Page 1

Adjustable
Frequency AC
Drive
FRN 7.xx
www.abpowerflex.com
User Manual
Page 2

Important User Information
Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of
electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for the Application, Installation
and Maintenance of Solid State Controls (Publication SGI-1.1 available from your
local Rockwell Automation sales office or online at http://
www.rockwellautomation.com/literature) describes some important differences
between solid state equipment and hard-wired electromechanical devices. Because
of this difference, and also because of the wide variety of uses for solid state
equipment, all persons responsible for applying this equipment must satisfy
themselves that each intended application of this equipment is acceptable.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or
consequential damages resulting from the use or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative
purposes. Because of the many variables and requirements associated with any
particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or
liability for actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of
information, circuits, equipment, or software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written
permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc. is prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary we use notes to make you aware of safety
considerations.
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or circumstances
that can cause an explosion in a hazardous environment, which may
lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
Important: Identifies information that is critical for successful application and
understanding of the product.
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances
that can lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic
loss. Attentions help you:
identify a hazard
avoid the hazard
recognize the consequences
Shock Hazard labels may be located on or inside the equipment (e.g.,
drive or motor) to alert people that dangerous voltage may be present.
Burn Hazard labels may be located on or inside the equipment (e.g.,
drive or motor) to alert people that surfaces may be at dangerous
temperatures.
PowerFlex is a registered trademark of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
DriveExplorer, DriveExecutive, and SCANport are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
PLC is a registered trademark of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Page 3

Summary of Changes
The information below summarizes changes made for the July 2017
PowerFlex 4 User Manual, Publication 22A-UM001K-EN-E.
Description of New or Updated Information See Page(s)
Line fuse footnote added to Fuse Rating column.
Low Voltage Directive updated. 1-20
Attention statement on Option 3 “2-W Lvl Sens” and Important statement
about Option 4 “2-W Hi Speed” added to parameter P036 [Start Source].
Specifications table Approvals column updated. A-2
Sound Pressure Level specification added. A-3
Product Environmental Information added. A-4
Dynamic Brake Fuse Rating column and new footnote added. B-2
Network Wiring topic updated. C-1
The information below summarizes changes made for the June 2013
PowerFlex 4 User Manual, Publication 22A-UM001J-EN-E.
1-7
3-9
Description of New or Updated Information See Page(s)
Minimum Enclosure Volume column and new footnotes added.
Drive, Fuse & Circuit Breaker Ratings topic updated. A-1
Electronic Motor Overload Protection description updated. A-3
1-7, A-2
The information below summarizes changes made for the September
2010 PowerFlex 4 User Manual, Publication 22A-UM001I-EN-E.
Description of New or Updated Information See Page(s)
Parameters A117 [Bus Reg Mode] and A118 [Comm Write Mode] added.
3-13
The information below summarizes changes made for the July 2010
PowerFlex 4 User Manual, Publication 22A-UM001H-EN-E.
Description of New or Updated Information See Page(s)
Start and Speed Reference Control 1-18
The information below summarizes changes made for the March 2007
PowerFlex 4 User Manual, Publication 22A-UM001G-EN-E.
Description of New or Updated Information See Page(s)
Minimum Mounting Clearances clarified.
Footnote (2) on Bulletin 140M catalog edited. 1-7
Graphic for Analog Input, PTC wiring example corrected. 1-14
1-2
Page 4

soc-2
Description of New or Updated Information See Page(s)
Stop Drive icon and related warning text removed for parameter
A110 [Anlg In 0-10V Lo].
New information on reading register address 8192 added. C-4
New information on reading register address 8193 added. C-5
3-25
The information below summarizes changes made for the September
2005 PowerFlex 4 User Manual, Publication 22A-UM001F-EN-E.
Description of New or Updated Information See Page(s)
Attention statement clarified.
240V AC – 3-Phase 3.7 kW (5.0 Hp) drive fuse rating revised to 30 amps. 1-7, A-2
Analog Input, PTC wiring example added. 1-14
Attention statement added to Multiple Digital Input Connections wiring
example.
Parameter P043 [Motor OL Ret] added. 3-12
Attention statement added to parameter A082 [DB Resistor Sel]. 3-18
External Comm Options, Compact I/O added to Ta b le B. G . B-4
Modbus function code 16 added. C-3
1-3
1-17
Page 5

Preface Overview
Chapter 1 Installation/Wiring
Chapter 2 Start Up
Table of Contents
Who Should Use this Manual? . . . . . . . . . P-1
Reference Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-1
Manual Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-2
Drive Frame Sizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-2
General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-3
Catalog Number Explanation . . . . . . . . . . P-4
Opening the Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Mounting Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
AC Supply Source Considerations . . . . . . 1-3
General Grounding Requirements . . . . . . 1-4
Fuses and Circuit Breakers . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Power Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
I/O Wiring Recommendations . . . . . . . . 1-11
Start and Speed Reference Control . . . . . 1-18
EMC Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-20
Prepare For Drive Start-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Integral Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Viewing and Editing Parameters. . . . . . . . 2-4
Chapter 3 Programming and Parameters
About Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Parameter Organization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Display Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Basic Program Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Advanced Program Group. . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Parameter Cross Reference – by Name. . 3-27
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting
Drive Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Fault Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Common Symptoms and Corrective Actions . .
4-5
Appendix A Supplemental Drive Information
Drive, Fuse & Circuit Breaker Ratings . . . A-1
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Product Environmental Information . . . . . A-4
Appendix B Accessories and Dimensions
Product Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Product Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-5
Page 6

ii
Appendix C RS485 (DSI) Protocol
Network Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
Parameter Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
Supported Modbus Function Codes . . . . . C-3
Writing (06) Logic Command Data. . . . . . C-4
Writing (06) Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Reading (03) Logic Status Data. . . . . . . . . C-5
Reading (03) Feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Reading (03) Drive Error Codes . . . . . . . . C-6
Reading (03) and Writing (06) Drive
Additional Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-6
Appendix D RJ45 DSI Splitter Cable
Connectivity Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-1
DSI Cable Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-2
Connecting an RS-485 Network . . . . . . . . D-3
Index
Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-6
Page 7

Preface
Overview
The purpose of this manual is to provide you with the basic information
needed to install, start-up and troubleshoot the PowerFlex 4 Adjustable
Frequency AC Drive.
For information on… See page…
Who Should Use this Manual? P-1
Reference Materials P-1
Manual Conventions P-2
Drive Frame Sizes P-2
General Precautions P-3
Catalog Number Explanation P-4
Who Should Use this Manual?
This manual is intended for qualified personnel. You must be able to
program and operate Adjustable Frequency AC Drive devices. In
addition, you must have an understanding of the parameter settings and
functions.
Reference Materials
The following manuals are recommended for general drive information:
Title Publication Available Online at …
Wiring and Grounding
Guidelines for Pulse Width
Modulated (PWM) AC Drives
Preventive Maintenance of
Industrial Control and Drive
System Equipment
Safety Guidelines for the
Application, Installation and
Maintenance of Solid State
Control
A Global Reference Guide for
Reading Schematic Diagrams
Guarding Against Electrostatic
Damage
DRIVES-IN001…
DRIVES-SB001…
SGI-1.1
0100-2.10
8000-4.5.2
www.rockwellautomation.com/
literature
Page 8

P-P-2 Overview
Manual Conventions
In this manual we refer to the PowerFlex 4 Adjustable Frequency AC
Drive as: drive, PowerFlex 4 or PowerFlex 4 Drive.
Parameter numbers and names are shown in this format:
P031 [Motor NP Volts]
The following words are used throughout the manual to describe an
action:
Name
Number
Group
d = Display Group
P = Basic Program Group
A = Advanced Program Group
Word Meaning
Can Possible, able to do something
Cannot Not possible, not able to do something
May Permitted, allowed
Must Unavoidable, you must do this
Shall Required and necessary
Should Recommended
Should Not Not Recommended
Drive Frame Sizes
Similar PowerFlex 4 drive sizes are grouped into frame sizes to
simplify spare parts ordering, dimensioning, etc. A cross reference of
drive catalog numbers and their respective frame sizes is provided in
Appendix B.
Page 9

Overview P-3
!
!
!
!
!
General Precautions
ATTENTION: The drive contains high voltage capacitors which take
time to discharge after removal of mains supply. Before working on
drive, ensure isolation of mains supply from line inputs [R, S, T (L1,
L2, L3)]. Wait three minutes for capacitors to discharge to safe voltage
levels. Failure to do so may result in personal injury or death.
Darkened display LEDs is not an indication that capacitors have
discharged to safe voltage levels.
ATTENTION: Only qualified personnel familiar with adjustable
frequency AC drives and associated machinery should plan or
implement the installation, start-up and subsequent maintenance of the
system. Failure to comply may result in personal injury and/or
equipment damage.
ATTENTION: This drive contains ESD (Electrostatic Discharge)
sensitive parts and assemblies. Static control precautions are required
when installing, testing, servicing or repairing this assembly.
Component damage may result if ESD control procedures are not
followed. If you are not familiar with static control procedures,
reference A-B publication 8000-4.5.2, “Guarding Against Electrostatic
Damage” or any other applicable ESD protection handbook.
ATTENTION: An incorrectly applied or installed drive can result in
component damage or a reduction in product life. Wiring or application
errors, such as, undersizing the motor, incorrect or inadequate AC
supply, or excessive ambient temperatures may result in malfunction of
the system.
ATTENTION: The bus regulator function is extremely useful for
preventing nuisance overvoltage faults resulting from aggressive
decelerations, overhauling loads, and eccentric loads. However, it can
also cause either of the following two conditions to occur.
1. Fast positive changes in input voltage or imbalanced input voltages
can cause uncommanded positive speed changes;
2. Actual deceleration times can be longer than commanded
deceleration times
However, a “Stall Fault” is generated if the drive remains in this state
for 1 minute. If this condition is unacceptable, the bus regulator must be
disabled (see parameter
dynamic brake resistor will provide equal or better performance in most
cases.
). In addition, installing a properly sized
A117
Page 10

P-P-4 Overview
Code Volt age Ph.
V 120V AC 1
A 240V AC 1
B 240V AC 3
D 480V AC 3
Code
Version
3 No Brake IGBT
4 Standard
Code
Interface Module
1 Fixed Keypad
Code
Enclosure
N Panel Mount - IP 20 (NEMA Type Open)
F Flange Mount - IP 20 (NEMA Type Open)
H Replacement Plate Drive - IP 20 (NEMA Type Open)
- Contact factory for ordering information.
1-3 4 5 6-8 9 10 11 12
(1)
13-14
22A - A 1P5 N 1 1 4 AA
Drive Dash Voltage Rating Rating Enclosure HIM Emission Class Type Optional
Output Current @ 100-120V Input
Code Amps kW (HP)
1P5 1.5 0.2 (0.25)
2P3 2.3 0.4 (0.5)
4P5 4.5 0.75 (1.0)
6P0 6.0 1.1 (1.5)
Code Rating
0 Not Filtered
1Filtered
Code
22A PowerFlex 4
Code Purpose
AA Reserved for
thru custom firmware
ZZ
Output Current @ 200-240V Input, NO BRAKE
Code Amps kW (HP)
1P4 1.4 0.2 (0.25)
2P1 2.1 0.4 (0.5)
3P6 3.6 0.75 (1.0)
6P8 6.8 1.5 (2.0)
9P6 9.6 2.2 (3.0)
Output Current @ 380-480V Input
Code Amps kW (HP)
1P4 1.4 0.4 (0.5)
2P3 2.3 0.75 (1.0)
4P0 4.0 1.5 (2.0)
6P0 6.0 2.2 (3.0)
8P7 8.7 3.7 (5.0)
Output Current @ 200-240V Input
Code Amps kW (HP)
1P5 1.5 0.2 (0.25)
2P3 2.3 0.4 (0.5)
4P5 4.5 0.75 (1.0)
8P0 8.0 1.5 (2.0)
012 12.0 2.2 (3.0)
017 17.5 3.7 (5.0)
(1)
Position 12 of the Catalog Number now indicates drive type. All PowerFlex 4 drives
are equipped with RS485 communication.
Catalog Number Explanation
Page 11

Chapter 1
!
Installation/Wiring
This chapter provides information on mounting and wiring the
PowerFlex 4 Drive.
For information on… See page For information on… See page
Opening the Cover 1-1 Fuses and Circuit Breakers 1-6
Mounting Considerations 1-2 Power Wiring 1-8
AC Supply Source Considerations 1-3 I/O Wiring
Recommendations
General Grounding Requirements 1-4 EMC Instructions 1-20
Most start-up difficulties are the result of incorrect wiring. Every
precaution must be taken to assure that the wiring is done as instructed.
All items must be read and understood before the actual installation
begins.
1-11
ATTENTION: The following information is merely a guide for proper
installation. Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility
for the compliance or the noncompliance to any code, national, local or
otherwise for the proper installation of this drive or associated
equipment. A hazard of personal injury and/or equipment damage
exists if codes are ignored during installation.
Opening the Cover
1. Press and hold in the tabs on each side of the cover.
2. Pull the cover out and up to release.
Page 12
1-2 Installation/Wiring
Mounting Option A
No clearance required between drives.
Mounting Option B
Closest object that
may restrict air flow
through the drive heat
sink and chassis
Mounting Considerations
Mount the drive upright on a flat, vertical and level surface.
– Install on 35 mm DIN Rail.
or
– Install with screws.
Table 1.A Screw Mounting Recommendations
Minimum Panel Thickness Screw Size Mounting Torque
1.9 mm (0.0747 in.) M4 (#8-32) 1.56-1.96 N-m (14-17 lb.-in.)
Protect the cooling fan by avoiding dust or metallic particles.
Do not expose to a corrosive atmosphere.
Protect from moisture and direct sunlight.
Minimum Mounting Clearances
Refer to
Appendix B for mounting dimensions.
120 mm
(4.7 in.)
120 mm
(4.7 in.)
120 mm
(4.7 in.)
120 mm
(4.7 in.)
25 mm
(1.0 in.)
Ambient Operating Temperatures
Table 1.B Enclosure and Clearance Requirements
Ambient Temperature Enclosure Rating Minimum Mounting
Minimum Maximum
-10°C (14°F)
(1)
Rating requires installation of the PowerFlex 4 IP 30/NEMA 1/UL Type 1 option kit.
40°C (104°F)
50°C (122°F) IP 20/Open Type Use Mounting Option B
Debris Protection
A plastic top panel is included with the drive. Install the panel to prevent
debris from falling through the vents of the drive housing during
installation. Remove the panel for IP 20/Open Type applications.
Clearances
IP 20/Open Type Use Mounting Option A
(1)
IP 30/NEMA 1/UL Type 1
Use Mounting Option B
Page 13
Installation/Wiring 1-3
!
Important:
Tighten screw after
jumper removal.
Storage
Store within an ambient temperature range of -40° to +85°C.
Store within a relative humidity range of 0% to 95%,
non-condensing.
Do not expose to a corrosive atmosphere.
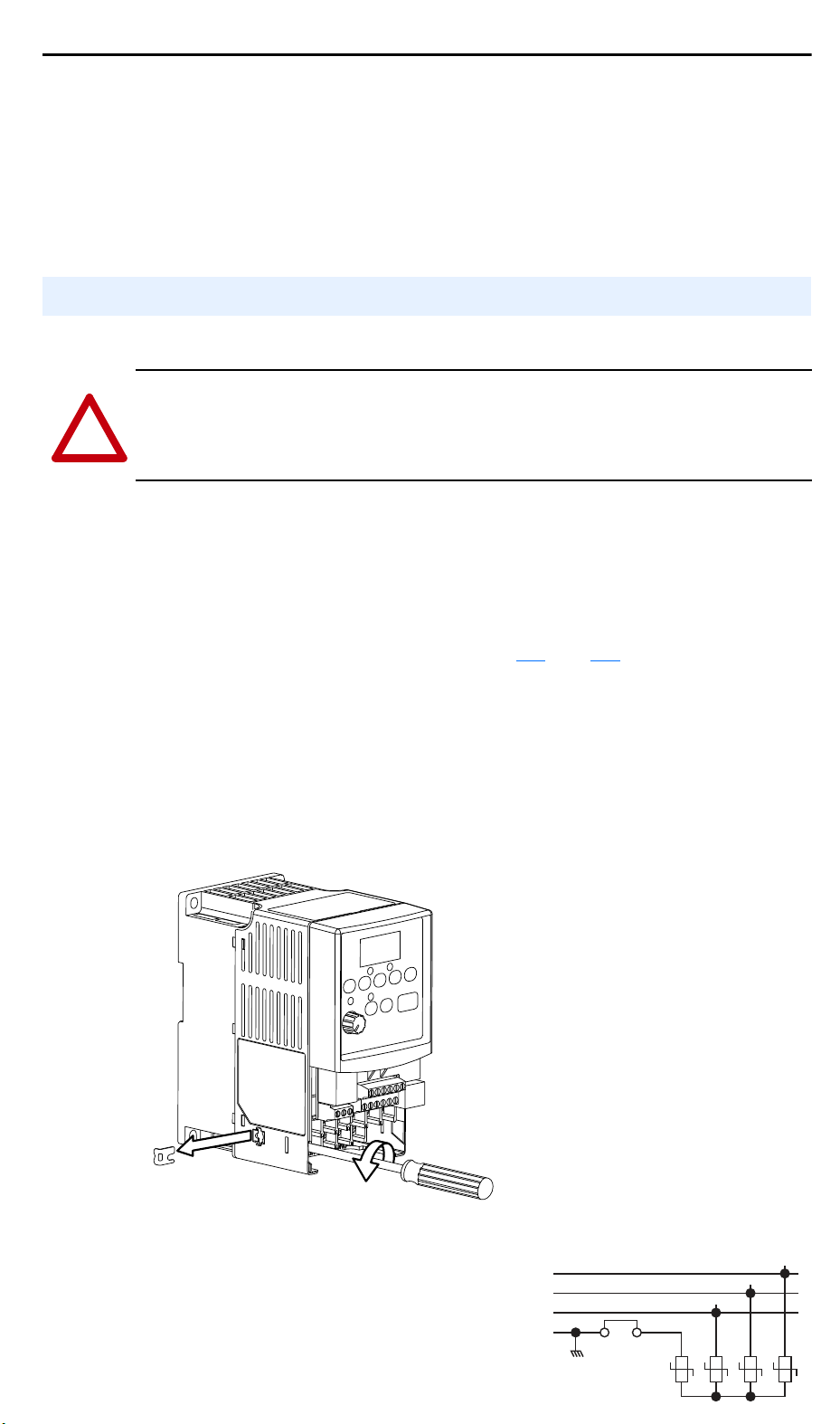
AC Supply Source Considerations
Ungrounded Distribution Systems
ATTENTION: PowerFlex 4 drives contain protective MOVs that are
referenced to ground. These devices must be disconnected if the drive is
installed on an ungrounded or resistive grounded distribution system.
Disconnecting MOVs
To prevent drive damage, the MOVs connected to ground shall be
disconnected if the drive is installed on an ungrounded distribution
system where the line-to-ground voltages on any phase could exceed
125% of the nominal line-to-line voltage. To disconnect these devices,
remove the jumper shown in the Figures
1.1 and 1.2.
1. Turn the screw counterclockwise to loosen.
2. Pull the jumper completely out of the drive chassis.
3. Tighten the screw to keep it in place.
Figure 1.1 Jumper Location (A Frame Shown)
Figure 1.2 Phase to Ground MOV Removal
Three-Phase
AC Input
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
Jumper
1234
Page 14

1-4 Installation/Wiring
Input Power Conditioning
The drive is suitable for direct connection to input power within the rated
voltage of the drive (see
input power conditions which may cause component damage or
reduction in product life. If any of the conditions exist, as described in
Table 1.C, install one of the devices listed under the heading Corrective
Action on the line side of the drive.
Important: Only one device per branch circuit is required. It should be
mounted closest to the branch and sized to handle the total
current of the branch circuit.
Table 1.C Input Power Conditions
Input Power Condition Corrective Action
Low Line Impedance (less than 1% line reactance) Install Line Reactor
Greater than 120 kVA supply transformer
Appendix A). Listed in Table 1.C are certain
(1)
or Isolation Transformer
Line has power factor correction capacitors
Line has frequent power interruptions
Line has intermittent noise spikes in excess of
6000V (lightning)
Phase to ground voltage exceeds 125% of normal
line to line voltage
Ungrounded distribution system
(1)
Refer to
Appendix B for accessory ordering information.
Remove MOV jumper to ground.
or Install Isolation Transformer
with grounded secondary if
necessary.
General Grounding Requirements
The drive Safety Ground - (PE) must be connected to system ground.
Ground impedance must conform to the requirements of national and
local industrial safety regulations and/or electrical codes. The integrity
of all ground connections should be periodically checked.
Figure 1.3 Typical Grounding
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
SHLD
Page 15

Installation/Wiring 1-5
Ground Fault Monitoring
If a system ground fault monitor (RCD) is to be used, only Type B
(adjustable) devices should be used to avoid nuisance tripping.
Safety Ground - (PE)
This is the safety ground for the drive that is required by code. One of
these points must be connected to adjacent building steel (girder, joist), a
floor ground rod or bus bar. Grounding points must comply with
national and local industrial safety regulations and/or electrical codes.
Motor Ground
The motor ground must be connected to one of the ground terminals on
the drive.
Shield Termination - SHLD
Either of the safety ground terminals located on the power terminal
block provides a grounding point for the motor cable shield. The motor
cable shield connected to one of these terminals (drive end) should also
be connected to the motor frame (motor end). Use a shield terminating or
EMI clamp to connect the shield to the safety ground terminal. The
conduit box option may be used with a cable clamp for a grounding point
for the cable shield.
When shielded cable is used for control and signal wiring, the shield
should be grounded at the source end only, not at the drive end.
RFI Filter Grounding
Using single phase drives with integral filter, or an external filter with
any drive rating, may result in relatively high ground leakage currents.
Therefore, the filter must only be used in installations with grounded
AC supply systems and be permanently installed and solidly
grounded (bonded) to the building power distribution ground. Ensure
that the incoming supply neutral is solidly connected (bonded) to the
same building power distribution ground. Grounding must not rely on
flexible cables and should not include any form of plug or socket that
would permit inadvertent disconnection. Some local codes may require
redundant ground connections. The integrity of all connections should
be periodically checked.
Page 16

