Page 1

AKG
REVERBERATION
BX20E
UNIT
Page 2

AKG
REVERBERATION
UNIT
BX
20E
Modern
pensable
reverberation
characteristics,
of
producing
While
some.
the
The
recording
in
instruments
high-quality
1.
2.
producing
To
obtain a range
re-recording
reverberatory
studio
added;
or
the
the
the
techniques
operations.
even
often
process
use
the
performance
reverberation:
echo
room
reverberatory
highest
of
is
plate
provides
have
With
those
done
additional
plate
sound
decay
susceptible
made
the
few
on
location
reverberation
as a whole.
quality,
times,
to
a
simpler
use
of
exceptions
There
the
echo
several
vibration
means
artificial
most
in
halls
to
are
chamber
rooms
and
of
producing
musical
with
enhance
currently
have
noise.
reverberation
recordings
excellent
individual
two
is
expensive
to
be
constructed
artificial
indis-
have
acoustic
groups
methods
and
reverbera-
of
cumber-
and
tion
albeit
considerably
often
large
in
great
of
often
beration
stud
A
deliberately
size
outdoor
variety
running
impossible
io.
portable
with
longer
and
weight
recording
of
special
unit
that
reverberation
slightly
than
with
used
in
and
or
with a mobile
acoustically
cables
because
is
of
portable
unit
lower
resultant
to
sound
natural
recording.
different
the
distance
yet
may
quality.
reverberation,
The
immovability.
van,
recording
plate
and
meets
be
developed
located
major
as
location.
all
the
1
Decay
disadvantage
This
the
sound
problems.
in
the
Hence
quality
on
the
time
but
this
has
engineer
studio
AKG
requirements
basis
at
higher
characteristic
of
proved a great
The
is
developed
of
the
frequencies
the
plate
has
to
customary
very
expensive
following
cope
a new
for
is
is
its
handicap
with
practice
rever-
use
in
techniques:
is
a
and
the
Page 3

a)
b)
c)
d)
production
recorders
production
mechanical
use
at
present
production
storage
production
torsion
of
artificial
of
artificial
plate
of
artificial
technique
of
artificial
transmission
that
reverberation
reverberation
is
much
reverberation
reverberation
line
(TTL)
smaller
by
by
than
using
by
means
means
the
electronic
means
of
of
one
of
tape
a
in
a
After
offers
space
some
critical
the
requirements
prejudices
beration
quirements.
When
judging
ways
uses
theory
a
following
ation
device
best
produced
the
the
natural
natural
essential
irrespective
1)
high
2)
high
consideration
means
in
for
are
small
connection
by
various
quality
room
room
exhibits
characteristics
density
pulse
of
all
the
realization
and
construction
with
types
of
reverberation
as a standard.
a
highly
of
the
means
of
resonance
density
to
these
this
of
coil
which
used:
duplicate
techniques,
of a portable
is
method
must
springs
the
listener,
From
complex
must
be
frequencies
the
AKG
reverberation
relatively
be
overcome
has
not
in
the
viewpoint
transmission
met
by
many
sound
has
economical.
met
the
pattern
any
artificial
paths
decided
as
so
studio
final
of
analysis,
communication
with
that
unit,
However,
far
rever-
quality
the
reverber-
TTL
as
re-
al-
3)
high
ranges
4)
reverberation
sound
5)
frequency
extremes
6)
a
cies,
7)
practical
degree
decay
-
time
while
i.e.
of
statistical
no
regularity
must
response
frequency
at
high
applications
start
that
20
falls
response
frequencies
require
diffusion
must
to
slightly
2
in
exist
50
milliseconds
that
has a slight
a
slight
variability
the
in
the
at
the high
fall
frequency
two
after
is
of
decay
and
ranges
the
and
rise
desirable
time
time
concerned
original
low
frequency
at
low
frequen-
Page 4

