Page 1

The Agilent E3633A and Agilent E3634A are high performance 200 watt single-
output dual range programmable DC power suppli es wi th both GPIB and RS-
232 interfaces. The combination of bench-top and system features in these
power supplies provides versatile solutions for your design and test
requirements.
Convenient bench-top features
• Single-output dual range
• Easy-to-us e knob control settings
• Highly visible vacuum-fluor escent display meters
• High accuracy and high resolution
• Remote voltage sensing
• Overvoltage and overcurrent protection
• Output on/off
• Excellent load and line regulation and low rip ple and noise
• Operating states storage
• Portable, ruggedized case with non-sk id feet
• Front and Rear output terminals
• Retrieving/Scrolling error messages on the display
Flexible system features
• GPIB (IEEE-488) and RS-232 interfaces are standard
• SCPI (Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments) compatibility
• I/O setup easily done from front-panel
• Software calibration, no internal adjustments required
Agilent E3633A and E3634A
DC Power Supplies
Page 2
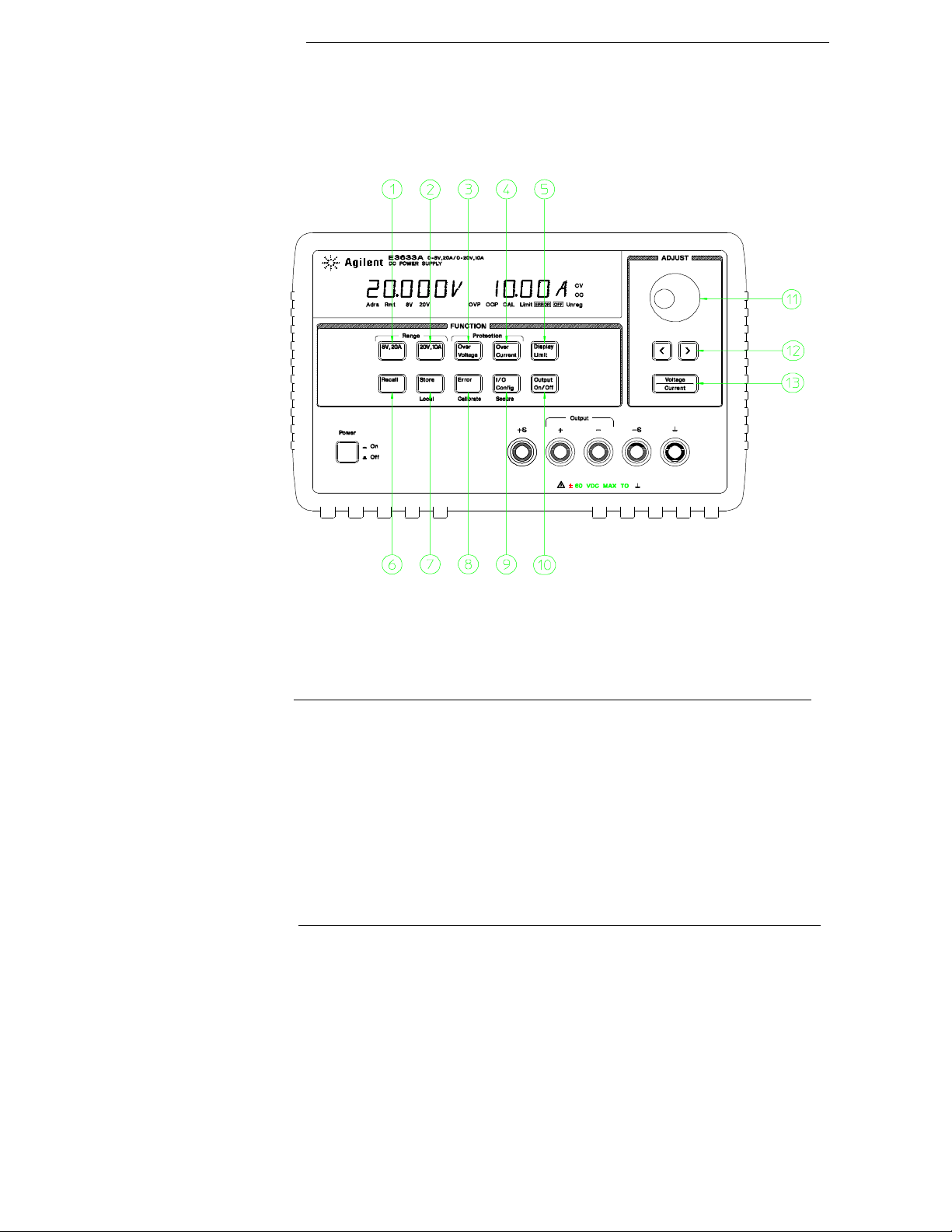
The Front Panel at a Glance
1 8V/20A range selection key (E3633A)
25V/7A range selection key (E3634A)
2 20V/10A range selection key (E3633A)
50V/4A range selection key (E3634A)
3 Overvoltage protection key
4 Overcurrent protection key
5 Display limit key
6 Recall operating state key
7 Store operating state/Local key
8 Error/Calibrate key
9 I/O Configuration/Secure key
10 Output On/Off key
11 Control knob
12 Resolution selection keys
13 Voltage/current adjust selection key
ii
Page 3

1 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range selection key Selects the 8V/20A or 25V/7A
range and allows the full rated output to 8V/20A or 25V/7A.
2 20V/10A* or 50V/4A** range selection key Selects the 20V/10A or
50V/4A range and allows the full rated output to 20V/10A or 50V/4A.
3 Overvoltage protection key Enables or disables the overvoltage protection
function, sets trip voltage level, and clears the overvoltage condition.
4 Overcurrent protection key Enables or disables the overcurrent protection
function, sets trip current level, and clears the overcurrent condition.
5 Display limit key Shows voltage and current limit values on the display and
allows knob adjustment for setting limit values.
6 Recall operating state key Recalls a previously stored operating state from
location ‘‘1’’, ‘‘2’’, or ‘‘3’’.
7 Store operating state / Local key1 Stores an operating state in location ‘‘1’’,
‘‘2’’, or ‘‘3’’ / or returns the power supply to local mode from remote interface
mode.
8 Error / Calibrate key2 Displays error codes generated during operation, self-
test and calibration / or enables calibration mode (the power supply must be
unsecured before performing calibration). See Service Guide for more details
on calibration.
9 I/O Configuration / Secure key3 Configures the power supply for remote
interfaces / or secure or unsecure the power supply for calibration. See
Service Guide for more details on how to secure or unsecure the power supply.
10 Output On/Off key Enables or disables the power supply output. This key
toggles between on and off.
11 Control knob Increases or decreases the value of the blinking digit by turning
clockwise or counter clockwise.
12 Resolution selection keys Move the blinking digit to the right or left.
13 Voltage/current adjust selection key Selects the knob control function for
voltage or current adjustment.
1
The key can be used as the ‘‘
Local
’’ key when the power supply is in the remote
interface mode.
2
You can enable the ‘‘calibration mode’’ by holding down this key when you
turn on the power supply.
3
You can use it as the ‘‘Secure’’ or ‘‘Unsecure’’ key when the power supply is
in the calibration mode.
*For Agilent E3633A Model **For Agilent E3634A Model
iii
Page 4
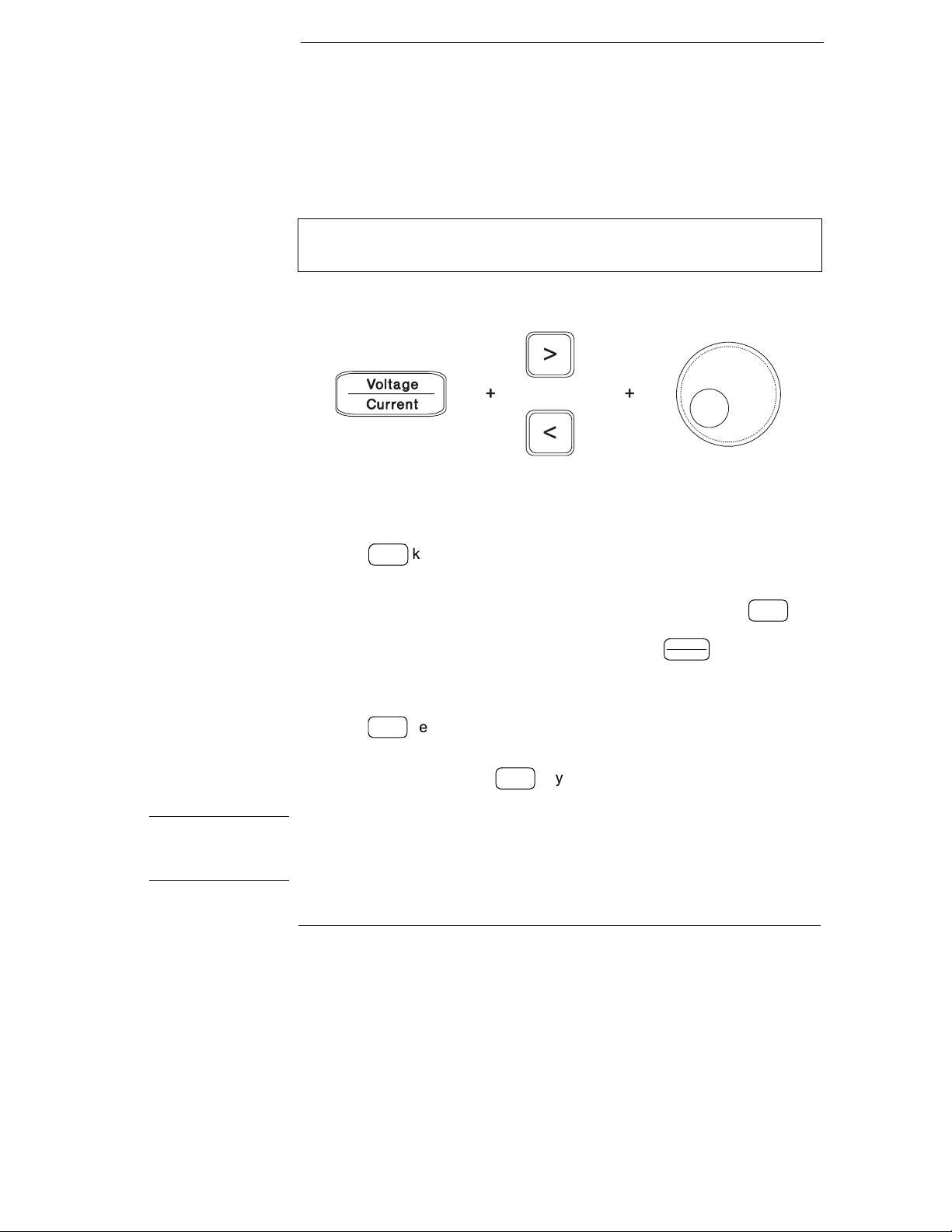
Front-Panel Voltage and Current Limit Settings
You can set the voltage and current limit values from the front panel using the
following method.
Use the voltage/current adjust selection key, the resolution selection keys,
and the control knob to change the voltage and current limit values.
1 Select the desired range using the range selection keys after turning on the
power supply.
2 Press the
3 Move the blinking digit to the appropriate position using the resolution
selection keys and change the blinking digit value to the desired voltage limit
by turning the control knob. If the display limit times out, press the
again.
4 Set the knob to current control mode by pressing the key.
5 Move the blinking digit to the appropriate position using the resolution
selection keys and change the blinking digit value to the desired current limit
by turning the control knob.
6 Press the
will go to output monitoring mode automatically to display the voltage and
current at the output or the display will go to output monitoring mode
immediately by pressing the
Display
key to show the limit values on the display.
Limit
Vol tage
Current
Output
key to enable the output. After about 5 seconds, the display
On/Off
Output
key again.
On/Off
Display
Limit
key
Note All front panel keys and controls can be disabled with remote interface commands.
The Agilent E3633A and Agilent E3634A must be in "Local" mode for the front panel
keys and controls to function.
iv
Page 5
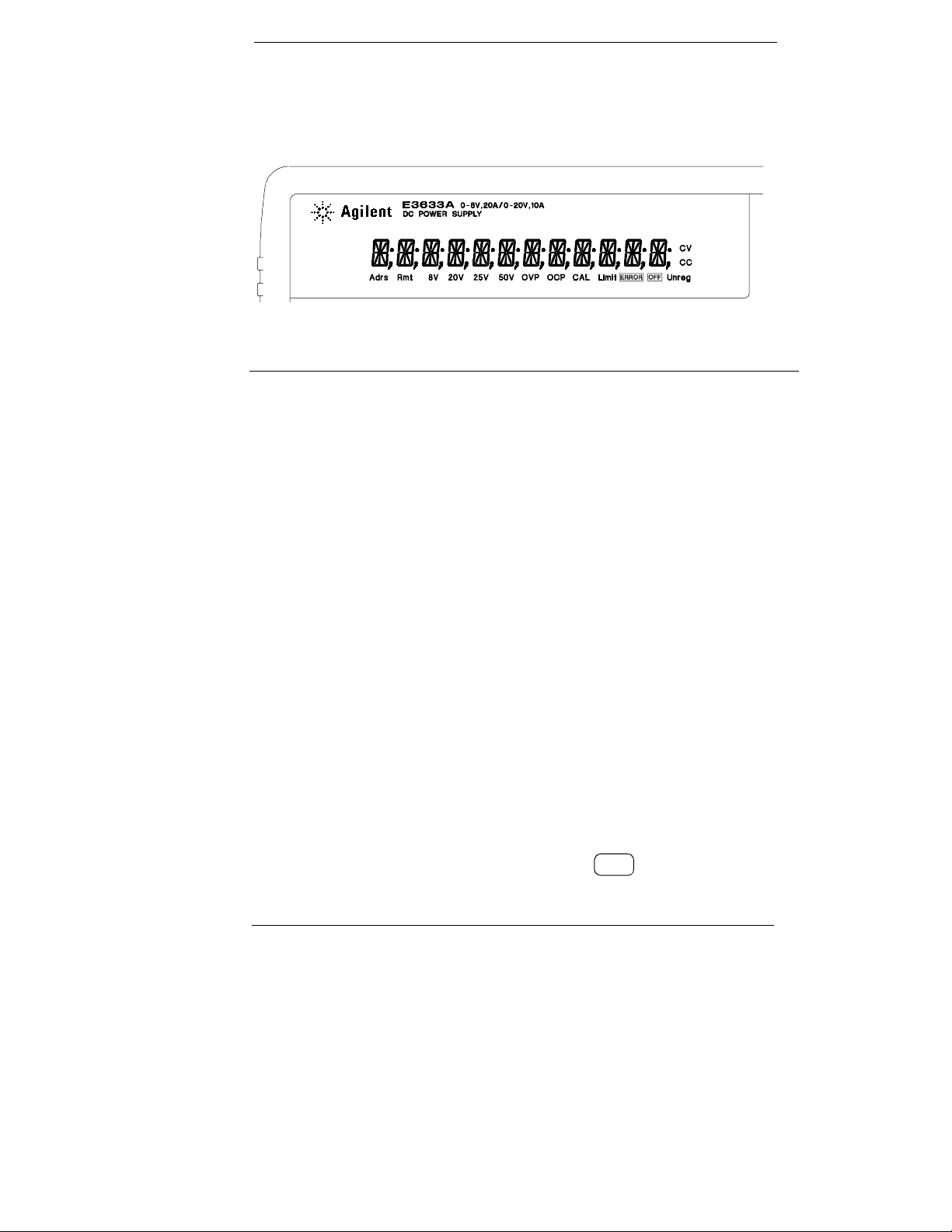
Display Annunciators
Adrs Power supply is addressed to listen or talk over a remote interface.
Rmt Power supply is in remote interface mode.
8V Shows the 8V/20A range is selected. (Agilent E3633A model)
20V Shows the 20V/10A range is selected. (Agilent E3633A model)
25V Shows the 25V/7A range is selected. (Agilent E3634A model)
50V Shows the 50V/4A range is selected. (Agilent E3634A model)
OVP The overvoltage protection function is enabled when the
annunciator turns on or the overvoltage protection circuit has
caused the power supply to shutdown when the annunciator blinks.
OCP The overcurrent protection function is enabled when the
annunciator turns on or the overcurrent protection circuit has
caused the power supply to shutdown when the annunciator blinks.
CAL The power supply is in calibration mode.
Limit The display shows the limit values of voltage and current.
ERROR Hardware or remote interface command errors are detected and
the error bit has not been cleared.
OFF The output of the power supply is disabled (See page 52 for more
information).
Unreg The output of the power supply is unregulated (output is neither CV
nor CC).
CV The power supply is in constant voltage mode.
CC The power supply is in constant current mode.
To review the display annunciators, hold down key as you turn on
Display
Limit
the power supply.
v
Page 6
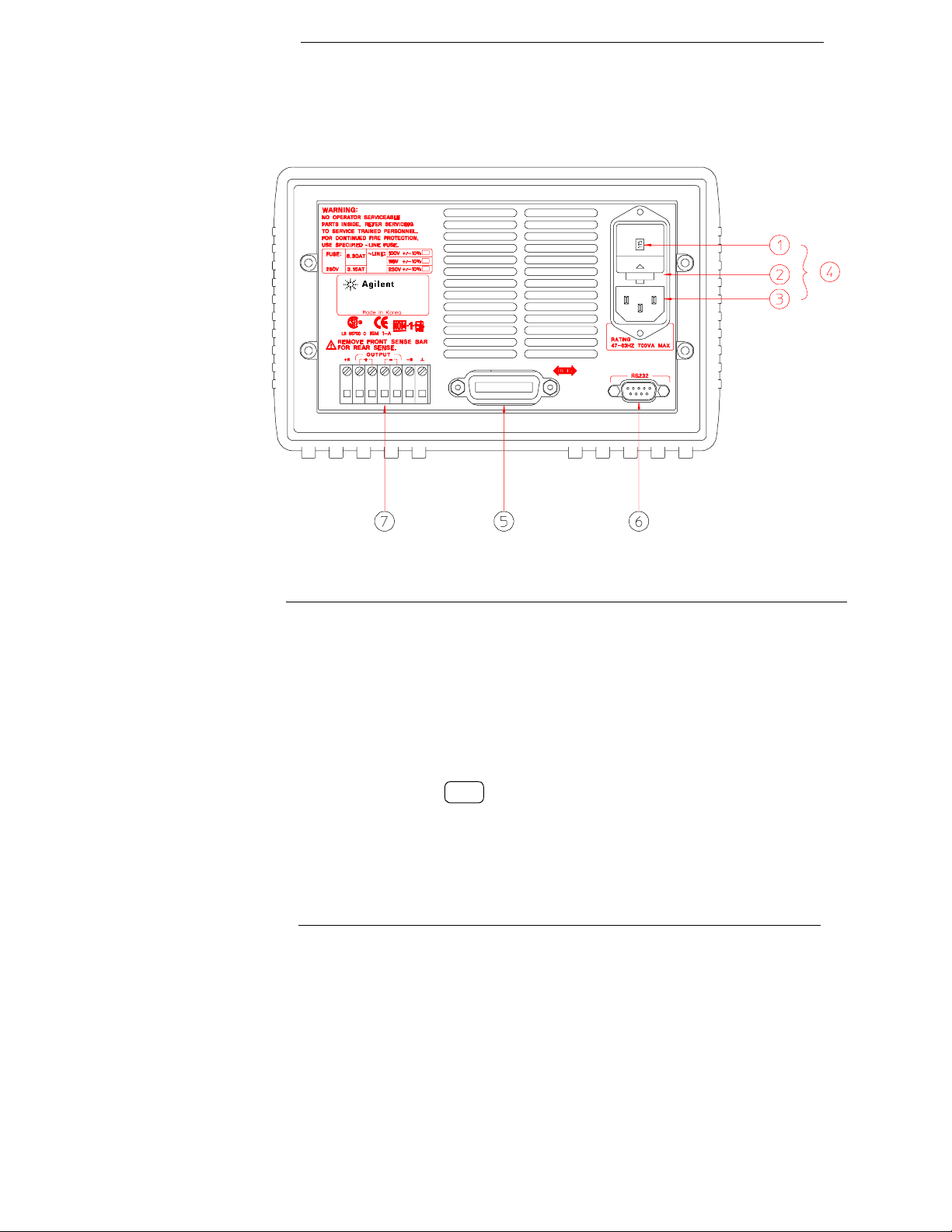
The Rear Panel at a Glance
1 Power-line voltage setting
2 Power-line fuse-holder assembly
3 AC inlet
5 GPIB (IEEE-488) interface connector
6 RS-232 interface connector
7 Rear output terminals
4 Power-line module
Use the front-panel key to:
I/O
Config
• Select the GPIB or RS-232 interface (see chapter 3).
• Set the GPIB bus address (see chapter 3).
• Set the RS-232 baud rate and parity (see chapter 3).
vi
Page 7