1-6 Installation/Wiring
!
Fuses and Circuit Breakers
The PowerFlex 4 does not provide branch short circuit protection. This
product should be installed with either input fuses or an input circuit
breaker. National and local industrial safety regulations and/or electrical
codes may determine additional requirements for these installations.
ATTENTION: To guard against personal injury and/or equipment
damage caused by improper fusing or circuit breaker selection, use only
the recommended line fuses/circuit breakers specified in this section.
Fusing
The PowerFlex 4 has been UL tested and approved for use with input
fuses. The ratings in the table that follows are the minimum
recommended values for use with each drive rating. The devices listed in
this table are provided to serve as a guide.
Bulletin 140M (Self-Protected Combination Controller)/UL489
Circuit Breakers
When using Bulletin 140M or UL489 rated circuit breakers, the
guidelines listed below must be followed in order to meet the NEC
requirements for branch circuit protection.
Bulletin 140M can be used in single and group motor applications.
Bulletin 140M can be used up stream from the drive without the
need for fuses.
Page 17

Installation/Wiring 1-7
Table 1.D Minimum Recommended Branch Circuit Protective Devices
Voltage
Rating
120V AC –
1-Phase
240V AC –
1-Phase
NO BRAKE
240V AC –
1-Phase
240V AC –
3-Phase
Drive Rating
kW (HP)
0.2 (0.25)
0.4 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.1 (1.5)
0.2 (0.25)
0.4 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
2.2 (3.0)
0.2 (0.25)
0.4 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
0.2 (0.25)
0.4 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
2.2 (3.0)
3.7 (5.0)
Fuse Rating
Amps
(Line Fuse)
10
15
30
40
6
10
15
25
30
10
10
15
30
3
6
10
15
25
30
(1)
140M
Catalog No.
(2)
140M-C2E-C10
140M-C2E-C16
140M-D8E-C20
140M-F8E-C32
140M-C2E-B40
140M-C2E-B63
140M-C2E-C16
140M-C2E-C16
140M-D8E-C25
140M-C2E-B63
140M-C2E-B63
140M-C2E-C16
140M-D8E-C20
140M-C2E-B25
140M-C2E-B40
140M-C2E-C10
140M-C2E-C16
140M-C2E-C16
140M-F8E-C25
(3) (4)
Recommended
MCS Contactors
Catalog No.
100-C09
100-C12
100-C23
100-C37
100-C09
100-C09
100-C12
100-C16
100-C23
100-C09
100-C09
100-C12
100-C23
100-C09
100-C09
100-C09
100-C12
100-C16
100-C23
Min. Enclosure
Volum e
Inches
(5)
3
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
480V AC –
3-Phase
0.4 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
2.2 (3.0)
3.7 (5.0)
(1)
Recommended Fuse Type: UL Class J, CC, T or Type BS88; 600V (550V) or equivalent.
(2)
EN61800-5-1 compliance
3
6
10
15
15
140M-C2E-B25
140M-C2E-B40
140M-C2E-B63
140M-C2E-C10
140M-C2E-C16
100-C09
100-C09
100-C09
100-C09
100-C16
1655
1655
1655
1655
1655
When using a dynamic brake resistor, the guidelines listed below must be followed.
– Only use input fuse UL Class T 600V or equivalent for branch circuit protection.
– Connect a series fuse, type PV 1000V fast-acting or equivalent, with the dynamic brake resistor.
– Recommended fuse rating is listed in
(3)
The AIC ratings of the Bulletin 140M Motor Protector Circuit Breakers may vary. See
Tab l e B .C .
Bulletin 140M
Motor Protection Circuit Breakers Application Ratings.
(4)
Manual Self-Protected (Type E) Combination Motor Controller, UL listed for 208 Wye or Delta, 240
Wye or Delta, 480Y/277 or 600Y/347. Not UL listed for use on 480V or 600V Delta/Delta, corner
ground, or high-resistance ground systems.
(5)
When using a Manual Self-Protected (Type E) Combination Motor Controller, the drive must be
installed in a ventilated or non-ventilated enclosure with the minimum volume specified in this
column. Application specific thermal considerations may require a larger enclosure.
Page 18
1-8 Installation/Wiring
!
!
Power Wiring
ATTENTION: National Codes and standards (NEC, VDE, BSI, etc.)
and local codes outline provisions for safely installing electrical
equipment. Installation must comply with specifications regarding wire
types, conductor sizes, branch circuit protection and disconnect
devices. Failure to do so may result in personal injury and/or equipment
damage.
ATTENTION: To avoid a possible shock hazard caused by induced
voltages, unused wires in the conduit must be grounded at both ends.
For the same reason, if a drive sharing a conduit is being serviced or
installed, all drives using this conduit should be disabled. This will help
minimize the possible shock hazard from “cross coupled” power leads.
Motor Cable Types Acceptable for 200-600 Volt Installations
General
A variety of cable types are acceptable for drive installations. For many
installations, unshielded cable is adequate, provided it can be separated
from sensitive circuits. As an approximate guide, allow a spacing of 0.3
meters (1 foot) for every 10 meters (32.8 feet) of length. In all cases,
long parallel runs must be avoided. Do not use cable with an insulation
thickness less than 15 mils (0.4 mm/0.015 in.). Do not route more than
three sets of motor leads in a single conduit to minimize “cross talk”. If
more than three drive/motor connections per conduit are required,
shielded cable must be used.
UL installations in 50°C ambient must use 600V, 75°C or 90°C wire.
UL installations in 40°C ambient should use 600V, 75°C or 90°C wire.
Use copper wire only. Wire gauge requirements and recommendations
are based on 75 degree C. Do not reduce wire gauge when using higher
temperature wire.
Unshielded
THHN, THWN or similar wire is acceptable for drive installation in dry
environments provided adequate free air space and/or conduit fill rates
limits are provided. Do not use THHN or similarly coated wire in wet
areas. Any wire chosen must have a minimum insulation thickness of
15 mils and should not have large variations in insulation concentricity.
Shielded
Location Rating/Type Description
Standard
(Option 1)
Standard
(Option 2)
Class I & II;
Division I & II
600V, 75°C or 90°C (167°F
or 194°F) RHH/RHW-2
Belden 29501-29507 or
equivalent
Tray rated 600V, 75°C or
90°C (167°F or 194°F)
RHH/RHW-2
Shawflex 2ACD/3ACD or
equivalent
Tray rated 600V, 75°C or
90°C (167°F or 194°F)
RHH/RHW-2
Four tinned copper conductors with XLPE insulation
Foil shield and tinned copper drain wire with 85% braid
coverage
PVC jacket
Three tinned copper conductors with XLPE insulation
5 mil single helical copper tape (25% overlap min.)
with three bare copper grounds in contact with shield
PVC jacket
Three tinned copper conductors with XLPE insulation
5 mil single helical copper tape (25% overlap min.)
with three bare copper grounds in contact with shield
PVC copper grounds on #10 AWG and smaller
Page 19

Installation/Wiring 1-9
Reflected Wave Protection
The drive should be installed as close to the motor as possible.
Installations with long motor cables may require the addition of external
devices to limit voltage reflections at the motor (reflected wave
phenomena). See
The reflected wave data applies to all frequencies 2 to 16 kHz.
For 240V ratings, reflected wave effects do not need to be considered.
Table 1.E Maximum Cable Length Recommendations
Reflected Wave
380-480V Ratings Motor Insulation Rating Motor Cable Only
Table 1.E for recommendations.
(1)
1000 Vp-p 15 meters (49 feet)
1200 Vp-p 40 meters (131 feet)
1600 Vp-p 170 meters (558 feet)
(1)
Longer cable lengths can be achieved by installing devices on the output of the drive.
Consult factory for recommendations.
Output Disconnect
The drive is intended to be commanded by control input signals that will
start and stop the motor. A device that routinely disconnects then
reapplies output power to the motor for the purpose of starting and
stopping the motor should not be used. If it is necessary to disconnect
power to the motor with the drive outputting power, an auxiliary contact
should be used to simultaneously disable drive control run commands.
Page 20
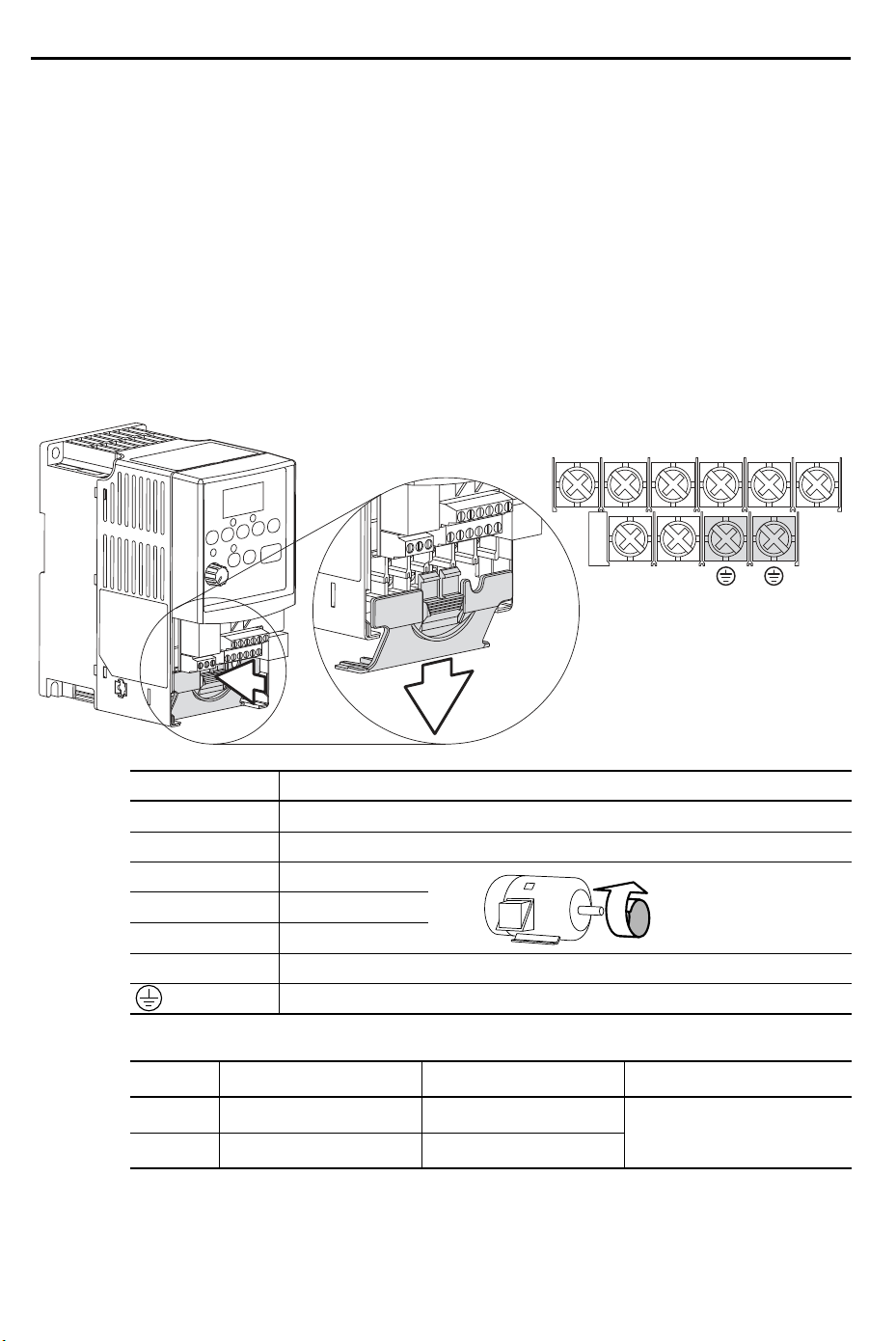
1-10 Installation/Wiring
V/T2T/L3S/L2R/L1 U/T1 W/T3
BR+ BR-
Power Terminal Block
The drive utilizes a finger guard over the power wiring terminals. To
remove:
1. Press in and hold the locking tab.
2. Slide finger guard down and out.
Replace the finger guard when wiring is complete.
Figure 1.4 Power Terminal Block (A Frame Shown)
Terminal Description
R/L1, S/L2 1-Phase Input
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3 3-Phase Input
U/T1 To Motor U/T1
V/T2 To Motor V/T2
W/T3 To Motor W/T3
=
Switch any two motor
leads to change
forward direction.
BR+, BR- Dynamic Brake Resistor Connection
Safety Ground - PE
Table 1.F Power Terminal Block Specifications
Frame Maximum Wire Size
(1)
Minimum Wire Size
(1)
Torq ue
A 3.3 mm2 (12 AWG) 0.8 mm2 (18 AWG)
B 5.3 mm
(1)
Maximum/minimum sizes that the terminal block will accept - these are not
2
(10 AWG) 1.3 mm2 (16 AWG)
1.7-2.2 N-m (16-19 lb.-in.)
recommendations.
Page 21

Installation/Wiring 1-11
!
!
!
I/O Wiring Recommendations
Motor Start/Stop Precautions
ATTENTION: A contactor or other device that routinely disconnects
and reapplies the AC line to the drive to start and stop the motor can
cause drive hardware damage. The drive is designed to use control input
signals that will start and stop the motor. If used, the input device must
not exceed one operation per minute or drive damage can occur.
ATTENTION: The drive start/stop control circuitry includes
solid-state components. If hazards due to accidental contact with
moving machinery or unintentional flow of liquid, gas or solids exist,
an additional hardwired stop circuit may be required to remove the AC
line to the drive. When the AC line is removed, there will be a loss of
any inherent regenerative braking effect that might be present - the
motor will coast to a stop. An auxiliary braking method may be
required.
Important points to remember about I/O wiring:
Always use copper wire.
Wire with an insulation rating of 600V or greater is recommended.
Control and signal wires should be separated from power wires by at
least 0.3 meters (1 foot).
Important: I/O terminals labeled “Common” are
safety ground (PE) terminal and are designed to greatly
reduce common mode interference.
ATTENTION: Driving the 4-20mA analog input from a voltage
source could cause component damage. Verify proper configuration
prior to applying input signals.
not referenced to the
Page 22

1-12 Installation/Wiring
Control Wire Types
Table 1.G Recommended Control and Signal Wire
Wire Type(s) Description Minimum
Belden 8760/9460
(or equiv.)
Belden 8770
(or equiv.)
(1)
If the wires are short and contained within a cabinet which has no sensitive circuits,
the use of shielded wire may not be necessary, but is always recommended.
0.8 mm2(18AWG), twisted pair, 100%
shield with drain.
0.8 mm2(18AWG), 3 conductor, shielded for
remote pot only.
(1)
(1)
Insulation Rating
300V
60 degrees C
(140 degrees F)
I/O Terminal Block
Table 1.H I/O Terminal Block Specifications
Maximum Wire Size
1.3 mm2 (16 AWG) 0.13 mm2 (26 AWG) 0.5-0.8 N-m (4.4-7 lb.-in.)
(1)
Maximum/minimum sizes that the terminal block will accept - these are not
recommendations.
(1)
Minimum Wire Size
(1)
Torque
Maximum Control Wire Recommendations
Do not exceed control wiring length of 30 meters (100 feet). Control
signal cable length is highly dependent on electrical environment and
installation practices. To improve noise immunity, the I/O terminal
block Common must be connected to ground terminal/protective earth.
If using the RS485 (DSI) port, I/O Terminal 16 should also be connected
to ground terminal/protective earth.
Page 23

Figure 1.5 Control Wiring Block Diagram
01
02
03
04
05
06
11
12
13
14
15
16
Stop
(1)
Start/Run FWD
(2)
Direction/Run REV
Digital Common
Digital Input 1
Digital Input 2
R1
R2
R3
Relay N.O.
Relay Common
Relay N.C.
+24V DC
+10V DC
0-10V In
Analog Common
4-20mA In
RS485 Shield
+24V
+10V
SRCSNK
Typical
SNK Wiring
Typical
SRC Wiring
18
RS485
(DSI)
R1 R2 R3
01 02 03 04 05 06
11 12 13 14 15 16
SNK
SRC
(1)
Potentiometer
must be
1-10k ohm
2 Watt Min.
30V DC 125V AC 240V AC
Resistive 3.0A 3.0A 3.0A
Inductive 0.5A 0.5A 0.5A
(1)
Important: I/O Terminal 01 is
always a coast to stop input except
when P036 [Start Source] is set to
“3-Wire” control. In three wire
control, I/O Terminal 01 is controlled
by P037 [Stop Mode]. All other stop
sources are controlled by P037
[Stop Mode].
Important: The drive is shipped with
a jumper installed between I/O
Terminals 01 and 11. Remove this
jumper when using I/O Terminal 01
as a stop or enable input.
(2)
Two wire control shown. For three
wire control use a momentary input
on I/O Terminal 02 to
command a start. Use a maintained
input for I/O Terminal 03 to
change direction.
P036
[Start Source]
Stop
I/O Terminal 01
Stop
Keypad Per P037 Coast
3-Wire Per P037 Per P037
2-Wire Per P037 Coast
RS485 Port Per P037 Coast
Installation/Wiring 1-13
No. Signal Default Description Param.
R1 Relay N.O. Fault Normally open contact for output relay.
R2 Relay Common – Common for output relay.
R3 Relay N.C. Fault Normally closed contact for output relay. A055
Sink/Source DIP Switch Source (SRC)
01 Stop
02 Start/Run FWD Not Active
03 Direction/Run REV Not Active
04 Digital Common –
05 Digital Input 1 Preset Freq Program with A051 [Digital In1 Sel].
06 Digital Input 2 Preset Freq Program with A052 [Digital In2 Sel]. A052
11 +24V DC –
12 +10V DC –
13 0-10V In
14 Analog Common –
15 4-20mA In
16 RS485 (DSI) Shield –
(3)
(1)
(3)
(3)
Only one analog frequency source may be connected at a time. If more than one reference is connected at the same
time, an undetermined frequency reference will result.
Coast
Not Active
Not Active
Inputs can be wired as Sink (SNK) or Source (SRC) via DIP Switch
setting.
The factory installed jumper or a normally closed input
must be present for the drive to start.
Command comes from the integral keypad by default. To
disable reverse operation, see A095 [Reverse Disable].
For digital inputs. Electronically isolated with digital inputs
from analog I/O.
Drive supplied power for digital inputs.
Maximum output current is 100mA.
Drive supplied power for 0-10V external potentiometer.
Maximum output current is 15mA.
For external 0-10V input supply
(input impedance = 100k ohm) or potentiometer wiper.
For 0-10V In or 4-20mA In. Electronically isolated with
analog inputs from digital I/O.
For external 4-20mA input supply
(input impedance = 250 ohm).
Terminal should be connected to safety ground - PE
when using the RS485 (DSI) communications por t.
A055
P036
P036, P037
P036, P037,
A095
A051
P038
P038
P038
(1)
Page 24
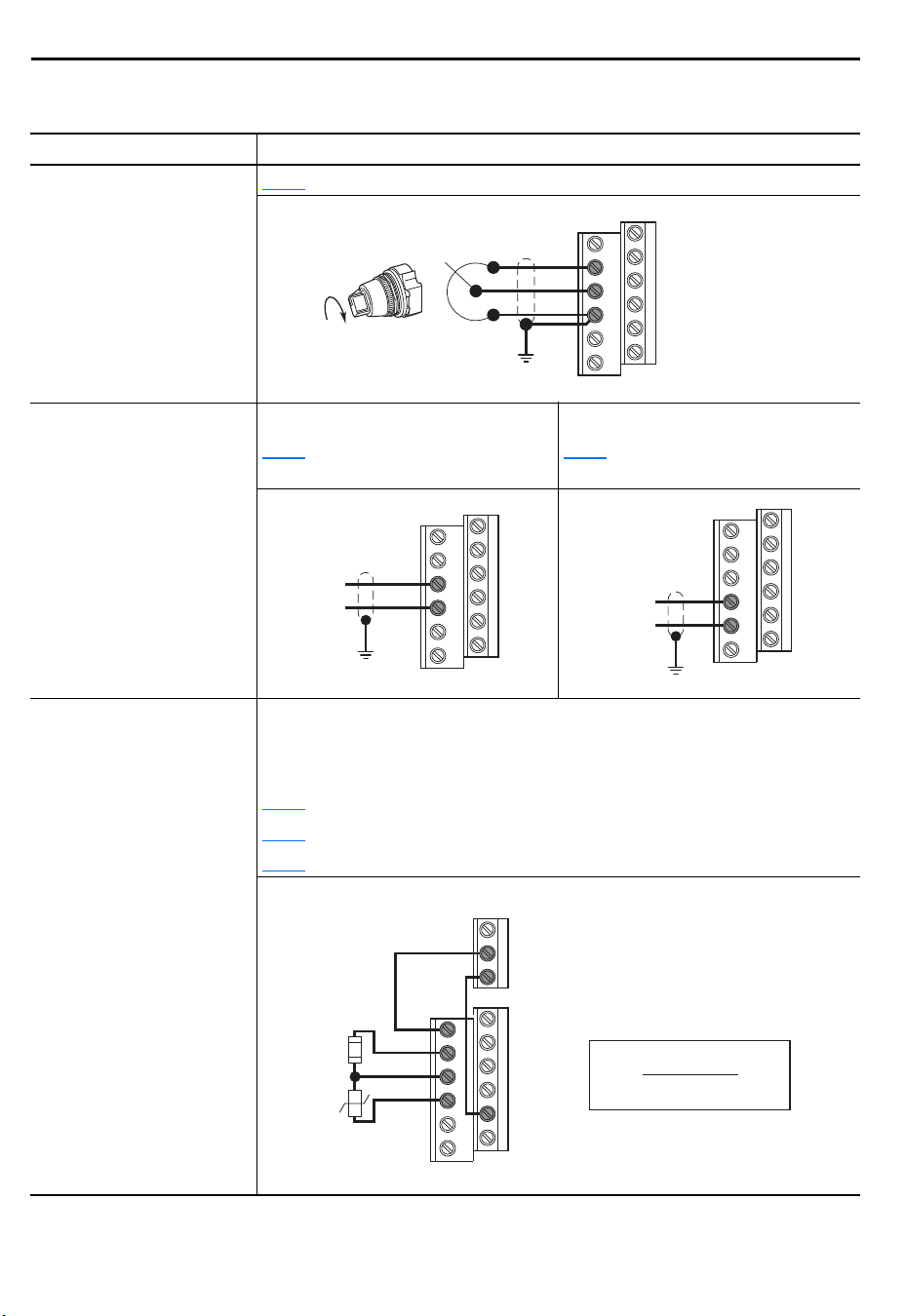
1-14 Installation/Wiring
13
14
+
Common
I/O Wiring Examples
Input Connection Example
Potentiometer
1-10k Ohm Pot.
Recommended
(2 Watt minimum)
P038 [Speed Reference] = 2 “0-10V Input”
12
13
14
Analog Input
0 to +10V, 100k ohm
impedance
4-20 mA, 100 ohm
impedance
Analog Input, PTC
For Drive Fault
Voltage
P038 [Speed Reference] = 2 “0-10V
Input”
Current
P038 [Speed Reference] = 3
“4-20mA Input”
Common
14
15
+
Wire the PTC and External Resistor (typically matched to the PTC Hot
Resistance) to I/O Terminals 12, 13, 14.
Wire R2/R3 Relay Output (SRC) to I/O Terminals 5 & 11.
A051
[Digital In1 Sel] = 3 “Aux Fault”
A055 [Relay Out Sel] = 10 “Above Anlg V”
A056 [Relay Out Level] = % Voltage Trip
R2
R3
11
R
e
R
PTC
12
13
14
05
R
=
PTC (hot)
R
PTC (hot)
+ R
×
100
e
V
Tr ip
Page 25

