Page 1

W-CDMA Programming Commands
Agilent Technologies E4406A VSA Series
Transmitter Tester
Manufacturing Part Number: E4406-90089
Printed in USA
April 2000
© Copyright 1999-2000 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Page 2

The information contained in this document is subject to change
without notice.
Agilent Technologiesmakesnowarrantyofanykindwithregard to this
material, including but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Agilent
Technologies shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for
incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
2
Page 3

Contents
SCPI Command Subsystems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
CALCulate Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Code Domain Power Measurement Power Offset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Code Domain Power Measurement Spread Code. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Code Domain Power Measurement Symbol Rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Code Domain Power Measurement Sweep Offset (Measurement Offset)
8
CodeDomainPowerMeasurementSweepTime(MeasurementInterval)
9
Query the Current Measurement Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Data Query . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Calculate/Compress Trace Data Query. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Calculate Peaks of Trace Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
CALCulate:MARKers Subsection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
CONFigure Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
DISPlay Subsystem. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement View Selection . . . . . . . . . . .22
Spectrum Measurement Y-Axis Reference Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Turn a Trace Display On/Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Waveform Measurement Y-Axis Reference Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
FETCh Subsystem. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
MEASure Group of Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Measure Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Configure Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Fetch Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Read Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Adjacent Channel Power Ratio (ACP) Measurement. . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Code Domain Power Measurement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Channel Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
3
Page 4

Contents
Power Statistics CCDF Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Rho (Waveform Quality) Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Spectrum (Frequency Domain) Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Waveform (Time Domain) Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
READ Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
SENSe Subsystem. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Code Domain Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Channel Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Correction for BTS RF Port External Attenuation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Correction for Mobile Station RF Port External Attenuation . . . . . . .78
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Power Statistics CCDF Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Radio Device Under Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Frequency Offset of MS to BTS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Radio Format (Standard). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Rho (Waveform Quality) Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Spectrum (Frequency-Domain) Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .91
Waveform (Time-Domain) Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
4
Page 5

1 W-CDMA Programming
Commands
These commands are only available when the W-CDMA mode has been
selected using INSTrument:SELect. If W-CDMA mode is selected,
commands that are unique to another mode are not available.
5
Page 6

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SCPI Command Subsystems
SCPI Command Subsystems
CALCulate on page 7
CONFigure on page 21
DISPlay on page 22
FETCh on page 26
MEASure on page 27
READ on page 52
SENSe on page 53
6 Chapter1
Page 7

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
CALCulate Subsystem
This subsystem is used to perform post-acquisition data processing. In
effect, the collection of new data triggers the CALCulate subsystem. In
this instrument, the primary functions in this subsystem are markers
and limits.
Code Domain Power Measurement Power Offset
:CALCulate:CDPower:PO1 <rel_power>
:CALCulate:CDPower:PO1?
Set the power offset value of the pilot bits.
:CALCulate:CDPower:PO2 <rel_power>
:CALCulate:CDPower:PO2?
Set the power offset value of the transmit control bits.
:CALCulate:CDPower:PO3 <rel_power>
:CALCulate:CDPower:PO3?
Set the power offset value of the transport format control indicator bits.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0 dB
Range: −20 to 50 dB
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Code Domain Power Measurement Spread Code
:CALCulate:CDPower:SPRead <integer>
:CALCulate:CDPower:SPRead?
Set a spread code.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0
Range: 0 to 511, when CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe = 8
0 to 255, when CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe = 16
0 to 127, when CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe = 32
0 to 63, when CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe = 64
0 to 31, when CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe = 128
Chapter 1 7
Page 8

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
0 to 15, when CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe = 256
0 to 7, when CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe = 512
0 to 3, when CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe = 1024
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Code Domain Power Measurement Symbol Rate
:CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe <integer>
:CALCulate:CDPower:SRATe?
Set a symbol rate.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 16
Range: 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, when
[SENSe:]RADio:FORMat = ARIB
16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, when
[SENSe:]RADio:FORMat = Trial
Unit: ksps
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Code Domain Power Measurement Sweep Offset (Measurement Offset)
:CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:OFFSet <integer>
:CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:OFFSet?
Set the timing offset of measurement interval in slots. (1 slot = 625 µs)
The sum of CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:TIME and
CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:OFFSet must be equal to or less than 32,
because data of 32 slots are acquired. If the sum becomes more than 32,
CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:TIME is adjusted automatically.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0
Range: 0 to 31
Unit: slots
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
8 Chapter1
Page 9

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
Code Domain Power Measurement Sweep Time (Measurement Interval)
:CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:TIME <integer>
:CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:TIME?
Set the length of measurement interval in slots. (1 slot = 625 µs)
The sum of CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:TIME and
CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:OFFSet must be equal to or less than 32,
because data of 32 slots are acquired. If the sum becomes more than 32,
CALCulate:CDPower:SWEep:OFFSet is adjusted automatically.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1
Range: 1 to 32
Unit: slots
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Query the Current Measurement Status
:CALCulate:CLIMits:FAIL?
Checks if the current measurement is outside its limits. It returns a 0
(zero) if it is passing or a 1 (one) if it is failing.
Front Panel
Access: None
Data Query
:CALCulate:DATA[n]?
Returns the designated measurement data for the currently selected
measurement and sub-opcode.
n = any valid sub-opcode for the current measurement. See the
“MEASure Group of Commands” on page 27 for information on the data
that can be returned for each measurement.
Calculate/Compress Trace Data Query
:CALCulate:DATA[n]:COMPress?
MAXimum|MEAN|MINimum|RMS|SAMPle|SDEViation|CFIT
{,<soffset>}{,<length>}{,<roffset>}
Returns the designated trace data for the currently selected
measurement. The command can be used with sub-opcodes (n) for
measurement results that are trace data. See the following table.
Chapter 1 9
Page 10

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
This command is used to compress/decimate a long trace to extract the
desired data and only return to the computer the necessary data. A
typical example would be to acquire N bursts of GSM data and return
the mean power of each burst.
The command can also be used to identify the best curve fit for the data.
Curve Fit - applies curve fitting routines to the data. Where
<soffset> and <length> are required, and <roffset> is an optional
parameter for the desired order of the curve equation. The query will
return the following values: the x-offset (in points) and the curve
coefficients ((order + 1) values).
<Start offset> - is an optional integer. It specifies the amount of data,
at the beginning of the trace, that will be ignored before the
decimation process starts. It is an integer index (that starts counting
at zero) for all the elements in the trace. The default value is zero.
<Length> - is an optional integer that defines how many trace
elements will be compressed into one value. This parameter has a
default value equal to the current trace length.
<Repeat offset> - is an optional real number.It defines the beginning
of the next field of trace elements to be compressed. This is relative
to the beginning of the previous field. This parameter has a default
value equal to the <length> variable. Select a number such that
repeated additions will round to the correct starting index.
Example: To query the mean power of a set of GSM bursts:
1. Set the waveform measurement sweep time to
acquire the required number of bursts.
2. Set the triggers such that acquisition happens at a
known position relative to a burst.
3. Then query the mean burst levels using,
CALC:DATA2:COMP? MEAN,62,1315,1442.3 (These
parameter values correspond to GSM signals.)
Remarks: The optional parameters must be entered in the
specified order. If you want to specify <length>, you
must also specify <soffset> or it’s default. (e.g.
CALC:DATA2:COMP? MEAN,62,1315
This command uses the data setting specified by the
FORMat:DATA command and can return binary or
ascii data.
10 Chapter1
Page 11

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
History: Added in revision A.03.00 and later
Measurement Available Traces Markers
Available?
ACP - adjacent channel power
(Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000,
W-CDMA, iDEN, NADC, PDC modes)
CDPower - code domain power
(W-CDMA mode)
CHPower - channel power
(Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA
mode)
EVMQpsk - QPSK error vector
magnitude
(cdma2000, W-CDMA modes)
PSTatistic - power statistics CCDF
(cdma2000, W-CDMA modes)
no traces no markers
CDPower (n=2)
EVM (n=4)
MERRor (n=5)
PERRor (n=6)
SPOWer (n=8)
a
a
a
a
SPECtrum (n=2)
EVM (n=2)
MERRor (n=3)
PERRor (n=4)
a
a
a
MEASured (n=2)
GAUSsian (n=3)
REFerence (n=4)
a
a
a
a
a
yes
no markers
yes
yes
RHO - modulation quality
(cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode)
SPECtrum - (frequency domain)
(all modes)
WAVEform - (time domain)
(all modes)
EVM (n=2)
MAGerror (n=3)
PHASe (n=4)
RFENvelope (n=2)
for Service mode
IQ (n=3)
SPECtrum (n=4)
ASPectrum (n=7)
RFENvelope (n=2)
IQ (n=8)
a
a
a
a
a
a
yes
a
yes
a
a
yes
Chapter 1 11
Page 12

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
a. The n number indicates the sub-opcode that corresponds to this
trace. Detailed descriptions of the trace data can be found in the
MEASure subsystem documentation by looking up the
sub-opcode for the appropriate measurement.
Calculate Peaks of Trace Data
:CALCulate:DATA[n]:PEAKs?
<threshold>,<excursion>[,AMPLitude|FREQuency|TIME]
Returns a list of peaks for the designated trace data n for the currently
selected measurement. The peaks must meet the requirements of the
peak threshold and excursion values.
The command can be used with sub-opcodes (n) for any measurement
results that are trace data. See the table above. Subopcode n=0, raw
trace data cannot be searched for peaks. Both real and complex traces
can be searched, but complex traces are converted to magnitude in
dBm.
Threshold - is the level below which trace data peaks are ignored
Excursion - To be defined as a peak, the signal must rise above the
threshold by a minimum amplitude change. Excursion is measured
from the lowest point above the threshold (of the rising edge of the
peak), to the highest signal point that begins the falling edge.
Amplitude - lists the peaks in order of descending amplitude, so the
highest peak is listed first. This is the default peak order listing if
the optional parameter is not specified.
Frequency - lists the peaks in order of occurrence, left to right across
the x-axis
Time - lists the peaks in order of occurrence, left to right across the
x-axis
Example: Select the spectrum measurement.
Use CALC:DATA4:PEAK? -40,10,FREQ to identify the
peaks above -40 dBm, with excursions of at least 10 dB,
in order of increasing frequency.
Query Results: Returns a list of floating-point numbers. The first value
in the list is the number of peak points that follow. A
peak point consists of two values: a peak amplitude
followed by the its corresponding frequency (or time).
If no peaks are found the peak list will consist of only
the number of peaks, (0).
The peak list is limited to 100 peaks. Peaks in excess of
100 are ignored.
12 Chapter1
Page 13

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
Remarks: This command uses the data setting specified by the
FORMat:DATA command and can return real 32-bit,
real 64-bit, or ASCII data. The default data format is
ASCII.
History: Added in revision A.03.00 and later
Chapter 1 13
Page 14

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
CALCulate:MARKers Subsection
When using the marker commands you must specify the measurement
in the SCPI command. We recommend that you use the marker
commands only on the current measurement. Many marker commands
will return invalid results, when used on a measurement that is not
current. (This is true for commands that do more than simply setting or
querying an instrument parameter.) No error is reported for these
invalid results.
You must make sure that the measurement is completed before trying
to query the marker value. Using the MEASure or READ command,
before the marker command, forces the measurement to complete
before allowing the next command to be executed.
Each measurement has its own instrument state for marker
parameters. Therefore, if you exit the measurement, the marker
settings in each measurement are saved and are then recalled when
you change back to that measurement.
W-CDMA Mode - <measurement> key words
• ACP - no markers
• CDPower - markers available
• CHPower - no markers
• EVMQpsk - markers available
• PSTatistic - markers available
• RHO - markers available
• SPECtrum - markers available
• WAVeform - markers available
Example:
Suppose you are using the Spectrum measurement. Toposition marker
2 at the maximum peak value, of the trace that marker 2 is currently
on, the command is:
:CALCulate:SPECtrum:MARKer2:MAXimum
You must make sure that the measurement is completed before trying
to query the marker value. Using the MEASure or READ command,
before the marker command, forces the measurement to complete
before allowing the next command to be executed.
14 Chapter1
Page 15

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
Markers All Off on All Traces
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer:AOFF
Turns off all markers on all the traces.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK:AOFF
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access:
Marker, More, Marker All Off
Marker Function
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:FUNCtion
BPOWer|NOISe|OFF
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:FUNCtion?
Selects the type of marker for the specified marker. A particular
measurement may not have all the types of markers that are commonly
available.
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
Band Power − is the integrated power between the two markers for
traces in the frequency domain and is the mean power between the
two markers for traces in the time domain.
Noise − is the noise power spectral density in a 1 Hz bandwidth. It is
averaged over 32 horizontal trace points.
Off − turns off the marker functions
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK3:FUNC Noise
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access:
Marker, Marker Function
Marker Function Result
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:FUNCtion:RESult?
Quires the result of the currently active marker function. The
measurement must be completed before querying the marker.A
particular measurement may not have all the types of markers
available.
Chapter 1 15
Page 16