We
The
can
high
use
density
the
technique
of
resonance
of
TTL
to
frequency
meet
these
requires
criteria
very
in
long
the
coil
following
spring
way:
elements.
L-
According
milliseconds
and
picked
resonance
~F
This
~
T
distance
density
delay
possible
development.
changes
in
described
to
experience,
from
up
at
the
frequency
~F
of
of
time
density
The
density
later.
beginning
other
of
0.6
I
two
adjacent
resonance
of
excellent
and
distribution
their
to
end
length
end.
of
based
poles
frequency
natural
reverberation
should
Provided
the
spring,
upon
the
where
in
resonances
of
these
formula.
the
frequency
is
quality
correspond
that
the
this
length
~F
the
starting
is
natural
to a delay
signal
yields
I
2T
spectrum
point
brought
resonances
is
about
by
time
fed
a
density
for
by
means
of
into
all
certain
300
one
of
further
which
end
are
:y
len-
In
order
the
time
of
the
spring.
The
onset
ing
circuit
be
explained
The
frequency
internal
rise
by
means
spring
in
to
obtain
and
of
based
friction
the
low
of
mechanical
the
high
frequency
statistically
reverberation
on
the
in
detail
response
of
the
frequency
pulse
range,
by
after
statistical
later
of
on.
the
spring.
response
damping.
density
it
is
necessary
changing
20
to
transmission
reverberated
Mechanical
of
the
The
frequency
as
well
the
mass
50
milliseconds
signal
vibrating
reverberated
3
as
to
vary
and
properties
is
response
the
statistical
the
transmission
spring
is
elements
effected
determined
systems
signal,
depends
of
the
primarily
generally
which
on
diffusion
in
properties
along
the
coil
by a compensat-
coil
and
will
by
the
display
can
be
corrected
the
mass
of
the
a
Page 5

transducer
From
the
way
the
This
additional
system
users
maximum
and
viewpoint
number
damping
the
spring
a
of
applications
is
parameters
linear
necessary
frequency
is
because
as
well
response
possible.
variation
as
is
on
most
of
the
desirable
decay
internal
time
friction.
as
which
in
this
is
based
only
provided
show
The
the
with
Depending
the
Having demonstrated
given a rough
tion
on
the
principle
permits a limited
mechanically.
the
longest
motional
transduction
the
mass,
unit
feedback
proper
on
the
compliance
outline
BX
20E
phasing,
of
control
decay
to
desired
developed
time
principle
an
analogues
and
the
of
motional
This
means
desired.
and
the
phase
friction
feasibility
the
various
by
AKG
feedback
range
and
and,
accordingly,
that
the
consists
electrical
electromechanical
frequency
of
will
of
the
mechanical
of
the
measures
be
TTL
described
and
carried
electronically
the
pickup
signal,
response,
used,
for
the
feedback
system.
high
the
in
out
at
initial
undamped
of
the
mechanical
amplification
to
we
can
in
quality
portable
detail.
the
spring
damping
the
this
reverberation
studio
must
system
of
pickup
way
ends,
be
must
signals,
the sig
system,
establish
and
reverbera-
nal
The
BX
main
The
BX
channel
inputs
20E
is
parts:
1)
2)
3)
20E
is
allowing max
can
be
based
the
the
the
a two
paralleled,
on
the
electromechanical
electronic
elastic
channel
imum
principle
circuits
support
unit
flexibility
and
either
of
reverberation
with
independent
in
channel
torsion
stereophonic
transmission
can
be
4
unit
control
or
used
and
proper
of
decay
monophonic
separately.
consists
time
use.
of
of
each
The two
three
Page 6

Reverberation
coil
spring.
The
transmission
line
equations.
is
produced
properties
For
the
Mass
by
the
of
per
torsional
the
unit
spring
length
vibration
can
be
of a specially
calculated
by
the
treated
well
known
.
.
e
al
sh
The
The
and
r
a
p
E
W
T
Compliance
Delay
the
Time
Limiting
spring
wire
density
modulus
number
delay
radius
time
L= 2rr
per
C
is
then
T = W
Frequency
a
F=~2
radius
of
elasticity
of
turns
232
ra
unit
Br
Ea
4
4
rr
a
in
~
length
given
2
r
fFp
spring
is
by
IJ
E
per
unit
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
length
As
the
is
used
to
provide
To
fit
special
to
be
and
reverberation
as
it
attention
reverberated
is
picked
illustrated
the
desired
into
a
up
element,
in
300
reasonable
paid
to
enters
by
similar
a
spring
figure
milliseconds
avoiding
both
size
ends
systems
1:
enclosure,
which
The
length
delay
unnecessary
of
the
after
reverberation.
5
has a double
of
time.
the
spring
reflections.
spring
by
the
spring
has
means
step
been
of
toward
is
bent
The
moving
1.2
signal
both
meters
twice
that
coil
ends
(47. 2")
with
is
systems
Page 7