Input Connection Example
11
01
02
Stop-Run
Each digital input draws 6 mA.
01
02
04
Stop-Run
11
01
02
03
Stop-Run
Forward
Stop-Run
Reverse
Common
01
02
03
04
Stop-Run
Forward
Stop-Run
Reverse
+24V
Each digital input draws 6 mA.
Stop-Run
Forward
Stop-Run
Reverse
01
02
03
04
2 Wire SRC Control -
Internal Supply (SRC) External Supply (SRC)
Non-Reversing
P036
[Start Source] = 2, 3
or 4
Input must be active for
the drive to run. When
input is opened, the drive
will stop as specified by
P037 [Stop Mode].
If desired, a User Supplied
24V DC power source can
be used. Refer to the
“External Supply (SRC)”
example.
2 Wire SNK Control -
Internal Supply (SNK)
Non-Reversing
Installation/Wiring 1-15
01
02
Stop-Run
04
+24V Common
2 Wire SRC Control Run FWD/Run REV
P036 [Start Source] = 2, 3
or 4
Input must be active for
the drive to run. When
input is opened, the drive
will stop as specified by
P037 [Stop Mode].
If both Run Forward and
Run Reverse inputs are
closed at the same time,
an undetermined state
could occur.
2 Wire SNK Control Run FWD/Run REV
Internal Supply (SRC) External Supply (SRC)
Internal Supply (SNK)
Page 26

1-16 Installation/Wiring
Each digital input draws 6 mA.
Stop
Start
01
02
03
04
11
01
02
03
Stop
Start
Direction
+24V Common
Stop
Start
Direction
01
02
03
04
Each digital input draws 6 mA.
Stop
Start
Direction
01
02
03
04
Input Connection Example
3 Wire SRC Control Non-Reversing
P036
[Start Source] = 1
A momentary input will
start the drive. A stop
input to I/O Terminal 01
will stop the drive as
specified by
P037
[Stop
Mode].
Internal Supply (SRC) External Supply (SRC)
Stop
11
Start
+24V
Stop
Start
Common
01
02
04
01
02
3 Wire SNK Control Non-Reversing
3 Wire SRC Control Reversing
P036 [Start Source] = 1
A momentary input will
start the drive. A stop
input to I/O Terminal 01
will stop the drive as
specified by
P037 [Stop
Mode]. I/O Terminal 03
determines direction.
Internal Supply (SNK)
Internal Supply (SRC) External Supply (SRC)
3 Wire SNK Control Reversing
Internal Supply (SNK)
Page 27

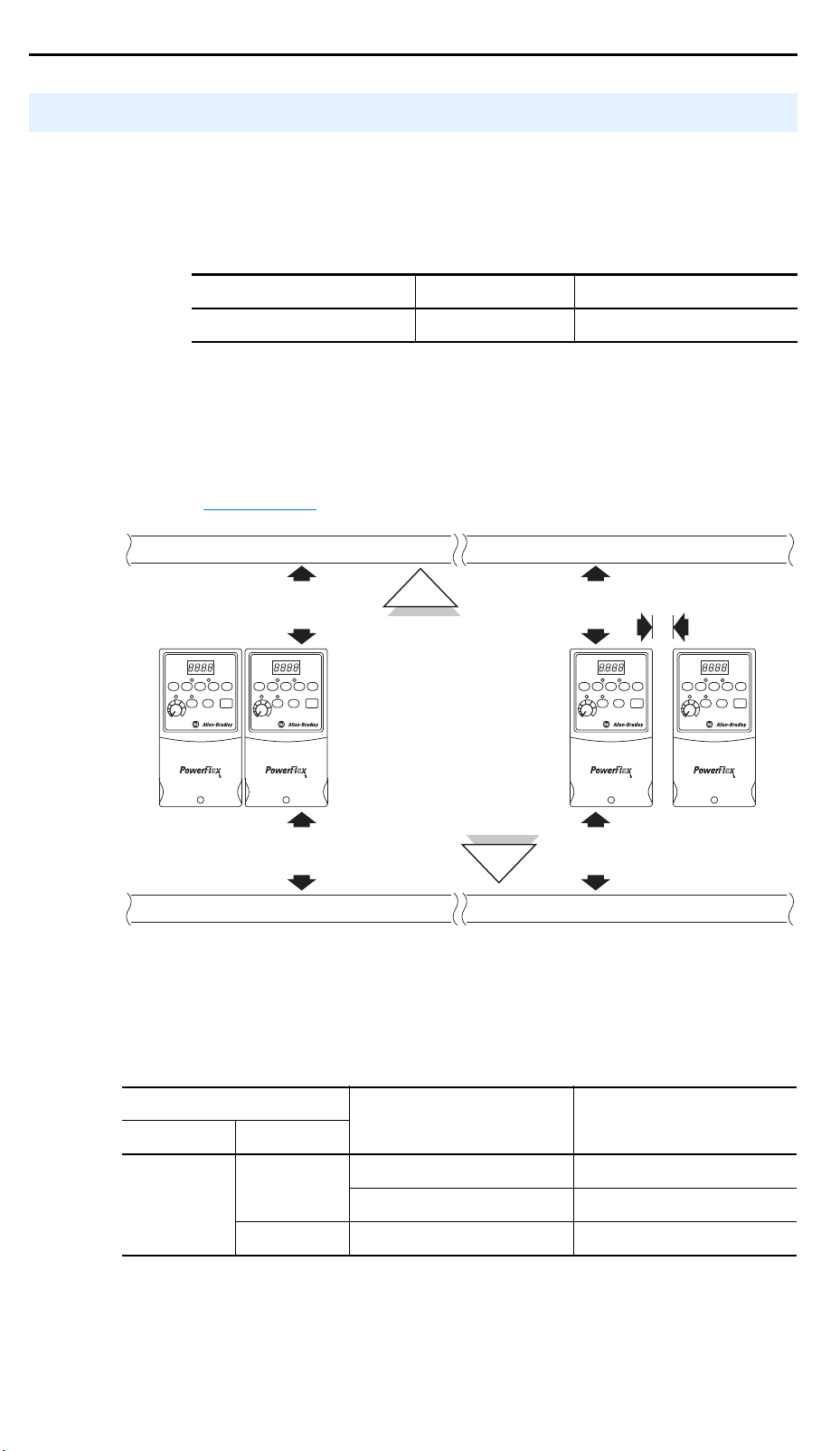
Typical Multiple Drive Connection Examples
!
ATTENTION: I/O Common terminals should not be tied
together when using SNK (Internal Supply) mode. In SNK
mode, if power is removed from one drive, inadvertent operation
of other drives that share the same I/O Common connection
may occur.
Input Connection Example
Multiple Digital
Input Connections
Customer Inputs can
be wired per
External Supply
(SRC) or Internal
Supply (SNK)
examples on
page 1-15.
Customer Inputs
When connecting a single input such as Run, Stop, Reverse or Preset Speeds
to multiple drives, it is important to connect I/O Terminal 04 common together
for all drives. If they are to be tied into another common (such as earth ground
or separate apparatus ground) only one point of the daisy chain of I/O Terminal
04 should be connected.
04
02 0402 0402 0402
Installation/Wiring 1-17
Optional Ground Connection
Multiple Analog
Connections
12 13 14 13 14 13 14 13 14
Remote Potentiometer Optional Ground Connection
When connecting a single potentiometer to multiple drives it is important to
connect I/O Terminal 14 common together for all drives. I/O Terminal 14
common and I/O Terminal 13 (potentiometer wiper) should be daisy-chained to
each drive. All drives must be powered up for the analog signal to be read
correctly.
Page 28
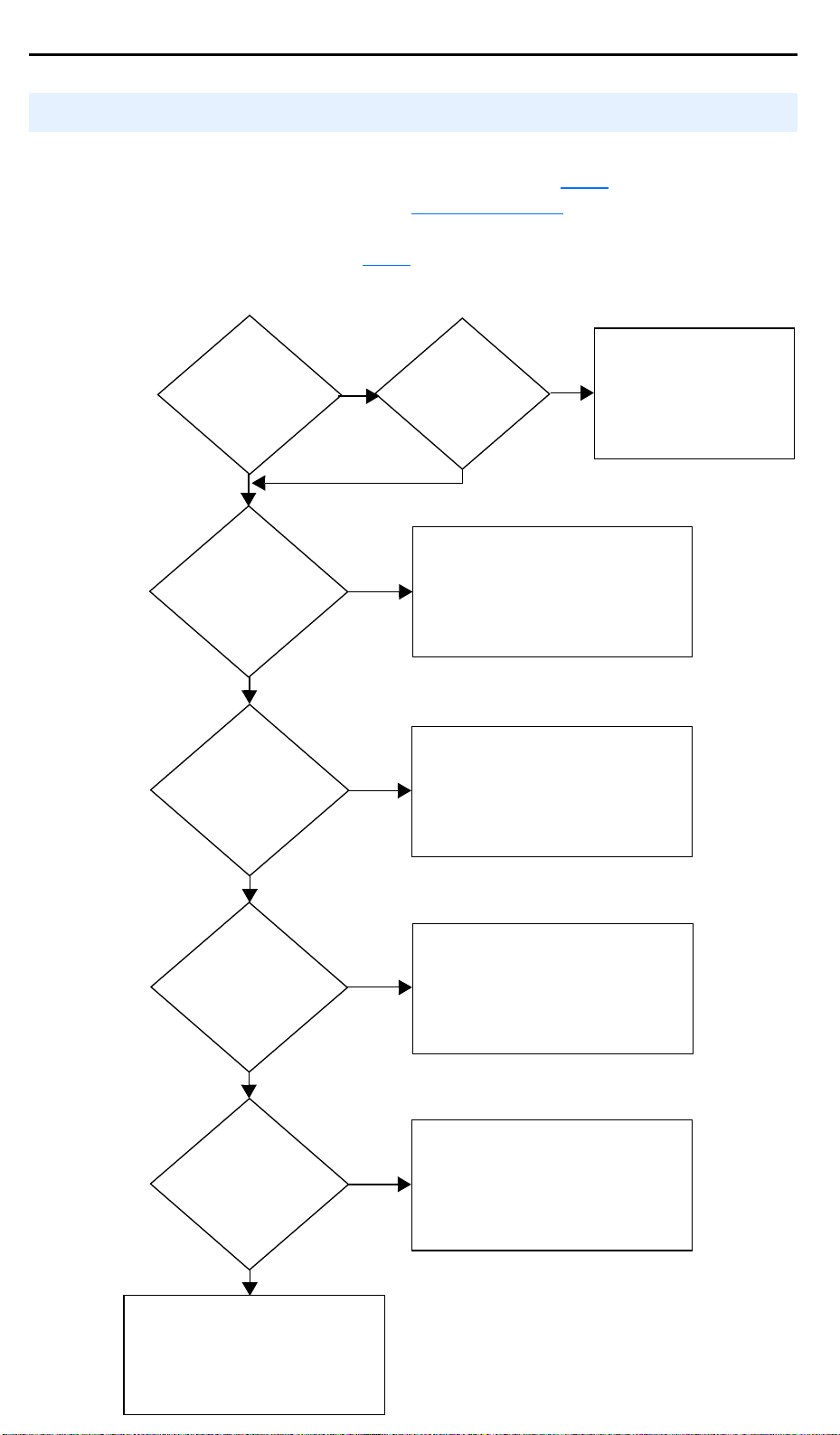
1-18 Installation/Wiring
Jog Input
Enabled and Active:
A051 or A052 = 2
Ye s
Drive will Start and Run at
Jog Speed.
Direction comes from
Terminal 03 Dir/Run REV
Local/Remote Input
Enabled and Active:
A051 or A052 = 5
Ye s
Start, Speed and Direction commands
come from Integral Keypad.
Comm Select Input
Enabled and Active:
A051 or A052 = 6
Ye s
Start, Speed and Direction commands
come from RS485 (DSI) port.
P038 [Speed Reference]
= 4 or 5
Ye s
Run as specified by
P038 [Speed Reference].
Start and Direction commands come
from P036 [Start Source].
A051 / A052
Preset Inputs Active
Ye s
Run as specified by
A071-A073 [Preset Freq 1-3].
Start and Direction commands come
from P036 [Start Source].
Run as specified by
P038 [Speed Reference].
Start and Direction commands
come from P036 [Start Source].
No
No
No
No
No
Drive stopped
(not Running)
Ye s
No
Start and Speed Reference Control
The drive speed command can be obtained from a number of different
sources. The source is normally determined by
However, when A051 or A052
6, and the digital input is active, A051 or A052 will override the speed
reference commanded by
for the override priority.
P038 [Speed Reference].
[Digital Inx Sel] is set to option 2, 4, 5 or
P038 [Speed Reference]. See the chart below
Page 29

Installation/Wiring 1-19
Jog Input
Enabled and Active:
A051 or A052 = 2
Ye s
A079 [Jog Accel/Decel] used.
P039 [Accel Time 1]/P040 [Decel Time 1]
are used.
RS485 (DSI) Port
Controls Speed
Active when
A067 [Accel Time 2]/A068 [Decel Time 2]
is selected by RS485 (DSI) port.
Input is programmed
as “Accel 2 & Decel 2”
A051 or A052 = 1
A067 [Accel Time 2]/A068 [Decel Time 2]
is active when input is active.
Speed is controlled
by [Preset Freq x]
A051 or A052 = 4
P039 [Accel Time 1]/P040 [Decel Time 1];
A067 [Accel Time 2]/A068 [Decel Time 2]
determined by the active Preset Frequency.
See A070-A073 [Preset Freq 0-3]
on page 3-16.
No
No
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
No
No
Accel/Decel Selection
The selection of Accel/Decel rates can be made through digital inputs,
RS485 (DSI) communications and/or parameters.
t
Page 30

1-20 Installation/Wiring
EMC Instructions
CE Conformity
Conformity with the Low Voltage (LV) Directive and Electromagnetic
Compatibility (EMC) Directive has been demonstrated using
harmonized European Norm (EN) standards published in the Official
Journal of the European Communities. PowerFlex Drives comply with
the EN standards listed below when installed according to the User
Manual.
CE Declarations of Conformity are available online at:
http://www.ab.com/certification/ce/docs.
Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU)
EN 61800-5-1 Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems –
Part 5-1: Safety requirements – Electrical, thermal and energy.
Pollution Degree Ratings According to EN 61800-5-1
Pollution Degree Description
1 No pollution or only dry, non-conductive pollution occurs. The
pollution has no influence.
2 Normally, only non-conductive pollution occurs. Occasionally,
however, a temporary conductivity caused by condensation is to
be expected, when the drive is out of operation.
EMC Directive (2014/30/EU)
EN61800-3 Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems Part 3:
EMC product standard including specific test methods.
General Notes
If the plastic top panel is removed or the optional conduit box is not
installed, the drive must be installed in an enclosure with side
openings less than 12.5 mm (0.5 in.) and top openings less than 1.0
mm (0.04 in.) to maintain compliance with the LV Directive.
The motor cable should be kept as short as possible in order to avoid
electromagnetic emission as well as capacitive currents.
Use of line filters in ungrounded systems is not recommended.
Conformity of the drive with CE EMC requirements does not
guarantee an entire machine installation complies with CE EMC
requirements. Many factors can influence total machine/installation
compliance.
Page 31

Installation/Wiring 1-21
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
EMI Fittings and Metal Conduit
IP 30/NEMA 1/UL Type 1
Option Kit
Shielded Enclosure
(1)
Building Structure Steel
Enclosure Ground Connection
(2)
EMI Filter
L1'
L2'
L3'
L1
L2
L3
Shielded Motor Cable
Essential Requirements for CE Compliance
Conditions 1-3 listed below must be satisfied for PowerFlex drives to
meet the requirements of EN61800-3.
1. Grounding as described in
Figure 1.6. Refer to page 1-5 for
additional grounding recommendations.
2. Output power, control (I/O) and signal wiring must be braided,
shielded cable with a coverage of 75% or better, metal conduit or
equivalent attenuation.
3. Allowable cable length in
Table 1.I
Table 1.I Allowable Cable Length
Filter Type EN61800-3 First Environment
Restricted Distribution or
Second Environment
Integral 10 meters (33 feet) 1 meter (3 feet)
(1)
External - S Type
External - L Type
(1)
Refer to
(2)
Equivalent to EN55011 Class A.
(3)
Equivalent to EN55011 Class B.
Appendix B for details on optional external filters.
10 meters (33 feet) 1 meter (3 feet)
(1)
100 meters (328 feet) 5 meters (16 feet)
is not exceeded.
EN61800-3 First Environment
Unrestricted Distribution
(2)
(3)
Figure 1.6 Connections and Grounding
(1)
First Environment Unrestricted Distribution installations require a shielded enclosure.
Keep wire length as short as possible between the enclosure entry point and the EMI
filter.
(2)
Integral EMI filters are available on 240V, 1-Phase drives.
Page 32

1-22 Installation/Wiring
EN61000-3-2
0.75 kW (1 HP) 240V 1-Phase and 3-Phase drives and 0.37 kW (0.5
HP) 240V 1-Phase drives are suitable for installation on a private low
voltage power network. Installations on a public low voltage power
network may require additional external harmonic mitigation.
Other drive ratings meet the current harmonic requirements of
EN61000-3-2 without additional external mitigation.
Page 33

Chapter 2
!
Start Up
This chapter describes how to start up the PowerFlex 4 Drive. To
simplify drive setup, the most commonly programmed parameters are
organized in a single Basic Program Group.
Important: Read the General Precautions section before proceeding.
ATTENTION: Power must be applied to the drive to perform the
following start-up procedures. Some of the voltages present are at
incoming line potential. To avoid electric shock hazard or damage to
equipment, only qualified service personnel should perform the
following procedure. Thoroughly read and understand the procedure
before beginning. If an event does not occur while performing this
procedure, Do Not Proceed. Remove All Power including user
supplied control voltages. User supplied voltages may exist even when
main AC power is not applied to the drive. Correct the malfunction
before continuing.
Prepare For Drive Start-Up
Before Applying Power to the Drive
❏ 1. Confirm that all inputs are connected to the correct terminals and are
secure.
❏ 2. Verify that AC line power at the disconnect device is within the rated
value of the drive.
❏ 3. Verify that any digital control power is 24 volts.
❏ 4. Verify that the Sink (SNK)/Source (SRC) Setup DIP Switch is set to
match your control wiring scheme. See
location.
Important: The default control scheme is Source (SRC). The Stop
terminal is jumpered (I/O Terminals 01 and 11) to allow
starting from the keypad. If the control scheme is changed
to Sink (SNK), the jumper must be removed from I/O
Terminals 01 and 11 and installed between I/O Terminals
01 and 04.
Figure 1.5 on page 1-13 for
❏ 5. Verify that the Stop input is present or the drive will not start.
Important: If I/O Terminal 01 is used as a stop input, the jumper
between I/O Terminals 01 and 11 must be removed.
Page 34

2-2 Start Up
Applying Power to the Drive
❏ 6. Apply AC power and control voltages to the drive.
❏ 7. Familiarize yourself with the integral keypad features (see
before setting any Program Group parameters.
Start, Stop, Direction and Speed Control
Factory default parameter values allow the drive to be controlled from
the integral keypad. No programming is required to start, stop, change
direction and control speed directly from the integral keypad.
Important: To disable reverse operation, see
If a fault appears on power up, refer to
for an explanation of the fault code.
Fault Descriptions on page 4-3
Variable Torque Fan/Pump Applications
For improved motor tuning performance when using a premium efficient
motor on a variable torque load, set
“35.0, VT”.
A084 [Boost Select] to option 2
A095 [Reverse Disable].
page 2-3)
Page 35

Start Up 2-3
FAULT
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
RUN
FWD
REV
PROGRAM
➊
➋
➍
➏
➒
➎
Menu Description
Display Group (View Only)
Consists of commonly viewed drive operating
conditions.
Basic Program Group
Consists of most commonly used
programmable functions.
Advanced Program Group
Consists of remaining programmable functions.
Fault Designator
Consists of list of codes for specific fault
conditions. Displayed only when fault is present.
➌
➑
➐
Integral Keypad
No. LED LED State Description
Run/Direction
➊
Status
Alphanumeric
➋
Display
Displayed Units Steady Red Indicates the units of the parameter value being displayed.
➌
Program Status Steady Red Indicates parameter value can be changed.
➍
Fault Status Flashing Red Indicates drive is faulted.
➎
Pot Status Steady Green Indicates potentiometer on Integral Keypad is active.
➏
Start Key Status Steady Green Indicates Start key on Integral Keypad is active.
➐
Steady Red Indicates drive is running and commanded motor direction.
Flashing Red Drive has been commanded to change direction. Indicates
actual motor direction while decelerating to zero.
Steady Red Indicates parameter number, parameter value, or fault code.
Flashing Red Single digit flashing indicates that digit can be edited.
All digits flashing indicates a fault condition.
The Reverse key is also active unless disabled by
[Reverse Disable].
A095
No. Key Name Description
Escape Back one step in programming menu.
Cancel a change to a parameter value and exit Program
Mode.
Select Advance one step in programming menu.
Select a digit when viewing parameter value.
Up Arrow
Down Arrow
Enter Advance one step in programming menu.
Potentiometer Used to control speed of drive. Default is active.
Start Used to start the drive. Default is active.
Scroll through groups and parameters.
Increase/decrease the value of a flashing digit.
Save a change to a parameter value.
Controlled by parameter
Controlled by parameter
Reverse Used to reverse direction of the drive. Default is active.
Controlled by parameters
[Reverse Disable].
Stop Used to stop the drive or clear a fault.
This key is always active.
Controlled by parameter P037 [Stop Mode].
➑
➒
P038 [Speed Reference].
P036 [Start Source].
P036 [Start Source] and A095
Page 36