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK:FUNC:RES?
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access:
Marker, Marker Function
Marker Peak (Maximum) Search
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:MAXimum
Places the selected marker on the highest point on the trace that is
assigned to that particular marker number.
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK1:MAX
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access: Search
Marker Peak (Minimum) Search
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:MINimum
Places the selected marker on the lowest point on the trace that is
assigned to that particular marker number.
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK2:MIN
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access: None
16 Chapter1
Page 17

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
Marker Mode
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:MODE
POSition|DELTa
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:MODE?
Selects the type of marker to be a normal position-type marker or a
delta marker.A specific measurement may not have both types of
markers. For example, several measurements only have position
markers.
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK:MODE DELTA
Remarks: For the delta mode only markers 1 and 2 are valid.
The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access:
Marker, Marker [Delta]
Marker On/Off
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4[:STATe] OFF|ON|0|1
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4[:STATe]?
Turns the selected marker on or off.
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK2: on
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, AREFerence, WAVeform)
The WAVeform measurement only has two markers
available.
Front Panel
Access: M
arker, Select then Marker Normal or Marker On Off
Chapter 1 17
Page 18

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
Marker to Trace
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe <trace_name>
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe?
Assigns the specified marker to the designated trace. Not all types of
measurement data can have markers assigned to them.
Example: With the WAVeform measurement selected, a valid
command is CALC:SPEC:MARK2:TRACE rfenvelope.
Range: The names of valid traces are dependent upon the
selected measurement. See the following table for the
available trace names. The trace name assignment is
independent of the marker number.
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access:
Marker, Marker Trace
Measurement Available Traces Markers
Available?
ACP - adjacent channel power
no traces no markers
(Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000,
W-CDMA, iDEN, NADC, PDC modes)
CDPower - code domain power
(W-CDMA mode)
CHPower - channel power
CDPower (n=2)
EVM (n=4)
MERRor (n=5)
PERRor (n=6)
SPOWer (n=8)
SPECtrum (n=2)
a
a
a
a
a
a
yes
no markers
(Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA
mode)
EVMQpsk - QPSK error vector
magnitude
(cdma2000, W-CDMA modes)
EVM (n=2)
MERRor (n=3)
PERRor (n=4)
a
a
a
yes
PSTatistic - power statistics CCDF
(cdma2000, W-CDMA modes)
MEASured (n=2)
GAUSian (n=3)
REFerence (n=4)
a
yes
a
a
18 Chapter1
Page 19

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
Measurement Available Traces Markers
Available?
RHO - modulation quality
(cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode)
SPECtrum - (frequency domain)
(all modes)
WAVEform - (time domain)
(all modes)
EVM (n=2)
MAGerror (n=3)
PHASe (n=4)
RFENvelope (n=2)
for Service mode
IQ (n=3)
SPECtrum (n=4)
ASPectrum (n=7)
RFENvelope (n=2)
IQ (n=8)
a
a
a
a
a
a
yes
a
yes
a
a
yes
a. The n number indicates the sub-opcode that corresponds to this
trace. Detailed descriptions of the trace data can be found in the
MEASure subsystem documentation by looking up the
sub-opcode for the appropriate measurement.
Marker X Value
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:X <param>
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:X?
Position the designated marker on its assigned trace at the specified X
value. The parameter value is in X-axis units (which is often frequency
or time).
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
The query returns the current X value of the designated marker. The
measurement must be completed before querying the marker.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK2:X 1.2e6 Hz
Default Unit: Matches the units of the trace on which the marker is
positioned
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access: Marker, <active marker>, RPG
Chapter 1 19
Page 20

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CALCulate Subsystem
Marker X Position
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:X:POSition
<integer>
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:X:POSition?
Position the designated marker on its assigned trace at the specified X
position. A trace is composed of a variable number of measurement
points. This number changes depending on the current measurement
conditions. The current number of points must be identified before
using this command to place the marker at a specific location.
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
The query returns the current X position for the designated marker.
The measurement must be completed before querying the marker.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK:X:POS 500
Range: 0 to a maximum of (3 to 920,000)
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
Front Panel
Access:
Marker, <active marker>, RPG
Marker Readout Y Value
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:Y?
Readout the current Y value for the designated marker on its assigned
trace. The value is in the Y-axis units for the trace (which is often dBm).
The marker must have already been assigned to a trace. Use
:CALCulate:<measurement>:MARKer[1]|2|3|4:TRACe to assign a
marker to a particular trace.
The measurement must be completed before querying the marker.
Example: CALC:SPEC:MARK1:Y -20 dB
Default Unit: Matches the units of the trace on which the marker is
positioned
Remarks: The keyword for the current measurement must be
specified in the command. (Some examples include:
SPECtrum, WAVeform)
20 Chapter1
Page 21

W-CDMA Programming Commands
CONFigure Subsystem
CONFigure Subsystem
:CONFigure:<measurement>
The CONFigure commands are used with several other commands and
are documented in the section on the “MEASure Group of Commands”
on page 27.
Chapter 1 21
Page 22

W-CDMA Programming Commands
DISPlay Subsystem
DISPlay Subsystem
The DISPlay controls the selection and presentation of textual,
graphical, and TRACe information. Within a DISPlay, information may
be separated into individual WINDows.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement View Selection
:DISPlay:ACP:VIEW BGRaph|SPECtrum
:DISPlay:ACP:VIEW?
Select the adjacent channel power measurement display of bar graph or
spectrum.
Factory Preset
and *RST: BGRaph
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000, W-CDMA, NADC or PDC
mode to use this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to
set the mode.
Spectrum Measurement Y-Axis Reference Level
:DISPlay:SPECtrum[n]:WINDow[m]:TRACe:Y[:SCALe]:RLEVel
<power>
:DISPlay:SPECtrum[n]:WINDow[m]:TRACe:Y[:SCALe]:RLEVel?
Sets the amplitude reference level for the y-axis.
n − selects the view, the default is Spectrum.
— n=1, Spectrum
— n=2, I/Q Waveform
— n=3, numeric data (service mode)
— n=4, RF Envelope (service mode)
m − selects the window within the view. The default is 1.
22 Chapter1
Page 23

W-CDMA Programming Commands
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0 dBm, for Spectrum
Range: −250 to 250 dBm, for Spectrum
Default Unit: dBm, for Spectrum
Remarks: May affect input attenuator setting.
To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Front Panel
Access: When in Spectrum measurement:
Level
Amplitude Y Scale, Ref
Turn a Trace Display On/Off
:DISPlay:TRACe[n][:STATe] OFF|ON|0|1
:DISPlay:TRACe[n][:STATe]?
DISPlay Subsystem
Controls whether the specified trace is visible or not.
n is a sub-opcode that is valid for the current measurement. See the
“MEASure Group of Commands” on page 27 for more information about
sub-opcodes.
Factory Preset
and *RST: On
Range: The valid traces and their sub-opcodes are dependent
upon the selected measurement. See the following
table.
The trace name assignment is independent of the
window number.
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Front Panel
Access: Display, Display Traces
Chapter 1 23
Page 24

W-CDMA Programming Commands
DISPlay Subsystem
Measurement Available Traces Markers
Available?
ACP - adjacent channel power
(Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000,
W-CDMA, iDEN, NADC, PDC modes)
CDPower - code domain power
(W-CDMA mode)
CHPower - channel power
(Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA
mode)
EVMQpsk - QPSK error vector
magnitude
(cdma2000, W-CDMA modes)
PSTatistic - power statistics CCDF
(cdma2000, W-CDMA modes)
no traces no markers
CDPower (n=2)
EVM (n=4)
MERRor (n=5)
PERRor (n=6)
SPOWer (n=8)
a
a
a
a
SPECtrum (n=2)
EVM (n=2)
MERRor (n=3)
PERRor (n=4)
a
a
a
MEASured (n=2)
GAUSian (n=3)
REFerence (n=4)
a
a
a
a
a
yes
no markers
yes
yes
RHO - modulation quality
(cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode)
SPECtrum - (frequency domain)
(all modes)
WAVEform - (time domain)
(all modes)
EVM (n=2)
MAGerror (n=3)
PHASe (n=4)
RFENvelope (n=2)
for Service mode
IQ (n=3)
SPECtrum (n=4)
ASPectrum (n=7)
RFENvelope (n=2)
IQ (n=8)
a
a
a
a
a
a
yes
a
yes
a
a
yes
a. The n number indicates the sub-opcode that corresponds to this
trace. Detailed descriptions of the trace data can be found in the
MEASure subsystem documentation by looking up the
sub-opcode for the appropriate measurement.
24 Chapter1
Page 25

W-CDMA Programming Commands
DISPlay Subsystem
Waveform Measurement Y-Axis Reference Level
:DISPlay:WAVEform[n]:WINDow[m]:TRACe:Y[:SCALe]:RLEVel
<power>
:DISPlay:WAVEform[n]:WINDow[m]:TRACe:Y[:SCALe]:RLEVel?
Sets the amplitude reference level for the y-axis.
n − selects the view, the default is RF envelope.
— n=1, RF Envelope
— n=2, I/Q Waveform
m − selects the window within the view. The default is 1.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0 dBm, for RF envelope
Range: −250 to 250 dBm, for RF envelope
Default Unit: dBm, for RF envelope
Remarks: May affect input attenuator setting.
To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Front Panel
Access: When in Waveform measurement:
Ref Level
Amplitude Y Scale,
Chapter 1 25
Page 26

W-CDMA Programming Commands
FETCh Subsystem
FETCh Subsystem
:FETCh:<measurement>[n]?
The FETCh? commands are used with several other commands and are
documented in the section on the “MEASure Group of Commands” on
page 27.
26 Chapter1
Page 27

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
This group includes commands used to make measurements and return
results. The different commands can be used to provide fine control of
the overall measurement process. Most measurements should be done
in single measurement mode, rather than doing the measurement
continuously.
Each measurement sets the instrument state that is appropriate for
that measurement. Other commands are available for each
allow changing settings, view, limits, etc. Refer to:
SENSe:<measurement>, SENSe:CHANnel, SENSe:CORRection,
SENSe:FREQuency, SENSe:POWer, SENSe:RADio, SENSe:SNYC
CALCulate:<measurement>, CALCulate:CLIMits/DATA
DISPlay:<measurement>
TRIGger
Mode to
Measure Commands
:MEASure:<measurement>[n]?
This is a fast single-command way to make a measurement using the
factory default instrument settings. These are the settings and units
that conform to the Standard.
• Stops the current measurement and sets up the instrument for the
specified measurement using the factory defaults
• Initiates the data acquisition for the measurement
• Blocks other SCPI communication, waiting until the measurement is
complete before returning results.
• After the data is valid it returns the scalar results, or the trace data,
for the specified measurement.
If the optional [n] value is not included, or is set to 1, the scalar
measurement results will be returned. If the [n] value is set to a
value other than 1, the selected trace data results will be returned.
See each command for details of what types of scalar results or trace
data results are available. The binary data formats should be used
for handling large blocks of data since they are smaller and faster
then the ASCII format.
Chapter 1 27
Page 28

