Page 1
0.5 – 4 GHz 3 V Low Current
GaAs MMIC LNA
Technical Data
MGA-87563
Features
• Lead-free Option Available
• Ultra-Miniature Package
• 1.6 dB Min. Noise Figure at
2.4 GHz
• 12.5 dB Gain at 2.4 GHz
• Single +3 V or 5 V Supply,
4.5 mA Current
Attention:
Observe precautions for
handling electrostatic
sensitive devices.
ESD Machine Model (Class A)
ESD Human Body Model (Class 0)
Refer to Agilent Application Note A004R:
Electrostatic Discharge Damage and Control.
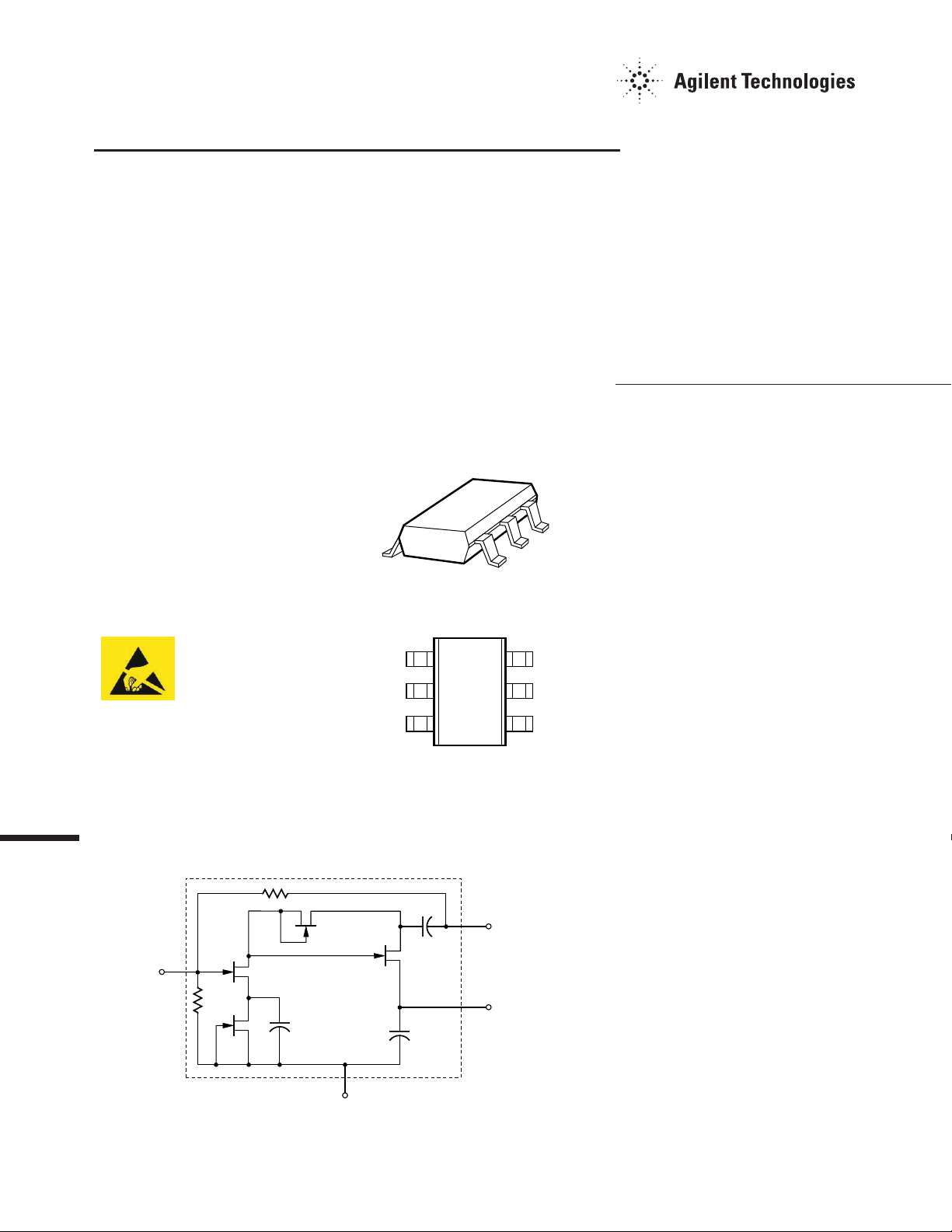
Equivalent Circuit
RF
INPUT
3
GROUND
Surface Mount SOT-363
(SC-70) Package
Pin Connections and
Package Marking
GND
1
87
GND
2
INPUT
Note:
Package marking provides orientation
and identification.
