Page 1

Ethernet
Network
®
Adapters
AT-2450FTX, AT-2451FTX,
AT-2700FX, AT-2701FX,
AT-2700FTX, AT-2701FTX,
AT-2745FX, AT-2746FX
Installation
Guide
PN 613-50669-00 Rev A
Page 2

Copyright © 2005 Allied Telesyn, Inc.
3200 North First Street, San Jose, CA 95134 USA
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesyn, Inc.
Microsoft is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation, Netscape Navigator is a registered trademark of Netscape
Communications Corporation. All other product names, company names, logos or other designations mentioned herein are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Allied Telesyn, Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without
prior written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied Telesyn, Inc. be
liable for any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not limited to lost profits, arising
out of or related to this manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesyn, Inc. has been advised of, known, or
should have known, the possibility of such damages.
Page 3
Electrical Safety and Emissions Standards
This product meets the following standards.
U.S. Federal Communications Commission
Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer Name: Allied Telesyn, Inc.
Declares that the product: Network Adapter Cards
Model Numbers: AT-2450FTX, AT-2451FTX, AT-2700FX, AT-2701FX, AT-2700FTX, AT-2701FTX, AT-2745FX,
AT-2746FX
These products comply with FCC Part 15B, Class B Limits:
These devices comply with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device
must not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
Radiated Energy
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device pursuant to Part 15
of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined
by turning the equipment off and on. The user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Changes and modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer or registrant of this equipment can void your
authority to operate this equipment under Federal Communications Commission rules.
Industry Canada
This Class Bdigital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du Canada.
RFI Emissions EN55022 Class B, EN61000-3-2, EN61000-3-3
Immunity EN55024
Electrical Safety EN60950 (TUV), UL 60950 (
CULUS
)
Laser Safety EN60825
3
Page 4
Translated Safety Statements
Important: Appendix E contains translated safety statements for installing this equipment. When
you see the , go to Appendix E for the translated safety statement in your language.
Wichtig: Anhang E enthält übersetzte Sicherheitshinweise für die Installation dieses Geräts. Wenn
Sie sehen, schlagen Sie in Anhang E den übersetzten Sicherheitshinweis in Ihrer Sprache nach.
Importante: El Apéndice E contiene mensajes de seguridad traducidos para la instalación de este
equipo. Cuando vea el símbolo , vaya al Apéndice E para ver el mensaje de seguridad traducido
a su idioma.
Important : L'annexe E contient les instructions de sécurité relatives à l'installation de cet
équipement. Lorsque vous voyez le symbole , reportez-vous à l'annexe E pour consulter la
traduction de ces instructions dans votre langue.
Importante: l’Appendice E contiene avvisi di sicurezza tradotti per l’installazione di questa
apparecchiatura. Il simbolo , indica di consultare l’Appendice E per l’avviso di sicurezza nella
propria lingua.
Важно: Приложение E содержит переведенную инструкцию по безопасности при установке
данного устройства. Если Вы встретите , перейдите к Приложению E для получения
переведенной инструкции по безопасности.
4
Page 5

Contents
Preface ................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
Document Conventions ....................................................................................................................................................... 10
Where to Find Web-based Guides ...................................................................................................................................... 11
Contacting Allied Telesyn .................................................................................................................................................... 12
Online Support ..............................................................................................................................................................12
Email and Telephone Support.......................................................................................................................................12
Returning Products........................................................................................................................................................12
For Sales or Corporate Information...............................................................................................................................12
Adapter Card Driver Updates ........................................................................................................................................12
Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview .................................................................................................................. 13
Overview.............................................................................................................................................................................. 14
AT-2450FTX and AT-2451FTX Series ................................................................................................................................ 16
Specifications ................................................................................................................................................................17
LEDs..............................................................................................................................................................................20
AT-2700FX and AT-2701FX Series..................................................................................................................................... 21
Specifications ................................................................................................................................................................22
LED ...............................................................................................................................................................................24
AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series ................................................................................................................................ 25
Specifications ................................................................................................................................................................26
LEDs..............................................................................................................................................................................28
AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series..................................................................................................................................... 30
Specifications ................................................................................................................................................................31
LEDs..............................................................................................................................................................................34
Additional Features.............................................................................................................................................................. 35
Wake on LAN ................................................................................................................................................................35
Driver Installation and the AT-Setup Utility....................................................................................................................36
Virtual LANs and the AT-MUX Protocol.........................................................................................................................37
Operating Statistics and the AT-Stat Utility ...................................................................................................................38
Diagnostics and the AT-Diag Utility...............................................................................................................................39
Load Balancing and Fail-over Protection ......................................................................................................................39
Managed Boot Agent.............................................................................................................
........................................43
Chapter 2: Installing a Network Adapter Card ............................................................................................................... 45
Verifying Package Contents ................................................................................................................................................ 46
Reviewing Safety Precautions............................................................................................................................................. 47
Installing the Low Profile Bracket......................................................................................................................................... 48
Installing a Network Adapter Card ....................................................................................................................................... 51
Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP ....................................................................................................... 57
Choosing a Network Adapter Card Driver ........................................................................................................................... 58
Installing or Updating a Driver Using the AT-Setup Utility ................................................................................................... 59
AT-Setup Guidelines .....................................................................................................................................................59
Running AT-Setup from the Installation CD ..................................................................................................................60
Running AT-Setup from a Driver Installation Diskette...................................................................................................66
Creating a Driver Installation Disk ....................................................................................................................................... 68
Manually Installing a Driver.................................................................................................................................................. 73
Manually Updating a Driver ................................................................................................................................................. 77
Removing a Driver............................................................................................................................................................... 85
Running AT-Setup to Complete Driver Installation.............................................................................................................. 90
Configuring the Network Adapter Card Settings.................................................................................................................. 91
5
Page 6

Contents
Configuring the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address .............................................................................. 92
Configuring Additional Network Adapter Card Settings................................................................................................ 96
Chapter 4: Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 .......................................................................................................................... 107
Installing the Driver on a Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 System ............................................................................................108
Removing the Driver from a Windows NT 4.0 System.......................................................................................................115
Chapter 5: Novell Netware 6.5 .......................................................................................................................................119
Installing the Network Adapter Driver on a Novell NetWare 6.5 System ...........................................................................120
Files Needed for Installation ....................................................................................................................................... 120
New Server Installation............................................................................................................................................... 120
Manual Installation...................................................................................................................................................... 121
Multiple Adapters........................................................................................................................................................ 122
Removing an Adapter Driver from Novell Netware 6.5 Server ................................................................................... 123
Chapter 6: Linux 2.4 and 2.6 ..........................................................................................................................................125
Installing the ATNIC Driver on Linux 2.4............................................................................................................................126
Limitations .................................................................................................................................................................. 126
Building the Driver ...................................................................................................................................................... 126
Installing the Driver..................................................................................................................................................... 126
Dynamic Loading........................................................................................................................................................ 127
Changing Configuration Settings................................................................................................................................ 127
Setting the Adapter’s Speed and Duplex Mode on Linux 2.6 ............................................................................................128
Phase 1 ...................................................................................................................................................................... 128
Phase 2 ...................................................................................................................................................................... 128
Chapter 7: Solaris 9 ........................................................................................................................................................129
Supported Operating System.............................................................................................................................................130
Installing the Driver ............................................................................................................................................................130
Configuring the Network Adapter Card..............................................................................................................................131
Removing the Driver ..........................................................................................................................................................132
Chapter 8: AT-Stat Utility ...............................................................................................................................................133
Installing the AT-Stat Utility................................................................................................................................................134
Installing with a CD Drive............................................................................................................................................ 134
Installing without a CD Drive....................................................................................................................................... 140
Using the AT-Stat Utility.....................................................................................................................................................142
Starting the AT-Stat Utility .......................................................................................................................................... 142
General Tab................................................................................................................................................................ 143
Statistics Tab.............................................................................................................................................................. 147
Ping Tab ..................................................................................................................................................................... 150
NetCheck Tab............................................................................................................................................................. 151
Support Tab................................................................................................................................................................ 152
Removing the AT-Stat Utility..............................................................................................................................................153
Chapter 9: AT-MUX Multiple VLAN Protocol ................................................................................................................ 157
AT-MUX Protocol Overview...............................................................................................................................................158
Installing the AT-MUX Protocol..........................................................................................................................................162
Adding, Changing, or Deleting VIDs ..................................................................................................................................168
Removing the AT-MUX Protocol........................................................................................................................................ 173
Chapter 10: AT-Diag Utility ............................................................................................................................................175
Starting the AT-Diag Utility.................................................................................................................................................176
Diagnostics Tests Option...................................................................................................................................................179
Communications Test Option............................................................................................................................................. 181
Hardware Information Option....................................................................................................
Settings Option .................................................................................................................................................................. 184
Speed/Duplex Selection ............................................................................................................................................. 184
Default Port................................................................................................................................................................. 184
BootROM.................................................................................................................................................................... 185
Select Adapter Option........................................................................................................................................................ 186
Technical Support Option .................................................................................................................................................. 187
......................................... 183
6
Page 7

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Chapter 11: Troubleshooting ......................................................................................................................................... 189
Appendix A: Technical Specifications .......................................................................................................................... 193
Physical Specifications ......................................................................................................................................................193
Operating Voltage.............................................................................................................................................................. 193
Environmental Specifications.............................................................................................................................................193
Electrical Safety and Emissions Standards ....................................................................................................................... 194
Twisted Pair Port Pin-outs ................................................................................................................................................. 194
Appendix B: Unattended Microsoft Windows Installations ........................................................................................ 195
Unattended Microsoft Windows XP Installation................................................................................................................. 196
What the Steps Do ......................................................................................................................................................196
Unattended Setup .......................................................................................................................................................196
Appendix C: Optional BootPROM Chip and DIP Switch Settings .............................................................................. 199
Installing a BootPROM Chip.............................................................................................................................................. 200
DIP Switch Settings ........................................................................................................................................................... 202
Appendix D: Cleaning Fiber Optic Connectors ........................................................................................................... 203
Using a Cartridge-Type Cleaner........................................................................................................................................ 204
Using a Swab .................................................................................................................................................................... 206
Appendix E: Translated Safety Statements ................................................................................................................. 209
Index ................................................................................................................................................................................ 235
7
Page 8

Contents
8
Page 9

Preface
This guide contains installation instructions for the following Allied Telesyn
network adapter card series:
AT-2450FTX
AT-2451FTX
AT-2700FX
AT-2701FX
AT-2700FTX
AT-2701FTX
AT-2745FX
AT-2746FX
Note
The AT-2450FTX, AT-2700FX, AT-2700FTX, and AT-2745FX Series
are no longer available from Allied Telesyn and have been replaced
by the AT-2451FTX, AT-2701FX, AT-2701FTX, and AT-2746FX
Series, respectively. They are described in this guide for reference
purposes for those networks where the cards are already installed.
9
Page 10

Preface
Document Conventions
This guide uses the following conventions:
Note
Notes provide additional information.
Caution
Cautions inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warning
Warnings inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in bodily injury.
10
Page 11

Where to Find Web-based Guides
The installation and user guides for all Allied Telesyn products are
available in Portable Document Format (PDF) from our web site at
www.alliedtelesyn.com. You can view the documents on-line or
download them onto a local workstation or server.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
11
Page 12

Preface
Contacting Allied Telesyn
This section provides Allied Telesyn contact information for technical
support as well as sales or corporate information.
Online Support You can request technical support online by accessing the Allied Telesyn
Knowledge Base from the following web site: www.alliedtelesyn.com/kb.
You can use the Knowledge Base to submit questions to our technical
support staff and review answers to previously asked questions.
Email and
Telephone
Support
Returning
Products
For Sales or
Corporate
Information
Adapter Card
Driver Updates
For Technical Support via email or telephone, refer to the Support &
Services section of the Allied Telesyn web site: www.alliedtelesyn.com.
Products for return or repair must first be assigned a Return Materials
Authorization (RMA) number. A product sent to Allied Telesyn without a
RMA number will be returned to the sender at the sender’s expense.
To obtain a RMA number, contact Allied Telesyn’s Technical Support at
our web site: www.alliedtelesyn.com.
You can contact Allied Telesyn for sales or corporate information at our
web site: www.alliedtelesyn.com. To find the contact information for your
country, select Contact Us -> Worldwide Contacts.
You can download new releases of network adapter card drivers from
either of the following Internet sites:
❑ Allied Telesyn web site: www.alliedtelesyn.com
❑ Allied Telesyn FTP server: ftp://ftp.alliedtelesyn.com
12
To download new firmware from the Allied Telesyn FTP server using your
workstation’s command prompt, you will need FTP client software and you
must log in to the server. Enter “anonymous” as the user name and your
email address for the password.
Page 13

Chapter 1
Network Adapter Card Overview
This chapter describes the features of the Allied Telesyn network adapter
cards. Sections in the chapter include:
“Overview” on page 14
“AT-2450FTX and AT-2451FTX Series” on page 16
“AT-2700FX and AT-2701FX Series” on page 21
“AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series” on page 25
“AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series” on page 30
“Additional Features” on page 35
13
Page 14

