Page 1

AlliedWareTM OS
How To |
Use DHCP Snooping, Option 82, and Filtering on
AT-9900 and x900-48 Series Switches
Introduction
It has increasingly become a legal requirement for service providers to identify which of their
customers were using a specific IP address at a specific time. This means that service
providers must be able to:
z Know which customer was allocated an IP address at any time.
z Guarantee that customers cannot avoid detection by spoofing an IP address that was not
actually allocated to them.
These security features provide a traceable history in the event of an official query. Three
components are used to provide this traceable history:
z DHCP snooping
z DHCP Option 82
z DHCP filtering
What information will you find in this document?
This document describes DHCP snooping, DHCP Option 82 and DHCP filtering, and takes
you through step-by-step configuration examples.
With DHCP snooping, an administrator can control port-to-IP connectivity by:
z permitting port access to specified IP addresses only
z permitting port access to DHCP issued IP addresses only
z dictating the number of IP clients on any given port
z passing location information about an IP client to the DHCP server
C613-16082-00 REV B
z permitting only known IP clients to ARP
www.alliedtelesis.com
Page 2

Introduction > What information will you find in this document?
This document explains each feature and provides the minimum configuration to enable
them. There are also two configuration examples that make advanced use of the features.
This document contains the following contents:
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 1
What information will you find in this document? ................................................................... 1
Which products and software version does this information apply to? .............................. 3
Related How To Notes ................................................................................................................... 3
DHCP snooping ....................................................................................................................................... 3
Minimum configuration ................................................................................................................... 4
The database ..................................................................................................................................... 5
Trusted and non-trusted ports ..................................................................................................... 7
Enabling DHCP snooping ............................................................................................................... 7
Static binding ..................................................................................................................................... 7
Completely removing the DHCP snooping database .............................................................. 8
DHCP Option 82 .................................................................................................................................... 9
Protocol details ................................................................................................................................. 9
Configuring Option 82 .................................................................................................................. 10
DHCP filtering ........................................................................................................................................ 11
Configuring filtering ....................................................................................................................... 12
Supporting multiple devices on a port ...................................................................................... 12
ARP security .................................................................................................................................... 13
Resource considerations .............................................................................................................. 14
Configuration examples ....................................................................................................................... 15
Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering, and Option 82, when it is
acting as a layer 2 switch ....................................................................................................... 15
Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering and Option 82, when it is
acting as a layer 3 BOOTP Relay Agent ............................................................................ 19
Troubleshooting ..................................................................................................................................... 23
No trusted ports configured ....................................................................................................... 23
The DHCP client continually sends requests instead of a discover ................................... 24
Maximum number of leases is exceeded .................................................................................. 24
Switch is dropping ARPs ............................................................................................................... 26
The DHCP ACK is dropped by the switch .............................................................................. 28
Cannot create a binding entry .................................................................................................... 34
Entries with client lease but no listeners .................................................................................. 36
Appendix
Page 2 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
1
: ISC DHCP server .......................................................................................................... 37
Page 3

DHCP snooping > Which products and software version does this information apply to?
Which products and software version does this information apply to?
The information provided in this document applies to the following switches, running
AlliedWare version 2.7.6 and above:
z AT-9900 series
z x900-48 series
z AT- 89 48
Related How To Notes
The following How To Note describes DHCP snooping on AT-8600, AT-8800, AT-8700XL,
Rapier, and Rapier i series switches:
z How To Use DHCP Snooping, Option 82, and Filtering on AT-8800, AT-8600, AT-8700XL, Rapier,
and Rapier i Series Switches
The following How To Notes also use DHCP snooping in their solutions:
z How To Use MAC-Forced Forwarding with DHCP Snooping to Create Enhanced Private VLANs
z How To Create A Secure Network With Allied Telesis Managed Layer 3 Switches
z How To Use DHCP Snooping and ARP Security to Block ARP Poisoning Attacks
How To Notes are available from the library at www.alliedtelesis.com/resources/literature/
howto.aspx.
DHCP snooping
DHCP snooping forces all DHCP packets to be sent up to the switch CPU before forwarding.
The switch CPU then keeps a database of the IP addresses that are currently allocated to
downstream clients and the switch ports that the relevant clients are attached to.
Note: The switch CPU does not store a history log. The DHCP server does this.
DHCP snooping performs two main tasks:
z Keeping a record of which IP addresses are currently allocated to hosts downstream of
the ports on the switch.
z Deciding which packets are candidates for having Option 82 information inserted, and
actively filtering out packets that are deemed to be invalid DHCP packets (according to
criteria described below).
Note: Option 82 must be enabled separately.
Page 3 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 4

DHCP snooping > Minimum configuration
Minimum configuration
On x900 and AT-9900 series switches, below is the minimum configuration required to use
DHCP snooping and provide unfiltered connectivity. With this configuration a client will be
able to receive a DHCP address, and access the IP network unfiltered. Also, the
administrator will be able to see the current valid entries in the DHCP snooping database.
Note: With this configuration, a client could manually change its IP and MAC address and
be able to access the IP network unfiltered.
# DHCP Snooping configuration - Pre QoS
enable dhcpsnooping
set dhcpsnooping port=24 trusted=yes
# CLASSIFR configuration
create classifier=50 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping protocol="ip"
ipsaddr=dhcpsnooping
# QOS configuration
create qos policy=1
create qos trafficclass=1
create qos flow=50 action=FORWARD
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=1
set qos port=1-23 policy=1
add qos trafficclass=1 flow=50
add qos flow=50 classifier=50
Page 4 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 5

DHCP snooping > The database
The database
The switch watches the DHCP packets that it is passing back-and-forth. It also maintains a
database that lists the DHCP leases it knows are being held by devices downstream of its
ports.
Each lease in the database holds the following information:
z the MAC address of the client device
z the IP address that was allocated to that client
z time until expiry
z VLAN to which the client is attached
z the port to which the client is attached
When inserting Option 82 information into the DHCP packets, the switch uses the
information it has stored in the database for filtering and for filling in the fields.
DHCP snooping database time-out
The CPU will time-out database entries if the lease, also stored in the database, expires.
Database survival across reboots
The database is periodically saved as a .dsn file into non-volatile storage, therefore the
database will survive a reboot.
DHCP snooping show commands
To verify the status of snooped users, use the command show dhcpsnooping database.
Manager > show dhcpsnooping database
DHCP Snooping Binding Database
------------------------------------------------------------------Full Leases/Max Leases ... 1/52
Check Interval ........... 60 seconds
Database Listeners ....... CLASSIFR
Current valid entries
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------00-03-47-6b-a5-7a 10.11.67.50 56 48 16 3 Dynamic
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with client lease but no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with no client lease and no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
Page 5 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 6

