Page 1
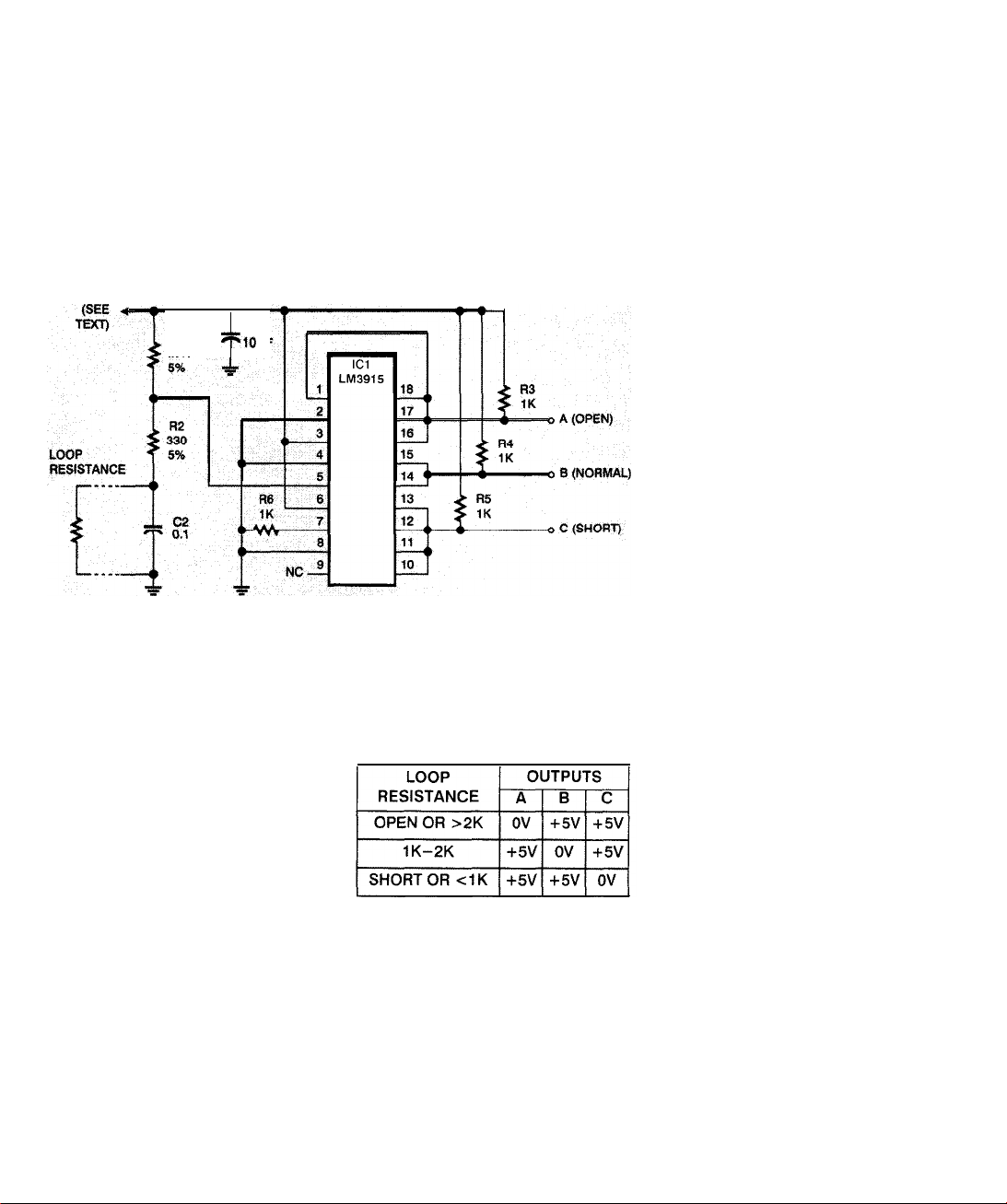
tance
into a voltage; that’s done by
Safer
I
presently have a
utilizing loops with a load resistance
between 1000 and 2000 ohms. Can you help
me
design
logic.-level outputs for “open, ” “shorted, ” and
“‘correct resistance”
Lakewood, CA
Security
simple
a sensing
circuit
conditions? - R. E.
System
security
that will give
system
putting it into a voltage divider with
resistors R1 and
tects the circuit against electromagnetic
noise-important because burglar alarms
use long wires, often running near heavy
electrical equipment.
F.,
Step 2 is to translate the voltage into
a logic signal indicating whether it’s in
R2.
Capacitor C2 pro-
+5V
+
__
R1
4.7K
FIG. l-ONE OF THREE OUTPUTS goes low depending on whether loop resistance is too
high, too low, or just right.
C1
C.10 µF
The truth table in Fig. 2 shows how
the outputs work. Note that they use
negative logic (OV for “yes”, +5V for
“no”), the opposite of ordinary logic circuits. You can use inverters such as the
74HC04
nals if that’s what you need.
actually work with any supply voltage
from 3 to 25 volts. Of course, if the supply isn’t 5 volts, the outputs will not be
compatible with j-volt logic circuits.
to produce positive logic sig-
Finally, note that the circuit will
Many security systems use a closed
loop of wires and switches arranged
A
so that whenever a door or window is
opened, the loop will be broken and the
alarm will sound. An obvious problem is
that someone can tamper with the sys-
tem, short out the loop, and later on,
come back and burglarize the premises
without sounding the alarm.
Hiding a known resistance in the
loop, as you propose, is a very good idea.
That way, the alarm can distinguish a
short circuit from a correctly functioning
closed loop.
Figure
1
shows a circuit that does the
job. It’s a somewhat unusual application
of a National Semiconductor LM3915
IC, normally used to drive LED’
graph displays. That chip happens to
contain
the right combination of comparators and logic circuits to do what you
need.
Step 1 is to translate the loop resis-
bar-
the correct range. That’s where the
LM3915 comes in. Normally, the
LM3 9 15 would drive ten
each of ten small ranges of voltage. To
FIG. P-THIS TRUTH TABLE shows the
states of outputs A, B, and C under different
loop-resistance conditions.
obtain
logic-level outputs, we have it
driving
Since we only need to distinguish three
situations, not ten, we tie some of the
outputs together. The LM3915 has
open-collector outputs that can be paralleled in that way.
1K
resistors instead of
LEDs,
one for
LEDs.
 Loading...
Loading...