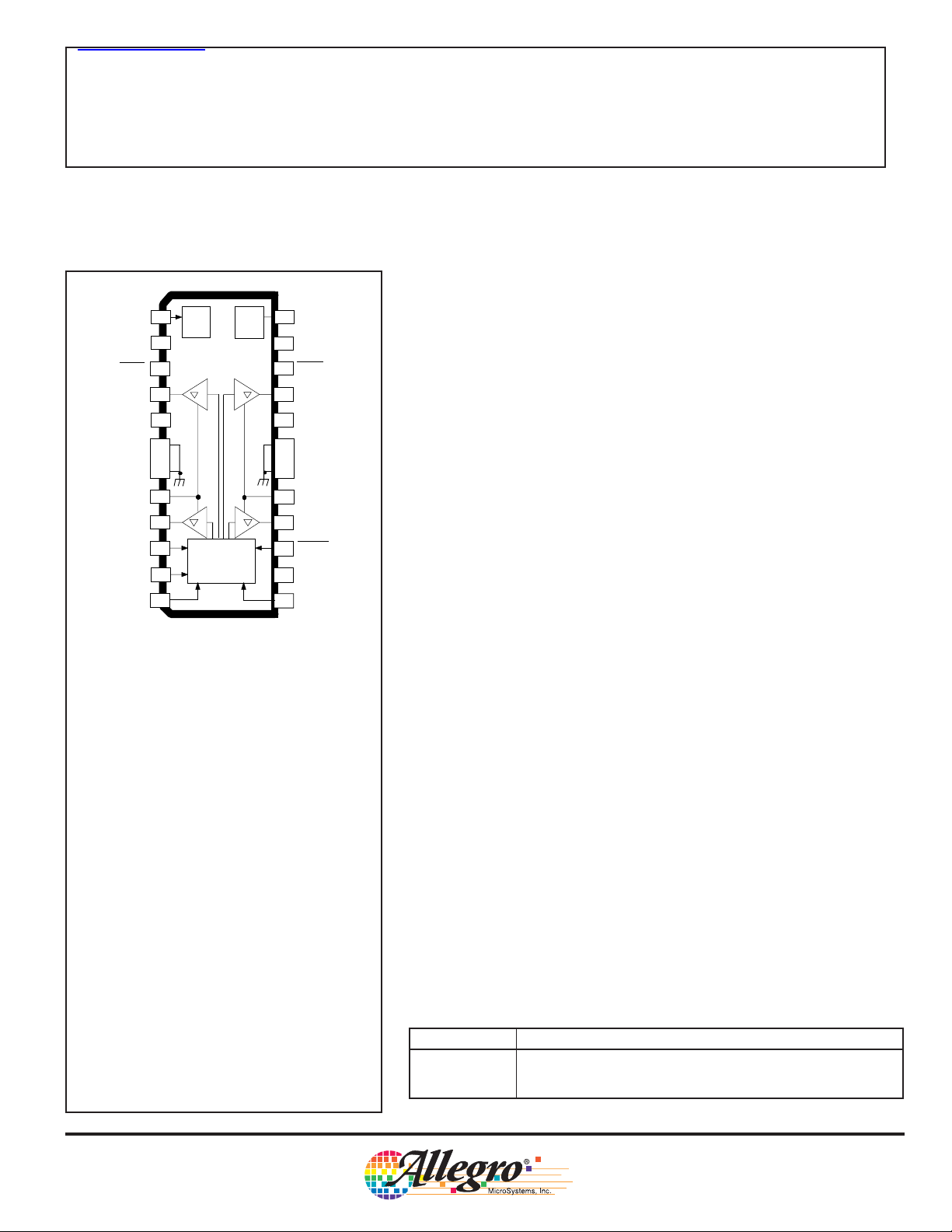
查询3967供应商
REF
RC
SLEEP
OUT
LOAD
SUPPLY
GND
GND
SENSE
OUT
STEP
DIR
MS
1
÷8
2
2
3
4
2B
5
BB2
V
2
6
7
2
8
9
2A
10
11
12
1
TIMER
TRANSLATOR
& CONTROL
LOGIC
PWM
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
at TA = +25°C
Load Supply Voltage, VBB............. 30 V
Output Current, I
Continuous ..................... ±750 mA
Peak................................. ±850 mA
Logic Supply Voltage, VCC........... 7.0 V
Logic Input Voltage Range, V
(tw >30 ns)............. -0.3 V to +7.0 V
(tw <30 ns)................ -1 V to +7.0 V
Sense Voltage, V
Reference Voltage, V
Package Power Dissipation,
PD................................. See page 8
Operating Temperature Range,
TA........................... -20°C to +85°C
Junction Temperature, TJ......... +150°C
Storage Temperature Range,
TS......................... -55°C to +150°C
* Output current rating may be limited by
duty cycle, ambient temperature, and heat
sinking. Under any set of conditions, do not
exceed the specified current rating or a
junction temperature of 150°C.
