ALCON Telecommunications 24005G03 User Manual

802.11g Wireless High Power
Ceiling Access Point
Revision 1.3
User Guide
1
U
Revision History
Version Date Notes
1.0 June 9, 2008 Initial Version
1.1 July 22, 2008 Update screen captures of status,
advanced wireless, and firmware upgrade
based on new firmware version.
1.2 September 22, 2008 Output power spec adjustment
1.3 April 24,2009 Add Spanning Tree Settings, AP detection
site survey in AP mode, Diagnostics
2
Introduction
This is a smoke detector looking Wireless ceiling Access Point / Repeater /
WDS that operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum
supporting the 802.11b (2.4GHz, 11Mbps) and faster 802.11g (2.4GHz,
54Mbps) wireless standards. It's the best way to add wireless capability to
your existing wired network, or to add bandwidth to your wireless
installation.
This device features high transmitted output power and high receivable
sensitivity along with antenna diversity. High output power and high
sensitivity can extend range and coverage to reduce the roaming between
Access Points to get more stable wireless connection. It also reduces the
expense of equipment in the same environment.
To protect your wireless connectivity, it can encrypt all wireless
transmissions through 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption and also
supports WPA/WPA2. The MAC address filter lets you select exactly which
stations should have access to your network. In addition, the User Isolation
function can protect the private network between client users.
The attractive design, high performance, and array of features make this a
suitable wireless solution for your residence or office.
This chapter describes the features & benefits, package contents,
applications, and network configuration
.
Features & Benefits
Features Benefits
High Speed Data Rate Up to 54Mbps
High Output Power up to 28 dBm
IEEE 802.11b/g Compliant
Embedded Antenna
WDS (Wireless Distributed System)
Universal Repeater
Support Multi-SSID function (4 SSIDs) in
AP mode
Diversity support
WPA2/WPA/ IEEE 802.1x support
Capable of handling heavy data payloads
such as MPEG video streaming
Extended excellent Range and Coverage
(fewer APs)
Fully Interoperable with IEEE
802.11b/IEEE802.11g compliant devices
Users won’t see antenna in your building
environment
Make wireless AP and Bridge mode
simultaneously as a wireless repeater up to
8 links
The easiest way to expand your wireless
network's coverage
Allow clients to access different networks
through a single access point and assign
different policies and functions for each
SSID by manager
Enhance the traffic signal
Powerful data security
3
MAC address filtering in AP mode(up to
50)
Ensures secure network connection
User isolation support (AP mode)
Power-over-Ethernet (IEEE802.3af)
Keep personal setting
SNMP Remote Configuration
Management
QoS (WMM) support Enhance user performance and density
Protect the private network between client
users.
Flexible Access Point locations and cost
savings
Keep the latest setting when firmware
upgrade
Help administrators to remotely configure or
manage the Access Point easily.