DHCP snooping > The database
List of terms: MAC Address: The MAC address of the snooped DHCP client.
IP Address: The IP address that has been allocated to the snooped DHCP client.
Expires: The time, in seconds, until the DHCP client entry will expire.
VLAN: The VLAN to which the snooped DHCP client is connected.
Port: The port to which the snooped DHCP client is connected.
ID: The unique ID for the entry in the DHCP snooping database. This ID is dynamically
allocated to all clients. (The same ID can be seen in show dhcpsnooping filter.)
Database Listeners: These are switch features (or modules) that have registered to listen
to the Binding Database. Database listeners are informed when an entry is added or
deleted from the database. In this case the Classifier module will be informed so the
dynamic classifiers can be updated.
Source: How the DHCP binding was entered into the database:
z User = static
z File = read from bindings. dsn (usually at boot time)
z Dynamic = it was snooped
To see port details, use the commands show dhcpsnooping port and show
dhcpsnooping count.
Manager > show dhcpsnooping port=16
DHCP Snooping Port Information:
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Port ..................... 16
Trusted .................. No
Full Leases/Max Leases ... 1/1
Subscriber-ID ............
Manager > show dhcpsnooping count
DHCP Snooping Counters
--------------------------------------------------------------------DHCP Snooping
InPackets .................... 1751
InBootpRequests ............... 908
InBootpReplies ................ 843
InDiscards ...................... 0
ARP Security
InPackets ....................... 0
InDiscards ...................... 0
NoLease ....................... 0
Invalid ....................... 0
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 6 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 7

DHCP snooping > Trusted and non-trusted ports
Trusted and non-trusted ports
The concept of trusted and non-trusted ports is fundamental to the operation of DHCP
snooping:
z Trusted ports connect to a trusted entity in the network, and are under the complete
control of the network manager.
z Non-trusted ports connect an untrusted entity to the trusted network.
z Non-trusted ports can connect to non-trusted ports.
In general, trusted ports connect to the network core, and non-trusted ports connect to
subscribers.
DHCP snooping will make forwarding decisions based on the trust status of ports:
z BOOTP packets that contain Option 82 information received on untrusted ports will be
dropped
z If Option 82 is enabled, the switch will insert Option 82 information into BOOTP
REQUEST packets received from an untrusted port.
z BOOTP REQUEST packets that contain Option 82 information received on trusted ports
will not have the Option 82 information updated with information for the receive port. It
will be kept.
z BOOTP REPLY packets (from servers) should come from a trusted source.
z The switch will remove Option 82 information from BOOTP REPLY packets destined to
an untrusted port.
z BOOTP REPLY packets received on non-trusted ports will be dropped.
Enabling DHCP snooping
DHCP snooping is enabled globally by the command enable dhcpsnooping. All ports are
untrusted by default. For DHCP snooping to do anything useful, at least one port must be
trusted.
Static binding
If there is a device with a statically set IP attached to a port in the DHCP snooping port
range, then, with filtering enabled it is necessary to statically bind it to the port. This will
ensure the device's IP connectivity to the rest of the network.
If a device with the IP
VLAN
1
on port 2 then a static binding is configured by adding the following command to the
1
72.16.1.202 and MAC address 00-00-00-00-00-ca is attached to
basic DHCP configuration (see "Minimum configuration" on page 4):
add dhcpsnooping binding=00-00-00-00-00-CA interface=vlan1 ip=172.16.1.202
port=2
Adding a static binding uses a lease on the port. If the maximum leases on the port is 1 (the
default), the static binding means that no device on the port can acquire an address by DHCP.
Page 7 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 8
DHCP snooping > Completely removing the DHCP snooping database
Completely removing the DHCP snooping database
To completely remove the database, it is necessary to delete the file nvs:bindings.dsn.
Manager > delete fi=nvs:bindings.dsn
nvs:bindings.dsn successfully deleted
1 file deleted.
Info (1056003): Operation successful.
Manager > enable dhcpsnooping
DHCPSN_DB: Reloading static entries...
Info (1137057): DHCPSNOOPING has been enabled.
Manager > DHCPSN_DB: Reading entries from file...
DHCPSN_DB: Full file name is: (nvs:bindings.dsn)
DHCPSN_DB: File nvs:bindings.dsn not present on device, nothing to load.
So the database is empty:
Manager > show dhcpsnooping database
DHCP Snooping Binding Database
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Database Version ..... 1
Full Leases/Max Leases ... 0/151
Check Interval ........... 60 seconds
Database Listeners ....... CLASSIFR
Current valid entries
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with client lease but no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with no client lease and no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 8 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 9

DHCP Option 82 > Protocol details
DHCP Option 82
DHCP Relay Agent Information Option 82 is an extension to the Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP), and is defined in RFC 3046 and RFC 3993.
DHCP Option 82 can be used to send information about DHCP clients to the authenticating
DHCP server. DHCP Option 82 will identify the VLAN number, port number and, optionally
a customer ID of a client, during any IP address allocation. When DHCP Option 82 is enabled
on the switch, it inserts the above information into the DHCP packets as they pass through
the switch on their way to the DHCP server. The DHCP server stores the IP allocation
record.
DHCP Option 82 can work in either layer 2 forwarding or layer 3 routing modes. There are
significant differences in operation and configuration of these two modes – the latter needing
BOOTP Relay support. Some configuration examples and operation descriptions are
provided in a later section of this document.
Although Option 82 is titled the DHCP Relay Agent Information Option, the device that
inserts the Option 82 information into a DHCP packet does not have to be acting as DHCP
relay. A layer 2 switch can insert the Option 82 information into the DHCP packets (if
snooping is enabled). The Option 82 information needs to be inserted into the DHCP
packets by a switch at the edge of the network, because only the edge switch knows the
information that uniquely identifies the subscriber that the IP address was allocated to.
It is quite likely that the edge switch will be a layer 2 switch, rather than a DCHP-relaying
layer 3 switch.
Protocol details
In the DHCP packet, the Option 82 segment is organized as a single DHCP option containing
one or more sub-options that convey information known by the relay agent. The format of
the option is shown below:
Code Len Agent Information Field
+------+------+------+------+------+------+---+------+
| 82 | N | i1 | i2 | i3 | i4 | | iN |
+------+------+------+------+------+------+---+------+
The sub-options within the DHCP option are constructed as follows:
SubOpt Len Sub-option Value
+------+------+------+------+------+------+---+------+
| 1 | N | s1 | s2 | s3 | s4 | | sN |
+------+------+------+------+------+------+---+------+
SubOpt Len Sub-option Value
+------+------+------+------+------+------+---+------+
| 2 | N | i1 | i2 | i3 | i4 | | iN |
+------+------+------+------+------+------+---+------+
Page 9 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 10

