
H
Reference
Guide
HP 81130A 400/660MHz
Pulse/Data Generator

Front Panel Display and Softkeys
Mode / Parameter Area Modify / Enter Area
Use the CURSOR keys to
move the entry focus to a
mode, parameter format,
Channel 1
Column
or
parameter value
Channel 2
Column
Use the KNOB to select a
mode or modify parameters
and formats
Press ENTER or a UNIT key to
confirm parameter changes
ON Freq 50.00MHz OFF
1
OFF OFF
Entry
Focus
Delay
DtyCyc
Press a SOFTKEY to access
the required entry screen
0ps
50.0%
Screen Selection Area
Delay 0ps
Width 100.0ns
TIMING PATTERNLEVELSMODE/TRG
2
MODIFY
50.0
%
GRAPH
MORE
Press MORE key to access
the additional screen menus:
LIMITS TRG-LEV MEMCARD CONFIG

Reference Guide
HP 81130A 400/660 MHz
Pulse/Data Generator
HP Part No. 81130-91011
Printed in Germany November 1998
Edition 1.0, E1198

Notice
Notice
Copyright
1998 Hewlett-Packard GmbH
Herrenberger Str. 110–140
71034 Boeblingen
Germany
All rights reserved. Reproduction, adaptation or translation without prior
written permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright
laws.
Warranty
This Hewlett-Packard product has a warranty against defects in material
and workmanship for a period of three years from date of shipment.
During the warranty period, Hewlett-Packard Company will, at its option,
either repair or replace products that prove to be defective. For warranty
service or repair, this product must be returned to a service facility
designated by Hewlett-Packard. The Buyer shall pay Hewlett-Packard's
round-trip travel expenses. For products returned to Hewlett-Packard for
warranty service, the Buyer shall prepay shipping charges to HewlettPackard and Hewlett-Packard shall pay shipping charges to return the
product to the Buyer. However, the Buyer shall pay all shipping charges,
duties and taxes for products returned to Hewlett-Packard from another
country. Hewlett-Packard warrants that its software and firmware
designated by Hewlett-Packard for use with an instrument will execute
its programming instructions when properly installed on that instrument.
Hewlett-Packard does not warrant that the operation of the instrument
software, or firmware, will be uninterrupted or error free.
6

Notice
Limitation of Warranty
The foregoing warranty shall not apply to defects resulting from
improper or inadequate maintenance by the Buyer, Buyer-supplied
software or interfacing, unauthorized modification or misuse, operation
outside of the environmental specifications for the product, or improper
site preparation or maintenance.
No other warranty is expressed or implied. Hewlett-Packard specifically
disclaims the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a
particular purpose.
Exclusive Remedies
The remedies supplied are the Buyer’s sole and exclusive remedies.
Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, special,
incidental, or consequential damages, whether based on contract, tort or
any other legal theory.
Assistance
Product maintenance agreements and other customer assistance
agreements are available for Hewlett-Packard products. For any
assistance, contact your nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales Office.
Certification
Hewlett-Packard Company certifies that this product met its published
specifications at the time of shipment. Hewlett-Packard further certifies
that its calibration measurements are traceable to the United States
Institute of Standards and Technology, to the extent allowed by the
Institute's calibrating facility, and to the calibration facilities of other
International Standards Organization members.
7

About this Book
About this Book
This guide provides reference information primarily for programming the
HP 81130A via remote control.
Chapter 1 “General Programming Aspects” on page 15 gives general
hints for programming instruments like the HP 81130A using SCPI
commands.
Chapter 2 “Programming Reference” on page 27 provides detailed
information on the SCPI commands supported by the instrument.
Chapter 3 “Specifications” on page 95 lists the instrument’s technical
specifications and provides exact definitions for the instrument’s
parameters.
For an introduction and information on the HP 81130A’s user interface,
please refer to the Quick Start Guide, p/n 81130-91010.
8

About this Book
Conventions Used in this Book
This book uses certain conventions to indicate elements of the
HP 81130A’s user interface. The following table shows some examples:
Softkeys Press the MODE/TRG softkey to access the Mode/
Trigger screen.
Hardkeys Press the MORE key to switch to the alternative
softkey layout.
Alternate Keys Press SHIFT + 0 (ON/OFF1) to switch on output1.
The alternate key label—which is selected by
pressing the SHIFT key—is given in parentheses.
Screen Quotes Move the entry focus down to P
turn the knob to select
INTERNAL
ULSE-PERIOD
PLL.
and
Entry Focus The highlight field, that can be moved with the
cursor keys, to change modes, parameters, or
parameter formats.
:VOLTage:HIGH 3V
Full command for programming a 3 V high level.
The upper case letters represent the short form
of the command, which results in faster programming times.
*RST Common IEEE 488 command, to reset instru-
ment to default status.
9

Safety Information
Safety Information
Safety
This is a Safety Class 1 instrument (provided with terminal for protective
earthing). Before applying power, verify that the correct safety
precautions are taken (see the following warnings). In addition, note the
external markings on the instrument that are described under Safety
Symbols. Do not operate the instrument with its covers removed.
Replace fuse only with specified type.
Warning
Before turning on the instrument, you must connect the protective earth
terminal of the instrument to the protective earth conductor of the
(mains) power cord. The mains plug must only be inserted in a socket
outlet with a protective earth contact. Do not negate the protective
action by using an extension power cord without a protective grounding
conductor. Grounding one conductor of a two-conductor outlet is not
sufficient protection.
Service instructions are for trained service personnel. To avoid
dangerous electric shock, do not perform any service unless qualified to
do so. Do not attempt internal service or adjustment unless another
person, capable of rendering first aid and resuscitation, is present.
If you energize this instrument using an auto-transformer (for voltage
reduction) make sure that the common terminal is connected to the earth
terminal of the power source.
Whenever it is likely that the ground protection is impaired, you must
make the instrument inoperative and secure it against any unintended
operation.
Do not operate the instrument in the presence of flammable gases or
fumes. Operation of any electrical instrument in such an environment
constitutes a definite safety hazard.
Do not install substitute parts or perform any unauthorized modification
to the instrument.
10

Safety Information
Capacitors inside the instrument may retain a charge even if the
instrument is disconnected from its source of supply.
Safety Symbols
Instruction Manual symbol: The instrument is marked with this symbol
when it is necessary for you to refer to the instruction manual in order to
protect against damage to the instrument.
Protected conductor symbol.
In the manuals:
WARNING
CAUTION Cautions call attention to a procedure, practice, or the like, which, if not
Warnings call attention to a procedure, practice, or the like,
which, if not correctly performed or adhered to, could result in
personal injury or loss of life. Do not proceed beyond a Warning
until the indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
correctly performed or adhered to, could result in damage to or
destruction of part or all of the equipment. Do not proceed beyond a
Caution until the indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
11