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
Overview
The Allied Telesyn Ethernet network adapter cards are designed to
simplify the task of building a new 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps Ethernet network
or expanding an existing one. Offered in a variety of port configurations,
these adapters give you the power and flexibility to build an Ethernet
network suited to the unique requirements of your business environment.
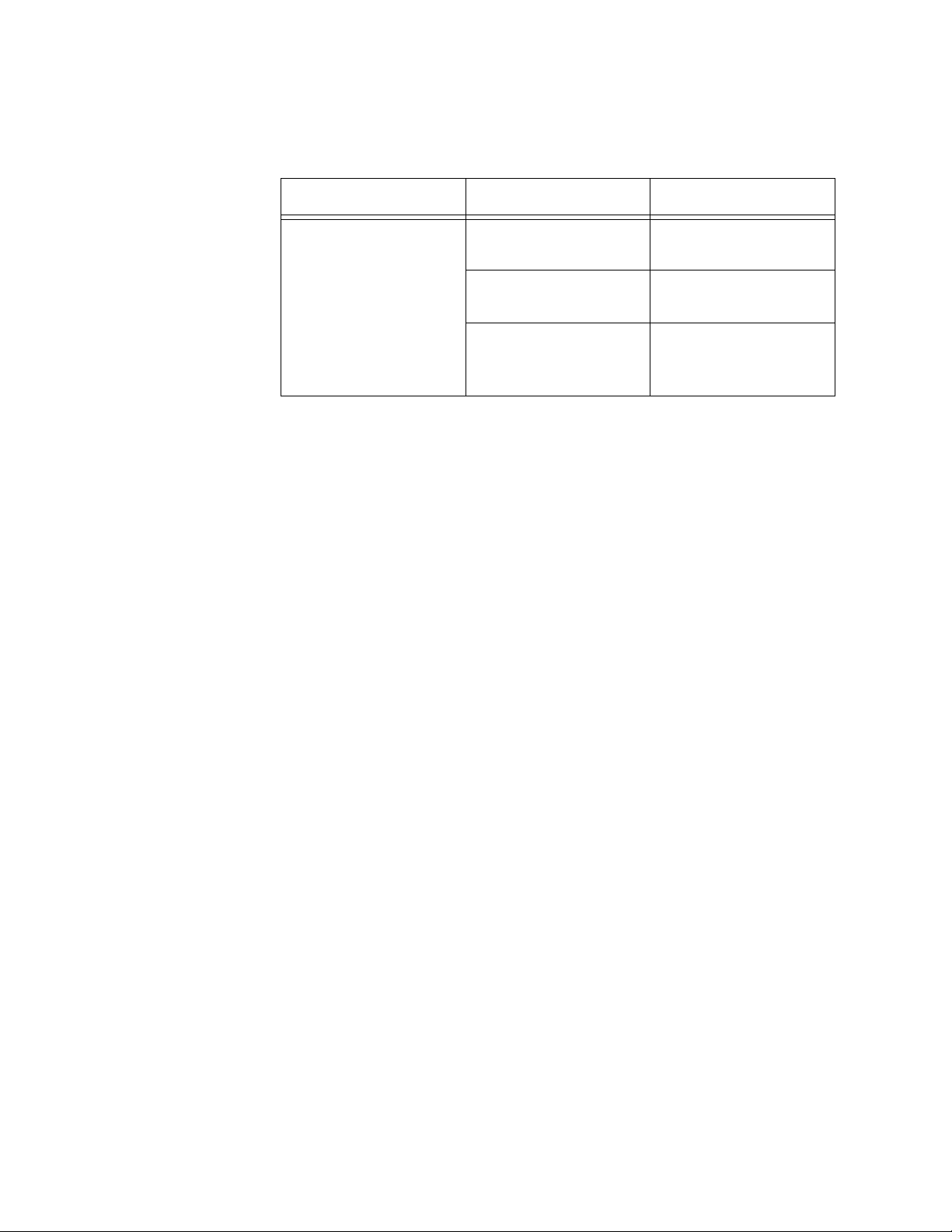
Table 1 lists the port configurations of the network adapter card series
described in this guide.
Table 1. Port Configurations
Series
AT-2450FTX 10/100Base-TX 10Base-FL -
AT-2451FTX 10/100Base-TX 10Base-FL -
AT-2700FX - 100Base-FX -
AT-2701FX - 100Base-FX -
AT-2700FTX 10/100Base-TX 100Base-FX -
AT-2701FTX 10/100Base-TX 100Base-FX -
AT-2745FX - 10Base-FL 100Base-FX
AT-2746FX - 10Base-FL 100Base-FX
Note
The AT-2450FTX, AT-2700FX, AT-2700FTX, and AT-2745FX Series
are no longer available from Allied Telesyn. They have been
replaced by the AT-2451FTX, AT-2701FX, AT-2701FTX, and
AT-2746FX Series, respectively. They are described in this guide for
reference purposes for those networks where the cards are already
installed.
Twisted Pair
Port
Fiber Optic
Port
Second Fiber
Optic Port
14
As shown in Table 1, most of the network adapter cards discussed in this
manual are dual port adapters. A dual port card has either a twisted pair
port and a fiber optic port or two fiber optic ports.
Dual port adapters can simplify the installation and maintenance of your
network because the same network adapter card can be used for either
twisted pair cable or fiber optic cable. This eliminates the need of
purchasing different cards for different cable media and so reduces the
number of types of adapters needed to build your network.
Page 15

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Dual port adapters also simplify the task of relocating nodes in a network.
When a node is moved to a new location that also involves a change to the
media connection, such as from twisted pair cable to fiber optic cable, no
change to the adapter is necessary since the adapter has ports for both
types of medium.
Selecting which port to use on a dual port adapter is usually dictated by
the distance of the node from the Ethernet switch of hub or the working
environment. The maximum operating distance for the twisted pair port is
100 meters, typically making this port appropriate for nodes within that
operating distance from the Ethernet switch or hub.
The fiber optic port is appropriate for nodes that are greater than 100
meters from the switch or hub or in working environments where
electromagnetic emissions from manufacturing or other heavy equipment
could affect network transmissions over twisted pair cabling.
All of the adapters described in this guide use the same network adapter
card drivers. This further simplifies the task of network maintenance by
reducing the number of drivers you need to maintain.
15
Page 16

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
AT-2450FTX and AT-2451FTX Series
The adapters in the AT-2450FTX Series are:
AT-2450FTX/SC
AT-2450FTX/ST
The adapters in the AT-2451FTX Series are:
AT-2451FTX/SC
AT-2451FTX/ST
These are dual port adapters. They feature a twisted pair port and a fiber
optic port. The twisted pair port has a standard RJ-45 connector and
operates at either 10 or 100 Mbps (10Base-T/100Base-TX), half- or fullduplex mode. The adapter features Auto-Negotiation, which allows the
network adapter port to automatically set its speed and duplex mode to
match the settings of the port on the remote device, such as an Ethernet
switch or hub.
The second port is a fiber optic port with either a duplex SC or duplex ST
connector, depending on the model. This port has a fixed operating speed
of 10 Mbps (10Base-FL), half- or full-duplex mode. The default setting is
full-duplex. The duplex mode must be set manually.
Note
You can use only one port on this adapter at a time. Do not attach
both ports to the network at the same time.
Differences between the two series are:
The AT-2450FTX Series is PCI 2.1-compliant.
The AT-2451FTX Series is PCI 2.2-compliant.
The AT-2450FTX Series was offered in two versions — a standard
version and a low profile version for systems that accept only low
profile adapters.
The AT-2451FTX Series can be installed in either a standard or low
profile system. The adapter comes with two brackets, one for a
standard system and another for a low profile system.
The BootPROM and Managed Boot Agent (MBA) were optional with
the AT-2450FTX Series.
16
The BootPROM and MBA come standard with the AT-2451FTX
Series.
Page 17
The AT-2450FTX Series supported the Wake on LAN feature only on
the twisted pair port.
The AT-2451FTX Series supports the Wake on LAN feature on both
ports.
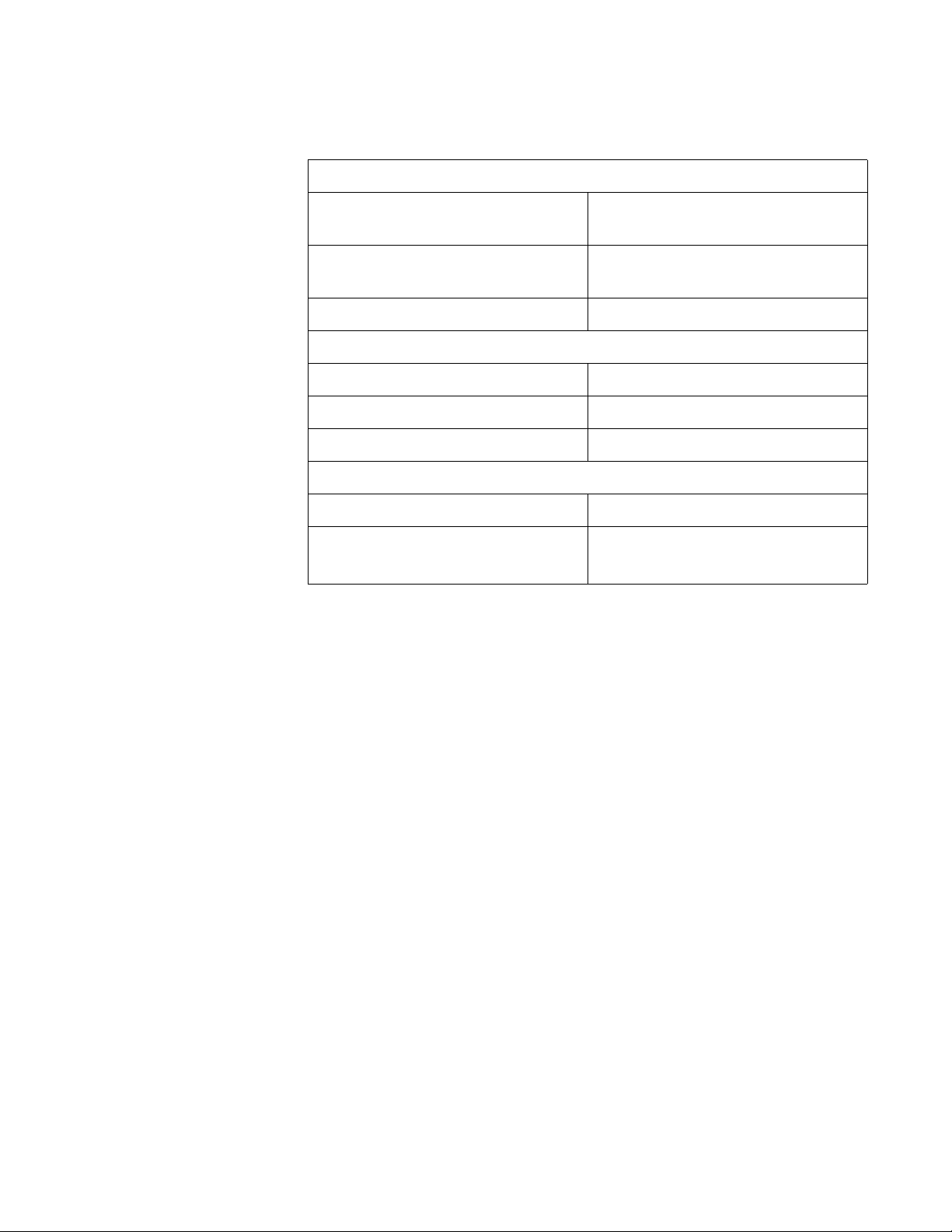
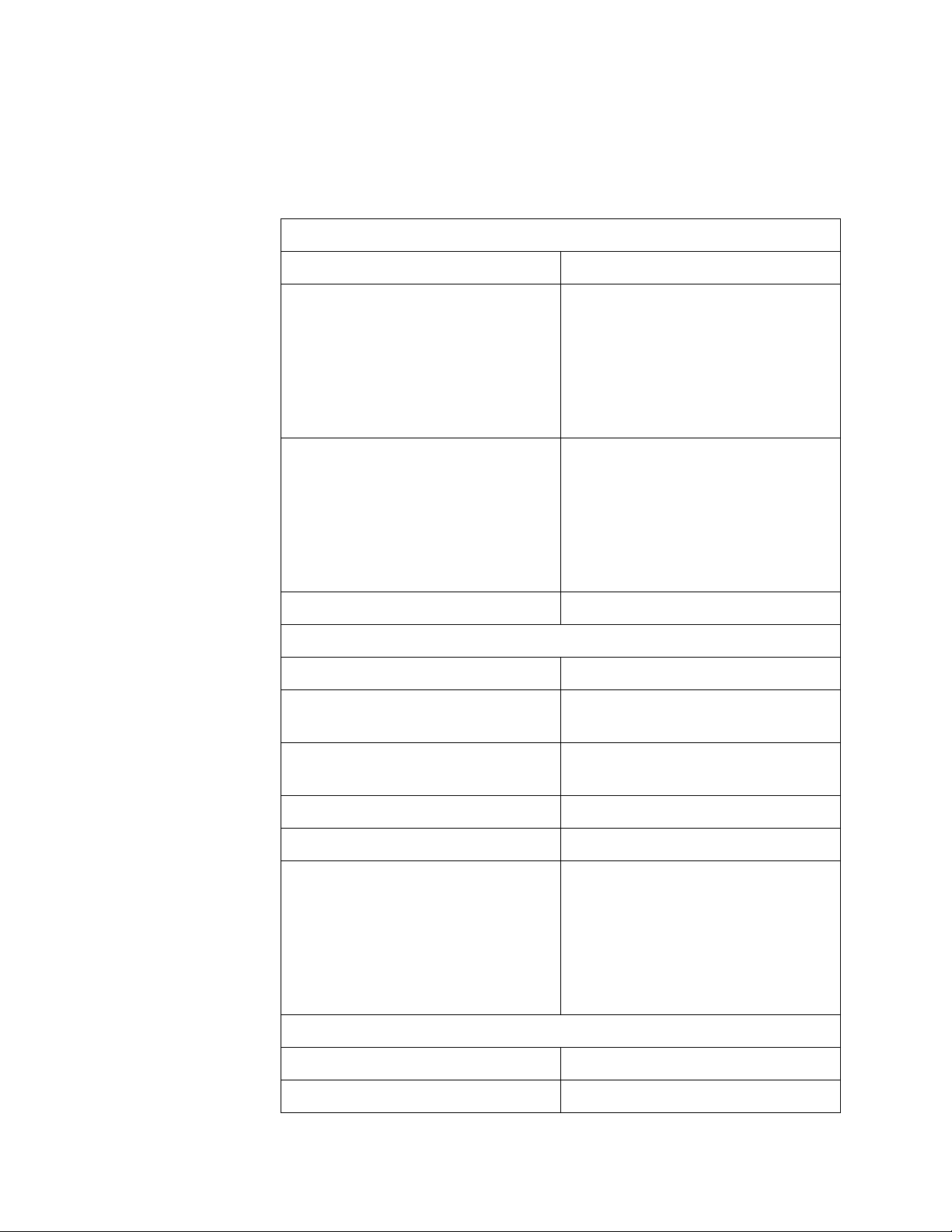
Specifications Table 2 lists the adapter specifications.
Table 2. AT-2450FTX and AT-2451FTX Series Network Adapter
Cards
Basic Features
Supported Platforms IBM PC or compatible
Supported Operating Systems Microsoft Windows 2000
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Microsoft Windows 2003
Microsoft Windows XP
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
Novell Netware 6.5
Linux 2.4 and 2.6
Solaris 9
Motherboard Connector AT-2450FTX Series:
PCI bus 2.1-compliant
(32-bit bus width)
AT-2451FTX Series:
PCI bus 2.2-compliant
(32-bit bus width)
Number of Ports 2
Twisted Pair Port
Standards 10Base-T and 100Base-TX
Speed 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps
(Default: Auto-Negotiation)
Duplex Mode Half- or full-duplex
(Default: Auto-Negotiation)
Type of Connector RJ-45
Maximum Operating Distance 100 meters (328 feet)
17
Page 18
Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
Type of Cabling 10Base-T operation:
Wiring Configuration MDI
Fiber Optic Port
Standard 10Base-FL
Speed 10 Mbps
Duplex Mode Half- or full-duplex
Table 2. AT-2450FTX and AT-2451FTX Series Network Adapter
Cards (Continued)
Category 3 or better 100 ohm
shielded or unshielded twisted
pair cable
100Base-TX operation:
Category 5 or better 100 ohm
shielded or unshielded twisted
pair cable
(Default: Full-duplex)
Type of Connector AT-2450FTX/SC - duplex SC
AT-2450FTX/ST - duplex ST
AT-2451FTX/SC - duplex SC
AT-2451FTX/ST - duplex ST
Maximum Operating Distance
1
2 kilometers (1.2 miles)
Type of Cabling 50/125 or 62.5/125 micron (core/
cladding) multimode fiber optic
cable
Operating Specifications Wavelength: 820 nm
Output power - 50/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -18.8 dBm
Maximum: -13.8 dBm
Output power - 62.5/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -15.0 dBm
Maximum: -10.0 dBm
18
Input sensitivity:
Typical: -4.4 dBm
Page 19
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Table 2. AT-2450FTX and AT-2451FTX Series Network Adapter
Cards (Continued)
Wake on LAN Feature
AT-2450FTX Series Supported on twisted pair port
only.
AT-2451FTX Series Supported on both twisted pair
port and fiber optic port.
Default Setting Disabled
BootPROM Chip and MBA Feature
AT-2450FTX Series Optional
AT-2451FTX Series Standard
Default Port 10/100Base-TX
Load Balancing and Fail-over Protection
AT-2450FTX Series Not supported
AT-2451FTX Series
Supported
2
Default setting: Disabled
1. Numerous factors, such as too many splices or poorly implemented splices,
can significantly reduce the maximum distance of a fiber optic port. Fiber optic
cable should only be installed by a qualified fiber optic cable contractor.
2. Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP.
19
Page 20
Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
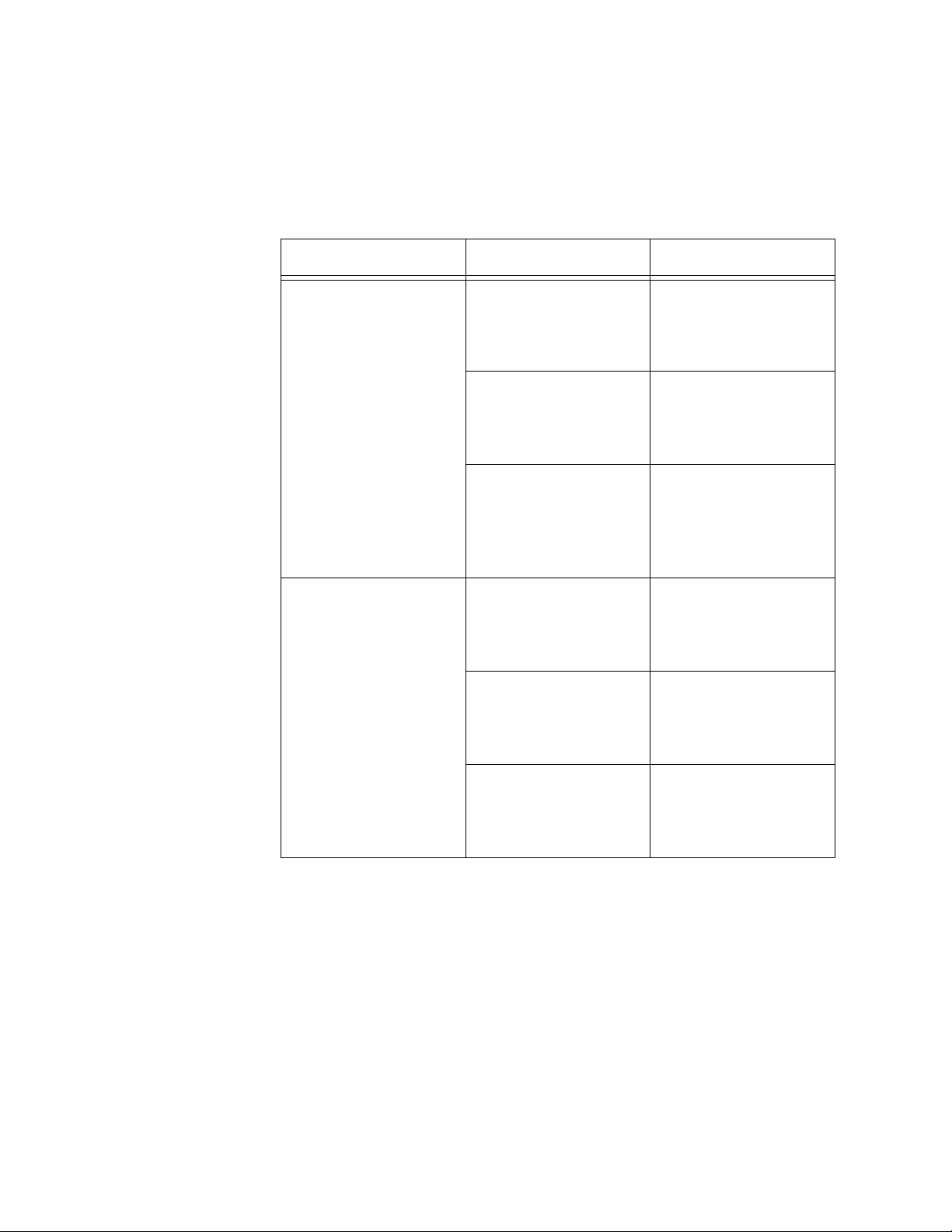
LEDs Table 3 describes the LEDs for the ports on the AT-2450FTX and
AT-2451FTX Series. The twisted pair port uses the 10 or 100 LED,
depending on its operating speed. The fiber optic port uses just the 10
LED.
10 Green The twisted pair port
Table 3. AT-2450FTX and AT-2451FTX Series LEDs
LED Status Description
or fiber optic port is
operating at 10 Mbps,
full-duplex mode.
Amber The twisted pair port
or fiber optic port is
operating at 10 Mbps,
half-duplex mode.
Flashing The twisted pair port
or fiber optic port is
receiving or
transmitting network
packets at 10 Mbps.
100 Green The twisted pair port
is operating at 100
Mbps, full-duplex
mode.
Amber The twisted pair port
is operating at 100
Mbps, half-duplex
mode.
Flashing The twisted pair port
is receiving or
transmitting network
packets at 100 Mbps.
20
Page 21