1, 2, 5
3
6
RF
OUTPUT
4
V
dd
6
5
4
OUTPUT
GND
V
dd
Applications
• LNA or Gain Stage for PCS,
ISM, Cellular, and GPS
Applications
Description
Agilent’s MGA-87563 is an
economical, easy-to-use GaAs
MMIC amplifier that offers low
noise and excellent gain for
applications from 0.5 to 4 GHz.
Packaged in an ultra-miniature
SOT-363 package, it requires half
the board space of a SOT-143
package.
With the addition of a simple
shunt-series inductor at the input,
the device is easily matched to
achieve a noise of 1.6 dB at
2.4 GHz. For 2.4 GHz applications
and above, the output is well
matched to 50 Ohms. Below
2 GHz, gain can be increased by
using conjugate matching.
The circuit uses state-of-the-art
PHEMT technology with selfbiasing current sources, a sourcefollower interstage, resistive
feedback, and on-chip impedance
matching networks. A patented,
on-chip active bias circuit allows
operation from a single +3 V or
+5 V power supply. Current
consumption is only 4.5 mA,
making this part ideal for battery
powered designs.
Page 2
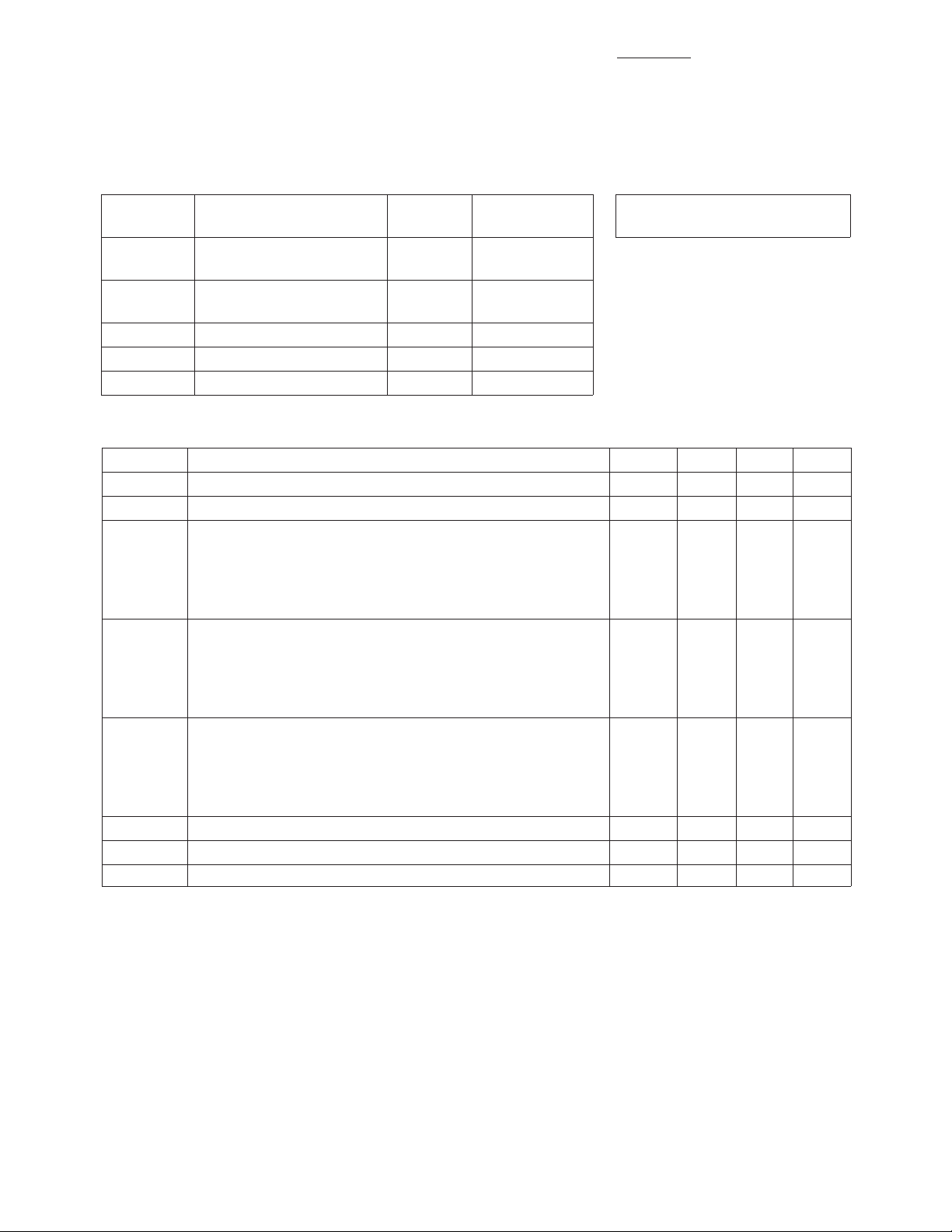
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute
Symbol Parameter Units Maximum
V
dd
V
in
V
out
P
in