Safety Information
12

Contents
Notice ......................................................................................... 6
About this Book ......................................................................... 8
Safety Information .................................................................. 10
Chapter 1
Chapter 2
General Programming Aspects
The HP-IB Interface Bus ......................................................... 16
HP 81130A Remote Control .................................................... 17
Programming Recommendations ............................................ 18
Common Command Summary ................................................. 20
Status Model ............................................................................ 21
Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary .................................... 28
Default Values, Standard Settings ......................................... 36
Programming the Instrument Trigger Modes ........................ 40
SCPI Instrument Command List ............................................ 44
xiii

Contents
Chapter 3 Specifications
Declaration of Conformity ..................................................... 96
HP 81130A Specifications ...................................................... 97
General ................................................................................................... 97
Timing Specifications ........................................................................... 99
Main Output Level Specifications ..................................................... 102
External Input, External Clock/PLL Reference Input .................... 103
Trigger Modes ...................................................................................... 105
Output Modes ...................................................................................... 106
Human Interface .................................................................................. 108
Memory ................................................................................................. 109
Remote Control ................................................................................... 109
Pulse Parameter Definitions ................................................ 111
xiv

1General Programming
1
Aspects
This chapter provides general information on writing HP-IB/SCPI
programs for instruments like the HP 81130A.
Detailed information on programming the HP 81130A can be found in
Chapter 2 “Programming Reference” on page 27.
15

General Programming Aspects
The HP-IB Interface Bus
The HP-IB Interface Bus
The Hewlett-Packard Interface Bus is the interface used for
communication between a controller and an external device, such as the
HP 81130A. The HP-IB conforms to IEEE standard 488-1987, ANSI
standard MC 1.1, and IEC recommendation 625-1.
If you are not familiar with the HP-IB, please refer to the following
books:
•
Hewlett-Packard Company: Publication 5952-0156, Tutor ial
Description of Hewlett-Packard Interface Bus.
•
The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers: IEEE Standard
488.1-1987, IEEE Standard Digital Interface for Programmable
Instrumentation.
•
The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers: IEEE Standard
488.2-1987, IEEE Standard Codes, Formats, and Common
Commands for Use with IEEE Standard 488.1-1987.
In addition, the commands not from the IEEE 488.2 standard are defined
according to the Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments
(SCPI). For an introduction to SCPI and SCPI programming techniques,
refer to the following documents:
•
Hewlett-Packard Press (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.):
A Beginners Guide to SCPI by Barry Eppler, 1991.
•
The SCPI Consortium: Standard Commands for Programmable
Instruments, published periodically by various publishers. To obtain a
copy of this manual, contact your Hewlett-Packard representative.
16

General Programming Aspects
HP 81130A Remote Control
HP 81130A Remote Control
HP-IB Address You can only set the HP-IB address from the front panel of the instrument
(refer to the Quick Start Guide).
The default HP-IB address is 10.
Modes of
Operation
The HP 81130A has two modes of operation:
•
Local
The instrument is operated using the front panel keys.
•
Remote
After receiving the first command or query via the HP-IB, the
instrument is put into remote state. The front panel is locked.
To return to local operating mode, press SHIFT (LOCAL).
17

General Programming Aspects
Programming Recommendations
Programming Recommendations
Here are some recommendations for programming the instrument:
•
Start programming from the default setting. The common command
for setting the default setting is:
*RST
•
Switch off the automatic update of the display to increase the
programming speed. The device command for switching off the
display is:
:DISPlay OFF
•
The SCPI standard defines a long and a short form of the commands.
For fast programming speed it is recommended to use the short
forms. The short forms of the commands are represented by upper
case letters. For example the short form of the command to set 100 ns
delay is:
:PULS:DEL 100NS
•
To improve programming speed it is also allowed to skip optional
subsystem command parts. Optional subsystem command parts are
depicted in square brackets, e.g.: set amplitude voltage of output 1:
[SOURce]:VOLTage[1][:LEV el][:IMMed iate][:A MPLitude] .
Sufficient to use: :VOLT 1.2V
•
For the commands to set the timing and level parameters, except of
period/frequency, you can explicitly specify the output to be
programmed (for compatibility reasons). If there is no output
specified, the commands will set the default output 1.
So, for setting a high level of 3 Volts for output 1 the commands are:
:VOLT:HIGH 3V # sets high level of 3 V at out 1
:VOLT1:HIGH 3V # sets high level of 3 V at out 1
18

General Programming Aspects
Programming Recommendations
• It is recommended to test a new setting that will be programmed on
the instrument by setting it up manually.
Enable the outputs so that the instrument’s error check system is on
and possible parameter conflicts are immediately displayed.
When you have found the correct setting, then use this to create the
program. In the program it is recommended to send the command for
enabling outputs (for example, :OUTPut ON) as the last command.
• Selftest of the instrument can be invoked by the common command
*TST
• If it is important to know whether the last command is completed,
then send the common command
*OPC?
19

General Programming Aspects
Common Command Summary
Common Command Summary
This table summarizes the IEEE 488.2 common commands supported by
the HP 81130A:
Command Parameter Description
*CLS – Clear the status structure
*ESE <0–255> Set the Standard Event Status register mask
*ESE? – Read the state of the Standard Event Status enable register
*ESR? – Read the state of the Standard Event Status event register
*IDN? – Read the Instrument's Identification string
*LRN? – Read the complete Instrument Setting
*OPC – Set the Operation Complete bit when all pending actions
are complete
*OPC? – Read the status of the Operation Complete bit
*OPT? – Read the installed options
*RCL <0–4> Recall a complete Instrument Setting from memory
*RST – Reset the instrument to standard settings
*SAV <1–4> Save the complete Instrument Setting to memory
*SRE <0–255> Set the Service Request Enable Mask
*SRE? – Read the Service Request Enable Mask
*STB? – Read the Status Byte
*TRG – Trigger
*TST? – Execute instrument’s selftest
*WAI – Wait until all pending actions are complete
20

Status Model
TIONABLE STATUS
QUES
Voltage Warning
Current Warning
Timi ng War ning
Frequency Warning
Pattern Warning
Operation Complete
Query Error
Device Dependent Error
Execution Error
Command Error
Power On
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
15
OPERation Status
(NOT USED)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
15
Standard Event Status
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
MAV
SRQ
Status
Byte
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
General Programming Aspects
Status Model
The instrument has a status reporting system conforming to IEEE 488.2
and SCPI. The above figure shows the status groups available in the
instrument.
Each status group is made up of component registers, as shown in the
following figure.
21

