Page 1

Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator
Programming Guide
sA
Page 2

Important Notice
CAUTION
WARNING
© Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2007
Manual Part Number
5988-7402EN
Revision
March 2007
Printed in Germany
Agilent Technologies
Herrenberger Straße 130
D-71034 Böblingen
Germany
Warranty
The material contained in this document is
provided "as is," and is subject to being changed,
without notice, in future editions. Further, to the
maximum extent permitted by applicable law,
Agilent disclaims all warranties, either express or
implied, with regard to this manual and any
information contained herein, including but not
limited to the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose. Agilent shall not be liable for errors or
for incidental or consequential damages in
connection with the furnishing, use, or
performance of this document or of any
information contained herein. Should Agilent and
the user have a separate written agreement with
warranty terms covering the material in this
document that conflict with these terms, the
warranty terms in the separate agreement shall
control.
Technology Licenses
The hardware and/or software described in this
document are furnished under a license and may
be used or copied only in accordance with the
terms of such license.
Restricted Rights Legend
If software is for use in the performance of a U.S.
Government prime contract or subcontract,
Software is delivered and licensed as
"Commercial computer software" as defined in
DFAR 252.227-7014 (June 1995), or as a
"commercial item" as defined in FAR 2.101(a) or
as "Restricted computer software" as defined in
FAR 52.227-19 (June 1987) or any equivalent
agency regulation or contract clause. Use,
duplication or disclosure of Software is subject to
Agilent Technologies' standard commercial
license terms, and non-DOD Departments and
Agencies of the U.S. Government will receive no
greater than Restricted Rights as defined in FAR
52.227-19(c)(1-2) (June 1987). U.S. Government
users will receive no greater than Limited Rights
as defined in FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987) or DFAR
252.227-7015 (b)(2) (November 1995), as
applicable in any technical data.
Safety Notices
A CAUTION notice denotes a hazard. It calls
attention to an operating procedure, practice, or
the like that, if not correctly performed or adhered
to, could result in damage to the product or loss
of important data. Do not proceed beyond a
CAUTION notice until the indicated conditions
are fully understood and met.
A WARNING notice denotes a hazard. It calls
attention to an operating procedure, practice, or
the like that, if not correctly performed or adhered
to, could result in personal injury or death. Do not
proceed beyond a WARNING notice until the
indicated conditions are fully understood and
met.
Trademarks
Windows NT ® and MS Windows ® are U.S.
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
2 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 3

About This Programming Guide
This guide provides information about programming the Agilent
81133A/81134A Pulse/Pattern Generator through the available
remote interfaces.
• “Introduction” on page 9 provides information about the
different remote programming interfaces.
• “Connecting to the Pulse/Pattern Generator for Remote
Programming” on page 11 provides information about how to
connect to the instrument and gives examples.
• “SCPI Commands Reference” on page 17 provides detailed
information about the available SCPI commands.
• “Troubleshooting” on page 97 lists the error messages and
shows how to solve the errors.
• “Differences between the 8133A and the 81133A/81134A” on
page 101 provides information on how to adapt a program
written for the 8133A to the 81133A/81134A instrument.
For examples for setting up generic and advanced signals, please
refer to the User Guide.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 3
Page 4

About This Programming Guide
4 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 5

Contents
Introduction 9
Connecting to the Pulse/Pattern Generator for Remote
Programming 11
SCPI Commands Reference 17
About This Programming Guide 3
Connecting to the Instrument via GPIB 11
Example for Connecting via GPIB 12
Connecting to the Instrument via LAN 13
Configuring the Agilent IO Libraries 13
Example for Connecting via LAN 14
Connecting to the Instrument via USB 15
Common Commands 19
Standard Settings 21
DIAGnostic Commands 23
:CAL:TIM 24
:DIAG:CHANnel[1|2]:PPERformance 24
DIGital Commands 25
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:PATTern[:DATa] 27
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:PATTern:LDATa 29
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:PATTern:LENGth 31
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:FORMat 31
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:POLarity 32
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:
CROSsover:[VALue] 32
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:
CROSsover:[STATe] 34
DISPlay Commands 35
:DISPlay[:WINDow][:STATe] 35
MEASure Commands 36
:MEASure:FREQuency? 37
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 5
Page 6

:MEASure:PERiod? 38
OUTPut Commands 39
:OUTPut[0|1|2]:DIVider 41
:OUTPut0:SOURce 42
:OUTPut[0|1|2][:STATe] 43
:OUTPut[1|2]:NEG 43
:OUTPut[1|2]:POS 44
:OUTPut:CENTral 44
SOURce Commands 45
[:SOURce]:FUNCtion[:SHAPe] 50
[:SOURce]:FUNCtion:MODe[1|2] 51
[:SOURce]:FREQuency[:CW|:FIXed] 52
[:SOURce]:PHASe[:ADJ][1|2] 53
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DCYCle[1|2] 54
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DELay[1|2] 55
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DESKew[1|2] 56
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DHOLd[1|2] 56
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:PERiod 57
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:POLarity[1|2] 57
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:WIDTh[1|2] 58
[:SOURce]:PM[1|2] 59
[:SOURce]:PM[1|2]:SENSitivity 59
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel]
[:IMMediate][:AMPLitude] 60
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel]
[:IMMediate]:OFFSet 61
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel]
[:IMMediate]:HIGH 62
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel]
[:IMMediate]:LOW 63
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel]
[:IMMediate]:TERM 64
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit
[:AMPLitude]? 64
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:OFFSet? 65
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:HIGH? 65
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:LOW? 65
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:STATe 66
Status Handling Commands 67
6 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 7

:STATus:OPERation 70
:STATus:PRESet 70
:STATus:QUEStionable 71
:STATus:QUEStionable:VOLTage 73
:STATus:QUEStionable:FREQuency 74
:STATus:QUEStionable:MONotony 76
SYSTem Commands 79
:SYSTem:ERRor? 81
:SYSTem:PRESet 81
:SYSTem:SET 82
:SYSTem:VERSion? 82
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:DHCP 83
:SYSTEM:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:NAME 83
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]
:ADDRess 84
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]
:SMASk 84
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]
:DGATeway 85
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDR 85
TRIGger Commands 86
:TRIGger:SOURce 87
:TRIGger:TERM 88
:TRIGger:TERM:STATE[?] 89
ARM Commands 90
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:LEVel 91
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:SLOPe 92
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:SOURce 93
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:TERM 94
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer][:STARt] 94
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:STOP 95
Troubleshooting 97
Differences between the 8133A and the 81133A/81134A 101
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 7
Page 8

8 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 9

Introduction
For controlling the Agilent 81133A/81134A remotely, the
instrument provides three different interfaces:
•GPIB
•LAN
•USB
NOTE Your instrument’s firmware might not be set up for USB. USB
functionality is not available with the first release but will be
included in a later release of the firmware. Check the Agilent Web
page for update information.
Using the GPIB connector, the instrument can be controlled from
a PC or a UNIX Workstation.
Using the LAN connector, the instrument can be connected to a
local area network and can be programmed from a PC.
USB is the replacement for GPIB when used on the bench. The
language is the same as with GPIB.
Firmware Server and SCPI Commands All interfaces use the same SCPI- like language to communicate
with the instrument’s firmware server. The firmware server
implements a client server architecture, allowing to connect
multiple clients simultaneously.
The GUI also uses this language to communicate with the firmware
server. Therefore, everything that can be done via the user
interface can also be done via the programming interfaces.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 9
Page 10

Introduction
10 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 11

Connecting to the Pulse/Pattern Generator for Remote Programming
The following sections show how to establish the connection
between your control PC and the instrument through the available
remote interfaces.
Connecting to the Instrument via GPIB
You can use GPIB connections only for controlling the instrument
by means of SCPI commands.
To connect to the instrument via GPIB you have to:
• Use GPIB cables to connect the instrument to the test
environment.
• Specify the instrument’s GPIB address.
The address is displayed on the user interface. The default
address is 13. It can be changed on the user interface in the
Config Page or with the command
“:SYSTem:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDR” on page 85
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 11
.
Page 12

Connecting to the Pulse/Pattern Generator for Remote Programming Connecting to the Instrument via GPIB
Example for Connecting via GPIB
The following code example shows how to use the VISA library to
connect to the instrument via GPIB.
This example queries a GPIB device for an identification string and
prints the results.
Implementation
#include <visa.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void main () {
ViSession defaultRM, vi;
char buf [256] = {0};
/* Open session to GPIB device at address 22 */
viOpenDefaultRM (&defaultRM);
viOpen (defaultRM, "GPIB0::22::INSTR", VI_NULL,VI_NULL, &vi);
/* Initialize device */
viPrintf (vi, "*RST\n");
/* Send an *IDN? string to the device */
viPrintf (vi, "*IDN?\n");
/* Read results */
viScanf (vi, "%t", &buf);
/* Print results */
printf ("Instrument identification string: %s\n", buf);
/* Close session */
viClose (vi);
viClose (defaultRM);
}
12 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 13

Connecting to the Instrument via LAN Connecting to the Pulse/Pattern Generator for Remote Programming
Connecting to the Instrument via LAN
For connecting over the LAN, you would do have the following:
• Connect the instrument to the LAN physically.
• Configure the Agilent IO Libraries on the remote machine.
• On the user interface, either specify the LAN address or—if a
DHCP server is available—enable the DHCP. The DHCP will
automatically set up the LAN connection.
• After the connection has been established, the following
commands can be used to modify the settings:
– Enable/disable DHCP with
:SYST:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:DHCP
– Set the instrument’s LAN name with
:SYST:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:NAME
– Set the instrument's IP address with
:SYST:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:ADDRess
– Set the instrument’s subnet mask with
:SYST:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:SMASk
– Set the instrument’s gateway with
:SYST:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:DGATeway
Configuring the Agilent IO Libraries
Suite 14 of the Agilent IO Libraries does not directly support
interfaces with a SICL name of “lan0”. When you add a LAN
interface, the default SICL name is “inst0”. To ensure compatability
with current code, it is recommended that you change the SICL
name to “lan0”.
To set up and configure the interface:
1 Run Agilent Connection Expert and configure your TCPIP
instrument according to the instructions provided with the
Agilent Connection Expert.
2 Close Agilent Connection Expert.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 13
Page 14

