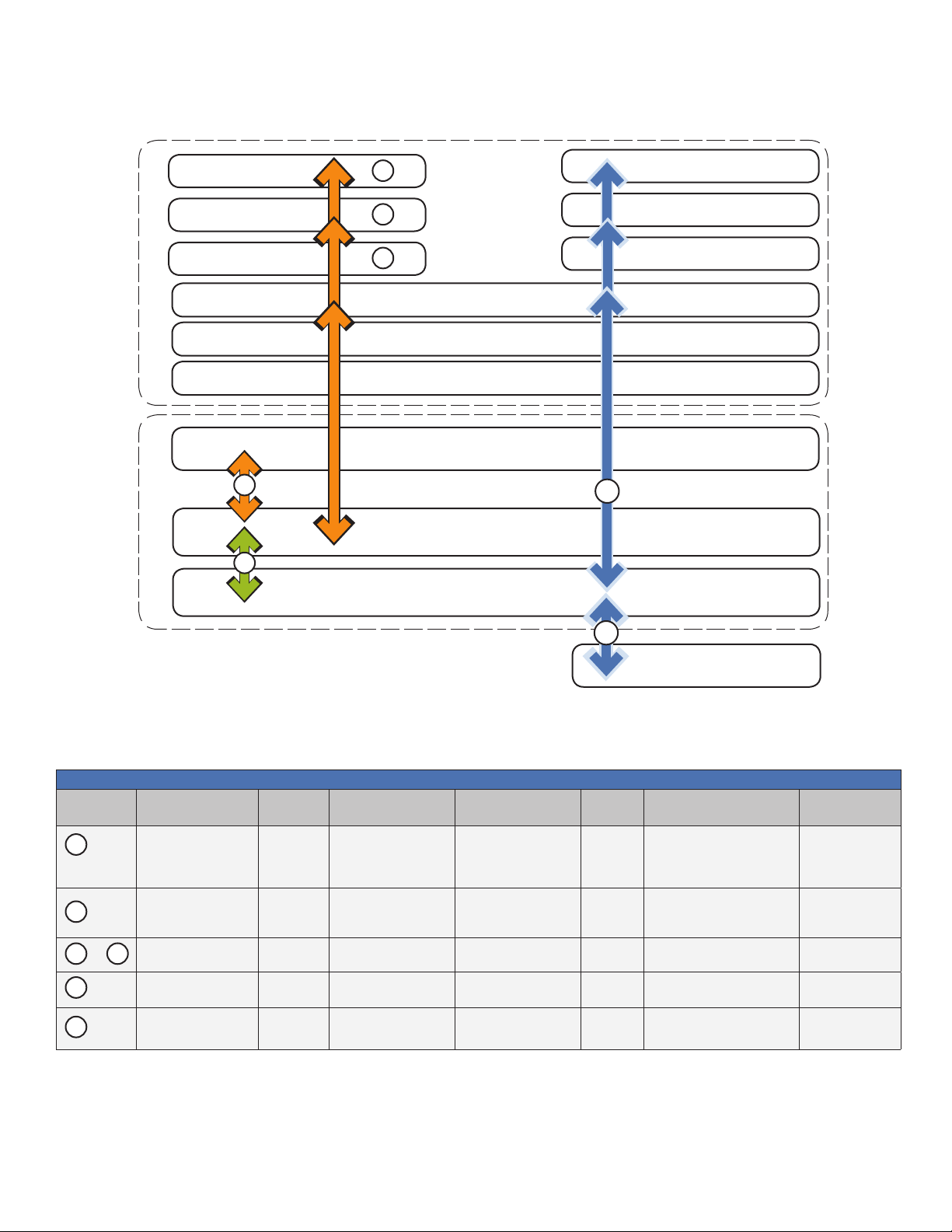
2.0 Overview
2.4 IDH4 Series Start-up and Reboot Routine
TFTP Server
TOD Server
DHCP Server
TCP/IP NetworkHFC Network
5
4
3
Routers
Switches
Firewalls
Network Management System
MIB Browser
Web Browser
CMTS
2
6
IDH4 Series
1
Power Supply
7
The above diagram, read left to right, indicates the order of operations as the transponder comes online.
There are certain conditions that must exist for each step to occur, resulting in successful data monitoring and
management. The numbers below correspond to the numbered arrows above.
LEDs and Indications
Ref #
1
2
3 5
to
6
7
Refer to Ref #6 in the above table for normal LED behavior when the IDH4 is fully functional.
• Blue Rx/Tx Power LED indicates Rx/Tx Power at a warning level. Make the necessary RF level adjustments.
• Red Rx/Tx Power LED indicates Rx/Tx Power at an alert level. Make the necessary RF level adjustments.
Communications
State
Transponder Initializing/
Searching for
Downstream DOCSIS
channel
DOCSIS Channel locked
- Completing upstream
and network registration
Online - Registration
Complete
IDH4 Series fully
functional
Laptop Connected to
local Ethernet port
ALM/RDY Downstream (DS) Registration (REG)
ON (Green) Flashing OFF OFF OFF OFF
ON (Green) ON Flashing ON (Green) OFF OFF
Flashing
(Green)
Flashing
(Green)
Flashing
(Green)
ON ON ON (Green) OFF and ON OFF
ON ON ON (Green)
ON ON ON (Green) Bursts
Rx/Tx
Power
Communications (COM) Ethernet (ETH)
Bursts when communicating to
multiple power supplies (IDH4X
Local Laptop
OFF
LNK - ON
ACT - Bursts
Table 2-1, LEDs and Indications
12 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
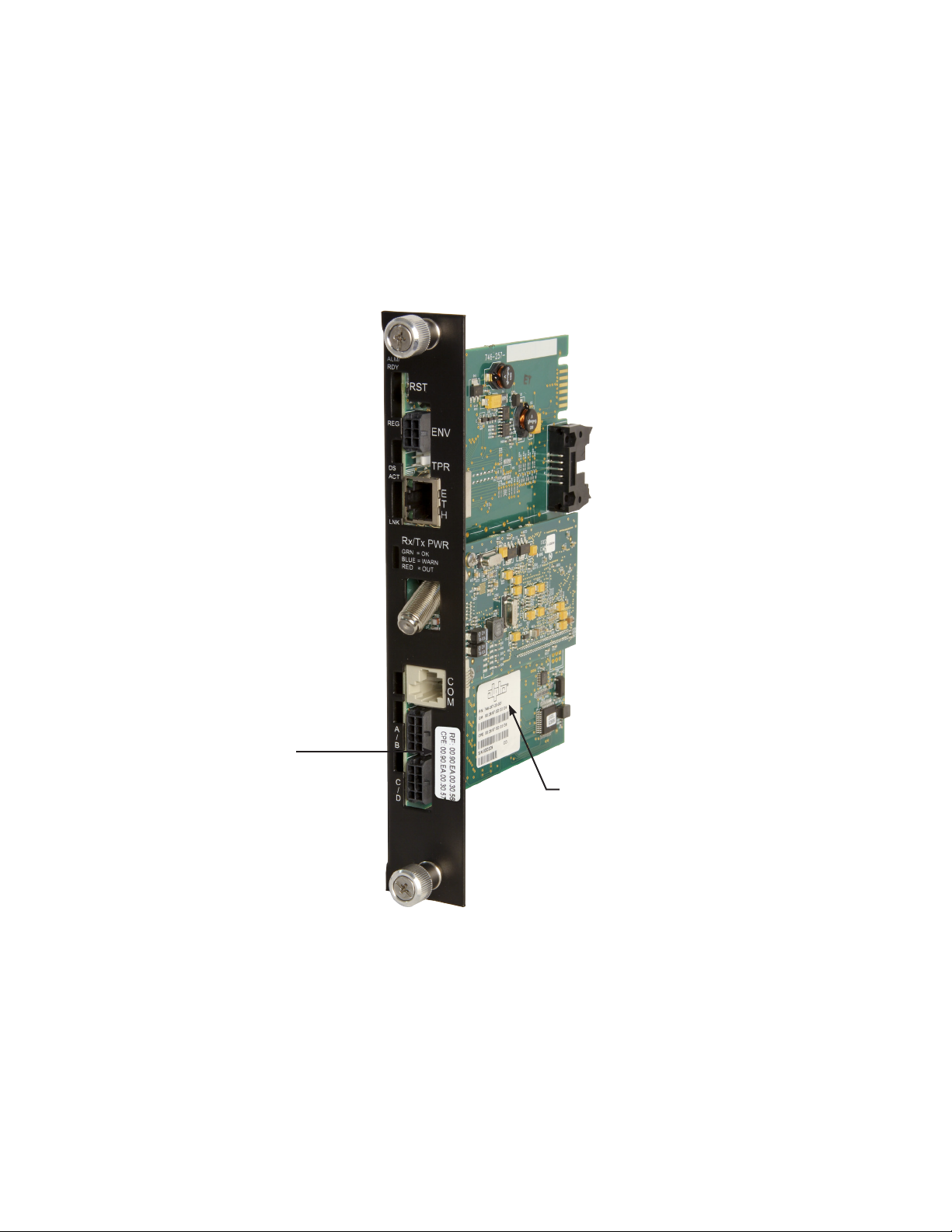
3.0 Network Conguration
3.1 Provisioning the DHCP Server with the MAC addresses
On the DHCP server, assign the cable modem’s RF MAC address with a DOCSIS Conguration File
to set modem communication options. (See Section 3.2 for instructions on how to create a DOCSIS
Conguration File).