DHCP Option 82 > Configuring Option 82
The following table shows a list of the sub-options that are used for identifying the subscriber
that the IP address was allocated to:
Sub-option RFC Description
1
2 RFC 3046 Agent Remote ID sub-option – used for defining the MAC address of
6 RFC 3993 Subscriber-ID sub-option – optionally configured per port using set
RFC 3046 Agent Circuit ID sub-option – used for defining the switch port and
VLAN number of the port user(s).
the switch that added the Option 82 information.
dhcpsnooping port=x subscriberid=x – can define port customer
name, or switch name.
Example Packet
The following shows an extract of a DHCP Request packet that includes Option 82 details:
DHCP Message Type = DHCP Request
Bootstrap Protocol
Option 82 – Agent Information (Option)
0000: 52 20 01 06 00 04 00 30 00 05 02 08 00 06 00 00 R ..............
0010: CD 11 B2 52 06 0C 55 73 65 72 49 64 30 31 32 33 ...R..UserId0123
0020: 34 35 45
Analysis
The following table provides an analysis of the strings in the above DHCP Request packet
extract:
Text Colour Analysis
Green This is the Agent Circuit ID
Blue This is the Agent
Red This is the subscriber ID sub-option
The Agent circuit ID string 00 30 00 05 translates as:
30 = vlan48
05 = switch port 5
Configuring Option 82
Different commands are used to turn on Option 82 depending on whether the switch is
performing DHCP snooping or DHCP relay. For the DHCP snooping, the command is:
enable dhcpsnooping option82
The subscriber ID to be used on any given port can be set using the command:
set dhcpsnooping port=x subscriberid=”xxxx”
Page 10 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 11
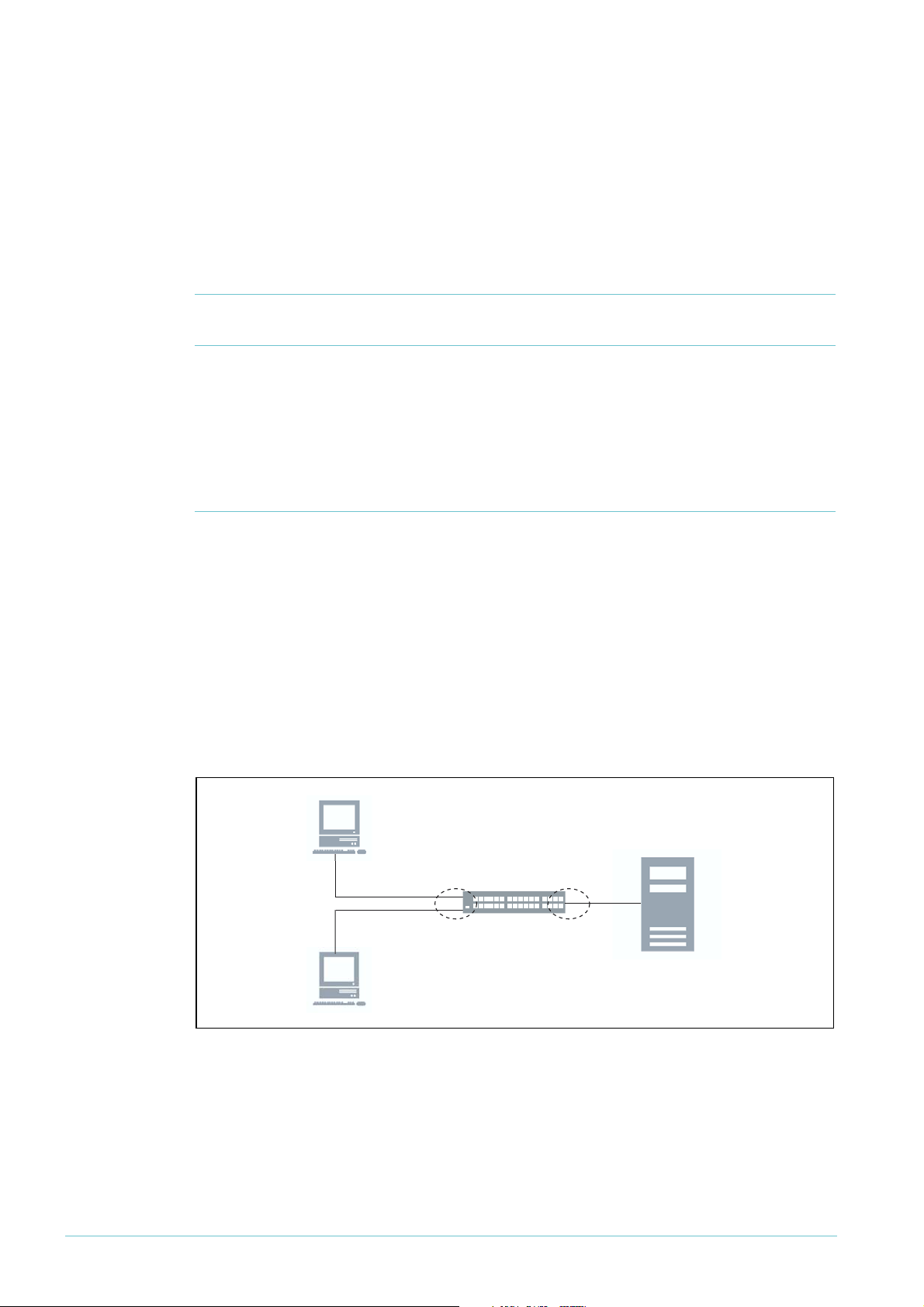
DHCP filtering > Configuring Option 82
Client A
Client B
Non-trusted Ports
Trusted Ports
Access Device
DHCP Server
If the switch is acting as a DHCP relay and there is no requirement to also maintain a DHCP
snooping database, then the DHCP relay process can be configured to insert option 82
information into the relayed packets:
enable bootp relay option82
The subscriber ID to be used on any given port can be configured with:
set bootp relay option82 subscriberid=”xxxx”
Note: The use of BOOTP relay without DHCP snooping will not be discussed any further
in this document.
Agent Circuit ID and Agent Remote ID are sub-options that are also sent as part of the
Option 82 data but they are not configurable.
DHCP filtering
The purpose of DHCP filtering is to prevent IP addresses from being falsified or ‘spoofed’.
This guarantees that customers cannot avoid detection by spoofing an IP address that was
not actually allocated to them.
DHCP filtering is achieved by creating dynamic classifiers. The dynamic classifiers are
configured with DHCP snooping placeholders for the source IP address (and possibly source
MAC address), to match on.
The dynamic classifiers are attached to filters, which are applied to a port. Only those
packets with a source IP address that matches one of the IP addresses allocated to the
devices connected to that port are allowed through.
Page 11 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 12
DHCP filtering > Configuring filtering
Configuring filtering
The switch can be configured to block all packets arriving from clients, unless their source
addresses are those known by the switch to have been allocated to the clients by DHCP.
Note: The filtering does not, of course, block DHCP packets. In fact, the DHCP snooping
process creates a filter which forces DHCP packets to the CPU before any other
filters can process the packet.
On the x900 switches, this is achieved by creating classifiers that have placeholder entries for
the source IP address and (optionally) the source MAC address parameter.
To create this type of classifier:
create classifier=1 ipsaddress=dhcpsnooping macsaddress=dhcpsnooping
<other-parameters>
These classifiers can be applied to hardware filters that will then allow through the
appropriate packets (and, a subsequent deny-all-else filter can ensure that packets with invalid
source addresses are discarded).
You can treat these classifiers like all other classifiers, and use them as part of any QoS or
filtering configuration.
How the switch uses these classifiers
These classifiers are attached to flow groups or filters, which are eventually written into
hardware tables. When the corresponding filters are written into the hardware tables, the
placeholder IP address DHCPsnooping is replaced by the IP address 0.0.0.0 and the
placeholder MAC address DHCPsnooping is replaced by the MAC address 00-00-00-00-
00-00.
As the DHCP snooping process detects DHCP leases being allocated to devices connected
to a port, the 0.0.0.0 and 00-00-00-00-00-00 IP and MAC addresses in the relevant filters
applied to that port are replaced by the actual IP address and MAC address of the device
receiving the DHCP lease.
Similarly, as the DHCP snooping notices a DHCP lease time out, it finds the filter’s entries
using the address of the expiring lease, and replaces them with the 0.0.0.0 and 00-00-00-00-
00-00 IP and MAC addresses again.
Supporting multiple devices on a port
If there are multiple devices downstream of a port on the switch, and all of those devices can
be allocated IP addresses by DHCP, then the ipsaddress=dhcpsnooping clause in the
above classifier should match any of the IP addresses allocated to a device connected to that
port.
This is achieved by replicating any filter or flowgroup that uses the classifier.
Page 12 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 13