Connecting to the Pulse/Pattern Generator for Remote Programming Connecting to the Instrument via LAN
3 Run IO Config.
The IO Config utility (iocfg32.exe) can be found at (default
location):
C:\Program Files\Agilent\IO Libraries Suite\bin
Note that you can also open the IO Config from the Agilent IO
Libraries Control icon in the task bar.
4 Edit “inst0” to “lan0”.
Select “TCPIP Lan”, then click Edit. This will bring up the list of
TCPIP devices already configured. Select the device you need to
change, then click Edit Device. You can now change the device
name to “lan0”.
NOTE You will see a red circle with “!” in the Agilent Connection Expert.
Example for Connecting via LAN
Implementation
The following code snippet shows how to use the VISA library to
connect to the instrument via LAN.
This example queries a device for an identification string and
prints the results.
#include <visa.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void main () {
ViSession defaultRM, vi;
char buf [256] = {0};
/* Open session to the device */
viOpenDefaultRM (&defaultRM);
viOpen (defaultRM,
"TCPIP0::123.123.123.123::lan0::INSTR"
VI_NULL,VI_NULL, &vi);
/* Initialize device */
viPrintf (vi, "*RST\n");
/* Send an *IDN? string to the device */
viPrintf (vi, "*IDN?\n");
/* Read results */
viScanf (vi, "%t", &buf);
/* Print results */
printf ("Instrument identification string: %s\n", buf);
/* Close session */
viClose (vi);
14 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 15

Connecting to the Instrument via USB Connecting to the Pulse/Pattern Generator for Remote Programming
viClose (defaultRM);
}
Connecting to the Instrument via USB
NOTE The control PC must have USB capability for USB connections
(Windows NT is not supported).
For connecting over the USB, please refer to the Help delivered
with the USB driver.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 15
Page 16

Connecting to the Pulse/Pattern Generator for Remote Programming Connecting to the Instrument via USB
16 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 17

SCPI Commands Reference
The following sections describe the SCPI Commands available to
program the 81133A/81134A remotely. The commands are divided
into the following functional blocks:
• “Common Commands” on page 19
• “DIAGnostic Commands” on page 23
• “DIGital Commands” on page 25
• “DISPlay Commands” on page 35
• “MEASure Commands” on page 36
• “OUTPut Commands” on page 39
• “SOURce Commands” on page 45
• “Status Handling Commands” on page 67
• “SYSTem Commands” on page 79
• “TRIGger Commands” on page 86
• “ARM Commands” on page 90
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 17
Page 18

SCPI Commands Reference
Command Structure Each command description has at least some of the following
items:
• Full command syntax
•Form
–Set
The command can be used to program the instrument.
–Query
The command can be used to interrogate the instrument. A
question mark (?) is added to the command, the parameters
may also change.
• Brief description
• Parameters
• Parameter Suffix
The suffixes that may follow the parameter.
• Functional Coupling
Any other commands that are implicitly executed by the
command.
•Value Coupling
Any other parameter that is also changed by the command.
•Range Coupling
Any other parameter whose valid ranges may be changed by the
command.
• *RST value
The value/state following a *RST command
•Specified Limits
•Short example
18 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 19

Common Commands SCPI Commands Reference
Common Commands
The following table shows the IEEE 488.2 Common Commands
available with the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator.
Command Parameter Description
*CLS
*ESE
*ESR?
*IDN?
*LRN?
*OPC
*OPT?
*RCL
*RCL
*RST
*SAV
*SRE
*STB?
*TST?
*WAI
- Clears the status register
<0–255> Sets the event status register mask
- Reads the event status register
- Reads the instrument's identification string
- Reads a complete instrument setting
- Sets the operation complete bit when all pending
actions are complete
- Reads the installed options
<1–9> Reads a complete instrument setting from memory
<0> Reads the standard settings from the memory.
For a list of standard settings, see “Standard
Settings” on page 21.
- Resets the instrument to standard settings.
For a list of standard settings, see “Standard
Settings” on page 21.
<1–9> Saves the complete instrument setting to the
memory
<0–255> Sets the service request enable mask
- Reads the status byte
- Executes the instrument's self-test
- Waits until all pending actions are complete
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 19
Page 20

SCPI Commands Reference Common Commands
*RCL
*TST
*SAV
Commands in the User Interface The following figure shows how the IEEE 488.2 Common
commands are implemented in the 81133A/81134A user interface.
20 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 21

Common Commands SCPI Commands Reference
Standard Settings
The following table shows the standard settings (Memory 0).
Parameter SCPI Command Reset Value Range
Outputs On/Off :OUTP[0|1|2] <value> 0 (OFF) 0 | 1| ON | OFF
Output Normal :OUTP[1|2]:POS <value> 0 (OFF) 0 | 1 | ON | OFF
Output Complement :OUTP[1|2]:NEG 0 (OFF) 0 | 1 | ON | OFF
Instrument Mode :FUNC <value> PATT PATTern|BURSt, <number>|RBURSt,
<number1>, <number2>
Burst :FUNC BURSt, <value> 1 1 … 16384
Repeated Burst :FUNC RBURS 4, 4 For both, 4 … 16384 in increments of 4
Frequency :FREQ <value> 15 MHz 15 MHz … 3.35 GHz
Period :PER <value> 66.666667ns 0.298507 ps … 66.666667 ns
Clock Mode :TRIG:SOUR Internal IMMediate, EXTernal, REFerence,
IDIRect, EDIRect
Channel Mode :FUNC:MOD[1|2]
<value>
PRBS Number :FUNC:MOD[1|2] PRBS,
<value>
Freq. Divider :OUTP[0|1|2]:DIV
<value>
Data Signal Mode :DIG[1|2]:SIGN:FORM
<value>
Var. Crossover :DIG[1|2]:SIGN:CROS
<value>
Var. Crossover mode :DIG[1|2]:SIGN:CROS:ST
AT <value >
Data Polarity :DIG[1|2]:SIGN:POL
<value>
Pulse Perf. DIAG:CHAN[1|2]:PPER
<value>
Delay Control Input :PM[1|2] <value> OFF OFF, ON
Delay Control Input
Sensitivity
Delay :DEL[1|2] <value> 0 ns -5 ns … +230 ns
Phase :PHAS[1|2] <value> 0 see Delay
Pulse Width :WIDT[1|2] <value> 33.333333 ns 100 ps … (period -100 ps)
Duty Cycle :DCYC[1|2] <value> 50 % See Pulse Width
Deskew :DESK[1|2] <value> 0ps -10 ns … +10 ns
Polarity :POL[1|2] <value> NORMal NORMal|COMPlement
:PM[1|2]:SENS <value> 25 ps 25 ps | 250 ps
PULSe PULSe |SQUAre |DATa |PRBS,
<numeric>
23 (223 - 1) 5|6|7|8|9|10|11|12|13|14|15|23|
31
1 1, 2, 4, … 128
NRZ R1, RZ, NRZ
50 % 30 … 70 %
0 (disabled) 0| 1 | OFF | ON
NORMal NORMal, INVerted
NORMal NORMal|FAST|SMOoth
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 21
Page 22

SCPI Commands Reference Common Commands
Parameter SCPI Command Reset Value Range
Low Level :VOLT[0|1|2]:LOW
<value>
High :VOLT[0|1|2]:HIGH
<value>
Offset :VOLT[0|1|2]:OFFS
<value>
Amplitude :VOLT[0|1|2] <value> 100 mV 50 mV … 2.00 V
Term. Voltage :VOLT[0|1|2]:TERM
<value>
Limit to current levels :VOLT[1|2]:LIM <value> OFF OFF, ON
Data Length :DIG:PATT:LENG <value> 32 32 … 8192 (in increments of 32)
Clock Input
Termination
Clock Input Term.
Voltage
Trigger Output Mode :OUTP0:SOUR <value> PERiodic PERiodic, BITStream
Trigger Output Divider :OUTP0:DIV <value> 1 1, 2, 3, … (231 - 1)
Trigger Output High see High Level 50 mV -1.95 V … +3.00 V
Trigger Output Low see Low Level -50 mV -2.00 … +2.95 V
Trigger Output Term.
Voltage
Start Input Start Mode :ARM:SOUR <value> IMMediate IMMediate|MANual|EXTernal
Start Input Term.
Voltage
Start Input Threshold :ARM:LEV <value> 100 mV -2.00 … +3.00 V
Start Input Start On :ARM:SLOP <value> POS (rising) POS, NEG (rising/falling)
:TRIG:TERM:STATE
<value>
:TRIG:TERM <value> 0 mV -2.00 … +3.00 V
see Term. Voltage 0 mV -2.00 … +3.00 V
:ARM:TERM <value> 0 mV -2.00 … +3.00 V
-50 mV -2.00 V … +2.95 V
50 mV -1.95 V … +3.00 V
0 mV -1.975 V … +2.975 V
0 mV -2.00 V … +3.00 V
OFF ON, OFF
22 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 23

DIAGnostic Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:CAL:TIM
:DIAG:CHANnel[1|2]
:PPERformance[?]
:TEST?
DIAGnostic Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator DIAGnostic Commands.
Command Parameter Description
:CAL:TIM
:DIAG
:CHANnel[1|2]
:PPERformance[?] NORMal | FAST
| SMOoth
Commands in the User Interface The following figure shows how the DIAGnostic commands are
implemented in the 81133A/81134A user interface.
Calibrates the timing system of
the instrument
Sets/reads channel peak
performance
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 23
Page 24

SCPI Commands Reference DIAGnostic Commands
:CAL:TIM
Syntax
Form Set
Description Calibrates the timing system of the instrument.
NOTE Execution of this command can take about 15 minutes.
*RST value –
:CAL:TIM
:DIAG:CHANnel[1|2]:PPERformance
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command is used to modify the specified transition time of
:DIAG:CHAN[1|2]:PPER[?]
the signal.
For the specified transition time, please refer to the Technical
Specification delivered on the product CD.
Parameter NORMal|FAST|SMOoth
•Normal
Produces pulses with the standard transition time specified for
the instrument.
For the specified transition time, please refer to the Technical
Specification delivered on the product CD.
•Fast
Reduces the transition time. This leads to a higher slew rate but
more overshoot.
• Smooth
Produces a rounder output pulse, with lower slew rate and less
overshoot.
*RST value Normal
Example Set the Peak Performance to Fast.
:DIAG:CHANnel:PPER FAST
24 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 25

DIGital Commands SCPI Commands Reference
DIGital Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator DIGital commands:
Command Parameter Description
:DIGital[1|2]
[:STIMulus]
:PATTern
[:DATa][?] <data>, [HEX |
BIN | DUAL]
:LDATa <data>
:LENGth[?]
:SIGNal
:FORMat[?] RZ | NRZ | R1
:POLarity[?] NORMal |
:CROSsover
:[VALUE][?]
:STATe[?] ON | OFF | 1 | 0Switches crossover on/off
Numeric Sets/reads data pattern length
COMPlement |
INVerted
Numeric Sets/reads crossover
Sets/reads data in hexadecimal
(default), binary or dual format;
this command is for data pat
terns with maximum 8192 bits
Sets data in hexadecimal format; this command is for data
patterns larger than 8192 bits
in bits (32 ... 8192) in steps of 32
Sets/reads the signal mode
Sets/reads data polarity
-
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 25
Page 26