The RF and CPE MAC addresses are located in two places on the IDH4 Series and on the packing slip,
see below.
Cable Modem
and CPE MAC
address label
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
Identier label
Fig. 3-1, Locations of MAC Address labels
13
3.0 Network Configuration
3.2 The DOCSIS Conguration File
A cable modem’s DOCSIS Conguration File is a type-length-value (TLV) le that contains important
operational parameters as dened by the DOCSIS standards. It provides certain settings for the cable
modem. In addition to standard entries, settings in the DOCSIS Conguration File should include the
modem’s community strings and, if an upgrade is necessary, rmware upgrade parameters. Place the
conguration le in the TFTP root directory.
To build a DOCSIS Conguration File use a DOCSIS TLV editor program.
See the example Conguration File in Section 3.2.3.
NOTE:
The modem community strings should be set in the DOCSIS Conguration File. Failure to set
community strings will result in a less secure system. For automatically updating modem rmware
with the DOCSIS Conguration File, see Section 5.1.
3.2.1 Setting Modem Community Strings
Set the modem community strings with the DOCSIS Conguration File by including the following
SNMP parameters:
MIB Parameter Object ID Description Value
docsDevNmAccessIp 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.2.x The IP address (or subnet) of the
network management station
docsDevNmAccessIpMask 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.3.x The IP subnet mask of the network
management stations
docsDevNmAccessCommunity 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.4.x The community string matched to
this IP/Mask entry
docsDevNmAccessControl 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.5.x The level of access granted 1= none
docsDevNmAccessInterfaces 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.6.x Specifies the set of interfaces from
which requests from this NMS will
be accepted
docsDevNmAccessStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.7.x Controls and reflects the status of
rows in this table
Note: X denotes the index of the SNMP entry
e.g. 10.20.30.0
e.g. 255.255.255.0
alphanumeric string
2= read only
3= read/write
0x40 : Cable interface
(typical)
0x80 : Ethernet interface
0xC0 or 0x00 : Both interfaces
4
Table 3-1, Modem Community String Parameters
14 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
3.0 Network Configuration
3.2 The DOCSIS Conguration File
3.2.2 Setting SNMP Trap Destination Addresses
Set the SNMP Trap Destination addresses via the DOCSIS Conguration File by including the
following SNMP parameters:
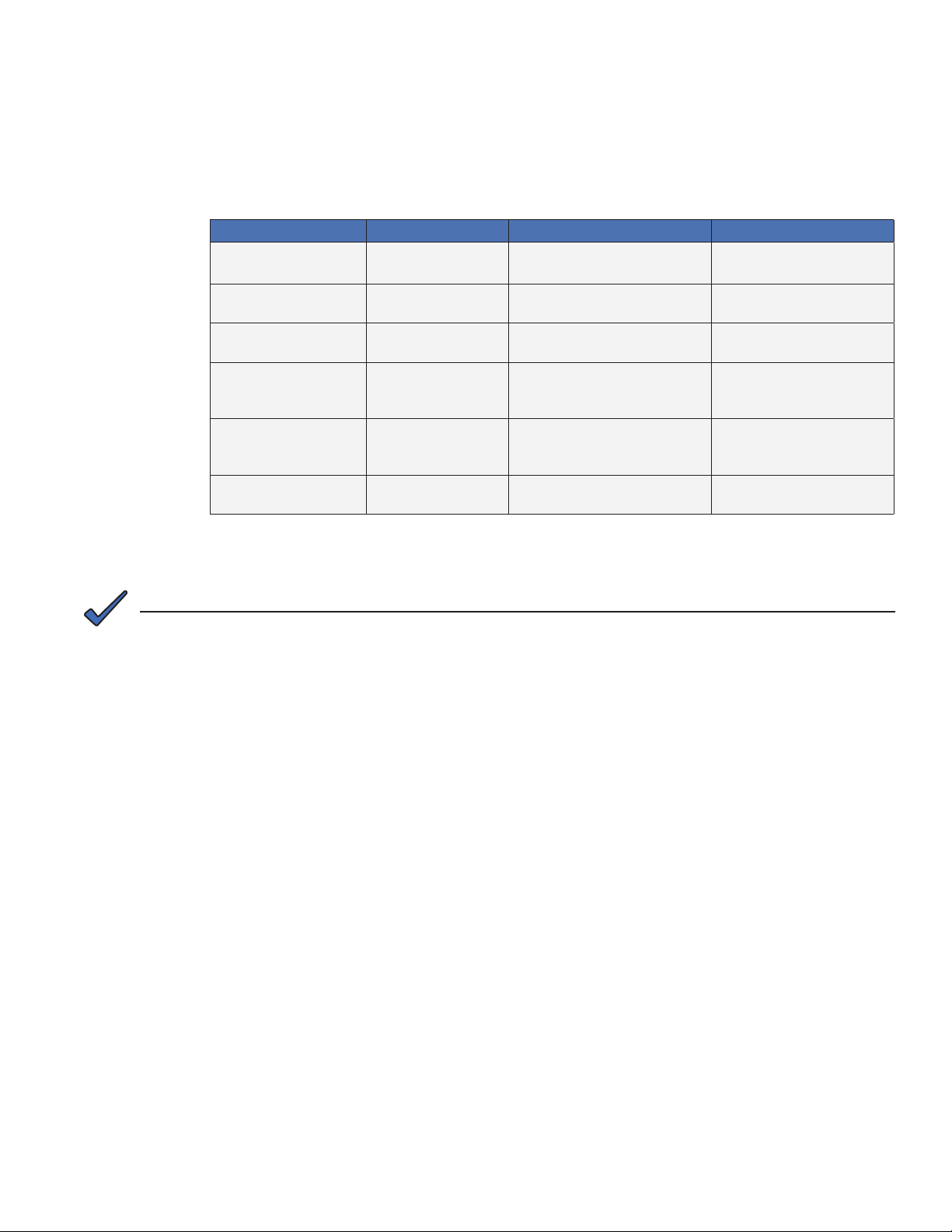
MIB Parameter Object ID Description Value
docsDevNmAccessIP 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.2.X IP address of trap destination, e.g.