AT-2700FX and AT-2701FX Series
The adapters in the AT-2700FX Series are:
AT-2700FX/SC
AT-2700FX/ST
AT-2700FX/MT
AT-2700FX/VF
The adapters in the AT-2701FX Series are:
AT-2701FX/SC
AT-2701FX/ST
AT-2701FX/MT
AT-2701FX/VF
These adapters feature a single fiber optic port with a fixed operating
speed of 100 Mbps with half- or full-duplex operation. The port has a
maximum operating distance of 2 kilometers in full-duplex mode and uses
50/125 or 62.5/125 micron (core/cladding) multimode fiber optic cable.
Maximum operating distance will be less for half-duplex mode.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
These adapters are appropriate in network environments where the
distance between an end node and an Ethernet hub or switch is more than
100 meters, the maximum allowed for twisted pair cable, or in
manufacturing areas or other heavy equipment environments where
electromagnetic emissions could interfere with nodes connected with
twisted pair cable.
Differences between the two series are:
The AT-2700FX Series is PCI 2.1-compliant.
The AT-2701FX Series is PCI 2.2-compliant.
The AT-2700FX Series was offered in two versions — a standard
version and a low profile version for systems that accept only low
profile adapters.
The AT-2701FX Series can be installed in either a standard or low
profile system. The adapter comes with two brackets, one for a
standard system and another for a low profile system.
The BootPROM chip and MBA were optional with the AT-2700FX
Series.
The BootPROM chip and MBA come standard with the AT-2701FX
Series.
21
Page 22
Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
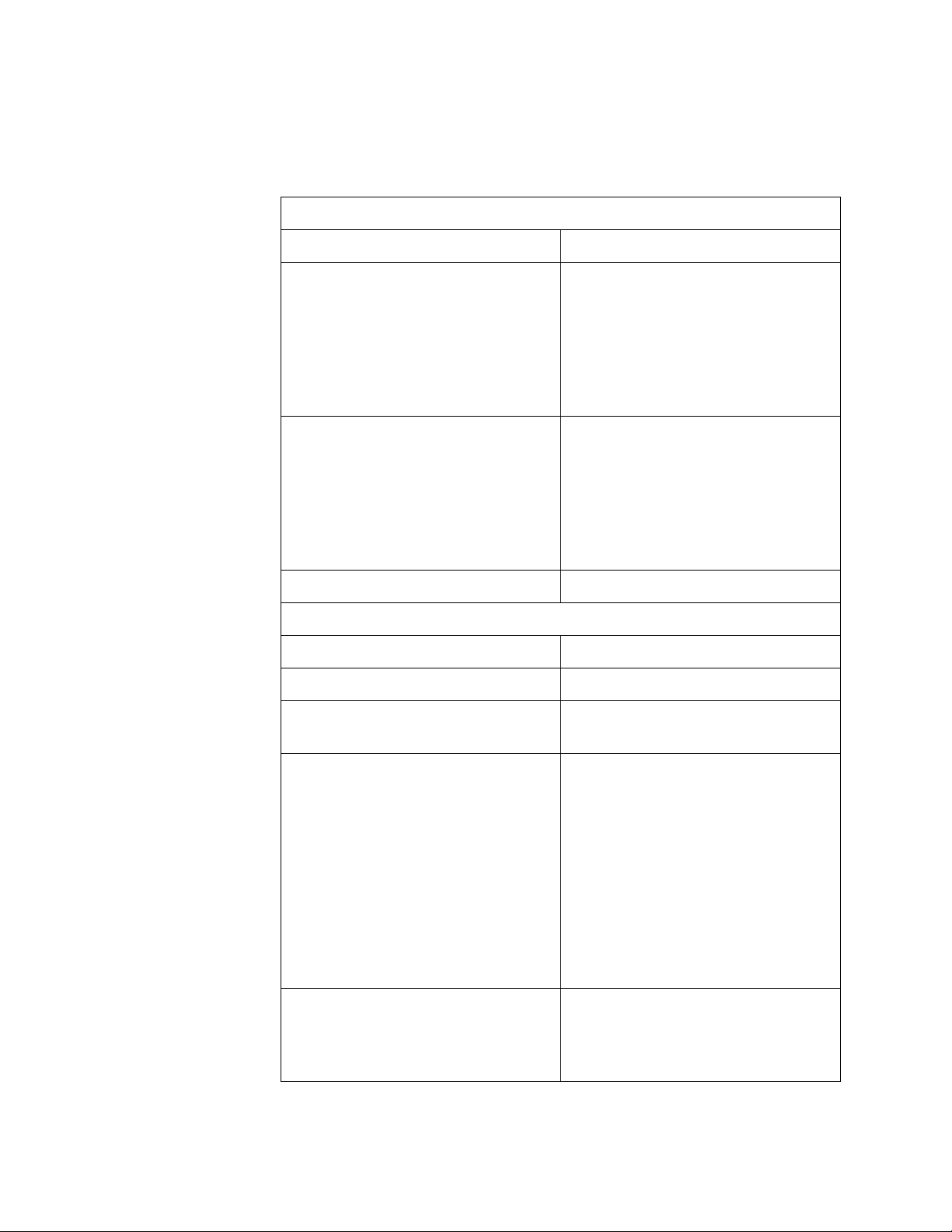
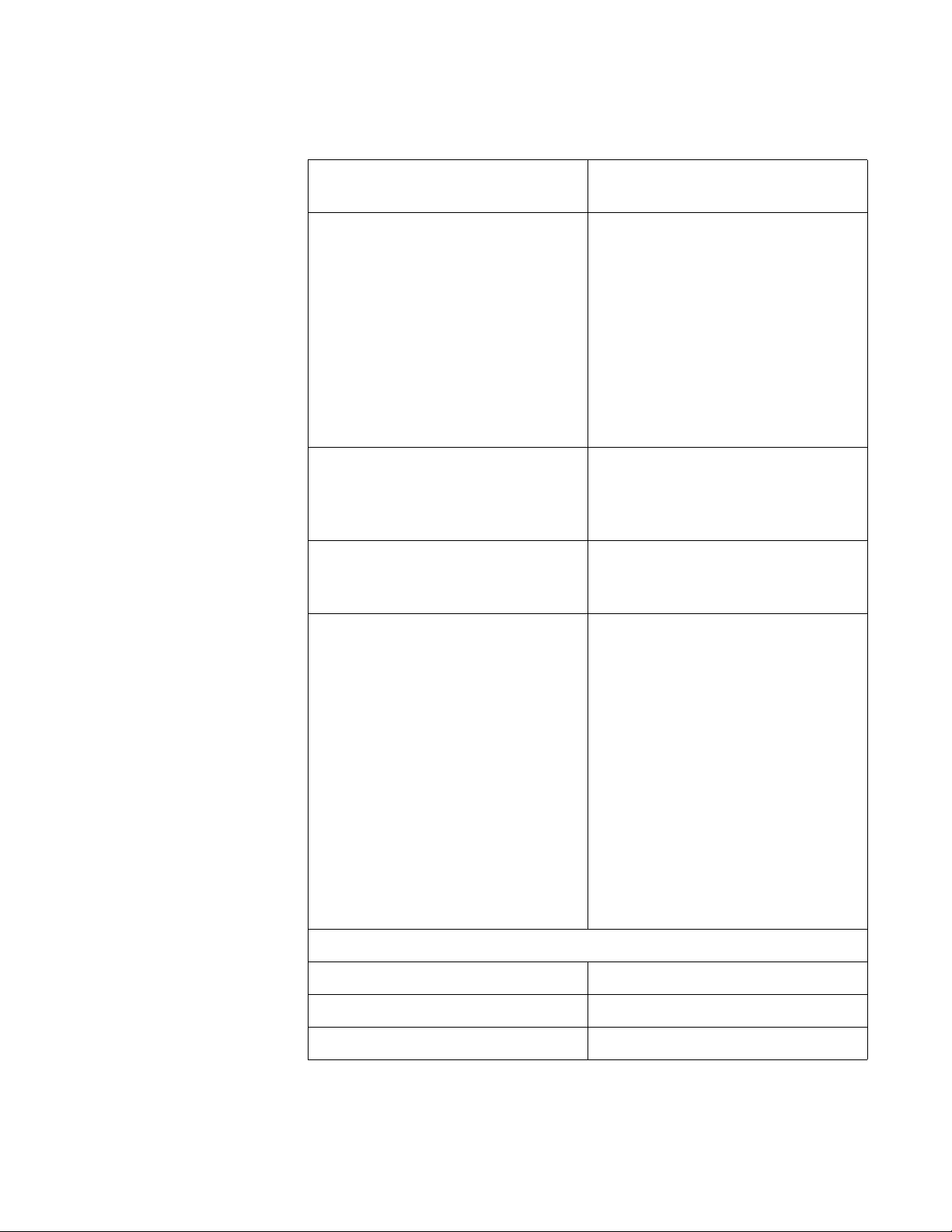
Specifications Table 4 lists the adapter specifications.
Table 4. AT-2700FX and AT-2701FX Series Network Adapter
Basic Features
Supported Platforms IBM PC or compatible
Supported Operating Systems Microsoft Windows 2000
Motherboard Connector AT-2700FX Series:
Cards
Microsoft Windows 2003
Microsoft Windows XP
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
Novell Netware 6.5
Linux 2.4 and 2.6
Solaris 9
PCI bus 2.1-compliant
(32-bit bus width)
AT-2701FX Series:
PCI bus 2.2-compliant
(32-bit bus width)
Number of Ports 1
Fiber Optic Port
Standard 100Base-FX
Speed 100 Mbps
Duplex Mode Half- or full-duplex
(Default: full-duplex)
Type of Connector AT-2700FX Series:
AT-2700FX/SC - duplex SC
AT-2700FX/ST - duplex ST
AT-2700FX/MT - MT-RJ
AT-2700FX/VF - VF-45
AT-2701FX Series
AT-2701FX/SC - duplex SC
AT-2701FX/ST - duplex ST
AT-2701FX/MT - MT-RJ
AT-2701FX/VF - VF-45
22
Maximum Operating Distance
1
2 kilometers (1.2 miles) in fullduplex mode
412 meters (1236 feet) in halfduplex mode
Page 23
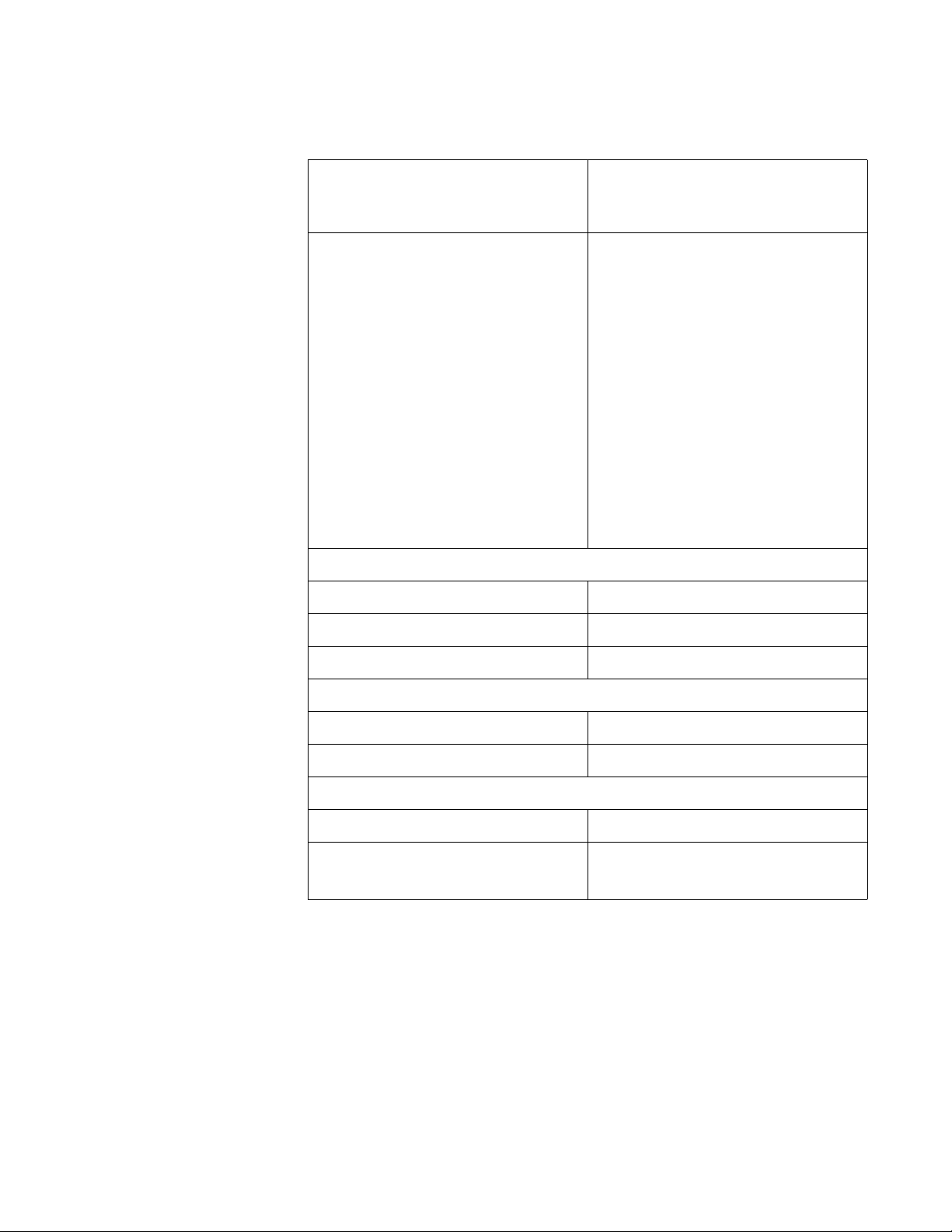
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Table 4. AT-2700FX and AT-2701FX Series Network Adapter
Cards (Continued)
Type of Cabling 50/125 or 62.5/125 micron (core/
cladding) multimode fiber optic
cable
Operating Specifications Wavelength: 1310 nm
Output power - 50/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -22.5 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Output power - 62.5/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -19.0 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Input sensitivity:
Minimum: -31 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Wake on LAN Feature
AT-2700FX Series Supported
AT-2701FX Series Supported
Default Setting Disabled
BootPROM Chip and MBA Feature
AT-2700FX Series Optional
AT-2701FX Series Standard
Load Balancing and Fail-over Protection
AT-2700FX Series Not supported
AT-2701FX Series
Supported
2
Default setting: Disabled
1. Numerous factors, such as too many splices or poorly implemented splices,
can significantly reduce the maximum distance of a fiber optic port. Fiber optic
cable should only be installed by a qualified fiber optic cable contractor.
2. Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP.
23
Page 24
Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
LED The AT-2700FX and AT-2701FX Series have one LED, defined in Table 5.
100 Green The port is operating
Table 5. AT-2700FX and AT-2701FX Series LED
LED Status Description
in full-duplex mode.
Amber The port is operating
in half-duplex mode.
Blinking The port is receiving
or transmitting
network traffic.
24
Page 25

AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series
The adapters in the AT-2700FTX Series are:
AT-2700FTX/SC
AT-2700FTX/ST
AT-2700FTX/MT
AT-2700FTX/VF
The adapters in the AT-2701FTX Series are:
AT-2701FTX/SC
AT-2701FTX/ST
AT-2701FTX/MT
AT-2701FTX/VF
These dual-port adapters feature a 10/100Base-TX twisted pair port and a
100Base-FX fiber optic port. The twisted pair port features AutoNegotiation and can operate at either 10 or 100 Mbps, half- or full-duplex
mode. The fiber optic port has a fixed operating speed of 100 Mbps
(100Base-FX), half- or full-duplex mode, and a maximum operating
distance of 2 kilometers (1.28 miles) in full-duplex mode. Maximum
distance for the fiber optic port is less for half-duplex mode.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Note
You can use only one port on this adapter at a time. Do not attach
both ports to the network at the same time.
Differences between the two series are:
The AT-2700FTX Series is PCI 2.1-compliant.
The AT-2701FTX Series is PCI 2.2-compliant.
The AT-2700FTX Series was offered in two versions — a standard
version and a low profile version for systems that accept only low
profile adapters.
The AT-2701FTX Series can be installed in either a standard or low
profile system. The adapter comes with two brackets, one for a
standard system and another for a low profile system.
The BootPROM chip and MBA were optional with the AT-2700FTX
Series.
The BootPROM chip and MBA come standard with the AT-2701FTX
Series.
25
Page 26
Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
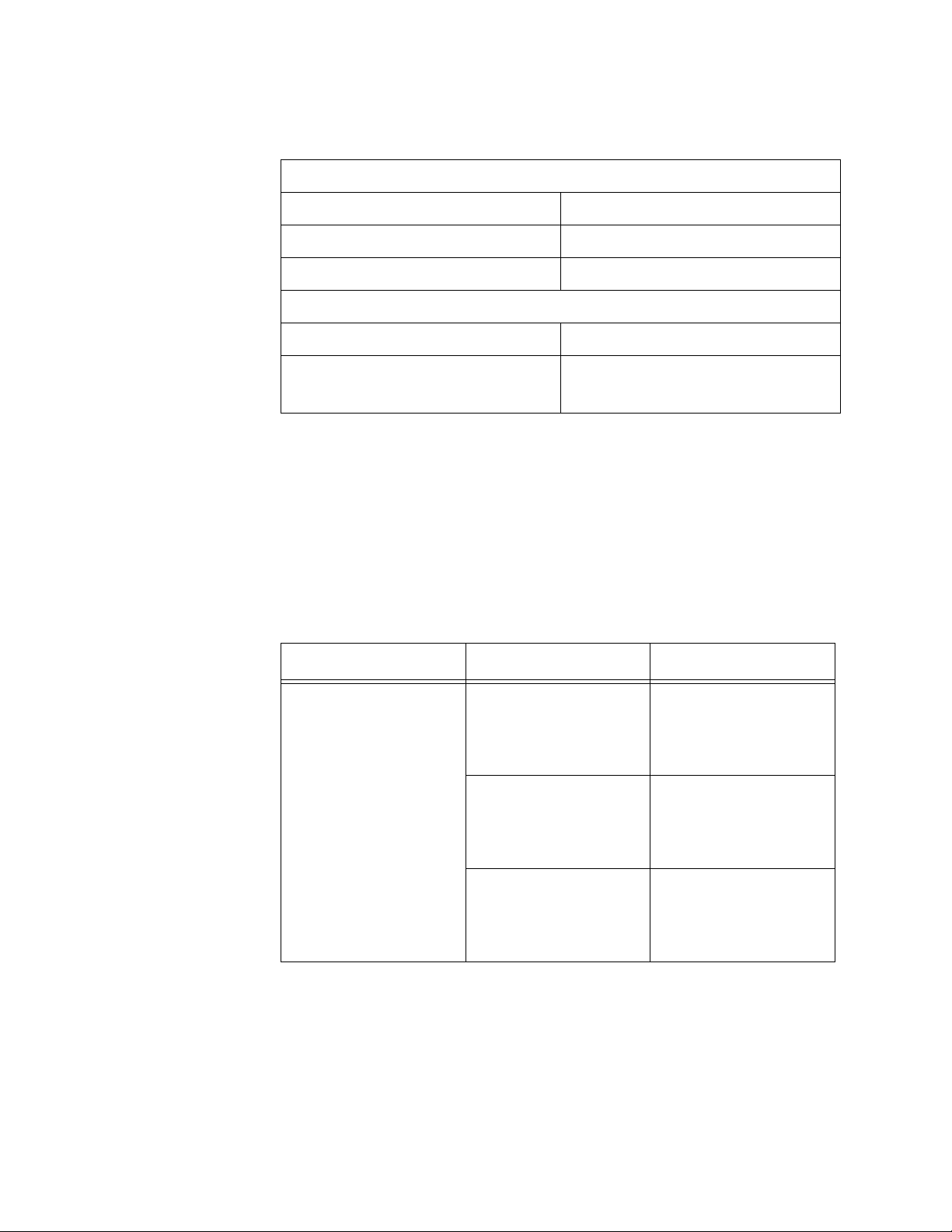
Specifications Table 6 lists the specifications of the AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX
Series adapter cards.
Table 6. AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series Network Adapter
Cards
Basic Features
Supported Platforms IBM PC or compatible
Supported Operating Systems Microsoft Windows 2000
Microsoft Windows 2003
Microsoft Windows XP
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
Novell Netware 6.5
Linux 2.4 and 2.6
Solaris 9
Type of Motherboard Connector AT-2700FTX Series:
PCI bus 2.1-compliant
(32-bit bus width)
AT-2701FTX Series:
PCI bus 2.2-compliant
(32-bit bus width)
Number of Ports 2
Twisted Pair Port
Standards 10Base-T and 100Base-TX
Speed 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps
(Default: Auto-Negotiation)
Duplex Mode Half- or full-duplex
(Default: Auto-Negotiation)
Type of Connector RJ-45
Maximum Operating Distance 100 m (328 ft.)
Type of Cabling 10Base-T operation:
100 Ohm shielded or
unshielded Category 3 or better
100Base-TX operation:
100 Ohm shielded or
unshielded Category 5 or better
26
Fiber Optic Port
Standard 100Base-FX
Speed 100 Mbps
Page 27
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Table 6. AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series Network Adapter
Cards (Continued)
Duplex Mode Half- or full-duplex
(Default: full-duplex)
Type of Connector AT-2700FTX Series:
AT-2700FTX/SC - duplex SC
AT-2700FTX/ST - duplex ST
AT-2700FTX/MT - MT-RJ
AT-2700FTX/VF - VF-45
AT-2701FTX Series:
AT-2701FTX/SC - duplex SC
AT-2701FTX/ST - duplex ST
AT-2701FTX/MT - MT-RJ
AT-2701FTX/VF - VF-45
Maximum Operating Distance
1
2 km (1.24 miles) in full-duplex
mode
412 m (1373 feet) in half-duplex
mode
Type of Cabling 50/125 or 62.5/125 micron (core/
cladding) multimode fiber optic
cable
Operating Specifications Wavelength: 1310 nm
Output power - 50/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -22.5 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Output power - 62.5/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -19.0 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Input sensitivity:
Minimum: -31 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Wake on LAN Feature
AT-2700FTX Series Supported on both ports.
AT-2701FTX Series Supported on both ports.
Default Setting Disabled
27
Page 28
Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
BootPROM Chip and MBA Feature
AT-2700FTX Series Optional
AT-2701FTX Series Standard
Default Port 100Base-FX
Load Balancing and Fail-over Protection
AT-2700FTX Series Not supported
Table 6. AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series Network Adapter
Cards (Continued)
AT-2701FTX Series
Supported
2
Default setting: Disabled
1. Numerous factors, such as too many splices or poorly implemented splices,
can significantly reduce the maximum distance of a fiber optic port. Fiber optic
cable should only be installed by a qualified fiber optic cable contractor.
2. Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP.
LEDs Table 7 describes the LEDs on the AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series
adapter cards. The twisted pair port uses either the 10 or 100 LED,
depending on its operating speed. The fiber optic port uses just the 100
LED.
Table 7. AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series LEDs
LED Status Description
10 Green The twisted pair port
is operating at 10
Mbps, full-duplex
mode.
Amber The twisted pair port
is operating at 10
Mbps, half-duplex
mode.
28
Flashing The twisted pair port
is receiving or
transmitting network
packets at 10 Mbps.
Page 29
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Table 7. AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series LEDs (Continued)
LED Status Description
100 Green The twisted pair port
or fiber optic port is
operating at 100
Mbps, full-duplex
mode.
Amber The twisted pair port
or fiber optic port is
operating at 100
Mbps, half-duplex
mode.
Flashing The twisted pair port
or fiber optic port is
receiving or
transmitting network
packets at 100 Mbps.
29
Page 30