In This Book
General Information
power supply. This chapter also provides instructions for checking your power
supply, connecting to ac power, and selecting power-li ne voltage.
Initial Operation
outputs and properly responds to operation from the front panel.
Front- Pa ne l O per ati on
keys and how they are used to operate the power supply from the front panel.
This chapter also shows how to configure the power supply for the remote
interface and gives a brief introduction to the calibration features.
Remo te Int e rf a c e R ef e r e nc e
help you program the power supply over the remote interface. This chapter
also explains how to program for status reporting.
Error Messages
are working with the power supply. Each listing contains information to help
you diagnose and solve the problem.
Application Programs
applications to help you develop programs for your application.
Tutorial
gives specific details on the operation and use of the Agilent E3633A and
Agilent E3634A power supplies.
Chapter 7 describes basic operation of linear power supplies and
Chapter 1 contains a general description of your
Chapter 2 ensures that the power supply develops its rated
Chapter 3 describes in detail the use of front-panel
Chapter 4 contains reference information to
Chapter 5 lists the error messages that may appear as you
Chapter 6 contains some remote interface
Specifications
If you have questions relating to the operation of the power supply, call
1-800-829-4444 in the United States, or contact your nearest Agilent
Technologies Sales Office.
If your Agilent E3633A or Agilent E3634A fails within one year of purchase,
Agilent will repair or replace it free of charge. Call 1-800-258-5165 ("Express
Exchange") in the United States, or contact your nearest Agilent Technologies
Sales Office.
Chapter 8 lists the power supply’s specifications .
vii
Page 8

viii
Page 9

Contents
Chapter 1 General Informatio n
Safety Considerations- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14
Safety and EMC Requirements - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14
Options and Accessories - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 15
Options- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 15
Accessories - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 15
Description - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16
Installation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19
Initial Inspection - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19
Cooling and Location - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19
Input Power Requirements- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
Power-Line Cord - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
Power-Line Voltage Selection - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22
Chapter 2 Initial Operation
Preliminary Checkout- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 27
Power-On Checkout - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 28
Output Checkout- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 29
Voltage Output Checkout - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 29
Current Output Checkout - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 30
Contents
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Front-Panel Operation Overview- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 35
Constant Voltage Operation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 36
Constant Current Operation- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 38
Storing and Recalling Operating States - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 40
Programming Overvoltage Protection- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 42
Setting the OVP Level and Enable the OVP Circuit - - - - - - - - 42
Checking OVP Operation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 43
Clearing the Overvoltage Condition - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 43
Programming Overcurrent Protection- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 46
Setting the OCP Level and Enable the OCP Circuit- - - - - - - - 46
Checking OCP Operation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 47
Clearing the Overcurrent Condition- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 47
Remote Voltage Sensing at the Front and Rear Terminals - - - - - 49
CV Regulation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 49
Output Rating - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 49
Output Noise - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 49
Stability - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 50
Remote Voltage Sensing Connections - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 50
Remote Voltage Sensing at the Rear Panel - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 51
ix
Page 10

Contents
Disabling the Output - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 52
Disablin g the Output Using an External Relay- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 53
Knob Locking- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 53
System-Related Operations- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 54
Self-Test - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 54
Error Conditions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 55
Display Control - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 56
Firmw are Revisi on Query - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 57
SCPI Language Version - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 57
Remote Interface Configuration - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 58
Remote Interface Selection - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 58
GPIB Address- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 59
Baud Rate Selection (RS-232) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 59
Parity Selection (RS-232)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 59
To Set the GPIB Address - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 60
To Set the Baud Rate and Parity (RS-232) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 61
GPIB Interface Configuration - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 63
RS-232 Interface Configuration- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 64
RS-232 Configurati on Overview - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 64
RS-232 Data Frame Format - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 64
Connection to a Computer or Termi nal - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 65
Contents
DTR / DSR Handshake Protocol - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 66
RS-232 Troubles hooti ng- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 67
Calibration Overview - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 68
Calibration Security- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 68
Calibration Count- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 72
Calibration Message- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 72
Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
SCPI Command Summary- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 75
Simpli fied Pro gramm in g Overview - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 80
Using the
Using the Low-Level Com mands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 80
Reading a Query Response - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 81
Selecting a Trigger Source - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 81
Power Supply Programm i ng Ranges- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 82
Using the
Output Setting and Operation Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 84
Triggering Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 91
Trigger Source Choices - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 91
Triggering Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 93
System-Related Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 94
x
APPLy
APPLy
Command - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 80
Command- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 83
Page 11

Contents
Calibration Commands- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 98
RS-232 Interface Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 101
The SCPI Status Registers - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 102
What is an
What is an
SCPI Status System - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 103
The Questionable Status Register- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 104
The Standard Event Register - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 105
The Status Byte Register- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 106
Using Service Request (SRQ) and Serial POLL - - - - - - - - - - 107
Using *STB? to Read the Status Byte- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 108
Using the Message Available Bit (MAV)- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 108
To Interrupt Your Bus Controll er Usi ng SRQ - - - - - - - - - - - 108
To Determine When a Command Sequence is Com pl eted - 109
Using *OPC to Signal When Data is in the Output Buffer - - 109
Status Reporting Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 110
An Introduction to the SCPI Language - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 113
Command Format Used in This Manual- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 114
Command Separators - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 115
Using the
Querying Parameter Settings - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 116
SCPI Command Terminators - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 116
IEEE-488.2 Common Commands - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 116
SCPI Parameter Types - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 117
Halting an Output in Progress - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 118
SCPI Conformance Information- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 119
IEEE-488 Conformance Information - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 122
Event
Enable
MIN
Register? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 102
Register? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 102
and
MAX
Parameters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 115
Contents
Chapter 5 Error Messages
Execution Errors - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 125
Self-Test Errors- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 130
Calibration Errors- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 131
Chapter 6 Application Programs
Example Program for C and C++- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 135
Example Program for Excel 97 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 139
Chapter 7 Tutorial
Overview of Agilent E3633A and Agilent E3634A Operation - - 147
Output Characteristics - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 149
Unregulated State - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 151
Unwanted Signals - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 151
Connecting the Load- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 153
xi
Page 12

Contents
Output Isolation- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 153
Multiple Loads - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 153
Remote Voltage Sensing - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 154
Load Consideration - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 155
Extending the Voltage and Current Range- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 157
Series Connections - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 157
Parallel Connections - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 157
Remote Programming- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 158
Reliability- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 160
Chapter 8 Specifications
Performance Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 163
Supplemental Ch aracteristi cs - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 165
Contents
xii
Page 13

1
General Information
Page 14

General Information
This is the User’s guide for your Agilent E3633A and E3634A DC power
supplies. Unless otherwise stated, the information in this manual applies to
both two models.
This chapter provides a general description of your power supply . This chapter
also contains instructions for initial inspection, location and cooling for bench
and rack operation, selecting the power-line voltage, and connecting your
power supply to ac power.
Safety Considerations
This power supply is a Safety Class I instrument, which means that it has a
protective earth terminal. That terminal must be connected to earth ground
through a power source with a 3-wire ground receptacle.
Before installation or operation , check the power supply and review this
manual for safety markings and instructions. Safety information for specific
procedures is located at the appropriate pl aces in this manual. See also
‘‘
Safety
’’ at the beginning of this manual for general safety information.
Safety and EMC Requirements
This power supply is designed to comply with the following safety and EMC
(Electromagnetic Compatibility) requirements:
• IEC 1010-1(1990)/EN 61010-1(1993) + A2 (1995): Safety Requirements for
Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Use
• CSA C22.2 No.1010.1-92: Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for
Measurement, Control, and L aboratory Use
• EN50082-1(1992):
IEC 1000-4-2(1995): Electrostatic Discharge Requirements
IEC 1000-4-3(1995): Radiated Electrom agnetic Field R equirem ents
IEC 1000-4-4(1995): Electrical Fast Trans ient/ Bu rst Requi rements
EN61000-4-5(1995): Surge Requirements
EN61000-4-6(1995): Conducted Radio Frequency Immunity Requir em ents
EN61000-4-8(1993): Magnetic Field Requirements
EN61000-4-11(1994): Voltage dips, short, interruption and var Requirement
• Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
• EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
2
Page 15

Chapter 1 General Information
Options and Accessories
• EN 55011(1991) Group 1, Class A/CISPR 11(1990): Limits and Methods of
Radio Interference Characteristics of Industrial, Scientific, and Medical
(ISM) Radio - Frequency Equipment.
• ICES/NMB-001
This ISM device complies with Canadian ICES-001.
Cet appareil ISM est conforme à la norme NMB -001 du Canada.
Options and Accessories
Options
Option 0EM, 0E3, and 0E9 determine whi ch power-line voltage is selected at
the factory. The standard unit is configured for 115 Vac ± 10%, 47-63 Hz input
voltage. For more information about changing the power-line voltage setting,
see ‘‘
Power-Line Voltage Selection
Option Description
0EM 115
0E3
0E9
1CM
0L2
Vac ± 10%, 47-63 Hz input voltage
230 Vac ± 10%, 47-63 Hz input voltage
100 Vac ± 10%, 47-63 Hz input voltage
Rack mount kit (Agilent part number 5063-9243)
Extra English manual set (local language manual fil es are included
on the CD-ROM, Agi lent part number 5964-8251)
’’, starting on page 22 in this ch ap ter.
1
Accessories
The accessories listed below may be ordered from your local Agilent
Technologies Sales Office either with the power supply or separately.
Agilent No. Description
10833A
10833B
34398A
34399A
GPIB cable, 1 m (3.3 ft.)
GPIB cable, 2 m (6.6 ft.)
RS-232, 9 pin (f) to 9 pin (f), 2.5 m (8.2 ft.) cable; plus 9 pin (m) to
25 pin (f) adapter
RS-232 adapter kit (contains 4 adapters):
9 pin (m) to 25 pin (m) for use with PC or printer
9 pin (m) to 25 pin (f) for use with PC or printer
9 pin (m) to 25 pin (m) for use with modem
9 pin (m) to 9 pin (m) for use with modem
3
Page 16

Chapter 1 General Information
Description
Description
The Agilent E3633A and Agilent E3634A DC power supplies feature a
combination of programming capabilities and linear power supply
performance that makes them ideal for power systems applications. The power
supply is programmable locally from the front panel or remotely over the GPIB
and RS-232 interfaces. This power supply has two ranges, allowing more
voltage at a lower current. An output range needed is selected from the front
panel or over the remote interfaces.
Operational features include:
• Dual range of single-output: 8V/20A and 20V/10A (Agilent E3633A),
25V/7A and 50V/4A (Agilent E3634A)
• Constant voltage (CV) or constant current (CC) operation
• Overvoltage protection (OVP) and overcurrent protection (OCP)
• Three storage locations (1 to 3) for user-defined operating states
• Automatic turn-on self-test
• Remote sensing for load voltage at the front or rear panel terminals
• User calibration from the front panel or over the remote interfaces
The front panel operation permits:
• Easy-to-use of knob control
• Output range selection
• Enabling or disablin g OVP and OCP features
• Setting the OVP and OCP trip levels
• Clearing OVP and OCP conditions
• Setting and displaying the voltage and current limit values
• Saving and recalling operating states
• Returning the power supply to l ocal mode from remote interface mode
• Retrieving/Scrolling error messages on the display
• Calibrating the power supply, includ ing changing the calibration secure
code
• Configuring the power supply for remote interfaces
• Enabling or disablin g the output
4
Page 17

Chapter 1 General Information
Description
When operated over the remote interface, the power supply can be both a
listener and a talker. Using an external controller, you can instruct the power
supply to set the output and to send the status data back over the GPIB or
RS-232. Capabili ties inclu de the followin g features:
• Voltage and current programming
• Voltage and current readback
• Present and stored status readback
• Programming syntax error detection
• Complete self-test
The front-panel VFD (Vacuum-Fluorescent Display) incl udes :
• Displaying actual values of output voltage and current (meter mode)
• Or displaying the limit values of voltage and current (limit mode)
• Checking the operating status from the annunciators
• Checking the type of error from the error codes (messages)
1
Connections to the power supply’s output and to chassis ground are made to
binding posts on the
Warning Floating the power supply output more than ±60 Vdc from the chassis presents an
electric shock hazard to the operator. Do not float the outputs more than ±60 Vdc
when metal shorting bars without insulation are used to connect the (+) output to the
(+) sense and the (-) output to the (-) sense terminals.
front panel
and to the
rear output
terminals.
5
Page 18
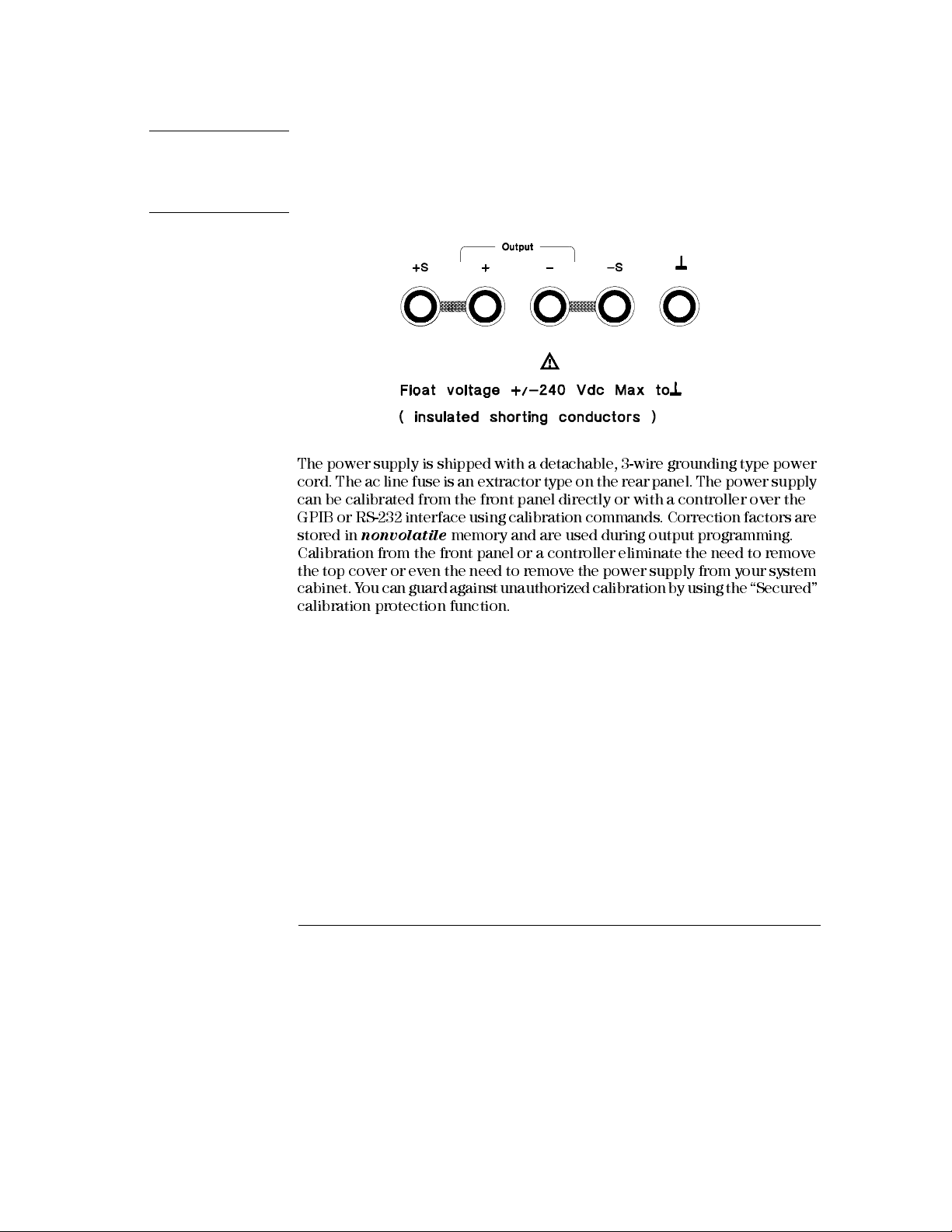
Chapter 1 General Information
Description
Warning Outputs can be floated to maximum of ±240 Vdc provided that the metal shorting bars
without insulation are either replaced with insulated conductors or they are removed
from the terminals so there is no operator access to the output conductors without
insulation. All field wiring insulation must be adequate for the voltage present.
The power supply is shipped with a detachable, 3-wire grounding type power
cord. The ac line fuse is an extractor type on the rear panel. The power supply
can be calibrated from the front panel di rectly or with a controller over the
GPIB or RS-232 interface using calibration commands. Correction factors are
stored in
Calibration from the front panel or a controller eliminate the need to remove
the top cover or even the need to remove the power supply from your system
cabinet. Y ou can guard against unauthorized calibration by using the “Secured”
calibration protection function.
nonvolatile
memory and are used during output programming.
6
Page 19