T
ch
T
STG
Device Voltage, RF V 6
Output to Ground
RF input or RF Output V +0.5
Voltage to Ground –1.0
CW RF Input Power dBm +13
Channel Temperature °C 150
Storage Temperature °C -65 to 150
[1]
2
Thermal Resistance
θ
= 160°C/ W
ch-c
Notes:
1. Operation of this device above any one
of these limits may cause permanent
damage.
= 25°C (TC is defined to be the
2. T
C
temperature at the package pins where
contact is made to the circuit board).
[2]
:
MGA-87563 Electrical Specifications
[3]
, TC = 25°C, ZO = 50 Ω, Vdd = 3 V
Symbol Parameters and Test Conditions Units Min. Typ. Max.
[3]
G
NF
test
NF
test
[3]
o
Optimum Noise Figure f = 0.9 GHz dB 1.9
f = 2.0 GHz 11 14
f = 2.0 GHz 1.8 2.3
(Tuned for lowest noise figure) f = 1.5 GHz 1.6
f = 2.0 GHz 1.6
f = 2.4 GHz 1.6
f = 4.0 GHz 2.0
G
a
Associated Gain at NF
O
f = 0.9 GHz dB 14.6
(Tuned for lowest noise figure) f = 1.5 GHz 14.5
f = 2.0 GHz 14.0
f = 2.4 GHz 12.5
f = 4.0 GHz 10.3
P
1dB
Output Power at 1 dB Gain Compression f = 0.9 GHz dBm -2.0
f = 1.5 GHz -1.8
f = 2.0 GHz -2.0
f = 2.4 GHz -2.0
f = 4.0 GHz -2.6
IP
3
Third Order Intercept Point f = 2.4 GHz dBm +8
VSWR Output VSWR f = 2.4 GHz 1.8
I
dd
Device Current mA 4.5
Note:
3. Guaranteed specifications are 100% tested in the circuit in Figure 10 in the Applications Information section.
Page 3
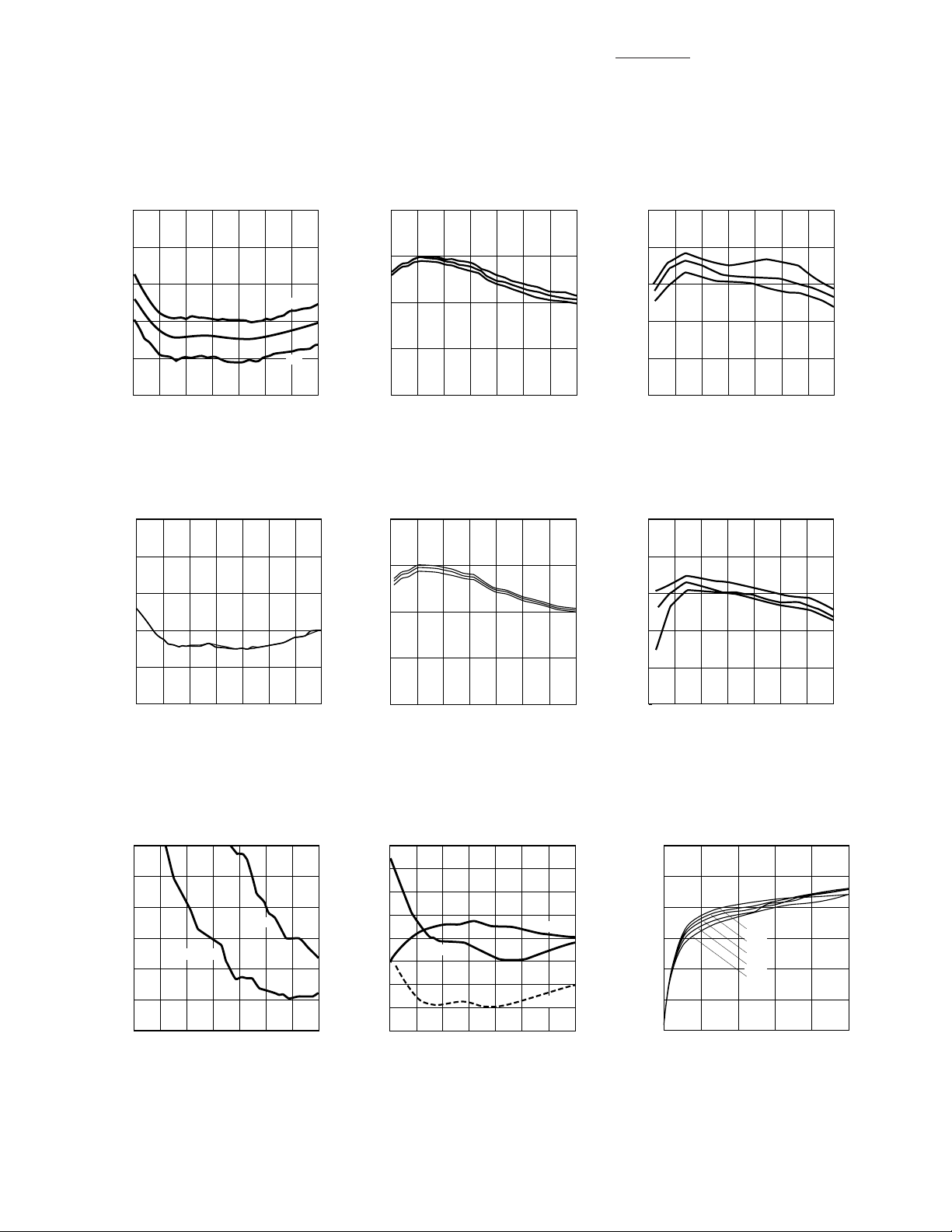
3
P 1dB (dBm)
0.5
-5
FREQUENCY (GHz)
2.0
0
-4
4.0
-2
3.0
1.5
3.0 V
2.7 V
-3
3.3 V
-1
1.0 2.5 3.5
MGA-87563 Typical Performance, T
5
4
3
+85
2
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
1
0
0.5
1.0
1.5 2.5 3.5
FREQUENCY (GHz)
2.0
3.0
+25
-40
4.0
Figure 1. Minimum Noise Figure
(Optimum Tuning) vs. Frequency and
Temperature.
5
4
3
2
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
1
3.3 V
3.0 V
2.7 V
20
15
10
5
ASSOCIATED GAIN (dB)
0
0.5
Figure 2. Associated Gain (Optimum
Tuning) vs. Frequency and
Temperature.