docsDevNmAccessIpMask 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.3.X Must be set to 255.255.255.255 per
docsDevNmAccessCommunity
docsDevNmAccessControl 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.5.X Level of SNMP access to IDH4
docsDevNmAccessInterfaces
docsDevNmAccessStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.7.X Controls and reflects the status of
Note: X denotes the index of the SNMP entry
NMS server
RFC 4639
1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.4.X Community string used by NMS to
query transponder
Series from IP address specified in
docsDevNmAccessIpMask
1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.6.X Specifies the set of interfaces from
which requests from this NMS will be
accepted
rows in this table
e.g. 10.20.30.40
255.255.255.255
alphanumeric string
4= Read/Only plus Trap
5= Read/Write plus Trap
6= Trap only, no SNMP access
0x40 : Cable interface (typical)
0x80 : Ethernet interface
0xC0 or 0x00 : Both interfaces
4
Table 3-2, Trap Destination Addresses
NOTE:
As an alternative to the docsDevNmAccessTable, SNMP Trap Destination Addresses may be set through the
IDH4 proprietary MIB atiMgmtSnmpTrapTable (OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.926.1.3.1.1) using an SNMP MIB Browser
or as an entry in the Proprietary Conguration File (see Section 3.2.4, Proprietary Conguration File
'idhdoc04.cfg').
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
15

3.0 Network Configuration
3.2 The DOCSIS Conguration File
3.2.3 Sample DOCSIS Conguration File Entries
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=21]:docsDevNmAccessStatus.1/4
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=21]:docsDevNmAccesslp.1/10.56.21.0
A
B
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=21]:docsDevNmAccesslpMask.1/255.255.255.0
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=25]:docsDevNmAccessCommunity.1/"RW STRING"
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=25]:docsDevNmAccessInterfaces.1/"@"
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=21]:docsDevNmAccessControl.1/3
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=21]:docsDevNmAccessStatus.2/4
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=21]:docsDevNmAccesslp.2/10.20.30.40
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=21]:docsDevNmAccesslpMask.2/255.255.255.255
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=25]:docsDevNmAccessCommunity.2/"RW Trap string"
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=25]:docsDevNmAccessInterfaces.2/"@"
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=21]:docsDevNmAccessControl.2/5
C
D
E
Legend:
A
B
C
Software Upgrade Filename(9) [Len=24]:"ModemFirmwareFile.bin"
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len=20]:docsDevSwAdminStatus.0/2
Software Upgrade TFTP Server (21) [Len=4]:10.56.48.15
Manufacturer Code Verification Certificate (32) [Len=254]: 30 82 03 1A 30 82...
Manufacturer Code Verification Certificate (32) [Len=254]: 04 0A 13 11 41 4D...
Manufacturer Code Verification Certificate (32) [Len=254]: 04 0C 30 0A 06 01...
Manufacturer Code Verification Certificate (32) [Len=36]: 11 A3 41 A6 A7 D9....
Fig. 3-2, Sample DOCSIS Conguration File
Sets Read-Write Community string. Set the IP address, Netmask and community string to t your system.
Sets the IP address of where the SNMP traps will be sent. This is typically set to match the IP address of the Network
Management System Server.
Sets rmware download parameters.
Species the IP Address of the TFTP server used for upgrading rmware.
D
Sets Code Verication Certicate (CVC) for rmware upgrade security per the DOCSIS specication.
E
NOTE:
DOCSIS conguration les vary from system to system. Take into consideration your company's policies and
test the le on a local system prior to widescale deployment.
16 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
3.0 Network Configuration
3.2 The DOCSIS Conguration File
3.2.4 Proprietary Conguration File ‘idhdoc04.cfg’
The IDH4 Series will attempt to download a TLV-formatted le ‘idhdoc04.cfg’ from the modem’s
provisioning TFTP server at start up and every 24 hours thereafter. The idhdoc04.cfg proprietary
conguration le is optional and provides an alternative method to the modem’s DOCSIS conguration
le for deploying Alpha proprietary SNMP MIB parameters to eld-installed IDH4 Series transponders.
The idhdoc04.cfg le should be used if the following conditions are true:
1. Non-default settings, such as SNMP Trap Destination Addresses need to be distributed to all
IDH4 Series transponders.
2. The operator does not desire to place Alpha-proprietary parameters into the modem’s DOCSIS
conguration le.
NOTE:
The recommended method for setting the SNMP trap address(es) is through the modem DOCSIS
conguration le (see Section 3.2, The DOCSIS Conguration File). Alpha-proprietary parameters may
also be set through the modem’s DOCSIS conguration le, eliminating the need for the idhdoc04.cfg
proprietary conguration le.
To build the idhdoc04.cfg le, enter the desired SNMP OIDs and values from the Alpha MIB into a TLV
le as TLV type-11 entries using a TLV editor (see sample entries below). The IDH4 Series proprietary
conguration Setup le must be named “idhdoc04.cfg” and placed in the root directory of the TFTP
server. IDH4 settings are updated according to values dened in this le at start up and after every 24
hours of operation.
Sample idhdoc04.cfg Entries:
Network Access Control (3) [Len = 1]: 1
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len = 24]: atiMgmtSnmpTrapAddress.1 / 10.20.30.40
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len = 24]: atiMgmtSnmpTrapAddress.2 / 10.20.30.50
SNMP MIB Object (11) [Len = 23]: atiMgmtSysTamperPolarity.0 / 1
3.2.5 Changing Default idhdoc04.cfg Download Settings
By default the IDH4 Series will download the idhdoc04.cfg le from the provisioning TFTP server
every 24 hours. However, these settings may be adjusted per the tables below by placing the
respective SNMP varbinds into the modem’s DOCSIS conguration le.