Chapter 1 General Information
Installation
Installation
Initial Inspection
When you receive your power supply, insp ect it for any obvious damage that
may have occurred during shipment. If any damage is found, notify the carrier
and the nearest Agilent Sales Office immediately. Warranty information is
shown in the front of this manual.
Keep the original packing materials in case the power supply has to be returned
to Agilent Technologies in the future. If you return the power supply for service,
attach a tag identifying the owner and model nu mber. Also include a brief
description of the problem.
Mechanical Check
This check confirms that there are no broken keys or knob, that the cabinet
and panel surfaces are free of dents and scratches, and that the display is not
scratched or cracked.
Electrical Check
Chapter 2 describes an initial operation procedure which, when successfully
completed, verifies to a high l evel of confidence that the power supply is
operating in accordance with its specifications. Detailed electrical verification
procedures are included in the
Service Guide
.
1
Cooling and Location
Cooling
The power supply can operate without loss of performance within the
temperature range of 0 °C to 40 °C, and with derated output current from
40 °C to 55 °C. A fan cools the power supply by drawing air through the rear
panel and exhausting it out the sides. Using an Agilent rack mount will not
impede the flow of air.
Bench Operation
Y our power supply must be installed in a location that allows sufficient space
at the sides and rear of the power supply for adequate air circulation. The
rubber bumpers must be removed for rack mounting.
7
Page 20
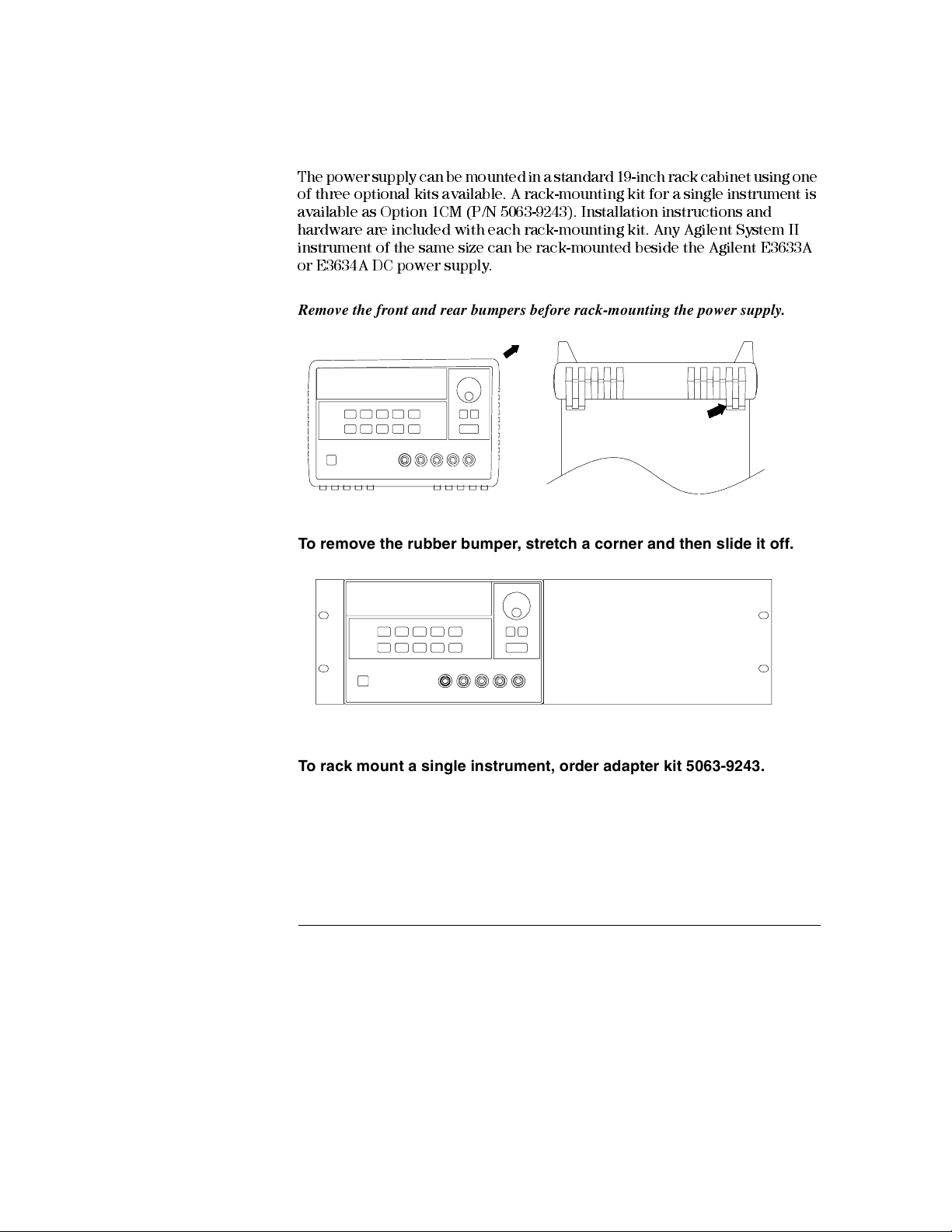
Chapter 1 General Information
Installation
Rack Mounting
The power supply can be mounted in a standard 19-inch rack cabinet using one
of three optional kits available. A rack-mounting kit for a single instrument is
available as Option 1CM (P/N 5063-9243). Installation instructions and
hardware are included with each rack-mounting kit. Any Agilent System II
instrument of the same size can be rack-mounted beside the Agilent E3633A
or E3634A DC power supply.
Remove the front and rear bumpers before rack-mounting the power supply.
To remove the rubber bumper, stretch a corner and then slide it off.
To rack mount a single instrument, order adapter kit 5063-9243.
8
Page 21
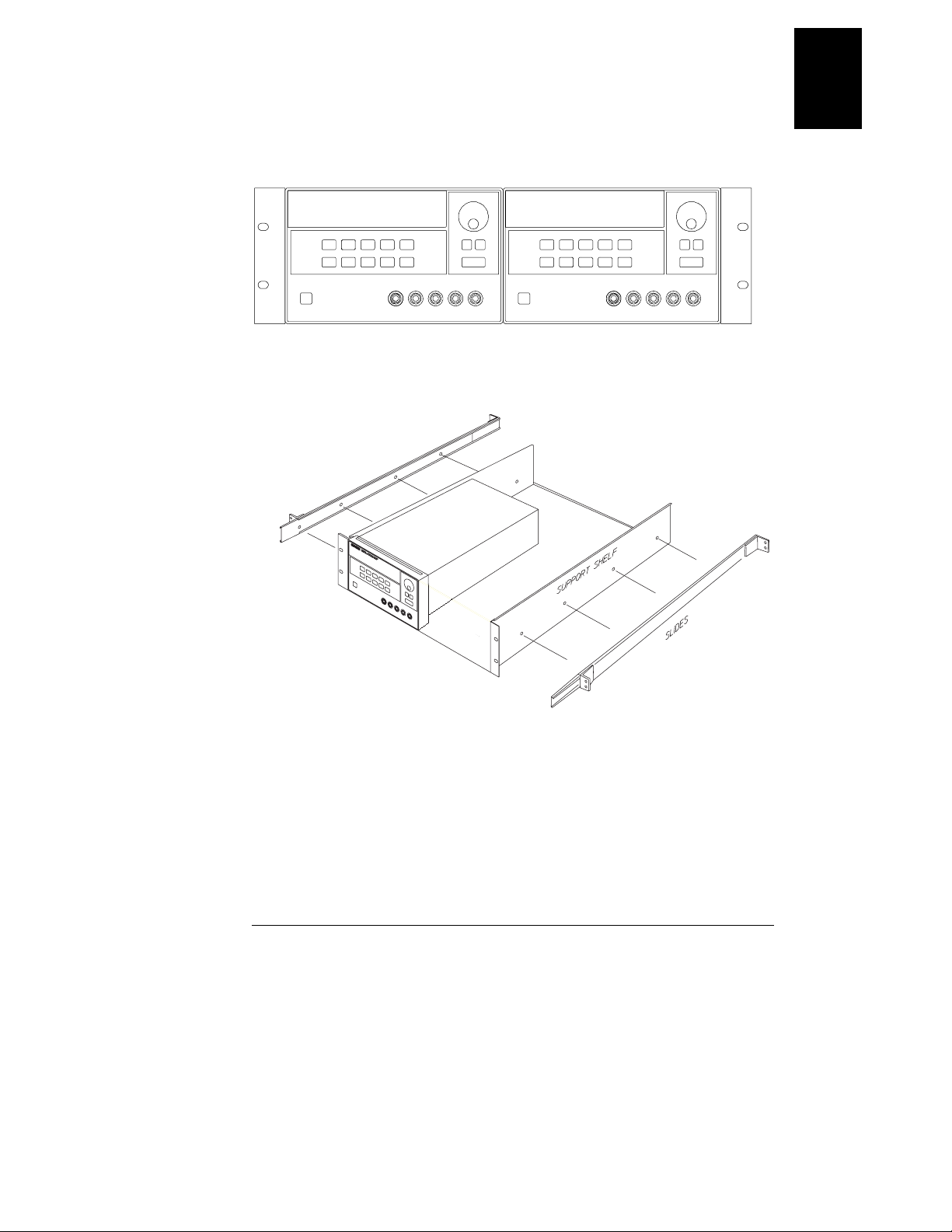
Chapter 1 General Information
Installation
To rack mount two instruments of the same depth side-by-side, order
lock-link kit 5061-9694 and flange kit 5063-9214.
1
To install two instruments in a sliding support shelf, order support shelf
5063-9256, and slide kit 1494-0015.
9
Page 22

Chapter 1 General Information
Input Power Requirements
Input Power Requirements
Y ou can operate your power supply from a nominal 100 V, 115 V , or 230 V single
phase ac power source at 47 to 63 Hz. An indication on the rear panel shows
the nominal input voltage set for the power supply at the factory . If necessary ,
you can change the power-line voltage setting according to the instructions on
the next page.
Power-Line Cord
The power supply is shipped from the factory with a power-line cord that has
a plug appropriate for your location. Contact the nearest Agilent Sales and
Service Office if the wrong power-line cord is included with your power supply.
Your power supply is equipped with a 3-wire grounding type power cord; the
third conductor being the ground. The power supply is grounded only when
the power-line cord is plugged into an appropriate receptacle. Do not operate
your power supply without adequate cabinet ground connection.
Power-Line Voltage Selection
Power-line voltage selection is accomplished by adjusting two components:
power-line voltage selector and power- line fuse on the power-line module of
the rear panel. To change the power-line voltage, proceed as fol lows:
10
Page 23
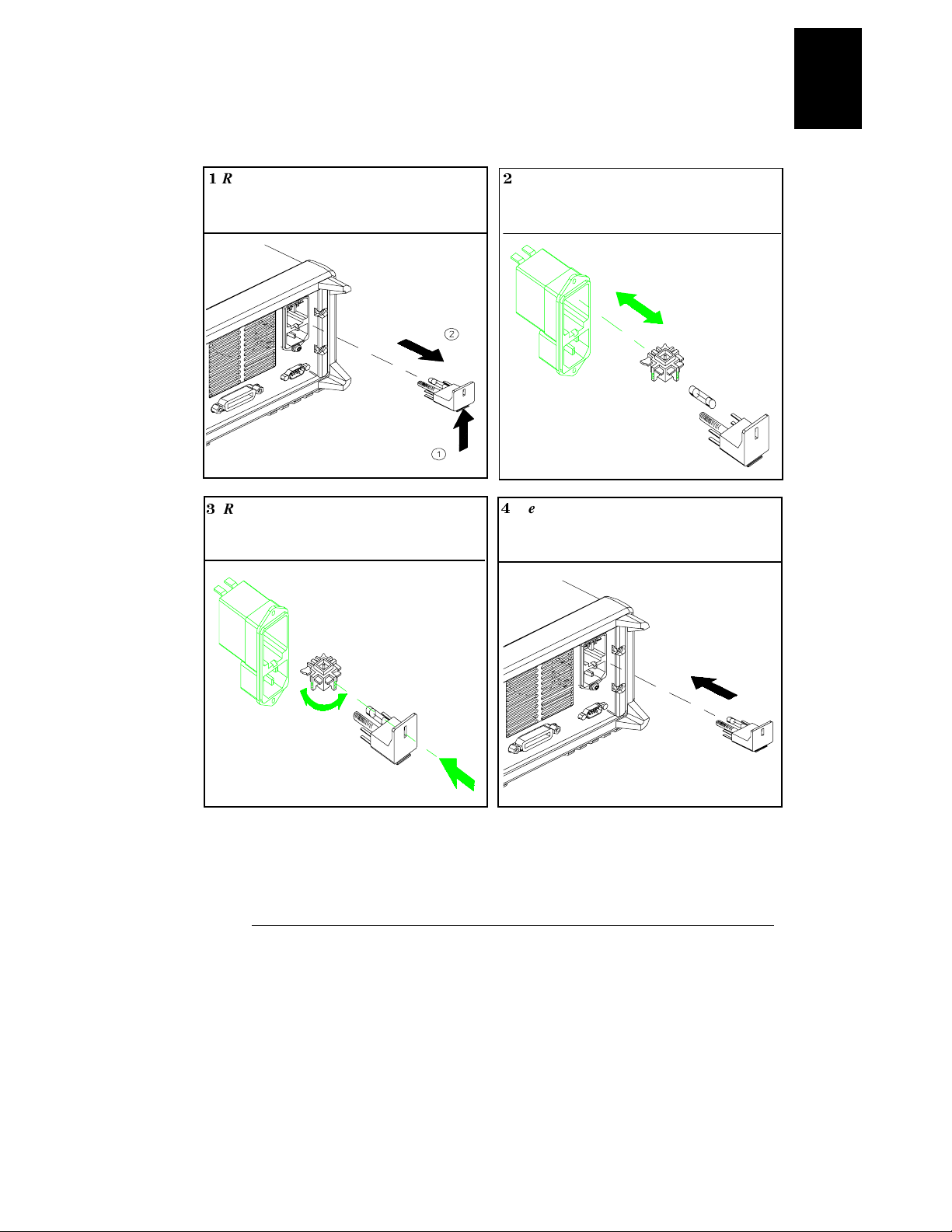
Chapter 1 General Information
Input Power Requirements
1
Remove the power cord. Remove the
fuse-holder assembly with a flat-blade
screwdriver from the rear panel.
2
Install the correct line fuse. Remove
the power-line voltage selector from the
power-line module.
100 or 115 Vac, 6.3 AT fuse
230 Vac, 3.15 AT fuse
1
3
Rotate the power-line voltage selector
until the correct voltage appears.
100, 115, or 230 Vac
4
Replace the power-line voltage selector
and the fuse-holder assembly in the rear
panel.
11
Page 24

Chapter 1 General Information
Input Power Requirements
12
Page 25

2
Initial Operation
Page 26

Initial Operation
There are three basic tests in this chapter. The automatic power-on test
includes a self-test that checks the internal microprocessors and allows the
user visually to check the display. The output check ensures that the power
supply develops its rated outputs and properly responds to operation from the
front panel. For complete performance and/or verification tests, refer to the
Service Guide
This chapter is intended for both the experienced and the inexperienced user
because it calls attention to certain checks that s hould be made prior to
operation.
Throughout this chapter the key to be pressed is shown in the left margin.
.
14
Page 27

Chapter 2 Initial Operation
Preliminary Checkout
Preliminary Checkout
The following steps help you verify that the power supply is ready for use.
1 Check the list of supplied items.
Verify that you have received the following item s with your power sup ply. If
anything is missing, contact yo ur nearest Agilent Technologies Sales Office.
One power cord for your location.
This User’s
One
Certificate of Calibration.
2 Verify the power-line voltage setting on the rear panel.
The power-line voltage is set to the proper value for your country when the
power supply is shipped from the factory. Change the voltage setting if it is not
correct. The settings are: 100, 115, or 230 Vac.
3 Verify that the correct power-line fuse is installed.
The correct fuse is installed for your country when the power supply is shipped
from the factory. For 100 or 115 Vac operation, you must use a 6.3 AT fuse. For
230 Vac operation, you must use a 3.15 AT fuse.
4 Connect the power-line cord and turn on your power supply.
The front-panel display wil l light up and a power-on self-test occurs
automatically when you turn on the power supply.
See ‘‘Power-Line Voltage Selection’’, starting on page 22 in chapter 1 if you
need to change the power-line voltage or the powe r-line fuse .
Service
Guide.
Guide.
2
To replace the 6.3 AT fuse, order A gile nt part nu m ber 2110-1030.
To replace the 3.15 AT fuse, order A gile nt par t num ber 2110-1031.
15
Page 28

Chapter 2 Initial Operation
Power-On Checkout
Power-On Checkout
The power-on test includes an automatic self-test that checks the internal
microprocesso rs and allow s the user visuall y to check the display. You will
observe the following sequence on the display after pressing the front panel
power switch to on.
1 The front-panel display will light up briefly while the instrument
performs its power-on self-test.
To review the power-on display with all annunciators turned on, hold down
Display
key as you turn on the power sup ply
Limit
2 The GPIB address or RS-232 is also displayed for abou t one second.
ADDR 05 (or RS-232)
The GPIB address is s et to ‘‘5’’ when the power supply is shipped from the
factory for remote interface configuration. If this is not the first time the power
supply is turned on, a different interface (RS-232) or a different GPIB address
may appear.
See "Remote Interface Configuration" in chapter 3 starting on page 58 if you
need to change the remote interface configuration.
.
3The “8V”* or “
25V
”**, “
OVP
”, “
OCP
” and “
OFF
” annunciators are on.
All others are off.
The power supply will go into the power-on / reset state; the output is disabled
(the
OFF
annunciator turns on); the 8/20A* or 25V/7A** range is selected (the
8V
* or
25V
** annunciator turns on); and the knob is selected for voltage
Output
On/Off
control. Notice that the
4 Enable the outputs.
The
OFF
annunciator turns off and the 8V* or
annunciators are lit. The
OVP
and
blinking
OCP
annunciator also turn on.
25V
**,
OVP, OCP
, and CV
digit can be adjusted by turning the knob.
Notice that the display is in the meter mode. ‘‘Meter mode’’ means that the
display shows the actual output voltage and current.
Note If the power supply detects an error during power-on self-test, the ERROR
annunciator will turn on.
See "Error Messages" for more information starting on page
123 in chapter 5
*For Agilent E3633A Model **For Agilent E3634A Model
16
Page 29

