Page 1

Raven CDMA/1x
User Guide
AirLink Communications, Inc.
version 2.23
May 2006
Page 2

Information in this document is subject to change without notice
©Copyright AirLink Communications, Inc., 1993-2006. All rights reserved.
WARNING
The antenna(s) used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at
least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
Important Notice
Because of the nature of wireless communications, transmission and reception of data can never
be guaranteed. Data may be delayed, corrupted (i.e., have errors) or be totally lost. Although sig
nificant delays or losses of data are rare when wireless devices such as the AirLink Communications modem are used in a normal manner with a well-constructed network, the AirLink modem
should not be used in situations where failure to transmit or receive data could result in damage of
any kind to the user or any other party, including but not limited to personal injury, death, or loss
of property. AirLink Communications, Inc., accepts no responsibility for damages of any kind
resulting from delays or errors in data transmitted or received using the AirLink Communications
modem, or for failure of the AirLink Communications modem to transmit or receive such data.
Safety and Hazards
Do not operate the AirLink Communications modem in areas where blasting is in progress, where
explosive atmospheres may be present, near medical equipment, near life support equipment, or
any equipment which may be susceptible to any form of radio interference. In such areas, the Air
Link Communications modem MUST BE POWERED OFF. The AirLink Communications
modem can transmit signals that could interfere with this equipment. Do not operate the AirLink
Communications modem in any aircraft, whether the aircraft is on the ground or in flight. In air
craft, the AirLink Communications modem MUST BE POWERED OFF. When operating, the
AirLink Communications modem can transmit signals that could interfere with various on board
systems. The driver or operator of any vehicle should not operate the AirLink Communications
modem while in control of a vehicle. Doing so will detract from the driver or operator's control
and operation of that vehicle. In some states and provinces, operating such communications
devices while in control of a vehicle is an offence.
-
-
-
Limitation of Liability
The information in this manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of AirLink Communications, Inc. AIRLINK COMMUNICATIONS, INC.
SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS LIABILITY FOR ANY AND ALL DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPE
CIAL, GENERAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR EXEMPLARY DAMAGES INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, LOSS OF PROFITS OR REVENUE OR
ANTICIPATED PROFITS OR REVENUE ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO
USE ANY AIRLINK COMMUNICATIONS, INC. PRODUCT, EVEN IF AIRLINK COMMU
NICATIONS, INC. HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES OR
THEY ARE FORESEEABLE OR FOR CLAIMS BY ANY THIRD PARTY.
ii Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
-
-
Page 3
Contents
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Raven CDMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
CDMA Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Establishing a Internet Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Using CDMA to Communicate with Your Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Common Uses for the Raven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
CHAPTER 2 Activation of the Raven CDMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Connecting the Raven to your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Quick Start Guide and Setup Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Activating the Raven using AT Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Raven Indicator Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
CHAPTER 3 Utilities for the Raven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
AirLink Configuration Executive (ACE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Wireless ACE 3G . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
AceNet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
AceView . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Modem Doctor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 iii
Page 4

Contents
CHAPTER 4 IP Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Fully Qualified Domain Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Dynamic Name Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Configuring the Raven for Dynamic IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Restrictions for Modem Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
DNS: Using Names Instead of IP addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Configuring DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
PPP-Peer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CHAPTER 5 Keepalive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Configuring Keepalive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Data usage using Keepalive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
CHAPTER 6 Host Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
AT Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
PassThru Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
PPP Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Slip Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
UDP Pad Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
UDP Auto Answer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Reliable UDP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Multicast UDP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
TCP PAD Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
TCP Auto Answer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Hybrid Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
CHAPTER 7 Modbus/BSAP Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Modbus Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Telemetry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Modbus TCP/IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Raven Modbus on UDP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Configuring the Raven at the Polling Host for Modbus on UDP . . . . . . . .35
Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Default Power-up Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
iv Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 5

Contents
IDs to IPs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Dynamic IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Configuring the Remote Ravens for Modbus with UDP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Default Power-up Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Host Raven IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Dynamic IPs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
RTU settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
CHAPTER 8 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) . . . . . . . . . . . 41
SNMP Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Management Information Base (MIB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
SNMP Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Raven SNMP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Listening Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Security Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
User Name and Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Trap Destination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
CHAPTER 9 Hardware Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Connecting the Antenna . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Connecting power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Connecting the Raven to a computer or other device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
APPENDIX 1 Specifications for the Raven CDMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Physical Characteristics: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Data Services & RF Features: CDMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Environmental: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Power Management: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Power consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
APPENDIX 2 Mounting Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
APPENDIX 3 AT Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Using Wireless Ace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Using Telnet Terminal Emulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Direct Serial Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
AT Command Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Information Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 v
Page 6

Contents
Basic Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Activation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Cellular Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Local Network and Host Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
PassThru . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Direct Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Time/Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Friends Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Keepalive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
IP Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Modbus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
SMTP/SMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Other . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
APPENDIX 4 Example of the MIB trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) and Solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
What is RSSI? Why is the RSSI for my Raven negative? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
What is the Proper RF Coverage for my Raven? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
What Type of Antenna is Best for my Raven? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
What do I need to power my Raven ? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Can I use a portable battery to power my Raven ? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
I’m Having Problems getting my Raven registered (activated or provisioned) with
Verizon, what could be the problem? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Why Can’t I reach my Raven from the Internet? What is a Restricted or Private IP?
103
What is the difference between Private Mode and Public Mode? . . . . . . . . . . . 103
How do I set up Private Mode? How do I connect to my Raven to my router or to
Linux? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
What is the COM1000? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
How can I update the PRL (Prefered Roaming List) for my CDMA modem? I have
activated my Raven but now cannot connect to Verizon, what can be wrong? . 106
Support web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
Contacting Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
vi Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 7

CHAPTER 1 Intr oduction to
Raven CDMA
The Raven's rugged form factor is ideal for industrial and commercial applications
that require real-time communications. The Raven provides cellular data communications for a variety of applications, such as telemetry, public safety, SCADA, traffic control, traffic metering, transit arrival systems and more.
FIGURE 1. Raven front and back
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 1
Page 8

Introduction to Raven CDMA
CDMA Overview
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) provides a digital cellular telephony system provides wireless Internet access at speeds between 60 and 80 kbps, with bursts
up to 144 kbps.
Establishing a Internet Connection
The Internet Service Provider (ISP) from you to the Internet is Verizon with your
Raven as the connection to Verizon.
When your Raven is powered on, it automatically searches for cellular service
using CDMA and establishes a PPP (Point to Point Protocol or “dial” up connection) link to Verizon’s network. As soon as the Raven receives its IP, it’s ready to
create a network between your computer or device and Verizon’s network so you
can use Verizon to communicate on the Internet.
To use your Raven to connect to the Internet from your computer, you need to connect the computer directly to the Raven’s serial port and use Dial-Up Networking
(DUN).
FIGURE 2. Using the Raven to connect to the Internet
2 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 9
Introduction to Raven CDMA
Note: Private network connections are unique for each configu-
ration and not covered as part of the standard installation.
Using CDMA to Communicate with Your Equipment
There are two types of addresses in TCP/IP, dynamic and static.
• Dynamic addresses are assigned on a “need to have” basis. Your Raven might
not always receive the same address each time it connects with Verizon.
• Static addresses are permanently assigned to a particular account and will
always be used whenever your
will not be given to anyone else.
If you need to contact the Raven, a device connected to the modem, or a host system using the modem, you need to have a known IP (such as one which is static) or
domain name (an IP address which is converted by a DNS server into a word based
name).
Raven connects to the Internet. The IP address
Most ISPs (cellular included) use dynamic IP addresses rather than static IP
addresses. A dynamic IP address is suitable for many common Internet uses, such
as web browsing, looking up data on another computer system, or other client func
tion (such as data only being sent out or only being received after an initial request).
Note: If you have a dynamic IP address for your Raven, you can
use a Dynamic DNS service (such as IP Manager coupled with a
Dynamic DNS Server, covered later in this User Guide) to trans
late a dynamic IP address to a fully qualified domain name so
you can contact the
Caution: The IP address given to your Raven by Verizon must
also be Internet routable if the computer you need to connect to
the
Raven is not connected directly to Verizon 's IP network.
Please check with Verizon to confirm you IP is scheme is correct
for your application and needs.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 3
Raven as if it had a static IP.
-
-
Page 10
Introduction to Raven CDMA
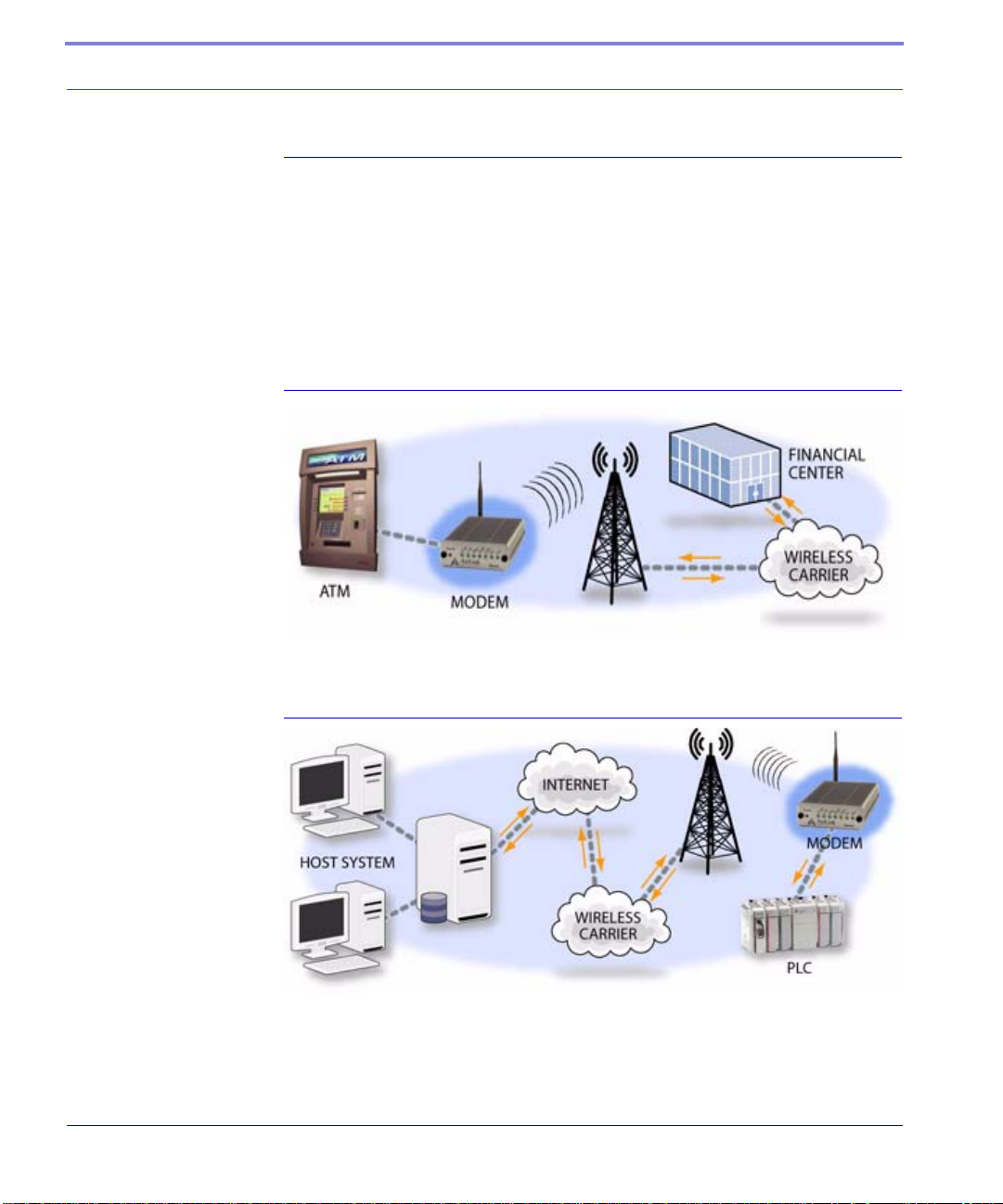
Common Uses for the Raven
The Raven’s rugged construction and cellular connection make it ideal for use in
remote and/or industrial locations.
The Raven can be used for telemetry and for more advanced communication to
the device or devices behind it.
FIGURE 3. Financial Point of Sale and Kiosk
FIGURE 4. Automation and Telemetry
4 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 11