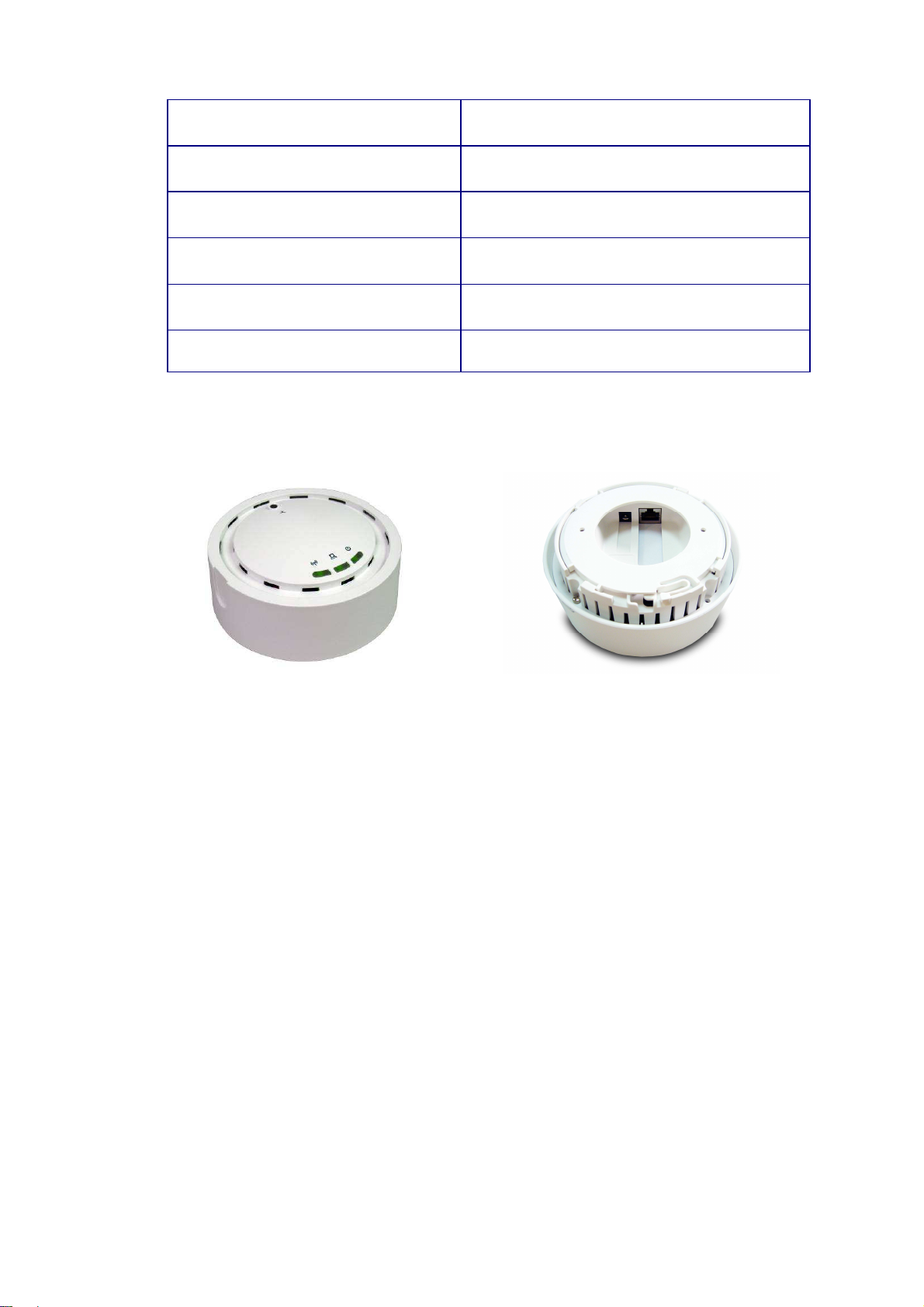
Access Point Description
Front Panel Real Panel
System Requirements
The following are the minimum system requirements in order configure the
device.
PC/AT compatible computer with an Ethernet interface.
Operating system that supports HTTP web-browser
Applications
The wireless LAN products are easy to install and highly efficient. The
following list describes some of the many applications made possible
through the power and flexibility of wireless LANs:
a) Difficult-to-wire environments
There are many situations where wires cannot be laid easily.
Historic buildings, older buildings, open areas and across busy
streets make the installation of LANs either impossible or very
expensive.
b) Temporary workgroups
Consider situations in parks, athletic arenas, exhibition centers,
4

disaster-recovery, temporary offices and construction sites where
one wants a temporary WLAN established and removed.
c) The ability to access real-time information
Doctors/nurses, point-of-sale employees, and warehouse
workers can access real-time information while dealing with
patients, serving customers and processing information.
d) Frequently changed environments
Show rooms, meeting rooms, retail stores, and manufacturing
sites where frequently rearrange the workplace.
e) Small Office and Home Office (SOHO) networks
SOHO users need a cost-effective, easy and quick installation of
a small network.
f) Wireless extensions to Ethernet networks
Network managers in dynamic environments can minimize the
overhead caused by moves, extensions to networks, and other
changes with wireless LANs.
g) Wired LAN backup
Network managers implement wireless LANs to provide backup
for mission-critical applications running on wired networks.
h) Training/Educational facilities
Training sites at corporations and students at universities use
wireless connectivity to ease access to information, information
exchanges, and learning.