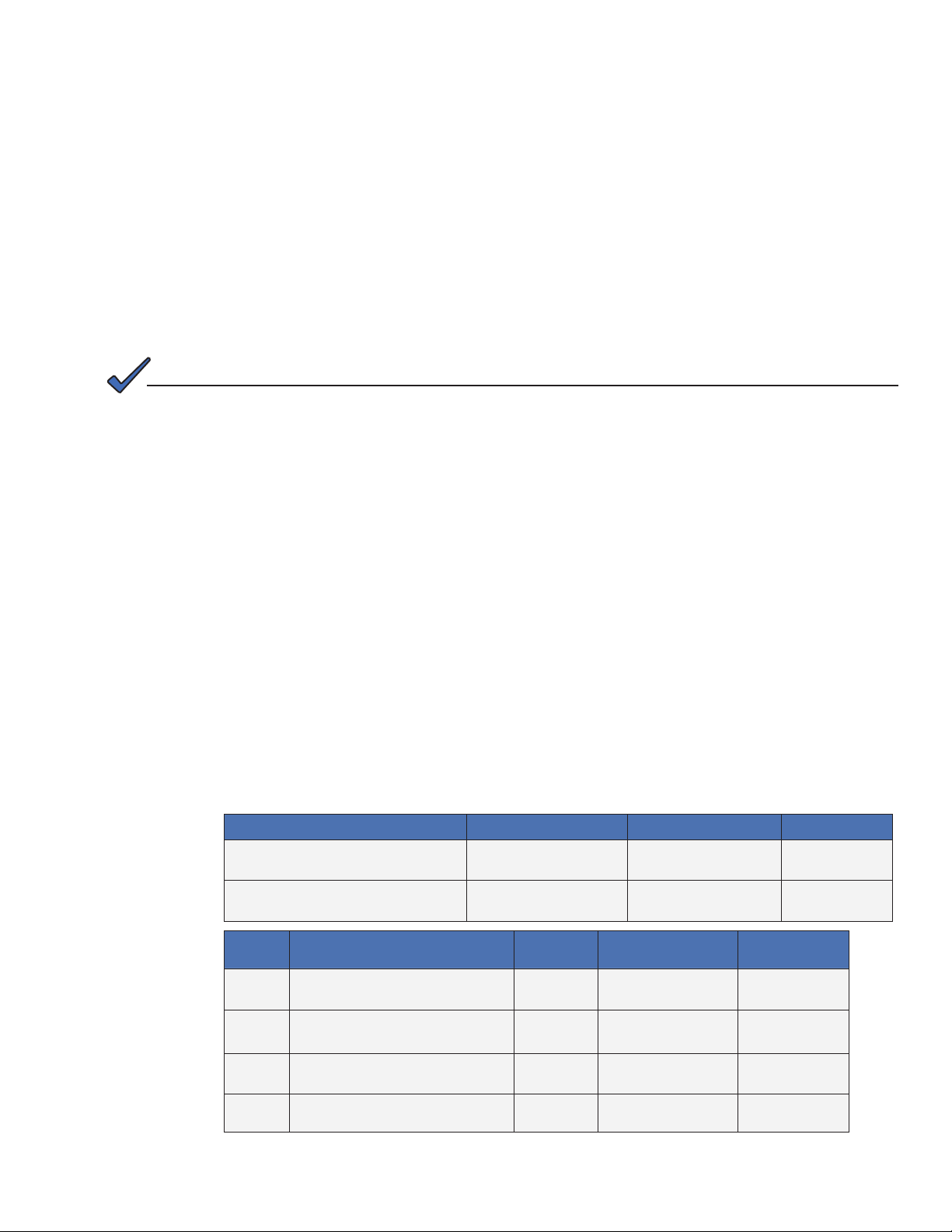
Parameter Type Description Value
atiMgmtSysDownloadCongName
1.3.6.1.4.1.926.1.3.2.1.9.0
atiMgmtSysDownloadReCfgTime
1.3.6.1.4.1.926.1.3.2.1.13.0
Search
Order
Parameter Type Description Value
atiMgmtSysDownloadCongAddress
1
OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.926.1.3.2.1.10.0
docsDevServerCongTftpAddress
2
1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.4.11.0
docsDevSwServerAddress
3
1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.3.7.0
4 Software Upgrade Server IP Address
Alphanumeric String
Integer
IP Address
IP Address
IP Address
Overrides default
location
Default location (No
change necessary)
Set via DOCSIS
conguration le
Set via DOCSIS
conguration le
Name of proprietary
conguration le
Download interval for
idhdoc04.cfg (hours)
"idhdoc04.cfg"
(Default)
24 (Default)
0.0.0.0 (Default)
CM's TFTP
Server Address
Congurable
Congurable
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
Table 3-3, Changing Default idhdoc04.cfg Download Settings
17
3.0 Network Configuration
3.3 Setting Communication Options
Communications Settings may be changed through the Alpha MIB remotely using an SNMP MIB browser
or automatically by placing the SNMP parameters into the DOCSIS cong le.
See Section 6, Data Management for an explanation of the Alpha MIB.
NOTE:
Before setting options, verify UDP ports 37, 69, 161, 162 and TCP port 80 are not blocked.
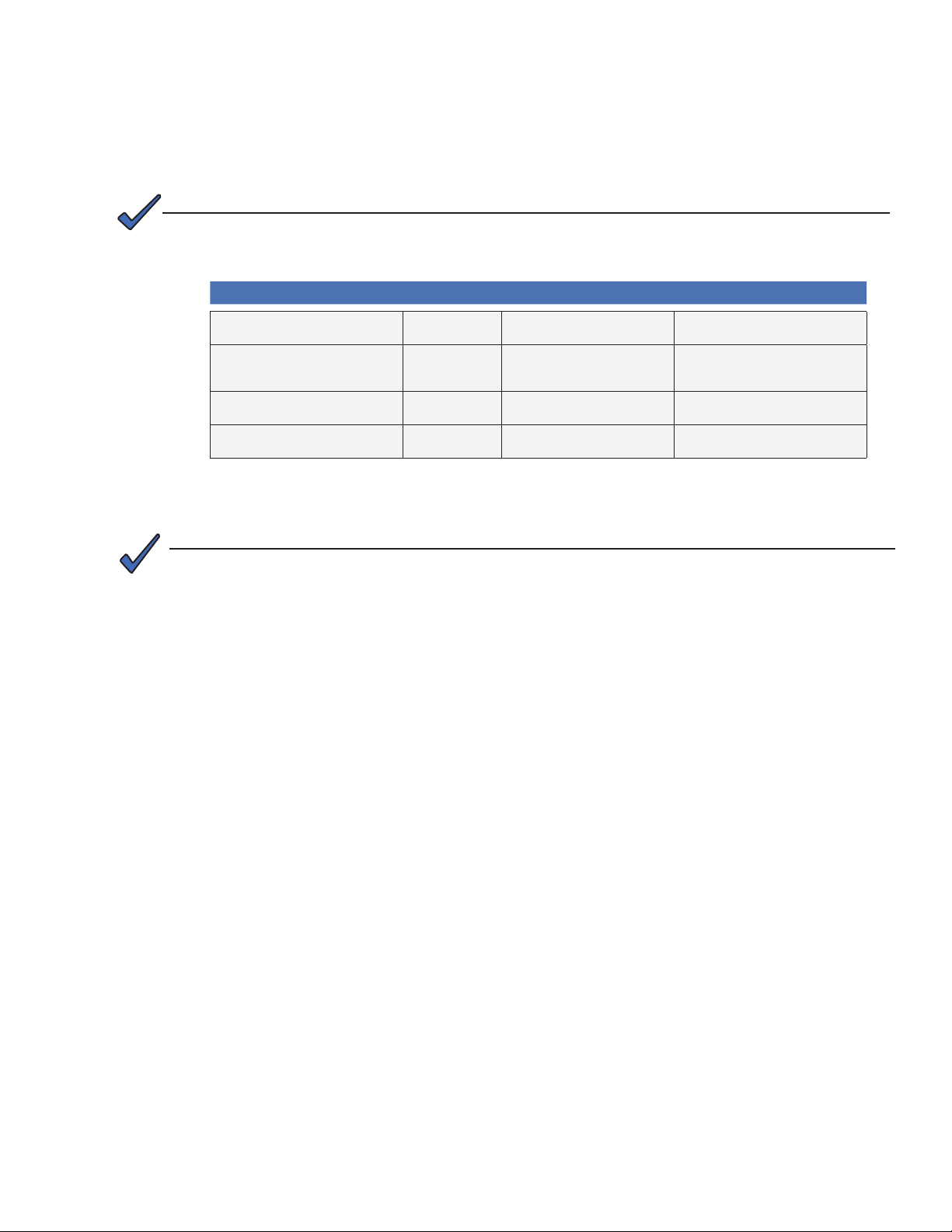
SNMP Parameter Type Description Value
atiMgmtSnmpTrapOnNormal
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.926.1.3.1.5.1.0
atiMgmtSysDownloadReCfgTime
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.926.1.3.2.1.13.0
atiMgmtSysSnmpTimeout
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.926.1.3.1.5.3.0
atiMgmtSysHttpAccess
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.926.1.3.2.2.4.1.0
See Section 10.0 for complete parameter denitions.
Integer Send SNMP trap when alarmed
Integer Download interval for IDH4 Series-
Integer Time IDH4 Series will wait before reset
Integer
condition returns to normal state
specic items in modem cong le
(hours)
if SNMP trafc is not detected (minutes)
HTTP Web Server
1 = Disabled
2 = Enabled (Default)
24 (Default)
1440 (Default)
Note: if set to zero, watchdog will be disabled.