OUT
............... 0.68 V
SENSE
REF
PFD
24
23
RC
1
22
RESET
21
OUT
1B
LOAD
20
V
BB1
SUPPLY
19
GND
18
GND
SENSE
1
17
OUT
16
1A
ENABLE
15
LOGIC
V
CC
14
SUPPLY
MS
2
13
Dwg. PP-075-2
IN
................ V
1
CC
Data Sheet
26184.24C
3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
The A3967SLB is a complete microstepping motor driver with
built-in translator. It is designed to operate bipolar stepper motors in
full-, half-, quarter-, and eighth-step modes, with output drive capability of 30 V and ±750 mA. The A3967SLB includes a fixed off-time
current regulator that has the ability to operate in slow, fast, or mixed
current-decay modes. This current-decay control scheme results in
reduced audible motor noise, increased step accuracy, and reduced
power dissipation.
The translator is the key to the easy implementation of the
A3967SLB. By simply inputting one pulse on the STEP input the
motor will take one step (full, half, quarter, or eighth depending on two
logic inputs). There are no phase-sequence tables, high-frequency
control lines, or complex interfaces to program. The A3967SLB
interface is an ideal fit for applications where a complex µP is unavailable or over-burdened.
Internal circuit protection includes thermal shutdown with hysteresis, under-voltage lockout (UVLO) and crossover-current protection.
Special power-up sequencing is not required.
The A3967SLB is supplied in a 24-lead SOIC with copper batwing
tabs. The tabs are at ground potential and need no insulation. A lead-
*
free (100% matte tin leadframe) version is also available.
FEATURES
■ ±750 mA, 30 V Output Rating
■ Satlington™ Sink Drivers
■ Automatic Current-Decay Mode Detection/Selection
■ 3.0 V to 5.5 V Logic Supply Voltage Range
■ Mixed, Fast, and Slow Current-Decay Modes
■ Internal UVLO and Thermal Shutdown Circuitry
■ Crossover-Current Protection
Always order by complete part number:
Part Number Package
A3967SLB 24-lead batwing SOIC
A3967SLB-T 24-lead batwing SOIC; Lead-free
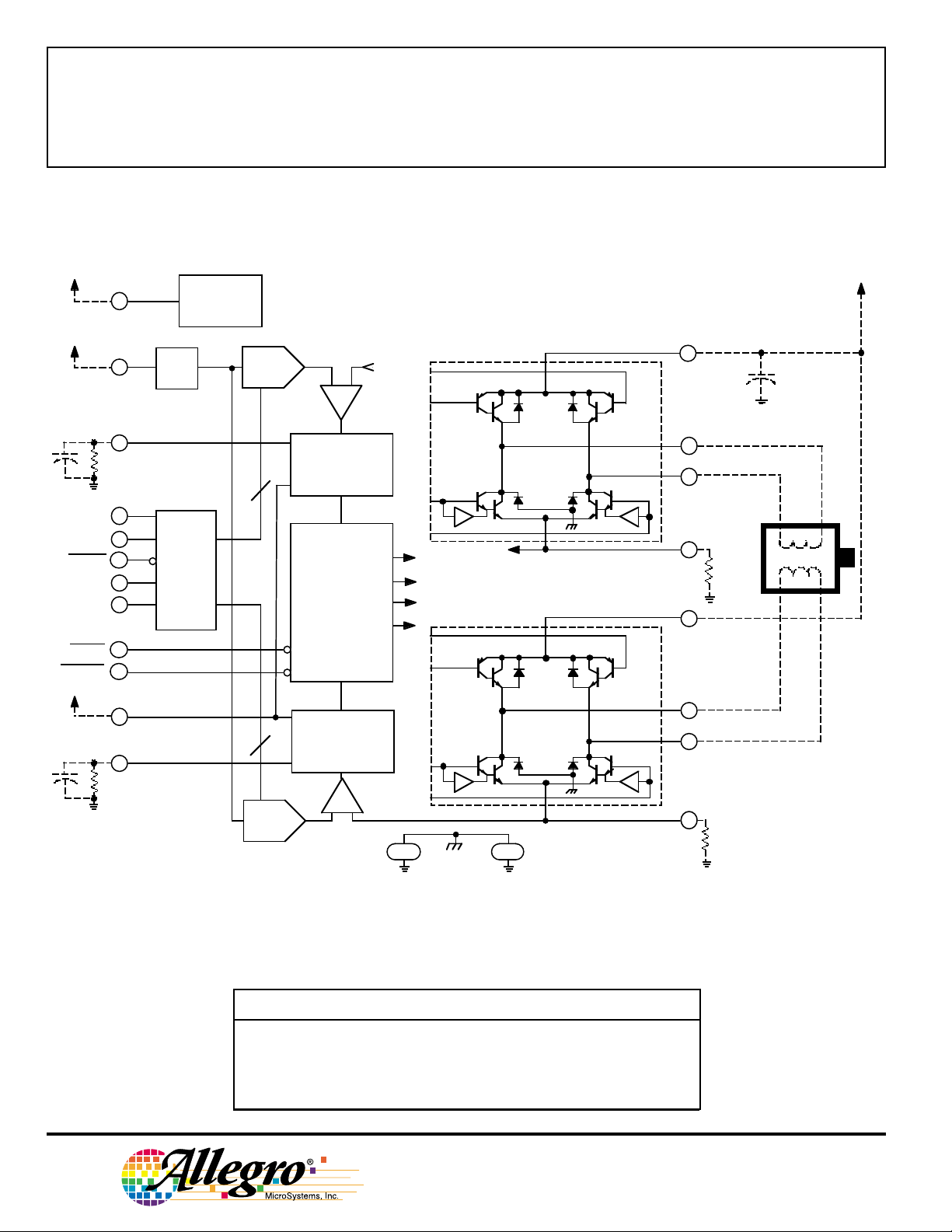
3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
LOGIC
SUPPLY
REF.