2-4 Start Up
or
or
or
or
or
or
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
FAULTPROGRAM
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
FAULTPROGRAM
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
FAULTPROGRAM
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
FAULTPROGRAM
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
FAULTPROGRAM
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
FAULTPROGRAM
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
FAULTPROGRAM
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
FAULTPROGRAM
Viewing and Editing Parameters
The last user-selected Display Group parameter is saved when power is removed and is displayed by
default when power is reapplied.
The following is an example of basic integral keypad and display functions. This example provides basic
navigation instructions and illustrates how to program the first Program Group parameter.
Step Key(s) Example Displays
1. When power is applied, the last user-selected
Display Group parameter number is briefly
displayed with flashing characters. The display
then defaults to that parameter’s current value.
(Example shows the value of d001 [Output
Freq] with the drive stopped.)
2. Press Esc once to display the Display Group
parameter number shown on power-up. The
parameter number will flash.
3. Press Esc again to enter the group menu. The
group menu letter will flash.
4. Press the Up Arrow or Down Arrow to scroll
through the group menu (d, P and A).
5. Press Enter or Sel to enter a group. The right
digit of the last viewed parameter in that group
will flash.
6. Press the Up Arrow or Down Arrow to scroll
through the parameters that are in the group.
7. Press Enter or Sel to view the value of a
parameter. If you do not want to edit the value,
press Esc to return to the parameter number.
8. Press Enter or Sel to enter program mode to
edit the parameter value. The right digit will
flash and the Program LED will illuminate if the
parameter can be edited.
9. Press the Up Arrow or Down Arrow to change
the parameter value. If desired, press Sel to
move from digit to digit or bit to bit. The digit or
bit that you can change will flash.
10. Press Esc to cancel a change. The digit will
stop flashing, the previous value is restored and
the Program LED will turn off.
Or
Press Enter to save a change. The digit will stop
flashing and the Program LED will turn off.
11. Press Esc to return to the parameter list.
Continue to press Esc to back out of the
programming menu.
If pressing Esc does not change the display,
then d001 [Output Frequency] is displayed.
Press Enter or Sel to enter the group menu.
The Basic Program Group (
page 3-8) contains the most commonly changed parameters.
Page 37

Chapter 3
32
Programming and Parameters
Chapter 3 provides a complete listing and description of the PowerFlex 4
parameters. Parameters are programmed (viewed/edited) using the
integral keypad. As an alternative, programming can also be performed
using DriveExplorer™ or DriveExecutive™ software, a personal
computer and a serial converter module. Refer to
numbers.
For information on… See page…
About Parameters 3-1
Parameter Organization 3-2
Basic Program Group 3-8
Advanced Program Group 3-13
Parameter Cross Reference – by Name 3-27
Appendix B for catalog
About Parameters
To configure a drive to operate in a specific way, drive parameters may
have to be set. Three types of parameters exist:
ENUM
ENUM parameters allow a selection from 2 or more items. Each item
is represented by a number.
Numeric Parameters
These parameters have a single numerical value (i.e. 0.1 Volts).
Bit Parameters
Bit parameters have four individual bits associated with features or
conditions. If the bit is 0, the feature is off or the condition is false. If
the bit is 1, the feature is on or the condition is true.
Some parameters are marked as follows.
= Stop drive before changing this parameter.
= 32 bit parameter. Parameters marked 32 bit will have two
parameter numbers when using RS485 communications and
programming software.
Page 38

3-2 Programming and Parameters
See page 3-8
Motor NP Volts P031
Motor NP Hertz P032
Motor OL Current P033
Minimum Freq P034
Maximum Freq P035
Start Source P036
Stop Mode P037
Speed Reference P038
Accel Time 1 P039
Decel Time 1 P040
Reset To Defalts P041
Motor OL Ret P043
See page 3-3
Output Freq d001
Commanded Freq d002
Output Current d003
Output Voltage d004
DC Bus Voltage d005
Drive Status d006
Fault 1 Code d007
Fault 2 Code d008
Fault 3 Code d009
Process Display d010
Control Source d012
Contrl In Status d013
Dig In Status d014
Comm Status d015
Control SW Ver d016
Drive Type d017
Elapsed Run Time d018
Testpoint Data d019
Analog In 0-10V d020
Analog In 4-20mA d021
Drive Temp d024
See page 3-13
Digital In1 Sel A051
Digital In2 Sel A052
Relay Out Sel A055
Relay Out Level A056
Accel Time 2 A067
Decel Time 2 A068
Internal Freq A069
Preset Freq 0 A070
Preset Freq 1 A071
Preset Freq 2 A072
Preset Freq 3 A073
Jog Frequency A078
Jog Accel/Decel A079
DC Brake Time A080
DC Brake Level A081
DB Resistor Sel A082
S Curve % A083
Boost Select A084
Maximum Voltage A088
Current Limit A089
Motor OL Select A090
PWM Frequency A091
Auto Rstrt Tries A092
Auto Rstrt Delay A093
Start At PowerUp A094
Reverse Disable A095
Flying Start En A096
Compensation A097
SW Current Trip A098
Process Factor A099
Fault Clear A100
Program Lock A101
Testpoint Sel A102
Comm Data Rate A103
Comm Node Addr A104
Comm Loss Action A105
Comm Loss Time A106
Comm Format A107
Anlg In 0-10V Lo A110
Anlg In 0-10V Hi A111
Anlg In 4-20mA Lo A112
Anlg In 4-20mA Hi A113
Slip Hertz @ FLA A114
Process Time Lo A115
Process Time Hi A116
Bus Reg Mode A117
Comm Write Mode A118
Parameter Organization
Display Group
Basic
Program Group
Advanced
Program Group
Page 39

Programming and Parameters 3-3
Display Group
d001 [Output Freq] Related Parameter(s): d002, d010, P034, P035, P038
Output frequency present at T1, T2 & T3 (U, V & W).
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0.0/
Display: 0.1 Hz
P035 [Maximum Freq]
d002 [Commanded Freq] Related Parameter(s): d001, d013, P034, P035, P038
Value of the active frequency command. Displays the commanded frequency even if the drive is not
running.
Important: The frequency command can come from a number of sources. Refer to
Reference Control on page 1-18 for details.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0.0/
Display: 0.1 Hz
[Maximum Freq]
P035
Start and Speed
d003 [Output Current]
The output current present at T1, T2 & T3 (U, V & W).
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0.00/(Drive Rated Amps 2)
Display: 0.01 Amps
d004 [Output Voltage] Related Parameter(s): P031, A084, A088
Output voltage present at terminals T1, T2 & T3 (U, V & W).
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/Drive Rated Volts
Display: 1 VAC
d005 [DC Bus Voltage]
Present DC bus voltage level.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: Based on Drive Rating
Display: 1 VDC
Page 40

3-4 Programming and Parameters
1 = Condition True, 0 = Condition False
Running Bit 0
Forward Bit 1
Accelerating Bit 2
Decelerating Bit 3
32
Output
Freq
Process
Factor
Process
Display
=
x
Display Group (continued)
d006 [Drive Status] Related Parameter(s): A095
Present operating condition of the drive.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/1
Display: 1
d007 [Fault 1 Code]
d008 [Fault 2 Code]
d009 [Fault 3 Code]
A code that represents a drive fault. The codes will appear in these parameters in the order they occur
(d007 [Fault 1 Code] = the most recent fault). Repetitive faults will only be recorded once.
Refer to
Values Default Read Only
Chapter 4 for fault code descriptions.
Min/Max: F2/F122
Display: F1
d010 [Process Display] Related Parameter(s): d001, A099, A115, A116
32 bit parameter.
The output frequency scaled by
[Process Time Hi].
Values Default Read Only
A099 [Process Factor] or by A115 [Process Time Lo] and A116
Min/Max: 0.00/9999
Display: 0.01 – 1
Page 41

Programming and Parameters 3-5
Start Command Digit 0
0 = Keypad
1 = 3-Wire
2 = 2-Wire
3 = 2-Wire Level Sensitive
4 = 2-Wire High Speed
5 = RS485 (DSI) Port
9 = Jog
Speed Command Digit 1
0 = Drive Potentiometer
1 =
A069
[Internal Freq]
2 = 0-10V Input/Remote Potentiometer
3 = 4-20mA Input
4 =
A070 - A073 [Preset Freq x]
(
A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Sel] must be set to 4)
5 = RS485 (DSI) Port
9 = Jog Freq
Reserved Digit 2
Reserved Digit 3
1 = Input Present, 0 = Input Not Present
Start / Run FWD Input (I/O Terminal 02) Bit 0
Direction / Run REV Input (I/O Terminal 03) Bit 1
Stop Input
(1)
(I/O Terminal 01) Bit 2
(1)
The stop input must be present in order to start the drive.
When this bit is a 1 the drive can be started.
When this bit is a 0 the drive will stop.
Reserved Bit 3
Display Group (continued)
d012 [Control Source] Related Parameter(s): P036, P038, A051, A052
Displays the active source of the Start Command and Speed Command which are normally defined
by the settings of
inputs. Refer to the flowcharts on pages
P036 [Start Source] and P038 [Speed Reference] but may be overridden by digital
1-18 and 1-19 for details.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/9
Display: 1
d013 [Contrl In Status] Related Parameter(s): d002, P034, P035
Status of the control terminal block control inputs.
Important: Actual control commands may come from a source other than the control terminal block.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/1
Display: 1
Page 42

3-6 Programming and Parameters
1 = Input Present, 0 = Input Not Present
Digital In1 Sel (I/O Terminal 05) Bit 0
Digital In2 Sel (I/O Terminal 06) Bit 1
Reserved Bit 2
Reserved Bit 3
1 = Condition True, 0 = Condition False
Receiving Data Bit 0
Transmitting Data Bit 1
RS485 (DSI) Based Option Connected Bit 2
(Allen-Bradley devices only.)
Communication Error Occurred Bit 3
Display Group (continued)
d014 [Dig In Status] Related Parameter(s): A051, A052
Status of the control terminal block digital inputs.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/1
Display: 1
d015 [Comm Status] Related Parameter(s): A103 - A107
Status of the communications ports.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/1
Display: 1
d016 [Control SW Ver]
Main Control Board software version.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 1.00/99.99
Display: 0.01
d017 [Drive Type]
Used by Rockwell Automation field service personnel.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 1001/9999
Display: 1
Page 43

Programming and Parameters 3-7
Display Group (continued)
d018 [Elapsed Run Time]
Accumulated time drive is outputting power. Time is displayed in 10 hour increments.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/9999 Hrs
Display: 1 = 10 Hrs
d019 [Testpoint Data] Related Parameter(s): A102
The present value of the function selected in A102 [Testpoint Sel].
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/FFFF
Display: 1 Hex
d020 [Analog In 0-10V] Related Parameter(s): A110, A111
The present value of the voltage at I/O Terminal 13 (100.0% = 10 volts).
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0.0/100.0%
Display: 0.1%
d021 [Analog In 4-20mA] Related Parameter(s): A112, A113
The present value of the current at I/O Terminal 15 (0.0% = 4mA, 100.0% = 20mA).
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0.0/100.0%
Display: 0.1%
d024 [Drive Temp]
Present operating temperature of the drive power section.
Values Default Read Only
Min/Max: 0/120 degC
Display: 1 degC
Page 44

3-8 Programming and Parameters
Basic Program Group
P031 [Motor NP Volts] Related Parameter(s): d004, A084
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Set to the motor nameplate rated volts.
Values Default Based on Drive Rating
Min/Max: 20/Drive Rated Volts
Display: 1 VAC
P032 [Motor NP Hertz] Related Parameter(s): A084, A090
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Set to the motor nameplate rated frequency.
Values Default 60 Hz
Min/Max: 10/240 Hz
Display: 1 Hz
P033 [Motor OL Current] Related Parameter(s): P043, A055, A089, A090, A098, A114
Set to the maximum allowable motor current.
The drive will fault on an F7 Motor Overload if the value of this parameter is exceeded by 150% for 60
seconds.
Values Default Based on Drive Rating
Min/Max: 0.0/(Drive Rated Amps 2)
Display: 0.1 Amps
P034 [Minimum Freq] Related Parameter(s): d001, d002, d013, P035, A110, A112, A115
Sets the lowest frequency the drive will output continuously.
Values Default 0.0 Hz
Min/Max: 0.0/240.0 Hz
Display: 0.1 Hz
P035 [Maximum Freq]
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Sets the highest frequency the drive will output.
Values Default 60 Hz
Min/Max: 0/240 Hz
Display: 1 Hz
Related Parameter(s):
d001, d002, d013, P034, A078,
A111, A113, A115
Page 45

Programming and Parameters 3-9
!
ATTENTION: Hazard of injury exists due to unintended operation. When
P036 [Start Source] is set to option 3, and the Run input is maintained, the
Run inputs do not need to be toggled after a Stop input for the drive to run
again. A Stop function is provided only when the Stop input is active (open).
ATTENTION: The drive must only be controlled from the Digital Input
Terminal Blocks and must NOT be used with any other DSI or
Network device.
Basic Program Group (continued)
P036 [Start Source] Related Parameter(s): d012, P037
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Sets the control scheme used to start the drive.
Refer to
can override the setting of this parameter.
Important: For all settings except option 3, the drive must receive a leading edge from the start input
for the drive to start after a stop input, loss of power or fault condition.
Options 0 “Keypad” (Default) Integral keypad controls drive operation.
Start and Speed Reference Control on page 1-18 for details about how other drive settings
I/O Terminal 1 “Stop” = coast to stop.
When active, the Reverse key is also active unless
disabled by
1 “3-Wire” I/O Terminal 1 “Stop” = stop according to the value set in
P037 [Stop Mode].
2 “2-Wire” I/O Terminal 1 “Stop” = coast to stop.
A095 [Reverse Disable].
3 “2-W Lvl Sens” Drive will restart after a “Stop” command when:
Stop is removed
and
Start is held active
4 “2-W Hi Speed” Important: There is greater potential voltage on the output
terminals when using this option.
Important: The drive may fault on an F5 OverVoltage if
[Start Source] is set to “2-W Hi Speed” and a Coast to Stop
command is given while the drive is running.
For example, a Coast to Stop command is given while the
P037
drive is running when
“Coast” and
Outputs are kept in a ready-to-run state. The drive will
respond to a “Start” command within 10 ms.
I/O Terminal 1 “Stop” = coast to stop.
P036 [Start Source] = 4.
[Stop Mode] = 1 “Coast, CF” or 5
P036
5 “Comm Port” Remote communications. Refer to
I/O Terminal 1 “Stop” = coast to stop.
Important: When commanding Jog via the RS485 communications port on drives with firmware
version 1.02 or earlier, the Jog command will follow the commanded direction from I/O Terminal 03.
On firmware versions 1.03 and later, the commanded direction will be provided via the RS485
communications port.
Important: When sending a continuous start command via the RS485 communications port on drives
with firmware version 1.02 or earlier, a maintained stop input is required to stop the drive. Once the
stop input is inactive, the drive will restart. On firmware versions 1.03 and later, once a stop input is
received, the start command must transition from high to low to high for the drive to start.
Appendix C for details.
Page 46

3-10 Programming and Parameters
Basic Program Group (continued)
P037 [Stop Mode] Related Parameter(s): P036, A080, A081, A082, A105
Active stop mode for all stop sources [e.g. keypad, run forward (I/O Terminal 02), run reverse (I/O
Terminal 03), RS485 port] except as noted below.
P036
Important: I/O Terminal 01 is always a coast to stop input except when
“3-Wire” control. When in three wire control, I/O Terminal 01 is controlled by
Hardware Enable Circuitry
By default, I/O Terminal 01 is a coast to stop input. The status of the input is interpreted by drive
software. If the application requires the drive to be disabled without software interpretation, a “dedicated” hardware enable configuration can be utilized. This is accomplished by removing the ENBL
enable jumper on the control board. In this case, the drive will always coast to a stop regardless of the
settings of
P036 [Start Source] and P037 [Stop Mode].
[Start Source] is set for
P037 [Stop Mode].
Options 0 “Ramp, CF”
1 “Coast, CF”
2 “DC Brake, CF”
3 “DCBrkAuto,CF”
4 “Ramp” Ramp to Stop.
5 “Coast” Coast to Stop.
6 “DC Brake” DC Injection Braking Stop.
7 “DC BrakeAuto” DC Injection Braking Stop with Auto Shutoff.
(1)
(Default) Ramp to Stop. “Stop” command clears active fault.
(1)
(1)
Coast to Stop. “Stop” command clears active fault.
DC Injection Braking Stop. “Stop” command clears active
fault.
(1)
DC Injection Braking Stop with Auto Shutoff.
Standard DC Injection Braking for value set in
Brake Time].
OR
Drive shuts off if the drive detects that the motor is
stopped.
“Stop” command clears active fault.
Standard DC Injection Braking for value set in A080
Brake Time].
OR
Drive shuts off if current limit is exceeded.
A080 [DC
[DC
(1)
Stop input also clears active fault.
Page 47

Programming and Parameters 3-11
Maximum Freq
Accel Time
Accel Rate=
Speed
0
Time
P035 [Maximum Freq]
P039 or A067
[Accel Time x]
P040 or A068
[Decel Time x]
0
Acceleration
D
eceleration
Basic Program Group (continued)
P038 [Speed Reference] Related Parameter(s): d001, d002, d012, P039, P040, A051, A052,
A069, A070-A073, A110, A111, A112, A113
Sets the source of the speed reference to the drive.
The drive speed command can be obtained from a number of different sources. The source is
normally determined by
to option 2, 4, 5, 6, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 and the digital input is active, the speed reference commanded
by
P038 [Speed Reference] will be overridden. Refer to the flowchart on page 1-18 for more
information on speed reference control priority.
Options 0 “Drive Pot” (Default) Internal frequency command from the potentiometer on the
P038 [Speed Reference]. However, when A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Sel] is set
integral keypad.
1 “InternalFreq” Internal frequency command from
A069 [Internal Freq].
2 “0-10V Input” External frequency command from the 0-10V analog input or
remote potentiometer.
3 “4-20mA Input” External frequency command from the 4-20mA analog input.
4 “Preset Freq” External frequency command as defined by
[Preset Freq x] when
A051 and A052 [Digital Inx Sel] are
A070
- A073
programmed as “Preset Frequencies” and the digital inputs
are active.
5 “Comm Port” External frequency command from the communications port.
P039 [Accel Time 1] Related Parameter(s): P038, P040, A051, A052, A067, A070-A073
Sets the rate of acceleration for all speed increases.
Values Default 10.0 Secs
Min/Max: 0.0/600.0 Secs
Display: 0.1 Secs
Page 48

3-12 Programming and Parameters
Maximum Freq
Decel Time
Decel Rate
=
Speed
0
Time
P035 [Maximum Freq]
P039 or A067
[Accel Time x]
P040 or A068
[Decel Time x]
0
Acceleration
D
eceleration
Basic Program Group (continued)
P040 [Decel Time 1] Related Parameter(s): P038, P039, A051, A052, A068, A070-A073
Sets the rate of deceleration for all speed decreases.
Values Default 10.0 Secs
Min/Max: 0.1/600.0 Secs
Display: 0.1 Secs
P041 [Reset To Defalts]
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Resets all parameter values to factory defaults.
Options 0 “Idle State” (Default)
1 “Reset Defaults” After the reset function is complete, this parameter will set
itself back to “0”.
Causes an F48
Params Defaulted fault.
P043 [Motor OL Ret] Related Parameter(s): P033
Enables/disables the Motor Overload Retention function. When Enabled, the value held in the motor
overload counter is saved at power-down and restored at power-up. A change to this parameter
setting resets the counter.
Options 0 “Disabled” (Default)
1 “Enabled”
Page 49

Advanced Program Group
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Programming and Parameters 3-13
A051 [Digital In1 Sel]
(I/O Terminal 5)
Related Parameter(s):
d012, d014, P038, P039, P040,
A067, A068, A070-A073, A078, A079
A052 [Digital In2 Sel]
(I/O Terminal 6)
Selects the function for the digital inputs. Refer to the flowchart on page 1-18 for more information on
speed reference control priority.
Options 0 “Not Used” Terminal has no function but can be read over network
communications via
1 “Acc 2 & Dec 2” When active,
2] are used for all ramp rates except Jog.
Can only be tied to one input.
Refer to the flowchart on
Accel/Decel selection.
2 “Jog” When input is present, drive accelerates according to the
value set in A079 [Jog Accel/Decel] and ramps to the
value set in
When input is removed, drive ramps to a stop according to
the value set in
A valid “Start” command will override this input.
3 “Aux Fault” When enabled, an F2
input is removed.
d014 [Dig In Status]
A067 [Accel Time 2] and A068 [Decel Time
page 1-19
A078 [Jog Frequency].
A079 [Jog Accel/Decel].
Auxiliary Input fault will occur when the
for more information on
4 “Preset Freq” (Default) Refer to
Important: Digital Inputs have priority for frequency control
when programmed as a Preset Speed and are active. Refer
to the flowchart on
reference control priority.
5 “Local” When active, sets integral keypad as start source and
potentiometer on the integral keypad as speed source.
6 “Comm Port” When active, sets communications device as default start/
Can only be tied to one input.
7 “Clear Fault” When active, clears an active fault.
8 “RampStop,CF” Causes drive to immediately ramp to a stop regardless of how
P037 [Stop Mode] is set.
9 “CoastStop,CF” Causes drive to immediately coast to a stop regardless of
how
10 “DCInjStop,CF” Causes drive to immediately begin a DC Injection stop
regardless of how
11 “Jog Forward” Drive accelerates to
[Jog Accel/Decel] and ramps to stop when input becomes
inactive. A valid start will override this command.
A070 - A073 [Preset Freq x].
1-18 for more information on speed
speed command source.
P037 [Stop Mode] is set.
P037 [Stop Mode] is set.
A078 [Jog Frequency] according to A079
12 “Jog Reverse” Drive accelerates to A078 [Jog Frequency] according to A079
[Jog Accel/Decel] and ramps to stop when input becomes
inactive. A valid start will override this command.
Page 50