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
If you need to change some of the measurement parameters from the
factory default settings you can set up the measurement with the
CONFigure command. Use the commands in the
SENSe:<measurement> and CALCulate:<measurement> subsystems
to change the settings. Then you can use the READ? command, or the
INITiate and FETCh? commands, to initiate the measurement and
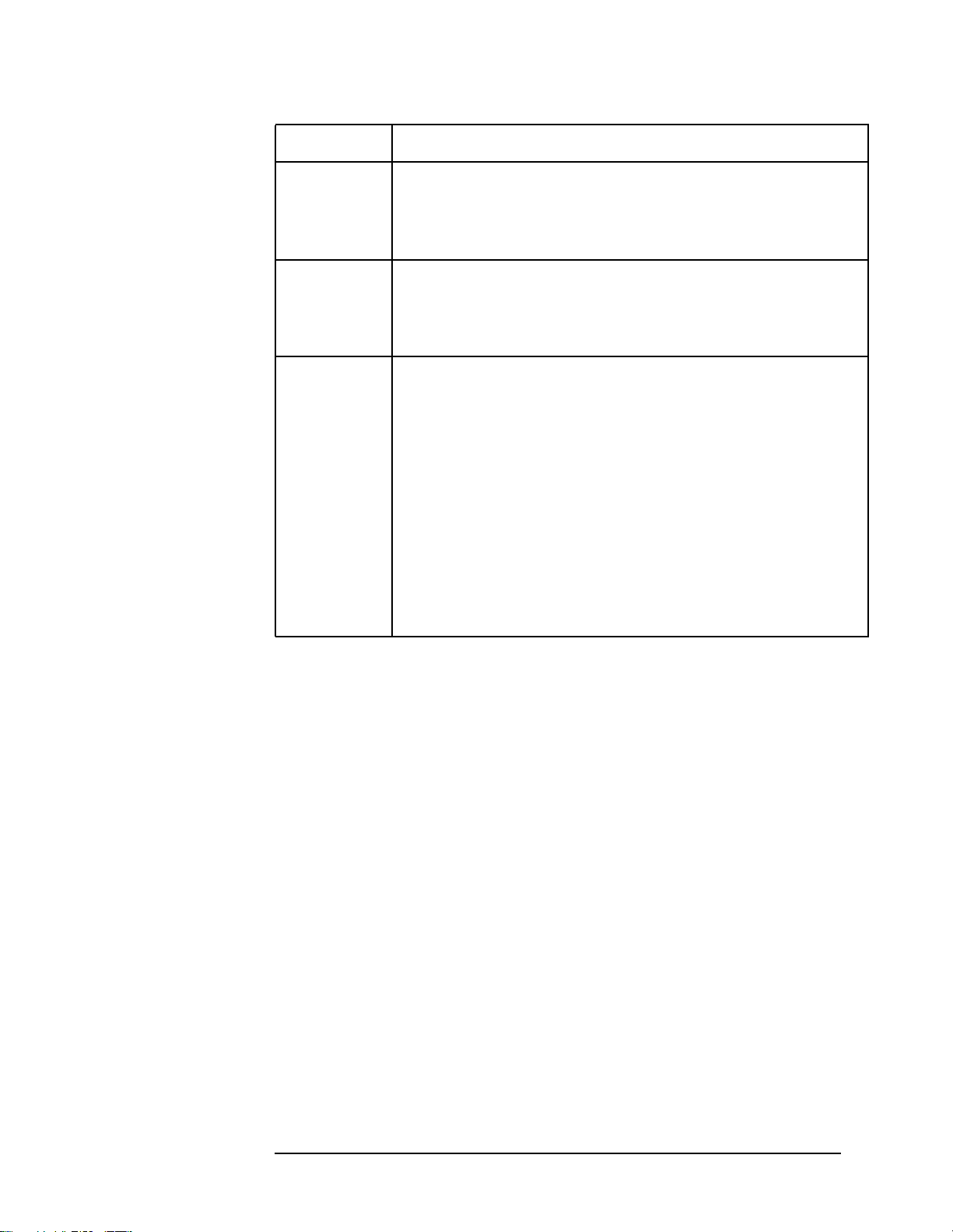
query the results. See Figure 1-1.
If you need to repeatedly make a given measurement with settings
other than the factory defaults, you can use the commands in the
SENSe:<measurement> and CALCulate:<measurement> subsystems
to set up the measurement. Then use the READ? command or INITiate
and FETCh? commands, to initiate the measurement and query results.
Measurement settings persist if you initiate a different measurement
and then return to a previous one. Use READ:<measurement>? if you
want to use those persistent settings. If you want to go back to the
default settings, use MEASure:<measurement>?.
Figure 1-1 Measurement Group of Commands
Start from
Any Inst State
Configure Commands
:CONFigure:<measurement>
This command sets up the instrument for the specified measurement
using the factory default instrument settings and stops the current
measurement. It does not initiate the taking of measurement data.
The CONFigure? query returns the current measurement name.
CONFigure
ABORt
returns
to this
point
Sets default
state then
waits
SENSe & CALCulate
commands
change the
settings from
the defaults
MEASure
INITiate
INITiate:RESTart
READ
Initialize
taking of
data
FETch
Acquired data
is calculated
and returned
ca81a
28 Chapter1
Page 29

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Fetch Commands
:FETCh:<measurement>[n]?
This command puts valid data into the output buffer, but does not
initiate data acquisition. Use the INITiate[:IMMediate] command to
acquire data before you use the FETCh command. You can only fetch
results from the measurement that is currently selected.
If the optional [n] value is not included, or is set to 1, the scalar
measurement results will be returned. If the [n] value is set to a value
other than 1, the selected trace data results will be returned. See each
command for details of what types of scalar results or trace data results
are available. The binary data formats should be used for handling
large blocks of data since they are smaller and faster then the ASCII
format.
Read Commands
:READ:<measurement>[n]?
• Does not preset the measurement to the factory defaults. (The
MEASure? command does preset.) It uses the settings from the last
measurement.
• Initiates the measurement and puts valid data into the output
buffer. If a measurement other than the current one is specified, the
instrument will switch to that measurement before it initiates the
measurement and returns results.
• Blocks other SCPI communication, waiting until the measurement is
complete before returning the results
If the optional [n] value is not included, or is set to 1, the scalar
measurement results will be returned. If the [n] value is set to a
value other than 1, the selected trace data results will be returned.
See each command for details of what types of scalar results or trace
data results are available. The binary data formats should be used
when handling large blocks of data since they are smaller and faster
then the ASCII format.
Measurement settings persist if you initiate a different measurement
and then return to a previous one. Use READ:<measurement>? if you
want to use those persistent settings. If you want to go back to the
default settings, use MEASure:<measurement>?.
Chapter 1 29
Page 30

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Adjacent Channel Power Ratio (ACP) Measurement
This measures the total rms power in the specified channel and in 5
offset channels. You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN, NADC or PDC mode to use these commands. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
The general functionality of CONFigure, FETCh, MEASure, and READ
are described at the beginning of this section. See the SENSe:ACP
commands for more measurement related commands.
:CONFigure:ACP
:FETCh:ACP[n]?
:READ:ACP[n]?
:MEASure:ACP[n]?
For Basic mode, a channel frequency and power level can be defined in
the command statement to override the default standard setting. A
comma must precede the power value as a place holder for the
frequency, when no frequency is sent.
History: Added to Basic mode, version A.03.00 or later
Front Panel
Access:
Measure, ACPR
After the measurement is selected, press Restore Meas
Defaults to restore factory defaults.
30 Chapter1
Page 31

Measurement Results Available
W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Measurement
Type
Total power
reference
n Results Returned
0 Returns unprocessed I/Q trace data, as a
series of comma-separated trace points, in
volts. The I values are listed first in each pair,
using the 0 through even-indexed values. The
Q values are the odd-indexed values.
not
specified or
n=1
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns 24 comma-separated scalar results,
in the following order:
Center freq - relative power (dB)
Center freq - absolute power (dBm)
Center freq - relative power (dB)
Center freq - absolute power (dBm)
Negative offset freq(1) - relative power
(dB),
Negative offset freq(1) - absolute power
(dBm)
Positive offset freq(1) - relative power (dB)
Positive offset freq(1) - absolute power
(dBm)
...
Positive offset freq(5) - relative power (dB)
Positive offset freq(5) - absolute power
(dBm)
Power spectral
density
reference
not
specified or
n=1
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns 24 comma-separated scalar results,
in the following order:
Center freq - relative power (dB)
Center freq - absolute power (dBm/Hz)
Center freq - relative power (dB)
Center freq - absolute power (dBm/Hz)
Negative offset freq(1) - relative power
(dB)
Negative offset freq(1) - absolute power
(dBm/Hz)
Positive offset freq(1) - relative power (dB)
Positive offset freq(1) - absolute power
(dBm/Hz)
...
Positive offset freq(5) - relative power (dB)
Positive offset freq(5) - absolute power
(dBm/Hz)
Chapter 1 31
Page 32

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Measurement
Type
Total power
reference
Power spectral
density
reference
n Results Returned
2
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
3
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns11 comma-separated scalar values (in
dBm) corresponding to the total power
histogram display. The values are returned in
ascending frequency order:
Negative offset frequency(5)
Negative offset frequency(4)
...
Center frequency
Positive Offset frequency(1)
...
Positive Offset frequency(5)
Returns11 comma-separated scalar values (in
dBm/Hz) corresponding to the power spectral
density histogram display. The values are
returned in ascending frequency order:
Negative offset frequency(5)
Negative offset frequency(4)
...
Center frequency
Positive Offset frequency(1)
...
Positive Offset frequency(5)
(For cdma2000
and W-CDMA
the data is only
available with
spectrum
display selected)
4
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns the frequency-domain spectrum trace
data for the entire frequency range being
measured.
With spectrum display selected
(DISPlay:ACP:VIEW SPEC):
• In FFT mode (SENSe:ACPR:SWEep:TYPE
FFT) the number of trace points returned
are 343 (cdma2000 SR1), 1029 (cdma2000
SR3) or 1715 (W-CDMA). This is with the
default span of 5 MHz (cdma2000 SR1), 15
MHz (cdma2000 SR3), or 25 MHz
(W-CDMA). The number of points also
varies if another offset frequency is set.
• In sweep mode
(SENSe:ACPR:SWEep:TYPE SWEep), the
number of trace points returned is 601 (for
cdma2000 or W-CDMA) for any span.
With bar graph display selected, one point of
–999.0 will be returned.
32 Chapter1
Page 33

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Measurement
Type
Total power
reference
Power spectral
density
reference
n Results Returned
5
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
5
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns12 comma-separated scalar values (in
dBm) of the absolute power of the center and
the offset frequencies:
Center frequency
Center frequency
Negative offset frequency(1)
Positive offset frequency(1)
...
Negative Offset frequency(5)
Positive Offset frequency(5)
Returns12 comma-separated scalar values (in
dBm/Hz) of the absolute power of the center
and the offset frequencies:
Center frequency
Center frequency
Negative offset frequency(1)
Positive offset frequency(1)
...
Negative offset frequency(5)
Positive offset frequency(5)
Total power
reference
Power spectral
density
reference
6
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
6
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns 12 comma-separated scalar values
(total power in dB) of the power relative to the
carrier at the center and the offset
frequencies:
Center frequency
Center frequency
Negative offset frequency(1)
Positive offset frequency(1)
...
Negative offset frequency(5)
Positive offset frequency(5)
Returns 12 comma-separated scalar values
(power spectral density in dB) of the power
relative to the carrier at the center and offset
frequencies:
Center frequency
Center frequency
Negative offset frequency(1)
Positive offset frequency(1)
...
Negative offset frequency(5)
Positive offset frequency(5)
Chapter 1 33
Page 34

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Measurement
Type
Total power
reference
Power spectral
density
reference
n Results Returned
7
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
7
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns 12 comma-separated scalar values of
the pass/fail (1=passed, or 0=failed) results
determined by testing the absolute power
limit of the center and offset frequencies
(measured as total power in dB):
Center frequency
Center frequency
Negative offset frequency(1)
Positive offset frequency(1)
...
Negative offset frequency(5)
Positive offset frequency(5)
Returns 12 comma-separated scalar values of
the pass/fail (1=passed, or 0=failed) results
determined by testing the absolute power
limit of the center and offset frequencies
(measured as power spectral density in dB):
Center frequency
Center frequency
Negative offset frequency(1)
Positive offset frequency(1)
...
Negative offset frequency(5)
Positive Offset frequency(5)
Total power
reference
8
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns 12 comma-separated scalar values of
the pass/fail (1=passed, or 0=failed) results
determined by testing the power limit relative
to the center frequency (measured as total
power spectral in dB):
Center frequency
Center frequency
Negative offset frequency(1)
Positive offset frequency(1)
...
Negative offset frequency(5)
Positive Offset frequency(5)
34 Chapter1
Page 35

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Measurement
Type
Power spectral
density
reference
n Results Returned
8
cdmaOne,
cdma2000,
or
W-CDMA
mode
Returns 12 comma-separated scalar values of
the pass/fail (1=passed, or 0=failed) results
determined by testing the power limit relative
to the center frequency (measured as power
spectral density in dB):
Center frequency
Center frequency
Negative offset frequency(1)
Positive offset frequency(1)
...
Negative offset frequency(5)
Positive Offset frequency(5)
Chapter 1 35
Page 36

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Code Domain Power Measurement
This measures the power for each of the 64 Walsh codes/channels,
relative to the total power in the pilot channel. You must be in the
cdmaOne or W-CDMA mode to use these commands. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
The general functionality of CONFigure, FETCh, MEASure, and READ
are described at the beginning of this section. See the SENSe:CDPower
commands for more measurement related commands.
:CONFigure:CDPower
:FETCh:CDPower[n]?
:READ:CDPower[n]?
:MEASure:CDPower[n]?
Front Panel
Access: Measure, Code Domain Power
After the measurement is selected, press Restore Meas
Defaults to restore factory defaults.
Measurement Results Available
n Results Returned
0 Returns unprocessed I/Q trace data, as a series of comma-separated trace
points, in volts. The I values are listed first in each pair, using the 0
through even-indexed values. The Q values are the odd-indexed values.
36 Chapter1
Page 37

n Results Returned
W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
not
specified
or n=1
W-CDM
A mode
Returns the following14 comma-separated scalar results:
1. RMS symbol EVM is a floating point number (in percent) of the EVM
over the entire measurement area.
2. Peak symbol EVM is a floating point number (in percent) of the peak
EVM in the measurement area.
3. Symbol magnitude error is a floating point number (in percent) of
the average magnitude error over the entire measurement area.
4. Symbol phase error is a floating point number (in degrees) of the
average phase error over the entire measurement area.
5. Total power is a floating point number with units of dBm. It is the
total RF power over the measurement interval.
6. Average power is a floating point number with units of dBm. It is the
power in the entire slot, for the selected code, averaged over the
measurement interval.
7. Tslot is an integer number (in symbols) of the frame timing offset
within the slot. It is the measured offset of the start of the radio frame
of the selected code. The code is determined by the current spread code
and symbol rate.
8. Tframe is an integer number (in slots) of the frame timing offset
within the frame. It is the measured offset of the start of the radio
frame of the selected code. The code is determined by the current
spread code and symbol rate.
9. Total power in slot is a floating point number in units of dBm. It is
the total RF power in the first slot timing in the acquired data. The slot
timing is determined by Perch. (The search code portion of Perch is
excluded.)
10. Perch power is a floating point number (in dB) of the average power of
the Perch code relative to the total slot power. The slot timing is
determined by Perch. (The search code portion of Perch is excluded.)
11. Maximum active traffic power is a floating point number (in dB) of
the maximum average power of the active traffic channels. If no active
code is detected the value returned is −999. The slot timing is
determined by Perch. (The search code portion of Perch is excluded.)
12. Average active traffic power is a floating point number (in dB) of the
average power of all the active traffic channels. If no active code is
detected the value returned is −999. The slot timing is determined by
Perch. (The search code portion of Perch is excluded.)
13. Maximum inactive traffic power is a floating point number (in dB)
of the maximum average power of the inactive traffic channels. The slot
timing is determined by Perch. (The search code portion of Perch is
excluded.)
14. Average inactive traffic power is a floating point number (in dB) of
the average power of the inactive traffic channels. The slot timing is
determined by Perch. (The search code portion of Perch is excluded.)
Chapter 1 37
Page 38