DHCP filtering > ARP security
X To configure how many times the filters or flowgroups will be replicated:
set dhcpsnooping port=<port-list> maxlease=<number>
Any filter or flowgroup that is using a classifier containing a DHCP snooping parameter, and is
applied to a port in the list, will be replicated maxlease times as it is written into the
hardware table. Then, as the IP addresses are allocated to devices on the port, the addresses
in the leases can be written in these replicated filter entries.
For example, when the first device on the port receives a lease, the first member of the
relevant set of replicated filters is filled in with the lease address. When a second device on
the port receives a lease, the second member of the set of replicated filters receives the new
lease address, and so on.
ARP security
It is also possible to enable DHCP snooping ARP security. If enabled this will ensure that ARP
packets received on non-trusted ports are only permitted if they originate from an IP address
that has been allocated by DHCP.
X To enable DHCP snooping ARP security:
enable dhcpsnooping arpsecurity
DHCP snooping filter show command
To see what addresses have been inserted into filters using DHCP snooping classifiers, use
the command show dhcpsnooping filter:
Manager > show dhcpsnooping filter
DHCPSnooping ACL ( 150 entries )
ClassID FlowID Port EntryID IP Address/Port/Mac
--------------------------------------------------------------------- 60161 150 16 3 10.11.67.50/16/00-03-47-6b-a5-7a
61161 150 16 3 10.11.67.50/16/00-03-47-6b-a5-7a
62161 151 16 3 10.11.67.50/16/00-03-47-6b-a5-7a
...
List of terms:
The FlowID refers to the associated QoS FlowGroup.
The EntryID refers to the associated entry in the DHCP snooping database.
The ClassID refers to the dynamically created classifier entry.
Page 13 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 14

DHCP filtering > Resource considerations
Resource considerations
Because of the potential for classifier replication, you need to be cautious about running out
of classifier resource. Some resource calculations are provided below.
When configuring DHCP classifiers you need to guard against running out of classifier
resource, especially when using a complex QoS classifier solution.
Calculations
X To calculate the number of snooping classifiers:
The number of rules used = number of classifiers * number of ports attached
* dhcpsn max lease per port
X To calculate the number of snooping classifiers when DHCP snooping ARP
security is also enabled:
The number of rules used = 2 * number of classifiers * number of ports attached
* dhcpsn max lease per port
X To see the number of rules used, and still available:
Manager > show switch
Traffic Control Unit, hardware resource usage:
Total system rule space ....... 2048
Total number of rules used .... 403
Total rule space usage ........ 408
Number of rules per application:
MLD Snooping ................ 51
DHCP Snooping ............... 102
QOS ......................... 250
MLD snooping = multicast listen discovery for Ipv6
As the above output shows, the command show switch gives a breakdown of the current
usage of rule resource.
Page 14 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 15

Configuration examples > Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering, and Option 82, when it is
(1). DHCP Client sends request
(2). Layer 2 Relay Agent appends
Option 82 to client sourced
packets
(4). Layer 2 Relay Agent strips
Option 82 from the offer packet
to client
(3). Option 82 enabled DHCP
to the layer 2 relay agent
Option 82 information
Option 82 echoed
Server sends offer, with
server allocates address
and stores the
and forwards
Configuration examples
This section contains the following examples:
z "Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering, and Option 82, when it is
acting as a layer 2 switch" on page 15
z "Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering and Option 82, when it is
acting as a layer 3 BOOTP Relay Agent" on page 19
Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering, and Option 82, when it is acting as a layer 2 switch
In a layer 2 switching environment, a switch configured with Option 82 snooping will snoop
any client-originated DHCP packets and insert Option 82 information into it before
forwarding the packet(s) to the DHCP server. In this sense it is a layer 2 relay agent; the
packet source and destination addresses are not altered.
DHCP servers that are configured to recognise the relay agent information option (Option
82) may use the information to keep a log of switches and port numbers that IP addresses
have been allocated to, and may also use the information for various address assignment
policies.
The DHCP server echoes the option back verbatim to the relay agent in server-to-client
replies, and the relay agent strips the option before forwarding the reply to the client. This
process is shown in the following figure.
Page 15 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
X Configure a private VLAN for customers:
create vlan="Customers" vid=48 private
A private VLAN provides security so customers will not be able to directly connect to or
detect each other.
Page 16

Configuration examples > Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering, and Option 82, when it is
X Add the tagged uplink ports to the VLAN:
add vlan="48" port=24 frame=tagged uplink
X Add the untagged ports for the customers:
add vlan="48" port=1-23
This is a layer 2 solution. The IP protocol does not need to be configured.
X Enable DHCP snooping and Option 82 support:
enable dhcpsnooping
enable dhcpsnooping option82
It is also possible to enable DHCP snooping ARP security. If enabled, this will ensure that
ARP packets received on non-trusted ports are only permitted if they originate from an IP
address that has been allocated and snooped by DHCP (enable dhcpsnooping
arpsecurity).
X Define the DHCP snooping trusted ports:
set dhcpsnooping port=24 trusted=yes
These ports can receive Option 82 information, and the switch will permit them to send
Option 82.
X Define the maximum number of DHCP leasees permitted on each port:
set dhcpsnooping port=1-23 maxlease=1
X Define the string that will be used in the subscriber-ID suboption portion of
the Option 82 inserted into DHCP packets:
set dhcpsnooping port=1 subscriberid="Ground Floor Room 1"
Page 16 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 17

Configuration examples > Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering, and Option 82, when it is
X Create a set of QoS Classifiers to capture all upstream traffic and include the
DHCP snooping placeholders.
These will be used to ensure that only traffic from DHCP allocated addresses is permitted,
while also allowing QoS prioritisation or shaping of traffic if desired.
This example classifies FTP and telnet. Classifier 54 is an open classifier, responsible for
discarding any traffic without a source address (found in the DHCP snooping database):
create classifier=50 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping ipsaddr=dhcpsnooping tcpdport=20
create classifier=51 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping ipsaddr=dhcpsnooping tcpdport=21
create classifier=52 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping ipsaddr=dhcpsnooping tcpdport=23
create classifier=53 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping prot="ip" ipsaddr=dhcps
create classifier=54 prot="ip"
X Define the upstream QoS flowgroups:
create qos flow=50 markvalue=10 premarking=usemarkvalue action=FORWARD
create qos flow=52 markvalue=11 premarking=usemarkvalue action=FORWARD
create qos flow=53 markvalue=12 premarking=usemarkvalue action=FORWARD
create qos flow=54 action=DISCARD
add qos flow=50 classifier=50
add qos flow=50 classifier=51
add qos flow=52 classifier=52
add qos flow=53 classifier=53
add qos flow=54 classifier=54
Mark values are used to reference into the DSCP mapping table, which is defined later.
X Create traffic classes for all upstream flow groups:
create qos trafficclass=1
create qos trafficclass=2
create qos trafficclass=3
create qos trafficclass=4
add qos trafficclass=1 flow=50
add qos trafficclass=2 flow=52
add qos trafficclass=3 flow=53
add qos trafficclass=4 flow=54
Page 17 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 18

