Page 1

AlliedWare PlusTM OS
How To |
Configure Hardware Filters on SwitchBlade x908,
x900-12XT/S, and x900-24 Series Switches
Introduction
The SwitchBlade x908, x900-12XT/S, and x900-24 series switches support a powerful
hardware based packet-filtering facility.
These switches can filter on a range of Layer 2, Layer 3, and Layer 4 packet attributes, and
perform a variety of different actions on the packets that match the filters.
Because the filters are hardware-based, they put no load on the CPU of the switch, and do
not affect the throughput of the switch. It is possible to configure over 1000 different filters,
and still have complete wire speed throughput on the switch.
On the AlliedWare Plus OS, hardware-based packet filtering is carried out by using hardware
ACLs (Access Control Lists). The following configuration methods are available:
1. To make a simple filter based on IP address, MAC address, TCP/UDP port, or ICMP type,
you simply create one or more ACLs and apply them to a port.
You can build up a filter hierarchy by applying multiple ACLs to a port (e.g. make one ACL
to allow traffic from a source IP address to a destination address, then a second ACL to
drop all (other) traffic from that source IP address).
This How To Note calls ACLs that are applied to ports interface ACLs.
2. To make a filter based on a range of other packet settings, you use QoS match commands
in one or more QoS class-maps, mostly in combination with ACLs. Then you use QoS to
apply the class-maps to a policy-map and port.
This note describes both approaches. Then it gives a series of examples, and ends by
discussing how many filters you can make.
C613-16119-00 REV A
www.alliedtelesis.com
Page 2

Introduction
Contents
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 1
Which products and software version does this Note apply to? ......................................... 2
Creating hardware ACLs ....................................................................................................................... 3
Creating IP hardware ACLs ........................................................................................................... 3
Creating MAC address hardware ACLs ...................................................................................... 6
The effects of the action keywords in ACLs ..................................................................................... 6
Making filters by applying hardware ACLs to ports ........................................................................ 7
Making filters by using QoS class-maps .............................................................................................. 8
Creating a class-map ........................................................................................................................ 9
Specifying what the class-map will match on ............................................................................. 9
Matching on “inner” keywords for nested VLANs ........................................................ 10
Matching on TCP flag ........................................................................................................... 11
Matching on eth-format and protocol .............................................................................. 12
Applying the class-maps to a policy-map .................................................................................. 12
Applying the policy-map to ports ............................................................................................... 12
The logic of the operation of the hardware filters ........................................................................ 13
Combining interface ACLs and QoS class-maps ............................................................................ 13
Examples .................................................................................................................................................. 14
Blocking all multicast traffic ......................................................................................................... 14
Blocking all multicast traffic except one address .................................................................... 15
Mirroring HTTP and SMTP traffic .............................................................................................. 15
Mirroring ARP packets .................................................................................................................. 16
Blocking TCP sessions in one direction .................................................................................... 17
How many filters can you create? ...................................................................................................... 18
1. The filter rules table ................................................................................................................. 18
2. The profile (mask) ..................................................................................................................... 19
Are there enough bytes for your set of filters? .............................................................. 20
Some protocols also use filters, so use some of the length ........................................ 21
Which products and software version does this Note apply to?
z Products: SwitchBlade x908, x900-12XT/S, and x900-24 series switches
z Software versions: 5.2.1-0.1 and above
Hardware filters are also available on Layer 3 switches running the AlliedWare OS. For
AlliedWare OS configurations, see the AlliedWare OS How To Notes:
z How To Use the Hardware Filters on the AT-8948 and AT-9900 Series Switches
z How To Configure Filtering Actions on QoS Flow Groups and Traffic Classes
These Notes are available from www.alliedtelesis.com/resources/literature/howto.aspx.
Page 2 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 3

Creating hardware ACLs
Creating hardware ACLs
Hardware ACLs contain both the match criteria and the action to take on matching traffic.
There are two types of hardware ACL: IP address and MAC address. These are indexed by
their ID number. IP hardware ACLs have a number in the range 3000 to 3699 and MAC
hardware ACLs have a number in the range 4000 to 4699.
The following table shows the available ACL ranges as displayed by the ? help, and highlights
the hardware ACLs.
Number range Description
1-99 IP standard access list
100-199 IP extended access list
1300-1999 IP standard access list (expanded range)
2000-2699 IP extended access list (expanded range)
3000-3699 Hardware IP access list
4000-4699 Hardware MAC access list
extended Named IP extended access list
standard Named IP standard access list
The ACLs give you the following choice of actions to take on matching traffic (see “The
effects of the action keywords in ACLs” on page 6 for details).
Action parameter Description
copy-to-cpu Specify packets to copy to the CPU
copy-to-mirror Specify packets to copy to the mirror port
deny Specify packets to reject
permit Specify packets to permit
send-to-cpu Specify packets to send to the CPU
Creating IP hardware ACLs
IP hardware ACLs filter packets from the following IP protocols:
z IP
z ICMP
z TCP
z UDP
This section describes how to create ACLs to filter packets from each of these protocols.
Page 3 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 4

