Page 1

How To |
U s e D y n a m i c D N S To A l l o w Yo u To H o s t S e r v e r s
Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address
Allied Telesis routers feature a dynamic DNS client, which allows you to host web domains,
FTP servers, and mail servers behind a dynamically-assigned public IP address that periodically
changes. The dynamic DNS client works with the service provided by DynDNS.com
(www.dyndns.com). When the public IP address changes, the client notifies DynDNS.com of
the change.
What information will you find in this document?
This How To Note begins with essential background information, in the following sections:
• “DynDNS.com hostnames” on page 2
• “DNS server assignment” on page 3
Then it describes the example configuration, in the following sections:
• “Configuring dynamic DNS” on page 3:
• “Network diagram” on page 4
• “Configure the network and firewall” on page 4
• “Configure dynamic DNS” on page 7
• “Check dynamic DNS configuration” on page 9
• “Troubleshooting” on page 11
Which products and software version does it apply to?
This configuration applies to the following Allied Telesis routers, running Software Version
2.9.1 or later:
• AR4
• AR440S, AR44
• AR750S, AR750S-DP, AR770S
1
5S
1
S, AR442S
C613-16100-00 REV A
www.alliedtelesis.com
Page 2

DynDNS.com hostnames
In order to use the dynamic DNS client on the router, you first need to register at least one
hostname (actually a fully qualified domain name—FQDN) with DynDNS.com.
The dynamic DNS client can work with the following three hostname types from
DynDNS.com:
• Dynamic Hosts
This is the option to use if you don't own a domain name, but you want to host a server
on your network and have people reach it by entering a domain name.
Dynamic hosts are free to register with DynDNS.com, and allow you to associate a
dynamic IP address with up to five of the static domain names that DynDNS.com provide.
Dynamic host IP associations require at least one update every 35 days to prevent them
from expiring.
• Static Hosts
This is the option to use if you have a fixed IP address, you want to host a server on your
network and have people reach it by entering a domain name, but you do not want to buy
your own domain name.
Like dynamic hosts, static hosts are free to register with DynDNS.com, and allow you to
associate your public IP address with up to five of the static domain names that
DynDNS.com provides. However, static hosts are designed for use with IP addresses that
rarely or never change. This means that static host IP associations do not expire, and that
dynamic DNS updates take longer to propagate through the DNS system with static hosts.
• Custom Hosts
This is the option to use if you already own your own domain name.
Custom hosts support both static and dynamic IP addresses. For custom hosts, in addition
to automatic updates via the dynamic DNS client, DynDNS.com also provides a web-based
interface where you can make updates directly. Such direct changes propagate through the
DNS system very quickly.
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 2
Page 3