General Programming Aspects
Status Model
Condition
Register
Hardware
and Firmware
condition
Transition
Filters
1
0
PTR NTR
1
0
Event
Register
Latched
Enable
Register
OR
Summary Bit
Condition Register
A condition register contains the current status of the hardware and
firmware. It is continuously updated and is not latched or buffered. You
can only read condition registers. If there is no command to read the
condition register of a particular status group, then it is simply invisible
to you.
Transition Filters
Transition filters are used to detect changes of state in the condition
register and set the corresponding bit in the event register. You can set
transition filter bits to detect positive transitions (PTR), negative
transitions (NTR) or both. Transition filters are therefore read/write
registers. They are unaffected by *CLS.
Event Register
An event register latches transition events from the condition register as
specified by the transition filters or records status events. Querying
(reading) the event register clears it, as does the *CLS command. There is
no buffering, so while a bit is set, subsequent transition events are not
recorded. Event registers are read only.
22

General Programming Aspects
Status Model
Enable Register
The enable register defines which bits in an event register are included in
the logical OR into the summary bit. The enable register is logically
ANDed with the event register and the resulting bits ORed into the
summary bit. Enable registers are read/write, and are not affected by
or querying.
*CLS
Although all status groups have all of these registers, not all status
groups actually use all of the registers. The following table summarizes
the registers used in the instrument status groups.
Registers in Group
Status Group
QUEStionable
*ESR?
*ESE
*STB?
*SRE
1
to query.
to set,
to query
to set,
OPERation
Standard Event Status
Status Byte
1 Present, but not used. COND and EVEN always 0.
2 Use
3 Use
4 Use
5 Use
CONDition NTR PTR EVENt ENABLe
√ √ √ √ √
xxxxx
xxx
xxx
to query
*ESE?
to query
*SRE?
2
√
4
√
3
√
5
√
23

General Programming Aspects
Status Model
Status Byte
The status byte summarizes the information from all other status groups.
The summary bit for the status byte actually appears in bit 6 (RQS) of the
status byte. When RQS is set it generates an SRQ interrupt to the
controller indicating that at least one instrument on the bus requires
attention. You can read the status byte using a serial poll or *STB?
Bit Description
0 Unused, always 0
1 Unused, always 0
2 Unused, always 0
3 QUESTionable Status Summary Bit
4 MAV—Message AVailable in output buffer
5 Standard Event Status summary bit
6 RQS; ReQuest Service
7 OPERation Status summary Bit, unused
Standard Event Status Group
Bit Description
0 Operation Complete, set by *OPC
1 Unused, always 0
2 Query Error
3 Device Dependent Error
4 Execution Error
5 Command Error
6 Unused, always 0
7 Power On
24

OPERation Status Group
This Status Group is not used in the instrument.
Bit Description
0 Unused, always 0
1 Unused, always 0
2 Unused, always 0
3 Unused, always 0
4 Unused, always 0
5 Unused, always 0
6 Unused, always 0
7 Unused, always 0
8 Unused, always 0
9 Unused, always 0
General Programming Aspects
Status Model
10 Unused, always 0
11 Unused, always 0
12 Unused, always 0
13 Unused, always 0
14 Unused, always 0
15 Always 0
25

General Programming Aspects
Status Model
QUEStionable Status Group
Bit QUEStionable
0 Voltage warning
1 Current warning
2 Time warning
3 Unused, always 0
4 Unused, always 0
5 Frequency warning
6 Unused, always 0
7 Unused, always 0
8 Unused, always 0
9 Pattern warning
10 Unused, always 0
11 Unused, always 0
12 Unused, always
13 Unused, always 0
14 Unused, always 0
15 Always 0
The QUEStionable Status group is used to report warning conditions
amongst the voltage, current, pulse timing, frequency and pattern
parameters. Warnings occur when a parameter, although not outside its
maximum limits, could be causing an invalid signal at the output because
of the actual settings and uncertainties of related parameters.
26

2
2Programming Reference
This chapter provides reference information on the following topics:
•
“HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary” on page 28
•
“Default Values, Standard Settings” on page 36
•
“Programming the Instrument Trigger Modes” on page 40
•
“SCPI Instrument Command List” on page 44
For general programming information, please refer to Chapter 1
“General Programming Aspects” on page 15.
27

Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
Command Parameter Description see page
:ARM
[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt]
[:LAYer[1]]
:LEVel
[:THReshold]
:TERMination
:MODE
:SENSe
:SOURce
:INITiate
:CONTinuous
:CHANnel
:MATH
(Trigger mode and source)
<value> Set/read threshold level at EXT INPUT
<value> Set/read the termination voltage at EXT IN-
PUT
GATed | STARted Set/read the trigger mode, if the source is
POSitive | NEGative Set/read trigger on edge or gate on level
EXT1| IMM | MAN Set/read trigger source
ON | OFF | 1 | 0 Starts or stops the instrument, if the arming
OFF|DIGital Set/read addition of channels of channels 1
IMMediate
not
(EXT INPUT| IMMediate | MAN key)
source is
& 2 at output 1
IMMediate
not
45
45
45
46
46
47
47
28

Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
Command Parameter Description see page
:DIGital
[:STIMulus]
:PATTern 50
:LOOP 47
:INFinite 48
[:STATe]
:STARt
[:LEVel[1]]
[:COUNt]
:STARt
:LENGth
:PRBS
:SEGMent[1|2|3|4]
:DATA[1|2]
:LENGth
:PRESet[1|2]
:TYPE[1|2]
[:STATe]
:UPDate
:SIGNal[1|2]
:FORMat
ON | OFF | 1 | 0 Enables/Disables the infinite loop
SEGM1 | SEGM2 |
SEGM3 | SEGM4
<value> Set/read the segment loop count
SEGM1 | SEGM2 |
SEGM3 | SEGM4
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 Set/read the number of segments within the
<base> Set/read the PRBS base (the same for all
<data> Set/read pattern data
<segment-length> Set/read the length of the segment (if the
[<n>,]<length> Set preset pattern with frequency CLOCK÷ n
DATA|
PRBS|HIGH|LOW
OFF|ON|0|1 Switch PATTERN pulse-mode on or off
OFF|ON|ONCE Update the hardware with pattern data
RZ | R1 | NRZ Set/read data format of output channel
Set/read the start of the infinite loop (the
segment to restart the output after the last
bit of the last used segment)
Set/read the start segment for the counted
segment loop
segment loop
PRBS segments!)
length is increased, ‘0’ bits are appended)
Set/read the type of the segment
49
49
50
50
51
53
54
55
55
56
29

Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
Command Parameter Description see page
:DISPlay 57
[:WINDow]
[:STATe]
:MMEMory
:CATalog?
:CDIRectory
:COPY
:DELete
:INITialize
:LOAD
:STATe
:STORe
:STATe
ON|OFF|1|0 Set/read frontpanel display state
[A:] Read directory of memory card
[<name>] Change directory on memory card
<source>[,A:],<dest>
[,A: ]
<name>[,A:] Delete a file from memory card
[A:[DOS]] Initialize memory card to DOS format
<n>,<name> Load file from memory card to memory n
<n>,<name> Store memory n to memory card
Copy a file on memory card
57
58
58
59
59
59
60
:OUTPut[1|2] 60
[:NORMal]
[:STATe]
:COMPlement 60
[:STATe]
OFF|ON|1|0 Set/read normal output state
OFF|ON|1|0 Set/read complement output state
30

Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
Command Parameter Description see page
[:SOURce]
:CORRection[1|2]
:EDELay 61
[:TIMe]
:CURRent[1|2]
[:LEVel]
[:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude]
:OFFSet
:HIGH
:LOW
:LIMit
:HIGH
:LOW
:STATe
:FREQency
[:CW]
[:FIXed]
:AUTO
:HOLD[1|2]
<value> Set/read channel delay deskew
The CURRent and VOLTage subsystem cannot be used at the same time. Use the :HOLD
command to select between them.
<value> Set/read channel amplitude current
<value> Set/read channel offset current
<value> Set/read channel high-level current
<value> Set/read channel low-level current
<value> Set/read maximum current limits
<value> Set/read minimum current limits
ON|OFF|1|0 Enable/Disable the current limits
<value> Set/read frequency of pulses
ONCE Do a frequency measurement at CLK IN
VOLT|CURR Switch between VOLTage and CURRent
command subtrees
61
62
63
64
64
65
65
66
67
67
31

Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
Command Parameter Description see page
[:SOURce]
:PHASe[1|2]
[:ADJust]
:PULSe
:DCYCle[1|2]
:DELay[1|2]
:HOLD
:UNIT
:HOLD[1|2]
:PERiod
:AUTO
:TDelay[1|2]
:TRANsition[1|2] 73
:UNIT
[:LEADing]
:TRAiling
:TRIGger[1]
:MODE
:POSition
:VOLTage 75
[:LEVel]
[:IMMediate]
:WIDTh[1|2]
<value>
<value> Set/read channel phase
<value> Set/read channel dutycycle
<value> Set/read channel delay (to leading edge)
TIME|PRATio Hold absolute delay|delay as period fixed
with varying frequency
S|SEC|PCT|DEG|
RAD
WIDTh | DCYCle |
TDELay
<value> Set/read pulse period
ONCE Measure pulse period at CLK IN
<value> Set/read trailing edge delay
S|SEC|PCT Set/read transition-time units
<value> Set/read leading-edge transition
<value> Set/read trailing-edge transition
CONTinuous | STARt Set/read the mode of the trigger output sig-
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 Set/read the trigger output signal position
TTL | PECL | SYM |
ECLGND | ECLN2V
<value> Set/read channel pulse-width
Set/read delay units
Hold Width|Dutycycle|Trailing edge delay
fixed with varying frequency
nal generation (ignored if not in pattern
mode)
Set/read TRIGGER OUTput levels
68
68
69
70
70
71
71
72
72
73
74
74
75
76
32

Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
Command Parameter Description see page
[:SOURce]
:ROSCillator
:SOURce
:EXTernal
:FREQuency
:VOLTage[1|2] 77
[:LEVel]
[:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude]
:OFFSet
:HIGH
:LOW
:LIMit
[:HIGH]
:LOW
:STATe
INTernal|EXTernal Set/read PLL reference source
<value> Set/read frequency of external PLL
reference. Value will be rounded to 1 MHz,
2MHz, 5MHz or 10MHz.
<value> Set/read channel amplitude voltage
<value> Set/read channel offset voltage
<value> Set/read channel high-level voltage
<value> Set/read channel low-level voltage
<value> Set/read maximum voltage limit
<value> Set/read minimum voltage limit
ON|OFF|1|0 Enable|Disable the voltage limits
76
77
78
79
79
80
81
81
33

Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
Command Parameter Description see page
:STATus
:OPERation 82
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition
:ENABle
:NTRansition
:PTRansition
:PRESet
:QUEStionable 83
[:EVENt]?
:CONDition?
:ENABle
:NTRansition
:PTRansition
Numeric Set/Read Operation enable register
Numeric Set/Read Operation negative-transition
Numeric Set/Read positive-transition register
Numeric Set/Read Questionable enable register
Numeric Set/Read Questionable negative-transition
Numeric Set/Read Questionable positive-transition
Read Operation event register
Read Operation condition register
register
Clear and preset status groups
Read Questionable event register
Read Questionable condition register
register
register
82
82
82
82
82
82
83
83
83
83
34

Programming Reference
HP 81130A SCPI Command Summary
Command Parameter Description see page
:SYSTem
:ERRor?
:KEY
:PRESet
:SECurity 87
[:STATe]
:SET
:VERSion?
:WARNing 88
[:COUNt]?
:STRing?
:BUFFer?
Numeric Simulate key press or read last key pressed
ON|OFF Switch security on and off
Block data Set/read complete instrument setting
Read error queue
no function
Read SCPI compliance setting
Read number of active warnings
Read active warnings as concatenated string
Read maximum possible length of
concatenated string
85
85
87
88
88
89
89
:TRIGger
[:SEQuence [1]] | :STARt]
:COUNt
:PULSes[1|2]
:LEVel
:TERMination
:SOURce
(Pulse mode and period source)
<value> Set/read number of triggered periods to be
generated per ARM event (BURST period)
<value> Set/red the number of pulses within the trig-
gered periods at OUTput 1 or OUTput 2
<value> Set/read termination voltage level at CLK IN
IMM | INT[1] | EXT2 Set/read trigger source (Immediate | PLL |
CLK IN)
89
92
92
93
35