Creating hardware ACLs
IP packets You can filter IP packets on the basis of their source and/or destination IP addresses. The
command syntax is:
awplus(config)#access-list <3000-3699> <action> ip <source-ip-address>
<destination-ip-address>
The source and destination IP addresses can be any of the following:
z a subnet. To specify this, enter the address and mask. You can specify the mask in slash
notation or with a wildcard (reverse) mask:
awplus(config)#access-list 3000 permit ip 192.168.0.0/16 ...
awplus(config)#access-list 3000 permit ip 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 ...
z a single host. To specify this, enter the keyword host and then the address:
awplus(config)#access-list 3000 permit ip host 192.168.0.1 ...
z all source IPs or all destination IPs. To specify this, enter the keyword any:
awplus(config)#access-list 3000 permit ip any ...
ICMP packets You can filter ICMP messages on the basis of:
z source IP address and/or destination IP address (using the same syntax as when filtering IP
packets)
z ICMP message type, by specifying a type number. Popular types to filter include Echo Reply
(0), Echo Request (8), Redirect (5), Destination Unreachable (3), Traceroute (30), and
Time Exceeded (11)
The command syntax is:
awplus(config)#access-list <3000-3699> <action> icmp
<source-ip-address> <destination-ip-address> [icmp-type <value>]
For example, the following ACL matches on all ICMP messages from 192.168.0.0/16:
awplus(config)#access-list 3000 permit icmp 192.168.0.0/16 any
For example, the following ACL matches on ICMP redirect messages to and from any
address:
awplus(config)#access-list 3000 permit icmp any any icmp-type 5
Page 4 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 5

Creating hardware ACLs
TCP and UDP
packets
You can filter TCP and UDP packets on the basis of:
z source IP address and/or destination IP address (using the same syntax as when filtering IP
packets)
z source and/or destination TCP/UDP ports.
The command syntax is:
awplus(config)#access-list <3000-3699> <action> {tcp|udp}
<source-ip-address>
[{eq|gt|lt|ne|range} <source-port> [<source-port>]]
<destination-ip-address>
[{eq|gt|lt|ne|range} <dest-port> [<dest-port>]]
To determine which ports to filter, use the following keywords:
Keyword Selects Example
no keyword All ports For example, to match packets that use any TCP source or
destination port:
access-list 3000 permit tcp any any
eq A single port Specify a single port number. For example, to match packets
from any IP address that use TCP source port 5100:
access-list 3000 permit tcp any eq 5100 any
Note that the TCP port parameter is optional. In this
example, the keyword any indicates that the ACL matches
on any source and destination IP address. The absence of a
port at the end of the command indicates that it matches on
any destination port.
gt All ports higher than the
specified port number
lt All ports lower than the
specified port number
ne All ports except the specified
port
range A contiguous range of ports Specify the lowest and highest numbers in the range,
Specify a single port number. For example, to match packets
that use a source TCP port of 5100 or higher:
access-list 3000 permit tcp any gt 5099 any
Specify a single port number. For example, to match packets
that use a source TCP port of 5100 or lower:
access-list 3000 permit tcp any lt 5101 any
Specify a single port number. For example, to match packets
that use any source TCP port except port 5100:
access-list 3000 permit tcp any ne 5100 any
separated by a space. For example, to match packets that use
TCP source ports 5100 to 5200 inclusive:
access-list 3000 permit tcp any range 5100 5200 any
Page 5 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 6

The effects of the action keywords in ACLs
Creating MAC address hardware ACLs
MAC address hardware ACLs filter packets on the basis of their source or destination MAC
address.
The command syntax is:
awplus(config)#access-list <4000-4699> <action> <source-mac-address>
<destination-mac-address>
The source and destination MAC addresses can be any of the following:
z a range of MAC addresses. To specify this, enter a MAC address and the mask. Specify the
mask as a wildcard mask:
awplus(config)#access-list 4000 permit 1234.1234.1234 0000.0000.000f
...
(this example selects MAC addresses from 1234.1234.1230 to 1234.1234.123f)
z a single MAC address. To specify this, enter the MAC address and a mask of
0000.0000.0000:
awplus(config)#access-list 4000 permit 1234.1234.1234 0000.0000.0000
...
z all MAC addresses. To specify this, enter the keyword any:
awplus(config)#access-list 4000 permit any ...
The effects of the action keywords in ACLs
Let us consider the effect of each the possible action keywords.
Action What it does When do you need this action?
deny Drops the traffic. Use this when the filtering policy is to disallow certain
traffic flows.
permit Forwards the traffic normally. Use this when you want to:
z discard a wide range of traffic, but still forward some
small subset of traffic within that range.
z use the ACL in a QoS class-map to select traffic for the
switch to apply QoS settings to (like queue shaping).
copy-to-cpu Forwards the traffic normally, and
also sends a copy of each packet to
the CPU.
send-to-cpu Drops the traffic, but also sends a
copy of each packet to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Forwards the traffic normally, and
also sends a copy of each packet to
the mirror port.
Use this when you want software monitoring of a certain
packet flow. If you want to log, or count, or output debug
pertaining to a certain stream, then create an ACL that
matches the packets in the stream, and specify the copyto-cpu action.
Use this when you want software monitoring of a certain
packet flow that is being dropped. If you want to log,
count, or output debug pertaining to a certain disallowed
stream, then create an ACL that matches the packets in
the stream, and specify the send-to-cpu action.
Use this when you want to mirror only a certain stream,
instead of mirroring all traffic on a port.
Page 6 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 7