DNS server assignment
For the dynamic DNS process on the router to work, the router itself must be able to
resolve the domain name dyndns.com. Therefore, the router needs to know the address of at
least one DNS server. The router can learn the addresses of DNS servers dynamically from
your ISP, or you can configure them statically.
Dynamically When ISPs supply IP address settings dynamically, they mostly supply DNS server settings as
well. They do this by setting one of the following:
• DHCP option 6 on Eth and VLAN interfaces
• IPCP options
You can check if your router has dynamically-assigned name servers, and if so, what the
server addresses are, by using the command:
show ip dns
Dynamically-assigned servers are identified by an * in the Domain column of the output of
this command.
If necessary, you can force the router to learn DNS servers over a particular Eth, PPP or
VLAN interface. Use the command:
add ip dns interface=interface
Statically If your ISP does not assign DNS servers dynamically, you need to enter their addresses
statically. Use the command:
add ip dns primary=ipadd secondary=ipadd
If you manually configure the DNS servers and you have a backup connection to a different
ISP, you may need to set up triggers so that when the primary WAN connection fails, the
router is re-configured with the correct DNS servers for the backup connection.
1
29 (Primary server) and 131 (secondary server) on PPP interfaces
Configuring dynamic DNS
In this example, an AR440S connects to the Internet through a primary ADSL connection to
ISP
1
, with a backup ISDN connection to ISP 2. The AR440S router also acts as a firewall.
Steps that relate to the backup link are labelled, so you can avoid them if you have a single
connection.
To configure this example, follow the steps in the following sections:
• “Configure the network and firewall” on page 4
• “Configure dynamic DNS” on page 7
• “Check dynamic DNS configuration” on page 9
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 3
Page 4
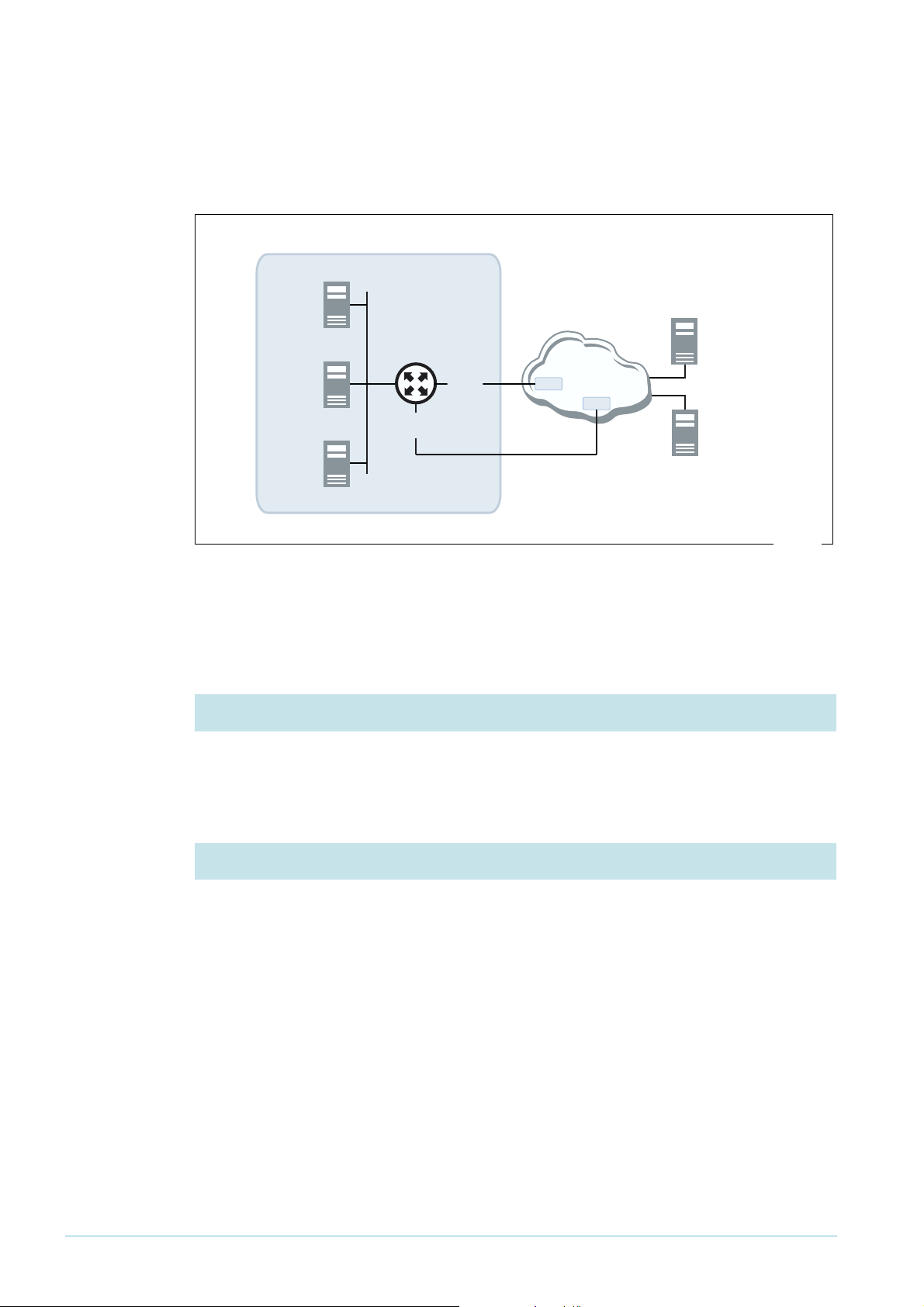
Network diagram
The following figure shows the network configuration.
web
server
AR440S router
FTP
server
ppp1
(ISDN)
mail
server
ppp0
(ADSL)
ISP 1
Internet
DNS
server
ISP 2
DynDNS.com
server
ddns.eps
Configure the network and firewall
This section describes how to configure the WAN links, IP, and the firewall.
1. Specify the country
Setting the country sets the ADSL defaults. Use the command:
set system country=your-country
2. Configure the WAN links
For the primary ADSL link, use the commands:
create atm=0 over=adsl0
add atm=0 channel=1
enable adsl=0
For the backup ISDN link, use the command:
add isdn call=backup num=isdn-number-of-isp prec=out
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 4
Page 5