5

FCC Notice
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
—Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
—Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
—Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
—Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/ TV technician for help.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
The antenna(s) used for this transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction
with any other antenna or transmitter.
The manufacture is not responsible for any radio or TV interference caused by unauthorized
modifications to this equipment. Such modifications could void the user’s authority to operate
the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must
accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
6

The Wireless Technology
Standard
The Wireless Access Point utilizes the 802.11b and the 802.11g standards.
The IEEE 802.11g standard is an extension of the 802.11b standard. It
increases the data rate up to 54 Mbps (108Mbps in Super G mode) within the
2.4GHz band, utilizing OFDM technology. This means that in most
environments, within the specified range of this device, you will be able to
transfer large files quickly or even watch a movie in MPEG format you’re your
network without noticeable delays. This technology works by transmitting
high-speed digital data over a radio wave utilizing OFDM (Orthogonal
Frequency Division Multiplexing) technology. OFDM works by splitting the
radio signal into multiple smaller sub-signals that are then transmitted
simultaneously at different frequencies to the receiver. OFDM reduces the
amount of cross talk (interference) in signal transmissions. The AP will
automatically sense the best possible connection speed to ensure the greatest
speed and range possible. 802.11g offers the most advanced network security
features available today, including: WPA, WPA2, TKIP, AES and Pre-Shared
Key mode.
U
Planning Your Wireless Network
Network Topology
A wireless network is a group of computers, each equipped with one wireless
adapter. Computers in a wireless network must be configured to share the
same radio channel. Several PCs equipped with wireless cards or adapters
can communicate with one another to form an ad-hoc network. The wireless
adapters also provide users access to a wired network when using an access
point or wireless router. An integrated wireless and wired network is called an
infrastructure network. Each wireless PC in an infrastructure network can talk
to any computer in a wired network infrastructure via the access point or
wireless router. An infrastructure configuration extends the accessibility of a
wireless PC to a wired network, and may double the effective wireless
transmission range for two wireless adapter PCs. Since an access point is
able to forward data within a network, the effective transmission range in an
infrastructure network may be doubled.
7

Roaming
Infrastructure mode also supports roaming capabilities for mobile users.
Roaming means that you can move your wireless PC within your network and
the access points will pick up the wireless PC's signal, providing that they both
share the same channel and SSID. Before enabling you consider roaming,
choose a feasible radio channel and optimum access point position. Proper
access point positioning combined with a clear radio signal will greatly
enhance performance.
Network Layout
The AP Access Point has been designed for use with 802.11g and 802.11b
products. With 802.11g products communicating with the 802.11b standard,
products using these standards can communicate with each other. The
Access point is compatible with 802.11g and 802.11b adapters, such at the
PC Cards for your laptop computers, PCI Card for your desktop PC, and USB
Adapters for when you want to enjoy USB connectivity. These wireless
products can also communicate with an 802.11g or 802.11b wireless Print
Server. When you wish to connect your wired network with your wireless
network, the Access Point’s network port can be used to connect to any of
switches or routers.
Installation Considerations
The AP lets you access your network, using a wireless connection, from
virtually anywhere within its operating range. Keep in mind, however, that the
number, thickness and location of walls, ceilings, or other objects that the
wireless signals must pass through, may limit the range. Typical ranges vary
depending on the types of materials and background RF (radio frequency)
noise in your home or business. The key to maximizing wireless range is to
follow these basic guidelines:
Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical
devices or appliances that generate RF noise.
Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the AP and other network
devices to a minimum - each wall or ceiling can reduce your AP’s range
from 3-90 feet (1-30 meters.) Position your devices so that the number of
walls or ceilings is minimized.
Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet
thick(.5 meters), at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1
meter) thick. At a 2-degree angle it looks over 42 feet (14 meters) thick!