3-14 Programming and Parameters
A051 &
A052
Options
(Cont.)
A055 [Relay Out Sel]
Sets the condition that changes the state of the output relay contacts.
Options 0 “Ready/Fault”
13 “10V In Ctrl” Selects 0-10V or ±10V control as the frequency reference.
Start source is not changed.
14 “20mA In Ctrl” Selects 4-20mA control as the frequency reference. Start
source is not changed.
15 - 25 Reserved
26 “Anlg Invert” Inverts the scaling of the analog input levels set in
A110 [Anlg In 0-10V Lo] and A111 [Anlg In 0-10V Hi] or
A112 [Anlg In4-20mA Lo] and A113 [Anlg In4-20mA Hi].
Related Parameter(s):
Relay changes state when power is applied. This indicates
(Default)
1 “At Frequency” Drive reaches commanded frequency.
2 “MotorRunning” Motor is receiving power from the drive.
3 “Reverse” Drive is commanded to run in reverse direction.
4 “Motor Overld” Motor overload condition exists.
that the drive is ready for operation. Relay returns drive to
shelf state when power is removed or a fault occurs.
P033, A056, A092
5 “Ramp Reg” Ramp regulator is modifying the programmed accel/decel
times to avoid an overcurrent or overvoltage fault from
occurring.
6 “Above Freq” Drive exceeds the frequency (Hz) value set in
Out Level].
7 “Above Cur” Drive exceeds the current (% Amps) value set in
Out Level].
Important: Value for
in percent of drive rated output current.
8 “Above DCVolt” Drive exceeds the DC bus voltage value set in
Out Level].
9 “Retries Exst” Value set in
10 “Above Anlg V” Analog input voltage (I/O Terminal 13) exceeds the value
set in
This parameter setting can also be used to indicate a PTC
trip point when the input (I/O Terminal 13) is wired to a
PTC and external resistor.
Use A056 to set threshold.
11-19 Reserved
20 “ParamControl” Enables the output to be controlled over network
communications by writing to
(0 = Off, 1 = On.)
A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries] is exceeded.
A056 [Relay Out Level].
A056 [Relay Out Level] must be entered
A056 [Relay Out Level].
A056 [Relay
A056 [Relay
A056 [Relay
21 “NonRec Fault”” Value set in
A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries] is exceeded.
Page 51
Programming and Parameters 3-15
32
A055 Setting A056 Min/Max
6
7
8
10
20
0/240 Hz
0/180%
0/815 Volts
0/100%
0/1
Maximum Freq
Accel Time
Accel Rate=
Speed
0
Time
P035 [Maximum Freq]
P039 or A067
[Accel Time x]
P040 or A068
[Decel Time x]
0
Acceleration
Deceleration
Maximum Freq
Decel Time
Decel Rate
=
Speed
0
Time
P035 [Maximum Freq]
P039 or A067
[Accel Time x]
P040 or A068
[Decel Time x]
0
Acceleration
Deceleration
Advanced Program Group
(continued)
A056 [Relay Out Level] Related Parameter(s): A055
32 bit parameter.
Sets the trip point for the digital output relay if the value of
A055 [Relay Out Sel] is 6, 7, 8, 10 or 20.
Values Default 0.0
Min/Max: 0.0/9999
Display: 0.1
A067 [Accel Time 2] Related Parameter(s): P039
When active, sets the rate of acceleration for all speed increases except jog. Refer to the flowchart on
page 1-19 for details.
Values Default 20.0 Secs
Min/Max: 0.0/600.0 Secs
Display: 0.1 Secs
A068 [Decel Time 2] Related Parameter(s): P040
When active, sets the rate of deceleration for all speed decreases except jog. Refer to the flowchart
page 1-19 for details.
on
Values Default 20.0 Secs
Min/Max: 0.1/600.0 Secs
Display: 0.1 Secs
Page 52

3-16 Programming and Parameters
Input State of Digital In 1
(I/O Terminal 05)
Input State of Digital In 2
(I/O Terminal 06) Frequency Source Accel / Decel Parameter Used
(2)
0 0 A070 [Preset Freq 0] [Accel Time 1] / [Decel Time 1]
1 0 A071 [Preset Freq 1] [Accel Time 1] / [Decel Time 1]
0 1 A072 [Preset Freq 2] [Accel Time 2] / [Decel Time 2]
1 1 A073 [Preset Freq 3] [Accel Time 2] / [Decel Time 2]
(2)
When a Digital Input is set to “Accel 2 & Decel 2”, and the input is active, that input overrides the settings in
this table.
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A069 [Internal Freq] Related Parameter(s): P038
Provides the frequency command to the drive when P038 [Speed Reference] is set to 1 “Internal
Freq”. When enabled, this parameter will change the frequency command in “real time” using the
integral keypad Up Arrow or Down Arrow when in program mode.
Important: Once the desired command frequency is reached, the Enter key must be pressed to store
this value to EEPROM memory. If the ESC key is used before the Enter key, the frequency will return
to the original value following the normal accel/decel curve.
Values Default 60.0 Hz
Min/Max: 0.0/240.0 Hz
Display: 0.1 Hz
A070 [Preset Freq 0]
(1)
Related Parameter(s):
P038, P039, P040, A051, A052,
A071 [Preset Freq 1]
A072 [Preset Freq 2]
A073 [Preset Freq 3]
Values A070 Default
A071 Default
A072 Default
A073 Default
Min/Max: 0.0/240.0 Hz
Display: 0.1 Hz
Provides a fixed frequency command value when
Frequencies”.
An active preset input will override speed command as shown in the flowchart on
(1)
To activate A070 [Preset Freq 0] set
0.0 Hz
5.0 Hz
10.0 Hz
20.0 Hz
A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Sel] is set to 4 “Preset
P038 [Speed Reference] to option 4 “Preset Freq 0-3”.
A067, A068
page 1-19.
A078 [Jog Frequency] Related Parameter(s): P035, A051, A052, A079
Sets the output frequency when a jog command is issued.
Values Default 10.0 Hz
Min/Max: 0.0/
Display: 0.1 Hz
P035 [Maximum Freq]
Page 53

Programming and Parameters 3-17
e
p
e
d
d
[
]
[
]
p
e
e
d
[
]
[
]
Voltage
Speed
!
ATT E NT ION : If a hazard of injury due to movement of equipment or material exists,
an auxiliary mechanical braking device must be used.
!
ATTENTION: This feature should not be used with synchronous or permanent
magnet motors. Motors may be demagnetized during braking.
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A079 [Jog Accel/Decel] Related Parameter(s): A051, A052, A078
Sets the acceleration and deceleration time when a jog command is issued.
Values Default 10.0 Secs
Min/Max: 0.1/600.0 Secs
Display: 0.1 Secs
A080 [DC Brake Time] Related Parameter(s): P037, A081
Sets the length of time that DC brake current is “injected” into the motor. Refer to parameter A081 [DC
Brake Level].
Values Default 0.0 Secs
Min/Max: 0.0/90.0 Secs
Display: 0.1 Secs
A081 [DC Brake Level] Related Parameter(s): P037, A080
Defines the maximum DC brake current, in amps, applied to the motor when P037 [Stop Mode] is set
to either “Ramp” or “DC Brake”.
Values Default Drive Rated Amps 0.05
Min/Max: 0.0/(Drive Rated Amps 1.8)
Display: 0.1 Amps
Ramp-to-Stop Mod
eed
olts/S
Stop Comman
DC Brake Time
DC Brake Level
Tim
DC Injection Braking Mod
Voltage
eed
Spee
olts/S
Stop Comman
DC Brake Time
DC Brake Level
Tim
Page 54

3-18 Programming and Parameters
Setting Min/Max
0
1
2
3-99
“Disabled”
“Normal RA Res” (5% Duty Cycle) - Refer to
Table B.C on page B-2
“No Protection” (100% Duty Cycle)
“x%Duty Cycle” Limited (3% – 99% of Duty Cycle)
!
ATTENTION: A risk of fire exists if external braking resistors are not protected. The
external resistor package must be self-protected from over temperature or the protective
circuit shown in
Figure B.7 on page B-9, or equivalent, must be supplied.
1/2 S Curve Time
2.5 Seconds
Total Time to Accelerate = Accel Time + S Curve Time
50% S Curve
Target
Target/2
Accel Time
10 Seconds
1/2 S Curve Time
2.5 Seconds
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A082 [DB Resistor Sel]
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Enables/disables external dynamic braking.
The drive is able to provide full braking indefinitely. Braking power is limited by the external DB
resistor. When this parameter is set to 1 “Normal RA Res” and an appropriate RA resistor is used (see
selection
cannot protect against a brake IGBT failure.
Tab l e B . C ), the drive provides calculated resistor overload protection. However, the drive
Values Default 0
Min/Max: 0/99
Display: 1
A083 [S Curve %]
Sets the percentage of acceleration or deceleration time that is applied to the ramp as S Curve. Time
is added, 1/2 at the beginning and 1/2 at the end of the ramp.
Values Default 0% (Disabled)
Min/Max: 0/100%
Display: 1%
Example:
Accel Time = 10 Seconds
S Curve Setting = 50%
S Curve Time = 10 0.5 = 5 Seconds
Total Time = 10 + 5 = 15 Seconds
Page 55

Programming and Parameters 3-19
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A084 [Boost Select] Related Parameter(s): d004, P031, P032
Sets the boost voltage (% of P031 [Motor NP Volts]) and redefines the Volts per Hz curve.
(1)
Drive may add additional voltage unless option 5 is selected.
Options 1 “30.0, VT”
(1)
100
2 “35.0, VT”
3 “40.0, VT”
4 “45.0, VT”
5 “0.0 no IR”
6 “0.0”
7 “2.5, CT”
[Default for 3.7kW
(5HP) Drives]
8 “5.0, CT” (Default)
9 “7.5, CT”
10 “10.0, CT”
11 “12.5, CT”
12 “15.0, CT”
13 “17.5, CT”
14 “20.0, CT”
Variable Torque
Constant Torque
1/2 [Motor NP Volts]
50
% P031 [Motor NP Volts]
Settings
5-14
0 50 100
% P032 [Motor NP Hertz]
4
3
2
1
1/2
[Motor NP Hertz]
A088 [Maximum Voltage]
Sets the highest voltage the drive will output.
Values Default Drive Rated Volts
Min/Max: 20/Drive Rated Volts
Display: 1 VAC
Page 56

3-20 Programming and Parameters
e
0
80
00
60
0
0
e
0
80
00
60
0
0
[
]
e
0
80
00
60
0
0
020017515012510075
5025
0200
5
5012510075
5025
0
00175150
5
5025
68
84
88
80
6
96
00
92
64
60
56
52
8765315
14
61310
9
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A089 [Current Limit]
Maximum output current allowed before current limiting occurs.
Values Default Drive Rated Amps 1.5
Min/Max: 0.1/(Drive Rated Amps 1.8)
Display: 0.1 Amps
A090 [Motor OL Select] Related Parameter(s): P032
Drive provides Class 10 motor overload protection. Settings 0-2 select the derating factor for the I2t
overload function.
Options 0 “No Derate” (Default)
1 “Min Derate”
2 “Max Derate”
1
4
2
No Derat
1
4
2
17
1
Min Derat
1
Motor OL Curent
4
2
of P033
1251007
2
Max Derat
A091 [PWM Frequency]
Sets the carrier frequency for the PWM output waveform. The chart below provides derating
guidelines based on the PWM frequency setting.
Important: Ignoring derating guidelines can cause reduced drive performance.
Values Default 4.0 kHz
Min/Max: 2.0/16.0 kHz
Display: 0.1 kHz
1
7
1
Page 57

Programming and Parameters 3-21
!
ATT E NT ION : Equipment damage and/or personal injury may result if this parameter
is used in an inappropriate application. Do not use this function without considering
applicable local, national and international codes, standards, regulations or industry
guidelines.
!
ATT E NT ION : Equipment damage and/or personal injury may result if this parameter
is used in an inappropriate application. Do not use this function without considering
applicable local, national and international codes, standards, regulations or industry
guidelines.
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries]
Sets the maximum number of times the drive attempts to reset a fault and restart.
Clear a Type 1 fault and restart the drive.
1. Set A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries] to a value other than “0”.
2. Set
Clear an OverVoltage, UnderVoltage or Heatsink OvrTmp fault without restarting the drive.
1. Set A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries] to a value other than “0”.
2. Set
A093 [Auto Rstrt Delay] to a value other than “0”.
A093 [Auto Rstrt Delay] to “0”.
Values Default 0
Min/Max: 0/9
Display: 1
A093 [Auto Rstrt Delay] Related Parameter(s): A092
Sets the time between restart attempts when A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries] is set to a value other than zero.
Values Default 1.0 Secs
Min/Max: 0.0/300.0 Secs
Display: 0.1 Secs
A094 [Start At PowerUp]
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Enables/disables a feature that allows a Start or Run command to automatically cause the drive to
resume running at commanded speed after drive input power is restored. Requires a digital input
configured for Run or Start and a valid start contact.
This parameter will not function if parameter
[Start Source] is set to 4 “2-W High Speed”.
P036
Options 0 “Disabled” (Default)
1 “Enabled”
Page 58

3-22 Programming and Parameters
Output
Freq
Process
Factor
Process
Display
=
x
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A095 [Reverse Disable] Related Parameter(s): d006
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Enables/disables the function that allows the direction of motor rotation to be changed. The reverse
command may come from a digital command, the keypad or a serial command. All reverse inputs
including two-wire Run Reverse will be ignored with reverse disabled.
Options 0 “Rev Enabled” (Default)
1 “Rev Disabled”
A096 [Flying Start En]
Sets the condition that allows the drive to reconnect to a spinning motor at actual RPM.
Options 0 “Disabled” (Default)
1 “Enabled”
A097 [Compensation]
Enables/disables correction options that may improve problems with motor instability.
Options 0 “Disabled”
1 “Electrical” (Default) Some drive/motor combinations have inherent instabilities
which are exhibited as non-sinusodial motor currents. This
setting attempts to correct this condition.
2 “Mechanical” Some motor/load combinations have mechanical resonances
which can be excited by the drive current regulator. This
setting slows down the current regulator response and
attempts to correct this condition.
3 “Both”
A098 [SW Current Trip] Related Parameter(s): P033
Enables/disables a software instantaneous (within 100 ms) current trip.
Values Default 0.0 (Disabled)
Min/Max: 0.0/(Drive Rated Amps 2)
Display: 0.1 Amps
A099 [Process Factor] Related Parameter(s): d010
Scales the value displayed by d010 [Process Display].
Values Default 30.0
Min/Max: 0.1/999.9
Display: 0.1
Page 59

Programming and Parameters 3-23
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A100 [Fault Clear]
Stop drive before changing this parameter.
Resets a fault and clears the fault queue. Used primarily to clear a fault over network communications.
Options 0 “Ready/Idle” (Default)
1 “Reset Fault”
-d009 [Fault x Code])
2 “Clear Buffer” (Parameters
A101 [Program Lock]
Protects parameters against change by unauthorized personnel.
Options 0 “Unlocked” (Default)
1 “Locked”
d007
A102 [Testpoint Sel]
Used by Rockwell Automation field service personnel.
Values Default 400
Min/Max: 0/FFFF
Display: 1 Hex
A103 [Comm Data Rate] Related Parameter(s): d015
Sets the serial port rate for the RS485 (DSI) port.
Important: Power to drive must be cycled before any changes will affect drive operation.
Options 0 “1200”
1 “2400”
2 “4800”
3 “9600” (Default)
4 “19.2K”
5 “38.4K”
A104 [Comm Node Addr] Related Parameter(s): d015
Sets the drive node address for the RS485 (DSI) port if using a network connection.
Important: Power to drive must be cycled before any changes will affect drive operation.
Values Default 100
Min/Max: 1/247
Display: 1
Page 60

3-24 Programming and Parameters
Advanced Program Group (continued)
A105 [Comm Loss Action] Related Parameter(s): d015, P037, A106
Selects the drive’s response to a loss of the communication connection or excessive communication
errors.
Options 0 “Fault” (Default) Drive will fault on an F81 Comm Loss and coast to stop.
1 “Coast to Stop” Stops drive via coast to stop.
2 “Stop” Stops drive via
3 “Continu Last” Drive continues operating at communication commanded
speed saved in RAM.
P037 [Stop Mode] setting.
A106 [Comm Loss Time] Related Parameter(s): d015, A105
Sets the time that the drive will remain in communication loss before implementing the option selected
in
A105 [Comm Loss Action].
Values Default 5.0 Secs
Min/Max: 0.1/60.0 Secs
Display: 0.1 Secs
A107 [Comm Format]
Selects the protocol (RTU only), data bits (8 data bits only), parity (N
stop bit only) used by the RS485 port on the drive.
Refer to
Important: Power to drive must be cycled before any changes will affect drive operation.
Options 0 “RTU 8-N-1” (Default)
Appendix C for details on using the drive communication features.
one, Even, Odd), and stop bits (1
1 “RTU 8-E-1”
2 “RTU 8-O-1”
3 “RTU 8-N-2”
4 “RTU 8-E-2”
5 “RTU 8-O-2”
Page 61

Programming and Parameters 3-25
0
P035 [Maximum Freq]
P034 [Minimum Freq]
A110 [Anlg In 0-10V Lo] A111 [Anlg In 0-10V Hi]
0
Speed Reference
A110 [Anlg In 0-10V Lo] Related Parameter(s):
d020, P034, P038, A051, A052
Sets the analog input level that corresponds to P034 [Minimum Freq] if a 0-10V input is used by P038
[Speed Reference].
Analog inversion can be accomplished by setting this value larger than
setting
A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Sel] to option 26 “Anlg Invert”
A111 [Anlg In 0-10V Hi] or by
Values Default 0.0%
Min/Max: 0.0/100.0%
Display: 0.1%
A111 [Anlg In 0-10V Hi] Related Parameter(s): d020, P035, P038, A051, A052
Sets the analog input level that corresponds to P035 [Maximum Freq] if a 0-10V input is used by P038
[Speed Reference].
Analog inversion can be accomplished by setting this value smaller than
setting
A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Sel] to option 26 “Anlg Invert”.
A110 [Anlg 0-10V In Lo] or by
Values Default 100.0%
Min/Max: 0.0/100.0%
Display: 0.1%
A112 [Anlg In4-20mA Lo] Related Parameter(s): d021, P034, P038, A051, A052
Sets the analog input level that corresponds to P034 [Minimum Freq] if a 4-20mA input is used by
P038 [Speed Reference].
Analog inversion can be accomplished by setting this value larger than
setting
A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Sel] to option 26 “Anlg Invert”.
A113
[Anlg In4-20mA Hi] or by
Values Default 0.0%
Min/Max: 0.0/100.0%
Display: 0.1%
A113 [Anlg In4-20mA Hi] Related Parameter(s): d021, P035, P038, A051, A052
Sets the analog input level that corresponds to P035 [Maximum Freq] if a 4-20mA input is used by
P038 [Speed Reference].
Analog inversion can be accomplished by setting this value smaller than
by setting
Values Default 100.0%
A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Sel] to option 26 “Anlg Invert”.
A112 [Anlg In4-20mA Lo] or
Min/Max: 0.0/100.0%
Display: 0.1%
Page 62

3-26 Programming and Parameters
!
ATTENTION: Risk of equipment damage exists. If a controller is
programmed to write parameter data to Non-Volatile Storage (NVS)
frequently, the NVS will quickly exceed its life cycle and cause the
drive to malfunction. Do not create a program that frequently uses
configurable outputs to write parameter data to NVS unless A164
[Comm Write Mode] is set to option 1.
A114 [Slip Hertz @ FLA] Related Parameter(s):
Compensates for the inherent slip in an induction motor. This frequency is added to the commanded
output frequency based on motor current.
Values Default 2.0 Hz
Min/Max: 0.0/10.0 Hz
Display: 0.1 Hz
P033
A115 [Process Time Lo] Related Parameter(s): d010, P034
Scales the time value when the drive is running at P034 [Minimum Freq]. When set to a value other
than zero,
Values Default 0.00
d010 [Process Display] indicates the duration of the process.
Min/Max: 0.00/99.99
Display: 0.01
A116 [Process Time Hi] Related Parameter(s): d010, P035
Scales the time value when the drive is running at P035 [Maximum Freq]. When set to a value other
than zero,
d010 [Process Display] indicates the duration of the process.
Values Default 0.00
Min/Max: 0.00/99.99
Display: 0.01
A117 [Bus Reg Mode]
Controls the operation of the drive voltage regulation, which is normally operational at decel or when
the bus voltage rises.
Refer to the Attention statement on page
Options 0 “Disabled”
1 “Enabled” (Default)
P-3 for important information on bus regulation.
A118 [Comm Write Mode]
Determines whether parameter changes made over communication port are saved and stored in
Non-Volatile Storage (NVS) or RAM only. If they are stored in RAM, the values will be lost at
power-down.
Options 0 “Save” (Default)
1“RAM Only”
Page 63

Programming and Parameters 3-27
Parameter Cross Reference – by Name
Parameter Name No. Group
Accel Time 1 P039 Basic Program
Accel Time 2 A067 Advanced Program
Analog In 0-10V d020 Display
Analog In 4-20mA d021 Display
Anlg In 0-10V Hi A111 Advanced Program
Anlg In 0-10V Lo A110 Advanced Program
Anlg In4-20mA Hi A113 Advanced Program
Anlg In4-20mA Lo A112 Advanced Program
Auto Rstrt Delay A093 Advanced Program
Auto Rstrt Tries A092 Advanced Program
Boost Select A084 Advanced Program
Bus Reg Mode A117 Advanced Program
Comm Data Rate A103 Advanced Program
Comm Format A107 Advanced Program
Comm Loss Action A105 Advanced Program
Comm Loss Time A106 Advanced Program
Comm Node Addr A104 Advanced Program
Comm Status d015 Display
Comm Write Mode A118 Advanced Program
Commanded Freq d002 Display
Compensation A097 Advanced Program
Contrl In Status d013 Display
Control Source d012 Display
Control SW Ver d016 Display
Current Limit A089 Advanced Program
DB Resistor Sel A082 Advanced Program
DC Brake Level A081 Advanced Program
DC Brake Time A080 Advanced Program
DC Bus Voltage d005 Display
Decel Time 1 P040 Basic Program
Decel Time 2 A068 Advanced Program
Dig In Status d014 Display
Digital Inx Sel A051, A052 Advanced Program
Drive Status d006 Display
Drive Temp d024 Display
Drive Type d017 Display
Elapsed Run Time d018 Display
Parameter Name
Fault x Code d007-d009 Display
Fault Clear A100 Advanced Program
Flying Start En A096 Advanced Program
Internal Freq A069 Advanced Program
Jog Accel/Decel A079 Advanced Program
Jog Frequency A078 Advanced Program
Maximum Freq P035 Basic Program
Maximum Voltage A088 Advanced Program
Minimum Freq P034 Basic Program
Motor NP Hertz P032 Basic Program
Motor NP Volts P031 Basic Program
Motor OL Current P033 Basic Program
Motor OL Ret P043 Basic Program
Motor OL Select A090 Advanced Program
Output Current d003 Display
Output Freq d001 Display
Output Voltage d004 Display
Preset Freq x A070-A073 Advanced Program
Process Display d010 Display
Process Factor A099 Advanced Program
Process Time Hi A116 Advanced Program
Process Time Lo A115 Advanced Program
Program Lock A101 Advanced Program
PWM Frequency A091 Advanced Program
Relay Out Level A056 Advanced Program
Relay Out Sel A055 Advanced Program
Reset To Defalts P041 Basic Program
Reverse Disable A095 Advanced Program
S Curve % A083 Advanced Program
Slip Compensation A114 Advanced Program
Speed Reference P038 Basic Program
Start At PowerUp A094 Advanced Program
Start Source P036 Basic Program
Stop Mode P037 Basic Program
SW Current Trip A098 Advanced Program
Testpoint Data d019 Display
Testpoint Sel A102 Advanced Program
No. Group
Page 64