1 = Disabled
2 = Enabled (default)
Table 3-4, Transponder Communications Parameters
NOTE:
The IDH4 Series will inherit the cable modem community string settings provided by the DOCSIS
Conguration File.
18 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
4.0 Web Interface
Overview
The IDH4 Series power supply transponder provides an embedded Web server interface to allow
operations personnel the ability to connect locally or remotely via TCP/IP over Ethernet with a laptop/
computer to verify the status of common data points and to congure various operating parameters.
4.1 Local Web Server Access
The IDH4 Series transponder’s Ethernet port (comparable to the Craft port on some transponder models)
will typically be used as a local connection point allowing the user to connect directly to the IDH4 Series
Web server interface to verify/congure common communication parameters and view power supply
status and battery values. The Ethernet port on the IDH4 Series is a fully functional standard Ethernet
port, capable of providing all the functionality of any standard Ethernet connection.
To access the IDH4 Series transponder Web server locally utilizing a Web browser, follow the procedure
outlined below:
1. Connect a standard Ethernet cable (CAT5) between the IDH4 Series transponder Ethernet port (ETH)
and a laptop or computer’s network interface port.
2. Launch a Web browser.
3. Enter the transponder's default IP address (192.168.100.1) into the Web browser’s address eld.
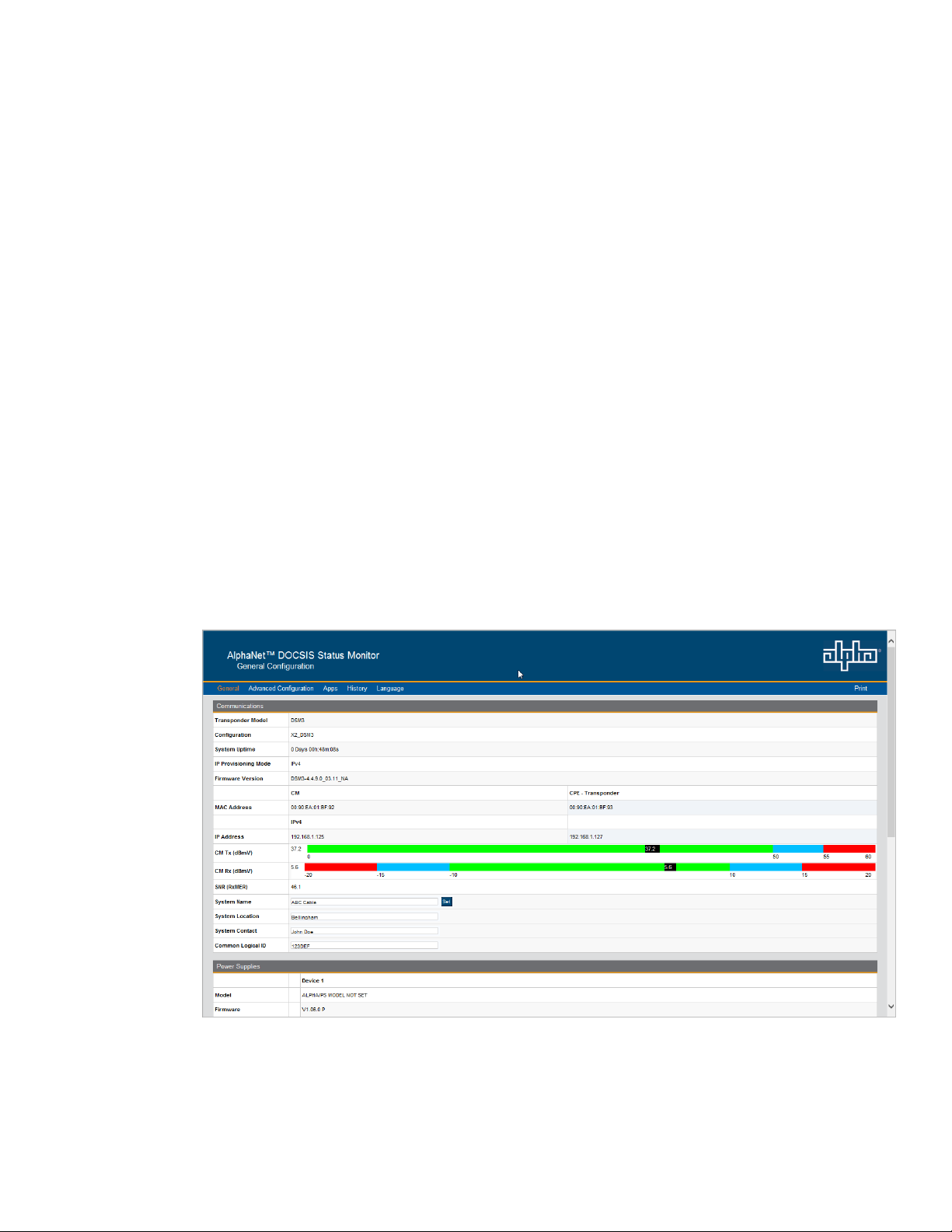
4. The transponder’s Web server home page will appear (Fig. 4-1). Note: For the IDH4 Series, this may
take up to 45 seconds when the transponder is initially powered up with no RF connection.
5. Click on the Language menu to select a desired language for the text information on the Web page.
The language choices are English (default), Spanish, Portuguese, French and German.
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
Fig. 4-1, IDH4 Series Web Page
(data values shown for illustration purposes only)
19
4.0 Web Interface
4.1 Local Web Server Access
NOTE:
If you are unable to view the home page of the IDH4 Series using IP Address 192.168.100.1, the network
conguration on the computer that is being used to connect to the IDH4 Series transponder may require a
temporary static IP address to be congured.
Use the following procedure to congure a static IP
address on a laptop or computer for Windows XP:
1. Click on the Start button (lower left button on most
Windows® computers).
2. When the window pops up, click on Control Panel
(usually about half the way down the second
column).
3. Click on Network Connections.
4. Right-Click on Local Area Connection to open
menu box.
5. Click the Properties button.
6. You will see a dialog box much like Fig. 4-2; scroll
down to the entry Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and
then click on the Properties button.
7. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
dialog box will open (Fig. 4-3). Select Use
the following IP address. Enter the values
as shown. Record the existing IP address
and Subnet mask in order to later return the
computer to its original state.
8. Click on the OK button and try to connect
to the IDH4 Series transponder once again
using 192.168.100.1 in your Web browser.
9. Once completed with the IDH4 Series
local Ethernet port connection, repeat the
above steps 1 to 6 to restore the computer's
network conguration back to the original
settings.