Making filters by applying hardware ACLs to ports
Making filters by applying hardware ACLs to ports
You can create a filter by simply applying one or more ACLs to a port, as long as you can
select the matching traffic through hardware ACL keywords, as described above.
ACLs can be applied to switch ports and static channel groups. To apply an ACL to a dynamic
(LACP) channel group, apply the ACL to all ports that can be in the channel group.
The hardware filters act on incoming traffic, so apply them to the ingress ports.
Attaching
ACLs
Viewing port
information
To apply ACLs to ports, enter interface mode for the port or ports you want to attach the
ACL to, and then use one of the following commands:
For IP hardware ACLs:
ip access-group <ip-acl-number>
For MAC hardware ACLs:
mac access-group <mac-acl-number>
If you have multiple ACLs on a port, attach them to the port in the order in which you want
the switch to check them—see “The logic of the operation of the hardware filters” on
page 13. You can alternate IP and MAC ACLs, like in the following example:
awplus(config-if)#ip access-group 3200
awplus(config-if)#ip access-group 3100
awplus(config-if)#mac access-group 4300
awplus(config-if)#ip access-group 3150
awplus(config-if)#mac access-group 4350
To see a list of the ACLs that are directly attached to a port, use the following command:
awplus#show interface <range> access-group
Changing
ACL order
It is not possible to change the order of ACLs once you have attached them to a port.
Instead, remove ACLs from the port by entering interface mode for the port and using the
commands:
no ip access-group <ip-acl-number>
no mac access-group <mac-acl-number>
Then re-enter them in the desired order.
Page 7 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 8
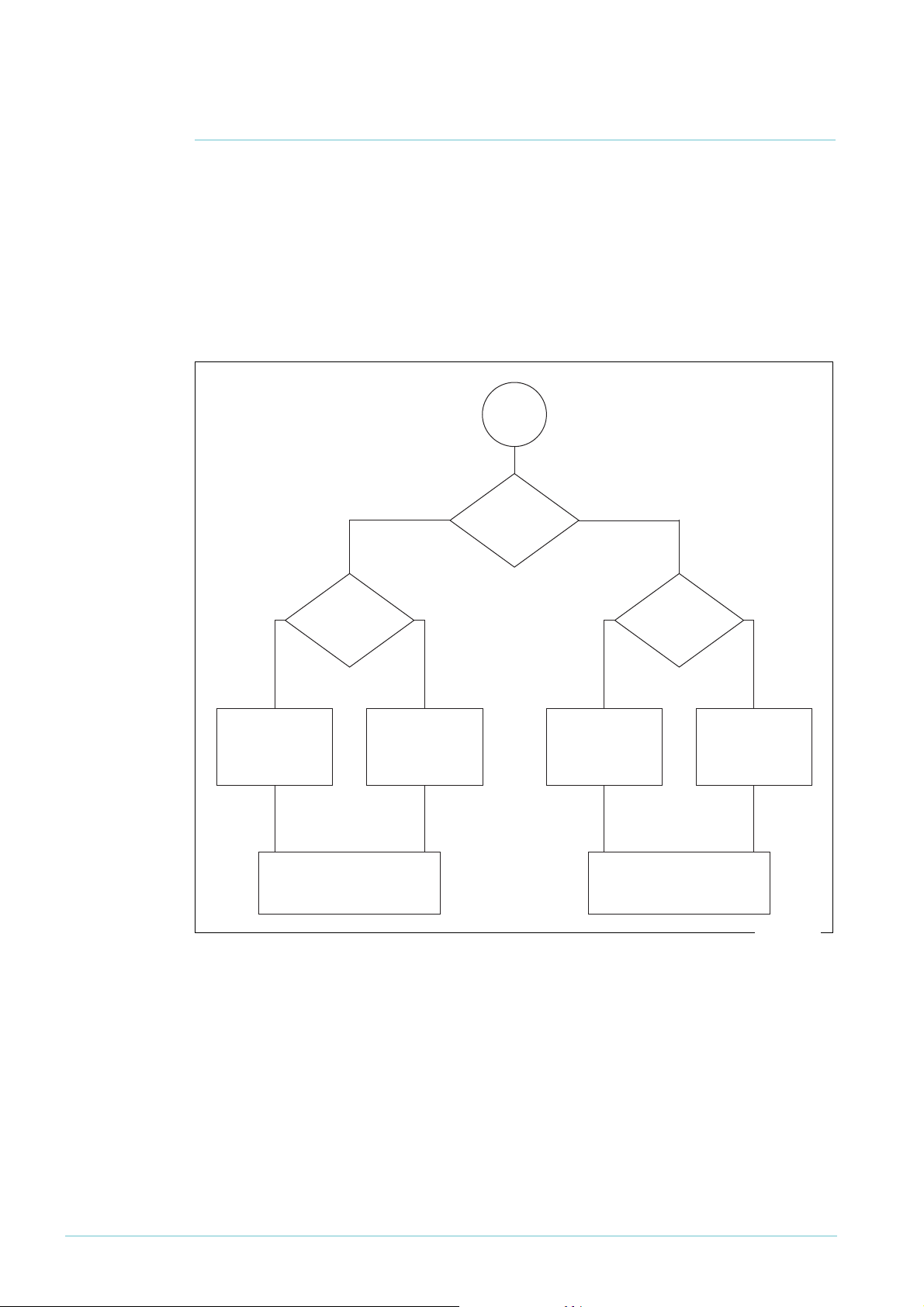
Making filters by using QoS class-maps
qos-match.eps
Making filters by using QoS class-maps
QoS class-maps allow you to match on a much wider range of packet attributes than ACLs by
themselves. They do this by determining the match criteria from an ACL, or from match
commands, or from both in combination. Also, they use an ACL to decide what action to
take on a packet, unless you want the default action of permit.
The following figure summarises the class-map logic flow. Note that a class-map with no
match commands (including no ACL match) matches on all traffic and forwards it. You could
use such a class-map to apply QoS policing to a port, but would not be likely to use it when
filtering.
Start
Also
yes yesno
Get criteria by
ANDing together
ACL and other
match commands
match on other
things?
using ACL settings
Apply action from ACL
(permit, deny, send-to-mirror,
send-to-cpu, copy-to-cpu)
yes
Get criteria by
Match
on ACL?
no
Get criteria by
ANDing together
other match
commands
Apply default action
Instead
match on other
things?
(permit)
no
Match all
packets
Therefore, the basic procedure for using a class-map as a filter is:
1. Make an ACL to match on MAC address or IP settings, and to specify the action that QoS
will take on traffic that matches the class-map.
You need an ACL to specify the action—unless the action is permit—even if you don’t
want to match on MAC address or IP settings. In that case, make an ACL with the desired
action and with both source and destination address of any. For example, if you want to
deny traffic from one VLAN ID, you need an ACL with action of deny and addresses of
any.
2. Create the class-map (see page 9).
Page 8 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 9