SUPPLY
STEP
RESET
SLEEP
ENABLE
V
PF
V
CC
REF
RC
DIR
MS
MS
1
1
2
14
1
23
10
11
22
12
13
3
15
24
PFD
2
RC
LOAD
UVLO
AND
FAULT
DETECT
V
BB1
20
16
21
17
5
9
4
8
OUT
OUT
SENSE
V
BB2
OUT
OUT
SENSE
1A
1B
1
2A
2B
2
3
3
DAC
DAC
+-
PWM LATCH
BLANKING
MIXED DECAY
PWM TIMER
PWM TIMER
PWM LATCH
BLANKING
MIXED DECAY
+-
SENSE
CONTROL LOGIC
÷8
TRANSLATOR
2
SUPPLY
76
1918
Dwg. FP-050-3A
Table 1. Microstep Resolution Truth Table
MS
1
MS
2
Resolution
L L Full step (2 phase)
H L Half step
L H Quarter step
H H Eighth step
2
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000
Copyright © 2002, 2003 Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
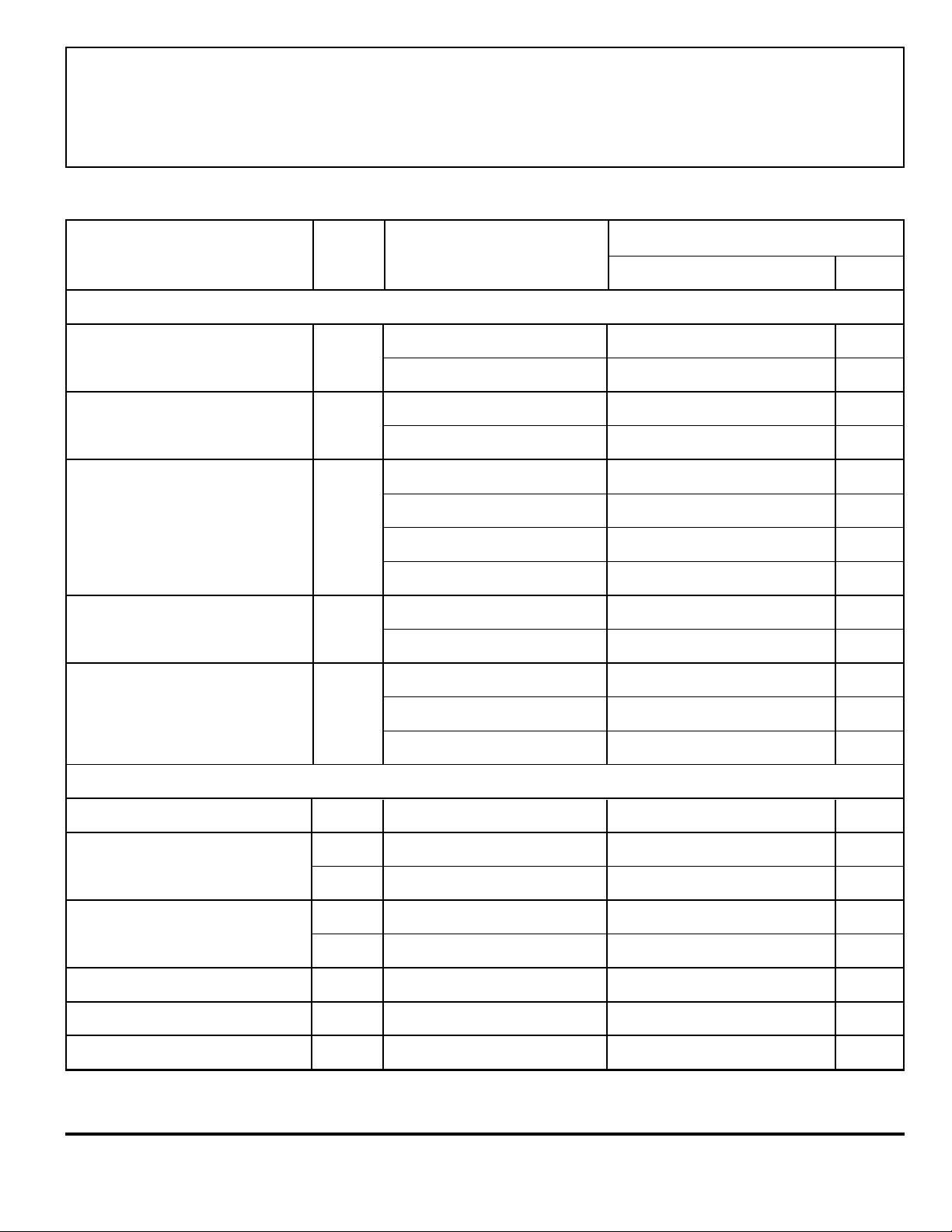
3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLAT OR
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS at T
= +25°C, V
A
= 30 V, VCC = 3.0 V to 5.5V (unless otherwise
BB
noted)
Limits
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Output Drivers
Load Supply Voltage Range V
BB
Operating 4.75 – 30 V
During sleep mode 0 – 30 V
Output Leakage Current I
Output Saturation Voltage V
CE(sat)
Clamp Diode Forward Voltage V
CEX
V
= V
OUT
V
OUT
Source driver, I
Source driver, I
Sink driver, I
Sink driver, I
IF = 750 mA – 1.4 1.6 V
F
BB
= 0 V – <-1.0 -20 µA
= -750 mA
OUT
= -400 mA
OUT
= 750 mA – 0.65 1.3 V
OUT
= 400 mA – 0.21 0.5 V
OUT
– <1.0 20 µA
– 1.9 2.1 V
– 1.7 2.0 V
Motor Supply Current I
Control Logic
Logic Supply Voltage Range V
Logic Input Voltage V
V
Logic Input Current I
I
Maximum STEP Frequency f