Programming Reference
Default Values, Standard Settings
Default Values, Standard Settings
Parameter *RST, Default Values
:ARM :LEVel [:THReshold] +1.0 V
:TERM +0.0 V
:MODE STARted
:SENSe POS
:SOURce IMM
:INITiate :CONTinuous ON
:CHANnel :MATH OFF
:DIGital :PATTern: OFF
:LOOP:INFinite ON
:LOOP:INFinite:STARt SEGM1
:LOOP 1
:LOOP:STARt SEGM1
:LOOP:LENGth 1
:PRBS 7
:SEGMent:DATA see
:SEGMent:LENGth 32, 0, 0, 0
:SEGMent:PRESet not applicable
:SEGMent:TYPE DATA
:UPDate ON
:SIGNal :FORMat RZ
:DISPlay ON
:MMEMory :CATatalog? not applicable
:CDIRectory not applicable
:COPY not applicable
:DELete not applicable
page 51
36

Programming Reference
Default Values, Standard Settings
Parameter *RST, Default Values
:INITialize not applicable
:LOAD :STATe not applicable
:STORe :STATe not applicable
:OUTPut OFF
:COMPlement OFF
:CORRection :EDELay 0.0 s
:CURRent
:OFFSet
:HIGH
:LOW
:LIMit [:HIGH] +10.0 mA
:LOW –10 mA
:STATe OFF
:FREQuency 1.00 MHz
:AUTO not applicable
:HOLD VOLT
:PHAS 0.0
:PULSe :DCYCle 10.0% (derived from Width and Period)
:DELay 0.00
:HOLD TIME
:UNIT SEC
:HOLD WIDTh
:PERiod 1µs
:AUTO not applicable
:TDELay 100 ns
:TRANsition :HOLD TIME
:UNIT SEC
20 mA (50
0.0
µ
+10 mA (50
–10 mA (50
into 50Ω)
Ω
A (50Ω into 50Ω)
into 50Ω)
Ω
into 50Ω)
Ω
37

Programming Reference
Default Values, Standard Settings
Parameter *RST, Default Values
[:LEADING] 0.8 ns (HP 81131A) or not applicable
:TRAiling 0.8 ns (HP 81131A) or not applicable
:TRAiling:AUTO ON
:TRIGger: :MODE STARt
:POSition 1
:VOLTage TTL
:WIDTh 100 ns
:ROSCillator :SOURce INT
:EXTernal :FREQuency 5 MHz
:VOLTage 1.00 V
:OFFSet 0.0 mV
:HIGH 500 mV
:LOW –500 mV
:LIMit [HIGH] +500 mV
:LOW –500 mV
:STATe OFF
:STATus :OPERation not applicable
:PRESet not applicable
:QUESTionable ON
:SYSTem :ERRor? not applicable
:KEY not applicable
:PRESet not applicable
:SECurity OFF
:SET not applicable
:VERSion? “1992.0”
:WARN? [:COUNt] not applicable
:STRing? not applicable
:BUFFer? not applicable
38

Programming Reference
Default Values, Standard Settings
Parameter *RST, Default Values
:TRIGger :COUNt 1
:PULSes 2
:LEVel :TERMination 0.0 V
:SOURce INT
39

Programming Reference
Programming the Instrument Trigger Modes
Programming the Instrument
Tri gg er M ode s
The following figure shows the instrument’s arming/triggering model:
*RST or power on
Trigger system
(1)
initiated
(still) initiated
ARM conditions
(1)
satisfied
For details of the
trigger count
command, refer to
“:TRIG:COUN” on
page 89.
Idle
loops
(1)
(2)
or
Notes:
(1) The instrument is always initiated in CONTINUOUS modes.
The instrument is automatically initiated in MANual started/gated modes.
(2) 1 in Pulses Mode (same as :TRIGger:COUNt)
:TRIGger:COUNt in Continuous/Gated Mode
Maximum of :TRIGger:COUNt:PULSes1 and :TRIGger:COUNt:PULSes2
in Started Burst mode
Depends on sequence in Pattern Mode (may be infinite)
no longer initiated
Initiated
wait for Arm
completed # of Trigger
no longer initiated
wait for Trigger
Trigger conditions
satisfied
You program the comprehensive triggering capabilities of the instrument
using the SCPI :ARM and :TRIGger subsystems. Using these two
command subsystems you can program the operating modes of the
instrument which are set up using the M
ODE/TRG
screen on the
frontpanel.
Use the :ARM subsystem to select the overall triggering mode of the
instrument (CONTINUOUS, STARTED, GATED), and the :TRIGger
subsystem to select the pulse period source, triggering and number of
pulse periods per :ARM event (BURST length). In pattern mode the
pattern length is the sum of each used segment’s length.
40

Programming Reference
Programming the Instrument Trigger Modes
Continuous
Set Continuous mode by arming the instrument from its internal PLL:
:ARM:SOURce IMMediate Arm from internal PLL
Started
Set Started mode by arming the instrument on low to high level transition
from the EXT INPUT:
:ARM:SOURce EXTernal1 Arm from EXT INPUT
:ARM:MODE STARted Start on the arm event
:ARM:SENSe POSitive Arm on positive (high) level
:ARM:LEVel:THReshold 1V Set EXT INPUT threshold
Gated
Set Gated mode by arming the instrument on levels from the EXT INPUT:
:ARM:SOURce EXTernal1 Arm from EXT INPUT
:ARM:MODE GATed Select gated mode
:ARM:SENSe POSitive Arm on positive level
Pulses
Set Pulses mode by setting the
:TRIGger:COUNt
triggered pulse period is generated for every :ARM event. The trigger
source sets the pulse period:
:TRIGger:COUNt 1 Single pulse period per arm event
:TRIGger:SOURce INTernal 1 Pulse period from internal PLL
:DIGital:PATTern OFF Disable pattern data.
Pulse period source :TRIGger SOURce
internal PLL
CLK-IN
INTernal[1] or IMMediate
EXTernal2
to 1 so that a single
41

Programming Reference
Programming the Instrument Trigger Modes
Burst
Set Burst mode by setting the :TRIGger:COUNt to the burst count
required. The trigger source sets the pulse period for the pulses within
the burst (See table in “Pulses” on page 41).
:TRIGger:COUNt 16 Burst of 16 pulse periods
:TRIGger:SOURce INTernal1 Pulse period from internal PLL.
:DIGital:PATTern OFF Disable pattern data
Pattern
Set Pattern mode by setting the
:DIGital[STIMulus]:PATTern:SEGMent[1|2|3|4]:LENGth to the
required pattern length, and switching on digital pattern data. The trigger
source sets the pulse period for the data pulses (See table in “Pulses” on
page 41):
#Pattern length 512
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:SEG Ment1:LENGth 512
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:SEG Ment2:LENGth 0
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:SEG Ment3:LENGth 0
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:SEG Ment4:LENGth 0
#Disable counted segment loop
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:LOO P:COUNt 1
#Jump back to start of segment 1 after the last bit of the last
segment (here: segment 1)
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:LOO P:INFinite[:STATe] ON
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:LOOP:INFinite:STARt SEGM1
:TRIGger:SOURce INTernal1 Pulse period from internal PLL
:DIGital:PATTern ON En ab le pattern data
:DIGital:SIGNal1:FORMat NRZ Set OUTPUT 1 data to NRZ
:ARM:MODE STARted
:ARM:SOURce EXT1 Switch to started by EXT1
42