Each
moving
coil
system
consists
of
two
coils
which
have a rigid
mechamical
connection
coils
half
Figure
are
and
2 shows
circular
The
statistical
statistically
individual
The
transmission
cited
on
on
the
the
are
third
fourth
between
electrically
picked
the
magnet.
changing
turns
determined
power
power
them
up
at
the
moving
diffusion
which
properties
by
of
the
of
and
which
and
magnetically
other.
coil
of
the
surface
are
distributed
of a coil
the
mass
mean
the
wire
vibrate
transducer
the
reverberated
and
diameter
diameter
decoupled.
of
the
irregularly
spring
compliance
of
(2).
in a strong
system
suspended
signal
spring
wire
along
in
which
per
the
coil
The
internal
magnetic
The
signal
is
achieved
and
torsion
unit
spring,
in
partly
the
length
length.
(1)
friction
field.
is
fed
the
airgap
partly
by
deforming
of
vibrations
The
compliance
of
The two
into
of
by
the
are
mass
the
coil
one
the
spring.
ex-
depends
depends
spring
variations
surface
tion
of
the
spring
lower
For
ones.
the
bending
be
deformed
is
realized.
The
spring
damping.
is
the
the
lower
parts
very
low.
by
relatively
maximum
diameter.
elements,
frequencies,
of
the
is
done
(See
is
adjusted
On
the
small
local
These
are
naturally
turns
statistically.
figure
3.)
to
basis
changes
removal
changes,
i.e.
toward
the
required
of
these
of
the
of
wire
material
which
more
effective
below 1 kHz,
the
spring
By
these
output
facts
wire
reduce
the
axis.
means
decay
it
is
possible
diameter.
results
the
mass
at
higher
individual
Selection
the
necessary
time
By
in
a 20
of
the
frequencies
turns
of
by means
to
achieve
etching
per
wire
are
turns
degree
of
large
the
wire
cent
reduc-
and
modify
than
deformed
that
are
of
diffusion
mechanical
at
by
to
6
Page 8

Without
and
10,000
these
cycles
mechanical
is
on
dampings
the
order
the
of
relation
10
:
1.
of
decay
Figure
time
4 shows
measured
the
damper
at
50
and
cycles
figure
,.
.s
5 shows
For
mary
obtain
6
seconds
consists
washers
disk
the
The
s
and
within
from
this
this
reason
effect
the
at
of a small
made
by
means
spring
choice
the
determination
limits.
them
remain
damper
is
to
desired
100 Hz,
of
of
at
various
of
diameter
built
additional
influence
output
4.5
disk
foam
material
Laminae.
places
of
The
dampers
within
into
dampers
low
reverberation
seconds
mounted
The
and
and
surface
the
pressure
do
tolerable
the
spring.
are
frequencies
at
on
which
disks
soldering
of
not
act
limits.
500
an
are
are
the
applied
inserted
under
frequency
Hz
and 2 seconds
axle.
in
The
turn
inserted
the
disk,
permit
as
impedances
Apart
along
1 kHz,
response,
disk
slightly
in
ends
the
from
the
coil
making
at
is
placed
pressed
the
spring
to
the
selection
frequency
on
the
providing
spring.
it
possible
whose
decay
5 kHz. The
between
against
by
disconnecting
ends
of
the
of
foam
independent
line
so
the
Their
time
damper
disk
material,
that
desired
pri-
to
is
two
the
axle.
damping
reflections
amount
o
ion
of
damping
the
reverberation
As
can
be
seen
channel,
consists
amplifiers.
half
of
each
The
"dry"
spring,
signal
the
amplified,
interdependent
transmission
they
also
unit
from
of
The
spring
of
the
is
reverberated
and
connected
and
system.
serve
to
the
an
moving
fed
related
as
be moved
block
input
is
excited
coil
in
phase,
signal
in
opposite
Signals
excellent
without
diagram
amplifier,
by
systems
to
is
picked
is
protectors
(figure
an
feeding
arranged
each
moving
up by
phase.
achieved,
7
special
6)
output
the
In
from
mechanical
locking.
the
electronic
amplifier,
original
at
either
coil
the
two
this
manner
TTL
being a reciprocal
end
half
on
remaining
shock
portion,
and
two
signal
of
the
into
the
ends
coil
compensation
allowing
for
each
attenuation
one
coil
spring.
of
the
halves,
of
all
and
passive
Page 9