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series
The adapters in the AT-2745FX Series are:
AT-2745FX/SC
AT-2745FX/ST
AT-2745FX/STSC
The adapters in the AT-2746FX Series are:
AT-2746FX/SC/SC
AT-2746FX/ST/ST
AT-2746FX/ST/SC
The AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series are dual port adapters. But unlike
the other dual port adapters discussed in this guide, which feature a
twisted pair port and a fiber optic port, these adapter cards have two fiber
optic ports. One port is 10Base-FL and the other 100Base-FX. These
adapters allow you to use the same network adapter card for either 10
Mbps or 100 Mbps over fiber optic cable. The cards are appropriate in
network environments whether there is a mix of 10Base-FL and 100BaseFX Ethernet hubs and switches. They can also be useful in 10Base-FL
environments where there are future plans to upgrade the switches and
hubs to 100Base-FX.
Note
You can use only one port on this adapter at a time. Do not attach
both ports to the network at the same time.
Differences between the two series are:
The AT-2745FX Series is PCI 2.1-compliant.
The AT-2746FX Series is PCI 2.2-compliant.
The AT-2745FX Series was offered in two versions — a standard
version and a low profile version for systems that accept only low
profile adapters.
The AT-2746FX Series can be installed in either a standard or low
profile system. The adapter comes with two brackets, one for a
standard system and another for a low profile system.
The AT-2745FX Series supported the Wake on LAN feature only on
the 100Base-FX port.
The AT-2746FX Series supports the Wake on LAN feature on both
ports.
30
Page 31

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
The BootPROM chip and MBA were optional with the AT-2745FX
Series.
The BootPROM chip and MBA come standard with the AT-2746FX
Series.
Specifications Table 8 lists the specifications of the AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series
adapter cards.
Table 8. AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series Network Adapter
Cards
Basic Features
Supported Platforms IBM PC or compatible
Supported Operating Systems Microsoft Windows 2000
Microsoft Windows 2003
Microsoft Windows XP
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
Novell Netware 6.5
Linux 2.4 and 2.6
Solaris 9
Type of Motherboard Connector AT-2745FX Series:
PCI bus 2.1-compliant
(32-bit bus width)
AT-2746FX Series:
PCI bus 2.2-compliant
(32-bit bus width)
Number of Ports 2
10Base-FL Fiber Optic Port
Standard 10Base-FL
Speed 10 Mbps
Duplex Mode Half- or full-duplex
(Default: full-duplex)
Type of Connector AT-2745FX Series:
AT-2745FX/SC: duplex SC
AT-2745FX/ST: duplex ST
AT-2745FX/STSC: duplex ST
AT-2746FX Series:
AT-2746FX/SC/SC: duplex SC
AT-2746FX/ST/ST: duplex ST
AT-2745FX/ST/SC: duplex ST
Maximum Operating Distance
1
2 kilometers (1.2 miles)
31
Page 32

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
Type of Cabling 50/125 or 62.5/125 micron (core/
Operating Specifications Wavelength: 820 nm
Table 8. AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series Network Adapter
Cards (Continued)
cladding) multimode fiber optic
cable
Output power - 50/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -18.8 dBm
Maximum: -13.8 dBm
Output power - 62.5/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -15.0 dBm
Maximum: -10.0 dBm
Input sensitivity:
Typical: -4.4 dBm
100Base-FX Fiber Optic Port
Standard 100Base-FX
Speed 100 Mbps
Duplex Mode Half- or full-duplex
(Default: full-duplex)
Type of Connector AT-2745FX Series:
AT-2745FX/SC: duplex SC
AT-2745FX/ST: duplex ST
AT-2745FX/STSC: duplex SC
AT-2746FX Series:
AT-2746FX/SC/SC: duplex SC
AT-2746FX/ST/ST: duplex ST
AT-2745FX/ST/SC: duplex SC
Maximum Operating Distance
1
2 kilometers (1.2 miles) in fullduplex mode
412 m (1373 feet) in half-duplex
mode
Type of Cabling 50/125 or 62.5/125 micron (core/
cladding) multimode fiber optic
cable
32
Page 33

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Table 8. AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series Network Adapter
Cards (Continued)
Operating Specifications Wavelength: 1310 nm
Output power - 50/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -22.5 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Output power - 62.5/125 micron
cabling:
Minimum: -19.0 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Input sensitivity:
Minimum: -31 dBm
Maximum: -14 dBm
Wake on LAN Feature
AT-2745FX Series Supported on 100Base-FX port
only.
AT-2746FX Series Supported on both ports.
Default Setting Disabled
BootPROM Chip and MBA Feature
AT-2745FX Series Optional
AT-2746FX Series Standard
Default Port 100Base-FX
Load Balancing and Fail-over Protection
AT-2745FX Series Not supported
AT-2746FX Series
Supported
2
Default setting: Disabled
1. Numerous factors, such as too many splices or poorly implemented splices,
can significantly reduce the maximum distance of a fiber optic port. Fiber optic
cable should only be installed by a qualified fiber optic cable contractor.
2. Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP.
33
Page 34

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
LEDs Table 9 describes the LEDs on the AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series
adapter cards. The 10Base-FL port uses the 10 LED and the 100Base-FX
port uses the 100 LED.
10 Green The 10Base-FL port
Table 9. AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series LEDs
LED Status Description
is operating at 10
Mbps, full-duplex
mode.
Amber The 10Base-FL port
is operating at 10
Mbps, half-duplex
mode.
Flashing The 10Base-FL port
is receiving or
transmitting network
packets at 10 Mbps.
100 Green The 100Base-FX port
is operating at 100
Mbps, full-duplex
mode.
Amber The 100Base-FX port
is operating at 100
Mbps, half-duplex
mode.
Flashing The 100Base-FX port
is receiving or
transmitting network
packets at 100 Mbps.
34
Page 35

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Additional Features
The following sections describe these network adapter card features:
❑ “Wake on LAN” on page 35
❑ “Driver Installation and the AT-Setup Utility” on page 36
❑ “Virtual LANs and the AT-MUX Protocol” on page 37
❑ “Operating Statistics and the AT-Stat Utility” on page 38
❑ “Diagnostics and the AT-Diag Utility” on page 39
❑ “Load Balancing and Fail-over Protection” on page 39
❑ “Managed Boot Agent” on page 43
Wake on LAN This feature can help automate many of your network administrator
functions, such as backing up workstation files and updating system files.
It allows a network adapter card to power ON a system that has been
powered OFF or is in a sleep mode.
The feature is activated whenever the network adapter card receives a
special signal, called a Magic Packet, from a network management
program. Once the card has received the Magic Packet and instructed the
system to power ON, the network management program can run whatever
network management function needs to be performed on the system,
automatically. If your network management program permits, you can
configure the program to run the tasks during non-business hours so as
not interrupt the work of the network users. This helps simplify your
network maintenance tasks and limits the impact the tasks have on your
network users.
There are several steps you need to perform before you can use the Wake
on LAN feature on the network adapter card. First, you need to determine
whether the system where you will be installing the card supports Wake on
LAN. Not all do. The best way to determine this is by referring to the
system’s documentation.
Next, you need to determine whether the system is PCI 2.1- or PCI 2.2compliant. (PCI is an acronym for Peripheral Component Interconnect.)
Again, the system’s documentation should tell you this. Computers that
are PCI 2.1-compliant and that support Wake on LAN control the feature
through a special Wake on LAN connector on the system’s motherboard.
As part of the installation procedure you will need to connect the network
adapter card to the special connector on the motherboard using the Wake
on LAN cable included with the adapter card.
35
Page 36

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
When you install a PCI 2.2-compatible adapter in a PCI 2.2-compliant
computer, the Wake on LAN cable is unnecessary because the feature is
controlled through the connector bus on the network adapter card and the
system’s motherboard.
The following table can help sort things out. To determine whether you
need to use the Wake on LAN cable, match the type of adapter you
purchased with the type of system in which you are installing it.
Note
Wake on LAN is not supported when a PCI 2.1-compliant adapter,
such as the AT-2450FTX Series, is installed in a PCI 2.2-compliant
computer. Additionally, Wake on LAN is not supported on the
10Base-FL ports on the AT-2450FTX and AT-2745FX Series
network adapter cards.
Table 10. When to Use the Wake on LAN Cable
Driver
Installation and
the AT-Setup
Utility
PCI 2.1-Compatible
System
PCI 2.1-compatible
adapter
PCI 2.2 compatible
adapter
This feature also requires a network management program capable of
sending out Magic Packets to the network adapter card. An example is HP
OpenView Network Node Manager. Of course, whatever program you
choose to use should also allow you to specify what network maintenance
functions you want performed once a system has powered ON.
The quickest and easiest way to install the driver for the network adapter
card on a Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP system is with the
AT-Setup utility. This utility, included on the Allied Telesyn Installation CD,
is also useful in updating an adapter driver already installed on a system
or correcting a driver installation. For systems without a CD driver, the
Installation CD comes with a utility program that creates a driver
installation diskette that contains the AT-Setup utility and the driver, so
you can run the program from a diskette drive rather than from a CD drive.
Install Wake on LAN
cable
Install Wake on LAN
cable
PCI 2-2 Compatible
System
Wake on LAN not
supported.
Connector bus
(Wake on LAN cable
not used)
36
For instructions on how to use the AT-Setup utility, refer to Chapter 3,
“Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP” on page 57.
Page 37