Fig. 4-2, Local Area Connection
Properties Screen
Fig. 4-3, Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties Screen
20 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
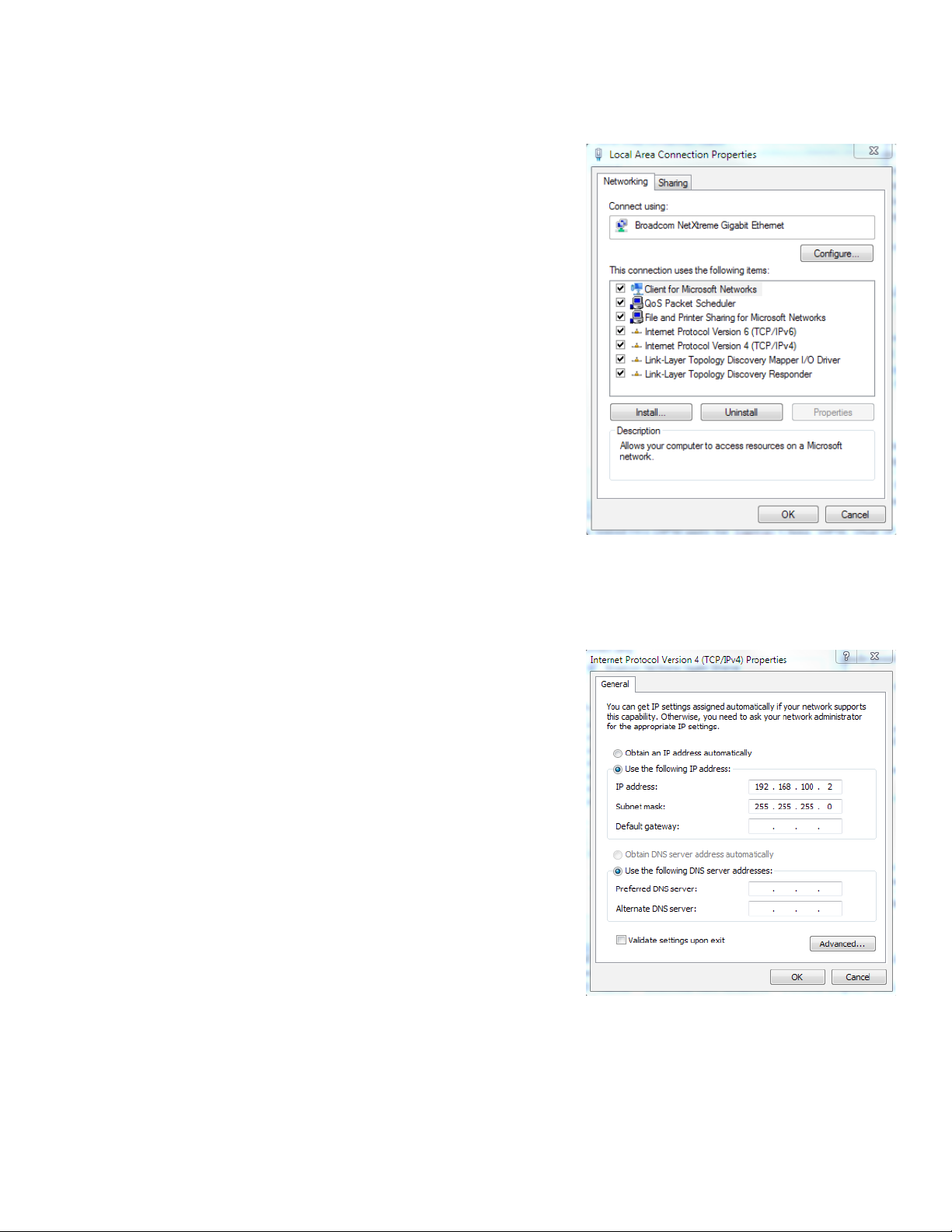
4.0 Web Interface
4.1 Local Web Server Access
Use the following procedure to congure a static IP
address on a laptop or computer with the Windows 7
operating system:
1. Click the Start button (lower left button on most
Windows® computers).
2. When the window pops up, click Control Panel
(usually about half the way down the second
column).
3. Click Network and Sharing Center.
4. Click Local Area Connection.
5. Click the Properties button.
6. You will see a dialog box much like Fig. 4-4; click
Internet Protocol (TCP/IPv4) and then click the
Properties button.
7. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
dialog box will open (Fig. 4-5). Select "Use
the following IP address". Enter the values
as shown (i.e. IP address 192.168.100.2
and Subnet mask 255.255.255.0). Record
the existing IP address and Subnet mask
in order to later return the computer to its
original state.
8. Click the OK button and try to connect to the
IDH4 Series transponder once again using
192.168.100.1 in the Web browser.
9. To restore network settings, repeat Steps 1
through 6.
Fig. 4-4, Local Area Connection
Properties Screen, Windows 7
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
Fig. 4-5, Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties Screen, Windows 7
21
4.0 Web Interface
4.2 Remote Web Server Access
To remotely access the IDH4 Series transponder Web server utilizing a Web browser, follow the
procedure outlined below:
NOTE:
For Web server (HTTP) access, port 80 must not be blocked.
1. Connect the laptop or computer’s network interface port to the company’s Ethernet network.
2. Open a Web browser.
3. Enter the IDH4 Series' designated IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.124) into the Web browser’s address
eld.
4. The IDH4 Series transponder’s Web server home page will appear (Fig. 4-6).
5. Click on the Language drop-down menu located on the top right of the page to select a desired
language for the text information on the Web page. The language choices are English (default),
Spanish, Portuguese, French and German.
Fig. 4-6, Web Server Home Page
(data values shown for illustration purposes only)
22 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)

4.0 Web Interface
4.3 Navigating the Web Page
Once the Web page has been successfully accessed, the operator is able to select a link on the header
bar and the page specic to the topic will open enabling real-time data to be observed.
See Fig. 4-7 for IDH4 Series navigation bar items.
Commonly used
parameters for
quick diagnostics
of Power Supply,
Communications,
Batteries and
Generator.
Communications: Comprehensive
communications diagnostic parameters
Power Supply: Comprehensive Power
Supply conguration and congurable
parameters
Generator: Comprehensive Generator
conguration and diagnostic parameters
IO - Environment: Status and conguration
of Tamper polarity and external I/O devices
HMS Alarms: Status of SCTE-HMS active
alarms, alarm history and alarm threshold
settings.
Modem Log: Web page
representation of the
DOCSIS modem event
log.
Apps menu is not
accessible for the XM2
CableUPS.
Fig. 4-7, IDH4 Series Navigation Bar Items
The Web page content
will be displayed in the
selected language
Sends the contents
of the selected
Web page to the
computer’s default
printer.
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
23

4.0 Web Interface
4.3 Navigating the Web Page
4.3.1 Web Interface Security Levels
Within the IDH4 Series transponder are two levels of function-specic security. General
operations are set at Level 1 and conguration-related functions are set at Level 2.
Default User ID and Passwords are shown in the gure below.