Introduction to Raven CDMA
FIGURE 5. Backup connection to the Internet
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 5
Page 12
CHAPTER 2 Activation of the Raven
CDMA
Your Raven needs specific parameters before it can operate on the CDMA network.
Generally Verizon will provide you with the necessary parameters to get the Raven
configured.
Connecting the Raven to your computer
Your Raven’s serial port can be connected directly to most computers or devices
using a standard straight through serial cable.
Quick Start Guide and Setup Wizard
The preferred way to configure and activate your Raven is via the AirLink Setup
Wizard for Verizon and CDMA. The Quick Start Guide will lead you through the
using the Setup Wizard.
• The Raven Setup Wizard for CDMA and Verizon is available from the AirLink
web site, http://www.airlink.com/support.
• The Quick Start Guide is also available at the AirLink web site.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 6
Page 13
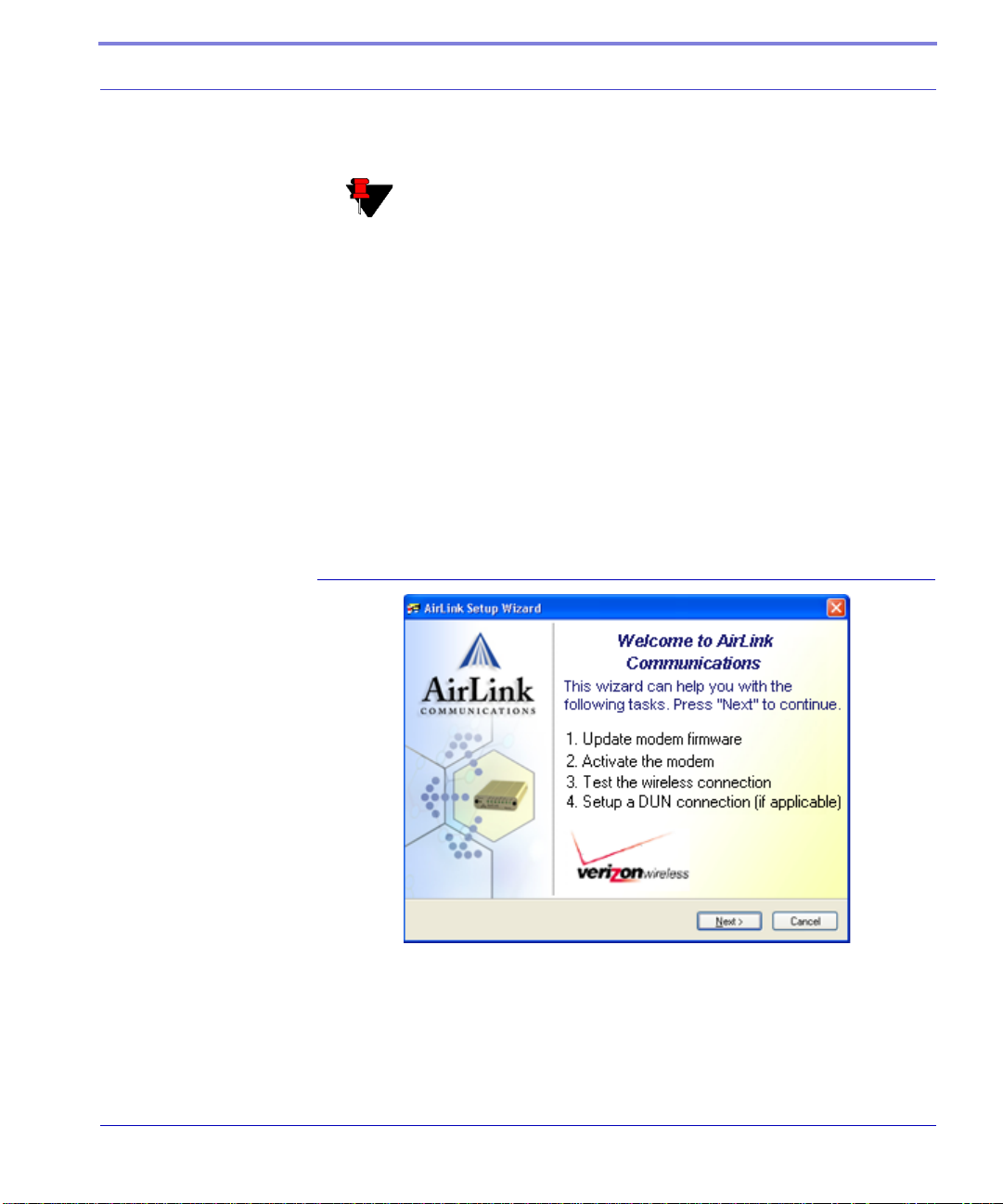
Activation of the Raven CDMA
Note: The web site may have a more recent Setup Wizard and
Quick Start Guide than those included with your Raven. It is rec
ommended that you check with the web site for the latest version
before installing your Raven. You will need to look for Verizon,
CDMA, and the Raven. Other Setup Wizards may not work to
connect you to Verizon.
To run the Setup Wizard, you will need the Microsoft .NET framework and
Microsoft Windows 98, Microsoft Windows 2000, Microsoft W indows XP , or later .
1. Select Start.
2. Select All Programs.
3. Select AirLink Communications.
4. Select Setup Wizard.
5. Select Setup Wizard.
FIGURE 1. Setup Wizard
The Quick Start Guide specifies the information you need and will lead you
through the steps.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 7
Page 14
Activation of the Raven CDMA
Activating the Raven using AT Commands
An alternate method to configure and activate your Raven is by AT commands (full
listing beginning on page 53) sent directly to the modem via a terminal application.
This method is recommended only in situations where the Setup Wizard is not
available and/or the configuration for the
Caution: While you can configure your Raven using Wireless
ACE (page
activate the Raven using either Wireless ACE or AceNet.
10) or AceNet (page 11), it is not recommended to
Raven is unusual.
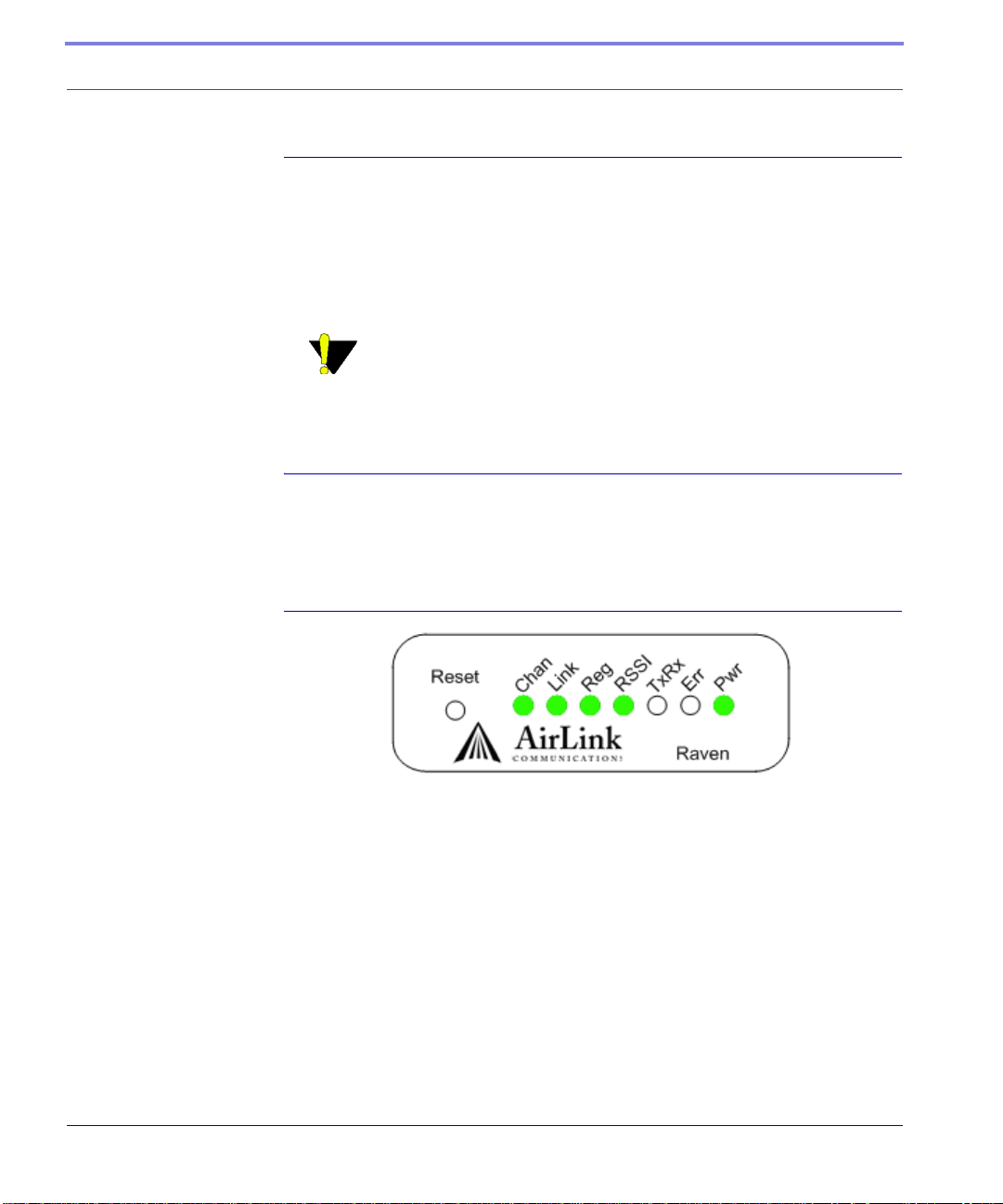
Raven Indicator Lights
When your Raven is connected to power and an antenna, there is a specific pattern
to the lights to indicate its operation mode.
FIGURE 2. Raven indicator lights
Tx (transmit) and Rx (receive) - Lights will flash as data is transferred to and
from the
RSSI - Light shows the strength of the signal and may be nearly solid (strong signal) or
flashing (weaker signal). A slow flash indicates a very weak signal.
Reg - Indicates the Raven has acquired an IP from Verizon.
Chan - Indicates the modem has acquired a network channel.
Link - Indicate a successful connection to the cellular network.
Raven on the remote network.
8 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 15