Configuration examples > Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering, and Option 82, when it is
X Apply the QoS policy to the downstream ingress ports (customer-facing
edge ports):
create qos policy=1
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=1
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=2
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=3
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=4
set qos port=1-23 policy=1
X Set up the upstream DSCP mapping table:
For FTP and Telnet traffic respectively:
set qos dscpmap=premarking dscp=10 bwclass=1 newqueue=7
set qos dscpmap=premarking dscp=11 bwclass=1 newqueue=6
set qos dscpmap=premarking dscp=12 bwclass=1 newqueue=3
This will be used to control the egress queues that all upstream traffic is sent to. Note that
the higher value egress queues have higher priority, so FTP traffic has priority over Telnet.
Traffic arriving into the switch at a non-trusted port will be dropped if it comes from an IP
address that is not in any DHCP snooping database entry associated with that ingress port.
Page 18 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 19

Configuration examples > Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering and Option 82, when it is
(1). DHCP client sends request.
(2). Relay agent appends
Option 82 to client sourced
packets.
(4). Relay agent strips
Option 82, and forwards
to client.
(3). Option 82 enabled DHCP
server allocates address
and stores the
to the relay agent.
Option 82 information.
Option 82 echoed
Server sends offer, with
Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering and Option 82, when it is acting as a layer 3 BOOTP Relay Agent
In a layer 3 routing environment, the switch takes on a role of BOOTP Relay Agent, with
support for DHCP Option 82. The relay agent inserts the information mentioned above
when forwarding client-originated DHCP packets to a DHCP server. DHCP servers that are
configured to recognise the relay agent information option may use the information to keep a
log of switches and port numbers that IP addresses have been allocated to, and may also use
this information for various address assignment policies.
The DHCP server echoes the option back to the relay agent in server-to-client replies, and
the relay agent strips the option before forwarding the reply to the client (RFC 3046). This
process is shown in the following figure.
Page 19 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
X Configure two VLANs for layer 3 access to the DHCP server:
create vlan="Customers" vid=48
create vlan="Network" vid=50
Here the DHCP Server is on VLAN 50, while the DHCP clients are on VLAN 48.
X Add ports to the VLANs:
add vlan="48" port=1-24
add vlan="50" port=25
Page 20

Configuration examples > Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering and Option 82, when it is
X Configure the switch’s IP:
enable ip
add ip int=vlan48 ip=10.11.67.254 mask=255.255.255.0
add ip int=vlan50 ip=10.50.1.254 mask=255.255.255.0
add ip rou=0.0.0.0 mask=0.0.0.0 int=vlan50 next=10.50.1.1
X For layer 3 support, enable the BOOTP Relay:
enable bootp relay
add bootp relay=10.50.1.100
Here the DHCP server is set to 10.50.1.100.
X Enable DHCP snooping and Option 82 support:
enable dhcpsnooping
enable dhcpsnooping option82
Note: It is also possible to enable DHCP snooping ARP security. If enabled this will ensure
that ARP packets received on un-trusted ports are only permitted if they originate
from an IP address that has been allocated and snooped by DHCP (enable
dhcpsnooping arpsecurity).
X Define the DHCP snooping trusted port:
set dhcpsnooping port=25 trusted=yes
This port is open for generating and receiving Option 82 information. By default, the other
ports are non-trusted.
X Define the maximum number of DHCP leasees permitted on each port:
set dhcpsnooping port=1-24 maxlease=1
X Define the string that will be used in the subscriber-ID suboption portion of
the Option 82 inserted into DHCP packets:
set dhcpsnooping port=1 subscriberid="Ground Floor Room 1"
Page 20 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 21

Configuration examples > Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering and Option 82, when it is
X Create a set of QoS classifiers (include the DHCP snooping placeholders):
create classifier=50 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping ipsaddr=dhcpsnooping tcpdport=20
create classifier=51 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping ipsaddr=dhcpsnooping tcpdport=21
create classifier=52 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping ipsaddr=dhcpsnooping tcpdport=23
create classifier=53 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping prot="ip" ipsaddr=dhcps
create classifier=54 prot="ip"
The QoS classifiers are used to ensure that only traffic from DHCP allocated addresses is
forwarded, while also allowing QoS prioritisation or traffic shaping.
The above example classifies FTP and telnet. Classifier 54 is an open classifier, responsible for
discarding any traffic without an allocated source address.
X Define the upstream QoS flowgroups:
create qos flow=50 markvalue=10 premarking=usemarkvalue action=FORWARD
create qos flow=52 markvalue=11 premarking=usemarkvalue action=FORWARD
create qos flow=53 markvalue=12 premarking=usemarkvalue action=FORWARD
create qos flow=54 action=DISCARD
add qos flow=50 classifier=50
add qos flow=50 classifier=51
add qos flow=52 classifier=52
add qos flow=53 classifier=53
add qos flow=54 classifier=54
Mark values are used to reference into the DSCP mapping table, which is defined later.
X Create traffic classes for all upstream flow groups:
create qos trafficclass=1
create qos trafficclass=2
create qos trafficclass=3
create qos trafficclass=4
add qos trafficclass=1 flow=50
add qos trafficclass=2 flow=52
add qos trafficclass=3 flow=53
add qos trafficclass=4 flow=54
Page 21 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 22

Configuration examples > Configuring the switch for DHCP snooping, filtering and Option 82, when it is
X Apply the QoS policy to the downstream ingress ports (customer-facing
edge ports):
create qos policy=1
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=1
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=2
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=3
add qos policy=1 trafficclass=4
set qos port=1-24 policy=1
X Set up the upstream DSCP mapping table:
For FTP and Telnet traffic respectively:
set qos dscpmap=premarking dscp=10 bwclass=1 newqueue=7
set qos dscpmap=premarking dscp=11 bwclass=1 newqueue=6
set qos dscpmap=premarking dscp=12 bwclass=1 newqueue=3
This will be used to control the egress queues that all upstream traffic is sent to. Note that
the higher value egress queues have higher priority, so FTP traffic has priority over Telnet.
Page 22 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 23

Troubleshooting > No trusted ports configured
Troubleshooting
Use the command enable dhcpsnooping debug=all to get the most verbose level of
debugging available. In the following sections, all debugging comes from that command.
Let’s look at how you can use debugging to investigate some common problem scenarios.
No trusted ports configured
In the following output, you can see that a DHCP request has arrived at the switch on port 1.
The switch does not forward this on to any other port.
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 1B
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] Forward ports (except 1)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] Tagged:None B
DHCPSN_Process: [0b4333cc] Untagged:None B
The reason for this behaviour is because there are no trusted ports configured. Your DHCP
server must be attached to a trusted port.
When a trusted port is configured, the debug shows a more complete conversation, as the
following output shows.
Manager > set dhcpsnooping port=48 trusted=yes
Info (1137260): DHCP Snooping port(s) 48 updated successfully.
Manager >
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 1B
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Forward ports (except 1)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Untagged:48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] On DHCP Snooping trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] Lookup result for CHAddr 00-06-5b-31-14-af: Port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] L2 forward using client port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] Forward ports (except 48)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43adac] Untagged:1
Page 23 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 24