Blank Time t
BLANK
Fixed Off Time t
BB
CC
IN(1)
IN(0)
IN(1)
IN(0)
STEP
off
IF = 400 mA – 1.1 1.4 V
Outputs enabled – – 5.0 mA
RESET high
– – 200 µA
Sleep mode – – 20 µA
Operating 3.0 5.0 5.5 V
VIN = 0.7V
VIN = 0.3V
CC
CC
0.7V
CC
– – 0.3V
-20 <1.0 20 µA
-20 <1.0 20 µA
––V
CC
V
500* – – kHz
R
= 56 kΩ, C
t
R
= 56 kΩ, Ct = 680 pF 30 38 46 µs
t
= 680 pF 700 950 1200 ns
t
continued next page …
www.allegromicro.com
3
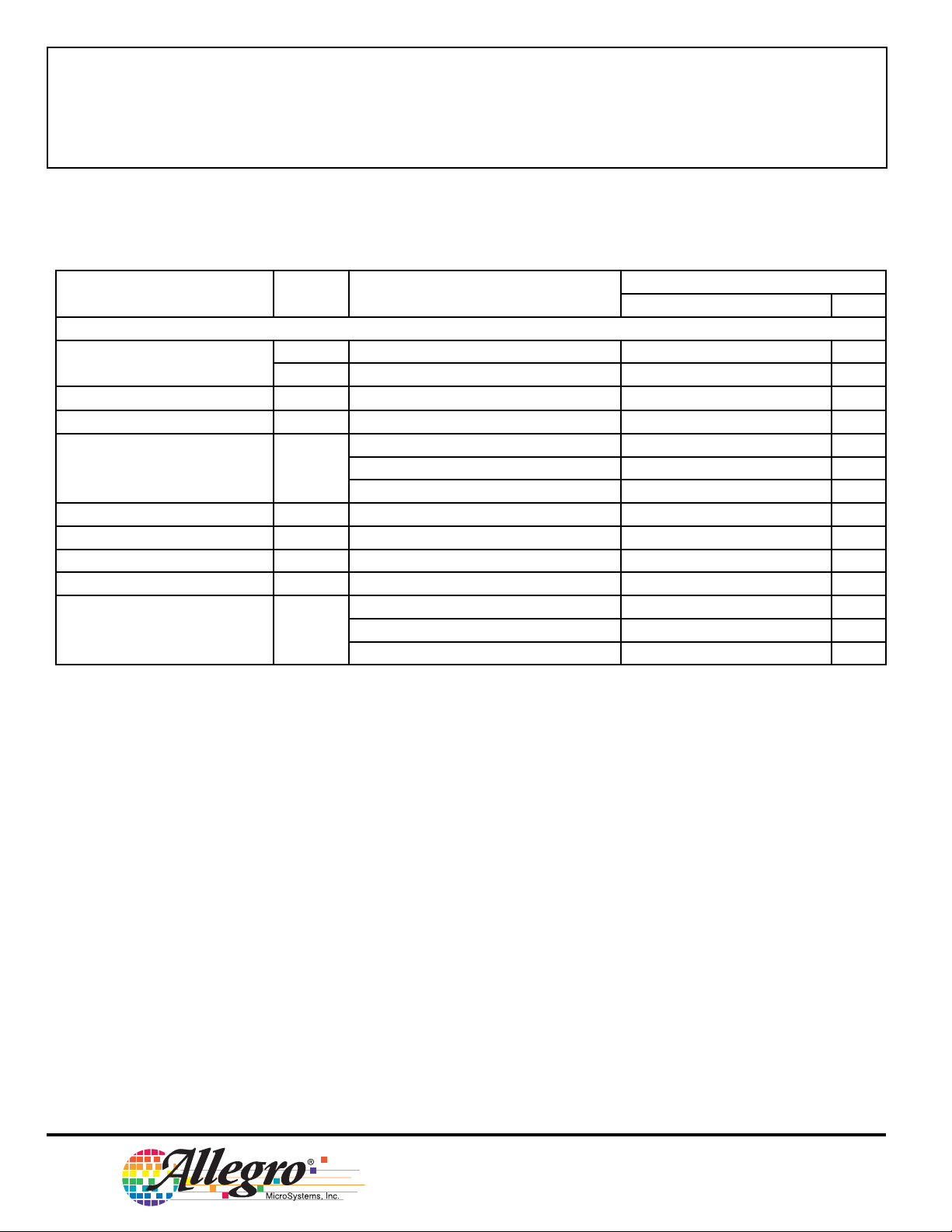
3967
MICROSTEPPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS at TA = +25°C, VBB = 30 V, VCC = 3.0 V to 5.5V (unless otherwise
noted)
Limits
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions
Control Logic (cont’d)
Mixed Decay Trip Point PFDH – 0.6V
PFDL – 0.21V
Ref. Input Voltage Range V
Reference Input Impedance Z
Gain (G
(note 3)
Thermal Shutdown Temp. T
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis ∆T
UVLO Enable Threshold V
UVLO Hysteresis ∆V
Logic Supply Current I
) Error
m
REF
REF
E
UVLO
UVLO
CC
Operating 1.0 – V
V
= 2 V, Phase Current = 38.37% † – – ±10 %
G
J
J
REF
V
= 2 V, Phase Current = 70.71% † – – ±5.0 %
REF
V
= 2 V, Phase Current = 100.00% † – – ±5.0 %
REF
Increasing V
Outputs enabled – 50 65 mA
Outputs off – – 9.0 mA
Sleep mode – – 20 µA
CC
* Operation at a step frequency greater than the specifi ed minimum value is possible but not warranteed.
† 8 microstep/step operation.
NOTES: 1. Typical Data is for design information only.
2. Negative current is defi ned as coming out of (sourcing) the specifi ed device terminal.