Activation of the Raven CDMA
Pwr - Indicates the power adapter is connected and there is power getting to
the modem.
The Reset button performs the same function as unplugging power from the
modem and plugging it back in. Reset will not alter any saved configuration
settings.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 9
Page 16
CHAPTER 3 Utilities for the Raven
AirLink offers a suite of utilities to optimize your Raven’s performance, allowing
you to remotely view status and make changes to the configuration as needed.
• AceView
• Wireless ACE 3G
• AceNet
• Modem Doctor
This section of the Raven User Guide covers basic information about these utilities.
For additional information on a specific utility, please refer to the user guide for
that utility.
These utilities, except AceNet, are free of charge to those who own AirLink
modems. You can download the utilities and their user guides from the AirLink
web site: http://www.airlink.com/support. Contact your dealer or AirLink repre
sentative for information on AceNet.
Note: AceView, Wireless ACE 3G, and AceNet require the
Microsoft .NET Framework and Microsoft Windows 98, Win
dows 2000, Windows XP, or later.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 10
-
-
Page 17
Utilities for the Raven
You can obtain the Microsoft .Net Framework, Microsoft Internet Explorer, and/or the latest ActiveX updates for Internet
Explorer from Microsoft at:
http://www.microsoft.com/.
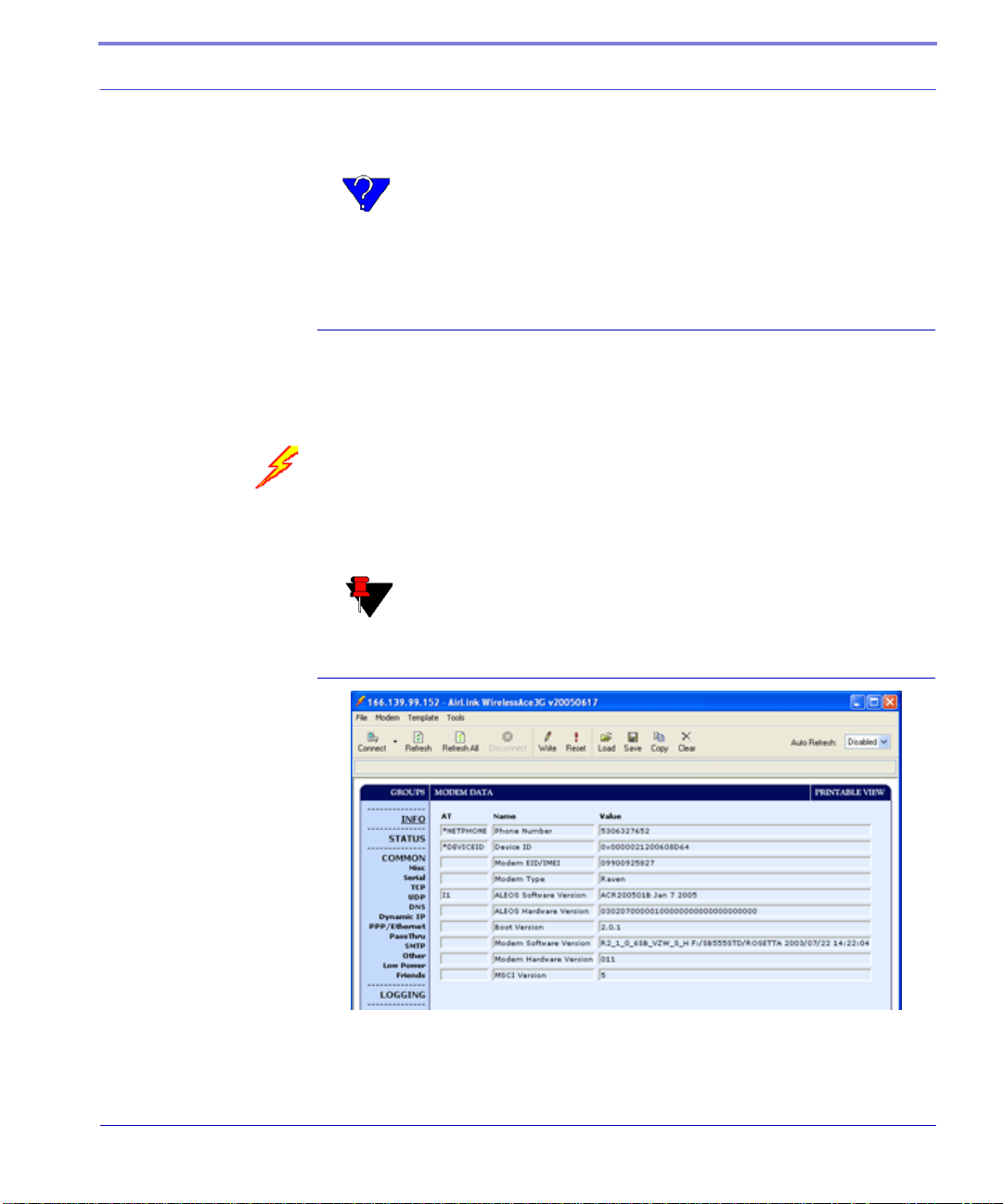
AirLink Configuration Executive (ACE)
The AirLink Configuration Executive provides a user friendly interaction with
ALEOS, the brains of your Raven.
Wireless ACE 3G
Wireless ACE 3G allow you to monitor your Raven either remotely or locally with
a direct connection to the modem.
Note: Most configuration screen shots in this guide are using
Wireless ACE 3G.
FIGURE 1. Wireless ACE 3G
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 11
Page 18
Utilities for the Raven
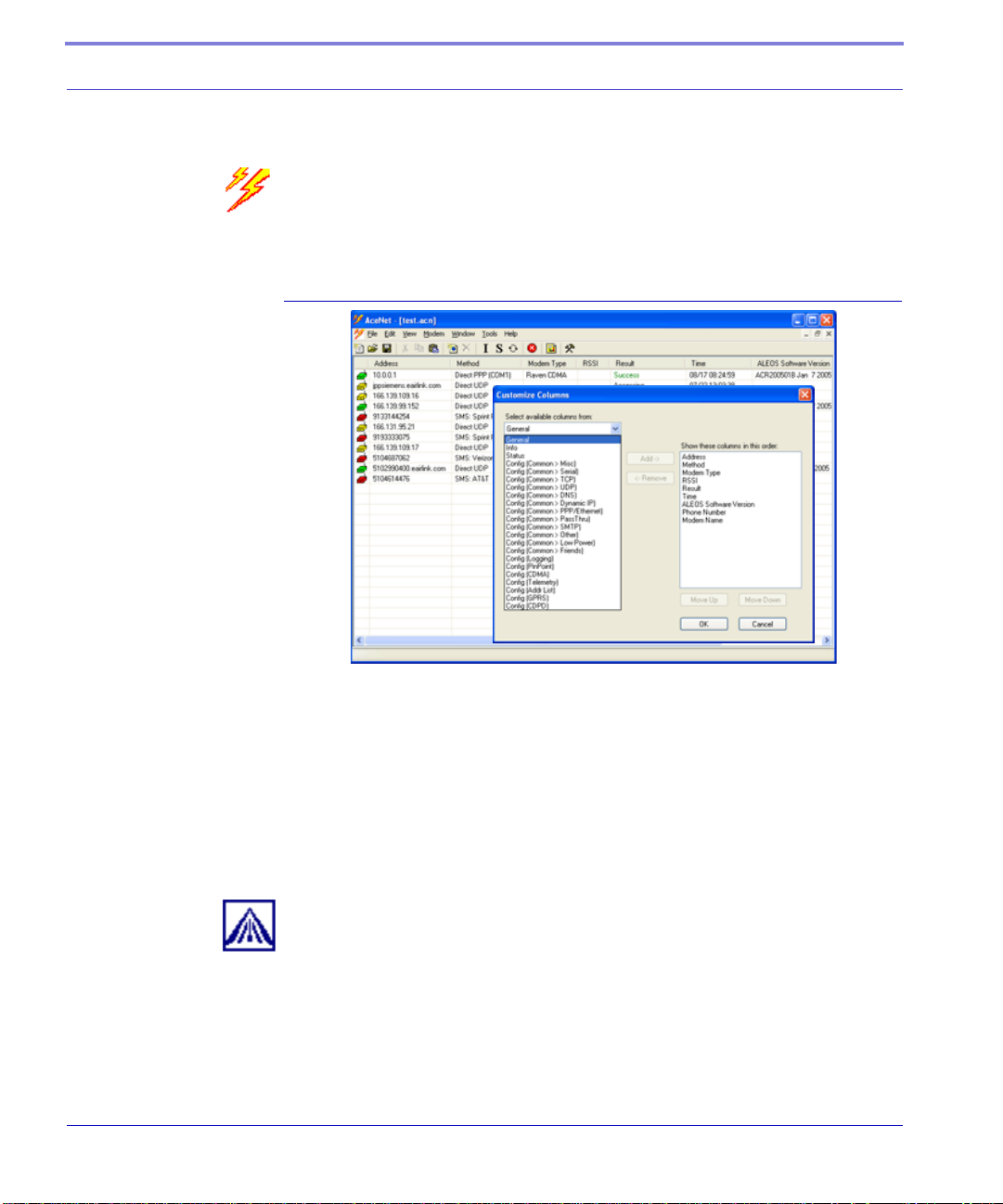
AceNet
With AceNet you can monitor several AirLink modems at the same time. The
modems can be connected locally or remote. Several features can be displayed and
logged. AceNet is a seperate product which can be purchased from AirLink.
FIGURE 2. AceNet
Using a template from Wireless ACE, you can change the configuration in several
modems at the same time and can check and update their firmware as well. AceNet
also features logging to a database and charting for the monitored modems.
With AceNet, you can connect to modems locally or remotely with TCP/IP or
SMS.
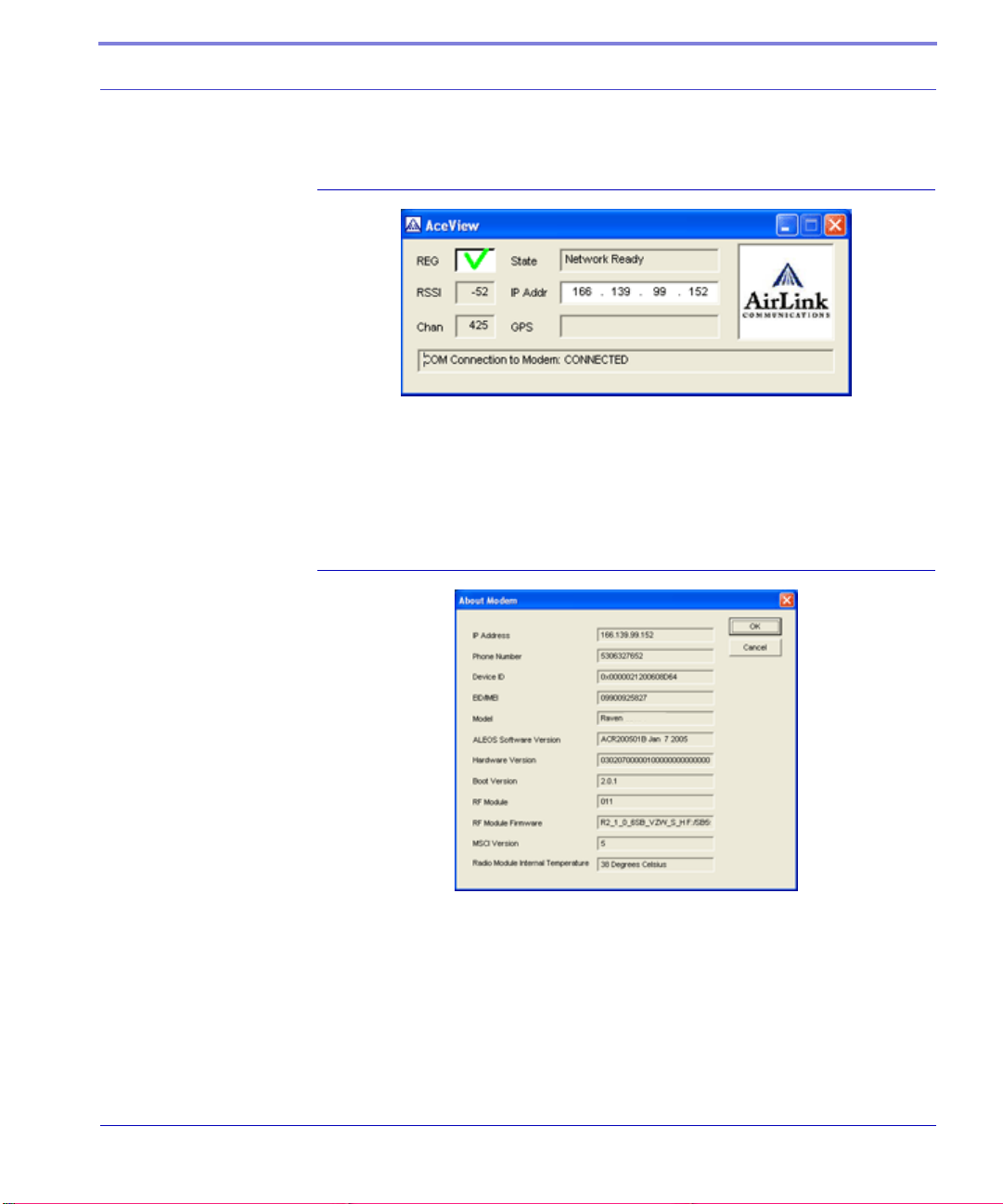
AceView
AceView is a low-profile monitoring tool to view the status of your AirLink Raven
and display network status, IP address, RSSI strength, firmware version, and other
basic information.
12 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 19
Utilities for the Raven
FIGURE 3. AceView
You can connect to your Raven locally or remotely using a known IP address or a
fully qualified domain name. The display is updated periodically as AceView polls
the Raven at a specified interval. GPS is available only for PinPoint and PinPoint-
E modems.
FIGURE 4. AceView: About Modem
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 13
Page 20
Utilities for the Raven
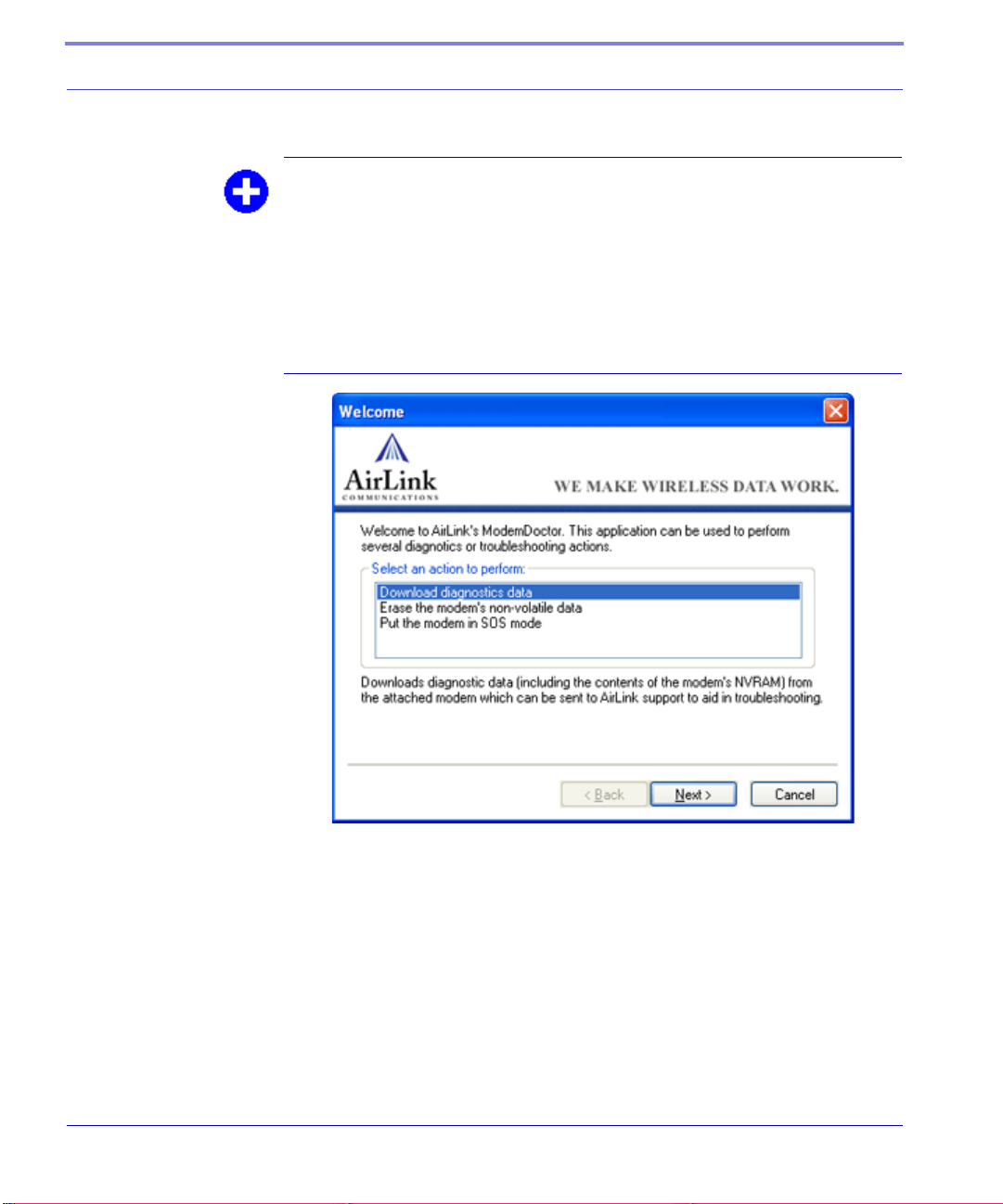
Modem Doctor
Modem Doctor is a troubleshooting utility. This utility will allow you to get a log
file of the Raven activity which you can then send to AirLink support, erase the
current configuration completely, and temporarily set the Raven to a known serial
configuration to aid in trouble shooting.
FIGURE 5. Modem Doctor
14 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 21
CHAPTER 4 IP Manager
IP Manager translates a dynamic IP address to a fully qualified domain name so
you can contact your
Since Wireless Service Providers frequently do not offer static IP addresses, IP
Manager is a free service provided by AirLink for your
dynamic IP address into a fully qualified domain name so it can be contacted
directly on the Internet.
Raven by name as if it had a static IP.
Raven to translate a
• Dynamic IP addresses are granted only when a modem or other device is con-
nected and can change each time the modem or device reconnects to the network.
• Static IP addresses are granted the same address every time the modem or
device is connected and are not in use when the associated device is not con
nected.
A dynamic IP address is suitable for many Internet activities such as web browsing,
looking up data on another computer system, data only being sent out, or data only
being received after an initial request. However, if you need to contact the
directly, a device connected to the modem, or a host system using the Raven, a
dynamic IP won’t give you a reliable address to contact (since it may have changed
since the last time it was assigned).
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 15
-
Raven
Page 22

IP Manager
Fully Qualified Domain Name
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) generally has several parts.
• Top Level Domain (TLD): The TLD is the ending suffix for a domain name
(.com, .net, .org, etc.)
• Country Code Top Level Domain (ccTLD): This suffix is often used after the
TLD for most countries except the US (.ca, .uk, .au, etc.)
• Domain name: This is the name registered with ICANN (Internet Corporation
for Assigned Names and Numbers) or the registry for a the country of the
ccTLD (i.e. if a domain is part of the .ca TLD, it would be registered with the
Canadian domain registry). It is necessary to have a name registered before it
can be used.
• Sub-domain or server name: A domain name can have many sub-domain or
server names associated with it. Sub-domains need to be registered with the
domain, but do not need to be registered with ICANN or any other registry . It is
the responsibility of a domain to keep track of its own subs.
A URL (Universal Resource Locator) is different from a domain name in that it
also indicates information on the protocol used by a web browser to contact that
address, such as http://www.airlink.com.
• .com is the TLD
• airlink is the domain (usually noted as airlink.com since the domain is specific
to the TLD)
• www is the server registered with AirLink.com
• http:// is the protocol (html or web) used to access the webpage for AirLink
Dynamic Name Resolution
When an IP address is not expected to change, the DNS server can indicate to all
queries that the address can be cached and not looked up for a long period of time.
Dynamic DNS servers, conversely, have a short caching period for the domain
information to prevent other Internet sites or queries from using the old informa
tion.
16 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
-
Page 23
IP Manager
If the Raven is configured for Dynamic IP, when the Raven first connects to the
Internet, it sends a IP change notification to IP Manager. IP Manger will acknowledge the change and update the DNS record. The changed IP address will then be
the address for the
Raven’s configured name.
Once the Raven’s IP has been updated in IP Manager, it can be contacted via name.
If the IP address is needed, you can use the domain name to determine the IP
address.
Note: The fully qualified domain name of the Raven will be a
subdomain of the domain used by the IP Manager server.
As a free service, Airlink maintains an IP Manager server which can be
used for any AirLink modem. The domain is earlink.com and is used
in all the samples below.
Configuring the Raven for Dynamic IP
T o configure the Dynamic IP settings in your Raven so that it will use IP Manager,
you can use AT commands (page 53), using direct serial communication or Telnet,
Wireless ACE (
less ACE.
To configure your AirLink modem to be addressed by name, the mo dem needs to
have 4 elements configured.
In Wireless ACE, select Dynamic IP to configure your modem to use IP Manager.
page 10), and ACE Net (page 11) using a template built from Wire-
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 17
Page 24

IP Manager
FIGURE 1. Wireless ACE: Dynamic IP (IP Manager configuration)
1. Modem name: The name you want for the modem.
2. Domain: The domain name to be used by the modem.
3. IP Manager IP Address: The IP or domain name of the dynamic DNS server
which is running IP Manager.
Note: To use the name here instead of the IP, you need to have
DNS set up in your
Raven (page 19).
4. IP Manager update interval: How often you want the address sent to IP Man-
ager. If this is set to zero, the modem will only send an update if the IP changes
(i.e. if the modem is reset or is assigned a different IP).
You can configure a second dynamic server as a backup, secondary, or alternate
server.
Note: For the Modem Name, you should use something which is
unique but also easy to remember. Your company name or the
intended function of the modem are recommended. If you have
more than one modem, you can append a number for each.
Restrictions for Modem Name
• Must begin with a letter or number
• Can include a hyphen (-)
• Cannot contain spaces
• Must be no longer than 20 characters total
18 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 25

IP Manager
DNS: Using Names Instead of IP addresses
A domain name is a name of a server or device on the Internet which is associated,
generally, with an IP address. In a way, a domain name is like the street address of
your house with the phone number being like the IP address. You can contact the
house either by going to the address (name) or by calling the phone number (IP
address).
Domain Name Service (DNS) is a network service which translates, or redirects,
the IP address, allowing someone to contact that address via the name. A DNS
server is registered to handle all addresses of a particular domain (much like the
post office for a particular town or city is known to the post offices of all other
towns and cities and is authorized to give the addresses of locations in its own loca
tion).
Configuring DNS
The Raven has an internal DNS resolver with which it can query DNS servers in
order to translate names into IP addresss which it can then use internally. Generally, when your Raven receives its IP address from Verizon, it will also be configured to use Verizon’s DNS servers to use for resolving (or translating) names to IP
addresses. In that case, the only one which is not overwritten is the alternate DNS.
-
You can use AT commands (page 53), Wireless ACE (page 10), and ACE Net
(page 11) using a template built from Wireless ACE to configure DNS in your
Raven.
FIGURE 2. Wireless ACE: DNS
*DNS1 and *DNS2 - Set these to your primary and secondary DNS servers.
These maybe be overwritten by
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 19
Verizon when your Raven gets its IP address.
Page 26

IP Manager
*DNSUSER - Set this, if desired, to an additional DNS server to query first
before the primary or secondary (just as a hosts file is queried first on a com
puter). If *DNSUSER is set to 0.0.0.0, it will be ignored.
*DNSUPDATE - This command sets how often you want DNS Updates to be
forced. Otherwise the
up, or the IP address granted by the network changes.
Note: If you will be using your Raven to communicate with
another AirLink modem and both are using IP Manager to translate dynamic IP addresss to domain names, it is recommended
that you set *DNSUSER to the IP address for IP Manager. IP
Manager’s updates occur more frequently than
servers decreasing the time between IP address change and
address resolution.
Raven will only send updates when it is reset, powered
Verizon’s DNS
-
PPP-Peer
The Raven uses the unqualified domain name of “ppp-peer” when it is PPP or SLIP
address mode to resolve the address of the device or computer connected via PPP or
SLIP address. If the
resolve to 0.0.0.0.
Raven is not in PPP or SLIP address mode, “ppp-peer” will
20 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 27
CHAPTER 5 Keepalive
It is not uncommon for your Raven to be disconnected from Verizon after an
extended period of inactivity. This is generally a feature intended to reduce your
charges for inactive use.
Keepalive is used to test and maintain the Raven’s connection to Verizon by pinging an IP address after a specified period of inactivity. Keepalive is recommended
for users who have a remote terminated modem that infrequently communicates to
the network. Keepalive is also recommended if you have experienced issues where
the modem can no longer be reached remotely.
When Keepalive pings the IP address, an acknowledgement indicates there is an
active connection to the network. If the modem does not receive a response from
the IP address, it will retry 5 times in 5 second intervals. The
the radio module after 5 failed attempts and reconnect to Verizon.
Raven will then reset
Configuring Keepalive
As with all other aspects of the Raven’s configuration, you can use Wireless Ace
(page 10), AceNet (page 11), direct serial communication (page 53), or Telnet
(page 53) to configure Keepalive.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 21
Page 28