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
n Results Returned
2
W-CDM
A mode
2
W-CDM
A mode
With a radio format (or band) of ARIB:
Returns a series of floating point numbers (in dB) with a multiplier of
8 ksymbols per second that represent all the code domain powers.
1st number = 1st code power relative to the total power over a slot
2nd number = 1st code symbol rate / 8 ksps
...
(2×N-1)th number = Nth code power relative to the total power over a
slot
(2×N)th number = Nth code symbol rate / 8 ksps
N = the number of codes detected. The total number of codes varies because
of the different symbol rates of each code.
With a radio format (or band) of Trial:
Returns a series of floating point numbers (in dB) with a multiplier of
16 ksymbols/second that represent all the code domain powers.
1st number = 1st code power relative to the total power over a slot
2nd number = 1st code symbol rate / 16 ksps
...
(2×N-1)th number = Nth code power relative to the total power over a
slot
(2×N)th number = Nth code symbol rate / 16 ksps
N = the number of codes detected. The total number of codes varies because
of the different symbol rates of each code.
3
W-CDM
A mode
4
W-CDM
A mode
5
W-CDM
A mode
6
W-CDM
A mode
Returns a series of floating point numbers that show either active or
inactive status for each of the code powers returned in n=2. (See above.) If a
code is inactive, the value returned is 0.0, otherwise a value >0.0 is
returned.
1st number = active or inactive flag of the 1st code
...
Nth number = active or inactive flag of the Nth code
(where N= the number of codes identified)
Returns a series of floating point numbers (in percent) that represent each
sample in the EVM trace. The first number is the symbol 0 decision point
and there are X points per symbol. Therefore, the decision points are at 0,
1×X, 2×X, 3×X...
(where X = the number of points per chip)
Returns a series of floating point numbers (in percent) that represent each
sample in the magnitude error trace. The first number is the symbol 0
decision point and there are X points per symbol. Therefore, the decision
points are at 0, 1×X, 2×X, 3×X...
(where X = the number of points per chip)
Returns a series of floating point numbers (in degrees) that represent each
sample in the phase error trace. The first number is the symbol 0 decision
point and there are X points per symbol. Therefore, the decision points are
at 0, 1×X, 2×X, 3×X...
(where X = the number of points per chip)
38 Chapter1
Page 39

n Results Returned
W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
7
W-CDM
A mode
8
W-CDM
A mode
Returns series of floating point numbers that alternately represent I and Q
pairs of the corrected measured trace. The magnitude of each I and Q pair is
normalized to 1.0. The first number is the in-phase (I) sample of symbol 0
decision point and the second is the quadrature-phase (Q) sample of symbol
0 decision point. As in the EVM, there are X points per symbol, so that:
1st number is I of the symbol 0 decision point
2nd number is Q of the symbol 0 decision point
...
(2×X)+1 number is I of the symbol 1 decision point
(2×X)+2 number is Q of the symbol 1 decision point
...
(2×X)×N+1th number is I of the symbol N decision point
(2×X)×N+2th number is Q of the symbol N decision point
where X = the number of points per symbol, and
N = the number of symbols
Returns series of floating point numbers (in dBm) that represent the trace
data of the symbol power vs. time.
Chapter 1 39
Page 40

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Channel Power Measurement
This measures the total rms power in a specified integration
bandwidth. You must be in the Basic, cdmaOne mode to use these
commands. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
The general functionality of CONFigure, FETCh, MEASure, and READ
are described at the beginning of this section. See the SENSe:CHPower
commands for more measurement related commands.
:CONFigure:CHPower
:FETCh:CHPower[n]?
:READ:CHPower[n]?
:MEASure:CHPower[n]?
History: Added to Basic mode, version A.03.00 or later
Front Panel
Access:
Measure, Channel Power
After the measurement is selected, press Restore Meas
Defaults to restore factory defaults.
Measurement Results Available
n Results Returned
0 Returns unprocessed I/Q trace data, as a series of
comma-separated trace points, in volts. The I values are
listed first in each pair, using the 0 through even-indexed
values. The Q values are the odd-indexed values.
not specified or
n=1
2 Returns comma-separated floating point numbers that are
Returns 2 comma-separated scalar results:
1. Channel power is a floating point number
representing the total channel power in the specified
integration bandwidth.
2. PSD (Power Spectral Density) is the power (in dBm/Hz)
in the specified integration bandwidth.
the captured trace data of the power (in dBm/resolution
BW) of the signal. The frequency span of the captured trace
data is specified by the Span key.
40 Chapter1
Page 41

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement
This measures the QPSK error vector magnitude of each symbol. You
must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use these commands.
Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
The general functionality of CONFigure, FETCh, MEASure, and READ
are described at the beginning of this section. See the SENSe:EVM
commands for more measurement related commands.
:CONFigure:EVMQpsk
:FETCh:EVMQpsk[n]?
:READ:EVMQpsk[n]?
:MEASure:EVMQpsk[n]?
History: Version A.03.00 or later
Front Panel
Access:
Measure, QPSK EVM
After the measurement is selected, press Restore Meas
Defaults to restore factory defaults.
Measurement Results Available
n Results Returned
0 Returns unprocessed I/Q trace data, as a data array of
comma-separated trace points, in volts.
Chapter 1 41
Page 42

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
n Results Returned
1 (default)
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
Returns 11 comma-separated scalar results, in the following
order.
1. RMS EVM – a floating point number (in percent) of EVM
over the entire measurement area
2. RMS EVM maximum – the maximum RMS EVM over the
averaged counts
3. Peak EVM error – a floating point number (in percent) of
peak EVM in the measurement area
4. Peak EVM maximum – the maximum peak EVM over the
averaged counts
5. Magnitude error – a floating point number (in percent) of
average magnitude error over the entire measurement area
6. Magnitude error maximum – the maximum magnitude error
over the averaged counts
7. Phase error – a floating point number (in degree) of average
phase error over the entire measurement area
8. Phase error maximum – the maximum phase error over the
averaged counts
9. Frequency error – a floating point number (in Hz) of the
frequency error in the measured signal
10.Frequency error maximum – the maximum frequency error
over the averaged counts
11.I/Q origin offset – a floating point number (in dB) of the I
and Q error (magnitude squared) offset from the origin
2
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
3
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
4
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
EVM trace − returns series of floating point numbers (in
percent) that represent each sample in the EVM trace. The first
number is the symbol 0 decision point. There are X points per
symbol (X = points/chip). Therefore, the decision points are at 0,
1 × X, 2 × X, 3 × X ...
Magnitude error trace − returns series of floating point
numbers (in percent) that represent each sample in the
magnitude error trace. The first number is the symbol 0
decision point. There are X points per symbol (X = points/chip).
Therefore, the decision points are at 0, 1 × X, 2 × X, 3 × X
...
Phase error trace − returns series of floating point numbers (in
degree) that represent each sample in the phase error trace.
There are X points per symbol (X = points/ chip). Therefore, the
decision points are at 0, 1 × X, 2 × X, 3 × X ...
42 Chapter1
Page 43

n Results Returned
W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
5
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
Corrected measured trace − returns series of floating point
numbers that alternately represent I and Q pairs of the
corrected measured trace. The magnitude of each I and Q pair
are normalized to 1.0. The first number is the in-phase (I)
sample of symbol 0 decision point and the second is the
quadrature-phase (Q) sample of symbol 0 decision point. There
are X points per symbol (X = points/chip), so the series of
numbers is:
1st number = I of the symbol 0 decision point
2nd number = Q of the symbol 0 decision point
...
(2 × X) + 1, number = I of the symbol 1 decision point
(2 × X) + 2, number = Q of the symbol 1 decision point
...
(2 × X) × Nth + 1 number = I of the symbol N decision point
(2 × X) × Nth + 2 number = Q of the symbol N decision point
Chapter 1 43
Page 44

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Power Statistics CCDF Measurement
This is a statistical power measurement of the complimentary
cumulative distribution function (CCDF). Youmust be in the cdma2000
or W-CDMA mode to use these commands. Use INSTrument:SELect to
set the mode.
The general functionality of CONFigure, FETCh, MEASure, and READ
are described at the beginning of this section. See the SENSe:PSTat
commands for more measurement related commands.
:CONFigure:PSTatistic
:FETCh:PSTatistic[n]?
:READ:PSTatastic[n]?
:MEASure:PSTatastic[n]?
History: Version A.03.00 or later
Front Panel
Access:
Measure, Power Stat CCDF
After the measurement is selected, press Restore Meas
Defaults to restore factory defaults.
Measurement Results Available
n
0
not specified
or n=1
Returns unprocessed I/Q trace data, as a series of comma-separated
trace points, in volts. The I values are listed first in each pair, using
the 0 through even-indexed values. The Q values are the
odd-indexed values,
Returns 10 comma-separated scalar results:
1. Average input power (in dBm)
2. Probability at the average input power level (in %)
3. Power level that has 10% of the power
4. Power level that has 1% of the power
5. Power level that has 0.1% of the power
6. Power level that has 0.01% of the power
7. Power level that has 0.001% of the power
8. Power level that has 0.0001% of the power
9. Peak power (in dB)
10. Count
44 Chapter1
Page 45

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
n
2
3
4
Returns a series of 5001 floating point numbers (in percent) that
represent the current measured power stat trace. This is the
probability at particular power levels (average power), in the
following order:
Probability at 0 dB power
Probability at 0.1 dB power
Probability at 0.2 dB power
...
Probability at 49.9 dB power
Probability at 50.0 dB power
Returns a series of 5001 floating point numbers (in percent) that
represent the Gaussian trace. This is the probability at particular
power levels (average power), in the following order:
Probability at 0 dB power
Probability at 0.1 dB power
Probability at 0.2 dB power
...
Probability at 49.9 dB power
Probability at 50.0 dB power
Returns a series of 5001 floating point numbers (in percent) that
represent the user-definable reference trace. This is the probability
at particular power levels (average power), in the following order:
Probability at 0 dB power
Probability at 0.1 dB power
Probability at 0.2 dB power
...
Probability at 49.9 dB power
Probability at 50.0 dB power
Chapter 1 45
Page 46

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Rho (Waveform Quality) Measurement
This measures the modulation accuracy of the transmitter by checking
the magnitude and phase error and the EVM (error vector magnitude).
You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use these
commands. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
The general functionality of CONFigure, FETCh, MEASure, and READ
are described at the beginning of this section. See the SENSe:RHO
commands for more measurement related commands.
:CONFigure:RHO
:FETCh:RHO[n]?
:READ:RHO[n]?
:MEASure:RHO[n]?
Front Panel
Access: Measure, Mod Accuracy (Rho)
After the measurement is selected, press Restore Meas
Defaults to restore factory defaults.
Measurement Results Available
n
0
1 (default)
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
2
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
Results Returned
Returns unprocessed I/Q trace data, as a data array of
comma-separated trace points, in volts.
Returns 7 comma-separated scalar results, in the following order.
1. RMS EVM – a floating point number (in percent) of EVM over the
entire measurement area
2. Peak EVM error – a floating point number (in percent) of peak
EVM in the measurement area
3. Magnitude error – a floating point number (in percent) of average
magnitude error over the entire measurement area
4. Phase error – a floating point number (in degree) of average phase
error over the entire measurement area
5. I/Q origin offset – a floating point number (in dB) of the I and Q
error (magnitude squared) offset from the origin
6. Frequency error – a floating point number (in Hz) of the frequency
error in the measured signal
7. Rho – a floating point number of Rho
EVM trace − returns series of floating point numbers (in percent) that
represent each sample in the EVM trace. The first number is the
symbol 0 decision point. There are X points per symbol (X =
points/chip). Therefore, the decision points are at 0, 1 × X, 2 × X, 3 × X
...
46 Chapter1
Page 47
W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
n
3
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
4
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
5
cdma2000,
W-CDMA
mode
Results Returned
Magnitude error trace − returns series of floating point numbers (in
percent) that represent each sample in the magnitude error trace. The
first number is the symbol 0 decision point. There are X points per
symbol (X = points/chip). Therefore, the decision points are at 0, 1 × X,
2 × X, 3 × X ...
Phase error trace − returns series of floating point numbers (in degree)
that represent each sample in the phase error trace. There are X points
per symbol (X = points/ chip). Therefore, the decision points are at 0, 1
× X, 2 × X, 3 × X ...
Corrected measured trace − returns series of floating point numbers
that alternately represent I and Q pairs of the corrected measured
trace. The magnitude of each I and Q pair are normalized to 1.0. The
first number is the in-phase (I) sample of symbol 0 decision point and
the second is the quadrature-phase (Q) sample of symbol 0 decision
point. There are X points per symbol (X = points/chip), so the series of
numbers is:
1st number = I of the symbol 0 decision point
2nd number = Q of the symbol 0 decision point
...
(2 × X) + 1, number = I of the symbol 1 decision point
(2 × X) + 2, number = Q of the symbol 1 decision point
...
(2 × X) × Nth + 1 number = I of the symbol N decision point
(2 × X) × Nth + 2 number = Q of the symbol N decision point
Chapter 1 47
Page 48