20
15
10
5
ASSOCIATED GAIN (dB)
= 25°C, Vdd = 3 V
C
1.5
1.0 2.5 3.5
2.0
FREQUENCY (GHz)
3.0
0
-1
-2
-3
P 1 dB (dBm)
-4
-5
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.5 3.5
FREQUENCY (GHz)
2.0
4.0
-40
+25
+85
Figure 3. Output Power for 1 dB Gain
Compression (into 50 Ω) vs.
Frequency and Temperature.
3.3 V
3.0 V
2.7 V
3.0
4.0
-40
+25
+85
0
0.5
1.0 1.5 2.5 3.5
2.0
FREQUENCY (GHz)
3.0
4.0
Figure 4. Minimum Noise Figure
(Optimum Tuning) vs. Frequency and
Voltage.
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
VSWR (n:1)
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
OUTPUT
1.0
1.5 3.52.5
FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 7. Input and Output VSWR
(into 50 Ω) vs. Frequency.
2.0
INPUT
3.0
4.0
0
0.5
1.5
1.0 2.5 3.5
2.0
FREQUENCY (GHz)
3.0
Figure 5. Associated Gain (Optimum
Tuning) vs. Frequency and Voltage.
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
1.5
1.0
0.5
NF 50
1.5
1.0 2.5 3.5
FREQUENCY (GHz)
2.0
3.0
Ga 50
NF OPT
4.0
Figure 8. 50 Ω Noise Figure and
Associated Gain vs. Frequency.
4.0
Figure 6. Output Power for 1 dB Gain
Compression (into 50 Ω) vs.
Frequency and Voltage.
20
15
10
5
ASSOCIATED GAIN (dB)
0
6
5
4
3
2
CURRENT (mA)
1
0
0
1
2
VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 9. Device Current vs. Voltage.
+85
+50
+25
-40
0
4
3
5
Page 4

4
MGA-87563 Typical Scattering Parameters
Freq. S
11
S
21
[4]
, T
= 25°C, ZO = 50 Ω, Vdd = 3 V
C
S
12
S
22
GHz Mag Ang dB Mag Ang dB Mag Ang Mag Ang Factor
0.1 0.92 -5 -5.6 0.53 -90 -22.7 0.073 -7 0.86 -11 0.41
0.2 0.91 -8 -0.7 0.92 -100 -22.7 0.073 -9 0.85 -18 0.29
0.5 0.88 -20 6.7 2.15 -131 -23.4 0.068 -18 0.78 -43 0.33
1.0 0.79 -35 10.1 3.22 -170 -25.2 0.055 -26 0.61 -75 0.72
1.5 0.73 -49 11.2 3.63 163 -26.2 0.049 -33 0.50 -100 1.02
2.0 0.67 -60 11.4 3.72 140 -26.6 0.047 -39 0.42 -122 1.32
2.5 0.59 -69 11.0 3.54 119 -29.1 0.035 -40 0.31 -141 2.38
3.0 0.50 -78 10.7 3.41 101 -32.5 0.024 -52 0.25 -167 4.29
3.5 0.43 -83 10.1 3.20 85 -35.1 0.018 -12 0.20 172 6.74
4.0 0.37 -96 10.0 3.16 71 -37.7 0.013 -10 0.24 143 9.83
4.5 0.31 -91 8.7 2.72 52 -26.1 0.050 20 0.11 123 3.33
5.0 0.30 -105 8.1 2.55 42 -25.9 0.050 -3 0.17 127 3.48
MGA-87563 Typical Noise Parameters
[4]
, T
= 25°C,
C
ZO = 50 Ω, Vdd = 3 V
ΓΓ
Γ
Frequency NF
o
ΓΓ
opt
(GHz) (dB) Mag. Ang. RN/50 Ω
0.5 2.6 0.71 1 1.57
1.0 1.7 0.68 17 0.96
1.5 1.6 0.68 28 0.75
2.0 1.6 0.66 36 0.67
2.5 1.6 0.63 42 0.56
3.0 1.6 0.59 49 0.53
3.5 1.8 0.56 55 0.55
4.0 2.0 0.53 62 0.58
K
Notes:
4. Reference plane per Figure 11 in Applications Information section.
Page 5

5
MGA-87563 Applications
Information
Introduction
The MGA-87563 low noise RF
amplifier is designed to simplify
wireless RF applications in the
0.5 to 4 GHz frequency range. The
MGA-87563 is a two-stage, GaAs
Microwave Monolithic Integrated
Circuit (MMIC) amplifier that
uses feedback to provide
wideband gain. The output is
matched to 50 Ω and the input is
partially matched for optimum
noise figure.
A patented, active bias circuit
makes use of current sources to
“re-use” the drain current in both
stages of gain, thus minimizing
the required supply current and
decreasing sensitivity to variations in power supply voltage.
Test Circuit
The circuit shown in Figure 10 is
used for 100% RF testing of Noise
Figure and Gain. The input of this
circuit is fixed tuned for a
conjugate power match (maximum power transfer, or, minimum Input VSWR) at 2 GHz.
Tests in this circuit are used to
guarantee the NF
parameters shown in the
Electrical Specifications table.
The 4.7 nH inductor, L1 (Coilcraft,
Cary, IL part number series
1008CT-040) placed in series with
C1
RF
INPUT
L1
4.7 nH50 Ω
test
V
and G
dd
10 Ω
50 Ω
test
RF
OUTPUT
the input of the amplifier is all
that is necessary to match the
input to 50 Ω at 2 GHz.
Phase Reference Planes
The positions of the reference
planes used to measure
S-Parameters and to specify Γ
opt
for the Noise Parameters are
shown in Figure 11. As seen in the
illustration, the reference planes
are located at the extremities of
the package leads.
Biasing
The MGA-87563 is a voltagebiased device and operates from
a single +3 volt power supply.
With a typical current drain of
only 4.5 mA, the MGA-87563 is
very well suited for use in battery
powered applications. All bias
regulation circuitry is integrated
into the MMIC, eliminating the
need for external DC components. RF performance is very
consistent for 3-volt battery
supplies that may range from 2.7
to 3.3 volts, depending on battery
“freshness” or state of charge for
rechargeable batteries. Operation
up to +5 volts is discussed at the
end of the Applications section.
The test circuit in Figure 10
illustrates a suitable method for
bringing bias into the MGA-87563.
The bias connection must be
designed so that it adequately
bypasses the Vdd terminal while
not inadvertently creating any
resonances at frequencies where
the MGA-87563 has gain.
REFERENCE
PLANES
TEST CIRCUIT
The 10 Ω resistor, R1, serves to
“de-Q” any potential resonances
in the bias line that could lead to
low gain, unwanted gain variations or device instability. The
power supply end of R1 is
bypassed to ground with
capacitor C1. The suggested value
for C1 is 100 pF. Significantly
higher values for C1 are not
recommended. Many higher value
chip capacitors (e.g., 1000 pF) are
not of sufficiently high quality at
these frequencies to function well
as a RF bypass without adding
harmful parasitics or selfresonances.
While the input and output
terminals are internally resistively
grounded, these pins should not
be considered to be current sinks.
Connection of the MGA-87563
amplifier to circuits that are at
ground potential may be made
without the additional cost and
PCB space needed for DC blocking capacitors. If the amplifier is
to be cascaded with active circuits
having non-zero voltages present,
the use of series blocking
capacitors is recommended.
Input Matching
The input of the MGA-87563 is
partially matched internally to
50 Ω. The use of a simple input
conjugate matching circuit (such
as shown in Figure 10 for 2 GHz),
will lower the noise figure
considerably. A significant advantage of the MGA-87563’s design is
that the impedance match for NF
(minimum noise figure) is very
close to a conjugate power
match. This means that a very
low noise figure can be realized
simultaneously with a low input
VSWR. The typical difference
o
Figure 10. Test Circuit for 2 GHz.
Figure 11. Reference Planes.