Keepalive
To set the Keepalive using Wireless ACE, select Other from the menu on the left.
FIGURE 1. Wireless ACE: Keepalive Configuration
*IPPING sets the interval, in minutes, you want Keepalive to test the network
connection. To disable Keepalive, set *IPPING to 0 (default setting).
Note: 15 minutes is the minimum time which can be set for Kee-
palive.
*IPPINGADDR sets the IP address you want to use for the test. If *PPINGADDR is left blank or is set to an invalid IP address (i.e. an IP which is
unreachable or one which is not a valid IP address), the modem will reset itself
on a regular interval.
Data usage using Keepalive
When using Keepalive, be aware that a ping moves approximately 66 bytes of data
over the network and is billable by the carrier. The following *IPPING settings
will incur approximate monthly data usage in addition to any other data usage:
15 minutes
30 minutes
60 minutes
120 minutes
22 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
400k / month
200k / month
100k / month
50k / month
Page 29
CHAPTER 6 Host Modes
The Raven plays the part of a host when its serial port is connected to a computer or
another device. As the host, the Raven can be in one of six communication modes.
AT: The Raven accepts and responds to standard, Hayes-style AT commands.
PassThru: Direct connection to internal hardware (OEM Module) of the
Raven.
PPP: The Raven uses PPP to communicate.
SLIP: The Raven uses SLIP to communicate.
UDP PAD: Any data received on the serial port is assembled into UDP packets
and send to the session's associated IP and Port (described later). Any responses
received from the associated IP and port destined for the modem's Device Port
are unwrapped and sent out the
TCP P AD: Any data received on the serial port is packaged into TCP messages
and sent to the associated connection's IP and Port (described later). Any data
received from the TCP peer is unwrapped and sent out the
serial port.
serial port.
By default, the Raven is in AT Mode and allows AT Commands to be entered via
T elnet (through the serial port connection) or remotely (through the cellular network).
The Raven can be programmed to enter any of the modes, except PassThru, automatically on power up. This is done setting the Startup Mode Default (refer to MD
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 23
Page 30
Host Modes
in the AT Command listing, page 66) to the desired mode. If this setting is nonzero, the modem will enter the specified mode after 5 seconds. If you want to cancel this behavior, the ATMD0 command can be used before the 5-second time-out
expires.
If the modem is in any mode other than AT or PassThru, the AT command mode
can be re-entered by:
• Deactivating DTR (if &D2 or Ignore DTR, S211, is not set).
• Issuing the +++ escape sequence (if Disable AT Escape, DAE, is not set).
• Resetting or Power cycling the modem.
PassThru Mode can only be exited by resetting the modem.
Note: DTR needs to be asserted (S211=1 or &D0) by the host
before PPP Mode, SLIP Mode, UDP PAD Mode, or TCP PAD
Mode can be entered.
AT Mode
AT commands are used to configure the modem, command it to do something, or
query a setting. For a full listing of the AT commands, refer to page
AT commands must always be terminated by <CR> (ASCII character 0x0D).
If E=1 (Echo On), the AT command (including the terminating <CR>) will be
displayed (output) before any responses.
Two settings affect the format of AT command output: V (Verbose) and Q (Quiet).
If Q=1 (Quiet On), no result codes are output whatsoever, so there is no
response generated by a (non query) command.
If Q=0 (Quiet Off), result codes are output. The format of this output is then
affected by the Verbose setting.
If Quiet mode is off, the result code is affected as follows:
For V=1 (Verbose mode), the textual result code is surrounded by <CR><LF>
and any AT query response is also surrounded by <CR><LF>.
24 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
53.
Page 31

Host Modes
For V=0 (Terse mode), a numeric result code is output with a single trailing
<CR> (no <LF> is output), while any AT query response is followed by
<CR><LF> (there is no preceding output).
For example, possible output to the AT command "AT<CR>" (assuming quiet
mode is not on) is:
<CR> - if V=0
<CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> - if V=1
PassThru Mode
In PassThru mode, the Raven does not behave normally, all serial port communication is passed directly between the internal hardware and the computer connected
directly to the modem. This mode can be used to configure hardware-specific set
tings (e.g., for provisioning, etc.).
Issuing the "AT\APASSTHRU" enters this mode. The modem responds with OK,
at which point a direct connection to the internal hardware is established.
-
Some internal hardware requires upwards of 20 seconds before AT commands can
be entered, so be patient if there seems to be no response to AT commands.
Caution: PassThru can only be exited by resetting or power-
cycling the modem. This mode cannot be entered via a Telnet
session.
PassThru Mode allows only specific AT commands. Those commands which are
used with ALEOS only will be unavailable. The commands usable also depend
heavily on the modem model number (found on the label on the top of the modem).
Caution: ALEOS is disabled in PassThru Mode. You cannot use
most ALEOS specific commands while the modem is in
PassThru Mode.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 25
Page 32

Host Modes
PPP Mode
In PPP mode, the Raven acts as a PPP server, providing an IP address, and DNS
servers (if available) to the Host.
PPP mode is entered from the AT mode by using any of the following commands:
AT\APPP<CR>
ATDT10.0.0.1<CR>
ATDT10001<CR>
ATD#19788<CR>
CLIENT<CR>
In response to any of the preceding commands, the modem will respond with
CONNECT<CR><lf> and is ready for the host to begin PPP negotiations.
The IP received by the host in the resulting negotiation will either be a private (nonroutable) IP or a public (network-routable) IP provided by the network, depending
on the settings of *HOSTPRIVMODE. If *HOSTPRIVMODE=1, the value of
the private IP an be determined beforehand by querying S110. The private IP to be
used can be defined with the command AT*HOSTPRIVIP=192.168.100.33 sub
stituting the desired IP address.
-
AT*HOSTPRIVIP=192.168.100.33Using a private IP insulates the PPP client
from changes in IP addresses of the underlying network. The
basic NAT-like address translation on all packets.
If a public IP address is being used, any changes in the IP (as determined by the
wireless network) will result in the PPP link to the host being disconnected, requir
ing the host to reinitiate it. The public IP is passed to the host in the PPP negotiations, so when the network forces a change, the modem has to force the host to
renegotiate the PPP link to make this happen.
Slip Mode
SLIP mode is entered be using the "AT\ASLIP" command. As in PPP Mode, the IP
address that the host assumes is affected by the setting of *HOSTPRIVMODE.
26 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Raven will perform
-
Page 33

Host Modes
SLIP does not negotiate the IP with the host, so before making a SLIP connection,
the host SLIP driver must be configured to use the IP specified by querying S110.
UDP Pad Mode
When the modem is in UDP PAD (Packet Assembly and Disassembly) Mode, all
characters received on the
the Raven’s remote IP address/port, and any packets received from the same IP/
port-destined for the Raven’s Device Port (see *DPORT)--are disassembled and
dumped onto the serial line.
A UDP session is initiated by one of the following events:
• Using the Dial UDP (DP) AT command (ex. ATDP192.168.3.23/3456)
• Setting the Startup Mode Default (MD) to 3 (UDP) so that a UDP session is
entered automatically when the modem powers up. Serial data will be sent to
the IP/port specified in S53.
• An incoming UDP packet is received and
• UDP auto answer is enabled (S82=2);
• The destination IP address matches that in S53;
• Or allow any IP is set (AIP=1);
• The modem is in AT mode (not in a current UDP or TCP session).
serial port are assembled into UDP packets and sent to
• • • • UDP packet assembly is affected by the values of S50 (PAD Forwarding
Time-out) and S51 (PAD Forwarding Character). Data received in the serial buffer
will be transmitted when the idle inter-character time-out specified in S50 (in tenths
of seconds) occurs or when a character is received that matches S51 (if non-zero).
UDP Auto Answer
UDP auto answer (previously called UDP half-open) is set with S82=2. When set,
the
Raven will automatically establish a UDP session to the source IP address and
port of the UDP packet received. The Raven will remain "locked" to this one
remote IP/port until no data is sent or received for the time interval defined in the
UDP auto answer time-out (S83). During this session, packets from other IP/port
addresses will be rejected, unless *UALL is set. Whether or not an incoming
packet will cause the modem to enter a UDP session is always dependent on the
S53 and AIP settings.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 27
Page 34

Host Modes
When idle, after the time-out has occurred, the Raven is in AT command mode on
the serial port, and any valid AT command may be entered during this time.
The Normal UDP Mode (MD3) can be combined with UDP auto answer to cause
the incoming serial data to be sent in UDP packets (instead of being treated as AT
commands), while allowing sessions to be established from different UDP sources.
A UDP session will be initiated either by incoming serial data or by an incoming
UDP packet. The session, started by either method, will be terminated when no data
has been sent or received for the S82 period. Once the session terminates, another
may be initiated by either means.
When the session is initiated by serial data, the new session will be established
using the destination address specified in S53. The S53 setting can be changed if
the connect to last UDP setting (*UDPLAST=1) is set. The address in S53 will be
updated to reflect the address of the last session initiated by an incoming UDP
packet. So that when new data is received over the host
state, a session will be re-established with the last address. (This behavior is the
same as the previous Hybrid2 (MD6) mode).
Note: TCP auto answer (S0) may also be set simultan eously with
UDP auto answer. Then, when in the idle state, the modem will
accept either a TCP or UDP incoming packet, and enter a TCP
or UDP session as appropriate.
serial port while in the idle
Reliable UDP
Reliable UDP adds a simple protocol on top of UDP to provide reliable deli v e ry of
data. When data is received from the host
data, containing a message type and a sequence number. The Raven will continue to
send this data (buffering any received data in the meantime) until it receives an
acknowledgement with this sequence number. If an acknowledgement is not
received within the time-out period (specified in S7), the data will be retransmitted.
This will continue until an acknowledgement is received or the modem is reset.
Likewise any UDP packets received by the
header. The Raven will issue an acknowledgement for any valid packets which are
received.
Configure the Raven as for a normal UDP session. Set the Startup Mode Default to
3, and the UDP Mode Default to 7 (ATMD73). If using two modems, configure the
Destination IP and Port in each to point to each other. Serial data will then be sent
reliably between the two
serial port, a 2 byte header is added to the
Raven are expected to have this simple
28 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 35

Host Modes
Note: Although it adds reliability, the simple implementation of
the Reliable UDP mode in the
cate packets.
Raven does not check for dupli-
Multicast UDP
Multicast UDP results in any data received from the host serial port being sent to all
the clients in the Modbus list. The remote port number is taken from S53. To avoid
flooding the network, the packets are sent to each client with a 20ms pause in
between. The receipt of UDP packets works as in normal UDP mode (i.e. bound by
the value S53 and/or AIP). Since it may take a while to transmit the data to all hosts
(especially if all 20 Modbus entries are used and name resolutions are required),
new data received from the host port is buffered until current transmissions to all
hosts are finished.
Enter the list of target IPs in the Modbus IP list. The index numbers in the IP list
aren't used. Configure the Raven as for a normal UDP session. Set the Startup
Mode Default to 3, and the UDP Mode Default to 8 (ATMD83). Configure the
Destination port to match the device port of the remote modems.
TCP PAD Mode
When the Raven is in a TCP session, all characters received on the serial port are
assembled into TCP packets and sent to the mode's remote IP address/port, and any
packets received from the remote end of the TCP connection are disassembled and
dumped onto the serial line.
• A TCP connection is established by one of the following methods:
• Using the Dial TCP (DT) AT command (for example, ATDT192.168.3.23/
3456)
• TCP auto answer is enabled (S0), a TCP connection request is received, and the
modem is not in a data session.
• Data is received on the serial port and
• The Startup Mode Default (MD) is 4 (auto TCP)
• The remote TCP destination, as defined in S53, successfully responds to the
TCP connection request.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 29
Page 36

Host Modes
The value of S7 (TCP Connection Time-out) specifies the number of seconds to
wait, after initiating a TCP connection attempt, for a successful connection to be
established. If the connection has not been successfully established before the timeout occurs, ERROR/BUSY is returned.
TCP packet assembly is affected by the values of S50 (PAD Forwarding Time-out)
and S51 (PAD Forwarding Character). Data received in the serial buffer will be
transmitted when the idle inter-character time-out specified in S50 (in tenths of sec
onds) occurs or when a character is received that matches S51 (if non-zero).
The TCP session will be terminated if no data is transmitted or received for the time
interval specified in TCPT and TCPS. TCPT is the number of minutes (TCPS=0)
or seconds (TCPS=1) used for this idle time-out.
Caution: TCPT should never be 0 when using the TCP mode. A
broken TCP session can result in the modem being left with a
TCP half-open connection that can only be terminated with a
reset.
-
TCP Auto Answer
TCP auto answer (S0=1|2) also allows a TCP connection request to be "answered"
when the modem is idle, not in a data session. The TCP connection request's desti
nation port has to match the modem's device port.
Note: UDP auto answer may also be set simultaneously with
TCP auto answer. Then, when in the idle state, the modem will
accept either a TCP connection request or UDP incoming
packet, and enter a TCP or UDP session as appropriate.
Hybrid Modes
Some previous hybrid modes (MD=5, 6) are no longer implemented as special,
unique modes. Now that UDP auto answer (UDP Half-open, S82=2) can be
enabled in conjunction with UDP P AD mode (MD3), effectively this is the same
30 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
-
Page 37

Host Modes
as MD5 and MD6 previously accomplished. Setting MD5 and MD6 are still sup-
ported, but not recommended.
TABLE 1. Hybrid Mode Settings
AT Hybrid (MD5) Hybrid2 (MD6)
MD 3 3
S82 2 2
S0 1 1
*UDPLAST 0 1
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 31
Page 38

CHAPTER 7 Modbus/BSAP
Configuration
The Raven supports Modbus ASCII, Modbus RTU, BSAP, and can also emulate
other protocols like DF1 or others using its Modbus Variable feature.
Modbus Overview
The Modbus Protocol, developed by Modicon in 1979, provides for client-server
(also referred to as master-slave) communications between intelligent devices. As
a de facto standard, it is the most widely used network protocol in the industrial
manufacturing environment to transfer discrete/analog I/O and register data
between control devices.
Modbus, BSAP, and other Modbus variations are often used in conjunction with
telemetry devices.
This section is just a brief overview of Modbus. For more information, refer to your Modbus equipment distributor or manufacturer or http://www.modbus.org.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 32
Page 39

Modbus/BSAP Configuration
Telemetry
T elemetry is an automated communications process by which data is collected from
instruments located at remote or inaccessible points and transmitted to receiving
equipment for measurement, monitoring, display, and recording. Transmission of
the information may be over physical pairs of wires, telecommunication circuits,
radios or satellite.
Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)
Modbus was originally designed to be used in a radio environment where packets
are broadcast from a central station (also called master or host) to a group of remote
units. Each remote unit, Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) , has a hexidecimal identifi
cation number (ID). The first part of the broadcast packet contains an RTU ID
which corosponds to the ID of one of the remote units. The Modbus host looks for
the ID and sends to only the unit with the matching ID. The RTU would then reply
back to the central station.
The RTU connects to physical equipment such as switches, pumps, and other
devices and monitors and controls these devices. The RTU can be part of a net
work set up for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition.
-
-
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) describes solutions across a
large variety of industries and is used in industrial and engineering applications to
monitor and control distributed systems from a master location. SCADA encom
passes multiple RTUs, a central control room with a host computer (or network),
and some sort of communication infrastructure.
SCADA allows for “supervisory” control of remote devices as well as acquiring
data from the remote locations. Pro grammable Logic Controllers allow for a higher
degree of automated SCADA.
-
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a small industrial computer which generally monitors several connected sensor inputs and controls attached devices
(motor starters, solenoids, pilot lights/displays, speed drives, valves, etc.) according
to a user-created program stored in its memory. Containing inputs and outputs sim
ilar to an RTU, PLCs are frequently used for typical relay control, sophisticated
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 33
-
Page 40