3. Configure PPP
Configure the PPP link to each ISP. Use the username and password settings that your ISP
provides.
For the primary ADSL link, use the commands:
create ppp=0 over=atm0.1 lqr=off echo=10
set ppp=0 bap=off iprequest=on username=username
password=password
For the backup ISDN link, use the commands:
create ppp=1 over=isdn-backup idle=300 iprequest=on
username=username password=password lqr=off echo=10 bap=off
4. Configure IP
Enable IP, allow the router to obtain its addresses remotely, and assign an IP address to the
WAN interface. Use the commands:
enable ip
enable ip remote
add ip int=vlan1 ip=your-private-side-ip-address
If your ISP does not provide DNS server addresses as part of the dynamic IP configuration,
specify DNS servers for the router to use. See “DNS server assignment” on page 3 for more
information.
add ip dns primary=ip-of-primary-dns-server
secondary=ip-of-secondary-dns-server
For the primary ADSL link, assign an unnumbered address to the link and create a default
route. Use the commands:
add ip int=ppp0 ip=0.0.0.0 mask=0.0.0.0
add ip rou=0.0.0.0 mask=0.0.0.0 int=ppp0 next=0.0.0.0
For the backup ISDN link, assign an unnumbered address to the link and create a default
route with a higher preference value than the route over the primary link. This ensures that
the backup link is only used if the primary link goes down. Use the command:
add ip int=ppp1 ip=0.0.0.0 mask=0.0.0.0
add ip rou=0.0.0.0 mask=0.0.0.0 int=ppp1 next=0.0.0.0 pref=500
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 5
Page 6

5. Configure the firewall
Create a firewall policy and enable it. Use the commands:
create firewall policy=internet
enable firewall
enable firewall policy=internet icmp_f=all
Add the private interface to it. Use the command:
add firewall policy=internet int=vlan1 type=private
Add the public interface to it and set up Network Address Translation (NAT) between the
private and public interfaces. For the primary ADSL link, use the commands:
add firewall policy=internet int=ppp0 type=public
add firewall policy=internet nat=enhanced int=vlan1 gblint=ppp0
For the backup ISDN link, use the commands:
add firewall policy=internet int=ppp1 type=public
add firewall policy=internet nat=enhanced int=vlan1 gblin=ppp1
6. Add firewall rules
Add firewall rules to allow traffic from the WAN to access the servers. In this example, there
are web, FTP and mail servers.
For the primary ADSL link, use the commands:
add firewall policy=internet rule=1 action=allow interface=ppp0
protocol=tcp port=80 ip=ip-address-of-web-server gblip=0.0.0.0
gblport=80
add firewall policy=internet rule=2 action=allow interface=ppp0
protocol=tcp port=21 ip=ip-address-of-ftp-server gblip=0.0.0.0
gblport=21
add firewall policy=internet rule=3 action=allow interface=ppp0
protocol=tcp port=25 ip=ip-address-of-smtp-server gblip=0.0.0.0
gblport=25
For the backup ISDN link, use the commands:
add firewall policy=internet rule=4 action=allow interface=ppp1
protocol=tcp port=80 ip=ip-address-of-web-server gblip=0.0.0.0
gblport=80
add firewall policy=internet rule=5 action=allow interface=ppp1
protocol=tcp port=21 ip=ip-address-of-ftp-server gblip=0.0.0.0
gblport=21
add firewall policy=internet rule=6 action=allow interface=ppp1
protocol=tcp port=25 ip=ip-address-of-smtp-server gblip=0.0.0.0
gblport=25
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 6
Page 7