Programming Reference
Programming the Instrument Trigger Modes
Manually Starting and Gating
When starting and gating with the MAN key use the following commands:
STARTED *TRG or :INITiate:CONTinuous ON to start the instrument
:INITiate:CONTinuous OFF to stop the instrument
GATED :INITiate:CONTinuous ON to 'open the gate'
:INITiate:CONTinuous OFF to 'close the gate'
*TRG to gate for approx. 10ms
43

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
SCPI Instrument Command List
The following reference sections list the instrument commands in
alphabetical order. In addition to a command description, the attributes
of each command are described under the following headings. Not all of
these attributes are applicable to all commands. The commands are
conform to the IEEE 488.2 SCPI standard.
Command Shows the short form of the command.
Long Shows the long form of the command.
Form Most commands can be used in different forms:
Set The command can be used to program the instrument
Query The command can be used to interrogate the instrument. Add a ? to
Event The command performs a one-off action.
Parameter The type of parameter, if any, accepted by the command. The minimum
and maximum value of numeric parameters can be accessed by the
option MINimum or MAXimum.
the command if necessary.
Parameter Suffix The suffixes that may follow the parameter.
Functional
Coupling
Value Coupling Any other parameter that is also changed by the command.
Range Coupling Any other parameters whose valid ranges may be changed by the
*RST value The value/state following a *RST command.
Specified Limits The specified limits of a parameter.
Absolute Limits Some parameters can be programmed beyond their specified limits.
Example Example programming statements.
Any other commands that are implicitly executed by the command.
command.
44

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :ARM:LEV[:THR]
Long
:ARM[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt][:LAYer]:LEVel[:THReshold]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter SuffixV with engineering prefixes.
*RST value +1.0 V
Specified Limits –1.4 V to +3.7 V
Description Use this command to program the triggering threshold of the EXT INPUT
connector.
Example
:ARM:LEV 2.5V
Set EXT INPUT threshold to 2.5 V
Command :ARM:LEV:TERM
Long
:ARM[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt][:LAYer]:LEVel:TERMination
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter SuffixV with engineering prefixes.
*RST value +0.0 V
Specified Limits –2.1 V to +3.3 V
Description Use this command to program the termination voltage compensation of
the EXT INPUT connector.
Example
:ARM:LEV:TERM 1.0V
Set EXT INPUT termination voltage to 1.0 V
Command :ARM:MODE
Long
:ARM[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt][:LAYer]:MODE
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
STARted | GATed
STARted
45

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Description Use this command to select STARTED or GATED mode.
In the gated mode, the instrument triggers as long as the arming signal is
above (:ARM:SENS POS), or below (:ARM:SENS NEG) the selected
threshold level (:ARM:LEV).
In started mode, the instrument triggers on positive edge
(:ARM:SENS POS) or negative edge (:ARM:SENS NEG).
Command :ARM:SENS
Long
:ARM[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt][:LAYer]:SENSe
Form Set & Query
Parameter POSitive | NEGative
*RST value POS
Description Use this command to select the edge or trigger level for the arming
signal.
The instrument triggers at the positive or negative cycle of the arming
signal.
Command :ARM:SOUR
Long
:ARM[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt][:LAYer]:SOURce
Form Set & Query
Parameter IMMediate | EXTernal1 | MANual
*RST value IMM
Description Use this command to select the triggering mode of the instrument by
selecting the source of the arming signal:
Triggering Source :ARM:SOURce Mode
Internal PLL
EXT INPUT
MAN key
IMMediate
EXTernal1
MANual
Continuous
Triggered | Gated by: EXT IN
Triggered | Gated by: MANKey
Use :ARM:MODE STARTed|GATed to select the mode.
46

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :INIT:CONT
Long
:INITiate:CONTinuous
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
ON | OFF | 1 | 0
ON
Description Use this command to enable/disable automatic restart of the instrument
(equal to start and stop the instrument). If
IMMediate
, the value of
:INITiate:CONTinuous
:ARM:SOURce
is ignored.
is set to
Command :CHAN:MATH
Long
:CHANnel:MATH
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
OFF | DIGital
OFF
Description Use this command to enable or disable digital channel addition in an
instrument with two Output channels installed.
:CHAN:MATH DIGital
With
the digital signals from both channels are
”xor’ed” (before the slopes are applied) at OUTPUT 1. The signal of
OUTPUT 2 can be used in parallel.
This allows you to for example to simulate single or repeated glitches.
Command :DIG:PATT:LOOP
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:LOOP[:LEVel[1]][:COUNt]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
*RST value 1
Specified Limits 1 to 2^20
Description Use this command to set up a counted loop across one or more
segments.
47

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
If nested loops are used, the counted loop must be embedded into the
infinite loop completely.
Example To set up an infinite loop over segment 2 to segment 4 and a counted loop
across segment 2 and segment 3:
:ARM:SOUR EXT1
:ARM:MODE STAR
:ARM:SENS POS
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:INF:STAR SEGM2
:DIG:PATT:LOOP 100
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:STAR SEGM2
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:LENG 2
:DIG:PATT ON
Set arming source to EXT-IN
Set arming mode to started
Arm on positive level
Set jump destination to segment 2
Set number of repetitions of
segment2 and segment 3
Set start of counted loop
Set length of counted loop
Switch on PATTERN mode
Command :DIG:PATT:LOOP:INF
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:LOOP:INFinite[:STATe]
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
ON | OFF | 1 | 0
ON
Description Use this command to set up an infinite loop from the last used segment
to the destination segment.
The infinite loop is ignored, if
:ARM:SOURce
IMMediate
is
(CONTINUOUS mode), since in continuous mode there has to be a jump
back to the start of the pattern (always from segment 4 to segment 1).
Example To setup an infinite loop over segment 2 to segment 4:
:ARM:SOUR EXT1
:ARM:MODE STAR
:ARM:SENS POS
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:INF ON
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:INF:STAR SEGM2
:DIG:PATT:LOOP 1
:DIG:PATT ON
Set arming source to EXT-IN
Set arming mode to started
Arm on positive level
Enable infinite loop
Set jump destination to segment 2
Disable counted loop
Switch on PATTERN mode
48

SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :DIG:PATT:LOOP:INF:STAR
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:LOOP:INFinite:STARt
Form Set & Query
Parameter
SEGM1 | SEGM2 | SEGM3 | SEGM4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4
*RST value SEGM1
Description Use this command to set up the destination segment.
The infinite loop is ignored, if :ARM:SOURce is IMMediate
(CONTINUOUS mode), since in continuous mode there has to be a jump
back to the start of the pattern (always from segment 4 to segment 1).
Example See previous example (page 48).
Command :DIG:PATT:LOOP:STAR
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:LOOP[:LEVel[1]]:STARt
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
SEGM1 | SEGM2 | SEGM3 | SEGM4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4
SEGM1
Programming Reference
Description Use this command to set the first segment within a counted loop. The
start of the counted loop must be within the infinite loop (if used).
Example To set up an infinite loop over segment 2 to segment 4 and a counted loop
across segment 2 and segment 3:
:ARM:SOUR EXT1
:ARM:MODE STAR
:ARM:SENS POS
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:INF ON
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:INF:STAR SEGM2
:DIG:PATT:LOOP 100
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:STAR SEGM2
:DIG:PATT:LOOP:LENG 2
:DIG:PATT ON
Set arming source to EXT-IN
Set arming mode to started
Arm on positive level
Switch on infinite loop
Set jump destination to segment 2
Set number of repetitions of
segment2 and segment 3
Set start of counted loop
Set length of counted loop
Switch on PATTERN mode
49

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :DIG:PATT:LOOP:LENG
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:LOOP[:LEVel[1]]:LENGth
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
1 | 2 | 3 | 4
1
Description Use this command to set the number of segments to be repeated within
the counted loop.
Example See previous example (page 49).
Command :DIG:PATT
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern[:STATe]
Form Set & query
Parameter
*RST value
ON | OFF | 1 | 0
OFF
Description Use this command to enable and disable PATTERN mode.
Command :DIG:PATT:PRBS
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:PRBS
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
*RST value 7
Specified Limits 7 to 15 (integer)
Description Use this command to set up PRBS polynom for all PRBS segments on all
channels.
50

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Example
To set up a repeating 2
:ARM:SOUR IMM
:DIG:PATT:SEGM1:LENG 1023
:DIG:PATT:SEGM2:LENG 0
:DIG:PATT:SEGM3:LENG 0
:DIG:PATT:SEGM4:LENG 0
:DIG:PATT:SEGM1:TYPE1 PRBS
:DIG:PATT:LOOP 1
:DIG:PATT:PRBS 10
:DIG:PATT ON
10
–1 PRBS on OUTPUT 1:
Set continuous mode
Set segment 1 pattern length (last
bit) to 1023
Set segment 2 to be ignored
Set segment 3 to be ignored
Set segment 4 to be ignored
Set type of segment 1 on channel 1
to PRBS
Disable segment looping
Set PRBS base to 10
Switch on PATTERN mode
Command :DIG:PATT:SEGM[1|2|3|4]:DATA[1|2]
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:SEGMent[1|2|3|4]:DATA[1|2]
Form Set & Query
Parameter <data>
*RST value Segment 1
Channel
[1|2] Description Bit 1 Bit 2
1 CH1 (OUTPUT 1) 1 0
2 CH2 (OUTPUT 2) 0 1
Segment 2 to Segment 4 set to all bits set to zero.
Description Use this command to set or read a segment’s data of one or all channels
starting from Bit 1. The <data> is an arbitrary block of program data as
defined in IEEE 488.2 7.7.6.2, for example:
#1511213
# Start of block
1 Length of the length of the data
5 Length of the data
11213 5 bytes of data
51

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
#2161000100010001000
# Start of block
2 Length of the length of the data
16 Length of the data
10...00 16 bytes of data
#011213
# Start of block
0 Replaces the data block length specification. Length is
calculated automatically.
11213 5 bytes of data
NOTE The data length meets the same restrictions, than the segment length
(see page 53).
Example :DIG:PATT:SEGM1:DATA #1511213
The instrument uses each byte of data set one Bit in the pattern memory.
If you don’t specify a particular channel, the lowest two bits of each byte
are used to set all three channels, and the top six bits are ignored. Note
that you can therefore use the ASCII characters ‘0’,‘1’,‘2’ and ‘3’, to
program Outputs 1 and 2 in binary:
DATA CH2
ASCII
0
1
2
3
ignored used
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 0 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
OUTPUT2
0
0
1
1
CH1
OUTPUT1
0
1
0
1
:DIG:PATT:SEGM1:DATA2 #1501011
If you specify a particular channel, the least significant bit of each byte is
used to set the selected channel, and the top seven bits are ignored. Note
52

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
that you can therefore use the ASCII characters ‘1’ and ‘0’ to set
individual bits to 1 and 0:
Example
DATA CH2
ASCII
0
1
:ARM:SOUR IMM
:DIG:PATT:SEGM1:DATA1 #1501011
:DIG:PATT:SEGM1:LENG 5
:DIG:PATT ON
ignored
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 0 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0 0
LSB
0
1
Set continuous mode
Set up pattern data for channel 1
Set pattern length (last bit) to 5
Switch on PATTERN mode
OUTPUT2
0
1
CH1
OUTPUT1
remains unchanged
remains unchange
Command :DIG:PATT:SEGM[1|2|3|4]:LENG
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:SEGMent[1|2|3|4]:LENGth
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
*RST value 32, 0, 0, 0 (segment 1 = 32, segments 2, 3, and 4 = 0)
Specified Limits 0 to 65504
Description Use this command to set up the number of bits within a segment. If a
segment is set to a length of 0, the segment will be skipped.
d
Restrictions:
• At least one segment’s length has to be > 0.
• The overall length of the pattern has to be <= 65504 and >= two times
segment length resolution.
• If at least one segment is used to generate a PRBS, the overall pattern
length has to be <= 32768.
53

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
• The segment length has a resolution that depends on the current set
frequency/period.
• The segment at the start of a counted loop has a minimum length of 2
times the resolution.
Pulse Period
< 3ns 16
3ns ... < 6ns 8
6ns ... < 12ns 4
12ns ... < 24ns 2
>= 24ns 1
Segment Length Resolution
(length must be multiple of ...)
NOTE Every change of a segment length will cause the unused pattern data to
be overwritten (no undo!).
Command :DIG:PATT:SEGM[1|2|3|4]:PRES[1|2]
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:SEGMent[1|2|3|4]:PRESet[1|2]
Form Set
Parameter <n>,<length>
*RST value Not applicable
Specified Limits <n> 0 to 32768 (integer)
<length> 1 to 65504 (integer)
Description Use this command to set up clock data starting from bit 1 with value 1.
The parameter <n> is used as the divider to generate a CLOCK÷n
sequence (squarewave if NRZ data is selected). The parameter <length>
determines the length of the segment.
54