Modbus/BSAP Configuration
motion control, process control, Distributed Control System and complex networking.
Modbus TCP/IP
Modbus TCP/IP simply takes the Modbus instruction set and wraps TCP/IP around
it. Since TCP/IP is the communications standard for the Internet and most net
worked computers, this provides a simpler installation. Modbus TCP/IP uses standard Ethernet equipment.
-
Raven Modbus on UDP
When Ravens are used in place of radios, a Raven is connected to the central station
(host) and a Raven is connected to each remote unit. When the Raven is configured
for Modbus with UDP, the Raven connected to the host can store a list of IP
addresses or names with matching IDs. When the host at the central station sends
serial data as a poll request, the Raven at the host matches the RTU ID to a corre
sponding IP of a Raven at a remote unit. A UDP packet is assembled encapsulating
the RTU ID and serial data transmitted from the host. The UDP packet is then
transmited to the specific Raven at the remote unit matching the RTU ID. The
remote Raven then disassembles the packet before transmiting the RTU ID and
serial data to the remote unit. The remote units operate in normal UDP mode and
their data is sent to the host via the remote Raven and host Raven.
-
FIGURE 1. Automation and Telemetry
34 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 41

Modbus/BSAP Configuration
Configuring the Raven at the Polling Host for Modbus on UDP
You can use either Wireless ACE (page 10) or direct serial communication or Telnet (page 53) to configure the modem using AT commands (page 53). This section
covers standard Modbus, variations may need additional commands.
Port
The destination port for the Raven at the host needs to match the device port in use
on all the Ravens at the remote sites. For example, if the remote Raven’s device
port (see below) is "12345", then the Modbus host Raven's S53 destination port
should be set to "12345".
In Wireless ACE, select Misc in the side menu.
FIGURE 2. Wireless ACE: Destination Port
Take note of (or set) the Device Port setting in *DPORT to configure the remote
Ravens.
Relevez ou réglez (le cas échéant) le numéro du port Device des modèles Raven
distants à l'aide de la commande *DPORT.
FIGURE 3. Wireless ACE: Device Port
Default Power-up Mode
The default power-up mode will need to be set. In Wireless ACE, select UDP in the
side menu. Select the appropriate MD (AT commands: page
drop down menu.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 35
66) mode from the
Page 42

Modbus/BSAP Configuration
FIGURE 4. Wireless ACE: MD Configuration
• ATMD13: Modbus ASCII
• ATMD23: Modbus RTU (Binary)
• ATMD33: BSAP
• ATMD63: Variable Modbus (individual parameters are set up manually)
IDs to IPs
The last step of configuring the Raven at the host is setting the IDs to their specific
IPs. In Wireless ACE, select the menu option Addr List.
FIGURE 5. Wireless ACE: Addr List
Addresses can be entered in decimal or hex. Wireless ACE will translate hex
entries into decimal. The number before the “=” is ID, the number after is the IP
address. There can be a total of 100 remote ID/Local addresses entered into the
Raven.
When using AT commands via telnet or direct serial connection, use ATMLIST for
decimal IDs and ATMLISTX for hexidecimal, ex. if the ID is 27 and the IP is
123.123.123.124, you would enter it as ATMLIST27=123.123.123.124 or
ATMLISTX1B=123.123.123.124.
Dynamic IP
If you do not have a static IP, the host Raven should be configured to report its current IP to a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) server (IP Manager: page 15).
36 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 43

Modbus/BSAP Configuration
In the Host Raven’s configuration, instead of IP address for the Addr List (ATMLIST or ATMLISTX), substitute a single unique name fo r each modem, i.e.
remote1, remote2, etc.
When you configure IPManager for the host Raven, make note of your modem
name and domain setting in W ire less ACE in the menu select ion Dynamic IP to be
used with the remote modems.
Lors de la configuration de IPManager pour le modèle Raven raccordé à l'hôte,
dans Wireless ACE, relevez le nom du modem ainsi que le nom de domaine corre
spondant à l'aide de l'option de menu Dynamic IP.
FIGURE 6. Wireless ACE: Modem Name and Domain
-
With names instead of IPs for the Address List, the host Raven will query the DNS
server for the current IP assigned to the specific name of a remote Raven to send a
message coroponding to the ID.
Configuring the Remote Ravens for Modbus with UDP
You can use either Wireless ACE (page 10), direct serial communication or Telnet
(page
53) to configure the modem using AT commands (page 53). This section
covers standard Modbus, variations may need additional commands.
Port
The destination port for the Raven at the host needs to match the device port in use
on all the Ravens at the remote sites. For example, if the remote Raven’s device
port (see below) is "12345", then the Modbus host Raven's S53 destination port
should be set to "12345".
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 37
Page 44

Modbus/BSAP Configuration
In Wireless ACE, select Misc in the side menu. Set the destination port (S53) to
match the device port of the host Raven (*DPORT, above). Make sure the device
port of the remote Raven (*DPORT) matches the destination port of the host
Raven (S53, above).
Default Power-up Mode
Each Raven at the remote locations will need to be configured to communicate with
the Raven at the host. In Wireless ACE, select UDP in the side menu. Select 03-
UDP (normal UDP operation) as the value for MD.
FIGURE 7. Wireless ACE: UDP Power-up Mode
Host Raven IP
If the Host Raven has a static IP, enter it in the Destination Address for S53. In
Wireless ACE, select Misc in the side menu.
FIGURE 8. Wireless ACE: Destination IP
Dynamic IPs
If you do not have static IPs, the remote Ravens need to be configured to report
their current IPs to a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) server (IP Manager: page
will need to match the name of the Raven to the names specified in the host Raven’s
MLIST or MLISTX for the connected RTU.
Instead of an IP, for S53, specify the name of the host Raven (*MODEMNAME).
If the remote Ravens are using a different DDNS than the host Raven, you will
need to specify the fully qualified domain name (*MODEMNAME+*DOMAIN).
With a name instead of IPs for the host Raven, the remote Ravens will query the
DNS server for the current IP assigned to the host Raven before sending data back
to the host.
38 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
15). You
Page 45

Modbus/BSAP Configuration
RTU settings
Other parameters may need to be changed, but this is dependent on the RTU type
being used. As a minimum, this typically involves setting the proper serial settings
to match your RTU.
FIGURE 9. Raven mounted in an enclosure with an RTU
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 39
Page 46

Modbus/BSAP Configuration
FIGURE 10. RTU to Raven setup
FIGURE 11. Power Connections
40 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 47

CHAPTER 8 Simple Network
Management Pr otocol
(SNMP)
The Raven can be configured as an SNMP agent and supports SNMPv2c and
SNMPv3.
SNMP Overview
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) was designed to allow remote
management and monitoring of a variety of devices from a central location. The
SNMP management system is generally composed of agents (such as your
router, a UPS, a web server, a file server, or other computer equipment) and a Network Management Station (NMS) which monitors all the agents on a specific network. Using the management information base (MIB), an NMS can include
reporting, network topology mapping, tools to allow traffic monitoring and trend
analysis, and device monitoring.
Authentication ensures SNMP messages coming from the agent, such as the Raven,
have not been modified and the agent may not be queried by unauthorized users.
SNMPv3 uses a User-Based Security Model (USM) to authenticate and, if desired
or supported, message encryption. USM uses a user name and password specific to
each device.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 41
Raven, a
Page 48

Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Management Information Base (MIB)
The management information base (MIB) is a type of database used to compile the
information from the various SNMP agents. Reports from various agents, such as
the
Raven, are sent as data in form designed to be parsed by the NMS into its MIB.
The data is hierarchical with entries addressed through object identifiers.
SNMP Traps
The trap is a “snap-shot” of the settings and status of the Agent’s device which is
sent as a report to the NMS in a form that can be parsed and stored in the MIB. For
an example of the trap from an AirLink modem refer to the Append ix,
page 91.
Raven SNMP Configuration
To configure your Raven to work as an SNMP agent, you can use either Wireless
ACE, direct serial communication or T elnet to configure the modem using AT commands (page 53). In Wireless ACE, the SNMP commands are all on the Other
menu option.
There are only three commands to set for SNMP in the Raven: the listening port,
the security level, and the trap destination.
Listening Port
*SNMPPORT sets the port for the SNMP agent to listen on. If set to zero, default,
SNMP is disabled.
FIGURE 1. Wireless ACE: *SNMPPORT
Note: SNMP generally uses port 161, however most Internet pro-
viders (including cellular) block all ports below 1024 as a security measure. You should be able to use a higher numbered port
such as 10161.
42 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 49

Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Security Level
*SNMPSECLVL sets the security level and which version of SNMP communications are used.
FIGURE 2. Wireless ACE: *SNMPSECLVL
0 - No security required. SNMPv2c and SMNPv3 communications are allowed.
1 - Authentication required. SNMPv3 is required to do authentication and
SNMPv2c transmissions will be silently discarded. Authentication is equivalent
to the authNoPriv setting in SNMPv3.
2 - Authentication required and messages are encrypted. SNMPv3 is required
to do authentication. SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 authNoPriv transmissions will be
silently discarded. Authentication and encryption is equivalent to the authPriv
setting in SNMPv3.
User Name and Password
The user name is 'user'. The user name cannot be changed.
The Raven's password is used as the SNMP password (default is '12345').
Note: The eight-character password requirement for SMNPv3 is
not enforced by the
to function. Your SNMP administrator or MIS may require you
to change to a more secure and/or longer password.
To change the password in the Raven, select Modem from the top menu line in
Wireless ACE.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 43
Raven's Agent to allow the default password
Page 50

Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
FIGURE 3. Wireless ACE: Changing the Raven Password - Menu Option
The current password will be pre-entered. As you type the new password and confirm it, the characters you type will be obscured by “x”.
FIGURE 4. Wireless ACE: Changing the Raven Password
For the password, you can use numbers, letters, and/or punctuation.
Caution: The password is case sensitive. “drowssaP” is not the
same as “drowssap”.
44 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 51

Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Trap Destination
*SNMPTRAPDEST needs to be set with the destination IP and port. If either are
set to zero or empty, SNMP traps are disabled.
FIGURE 5. Wireless ACE: *SNMPPORT
Note: Traps are sent out according to the SNMP security level
(i.e. if the security level is 2, traps will be authenticated and
encrypted). Currently, the only trap supported is LinkUp.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 45
Page 52

CHAPTER 9 Har dwar e Installation
Y our AirLink Raven should be mounted in a position that allows easy access for the
cables so they are not bent or constricted. The LEDs on the front panel should be
visible for ease of operational verification. You should ensure that there is adequate
airflow around the modem but that it is kept free from direct exposure to the ele
ments (sun, rain, etc.). The exterior of the case should also be grounded.
An optional accessory for your modem is a mounting kit. The bracket is designed
to snugly cradle the modem and hold it in place where you need it.
Kit” on page 51.
-
See “Mounting
Connecting the Antenna
Your Raven will work with most standard cellular antennas with a TNC connector
and rated to work with CDMA technology. Connect the antenna or RF cable
directly to the TNC connector on the back of the Raven.
FIGURE 1. Raven connecters
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 46
Page 53

Hardware Installation
Connecting power
Your Raven can be used with either DC (available in most automobiles) or 110 AC
(standard US wall power) with the appropriate power adapter (available from AirLink).
The power cable positive lead should be connected to the battery or power source
positive terminal. The power cable negative lead should be connected to the battery
or power source negative terminal. The
breaker that opens at 0.5 to 1.0 amps of current.
Raven has an internal polysilicon circuit
Connecting the Raven to a computer or other device
Your Raven’s serial port can be connected directly to most computers or other
devices using a standard straight through cable. If you have a DCE device, you will
need a null modem or null modem cable. Raven
Your Raven can also be connected to a USB to serial device connected to a computer or other device which does not hav e an available serial port but does have
USB.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 47
Page 54

APPENDIX 1 Specifications for the
Raven CDMA
Physical Characteristics:
• Weight: < 1 lb.
• Size: 3” x 1.1” x 5.1"
• RF Antenna Connector: 50 Ohm TNC
• Serial Interface: RS232 DB-9F with 1200-115200 bps
• Status LEDs
Data Services & RF Features: CDMA
• Full duplex transceiver
• Dual-band support for both 800 MHz cellular and 1.9 GHz PCS bands
• Dual band Receive Diversity
• Adheres to CDMA authentication as specified in CDMA2000 1X
• 224 mW RF output (+23.5 dBm)
• Data rates up to 153.6 kbps (forward channel) and 76.8 kbps (reverse channel)
Environmental:
• Operating ranges: -30°C to +70°C
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 48
Page 55

• Humidity: 5%-95% Non-condensing
Power Management:
• Low power consumption
• Dormant connection (idle for 10-20 seconds): at 12 VDC
• Input Voltage: 10 VDC to 28 VDC
• Input Current: 20 mA to 350 mA
• Low power mode: at 12 VDC
Power consumption
Modem Idle Transmitting
Raven C3211 50 mAh 200-300 mAh
Raven C3210 50 mAh 250-300 mAh
Serial Port Pin-outs
The cable between the modem and a computer or other serial device needs to be
wired straight-through (pin 1 goes to pin 1, pin 2 to pin 2, etc).
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 49
Page 56

50 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 57

APPENDIX 2 Mounting Kit
An optional accessory for your modem is a mounting kit. The bracket is designed
to snugly cradle the modem and hold it in place where you need it.
The Raven “snaps” into place in the bracket locking into the grooves on the Raven
case. The bracket can be further secured with a twist-tie set into the grooves on the
top for situations where the modem may be subjected to violent movement, such as
in the back of an automobile. In most stationary installations, such as in a field or
pipe, the
Raven and bracket shouldn’t require a twist-tie.
The bracket can be attached to the location using #6 screws (mounting hole diameter approximately 0.150").
FIGURE 1. Raven Mounting Bracket, part number 100-170-1009 A
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 51
Page 58

52 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 59

APPENDIX 3 A T Commands
Just as with a Hayes compatible analog modem, the Raven parameters can all be
configured with AT commands.
Using Wireless Ace
Wireless ACE is a graphical interface for the AT commands and it is highly recommended that you this utility to modify any parameters, however a terminal emulation application, such as Telnet, see below, can be used instead.
With Wireless ACE, you only need to find the command listed and then enter the
new value in the space provided. For those commands which have specific param
eters, the choices will be in a drop down menu.
Note: Nearly all examples of entering commands in this User
Guide are using Wireless ACE.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 53
-
Page 60

FIGURE 1. Wireless ACE: Using AT Commands
To set or commit the changes in the modem, use the Write button at the top of
Wireless ACE interface.
FIGURE 2. Wireless ACE: Toolbar
For more information on using Wireless ACE 3G or Wireless ACE Web, please
refer to the Wireless ACE 3G User Guide.
Note: Some of the AT Commands are not able to be configured
in Wireless ACE 3G.
With Wireless ACE, you can create a template from one modem and
then use that template to configure other modems in the exact same
way. You can use a in AceNet, too, to configure several modems the
same all at once.
Using Telnet Terminal Emulation
It is possible to communicate with the Raven across a TCP/IP network. Telnet provides a terminal style connection to the Raven.
Most installations of Microsoft Windows come with a version of HyperTerminal
(used here for specific directions), but you can use any other Telnet application,
such as Putty.
54 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 61