IDH4 Series Web Page Security
OID Function Value
1.3.6.1.4.1.4413.2.2.2.1.1.3.3.0 Level 1 User Name Alpha
1.3.6.1.4.1.4413.2.2.2.1.1.3.4.0 Level 1 Security Password AlphaGet
1.3.6.1.4.1.4413.2.2.2.1.1.3.1.0 Level 2 User Name Alpha
1.3.6.1.4.1.4413.2.2.2.1.1.3.2.0 Level 2 Security Password AlphaSet
Web Page Function Security Level
System Name, System Contact, System Location,
General
Advanced Communications
Advanced Power Supply Congure/Save 2
Advanced Generator
Modem Log [Event Log] Reset Log 1
Advanced I/O
Common Logical ID
Power Supply Self Test 1
Generator Self Test 1
Reset Transponder 1
Provisioning Mode - Single IP or Dual IP 2
Congure Static IP Address 2
Congure Proprietary Trap Addresses 2
Power Supply Self Test 1
Reset Output 1/2 2
Generator Self Test 1
Reset Latched Alarms 1
Tamper Switch Polarity 1
Enclosure Heater/Cooler Installed 1
1
Fig. 4-8, IDH4 Series Transponder Security Levels
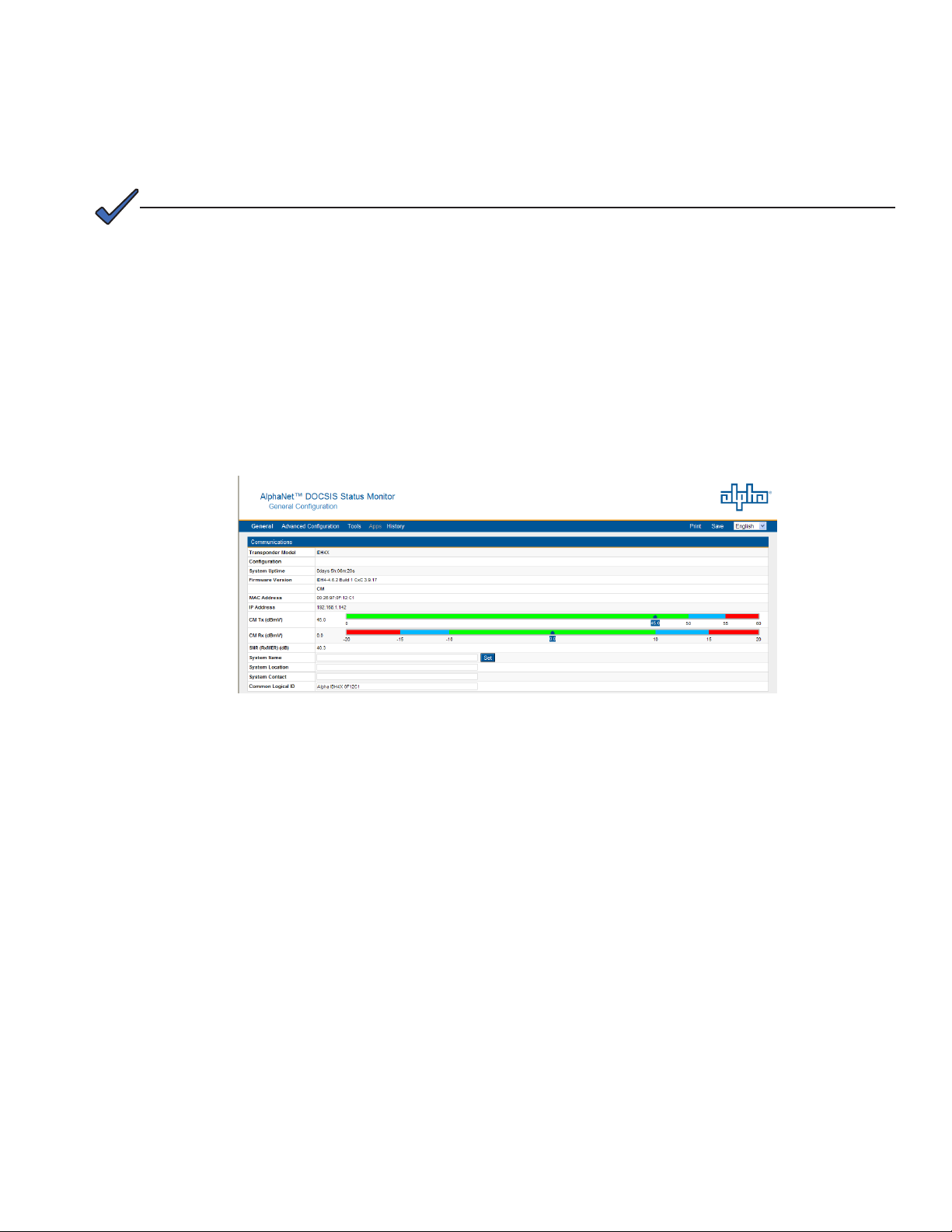
4.4 Verifying Communication Parameters
Click the General menu of the web page to display common communication settings and values. Click
the Advanced Communication menu to view additional communication parameters.
Fig. 4-9, Communication Parameters
(data values shown for illustration purposes only)
24 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
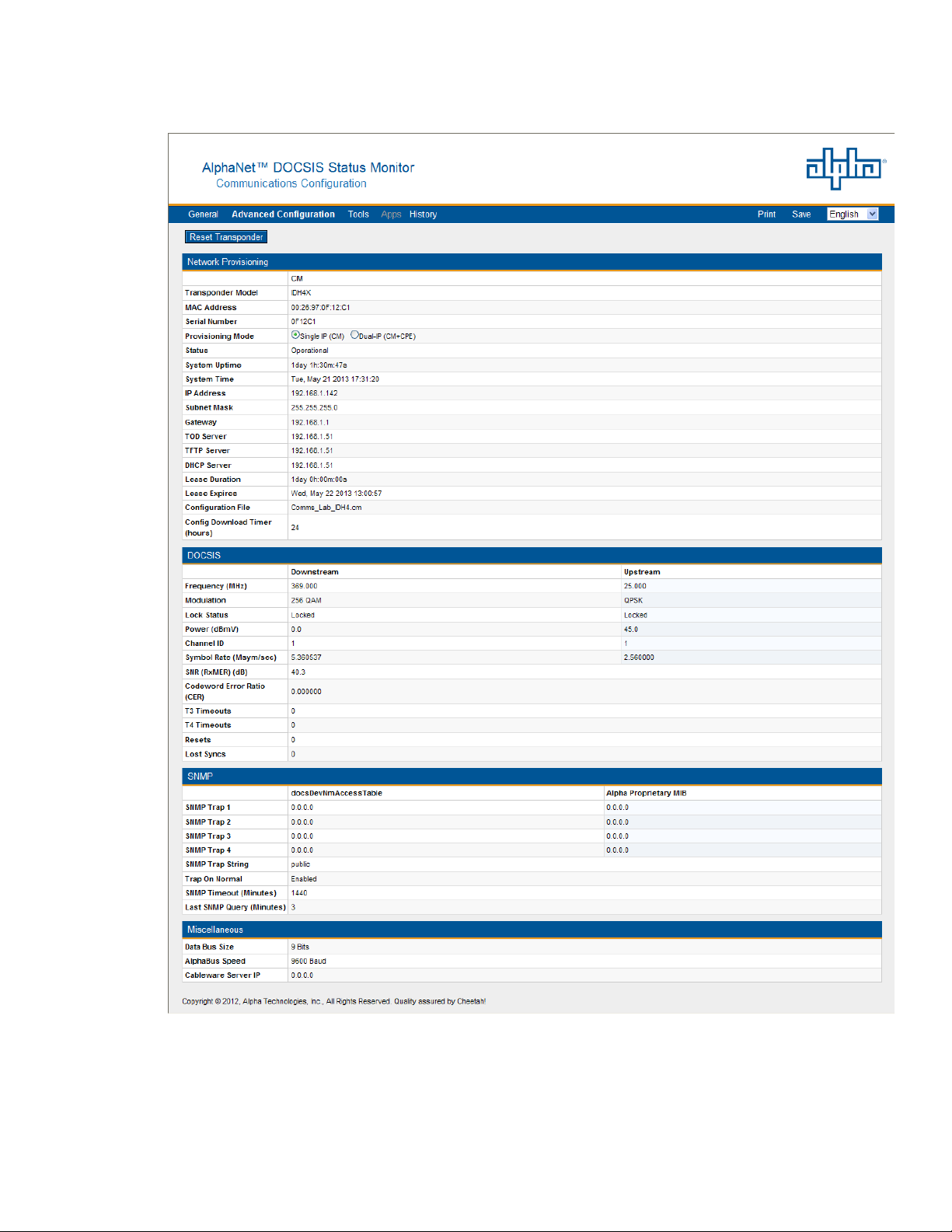
4.0 Web Interface
4.4 Verifying Communication Parameters