8

Position devices so that the signal will travel straight through a wall or
ceiling (instead of at an angle) for better reception.
Building materials can impede the wireless signal - a solid metal door or
aluminum studs may have a negative effect on range. Try to position
wireless devices and computers with wireless adapters so that the signal
passes through drywall or open doorways and not other materials.
Applications
The wireless LAN products are easy to install and highly efficient. The
following list describes some of the many applications made possible
through the power and flexibility of wireless LANs:
Difficult-to-wire environments
There are many situations where wires cannot be laid easily. Historic
buildings, older buildings, open areas and across busy streets make the
installation of LANs either impossible or very expensive.
Temporary workgroups
Consider situations in parks, athletic arenas, exhibition centers,
disaster-recovery, temporary offices and construction sites where one
wants a temporary WLAN established and removed.
The ability to access real-time information
Doctors/nurses, point-of-sale employees, and warehouse workers can
access real-time information while dealing with patients, serving
customers and processing information.
Frequently changed environments
Show rooms, meeting rooms, retail stores, and manufacturing sites where
frequently rearrange the workplace.
Small Office and Home Office (SOHO) networks
SOHO users need a cost-effective, easy and quick installation of a small
network.
Wireless extensions to Ethernet networks
Network managers in dynamic environments can minimize the overhead
caused by moves, extensions to networks, and other changes with
wireless LANs.
Wired LAN backup
Network managers implement wireless LANs to provide backup for
mission-critical applications running on wired networks.
9
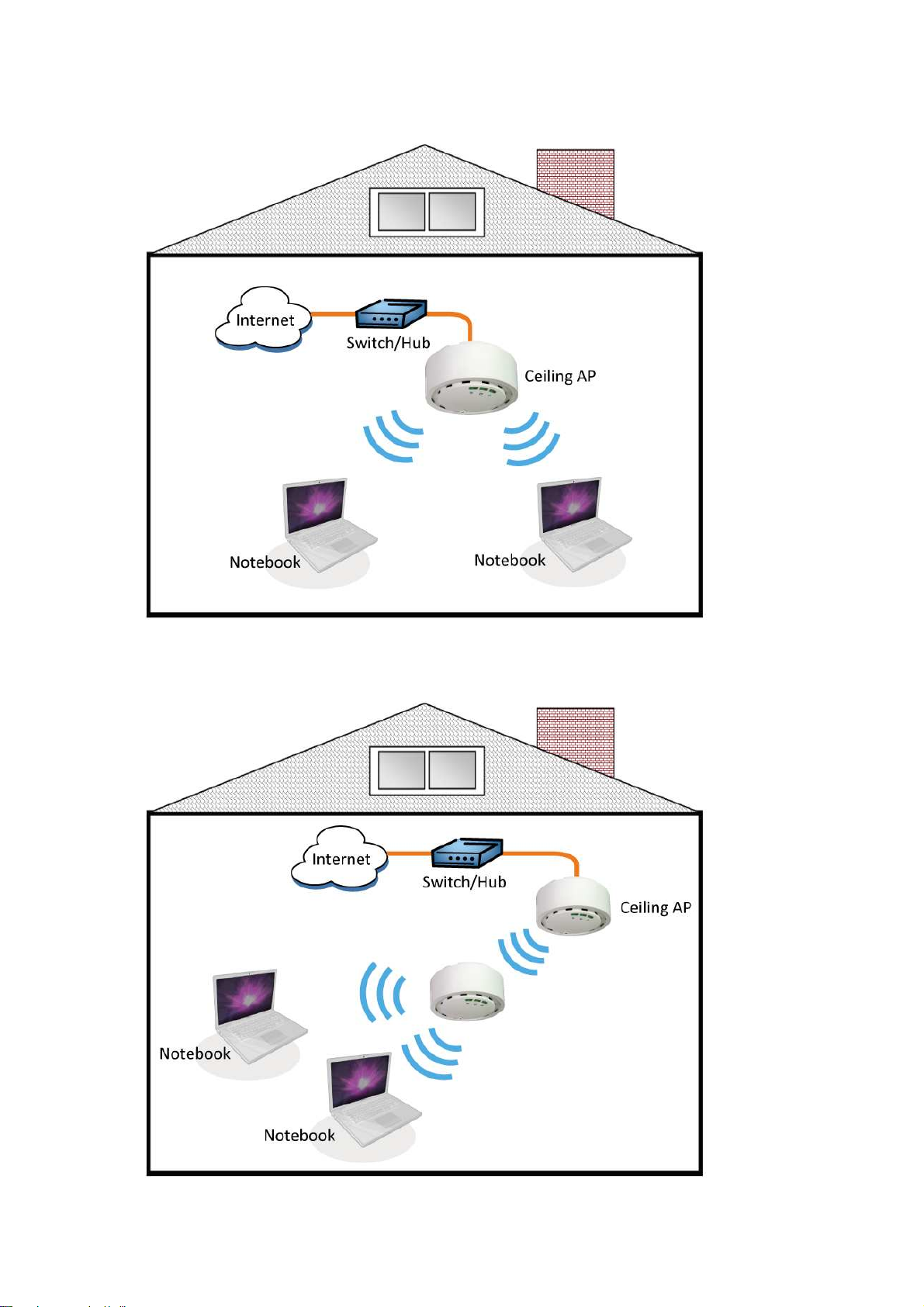
Network Topology – AP Mode
Network Topology – Repeater Mode
Repeat
er
10

Installation Diagram for Power & Cable
1. For 12V / 2A Adaptor
2. For 48V / 0.4A PoE
Note
2M RJ-45 cable is an optional accessory.
11

Ceiling AP Installation Diagram
Attention:
The cable distance between the Router and PC/hub/Switch
should not exceed 100 meters.
Make sure the wiring is correct. In 10Mbps operation, Category
3/4/5 cable can be used for connection. To reliably operate your
network at 100Mbps, you must use Category 5 cable, or better
Data Grade.
12

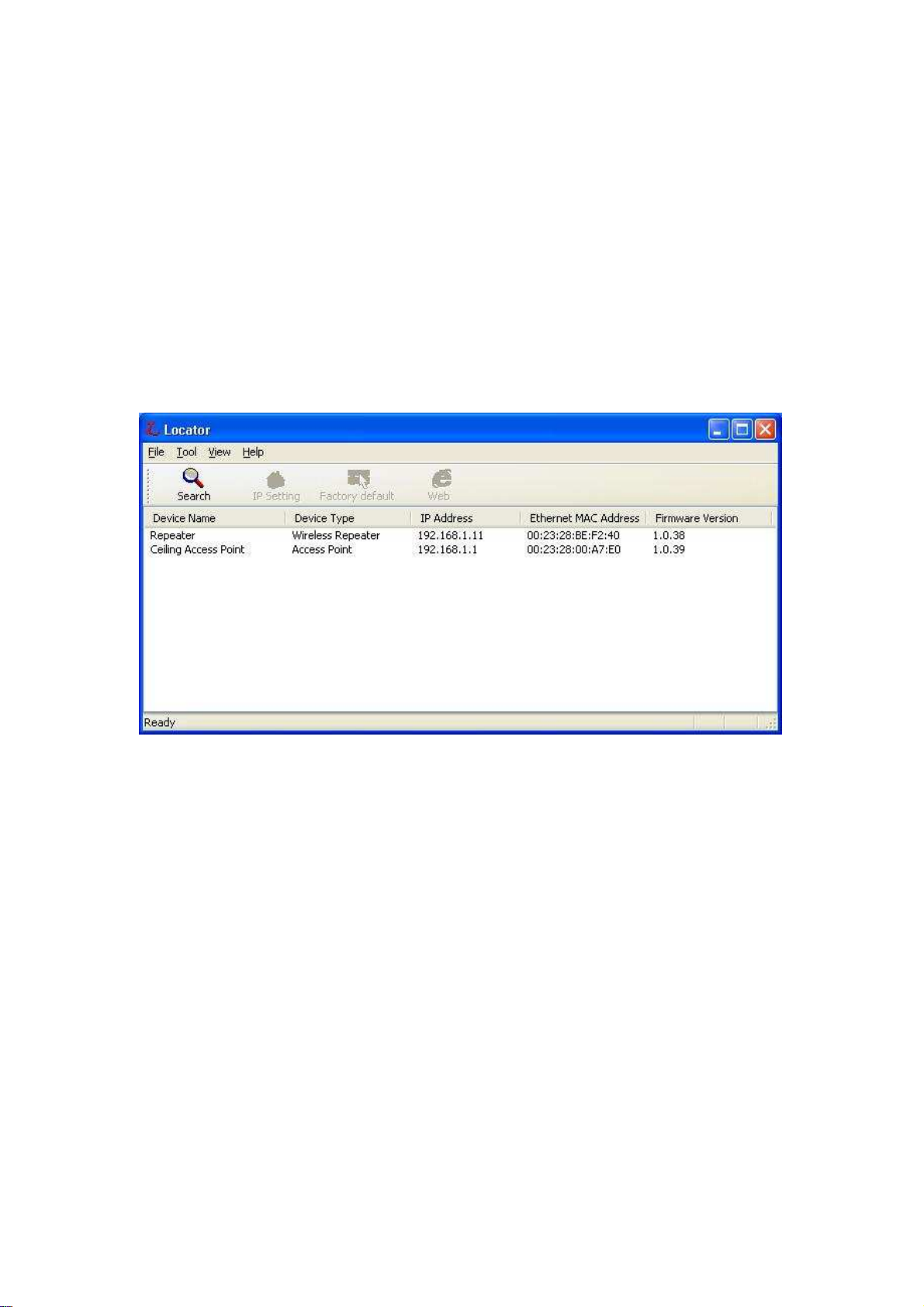
AP Configuration Using Locator
While entering the Locator utility, the Locator will automatically search the AP
available on the same network. Locator will show the Device Name, Device
Type, IP Address, Ethernet MAC Address and Firmware Version in first page.
Before start using Locator, make sure you disable personal firewall installed in
you PC. (Ex. Windows XP personal firewall)
If you have 2 Fast Ethernet Adapter or more, you can choose enable one Fast
Ethernet Adapter for enter with Locator utility.
AP Configuration Using Web User Interface
Before Setup…
Verify the IP address setting
You need to configure your PC’s network settings to obtain an IP address.
Computer use IP addresses to communicate with each other across a network,
such as the Internet.
1. From the taskbar, click the Start button, select Settings > Control
Panel. From there, double-click the Network connections icon.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection icon Properties; select the
TCP/IP line for the applicable Ethernet adapter. Then, click the
Properties button.
3. Click the IP Address tab page, select USE the following IP address,
type 192.168.254.254 (but, 192.168.x.x for the device use) in the IP
Address field and 255.255.0.0 in the Subnet Mask field, then click
OK button.
Start Setup by Browser...
1. After getting the correct connection, start the web browser (make
sure you disable the proxy) and type 192.168.x.x (x is outdoor unit IP
Address) in the Address field. Press Enter.
13
2. Enter the factory default User name and Password fields:
User Name: Admin
Password: (leave blank)
then click OK button.
3. You will enter the Utility homepage.
Start Setup by Locator...