Start>All Programs>Accessories>Communications>HyperTerminal
1. Choose a name for your connection, such as Raven or AirLink. The name and
icon are only for your own reference so you can find the connection at a later
date (if you want to have a connection saved for both local and remote, it is rec
ommended the connection name reflect the connection type, i.e. Raven
Remote).
FIGURE 3. HyperTerminal: Connection Name
2. Select TCP/IP (Winsock) for Connect Using. Then, if the modem is connected
directly to your computer’s Ethernet port, put in the host address of
192.168.13.31 or the *HOSTIP. If the modem is remote, the host address will
be the current Internet IP of the Raven. Change the port number to 2332
(default telnet port for the Raven).
FIGURE 4. HyperTerminal: TCP/IP Settings
-
3. When HyperT erminal connects to the Raven, you may be prompted for a pass-
word. The default password is 12345. When you press Enter, you should get
back a reply of “OK”.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 55
Page 62

FIGURE 5. HyperTerminal: AT mode via Telnet
4. Type AT and press Enter. You should get a reply of “OK” or “0”.
5. To see what you are typing as you type it, you will need to turn on the echo and
verbose mode. Type ATE1V1 and press Enter.
If you get a reply of “OK”, then you entered the command successfully. If you get
a reply of “0” or “ERROR”, try entering the command again.
Direct Serial Connection
Using HyperTerminal included with most installations of Microsoft Windows:
Start>All Programs>Accessories>Communications>HyperTerminal
1. Choose a name for your connection, such as Raven or AirLink (if you want to
have a connection saved for both local and remote, it is recommended the con
nection name reflect the connection type, i.e. Raven local). The name and icon
are only for your own reference so you can find the connection at a later date.
FIGURE 6. HyperTerminal: Connection Name
56 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
-
Page 63

2. Select COM1 for the Connect Using.
FIGURE 7. HyperTerminal: Comport Setting
3. Change the Bits per Second to 115200 (default), Data Bits to 8, Parity to
None, Stop Bit s to 1, and Flow Control to Hardware.
FIGURE 8. HyperTerminal: Comport Settings
4. Type AT and press Enter. You should get a reply of “OK” or “0”. .
5. To see what you are typing as you type it, you will need to turn on the echo and
verbose mode. Type ATE1V1 and press Enter.
6. If you get a reply of “OK”, then you entered the command successfully. If you
get a reply of “0” or “ERROR”, try entering the command again.
AT Command Tables
The tables below list the AT commands, their parameters, and explain what they do.
• For most commands, you need to preface the command with AT (exceptions are
noted), i.e. ATA which listed as A
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 57
Page 64

• Some commands have specific parameters while other commands will take
whatever your type.
• Acceptable parameters and/or specific formats are in the parameters column.
• Required variable parameters are denoted with italicized text, ex. Dn. The n is
variable and noted in the parameters column.
• Optional parameters are denoted with square brackets [ ].
• Most commands with parameters can be entered with ? to read the current value
(for example, AT&D? will respond with “2” if the default has not been
changed).
• AT Commands are not case sensitive. A capital “E” is the same as a lower-case
“e”.
• If you enter a command which is recognized by the Raven, it will respond with
“OK”. If the command is not recognized, the response will be “ERROR”.
• Those commands applicable only to certain model numbers of the Raven will be
noted in the command column.
Caution: Symbols listed with commands, such as *, /, &, or ?,
are part of the command and must be included. Commands with
symbols other than * may require PassThru mode.
Note: Some commands may be presented on more than one
table.
Information Commands
Most of the Commands in the “Information and Status” table, only, do not have any
parameters. They only provide information. These commands are repeated else
where in their respective categories as well.
58 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
-
Page 65

TABLE 1. Information and Status
Command Details
I[n]
&V View active profile (the contents of the active registers).
*HOSTMODE?
*NETCHAN? The current active CDMA channel number.
*NETERR? The EVDO or CDMA network frame error rate.
*NETIP? The current IP address of the modem reported by the
*NETOK Checks the CDMA network connection.
*NETPHONE? The modem's phone number (if applicable or obtainable).
*NETRSSI? The current RSSI (Receive Signal Strength Indicator) of
n=0 Product name (for example, Raven).
n=1 The Raven’s firmware (ALEOS) version, hardware
ID, and copyright.
n=2 The internal hardware's firmware version and relevant
hardware ID.
n=3 The hardware module's unique ID (ESN).
n=5 View active profile (the contents of the active regis-
ters).
The current host mode (AT, PPP, UDP, etc.). If the Raven
is not in AT mode, telnet into the modem to execute this
command.
embedded OEM module (generally obtained from Car
rier). This is the address to which packets can be sent in
order to contact the
there is no current network IP, 0.0.0.0 may be displayed.
Use *NETALLOWZEROIP if you need to allow the dis-
play of an IP ending in a zero .
OK if connected.
ERROR if not connected.
the
Raven as a negative dBm value.
The same information is displayed with the command
S202?.
Raven from the Internet. Note: If
-
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 59
Page 66

TABLE 1. Information and Status
Command Details
*NETST ATE? The current network state:
Connecting T o Network = The Raven is in the process of
trying to connect to the CDMA network.
Network Authentication Fail = Authentication to the
CDMA network has failed. Verify settings to activate the
Raven.
Network Negotiation Fail = Network connection negotiation failed. This is usually temporary and often clears up
during a subsequent attempt.
Network Ready = Raven is connected to the CDMA net-
work and ready to send data.
Network Dormant = Raven is connected to the CDMA
network, but the link is dormant. It will be woken up when
data is sent or received.
No Service = There is no CDMA network detected.
Hardware Reset = The hardware module is being reset.
This is a temporary state.
*SMTPSTATUS? The status of the last issued SMTP messa g e
(*SMTPSEND). If no status is available 0 is returned.
Once read, the status is cleared.
The status codes are received from the SMTP server the
modem attempted to send the request. Example: 354 =
send in progress, 250 = sent ok.
*SNTPQUERY? The current SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) time
and date.
+ECIO? The EC/IO value.
+PRL? Preferred Roaming List (PRL) version. Version de la PRL
(Preferred Roaming List, liste des partenaires d'itinéranc e).
TABLE 2.
For most of the commands in the rest of the tables, you can query the current status
of the associated register by substituting a “?” for any parameters, omitting the “=”
if there is one, i.e. for the command *DPORT=n, you would enter AT*DPORT?.
60 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 67

Basic Commands These commands are common to most communication devices using AT Com-
mands.
TABLE 3. Basic Commands (common AT commands)
Command Parameters Details
+++
The "+" is ASCII 0x2B.
A/ none Re-execute last command.
A none Answer - manual
DAE=n n=0 or 1 Disable AT Escape Sequence detection.
En n=0 or 1 Toggle AT command echo mode.
Hn n=1 Hang-Up Command.
O none Online (Remote): Causes the Raven to go from Com-
none AT Escape sequence.
Not proceeded by AT.
If the Raven is in a data mode (any mode other than
PassThru), this command causes the modem to re-enter
AT command mode.
There must be an idle time (set by S50) on the serial port
before and after this command.
The detection of +++ is disabled if DAE=1.
Not proceeded by AT.
0 : Enable +++ AT escape sequence detection.
1 : Disable +++ AT escape sequence detection.
0 : Echo Off
1 : Echo On
1: Hang-up
Note: With an AT telnet connection, this command will
terminate the host data mode and return the Raven to an
AT mode.
mand State to data state.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 61
Page 68

TABLE 3. Basic Commands (common AT commands)
Command Parameters Details
Qn n=0 or 1 The AT quiet-mode setting. If quiet mode is set, there
will be no responses to AT commands except for data
queried.
0 : Off (Default)
1 : Quiet-mode on
Vn n=0 or 1 Command Response Mode.
0 : Terse (numeric) co mmand responses
1 : Verbose command responses (Default).
Xn n=0 or 1 Extended Call Progress Result mode.
0 : Turn off extended result codes (Default).
1 : Turn on result codes. This adds the text 19200 to the
CONNECT response.
Z none Reset the Raven.
Note: This command does nothing if *DATZ=1.
&F none Restore Factory Setting.
&W none Write s all changed modem settings. If this command is
not issued, any modified values will revert back to their
previous values at modem reset.
*DATZ=n n=0 or 1 Enables or disables reset on ATZ.
0 : Normal Reset (Default)
1 : Disable Reset on ATZ
Activation
The preferred method of activating (provisioning) the modem is using the Setup
Wizard. However, there are special circumstances when commands may be used
instead.
Caution: You may need go into PassThru mode to use some of
the commeands in this section to activate the Raven.
62 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 69

TABLE 4. Activation (Provisioning)
Command Parameters Details
OPRG=n n=0 or 1 Enables/disables over-the-air firmware upgrading of the
Raven.
0 : Disables over-the-air programming.
1 : Enables over-the-air programming.
*DEVICEID=n n=number string Sets or queries the 64-bit Device ID that is used by the
modem to identify itself to the server. The default is a
value that depends on the underlying communications
technology being used.
*NETPHONE? none Aucun The modem's phone number , if applicable or obtainable.
*NETPW=pw pw=password
*NETUID=uid uid=user id (up
to 64 bytes)
*NETROAMPREF=n n=0 or 1 Allow configuration of the roaming preference.
*PROVISION=
[MSL],[MDN/MIN],[SID],
[NID]
*PROVISION2=
[MSL],[MDN],[MIN],[SID],
[NID]
*STATI CIP=d.d.d.d d.d.d.d=IP Set the static IP required to be received from the net-
MSL=master
lockcode
MDN/MIN=
phone number
SID=network
ID*
NID=system
ID*
Same as above
but with MDN
and MIN “split”
The password that is used to login to Verizon’s cellular
network
The login that is used to login to the Verizon’s cellular
network
0 : Restrict to home network only.
1 : Allow roaming to affiliated networks.
Provision the modem with the lock code and phone num-
ber.
Note: It is recommended to use the Verizon Setup Wiz-
ard for Verizon to provision the modem. *Note: Verizon
may not support this function.
A second set of modem provision parameters, when the
MDN and MIN (MSID) are different or “split”.
Note: SID and NID are optional, however if you include
SID you must include NID.
work. If the modem does not get this IP address from the
network, it will reset the module and try again. The
default is 0.0.0.0, which allows any IP address from the
network. Example: AT*STATICIP=192.168.1.23
, when required.
, when required.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 63
Page 70

Cellular Network
The Raven’s cellular network is the connection to CDMA and remote devices or
computers.
TABLE 5. Cellular Network (Verizon’s CDMA)
Command Parameters Details
*NET ALLOWZEROIP=n n=0 or 1 Allows the displayed IP address in *NETIP to end in
zero (ex. 192.168.1.0).
0 : Do not allow
1 : Allow
*NETCHAN? none The current active CDMA channel number.
*NETERR? none The EVDO or CDMA network frame error rate.
*NETIP? none The current IP address of the modem reported by the
embedded hardware module (generally obtained from
Carrier). This is the address to which packets can be
sent in order to contact the Raven from the Internet.
Note: If there is no current network IP, 0.0.0.0 may be
displayed.
Refer to *NETALLOWZEROIP if you need to allow
the display of an IP ending in a zero.
*NETOK? none Checks the CDMA connection.
OK if connected.
ERROR if not connected.
*NETRSSI? none The current RSSI (Receive Signal Strength Indicator) of
the Raven as a negative dBm value. The same informa
tion is displayed with the command S202?.
*NETSTATE? none See *NETSTATE?.
*NETWDOG=n n=minutes Network connection watchdog: The number of minutes
to wait for a network connection. If no connection is
established within the set number of minutes, the Raven
resets.
Default = 20 min. 0 = Disable.
-
64 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 71

TABLE 5. Cellular Network (Verizon’s CDMA)
Command Parameters Details
!STATUS
C3210
!RSSI C3210 none Received Signal Strength Indicator Puissance du signal
+CBIP? none Mobile Station IP Address.
+CGSN none ESN (Electronic Serial Number).
+CICB
C3211
none Displays the current modem status. Format of response:
Current band: <band>
Current channel: <chan>
SID:<sid> NID:<nid> Roaming:<n>
Temp:<temp>
Pilot [NOT] acquired
Modem has [NOT] registered
reçu.
n=0 | 2 | 3 The mode for answering data/fax calls with A (Answer)
or autoanswer via S0=1.
0 : Answer as voice (Default)
2 : Voi ce
3 : Async data for next call, then revert to Voice.
Local Network and Host Modes
The Local network for the Raven is the one to which it is connected physically via
the serial port to your computer, device, hub, or switch. The
Raven has the ability to
provide some NAT (network address translation) to pass communication from the
CDMA network and the Internet to the local device(s) and network. On the local
network, the
Raven acts as a Host.
PassThru
PassThru Mode is used to communicate directly to the Raven’s internal hardware
(OEM module).
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 65
Page 72

TABLE 6. Local Network and Host Modes
Command Parameters Details
+++
The "+" is ASCII 0x2B.
This command is not proceeded by AT.
AIP=n n=0
HOR=n
MDhh hh (hex byte) =
none AT Escape sequence.
If the Raven is in a data mode (any mode other than
PassThru), this command causes the modem to re-enter
AT command mode.
Note: There must be an idle time (set by S50) on the
serial port before and after this command. The detection
of +++ is disabled if DAE=1.
Allow only the IP specified in S53 to connect when UDP
auto answer is enabled (S82=2).
Allow any incoming IP to connect when UDP auto
answer is enabled (S82=2).
n=1
Always subject to any Friends filters that may be
defined.
Half-Open Response - In UDP auto answer (half-open)
mode:
No response codes when UDP session is initiated.
n=0
RING CONNECT response codes sent out serial link
before the data from the first UDP packet.
n=1
Note: Quiet Mode must be Off.
Default power-up mode.
00 - normal
mode
01 - SLIP mode
02 - PPP mode
03 - UDP mode
04 - TCP mode
07 - PassThru
mode
When the PinPoint is power-cycled, it may enter the
mode specified by this command after 5 seconds. On
startup, typing ATMD0 within 5 seconds changes the
mode to normal (AT command) mode.
See also S53 to set the port for UDP or TCP.
66 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 73

TABLE 6. Local Network and Host Modes
Command Parameters Details
S0=n n=0 | 1 | 2 | 3 This register determines how the Raven responds to an
incoming TCP connection request. The Raven remains
in AT Command mode until a connection request is
received. DTR must be asserted (S211=1 or &D0) and
the Raven must be set for a successful TCP connection.
The modem will send a "RING" string to the host. A
"CONNECT" sent to the host indicates acknowledge
ment of the connection request and the TCP session is
established.
0 : Off (Default)
1 : On
2 : Use Telnet server mode on TCP connections.
3 : With a Telnet connection, overrides the client's
default echo, allowing the server on the host port to per-
form the echo. CRLF sequences from the telnet client
will also be edited to simply pass CRs to the server on
the host port.
S7=n n = seconds Specifies the number of seconds to wait for a TCP con-
nection to be established when dialing out.
S23=[speed],[databits]
[parity][stop bits]
S50=n n = tenths of
speed =
300 | 1200 |
2400 | 4800 |
9600 | 19200 |
38400 | 57600 |
115200 | 230400
databits = 7 or 8
parity =
O | E | N | M
stopbits =
1 | 1.5 | 2
seconds
Serial line parameters. The settings take affect after
reset.
Ex. ATS23=19200,8N1 (sets modem to 19200, etc.)
Note: Databits MUST be 8 data bits for PPP mode.
Can also be set using &L=[speed],[databits] [par-
ity][stop bits]
O=Odd E=Even N=None M=Mark
Data forwarding idle time-out. If set to 0, a forwarding
time-out of 10ms is used.
(Used in UDP or TCP PAD mode)
-
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 67
Page 74