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Spectrum (Frequency Domain) Measurement
This measures the amplitude of your input signal with respect to the
frequency. It provides spectrum analysis capability using FFT (fast
Fourier transform) measurement techniques. You must select the
appropriate mode using INSTrument:SELect, to use these commands.
The general functionality of CONFigure, FETCh, MEASure, and READ
are described at the beginning of this section. See the
SENSe:SPECtrum commands for more measurement related
commands.
:CONFigure:SPECtrum
:FETCh:SPECtrum[n]?
:READ:SPECtrum[n]?
:MEASure:SPECtrum[n]?
Front Panel
Access:
Measure, Spectrum (Freq Domain)
After the measurement is selected, press Restore Meas
Defaults to restore factory defaults.
Measurement Results Available
n
0
Results Returned
Returns unprocessed I/Q trace data, as a series of comma-separated trace
points, in volts. The I values are listed first in each pair, using the 0 through
even-indexed values. The Q values are the odd-indexed values.
48 Chapter1
Page 49

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
n
not
specified
or n=1
Results Returned
Returns the following comma-separated scalar results:
1. FFT peak is the FFT peak amplitude.
2. FFT frequency is the FFT frequency of the peak amplitude.
3. FFT points is the Number of points in the FFT spectrum.
4. First FFT frequency is the frequency of the first FFT point of the
spectrum.
5. FFT spacing is the frequency spacing between the FFT points of the
spectrum.
6. Time domain points is the number of points in the time domain trace
used for the FFT.
7. First time point is the time of the first time domain point, where time
zero is the trigger event.
8. Time spacing is the time spacing between the time domain points.
9. Time domain returns a 1, if time domain is complex (I/Q), or 0 if it is
real. (raw ADC samples)
10. Scan time is the total scan time of the time domain trace used for the
FFT. The total scantime = (time spacing) x (time domain points − 1)
11. Current average count is the current number of data measurements
that have already been combined, in the averaging calculation.
2, Service
mode
only
3
4
5, Service
mode
only
6
7
8
9, Service
mode
only
10,
Service
mode
only
Returns the trace data of the log-magnitude versus time. (That is, the RF
envelope.)
Returns the I and Q trace data. It is represented by I and Q pairs (in volts)
versus time.
Returns spectrum trace data. That is, the trace of log-magnitude versus
frequency. (The trace is computed using a FFT.)
Returns the averaged trace data of log-magnitude versus time. (That is, the
RF envelope.)
Not used.
Returns the averaged spectrum trace data. That is, the trace of the averaged
log-magnitude versus frequency.
Not used.
Returns a trace containing the shape of the FFT window.
Returns trace data of the phase of the FFT versus frequency.
Chapter 1 49
Page 50
W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
Waveform (Time Domain) Measurement
This measures the power in your input signal with respect to time and
is equivalent to zero-span operation in a traditional spectrum analyzer.
You must select the appropriate mode using INSTrument:SELect, to
use these commands.
The general functionality of CONFigure, FETCh, MEASure, and READ
are described at the beginning of this section. See the
SENSe:WAVeform commands for more measurement related
commands.
:CONFigure:WAVeform
:FETCh:WAVeform[n]?
:READ:WAVeform[n]?
:MEASure:WAVeform[n]?
Front Panel
Access:
Measure, Waveform (Time Domain)
After the measurement is selected, press Restore Meas
Defaults to restore factory defaults.
Measurement Results Available
n
0
Results Returned
Returns unprocessed I/Q trace data, as a series of comma-separated trace
points, in volts. The I values are listed first in each pair, using the 0 through
even-indexed values. The Q values are the odd-indexed values.
50 Chapter1
Page 51

W-CDMA Programming Commands
MEASure Group of Commands
n
not
specifie
d or
n=1
Results Returned
Returns the following comma-separated scalar results:
1. Sample time is a floating point number representing the time between
samples when using the trace queries (n=0,2,etc).
2. Mean power is the mean power (in dBm). This is either the power across
the entire trace, or the power between markers if the markers are
enabled. If averaging is on, the power is for the latest acquisition.
3. Mean power averaged is the power (in dBm) for N averages, if
averaging is on. This is either the power across the entire trace, or the
power between markers if the markers are enabled. If averaging is on, the
power is for the latest acquisition. If averaging is off, the value of the
mean power averaged is the same as the value of the mean power.
4. Number of samples is the number of data points in the captured signal.
This number is useful when performing a query on the signal (i.e. when
n=0,2,etc.).
5. Peak-to-mean ratio has units of dB. The peak is defined to be the
maximum level of the signal (non-averaged). The mean is the mean power
(non-averaged). If averaging is on, the peak-to-mean ratio is invalid.
6. Maximum value is the maximum of the most recently acquired data (in
dBm).
7. Minimum value is the minimum of the most recently acquired data (in
dBm).
2
Returns comma-separated trace points of the entire captured trace data.
These data points are floating point numbers representing the power of the
signal (in dBm). There are N data points, where N is the number of
samples. The period between the samples is defined by the sample time.
Chapter 1 51
Page 52

W-CDMA Programming Commands
READ Subsystem
READ Subsystem
:READ:<measurement>[n]?
The READ? commands are used with several other commands and are
documented in the section on the “MEASure Group of Commands” on
page 27.
52 Chapter1
Page 53

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
SENSe Subsystem
Sets the instrument state parameters so that you can measure the
input signal.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement
Commands for querying the adjacent channel power measurement
results and for setting to the default values are found in the “MEASure
Group of Commands” on page 27. The equivalent front panel keys for
the parameters described in the following commands, are found under
the
Meas Setup key, after the ACP measurement has been selected from
the
MEASURE key menu.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Average Count
[:SENSe]:ACP:AVERage:COUNt <integer>
[:SENSe]:ACP:AVERage:COUNt?
Set the number of data acquisitions that will be averaged. After the
specified number of average counts, the average mode (termination
control) setting determines the average action.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 10, for cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
20, for Basic, cdmaOne, iDEN mode
Range: 1 to 10,000
Remarks: Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Averaging State
[:SENSe]:ACP:AVERage[:STATe] OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:ACP:AVERage[:STATe]?
Turn average on or off.
Factory Preset
and *RST: On
Off, for iDEN mode
Remarks: Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Averaging Termination
Control
[:SENSe]:ACP:AVERage:TCONtrol EXPonential|REPeat
[:SENSe]:ACP:AVERage:TCONtrol?
Chapter 1 53
Page 54

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Select the type of termination control used for averaging. This
determines the averaging action after the specified number of data
acquisitions (average count) is reached.
Exponential – Each successive data acquisition after the average
count is reached, is exponentially weighted and combined with the
existing average.
Repeat – After reaching the average count, the averaging is reset
and a new average is started.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Repeat, for basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
Exponential, for NADC, PDC, iDEN mode
Remarks: Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Channel Integration
BW
Basic, iDEN mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:BANDwidth|BWIDth:INTegration <freq>
[:SENSe]:ACP:BANDwidth|BWIDth:INTegration?
cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CMDA mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:BANDwidth|BWIDth[n]:INTegration[n] <freq>
[:SENSe]:ACP:BANDwidth|BWIDth[n]:INTegration[n]?
Set the Integration bandwidth that will be used for the main (carrier)
channel.
cdmaOne mode
Bandwidth [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default
is base station (1).
Integration [n] - Where 1 is cellular bands and 2 is pcs bands. The
default is cellular (1).
cdma2000 mode
Bandwidth [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default
is base station (1).
Integration [n] - Where 1 is SR1, 2 is SR3 DS, and 3 is SR3 MC. The
default is SR1 (1).
54 Chapter1
Page 55

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
W-CDMA mode
Bandwidth [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default
is base station (1).
Integration [n] - Where 1 is ARIB, 2 is 3GPP, and 3 is Trial. The
default is ARIB (1).
Factory Preset
and *RST:
Mode Format
(Modulation Standard)
Basic 1.23 MHz
cdmaOne 1.23 MHz
iDEN 18 kHz
cdma2000 SR1 (n=1) SR3 DC (n=2) SR3 MC (n=3)
1.23 MHz 3.69 MHz 3.69 MHz
W-CDMA ARIB (n=1) 3GPP (n=2) Trial (n=3)
4.069 MHz 3.84 MHz 4.096 MHz
Range: 300 Hz to 20 MHz for Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000,
W-CDMA mode
1 kHz to 5 MHz for iDEN
Default Unit: Hz
Remarks: With measurement type set at (TPR) total power
reference, 1.40 MHz is sometimes used. Using 1.23
MHz will give a power that is very nearly identical to
the 1.40 MHz value, and using 1.23 MHz will also yield
the correct power spectral density with measurement
type set at (PSD) reference. However, a setting of 1.40
MHz will not give the correct results with
measurement type set at PSD reference.
You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 55
Page 56

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Absolute Amplitude
Limits
iDEN mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:ABSolute <power>
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:ABSolute?
Basic mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:ABSolute <power>{,<power>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:ABSolute?
cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:ABSolute <power>{,<power>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:ABSolute?
Sets the absolute amplitude levels to test against for each of the custom
offsets. The list contains five (5) entries. If there is more than one offset,
the offset closest to the carrier channel is the first one in the list.
ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:TEST selects the type of testing to be done at
each offset.
The query returns five (5) real numbers that are the current absolute
amplitude test limits.
cdmaOne, Basic mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is cellular bands and 2 is pcs bands. The default is
cellular.
cdma2000 mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is SR1, 2 is SR3 DS, and 3 is SR3 MC. The default
is SR1 (1).
W-CDMA mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is ARIB, 2 is 3GPP, and 3 is Trial. The default is
ARIB (1).
56 Chapter1
Page 57

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset and *RST:
Offset A Offset B Offset C Offset D Offset E
Basic
0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm
cdmaOne
BS cellular 0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm
BS pcs 0 dBm −13 dBm −13 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm
MS cellular 0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm
MS pcs 0 dBm −13 dBm −13 dBm 0 dBm 0 dBm
cdma2000
50 dBm 50 dBm 50 dBm 50 dBm 50 dBm
W-CDMA
50 dBm 50 dBm 50 dBm 50 dBm 50 dBm
iDEN
0 dBm n/a n/a n/a n/a
Range: −200 dBm to 50 dBm
Default Unit: dBm
Remarks: You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 57
Page 58

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Define Resolution
Bandwidth List
iDEN mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:BANDwidth|BWIDth <res_bw>
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:BANDwidth|BWIDth?
Basic mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:BANDwidth|BWIDth
<res_bw>{,<res_bw>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:BANDwidth|BWIDth?
cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:BANDwidth|BWIDth
<res_bw>{,<res_bw>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:BANDwidth|BWIDth?
Define the custom resolution bandwidth(s) for the adjacent channel
power testing. If there is more than one bandwidth, the list contains
five (5) entries. Each resolution bandwidth in the list corresponds to an
offset frequency in the list defined by ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n][:FREQ.
cdmaOne mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is cellular bands and 2 is pcs bands. The default is
cellular.
cdma2000 mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is SR1, 2 is SR3 DS, and 3 is SR3 MC. The default
is SR1 (1).
W-CDMA mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is ARIB, 2 is 3GPP, and 3 is Trial. The default is
ARIB (1).
58 Chapter1
Page 59
W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset and *RST:
Offset A Offset B Offset C Offset D Offset E
iDEN
10 kHz n/a n/a n/a n/a
Basic
30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz
cdmaOne
BS cellular 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz
BS pcs 30 kHz 12.5 kHz 1 MHz 30 kHz 30 kHz
MS cellular 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz
MS pcs 30 kHz 12.5 kHz 1 MHz 30 kHz 30 kHz
cdma2000
30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz 30 kHz
W-CDMA
Trial and ARIB 4.096
MHz
3GPP 3.84 MHz 3.84 MHz 3.84 MHz 3.84 MHz 3.84 MHz
4.096
MHz
4.096
MHz
4.096
MHz
4.096
MHz
Range: 300 Hz to 20 MHz for cdmaOne, Basic, cdma2000,
W-CDMA mode
1 kHz to 5 MHz for iDEN mode
Default Unit: Hz
Remarks: You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 59
Page 60