Power
Output
On/Off
Chapter 2 Initial Operation
Output Checkout
Output Checkout
The following procedures check to ensure that the power supply develops its
rated outputs and properly responds to operation from the front panel. For
complete performance and verification tests, refer to the
For each step, use the keys shown on the left margins.
Voltage Output Checkout
The following steps verify bas ic voltage functions with no load.
1 Turn on the power supply.
The power supply will go into the power-on / reset state; the output is disabled
(the
OFF
annunciator turns on); the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range is selected (the
8V
* or
25V
** annunciator turns on); and the knob is selected for voltage
control.
2 Enable the outpu ts.
The
OFF
annunciator turns off and the 8V* or
annunciators are lit. The blinki ng digit can be adjusted by turning the knob.
Notice that the display is in the meter mode. ‘‘Meter mode’’ means that the
display shows the actual output voltage and current.
25V
**,
Service Guide
OVP, OCP
, and CV
.
2
3 Check that the front-pa nel voltmeter properly responds to knob
control for the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A ** range.
Turn the knob clockwise or counter clockwise to check that the voltmeter
responds to knob control and the ammeter indicates nearly zero.
1
4 Ensure that the voltage can be adjusted from zero to the full rated
value.
Adjust the knob until the voltmeter indicates 0 volts and then adjust the knob
8.0
until the voltmeter indicates ‘‘
1
You can use the resolution selection keys to move the blinking digit to the
volts’’* or ‘‘
25.0
vol t s ’’**
right or left when settin g the voltage.
*For Agilent E3633A Model **For Agilent E3634A Model
17
Page 30

Power
Output
On/Off
Display
Limit
Vol tage
Current
Chapter 2 Initial Operation
Output Checkout
Current Output Checkout
The following steps check basic current functions with a short across the
power supply’s output.
1 Turn on the power supply.
The power supply will go into the power-on / reset state; the output is disabled
(the
OFF
annunciator turns on); the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range is selected (the
8V
* or
25V
** annunciator turns on); and the knob is selected for voltage
control.
2 Conn e c t a s hor t a c r os s (+) and (-) output te r mi n a l s w i th a n i n sulated
test lead.
Use a wire size sufficient to handle the maximum current (See "Table 7-1 Wire
Rating" on page 153 in chapter 7).
3 Enable the outpu t.
The
OFF
annunciator turns off and the 8V* or
annunciators are lit. The
CV
or CC annunciator turns on depending on the
resistance of the test lead. The blinking digit can be adjusted by turning the
knob. Notice that the display is in the meter m ode. ‘‘Meter mode’’ means that
the display shows the actual output vo ltage and current.
4 Adjust the voltage limit value to 1.0 volt.
Set the display to the limit mode (the
Limit
the voltage limit to 1.0 volt to assure CC operation. The
turn on. To go back to normal mode, press the
time out for several seconds .
5 Set the knob to the current control to check that the front-panel
ammeter properly responds to knob control.
T urn the knob clockwise or counter clockwise when the display is in the meter
Limit
mode (the
annunciator is off). Check that the ammeter responds to knob
control and the voltmeter indicates nearly zero (the voltmeter will show the
voltage drop caused by the test lead).
25V
**,
OVP
, and
OCP
annunciator will be blinking). Adjust
CC
Display
key again or let the display
Limit
annunciator will
*For Agilent E3633A Model **For Agilent E3634A Model
18
Page 31

Chapter 2 Initial Operation
Output Checkout
1
6 Ensure that the current can be adjusted from zero to the full rated
value.
Adjust the knob until the ammeter indicates 0 amps and then until the ammeter
indicates 20.0 amps* or 7.0 amps**.
7 Turn off the power supply and remove the short from the output.
1
You can use the resolution selection keys to move the blinking digit to the
right or left when settin g the cur ren t.
Note If an error has been detected during the output checkout procedures, the ERROR
annunciator will turn on.
123 in chapter 5
See "Error Messages" for more information starting on page
2
*For Agilent E3633A Model **For Agilent E3634A Model
19
Page 32

Chapter 2 Initial Operation
Output Checkout
20
Page 33

3
Front-Panel Operation
Page 34

Front-Panel Operation
So far you have learned how to install your power supply and perform initial
operation. During the initial operation , you were briefly introduced to
operating from the front panel as you learned how to check basic voltage and
current functions. This chapter will describe in detail the use of these front-
panel keys and show how they are used to accomplish power supply operation.
• Front - Panel Op eration O v ervi e w , on p a g e 2 3
• Constant Voltage Operation, on page 24
• Constant Current Operation, on page 26
• Storing and Recalling Operating States, on page 28
• Programmin g Overvoltage Protection, on page 30
• Programming Overcurrent Protection, on page 34
• Remote Voltage Sensing at the Front and Rear Terminals, on page 37
• Disabling the Output, on page 40
• Disabling the Output Using an External Relay, on page 41
• Knob Locking, on page 41
• System-Related Operations, on page 42
• Remote Interface Configuration, on page 46
• HP-IB Interface Configuration, on page 51
• RS-232 Interface Configuration, on page 52
• Calibration Overview, on page 56
Throughout this chapter the key to be pressed is shown in the left margin.
Note See "Error Messages", starting on page 123 in chapter 5 if you encounter any errors
during front-panel operation.
22
Page 35

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Front-Panel Operation Overview
Front-Panel Operation Overview
The following section describes an overview of the front-panel keys before
operating your power supply.
• The power supply is shipped from the factory configured in the front-panel
operation mode. At power-on, the power supply is autom aticall y set to
operate in the front-panel operation mode. When in this mode, the front-
panel keys can be used. When the power supply is in remote operation mode,
you can return to front-panel operation m ode at any time by pressing the
Store
(Local
Local
command. A change between front-panel and remote operation modes will
not result in a change in the output p aram eters.
• The power supply has two output ranges. This feature allows more voltage
at a lower current or more current at a lower voltage. The desired output
range is selected from the front panel or over the remote interfaces. The
or
20V
the presently selected range.
• When you press key (the
power supply goes to the
displayed. In this mode, you can also observe the change of t he limit values
when adjusting the knob. If you press the
time-out after several seconds, the pow er supply will return the display to
the meter mode (the
output voltage and current will be displayed.
• The output of the power supply can be en ab led or disabled from the front
panel by pressing
turns on and the output is disabled.
• The display provides the present operating status of the power supply with
annunciators and also informs the user of error codes. For example, the
power supply is operating in CV mode in the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range and
controlled from the front panel, then the
will turn on. If, however, the power supply is remotely controlled, the
annunciator will also turn on, and when the power supply is being addressed
over HP-IB interface, the
Annunciators
) key if you did not previousl y send the front-panel lockout
for the E3633A and
Display
Limit
Output
On/Off
25V
or
50V
for the E3634A annunciator indicates
Limit
annunciator blinks), the display of the
limit
mode and the present limit values will be
Display
key again or let the display
Limit
Limit
annunciator turns off). In this mode, the actual
key. When the output is off, the
CV
and 8V* or
Adrs
annunciator will turn on. See “
OFF
25V
’ on page 5 for more information.
8V
annunciator
** annunciators
Rmt
Display
3
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
23
Page 36

Power
Display
Limit
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Constant Voltage Operation
Constant Voltage Operation
To set up the power supply for constant voltage (CV) operation, proceed as
follows.
• Front-panel operation:
1 Connect a load to the output terminals.
With power-off, connect a load to the (+) and (-) output terminals.
2 Turn on the power supply.
The power supply will go into the
(the
OFF
annunciator turns on); the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range is selected (the
8V
* or
25V
** annunciator turns on); and the knob is selected for
20V,10A 50V,4A
Press * or ** key to operate the power supply in the 20V/10A* or
50V/4A** range before proceeding to the next step. The
annunciator turns on.
3 Set the display to the limit mode.
Not i c e that th e
Limit
annunciator blinks, i ndicating that the display is in the
limit mod e. Wh en the dis pla y is in t he
current limit values of the power supply.
power-on / reset
limit
mode, you can see the voltage and
state; the output is disabled
20V
voltage
* or
50V
control.
**
Vol tage
Current
In
constant voltage
mode, the voltage valu es betwee n the m ete r and
limit modes are the same, but the current values are not. Moreover, if the
display is in the meter mode, you cannot see the change of current limit
value when adjusting the knob. We recommend that you should set the
display to “lim it” m ode to see the chan ge of curr en t lim it valu e in the
constant voltage mode whenever adjusting the knob.
1
4 Adjust the knob for the desired current limit.
Check that the
Limit
annunciator still blinks. Set the knob for
current
control.
The second digit of the ammeter wi ll be blinking. The blinking digit can be
changed using the resolution selection keys and the blinking digit can be
adjusted by turning the knob. Adjust the knob to the desired current limit.
1
You can use the resolution selection keys to move the blinking digit to the
right or left when settin g curr en t.
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
24
Page 37

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Constant Voltage Operation
Vol tage
Current
Display
Limit
Output
On/Off
1
5 Adjust the knob for the desired output voltage.
Check that the
The second digit of the voltmeter will be
Limit
annunciator still blinks. Set the knob for
blinking
. Change the blinking digit
voltage
control.
using the resolution selection keys and adjust the knob to the desired output
voltage.
6 Return to the meter mode.
Display
Press key or let the display time-out after several seconds to return to
Limit
the meter mode. Notice that the
Limit
annunciator turns off and the display
shows “OUTPUT OFF” mes sage.
3
7 Enable the outpu t.
The
OFF
annunciator turns off and the 8V* (or
OCP
and CV annunciators are lit. Notice that the display is in the
In the meter mode, the display shows the actual output voltage and current.
Refer to “Programming Overvoltage Protection” and “Programming
Overcurrent Protection” sections, starting on
information on
OVP
and
OCP
annunciators.
8 Verify that the power supply is in the constant voltage mode.
If you operate t he power supply in the constant v oltage (CV) mode, verify that
the
CV
annunciator is lit. If the CC annunciator is lit, choose a higher current
limit.
25V
**) o r
20V
* (or
50V
**),
OVP
meter
mode.
page 30 and page 34 for more
,
Note During actual CV operation, if a load change causes the current limit to be exceeded,
the power supply will automatically crossover to the constant current mode at the
preset current limit and the output voltage will drop proportionately.
• Remote interface operation:
CURRent {<current>|MIN|MAX} Set the current
VOLTage {<voltage>|MIN|MAX} Set the voltage
OUTPut ON Enable the output
1
You can use the resolution selection keys to move the blinking digit to the
right or left when settin g voltage.
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
25
Page 38

Power
Display
Limit
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Constant Current Operation
Constant Current Operation
To set up the power supply for constant current (CC ) operation, proceed as
follows.
• Front-panel operation:
1 Connect a load to the output terminals.
With power-off, connect a load to the (+) and (-) output terminals.
2 Turn on the power supply.
The power supply will go into the
(the
OFF
annunciator turns on); the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range is selected (the
8V
* or
25V
** annunciator turns on); and the knob is selected for
T o operate the power supply in the 20V/10A* or 50V/4A** range, press *
50V,4A
or ** key before proceeding to the next step. The
annunciator turns on.
3 Set the display to the limit mode.
Not i c e that th e
Limit
annunciator blinks, i ndicating that the display is in the
limit mod e. Wh en the dis pla y is in t he
current limit values of the selected supply.
power-on / reset
limit
mode, you can see the voltage and
state; the output is disabled
20V
voltage
* or
50V
control.
**
20V,10A
In
constant current
mode, the cur re nt valu es betw ee n the m ete r m ode
and limit mode are the same, but the voltage values are not. Moreover, if
the display is in the meter mode, you cannot see the change of voltage
limit v al ue wh en ad j u s t in g t h e k n o b . We recommend t h a t you should se t
the display to “limit” mode to see the change of voltage limit value in the
constant current mode whenever adjusting the knob.
1
4 Adjust the knob for the desired voltage limit.
Check that the
Limit
annunciator still blinks and the second digit of voltmeter
blinks to indicate the knob i s selected for voltage control. The blinking digit
can be changed using the resolution keys and the blinking digit can be adjusted
by turning the knob. Adjust the knob for the desired voltage limit.
1
You can use the resolution selection keys to move the blinking digit to the
right or left when settin g the voltage.
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
26
Page 39

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Constant Current Operation
Vol tage
Current
Display
Limit
Output
On/Off
1
5 Adjust the knob for the desired output current.
Check that the
Limit
annunciator still blinks. Set the knob for current
control
.
The second digit of the ammeter wi ll be blinking. Change the blinking digit
using the resolution selection keys and adjust the knob to the desired output
current.
6 Return to the meter mod e.
Display
Press key or let the display time-out after several seconds to return the
Limit
meter mode. Notice that the
Limit
annunciator turns off and the display shows
“OUTPUT OFF” message.
3
7 Enable the outpu t.
The
OFF
annunciator turns off and the 8V* (or
OCP
and CC annunciators are lit. Notice that the display is in the meter mode.
In the
meter
mode, the display shows the actual output voltage and current.
Refer to “Programming Overvoltage Protection” and “Programming
Overcurrent Protection” sections, starting on
information on
OVP
and
OCP
annunciators.
8 Verify that the power supply is in the constant current mode.
If you operate the power supply in the constant current (CC) mode, verify that
the
CC
annunciator is lit. If the CV annunciator is lit, choose a higher voltage
limit.
25V
**) o r
20V
* (or
50V
**),
OVP
page 30 and page 34 for more
,
Note During actual CC operation, if a load change causes the voltage limit to be exceeded,
the power supply will automatically crossover to constant voltage mode at the preset
voltage limit and the output current will drop proportionately.
• Remote interface operation:
VOLTage {<voltage>|MIN|MAX} Set the voltage
CURRent {<current>|MIN|MAX} Set the current
OUTPut ON Enable the output
1
You can use the resolution selection keys to move the blinking digit to the
right or left when settin g the cur ren t.
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
27
Page 40

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Storing and Recalling Operating States
Storing and Recalling Operating States
Store
You can store up to three different operating states in
non-volatile
memory.
This also enables you to recall the entire instrument configuration with just a
few key presses from the front panel.
The memory locations are suppli ed with the reset states from the factory for
*RST
front-panel operation. Refer to the description of
command, starting on
page 96 in chapter 4 for more information. The following steps show you how
to store and recall an operating state.
• Front-panel operation:
1 Set up the power supply for the desired operating state.
The storage feature “remembers” output range selection, the limit value
settings of voltage and current, output on/off state, OVP and OCP on/off state,
and OVP and OCP trip levels.
2 Turn on the storage mode.
Three memory locations (numbered 1, 2 and 3) are available to store the
operating states. The operating states are stored in
non-volatile
memory and
are remembered when being recalled.
STORE 1
This message appears on the di splay for approximately 3 seconds.
3 Store the operating state in memory location “3”.
Turn the knob to the right to specify the memory location 3.
STORE 3
To cancel the store operation
or press any other function key except the
to the normal operating mode and to the function pressed.Save the operating
state.
28
, let the display time-out after about 3 seconds
Store
key. The power supply returns
Page 41

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Storing and Recalling Operating States
Store
Recall
Recall
4 Save the operating state.
The operating state is now stored. To recall the stored state, go to the following
steps.
DONE
5 Turn on the recall mode.
Memory location “1” will be displ ayed in the recall mode.
RECALL 1
This message appears on the di splay for approximately 3 seconds.
6 Recall the stored operating stat e.
Turn the knob to the right to change the displayed storage location to 3.
RECALL 3
If this setting is not followed within 3 seconds with key stroke, the power
supply returns to normal operating mode and will not recall the instrument
state 3 from memory.
7 Restore the operating stat e.
The power supply should now be configured in the same state as when you
stored the state on the previous steps.
Recall
3
DONE
This message appears on the di splay for approximately 1 second.
• Remote interface operation:
*SAV {1|2|3} Store an operating state to a specified location
*RCL {1|2|3} Recall a previously stored state from a specified location
29
Page 42

Power
Output
On/Off
Over
Vol tage
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Programming Overvoltage Protection
Programming Overvoltage Protection
Overvoltage protection guards the load against output vol tages that reach a
specified value greater than the programmed protection level. It is
accomplished by shorting the output via an internal SCR when the trip level is
set to equal or greater than 3 volts, or by progamming the output to 1 volt when
the trip level is set to less than 3 volts.
The following steps show how to set the OVP trip level, how to check OVP
operation, and how to clear overvoltage condition.
• Front-panel operation:
Setting the OVP Level and Enable the OVP Circuit
1 Turn on the power supply.
The power supply will go into the
(the
OFF
annunciator turns on); the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range is selected (the
8V
* or
25V
** annunciator turns on); and the knob is selected for
2 Enable the outpu t.
The
OFF
annunciator turns off and the display will go to the meter mode.
3 Enter the OVP menu and set th e trip level.
power-on / reset
state; the output is disabled
voltage
control.
Over
Vol tage
LEVEL 22.0V (E3633A)
LEVEL 55.0V (E3634A)
Y ou will see the above message on the display when you enter the OVP menu.
Adjust the control knob for the desired OVP trip level.
Note that you cannot set the trip level s to lower than 1.0 volt.
4 Enable the OVP circuit.
OVP ON
You will see the above message after pressing key.
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
30
Over
Vol tage
Page 43