SCPI Commands Reference DIGital Commands
:DIGital[1|2]:PATTern:LENGth[?]
:DIGital[1|2]:PATTern:[DATa][?]
:DIGital[1|2]:SIGNal:FORMat[?]
:DIGital[1|2]:SIGNal:POLarity[?]
:DIGital[1|2]:SIGNal:CROSsover:[VALue][?]
:DIGital[1|2]:SIGNal:CROSsover:STATE[?]
Commands in the User Interface The following figures show how the DIGital commands are
implemented in the 81133A/81134A user interface.
26 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 27

DIGital Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:PATTern[:DATa]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command is used to set or read the pattern data of one of
:DIG[1|2][:STIM]:PATT[:DAT][?]
the channels. The minimum length of these patterns is 32 bits, the
maximum length is 8192 bits, the granularity is 32 bits. For
patterns larger than 8192 bits, see
“:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:PATTern:LDATa” on page 29.
The data can be written in either hexadecimal, binary or dual
format. The query returns the data in hexadecimal format.
For the command, the format is specified by the format parameter;
HEX is the default.
• Hexadecimal
With the hexadecimal format, the characters passed as the data
pattern will be interpreted as hexadecimal values.
The MSB of the first character becomes bit 0 of the data
pattern.
•Binary
With the binary format, the ASCII values of the characters
passed are used to build the data pattern.
•Dual
With the dual format, you can use “0” and “1” to build the data
pattern.
Parameter <data>, [HEX | BIN | DUAL]
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 27
Page 28

SCPI Commands Reference DIGital Commands
The <data> is an arbitrary block of program data as defined in
IEEE 488.2 7.7.6.2, for example:
#181CF1011E, HEX
# Start of block
1 Length of the length of the data
8 Length of the data (in bytes)
1CF1011E 32 bits of pattern data
HEX Data in hex format
#23201001001001001010100101010100110, DUAL
# Start of block
2 Length of the length of the data
32 Length of the data (in bytes)
010...110 32 bits of pattern data
DUAL Data in dual format
#14@@@@, BIN
# Start of block
1 Length of the length of the data
4 Length of the data (in bytes)
@@@@ 32 bits of pattern data
BIN Data in binary format
*RST value 4 bytes with the binary value 00010001
Example The examples above would be sent as follows:
:DIG:PATT #181CF1011E[, HEX]
:DIG:PATT?
>#181CF1011E
:DIG:PATT #23201001001001001010100101010100110, DUAL
:DIG:PATT?
>#1849254AA6
:DIG:PATT #14@@@@, BIN
:DIG:PATT?
>#1840404040
28 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 29

DIGital Commands SCPI Commands Reference
Max. pattern size =
Max. pattern size (@ freq)
Frequency divider
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:PATTern:LDATa
Syntax
Form Set
Description This command is used to program long data patterns in
Parameter <data>
:DIG[1|2][:STIM]:PATT:LDAT
hexadecimal format. The minimum length of these patterns is 128
bits, the maximum length is 12 Mbits, the granularity is 128 bits.
Patterns generated with this command are subject to various
restrictions (see below). See also
“:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:PATTern[:DATa]” on page 27.
The <data> is an arbitrary block of hex program data as defined in
IEEE 488.2 7.7.6.2, for example:
#532768AB03CDAD......
# Start of block
5 Length of the length of the data
32768 Length of the data
AB03CD... 32768 bytes of data for pattern
length of 131072 bits
Restrictions This command is subject to the following restrictions:
• Only pattern up to 12 Mbits and a granularity of 128 bits are
allowed.
• Because of hardware restrictions, a complete 12 Mbit pattern
can only be sent at higher frequency ranges:
Range Maximum Pattern Length
60 – 3360 Mhz 12 Mbit
30 – 60 Mhz 6 Mbit
15 – 30 Mhz 3 Mbit
• The frequency divider of a two- channel instrument also restricts
the maximum pattern. The following equation is valid:
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 29
Page 30

SCPI Commands Reference DIGital Commands
• The complete pattern is stored temporarily in the instrument. If
there are no restrictions to the maximum pattern length
regarding frequency and frequency divider, the complete pattern
will always be continually emitted. If there are restrictions to
the maximum pattern length, the stored pattern will be emitted
up to the maximum pattern length and then repeated from the
beginning.
• The channel mode must be data mode.
• The main mode of the instrument must be Pulse/Pattern. Burst
and RBurst mode are not allowed.
• The extended pattern is lost by any of the following actions:
– Modifying the pattern in the pattern editor of the user
interface
– Sending another pattern by :DIG:PATT:DATA or
:DIG:PATT:LDAT
– Changing channel mode or main mode of the instrument
– Recalling a setting or resetting the instrument
– Restarting the instrument
In all these cases, the pattern length is set to the actual data
length.
*RST value –
Example The above example would be sent as:
:DIG:PATT:LDAT #532768AB03CDAD......
30 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 31

DIGital Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:PATTern:LENGth
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Defines the length of the data pattern. If the current pattern is
Parameter Numeric
*RST value 32
Example Define a data pattern length of 64 bits.
:DIG[1|2][:STIM]:PATT:LENG[?]
longer than the new value for :LENGth, the pattern is truncated. If
the current pattern is shorter than the new value for :LENGth, the
pattern is lengthened and the new bits are set to ’0’.
Valid values are:
32 … 8192 in steps of 32.
:DIG:PATT:LENG 64
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:FORMat
Syntax
:DIG[1|2][:STIM]:SIGN:FORM[?]
Form Set & Query
Description This command is used to program the signal format for data and
PRBS signals:
Parameter RZ|NRZ|R1
•RZ
Return to Zero. A pulse of 50% duty cycle is generated for each
1.
•NRZ
Non- Return to Zero. A pulse of 100% duty cycle is generated for
each 1.
•R1
Return to One. A pulse of 100% duty cycle is generated for each
0.
*RST value NRZ
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 31
Page 32

SCPI Commands Reference DIGital Commands
Example Set data format to R1.
:DIG:SIGN:FORM R1
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:POLarity
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command is used to program the data polarity for Data and
NOTE This is not the same as the
Parameter NORMal|COMPlement|INVerted
*RST value NORMal
Example Logically invert the 32- bit data.
:DIG[1|2][:STIM]:SIGN:POL[?]
PRBS signals. The 32- bit data pattern is logically inverted, that is,
1 s are replaced with 0 s and vice versa.
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:POLarity[1|2]
command, which physically inverts the signal by swapping the
OUTPUT and
INVerted are synonyms (INVerted is included for backwards
compatibility).
:DIG:SIGN:POL INV
OUTPUT signals.
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal: CROSsover:[VALue]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description If variable crossover mode is enabled, this command specifies a
32 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
:DIG[1|2][:STIM]:SIGN:CROS[?]
value to adjust the crossover point of the NRZ signal in PRBS or
data mode, individually for each channel.
To enable the variable crossover mode, use
“:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal: CROSsover:[STATe]” on page 34.
The variable crossover is used to artificially close the eye pattern,
which simulates distortion.
Page 33

DIGital Commands SCPI Commands Reference
50 %
Normal
Out
50 %
Compl.
Out
70 %
Compl.
Out
Normal
Out
70 %
NOTE This parameter has no influence if the delay control input for the
channel is switched on (
:PM[1|2] ON
).
The figure below shows the normal and complement output with
the crossover point set to 50% and 70% respectively.
Parameter Numeric values (in %) in the range of 20 … 80.
*RST value 50
Example Set the variable crossover point to 70%.
:DIG:SIGN:CROS 70
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 33
Page 34

SCPI Commands Reference DIGital Commands
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal: CROSsover:[STATe]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description For each channel, the crossover mode of the NRZ signal in PRBS
Parameter ON|OFF|1|0
*RST value OFF|0
Example Enable the variable crossover mode.
:DIG[1|2][:STIM]:SIGN:CROS:STAT[?]
or data pattern mode can be enabled. This is used to artificially
close the eye pattern, simulating distortion.
If you enabled the variable crossover mode, specify the variable
crossover point with
CROSsover:[VALue]” on page 32.
:DIG:SIGN:CROS:STAT ON
“:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:
34 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 35

DISPlay Commands SCPI Commands Reference
DISPlay Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator DISPlay commands.
Command Parameter Description
:DISPlay
[:WINDow]
[:STATe][?] ON | OFF | 1 | 0Sets/reads front panel display
state
:DISPlay[:WINDow][:STATe]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command is used to turn the front panel display on and off.
NOTE The display is switched back on if a key on the instrument is
Parameter ON|OFF|1|0
*RST value ON
Example Switch off the front panel display.
:DISP[:WIND][:STAT][?]
Switching off the display improves the programming speed of the
instrument.
pressed. The command
:SYSTem:PRESet
back on.
:DISP OFF
to perform a
*RST
switches the display back on. Use
*RST
without switching the display
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 35
Page 36

SCPI Commands Reference MEASure Commands
:MEASure:FREQuency?
:MEASure:PERiod?
MEASure Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator MEASure commands:
Command Parameter Description
:MEASure
:FREQuency?
:PERiod?
Commands in the User Interface The following figure shows how the MEASure commands are
implemented in the 81133A/81134A user interface.
Read time base frequency
Read time base period
36 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 37

MEASure Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:MEASure:FREQuency?
Syntax
Form Query
Description This command is used to measure the operating frequency of the
NOTE The instrument is stopped when this command is executed. Thus,
NOTE When working in an automated test system, if the clock frequency
:MEAS:FREQ?
instrument.
In internal mode (
returned is the measured internal clock frequency (not the
programmed value).
In external mode (
is that measured at the Clock Input connector. If an invalid signal,
or no signal, is present at the Clock Input connector, a value of
zero is returned.
The query does not return a value immediately, but waits for the
internal frequency counter to complete its next measurement cycle.
This can take about half a second.
during the measurement, no signals will be output.
is known, it is better to set it directly instead of reading it from
the instrument. This is because:
:TRIGger:SOURce IMMediate
:TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal
) the frequency
) the frequency returned
• This method is faster since it eliminates the measurement time.
• The instrument is not stopped.
Parameter –
*RST value –
Example
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 37
:MEAS:FREQ?
Page 38

SCPI Commands Reference MEASure Commands
:MEASure:PERiod?
Syntax
Form Query
Description This command is used to read the operating period of the
NOTE The instrument is stopped when this command is executed. Thus,
NOTE When working in an automated test system, if the clock frequency
:MEAS:PER?
instrument.
In internal mode (
the internal clock period.
In external mode (
that measured at the Clock Input connector. If an invalid signal, or
no signal, is present at the Clock Input connector, a value of zero
is returned.
The query does not return a value immediately, as it waits for the
internal frequency counter to complete its next measurement cycle.
This can take about half a second.
during the measurement, no signals will be output.
is known, it is better to set it directly instead of reading it from
the instrument. This is because:
:TRIGger:SOURce IMMediate
:TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal
) the period returned is
) the period returned is
• This method is faster since it eliminates the measurement time.
• The instrument is not stopped.
Parameter –
*RST value –
Example
:MEAS:PER?
38 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 39