3. EG = ([V
REF
/8] – V
SENSE
)/(V
REF
/8)
Min. Typ. Max. Units
CC
CC
120 160 200 kΩ
– 165 – °C
–15–°C
2.45 2.7 2.95 V
0.05 0.10 – V
–V
–V
CC
V
4
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000

Functional Description
3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLAT OR
Device Operation. The A3967 is a complete
microstepping motor driver with built in translator for
easy operation with minimal control lines. It is designed
to operate bipolar stepper motors in full-, half-, quarterand eighth-step modes. The current in each of the two
output H-bridges is regulated with fixed off time pulsewidth modulated (PWM) control circuitry. The H-bridge
current at each step is set by the value of an external
current sense resistor (R
), a reference voltage (V
S
REF
), and
the DAC’s output voltage controlled by the output of the
translator.
At power up, or reset, the translator sets the DACs and
phase current polarity to initial home state (see figures for
home-state conditions), and sets the current regulator for
both phases to mixed-decay mode. When a step command
signal occurs on the STEP input the translator automatically sequences the DACs to the next level (see table 2 for
the current level sequence and current polarity). The
microstep resolution is set by inputs MS
and MS2 as
1
shown in table 1. If the new DAC output level is lower
than the previous level the decay mode for that H-bridge
will be set by the PFD input (fast, slow or mixed decay).