Over
Vol tage
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Programming Overvoltage Protection
5 Exit the OVP menu.
CHANGED
The “CHANGED” mess age is highli ghted for a second to show that the new
OVP trip level is now in effect. If the OVP settings are not changed, “NO
CHANGE” will be displayed. The power supply will exit the OVP menu and the
OVP
display will return to the meter mode. Check that the
on.
annunciator turns
Display
Limit
Over
Vol tage
Checking OVP Operation
3
To check OVP operation, raise the output voltage to near the trip point. Then
very gradually increase the output by turning the knob until the OVP circuit
OVP
trips. This wil l cause the power supply output to drop to near zero, the
annunciator to blink, and the
CC
annunciator to turn on. The “OVP TRIPPED”
message also appears on the display.
Clearing the Overvoltage Condition
When the OVP condition occurs (the “OVP T RIPPED” message is shown on
the display), the OVP annunciator blinks. When it was caused by an external
voltage source such as a battery, disconnect it first. Clear the overvoltage
condition by adjusting output vol tage level or by adjusting OVP trip level.
The following steps show how to clear the overvoltage condition and get back
to normal mode operation. In the following steps, the display will go back to
“OVP TRIPPED” if you let the display time out after about several seconds.
• Adjust output voltage level
1 Lower the output voltage level.
Lower the output voltage level below the OVP trip point after pressing
key. The
OVP
and
Limit
annunciators are blinking.
2 Move to the clear mode.
Display
Limit
OVP CLEAR
Over
Press key twice to move to the OVP CLEAR m ode. The “OVP ON”
Vol tage
message appears on the display. Turn the knob to the right until the above
message appears on the display.
31
Page 44

Over
Vol tage
Over
Vol tage
Over
Vol tage
Over
Vol tage
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Programming Overvoltage Protection
3 Clear the overvoltage condit ion and exit this menu.
Now, when you press key again, the “DONE” message is displayed for a
second and the
OVP
Over
Vol tage
annunciator will not blink any more. The output will return
to meter mode.
• Adjust OVP trip level
1 Raise the OVP trip level.
Over
Press key and turn the knob to raise the OVP trip level.
Vol tage
2 Move to the OVP C LEAR mode.
OVP CLEAR
Over
Press key to move to the OVP CLEAR mode. The “OVP ON” message
Vol tage
appears on the display. Turn the knob to the right until the above message
appears on the display.
3 Clear the overvoltage condit ion and exit this menu.
Now, when you press key again, the “DONE’’ message is displayed for
a second and the
return to the meter mode.
Over
Vol tage
OVP
annunciator will not blink any more. The output wil l
• Remote interface operation:
VOLT:PROT {<voltage>|MIN|MAX} Set the OVP level
VOLT:PROT:STAT {OFF|ON) Disable or enable the OVP circuit
VOLT:PROT:CLE Clear the tripped OVP circuit
Note The power supply’s OVP circuit contains a crowbar SCR, which effectively shorts the
output of the power supply whenever the overvoltage condition occurs. If external
voltage source such as a battery is connected across the output, and the overvoltage
condition inadvertently occurs, the SCR will continuously sink a large current from
the source; possibly damaging the power supply. To avoid this a diode must be
connected in series with the output as shown in Figure 3-1 on next page.
32
Page 45

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Programming Overvoltage Protection
Figure 3-1. Recommended Protection Circuit for Battery Charging
3
33
Page 46

Power
Output
On/Off
Over
Current
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Programming Overcurrent Protection
Programming Overcurrent Protection
Overcurrent protection guards the load against output currents that reach a
specified value greater than the programmed protection level. It is
accomplished by programm ing the output current to zero.
The following steps show how to set the overcurrent protection trip level, how
to check OCP operation and how to clear overcurrent condition.
• Front-panel operation:
Setting the OCP Level and Enable the OCP Circuit
1 Turn on the power supply.
The power supply will go into the
(the
OFF
annunciator turns on); the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range is selected (the
8V
* or
25V
** annunciator turns on); and the knob is selected for
2 Enable the outpu t.
The
OFF
annunciator turns off and the display will go to the meter mode.
3 Enter the OCP menu and set t he trip level.
power-on / reset
state; the output is disabled
voltage
control.
Over
Current
LEVEL 22.0 A
LEVEL 7.5 A
(E3633A)
(E3634A)
Y ou will see the above message on the display when you enter the OCP menu.
Adjust the knob for the desired OCP trip level.
4 Enable the OCP circuit.
OCP ON
You will see the above message after pressing the key.
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
34
Over
Current
Page 47

Over
Current
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Programming Overcurrent Protection
5 Exit the OCP menu.
CHANGED
The “CHANGED” message is displayed for a second to show that the new OCP
trip level is now in effect. If the OCP settings are not changed, “NO CHANGE”
will be displayed. T he power supply will exit the OCP menu and the display
OCP
will return to the meter mode. Check that the
annunciator turns on.
Display
Limit
Over
Current
Checking OCP Operation
To check OCP operation, raise the output current to near the trip point. Then
3
very gradually increase the output by turning the knob until the OCP circuit
trips. This will cause the power supply’s output current to drop to zero and the
OCP
annunciator to blink. The “OCP TRIPPED” message also appears on the
display.
Clearing the Overcurrent Condition
When the OCP condition occurs (the “OCP TRIPPED” message is shown on
the display), the OCP annunciator blinks. When it was caused by external
voltage sources such as a battery, disconnect it first. Clear the overcurrent
condition by adjusting output current level or by adjusting OCP trip level.
The following steps show how to clear the overcurrent condition and get back
to normal mode operation. In the following steps, the display will go back to
“OCP TRIPPED” if you let the display time out after about several seconds.
• Adjust output current level
1 Lower the output current level.
Display
Press key and set the knob for
Limit
current
control by pressing key,
then lower the output current level below the OCP trip point.
2 Move to the clear mode.
Vol tage
Current
OCP CLEAR
Over
Press key twice to move to the OCP CLEAR mode. The “OCP ON”
Current
message appears on the display. Turn the knob to the right until the above
message appears on the display.
35
Page 48

Over
Current
Over
Current
Over
Current
Over
Current
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Programming Overcurrent Protection
3 Clear the overcurrent condition and exit this menu.
Now, when you press key again, the “DONE’’ message is displayed for
a second and the
return to meter mode. The knob is selected for
Over
Current
OCP
annunciator will not blink any more. The output wil l
current
control.
Notice that the power supply is operated in the constant current (CC) mode.
• Adjust OCP trip level
1 Raise the OCP trip level.
Over
Press key and turn the knob to raise the OCP trip level.
Current
2 Move to the OC P CLEAR mode.
OCP CLEAR
Press the key to move to the OCP CLE AR mod e. The “OCP ON” mes sage
appears on the display. Turn the knob to the right until the above message
appears on the display.
3 Clear the overcurrent condition and exit this menu.
Now, when you press key again, the “DONE’’ message is displayed for
a second and the OCP annunciator will not blink any more. The output will
return to the meter mode.
Over
Current
• Remote interface operation:
CURR:PROT {<current>|MIN|MAX} Set the OCP level
CURR:PROT:STAT {OFF|ON} Disable or enable the OCP circuit
CURR:PROT:CLE Clear the tripped OCP circuit
36
Page 49

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Remote Voltage Sensing at the Front and Rear Terminals
Remote Voltage Sensing at the Front and Rear Terminals
Remote voltage sensing is used to maintain regulation at the load and reduce
the degradation of regulation that would occur due to the voltage drop in the
leads between the power supply and the load.
By connecting the power supply for remote voltage sensing, voltage is sensed
at the load rather than at the power supply’s output terminals. This will allow
the power supply to automatically compensate for the voltage drop in
applications with lo ng lead lengths as well as to accurately read back the
voltage directly across the load.
When the power supply is connected for remote sensing, the OVP circuit senses
the voltage at the
CV Regulation
The voltage load regulation specification in chapter 8 applies at the output
terminals of the power supply. When remote sensing, add 5 mV to this
specification for each 1 V drop between the positive sensi ng point and (+)
output terminal due to the change in load current. Because the sense leads are
part of the power supply’s feedback path, keep the resistance of the sense leads
at or below 0.5
sensing
Ω
per lead to maintain the above specified performance.
points (load) and not the output terminals.
3
Output Rating
The rated output voltage and current specifications in chapter 8 apply at the
output terminals of the power supply. With remote sensing, any voltage
dropped in the load leads must be added to the load voltage to calculate
maximum output voltage. The performance specifications are not guaranteed
when the maximum output voltage is exceeded. If the excessive demand on
Unreg
the power supply forces the power supply to lose regulation, the
annunciator will turn on to indicate that the output is unregulated.
Output Noise
Any noise picked up on the sense leads also appears at the output of the power
supply and may adversely affect the voltage load regulation. Twist the sense
leads to minimize external noise pickup and run them parallel and close to the
load leads. In noisy environments it may be necessary to shield the sense leads.
Ground the shield at the power supply end only.
of the sense conductors
.
Do not use the shield as one
37
Page 50

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Remote Voltage Sensing at the Front and Rear Terminals
Stability
Using remote sensing under certain combinations of load lead lengths and
large load capacitances may cause your application to form a filter, which
becomes part of the voltage feedback loop. The extra phase shift created by
this filter can degrade the power supply’s stability, resulting in poor transient
response or loop instability. In severe cases, it may cause oscillations. To
minimize this possibility, keep the load leads as short as possible and twist
them together. As the sense leads are part of the power supply’s programming
feedback loop, accidental open-connections of sense or load leads during
remote sensing operation have various unwanted effects. Provide secure and
permanent connections.
Remote Voltage Sensing Connections
Connections between the power supply sensing and output terminals should
be removed, and using shielded two-wire cable, the power supply sensing
terminals should be connected to the load as shown in Figure 3-2.
the shield as one of the sen si ng condu ctors and the other end sh ould be left
unconnected
⊥
) only. Opening a sensing lead causes the power supply output voltage to
(
decrease at the load leads. Observe polarity when connecting the sensing leads
to the load.
For local voltage sensing connections, the (+) and (-) sense terminals must be
connected to the (+) and (-) output terminals respectively.
. Connect one end of the sensing lead shield to the chassis ground
Do not use
Note When you make the remote voltage sensing connections at the front or rear panel
terminals, make sure to disconnect all the connections to the load and sense leads
at the other end terminals. Do not make the sensing connections at both front and
rear terminals at the same time. It will cause to damage the power supply seriously.
Not e During remote sensing setup, it is strongly recommended to power off (by presssing
power ON/OFF button) the power supply to avoid undesirable damage to the load
or the power supply.
38
Page 51

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Remote Voltage Sensing at the Front and Rear Terminals
Figure 3-2. Remote Voltage Sensing Connections
Remote Voltage Sensing at the Rear Panel
External sense terminals are also available on the back of the power supply
that allow the rear output voltages to be sensed at the load, which compensates
for impedance losses in the load wiri ng. The front panel bindin g posts are
paralleled with the rear output terminals .
The rear output terminals accept wires sizes from AWG 22 to AWG 10.
T o minimize the possibility of instability on the output, keep load leads as short
as possible and bundle or twist the leads tightly together to minimize
inductance.
3
Figure 3-3. Rear local sensing connections
Note For rear local voltage sensing connections, the front shorting bars must be removed
first and connect the sense wires as shown in Figure 3-3.
39
Page 52

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Disabling the Output
Disabling the Output
The output of the power supply can be disabled or enabled from the front panel.
When the power supply is in the “Off” state, the
the output is disabled. The
OFF
annunciator turns off when the power supply
returns to the “On” state. When the output is disabled, the voltage value is 0
volts and the current value is 0.02 amps.
The output state is stored in
volatile
memory; the output is always disabled
when power has been off or after a remote interface reset.
While the output is disa bled , the ra nge se le ction keys, the control knob,
resol utio n sele ctio n key s, and ad just select io n key a re sti ll wor king . If the
display is in the me ter mode , you ca nn ot see the ch anges of output
voltage and current settings on the display when turning the knob. To see
or ch eck th e cha ng es wh en t he out pu ts a re d isa bl ed, t he dis pla y sh ou ld b e
in the limit mode.
OFF
annunciator turns on and
• Front-panel operation:
You can disable the output by pressing key. This key toggles between
Output
On/Off
output “Off” and “On” states.
• Remote interface operation:
OUTP {OFF|ON} Disable or enable the output
40
Page 53

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Disabling the Output Using an External Relay
Disabling the Output Using an External Relay
When the output of the power supply is turned off, it is implemented by setting
the output to 0 volts and 0.02 amps. This gives a zero output voltage without
actually disconnecting the output. To disconnect the output an external relay
must be connected between the output and the load. A TTL signal of either low
true or high true is provided to control an external relay. This signal can only
be controlled with the remote command
output is available on the RS-232 connection pin 1 and pin 0.
When the
(4.5 V) and pin 9 is low (0.5 V). The levels are reversed when the
OUTPut:RELay
Note TTL output of pin 1 or pin 9 of the RS-232 connector is available only after installing
two jumpers inside the power supply. See the Service Guide for more information.
OUTPut:RELay
state is “OFF”.
state is “ON”, the TTL output of pin 1 is high
OUTPut:RELay {OFF|ON}
. The TTL
3
Note Do not use the RS-232 interface if you have configured the power supply to output
relay control signals. Internal components on the RS-232 circuitry may be damaged.
Knob Locking
The control knob can be locked to prevent from any unwanted changes
occurring during an experiment, or when you leave the power supply
unattended. To lock the knob, move the blinking digit to the right or left using
< >
the resolution selection key
Notice that the knob and front panel keys are disable d whe n in the re m ote
interface m ode.
or until the blinki ng digit dis appears.
41
Page 54

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
System-Related Operations
System-Related Operations
This section gives information on topics such as self-test, error conditions, and
front-panel display control. This information is not directly related to setting
up the power supply but is an important part of operating the power supply.
Self-Test
A
power-on
This test assures you that the power supply is operational. This test does not
perform the extensive set of tests that are included as part of the complete self-
test described below. If the power-on self- test fails, the
turns on.
•A
seconds to execute. If all tests pass, you can have a high confidence that the
power supply is operational.
• If the
If the self-test fails, “FA IL” is displayed and the
on. See the
Hewlett-Packard for service.
self-test occurs automatically when you turn on the power supply.
ERROR
complete
self-test performs a series of tests and takes approximately 2
complete
self-test is successful, “PASS” is displayed on the front panel.
Serv ice G ui de
ERROR
for instructions on returning the power supply to
annunciator turns
annunciator
• Front-panel operation:
T o perform the c omplete front panel
turn on the power supply and
The self-test will begin when you release the key following the beep.
• Remote interface operation:
self- t est
hold down
, hold down the key as you
the key
until you hear a lon g beep
Recall
*TST?
Returns “0” if the complete self-tes t passes or “1” if it fails.
42
.
Page 55

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
System-Related Operations
Error Conditions
When the front-panel
syntax or hardware errors have been detected. A record of up to 2 0 errors can
be stored in the power supply’s error queue. See chapter 5 “Error Messages”,
starting on
page 123 for a complete listing of the errors.
• Errors are retrieved in first-in-first-out (FIFO) order. The first error returned
is the first error that was stored. Errors are cleared as you read them over
the remote interface. When you have read all errors from the queue, the
ERROR
annunciator turns off. The power supply beeps once each time an
error is generated.
• If more than 20 errors have occurred when you operate the power supply
over the remote interface, the last error stored in the queue (the most recent
error) is replaced with -350, “
stored until you remove errors from the queue. If no errors have occurred
when you read the error queue, the power supply responds wi th +0, “
error
” over the remote interface or “NO ERROR S” from the front panel.
• The error queue is cleared when power has been off or after a
status) command has been executed. The
clear the error queue.
ERROR
annunciator turns on, one or m ore command
Too many errors
”. No additional errors are
No
*CLS
(clear
*RST
(reset) command does not
3
• Front-panel operation:
Store
Press (
supply is in remote operation mode.
Local
Local
) key to return to front-panel operation mode if the power
3: ERR -102
If the ERROR annunciator is on, press key to view the errors. Use the
knob to scroll through the error numbers. Press to view the text of the
error message. Press or key to increase or decrease the scrolling
< >
speed of the text on the display . All errors are cleared when you exit the menu
or let the display time out for about 30 seconds.
• Remote interface operation:
SYSTem:ERRor? Read and clear one error from the error queue
Errors have the following format (the error string may contain up to 80
characters).
-102, ‘‘Syntax error
’’
Error
>
43
Page 56

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
System-Related Operations
Display Control
For security reasons, you may want to turn off the front-panel display. From
the remote interface, you can display a 12-character m essage on the front
panel.
• The display can be
• When the display is turned off, outputs are not sent to the display and all
annunciators are disabled except the
operation is otherwise unaffected by turni ng off the display.
• The display state is stored in volatile memory; the display is always enabled
when power has been off, after a remote interface reset, or after returning
to local from remote.
• You can display a message on the front panel by sending a command from
the remote interface. The power supply can display up to 12 characters of
the message on the front panel; any additional characters are truncated.
Commas, periods, and semicolons share a display space with the preceding
character, and are not considered individual characters. When a message is
displayed, outputs are not sent to the display.
• Sending a message to the display fro m the remote interface overrides the
display state; this means that you can display a message even if the display
is turned off.
• The display state is automatically turned on when you return to the local
(front panel) operation. Press
from the remote interface.
enabled / disabl ed
Store
Local
from the remote interface only.
ERROR
(
Local
annunciator. Front-panel
) key to return to the local state
• Remote interface operation:
DISP {OFF|ON} Disable / enable the display
DISP:TEXT <quoted string> Display the string enclosed in quotes
DISP:TEXT:CLE Clear the displayed message
The following statement shows how to display a message on the front panel
from a Hewlett-Packard controller.
‘‘
DISP:TEXT ‘HELLO
’ ’’
44
Page 57

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
System-Related Operations
Firmware Revision Query
The power supply has three microprocessor s for control of various internal
systems. You can query the power supply to d etermine which revision of
firmware is installed for each microprocessor.
• You can query the firm w are revi sion from the re m ote inte rfac e onl y.
• The power supply returns four fi elds separated by commas and the fourth
field is a revision code w hich contains three numbers. The first number is
the firmware revision number for the main processor; the second is for the
input/output processor ; and the third is for the front-panel processor.
• Remote interface operation:
*IDN? Returns
‘‘HEWLETT-PACKARD,E3633A,0,X.X-X.X-X.X’’ (E3633A)
‘‘HEWLETT-PACKARD,E3634A,0,X.X-X.X-X.X’’ (E3634A)
Be sure to dimension a string variable with at least 40 characters.
SCPI Language Version
The power supply compli es with the rules and regulations of the present
version of SCPI (Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments). You
can determine the SCPI version with which the power supply is in compliance
by sending a command from the remote interface.
You can query the SCPI version from the remote interface only.
3
• Remote interface operation:
SYST:VERS? Query the SCPI version
Returns a string in the form “YYYY .V” where the “Y’s” represent the year of the
version, and the “V” represents a version number for that year (for example,
1996.0).
45
Page 58