Page 6

6
between the noise figure obtainable with a conjugate power
match at the input and NFo is only
about 0.2 dB.
Output Matching
The output of the MGA-87563 is
matched internally to 50 Ω above
1.8 GHz. The use of a conjugate
matching circuit, such as a simple
series inductor, can increase the
gain considerably at lower
frequencies. Matching the output
will not affect the noise figure.
Stability
If the MGA-87563 is cascaded
with highly reactive stages (such
as filters) some precautions may
be needed to ensure stability. The
low frequency stability (under
1.5 GHz) of the MGA-87563 can
be enhanced by adding a series
R-L network in shunt with the
output, as shown in Figure 12.
The inductor can be either a chip
component or a high impedance
transmission line as shown in the
figure. Component values are
selected such that the output of
the MGA-87563 will be resistively
loaded at low frequencies while
allowing high frequency signals to
pass the stability load with
minimal loss.
Typical values for the resistor are
in the 25 to 50 Ω range. A
suggested starting place for the
inductor is a 0.35 to 0.40-inch long
microstripline with a width of
DC BLOCKING
MGA
87563
Figure 12. Output Circuitry for Low
Frequency Stability.
CAPACITOR
25-50 Ω
HIGH IMPEDANCE
TRANSMISSION
OR INDUCTOR
OUTPUT
RF
0.020 inches, using 0.031-inch
thick FR-4 (ε
= 4.8) circuit board
r
as the substrate.
For applications near 1.5 GHz,
gain (and output power) may be
traded off for increased stability.
Some precautions regarding the
V
connection of the MGA-87563
dd
are also recommended to ensure
stability within the operating
frequency range of the device. It
is important that the connection
to the power supply be properly
bypassed to realize full amplifier
performance. Refer to the Biasing
section above for more
information.
SOT-363 PCB Layout
A PCB pad layout for the miniature SOT-363 (SC-70) package is
shown in Figure 13 (dimensions
are in inches). This layout provides
ample allowance for package
placement by automated assembly equipment without adding
parasitics that could impair the
high frequency RF performance
of the MGA-87563. The layout is
shown with a nominal SOT-363
package footprint superimposed
on the PCB pads.
0.026
0.079
0.039
0.018
Dimensions in inches.
Figure 13. Recommended PCB Pad
Layout for Agilent’s SC70 6L/SOT-363
Products.
RF Layout
The RF layout in Figure 14 is
suggested as a starting point for
designs using the MGA-87563
amplifier. Adequate grounding is
needed to obtain maximum performance and to obviate potential
instability. All three ground pins
of the MMIC should be connected
to RF ground by using plated
through holes (vias) near the
package terminals.
It is recommended that the PCB
traces for the ground pins NOT be
connected together underneath
the body of the package. PCB
pads hidden under the package
cannot be adequately inspected
for SMT solder quality.
FR-4 or G-10 PCB material is a
good choice for most low cost
wireless applications. Typical
board thickness is 0.025 or
0.031 inches. The width of 50 Ω
microstriplines in these PCB
thicknesses is also convenient for
mounting chip components such
as the series inductor at the input
for impedance matching or for
DC blocking capacitors. For noise
figure sensitive applications, the
use of PTFE/glass dielectric
materials may be warranted to
minimize transmission line losses
at the amplifier input.
Higher Bias Voltages
While the MGA-87563 is designed
for use in +3 volt battery powered
applications, the internal bias
regulation circuitry allows it to be
V
DD
RF OUTPUT
50 Ω
87
50 Ω
RF INPUT
Figure 14. RF Layout.
Page 7

7
easily operated with any power
supply voltage from +2.7 to
5 volts. Figure 15 shows an
increase of approximately 1 dB in
the associated gain with +5 volts
applied. The P
output power
1dB
(Figure 17) is also higher by
about 1 dBm. The effect of higher
Vdd on noise figure is negligible as
indicated in Figure 16.
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
ASSOCIATED GAIN (dB)
10
9
0.5
1.0
1.5 3.0 3.5
FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 15. Associated Gain vs.
Frequency at Vdd = 5 Volts.