OUTPut Commands SCPI Commands Reference
OUTPut Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator OUTPut commands.
Command Parameter Description
:OUTPut
[0|1|2]:DIVider[?] Numeric | MIN |
MAX
[0]:SOURce[?] PERiodic |
BITStream
[0|1|2][:STATe][?] ON | OFF | 1 | 0
[1|2]:NEG[?] ON | OFF | 1 | 0
[1|2]:POS[?] ON | OFF | 1 | 0
:CENTral[?] ON | OFF | 1 | 0
Set/read channel frequency
divider
Set/read trigger source mode
Set/read channel outputs on
and off
Set/read negative channel
output on and off
Set/read positive channel output on and off
Set/read central output settings
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 39
Page 40

SCPI Commands Reference OUTPut Commands
:OUTPut[0]:DIVider[?]
:OUTPut[1]:DIVider[?]
:OUTPut:CENTral[?]
OUTPut[1]:NEG[?]
OUTPut[1]:POS[?]
:OUTPut[0|1|2][:STATe][?]
Commands in the User Interface The following figures show how the DIAGnostic commands are
implemented in the 81133A/81134A user interface.
40 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 41

OUTPut Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:OUTPut[0|1|2]:DIVider
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command is used to program the frequency divider
Parameter Numeric|MIN|MAX
:OUTP[0|1|2]:DIV[?]
parameters of the trigger output (0) and the channel outputs (1,
2).
The trigger output frequency is divided only when the trigger
output is in Pulse mode (
You can program the divider in Data mode (
BITstream
output to pulse mode.
The channel output frequency is divided in square and pulse
pattern mode only (
You can program the divider in data and PRBS pattern mode
(
[SOURce]:FUNCtion:MODe[1|2] DATa|PRBS
until you select the square or pulse pattern mode.
) but it will have no effect until you select the trigger
:OUTPut0:SOURce PERiodic
[SOURce]:FUNCtion:MODe[1|2] SQUare|PULSe
), but it will have no effect
).
:OUTPut0:SOURce
).
*RST value 1
Specified Limits For trigger output (channel 0): 1 ... 231 – 1
For channels 1 and 2: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128
Example Set Trigger Output Divider to 8.
:OUTP0:DIV 8
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 41
Page 42

SCPI Commands Reference OUTPut Commands
:OUTPut0:SOURce
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command programs the trigger output source mode.
:OUTP0:SOUR[?]
•PERiodic
This corresponds to Pulse mode on the front panel.
The trigger source is the internal clock, and a trigger pulse is
generated every clock period, unless the divider parameter has
been set to a value other than 1. The trigger signal always has
50% nominal duty cycle.
•BITStream
This corresponds to the Data mode on the front panel.
If the clock source is external, the trigger is always synchronized
to the clock with a fixed delay (± a few picoseconds over the
frequency range). PERiodic means that a trigger pulse is
generated for every X clocks, BITStream means that X is set to
the data length.
The trigger divider does not take the frequency divider of the
channels into account. For a frequency divider of n, n trigger
pulses are generated for each data packet, starting with the first
edge of bit 0 of the data packet.
To get one trigger pulse per data packet when the channel
divider factor is not equal to 1, the trigger mode must set to
Trigger on pulse and the divider to n x X, where n is the
frequency divider and X is the data length. For example, if the
data length = 32 bits and the frequency divider of channel 1 = 2,
the frequency divider of the trigger output has to be 64.
Parameter PERiodic|BITStream
*RST value PERiodic
Example Synchronize the trigger output signal to the data.
:OUTP0:SOUR BITS
42 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 43

OUTPut Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:OUTPut[0|1|2][:STATe]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Switches the trigger output and channel outputs on or off, where 0
Parameter ON|OFF|1|0
*RST value OFF
Example Switch on the channel 1 outputs.
:OUTP[0|1|2][:STAT][?]
is the trigger output.
For the two channel outputs, both OUTPUT and OUTPUT are
switched simultaneously. In query form, OFF is returned only if
both OUTPUT and
separately from the front panel, or by adding
command.
:OUTP1 ON
OUTPUT are off. They can be controlled
:POS
or
:NEG
to the
:OUTPut[1|2]:NEG
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Switches the specified channel OUTPUT on or off.
Parameter ON|OFF|1|0
*RST value OFF
Example Switch off the channel 1 OUTPUT.
:OUTP[1|2]:NEG[?]
:OUTP1:NEG OFF
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 43
Page 44

SCPI Commands Reference OUTPut Commands
:OUTPut[1|2]:POS
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Switches the specified channel OUTPUT on or off.
Parameter ON|OFF|1|0
*RST value OFF
Example Switch off the channel 1 OUTPUT.
:OUTP[1|2]:POS[?]
:OUTP1:POS OFF
:OUTPut:CENTral
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or reads the central output settings.
:OUTP:CENT[?]
The OFF command forces all outputs (trigger output and channel
outputs) to be switched off, the ON command switches on every
output that is set to on by the other
:OUTPut
commands.
Parameter ON|OFF|1|0
*RST value 1
Example Switches off all output channels.
:OUTP:CENT OFF
44 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 45
SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
SOURce Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator SOURce commands:
Command Parameter Description
[:SOURce]
:FUNCtion
[:SHAPe][?] PATTern|
BURSt, <numeric>|
RBURSt, <numeric>,
<numeric>
:MODE[1|2][?] PULSe|SQUare|
DATa|PRBS
<numeric>
:FREQuency
[:CW|:FIXed][?] Numeric
[GHz|MHz|kHz|Hz] |
MIN|MAX
:PHASe
[:ADJ][1|2][?] Numeric|MIN|MAX
[:PULSe]
:DCYCle[1|2][?] Numeric|MIN|MAX
:DELay[1|2][?] Numeric
[ps|ns|us|ms|s] |
MIN|MAX
:DESKew[1|2][?] Numeric
[ps|ns|us|ms|s]|
MIN|MAX
:DHOLd[1|2][?] DELay|PHASe
:PERiod[?] Numeric
[ps|ns|us|ms|s] |
MIN|MAX
:POLarity[1|2][?] NORMal|
COMPlement|
INVerted
:WIDTh[1|2][?] Numeric
[ps|ns|us|ms|s] |
MIN|MAX
Sets/reads instrument
mode
Sets instrument main
mode
Sets/reads internal
clock frequency
Sets/reads channel
phase
Sets/reads channel duty
cycle
Sets/reads channel delay
Sets/reads channel
deskew
Holds Delay|Phase fixed
with varying frequency
Sets/reads internal
clock period
Sets/reads channel
polarity
Sets/reads channel
width
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 45
Page 46

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
Command Parameter Description
PM[1|2][?] OFF|ON
:SENSitivity 25ps|250ps
:VOLTage
[0|1|2][:LEVel]
[:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude][?] Numeric [uV|mV|V]
|MIN|MAX
:OFFSet[?] Numeric [uV|mV|V]
|MIN|MAX
:HIGH[?] Numeric [uV|mV|V]
|MIN|MAX
:LOW[?] Numeric [uV|mV|V]
|MIN|MAX
:TERM[?] Numeric [uV|mV|V]
[1|2]:LIMit
[:AMPLitude]?
:OFFSet?
:HIGH?
:LOW?
:STATe[?] ON|OFF|1|0
Sets/reads jitter
modulation
Sets jitter modulation
sensitivity
Sets/reads channel
amplitude
Sets/reads channel
offset
Sets/reads channel
high-level
Sets/reads channel lowlevel
Sets/reads termination
voltage
Reads channel
amplitude limit
Reads channel offset
limit
Reads channel high-level
limit
Reads channel low-level
limit
Sets/reads limited
output mode on and off
46 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 47
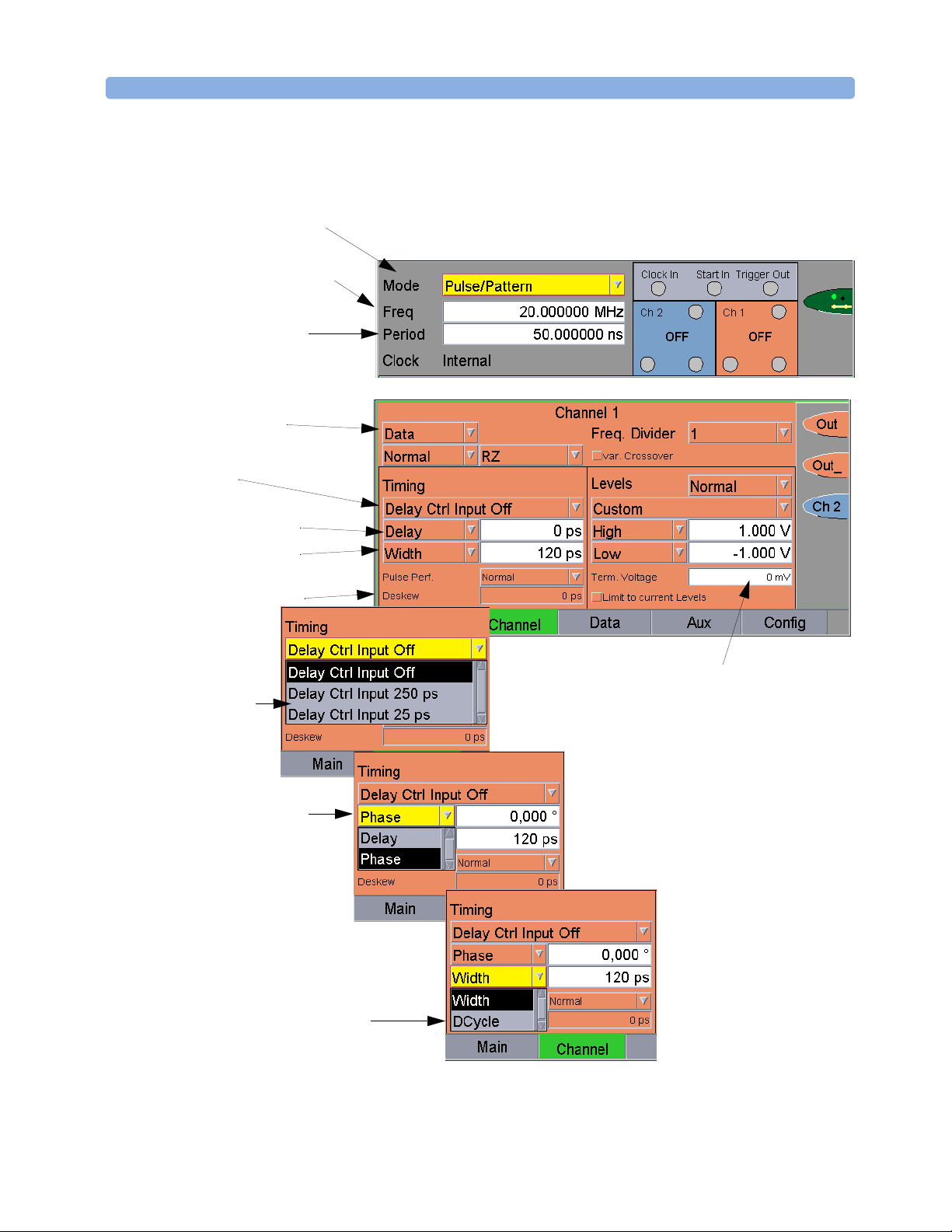
SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce]:FUNCtion[:SHAPe]
[:SOUR]:FREQ[:CW|:FIX][?]
[:SOUR][:PULS]:PER[?]
[:SOUR]:FUNC:MOD[1|2][?]
[:SOUR]:PHAS[:ADJ][1|2][?]
[:SOUR][:PULS]:DEL[1|2][?]
[:SOUR][:PULS]:DESK[1|2][?]
[:SOUR][:PULS]:DCYC[1|2][?]
[:SOUR][:PULS]:WIDT[1|2][?]
[:SOUR]:PM[1|2][?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT[0|1|2][:LEV][:IMM]:TERM[?]
Commands in the User Interface The following figures show how the DIAGnostic commands are
implemented in the 81133A/81134A user interface.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 47
Page 48