Making filters by using QoS class-maps
3. Specify what the class-map will match on (see page 9). This involves:
z attaching the ACL to the class-map
z using other match commands to further limit what the traffic will match the class-map
(unless the ACL’s settings were enough)
4. Attach the class-maps to a policy-map (see page 12).
5. Attach the policy-map to the ingress port or ports (see page 12).
The following sections describe how to do each of these steps (except creating ACLs—that’s
described from page 3).
Creating a class-map
To create a class-map, enter global configuration mode and use the command:
awplus(config)#class-map <name>
This puts you into class-map configuration mode.
Specifying what the class-map will match on
To do this, first attach the ACL to the class-map (unless you don’t need an ACL). In class-map
configuration mode, use the command:
awplus(config-cmap)#match access-group <number>
Next, use other match commands to further limit which traffic will match the class-map
(unless the ACL’s settings were enough). This means that you select the matching traffic by
using a combination of the ACL’s settings and the QoS match commands. The ACL and match
commands are ANDed together to make the class-map’s filtering rule. The available match
commands are:
match cos
match ip-dscp
match ip-precedence
match eth-format protocol (or match protocol eth-format)
match tpid
match inner-cos
match inner-tpid
match inner-vlan
match mac-type
match tcp-flags
match vlan
Most of these options are self-evident, but the following sections give more information
about the “inner” options, the TCP flags, and the eth-format and protocol options.
Except for TCP flags, each class-map can only match on one instance of each match type. If
you enter multiple matches of the same type, the class-map uses the last match you specify.
If you need more than one filtering rule on the port, create class-maps for each other filter.
Page 9 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 10