Troubleshooting > The DHCP client continually sends requests instead of a discover
The DHCP client continually sends requests instead of a discover
This happens when the client is renewing its lease or, for whatever reason, believes that
should be issued a specific address. If the client does not receive either an ACK or NACK
(from a DHCP server) then the client will continue to request the address.
A NACK should cause the client to send a discover packet instead of a request. Hence, if
NACK is not received, the client (depending on its DHCP software) may continue to request
an address and never send a discover.
Maximum number of leases is exceeded
By default, there is one lease per switch port. If there is already an entry for a port in the
DHCP snooping database (in the current valid entries), then the next request on that port
from a different MAC address will see the DHCP server ACK discarded:
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 3
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 3
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] Forward ports (except 3)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47d60c] Untagged:48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] On DHCP Snooping trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] Lookup result for CHAddr 00-00-00-00-00-01: Port 3
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] L2 Dest MAC is unicast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] Using chaddr lookup result for dest port(s)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] L2 forward packet directly to port 3
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] Forward ports (except 48)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47de2c] Untagged:3
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 3
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 3
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] Forward ports (except 3)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47e64c] Untagged:48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47ee6c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47ee6c] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47ee6c] On DHCP Snooping trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47ee6c] Lookup result for CHAddr 00-00-00-00-00-01: Port 3
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47ee6c] DHCP ACK Found...
DHCPSN_DB: Updating entryId 7. Flags 00000010
DHCPSN_DB: Couldn't update: Listener error or will exceed MAXLEASES on port 3 (Current/
MAX 1/1)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47ee6c] Error adding entry to DB
DHCPSN_Process: [0b47ee6c] Discard packet, DHCP ACK not forwarded
Page 24 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 25

Troubleshooting > Maximum number of leases is exceeded
Increasing the port’s maximum leases will permit multiple clients per port. Before changing
the maximum leases the port must be removed from the QoS policy:
Manager > set dhcpsnooping port=3 maxleases=2
Error (3137259): QoS policy must be detached from port(s) 3 before changing MAXLEASES.
Manager > set qos port=3 policy=none
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindAllByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=3
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 1 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindAllByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=3 items=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingDestroyFoundList >> destroying list with 1 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingDestroy >> classifierId=46561 notifyDB=0
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFind >> classifierId=46561
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFind >> finding binding classifierId=46561
bindingPt=0x0bf82494
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingDestroy >> destroyed binding classifierId=46561
Info (1099274): Policy 1 has been removed from PORT 3.
Info (1099003): Operation successful.
Manager >
DHCPSN_DB: Timer expired (23:26:03), checking entries...
DHCPSN_DB: Deleted 0 entries (7)
Manager > policy=noneDHCPSN_DB: No change has occured in DB, so no need to update the file
BManager > set dhcpsnooping port=3 maxleases=2
Info (1137260): DHCP Snooping port(s) 3 updated successfully.
BManager > set qos port=3 policy=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> templateId=1 flowId=1 port=3 num=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> created child-1 bindings of templateId=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> templateId=1 flowId=1 port=3 num=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> created child-2 bindings of templateId=1
Info (1099003): Operation successful.
Page 25 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 26

Troubleshooting > Switch is dropping ARPs
Switch is dropping ARPs
If you have DHCP snooping in ARP security mode, then unknown clients on untrusted ports
will not be able to ARP.
DHCPSN_ARP: [0193a9ec] ARP Received on untrusted port 24 VLAN 1
DHCPSN_ARP: [0193a9ec] ARP Discarded, sender not found in DHCP Snoop DB
Known clients on untrusted ports will be able to ARP.
DHCPSN_ARP: [01a6f5ec] ARP Received on untrusted port 1 VLAN 1
DHCPSN_ARP: [01a6f5ec] ARP to be forwarded, sender validated
DHCPSN_ARP: [01a6f5ec] Forwarding ARP at L2 for VLAN 1
DHCPSN_ARP: [01a6f5ec] Forward ports (except 1)
DHCPSN_ARP: [01a6f5ec] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_ARP: [01a6f5ec] Untagged:24
A client is known on an untrusted port if it has an IP/MAC entry in the DHCP snooping
database (show dhcpsnooping database). Your DHCP server must be on a trusted port.
Manager > set dhcpsnooping port=24 trusted=yes
Info (1137260): DHCP Snooping port(s) 24 updated successfully.
Manager >
DHCPSN_ARP: [023a218c] ARP Received on trusted port 24 VLAN 1
DHCPSN_ARP: [023a218c] Forwarding ARP at L2 for VLAN 1
DHCPSN_ARP: [023a218c] Forward ports (except 24)
DHCPSN_ARP: [023a218c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_ARP: [023a218c] Untagged:1
You cannot work around dropped ARPs (from the DHCP server) by statically binding the
DHCP server’s IP and MAC address to a port, instead of setting it as trusted. The switch will
not send the DHCP server the DHCP request. The switch will not flood the DHCP request
to any ports other than trusted ones. So although the switch will let the DHCP server send
ARP requests, the DHCP server will not receive any DHCP requests.
Page 26 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 27

Troubleshooting > Switch is dropping ARPs
Manager > add dhcpsnooping binding=00-50-FC-EE-F5-13 ip=172.16.1.1 int=vlan1 port=24
DHCPSN_DB: Creating new entry with entryId 3.
DHCPSN_DB: Notifying DB listener: CLASSIFR
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> dbEntryPt=0x010caed4 flags=0x00000080
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=3
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=3 it0
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindAllByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=24
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindAllByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=20
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> templateId=10001 flowId=0 port=24 num=3
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> created child-3 bindings of templateId1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingBinds >> bclassId=20003 portNum=24 entryId=3
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingBinds >> success, classifierId=20003 flowGroupId3
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> NEW, returns=1
DHCPSN_DB: Change state for 00-50-fc-ee-f5-13, in NONE for event LISTENER_OK
DHCPSN_DB: Changed state for 00-50-fc-ee-f5-13, to FULL
Info (1137003): Operation successful.
Manager >
DHCPSN_ARP: [02680e6c] ARP Received on untrusted port 24 VLAN 1
DHCPSN_ARP: [02680e6c] ARP to be forwarded, sender validated
DHCPSN_ARP: [02680e6c] Forwarding ARP at L2 for VLAN 1
DHCPSN_ARP: [02680e6c] Forward ports (except 24)
DHCPSN_ARP: [02680e6c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_ARP: [02680e6c] Untagged:1
Manager >
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 1
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] Forward ports (except 1)
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [026ef9ac] Untagged:None
Page 27 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 28