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LIM:STAT[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LEV[:IMM]:AMPL[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LEV[:IMM]:OFFS[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LEV[:IMM]:HIGH[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LEV[:IMM]:LOW[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LEV[:IMM]:TERM[?]
48 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 49

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOUR]:VOLT0:LEV[:IMM]:OFFS[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT0:LEV[:IMM]:AMPL[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT0:LEV[:IMM]:HIGH[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT0:LEV[:IMM]:LOW[?]
[:SOUR]:VOLT0:LEV[:IMM]:TERM[?]
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 49
Page 50

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOURce]:FUNCtion[:SHAPe]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Defines the main mode of the signal to be generated
Parameter PATTern|BURSt, <numeric>|RBURSt, <numeric>, <numeric>
[:SOUR]:FUNC[:SHAP][?]
(pulse/pattern, burst, or repetitive burst mode).
•PATTern
In this mode, each channel can be set independently to generate:
– Square waves of fixed width
– Pulses with selectable width or duty cycle
– Data in either RZ, R1 or NRZ format
– Pseudo random bit stream (PRBS) polynomials
To generate these signals, use “[:SOURce]:FUNCtion:MODe[1|2]”
on page 51.
• BURSt, <number of repeated data>
This mode enables you to generate a burst consisting of data
repeated n times followed by continuous zero data.
*RST value: 1
• RBURSt, <number of repeated data>, <p>
This mode enables you to generate a repeated burst consisting of
data repeated n times. A pause of zeros is inserted between two
successive bursts. The pause of zeros is calculated by:
Length of the pause = Burst Length × p
*RST values: 4, 4
*RST value PAT T
Example Generate a burst of data repeated 5 times:
:FUNC BURSt, 5
50 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 51

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce]:FUNCtion:MODe[1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Use this command to set the pattern mode for each channel. The
Parameter PULSe | SQUare | DATa | PRBS, <numeric>
[:SOUR]:FUNC:MOD[1|2][?]
pattern modes specify pulses, clocks, data patterns or PRBS
signals.
•SQUare
Generates a square wave (clock) of fixed width (50% duty cycle).
The frequency of the square wave can optionally be divided by
1,
2, 4, …, 128 with
•PULSe
Generates pulses with selectable width or duty cycle. The
frequency of the pulses can optionally be divided by 1, 2, 4,
…,
128 with
•DATa
Generates data in either RZ, R1 or NRZ format as specified with
:DIG[1|2][:STIM]:SIGN:FORM[?]
In RZ and R1 mode, the pulse width can be set. Set the pulse
width with
The frequency of the data can optionally be divided by 1, 2, 4,
…, 128 with
:OUTPut[1|2]:DIVider
[:SOUR][:PULS]:WIDT[1|2][?]
:OUTPut[1|2]:DIVider
:OUTPut[1|2]:DIVider
.
.
.
.
.
• PRBS, <numeric>
Generates a PRBS polynomial of selectable type in either RZ, R1
or NRZ format. In RZ and R1 mode, the pulse width can be set.
Set the pulse width with
The frequency of the PRBS signals can optionally be divided by
1,
2, 4, …, 128 with
Valid values are: 25–1 ... 231–1
*RST value PULSe
Example Generate a PRBS signal of 25–1 on channel 1:
1. Set the Pulse/Pattern mode:
[:SOUR]:FUNC[:SHAP] PATT
2. Set the PRBS signal:
[:SOUR]:FUNC:MOD[1|2] PRBS, 31
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 51
[:SOUR][:PULS]:WIDT[1|2][?]
:OUTPut[1|2]:DIVider
.
.
Page 52

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOURce]:FREQuency[:CW|:FIXed]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command programs the internal clock frequency, and also
Parameter Numeric [GHz|MHz|kHz|Hz] | MIN|MAX
Value coupling Period = 1 / Frequency
*RST value 15.0E6 Hz
Specified limits 15E6 ... 3.35E9 Hz, with overclocking up to 3.35E9 Hz
Example Select the clock with frequency 1.2 GHz.
[:SOUR]:FREQ[:CW|:FIX][?]
selects the internal clock as time base if it is not already selected.
:FREQ 1.2GHz
52 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 53

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce]:PHASe[:ADJ][1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command programs the pulse phase for a channel.
Parameter Numeric | MIN|MAX
Parameter Suffix DEG or RAD. A parameter without suffix is interpreted as degrees.
Functional coupling Programming the pulse phase also executes
Value coupling Delay = (Phase / 360) * Period
Range coupling Deskew
*RST value 0.0
Specified limits –6000° … +279000°, constrained by delay and period limits.
Absolute limits –6000° … +279000°, constrained by delay and period limits.
[:SOUR]:PHAS[:ADJ][1|2][?]
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:HOLD PHASe
constant when the signal frequency is changed.
so that the pulse phase is held
Example Set channel 1 phase delay to –180°.
:PHAS1 -180
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 53
Page 54

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DCYCle[1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command programs the duty cycle for a channel.
NOTE The duty cycle cannot be set:
Parameter Numeric|MIN|MAX
Functional coupling Programming the pulse duty cycle also executes
Value coupling Width = (duty cycle / 100) * Period
Range coupling Frequency, Period
[:SOUR][:PULS]:DCYC[1|2][?]
• In direct mode. To query the clock source, see
“:TRIGger:SOURce” on page 87.
• If signal mode is set to NRZ. To query the signal mode, see
“:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:FORMat” on page 31.
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:HOLD DCYCLE
constant when the signal frequency is changed.
so that the pulse duty cycle is held
*RST value 50% (derived from WIDth and PERiod)
NOTE The DCYCle command holds the PERiod and WIDth values in
proportion (if one value is increased 50 %, the other value is also
increased 50 %). Its limits are therefore dependent on the limits of
PERiod and WIDth.
Example Set channel 1 duty cycle to 66%.
:DCYC1 66
54 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 55

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DELay[1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command programs the pulse delay for a channel.
Parameter Numeric [ps|ns|us|ms|s]|MIN|MAX
Functional coupling Programming the pulse delay also executes the
Value coupling Phase = (Delay / Period) * 360
Range coupling Deskew
*RST value 0.0
Specified limits –5 ns … + 230 ns
Absolute limits –5 ns <= <value in absolute delay time> + <Deskew> <= 230 ns
Example Set Channel 1 Delay to 500 ps.
[:SOUR][:PULS]:DEL[1|2][?]
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DHOLD DELay
constant when the signal frequency is changed.
s so that the pulse delay is held
:DEL1 500PS
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 55
Page 56

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DESKew[1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command programs the deskew for a channel. The deskew
Parameter Numeric [ps|ns|us|ms|s]|MIN|MAX
Range coupling Delay, Phase
*RST value 0.0
Specified limits –10E–9 … 10E–9, but deskew and delay must be within the delay
Absolute limits –10E–9 … 10E–9
Example Set Channel 1 deskew to –155 ps.
[:SOUR][:PULS]:DESK[1|2][?]
allows you to move the zero-point of the delay (and phase)
parameter by ±
The final delay at the output is Delay + Deskew.
limits.
:DESK1 -155PS
10 ns.
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:DHOLd[1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Defines whether the pulse delay or the pulse phase of a channel is
Parameter DELay|PHASe
*RST value DELay
Example Hold Channel 1 Delay fixed when frequency varies.
56 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
[:SOUR][:PULS]:DHOL[1|2][?]
held constant when the signal frequency is changed.
:DHOL1 DEL
Page 57

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:PERiod
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command programs the internal clock period, and also selects
Parameter Numeric [ps|ns|us|ms|s]|MIN|MAX
Functional coupling Programming the signal period, or frequency, also executes
Value coupling Frequency = 1 / Period
Range coupling Width, Dutycycle, Phase and Pulse/Data mode selection.
*RST value 66.6 ns
Specified limits 299E–12 sec … 66.6E–9 sec
Instrument limits 297.61905E–12 sec … 66.66667E–9 sec
Example Select internal clock with period 750 ps.
[:SOUR][:PULS]:PER[?]
the internal clock time base if it has not already been selected.
:TRIGger:SOURce IMMediate
to select the internal clock.
:PER 750PS
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:POLarity[1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command programs the output polarity of a channel.
Parameter NORMal|COMPlement|INVerted
*RST value NORMal
Example Invert the Channel 1 outputs.
[:SOUR][:PULS]:POL[1|2][?]
COMPlement and INVerted are synonyms (INVerted is included for
backwards compatibility).
:POL1 INV
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 57
Page 58

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
NOTE This is not the same as the
:DIGital[1|2][:STIMulus]:SIGNal:POLarity
inverts the 32- bit data on the channels by swapping 1s with 0s
and vice- versa.
command, which logically
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:WIDTh[1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Programs the pulse width for a channel.
Parameter Numeric [ps|ns|us|ms|s]|MIN|MAX
Functional coupling Programming the pulse width also executes
Value coupling Dutycycle = (Width / Period) * 100
Range coupling Frequency, Period
*RST value 50% of Period
Specified limits 100E–12 … (Period – 100E–12) sec
Absolute limits 100 ps <= <value> <= <Period value> –100 ps && <value> < 10 ns
Example Set Channel 1 pulse width to 1 ns.
[:SOUR][:PULS]:WIDT[1|2][?]
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:HOLD WIDTh
constant when the signal frequency is changed.
so that the pulse width is held
:WIDT1 1NS
58 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 59