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Remote Interface Configuration
Remote Interface Configuration
Before you can operate the power supply over the remote interface, you must
configure the power supply for the remote interface. This section gives
information on configuring the remote interface. For additional information
on programming the power supply over the remote i nterface,
Interface Reference", starting on page 73 in chapter 4.
Remote Interface Selection
The power supply is shipped with both an HP-IB (IEEE-488) interface and an
RS-232 interface on the rear panel. Only one interface can be enabled at a time.
The HP-IB interface is selected when the power supply is shipp ed from the
factory.
The remote interface can be selected from the front-panel only.
• The interface selection is stored in non-volatile memory, and does not
change when power has been off or after a remote interface reset.
• If you select the HP-IB interface, you m ust select a unique address for the
power supply. The current address is displayed momentarily on the front
panel when you turn on the power supply.
• Your HP-IB bus controll er has its own address . B e sure to avoid using the
bus controller’s address for any instrument on the interface bus. Hewlett-
Packard controllers generally use address “21”.
• If you enable the RS-232 interface, you must select the baud rate and parity
to be used. “RS-232” is displayed momentarily on the front panel when you
turn on the power supply if you have selected this interface.
1
See "Remote
2
1
Refer to "HP-IB Interface Configuration" starting on page 51 for more information
on connecting the power supply to a computer over the HP-IB interface.
2
Refer to "RS-232 Interface Configuration" starting on page 52 for more information
on connecting the power supply to a computer over the RS-232 interface.
46
Page 59

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Remote Interface Configuration
HP-IB Address
Each device on the HP-IB (IEEE-488) interface must have a unique address.
You can set the power supply’s address to any value between 0 and 30. The
current address is displayed momentarily on the front panel when you turn on
the power supply . The address is set to “05” when the power supply is shipped
from the factory.
The HP-IB address can be set from the front-panel only.
• The address is stored in non-volati le mem ory, and does not change when
power has been off or after a remote interface reset.
• Your HP-IB bus controller has its own address. Be sure to avoid the bus
controller’s address for any instrument on the interface bus. Hewlett-
Packard controllers generally use address “21”.
Baud Rate Selection (RS-232)
You can select one of six baud rates for RS-232 operation. The rate is set to
9600 baud when the power supply is shipped from the factory.
The baud rate can be set from the front-panel only.
• Select one of the following: 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600 baud. The factory
setting is
• The baud rate selection is stored in
change when power has been off or after a remote interface reset.
9600
baud.
non-volatile
memory, and does not
3
Parity Selection (RS-232)
Y ou can select the parity for RS-232 operation. The power supply is configured
for no parity and 8 data bits when s hipped from the factory.
The parity can be set from the front-panel only.
• Select one of the following:
bits), or Odd (7 data bits). When you set the parity, you are indirectly setting
the number of data bits.
• The parity selection is stored in
when power has been off or after a remote interface reset.
None
(8 da ta bits ,
non-volatile
factory setting
memory, and does not change
), Even (7 data
47
Page 60

I/O
Config
I/O
Config
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Remote Interface Configuration
To Set the HP-IB Address
To configure the power supply for the HP-IB interface, proceed as follows:
1 Turn on the remote configuration mode.
HP-IB / 488
Y ou will see the above message on the front-panel display if the power supply
has not been changed from the factory setting. If “RS-232” appears, choose
“HP-IB / 488” by turning the knob to the right.
2 Move to the HP-IB address setting mode.
ADDR 05
The address is set to “05” when the power supply is shipped from the factory.
Notice that a different HP-IB address may appear if the power supply has been
changed from the factory setting.
3 Turn the knob to change t he HP-IB address.
The displayed address is changed when turning the knob to the right or left.
I/O
Config
4 Save the change and turn off the I/O configuration mode.
CHANGE SAVED
The address is stored in non-volatile memory, and does not change when power
has been off or after a remote interface reset. The power supply displays a
message to show that the change is now in effect. If the HP-IB address is not
changed, “NO CHANGE” will be displayed for one second.
Note To exit the I/O configuration mode without any further changes, press the “I/O
Config” key until the “NO CHANGE” message is displayed.
48
Page 61

I/O
Config
I/O
Config
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Remote Interface Configuration
To Set the Baud Rate and Parity (RS-232)
To configure the power supply for the RS-232 interface, proceed as follows:
1 Turn on the remote configuration mode.
HP-IB / 488
Y ou will see the above message on the display if the power supply has not been
changed from the factory setting.
Notice that if you changed the rem ote inte rfac e se le ction to RS-232 before,
“RS-232” me ss age wil l be dis pla yed.
2 Choose the RS-232 interface.
RS-232
You can choose the RS-232 interface by turning the knob to the left.
3 Move to the RS-232 interface setting mode and select the baud rate.
3
I/O
Config
9600 BAUD
The rate is set to 9600 baud when the power supply is shipped from the factory.
Choose from one of the following by turning the knob to the right or left: 300,
600, 1200, 2400, 4800, or
4 Save the change and choose th e parity.
9600
baud.
NONE 8 BITS
The power supply is configured for 8 data bits with no parity when shipped
from the factory. Choose from one of the following by turning the knob to the
right or left:
are indirectly setting the number of the data bits.
None 8 Bit s
, Odd 7 Bits, or Even 7 Bits. When you set parity, you
49
Page 62

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Remote Interface Configuration
I/O
Config
5 Save the change and turn off the I/O configuration mode.
CHANGE SAVED
The RS-232 baud rate and parity selections are stored in non-volatile memory,
and does not change when power has been off or after a remote interface reset.
The power supply displays a message to show that the change is now in effect.
If the baud rate and the parity are not changed, “NO CHANGE” will be displayed
for one second.
Note To exit the I/O configuration mode without any further changes, press the “I/O
Config” key until the “NO CHANGE” message is displayed.
50
Page 63

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
HP-IB Interface Configuration
HP-IB Interface Configuration
The HP-IB connector on the rear panel connects your power supply to the
computer and other HP-IB devices. Chapter 1 lists the cables that are available
from Hewlett-Packard. An HP- IB system can be connected together in any
configuration (star, linear, or both) as long as the following rules are observed:
• The total number of devices inclu ding the computer is no more than 15.
• The total length of all the cables used is no more than 2 meter times the
number of devices connected together, up to a maximum of 20 meters.
Note IEEE-488 states that you should exercise caution if your individual cable lengths
exceed 4 meters.
Do not stack more than three connector blocks together on any HP-IB
connector. Make sure that all connectors are fully seated and that the lock
screws are firmly finger tightened.
3
51
Page 64

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
RS-232 Interface Configuration
RS-232 Interface Configuration
You connect the power supply to the RS-232 interface using the 9-pin (DB-9)
serial connector on the rear panel. The power supply is configured as a DTE
(Data Terminal Equipment) device. For all communications over the RS-232
interface, the power supply uses two handshake lines: DTR (Data Terminal
Ready, on pin 4) and DSR (Data Set Ready, on pin 6).
The following sections contain information to help you use the power supply
over the RS-232 interface. The programming commands for RS-232 are
explained on
RS-232 Configuration Overview
Configure the RS-232 interface using the parameters shown below. Use the
front-panel
(see page 47 for more inform atio n to configure from the front panel).
page 101.
I/O
key to select the baud rate, parity, and number of data bits
Config
• Baud Rate: 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, or
• Parity and Data Bits:
• Number of Start Bits:
• Number of Stop Bits:
None / 8 data bits (factory setting
Even / 7 data bits, or
Odd / 7 data bits
1 bit (fixed
2 bits (fixed
9600
baud (
factory setting
)
)
)
)
RS-232 Data Frame Format
A character
character. The frame is defined as the characters from the
stop bit
data bits, and parity type. The power supply uses the following frame formats
for seven and eight data bits.
frame
consists of all the transm itted bits that make up a single
start bit
, inclusively. Within the frame, you can select the baud rate, number of
to the last
52
Page 65

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
RS-232 Interface Configuration
Connection to a Computer or Terminal
To connect the power supply to a computer or terminal, you must have the
proper interface cable. Most computers and terminals are DTE (
Equipment
use a DTE-to-DTE interface cable. These cables are also called null-modem,
modem-eli m inator, or crossover cables.
The interface cable must also have the proper connector on each end and the
internal wiring must be correct. Connectors typically have 9 pins (DB-9
connector) or 25 pins (DB-25 connector) with a “male” or “female” pin
configuration. A male connector has pins inside the connector shell and a
female connector has holes inside the connector shell.
If you cannot find the correct cable for your configuration, you may have to
use a
adapter is a “
null-m odem adapters, and D B- 9 to DB-25 adapters.
The cable and adapter diagrams shown below can be used to connect the
power supply to most computers or terminals. If your configuration is different
than those described, order the HP 34399A Adapter Kit. This kit contains
adapters for connection to other computers, term inals, and modems.
Instructions and pin diagrams are includ ed with the adapter kit.
) devices. Since the power suppl y is also a DTE device, you must
wiring adapter
straight-through
. If you are using a DTE- to-DTE cable, make sure the
” type. T ypical adapters include gender changers,
Data Terminal
3
DB-9 Serial Connection
port with a male connector, use the null-modem cable included with the HP
34398A Cable Kit. This cable has a 9-pin female connector on each end. The
cable pin diagram is shown bel ow.
If your computer or terminal has a 9-pin serial
53
Page 66

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
RS-232 Interface Configuration
DB-25 Serial Connection
port with a male conn ec tor, use the null-m ode m cable and 25-pin adapter
included with the HP 34398A Cable Kit. The cable and adapter pin diagram
are shown below.
If your computer or terminal has a 25-pin serial
DTR / DSR Handshake Protocol
The power supply is configured as a DTE (
and uses the DTR (
the RS-232 interface to handshake. The power supply uses the DTR line to send
a hold-off signal. The DTR line must be TRUE before the power supply will
accept data from the interface. When the power supply sets the DTR line
FALSE, the data must cease within 10 characters.
To disable the DTR/DSR handshake, do not connect the DTR line and tie the
DSR line to logic TRUE. If you disable the DTR/DSR handshake, also select a
slower baud rate to ensure that the data is transmitted correctly.
The power supp ly se ts the DTR li ne FALSE in the following two cases :
1
When the power supply’s input buffer is full (when approximately 100
characters have been received), it sets the DTR line FAL SE (pi n 4 on the RS-
232 connector). When enough characters have been removed to make space
in the input buffer, the power supply sets the DTR line TRUE, unless the
second case (see next) prevents this.
2
When the power supply wants to “talk” over the interface (which means that
it has processed a query) and has received a
it will set the DTR line FALSE. This implies that once a query has been sent to
the power supply, the bus controller should read the response before
attempting to send more data. It also means that a
the command string. After the response has been output, the power supply sets
the DTR line TRUE again, unl ess the first case (see above) prevents this.
Data Terminal Ready
Data Terminal Equipment
) and DSR (
<new line>
Data Set Ready
message terminator,
<new line>
must terminate
) device
) lines of
54
Page 67

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
RS-232 Interface Configuration
The power supply monitors the DSR line to determine when the bus controller
is ready to accept data over the interface. The power supply monitors the DSR
line (pin 6 on the RS-232 connector) before each character is sent. The output
is suspended if the DSR line is FALSE. When the DSR line goes TRUE,
transmission will resume.
The power supply holds the DTR line FALSE while output is suspended. A form
of interface deadlock exists until the bus controller asserts the DSR line TRUE
to allow the power supply to complete the transmission. You can break the
interface deadlock by sending the
operation in progress and dis cards pending output (this is equivalent to the
IEEE- 488 device clear action).
For the <Ctrl-C> character to be recognized reliably by the power supply
while it holds DTR FALSE, the bus controll er m us t first set DSR FALSE.
<Ctrl-C>
character, which clears the
RS-232 Troubleshooting
Here are a few things to check if you are having problems communicating over
the RS-232 interface. If you need additional help, refer to the documentation
that came with your computer.
• Verify that the power supply and your computer are configured for the same
baud rate, parity, and number of data bits. Make sure that your computer is
set up for 1 start bit and 2 stop bits (these values are fixed on the power
supply).
• Make sure to execute the
supply in the remote mode.
• Verify that you have connected the correct interface cable and adapters.
Even if the cable has the proper connectors for your system, the internal
wiring may be incorrect. The
the power supply to most computers or terminals.
• Verify that you have connected the interface cable to the correct serial port
on your computer (COM1, COM2, etc).
SYSTem:REMote
HP 34398A Cable Kit
command to place the power
can be used to connect
3
55
Page 68

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Calibration Overview
Calibration Overview
This section gives an overview of the calibration features of the power supply.
For more detailed discussion of the calibration procedures, see the
Guide
.
Calibration Security
This feature allows you to enter a security code to prevent accidental or
unauthorized calibrations of the power supply. When you first receive your
power supply, it is secured. Before you can calibrate the power supply, you
must unsecure it by entering the correct security code.
•The
• To secure the power supply from the remote interface, the security code
security code
supply is shipped from the
volatile
remote interface reset.
may contain up to 12 alphanumeric characters as shown below. The first
character must be a letter, but the remaining characters can be letters or
numbers. You do not have to use all 12 characters but the first character
must always be a letter.
memory, and does not change when power has been off or after a
is set to “HP003633”* or “HP003634”** when the power
factory
. The security code is stored in
Service
non-
A _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ (12 characters)
• To secure the power supply from the remote interface so that it can be
unsecured from the front panel, use the eight-character format shown
below. The first two characters must be “H P” and the remaining characters
must be numbers. Only the last six characters are recognized from the front
panel, but all eight characters are required.
To
unsecure
the remaining numbers as shown on the following pages.
If you forget your securi ty code, you can disabl e the se cu rity featu re by
adding a jumper inside the power supply, and then entering a new code.
See the Servic e Gui de for m ore in form ation.
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
56
the power supply from the front panel, omit the “H P” and enter
H P _ _ _ _ _ _ (8 characters)
Page 69

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Calibration Overview
To Unsecure for Calibration
You can unsecure the power supply for
calibration either from the front panel or over the remote interface.
The p ower suppl y is se cured when sh ipp ed fr om th e fac tory , an d th e securi ty
code is set to “HP003633”* or “HP0 03634” **
• Front-Panel Operation:
SECURED
If the power supply is secured, you will see the above message for one second
by holding
supply. To unsecure the power suppl y, press (
“CAL MODE” message is displayed in the calibration mode, enter the security
code using the knob and resolution selection keys, and then press the
(
Secure
) key.
Error
Calibrate
(
Calibrate
) key for 5 seconds when you turn on the power
I/O
Config
Secure
Secure
) key after the
000000 CODE
I/O
When you press (
message below for one second if the security code is correct. The unsecured
setting is stored in
been off or after a remote interface reset.
the power off and on.
Config
Secure
Secure
non-volatile
) key to save the change, you will see the
memory, and does not change when power has
To exit the calibration mode, turn
I/O
Config
Secure
3
UNSECURED
Notice that if the security is incor re ct, the power suppl y displays an
“INVALID” message for a second and returns to the code entering mode for
you to enter the correct code.
• Remote Interface Operation:
CAL:SEC:STAT {OFF|ON},<code> Secure or unsecure the power supply
To unsecure the power supply, send the above command with the same code
used to secure. For example,
‘‘
CAL:SEC:STAT OFF, HP003633’’ (E3633A)or
‘‘
CAL:SEC:STAT OFF, HP003634’’ (E3634A)
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
57
Page 70

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Calibration Overview
To Secure Against Calibration
You can secure the power supply against
calibration either from the front panel or over the remote interface. The power
supply is secured when shipped from the factory, and the security code is set
to “HP003633”* or “HP003634”**.
Be sure to re ad t he secu rity cod e rules o n pa ge 56 before attempting to secure
the power suppl y.
• Front-Panel Operation:
UNSECURED
If the power supply is unsecured, you will see the above message for one
second by holding
power supply. To secure the power supply, press (
“CAL MODE” message is displayed in the calibration mode, enter the security
code using the
(
Secure
) key.
Notice that you should omit the “HP ” and en ter the rem ai nin g num ber s as
shown below.
Error
(
Calibrate
control knob
Calibrate
and
) key for 5 seconds when you turn on the
resolution selection keys
I/O
Config
Secure
Secure
, and then press
) key after the
000000 CODE
I/O
When you press (
message below. The secured setting is stored in
not change when power has been off or after a remote interface reset. To exit
the calibration mode, turn the power off and on.
Config
Secure
Secure
) key to save the change, you will see the
non-volatile
memor y, and do es
I/O
Config
Secure
SECURED
• Remote Interface Operation:
CAL:SEC:STAT {OFF|ON},<code> Secure or unsecure the power supply
T o secure the power supply, send the above command with the same code as
used to unsecure. For example,
‘‘
CAL:SEC:STAT ON, HP003633’’ (E3633A) or
‘‘
CAL:SEC:STAT ON, HP003634’’ (E3634A)
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
58
Page 71

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Calibration Overview
To Change the Security Code
To change the security code, you must first
unsecure the power supply, and then enter a new code.
Be sure to re ad t he secu rity cod e rules o n pa ge 56 before attempting to secure
the power suppl y.
• Front-Panel Operation:
To change the security code, first make s ure that the power supply is
unsecured. Press
displayed in the calibration mode, enter the new security code using the
knob
and
resolution se le ction keys
I/O
Config
Secure
(
Secure
) key after the “CAL MODE” message is
control
, then press
I/O
Config
Secure
(
Secure
) key.
Changing the code from the front panel also changes the code required from
the remote inte rfac e.
• Remote Interface Operation:
CAL:SEC:CODE <new code> Change the security code
To change the security code, first unsecure the power supply using the old
security code. Then, enter the new code. For example,
‘‘
CAL:SEC:STAT OFF, HP003633* or HP003634**
‘‘
CAL:SEC:CODE ZZ001443
‘‘
CAL:SEC:STAT ON, ZZ001443
’’
’’
’’
Unsecure with old code
Enter new code
Secure with new code
3
*For HP E3633A Model **For HP E3634A Model
59
Page 72