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Define Offset Frequency
List
iDEN mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[:FREQuency] <offset_freq>
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[:FREQuency]?
Basic mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST[:FREQuency]
<offset_freq>{,<offset_freq>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST[:FREQuency]?
cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n][:FREQuency]
<offset_freq>{,<offset_freq>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n][:FREQuency]?
Define the custom set of offset frequencies at which the switching
transient spectrum part of the ACP measurement will be made. The list
contains five (5) entries for offset frequencies. Each offset frequency in
the list corresponds to a resolution bandwidth in the bandwidth list. An
offset frequency of zero turns “off” the measurement for that offset.
cdmaOne mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is cellular frequency bands and 2 is pcs frequency
bands. The default is cellular bands (1).
cdma2000 mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is SR1, 2 is SR3 DS, and 3 is SR3 MC. The default
is SR1 (1).
W-CDMA mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is ARIB, 2 is 3GPP, and 3 is Trial. The default is
ARIB (1).
60 Chapter1
Page 61
W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset and *RST:
Offset A Offset B Offset C Offset D Offset E
iDEN
25 kHz n/a n/a n/a n/a
Basic
750 kHz 1.98 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
cdmaOne
BS cellular 750 kHz 1.98 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
BS pcs 885 kHz 1.25625
MHz
MS cellular 885 kHz 1.98 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
MS pcs 885 kHz 1.25625
MHz
cdma2000
BTS SR1 750 kHz 1.98 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
BTS SR3 DS 2.655
MHz
BTS SR3 MC 2.135
kHz
MS SR1 885 kHz 1.98 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
MS SR3 DS 2.655
MHz
MS SR3 MC 2.655
kHz
W-CDMA
3.75 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
2.5 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
3.75 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
3.75 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz 0 Hz
2.75 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz
2.75 MHz 0 Hz 0 Hz
5 MHz 10 MHz 15 MHz 20 MHz 25 MHz
Range: 0 Hz to 20 MHz for cdmaOne, iDEN, Basic mode
0 Hz to 100 MHz for cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
Default Unit: Hz
Remarks: You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 61
Page 62

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Amplitude Limits
Relative to the Carrier
iDEN mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:RCARrier <rel_power>
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:RCARrier?
Basic mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:RCARrier <rel_power>{,<rel_power>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:RCARrier?
cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:RCARrier
<rel_power>{,<rel_power>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:RCARrier?
Sets the amplitude levels to test against for any custom offsets. This
amplitude level is relative to the carrier amplitude. If multiple offsets
are available, the list contains five (5) entries. The offset closest to the
carrier channel is the first one in the list. ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:TEST
selects the type of testing to be done at each offset.
The query returns five (5) real numbers that are the current amplitude
test limits, relative to the carrier, for each offset.
cdmaOne, Basic mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is cellular frequency bands and 2 is pcs frequency
bands. The default is cellular bands (1).
cdma2000 mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is SR1, 2 is SR3 DS, and 3 is SR3 MC. The default
is SR1 (1).
W-CDMA mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is ARIB, 2 is 3GPP, and 3 is Trial. The default is
ARIB (1).
62 Chapter1
Page 63

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset and *RST:
Offset A Offset B Offset C Offset D Offset E
iDEN
0 dBc n/a n/a n/a n/a
Basic
−45 dBc −60 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc
cdmaOne
BS cellular −45 dBc −60 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc
BS pcs −45 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc
MS cellular −42 dBc −54 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc
MS pcs −42 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc
cdma2000
0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc
W-CDMA
0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc 0 dBc
Range: −150 dB to 50 dB for cdmaOne, Basic mode
−200 dB to 50 dB for cdma2000, W-CDMA, iDEN mode
Default Unit: dB
Remarks: You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 63
Page 64

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Amplitude Limits
Relative to the Power Spectral Density
iDEN mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:RPSDensity <rel_power>
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:RPSDensity?
Basic mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:RPSDensity
<rel_power>{,<rel_power>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:RPSDensity?
cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:RPSDensity
<rel_power>{,<rel_power>}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:RPSDensity?
Sets the amplitude levels to test against for any custom offsets. This
amplitude level is relative to the power spectral density. If multiple
offsets are available, the list contains five (5) entries. The offset closest
to the carrier channel is the first one in the list.
ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:TEST selects the type of testing to be done at
each offset.
The query returns five (5) real numbers that are the current amplitude
test limits, relative to the power spectral density, for each offset.
cdmaOne, Basic mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is cellular frequency bands and 2 is pcs frequency
bands. The default is cellular bands (1).
cdma2000 mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is SR1, 2 is SR3 DS, and 3 is SR3 MC. The default
is SR1 (1).
W-CDMA mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is ARIB, 2 is 3GPP, and 3 is Trial. The default is
ARIB (1).
64 Chapter1
Page 65

Factory Preset and *RST:
Offset A Offset B Offset C Offset D Offset E
iDEN
0 dB n/a n/a n/a n/a
Basic
W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
−28.87
dB
cdmaOne
BS cellular −28.87
dB
BS pcs −28.87
dB
MS cellular −25.87
dB
MS pcs −25.87
dB
cdma2000
0 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
W-CDMA
0 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
−43.87 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
−43.87 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
0 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
−37.87 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
0 dB 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Range: −150 dB to 50 dB for cdmaOne, Basic, cdma2000,
W-CDMA mode
−200 dB to 50 dB for iDEN mode
Default Unit: dB
Remarks: You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 65
Page 66

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Control Offset
Frequency List
iDEN mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:STATe OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:STATe?
Basic mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:STATe OFF|ON|0|1{, OFF|ON|0|1}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:STATe?
cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:STATe OFF|ON|0|1
{, OFF|ON|0|1}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:STATe?
Selects whether testing is to be done at the custom offset frequencies.
The measured powers are tested against the absolute values defined
with ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:ABS, or the relative values defined with
ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:RPSD and ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:RCAR.
cdmaOne mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is cellular frequency bands and 2 is pcs frequency
bands. The default is cellular bands (1).
cdma2000 mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is SR1, 2 is SR3 DS, and 3 is SR3 MC. The default
is SR1 (1).
W-CDMA mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is ARIB, 2 is 3GPP, and 3 is Trial. The default is
ARIB (1).
66 Chapter1
Page 67

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset and *RST:
Offset A Offset B Offset C Offset D Offset E
iDEN
On n/a n/a n/a n/a
Basic
On On On On On
cdmaOne
BS cellular On On On On On
BS pcs On On On On On
MS cellular On On On On On
MS pcs On On On On On
cdma2000
On On Off Off Off
W-CDMA
On On Off Off Off
Remarks: You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 67
Page 68

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Define Type of Offset
Frequency List
iDEN mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:TEST ABSolute|AND|RELative|OR
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:TEST?
Basic mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:TEST ABSolute|AND|RELative|OR
{, ABSolute|AND|RELative|OR}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet:LIST:TEST?
cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA mode
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:TEST
ABSolute|AND|RELative|OR{, ABSolute|AND|RELative|OR}
[:SENSe]:ACP:OFFSet[n]:LIST[n]:TEST?
Defines the type of testing to be done at any custom offset frequencies.
The measured powers are tested against the absolute values defined
with ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:ABS, or the relative values defined with
ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:RPSD and ACP:OFFS[n]:LIST[n]:RCAR.
cdmaOne, Basic mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is cellular frequency bands and 2 is pcs frequency
bands. The default is cellular bands (1).
cdma2000 mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is SR1, 2 is SR3 DS, and 3 is SR3 MC. The default
is SR1 (1).
W-CDMA mode
Offset [n] - Where 1 is base station and 2 is mobiles. The default is
base station (1).
List [n] - Where 1 is ARIB, 2 is 3GPP, and 3 is Trial. The default is
ARIB (1).
The types of testing that can be done for each offset include:
• And - Test both the absolute power measurement and the power
relative to the carrier. If they both fail, then return a failure for the
measurement at this offset.
68 Chapter1
Page 69

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
• Absolute - Test the absolute power measurement. If it fails, then
return a failure for the measurement at this offset.
• Or - Test both the absolute power measurement and the power
relative to the carrier.If either one fails, then return a failure for the
measurement at this offset.
• Relative - Test the power relative to the carrier. If it fails, then
return a failure for the measurement at this offset.
Factory Preset
and *RST:
Offset A Offset B Offset C Offset D Offset E
iDEN
REL n/a n/a n/a n/a
Basic
REL REL REL REL REL
cdmaOne
BS cellular REL REL REL REL REL
BS pcs REL ABS ABS REL REL
MS cellular REL REL REL REL REL
MS pcs REL ABS ABS REL REL
cdma2000
REL REL REL REL REL
W-CDMA
REL REL REL REL REL
Remarks: You must be in Basic, cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
iDEN mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 69
Page 70

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Sweep Mode Resolution
Bandwidth
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution] <freq>
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution]?
Sets the resolution bandwidth when using the spectrum analyzer type
sweep mode. See [:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:TYPE.
Factory Preset
and *RST: In the automatic mode, the resolution bandwidth is set
based on the current span, which is determined by the
furthest selected offset.
Range: 1.0 kHz to 1.0 MHz
Default Unit: Hz
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000, W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Sweep Mode Resolution
BW Control
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution]:AUTO
OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution]:AUTO?
Sets the resolution bandwidth to automatic, when using the spectrum
analyzer type sweep mode. See [:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:TYPE.
Factory Preset
and *RST: On
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000, W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Sweep Mode Detection
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:DETector[:FUNCtion] AAVerage|POSitive
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:DETector[:FUNCtion]?
Selects the detector type when using the sweep mode. See
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:TYPE.
Absolute average - the absolute average power in each frequency is
measured across the spectrum
Positive - the positive peak power in each frequency is measured
across the spectrum
70 Chapter1
Page 71

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset
and *RST: Positive
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000, W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Sweep Time
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:TIME <time>
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:TIME?
Sets the sweep time when using the sweep mode. See
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:TYPE.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 625 µs (1 slot)
Range: 500 µs to 10 ms
Default Unit: seconds
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000, W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Sweep Type
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:TYPE FFT|SWEep
[:SENSe]:ACP:SWEep:TYPE?
Selects the type of sweeping. This can be either FFT or conventional
spectrum analyzer sweeping.
FFT - makes fast ACP measurements
Sweep - is slower than FFT, but the results correlate with traditional
spectrum analyzer measurements though the signals peak/average
ratio is higher. See [SENSe:]ACP:SWEep:DETector[:FUNCtion]
Factory Preset
and *RST: FFT
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000, W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Chapter 1 71
Page 72

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement Power Reference
[:SENSe]:ACP:TYPE TPRef|PSDRef
[:SENSe]:ACP:TYPE?
Selects the measurement type. This allows you to make absolute and
relative power measurements of either total power, or the power
normalized to the measurement bandwidth.
Total Power Reference - the total power is used as the power
reference
Power Spectral Density Reference - the power spectral density is
used as the power reference
Factory Preset
and *RST: Total power reference
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA,
NADC, PDC mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
72 Chapter1
Page 73

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Code Domain Power Measurement
Commands for querying the code domain power measurement results
and for setting to the default values are found in the “MEASure Group
of Commands” on page 27. The equivalent front panel keys for the
parameters described in the following commands, are found under the
Meas Setup key, after the Code Domain Power measurement has been
selected from the
Code Domain Power Measurement Demod Alpha
[:SENSe]:CDPower:ALPHa <float>
[:SENSe]:CDPower:ALPHa?
Set alpha for the root nyquist filter.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0.22
Range: 0.01 to 0.5
MEASURE key menu.
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Code Domain Power Measurement Chip Rate
[:SENSe]:CDPower:CRATe <freq>
[:SENSe]:CDPower:CRATe?
Set chip rate.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 4.096 MHz
Range: 3.6864 to 4.5056 MHz
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Code Domain Power Measurement Spectrum Normal/Invert
[:SENSe]:CDPower:SPECtrum NORMal|INVert
[:SENSe]:CDPower:SPECtrum?
Select normal or inverted spectrum for demodulation.
Normal - normal spectrum is used
Invert - inverted spectrum is used
Factory Preset
and *RST: Normal
Remarks You must be in the cdmaOne mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 73
Page 74

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Code Domain Power Measurement Scramble Code
[:SENSe]:CDPower:SYNC:SCRamble <integer>
[:SENSe]:CDPower:SYNC:SCRamble?
Set the scramble code for synchronization.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1
Range: 0 to 262143 (0h to 3FFFFh) (0 is for no-scramble)
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Code Domain Power Measurement Trigger Source
[:SENSe]:CDPower:TRIGger:SOURce
EXTernal[1]|External2|FRAMe|IF|IMMediate|IF|RFBurst
[:SENSe]:CDPower:TRIGger:SOURce?
Select the trigger source used to control the data acquisitions.
External 1 – front panel external trigger input
External 2 – rear panel external trigger input
Frame – internal frame trigger from front panel input
IF – internal IF envelope trigger
Immediate – the next data acquisition is immediately taken,
capturing the signal asynchronously (also called free run).
RF Burst – internal wideband RF burst envelope trigger that has
automatic level control for periodic burst signals.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Immediate
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Front Panel
Access:
Meas Setup, Trig Source
74 Chapter1
Page 75