Configure dynamic DNS
This section describes how to configure dynamic DNS.
1. Enable dynamic DNS
Use the command:
enable ddns
2. Specify the DynDNS.com host or hosts
Depending on the kind of DynDNS.com host you have (see “DynDNS.com hostnames” on
page 2), use one of the commands:
set ddns dynamichost=your-hostname.dyndns-domain
or
set ddns statichost=your-hostname.dyndns-domain
or
set ddns customhost=your-hostname.your-domain
Note that the dynamic DNS client only supports one type of hostname at a time, but
supports multiple hostnames of that type. If you have multiple hostnames, specify them as a
comma-separated list. For example:
set ddns dynamichost=myhost1.dyndns.org,myhost2.dnsalias.org
3. Specify the dynamic DNS interface
Specify the interface that the WAN link uses.
For the primary ADSL link, use the command:
set ddns primaryinterface=ppp0
If you also have the backup ISDN link, also use the command:
set ddns secondaryinterface=ppp1
Note that the dynamic DNS client only supports one active WAN interface at a time.
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 7
Page 8

4. Specify the TCP port, if necessary
The router sends dynamic DNS updates to DynDNS.com. If necessary, you can specify the
port number that it uses for these. The DynDNS.com server listens to the following TCP
ports:
• 80 (for HTTP)—the default
• 8245 (an alternative for HTTP)
• 443 (for HTTPS)
To use TCP port 8245, use the command:
set ddns port=8245
To use TCP port 443, use the command:
set ddns port=443
5. Enable wildcard host look-ups
Wildcard hosts allow DNS look-ups for any hosts on your registered domain, even if
DynDNS.com and the DNS server do not know about those specific hosts.
For example, if the domain name you registered with DynDNS.com is:
mysite.dyn-o-saur.com
and wildcard hosts are enabled, the DNS look-ups to any-hostname.mysite.dyn-o-saur.com
resolve to the current IP address of mysite.dyn-o-saur.com.
You must also enable wildcard hosts on DynDNS.com.
To enable wildcard hosts, use the command:
set ddns wildcard=on
6. Specify the username and password
Specify the username and password that you have registered with DynDNS.com.
set ddns user=username-for-DynDNS password=password-for-DynDNS
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 8
Page 9

Check dynamic DNS configuration
show ddns After you have entered the DDNS configuration, you can check it by using the command:
show ddns
The following figure shows an example output from the command show ddns once the
public IP address has been assigned, but before a dynamic DNS update has occurred.
DDNS Config Information:
Client State ....................... ENABLED
Debug .............................. ENABLED
Server ............................. members.dyndns.org
Port ............................... 80
User ............................... test
Password ........................... ****
system name ........................ dyndns
hosts ............................ test.dyndns.org
Wildcard ........................... off
Offline ............................ no
Primary WAN Interface .............. ppp0
Secondary WAN Interface ............ ppp1
DDNS Operation Information:
Server IP .......................... 0.0.0.0
IP in DynDns ....................... 0.0.0.0
Current IP ......................... 222.152.186.174
In the above output of show ddns, the fields show the settings you have configured, except
the system name field and probably the Server field—you can configure the server setting
but do not need to. The following table has more information about these two fields.
Field Meaning Configurable?
Server The server that the dynamic DNS client
connects to at DynDNS.com, which is
members.dyndns.org.
Yes, by using the command set ddns, but
you do not need to configure it because
the only valid value is the default value of
members.dyndns.org.
System name The DynDNS.com system that update
messages use: one of dyndns, statdns, or
custom, depending on the type of
No. The router automatically sets the
system name to an appropriate value for
your hostname type.
hostname you chose.
When your ISP assigns a public IP address to your WAN interface, dynamic DNS waits for 30
seconds, then initiates a dynamic DNS update. The wait allows time for the PPP interface to
become fully open and means that the ISP’s DNS server is reachable. The dynamic DNS client
can then resolve the IP address for members.dyndns.org and send the dynamic DNS update.
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 9
Page 10

The following figure shows an example output from the command show ddns once a
dynamic DNS update has occurred.
DDNS Config Information:
Client State ....................... ENABLED
Debug .............................. ENABLED
Server ............................. members.dyndns.org
Port ............................... 80
User ............................... test
Password ........................... ****
system name ........................ dyndns
hosts ............................ test.dyndns.org
Wildcard ........................... off
Offline ............................ no
Primary WAN Interface .............. ppp0
Secondary WAN Interface ............ ppp1
DDNS Operation Information:
Server IP .......................... 63.208.196.95
IP in DynDns ....................... 222.152.186.174
Current IP ......................... 222.152.186.174
log entry You can also check the router log to see information about the dynamic DNS update. Use
the command:
show log
The following figure shows the log entry for a successful dynamic DNS update.
07 10:36:18 5 DDNS MSG INFO Dynamic DNS update succeed. Host test.dyndns.org
is 222.152.186.174.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 10
Page 11