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce]:PM[1|2]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Enables the jitter modulation.
Parameter OFF|ON
*RST value OFF
Example Enable the jitter modulation on channel 1.
[:SOUR]:PM[1|2][?]
PM1 ON
[:SOURce]:PM[1|2]:SENSitivity
Syntax
Form Set
Description Sets jitter modulation sensitivity.
[:SOUR]:PM[1|2]:SENS
You now have to apply an external source (–0.5 V … 0.5 V max)
for jitter modulation to the Delay Control Input at the instrument’s
front panel:
• If you apply a source of 500 mV, the signal delay will be
increased by 250 ps/25 ps.
• If you apply a source of –500 mV, the signal delay will be
decreased by 250 ps/25 ps.
Between –500 mV and +500 mV, the signal delay
increases/decreases lineally to the Delay Control Input, for
example, a source of +200 mV results in a delay of 250 ps/V * 200
mV = 50 ps.
Parameter 25ps|250ps
Jitter modulation is turned on with fixed sensitivity of 50 ps/V or
500
ps/V.
*RST value 25 ps
Example Set the delay control input to 25 ps.
[:SOUR]:PM[1|2]:SENS 25ps
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 59
Page 60

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel] [:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Programs the amplitude of the output signal for the trigger output
Parameter Numeric [uV|mV|V] |MIN|MAX
Value coupling High = Offset + (Amplitude / 2)
Range coupling Offset
*RST value Trigger output (0): 100 mV
Specified limits Trigger output (0): 50 mV... 2.0 V
Absolute limits Trigger output (0): 2.0 V
[:SOUR]:VOLT[0|1|2][:LEV][:IMM][:AMPL][?]
and the channels.
Low = Offset – (Amplitude / 2)
Channels 1 and 2: 100 mV
Channels 1 and 2: 50 mV… 2.0 V
Channels 1 and 2: 2.0 V
Example Set Trigger Output amplitude to 1 V.
:VOLT0 1V
60 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 61

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel] [:IMMediate]:OFFSet
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Programs the offset of the output signal for the trigger output and
Parameter Numeric [uV|mV|V] |MIN|MAX
Value coupling High = Offset + (Amplitude / 2)
Range coupling Amplitude
*RST value Trigger output (0): 0 V
Specified limits Trigger channel (0): –1.975 V … +2.975 V
Example Set Trigger Output offset to –100 mV.
[:SOUR]:VOLT[0|1|2][:LEV][:IMM]:OFFS[?]
the channels.
Low = Offset – (Amplitude / 2)
Channels 1 and 2: 0 V
Channels 1 and 2: –1.975 V … +2.975 V
:VOLT0:OFFS -100MV
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 61
Page 62

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel] [:IMMediate]:HIGH
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Programs the high- level of the output signal for the trigger output
Parameter Numeric [uV|mV|V] |MIN|MAX
Value coupling Amplitude = High – Low
Range coupling Low- level
*RST value Trigger channel (0): 0.1 V
Specified limits Trigger channel (0): –1.95 … +3.0 V
Absolute limits Trigger output (0): –2.2 … +3.2 V
[:SOUR]:VOLT[0|1|2][:LEV][:IMM]:HIGH[?]
and the channels.
Offset = (High – Low) / 2
Channels 1 and 2: 0.1 V
Channels 1 and 2: –1.95 ... +3.0 V
Channels 1 and 2: –2.2 … +3.2 V
Example Set Channel 1 high- level to –200 mV.
:VOLT1:HIGH -200MV
62 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 63

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel] [:IMMediate]:LOW
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Programs the low- level of the output signal for the trigger output
Parameter Numeric [uV|mV|V] |MIN|MAX
Value coupling Amplitude = High – Low
Range coupling High- level
*RST value Trigger channel (0): 0.0 V
Specified limits Trigger channel (0): –2.0 … +2.95 V
Absolute limits Trigger output (0): –2.2 … +3.2 V
[:SOUR]:VOLT[0|1|2][:LEV][:IMM]:LOW[?]
and the channels.
Offset = (High – Low) / 2
Channels 1 and 2: 0.0 V
Channels 1 and 2: –2.0 … +2.95 V
Channels 1 and 2: –2.2 … +3.2 V
Example Set Channel 1 low-level to –1 V.
:VOLT1:LOW -1V
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 63
Page 64

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0|1|2][:LEVel] [:IMMediate]:TERM
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Programs the termination voltage of the output signal for the
Parameter Numeric [uV|mV|V]
*RST value Trigger output (0): 0.0 V
Specified limits Trigger output (0): –2.0 V … +3.0 V
Example Set Channel 1 termination voltage to 1 V.
[:SOUR]:VOLT[0|1|2][:LEV][:IMM]:TERM[?]
trigger output and the channels.
Channels 1 and 2: 0.0 V
Channels 1 and 2: –2.0 V … +3.0 V
:VOLT1:TERM 1V
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit [:AMPLitude]?
Syntax
Form Query
Description Reads the current setting of the amplitude limit. The result is only
*RST value 100 mV
Example Read Channel 1 amplitude limit.
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LIM[:AMPL]?
valid if the “Limit to current levels” output mode is currently on
(
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:STATe ON
:VOLT1:LIM?
).
64 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 65

SOURce Commands SCPI Commands Reference
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:OFFSet?
Syntax
Form Query
Description This command reads the current setting of the offset limit. The
*RST value 0 mV
Example Read Channel 1 offset limit.
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LIM:OFFS?
result is only valid if “Limit to current levels” output mode is
currently on (
:VOLT1:LIM:OFFS?
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:STATe ON
).
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:HIGH?
Syntax
Form Query
Description This command reads the current setting of the high- level limit. The
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LIM:HIGH?
result is only valid if Limited output mode is currently on
(
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:STATe ON
).
*RST value 100 mV
Example Read Channel 1 high- level limit.
:VOLT1:LIM:HIGH?
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:LOW?
Syntax
Form Query
Description This command reads the current setting of the low- level limit. The
*RST value 0 V
Example Read Channel 1 low-level limit.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 65
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LIM:LOW?
result is only valid if “Limit to current values” mode is currently
on (
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:STATe ON
:VOLT1:LIM:LOW?
).
Page 66

SCPI Commands Reference SOURce Commands
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:STATe
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Switches the “Limit to current values” output mode on or off.
Parameter ON|OFF|1|0
*RST value OFF
Example Switch on Channel 1 Limited output mode.
[:SOUR]:VOLT[1|2]:LIM:STAT[?]
When you switch on Limited output mode the current high-level
and low-level parameters are taken as limit values restricting the
available ranges of all output- level parameters. You cannot program
the output- levels beyond these temporary limits, until you switch
off Limited output mode. The limits apply whether you program
high/low levels or amplitude/offset levels.
:VOLT1:LIM:STAT ON
66 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 67

Status Handling Commands SCPI Commands Reference
+
+
+
0
1
2
15
0
1
2
15
:QUEStionable:VOLTage
(not used)
:QUEStionable:FREQuency
Frequency Range
PLL Unlocked
Ext. Ref. Missing
0
1
2
15
:QUEStionable:MONotony
(not used)
0
1
2
3
*ESR?
Operation Complete
Query Error
Standard Event Status
4
5
6
7
Device Dep. Error
Execution Error
Command Error
Power On
0
1
2
3
Questionable Status
4
5
6
7
8
9
15
0
1
2
15
Operation Status
(not used)
+
+
+
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
*STB?
Standard Byte
Status Handling Commands
The IEEE 488.2 specification requires status registers that contain
information about the instrument’s hardware and firmware. For
the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator, the status registers
have the following structure:
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 67
Page 68

SCPI Commands Reference Status Handling Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator Status Handling Commands:
Command Parameter Description
:STATus
:OPERation
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:ENABle[?]
:NTRansition[?]
:PTRansition[?]
:PRESet
:QUEStionable
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:ENABle[?]
:NTRansition[?]
:PTRansition[?]
:VOLTage
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:ENABle[?]
:NTRansition[?]
:PTRansition[?]
:FREQuency
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:ENABle[?]
Numeric Sets/reads operation enable register
Numeric Sets/reads operation negative-
Numeric Sets/reads operation positive-
Numeric Sets/reads questionable enable
Numeric Sets/reads questionable negative-
Numeric Sets/reads questionable positive-
Numeric Sets/reads questionable voltage
Numeric Sets/reads questionable voltage
Numeric Sets/reads questionable voltage
Numeric Sets/reads questionable frequency
Reads operation event register
Reads operation condition register
transition filter
transition filter
Clears and presets status groups
Reads questionable event register
Reads questionable condition
register
register
transition filter
transition filter
Reads questionable voltage event
register
Reads questionable voltage condition
register
enable register
negative-transition register
positive-transition register
Reads questionable frequency event
register
Reads questionable frequency
condition register
enable register
68 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 69

Status Handling Commands SCPI Commands Reference
Command Parameter Description
:NTRansition[?]
:PTRansition[?]
:MONotony
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:ENABle[?]
:NTRansition[?]
:PTRansition[?]
Numeric Sets/reads questionable frequency
negative-transition register
Numeric Sets/reads questionable frequency
positive-transition register
Reads questionable monotony event
register
Reads questionable monotony
condition register
Numeric Sets/reads questionable monotony
enable register
Numeric Sets/reads questionable monotony
negative-transition register
Numeric Sets/reads questionable monotony
positive-transition register
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 69
Page 70

SCPI Commands Reference Status Handling Commands
:STATus:OPERation
This command tree accesses the OPERation status group.
The OPERation status group is not used by the Agilent
81133A/81134A Pulse Generator, therefore this command tree is
redundant.
:STATus:PRESet
Syntax
Form Event
Description This command
:STAT:PRES
• clears all status group event- registers
• clears the error queue
• presets the status group enable, PTR, and NTR registers as
follows
Status Group Register Preset Value
OPERation ENABle 0000000000000000
QUEStionable ENABle 0000000000000000
QUEStionable:VOLTage ENABle 0111111111111111
QUEStionable:FREQuency ENABle 0111111111111111
QUEStionable:MONotony ENABle 0111111111111111
:
PTR 0111111111111111
NTR 0000000000000000
PTR 0111111111111111
NTR 0000000000000000
PTR 0111111111111111
NTR 0000000000000000
PTR 0111111111111111
NTR 0000000000000000
PTR 0111111111111111
NTR 0000000000000000
Parameter –
*RST value –
70 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 71

Status Handling Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:STATus:QUEStionable
This command tree accesses the QUEStionable status group.
The QUEStionable status group contains the summary bits from
the QUEStionable:VOLTage, :FREQuency and MONotony status
group.
The following commands are used to access the registers within
the status group.
:STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt]?
Syntax
Form Query
Description Reads the event register in the QUEStionable status group.
Parameter –
*RST value –
:STAT:QUES[:EVEN]?
:STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Syntax
Form Query
Description Reads the condition register in the QUEStionable status group.
NOTE The Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator does not use this
:STAT:QUES:COND?
condition register, therefore, this command is redundant.
Parameter –
*RST value –
:STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the enable register in the QUEStionable status
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 71
:STAT:QUES:ENAB[?]
group.
Page 72