To
illustrate
this:
If
the
circuit
were
to
be
applied
to
an
ideal
line
the
reflections
out
of
ties
of
frequency
coherence
of
phase
Owing
cuit
after
of
to
also
the
diffusion
deformation
the
absolute
would
phase
the
spring
independent
whatsoever.
output.
the
provides
input
of
connection
diffuse
of
provided
the
value
Figure 7 illustrates
all
be
of
are
statistically
reflections
Therefore,
transmission
for
20
the
original
for
ends
of
of
the
the
in
phase
the
to
the
the
start
above
at
output.
which
these
properties
50
milliseconds
signal.
spring,
elements
of
the
with
the
output
However,
changed,
appear
signals
This
as
through
the
reverberated
the
use
and
since
it
produces
at
the
will
of
the
delay
interval
the
frequency
of
tonebursts
would
be
the
irregular,
ends
not
be
spring
in
the
start
is
influenced
intensity
characteristics
signal
of
cancelled
transmission
of
the
spring
cancelled
this
compensation
of
reflections
of
etching
can
be
controlled.
300,
600
by
the
proper-
statistical,
with
at
the
by
the
degree
and
as
well
and
2000
no
out
cir-
the
as
Hz.
used
of
20
milliseconds.
50
milliseconds
cies
at
which
Using
time
systems
the
by
tance
time
motional
within a certain
are
greatest
its
characteristic
is
will
possible
limitations
as
signal
frequencies.
The maximum
for
low
value
it
feedback
range.
deliberately
possible
control
impedance
inserted
not
be
zero
in a line
but
with a frequency
on
the
control
frequencies
remains
the
attenuation
The
arranged
of
having a large
only
independent
range.
One
division
value
and
constant.
explanation
at
the
decay
the
decay
approach
The
for
the
falls
amplifier
spring
time.
time
number
a minimum
real
resistance.
insertion
on
the
onset
to
20
is
as
ends
We
know
is
of a real
screen
of
reverberation
milliseconds
permits
the
follows:
to
obtain -inter
that
zero.
of
because
If a simple
inhomogeneities
ideal
This
corresponds
for
variation
The
moving
in
an
ideal
matching
accounts
to a delay
is
approximately
higher
of
decay
coil
alia
line
real
resis-
the
decay
is
for
the
frequen-
-
loaded
not
frequency-independent
8
Page 10

resistance
-
is
obtained
in
the
following
way:
. y
signal
The
system,
into
tion
picked
the
can
decoupling
functioning.
The
amplification
d.c.
voltage.
decay
to
vary
time
decay
Particular
to
the
music
and
the
like.
that
first
be
introduced
and
is
insensitive
time
importance
without
is
to
up
at
coil
half.
in-phase
of
This
has
from
Thus
"true
be
reverberated
the
other
at
the
mechanical
the
attenuation
many
to
the
must
running
to
half,
By
varying
spring
advantages
interference
control
be
attached
the
risk
the
score"
is
fed
and
after
the
end.
vibration
amplifier
in
board
to
of
picking
reverberation
into
one
a 1800 phase
amplification
Complete
of
both
is
electronically
that
remote
on
the
control
during
the
recording.
last,
up
half
a
larger
electrical
coils
control
line
as
decay
undesired
is
possible
of
the
inversion
and
is
essential
is
and
time
and
moving
again
or
smaller
mechanical
to
controlled
possible,
it
is
possible
can
be
disturbing
•
coil
fed
fric-
their
by
the
adjusted
noise
a
lately
len-
d
The
amplifier
channel
output
with
the
nels
are
The
elastic
isolation
shock
careful
The
two
securing
and
levels
input
completely
from
during
insulation
springs
elements
is
mounted
uses
integrated
are
adjusted
impedance
symmetrical.
suspension
footsteps
transportation
against
together
form a unit
on a plug-in
circuits
to
the
at 1 kn
of
the
reverberation
and
floorborne
on
air
with
the
which
for
requirements
and
the
other
borne
sound,
magnet
is
printed
maximum
an
output
sounds
hand.
systems
mounted
9
circuit
reliability.
of
studio
impedance
unit
has
on
one
Attention
as
undesired
and
in a cardboard
board
to
hand
the
fulfill
with
The
techniques
of
SOn
and
protection
must
also
feedback
various
tube.
one
board
input
at + 6db,
Both
two
functions;
be
might
supporting
The
and
from
paid
occur.
inside
per
chan-
to
and
Page 11