Tro ubl es ho ot in g
To diagnose issues with dynamic DNS updates, try:
• checking the output of the show ddns command
• looking for log entries
• using the enable ddns debug command
You can manually activate a dynamic DNS client update. You should only do this when your
public IP address has changed but the dynamic DNS client has not been able to automatically
update. DynDNS.com treats repeated updates with no changes as abuse, and may blacklist
and disable your account. Therefore, the router requires confirmation whenever you activate
a dynamic DNS client update manually. To activate an update manually, use the command:
activate ddns update
The “show ddns” command
If the dynamic DNS update fails for any reason, the output from the show ddns command
includes a statement that the update failed, and suggested actions to resolve the issue. This
information appears at the bottom of the command, like in the following figure.
.
.
.
DDNS Operation Information:
Server IP .......................... 0.0.0.0
IP in DynDns ....................... 0.0.0.0
Current IP ......................... 222.152.186.174
Update failed - Suggested actions:
Config IP DNS or Set DDNS Server
Log entries
After every dynamic DNS update, a log entry indicates whether or not the update
succeeded. To see log entries, use the command:
show log
The following figure shows the log entry you might see if an update fails. In this case, the user
configured a domain name that DynDNS.com did not recognise, instead of using a domain
name from the list of domains that DynDNS.com owns (see Step 2 on page 7 and
www.dyndns.com).
Date/Time S Mod Type SType Message
------------------------------------------------------------------------------07 10:31:37 5 DDNS MSG WARN Dynamic DNS update failed. Host
fail_dyn_host_test is malformed.
Use Dynamic DNS To Allow You To Host Servers Behind A Dynamically-Assigned Public IP Address 11
Page 12

Debugging
The dynamic DNS client debug facility gives more information about rejected updates. When
DynDNS.com rejects an update it returns an error code, which is displayed in the debug
output. To enable debugging, use the command:
enable ddns debug
The figure on the next page shows debugging output for an update that failed because of an
incorrect username or password. The “return code” section of the output shows the error
code (“badauth” in this example, as shown in bold), and further down in the output is more
information about the cause of the return code (“Incorrect userid or path” in this example).
Manager >
ddnsIpgSetDynamicIpAddrNotify int=ppp0, ip=222.152.180.63
Manager >
ddnsReadDdnsRecord:
DynDns record file read IP=219.89.51.70, unicode=0x44444353
ddnsIpDNSServerName
ddnsIpDNSCallback server ip 63.208.196.95
idleflag=0x00000030, result=0x01000000
ddnsStartRequest
Manager >
ddnsHttpCreateRequestHeader
Manager >
ddnsHttpClientCallback sessionid=0x01581adc statusCode=401
ddnsHttpClientCallback sessionid=0x01581adc statusCode=1
HTTP Done
ddnsProcessReturnCodeTop
return code:
7
badauth
0
search for numhost
search for dnserr
search for 911
search for badsys
search for badagent
search for badauth
Incorrect userid or password.
result=0x00004000
action=0x00000400
ddnsProcessUpdateResult
USA Headquar ters | 19800 Nor th Cr eek Parkwa y | Suite 200 | Bothell | WA 98011 | USA | T: +1 800 424 4284 | F: +1 425 481 3895
Eur opean Headquar ters | Via Motta 24 | 6830 Chiasso | Switzerland | T: +41 91 69769.00 | F: +41 91 69769.11
Asia-Pacific Headquar ters | 11 T ai Seng Link | Singapor e | 534182 | T: +65 6383 3832 | F: +65 6383 3830
www .alliedtelesis.com
© 2006 Allied Tel esis Inc. All rights reser ved. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. All company names, logos, and product designs that are trademarks or registered trademarks are the proper ty of their respective owners.
C613-16100-00 REV A
 Loading...
Loading...