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Operation
Calibration Overview
Calibration Count
You can determine the number of times that your power supply has been
calibrated. Your power supply was calibrated before it left the factory. When
you receive your power supply, read the count to determine its initial value.
The calibration count feature can be performed from the remote interface
only.
• The calibration count is stored in
when power has been off or after a remote interface reset.
• The calibration count increments up to a maximum of 32,767 after which it
wraps-around to 0. Since the value increments by one for each calibration
point, a complete calibration wil l incr ease the value by 5 counts.
• Remote Interface Operation:
CAL:COUN? Query the number of times of calibration
non-volatile
memory, and does not change
Calibration Message
Y ou can use the calibration message feature to record calibration information
about your power supply. For example, you can store such information as the
last calibration date, the next calibrati on due date, the power supply’s serial
number, or even the name and phone number of the person to contact for a
new calibration.
You can recor d and re ad inform a tion in the cal ibr ation m es sage from the
remote inte rfac e only.
• The power supply should be unsecured before sending a calibration
message.
• The calibration message may contain up to 40 characters.
• The calibration message is stored in non- volatile mem ory, and does not
change when power has been off or after a remote interface reset.
• Remote Interface Operation:
CAL:STR <quoted string> Store the cal message
The following command string shows how to store a calibration message.
‘‘
CAL:STR ‘CAL 12-05-98
60
’ ’’
Page 73

4
Remote Interface Reference
Page 74

Remote Interface Reference
• SCPI Command Summary, on page 63
SCPI
• Simplified Programming Overview, on page 68
• Using the
• Output Setting and Operation Commands, on page 72
• Triggering Commands, on page 79
• System-Related Commands, on page 82
• Calibration C om mands , on page 86
• RS-232 Interface Commands, on page 89
• The SCPI Status Registers, on page 90
• Status Reporting Commands, on page 98
SCPI
• An Introduction to the SCPI Language, on page 101
• Halting an Output in Progress, on page 106
• SCPI Conformance Informati on, on page 107
• IEEE- 488 Conformance Informati on, on page 110
APPLy
Command, on page 71
SCPI
If you are a first-time us er of the SCPI la nguage , you m ay wan t to refer to
these section s to becom e fam il iar wi th the langu age before attem pting to
program the power supply.
62
Page 75

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
SCPI Command Summary
SCPI Command Summary
SCPI
This section summarizes the SCPI (
Instruments
remote interface. Refer to the later sections in this chapter for more complete
details on each command.
Throughout this manual, the following conventions are used for SCPI
command syntax.
• Square brackets ([ ]) indicate optional keywords or parameters.
• Braces ({ }) enclose parameters wi thin a command string.
• Triangle brackets (< >) indicate that you must substitute a value or a code
for the enclosed parameter.
• A vertical bar ( | ) separates one of two or more alternative parameters.
First-time SCPI users, see page 101.
) commands available to program the power supply over the
Standard Commands for Programmable
4
63
Page 76

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
SCPI Command Summary
Output Setting and Measurement Commands
APPLy {<voltage>|DEF|MIN|MAX}[,{<current>|DEF|MIN|MAX}]
APPLy?
[SOURce:]
CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]{<current>|MIN|MAX|UP|DOWN}
CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]? [MIN|MAX]
CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate]:STEP[:INCRement]
{<numeric value> |DEFault}
CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate]:STEP[:INCRement]? {DEFault}
CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude] {<current>|MIN|MAX}
CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude]? [MIN|MAX]
CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel] {<current>|MIN|MAX}
CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel]? {MIN|MAX}
CURRent:PROTection:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
CURRent:PROTection:STATe?
CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped?
CURRent:PROTection:CLEar
VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]
{<voltage>|MIN|MAX|UP|DOWN}
VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]? [MIN|MAX]
VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate]:STEP[:INCRement]
{<numeric value>|DEFault}
VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate]:STEP[:INCRement]? {DEFault}
VOLTage[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude] {<voltage>|MIN|MAX}
VOLTage[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude]? [MIN|MAX]
VOLTage:PROTection[:LEVel] {<voltage>|MIN|MAX}
VOLTage:PROTection[:LEVel]? {MIN|MAX}
VOLTage:PROTection:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
VOLTage:PROTection:STATe?
VOLTage:PROTection:TRIPped?
VOLTage:PROTection:CLEar
VOLTage:RANGe {P8V*|P20V*|P25V**|P50V**|LOW|HIGH}
VOLTage:RANGe?
MEASure
:CURRent[:DC]?
[:VOLTage][:DC]?
*For Agilent E3633A Model **For Agilent E3634A Model
64
Page 77

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
SCPI Command Summary
Triggering Commands
INITiate[:IMMediate]
TRIGger[:SEQuence]
:DELay {<seconds>|MIN|MAX}
:DELay?
:SOURce {BUS|IMM}
:SOURce?
*TRG
System-Related Commands
DISPlay[:WINDow]
[:STATe] {OFF|ON}
[:STATe]?
:TEXT[:DATA] <quoted string>
:TEXT[:DATA]?
:TEXT:CLEar
SYSTem
:BEEPer[:IMMediate]
:ERRor?
:VERSion?
OUTPut
:RELay[:STATe] {OFF|ON}
:RELay[:STATe]?
[:STATe] {OFF|ON}
[:STATe]?
4
*IDN?
*RST
*TST?
*SAV {1|2|3}
*RCL {1|2|3}
65
Page 78

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
SCPI Command Summary
Calibration Commands
CALibration
:COUNt?
:CURRent[:DATA] <numeric value>
:CURRent:LEVel {MIN|MID|MAX}
:CURRent:PROTection
:DAC:ERRor
:SECure:CODE <new code>
:SECure:STATe {OFF|ON},<code>
:SECure:STATe?
:STRing <quoted string>
:STRing?
:VOLTage[:DATA] <numeric value>
:VOLTage:LEVel {MIN|MID|MAX}
:VOLTage:PROTection
Status Reporting Commands
STATus:QUEStionable
:CONDition?
[:EVENt]?
:ENABle <enable value>
:ENABle?
SYSTem:ERRor?
*CLS
*ESE <enable value>
*ESE?
*ESR?
*OPC
*OPC?
*PSC {0|1}
*PSC?
*SRE <enable value>
*SRE?
*STB?
*WAI
66
Page 79

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
SCPI Command Summary
RS-232 Interface Commands
SYSTem
:LOCal
:REMote
:RWLock
IEEE-488.2 Common Commands
*CLS
*ESR?
*ESE <enable value>
*ESE?
*IDN?
*OPC
*OPC?
*PSC {0|1}
*PSC?
*RST
*SAV {1|2|3}
*RCL {1|2|3}
*STB?
*SRE <enable value>
*SRE?
*TRG
*TST?
*WAI
4
67
Page 80

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Simplified Programming Overview
Simplified Programming Overview
This section gives an overview of the basic techniques used to program the
power supply over the remote interface. This section is only an overview and
does not give all of the details you will need to write your own application
programs. Refer to the remainder of this chapter and also chapter 6,
“Application Programs ”, for mor e details and examples . Al so refer to the
programming reference manual that came with your computer for details on
outputting command strings and entering data.
Using the APPLy Command
The
APPLy
command provides the most straightforward method to program
the power supply over the remote interface. For example, the following
statement executed from your computer will set the power supply to an output
of 3 V rated at 1 A:
‘‘APPL 3.0, 1.0
’’
Using the Low-Level Commands
Although the
program the power supply, the low-level commands give you more fl ex ibility
to change individual parameters. For example, the following statements
executed from your computer will set the power supply to an output of 3 V
rated at 1 A:
‘‘VOLT 3.0
‘‘CURR 1.0
APPLy
’’
’’
command provides the most straightforward method to
Set output voltage to 3.0 V
Set output current to 1.0 A
68
Page 81

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Simplified Programming Overview
Reading a Query Response
Only the query commands (commands that end with “ ? ” ) will instruct the
power supply to send a response message. Queries return either output values
or internal instrument settings . For exampl e, the follow ing statements
executed from your computer will read the power supply’s error queue and
print the most recent error:
dimension statement Dimension string array (80 elements)
‘‘SYST:ERR?
bus enter statement Enter error string into computer
print statement Print error string
’’
Read error queue
Selecting a Trigger Source
The power supply will accept a ‘‘bus’’ (software) trigger or an immediate
internal trigger as a trigger source. By default, the ‘‘BUS’’ trigger source is
selected. If you want the power supply to use an immediate internal trigger,
you must select ‘‘
executed from your computer will set to an output of 3 V/1 A immediately:
‘‘VOLT:TRIG 3.0
‘‘CURR:TRIG 1.0
‘‘TRIG:SOUR IMM
‘‘INIT
IMMediate
’’
’’ . F o r ex ample, the fo l lowin g s t a t em e n t s
’’
’’
’’
Set the triggered voltage level to 3.0 V
Set the triggered current level to 1.0 A
Select the immediate trigger as a source
Cause the trigger system to initiate
4
69
Page 82

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Simplified Programming Overview
Power Supply Programming Ranges
The
SOURce
available programming value for a parameter varies according to the desired
output range of the power supply. The following table lists the programming
values available and
Agilent E3633A and E3634A power suppl ies.
Refer to this table to identify programming values when programming the power
supply.
Table 4-1. Agilent E3633A Programming Ranges
Voltage Programming Range 0 V to 8.24V 0 V to 20.60 V
Current Programming Range 0 A to 20.60 A 0 A to 10.30 A
subsystem requires parameters for programming values. T he
MINimum, MAXimum, DEFault
0 - 8V/20A Range 0 - 20V/10A Range
MAX Value 8.24 V 20.60 V
MIN Value 0 V 0 V
DEFault Value 0 V 0 V
*RST Value 0 V
MAX Value 20.60 A 10.30 A
MIN Value 0 A 0 A
DEFault Value 20 A 10 A
*RST Value 20.00 A
and reset values of the
Table 4-2. Agilent E3634A Programming Ranges
0 - 25V/7A Range 0 - 50V/4A Range
Voltage Programming Range 0 V to 25.75V 0 V to 51.5 V
MAX Value 25.75 V 51.5 V
MIN Value 0 V 0 V
DEFault Value 0 V 0 V
*RST Value 0 V
Current Programming Range 0 A to 7.21 A 0 A to 4.12 A
MAX Value 7.21 A 4.12 A
MIN Value 0 A 0 A
DEFault Value 7.0 A 4.0 A
*RST Value 7.00 A
70
Page 83

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Using the APPLy Command
Using the APPLy Command
The
APPLy
command provides the most straightforward method to program
the power supply over the remote interface. You can select the output voltage
and current in one command.
APPLy {<voltage>| DEF | MIN | MAX}[,{<current>| DEF | MIN | MAX}]
This command is combination of
as the newly programmed values are within the presently selected range, the
output voltage and current are changed as soon as the command is executed.
The
APPLy
command changes the power supply’s output to the newly
programmed values only if the programmed values are valid within the
presently selected range. An execution error will occur if the programmed
values are not valid within the selected range.
You can substitute ‘‘
specific value for the
values of ‘‘0’’ volts and ‘‘0’’ amps.
the selected range.
The
default
regardless of the presently selected range. For more details of parameters, see
Table 4-1 for the Agilent E3633A model and Table 4-2 for the Agilent E3634A
model.
If you specify only one parameter of the
regards it as voltage setting value.
values of voltage and current are ‘‘0’’ volts and ‘‘20’’* or ‘‘7’’** amps
MINimum
voltage
’’, ‘‘
and
VOLTage
MAXimum
current
MAX
and
CURRent
’’, or ‘‘
DEFault
parameters.
selects the highest values allowed for
APPLy
command, the power supply
commands. As long
’’ in place of a
MIN
selects the lowest
4
APPLy?
This command queries the power supply’s present voltage and current setting
values and returns a quoted string. The voltage and current are returned in
sequence as shown in the sample string below (the quotation marks are
returned as part of the string).
‘‘8.00000,20.00000’’* or ‘‘25.00000,7.00000’’**
In the above string, the first number 8.00000 is the voltage setting value and
the second number 20.00000 is the current setting value.
*For Agilent E3633A Model **For Agilent E3634A Model
71
Page 84

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Output Setting and Operation Commands
Output Setting and Operation Commands
This section describes low-level commands used to program the power supply.
’’ or ‘‘
APPLy
DOWN
Although the
program the power supply, the low-level output setting comm ands give you
more flexibility to change the individual parameters.
CURRent{<current>|MINimum | MAXimum|UP|DOWN}
This command programs the immediate current level of the power supply. The
immediate level is the current value of the output terminals.
The
CURRent
programmed value regardless of the output range presently selected.
You can substitute ‘‘
the current parameter.
selects the highest current values allowed for the selected range.
This command also increases or decreases the immediate current level using
the ‘‘
UP
CURRent:STEP
increment setting will cause an execution error -222 (Data out of range) when
the maximum or the minimum rated cur rent is exceeded.
command provides the most straightforward method to
command changes the output of the power supply to the newly
MINimum
MIN
’’ parameter by a predetermined amount. The command
sets the amount of increase or decrease. Notice that a new
’’ or ‘‘
MAXimum
selects the lowest current values of ‘‘0’’ amps.
’’ in place of a specific value for
MAX
CURRent
Example
The following program segm ents show how to use the
CURR DOWN
CURR:STEP
‘‘
CURR:STEP 0.01
‘‘
CURR UP
‘‘
CURR:STEP 0.02
‘‘
CURR DOWN
72
command to increase or decrease the output current with the
command.
’’
’’
’’
’’
Set the step size to 0.01 A
Increase the output current
Set the step size to 0.02 A
Decrease the output current
CURR UP
or
Page 85

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Output Setting and Operation Commands
CURRent? [MINimum | MAXimum]
This query returns the presently program med current level of the power
supply.
programmable current levels for the selected range.
CURRent:STEP {<numeric value>|DEFault}
This command sets the step size for current programming with the
UP
T o set the step size to the minimum resolution, set the step size to ‘‘
The minimum resol utio n of the step size is approxim ately 0.32 mA (E3633A)
and 0.13 mA (E3634A) respectively. The
minimum resolution of your instrument. The immediate current level increases
or decreases by the value of the step size. For example, the output current will
increase or decrease 10 mA if the step size is 0.01.
This command is useful when you program the power suppl y to the allowed
minimu m resoluti on. At
resolution.
CURR? MAX
and
CURRent DOWN
and
CURR? MIN
commands. See the example in the previous page.
*RST
return the highest and lowest
CURR:STEP? DEF
, the step size is the value of the minimum
returns the
CURRent
DEFault
’’.
CURRent:STEP? {DEFault}
This query returns the value of the step size currently specified. The returned
parameter is a numeric value. ‘‘
step size in unit of amps.
CURRent:TRIGgered {<current>| MINimum | MAXimum}
This command program s the pending triggered current level. The pending
triggered current level is a stored value that is transferred to the output
terminals when a trigger occurs. A pending triggered level is not affected by
subsequent
CURRent:TRIGgered? [MINimum | MAXimum]
This query returns the triggered current level presently programmed. If no
triggered level is programmed, the
:TRIG? MAX
programmable
CURRent
and
commands.
CURR:TRIG? MIN
triggered current levels.
DEFault
CURRent
ret u r n t h e h i ghes t an d l o wes t
’’ gives the minimum resolution of the
level is returned.
CURR
4
73
Page 86

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Output Setting and Operation Commands
CURRent:PROTection {<current>|MINimum|MAXimum}
This command sets the current level at which the overcurrent protection
(OCP) circuit will trip. If the peak output current exceeds the OCP level, then
the output current is programmed to zero. The Questionable Status register
‘‘OC’’ bit is set (see
CURR:PROT:CLE
removed.
page 91). An overcurrent condition can be cleared with the
command after the condition that caused the OCP trip i s
CURRent:PROTection? {MINimum|MAXimum}
This query returns the overcurrent protection trip level presently programmed.
CURR:PROT? MAX
programmable overcurrent trip levels.
and
CURR:PROT? MIN
ret urn the max imum a nd min imum
CURRent:PROTection:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
This command enables or disables the overcurrent protection function of the
power supply. An overcurrent condition can be cleared with the
CURR:PROT:CLE
removed. At
command after the condition that caused the OCP trip i s
*RST
, this value is set to ‘‘ON’’.
CURRent:PROTection:STATe?
This query returns the state of the overcurrent pr otection function. The
returned parameter is ‘‘0’’ (OFF) or ‘‘1’’ (ON).
CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped?
This query returns a ‘‘1’’ if the overcurrent protection circuit is tripped and not
cleared or a ‘‘0’’ if not tripped.
CURRent:PROTection:CLEar
This command causes the overcurrent protection circuit to be cleared. After
this command, the output current is restored to the state it was in before the
current protection tripped and the OCP trip level remains unchanged to the
value presently programmed. Before sending this command, lower the output
current below the trip OCP point, or raise the OCP trip level above the output
setting.
must be removed first before proceeding this command.
Note that the overcurrent condition caused by an external source
74
Page 87

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Output Setting and Operation Commands
VOLTage {<voltage>| MINimum | MAXimum|UP|DOWN}
This command programs the immediate voltage level of the power supply. The
immediate level is the voltage value of the output terminals.
The
VOLTage
programmed value regardless of the output range presently selected.
You can substitute ‘‘
the voltage parameter.
selects the highest voltage values allowed for the selected range.
This command also increases or decreases the immediate voltage level using
the ‘‘
UP
VOLTage:STEP
increment setting will cause an execution error -222 (Data out of range) when
the maximum or the minimum rated vol tage is exceeded.
command changes the output of the power supply to the newly
’’ or ‘‘
MINimum
MIN
DOWN
’’ parameter by a predetermined amount. The command
sets the amount of increase or decrease. Notice that a new
’’ or ‘‘
MAXimum
selects the lowest voltage values of ‘‘0’’ volts.
’’ in place of a specific value for
MAX
VOLTage
Example
The following program segm ents show how to use the
VOLT DOWN
VOLT:STEP
‘‘
VOLT:STEP 0.01
‘‘
VOLT UP
‘‘
VOLT:STEP 0.02
‘‘
VOLT DOWN
VOLTage? [MINimum | MAXimum]
This query returns the presently program med voltage level of the power
supply.
programmable
command to increase or decrease the output voltage with the
command.
’’
’’
VOLT? MAX
voltage levels for the selected range.
’’
’’
and
VOLT? MIN
return the highest and lowest
Set the step size to 0.01 V
Increase the output voltage
Set the step size to 0.02 V
Decrease the output voltage
VOLT UP
or
4
75
Page 88