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Channel Power Measurement
Commands for querying the channel power measurement results and
for setting to the default values are found in the “MEASure Group of
Commands” on page 27. The equivalent front panel keys for the
parameters described in the following commands, are found under the
Meas Setup key, after the Channel Power measurement has been selected
from the
std-compliant CPOWer, as that syntax was already used for Carrier
Power measurement (but has since been renamed).
Channel Power Measurement Average Count
[:SENSe]:CHPower:AVERage:COUNt <integer>
[:SENSe]:CHPower:AVERage:COUNt?
Set the number of data acquisitions that will be averaged. After the
specified number of average counts, the averaging mode (terminal
control) setting determines the averaging action.
MEASURE key menu. CHPower used instead of the more
Factory Preset
and *RST: 20
Range: 1 to 10,000
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA, or
Basic mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Channel Power Measurement Averaging State
[:SENSe]:CHPower:AVERage[:STATe] OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:CHPower:AVERage[:STATe]?
Turn averaging on or off.
Factory Preset
and *RST: On
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA, or
Basic mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 75
Page 76

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Channel Power Measurement Averaging Termination Control
[:SENSe]:CHPower:AVERage:TCONtrol EXPonential|REPeat
[:SENSe]:CHPower:AVERage:TCONtrol?
Select the type of terminal control used for averaging. This determines
the averaging action after the specified number of data acquisitions
(average count) is reached.
Exponential - Each successive data acquisition after the average
count is reached, is exponentially weighted and combined with the
existing average.
Repeat - After reaching the average count, the averaging is reset and
a new average is started.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Repeat
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA, or
Basic mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Channel Power Measurement Integration BW
[:SENSe]:CHPower:BANDwidth|BWIDth:INTegration <freq>
[:SENSe]:CHPower:BANDwidth|BWIDth:INTegration?
Set the Integration BW (IBW) that will be used.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1.23 MHz for Basic, cdmaOne, SR1 of cdma2000
3.69 MHz for SR3 of cdma2000
5 MHz for W-CDMA
Range: 1 kHz to 10 MHz
Default Unit: Hz
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA, or
Basic mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Channel Power Measurement Span
[:SENSe]:CHPower:FREQuency:SPAN <freq>
[:SENSe]:CHPower:FREQuency:SPAN?
Set the frequency span that will be used.
76 Chapter1
Page 77

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset
and *RST: 2 MHz for Basic, cdmaOne, SR1 of cdma2000
5 MHz for SR3 of cdma2000
6 MHz for W-CDMA
Range: 1 kHz to 10 MHz
Default Unit: Hz
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA, or
Basic mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Channel Power Measurement Data Points
[:SENSe]:CHPower:POINts <integer>
[:SENSe]:CHPower:POINts?
Set the number of data points that will be used. Changing this will
change the time record length and resolution BW that are used.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 512
n
Range: 64 to 32768, in a 2
sequence
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA, or
Basic mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Channel Power Measurement Data Points Auto
[:SENSe]:CHPower:POINts:AUTO OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:CHPower:POINts:AUTO?
Select auto or manual control of the data points. This is an advanced
control that normally does not need to be changed. Setting this to a
value other than the factory default, may cause invalid measurement
results.
Auto - couples the Data Points to the Integration BW.
Manual - the Data Points is uncoupled from the Integration BW.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Auto
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA, or
Basic mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Chapter 1 77
Page 78

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Channel Power Measurement Trigger Source
[:SENSe]:CHPower:TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal[1]|EXTernal
2|IMMediate
[:SENSe]:CHPower:TRIGger:SOURce?
Select the trigger source used to control the data acquisitions. This is
an Advanced control that normally does not need to be changed.
External 1 - front panel external trigger input
External 2 - rear panel external trigger input
Immediate - the next data acquisition is immediately taken (also
called Free Run).
Factory Preset
and *RST: Immediate (Free Run)
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA, or
Basic mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Correction for BTS RF Port External Attenuation
[:SENSe]:CORRection:BTS[:RF]:LOSS <rel_power>
[:SENSe]:CORRection:BTS[:RF]:LOSS?
Set equal to the external attenuation used when measuring base
transmit stations.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0 dB
Range: 0 to 100 dB for GSM
−50 to 50 dB for cdma2000, W-CDMA
Default Unit: dB
Remarks: Global to the current mode.
You must be in the GSM, cdma2000, or W-CDMA mode
to use this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set
the mode.
Correction for Mobile Station RF Port External Attenuation
[:SENSe]:CORRection:MS[:RF]:LOSS <rel_power>
[:SENSe]:CORRection:MS[:RF]:LOSS?
Set the correction equal to the external attenuation used when
measuring mobile stations.
78 Chapter1
Page 79

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0 dB
Range: −50 to 50 dB for cdma2000, W-CDMA, iDEN, NADC or
PDC
Default Unit: dB
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000, W-CDMA, iDEN, NADC
or PDC mode to use this command. Use
INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Value is global to the current mode.
Chapter 1 79
Page 80

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement
Commands for querying the QPSK error vector magnitude
measurement results and for setting to the default values are found in
the “MEASure Group of Commands” on page 27. The equivalent front
panel keys for the parameters described in the following commands, are
found under the
selected from the
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement Demod Alpha
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:ALPHa <float>
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:ALPHa?
Set alpha for the root nyquist filter.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0.22
Range: 0.01 to 0.5
Meas Setup key, after the EVM measurement has been
MEASURE key menu.
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement Average Count
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:AVERage:COUNt <integer>
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:AVERage:COUNt?
Set the number of data acquisitions that will be averaged. After the
specified number of average counts, the average mode (termination
control) setting determines the average action.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 10
Range: 1 to 10,000
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
80 Chapter1
Page 81

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement Averaging State
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:AVERage[:STATe] OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:AVERage[:STATe]?
Turn average on or off.
Factory Preset
and *RST: On
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement Averaging
Termination Control
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:AVERage:TCONtrol EXPonential|REPeat
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:AVERage:TCONtrol?
Select the type of termination control used to averaging. This
determines the averaging action after the specified number of data
acquisitions (average count) is reached.
Exponential – Each successive data acquisition after the average
count is reached, is exponentially weighted and combined with the
existing average.
Repeat – After reaching the average count, the averaging is reset
and a new average is started.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Repeat
Remarks: You must be in the cdam2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement Chip Rate
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:CRATe <freq>
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:CRATe?
Set chip rate.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1.2288 MHz for SR1 and SR3 MC BTS of cdma2000
3.6864 MHz for SR3 MC MS and SR3 DS of cdma2000
3.84 MHz for 3GPP of W-CDMA
4.096 MHz for Trial and ARIB of W-CDMA
Chapter 1 81
Page 82

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Range: 1.10592 to 1.35168 MHz for SR1 and SR3 MC BTS of
cdma2000
3.31776 to 4.05504 MHz for SR3 MC MS and SR3 DS of
cdma2000
3.456 to 4.224 MHz for 3GPP of W-CDMA
3.6864 to 4.5056 MHz for Trial and ARIB of W-CDMA
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement Length
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:SWEep:POINts <integer>
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:SWEep:POINts?
Set the number of data points that will be used.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 256
Range: 128 to 1536 for cdma2000
128 to 512 for W-CDMA
Unit: chips
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
QPSK Error Vector Magnitude Measurement Trigger Source
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:TRIGger:SOURce
EXTernal[1]|EXTernal2|FRAMe|IF|IMMediate|RFBurst
[:SENSe]:EVMQpsk:TRIGger:SOURce?
Select the trigger source used to control the data acquisitions.
External 1 – front panel external trigger input
External 2 – rear panel external trigger input
IF – internal IF envelope (video) trigger
Immediate – the next data acquisition is immediately taken,
capturing the signal asynchronously (also called free run)
Frame – internal frame trigger from front panel input
RF Burst – internal wideband RF burst envelope trigger that has
automatic level control for periodic burst signals
82 Chapter1
Page 83

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset
and *RST: Immediate
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Chapter 1 83
Page 84

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Power Statistics CCDF Measurement
Commands for querying the statistical power measurement of the
complimentary cumulative distribution function (CCDF) measurement
results and for setting to the default values are found in the “MEASure
Group of Commands” on page 27. The equivalent front panel keys for
the parameters described in the following commands, are found under
the
Meas Setup key, after the Power Stat CCDF measurement has been
selected from the
Power Statistics CCDF Measurement Channel Bandwidth
[:SENSe]:PSTatistic:BANDwidth|BWIDth <freq>
[:SENSe]:PSTatistic:BANDwidth|BWIDth?
Set the bandwidth that will be used for acquiring the signal.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 5.0 MHz
Range: 10.0 kHz to 6.7 MHz
MEASURE key menu.
Resolution: 0.1 kHz
Step: 1.0 kHz
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Power Statistics CCDF Measurement Sample Counts
[:SENSe]:PSTatistic:COUNts <integer>
[:SENSe]:PSTatistic:COUNts?
Set the counts. Measurement stops when the sample counts reach this
value.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 10,000,000
Range: 1,000 to 2,000,000,000
Unit: counts
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
84 Chapter1
Page 85

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Power Statistics CCDF Measurement Sweep Time
[:SENSe]:PSTatistic:SWEep:TIME <time>
[:SENSe]:PSTatistic:SWEep:TIME?
Set the length of measurement interval that will be used.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1.0 ms
Range: 0.1 ms to 10 ms
Resolution: 0.001 ms
Step: 0.001 ms
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Power Statistics CCDF Measurement Trigger Source
[:SENSe]:PSTatistic:TRIGger:SOURce
EXTernal[1]|EXTernal2|FRAMe|IF|IMMediate|RF Burst
[:SENSe]:PSTatistic:TRIGger:SOURce?
Set the trigger source used to control the data acquisitions.
External 1 - front panel external trigger input
External 2 - rear panel external trigger input
Frame - uses the internal frame timer, which has been synchronized
to the selected burst sync.
IF - internal IF envelope (video) trigger
Immediate - the next data acquisition is immediately taken,
capturing the signal asynchronously (also called Free Run).
RF Burst - internal wideband RF burst envelope trigger that has
automatic level control for periodic burst signals.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Immediate
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Chapter 1 85
Page 86

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Radio Device Under Test
[:SENSe]:RADio:DEVice BTS|MS
[:SENSe]:RADio:DEVice?
Select the type of radio device to be tested.
BTS - Base station transmitter test
MS - Mobile station transmitter test
Factory Preset
and *RST: BTS
Remarks: Global to the current mode.
You must be in cdma2000, W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
History: Version A.03.00 or later
Front Panel
Access:
Mode Setup, Radio, Device
Frequency Offset of MS to BTS
[:SENSe]:RADio:FOFFset <freq>
[:SENSe]:RADio:FOFFset?
Set the amount of frequency offset (MS freq − BTS freq).
Factory Preset
and *RST: 190 MHz
Range: −500 MHz to 500 MHz
Remarks: Global to the current mode.
You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
History: Version A.03.00 or later
Front Panel
Access:
Mode Setup, Radio, MS-BTS Offset
86 Chapter1
Page 87

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Radio Format (Standard)
[:SENSe]:RADio:FORMat ARIB|TGPP|TRIal
[:SENSe]:RADio:FORMat?
Select the format that testing will be compliant with when
measurements are made.
ARIB, is the standard format defined by the Association of Radio
Industries and Business in Japan
TGPP, is the standard format defined by the Third Generation
Partnership Projects (3GPP)
Trial, is a 1998 trial format being evaluated
Factory Preset
and *RST: Trial
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
History: Version A.03.00 or later
Front Panel
Access:
Mode Setup, Radio, Standard
Chapter 1 87
Page 88

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Rho (Waveform Quality) Measurement
Commands for querying the rho measurement results and for setting to
the default values are found in the “MEASure Group of Commands” on
page 27. The equivalent front panel keys for the parameters described
in the following commands, are found under the
the
Mod Accuracy (Rho) measurement has been selected from the
MEASURE key menu.
Rho Measurement Demod Alpha
[:SENSe]:RHO:ALPHa <float>
[:SENSe]:RHO:ALPHa?
Set alpha for the root nyquist filter.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0.22
Range: 0.01 to 0.5
Meas Setup key, after
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Rho Measurement Average Count
[:SENSe]:RHO:AVERage:COUNt <integer>
[:SENSe]:RHO:AVERage:COUNt?
Set the number of frames that will be averaged. After the specified
number of frames (average counts), the averaging mode (terminal
control) setting determines the averaging action.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 10
Range: 1 to 10,000
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA
mode to use this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to
set the mode.
Rho Measurement Averaging State
[:SENSe]:RHO:AVERage[:STATe] OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:RHO:AVERage[:STATe]?
Turn averaging on or off.
Factory Preset
and *RST: On
88 Chapter1
Page 89