TABLE 6. Local Network and Host Modes
Command Parameters Details
S51=n n=0 | ASCII
code
S82=n n=0 or 2 Enables UDP auto answer (half-open) mode.
S83=n n=0-255 Set or query UDP auto answer idle time-out. If no data is
S211=n n=0 | 1 | 3 For applications or situations where hardware control of
S221=n n = 0 - 255 Connect Delay
PAD data forwarding character.
0 : No forwarding character.
ASCII code of character that will cause data to be for-
warded.
(Used in UDP or TCP PAD mode.)
0 : Normal mode
2 : Enable UDP auto answer mode.
sent or received before the time-out occurs, the current
UDP session will be terminated. While a session is
active, packets from other IPs will be discarded (unless
*UALL is set).
Time-out in seconds.
0 : No idle time-out (Default).
the DTR signal is not possible, the modem can be con
figured to ignore DTR. When Ignore DTR is enabled,
the modem operates as if the DTR signal is always
asserted.
0 : Use hardware DTR. (default).
1 : Ignore DTR.
3 : Ignore DTR and assert DSR. This value is depre-
cated, and it is recommended to use &S to control the
DSR instead. When this value is set to 3, &S will auto
matically be set to 0. See also: &D and &S.
Number of seconds to delay the "CONNECT' response
upon establishing a TCP connection.
OR
Number of tenths of seconds to delay before outputting
ENQ on the serial port after the CONNECT when the
ENQ feature is enabled (see *ENQ).
-
-
68 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 75

TABLE 6. Local Network and Host Modes
Command Parameters Details
TCPS=n n = minutes
(TCPS=0) or
seconds
(TCPS=1)
TCPT=n n = minutes
(TCPT=0) or
seconds
(TCPT=1)
TCP connection time-out (TCPS) units. Specifies a time
interval upon which if there is no in or outbound traffic
through a TCP connection, the connection will be termi
nated.
TCP connection time-out (TCPT) units. Specifies a time
interval upon which if there is no in or outbound traffic
through a TCP connection, the connection will be termi
nated.
This value only affects the TCP connection in TCP PAD
mode.
&Cn n=0 | 1 | 2 Set DCD mode.
0 : Always assert DCD.
1 : Assert DCD when in a data mode (UDP, TCP , PPP, or
SLIP) (Default).
2 : Assert DCD when the modem has network coverage.
&Dn n=0 or 2 Set DTR mode.
0 : Ignore DTR, same effect as HW DTR always
asserted (same as S211=1).
2 : Use hardware DTR (same as S211=0).
&Sn n=0 | 1 | 2 Set DSR mode.
0 : Always assert DSR.
1 : Assert DSR when in a data mode (UDP , TCP, PPP, or
SLIP) (Default).
2 : Assert DSR when the modem has network coverage.
Note: S211 can also be used to request that DSR is
always asserted. If S211 is set to 3 and &S is changed to
a non-zero value, S211 will be changed to 1.
-
-
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 69
Page 76

TABLE 6. Local Network and Host Modes
Command Parameters Details
*CTSE=n n=0 or 1 Clear To Send Enable
This feature asserts CTS when there is a network connection.
0 : Disabled (Default).
1 : Enable assertion of CTS when there is network cov-
erage.
Note: Flow control (AT\Q) will override this indication,
so if you want to use CTS to indicate network coverage,
flow control has to be off (AT\Q0).
RS232 voltage levels:
Positive = Network coverage.
Negative = No coverage.
*DU=n n=0 or 1 The dial command always uses UDP, even when using
ATDT.
0 : Dial using the means specified (default).
1 : Dial UDP always, even when using ATDT.
Note: When this parameter is set you cannot establish a
TCP PAD connection.
*ENQ=n n=0 or 1 Outputs an ENQ [0x05] after the TCP CONNECT
delayed by the Delay Connect Response time (S221).
0 : Disabled (Default).
1 : Enables ENQ on CONNECT.
*HOSTCOMLVL none Displays the current signal levels of the host serial port.
*HOSTMODE? none The current host mode (AT, PPP, UDP, etc.) which the
modem is in. If the modem is not in AT mode, telnet into
the modem to execute this command.
*HOSTNETMASK=n.n.n.n n.n.n.n = subnet
mask, example
255.255.255.0
*HOSTPAP=n n=0 or 1 Use PAP to request the user login and password during
Netmask for the host interface. Allows communication
with a subnet behind the host interface.
PPP negotiation on the host connection.
0 : Disable PAP request (Default).
1 : Takes user login and password from Windows DUN
connection and copies to *NETUID and *NETPW.
70 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 77

TABLE 6. Local Network and Host Modes
Command Parameters Details
*HOSTPEERIP =d.d.d.d d.d.d.d=local or
peer IP of
modem
Set or query the IP address that can be used to directly
contact the Raven once a PPP connection is established.
If this value is not specified, 192.168.13.31 will be used.
Note: This is not normally used nor needed by user
applications. PPP
*HOSTPRIVIP =d.d.d.d d.d.d.d=IP Set or query the private IP address that is to be negoti-
ated by the PPP connection if *HOSTPRIVMODE =1.
PPP
*HOSTPRIVMODE =n n=0 or 1 Set or query whether a private or public (network) IP is
to be used when the Host initiates a PPP connection to
the modem. PPP
0 : Public (network) IP Mode: When the Host initiates a
PPP connection, the host will be given the public IP that
was obtained from the OEM module. If the network
issues a new IP, the PPP connection will be closed (since
the IP has changed) and has to be re-initiated. (default).
PPPPPP
1 : Private IP Mode: When the Host initiates a PPP con-
nection, the host will be given the IP address specified in
*HOSTPRIVIP. The modem will then perform NAT -like
address translation, which shields the Host from network
IP changes. PPP
*MODEMHISPEED=n n=0 or 1 Set the internal serial link speed to the radio (modem)
module.
0 : 115200 (default)
1 : 230400
*UALL=n n=0 or 1 Accepts UDP packets from any IP address when a UDP
session is active. If there is no UDP session active, an
incoming UDP packet will be treated according to the
UDP auto answer and AIP settings.
0 : No effect (Default).
1 : Accept UDP data from all IP addresses when in a
UDP session.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 71
Page 78

TABLE 6. Local Network and Host Modes
Command Parameters Details
*UDPLAST=n n=0 or 1 If enabled, sets S53 to the last accepted IP address
through UDP auto answer. This can be used in conjunction with MD3 so that when there is no UDP session,
new ethernet host data will cause a connection to be
restored to the last IP accepted through UDP auto
answer. .
0 : Does not change S53 setting. (Default).
1 : Set S53 to the last accepted IP.
Note: This does not change the S53 setting in NVRAM.
If the modem is reset, the original S53 setting will be
restored from NVRAM.
*USD=n n=1-255 Waits the specified delay before sending the first UDP
packet and the subsequent UDP packets out to the serial
port.
0 : No UDP packet delay (Default).
Delay in 100ms units, from 100 ms to 25.5 sec.
\Qn n=0 | 2 | 4 Set or query the serial port flow control setting.
0 : No flow control is being used.
1 : RTS/CTS hardware flow control is being used.
4: Transparent software flow control. Uses escaped
XON and XOFF for flow control. XON and XOFF characters in data stream are escaped with the @ character
(0x40). @ in data is sent as @@.
\APPP none Set modem operation to PPP mode.
\ASLIP none Set modem operation to SLIP mode. DTR must be
asserted (&D0 or S211=1).
Caution: Not all AT Commands can be used while in PassThru
mode.
Direct Communication
Direct Communication can be used with the Raven to contact other Internet devices
to pass information or other tasks.
72 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 79

TABLE 7. PassThru Mode
Command Parameters Details
\APASSTHRU
Note: This mode is not
available through the remote
AT telnet server.
*CSX1=n n=0 or 1 0 : Data will be passed to the host.
*PTINIT=n n=AT command Any AT Command string to be passed to the OEM mod-
*PTREFRESH=n n=0-255 min-
*RESETPERIOD=n n=0-255 hours In PASSTHRU mode, modem will be reset after this
none Set modem operation to pass through mode. This will
pass any characters received on the serial port directly to
the internal hardware module and output any characters
from the internal hardware module out the serial port.
This allows direct access/configuration of the hardware
module. Once this mode is entered, the unit must be
physically reset to return to normal operation.
Note: It may take up to 30 seconds for the hardware
module to respond after CONNECT is output.
1 : PASSTHRU mode will echo all host received data
and will not pass the data to the modem while the
modem is not asserting DCD.
Note: If the modem is asserting DCD, data will be
passed from the host to the modem as it normally is
when *CSX1=0.
ule before entering PASSTHRU mode, e.g. AT&S1V1,
etc.
Number of minutes of inactivity in P ASSTHRU mode to
utes
resend the *PTINIT string to the hardware module.
0 : Disabled
period if no data has been sent or received. . Value is in
hours.
0 : Disabled
Telnet
It is possible to communicate with the Raven across a TCP/IP network. Telnet provides a terminal style connection to the Raven.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 73
Page 80

TABLE 8. Direct Communication
Command Parameters Details
D[method][d.d.d.d][/ppppp]
or
D[method][@name][/ppppp]
D continued see above The defualt connetion is set in S53.
PINGd.d.d.d[,n]
or
PING domain_name[,n]
method = P, T, N
d.d.d.d = IP
address to contact
name = domain
name to contact
ppppp = IP port
to contact
d.d.d.d = IP
address to con
tact
n = amount of
data to send
Dial a connection to a remote IP and Port using method.
P - Establish a UDP connection
T - Establish a TCP connection
N - Establish a Telnet connection
ATD - Dial (establish) default connection.
ATDP192.168.13.31/2332 - Dial (establish) UDP ses-
sion to 192.168.13.31, at port 2332.
To end the connection, issue the +++ escape sequence or
drop the DTR line (if Ignore DTR S211=0 or &D2).
If a domain name is specified, the '@' symbol can be
used to explicitly indicate the start of the name. For
example, if ATDPHONY is issued, this will be inter-
preted as dial a UDP connection to "HONY". To dial
using the default method to host "PHONY", one would
issue ATD@PHONY. .
If the method, IP address, or port is omitted, the values
from S53 are used. If a telnet connection is requested (N)
and the port is not supplied, port 23 will be used instead
of the value from S53.
Several special dialing numbers exist to make it easy to
establish a PPP or SLIP connection with the modem.
ATD#19788 or ATDT#19788 will establish a PPP con
nection (see \APPP) and ATDT#7547 will establish a
SLIP connection (see \ASLIP).
Note: The source port of the session is the Device Port
(set by S110 or *DPORT).
Ping the specified IP address.
-
Sends a single ping, returns either OK or ERROR
depending on result. Times out in 10 seconds. If n is pro
vided, it specifies the amount of data to send with the
ping. If n is not provided, the default, 50 bytes is used.
-
-
74 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 81

TABLE 8. Direct Communication
Command Parameters Details
S53=[method][d.d.d.d][/
ppppp]
method =
P - UDP
T - TCP
N - Telnet
d.d.d.d = IP
address or name
ppppp = the port
address
Destination IP address, port, and method. These are used
as defaults for the D (Dial) AT command.
Examples:
ATS53=T192.168.100.23/12345
ATS53=foo.earlink.com
Te lnet to the specified IP at port 12345.
ATS53=192.168.100.23/12345
Query the specified IP at port 12345.
ATS53=/12345
Query port 12345.
*DPORT=n n=1-65535 The modem's Device Port. Can also be set with the com-
mand S110.
*MSCIUPDADDR=name
[/port]
name = domain
name
port=port
Modem Status Update Address - where Name/Port is the
domain name and port of the machine where the modem
status updates will be sent. The Raven's status parame
-
ters are sent in an XML format.
*MSCIUPDPERIOD=n n=0-255 Modem Status Update Period - where n defines the
update period in seconds.
0 : Disabled.
Caution: Telnet is not a secure communications protocol.
TABLE 9. Telnet
Command Parameters Details
S60=n n=0 | 1 |2 Telnet Client Echo Mode.
0 : No Echo
1 : Local Echo (Default)
2 : Remote Echo
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 75
Page 82

TABLE 9. Telnet
Command Parameters Details
*TELNETTIMEOUT=n n=minutes Telnet port inactivity time out.
By default, this value is set to close the AT telnet con-
nection if no data is received for 2 minutes.
*TPORT=p p=0-65535 Sets or queries the port used for the AT Telnet server. If 0
is specified, the AT Telnet server will be disabled. The
default value is 2332.
Time/Date
Time and Date in the Raven is set to UTC (Coordinated Universal Time). Time is
expressed in 24-hour format, i.e. 13:23:57 would be 1:23pm. You can set time and
date manually or you can have it set automatically with a regular query to an Inter
net time server (such as time.nist.gov) using SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol).
TABLE 10. Time and Date
Command Parameters Details
*DATE=[mm/dd/
yyyy],[hh:mm:ss]
*SNTP=n n=0 or 1 Enables daily SNTP update of the system time.
*SNTPADDR=
[d.d.d.d][name]
*SNTPQUERY? none The current SNTP time and date.
mm/dd/yyyy =
month, day, year
hh:mm:ss =
time in 24-hour
notation
d.d.d.d=IP
name=domain
name
Sets and queries the clock in the unit. Either the date and
time can be specified, or simply one of the two can be
specified in which case the unspecified value will remain
unchanged. The date and time are always specified 24-
hour notation.
0 : Off
1 : On
SNTP Server IP address, or fully-qualified domain
name, to use if *SNTP=1.
Note: If blank, time.nist.gov is used.
-
76 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 83

Friends Mode
Friends Mode can limit access to the Raven from the Carrier network and the Internet. Friends Mode is a limited form of security.
TABLE 11. Friends Mode
Command Parameters Details
FM=[n] n=0 or 1 Friends Mode - Only allow specified IPs to access the
Raven.
0 : Disable Friends mode
1 : Enable Friends mode - Only packets from friends will
be accepted (see below); packets from other IP addresses
are ignored.
Fn=[d.d.d.d] n = Friends list
index [0 - 9]
d.d.d.d = IP
address
Friends mode IP address.
255 = allow any number 0-255
Example: 166.129.2.255 allows access by all IPs in the
range 166.129.2.0-166.129.2.255.
Note: ATF? will return a list of all the current Fn set-
tings.
DNS
DNS settings in the Raven allow the modem to use domain names instead of IPs to
contact other Internet hosts.
TABLE 12. DNS
Command Parameters Details
*DNSn=d.d.d.d n=1 or 2
d.d.d.d = IP of
domain server
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 77
Sets the DNS addresses to be returned during PPP negotiation. If the underlying communications network provides DNS addresses, they replace those specified by
this command.
You can only set *DNS1 and *DNS2.
Page 84

TABLE 12. DNS
Command Parameters Details
*DNSUPDATE=n n=0 or 1 Indicates whether the modem should send DNS updates
to the DNS server specified by *DNSUSER. These
updates are as per RFC2136. They are not secure and are
recommended only for a private network. In a public
network, the IP Logger services should be used instead.
0 : DNS updates disabled (Default).
1 : DNS updates enabled.
*DNSUSER=d.d.d.d d.d.d.d = IP of
domain server
Sets a user-provided DNS to query first when perform-
ing name resolutions in the modem.
Keepalive
Keepalive (page 21) allows the Raven to stay connected to the cellular network even
when there are periods of inactivity.
TABLE 13. Keepalive
Command Parameters Details
*IPPING=n n=0, 15-255 Set the period to ping (if no valid packets have been
received) a specified address (*IPPINGADDR) to keep
the modem alive (online). 15 minuted is the minimum
intervale which can be set for Keepalive.
0 : Disable pinging (default)
See also *MINXMIT which can override this value.
*IPPINGADDR=
[d.d.d.d][name]
d.d.d.d = IP
name= domain
name
Set the IP address or valid internet domain name for the
Raven to ping to keep itself alive (online). *IPPING
must to be set to a value other than 0 to enable pinging.
78 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 85