Making filters by using QoS class-maps
Matching on “inner” keywords for nested VLANs
The match tpid, match inner-tpid, match inner-vlan, and match inner-cos
commands all apply to nested VLAN configuration. In this situation, the packets arriving at
the core-facing port can have two VLAN tags configured on them.
z The match tpid command matches on the first Tag Protocol Identifier field in the packet.
z The match inner-tpid command matches on the TPID in the second 802.1Q tag in the
packet.
z The match inner-vlan command matches on the tunnelled VLAN ID in the second
802.1Q tag in the packet.
z The match inner-cos command matches on the 802.1P field in the second tag in the
packet.
The following table shows where in the packet the inner and outer tags will be matched.
Outer VLAN parameters
(normal)
Customer port VLAN 1st tag
Core port 1st tag 2nd tag
Nested VLANs disabled 1st tag 2nd tag
Inner VLAN parameters
Some important points to keep in mind while configuring the “inner” commands are:
z When packets arrive at a customer port of a nested VLAN, the command match vlan
will match the VID of the nested VLAN that the port is a member of, which is just how
this command normally operates.
z When packets arrive at a customer port of a nested VLAN, the “inner” commands will
match the attributes of the first tag in the packets. This is because when the packet is
forwarded from the core port, that first tag will have become the inner tag. So, from the
point of view of the nested VLAN, the tag that is on the packet when it arrives into the
customer port is the inner tag.
z When nested VLANs are disabled, and “inner” commands have been configured in class-
maps, these parameters will be applied as though all packets arriving at the switch were
double tagged. In other words, there will be no attempt to make a distinction between
“customer” and “core” ports. So, if the packets arriving at the switch are not double
tagged, then the “inner” commands will just match on whatever data happens to be in the
packets at the position where an inner tag would have been.
Therefore, when you disable nested VLANs, you should also remove the match
commands.
z When nested VLANs are being used, the commands match tpid and match cos cannot
be used in class-maps applied to customer ports.
z If you attach the class-map to a number of ports, they will all be treated like core ports if
at least one of the ports is a core port.
Page 10 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 11

Making filters by using QoS class-maps
Matching on TCP flag
Unlike the other match commands, you can match on multiple TCP flags. The switch
combines the specified flags by ANDing them together. To specify the multiple flags, either
make multiple match tcp-flags commands or specify the flags in one command as a space-
separated list. For example, the following series of commands will match on a packet that has
all of ACK, SYN and FIN set:
awplus(config)#class-map tcp-flags
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags ack
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags syn
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags fin
So will the following single match command:
awplus(config)#class-map tcp-flags
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags ack syn fin
Note that QoS only checks that the specified flags are set, not that the other flags are not
set. For example, the following commands will match on a packet that has both SYN and
ACK set, as well as a packet that has SYN but not ACK set:
awplus(config)#class-map tcp-flags
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags syn
To drop packets with SYN only, but not with ACK and SYN, you could use the following two
class-maps. Note that access-list 3000 is used to get a deny action. This example is explained
fully in "Blocking TCP sessions in one direction" on page 17.
awplus(config)#access-list 3000 deny tcp any any
awplus(config)#class-map ack-syn-flags
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags ack syn
awplus(config-cmap)#class-map syn-flags
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags syn
awplus(config-cmap)#match access-group 3000
awplus(config-cmap)#policy-map flags
awplus(config-pmap)#class ack-syn-flags
awplus(config-pmap-c)#class syn-flags
Page 11 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 12

Making filters by using QoS class-maps
Matching on eth-format and protocol
Ethernet format and protocol are specified together, as a pair. You can either specify the
command as:
match eth-format <keyword> protocol <keyword-or-number>
or
match protocol <keyword-or-number> eth-format <keyword>
The switch allows you to match on any of the Ethernet formats, as the following output
shows:
awplus(config-cmap)#match eth-format ?
802dot2-tagged 802.2 Tagged Packets
802dot2-untagged 802.2 Untagged Packets
ethii-tagged EthII Tagged Packets
ethii-untagged EthII Untagged Packets
netwareraw-tagged Netware Raw Tagged Packets
netwareraw-untagged Netware Raw Untagged Packets
snap-tagged SNAP Tagged Packets
snap-untagged SNAP Untagged Packets
Protocol options are also extremely flexible. You can identify common protocols by their
name, or you can identify any protocol by using its hexadecimal protocol number.
Applying the class-maps to a policy-map
To create a policy-map, enter global configuration mode and use the command:
awplus(config)#policy-map <name>
Then add the class-maps to the policy-map. Make sure you add them in the order in which
you want the switch to check them—see “The logic of the operation of the hardware filters”
on page 13. For each class-map, use the command:
awplus(config-pmap)#class <name>
Applying the policy-map to ports
To apply the policy-map to ports, enter interface mode for the ports you want to apply it to.
Use the commands:
awplus(config)#interface port1.0.11
awplus(config-if)#service-policy input <policy-name>
Page 12 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 13