Troubleshooting > The DHCP ACK is dropped by the switch
The DHCP ACK is dropped by the switch
When you enable dhcpsnooping debug=all and a client does its first DHCP request you
get the following:
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] Forward ports (except 1)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b438d2c] Untagged:48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43954c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43954c] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43954c] On DHCP Snooping trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43954c] Lookup result for CHAddr 00-06-5b-31-14-af: Port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43954c] DHCP ACK Found...
DHCPSN_DB: Creating new entry with entryId 2.
DHCPSN_DB: Notifying DB listener: CLASSIFR
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> dbEntryPt=0x195de05c flags=0x00000080
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2 items=0
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=1 items=0
DHCPSN_DB: Change state for 00-06-5b-31-14-af, in NONE for event LISTENER_FAIL
DHCPSN_DB: Notifying DB listener: CLASSIFR
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> dbEntryPt=0x195de05c flags=0x00000100
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2 items=0
DHCPSN_DB: Changed state for 00-06-5b-31-14-af, to NOLEASE_NOLISTEN
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43954c] Error adding entry to DB
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43954c] Discard packet, DHCP ACK not forwarded
Page 28 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 29

Troubleshooting > The DHCP ACK is dropped by the switch
The second DHCP request will look slightly different:
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] Forward ports (except 1)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b439d6c] Untagged:48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] On DHCP Snooping trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Lookup result for CHAddr 00-06-5b-31-14-af: Port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] DHCP ACK Found...
DHCPSN_DB: Updating entryId 2. Flags 00000010
DHCPSN_DB: Notifying DB listener: CLASSIFR
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> dbEntryPt=0x195de05c flags=0x00000080
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2 items=0
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=1 items=0
DHCPSN_DB: Change state for 00-06-5b-31-14-af, in NOLEASE_NOLISTEN for event
LISTENER_FAIL
DHCPSN_DB: Changed state for 00-06-5b-31-14-af, to NOLEASE_NOLISTEN
DHCPSN_DB: Couldn't update: Listener error or will exceed MAXLEASES on port 1 (Current/
MAX 0/100)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Error adding entry to DB
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43a58c] Discard packet, DHCP ACK not forwarded
But the result is the same: the DHCP ACK has been dropped by the switch.
Page 29 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 30

Troubleshooting > The DHCP ACK is dropped by the switch
The DHCP snooping database will indicate that the DHCP process has not been completed
but that the IP has been seen:
Manager > sh dhcpsnooping database
DHCP Snooping Binding Database
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Database Version ..... 1
Full Leases/Max Leases ... 0/151
Check Interval ........... 60 seconds
Database Listeners ....... CLASSIFR
Current valid entries
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with client lease but no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with no client lease and no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------00-06-5b-31-14-af 172.16.1.100 3174 1 1 2 Dynamic
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
This can be caused when the ACK packet is dropped by the QoS process. It has failed to
match a policy for that port and as a result the traffic is dropped.
Manager > show conf dyn=classifier
# CLASSIFR configuration
create classifier=1 macsaddr=dhcpsnooping prot="ip" ipsaddr=dhcps
create classifier=99 prot="ip"
Manager > show conf dynamic=qos
# QOS configuration
create qos policy=1
create qos trafficclassifier=1
create qos flow=1 action=FORWARD
create qos flow=99 action=DISCARD
add qos policy=1 trafficclassifier=1
add qos trafficclassifier=1 flow=1
add qos trafficclassifier=1 flow=99
add qos flow=1 classifier=1
add qos flow=99 classifier=99
Page 30 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 31

Troubleshooting > The DHCP ACK is dropped by the switch
In this scenario we have the most basic QoS config possible to permit all IP traffic, but it has
not been applied to any port, so the solution is to set policy
Manager > set qos port=1 policy=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> templateId=1 flowId=1 port=1 num=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> created child-1 bindings of templateId=1
<snip>
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> templateId=1 flowId=1 port=1 num=n
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> created child-n bindings of templateId=1
1
Where n is the number of leases permitted on port
.
1
to port 1:
Now our DHCP ACK is forwarded:
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] Forward ports (except 1)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43ce2c] Untagged:48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] On DHCP Snooping trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] Lookup result for CHAddr 00-06-5b-31-14-af: Port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] DHCP ACK Found...
DHCPSN_DB: Updating entryId 2. Flags 00000010
DHCPSN_DB: Notifying DB listener: CLASSIFR
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> dbEntryPt=0x195de05c flags=0x00000080
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2 items=0
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 1 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=1 items=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingBinds >> bclassId=45521 portNum=1 entryId=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingBinds >> success, classifierId=45521 flowGroupId=1
portNum=1 entryId=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingDestroyFoundList >> destroying list with 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> NEW, returns=1
DHCPSN_DB: Change state for 00-06-5b-31-14-af, in NOLEASE_NOLISTEN for event LISTENER_OK
DHCPSN_DB: Changed state for 00-06-5b-31-14-af, to FULL
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] L2 Dest MAC is unicast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] Using chaddr lookup result for dest port(s)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] L2 forward packet directly to port 1
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] Forward ports (except 48)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b43d64c] Untagged:1
Page 31 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 32

Troubleshooting > The DHCP ACK is dropped by the switch
Notice that the entry has moved in the database:
Manager > sh dhcpsnooping database
DHCP Snooping Binding Database
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------Database
Version ..... 1
Full Leases/Max Leases ... 1/151
Check Interval ........... 60 seconds
Database Listeners ....... CLASSIFR
Current valid entries
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------00-06-5b-31-14-af 172.16.1.100 86343 1 1 2 Dynamic
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with client lease but no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with no client lease and no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 32 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 33

Troubleshooting > The DHCP ACK is dropped by the switch
Another possibility for dropping an ACK is when there is already an entry for the port in the
DHCP snooping database.
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44ca0c] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44ca0c] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44ca0c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 2
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44ca0c] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44ca0c] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44ca0c] Forward ports (except 2)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44ca0c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44ca0c] Untagged:48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] On DHCP Snooping trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] Lookup result for CHAddr 00-00-00-00-00-02: Port 2
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] L2 Dest MAC is unicast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] Using chaddr lookup result for dest port(s)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] L2 forward packet directly to port 2
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] Forward ports (except 48)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44d22c] Untagged:2
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 2
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] Type: REQUEST
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] On DHCP Snooping non-trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] DHCP Snoop forwarding pkt at L2 for VLAN 1 InPort 2
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] L2 Dest MAC is broadcast
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] Type: REQUEST, L2 forward to trusted ports
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] Forward ports (except 2)
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] Tagged:None
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44da4c] Untagged:48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44e26c] DHCP Snooping pkt for VLAN 1 from port 48
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44e26c] Type: REPLY
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44e26c] On DHCP Snooping trusted port
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44e26c] Lookup result for CHAddr 00-00-00-00-00-02: Port 2
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44e26c] DHCP ACK Found...
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44e26c] Error adding entry to DB
DHCPSN_Process: [0b44e26c] Discard packet, DHCP ACK not forwarded
In the example above, a client on port 2 has attempted a DHCP request but the server’s
ACK was dropped by the switch because there is already an entry on port 2. The entry on
port 2 is static. Even though the server offered the same IP to the same MAC (as appears in the
DHCP snooping database) the static entry causes the DHCP process to not be completed.
Page 33 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 34