If the new DAC level is higher or equal to the previous
level then the decay mode for that H-bridge will be slow
decay. This automatic current-decay selection will
improve microstepping performance by reducing the
distortion of the current waveform due to the motor
BEMF.
Reset Input (RESET). The RESET input (active low)
sets the translator to a predefined home state (see figures
for home state conditions) and turns off all of the outputs.
STEP inputs are ignored until the RESET input goes high.
Step Input (STEP). A low-to-high transition on the
STEP input sequences the translator and advances the
motor one increment. The translator controls the input to
the DACs and the direction of current flow in each winding. The size of the increment is determined by the state
of inputs MS
and MS2 (see table 1).
1
Microstep Select (MS1 and MS
MS1 and MS
select the microstepping format per
2
). Input terminals
2
table 1. Changes to these inputs do not take effect until
the STEP command (see figure).
Direction Input (DIR). The state of the DIRECTION
input will determine the direction of rotation of the motor.
Internal PWM Current Control. Each H-bridge is
controlled by a fixed off time PWM current-control circuit
that limits the load current to a desired value (I
TRIP
).
Initially, a diagonal pair of source and sink outputs are
enabled and current flows through the motor winding and
. When the voltage across the current-sense resistor
R
S
equals the DAC output voltage, the current-sense comparator resets the PWM latch, which turns off the source
driver (slow-decay mode) or the sink and source drivers
(fast- or mixed-decay modes).
The maximum value of current limiting is set by the
selection of R
and the voltage at the V
S
input with a
REF
transconductance function approximated by:
max = V
I
TRIP
The DAC output reduces the V
REF
/8R
REF
S
output to the
current-sense comparator in precise steps (see table 2 for
% I
max at each step).
TRIP
= (% I
I
TRIP
max/100) x I
TRIP
TRIP
max
Fixed Off-Time. The internal PWM current-control
circuitry uses a one shot to control the time the driver(s)
remain(s) off. The one shot off-time, t
the selection of an external resistor (R
) connected from the RC timing terminal to ground.
(C
T
The off time, over a range of values of C
1500 pF and R
= 12 kΩ to 100 kΩ is approximated by:
T
= RTC
t
off
, is determined by
off
) and capacitor
T
= 470 pF to
T
T
www.allegromicro.com
5

3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
Functional Description (cont’d)
RC Blanking. In addition to the fixed off time of the
PWM control circuit, the C
component sets the compara-
T
tor blanking time. This function blanks the output of the
current-sense comparator when the outputs are switched
by the internal current-control circuitry. The comparator
output is blanked to prevent false over-current detection
due to reverse recovery currents of the clamp diodes, and/
or switching transients related to the capacitance of the
load. The blank time t
t
BLANK
can be approximated by:
BLANK
= 1400C
T
Enable Input (ENABLE). This active-low input
enables all of the outputs. When logic high the outputs are
disabled. Inputs to the translator (STEP, DIRECTION,
, MS2) are all active independent of the ENABLE
MS
1
input state.
Shutdown. In the event of a fault (excessive junction
temperature) the outputs of the device are disabled until
the fault condition is removed. At power up, and in the
event of low V
, the under-voltage lockout (UVLO)
CC
circuit disables the drivers and resets the translator to the
home state.
Percent Fast Decay Input (PFD). When a STEP
input signal commands a lower output current from the
previous step, it switches the output current decay to either
slow-, fast-, or mixed-decay depending on the voltage
level at the PFD input. If the voltage at the PFD input is
greater than 0.6V
the voltage on the PFD input is less than 0.21V
then slow-decay mode is selected. If
CC
then
CC
fast-decay mode is selected. Mixed decay is between
these two levels.
Mixed Decay Operation. If the voltage on the PFD
input is between 0.6V
and 0.21VCC, the bridge will
CC
operate in mixed-decay mode depending on the step
sequence (see figures). As the trip point is reached, the
device will go into fast-decay mode until the voltage on
the RC terminal decays to the voltage applied to the PFD
terminal. The time that the device operates in fast decay is
approximated by:
= RTCTIn (0.6VCC/V
t
FD
After this fast decay portion, t
, the device will
FD
PFD
)
switch to slow-decay mode for the remainder of the fixed
off-time period.
Sleep Mode (SLEEP). An active-low control input
used to minimize power consumption when not in use.
This disables much of the internal circuitry including the
outputs. A logic high allows normal operation and startup
of the device in the home position.
Typical output saturation
voltages showing Satlington™
sink-driver operation.