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Note
The Installation CD that comes with your network adapter card has
two drivers for Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP system. There
is a regular driver and an enhanced driver that supports load
balancing and fail-over (LBFO) protection. The AT-Setup utility can
be used to install the regular driver. To install the LBFO driver, you
must install it manually. For further information, refer to “Load
Balancing and Fail-over Protection” on page 39 and “Choosing a
Network Adapter Card Driver” on page 58.
Virtual LANs and
the AT-MUX
Protocol
All of the adapters discussed in this guide are IEEE 802.1Q-compliant and
are designed to support virtual LANs (VLANs) and tagged packets. A
VLAN is an independent traffic domain where traffic generated by the
nodes of a VLAN is restricted only to nodes that are members of the same
VLAN. Traffic within a VLAN cannot cross over a VLAN boundary unless
there is an interconnection device, such as a router or a Layer 3 switch, in
the network.
VLANs are often used to group nodes with related functions into their own
separate, logical LAN segments. These VLAN groupings can be based on
similar data needs or security requirements. VLANs can increase network
performance and security by restricting traffic to specific devices or areas
of a network.
A tagged VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) contains one or more network links that
carry traffic from more than one VLAN. The VLAN traffic is identified by a
header tag, or simply tag, that follows the source and destination
addresses in a packet. The tag contains a VLAN identifier (VID) that
uniquely identifies the VLAN to which a packet belongs.
The Allied Telesyn network adapter cards are capable of reading the
header tag in tagged packets as they arrive on the port, as well as adding
tags to packets when transmitting packets.
Before a network adapter card can handle tagged packets, you must
configure it by specifying the appropriate VIDs of the VLANs whose tagged
packets the adapter is to process.
There are two ways to add VIDs to a network adapter card in a Microsoft
Windows 2000, 2003, or XP system. If the card will be handling tagged
traffic from only one tagged VLAN, you can specify the VID using the
Network Connections window in Microsoft Windows, as explained in
“Configuring Additional Network Adapter Card Settings” on page 96.
If the network adapter card will be handling tagged traffic from more than
one VLAN, you can use the AT-MUX protocol, which is included on the
Installation CD shipped with the network adapter card. The protocol allows
you to assign up to 16 VIDs to a single adapter, enabling a network
37
Page 38

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
adapter card to process tagged traffic from up to 16 different VLANs. The
protocol is described in Chapter 9, “AT-MUX Multiple VLAN Protocol” on
page 157.
The following briefly outlines the behavior of a network adapter card when
handling tagged and untagged VLAN traffic:
An adapter where no VIDs have been assigned accepts and transmits
An adapter where at least one VID has been assigned accepts only
Note
The AT-MUX protocol is compatible with Microsoft Windows 2000,
2003, and XP operating systems. You cannot use this protocol with
any other operating system.
only untagged packets. (An untagged packet does not contain a
header tag and, consequently, lacks VLAN identification.) The adapter
discards any tagged packets that arrive on the port.
those tagged packets with header tags that match the assigned VIDs.
The adapter discards all untagged packets as well as any tagged
packets with VIDs that do not match the VIDs assigned to the card.
Operating
Statistics and the
AT-Stat Utility
The AT-Stat utility can used to configure a card’s operating specifications
and display operating statistics. Functions include:
Displaying performance statistics, such as the number of packets sent
and received by a network adapter card.
Displaying the number of packet errors, such as CRC errors and
alignment errors.
Configuring the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address.
Pinging another network device.
Performing a throughput test.
For instructions, refer to Chapter 8, “AT-Stat Utility” on page 133.
Note
The AT-Stat utility is compatible with Microsoft Windows 2000,
2003, and XP operating systems. This utility cannot be used with
any other operating system.
38
Page 39

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Diagnostics and
the AT-Diag
Utility
Load Balancing
and Fail-over
Protection
Included on the Allied Telesyn Installation CD is the AT-Diag utility. This
program is useful in testing and configuring a network adapter card.
Functions include:
Testing a network adapter card.
Performing a link test between an adapter port and a remote device,
such as an Ethernet switch or hub.
Setting the speed and duplex mode of an adapter port.
Enabling or disabling the BootPROM chip and MBA.
Specifying the default port for MBA.
Viewing hardware information.
For instructions, refer to Chapter 10, “AT-Diag Utility” on page 175.
Allied Telesyn offers two drivers for an adapter card installed in a Microsoft
Windows 2000, 2003, or XP system. There is a regular driver and an
enhanced driver with load balancing and fail-over (LBFO) protection.
These latter features are described in the following subsections.
Load Balancing
The load balancing feature of the LBFO driver is primarily intended for
adapters in network servers. It enhances network performance by
distributing the traffic over two adapters and also increases network
resiliency by providing a redundant link from the server to the network
should a link fail.
The LBFO driver allows you to increase the bandwidth from a network
server by configuring two network adapters to function as one virtual
adapter. The two adapters distribute traffic between themselves by taking
turns transmitting packets in a round-robin fashion. One adapter transmits
a packet, the next packet is transmitted by the other adapter, and so on.
Note the following before using the LBFO driver:
This driver is supported only on Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and
XP systems.
The driver is supported on the AT-2451FTX, AT-2701FX, AT-2701FTX,
and AT-2746FX Series cards. It is not supported on the older versions
of these adapters (for example, AT-2450FTX, AT-2700FX, etc.).
Note
The LBFO driver has not been certified by Microsoft Corporation.
39
Page 40

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
There are two versions of the load balancing feature: mode 1 and mode 2.
The basic characteristics of mode 1 are:
Both adapters use the same MAC address, but different IP addresses.
The ports on the two adapter cards must be connected to the same
The basic characteristics of mode 2 are:
Both adapters use different MAC addresses and IP addresses.
The ports on the two adapter cards can be connected to the same
While Mode 1 typically offers the best in terms of performance, you might
not be able to use it in all situations. It all depends on the capability of the
Ethernet switch to which the ports on the adapters are connected. If the
switch cannot handle learning the same MAC address on more than one
port, you will probably need to use Mode 2.
Here are the steps to implementing load balancing:
remote device.
remote device or to different remote devices.
1. Install two adapter cards into the system. The two cards must be
identical (for example, two AT-2701FX Series cards).
2. Manually load the LBFO driver onto the cards. Be sure to install the
LBFO driver instead of the regular driver. You must install the driver
twice, once for each card. For instructions, refer to “Manually Installing
a Driver” on page 73.
Note
You cannot use the AT-Setup utility to load the LBFO driver.
3. Manually assign both cards an IP address or activate the DHCP client.
The IP addresses must be different for the two cards, even if you are
using mode 1. The addresses must belong to the same subnet.
Consequently, the network portion of the addresses must be the same
as well as the subnet masks. For instructions, refer to “Configuring the
IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address” on page 92. (In
mode 1, both adapters use the same MAC address. The MAC address
assignment is handled automatically by the driver.)
4. Assign both adapter cards to the same team. For instructions, refer to
“Configuring Additional Network Adapter Card Settings” on page 96.
40
Page 41

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Fail-over Protection
Another feature of the LBFO driver is fail-over protection. This feature is
useful in situations where a network device could benefit from link
redundancy, but not necessarily load balancing. The fail-over feature
protects against a loss of network connectivity should an adapter lose its
link to a remote device or the remote device loses power or is taken out of
service, such as for maintenance. When the link is lost on the primary
adapter, the redundant adapter automatically takes over the task of
sending and receiving network traffic.
There are two possible configurations for this feature. In the first
configuration both the primary link and the redundant link are connected to
the same remote node. This is illustrated in Figure 1 where the links from a
server containing two network adapter cards both go to the same Ethernet
switch. If the primary link should fail, the redundant link automatically takes
over, preventing a loss of network connectivity to the server.
Primary
Link
Redundant
Link
Figure 1. Fail-over Protection - Configuration #1
The drawback to this configuration is that it does not protect against a loss
of network access to the server should the switch lose power or be
removed from service. Fortunately, with fail-over protection the links can
go to different remote nodes. An example is illustrated in Figure 2 where
the primary and redundant links of the two adapters in the server go to
different Ethernet switches. Now, if the switch where the primary link is
connected loses power or is removed from service, network connectivity to
the server continues uninterrupted through the other Ethernet switch.
Primary
Link
Redundant
Link
Figure 2. Fail-over Protection - Configuration #2
41
Page 42

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
The selection of the active adapter is determined by the network driver
and the computer’s operating system. The active, primary adapter is
determined by whichever adapter establishes a link with its remote device
first. If the primary adapter loses its link with its remote device, the
redundant adapter automatically changes to the primary function and
remains as the primary adapter until such time as the status of its link
changes.
When an adapter card driver notes that it has changed from the redundant
to the active status, it sends out a Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
packet. The purpose of the packet is to notify the network nodes of the
system’s new MAC address and IP address.
To implement this feature, you need to install two identical adapters into
the system and create a team of the cards. Both adapters must be
members of the same team. One adapter will function as the active,
primary adapter and the second adapter will function as the redundant
adapter. There can be only one active and one redundant adapter per
team. You must also assign each adapter a unique IP address.
Implementing port redundancy requires the following steps:
1. Install two identical adapters in the network device.
2. Manually load the LBFO driver onto the cards. Be sure to install the
LBFO driver instead of the regular driver. You must install the driver
twice, once for each card. For instructions, refer to “Manually Installing
a Driver” on page 73.
Note
You cannot use the AT-Setup utility to load the LBFO driver.
3. Assign each adapter a unique IP address. The IP addresses must be
in the same subnet. Consequently, the network portion of the
addresses must be the same as well as the subnet masks. For
instructions, refer to “Configuring the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and
Gateway Address” on page 92.
4. Create a team consisting of the two adapter cards. For instructions,
refer to “Configuring Additional Network Adapter Card Settings” on
page 96.
42
Page 43

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Managed Boot
Agent
The managed boot agent (MBA) and the BootPROM chip allow you to
perform pre-boot procedures on a system, such as installing an operating
system, running a virus checker, or downloading a predefined system
configuration. You can couple this feature with the Wake on LAN feature to
perform configuration and maintenance tasks during non-work hours so as
not to interfere with the work of your network users.
Note
The MBA and BootPROM chip come standard with the AT-2451FTX,
AT-2701FX, AT-2701FTX, and AT-2746FX Series cards. They are
sold separately for the AT-2450FTX, AT-2700FX, AT-2700FTX, and
AT-2745FX Series adapters.
In order to use MBA on a dual port card you must specify which port is
connected to the network. This is made with the AT-Diag utility, described
in Chapter 10 on page 175. The MBA can address only one port at a time
and it cannot change ports automatically. The selected port is referred to
as the default MBA port. The factory settings of the default MBA port on
the dual port adapter cards are:
AT-2450FTX and AT-2451FTX Series cards — 10/100Base-TX twisted
pair port
AT-2700FTX and AT-2701FTX Series cards — 100Base-FX fiber optic
port
AT-2745FX and AT-2746FX Series cards — 100Base-FX fiber optic
port
For example, to use MBA on the 10Base-FL port on the AT-2746FX Series
card, you would run the AT-Diag utility and specify that port as the default
MBA port.
43
Page 44

Chapter 1: Network Adapter Card Overview
44
Page 45

Chapter 2
Installing a Network Adapter Card
This chapter contains instructions for installing an Allied Telesyn network
adapter card. Sections in the chapter include:
“Verifying Package Contents” on page 46
“Reviewing Safety Precautions” on page 47
“Installing the Low Profile Bracket” on page 48
“Installing a Network Adapter Card” on page 51
45
Page 46

Chapter 2: Installing a Network Adapter Card
Verifying Package Contents
Make sure the following items are included in your package. If any item is
missing or damaged, contact your Allied Telesyn sales representative for
assistance.
❑ Allied Telesyn Network Adapter Card
❑ Allied Telesyn Installation CD
❑ Wake on LAN Cable
❑ Low Profile Bracket (AT-2451FTX, AT-2701FX, AT-2701FTX, and
AT-2746FX Series)
❑ Warranty Card
46
Page 47

Reviewing Safety Precautions
Please review the following safety precautions before you begin to install
the network adapter card. Refer to Appendix E, “Translated Safety
Statements” on page 209 for translated safety statements in your
language.
Warning
This is a “Class 1 LED product”. 1
Warning
Do not stare into the laser beam. 2
Warning
Warning: Do not look directly at the fiber optic cable ends or inspect
the cable ends with an optical lens. 31
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Warning
Do not work on this equipment or cables during periods of lightning
activity. 4
Warning
Operating Temperature: This product is designed for a maximum
ambient temperature of 40 degrees C. 9
Note
All Countries: Install this product in accordance with local and
National Electric Codes. 10
47
Page 48

Chapter 2: Installing a Network Adapter Card
Installing the Low Profile Bracket
The AT-2451FTX, AT-2701FX, AT-2701FTX and AT-2746FX Series
network adapter cards come with two brackets, a pre-installed standard
bracket and a low profile bracket for systems that require low profile
adapters. If you are installing the card in a low profile system, you must
replace the standard bracket on the card with the low profile bracket.
Replacing the bracket must be performed with extreme care to avoid
damaging the network adapter card.
Caution
Wear a grounding device and observe electrostatic discharge
precautions when installing the bracket. Failure to observe this
caution could result in damage to the network adapter card.
48
Page 49

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
To install the low profile bracket, perform the following procedure:
1. Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, carefully remove the two screws
that secure the standard bracket to the network adapter card and
remove the bracket, as shown in Figure 3.
T
X
R
TX
X
RX
100
T
X R
X
TX
R
X
100
Figure 3. Removing the Standard Bracket
49
Page 50

2. Position the low profile bracket on the adapter card and secure with the
two screws, as shown in Figure 4.
T
X RX
T
X
RX
100
T
X R
TX
T
X
X
RX
RX
100
100
Figure 4. Installing the Low Profile Bracket
Page 51

Installing a Network Adapter Card
This section explains how to install a network adapter card in most
PC-compatible systems. Refer to system’s instruction manual for specific
information on installing peripheral devices.
Note
The optional BootPROM chip for an AT-2450FTX, AT-2700FX,
AT-2700FTX, or AT-2745FX Series card should be installed before
the card is installed in the system. For instructions, go to “Installing a
BootPROM Chip” on page 200.
To install the network adapter card, perform the following procedure:
1. Shutdown your system and disconnect the power cord from the outlet.
Warning
High voltage inside the system presents a safety hazard. Make sure
the power is off before removing the cover.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
2. Remove the system’s cover by removing the screws from the chassis
and gently sliding off the cover. See Figure 5.
Figure 5. Removing the PC Cover
51
Page 52