Troubleshooting > Cannot create a binding entry
Cannot create a binding entry
When you want to add a static entry to the DHCP snooping database you need to create a
binding entry.
Manager > add dhcpsnooping binding=00-00-00-00-00-02 int=vlan1 ip=172.16.1.202 port=2
DHCPSN_DB: Creating new entry with entryId 2.
DHCPSN_DB: Notifying DB listener: CLASSIFR
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> dbEntryPt=0x141ecef8 flags=0x00000080
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2 items=0
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=2 items=0
DHCPSN_DB: Change state for 00-00-00-00-00-02, in NONE for event LISTENER_FAIL
DHCPSN_DB: Notifying DB listener: CLASSIFR
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> dbEntryPt=0x141ecef8 flags=0x00000100
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=2 items=0
DHCPSN_DB: Changed state for 00-00-00-00-00-02, to NONE
Error (3137258): Static DHCP Snooping entry could not be added. Check log for details.
This error is caused, once again, by the port not being a part of a QoS policy, so the port is
rejected admission to the DHCP snooping database.
Manager > show conf dyn=qos
# QOS configuration
create qos policy=1
create qos trafficclassifier=1
create qos flow=1 action=FORWARD
create qos flow=99 action=DISCARD
add qos policy=1 trafficclassifier=1
set qos port=1 policy=1
add qos trafficclassifier=1 flow=1
add qos trafficclassifier=1 flow=99
add qos flow=1 classifier=1
add qos flow=99 classifier=99
Page 34 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 35

Troubleshooting > Cannot create a binding entry
The solution is to add the port to a relevant policy.
Manager > set qos port=2 policy=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> templateId=1 flowId=1 port=2 num=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingCreate >> created child-1 bindings of templateId=1
Manager > add dhcpsnooping binding=00-00-00-00-00-02 int=vlan1 ip=172.16.1.22 port=2
DHCPSN_DB: Creating new entry with entryId 3.
DHCPSN_DB: Notifying DB listener: CLASSIFR
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> dbEntryPt=0x141ecef8 flags=0x00000080
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=3
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindByEntryIndex >> finding binding entryId=3 items=0
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=2
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindGroup >> found 1 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingFindFreeByPortNumber >> finding binding portNum=2 items=1
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingBinds >> bclassId=46041 portNum=2 entryId=3
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingBinds >> success, classifierId=46041 flowGroupId=1
portNum=2 entryId=3
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclBindingDestroyFoundList >> destroying list with 0 items
DHCPSN_ACL: dhcpSnoopAclListener >> NEW, returns=1
DHCPSN_DB: Change state for 00-00-00-00-00-02, in NONE for event LISTENER_OK
DHCPSN_DB: Changed state for 00-00-00-00-00-02, to FULL
Info (1137003): Operation successful.
Manager > sh dhcpsnooping database
DHCP Snooping Binding Database
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Database Version ..... 1
Full Leases/Max Leases ... 1/151
Check Interval ........... 60 seconds
Database Listeners ....... CLASSIFR
Current valid entries
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------00-00-00-00-00-02 172.16.1.202 Static 1 2 3 User
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with client lease but no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with no client lease and no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 35 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 36

Troubleshooting > Entries with client lease but no listeners
Entries with client lease but no listeners
Entries are not being written to the Current valid leases section of the DHCP snooping
database:
Manager 8948> show dhcpsnooping database
DHCP Snooping Binding Database
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Database Version ..... 1
Full Leases/Max Leases ... 0/52
Check Interval ........... 60 seconds
Database Listeners ....... CLASSIFR
Current valid entries
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with client lease but no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------00-00-00-00-00-04 172.16.1.204 Static 1 4 1 User
00-00-cd-11-b2-4c 172.16.1.123 2432 1 17 2 File
00-06-5b-31-14-af 172.16.1.100 3084 1 1 3 File
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Entries with no client lease and no listeners
MAC Address IP Address Expires(s) VLAN Port ID Source
----------------------------------------------------------------------------None...
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
This is caused by partial or incorrect QoS configuration. Check you have classifiers to match
dhcpsnooping addresses. Those classifiers must be attached to policies with forwarding flow
groups or traffic classes. Finally, check that you have a QoS policy applied to untrusted ports.
Page 36 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 37

Appendix 1: ISC DHCP server > Entries with client lease but no listeners
Appendix 1: ISC DHCP server
One DHCP server that has been tested against x900 DHCP snooping is ISC DHCP. This is
free software with an option of a support contract. At the time of writing this document, ISC
DHCP did not support the logging of RFC3993 sub-option 6. For convenience, here is a
sample configuration (dhcpd.conf) for ISC DHCP.
This configuration lets you specify the IP that is given to each MAC address. You may easily
write a range statement to assign to any client.
ddns-update-style ad-hoc;
option domain-name "test.yourdomain.com";
option domain-name-servers 172.16.1.253;
option broadcast-address 172.16.1.255;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
use-host-decl-names on;
subnet 172.16.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
#filename "/vmlinuz ";
default-lease-time 86400;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option domain-name "test.yourdomain.com";
option domain-name-servers 172.16.1.1;
option routers 172.16.1.1;
option broadcast-address 172.16.1.255;
host linux {
hardware ethernet 00:06:5b:31:14:af;
fixed-address 172.16.1.100;
filename "/vmlinuz ";
}
host test01 {
hardware ethernet 00:00:00:00:00:01;
fixed-address 172.16.1.201;
}
host test02 {
hardware ethernet 00:00:00:00:00:02;
fixed-address 172.16.1.202;
}
host test03 {
hardware ethernet 00:00:00:00:00:03;
fixed-address 172.16.1.203;
}
host AT8800 {
hardware ethernet 00:00:cd:11:b2:4c;
fixed-address 172.16.1.123;
Page 37 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: DHCP snooping on AT-9900-style switches
Page 38

USA Headquar ters | 19800 Nor th Cr eek Parkwa y | Suite 200 | Bothell | WA 98011 | USA | T: +1 800 424 4284 | F: +1 425 481 3895
Eur opean Headquar ters | Via Motta 24 | 6830 Chiasso | Switzerland | T: +41 91 69769.00 | F: +41 91 69769.11
Asia-Pacific Headquar ters | 11 T ai Seng Link | Singapor e | 534182 | T: +65 6383 3832 | F: +65 6383 3830
www .alliedtelesis.com
© 2007 Allied Tel esis,
Inc. All rights reser ved.Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
All company names, logos,and product designs that are trademar ks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis is a trademark or registered trademark of Allied Telesis, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
The following configuration (thanks to www.thtech.net/article/10) will record Option 82
information in syslog. This part is ignored if no Option 82 information is passed on. The
logfile location is configured in syslog.
if exists agent.circuit-id
{
log ( info, concat( "NEW LEASE - IP: ", binary-to-ascii (10, 8, ".", leased-address),
", PORT: ", binary-to-ascii (10, 8, ":", suffix ( option agent.circuit-id, 2)),
", VLAN: ", binary-to-ascii(10, 16, "", substring( option agent.circuit-id, 2, 2)),
", SWITCH: ", binary-to-ascii(16, 8, ":", substring( option agent.remote-id, 2, 6))));
log ( info, concat( "IP ", binary-to-ascii (10, 8, ".", leased-address),
" raw option-82 info is CID: ", binary-to-ascii (10, 8, ".", option agent.circuit-id), "
AID: ",
binary-to-ascii(16, 8, ".", option agent.remote-id)));
C613-16082-00 REV B
 Loading...
Loading...