of
is
the
cardboard
tightly
tube
mounted.
is
This
lined
results
with a porous
in
both
excellent
foam
material
damping
into
and
which
the
the
absence
unit
of
membranelike
so
high.
The
cardboard
whose
of
resonance
tion
The
insulating
the
Intercepting
prevent
overturned.
natural
the
unit,
sprin
whole
amplifiers
it
frequencies
gs show
unit
vibrations
unit
resonances,
and
is
effect.
are
drums
from
They
is
the
spring
natural
mounted
The
mounted
are
striking
have
of
the
mounted
determined
constants,
are
necessary
resonances
in a strong
back
and
elastically
the
the
disadvantage
wall
inside
panel
on
wooden
since
because,
of
the
arranged
wall
the
an
elastic
by
the
is
below
between 5 and
wooden hOUSing
the
housing
outside
under
that
internal
length
owing
the
above
extreme
in
normal
single
of
1 Hz.
to
10
which
is a door
connector
and
friction
point
the
pendulum,
These
their
Hz
even
has
below
shock
operation
of
pendulum
low
suspension
length,
with
an
on
the
plate
the
cardboard
or
when
the
cardboard
suspension
the
weight
the
reverbera-
dampers
additional
inside
is
fastened.
the
maximum
inserted.
of
which
tube
unit
angle
is
sound
to
is
*
Fi
of
inclination
it
has
become
danger
constant
duced.
With
verberation
excellent
coloration,
The
quality
of
(See
the
unit
of
pOSSible
minor
motion
figure
BX
ZOE
meets
acoustic
flutter
has
met
of
reverberation
the
jerks
has
AKG
all
with
housing
to
acting
been
8 and
has
succeeded
the
fidelity
echoes,
considerable
is
restricted.
avoid
avoided
figure
requirements
has
directly
of
and
been
locking
and
9.)
the
similar
the
upon
the
danger
in
developing
and demands
reverberated
disturbances.
success
favorably
10
Owing
unit
the
system
of
a
sounds,
both
in
compared
to
during
and
fatigue
remotely
of
studio
Network
to
these
mounting
transportation.
keeping
breaks
operated
technique,
and
is
entirely
and
Studio
that
of a concert
the
is
greatly
unit
techniques
Thus
spring
use
in
re-
whose
guarantees
free
of
where
hall.
the
re-
its
F:
Page 12

~
---------------L
------------
----~
Figure
1
1
/
t
Figure
2
Figure
4
:s
Figure
3
11
Figure
5
Page 13