6
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000
2.5
TA = +25°C
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
OUTPUT SATURATION VOLTAGE IN VOLTS
0
200
SOURCE DRIVER
300
OUTPUT CURRENT IN MILLIAMPERES
500 800400
600
SINK DRIVER
700
Dwg. GP-064-4

(T
= +25°C, V
A
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLAT OR
Timing Requirements
= 5 V, Logic Levels are VCC and Ground)
CC
3967
STEP
MS1/MS2/
DIR/RESET
SLEEP
50%
C D
A
E
B
A. Minimum Command Active Time
Before Step Pulse (Data Set-Up Time) ..... 200 ns
Dwg. WP-042
www.allegromicro.com
B. Minimum Command Active Time
After Step Pulse (Data Hold Time)............ 200 ns
C. Minimum STEP Pulse Width ...................... 1.0 µs
D. Minimum STEP Low Time ......................... 1.0 µs
E. Maximum Wake-Up Time ......................... 1.0 ms
7

3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
Applications Information
Layout. The printed wiring board should use a heavy
ground plane.
For optimum electrical and thermal performance, the
driver should be soldered directly onto the board.
The load supply terminal, V
, should be decoupled
BB
with an electrolytic capacitor (>47 µF is recommended)
placed as close to the device as possible.
To avoid problems due to capacitive coupling of the
high dv/dt switching transients, route the bridge-output
traces away from the sensitive logic-input traces. Always
drive the logic inputs with a low source impedance to
increase noise immunity.
Grounding. A star ground system located close to the
driver is recommended.
The 24-lead SOIC has the analog ground and the
power ground internally bonded to the power tabs of the
package (leads 6, 7, 18, and 19).
Current Sensing. To minimize inaccuracies caused by
ground-trace IR drops in sensing the output current level,
the current-sense resistor (R
) should have an independent
S
ground return to the star ground of the device. This path
should be as short as possible. For low-value sense
resistors the IR drops in the printed wiring board sense
resistor’s traces can be significant and should be taken
into account. The use of sockets should be avoided as
they can introduce variation in R
due to their contact
S
resistance.
Allegro MicroSystems recommends a value of R
S
given by
= 0.5/I
R
S
TRIP
max
Thermal protection. Circuitry turns off all drivers
when the junction temperature reaches 165°C, typically.
It is intended only to protect the device from failures due
to excessive junction temperatures and should not imply
that output short circuits are permitted. Thermal shutdown has a hysteresis of approximately 15°C.
*R
= 35°C/W on JEDEC standard
θJA
“High-K” four-layer board per JESD 51-7.
†R
= 50°C/W on typical two-sided PCB with
θJA
1.3 square inches copper ground on each side.
See also, Application Note 29501.5,
Improving Batwing Power Dissipation.
8
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000

MICROSTEPPPING DRIVER
Table 2. Step Sequencing
Home State = 45º Step Angle, DIR = H
3967
WITH TRANSLATOR
Phase 1 Current
Full Step Half Step ¼ Step ⅛ Step
1 1 1 100.00 0.00 0.0
2 98.08 19.51 11.3
2 3 92.39 38.27 22.5
4 83.15 55.56 33.8
1 2 3 5 70.71 70.71 45.0
6 55.56 83.15 56.3
4 7 38.27 92.39 67.5
8 19.51 98.08 78.8
3 5 9 0.00 100.00 90.0
10 –19.51 98.08 101.3
6 11 –38.27 92.39 112.5
12 –55.56 83.15 123.8
2 4 7 13 –70.71 70.71 135.0
14 –83.15 55.56 146.3
8 15 –92.39 38.27 157.5
16 –98.08 19.51 168.8
5 9 17 –100.00 0.00 180.0
18 –98.08 –19.51 191.3
10 19 –92.39 –38.27 202.5
20 –83.15 –55.56 213.8
3 6 11 21 –70.71 –70.71 225.0
22 –55.56 –83.15 236.3
12 23 –38.27 –92.39 247.5
24 –19.51 –98.08 258.8
7 13 25 0.00 –100.00 270.0
26 19.51 –98.08 281.3
14 27 38.27 –92.39 292.5
28 55.56 –83.15 303.8
4 8 15 29 70.71 –70.71 315.0
30 83.15 –55.56 326.3
16 31 92.39 –38.27 337.5
32 98.08 –19.51 348.8
(%I
trip
(%)
max)
Phase 2 Current
(%I
max)
trip
(%)
Step Angle
(º)
www.allegromicro.com
9

3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
STEP
INPUT
70.7%
PHASE 1
CURRENT
Full Step Operation
MS1 = MS2 = L, DIR = H
SLOW
DECAY
–70.7%
70.7%
PHASE 2
CURRENT
–70.7%
SLOW
DECAY
Dwg. WK-004-19
10
The vector addition of the output currents at any step is
100%.