3-28 Programming and Parameters
Notes:
Page 65
Chapter 4
Troubleshooting
Chapter 4 provides information to guide you in troubleshooting the
PowerFlex 4 drive. Included is a listing and description of drive faults
(with possible solutions, when applicable).
For information on… See page… For information on… See page…
Drive Status 4-1 Fault Descriptions 4-3
Faults 4-1 Common Symptoms and
Corrective Actions
Drive Status
4-5
The condition or state of your drive is constantly monitored. Any
changes will be indicated through the integral keypad.
LED Indications
page 2-3 for information on drive status indicators and controls.
See
Faults
A fault is a condition that stops the drive. There are two fault types.
Type Fault Description
Auto-Reset/Run When this type of fault occurs, and
➀
set to a value greater than “0,” a user-configurable timer,
[Auto Rstrt Delay], begins. When the timer reaches zero, the
drive attempts to automatically reset the fault. If the condition
that caused the fault is no longer present, the fault will be reset
and the drive will be restarted.
Non-Resetable This type of fault may require drive or motor repair, or is
➁
caused by wiring or programing errors. The cause of the fault
must be corrected before the fault can be cleared.
A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries] is
A093
Page 66

4-2 Troubleshooting
FAULT
VOLTS
AMPS
HERTZ
RUN
FWD
REV
PRGOGRAM
Fault Indication
Condition Display
Drive is indicating a fault.
The integral keypad provides visual notification of a
fault condition by displaying the following.
Flashing fault number
Flashing fault indicator
Press the Escape key to regain control of the
integral keypad.
Manually Clearing Faults
Step Key(s)
1. Press Esc to acknowledge the fault. The fault information will be
removed so that you can use the integral keypad.
Access d007
2. Address the condition that caused the fault.
The cause must be corrected before the fault can be cleared.
See Tab l e 4 .A .
3. After corrective action has been taken, clear the fault by one of these
methods.
Press Stop if
Cycle drive power.
Set
Cycle digital input if
A100 [Fault Clear] to “1” or “2”.
“Clear Fault”.
[Fault 1 Code] to view the most recent fault information.
P037 [Stop Mode] is set to a value between “0” and “3”.
A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Select] is set to option 7
Automatically Clearing Faults
Option / Step
Clear a Type 1 fault and restart the drive.
1. Set
2. Set
A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries] to a value other than “0”.
A093 [Auto Rstrt Delay] to a value other than “0”.
Clear an OverVoltage, UnderVoltage or Heatsink OvrTmp fault
without restarting the drive.
1. Set
2. Set
A092 [Auto Rstrt Tries] to a value other than “0”.
A093 [Auto Rstrt Delay] to “0”.
Auto Restart (Reset/Run)
The Auto Restart feature provides the ability for the drive to
automatically perform a fault reset followed by a start attempt without
user or application intervention. This allows remote or “unattended”
operation. Only certain faults are allowed to be reset. Certain faults
(Type 2) that indicate possible drive component malfunction are not
resettable.
Caution should be used when enabling this feature, since the drive will
attempt to issue its own start command based on user selected
programming.
Page 67

Fault Descriptions
Table 4.A Fault Types, Descriptions and Actions
(1)
Troubleshooting 4-3
No. Fault
F2 Auxiliary Input
F3 Power Loss
F4 UnderVoltage
F5 OverVoltage
F6 Motor Stalled
F7 Motor Overload
F8 Heatsink
OvrTmp
F12 HW OverCurrent
F13 Ground Fault
Description Action
Type
Auxiliary input interlock is open. 1. Check remote wiring.
➀
2. Verify communications
programming for intentional fault.
DC bus voltage remained below
➁
85% of nominal.
DC bus voltage fell below the
➀
minimum value.
DC bus voltage exceeded
➀
maximum value.
Drive is unable to accelerate
➀
motor.
Internal electronic overload trip. 1. An excessive motor load exists.
➀
Heatsink temperature exceeds a
➀
predefined value.
The drive output current has
➁
exceeded the hardware current
limit.
A current path to earth ground
➁
has been detected at one or
more of the drive output
terminals.
1. Monitor the incoming AC line for
low voltage or line power
interruption.
2. Check input fuses.
Monitor the incoming AC line for low
voltage or line power interruption.
Monitor the AC line for high line
voltage or transient conditions. Bus
overvoltage can also be caused by
motor regeneration. Extend the
decel time or install dynamic brake
option.
Increase
or reduce load so drive output
current does not exceed the current
set by parameter A089 [Current
Limit].
2. Verify
1. Check for blocked or dirty heat
2. Check fan.
Check programming. Check for
excess load, improper
Select] setting, DC brake volts set
too high or other causes of excess
current.
Check the motor and external wiring
to the drive output terminals for a
grounded condition.
P039 - A067 [Accel Time x]
Reduce load so drive output
current does not exceed the
current set by parameter
[Motor OL Current].
A084 [Boost Select]
setting
sink fins. Verify that ambient
temperature has not exceeded
40C (104F) for IP 30/NEMA 1/UL
Type 1 installations or 50°C (122°F)
for IP20/Open type installations.
A084 [Boost
P033
(1)
page 4-1 for a description of fault types.
See
Page 68

4-4 Troubleshooting
(1)
No. Fault
F33 Auto Rstrt Tries
F38 Phase U to Gnd
F39 Phase V to Gnd
F40 Phase W to Gnd
F41 Phase UV Short
F42 Phase UW Short
F43 Phase VW Short
F48 Params
Defaulted
F63 SW OverCurrent
F64 Drive Overload
F70 Power Unit
F71 Net Loss The communication network has
F81 Comm Loss
F100 Parameter
Checksum
F122 I/O Board Fail
Description Action
Typ e
Drive unsuccessfully attempted
➁
to reset a fault and resume
running for the programmed
number of
Tr ie s] .
A phase to ground fault has been
➁
detected between the drive and
motor in this phase.
Excessive current has been
➁
detected between these two
output terminals.
The drive was commanded to
write default values to EEPROM.
Programmed
➀
Trip] has been exceeded.
Drive rating of 150% for 1 minute
➁
or 200% for 3 seconds has been
exceeded.
Failure has been detected in the
➁
drive power section.
faulted.
RS485 (DSI) port stopped
➁
communicating.
The checksum read from the
➁
board does not match the
checksum calculated.
Failure has been detected in the
➁
drive control and I/O section.
A092 [Auto Rstrt
A098 [SW Current
Correct the cause of the fault and
manually clear.
1. Check the wiring between the
drive and motor.
2. Check motor for grounded
phase.
3. Replace drive if fault cannot be
cleared.
1. Check the motor and drive output
terminal wiring for a shorted
condition.
2. Replace drive if fault cannot be
cleared.
1. Clear the fault or cycle power to
the drive.
2. Program the drive parameters as
needed.
Check load requirements and A098
[SW Current Trip] setting.
Reduce load or extend Accel Time.
1. Cycle power.
2. Replace drive if fault cannot be
cleared.
1. Cycle power.
2. Check communications cabling.
3. Check network adapter setting.
4. Check external network status.
1. If adapter was not intentionally
disconnected, check wiring to the
port. Replace wiring, port
expander, adapters or complete
drive as required.
2. Check connection.
3. An adapter was intentionally
disconnected.
4. Turn off using
Action].
P041 [Reset To Defalts] to
Set
option 1 “Reset Defaults”.
1. Cycle power.
2. Replace drive if fault cannot be
cleared.
A105 [Comm Loss
(1)
See
page 4-1 for a description of fault types.
Page 69
Troubleshooting 4-5
Common Symptoms and Corrective Actions
Motor does not Start.
Cause(s) Indication Corrective Action
No output voltage to the motor. None Check the power circuit.
Check the supply voltage.
Check all fuses and disconnects.
Check the motor.
Verify that the motor is
connected properly.
Check the control input signals.
Verify that a Start signal is
present. If 2-Wire control is used,
verify that either the Run
Forward or Run Reverse signal is
active, but not both.
Verify that I/O Terminal 01 is
active.
Verify that P036 [Start Source]
matches your configuration.
Improper boost setting at initial
start-up.
Verify that
Disable] is not prohibiting
movement.
None Set A084 [Boost Select] to option 2
“35.0, VT”.
A095 [Reverse
Drive does not Start from Integral Keypad.
Cause(s) Indication Corrective Action
Integral keypad is not enabled. Green LED above Start key is
not illuminated.
I/O Terminal 01 “Stop” input is
not present.
None Wire inputs correctly and/or install
Set parameter
Source] to option 0 “Keypad”.
Set parameter
[Digital Inx Select] to option 5
“Local” and activate the input.
jumper.
P036 [Start
A051 - A052
Page 70
4-6 Troubleshooting
Drive does not Start from Start or Run Inputs wired to the terminal block.
Cause(s) Indication Corrective Action
Drive is Faulted Flashing red status light Clear fault.
Press Stop
Cycle power
[Fault Clear] to option 1
Incorrect programming.
P036
A051 - A052 [Digital Inx Select]
Incorrect input wiring.
See
2 wire control requires Run
3 wire control requires Start and
Stop input is always required.
Incorrect Sink/Source DIP switch
setting.
[Start Source] is set to
option 0 “Keypad” or option 5
“RS485 (DSI) Port”.
is set to option 5 “Local” and the
input is active.
1-14 for wiring examples.
Forward, Run Reverse or Jog
input.
Stop inputs
Set A100
“Clear Faults”.
Cycle digital input if
[Digital Inx Select] is set to option
7 “Clear Fault”.
None Check parameter settings.
None Wire inputs correctly and/or install
jumper.
None Set switch to match wiring scheme.
A051 - A052
Drive does not respond to changes in speed command.
Cause(s) Indication Corrective Action
No value is coming from the
source of the command.
Incorrect reference source is
being selected via remote
device or digital inputs.
The drive “Run” indicator is lit
and output is 0 Hz.
None Check
Check d012
Source] for correct source.
If the source is an analog input,
check wiring and use a meter to
check for presence of signal.
Check
to verify correct command.
correct source.
Check
see if inputs are selecting an
alternate source. Verify settings
A051
for
Select].
Check
for the source of the speed
reference. Reprogram as
necessary.
Review the Speed Reference
Control chart on
d002 [Commanded Freq]
d012 [Control Source] for
d014 [Dig In Status] to
- A052 [Digital Inx
P038 [Speed Reference]
d012 [Control
page 1-18.
Page 71

Troubleshooting 4-7
Motor and/or drive will not accelerate to commanded speed.
Cause(s) Indication Corrective Action
Acceleration time is excessive. None Reprogram
A067 [Accel Time 2].
Excess load or short
acceleration times force the
drive into current limit, slowing
or stopping acceleration.
Speed command source or
value is not as expected.
Programming is preventing the
drive output from exceeding
limiting values.
None Compare
A089 [Current Limit].
Remove excess load or reprogram
P039 [Accel Time 1] or A067 [Accel
Time 2].
Check for improper
Select] setting.
None Verify
Check
proper Speed Command.
None Check
insure that speed is not limited by
programming.
P039 [Accel Time 1] or
d003
[Output Current] with
d002 [Commanded Freq].
d012 [Control Source] for the
P035
[Maximum Freq] to
A084
[Boost
Motor operation is unstable.
Cause(s) Indication Corrective Action
Motor data was incorrectly
entered.
None 1. Correctly enter motor nameplate
data into
2. Enable
3. Use
reduce boost level.
P031, P032 and P033.
A097 [Compensation].
A084
[Boost Select] to
Drive will not reverse motor direction.
Cause(s) Indication Corrective Action
Digital input is not selected for
reversing control.
Digital input is incorrectly
wired.
Motor wiring is improperly
phased for reverse.
Reverse is disabled. None Check
None Check [Digital Inx Sel]
page 3-13). Choose correct input
and program for reversing mode.
None Check input wiring.
None Switch two motor leads.
A095 [Reverse Disable].
(See
(See page 1-13)
Page 72

4-8 Troubleshooting
Notes:
Page 73

Appendix A
Supplemental Drive Information
For information on… See page…
Drive, Fuse & Circuit Breaker Ratings A-1
Specifications A-2
Drive, Fuse & Circuit Breaker Ratings
The tables on the following pages provide recommended AC line input
fuse and circuit breaker information. See Fusing and Circuit Breakers
below for UL and IEC requirements. Sizes listed are the recommended
sizes based on 40 °C (104 °F) and the U.S. N.E.C. Other country, state or
local codes may require different ratings.
Fusing
The recommended fuse types are listed below. If available current ratings
do not match those listed in the tables provided, choose the next higher
fuse rating.
(1)
IEC – BS88 (British Standard) Parts 1 & 2
2, type gG or equivalent should be used.
UL – UL Class CC, T or J must be used.
, EN60269-1, Parts 1 &
(2)
Circuit Breakers
The “non-fuse” listing in the following tables include inverse time circuit
breakers, instantaneous trip circuit breakers (motor circuit protectors)
and 140M self-protected combination motor controllers. If one of these
is chosen as the desired protection method, the following requirements
apply:
IEC – Both types of circuit breakers and 140M self-protected
combination motor controllers are acceptable for IEC installations.
UL – Only inverse time circuit breakers and the specified 140M
self-protected combination motor controllers are acceptable for UL
installations.
(1)
Typical designations include, but may not be limited to the following; Parts 1 & 2: AC,
AD, BC, BD, CD, DD, ED, EFS, EF, FF, FG, GF, GG, GH.
(2)
Typical designations include; Type CC - KTK-R, FNQ-R
Type J - JKS, LPJ
Type T - JJS, JJN
Page 74

A-2 Supplemental Drive Information
U
L
®
L
I
S
T
E
D
9
6
6
X
UL508C
U
L
®
L
I
S
T
E
D
9
6
6
X
I
N
D
C
O
N
T
E
Q
C
CSA 22.2
EMC Directive: 2014/30/EU: EN 61800-3
LV Directive: 2014/35/EU: EN 61800-5-1
Low Voltage TR CU 004/2011
EMC TR CU 020/2011
KCC-REM-RAA-22B
Specifications
Drive Ratings
Catalog
Number
100 - 120V AC (±10%) – 1-Phase Input, 0 - 230V 3-Phase Output
22A-V1P5N104 0.2 (0.25) 1.5 90-126 0.75 6.0 10 140M-C2E-C10 100-C09 1655
22A-V2P3N104 0.4 (0.5) 2.3 90-126 1.15 9.0 15 140M-C2E-C16 100-C12 1655
22A-V4P5N104 0.75 (1.0) 4.5 90-126 2.25 18.0 30 140M-D8E-C20 100-C23 1655
22A-V6P0N104 1.1 (1.5) 6.0 90-126 3.0 24.0 40 140M-F8E-C32 100-C37 1655
200 - 240V AC (±10%) – 1-Phase
22A-A1P4N103 0.2 (0.25) 1.4 180-265 0.7 3.2 6 140M-C2E-B40 100-C09 1655
22A-A2P1N103 0.4 (0.5) 2.1 180-265 1.05 5.3 10 140M-C2E-B63 100-C09 1655
22A-A3P6N103 0.75 (1.0) 3.6 180-265 1.8 9.2 15 140M-C2E-C16 100-C12 1655
22A-A6P8N103 1.5 (2.0) 6.8 180-265 3.4 14.2 25 140M-C2E-C16 100-C16 1655
22A-A9P6N103 2.2 (3.0) 9.6 180-265 4.8 19.6 30 140M-D8E-C25 100-C23 1655
200 - 240V AC (±10%) – 1-Phase
22A-A1P5N104 0.2 (0.25) 1.5 180-265 0.75 5.0 10 140M-C2E-B63 100-C09 1655
22A-A2P3N104 0.4 (0.5) 2.3 180-265 1.15 6.0 10 140M-C2E-B63 100-C09 1655
22A-A4P5N104 0.75 (1.0) 4.5 180-265 2.25 10.0 15 140M-C2E-C16 100-C12 1655
22A-A8P0N104 1.5 (2.0) 8.0 180-265 4.0 18.0 30 140M-D8E-C20 100-C23 1655
200 - 240V AC (±10%) – 3-Phase Input, 0 - 230V 3-Phase Output
22A-B1P5N104 0.2 (0.25) 1.5 180-265 0.75 1.8 3 140M-C2E-B25 100-C09 1655
22A-B2P3N104 0.4 (0.5) 2.3 180-265 1.15 2.5 6 140M-C2E-B40 100-C09 1655
22A-B4P5N104 0.75 (1.0) 4.5 180-265 2.25 5.2 10 140M-C2E-C10 100-C09 1655
22A-B8P0N104 1.5 (2.0) 8.0 180-265 4.0 9.5 15 140M-C2E-C16 100-C12 1655
22A-B012N104 2.2 (3.0) 12.0 180-265 5.5 15.5 25 140M-C2E-C16 100-C16 1655
22A-B017N104 3.7 (5.0) 17.5 180-265 8.6 21.0 30 140M-F8E-C25 100-C23 1655
380 - 480V AC (±10%) – 3-Phase
22A-D1P4N104 0.4 (0.5) 1.4 340-528 1.4 1.8 3 140M-C2E-B25 100-C09 1655
22A-D2P3N104 0.75 (1.0) 2.3 340-528 2.3 3.2 6 140M-C2E-B40 100-C09 1655
22A-D4P0N104 1.5 (2.0) 4.0 340-528 4.0 5.7 10 140M-C2E-B63 100-C09 1655
22A-D6P0N104 2.2 (3.0) 6.0 340-528 5.9 7.5 15 140M-C2E-C10 100-C09 1655
22A-D8P7N104 3.7 (5.0) 8.7 340-528 8.6 9.0 15 140M-C2E-C16 100-C16 1655
Input/Output Ratings
Output Frequency: 0-240 Hz (Programmable)
Efficiency: 97.5% (Typical)
Output Ratings Input Ratings Branch Circuit Protection
kW (HP) Amps
Voltage
Range kVA Amps Fuses
(1)
Input, 0 - 230V 3-Phase Output, NO BRAKE
(1)
Input, 0 - 230V 3-Phase Output
Input, 0 - 460V 3-Phase Output
140M Motor
Protectors
(2) (3)
Approvals
Contactors
Min. Enclosure
Vol um e
(4)
(in.3)
Digital Control Inputs (Input Current = 6mA) Analog Control Inputs
SRC (Source) Mode:
18-24V = ON
0-6V = OFF
SNK (Sink) Mode:
0-6V = ON
18-24V = OFF
4-20mA Analog: 250 ohm input impedance
0-10V DC Analog: 100k ohm input impedance
External Pot: 1-10k ohms, 2 Watt minimum
Control Output (Programmable Output, form C relay)
Resistive Rating: 3.0A at 30V DC, 125V AC and 240V AC Inductive Rating: 0.5A at 30V DC, 125V AC, and 240V AC
Recommended Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Fuse: UL Class J, CC, T or Type BS88; 600V (550V) or equivalent. Circuit Breakers: HMCP or Bulletin 140U or equivalent.
Protective Features
Motor Protection: I2t overload protection - 150% for 60 Secs, 200% for 3 Secs (Provides Class 10 protection)
Overcurrent: 200% hardware limit, 300% instantaneous fault
Over Voltage: 100-120V AC Input – Trip occurs at 405V DC bus voltage (equivalent to 150V AC incoming line)
Under Voltage: 100-120V AC Input – Trip occurs at 210V DC bus voltage (equivalent to 75V AC incoming line)
Control Ride Through: Minimum ride through is 0.5 Secs - typical value 2 Secs
Faultless Power Ride Through: 100 milliseconds
Dynamic Braking
Internal brake IGBT included with all ratings except No Brake versions. Refer to Appendix B of the PowerFlex 4 User Manual
on CD for ordering information.
200-240V AC Input – Trip occurs at 405V DC bus voltage (equivalent to 290V AC incoming line)
380-460V AC Input – Trip occurs at 810V DC bus voltage (equivalent to 575V AC incoming line)
200-240V AC Input – Trip occurs at 210V DC bus voltage (equivalent to 150V AC incoming line)
380-480V AC Input – Trip occurs at 390V DC bus voltage (equivalent to 275V AC incoming line)
Page 75
Supplemental Drive Information A-3
(1)
200-240V AC - 1-Phase drives are also available with an integral EMC filter. Catalog suffix changes from N103 to N113
and N104 to N114.
(2)
The AIC ratings of the Bulletin 140M Motor Protector Circuit Breakers may vary. See Bulletin 140M Motor Protection
Circuit Breakers Application Ratings.
(3)
Manual Self-Protected (Type E) Combination Motor Controller, UL listed for 208 Wye or Delta, 240 Wye or Delta, 480Y/
277 or 600Y/347. Not UL listed for use on 480V or 600V Delta/Delta, corner ground, or high-resistance ground systems.
(4)
When using a Manual Self-Protected (Type E) Combination Motor Controller, the drive must be installed in a ventilated or
non-ventilated enclosure with the minimum volume specified in this column. Application specific thermal considerations
may require a larger enclosure.
Category Specification
Environment Altitude: 1000 m (3300 ft) max. without derating
Maximum Surrounding Air
Temperature without derating:
IP20:
NEMA 1:
Flange Mount:
Cooling Method
Convection:
Fan:
Storage Temperature: –40 to 85 degrees C (–40 to 185 degrees F)
Atmosphere: Important: Drive must
Relative Humidity: 0 to 95% non-condensing
Shock (operating): 15G peak for 11ms duration (±1.0ms)
Vibration (operating): 1G peak, 5 to 2000 Hz
Sound Pressure Level
(A-weighted)
Frame A:
Frame B:
Control Carrier Frequency 2-16 kHz. Drive rating based on 4 kHz.
Frequency Accuracy
Digital Input:
Analog Input:
Speed Regulation - Open Loop
with Slip Compensation:
Stop Modes: Multiple programmable stop modes including -
Accel/Decel: Two independently programmable accel and
Intermittent Overload: 150% Overload capability for up to 1 minute
Electronic Motor Overload
Protection
–10 to 50° C (14 to 122° F)
–10 to 40° C (14 to 104° F)
Heatsink: –10 to 40° C (14 to 104° F)
Drive: –10 to 50° C (14 to 122° F)
0.2 kW (0.25 HP) drives
Flange Mount drives, all ratings
All other drive ratings.
not be installed in an
area where the ambient atmosphere contains
volatile or corrosive gas, vapors or dust. If the
drive is not going to be installed for a period of
time, it must be stored in an area where it will not
be exposed to a corrosive atmosphere.
Measurements are taken 1 m from the drive.
Maximum 50 dBA
Maximum 51 dBA
Within ±0.05% of set output frequency.
Within 0.5% of maximum output frequency.
±2% of base speed across a 40:1 speed range.
Ramp, Coast, DC-Brake, Ramp-to-Hold and
S Curve.
decel times. Each time may be programmed from
0 - 600 seconds in 0.1 second increments.
200% Overload capability for up to 3 seconds
Provides class 10 motor overload protection
according to NEC article 430 and motor
over-temperature protection according to NEC
article 430.126 (A) (2). UL 508C File 29572.
Page 76