TABLE 13. Keepalive
Command Parameters Details
*MINXMIT=n n=seconds Minimum transmit period enforcement. When set to n
seconds, will not let the *IPPING, *PPMINTIME, and
the *MSCIUPDPERIOD timers to be set less than n sec
onds.
Note that the *PPTIME can still be set to less than
*MINXMIT, bu t the pa cke ts will stil l be tra nsmitted no
more often than the *PPMINTIME.
Warning: The *MINXMIT value is can only be set one
time and AirLink must be contacted to reset it.
IP Manager
IP Manager (page 15) is a service from AirLink which allows a Raven with a
dynamic IP to be contacted as if it had a static IP by using a Fully Qualified
Domain Name.
TABLE 14. IP Manager
Command Parameters Details
*DOMAIN=[name] name = domain
name (i.e. eair
link.com)
*IPMANAGERn=[name] n= 1 or 2
name = domain
name
Domain (or domain zone) of which the Raven is a part.
-
This value is used during name resolutions if a fully
qualified name is not provided and also for DNS
updates. This value can be up to 20 characters long.
If *DOMAIN=eairlink.com, then when
ATDT@remote1 is entered, the fully qualified name
remote1.eairlink.com will be used to perform a DNS
query to resolve the name to an IP address.
Note: Only letters, numbers, hyphens, and periods can
be used.
Sets a domain name or IP address to send IP change notifications to. Up to two independent IP Manager servers
can be set, using either AT*IPMANAGER1 or
A T*IPMANAGER2. Updates to a server can be disabled
by setting that entry to nothing (i.e.
"AT*IPMANAGER1=").
-
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 79
Page 86

TABLE 14. IP Manager
Command Parameters Details
*IPMGRKEYn=[key] n= 1 or 2
key = 128-bit
key in hexadecimal [32 hex
characters]
*IPMGRUPDATEn=m n= 1 or 2
m=5-255
*MODEMNAME=[name] name = domain
name (i.e. eair
link.com)
Sets the 128-bit key to use to authenticate the IP update
notifications. If the key's value is all zeros, a default key
will be used. If all the bytes in the key are set to FF, then
no key will be used (i.e. the IP change notifications will
not be authenticated). AT*IPMGRKEY1 is used to set
the key to use with AT*IPMANAGER1, while
AT*IPMGRKEY2 is used to the key with
AT*IPMANAGER2.
Sets the number of minutes to periodically send an IP
update notification to the corresponding server . This will
occur even if the IP address of the Raven doesn't change.
*IPMGRUPDATE1 is used to set the refresh rate to
*IPMANAGER1, while *IPMGRUPDATE2 is used
with *IPMANAGER2.
If the value is set to 0, then periodic updates will not be
issued (i.e. IP change notifications will only be sent
when the IP actually changes).
Name of the Raven (up to 20 characters long) to use
-
when performing IP change notifications to IPManager.
The value in *DOMAIN provides the domain zone to
add to this name.
Example: if *MODEMNAME=mymodem and
*DOMAIN=eairlink.com, then the modem's fully qual
ified domain name is mymodem.eairlink.com.
Note: Each modem using IPManager needs a unique
name. Two modems cannot be called “mymodem”. One
could be “mymodem1” with the other as “mymodem”.
Automatically Generated Names:
#I3 - The ESN/IMEI will be used as the name.
#NETPHONE - The phone number be used as the
name.
Note: Only letters, numbers, hyphens, and periods can
be used.
-
80 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 87

Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 81
Page 88

Logging
The Raven allows several different levels of logging.
TABLE 15. Logging
Command Parameters Details
*DBGCOM1000=n n=0 or 1 Turn on debugging for COM1000.
0 : No logging
1 : Logging
*DBGCOMLVL=n n=0 | 1 | 2 Set the logging level for the host or module COM port.
0 : No logging
1 : Host COM
2 : Module COM
*DBGEVTLOGCLEAR none Clears the content of the logs in the modem.
*DBGIPLVL=n n=0 | 1 | 2 Sets the logging level for the IP subsystem.
0 : No logging
1 : Log errors (i.e. invalid/corrupt packets, etc.).
2 : Log the header of all received packets. Note that this
can quickly exhaust the event log.
*DBGPPPLVL=n n=0-3 Sets the logging level for the PPP stack.
Enables logging at different levels of detail. (default =
1).
0 : No logging
Modbus
Modbus, commonly used with telemetry devices, allows a connection via serial
port to the modem (page
32).
82 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 89

TABLE 16. Modbus Settings
Command Parameters Details
IPL=n n=0 or 1 IP List Dial
This allows access the Modbus IP list using the first two
digits of the dial string. Example: ATDT1234567 would
go to ID "12" on the Modbus list and use the associated
IP as the destination.
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
Cannot be configured in Wireless ACE.
MDhh hh (hex byte) =
00 - normal
mode
01 - SLIP mode
02 - PPP mode
Default power-up mode.
When the PinPoint is power-cycled, it may enter the
mode specified by this command after 5 seconds. On
startup, typing ATMD0 within 5 seconds changes the
mode to normal (AT command) mode.
See also S53 to set the port for UDP or TCP.
03 - UDP mode
04 - TCP mode
07 - PassThru
mode
MLISTid=d.d.d.d id=ID
d.d.d.d=IP or
name adresse
Enters an ID and IP address into the Modbus List. ID is
a decimal value (1 to 100).
Note: In Wireless ACE, this command (and MLISTX) is
the Addr List menu option.
MLISTXhexid=d.d.d.d hexid=ID
d.d.d.d=IP or
name adresse
Enters an ID and IP address into the Modbus List. ID is a
hexadecimal value (0 to 64).
Note: This value is entered via Wireless ACE as 0xHex.
MVLEN=n n= 1 or 2 Modbus Va riant ID Length.
Length of the RTU ID in a modbus-variant protocol, in
bytes. This parameter is used to define the length of the
RTU ID in Mod bus-like protocol data packets. This
parameter is used when the when the MD is set to hex
63.
Cannot be configured in Wireless ACE.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 83
Page 90

TABLE 16. Modbus Settings
Command Parameters Details
MVMSK=hh hh=hex value
00 - no mask, all
8 bits (default)
0F - only the
low order 4 bits
MVOFF=n n = 0 - 255 Modbus (variable mode) Offset.
MVOPT=n n= 0 or Modbus Variant Option.
MVTYP=n n=0 | 1 | 2 Modbus Variant Type.
Modbus Variant ID Mask.
Byte hex mask to use when extracting the ID. Specify
which bits in the ID field to use. This parameter is used
when the when the Mode Default (MD) is set to hex 63.
Cannot be configured in Wireless ACE.
Indicates the offset in the data of where the Modbus ID
starts.
Cannot be configured in Wireless ACE.
Sets various behavioral options when dealing with a
Modbus-variant protocol. This parameter is used when
the when MD is set to hex 63.
0 : No special action (Default).
1 : Skip leading zeroes in Modbus packets.
Cannot be configured in Wireless ACE.
The data-type of the RTU ID in a modbus-variant proto-
col. This parameter is used to define the data-type of the
RTU ID in Mod bus-like protocol data packets. This
parameter is used when MD is set to 63.
0 : Binary (Default)
1 : ASCII Hex
2 : ASCII Decimal
Cannot be configured in Wireless ACE.
84 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 91

TABLE 16. Modbus Settings
Command Parameters Details
RKEY=n n= 0 or Radio Transceiver Keying.
0 : Off (Default)
1 : On
Enable/disable MDS Radio transceiver keying. Radio
keying is designed to assert CTS when a packet is
received, delay the time as specified, send the data out
the serial port, wait the same amount time, drop CTS.
This way, the CT S signa l can be used to key a transmit
ter on and give it time to reach its power level before
data is sent to it. Delay interval is specified in S221.
Cannot be configured in Wireless ACE.
S53=[method][][d.d.d.d][/
ppppp]
*DPORT=n n=1-65535 The modem's Device Port. Can also be set with the com-
method =
P - UDP
T - TCP
N - Telnet
d.d.d.d = IP or
name adresse
ppppp = the port
address
Destination IP address, port, and method. These are used
as defaults for the D (Dial) AT command.
Examples:
ATS53=T192.168.100.23/12345
ATS53=foo.earlink.com
Te lnet to the specified IP at port 12345
ATS53=192.168.100.23/12345
Query the specified IP at port 12345
ATS53=/12345
Query port 12345
mand S110.
-
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) can be used to monitor devices
connected to a network for any conditions which warrant administration attention.
By default, SNMP uses port 161, however most Internet providers (including cellu
lar) block all ports below 1024 as a security measure.
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 85
-
Page 92

TABLE 17. SNMP
Command Parameters Details
\ACEPW=pw pw=password Change the ACE password to a new value. Password is
case-sensitive. Default password is 12345.
Example: AT\ACEPAW=new123
*SNMPPORT=n n=0-65535 This controls which port the SNMP Agent listens on.
0 : SNMP is disabled.
Port for SNMP agent to listen on.
*SNMPSECLVL=n n=0 | 1 | 2 Selects the security level requirements for SNMP com-
munications as follows:
0 : No security required. SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 com-
munications are allowed.
1 : Authentication equivalent to 'authNoPriv' setting in
SNMPv3. SNMPv3 is required to do authentication,
SNMPv2c transmissions will be silently discarded.
2 : Authentication and encryption, equivalent to 'auth-
Priv' setting in SNMPv3. SNMPv3 is required to do
authentication and encryption, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3
authNoPriv transmissions will be silently discarded.
-
*SNMPTRAPDEST=host/
[port]
host=IP address
port=TCP port
Messages are both authenticated and encrypted to pre
vent a hacker from viewing its contents.
Controls destination for SNMP Trap messages.
If port is 0 or host is empty, traps are disabled.
Traps are sent out according to the SNMP security level
(i.e. if the security level is 2, traps will be authenticated
and encrypted). Currently, the only trap that can be gen
erated is linkup.
-
SMTP/SMS
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is the de facto standard for email transmission across the Internet. The Raven can send messages using SMTP if it has been
configured to use a mail server.
SMS (Simple Message Service) is another way to send messages via your Wireless
Service Provider’s cellular network.
86 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 93

Caution: Your account with Verizon may not support message
sending. For most SMS commands (those not preceeded by *),
you will need to have the modem in PassThru mode.
TABLE 18. SMTP (email) an d SMS (messaging)
Command Parameters Details
*NETSMS2EMAIL=
[number]
*SMTPADDR=
[d.d.d.d][name]Maximum:
40 characters
*SMTPFROM=[email]Max-
imum: 30 characters
*SMTPPW=[pass] pass= password Sets the password to use when authenticating the email
*SMTPSEND=[email][body]email= email
*SMTPSTATUS? none Returns the status of the last issued SMTP message
*SMTPSUBJ=[subject] subject= S MTP
number= SMS/
E-mail server
d.d.d.d=IP
name=
domain name
email= email
address
address
body= message
body
message subject
Specify the SMS/E-mail server number. This is necessary to send an SMS message to an email address
(+CMGS).
Specify the IP address or Fully Qualified Domain Name
(FQDN) of the SMTP server to use.
Sets the email address from which th e SMTP messag e is
being sent.
account (*SMTPFROM) with the server (*SMT
PADDR).
Note: Not required to use SMTP settings but may be
required by carrier.
Sends an email to the address specified, followed by the
body of the email message.
The email message is terminated and sent by entering a .
or Ctrl-Z on an empty line.
See also *SMTPSUBJ, *SMYPFROM, and *SMTPADDR.
(*SMTPSEND). If no status is available 0 is returned.
Once read, the status is cleared out.
The status codes are received from the SMTP server the
modem attempted to send the request.
Example: 354 = send in progress, 250 = sent ok.
Allows configuration of the default Subject to use if one
isn't specified in the message by providing a "Subject:
xxx" line as the initial message line.
-
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 87
Page 94

TABLE 18. SMTP (email) an d SMS (messaging)
Command Parameters Details
*SMTPUSER=[user]Maximum: 40 characters
+CMGD=index[,flag]
C3211
+CMGR=index C3211 index=0-9 Read a message.
+CMGS=[email][body]
C3211
!CNTSMS
C3210
!DASMS
C3210
user= username The email account username to authenticate with the
SMTP server (*SMTPADDR) for sending email.
Note: not required to use SMTP settings but may be
required by carrier.
index=0-9
flag=0
flag=1
flag=2
flag=3
flag=4
email= email
address or
phone number
body= message
body
none Reports the number of messages stored:
none Deletes all SMS messages from all three index lists.
This command is used to delete one or several messages.
Delete message at location.
Delete All READ messages.
Delete All READ and SENT messages.
Delete All READ, SENT and UNSENT messages.
Delete All messages.
Note: There is no confirmation required.
Sends an email using SMS. The phone number or email
address is specified first. Then the body of the message
is entered. E-mail is only available if
*NETSMS2EMAIL has been configured correctly.
The message is terminated and sent by entering Ctrl-Z
on an empty line.
New Urgent Msg {Index = 1}: <n>
New Regular Msg {Index = 2}: <r>
Voice Messages {Index = 3}: <v>
The Index number corresponds to the SMS list index
used to retrieve messages. The counters n, r, and v indi
cate the number of messages in each list.
When retrieving (!GSMS) or deleting (!DSMS), the
message number is base 0, so the highest message num
ber in any list is the reported count minus one.
Note: There is no confirmation required. Use this with
caution.
-
-
88 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 95

TABLE 18. SMTP (email) an d SMS (messaging)
Command Parameters Details
!DSMS =index[,message]
C3210
!GSMS?index,message
C3210
!SSMS=priority,destination,[cb],”text”
C3210
!SSMS?
C3210
index= index list
(0, 1, 2)
message=mes-
sage number
index= index list
(0, 1, 2)
message= message number
priority=0, 1, 2)
destination=
phone number
of destination
cb= call back
number
text= text of
message
enclosed in
quotes
none The progress of the last message sent. Possible responses
Deletes one or all messages from one of the index lists.
The message number is a base 0 index into the list,
where 0 is the oldest message, and the number reported
by !CNTSMS minus one, is the most recent message.
If the message number parameter is omitted, then all
messages in the index list are deleted.
Note: There is no confirmation required.
Read an SMS message from the modem. The message
read is determined by the parameters:
The message number is a base 0 index into the list,
where 0 is the oldest message, and the number reported
by !CNTSMS minus one, is the most recent message.
Send an SMS message.
Note: The text is enclosed in quotations. The quote char-
acter cannot appear in the body text. Messages with over
160 bytes of body text will be truncated and sent anyway.
are:
Pending message has not left the modem
Sent successfully
Sent to the network
Delivered successfully
Delivered by the network
Failed sending
Failed and should be retried
Other
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 89
Page 96

TABLE 19. Other Settings
Command Parameters Details
*NUMTOIP=n n=0 or 1 Convert 12 digit number to IP.
0 : Use as name.
1 : Use as IP.
+CT A= n n=seconds Inactivity timer, in seconds.
Typical network sett ings cause a link to go dormant after
10 to 20 seconds of inactivity, no packets transmitted or
received. This time can be shortened to release the phys-
ical RF link sooner when the application only transmits
short bursts.
90 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 97

APPENDIX 4 Example of the MIB trap
AIRLINK-MIB DEFINITIONS ::= BEGIN
IMPORTS
ObjectNameFROM SNMPv2-SMI
MODULE-COMPLIANCEFROM SNMPv2-CONF;
org OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { iso 3 }
dod OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { org 6 }
internet OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { dod 1 }
private OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { internet 4 }
enterprises OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { private 1 }
airlink OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { enterprises 20542 }
general OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { airlink 1 }
common OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { airlink 2 }
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 91
Page 98

status OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { airlink 3 }
gps OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { airlink 4 }
-- GENERAL -phoneNumber OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString (SIZE (10))
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { general 1 }
deviceID OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { general 2 }
electronicID OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { general 3 }
modemType OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { general 4 }
92 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
Page 99

aleosSWVer OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { general 5 }
aleosHWVer OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { general 6 }
modemSWVer OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { general 7 }
modemHWVer OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { general 8 }
-- COMMON -date OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23 93
Page 100

STATUS current
::= { common 1 }
otaProgrammingEnable OBJECT-TYPE
SYNT AX INTEGER {
disabled(0),
enabled(1) }
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { common 2 }
devicePort OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER(0..65535)
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { common 3 }
netUID OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { common 4 }
netPW OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
::= { common 5 }
94 Raven CDMA User Guide for Verizon, version 2.23
 Loading...
Loading...