The logic of the operation of the hardware filters
The logic of the operation of the hardware filters
The operation of the filters follows the standard ACL logic: if a packet matches an ACL on
the port, the comparison process stops and the action attached to the ACL is performed.
The switch checks ACLs in the order in which you attach them to the port.
For example, to reject all multicast traffic except 236.5.8.213, make one ACL to permit that
address and another ACL to deny all multicast traffic. Then attach the permit ACL to the
port before attaching the deny ACL.
If a packet fails to match any of the port’s ACLs, then the switch moves to the next stage of
comparison. The next stage is matching against QoS class-maps, if they exist. If the packet
matches a QoS class-map, it will be processed appropriately. If it does not match a class-map,
it will be processed as normal. Therefore, ACLs do not end in an implicit deny action to drop
non-matching traffic. But they also do not end in an implicit permit action that would bypass
other processing and forward non-matching traffic. The switch simply continues processing
non-matching traffic as normal.
Note: ACLs will match on packets that are destined for the switch itself (packets that would
be passed up to the switch's own CPU) in exactly the same way as they act on
packets that were destined to be forwarded directly by the switching chip.
Combining interface ACLs and QoS class-maps
The switch compares the packet with every interface ACL before it compares the packet
with any QoS class-maps. If the packet matches an interface ACL, the switch takes the action
specified by that ACL and stops the comparison process. If a packet matches both an
interface ACL and a QoS class-map, the packet only gets matched against the interface ACL.
It bypasses the QoS process.
If the action on the interface ACL is deny or send-to-cpu, then this is not a problem,
because the packet was never going to get into the QoS system anyway (given that it was
being discarded). But, if the action on the interface ACL is permit, copy-to-cpu, or copy-
to-mirror, and the packet would also be matched by a QoS class-map, then this is a problem.
The packet will not be matched by the QoS class-map, so the switch will not apply any
intended QoS-based filtering, policing, queue redirection, etc to the packet. Instead the
switch will forward the packet as if it belongs to the default class-map.
For this reason, we only recommend combining interface ACLs and QoS class-map filtering if
all your interface ACLs result in traffic being dropped. For traffic that you want forwarded
with QoS control, use QoS class-maps for both the filtering and the QoS actions. Of course,
you can also use QoS class-maps to drop traffic.
Page 13 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 14

Examples
Examples
Blocking all multicast traffic
This example uses an interface ACL with an action of deny.
Consider a situation where multiple clients are attached to the switch, with each client
attached to a different port. Each client has a specific service, which includes a set of allowed
traffic types.
The client on port 1.0.10 is using a service that does not allow any multicast packets to be
sent. To configure this:
1. Create an ACL to match and deny all packets with a multicast destination address. To do
this, enter global configuration mode and use the command:
awplus(config)#access-list 3100 deny ip any 224.0.0.0/4
2. Attach the ACL to port 1.0.10. To do this, use the commands:
awplus(config)#interface port1.0.10
awplus(config-if)#ip access-group 3100
3. Verify the configuration.
To see the ACL ID number and keywords, return to privileged exec mode and enter the
command:
awplus#show access-list
To see the ACLs that are attached to port 1.0.10, enter the command:
awplus#show interface port1.0.10 access-group
Page 14 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 15

Examples
Blocking all multicast traffic except one address
This example uses two interface ACLs, one with an action of permit and one with an action
of deny.
Use this type of configuration when you want to discard a wide range of traffic but want to
forward a subset of traffic within that range.
Consider a situation where you want to prevent the forwarding of multicast traffic in general,
but wish to support an application that needs to send packets to one particular multicast
address (236.5.8.213 in this example). To configure this:
1. Create an ACL to match and permit packets with the multicast destination address
236.5.8.213. To do this, enter global configuration mode and use the command:
awplus(config)#access-list 3050 permit ip any 236.5.8.213/32
2. Create an ACL to match and deny all packets with a multicast destination address. To do
this, use the command:
awplus(config)#access-list 3100 deny ip any 224.0.0.0/4
3. Attach the ACLs to the port (for example, 1.0.10). You must first attach the permit ACL,
then the deny ACL. To do this, use the commands:
awplus(config)#interface port1.0.10
awplus(config-if)#ip access-group 3050
awplus(config-if)#ip access-group 3100
Mirroring HTTP and SMTP traffic
This example uses two interface ACLs with actions of copy-to-mirror.
Use this type of configuration when you want to mirror a subset of the incoming traffic on a
port, instead of mirroring all incoming traffic.
Consider a situation where you want to capture the HTTP (TCP port 80) and SMTP (TCP
port 25) traffic coming to users who are connected to ports 1.0.1-1.0.2. To configure this:
1. Set port 1.0.20 as the mirror port. To do this, enter global configuration mode and use the
commands:
awplus(config)#interface port1.0.20
awplus(config-if)#mirror interface none direction both
2. Create ACLs to match HTTP and SMTP traffic. To do this, return to global configuration
mode and use the commands:
awplus(config)#access-list 3100 copy-to-mirror tcp any any eq 25
awplus(config)#access-list 3200 copy-to-mirror tcp any any eq 80
3. Attach the ACLs to ports 1.0.1-1.0.2. To do this, use the commands:
awplus(config)#interface port1.0.1-1.0.2
awplus(config-if)#ip access-group 3100
awplus(config-if)#ip access-group 3200
Page 15 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 16