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA
mode to use this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to
set the mode.
Rho Measurement Averaging Termination Control
[:SENSe]:RHO:AVERage:TCONtrol EXPonential|REPeat
[:SENSe]:RHO:AVERage:TCONtrol?
Select the type of terminal control used for averaging. This determines
the averaging action after the specified number of frames (average
count) is reached.
Exponential - Each successive data acquisition after the average
count is reached, is exponentially weighted and combined with the
existing average.
Repeat - After reaching the average count, the averaging is reset and
a new average is started.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Exponential
Repeat for cdma2000 and W-CDMA mode
Remarks: You must be in the cdmaOne, cdma2000, W-CDMA
mode to use this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to
set the mode.
Rho Measurement Spectrum Normal/Invert
[:SENSe]:RHO:SPECtrum NORMal|INVert
[:SENSe]:RHO:SPECtrum?
Select normal or inverted spectrum for demodulation.
Normal - normal spectrum is used
Invert - inverted spectrum is used
Factory Preset
and *RST: Normal
Remarks You must be in the cdmaOne, cama2000, W-CDMA
mode to use this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to
set the mode.
Chapter 1 89
Page 90

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Rho Measurement Scramble Code
[:SENSe]:RHO:SYNC:SCRamble <integer>
[:SENSe]:RHO:SYNC:SCRamble?
Set the scramble code for synchronization.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1
Range: 0 to 262143 (0h to 3FFFFh) (0 is for no-scramble)
Remarks: You must be in the W-CDMA mode to use this
command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the mode.
Rho Measurement Trigger Source
[:SENSe]:RHO:TRIGger:SOURce
EXTernal[1]|External2|FRAMe|IF|IMMediate|IF|RFBurst
[:SENSe]:RHO:TRIGger:SOURce?
Select the trigger source used to control the data acquisitions.
External 1 – front panel external trigger input
External 2 – rear panel external trigger input
Frame – internal frame trigger from front panel input
IF – internal IF envelope trigger
Immediate – the next data acquisition is immediately taken,
capturing the signal asynchronously (also called free run).
RF Burst – internal wideband RF burst envelope trigger that has
automatic level control for periodic burst signals.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Immediate
Remarks: You must be in the cdma2000 or W-CDMA mode to use
this command. Use INSTrument:SELect to set the
mode.
Front Panel
Access:
Meas Setup, Trig Source
90 Chapter1
Page 91

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Spectrum (Frequency-Domain) Measurement
Commands for querying the spectrum measurement results and for
setting to the default values are found in the “MEASure Group of
Commands” on page 27. The equivalent front panel keys for the
parameters described in the following commands, are found under the
Meas Setup key, after the Spectrum (Freq Domain) measurement has been
selected from the
Spectrum Measurement Data Acquisition Packing
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:ACQuisition:PACKing
AUTO|LONG|MEDium|SHORt
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:ACQuisition:PACKing?
Select the amount of data acquisition packing. This is an advanced
control that normally does not need to be changed.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Auto
MEASURE key menu.
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement ADC Dither
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:ADC:DITHer[:STATe] AUTO|ON|OFF|2|1|0
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:ADC:DITHer[:STATe]?
Turn the ADC dither on or off. This is an advanced control that
normally does not need to be changed.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Auto
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Chapter 1 91
Page 92

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Spectrum Measurement ADC Range
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:ADC:RANGe
AUTO|APEak|APLock|M6|P0|P6|P12|P18|P24|
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:ADC:RANGe?
Select the range for the gain-ranging that is done in front of the ADC.
This is an advanced control that normally does not need to be changed.
Auto peak ranging is the default for this measurement. If you are
measuring a CW signal please see the description below.
• Auto - automatic range
For FFT spectrums - auto ranging should not be not be used. An
exception to this would be if you know that your signal is
“bursty”. Then you might use auto to maximize the time domain
dynamic range as long as you are not very interested in the FFT
data.
• Auto Peak - automatically peak the range
ForCW signals, the default of auto-peak ranging can be used, but
a better FFT measurement of the signal can be made by selecting
one of the manual ranges that are available: M6, P0 - P24.
Auto peaking can cause the ADC range gain to move
monotonically down during the data capture. This movement
should have negligible effect on the FFT spectrum, but selecting a
manual range removes this possibility. Note that if the CW signal
being measured is close to the auto-ranging threshold, the noise
floor may shift as much as 6 dB from sweep to sweep.
• Auto Peak Lock - automatically peak lock the range
— For CW signals, auto-peak lock ranging may be used. It will find
the best ADC measurement range for this particular signal and
will not move the range as auto-peak can. Note that if the CW
signal being measured is close to the auto-ranging threshold, the
noise floor may shift as much as 6 dB from sweep to sweep.
— For “bursty” signals, auto-peak lock ranging should not be used.
The measurement will fail to operate, since the wrong (locked)
ADC range will be chosen often and overloads will occur in the
ADC.
• M6 - manually selects an ADC range that subtracts 6 dB of fixed
gain across the range. Manual ranging is best for CW signals.
• P0 to 24 - manually selects ADC ranges that add 0 to 24 dB of fixed
gain across the range. Manual ranging is best for CW signals.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Auto peak
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
92 Chapter1
Page 93

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Spectrum Measurement Average Clear
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage:CLEAr
The average data is cleared and the average counter is reset.
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement Number of Averages
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage:COUNt <integer>
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage:COUNt?
Set the number of ‘sweeps’ that will be averaged. After the specified
number of ‘sweeps’ (average counts), the averaging mode (terminal
control) setting determines the averaging action.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 25
Range: 1 to 10,000
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement Averaging State
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage[:STATe] OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage[:STATe]?
Turn averaging on or off.
Factory Preset
and *RST: On
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Chapter 1 93
Page 94

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Spectrum Measurement Averaging Mode
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage:TCONtrol EXPonential|REPeat
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage:TCONtrol?
Select the type of terminal control used for averaging. This determines
the averaging action after the specified number of ‘sweeps’ (average
count) is reached.
Exponential - Each successive data acquisition after the average
count is reached, is exponentially weighted and combined with the
existing average.
Repeat - After reaching the average count, the averaging is reset and
a new average is started.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Exponential
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement Averaging Type
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage:TYPE
LOG|MAXimum|MINimum|RMS|SCALar
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:AVERage:TYPE?
Select the type of averaging.
Log − The log of the power is averaged. (This is also known as video
averaging.)
Maximum − The maximum values are retained.
Minimum − The minimum values are retained.
RMS − The power is averaged, providing the rms of the voltage.
Scalar − The voltage is averaged.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Log
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
94 Chapter1
Page 95

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Spectrum Measurement pre-ADC Bandpass Filter
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth:PADC OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth:PADC?
Turn the pre-ADC bandpass filter on or off. This is an advanced control
that normally does not need to be changed.
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement pre-FFT BW Auto
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth:PFFT:AUTO OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth:PFFT:AUTO?
Select auto or manual control of the pre-FFT BW. This is an advanced
control that normally does not need to be changed.
Auto - couples the pre-FFT BW to the frequency span.
Manual - the pre-FFT BW is uncoupled from the frequency span.
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement pre-FFT BW
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth:PFFT[:SIZE] <freq>
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth:PFFT[:SIZE]?
Set the pre-FFT bandwidth. This is an advanced control that normally
does not need to be changed.
Frequency span, resolution bandwidth, and the pre-FFT bandwidth
settings are normally coupled. If you are not auto-coupled, there can be
combinations of these settings that are not valid.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1.55 MHz
1.25 MHz for cdmaOne
155 kHz, for iDEN mode
Range: 1 Hz to 10 MHz
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Chapter 1 95
Page 96

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Spectrum Measurement Pre-FFT BW Filter Type
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth:PFFT:TYPE FLAT|GAUSsian
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth:PFFT:TYPE?
Select the type of pre-FFT filter that is used. This is an advanced
control that normally does not need to be changed.
Flat top- a filter with a flat amplitude response, which provides the
best amplitude accuracy.
Gaussian - a filter with Gaussian characteristics, which provides the
best pulse response.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Flat top
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement Resolution BW
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution] <freq>
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution]?
Set the resolution bandwidth for the FFT. This is the bandwidth used
for resolving the FFT measurement. It is not the pre-FFT bandwidth.
This value is ignored if the function is auto-coupled.
Frequency span, resolution bandwidth, and the pre-FFT bandwidth
settings are normally coupled. If you are not auto-coupled, there can be
combinations of these settings that are not valid.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 20 kHz
250 Hz, for iDEN mode
Range: 0.10 Hz to 3 MHz
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement Resolution BW Auto
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution]:AUTO
OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution]:AUTO?
Select auto or manual control of the resolution BW. The automatic mode
couples the resolution bandwidth setting to the frequency span.
96 Chapter1
Page 97

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Factory Preset
and *RST: On
Off, for iDEN mode
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Decimation of Spectrum Display
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:DECimate[:FACTor] <integer>
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:DECimate[:FACTor]?
Set the amount of data decimation done by the hardware and/or the
software. Decimation by 3 keeps every third sample, throwing awaythe
two in between. Similarly, decimation by 5 keeps every fifth sample,
throwing away the four in between.
Using zero (0) decimation selects the automatic mode. The
measurement will then automatically choose decimation by “1” or “2” as
is appropriate for the bandwidth being used. This is an advanced
control that normally does not need to be changed.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 0
Range: 0 to 1000, where 0 sets the function to automatic
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
History: Version A.02.00 or later
Spectrum Measurement FFT Length
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FFT:LENGth <integer>
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FFT:LENGth?
Set the FFT length. This value is only used if length control is set to
manual. The value must be greater than or equal to the window length
value. Any amount greater than the window length is implemented by
zero-padding. This is an advanced control that normally does not need
to be changed.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 4096
32768, for iDEN mode
Range: 8 to 1,048,576
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
History: Short form changed from LENgth to LENGth, A.03.00
Chapter 1 97
Page 98

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Spectrum Measurement FFT Length Auto
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FFT:LENGth:AUTO OFF|ON|0|1
[:SENSe]:SPECtum:FFT:LENGth:AUTO?
Select auto or manual control of the FFT and window lengths.
This is an advanced control that normally does not need to be changed.
Auto - the window lengths are coupled to resolution bandwidth,
window type (FFT), pre-FFT bandwidth (sample rate) and
SENSe:SPECtrum:FFT:RBWPoints.
Manual - lets you set SENSe:SPECtrum:FFT:LENGth and
SENSe:SPECtrum:FFT:WINDow:LENGth.
Factory Preset
and *RST: Auto
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
History: Short form changed from LENgth to LENGth, A.03.00
Spectrum Measurement FFT Minimum Points in Resolution BW
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FFT:RBWPoints <real>
[:SENSe]:SPECtum:FFT:RBWPoints?
Set the minimum number of data points that will be used inside the
resolution bandwidth. The value is ignored if length control is set to
manual. This is an advanced control that normally does not need to be
changed.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1.30
Range: 0.1 to 100
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement Window Length
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FFT:WINDow:LENGth <integer>
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FFT:WINDow:LENGth?
Set the FFT window length. This value is only used if length control is
set to manual. This is an advanced control that normally does not need
to be changed.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 706
5648, for iDEN mode
98 Chapter1
Page 99

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Range: 8 to 1,048,576
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
History: Short form changed from LENgth to LENGth, A.03.00
Spectrum Measurement FFT Window
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FFT:WINDow[:TYPE]
BH4Tap|BLACkman|FLATtop|GAUSsian|HAMMing|HANNing|KB70|KB90
|KB110|UNIForm
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FFT:WINDow[:TYPE]?
Select the FFT window type.
BH4Tap - Blackman Harris with 4 taps
Blackman - Blackman
Flat Top - flat top, the default (for high amplitude accuracy)
Gaussian - Gaussian with alpha of 3.5
Hamming - Hamming
Hanning - Hanning
KB70, 90, and 110 - Kaiser Bessel with sidelobes at −70, −90, or −110
dBc
Uniform - no window is used. (This is the unity response.)
Factory Preset
and *RST: Flat top
Remarks: This selection affects the acquisition point quantity and
the FFT size, based on the resolution bandwidth
selected.
To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Chapter 1 99
Page 100

W-CDMA Programming Commands
SENSe Subsystem
Spectrum Measurement Frequency Span
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FREQuency:SPAN <freq>
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:FREQuency:SPAN?
Set the frequency span to be measured.
Factory Preset
and *RST: 1 MHz
100 kHz for iDEN mode
Range: 10 Hz to 10 MHz (15 MHz when Service mode is
selected)
Default Unit: Hz
Remarks: The actual measured span will generally be slightly
wider due to the finite resolution of the FFT.
To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
Spectrum Measurement Trigger Source
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal[1]|EXTernal
2|FRAMe|IF|LINE|IMMediate|RFBurst
[:SENSe]:SPECtrum:TRIGger:SOURce?
Select the trigger source used to control the data acquisitions.
External 1 - front panel external trigger input
External 2 - rear panel external trigger input
Frame - internal frame timer from front panel input
IF - internal IF envelope (video) trigger
Line - internal line trigger
Immediate - the next data acquisition is immediately taken (also
called free run)
RF Burst - internal wideband RF burst envelope trigger that has
automatic level control for periodic burst signals
Factory Preset
and *RST: Immediate (free run)
RF burst, for GSM, iDEN mode
Remarks: To use this command, the appropriate mode should be
selected with INSTrument:SELect.
100 Chapter1
 Loading...
Loading...