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
Fig. 4-10, Communication Parameters
(data values shown for illustration purposes only)
25
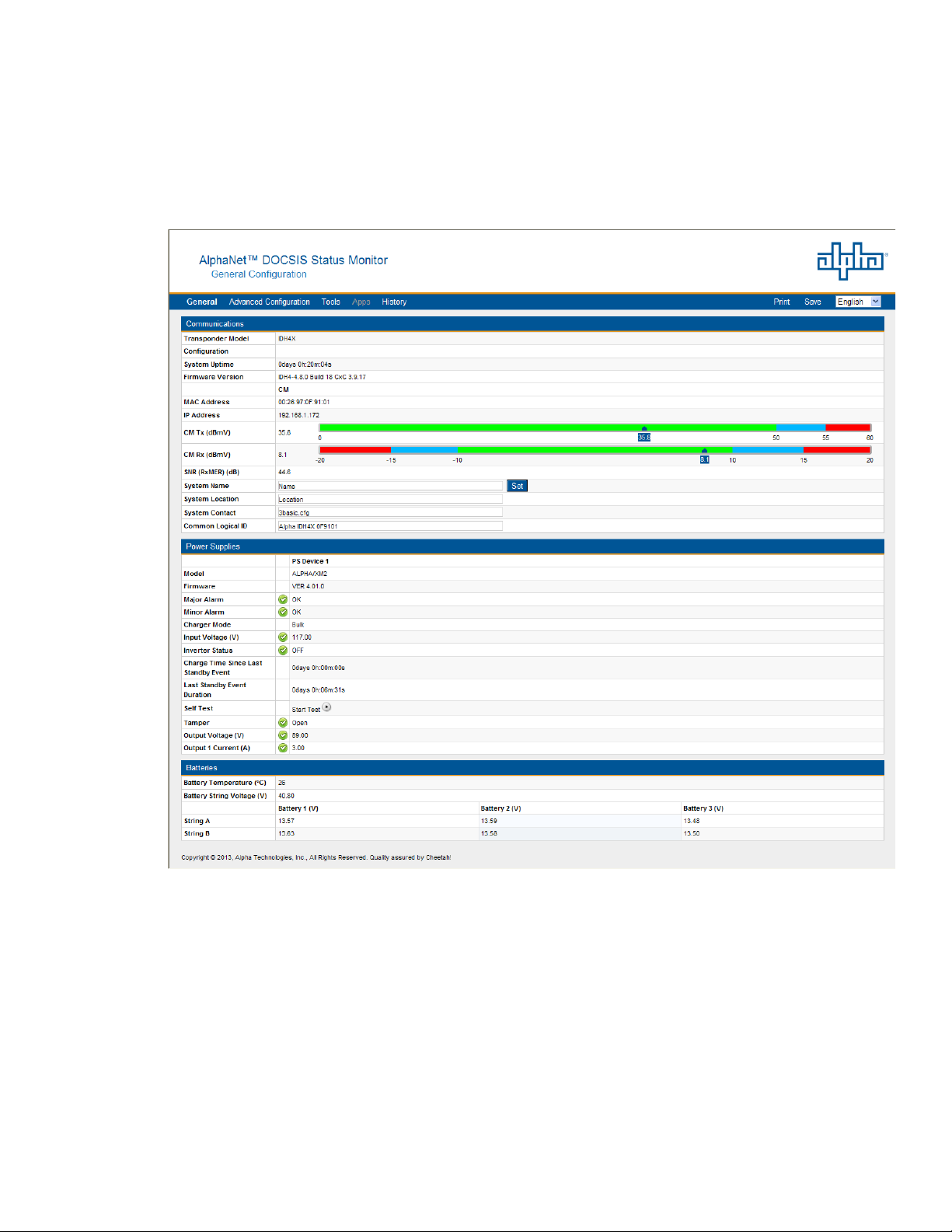
4.0 Web Interface
4.5 Verifying Power Supply and Battery Parameters
The General tab of the Web page also displays the common power supply and battery parameter values.
Important parameters such as current alarm status, inverter status and tamper status can be quickly
veried on this page. Additional power supply parameters can be viewed and edited on the Power Supply
page located in the Advanced Conguration menu.
Fig. 4-11, Power Supply and Battery Parameters
(data values shown for illustration purposes only)
26 746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
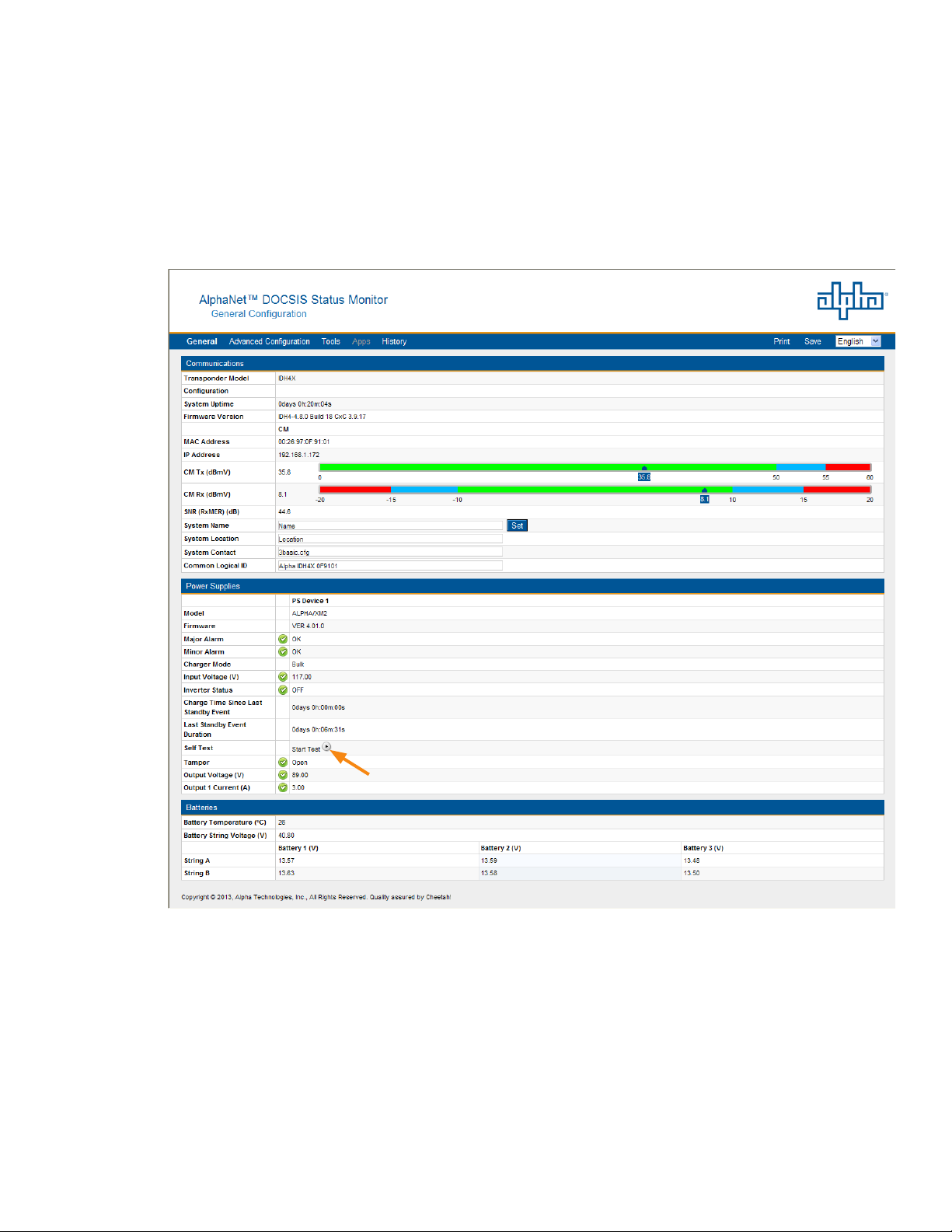
4.0 Web Interface
4.6 Remote Self Tests via the Web Page
Remote Self Tests on power supplies may be started and stopped via the IDH4 Series Web page. This
requires a Level 1 login. Refer to Section 4.3.1, Web Interface Security Levels for User Name and
Security Password.
To launch a remote Self Test, click on the Start Test button.
To stop a remote Self Test before the predened test duration, click on the Stop Test button.
746-257-B2-001, Rev. B (01/2014)
Fig. 4-13, Location of Start Button for Self Test
(data values shown for illustration purposes only)
27
 Loading...
Loading...