Chapter 2: Installing a Network Adapter Card
3. Select an empty, non-shared PCI slot and remove the faceplate. Keep
the faceplate in a safe place. You may need it for future use. See
Figure 6.
Figure 6. Removing the Faceplate From PCI Slot
If you are installing the network adapter card in a PCI 2.1-compliant
system and want to use the Wake on LAN feature, choose a slot that is
near the Wake on LAN connector on the system’s motherboard. This
will make installing the Wake on LAN cable easier.
Note
If you cannot locate or know how to find an PCI slot, refer to the
documentation that came with your system.
4. Remove the network adapter card from the shipping package and
store the packaging material in a safe location.
Caution
Wear a grounding device and observe electrostatic discharge
precautions when installing the network adapter card in a system.
Failure to observe this caution could result in damage to the card.
52
Page 53

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
5. To use the Wake on LAN feature in a PCI 2.1-compatible system,
connect one end of the Wake on LAN cable included with the network
adapter card to the Wake on LAN connector on the card, as shown in
Figure 7. If you are installing the card in a PCI 2.2-compliant system or
do not intend to use this feature, skip this step. For background
information on this feature, refer to “Wake on LAN” on page 35.
Figure 7. Connecting the Wake on LAN Cable to the Adapter Card
53
Page 54

Chapter 2: Installing a Network Adapter Card
6. Gently insert the network adapter card into the PCI slot. Make sure the
7. Secure the network adapter card to the chassis with a Phillips-head
card is securely seated.
Figure 8. Inserting the Network Adapter Card
screw, not provided.
54
Figure 9. Securing the Adapter Card
8. To use the Wake on LAN feature in a PCI 2.1-compatible system,
connect the other end of the Wake on LAN cable to the Wake on LAN
connector on the system’s motherboard. Refer to the system’s
documentation for the location of the connector. If you are installing
the card in a PCI 2.2-compliant system or do not want to use the Wake
on LAN feature, skip this step.
9. Replace the system’s cover and secure it with the screws removed in
Step 2.
10. Connect the network adapter card to the network by connecting the
appropriate network cable.
Page 55

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Note
If you installed a dual port network adapter card, connect only one
port to the network.
11. Power ON the system.
If you installed the adapter card in a Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or
XP system and did not pre-install the driver, the Found New Hardware
Wizard launches automatically once the system detects the new card.
Figure 10 illustrates the first window of the wizard.
Figure 10. Found New Hardware Wizard Window
12. At this point, you have a choice on how to install the adapter card’s
driver. If you prefer to use the AT-Setup utility, click Cancel in the
wizard and perform the procedure “Installing or Updating a Driver
Using the AT-Setup Utility” on page 59. Alternatively, you can use the
wizard to manually install the driver by performing the procedure
“Manually Installing a Driver” on page 73.
This completes the installation of the network adapter card. Go to the
appropriate chapter in this guide for installation instructions for the
adapter card’s driver.
55
Page 56

Chapter 2: Installing a Network Adapter Card
56
Page 57

Chapter 3
Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
This chapter contains instructions on how to install, update, and remove
the network adapter driver on a Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP
system. This chapter also contains the procedure for adjusting a network
adapter card’s parameters, such as assigning an IP address and changing
port speed and duplex mode. Procedures in the chapter include:
“Choosing a Network Adapter Card Driver” on page 58
“Installing or Updating a Driver Using the AT-Setup Utility” on page 59
“Creating a Driver Installation Disk” on page 68
“Manually Installing a Driver” on page 73
“Manually Updating a Driver” on page 77
“Removing a Driver” on page 85
“Running AT-Setup to Complete Driver Installation” on page 90
“Configuring the Network Adapter Card Settings” on page 91
57
Page 58

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
Choosing a Network Adapter Card Driver
The first step to installing the driver for your new network adapter card is to
select a driver. Allied Telesyn offers two drivers for Microsoft Windows
2000, 2003, and XP systems. There is a regular driver and an enhanced
driver that features load balancing and fail-over (LBFO) protection. The
LBFO driver is primarily intended for adapters in network servers. It
enhances network performance by distributing the traffic from the server
over two adapters. It also increases the resiliency of your network by
providing a redundant link from the server to the network. For background
information on the LBFO driver, refer to “Load Balancing and Fail-over
Protection” on page 39.
You can install the regular driver using the AT-Setup utility, as explained in
“Installing or Updating a Driver Using the AT-Setup Utility” on page 59 or
manually with the procedure “Manually Installing a Driver” on page 73.
To install the LBFO driver, you must use the procedure “Manually
Installing a Driver” on page 73. The LBFO driver cannot be installed using
the AT-Setup utility.
Note
The LBFO driver has not been certified by Microsoft Corporation.
58
Page 59

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Installing or Updating a Driver Using the AT-Setup Utility
Included on the Allied Telesyn Installation CD is the AT-Setup utility. This
utility is a quick and easy way to install the regular adapter driver on a
Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP system.
Note
Do not perform this procedure to install the LBFO driver. Instead, go
to “Manually Installing a Driver” on page 73.
You can run the AT-Setup utility either before or after you install the
network adapter card. Running the AT-Setup utility before installing the
card pre-loads the driver.
If you install an adapter card in your system before running the AT-Setup
utility, your operating system will attempt to install an adapter driver
automatically. Microsoft’s New Hardware Installation Wizard will prompt
you for the location of the appropriate driver for the adapter card. You can
either instruct the installation wizard to the proper location on the Allied
Telesyn Installation CD, given in Step 11 in the procedure “Manually
Installing a Driver” on page 73, or cancel the hardware wizard and perform
the AT-Setup utility.
AT-Setup
Guidelines
You can also use the AT-Setup utility to update the regular driver or to
correct problems during installation. If an error message occurs, simply
run AT-Setup again. The utility will scan your operating system and fix any
known issues.
Before running the AT-Setup utility, please review the following guidelines:
The AT-Setup utility is designed for Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003,
and XP operating systems. Do not use this program with any other
operating system.
If the system contains more than one adapter card, you must install the
adapter driver on each card. You can either run the AT-Setup utility,
which automatically installs the driver on all of the adapter cards that it
detects in the system, or you can install the driver manually for each
card.
If the system where you installed the adapter card does not have a CD
drive, you can create a driver installation diskette and run the AT-Setup
utility from the diskette. Refer to “Creating a Driver Installation Disk” on
page 68 for instructions.
Allied Telesyn network adapter cards are PCI-compliant. The adapter
card’s operating parameters, such as interrupt level and memory
range, are set automatically by the computer to avoid conflict with
other devices in your system. Do not change any of the operating
59
Page 60

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
parameters of an adapter card without a full understanding of the
parameters’ functions.
Running
AT-Setup from
the Installation
CD
To install or update the regular adapter card driver using the AT-Setup
utility from the Installation CD, perform the following procedure:
1. Insert the Allied Telesyn Installation CD into the CD drive.
Your system should automatically launch the CD and display the main
window, shown in Figure 11. If this window does not appear, doubleclick on the My Computer icon, then double-click on the Allied Telesyn
Installation CD icon.
60
Figure 11. Installation CD Main Window
Page 61

2. Select Tools.
The Tools window is shown in Figure 12.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Figure 12. Tools Window
3. Select AT-Setup Utility.
The AT-Setup Utility window is shown in Figure 13.
Figure 13. AT-Setup Utility Window
61
Page 62

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
4. Select Start AT-Setup.
Note
The security prompts in Steps 4, 5, and 6 are from Microsoft Internet
Explorer version 6.0. These security prompts may not appear or you
may see different prompts if you are using a different version of
Microsoft Internet Explorer or a different web browser.
The following prompt is displayed.
Figure 14. Active Content Warning Prompt
5. Select Yes.
The following prompt is displayed:
Figure 15. File Download - Security Warning Prompt
62
Page 63

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
6. Select Run to run the AT-Setup utility from the Installation CD.
The following security warning prompt is displayed.
Figure 16. Internet Explorer - Security Warning Prompt
7. Select Run to launch the AT-Setup utility.
If you are updating a driver, the program displays the Overwrite
Protection window, shown in Figure 17.
Figure 17. Overwrite Protection Window
63
Page 64

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
8. If the Overwrite Protection window appears, select Yes to All. The
utility searches the system for any network adapter cards. If it detects
a card(s), the utility displays the card model name(s) in the ATSetup
window. (In some cases, the utility might omit the model name and
display just the words “Ethernet Controller.”) An example of the
window is shown in Figure 18.
Figure 18. AT-Setup Window (Card Installed)
If the adapter card has not been installed, the window in Figure 19 is
displayed:
64
Figure 19. AT-Setup Window (No Card Installed)
Page 65

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
9. Select OK.
The AT-Setup utility copies the adapter driver from the Installation CD
to the system’s hard disk and integrates it with the system’s operating
system. The entire process can take up to 30 seconds to complete.
Note
If you see the error message “Failed to remove network adapter for
update. The data is invalid.”, click OK. The message can be ignored.
10. If the card is already installed in the system, the AT-Setup utility
displays the message in Figure 20 once the driver is installed. Click
OK. To complete the installation, connect the twisted pair cable or the
fiber optic cable to the port on the adapter.
Figure 20. AT-Setup Window - Completion
Note
To configure the adapter’s settings, refer to “Configuring the
Network Adapter Card Settings” on page 91.
65
Page 66

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
11. If the card has not been installed, the prompt in Figure 21 is displayed.
Remove the CD from the CD driver and click Yes. The Windows
operating system and the system are automatically shut down. You
can now install the adapter card. For instructions, refer to Chapter 2,
“Installing a Network Adapter Card” on page 45.
Figure 21. Shut Down Prompt
Running
AT-Setup from a
Driver
Installation
Diskette
To install the network adapter driver using the AT-Setup utility from a
driver installation diskette, perform the following procedure:
1. Insert the driver installation disk into the floppy drive.
Note
For instructions on how to create a driver installation disk, refer to
“Creating a Driver Installation Disk” on page 68.
2. From the Start menu on the Window’s toolbar, select Run, as shown in
Figure 22.
66
Figure 22. Run Selection in the Start Menu
Page 67

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
The Run window is shown in Figure 23.
Figure 23. Run Window
3. In the Open field, type: x:\Win_XP_200X\atsetup where ‘x’ is the drive
letter of the floppy drive.
4. Select OK.
5. To complete the installation of the adapter card driver, perform Steps 8
to 11 in the procedure “Running AT-Setup from the Installation CD” on
page 60.
67
Page 68

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
Creating a Driver Installation Disk
This procedure creates a driver installation diskette. You can use the
diskette to run the AT-Setup utility on those systems that do not have a CD
drive.
To create a driver installation disk, perform the following procedure on a
system that has both a CD drive and floppy drive:
1. Make sure your system is turned ON and the Windows operating
system is running.
2. Insert the Allied Telesyn Installation CD into the CD drive.
The Installation CD main window is shown in Figure 24. If this window
does not appear, double-click on the My Computer icon, then doubleclick on the Allied Telesyn Installation CD icon.
68
Figure 24. Allied Telesyn Installation CD Main Window
Page 69

3. Select Tools.
The Tools window is shown in Figure 25.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Figure 25. Installation CD Tools Window
4. Select Driver Installation Diskette.
The Driver Installation Diskette window is shown in Figure 26.
Figure 26. Driver Diskette Utility Window
69
Page 70

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
5. Insert a blank, formatted floppy disk into the floppy drive.
6. Select Create driver diskette.
Note
The security prompts in Steps 4, 5, and 6 are from Microsoft Internet
Explorer version 6.0. These security prompts may not appear or you
may see different prompts if you are using a different version of
Microsoft Internet Explorer or a different web browser.
The prompt in Figure 27 is displayed.
Figure 27. Active Content Warning Prompt
7. Select Yes.
The prompt in Figure 28 is displayed.
Figure 28. File Download - Security Warning Prompt
70
Page 71

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
8. Select Run to run the utility from the Installation CD.
The following security warning prompt is displayed.
Figure 29. Internet Explorer - Security Warning Prompt
9. Select Run.
The prompt in Figure 30 is displayed.
Figure 30. InstallShield Wizard
71
Page 72

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
10. Specify the floppy drive containing the blank disk.
11. Select Next. The adapter drivers and the AT-Setup utility are saved to
the floppy disk. The program displays the message in Figure 31when
the process is complete.
Figure 31. Driver Installation Diskette Completion Message
This completes the procedure for creating a driver installation disk. To
use the diskette to install the driver on a Microsoft Windows 2000,
2003, or XP system, refer to “Running AT-Setup from a Driver
Installation Diskette” on page 66 or “Manually Installing a Driver” on
page 73.
72
Page 73

Manually Installing a Driver
This section contains the procedure for manually installing the regular or
LBFO network adapter driver on a Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP
operating system. You can perform the procedure using the Allied Telesyn
Installation CD or, for those systems without a CD drive, a driver
installation diskette. For instructions on how to create a driver installation
diskette, refer to “Creating a Driver Installation Disk” on page 68.
1. Shutdown the Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP operating system
and power OFF your computer.
2. Install the network adapter card. Refer to Chapter 2, “Installing a
Network Adapter Card” on page 45 and the documentation that came
with your computer for instructions.
3. Power ON the computer.
After detecting the new adapter card, the system launches the Found
New Hardware Wizard, which displays the window shown in Figure 32.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Figure 32. Found New Hardware Wizard Window (1 of 4)
73
Page 74

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
4. Insert the Installation CD or the driver installation diskette into the
appropriate drive on the system.
Note
If you system launches the web browser when you insert the
Installation CD, minimize or close the web browser window.
5. In the Found New Hardware Wizard window, select No, not this time.
6. Select Next.
The window shown in Figure 33 is displayed.
74
Figure 33. Found New Hardware Wizard Window (2 of 4)
7. Select Install from a list or specific location (Advanced).
Page 75