A-4 Supplemental Drive Information
PowerFlex 4 Estimated Watts Loss (Rated Load, Speed & PWM)
Voltage kW (HP) External Watts Internal Watts Total Watts Loss
100–120V 0.2 (0.25)
0.4 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.1 (1.5)
200–240V 0.2 (0.25)
0.4 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
2.2 (3.0)
3.7 (5.0)
380–480V 0.4 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
2.2 (3.0)
3.7 (5.0)
Product Environmental Information
16
22
35
58
16
22
35
63
100
150
17
30
48
75
125
16
18
20
22
16
18
20
22
25
30
18
20
22
25
25
32
40
55
80
32
40
55
85
125
180
35
50
70
100
150
Rockwell Automation maintains current product environmental
information on its website at:
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/rockwellautomation/about-us/
sustainability-ethics/product-environmental-compliance.page.
At the end of its life, this equipment should be collected separately from any
unsorted municipal waste.
Page 77

Appendix B
Accessories and Dimensions
For information on… See page
Product Selection B-1
Product Dimensions B-5
Product Selection
Table B.A Catalog Number Description
22A - A 1P5 N 1 1 4
Drive Voltage Rating Rating Enclosure HIM Emission Class Type
Table B.B PowerFlex 4 Drives
Drive Ratings Catalog Number
Output
Current Panel Mount Flange Mount
120V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
No Filter
240V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
NO BRAKE
With Integral “S Type”
EMC Filter
240V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
NO BRAKE
No Filter
240V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
With Integral “S Type”
EMC Filter
240V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
No Filter
240V 50/60 Hz
3-Phase
No Filter
480V 50/60 Hz
3-Phase
No Filter
(1)
Replacement Plate drives are also available. Contact factory for ordering information.
0.2 0.25 1.5A 22A-V1P5N104 22A-V1P5F104 A
0.4 0.5 2.3A 22A-V2P3N104 22A-V2P3F104 A
0.75 1.0 4.5A 22A-V4P5N104 22A-V4P5F104 B
1.1 1.5 6.0A 22A-V6P0N104 22A-V6P0F104 B
0.2 0.25 1.4A 22A-A1P4N113 – A
0.4 0.5 2.1A 22A-A2P1N113 – A
0.75 1.0 3.6A 22A-A3P6N113 – A
1.5 2.0 6.8A 22A-A6P8N113 – B
2.2 3.0 9.6A 22A-A9P6N113 – B
0.2 0.25 1.4A 22A-A1P4N103 22A-A1P4F103 A
0.4 0.5 2.1A 22A-A2P1N103 22A-A2P1F103 A
0.75 1.0 3.6A 22A-A3P6N103 22A-A3P6F103 A
1.5 2.0 6.8A 22A-A6P8N103 22A-A6P8F103 B
2.2 3.0 9.6A 22A-A9P6N103 22A-A9P6F103 B
0.2 0.25 1.5A 22A-A1P5N114 – A
0.4 0.5 2.3A 22A-A2P3N114 – A
0.75 1.0 4.5A 22A-A4P5N114 – A
1.5 2.0 8.0A 22A-A8P0N114 – B
0.2 0.25 1.5A 22A-A1P5N104 22A-A1P5F104 A
0.4 0.5 2.3A 22A-A2P3N104 22A-A2P3F104 A
0.75 1.0 4.5A 22A-A4P5N104 22A-A4P5F104 A
1.5 2.0 8.0A 22A-A8P0N104 22A-A8P0F104 B
0.2 0.25 1.5A 22A-B1P5N104 22A-B1P5F104 A
0.4 0.5 2.3A 22A-B2P3N104 22A-B2P3F104 A
0.75 1.0 4.5A 22A-B4P5N104 22A-B4P5F104 A
1.5 2.0 8.0A 22A-B8P0N104 22A-B8P0F104 A
2.2 3.0 12.0A 22A-B012N104 22A-B012F104 B
3.7 5.0 17.5 22A-B017N104 22A-B017F104 B
0.4 0.5 1.4A 22A-D1P4N104 22A-D1P4F104 A
0.75 1.0 2.3A 22A-D2P3N104 22A-D2P3F104 A
1.5 2.0 4.0A 22A-D4P0N104 22A-D4P0F104 A
2.2 3.0 6.0A 22A-D6P0N104 22A-D6P0F104 B
3.7 5.0 8.7A 22A-D8P7N104 22A-D8P7F104 B
(1)
Frame
SizeInput Voltage kW HP
Page 78

B-2 Accessories and Dimensions
Table B.C Dynamic Brake Modules
Drive Ratings
Input Voltage kW HP
120V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
240V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
240V 50/60 Hz
3-Phase
480V 50/60 Hz
3-Phase
0.2 0.25 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.4 0.5 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.75 1.0 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
1.1 1.5 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.2 0.25 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.4 0.5 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.75 1.0 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
1.5 2.0 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.2 0.25 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.4 0.5 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.75 1.0 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
1.5 2.0 60 10 AK-R2-091P500
2.2 3.0 48 12 AK-R2-047P500
3.7 5.0 32 20 AK-R2-047P500
0.4 0.5 121 10 AK-R2-091P500
0.75 1.0 121 10 AK-R2-360P500
1.5 2.0 121 10 AK-R2-360P500
2.2 3.0 97 12 AK-R2-120P1K2
3.7 5.0 97 12 AK-R2-120P1K2
Minimum
Resistance
Dynamic
Brake Fuse
(1)
Rating
Catalog Number
(2) (3)
(1)
Refer to
(2)
The resistors listed in this table are rated for 5% duty cycle.
(3)
Use of Rockwell resistors is always recommended. The resistors listed have been carefully
EN61800-5-1 compliance in Table 1.D for more information.
selected for optimizing performance in a varity of applications. Alternative resistors may be used,
however care must be taken when making a selection. Refer to the
Resistor Calculator
, publication PFLEX-AT001….
PowerFlex Dynamic Braking
Table B.D Bulletin 1321-3R Series Line Reactors
Maximum
Input Voltage kW HP
240V 50/60 Hz
3-Phase
0.2 0.25 2 3 12.0 mh 7.5 W 1321-3R2-A
0.4 0.5 4 6 12.0 mh 21 W 1321-3R4-D
0.75 1.0 8 12 3.0 mh 29 W 1321-3R8-B
1.5 2.0 8 12 1.5 mh 19.5 W 1321-3R8-A
2.2 3.0 12 18 1.25 mh 26 W 1321-3R12-A
3.7 5.0 18 27 0.8 mh 36 W 1321-3R18-A
480V 50/60 Hz
3-Phase
0.4 0.5 2 3 20.0 mh 11.3 W 1321-3R2-B
0.75 1.0 4 6 9.0 mh 20 W 1321-3R4-C
1.5 2.0 4 6 6.5 mh 20 W 1321-3R4-B
2.2 3.0 8 12 5.0 mh 25.3 W 1321-3R8-C
3.7 5.0 18 27 3.0 mh 29 W 1321-3R-12-B
Fundamental
Amps
Continuous
Amps Inductance
Watts
Loss
Catalog
Number
(1)
(1)
Catalog numbers listed are for 3% impedance open style units. NEMA Type 1 and 5% impedance
reactor types are also available. Refer to publication 1321-TD001….
Page 79

Table B.E EMC Line Filters
Accessories and Dimensions B-3
Drive Ratings
Input Voltage kW HP
120V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
0.2 0.25 – 22-RF010-AL
0.4 0.5 – 22-RF010-AL
S Type Filter
Catalog Number
L Type Filter
(1)
Catalog Number
0.75 1.0 – 22-RF018-BL
1.1 1.5 – 22-RF025-CL
240V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
240V 50/60 Hz
1-Phase
NO BRAKE
240V 50/60 Hz
3-Phase
0.2 0.25
0.4 0.5
0.75 1.0
1.5 2.0
0.2 0.25
0.4 0.5
0.75 1.0
1.5 2.0
2.2 3.0
0.2 0.25 22-RF9P5-AS 22-RF9P5-AL
0.4 0.5 22-RF9P5-AS 22-RF9P5-AL
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
22-RF010-AL
22-RF010-AL
22-RF010-AL
22-RF018-BL
22-RF010-AL
22-RF010-AL
22-RF010-AL
22-RF018-BL
22-RF025-CL
0.75 1.0 22-RF9P5-AS 22-RF9P5-AL
1.5 2.0 22-RF9P5-AS 22-RF9P5-AL
2.2 3.0 22-RF021-BS 22-RF021-BL
3.7 5.0 22-RF021-BS 22-RF021-BL
480V 50/60 Hz
3-Phase
0.4 0.5 22-RF5P7-AS 22-RF5P7-AL
0.75 1.0 22-RF5P7-AS 22-RF5P7-AL
1.5 2.0 22-RF5P7-AS 22-RF5P7-AL
2.2 3.0 22-RF012-BS 22-RF012-BL
3.7 5.0 22-RF012-BS 22-RF012-BL
(1)
This filter is suitable for use with a cable length up to 10 meters (33 feet) for Class A and 1 meter
for Class B environments.
(2)
These ratings can be ordered with internal “S Type” filters. Refer to the Catalog Number
explanation on
(3)
This filter is suitable for use with a cable length up to 100 meters for Class A and 5 meters for
page P-4 and Ta b l e B. B for details.
Class B environments.
(4)
The piggyback mounting option cannot be used with Frame B PowerFlex 4 drives and Frame C
EMC Line Filters.
(3)
(4)
(4)
Table B.F Human Interface Module (HIM) Option Kits and Accessories
Item Description Catalog Number
LCD Display, Remote Panel
Mount
LCD Display, Remote Handheld Digital speed control
Bezel Kit Panel mount for LCD Display, Remote
DSI HIM Cable
(DSI HIM to RJ45 cable)
(1)
The 22-HIM-C2S is smaller than the 22-HIM-C2 and cannot be used as a direct replacement.
Digital speed control
CopyCat capable
IP66 (NEMA Type 4X/12) indoor use only
22-HIM-C2 includes 2.9 meter cable.
22-HIM-C2S includes 2 meter cable.
Full numeric keypad
CopyCat capable
IP30 (NEMA Type 1)
Includes 1.0 meter cable
Panel mount with optional Bezel Kit
Handheld unit, IP30 (NEMA Type 1)
1.0 Meter (3.3 Feet)
2.9 Meter (9.51 Feet)
22-HIM-C2
22-HIM-C2S
22-HIM-A3
22-HIM-B1
22-HIM-H10
22-HIM-H30
(1)
Page 80

B-4 Accessories and Dimensions
Table B.G Communication Option Kits
Item Description Catalog Number
External DSI™
Communications Kit
External Comms Power
Supply
Compact I/O Module Three channel. 1769-SM2
Serial Converter Module
(RS485 to RS232)
DSI Cable 2.0 meter RJ45 to RJ45 cable, male to male
Serial Cable 2.0 meter serial cable with a locking low profile
Null Cable Converter For use when connecting the serial converter to
Splitter Cable RJ45 one to two port splitter cable AK-U0-RJ45-SC1
Terminating Resistors RJ45 120 Ohm resistors (2 pieces) AK-U0-RJ45-TR1
Terminal Block RJ45 Two position terminal block (5 pieces) AK-U0-RJ45-TB2P
DriveExplorer Software
(CD-ROM) Version 3.01
or later
DriveExecutive software
(CD-ROM) Version 1.01
or later
External mounting kit for 22-COMM-C, -D, -E, -P. 22-XCOMM-DC-BASE
Optional 100-240V AC Power Supply for External
DSI Communications Kit.
Provides serial communication via DF1 protocol
for use with DriveExplorer and DriveExecutive
software. Includes:
DSI to RS232 serial converter (1)
1203-SFC serial cable (1)
22-RJ45CBL-C20 cable (1)
DriveExplorer Lite CD (1)
connectors.
connector to connect to the serial converter and a
9-pin sub-miniature D female connector to connect
to a computer.
DriveExplorer on a handheld PC.
Windows based software package that provides
an intuitive means for monitoring or configuring
Allen-Bradley drives and communication adapters
online.
Compatibility:
Windows 95, 98, ME, NT 4.0 (Service Pack 3 or
later), 2000, XP and CE
Windows based software package that provides
an intuitive means for monitoring or configuring
Allen-Bradley drives and communication adapters
online and offline.
Compatibility:
Windows 98, ME, NT 4.0 (Service Pack 3 or
later), 2000 and XP
(2)
20-XCOMM-AC-PS1
22-SCM-232
22-RJ45CBL-C20
1203-SFC
1203-SNM
9306-4EXP01ENE
(1)
9303-4DTE01ENE
(1)
See www.ab.com/drives/driveexplorer.htm for supported devices.
(2)
For pricing information, refer to the PowerFlex 4-Class
Table B.H IP30/NEMA 1/UL Type 1 Kit
Item Description
IP30/NEMA 1/UL Type 1
Kit
(1)
For pricing information, refer to the PowerFlex 4-Class
Field installed kit. Converts drive to IP30/
NEMA 1/UL Type 1 enclosure. Includes
conduit box with mounting screws and
plastic top panel.
Price List, Publication 22-PL001….
Drive
Frame Catalog Number
A22-JBAA
B22-JBAB
Price List, Publication 22-PL001….
(1)
Page 81

Accessories and Dimensions B-5
a
ge
d
c
b
f
5.5 (0.22)
59.2
(2.33)
40.0
(1.57)
20.7
(0.81)
75.3
(2.96)
109.3
(4.30)
74.3
(2.93)
109.9
(4.33)
64.1
(2.52)
79.1
(3.11)
40.6
(1.60)
25.6
(1.01)
∅ 22.2
(0.87)
∅ 22.2
(0.87)
Frame A - 22-JBAA Frame B - 22-JBAB
Product Dimensions
Table B.I PowerFlex 4 Panel Mount Drives – Ratings are in kW and (HP)
120V AC – 1-Phase
Frame
A 0.2 (0.25)
0.37(0.5)
B 0.75(1.0)
1.1 (1.5)
Figure B.1 PowerFlex 4 Panel Mount Drives – Dimensions are in millimeters and
(inches). Weights are in kilograms and (pounds).
240V AC – 1-Phase
No Brake
0.2 (0.25)
0.37 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
2.2 (3.0)
240V AC – 1-Phase 240V AC – 3-Phase 480V AC – 3-Phase
0.2 (0.25)
0.37 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0) 2.2 (3.0)
0.2 (0.25)
0.37 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
3.7 (5.0)
0.37 (0.5)
0.75 (1.0)
1.5 (2.0)
2.2 (3.0)
3.7 (5.0)
Frame a b
A 80 (3.15) 185 (7.28) 136 (5.35) 67 (2.64) 152 (5.98) 59.3 (2.33) 140 (5.51) 1.4 (3.1)
B 100 (3.94) 213 (8.39) 136 (5.35) 87 (3.43) 180 (7.09) 87.4 (3.44) 168 (6.61) 2.2 (4.9)
(1)
Overall height of drive with IP 30/NEMA 1/UL Type 1 option kit installed.
(2)
Overall height of standard IP 20/Open Type drive.
(1)
cde
(2)
fg
Figure B.2 IP 30/NEMA 1/UL Type 1 Option Kit – Dimensions are in millimeters and
(inches)
Shipping
Weight
Page 82

B-6 Accessories and Dimensions
175
(6.89)
210
(8.27)
54.7
(2.15)
92.8
(3.65)
145
(5.71)
244
(9.61)
250
(9.84)
94.3
(3.71)
63.1
(2.48)
214
(8.43)
Frame A
Frame B
Figure B.3 PowerFlex 4 Flange Mount Drives – Dimensions are in millimeters and
(inches)
Page 83

Accessories and Dimensions B-7
195
(7.68)
97.5
(3.84)
179
(7.05)
8
(0.31)
130
(5.12)
114
(4.49)
5.3
(0.21)
8
(0.31)
98
(3.86)
49
(1.93)
16
(0.63)
210
(8.27)
98
(3.86)
160
(6.30)
145
(5.71)
49
(1.93)
31
(1.22)
7.5
(0.30)
14
(0.55)
98.5
(3.88)
197
(7.76)
6.5
(0.26)
225
(8.86)
23.5
(0.93)
5.3
(0.21)
Frame A
Frame B
Figure B.4 PowerFlex 4 Cutout Dimensions – Dimensions are in millimeters and
(inches)
Page 84
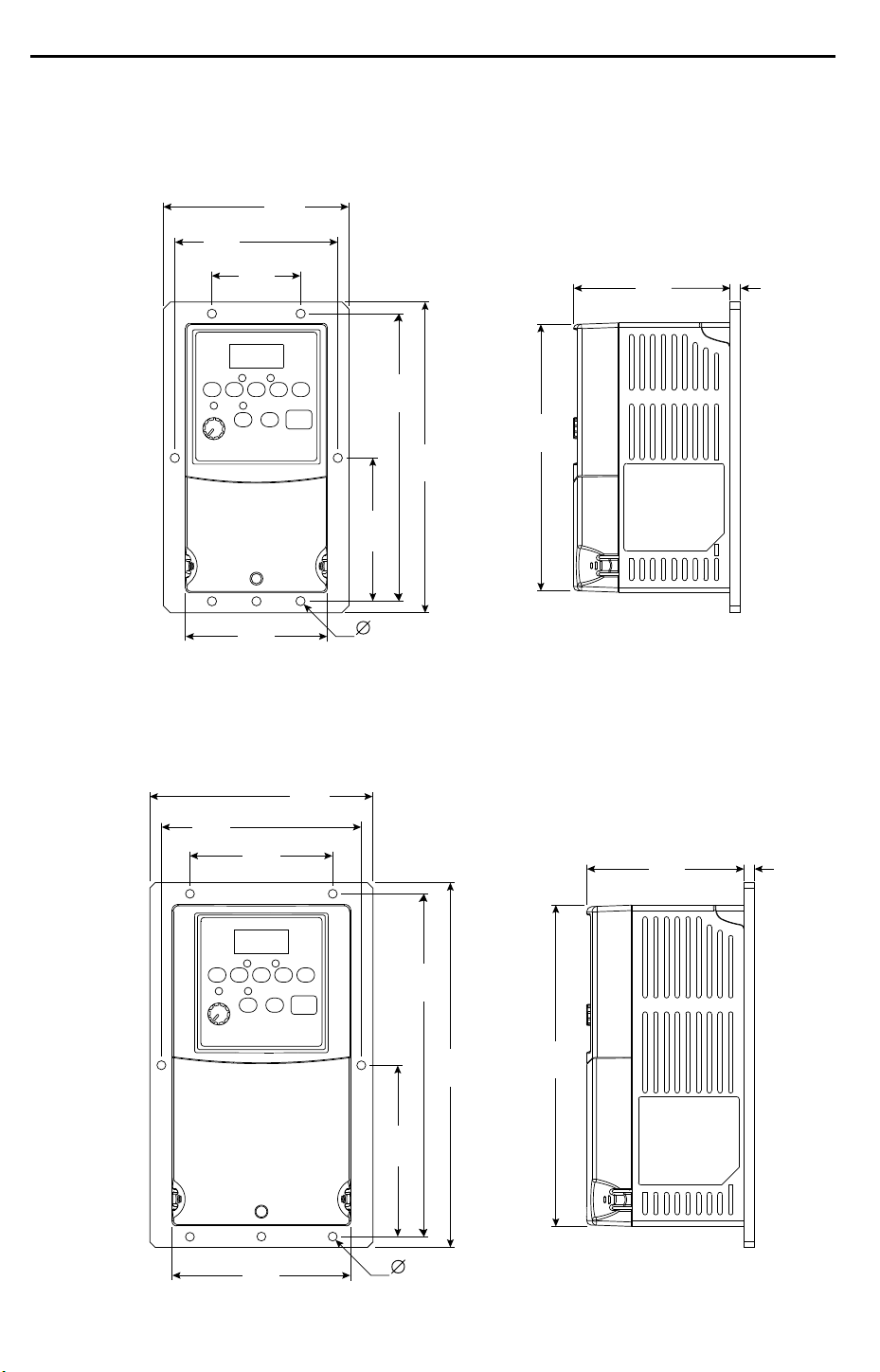
B-8 Accessories and Dimensions
104.8
(4.13)
175
(6.89)
152
(5.98)
163
(6.42)
81.5
(3.21)
6
(0.24)
88
(3.46)
92
(3.62)
80
(3.15)
50
(1.97)
5.3
(0.21)
Frame A
Frame B
Figure B.5 PowerFlex 4 Replacement Plate Drive Dimensions – Dimensions are in
millimeters and (inches)
112
(4.41)
80
(3.15)
100
(3.94)
125
(4.92)
96
(3.78)
(0.21)
192
(7.56)
5.3
204
(8.03)
180
(7.09)
88
(3.46)
9.5
(0.37)
Page 85

Accessories and Dimensions B-9
335.0
(13.19)
60.0
(2.36)
30.0
(1.18)
17.0
(0.67)
59.0
(2.32)
13.0
(0.51)
405.0
(15.94)
386.0
(15.20)
316.0
(12.44)
61.0
(2.40)
31.0
(1.22)
ROCKWELL
AUTOMATION
CUS
SURFACES MAY BE
ROCKWELL
AUTOMATION
CUS
Frame A Frame B
Power On
R (L1)
S (L2)
T (L3)
Power Source DB Resistor Thermostat
Power Off
M
M
(Input Contactor) M
Three-Phase
AC Input
Figure B.6 Dynamic Brake Modules – Dimensions are in millimeters and (inches)
Frame Catalog Number
A AK-R2-091P500, AK-R2-047P500, AK-R2-360P500
B AK-R2-030P1K2, AK-R2-120P1K2
Figure B.7 Recommended External Brake Resistor Circuitry
Page 86