SCPI Commands Reference Status Handling Commands
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STATus:QUEStionable:NTRansition
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the negative- transition register in the QUEStionable
NOTE The Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator does not use the
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STAT:QUES:NTRansition[?]
status group.
transition registers of the QUEStionable status group, therefore,
this command is redundant.
:STATus:QUEStionable:PTRansition
Syntax
:STAT:QUES:PTRansition[?]
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the positive- transition register in the QUEStionable
status group.
NOTE The Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator does not use the
transition registers of the QUEStionable status group, therefore,
this command is redundant.
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
72 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 73

Status Handling Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:STATus:QUEStionable:VOLTage
This command tree accesses the QUEStionable:VOLTage status
group.
The QUEStionable:VOLTage status group monitors the currently
programmed output voltage levels against their specified ranges.
The following commands are used to access the registers within
the status group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:VOLTage[:EVENt]?
Syntax
Form Query
Description Reads the event register in the QUEStionable:VOLTage status
Parameter –
*RST value –
:STAT:QUES:VOLT[:EVEN]?
group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:VOLTage:CONDition?
Syntax
Form Query
Description Reads the condition register in the QUEStionable:VOLTage status
Parameter –
*RST value –
:STAT:QUES:VOLT:COND?
group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:VOLTage:ENABle
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the enable register in the QUEStionable:VOLTage
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 73
:STAT:QUES:VOLT:ENAB[?]
status group.
Page 74

SCPI Commands Reference Status Handling Commands
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STATus:QUEStionable:VOLTage:NTRansition
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the negative- transition register in the
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STAT:QUES:VOLT:NTR[?]
QUEStionable:VOLTage status group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:VOLTage:PTRansition
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the positive- transition register in the
:STAT:QUES:VOLT:PTR[?]
QUEStionable:VOLTage status group.
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STATus:QUEStionable:FREQuency
This command tree accesses the QUEStionable:FREQuency status
group.
The QUEStionable:FREQuency status group monitors the currently
programmed frequency against the specified range, detects if the
PLL in unlocked and indicates if there is a valid signal at the time
base external input.
The following commands are used to access the registers within
this status group.
74 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 75

Status Handling Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:STATus:QUEStionable:FREQuency[:EVENt]?
Syntax
Form Query
Description Reads the event register in the QUEStionable:FREQency status
Parameter –
*RST value –
:STAT:QUES:FREQ[:EVEN]?
group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:FREQuency:CONDition?
Syntax
Form Query
Description Reads the condition register in the QUEStionable:FREQency status
Parameter –
:STAT:QUES:FREQ:COND?
group.
*RST value –
:STATus:QUEStionable:FREQuency:ENABle
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the enable register in the QUEStionable:FREQency
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STAT:QUES:FREQ:ENAB[?]
status group.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 75
Page 76

SCPI Commands Reference Status Handling Commands
:STATus:QUEStionable:FREQuency:NTRansition
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the negative- transition register in the
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STAT:QUES:FREQ:NTR[?]
QUEStionable:FREQency status group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:FREQuency:PTRansition
Syntax
FormForm Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the positive- transition register in the
:STAT:QUES:FREQ:PTR[?]
QUEStionable:FREQency status group.
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STATus:QUEStionable:MONotony
This command tree accesses the QUEStionable:MONotony status
group.
The QUEStionable:MONotony status group monitors the frequency,
width, delay and amplitude parameters. The range of these
parameters is made up of several internal ranges and when the
parameter moves from one internal range to the next a
discontinuity can occur. For example, increasing the frequency at a
range boundary could cause the actual output frequency to
decrease slightly. The range boundaries also vary with temperature,
and a significant temperature change could cause the instrument
to move to the next range in order to maintain the current
parameter within specification.
76 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 77

Status Handling Commands SCPI Commands Reference
When a parameter range change occurs, the corresponding bit in
the QUEStionable:MONotony status event register is set to indicate
that the output signal may not vary monotonically with the
programmed parameter value.
The following commands are used to access the registers within
the status group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:MONotony[:EVENt]?
Syntax
Form Query
Description This command reads the event register in the
Parameter –
*RST value –
:STAT:QUES:MON[:EVEN]?
QUEStionable:MONotony status group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:MONotony:CONDition?
Syntax
Form Query
Description This command reads the condition register in the
NOTE The Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator does not use the
:STAT:QUES:MON:COND?
QUEStionable:MONotony status group.
condition register of the QUEStionable:MONotony status group,
therefore, this command is redundant.
Parameter –
*RST value –
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 77
Page 78

SCPI Commands Reference Status Handling Commands
:STATus:QUEStionable:MONotony:ENABle
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the enable register in the QUEStionable:MONotony
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STAT:QUES:MON:ENAB[?]
status group.
:STATus:QUEStionable:MONotony:NTRansition
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets or queries the negative- transition register in the
:STAT:QUES:MON:NTR[?]
QUEStionable:MONotony status group.
NOTE The Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator does not use the
transition registers of the QUEStionable:MONotony status group,
therefore, this command is redundant.
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
:STATus:QUEStionable:MONotony:PTRansition
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command sets or queries the positive- transition register in
:STAT:QUES:MON:PTR[?]
the QUEStionable:MONotony status group.
78 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 79

SYSTem Commands SCPI Commands Reference
NOTE The Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator does not use the
transition registers of the QUEStionable:MONotony status group,
therefore, this command is redundant.
Parameter Numeric
*RST value –
Specified limits 0 … 32767
SYSTem Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator SYSTem Commands:
Command Parameter Description
:SYSTem
:ERRor?
:KEY[?]
:PRESet
:SET[?]
:VERSion?
:COMMunicate
:LAN
[:SELF]
:ADDRess
:SMASk
:DGATeway
Numeric Simulates key press or reads key
Block data Sets/reads complete instrument
String Sets/reads instrument's LAN
String Sets/reads subnet mask of current
String Sets/reads default Gateway for the
Reads error queue
queue
*RST without changing display state
setting
Reads SCPI compliance version
address. String format is A.B.C.D
with A,B,C,D is number between 1
and 255
LAN. String format is similar to
:ADDR
instrument. String format is similar
to :ADDR
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 79
Page 80

SCPI Commands Reference SYSTem Commands
:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDR
:COMMunicate::LAN[:SELF]:ADDRess
:COMMunicate::LAN[:SELF]:SMASk
:COMMunicate::LAN[:SELF]:DHCP
:COMMunicate::LAN[:SELF]:DGATeway
Command Parameter Description
:HADDRess
:NAME
:DHCP 1|0|ON|OFF
:GPIB
[:SELF]
:ADDR
String Set/read host LAN address for the
alphanumeric Sets the LAN name for the
Numeric Sets/reads GPIB bus No. A value
instrument. This setting is important
for FTP transfer
instrument
Enables/disables DHCP
configuration
between 0 to 30 is required
80 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 81

SYSTem Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:SYSTem:ERRor?
Syntax
Form Query
Description This command is used to read the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Parameter –
*RST value –
:SYST:ERR?
Generator error queue. The Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator error queue can store up to 32 error codes on a firstin- first- out basis. When you read the error queue, the error
number and associated message are put into the instrument’s
output buffer.
If the error queue is empty, the value 0 is returned, meaning No
Error. If the queue overflows at any time, the last error code is
discarded and replaced with –350 meaning Queue Overflow.
Refer to “Troubleshooting” on page 97 for a list of the error
messages.
:SYSTem:PRESet
Syntax
Form Event
Description This command is equivalent to
Parameter –
*RST value –
:SYST:PRES
to the
if you want the display to remain switched off during program
execution.
:DISPlay[:WINDow][:STATe]
*RST
, except that there is no change
. Use this command instead of
*RST
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 81
Page 82

SCPI Commands Reference SYSTem Commands
:SYSTem:SET
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description In query form, the command reads a block of data containing the
Parameter Block data
:SYST:SET[?]
instrument’s complete setup. The setup information includes all
parameter and mode settings, but does not include the contents of
the instrument setting memories, the status group registers or the
:DISPlay[:WINDow][:STATe]
ASCII, and cannot be edited.
In set form, the block data must be a complete instrument setup
that was produced with the query form of this command.
. The data is in a binary format, not
:SYSTem:VERSion?
Syntax
Form Query
:SYST:VERS?
Description This command reads the SCPI revision to which the instrument
complies.
*RST value –
82 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 83

SYSTem Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:DHCP
Syntax
Form Set
Description Enables/disables the DHCP.
Parameter 1|0|ON|OFF
*RST value –
:SYST:COMM:LAN[:SELF]:DHCP
•DHCP enabled
If DHCP is enabled, the instrument will request its own LAN
settings from the network. You only need to specify the LAN
name with
page 83.
•DHCP disabled
If DHCP is disabled, you have to set the instrument IP address,
subnet mask, gateway and host address with:
– “:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF] :ADDRess” on page 84
– “:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF] :SMASk” on page 84
– “:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF] :DGATeway” on page 85
“:SYSTEM:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:NAME” on
Example
Disable DHCP:
:SYST:COMM:LAN[:SELF]:DHCP OFF
:SYSTEM:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:NAME
Syntax
Form Set
Description Sets the LAN name. This command is only necessary for DHCP.
Parameter alphanumeric
*RST value –
Example
:SYST:COMM:LAN[:SELF]:NAME <LAN name>
:SYST:COMM:LAN:NAME PP81134A01
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 83
Page 84

SCPI Commands Reference SYSTem Commands
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF] :ADDRess
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets the instrument's IP address.
NOTE This parameter must only be set if DHCP is not available. See
Parameter String <no>.<no>.<no>.<no> in quotes, where <no> is in the range 1
*RST value –
Example
:SYST:COMM:LAN[:SELF]:ADDR[?]
“:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:DHCP” on page 83.
… 255.
:SYST:COMM:LAN:ADDR "150.215.17.9"
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF] :SMASk
Syntax
:SYST:COMM:LAN[:SELF]:SMAS[?]
Form Set & Query
Description Sets the instrument’s subnet mask.
NOTE This parameter must only be set if DHCP is not available. See
“:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:DHCP” on page 83.
Parameter String <no>.<no>.<no>.<no> in quotes, where <no> is in the range 0
… 255.
*RST value –
Example
:SYST:COMM:LAN:SMAS "255.255.240.000"
84 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 85