Examples
Mirroring ARP packets
This example uses a QoS class-map.
Use this type of configuration when you want to mirror a subset of the incoming traffic on a
port, and you need to use QoS match commands to select the mirrored traffic.
Consider a situation where you want to capture ARP packets that arrive at port 1.0.10. To
configure this:
1. Set port 1.0.20 as the mirror port. To do this, enter global configuration mode and use the
commands:
awplus(config)#interface port1.0.20
awplus(config-if)#mirror interface none direction both
2. Create an ACL with an action of copy-to-mirror. This ACL will only be used to set the
action taken on the ARP traffic, not to select the traffic, so it needs to match all IP traffic.
To do this, return to global configuration mode and use the commands:
awplus(config)#access-list 3400 copy-to-mirror ip any any
3. Create a class-map that matches on ARP traffic and uses the ACL. To do this, use the
commands:
awplus(config)#class-map mirror-arp
awplus(config-cmap)#match protocol arp eth-format ethii-untagged
awplus(config-cmap)#match access-group 3400
4. Create a policy-map and add the class-map to it. To do this, use the commands:
awplus(config-cmap)#policy-map mirror-arp
awplus(config-pmap)#class mirror-arp
5. Apply the policy-map to port 1.0.10. To do this, use the commands:
awplus(config-pmap-c)#interface port1.0.10
awplus(config-if)#service-policy input mirror-arp
Page 16 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 17

Examples
Blocking TCP sessions in one direction
This example uses two QoS class-maps.
Administrators often want to block the establishment of TCP sessions in one direction, but
allow TCP sessions to be established in the opposite direction. To do this, it is necessary to
block the very first packet of an outgoing TCP session from being forwarded, but to allow
any packets that reply to the initiation of an incoming TCP session to be forwarded.
The very first packet of a TCP session has the SYN flag set, and no other flags. The reply to
that packet has the SYN and ACK flags set, and no other flags. So, to block TCP sessions
from being established in one direction, but not the other direction, we must block packets
that have only the SYN flag set, but allow packets that have both the SYN and ACK flags set.
To configure this on port 1.0.10:
1. Create an ACL with an action of deny. This ACL will only be used to set the action taken
on packets with only the SYN flag set, not to select the traffic, so it needs to match all IP
traffic. To do this, enter global configuration mode and use the command:
awplus(config)#access-list 3000 deny tcp any any
2. Create a class-map that matches on packets that have both the SYN and ACK flags set. To
do this, use the commands:
awplus(config)#class-map ack-syn-flags
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags ack syn
You want to permit this traffic, so you do not need to make an ACL to specify an action.
3. Create a second class-map that matches on packets that have only the SYN flag set. Use
the ACL to give this class-map an action of drop. To do this, use the commands:
awplus(config-cmap)#class-map syn-flags
awplus(config-cmap)#match tcp-flags syn
awplus(config-cmap)#match access-group 3000
4. Create a policy-map and add both class-maps to it. Add the class-map that matches both
flags first, followed by the class-map that drops packets with only the SYN flag. To do this,
use the commands:
awplus(config-cmap)#policy-map flags
awplus(config-pmap)#class ack-syn-flags
awplus(config-pmap-c)#class syn-flags
5. Apply the policy-map to port 1.0.10. To do this, use the commands:
awplus(config-pmap-c)#interface port1.0.10
awplus(config-if)#service-policy input flags
Page 17 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 18
How many filters can you create?
How many filters can you create?
The total number of filters that can be created is not an exact number, but depends on which
fields the various filters are matching on. So, to understand how to work out whether the set
of filters you are creating might run out of space, it is necessary to understand the way in
which the filters operate in the switch hardware.
There are two items within the switch hardware which set limits on the number of filters that
can be created: the filter rules table and the profile (mask).
Filters share the same filter rules table and mask whether they are made by applying ACLs
directly to ports or are made through QoS class-maps.
1. The filter rules table
One item that sets a limit on the number of filters is the table that contains the list of filter
rules. This has a strict limit of 1024 entries. An entry gets made when:
z You apply an ACL to a port (with the ip access-group or mac access-group command)
z You apply a QoS class-map to a port by applying its policy-map to a port (with the service-
policy input command). For each class-map, its ACL and any match commands are
ANDed together to make a single filter entry.
Therefore, every ACL or class-map uses up one table entry for every port that it is applied
to. Interface ACL rules come before QoS class-map rules. Conceptually, the table looks like:
port1.0.1 Interface ACL rule
Interface ACL rule
...
QoS class-map rule
QoS class-map rule
...
port1.0.2 Interface ACL rule
Interface ACL rule
...
QoS class-map rule
QoS class-map rule
...
... ...
If you specify a TCP or UDP port range, this may use multiple filter entries. The switch
converts the range to a series of single TCP/UDP port numbers plus masks. It uses as few
entries as possible to cover the range.
Also, the protocols that use filters (CPU protection and EPSR—see page 21) create one
entry per port.
Page 18 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 19