8. Select Next.
The window shown in Figure 34 is displayed.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Figure 34. Found New Hardware Wizard Window (3 of 4)
9. If selected, deselect Search removable media (floppy, CD-ROM...).
10. Select Include this location in the search.
11. Specify the location of the driver file using the Browse button or by
entering the drive letter and path in the field.
If you are installing the regular driver, the driver files are stored in
this subdirectory on the Installation CD and the driver installation
diskette:
x:\drivers\Win_XP_200x
If you are installing the LBFO adapter driver, the files are stored in
this subdirectory on the Installation CD and the driver installation
diskette:
x:\drivers\Win_XP_200X_lbfo
Where X: is the driver letter of the CD drive or the diskette drive.
12. After you have specified the location, select Next.
75
Page 76

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
13. If you are installing the LBFO driver, a message is displayed stating
that the driver has not been certified by Microsoft. If you see the
message, click Continue Anyway.
The wizard installs the adapter driver. The installation process can
take up to 30 seconds to complete.
Once installed, the window in Figure 35 is displayed.
76
Figure 35. Found New Hardware Wizard Window (4 of 4)
14. Select Finish.
15. Reboot your system.
This completes the procedure for manually installing the driver on a
Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP system. To adjust the adapter’s
parameters, refer to “Configuring the Network Adapter Card Settings”
on page 91.
Page 77

Manually Updating a Driver
This section contains the procedure for updating a regular or LBFO
network adapter driver on a Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP system.
You can perform the procedure using the Allied Telesyn Installation CD or,
if the system does not have a CD driver, a driver installation disk. For
instructions on how to create a driver installation disk, refer to “Creating a
Driver Installation Disk” on page 68.
Note
Since the regular adapter driver and LBFO driver are considered
different drivers, you cannot use this procedure to convert a regular
driver already installed on a system into an LBFO driver, or vice
versa. If one of the adapter drivers is already installed, you must
uninstall it prior to installing the other driver. For background
information on the two drivers, refer to “Load Balancing and Failover Protection” on page 39 and “Choosing a Network Adapter Card
Driver” on page 58.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Note
You should have the Windows Installation CD or floppy disk(s)
available. You may be prompted to copy support files for networking.
To update a driver, perform the following procedure:
1. From the desktop, right-click the My Computer icon and select
Properties from the menu, as shown in Figure 36.
Figure 36. My Computer Icon and Menu
77
Page 78

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
The System Properties window is shown in Figure 37.
78
Figure 37. System Properties Window
Page 79

2. Select the Hardware tab.
The Hardware tab is shown in Figure 38.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Figure 38. Device Manager Tab Window
79
Page 80

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
3. Click the Device Manager button.
The Device Manager window is shown in Figure 39.
80
Figure 39. Device Manager Window
4. Expand Network adapters by either double-clicking on it or by clicking
once on the expansion box next to it.
The network adapter cards installed on the system are listed under
Network adapters. An example is shown here.
Note
The branch under Network Adapters will include VLANs if VIDs were
added to the adapter with the AT-MUX protocol. The VLANs are
labelled as “Allied Telesyn VLAN-Tagging miniport Driver.” In the
next step you must choose the selection for the network adapter
card and not a VLAN. The adapter card selection has the adapter’s
model number in the label.
Page 81

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
5. Right-click on the network adapter card whose driver you want to
update and select Update Driver from the pop-up menu, as shown
in.Figure 40.
Figure 40. Update Driver Menu Selection
The first of the Hardware Update Wizard windows is shown in Figure
41.
Figure 41. Welcome to the Hardware Update Wizard Window (1 of 4)
6. Select No, not this time.
81
Page 82

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
7. Click Next.
The window shown in Figure 42 is displayed.
Figure 42. Hardware Update Wizard Window (2 of 4)
8. Insert the Installation CD or the driver installation diskette into the
appropriate drive on the system.
Note
If, when you insert the CD, the system launches the web browser,
minimize or close the web browser window.
9. Select Install from a list of specific location (Advanced).
10. Click Next.
82
Page 83

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
The Hardware Update Wizard window shown in Figure 43 is displayed.
Figure 43. Hardware Update Wizard Window (3 of 4)
11. If selected, deselect Search removable media (floppy, CD-ROM...).
12. Select Include this location in the search.
If you are updating the regular driver, the driver files are stored in
this subdirectory on the Installation CD and the driver installation
diskette:
x:\drivers\Win_XP_200x
If you are updating the LBFO adapter driver, the files are stored in
this subdirectory on the Installation CD and the driver installation
diskette:
x:\drivers\Win_XP_200X_lbfo
Where X: is the driver letter of the CD drive or diskette drive.
13. Click Next.
83
Page 84

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
Microsoft Windows updates the driver and displays the window in
Figure 44
Figure 44. Hardware Update Wizard Window (4 of 4)
If the new driver is the same or older than the driver that is already
installed, the system cancels the update and displays a window stating
that it could not find a better match.
14. Click Finish.
This completes the procedure for updating an adapter card driver on a
Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, or XP system.
84
Page 85

Removing a Driver
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
To remove a network adapter driver from a Windows 2000, 2003 or XP
operating system, perform the following procedure.
1. From the desktop, right-click My Computer, then select Properties
from the pop-up menu.
Figure 45. My Computer Icon and Menu
85
Page 86

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
The System Properties window is shown in Figure 46.
86
Figure 46. Properties Window
Page 87

2. Select the Hardware tab.
The Hardware tab is shown in Figure 47.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Figure 47. Hardware Tab
87
Page 88

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
3. Select Device Manager.
The Device Manager window is shown in Figure 48.
88
Figure 48. Device Manager Window
4. Expand Network adapters by either double-clicking on it or by clicking
once on the expansion box next to it. The adapter drivers installed on
the switch are listed under Network adapters. An example is shown
here.
Note
The branch under Network Adapters will include VLANs if VIDs were
added to the adapter with the AT-MUX protocol. The VLANs are
labelled “Allied Telesyn VLAN-Tagging miniport Driver.” In the next
step you must choose the selection for the network adapter card and
not one of the VLANs. The adapter card selection has the adapter’s
model number in the label. For instructions on how to remove a VID
from the card, refer to “Adding, Changing, or Deleting VIDs” on
page 168.
Page 89

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
5. Right-click on the adapter driver you want to remove and select either
Remove or Uninstall from the pop-up menu, as shown in Figure 49.
Figure 49. Uninstall Menu Selection
A confirmation window is displayed.
Figure 50. Confirm Device Removal Window
6. Select OK.
If you intend to remove the adapter card from the system, go to the
next step. If you removed the adapter driver with the intent of replacing
it with another driver (for example, if you are replacing the regular
adapter driver with the LBFO driver), some additional steps might be
required, depending on the operating system. For instance, on a
Microsoft Windows XP system you might need to delete OEM.INF and
OEM.PNF files from the \WINDOWS\INF system folder before you can
load the new driver. For further information, refer to the documentation
included with the system.
7. Shutdown the Microsoft Windows operating system and power OFF
the system.
8. Remove the network adapter card from the system. For instructions,
refer to the documentation that came with your computer.
9. Power ON your computer.
This completes the procedure for removing a driver and network
adapter card from a system.
89
Page 90

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
Running AT-Setup to Complete Driver Installation
If you were unable to complete the installation of the regular adapter card
driver or if an error occurred during the installation, run AT-Setup again.
AT-Setup will scan your operating system and correct any known
problems. Refer to “Installing or Updating a Driver Using the AT-Setup
Utility” on page 59 for instructions.
90
Page 91

Configuring the Network Adapter Card Settings
A network adapter card has a number of parameters that you can adjust.
In some cases, the default configuration of the network adapter card will
be sufficient for it to operate without any adjustments. In other cases, you
might need to adjust one or more parameters.
Here are three of the parameters that you can set on an adapter.
IP address - Specifies a unique Internet Protocol address for the
adapter.
Subnet mask - Delineates the network portion of the IP address from
the node portion.
Gateway address - Specifies the IP address of a router or Layer 3
switch to be used by the node for traffic destined outside its virtual LAN
or network.
You can set these parameters manually or you can activate the DHCP
client software on the network adapter card and have the card retrieve this
information automatically from a DHCP or BOOTP server on your network
whenever the system is reset or power cycled. (Of course, the latter does
require that there be a DHCP or BOOTP server somewhere on your
network.) For instructions on how to set these parameters, refer to
“Configuring the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address” on
page 92.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Listed here are additional adapter card parameters you might need to
adjust, depending on the operating characteristics of the device to which
the port on the network adapter card is connected and the network
environment:
Port speed and duplex mode - The default speed and duplex mode
setting for a twisted pair port on an Allied Telesyn adapter card is AutoNegotiation. The default duplex mode setting for a fiber optic port is
full-duplex.
Magic packet - Enables and disables the Wake on LAN feature on the
adapter card. The default setting for this feature is disabled.
QoS tagging - Enables and disables the card’s ability to pass a Class
of Service level to packets. The default setting for this feature is
disabled.
VLAN ID - Specifies a VLAN identifier if the adapter card is to handle
tagged packets.
Network Address (LAA) - Specifies an alternate MAC address for the
adapter card.
Load balancing and fail over teams - Selects a load balancing mode
and assigns the adapter card to a team. These parameters are
91
Page 92

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
available only with the LBFO adapter driver. For background
information, refer to “Load Balancing and Fail-over Protection” on
page 39.
For instructions on how to set these parameters, refer to “Configuring
Additional Network Adapter Card Settings” on page 96.
Configuring the
IP Address,
Subnet Mask, and
Gateway Address
To configure the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address or to
activate the DHCP client software, perform the following procedure:
1. From the desktop, right-click the My Network Places icon and select
Properties from the menu, as shown in Figure 51.
Figure 51. My Network Places Icon Menu
An example of the Network Connections window is shown in Figure
52.
92
Figure 52. Network Connections Window
Page 93

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Note
The Network Connections window will contain more than one LAN
connection if the system contains more than one adapter or if VIDs
were added to an adapter using the AT-MUX protocol.
2. Do one of the following:
If you are not using the AT-MUX protocol, right-click the Local
Area Connections of the LAN connection icon for the network
adapter card and then select Properties, as shown in Figure 53.
The LAN connection icon for the network adapter card has the
adapter card model number in the icon’s label. (To view an icon’s
label, select the Tile menu selection under the View menu in the
Network Connections window. Alternately, you can open the
Properties window of a LAN connection.)
Figure 53. Local Area Connections Pop-up Menu
If you are using the AT-MUX protocol, right-click the Local Area
Connections of the LAN connection icon for the VLAN you want to
configure and then select Properties. The IP information on a
system using the AT-MUX protocol must be set on each VLAN
individually, and not on the adapter. For further information on the
protocol, refer to Chapter 9, “AT-MUX Multiple VLAN Protocol” on
page 157.
93
Page 94

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
An example of the Local Area Connection Properties window is shown
in Figure 54.
Figure 54. Local Area Connection Properties Window
3. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then click Properties.
Note
If the Properties button is greyed out and cannot be selected, it
probably means the system has the AT-MUX protocol and in Step 2
above you selected the icon for the adapter card instead of for a
VLAN. It is important to remember when setting the IP address,
subnet mask, and default gateway address on a system that has the
protocol that you must set this information on the individual VLANs
and not on the adapter card. To recover, simply close the Properties
window and repeat Step 2, this time selecting a VLAN icon.
94
Page 95

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window is shown in Figure 55.
Figure 55. Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Window
4. If you want the adapter to obtain its IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway from a DHCP or BOOTP server, select Obtain an IP
address automatically. If you want to set these parameters manually,
select Use the following IP address and enter the information into
the fields.
5. If your network has a domain name service, which converts domain
names into IP addresses, and you want the computer to obtain the IP
address of the domain name server from a DHCP or BOOTP server,
select Obtain DNS server address automatically. To enter the IP
address of a domain name server manually, select Use the following
DNS server addresses and enter the IP address in the field. You can
enter up to two IP addresses of domain name servers. The alternate
DNS server address is used only if the server specified as the
preferred DNS server does not respond.
Note
The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window has other
parameters that you can set. Do not set any other parameters
unless you have an complete understanding of their function.
95
Page 96

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
6. Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
7. Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
This completes the procedure for configuring the IP address and
subnet mask of a network adapter card.
Configuring
Additional
Network Adapter
Card Settings
This procedure explains how to change these parameters on a network
adapter card:
Port speed and duplex mode
Magic packet
QoS tagging
VLAN ID
Locally administered MAC address
Load balancing mode and fail-over protection
Note
For a dual port adapter Allied Telesyn recommends connecting the
appropriate port on the adapter to the network before performing this
procedure. Additionally, check to be sure that the remote device to
which the port on the adapter is connected is powered ON.
Caution
If you are planning to use the load balancing or fail-over protection
feature of the LBFO driver, do not connect both adapters to the
network at the same time until after you have configured the feature.
96
To configure these parameters, perform the following procedure:
1. From the desktop, right-click My Computer, then select Properties.
Page 97

Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
The System Properties window is shown in Figure 56.
Figure 56. Properties Window
97
Page 98

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
2. Select the Hardware tab.
The Hardware tab is shown in Figure 57.
98
Figure 57. Hardware Tab Window
Page 99

3. Select Device Manager.
The Device Manager window is shown in Figure 58.
Network Adapter Card Installation Guide
Figure 58. Device Manager Window
4. Expand Network adapters by either double-clicking on it or by clicking
once on the expansion box next to it.
The selection expands to display the network adapter cards installed in
the system. An example is shown here.
Note
The branch under Network Adapters will include VLANs if VIDs were
added to the adapter with the AT-MUX protocol. The VLANs are
labelled “Allied Telesyn VLAN-Tagging miniport Driver.” In the next
step you must select the network adapter card and not a VLAN. The
adapter card selection has the adapter’s model number in the label.
99
Page 100

Chapter 3: Microsoft Windows 2000, 2003, and XP
5. Right-click on the adapter driver you want to configure and select
Properties from the pop-up menu, as shown in Figure 59.
The Properties window is shown in Figure 60.
Figure 59. Properties Menu Selection
100
Figure 60. General Tab of the Network Adapter Card Properties Window
 Loading...
Loading...