SYSTem Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF] :DGATeway
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets the instrument’s gateway.
NOTE This parameter must only be set if DHCP is not available. See
Parameter String <no>.<no>.<no>.<no> in quotes, where <no> is in the range 1
*RST value –
Example
:SYST:COMM:LAN[:SELF]:DGAT[?]
“:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN[:SELF]:DHCP” on page 83.
… 255.
:SYST:COMM:LAN:DGAT "150.215.001.001"
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDR
Syntax
Form Set & Query
:SYST:COMM:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDR[?]
Description Sets/reads the instrument’s GPIB bus number.
Parameter Numeric
*RST value 13
Example
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 85
:SYST:COMM:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDR 15
Page 86

SCPI Commands Reference TRIGger Commands
:TRIG:SOUR[?]
:TRIG::TERM[?]
:TRIG::TERMSTATe[?]
TRIGger Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator TRIGger Commands:
Command Parameter Description
:TRIGger
:SOURce[?] IMMediate|EXTernal
|
REFerence|
IDIRect|
EDIRect
:TERM[?] Numeric [uV|mV|V]
:TERMSTATe[?] ON|OFF
Sets/reads timebase mode
internal, external, external 10 MHz
reference, internal direct and
external direct
Sets/reads termination voltage
Sets/reads termination state.
Defines whether the external clock
input (Clock In) connector is AC or
DC terminated
86 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 87

TRIGger Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:TRIGger:SOURce
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description This command is used to switch the timebase mode between
Parameter IMMediate|EXTernal|REFerence|IDIRect|EDIRect
:TRIG:SOUR[?]
Internal (
With
(or period) is controlled with the
[:SOURce][:PULSe]:PERiod
With
controlled by the external signal applied to the external clock
input connector (Clock In).
•IMMediate
The clock is derived from the internal oscillator.
•EXTernal
Enables the external clock input (Clock In) to accept an external
clock signal that forms the time base. The frequency is measured
once by selecting the Measure function from the user interface
or as a remote SCPI command (
This value is then used to calculate frequency- dependent values,
like the pulse width or the phase (available at the Channel
page).
IMMediate
:TRIGger:SOURce IMMediate
:TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal
) and External (
) command.
EXTernal
(internal timebase) the frequency
[:SOURce]:FREQuency
, the frequency (or period) is
:MEASure:FREQuency?
).
(or
).
•REFerence
Enables the external clock input (Clock In) to apply a 10 MHz
reference clock. This clock is used as a reference for all timing
parameters.
• IDIRect|EDIRect
The direct modes allow changes of frequency without dropouts
in the range of 1:2. They are used for applications (precise clock
source), where dropouts would make a measurement impossible,
for example, PLL frequency sweep and micro processor clock
sweep.
–IDIRect
Allows you to vary the clock derived from the internal
oscillator in the range of one octave.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 87
Page 88

SCPI Commands Reference TRIGger Commands
–EDIRect
Allows you to vary the frequency of the external clock signal
in the range of one octave.
Range switching occurs at the following frequency values:
• 1680 MHz
• 840 MHz
• 420 MHz
• 210 MHz
• 105 MHz
• 51.5 MHz
• 25.75 MHz
These values are based on 1680 MHz, subject to the frequency
divider.
*RST value IMMediate
Example Select the external timebase mode.
:TRIG:SOUR EXT
:TRIGger:TERM
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets/reads the termination voltage for the external clock input. See
NOTE The termination voltage can only be specified if the Clock In
Parameter Numeric [uV|mV|V]
*RST value 0 mV
:TRIG:TERM[?]
“:TRIGger:SOURce” on page 87.
connector is DC terminated.
Specified limits –2.0 V … 3.0 V
Example Set the termination voltage of the signal applied to the external
clock input to 1V.
:TRIG:TERM 1V
88 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 89

TRIGger Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:TRIGger:TERM:STATE[?]
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Defines whether the external clock input connector (Clock In) is
Parameter ON|OFF where ON = DC and OFF = AC terminated.
*RST value OFF
Example Set the coupling of the external clock input connector to DC.
:TRIG:TERM:STATE[?]
AC or DC terminated.
:TRIG:TERM:STATE ON
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 89
Page 90

SCPI Commands Reference ARM Commands
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:LEV
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:TERM[?]
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:SLOP
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY][:START]
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:SOURce
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:STOP
ARM Commands
The following table shows the Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse
Generator ARM Commands:
Command Parameter Description
:ARM
[:SEQuence]
[:LAYer]
:LEVel Numeric[mV|V]
:SLOPe POSitive|NEGative
:SOURce IMMediate|
MANual|EXTernal
:TERM[?] Numeric [mV|V]
[:STARt]
:STOP
The following figure shows how the ARM commands are
implemented in the 81133A/81134A user interface.
External start input
Sets the trigger threshold
Trigger set to leading/trailing edge
of external signal
Sets the start input to
disabled/manual (by key)/external
started
Sets/reads termination voltage
Starts signal output
Stops signal output
90 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 91

ARM Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:LEVel
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Specifies the threshold voltage for the external start signal.
NOTE The threshold can only be specified if the external start mode is
Parameter Numeric [mV|V]
Specified limits –2 V … 3.0 V
Absolute limits –2.0 V … 3.0 V
*RST value 100 mV
Example Sets the threshold voltage to 2.0 V.
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:LEV
selected (
:ARM:LEV 2.0 V
“:ARM:SOURce EXT”)
.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 91
Page 92

SCPI Commands Reference ARM Commands
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:SLOPe
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Specifies whether the signal is generated at the rising or falling
NOTE The threshold can only be specified if the external start mode is
Parameter POSitive|NEGative
*RST value POS
Example Specifies that the signal is generated at the falling edge.
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:SLOP
edge of the external start signal.
selected (
•POSitive
The signal is generated at the rising edge.
•NEGative
The signal is generated at the falling edge.
:ARM:SLOP NEG
“:ARM:SOURce EXT”)
.
92 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 93

ARM Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:SOURce
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Specifies when the generated signal is output immediately, by
Parameter IMMediate|MANual|EXTernal
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:SOUR
manual start or depending on an external signal at the Start In
connector.
The instrument provides the following start modes:
•IMMediate
The generated signal is always available at the outputs (assumed
that the outputs are enabled).
•MANual
The generated signal is output after Start at the instrument
panel is pressed.
•EXTernal
Select this start mode to send the generated signal to the
outputs depending on the external signal applied at the Start In
connector.
You can define the following parameters that the external signal
must meet:
– Threshold (voltage)
Set the threshold with “:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:LEVel” on
page 91.
– Termination voltage
Set the termination voltage with
“:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:TERM” on page 94.
– Edge (rising/falling)
Set the edge with “:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:SLOPe” on
page 92.
*RST value
Example Set the start mode to external.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 93
IMMediate
:ARM:SOUR EXT
Page 94

SCPI Commands Reference ARM Commands
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:TERM
Syntax
Form Set & Query
Description Sets/reads the termination voltage for the start input signal.
Parameter Numeric [mV|V]
Specified limits –2.0 V … 3.0 V
*RST value 0 mV
Example Set the termination voltage to 1 V.
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:TERM[?]
:ARM:TERM 1V
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer][:STARt]
Syntax
Form Event
Description Puts the instrument in armed mode. This means, that the
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY][STAR]
instrument waits for the selected edge to appear.
NOTE The instrument can only be put in armed mode if the external
start mode is selected (
Parameter –
*RST value –
Example Set the armed mode:
:ARM
“:ARM:SOURce EXT”)
.
94 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 95

ARM Commands SCPI Commands Reference
:ARM[:SEQuence][:LAYer]:STOP
Syntax
Form Event
Description Deactivates the armed mode for the instrument.
Parameter –
*RST value –
Example Deactivate the armed mode:
:ARM[:SEQ][:LAY]:STOP
:ARM:STOP
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 95
Page 96

SCPI Commands Reference ARM Commands
96 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 97

Troubleshooting
This chapter provides basic troubleshooting tips that you can use if
the instrument is not performing as expected.
Error Generated
The instrument generates error messages as follows:
-221:Settings conflict:String describing the error
The string describing the error could be one of the following:
• "divider of channel [1|2] leads to a frequency below minimum
frequency"
This occurs if the frequency below one of the channels is set
below the minimum (15 MHz). This could happen if the
frequency is decreased or if the frequency divider is increased.
• "pulsewidth of channel [1|2] is too small"
May happen:
– If the frequency is decreased and the channel is in duty
mode, or
– if the signal mode is switched from NRZ to RZ or R1, or
– if clock mode is switched from internal/external direct to a
none direct mode
• "pulse width of channel [1|2] is too large"
May happen:
– If the frequency is increased and the channel is in duty mode,
or
– if the signal mode is switched from NRZ to RZ or R1, or
– if clock mode is switched from internal/external direct to a
none direct mode.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 97
Page 98

Troubleshooting
• "delay of channel [1|2] below minimum"
May happen:
– If the frequency is decreased and the channel is in phase
mode, or
– if the square mode is switched from square to another mode,
or
– if clock mode is switched from internal/external direct to a
none direct mode.
• "delay of channel [1|2] above maximum"
May happen:
– If the frequency is increased and the channel is in phase
mode, or
– if the channel mode is switched from SQUARE to another
mode, or
– if clock mode is switched from internal/external direct to a
none direct mode.
• "amplitude of trigger is too small"
May happen:
– If the trigger high level is decreased, or
– if the low level is increased.
• "amplitude of channel [1|2] is too small"
May happen:
– If the channel high level is decreased, or
– if the low level is increased.
• "amplitude of trigger is too large"
May happen:
– If the trigger high level is increased, or
– if the low level is decreased.
• "amplitude of channel [1|2] is too large"
May happen
– If the channel high level is increased, or
– if the low level is decreased.
• "low level of trigger is below minimum"
May happen:
98 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
Page 99

– If the trigger amplitude is increased, or
– if the offset is decreased.
• "low level of channel [1|2] is below minimum"
May happen:
– If the channel amplitude is increased, or
– if the offset is decreased.
• "high level of trigger exceeds maximum"
May happen:
– If the trigger amplitude is increased, or
– if the offset is increased.
• "high level of channel [1|2] exceeds maximum"
May happen:
– If the channel amplitude is increased, or
Troubleshooting
– if the offset is increased.
• "high level of trigger is lower than low level"
May happen:
– If the trigger amplitude is set to a negative value, or
– if high level and low level are set in parallel by list of
semicolon- separated SCPI commands.
• "high level of channel [1|2] is lower than low level"
May happen:
– If the channel amplitude is set to a negative value, or
– if high level and low levels are set in parallel by list of
semicolon- separated SCPI commands.
Instrument not Operable via LAN
If the instrument cannot be programmed via LAN, make sure that
you have installed the latest Agilent I/O library on your computer.
Visit the Agilent web site for the newest version.
Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007 99
Page 100

Troubleshooting
100 Agilent 81133A/81134A Pulse Generator Programming Guide, March 2007
 Loading...
Loading...