'
~'
-'
I
-'-'-
'-'
-'-'-I
Inpul
BLOCK
I
DIAGRAM
I
I
r-._
.-
I
I
I
I
~
I
4.
Re
Figure
5IrOmy-ers-o,-gU-n9
Power
_b_lo_c_d.
mote control
6
~
:n-h.-II-t
supply
un,1
ah_m8_n_ld_t,on
unit R 20E
__
-
'
--
~
. .
__
·
-
rT71-
with
·
-·-~~-c---:~~~I
.
'
---
_r-_-_-
---
.
~-_-_-
remote
I-----t----+-c
51
1----4---4--<::
. I.
.
~~~-_-~-_-_-
control
.
line
OUlpul
I
Inpul
II
"
OUlpul
C-jH4
C - ®
-J+-~C
+~
220V1110V
5.
Autom
mains
V}
atic
supply swto
l.
Feedback
2.
Driving
3.
Pick-up
itc
h-o
battery
amplifier
amplifier
ver
amplifier
from
supply
Figure
7
Figure
12
8
Page 14
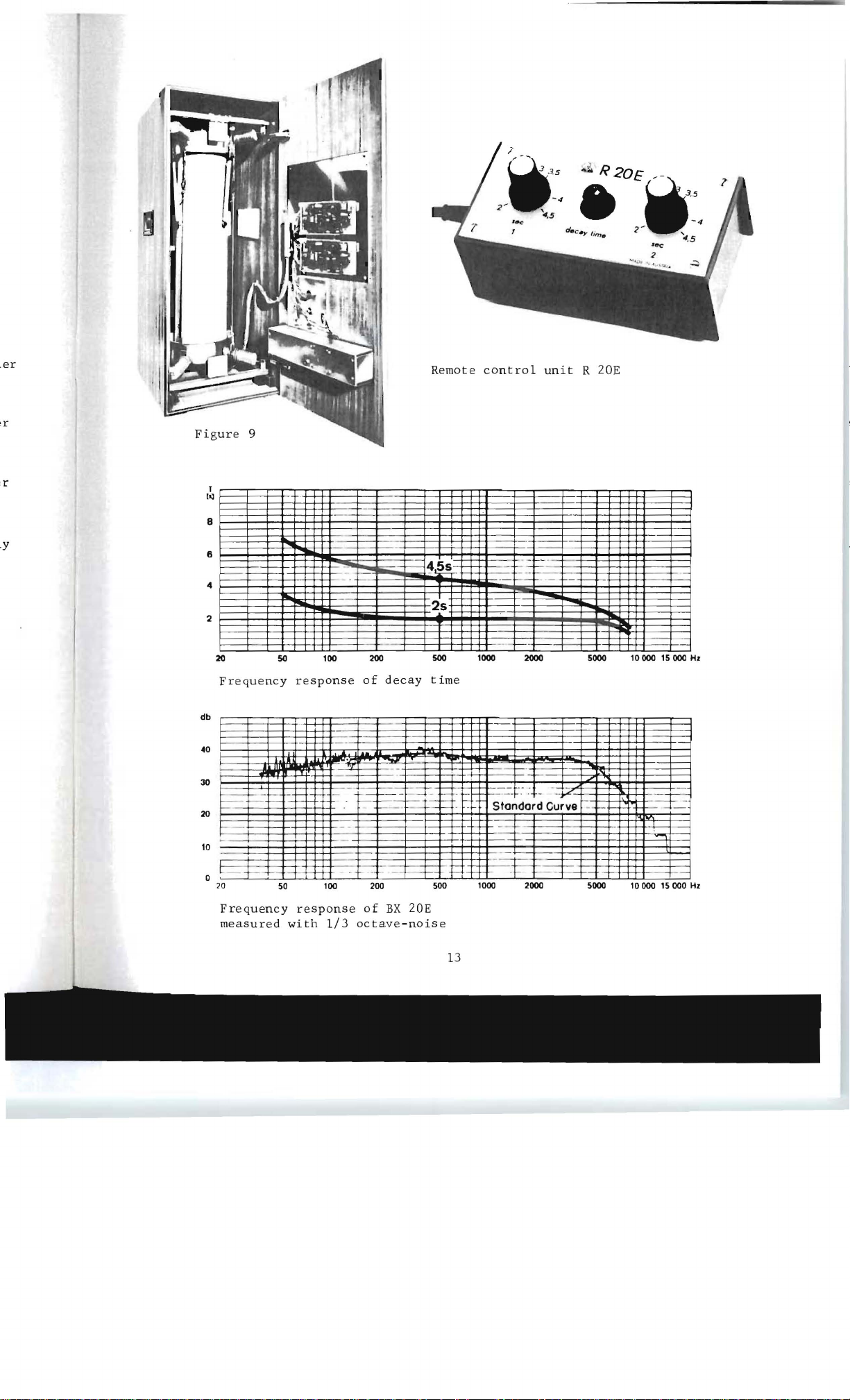
.er
Remote
control
unit
R
20E
-y
Figure
1
(I]
8
6
-
4
2
20
Frequency
db
40
30
f=='
"-
20
- .
~
10
1..
20
Frequency
measured
9
-
'
-
-
_.
-1
~~
2s
50
response
100
200
of
decay
~
--
500
time
-
1000
-
I--
- . -- f--
=....
-
i -
-
-
- - .- -
I -
-
-
-
50
response
with
-
f-
100
1/3
octave-noise
of
--
200
BX
I---
20E
1--
500
~
Standard Curve
--
-
~
1000 2000
--1- -
-
--
-
-I-
--
~
-
- -
..
--
-.
2000
"-
l-
--
-
-
--
5000
--I--
-
--
-
-
f--
I---
5000
10000
l-
10000
--
.-
IS
000
--
f--
f--
15000
.-
Hz
Hz
13
 Loading...
Loading...