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Output Setting and Operation Commands
VOLTage:STEP {<numeric value>|DEFault}
This command sets the step si ze for voltage programming with the
and
VOLT DOWN
To set the step size to the minimum resolution, set the step size to ‘‘
The minimum resol utio n of the step size is approxim ately 0.36 mV (E3633A)
and 0.95 mV (E3634A) respectively. The
minimum resolution of your instrument. The immediate voltage level increases
or decreases by the value of the step size. For example, the output voltage will
in crease or d e crease 10 m V i f the st e p s ize is 0 . 0 1 .
This command is useful when you program the power suppl y to the allowed
minimu m resoluti on. At
resolution.
commands. See the above example in the previous page.
VOLT:STEP? DEF
*RST
, the step size is the value of the minim um
returns the
VOLT UP
DEFault
’’.
VOLTage:STEP? {DEFault}
This query returns the value of the step size currently specified. The returned
parameter is a numeric value. ‘‘
size in unit of volts.
DEFault
’’ gives the minimum resolution step
VOLTage:TRIGgered {<voltage>| MINimum | MAXimum}
This command program s the pending triggered voltage level. The pending
triggered voltage level is a stored value that is transferred to the output
terminals when a trigger occurs. A pending triggered level is not affected by
subsequent
VOLTage
commands.
VOLTage:TRIGgered? [MINimum | MAXimum]
This query returns the triggered voltage level presently programmed. If no
triggered level is programmed, the
and
VOLT:TRIG? MIN
voltage levels.
return the highest and lowest programmable triggered
VOLT
level is returned.
VOLT:TRIG? MAX
VOLTage:PROTection {<voltage>|MINimum|MAXimum}
This command sets the voltage level at which the overvoltage protection (OVP)
circuit will trip. If the peak output voltage exceeds the OVP level, then the
power supply output is shorted by an internal SCR. The Questionable Status
register ‘‘OV’’ bit is set (see
with the
trip is removed.
VOLT:PROT:CLE
page 91). An overvoltage condition can be cleared
command after the condition that caused the OVP
76
Page 89

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Output Setting and Operation Commands
VOLTage:PROTection? {MINimum|MAXimum}
This query returns the overvoltage protection trip level presently programmed.
VOLT:PROT? MAX
programmable overvoltage trip levels.
VOLTage:PROTection:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
This command enables or disabl es the overvoltage protection function. An
overvoltage condition can be cleared with the
after the condition that caused the OVP trip is removed. At
set to ‘‘ON’’.
VOLTage:PROTection:STATe?
This query returns the state of the overvoltage protection function. The
returned parameter is ‘‘0’’ (OFF) or ‘‘1’’ (ON).
VOLTage:PROTection:TRIPped?
This query returns a ‘‘1’’ if the overvoltage protection circuit is tripped and not
cleared or a ‘‘0’’ if not tripped.
VOLTage:PROTection:CLEar
This command causes the overvoltage protection circuit to be cleared. After
this command, the output voltage is restored to the s tate it was in before the
protection feature occurred and the OVP trip level remains unchanged to the
value presently programmed. Before sending this command, lower the output
voltage below the trip OVP point, or raise the OVP trip level above the output
setting.
be removed firs t before proc ee ding this c omm a nd.
Note that the overvoltage condition caused by an external source must
and
VOLT:PROT? MIN
ret urn the max imum a nd min imum
VOLT:PROT:CLE
command
*RST
, thi s v alue is
4
VOLTage:RANGe {P8V|P20V||LOW|HIGH} (For E3633A model)
or {P25V|P50V|LOW|HIGH} (For E3634A model)
This command selects an output range to be programmed by the identifier. For
example, when 8V/20A* range is selected, the
voltage and current are limited to 8.24 volts and 20.60 amps. When 20V/10A *
range is selected, the
limited to 20.60 volts and 10.30 amps. See
programming ranges of the Agilent E3634A model . ‘‘P20V’ ’* or ‘‘HIGH’’ is the
identifier for the 20V/10A* range and ‘‘P8V’’* or ‘‘LOW’’ is for the 8V/20A* range.
*RST
At
*For Agilent E3633A Model **For Agilent E3634A Model
, the 8V/20A* or 25V/7A** range is selected.
maxim um programmable
maximu m program mable
voltage and current are
page 70 for more details of the
77
Page 90

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Output Setting and Operation Commands
VOLTage:RANGe?
This query returns the currently sel ected range. The returned parameter for
the Agilent E3633A is ‘‘P20V’’ (HIGH) or ‘‘P8V’’ (LOW) and the parameter for
the Agilent E3634A is ‘‘P50V’’ (HIGH) or ‘‘P25V’’ (LOW).
MEASure:CURRent?
This command queries the current measured across the current sense resistor
inside the power supply.
MEASure[:VOLTage]?
This command queries the voltage measured at the sense terminals of the
power supply.
78
Page 91

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Triggering Commands
Triggering Commands
The power supply’s triggering system allow s a change in voltage and current
when receiving a trigger, to select a trigger source, and to insert a trigger.
Triggering the power supply is a multi- step process .
• First, you must specify the source from which the power supply will accept
the trigger. The power supply will accept a bus (software) trigger or an
immediate trigger from the remote interface.
• Then, you can set the time delay between the detection of the trigger on the
specified trigger source and the start of any corresponding output change.
Notice that the time delay is valid for only the bus trigger source.
• Finally, you must provide an
source is selected, the selected output is set to the triggered level
immediately. But if the trigger source is the bus, the power s upply is set to
the triggered level after receiving the Group Execute Trigger (GET) or
command.
Trigger Source Choices
You must specify the source from which the power supply will accept a trigger.
The trigger is stored in volatile memory; the source is set to bus when the power
supply has been off or after a remote interface reset.
INITiate
command. If the
IMMediate
*TRG
4
Bus (Software) Triggering
• To select the bus trigger source, send the following command.
TRIG:SOUR BUS
• To trigger the power supply from the remote interface (GPIB or RS-232)
after selecting the bus source, send t he
*TRG
is sent, the trigger action starts after the specified time delay if any
delay is given.
• You can also trigger the power supply from the GPIB interface by sending
the IEEE-488 Group Execute Trigger (GET) mess age. The following
statement shows how to send a GET from a Agilent Technologies controller.
TRIGGER 705
(group execute trigger)
*TRG
(trigger) command. When the
79
Page 92

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Triggering Commands
• To ensure synchronization when the bus source is selected, send the
*WAI
(wait) command. When the
waits for all pending operations to complete before executing any additional
commands. For example, the following command string guarantees that the
first trigger is accepted and is executed before the second trigger is
recognized.
command is executed, the power supply
TRIG:SOUR BUS;*TRG;*WAI;*TRG;*WAI
• You can use the
(operation complete) command to s ignal when the operation is complete.
*OPC?
The
is co mp le te. The
Event register when the operation is complete.
*OPC?
command returns ‘‘1’’ to the output buffer when the operation
(operation complete query) command or the
*OPC
command sets the ‘‘OPC’’ bit (bit 0) in the Standard
Immediate Triggering
• To select the immediate trigger s ource, send the following command.
TRIG:SOUR IMM
• When the
command imm ediately transfers the
VOLT
IMMediate
or
CURR
is selected as a trigger so urce, an
VOLT:TRIG
value. Any delay is ignored.
or
CURR:TRIG
INITiate
value to
*WAI
*OPC
80
Page 93

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Triggering Commands
Triggering Commands
INITiate
This command causes the trigger system to initiate. This command completes
one full trigger cycle when the trigger source is an immediate and initiates the
trigger subsystem when the trigger source is bus.
TRIGger:DELay {<seconds>| MINimum | MAXimum}
This command sets the time delay between the detection of an event on the
specified trigger source and the start of any corresponding trigger action on
the power supply output. Select from 0 to 3600 seconds.
MAX
= 3600 seconds. At
TRIGger:DELay?
This command queries the trigger delay.
TRIGger:SOURce {BUS | IMMediate}
This command selects the source from which the power supply wi ll accept a
trigger. The power supply will accept a bus (software) trigger or an internal
immediate trigger. At
*RST
, this value is set to 0 seconds.
*RST
, the bus trigger source is selected.
MIN
= 0 seconds.
4
TRIGger:SOURce?
This command queries the present trigger source. Returns ‘‘BUS’’ or ‘‘IMM’’.
*TRG
This command generates a trigger to the trigger subsystem that has selected a
bus (software) trigger as its source
the same effect as the Group Execute Trigger (GET) command. For RS-232
operation, make sure the power supply is in the remote interface mode by
sending the
SYST:REM
command first.
(TRIG:SOUR BUS)
. The command has
81
Page 94

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
System-Related Commands
System-Related Commands
DISPlay {OFF | ON}
This command turns the front-panel display off or on. When the display is
turned off, outputs are not sent to the display and all annunciators are disabled
except the
The display state is automatically turned on when you return to the local mode.
Press
DISPlay?
This command queries the front-panel display setting. Returns ‘‘0’’ (OFF) or
‘‘1’’ (ON).
DISPlay:TEXT <quoted string>
This command dis pl ays a message on the front panel. The power supply will
display up to 12 characters in a message; any additional characters are
truncated. Commas, periods, and semicolons share a display space with the
preceding character, and are not considered indi vidual characters.
Store
Local
ERROR
(
Local
annunciator.
) key to return to the local state from the remote interface.
DISPlay:TEXT?
This command queries the message sent to the front panel and returns a quoted
string.
DISPlay:TEXT:CLEar
This command clears the mess age displayed on the front panel.
OUTPut {OFF | ON}
This command enables or disables the outputs of the power supply. When the
output is disabled, the voltage valu e is 0 V and the current value is 1 mA.
At
*RST
, the output state is OFF.
OUTPut?
This command queries the output state of the power supply. The returned value
is ‘‘0’’ (OFF) or ‘‘1’’ (ON).
82
Page 95

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
System-Related Commands
OUTPut:RELay {OFF | ON}
This command sets the state of two TTL signals on the RS-232 connector. These
signals are intended for use with an external relay and relay driver. The TTL
output is available on the RS-232 connector pin 1 and pin 9. When the
OUTPut:RELay
9 is low (0.5 V). The levels are reversed when the
‘‘OFF’’. At
Note TTL output of pin 1 or pin 9 of the RS-232 connector is available only after installing
two jumpers inside the power supply. See the Service Guide for more information.
Note Do not use the RS-232 interface if you have configured the power supply to output
relay control signals. Internal components on the RS-232 circuitry may be damaged.
OUTPut:RELay?
This command returns the state of the TTL relay logic signals. See also
OUTP:REL
SYSTem:BEEPer
This command issues a single beep immediately.
state is ‘‘ON’’, the TTL output of pi n 1 is high (4.5 V) and pin
OUTPut:RELay
*RST
, the
OUTPut:RELay
command.
state is OFF.
state is
4
SYSTem:ERRor?
This command queries the power supply’s error queue. When the front-panel
ERROR
errors have been detected. Up to 20 errors can be stored in the error queue.
See ‘‘Error Messages’’ for a complete listing of the errors in chapter 5.
• Errors are retrieved in first-in-first-out (FIFO) order. The first error returned
• If more than 20 errors have occurred, the last error stored in the queue (the
• The error queue is cleared when power has been off or after a
annunciator turns on, one or more command syntax or hardware
is the first error that was stored. When you have read all errors from the
queue, the
time an error is generated.
most recent error) is replaced with -350, ‘‘Too many errors’’. No additional
errors are stored until you remove errors from the queue. If no errors have
occurred when you read the error queue, the power supply responds with
+0, ‘‘No error’’.
status) command has been executed. The
clear the error queue.
ERROR
annunciator turns off. The power supply beeps once each
*CLS
(clear
*RST
(reset) command
does not
83
Page 96

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
System-Related Commands
SYSTem:VERSion?
This command queries the power supply to determine the present SCPI
version. The returned value is of a string in the form YYYY.V where the ‘‘Y’s’’
represent the year of the version, and the ‘‘V’’ represents a version number for
that year (for example, 1996.0).
*IDN?
This query command reads the power supply’s identification string. The power
supply returns four fields separated by commas. The first field is the
manufacturer’s name, the second field is the model number, the third field is
not used (always ‘‘0’’), and the
fourth field
is a revision code whi ch contains
three numbers. The first number is the firmware revision number for the main
power supply processor; the second is for the
input/output
processor; and the
third is for the front-panel processor.
The command returns a string with the following format (be sure to dimension
a string variable with at least
40 characters
):
HEWLETT-PACKARD,E3633A or E3634A,0,X.X-X.X-X.X
*RST
This command resets the power suppl y to its power-on state as follow s:
Command E3633A state E3634A state
CURR
CURR:STEP
CURR:TRIG
CURR:PROT
CURR:PROT:STAT
DISP
OUTP
OUTP:REL
TRIG:DEL
TRIG:SOUR
VOLT
VOLT:STEP
VOLT:TRIG
VOLT:PROT
VOLT:PROT:STAT
VOLT:RANG
20 A 7 A
0.32 mA (typical value) 0.13 mA (typical value)
20 A 7 A
22.0 A 7.5 A
ON ON
ON ON
OFF OFF
OFF OFF
0 0
BUS BUS
0 V 0 V
0.36 mV (typical value) 0.95 mV (typical value)
0 V 0 V
22.0 V 55.0 V
ON ON
P8V (Low) P25V (Low)
84
Page 97

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
System-Related Commands
*TST?
This query performs a
the self-test passes or ‘‘1’’ or any non-zero value if it fails. If the self-test fails,
an error message is also generated with additional information on why the test
failed.
*SAV { 1 | 2 | 3 }
This command stores the present state of the power supply to the specified
location in
3) are available to store operating states of the power supply. The state storage
feature ‘‘remembers’’ the states or values of the following commands:
CURR, CURR:STEP, CURR:TRIG, CURR:PROT, CURR:PROT:STAT
DISP, OUTP, OUTP:REL, TRIG:DEL, TRIG:SOUR, VOLT,
VOLT:STEP, VOLT:TRIG, VOLT:PROT, VOLT:PROT:STAT,
VOLT:RANG
To recall a stored state, you must use the same memory location used
previously to store the state.
non-volatile
complete
memory. Three memory locations (numbered 1, 2 and
self-test of the power supply. Returns ‘‘0’’ if
and
*RCL { 1 | 2 | 3 }
This command recall s a previousl y stored state. To recall a stored state, you
must use the same memory location used previously to store the state.
Note DISP {OFF|ON} can be stored and recalled in remote interface mode only. Going
to local mode automatically sets the display state to ON.
4
85
Page 98

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Calibration Commands
Calibration Commands
See chapter 3 ‘‘C al ibration Overvie w’’, star ting on page 56 for an overview
of the calibration features of the power supply. For more detailed discussion
of the calibration procedures, see the Service Guide.
Note When you calibrate the power supply, you should not set the OVP and OCP to ON
state in order to prevent OVP or OCP from tripping.
CALibration:COUNt?
This command queries the power supply to determine the number of times it
has been calibrated. Your power supply was calibrated before it left the factory.
When you receive your power supply, read the count to determine its initial
value. Since the value increments by one for each calibration point, a complete
calibration will increase the value by 5 counts.
CALibration:CURRent[:DATA] <numeric value>
This command can only be used after calibration is unsecured and the output
state is ON. It enters a current value that you obtained by reading an external
meter. You must first select the minimum calibration level (
) for the value being entered. You must then select the middle and
MIN
maximum calibration levels (
) for the value being entered. Three successi ve values must be selected and
entered. The power supply then computes new calibration constants. These
constants are then stored in
CAL:CURR:LEV MID
non-volatile
memory.
and
CAL:CURR:LEV
CAL:CURR:LEV MAX
CALibration:CURRent:LEVel {MINimum | MIDdle|MAXimum}
This command can only be used after calibration is unsecured and the output
state is ON. It sets the power supply to a calibration point that is entered with
CAL:CURR
low-end point (MIN) must be selected and entered fi rst.
CALibration:CURRent:PROTection
This command cali brates the overcurrent protection circuit of the power
supply. It takes about 10 seconds to execute the command. The calibration
must be unsecured and the output shorted before calibrating the overcurrent
protection. The power supply automatically performs the calibration and
stores the new overcurrent constant in
curren t cali bration pr ec ede s before sen din g this com mand.
86
command. During calibration, three points must be entered and the
nonvolatile
memory.
Notice that
Page 99

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Calibration Commands
CALibration:DAC:ERRor
This command corrects the differential nonlinearity error of the internal DAC
without an external meter. You must send this command before calibrating the
voltage. It takes about 30 seconds to execute the command.
CALibration:SECure:CODE <new code>
This command enters a new security code. To change the security code, first
unsecure the power supply using the old security code. Then, enter the new
code. The calibration code may contain up to 12 characters over the remote
interface but the first character must always be a letter.
CALibration:SECure:STATe {OFF | ON},<code>
This command unsecures or secures the power supply for calibration. The
calibration code may contain up to 12 characters over the remote interface.
CALibration:SECure:STATe?
This command queries the secured state for calibration of the power supply.
The returned parameter is ‘‘0’’ (OFF) or ‘‘1’’ (ON).
CALibration:STRing <quoted string>
This command records calibration information about your power supply. For
example, you can store such information as the last calibration date, the next
calibration due date, or the power supply’s serial number. The calibration
message may contain up to 40 characters. The power supply shou ld be
unsecured before sending a calibration message.
4
CALibration:STRing?
This command queries the calibration message and returns a quoted string.
CALibration:VOLTage[:DATA] <numeric value>
This command can only be used after calibration is unsecured and the output
state is ON. It enters a voltage value that you obtained by reading an external
meter. You must first select the minimum calibration level (
) for the value being entered. You must then select the middle and
MIN
maximum calibration levels (
for the value being entered. Three successive values must be selected and
entered. The power supply then computes new voltage calibration constants.
These constants are then stored in
CAL:VOLT:LEV MID
non-volatile
and
memory.
CAL:VOLT:LEV
CAL:VOLT:LEV MAX
87
)
Page 100

Chapter 4 Remote Interface Reference
Calibration Commands
CALibration:VOLTage:LEVel {MINimum | MIDdle|MAXimum}
This command can only be used after calibration is unsecured and the output
state is ON. It sets the power supply to a calibration point that is entered with
CAL:VOLT
low-end point (MIN) must be selected and entered fi rst.
command. During calibration, three points must be entered and the
CALibration:VOLTage:PROTection
This command cali brates the overvoltage protection circuit of the power
supply. It takes about 10 seconds to execute the command. The calibration
must be unsecured and the output be opened before calibrating the overvoltage
protection circuit. The power supply automati cally perform s the calibration
and stores the new overvoltage constant in
voltage calibration pre ce des before sen ding this c omm a nd.
nonvolatile
memory.
Notice that
88
 Loading...
Loading...