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
OPTIMUM NF (dB)
1.0
2.0
2.5
4.0
Package Dimensions
Outline 63 (SOT-363/SC-70)
HE
e
D
A1
b
DIMENSIONS (mm)
SYMBOL
E
D
HE
A
A2
A1
Q1
e
b
c
L
MIN.
1.15
1.80
1.80
0.80
0.80
0.00
0.10
0.15
0.10
0.10
MAX.
1.35
2.25
2.40
1.10
1.00
0.10
0.40
0.650 BCS
0.30
0.20
0.30
E
Q1
A2
A
L
NOTES:
1. All dimensions are in mm.
2. Dimensions are inclusive of plating.
3. Dimensions are exclusive of mold flash & metal burr.
4. All specifications comply to EIAJ SC70.
5. Die is facing up for mold and facing down for trim/form,
ie: reverse trim/form.
6. Package surface to be mirror finish.
c
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.5 3.0 3.5
FREQUENCY (GHz)
2.0
2.5
4.0
Figure 16. Optimum Noise Figure vs.
Frequency at Vdd = 5 Volts.
0.00
-0.50
-1.00
P 1 dB (dBm)
-1.50
-2.00
0.6
2.41.2
1.8 3.0 3.6 4.2
FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 17. Output Power at 1 dB Gain
Compression vs. Frequency at Vdd =
5 Volts.
Part Number Ordering Information
No. of
Part Number Devices Container
MGA-87563-TR1 3000 7" Reel
MGA-87563-TR2 10000 13" Reel
MGA-87563-BLK 100 antistatic bag
MGA-87563-TR1G 3000 7" Reel
MGA-87563-TR2G 10000 13" Reel
MGA-87563-BLKG 100 antistatic bag
Note: For lead-free option, the part number will have the
character “G” at the end.
Page 8

Device Orientation
REEL
CARRIER
8 mm
TAPE
USER
FEED
DIRECTION
COVER TAPE
Tape Dimensions and Product Orientation
For Outline 63
P
P
0
C
D
TOP VIEW
4 mm
87 87 87 87
P
2
END VIEW
E
F
W
CAVITY
PERFORATION
CARRIER TAPE
COVER TAPE
DISTANCE
t
(CARRIER TAPE THICKNESS) Tt (COVER TAPE THICKNESS)
1
10° MAX.
A
0
DESCRIPTION SYMBOL SIZE (mm) SIZE (INCHES)
A
LENGTH
WIDTH
DEPTH
PITCH
BOTTOM HOLE DIAMETER
DIAMETER
PITCH
POSITION
WIDTH
THICKNESS
WIDTH
TAPE THICKNESS
CAVITY TO PERFORATION
(WIDTH DIRECTION)
CAVITY TO PERFORATION
(LENGTH DIRECTION)
0
B
0
K
0
P
D
1
D
P
0
E
W
t
1
C
T
t
F
P
2
2.40 ± 0.10
2.40 ± 0.10
1.20 ± 0.10
4.00 ± 0.10
1.00 + 0.25
1.55 ± 0.10
4.00 ± 0.10
1.75 ± 0.10
8.00 + 0.30 - 0.10
0.254 ± 0.02
5.40 ± 0.10
0.062 ± 0.001
3.50 ± 0.05
2.00 ± 0.05
K
0
0.094 ± 0.004
0.094 ± 0.004
0.047 ± 0.004
0.157 ± 0.004
0.039 + 0.010
0.061 + 0.002
0.157 ± 0.004
0.069 ± 0.004
0.315 + 0.012
0.0100 ± 0.0008
0.205 + 0.004
0.0025 ± 0.0004
0.138 ± 0.002
0.079 ± 0.002
D
1
10° MAX.
B
0
For product information and a complete list of Agilent
contacts and distributors, please go to our web site.
www.agilent.com/semiconductors
E-mail: SemiconductorSupport@agilent.com
Data subject to change.
Copyright © 2004 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Obsoletes 5965-9688E
November 16, 2004
5989-1803EN
 Loading...
Loading...