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000

STEP
INPUT
Half Step Operation
= H, MS2 = L, DIR = H
MS
1
3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLAT OR
100%
70.7%
PHASE 1
CURRENT
–70.7%
–100%
100%
70.7%
PHASE 2
CURRENT
SLOW
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
–100%
www.allegromicro.com
70.7%
Dwg. WK-004-18
The mixed-decay mode is controlled by the percent fast
decay voltage (V
). If the voltage at the PFD input is
PFD
greater than 0.6VCC then slow-decay mode is selected. If
the voltage on the PFD input is less than 0.21VCC then
fast-decay mode is selected. Mixed decay is between
these two levels.
11

3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
STEP
INPUT
Quarter Step Operation
MS
= L, MS2 = H, DIR = H
1
100%
70.7%
38.3%
PHASE 1
CURRENT
–38.3%
–70.7%
–100%
100%
70.7%
38.3%
PHASE 2
CURRENT
SLOW
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
12
–38.3%
–70.7%
–100%
Dwg. WK-004-17
The mixed-decay mode is controlled by the percent fast
decay voltage (V
). If the voltage at the PFD input is
PFD
greater than 0.6VCC then slow-decay mode is selected. If
the voltage on the PFD input is less than 0.21VCC then
fast-decay mode is selected. Mixed decay is between
these two levels.
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000

STEP
INPUT
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
8 Microstep/Step Operation
MS
= MS2 = H, DIR = H
1
3967
WITH TRANSLAT OR
100%
70.7%
38.3%
PHASE 1
CURRENT
–38.3%
–70.7%
–100%
100%
70.7%
38.3%
PHASE 2
CURRENT
SLOW
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
MIXED
DECAY
SLOW
DECAY
–38.3%
–70.7%
–100%
www.allegromicro.com
Dwg. WK-004-16
The mixed-decay mode is controlled by the percent fast
decay voltage (V
). If the voltage at the PFD input is
PFD
greater than 0.6VCC then slow-decay mode is selected. If
the voltage on the PFD input is less than 0.21VCC then
fast-decay mode is selected. Mixed decay is between
these two levels.
13

3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
Terminal List
Terminal Terminal
Name Terminal Description Number
REF Gm reference input 1
RC
2 Analog input for fixed offtime – bridge 2 2
SLEEP Logic input 3
OUT
2B H bridge 2 output B 4
LOAD SUPPLY
GND Analog and power ground 6, 7
SENSE
OUT
2 Sense resistor for bridge 2 8
2A H bridge 2 output A 9
STEP Logic input 10
DIR Logic Input 11
MS
1 Logic input 12
MS
2 Logic input 13
LOGIC SUPPLY V
ENABLE Logic input 15
OUT
1A H bridge 1 output A 16
SENSE
1 Sense resistor for bridge 1 17
GND Analog and power ground 18, 19
LOAD SUPPLY
OUT
1B H bridge 1 output B 21
RESET Logic input 22
RC
1 Analog Input for fixed offtime – bridge 1 23
PFD Mixed decay setting 24
2 VBB2, the load supply for bridge 2 5
CC, the logic supply voltage 14
1 VBB1, the load supply for bridge 1 20
14
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000

3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLAT OR
0.2992
0.2914
0.020
0.013
0.0926
0.1043
24 13
1
2
3
0.6141
0.5985
0.0040
MIN.
0.050
BSC
NOTE 1
NOTE 3
0.419
0.394
0° TO 8°
0.0125
0.0091
0.050
0.016
Dwg. MA-008-25A in
0.32
0.23
Dimensions in Inches
(for reference only)
7.60
7.40
0.51
0.33
2.65
2.35
1242
0.10
MIN.
3
15.60
15.20
1.27
BSC
NOTE 1
NOTE 3
10.65
10.00
NOTES: 1. Exact body and lead configuration at vendor’s option within limits shown.
2. Lead spacing tolerance is non-cumulative.
3. Webbed lead frame. Leads 6, 7, 18, and 19 are internally one piece.
4. Supplied in standard sticks/tubes of 31 devices or add “TR” to part number for tape and reel.
www.allegromicro.com
0° TO 8°
Dwg. MA-008-25A mm
1.27
0.40
Dimensions in Millimeters
(controlling dimensions)
15

3967
MICROSTEPPING DRIVER
WITH TRANSLATOR
16
The products described here are manufactured under one or more
U.S. patents or U.S. patents pending.
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc. reserves the right to make, from time to
time, such departures from the detail specifications as may be
required to permit improvements in the performance, reliability, or
manufacturability of its products. Before placing an order, the user is
cautioned to verify that the information being relied upon is current.
Allegro products are not authorized for use as critical components
in life-support devices or systems without express written approval.
The information included herein is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, Allegro MicroSystems, Inc. assumes no responsibility for its use; nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of
third parties which may result from its use.
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000
 Loading...
Loading...