B-10 Accessories and Dimensions
Figure B.8 Bulletin 1321-3R Series Line Reactors
– Dimensions are in millimeters and (inches). Weights are in kilograms and (pounds).
a
b
e
Catalog Number a b c d e Weight
1321-3R2-A 112 (4.40) 104 (4.10) 70 (2.75) 50 (1.98) 37 (1.44) 1.8 (4)
1321-3R2-B 112 (4.40) 104 (4.10) 70 (2.75) 50 (1.98) 37 (1.44) 1.8 (4)
1321-3R4-B 112 (4.40) 104 (4.10) 76 (3.00) 50 (1.98) 37 (1.44) 1.8 (4)
1321-3R4-C 112 (4.40) 104 (4.10) 86 (3.38) 60 (2.35) 37 (1.44) 2.3 (5)
1321-3R4-D 112 (4.40) 104 (4.10) 92 (3.62) 66 (2.60) 37 (1.44) 2.7 (6)
1321-3R8-A 152 (6.00) 127 (5.00) 76 (3.00) 53 (2.10) 51 (2.00) 3.1 (7)
1321-3R8-B 152 (6.00) 127 (5.00) 76 (3.00) 53 (2.10) 51 (2.00) 3.6 (8)
1321-3R8-C 152 (6.00) 127 (5.00) 85 (3.35) 63 (2.48) 51 (2.00) 4.9 (11)
1321-3R12-A 152 (6.00) 127 (5.00) 76 (3.00) 53 (2.10) 51 (2.00) 4.1 (9)
1321-3R18-A 152 (6.00) 133 (5.25) 79 (3.10) 54 (2.13) 51 (2.00) 4.1 (9)
d
c
Page 87

Accessories and Dimensions B-11
5.5 (0.22)
17.8
(0.70)
24
(0.94)
60
(2.36)
80
(3.15)
50
(1.97)
29.8
(1.17)
220
(8.66)
208
(8.19)
208
(8.19)
5.5 (0.22)
17.8
(0.70)
24.0
(0.94)
78
(3.07)
100
(3.94)
50
(1.97)
29.8
(1.17)
229
(9.02)
216
(8.50)
217
(8.54)
Figure B.9 Frame A EMC Line Filters – Dimensions are in millimeters and (inches)
Catalog Numbers: 22-RF5P7-AS, -AL; 22-RF9P5-AS, -AL; 22-RF010-AL
Figure B.10 Frame B EMC Line Filters – Dimensions are in millimeters and (inches)
Catalog Numbers: 22-RF012-BS, -BL (Series B); 22-RF018-BS; 22-RF021-BS, -BL
Page 88

B-12 Accessories and Dimensions
5.5 (0.22)
17
(0.67)
30
(1.18)
90
(3.54)
130
(5.12)
60
(2.36)
32
(1.26)
309
(12.17)
297
(11.69)
297
(11.69)
Figure B.11 Frame C EMC Line Filters – Dimensions are in millimeters and (inches)
Catalog Number: 22-RF025-CL
Important: The piggyback mounting option cannot be used with
Frame B PowerFlex 4 drives and Frame C EMC Line
Filters.
Page 89

Accessories and Dimensions B-13
04
(
)
6
(
)
9m
0
(
)
5
(4.92)
60.5
(2.38)
38
(1.50)
8
(
)
66
(
)
1
(
)
8
(
)
Figure B.12 Remote (Panel Mount) HIM – Dimensions are in millimeters and (inches)
Catalog Number: 22-HIM-C2
17.
0.69
2.
1
4.09
22
8.66
7
3.07
2.60
19.
0.75
194
(7.64)
12
4.
0.19
Page 90

B-14 Accessories and Dimensions
93
(
)
5
(
)
80
(
)
54
(6.06)
(3.03)
5
(
)
67
(
)
60
(
)
1
(
)
8
(
)
Figure B.13 Remote (Panel Mount) Small HIM – Dimensions are in millimeters and
(inches) Catalog Number: 22-HIM-C2S
2
0.98
3.66
1
7.09
2.64
2.36
1
19.
0.75
4.
0.19
23.
0.93
Important: The 22-HIM-C2S is smaller than the 22-HIM-C2 and
cannot be used as a direct replacement.
Page 91
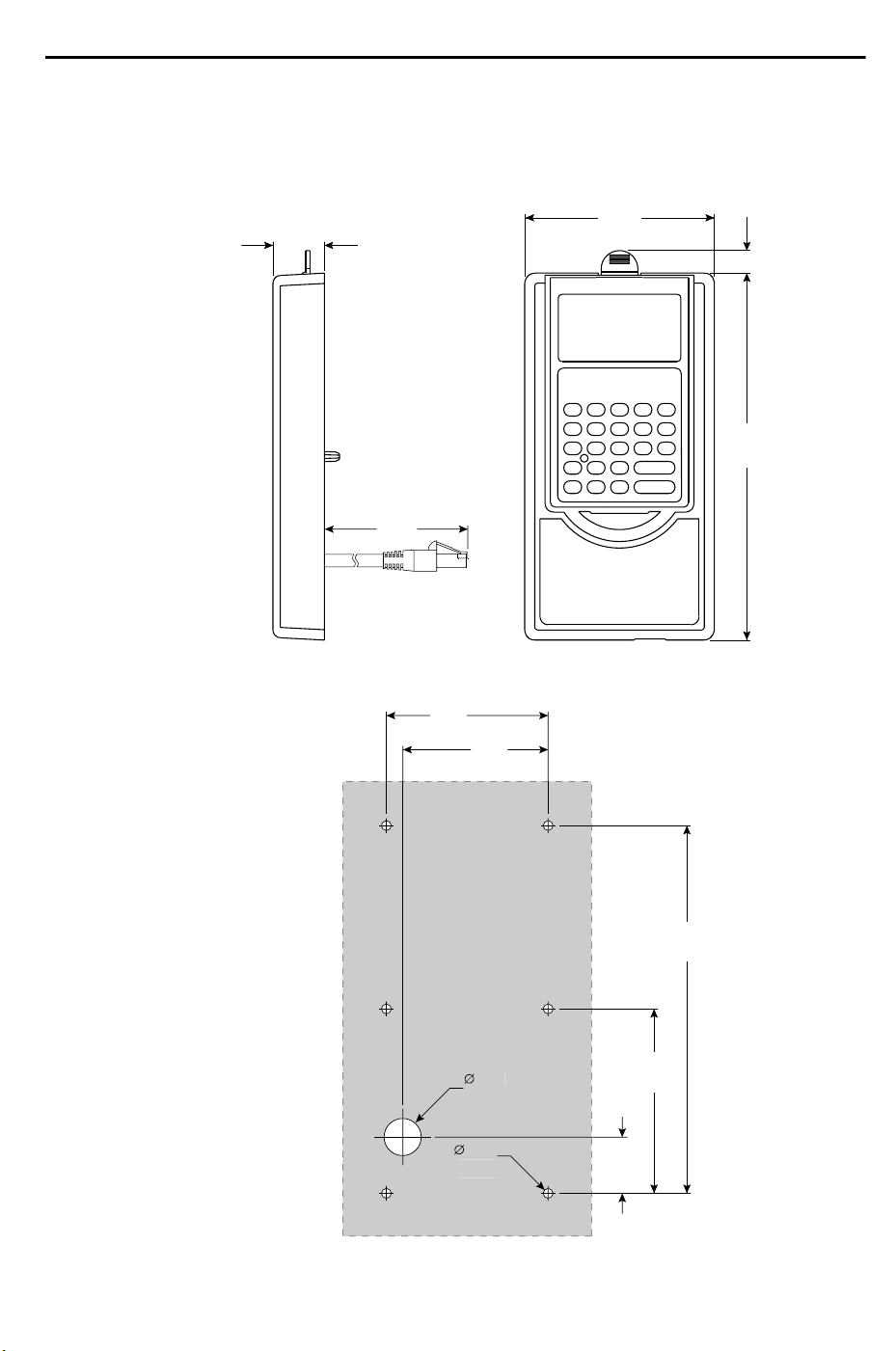
Accessories and Dimensions B-15
93
(3.66)
25.2
(0.99)
180
(7.09)
11. 1
(0.44)
154
(6.06)
77
(
)
5
(
)
67
(
)
60
(
)
1
(
)
8
(
)
Figure B.14 NEMA Type 1 Bezel – Dimensions are in millimeters and (inches)
Catalog Number: 22-HIM-B1
2.64
2.36
19.
0.75
4.
0.19
3.03
23.
0.93
Page 92

B-16 Accessories and Dimensions
Notes:
Page 93

Appendix C
Controller
RS485 (DSI) Protocol
PowerFlex 4 drives support the RS485 (DSI) protocol to allow efficient
operation with Rockwell Automation peripherals. In addition, some
Modbus functions are supported to allow simple networking. PowerFlex
4 drives can be multi-dropped on an RS485 network using Modbus
protocol in RTU mode.
For information regarding DeviceNet or other communication protocols,
refer to the appropriate usr manual.
Network Wiring
Network wiring consists of a shielded 2-conductor cable that is
daisy-chained from node to node.
Figure C.1 Network Wiring Diagram
PowerFlex 4
Master
TxRxD-
120 ohm resistor
TxRxD+
Shield Shield Shield
Node 1
5
4
X X X
TxRxD-
TxRxD+
NOTE: The shield is connected at ONLY ONE end of each cable segment.
01 02 03 04 05
11 12 13 14 15
06 07 08 09
16 17 18 19
W/T3
V/T2T/L3S/L2R/L1 U/T1
RS485
(DPI)
PowerFlex 4
Node 2
5
4
AK-00-RJ45-TB2P
TxRxDTxRxD+
PowerFlex 4
Node "n"
TxRxD-
TxRxD+
01 02 03 04 05
11 12 13 14 15
V/T2T/L3S/L2R/L1 U/T1 W/T3
120 ohm resistor
5
4
06 07 08 09
16 17 18 19
PIN 8
FRONT
RS485
(DPI)
PIN 1
TxRxDTxRxD+
BR+ BR-DC- DC+
BR+ BR-DC- DC+
Page 94

C-2 RS485 (DSI) Protocol
Only pins 4 and 5 on the RJ45 plug should be wired. The other pins on
the PowerFlex 4 RJ45 socket must not be connected because they
contain power, etc. for other Rockwell Automation peripheral devices.
Wiring terminations on the master controller will vary depending on the
master controller used and “TxRxD+” and “TxRxD-” are shown for
illustration purposes only. Refer to the master controller’s user manual
for network terminations. Note that there is no standard for the “+” and
“-” wires, and consequently Modbus device manufacturers interpret
them differently. If you have problems with initially establishing
communications, try swapping the two network wires at the master
controller.
Standard RS485 wiring practices apply.
Termination resistors need to be applied at each end of the network
cable.
RS485 repeaters may need to be used for long cable runs, or if
greater than 32 nodes are needed on the network.
Network wiring should be separated from power wires by at least 0.3
meters (1 foot).
Network wiring should only cross power wires at a right angle.
I/O Terminal 16 (RS485 Shield) on the PowerFlex 4 must also be
connected to PE ground (there are two PE terminals on the drive). See
Figure 1.5
Network Common is internally tied to I/O Terminal 04 (Digital
Common). Tying I/O Terminal 04 to PE ground may improve noise
immunity in some applications.
for more information.
Page 95

RS485 (DSI) Protocol C-3
Parameter Configuration
The following PowerFlex 4 parameters are used to configure the drive to
operate on a network.
Parameter Details Reference
P036 [Start Source] Set to 5 “RS485 (DSI) Port” if Start is controlled from
the network.
P038 [Speed Reference] Set to 5 “RS485 (DSI) Port” if the Speed Reference is
controlled from the network.
A103 [Comm Data Rate] Sets the data rate for the RS485 (DSI) Port. All nodes
on the network must be set to the same data rate.
A104 [Comm Node Addr] Sets the node address for the drive on the network.
Each device on the network requires a unique node
address.
A105 [Comm Loss Action] Selects the drive’s response to communication
problems.
A106 [Comm Loss Time] Sets the time that the drive will remain in
communication loss before the drive implements A105
[Comm Loss Action].
A107 [Comm Format] Sets the transmission mode, data bits, parity and stop
bits for the RS485 (DSI) Port. All nodes on the network
must be set to the same setting.
Page 3-9
Page 3-11
Page 3-23
Page 3-23
Page 3-24
Page 3-24
Page 3-24
Supported Modbus Function Codes
The peripheral interface (DSI) used on PowerFlex 4 drives supports
some of the Modbus function codes.
Modbus Function Code (Decimal) Command
03 Read Holding Registers
06 Preset (Write) Single Register
16 (10 Hexadecimal) Preset (Write) Multiple Registers
Important: Modbus devices can be 0-based (registers are numbered
starting at 0) or 1-based (registers are numbered starting at
1). Depending on the Modbus Master used, the register
addresses listed on the following pages may need to be
offset by +1. For example, Logic Command may be register
address 8192 for some master devices (e.g. ProSoft
3150-MCM SLC Modbus scanner) and 8193 for others
(e.g. PanelViews).
Page 96

C-4 RS485 (DSI) Protocol
Writing (06) Logic Command Data
The PowerFlex 4 drive can be controlled via the network by sending
Function Code 06 writes to register address 8192 (Logic Command).
P036 [Start Source] must be set to 5 “RS485 (DSI) Port” in order to
accept the commands. In addition to being written, register address 8192
can be read using Function Code 03.
Address (Decimal) Bit(s) Description
0 1 = Stop, 0 = Not Stop
1 1 = Start, 0 = Not Start
2 1 = Jog, 0 = No Jog
3 1 = Clear Faults, 0 = Not Clear Faults
5,4
6 Not Used
7 Not Used
9,8
8192
11,10
14,13,12
15 Not Used
Logic Command
00 = No Command
01 = Forward Command
10 = Reverse Command
11 = No Command
00 = No Command
01 = Accel Rate 1 Enable
10 = Accel Rate 2 Enable
11 = Hold Accel Rate Selected
00 = No Command
01 = Decel Rate 1 Enable
10 = Decel Rate 2 Enable
11 = Hold Decel Rate Selected
000 = No Command
001 = Freq. Source = P036 [Start Source]
010 = Freq. Source = A069 [Internal Freq]
011 = Freq. Source = Comms (Addr 8193)
100 = A070 [Preset Freq 0]
101 = A071 [Preset Freq 1]
110 = A072 [Preset Freq 2]
111 = A073 [Preset Freq 3]
Page 97

RS485 (DSI) Protocol C-5
Writing (06) Reference
The Speed Reference to a PowerFlex 4 drive can be controlled via the
network by sending Function Code 06 writes to register address 8193
(Reference). P038 [Speed Reference] must be set to 5 “RS485 (DSI)
Port” in order to accept the Speed Reference. In addition to being
written, register address 8193 can be read using Function Code 03.
Reference
Address (Decimal) Description
8193
A decimal value entered as xxx.x where the decimal point is fixed. For
example, a decimal “100” equals 10.0 Hz and “543” equals 54.3 Hz.
Reading (03) Logic Status Data
The PowerFlex 4 Logic Status data can be read via the network by
sending Function Code 03 reads to register address 8448 (Logic Status).
Logic Status
Address (Decimal) Bit(s) Description
0 1 = Ready, 0 = Not Ready
1 1 = Active (Running), 0 = Not Active
2 1 = Cmd Forward, 0 = Cmd Reverse
3 1 = Rotating Forward, 0 = Rotating Reverse
4 1 = Accelerating, 0 = Not Accelerating
5 1 = Decelerating, 0 = Not Decelerating
6 1 = Alarm, 0 = No Alarm
8448
7 1 = Faulted, 0 = Not Faulted
8 1 = At Reference, 0 = Not At Reference
9 1 = Reference Controlled by Comm
10 1 = Operation Cmd Controlled by Comm
11 1 = Parameters have been locked
12 Digital Input 1 Status
13 Digital Input 2 Status
14 Not Used
15 Not Used
Reading (03) Feedback
The Feedback (Output Frequency) from the PowerFlex 4 drive can be
read via the network by sending Function Code 03 reads to register
address 8451 (Feedback).
Feedback
Address (Decimal) Description
8451
(1)
Returns the same data as Reading (03) Parameter d001 [Output Freq].
A xxx.x decimal value where the decimal point is fixed. For example, a decimal
“123” equals 12.3 Hz and “300” equals 30.0 Hz.
(1)
Page 98

C-6 RS485 (DSI) Protocol
Reading (03) Drive Error Codes
The PowerFlex 4 Error Code data can be read via the network by sending
Function Code 03 reads to register address 8449 (Drive Error Codes).
Address (Decimal) Value (Decimal) Description
0 No Fault
2 Auxiliary Input
3 Power Loss
4 Undervoltage
5 Overvoltage
6 Motor Stalled
7 Motor Overload
8 Heatsink Overtemperature
12 HW Overcurrent (300%)
13 Ground Fault
29 Analog Input Loss
33 Auto Restart Tries
8449
38 Phase U to Ground Short
39 Phase V to Ground Short
40 Phase W to Ground Short
41 Phase UV Short
42 Phase UW Short
43 Phase VW Short
63 Software Overcurrent
64 Drive Overload
70 Power Unit Fail
80 AutoTune Fail
81 Communication Loss
100 Parameter Checksum Error
122 I/O Board Fail
Logic Status
Reading (03) and Writing (06) Drive Parameters
To access drive parameters, the Modbus register address equals the
parameter number. For example, a decimal “1” is used to address
Parameter d001 [Output Freq] and decimal “39” is used to address
Parameter P039 [Accel Time 1].
Additional Information
Refer to http://www.ab.com/drives/ for additional information.
Page 99

Appendix D
!
RJ45 DSI Splitter Cable
The PowerFlex 4 drive provides a RJ45 port to allow the connection of a
single peripheral device. The RJ45 DSI Splitter Cable can be used to
connect a second DSI peripheral device to the drive.
Connectivity Guidelines
ATTENTION: Risk of injury or equipment damage exists. The
peripherals may not perform as intended if these Connectivity
Guidelines are not followed. Precautions should be taken to follow
these Connectivity Guidelines.
Two peripherals maximum can be attached to a drive.
If a single peripheral is used, it must be connected to the Master port
(M) on the splitter and configured for “Auto” (default) or “Master.”
Parameter 9 [Device Type] on the DSI / MDI keypads and Parameter
1 [Adapter Cfg] on the Serial Converter are used to select the type
(Auto / Master / Slave).
If two peripherals will be powered up at the same time, one must be
configured as the “Master” and connected to the Master port (M) and
the other must be connected as the “Slave” and connected to the
Slave port (S).
Page 100
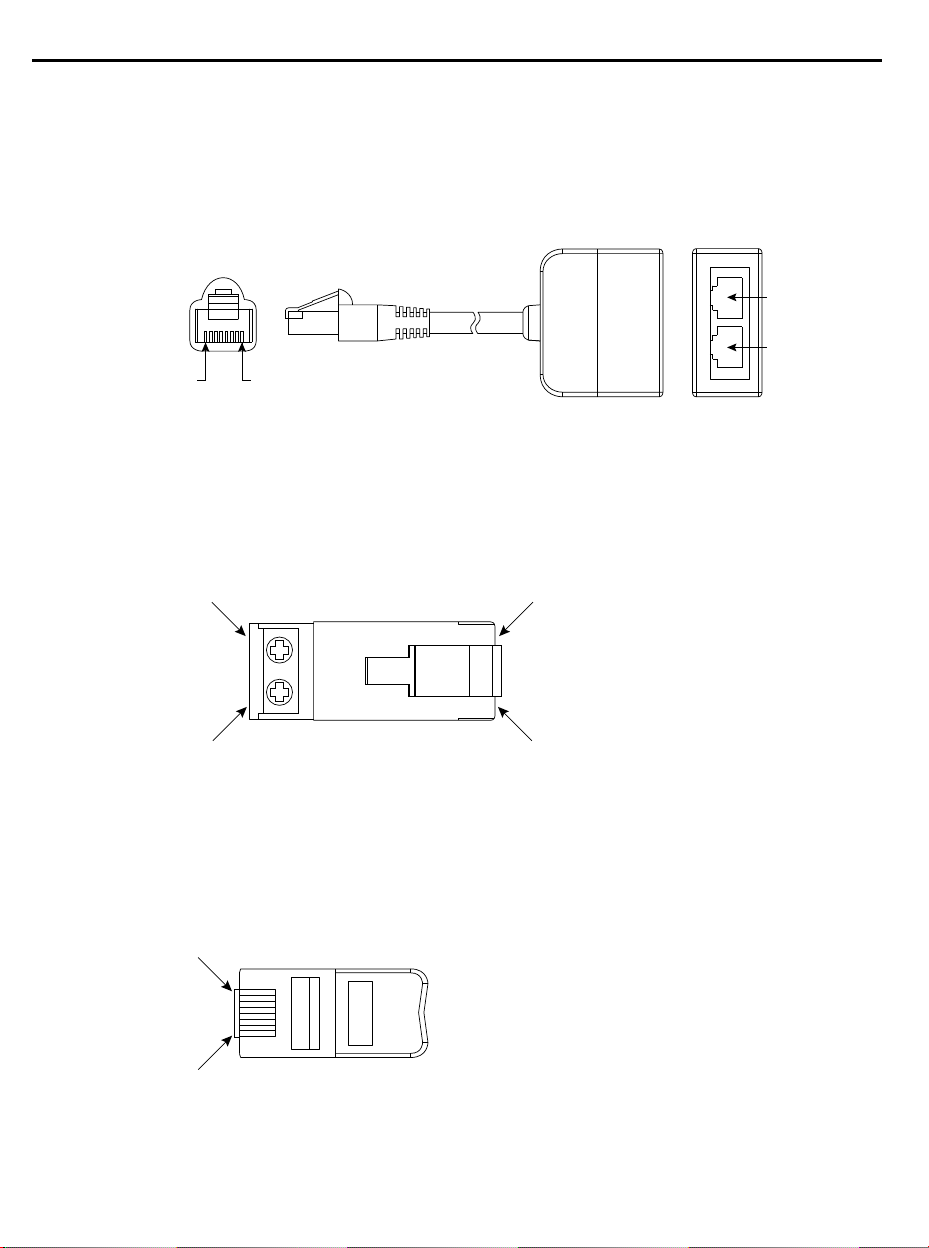
D-2 RJ45 DSI Splitter Cable
Slave Port
Master Port
PIN 8
PIN 1
M
S
TB2
(PIN 5)
TB1
(PIN 4)
PIN 8
PIN 1
PIN 8
PIN 1
DSI Cable Accessories
RJ45 Splitter Cable – Catalog Number: AK-U0-RJ45-SC1
RJ45 Two-Position Terminal Block Adapter –
Catalog Number: AK-U0-RJ45-TB2P
RJ45 Adapter with Integrated Termination Resistor –
Catalog Number: AK-U0-RJ45-TR1
 Loading...
Loading...