How many filters can you create?
2. The profile (mask)
The other item is called the profile. Conceptually, this is a 16-byte mask that decides which
set of bytes should be extracted from a packet as it enters the filtering process, to be
compared against all the interface ACLs and the QoS class-maps. All filters share a single
mask.
In effect, the mask is the sum of all the individual bytes required for each individual ACL or
QoS match command. The number of bytes required by each ACL or match command
depends on what fields it maps on. For example:
source MAC address—6 bytes
destination MAC address—6 bytes
Protocol type—2 bytes
Ethernet format—2 bytes
VLAN ID—2 bytes
IP protocol type (TCP, UDP, etc)—1 byte
source IP address—4 bytes
destination IP address—4 bytes
TCP port number—2 bytes
UDP port number—2 bytes
DSCP—1 byte
For example, if you make an ACL that matches on destination IP address and source TCP
port, this adds 7 bytes to the mask:
1 byte for the IP protocol field (to indicate TCP)
4 bytes for the destination IP address
2 bytes for the source TCP port number.
If you next make an ACL that matches on source MAC address, this adds 6 more bytes to the
mask.
If you next make a QoS class-map that matches on destination IP address (4 bytes) and DSCP
(1 byte), this adds 1 more byte to the mask, for the DSCP. It does not add 4 more bytes for
the destination IP address because the switch already matches on that field.
If you next make an ACL that matches on source IP address and source TCP port, then that
does not change the mask, because the switch already matches on those fields.
If you next make an ACL that matches on source UDP port, this also does not add any length
to the mask, because it shares the same 2 bytes as the source TCP port. However, if you next
make an ACL that matches on destination TCP or UDP port, that uses another 2 bytes.
Page 19 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 20

Are there enough bytes for your set of filters?
Of course, the mask cannot increase without limit—it has a maximum size of 16 bytes.
When it reaches the 16-byte limit, no more ACLs or QoS match commands can be created
which would cause the mask to increase in size. The switch can still accept ACLs or QoS
match commands that use fields that have already been included in the mask.
There is no particular number of ACLs or QoS match commands that will cause the mask to
reach its 16-byte limit—it could happen after a few ACLs, or you might be able to create
hundreds of ACLs and QoS match commands without the mask reaching its limit.
So to determine whether you will have enough filter length, look at the fields you want to
filter, determine the number of bytes for each field, and sum up the total number of
bytes. If that number is less than 16, there is enough filter length. Don’t forget to count TCP
and UDP source port as a single field, and likewise to count TCP and UDP destination port
as a single field.
Okay length For example, this set of ACLs would work:
source MAC address
source UDP port
destination IP address + destination TCP port
How many filters can you create?
The total number of bytes for the switch to check in a packet would be:
source MAC address + IP protocol type + source TCP/UDP port +
destination IP address + destination TCP/UDP port =
6 + 1 + 2 + 4 + 2 = 15 bytes
Too long But this set of ACLs would not work:
source MAC address
destination MAC address
destination IP address + destination TCP port
The total number of bytes for the switch to check in a packet would be:
source MAC address + destination MAC address + IP protocol type +
destination IP address + destination TCP/UDP port =
6 + 6 + 1 + 4 + 2 = 19 bytes
Page 20 | AlliedWare Plus™ OS How To Note
Page 21

USA Headquar ters | 19800 Nor th Cr eek Parkwa y | Suite 200 | Bothell | WA 98011 | USA | T: +1 800 424 4284 | F: +1 425 481 3895
Eur opean Headquar ters | Via Motta 24 | 6830 Chiasso | Switzerland | T: +41 91 69769.00 | F: +41 91 69769.11
Asia-Pacific Headquar ters | 11 T ai Seng Link | Singapor e | 534182 | T: +65 6383 3832 | F: +65 6383 3830
www .alliedtelesis.com
© 2007 Allied Te l esis,
Inc. All rights reser ved.Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
All company names, logos,and product designs that are trademar ks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis is a tr ademark or registered trademark of Allied Telesis, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
Some protocols also use filters, so use some of the length
The following protocols use filters, and therefore use up some of the available profile length
and filter entries:
CPU
protection
CPU protection is enabled by default. It controls the rate at which packets reach the CPU,
and uses filters to ensure that ARP and unregistered multicast packets get prioritised
appropriately.
It matches on:
Ethertype—2 bytes to check for ARP, and
VLAN tagging—2 bytes to check for tagged ARPs, and
destination MAC address—6 bytes to check for unregistered multicasts (01-00-5E-00-00-xx),
or
destination IP address—4 bytes to check for unregistered multicasts (224.0.0.x).
CPU protection automatically changes from using the destination MAC address to the
destination IP address if you configure a filter that uses destination IP address (as long as no
other filter already uses destination MAC address). This minimises the impact CPU
protection has on the number of filters available. However, it still uses 8-10 bytes of width.
If you are sure your network will not have an excessive rate of broadcast and multicast traffic,
you can turn off CPU protection by using the command no platform cpuprotection.
EPSR EPSR matches on VLAN ID, which uses 2 bytes. EPSR is disabled by default.
C613-16119-00 REV A
 Loading...
Loading...