1. You just need to click on the “Web” icon in Locator main page. The
Locator will launch a default browser for you and lead you into web UI
directly
14
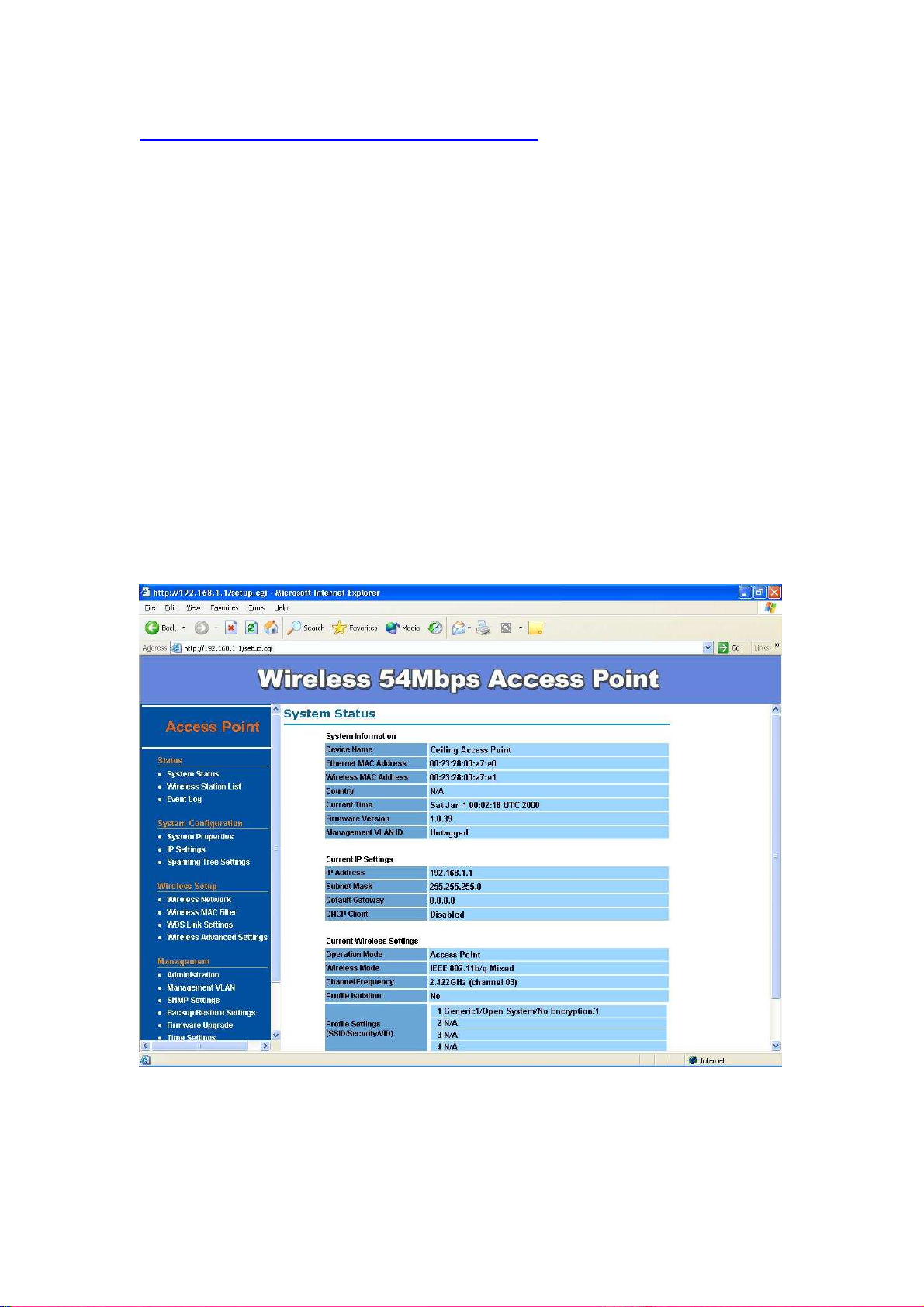
Wireless Configuration - AP Mode
System Status –
The first page appears in main page will show “System Status -> System
Summary” automatically, you can find detail system configuration in this page
including
System Information – This will display system name and both Ethernet
MAC address and Wireless MAC address. Current country setting and
Current time. firmware version and Management VLAN ID
Current IP Settings – This section show current IP address setting
including IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway and DHCP status.
Current Wireless Settings – This area show current wireless setting
including operation mode, wireless mode, Channel/Frequency, profile
isolation, profile settings (SSID/Security/VID), Spanning Tree Protocol.
15
 Loading...
Loading...