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
n=0 Fill with 0
n=1 Fill with 1
n=2 Sequence = 101010101010101....
n=4 Sequence = 110011001100110....
n=6 Sequence = 111000111000111....
n=8 Sequence = 111100001111000....
and so on.
NOTE The data length meets the same restrictions, than the segment length
(see page 53).
Command :DIG:PATT:SEGM[1|2|3|4]:TYPE[1|2]
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:SEGMent[1|2|3|4]:TYPE[1|2]
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
DATA | PRBS | HIGH | LOW
DATA
Description Use this command to set the type of the segment for one channel.
If the segment type of one channel is set to PRBS the other channel may
not be set to DATA.
If at least one channel uses PRBS, then the segment type combination
used in this segment has to be used in every segment that shall generate a
PRBS.
Command :DIG:PATT:UPD
Long :DIGital[:STIMulus]:PATTern:UPDate
Form Set & query
Parameter
ON | OFF | ONCE
55

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
*RST value ON
Description Use this command to enable and disable the automatic updating of the
pattern generating hardware following a
:DIG:PATT:SEGM[1|2|3|4]:DATA command. Disable the automatic
updating if you want to set up new pattern data in the instrument without
affecting the pattern which is currently being generated. You can then
update the hardware with the new pattern data by sending a
:DIG:PATT:UPD ONCE command.
Command :DIG:SIGN[1|2]:FORM
Long
:DIGital[:STIMulus]:SIGNal[1|2]:FORMat
Format Set & Query
Parameter RZ | NRZ | R1
Range Coupling Period, Frequency
*RST value RZ
Description Use this command to set and read the data format of channels 1 and 2
when using PATTERN mode. If you don’t specify a channel number in the
command, channel 1 is assumed.
Example
RZ Return to Zero. An RZ pulse is generated for each ‘1’ in
the data. You can vary the width, edges and levels of the
pulse.
R1 Return to One. An R1 pulse is generated for each ‘0’ in
the data. You can vary the width, edges and levels of the
pulse.
NRZ Non Return to Zero. A pulse of 100% dutycycle is
generated for each ‘1’ in the data. You can vary the
edges and levels of the pulse.
:DIG:SIGN:FORM NRZ
Set channel 1 data format to NRZ
56

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :DISP
Long
:DISPlay[:WINDow][:STATe]
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
ON | OFF | 1 | 0
ON
Description This command is used to turn the frontpanel display on and off.
Switching off the display improves the programming speed of the
instrument.
NOTE *RST switches the display back on.
Example
DISP OFF
Switch off the frontpanel display
Command :MMEM:CAT?
Long
:MMEMory:CATalog?
Form Query
Parameter ["A:"]
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to get a listing of the contents of the currently
selected directory on the memory card. As there is only one memory card
slot, the parameter A: is optional. The information returned is:
BYTES_USED
<
BYTES_FREE
>,<
FILE_ENTRY
>{,<
>}
<bytes_used> The total number of bytes used on the memory card.
<bytes_free> The total number of bytes still available on the memory
card.
<file_entry> String containing the name, type and size of one file:
FILE_NAME
"<
FILE_TYPE
>,<
FILE_SIZE
>,<
>"
NOTE The <file_type> is always blank. A directory name has <file_size> = 0
57

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :MMEM:CDIR
Long
:MMEMory:CDIRectory
Form Event
Parameter ["directory_name"]
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to change the current directory on the memory card.
If you don’t specify a directory name parameter, the root directory is
selected.
NOTE Note that you cannot use DOS pathnames as directory names, you can
only select a directory name within the current directory.
Use the directory name ".." to move back to the parent directory of the
current directory, unless you are already in the root directory "\".
Examples
:MMEM:CDIR
:MMEM:CDIR ""PERFORM""
:MMEM:CDIR ""..""
Select root directory
Select directory "PERFORM"
Select parent directory
Command :MMEM:COPY
Long
:MMEMory:COPY
Form Event
Parameter "filename"[,"A:"],"copyname"[,"A:"]
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to copy an existing file filename in the current
directory to a new file copyname. If copyname is the name of a subdirectory in the current directory, a copy of the file filename is made in
the sub-directory. Use ".." as copyname to copy a file into the parent
directory of the current directory.
Examples
:MMEM:COPY ""test1"",""test2""
:MMEM:COPY ""test1"",""..""
Copy test1 to test2
Copy test1 into parent directory
58

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :MMEM:DEL
Long
:MMEMory:DELete
Form Event
Parameter "filename"
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to delete file filename from the currently selected
directory.
Command :MMEM:INIT
Long
:MMEMory:INITialize
Form Event
Parameter ["A:"[,"DOS"]]
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to initialize a memory card to DOS format.
CAUTION Initializing a memory card destroys any existing data on the card.
Command :MMEM:LOAD:STAT
Long
:MMEMory:LOAD:STATe
Form Event
Parameter <n>,"filename"[,"A:"]
*RST value Not applicable
Specified Limits <n> = 0 to 4 (integer)
Description Use this command to load a complete instrument setting from file
filename in the current directory into memory <n> in the instrument.
Memories 1 to 4 are the internal memories. Use memory 0 to load a
setting as the current instrument setting.
Examples See next command
59

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :MMEM:STOR:STAT
Long
:MMEMory:STORe:STATe
Form Event
Parameter <n>,"filename"[,"A:"]
*RST value Not applicable
Specified Limits <n> = 0 to 4 (integer)
Description Use this command to store a complete instrument setting from memory
<n> to file filename in the current directory on the memory card.
Memories 1 to 4 are the internal memories. Use memory 0 to store the
current instrument setting to a file.
Examples
:MMEM:LOAD:STAT 1,""FREQPERF""
:MMEM:LOAD:STAT 0,""AMPTEST""
:*SAV 2
:MMEM:STOR:STAT 2,""SETTING2""
:*RCL 3
Load FREQPERF into memory 1
Load AMPTEST as current setting
Save current setting in memory 2
Store memory 2 to file “SETTING2”
Recall memory 3 as current setting
Command :OUTP[1|2]
Long
:OUTPut[1|2][:NORMal][:STATe]
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
ON | OFF | 1 | 0
OFF
Description Use this command to switch the normal OUTPUTs on or off.
Example
:OUTP1 ON
:OUTP2 OFF
Switch on OUTPUT 1
Switch off OUTPUT 2
Command :OUTP[1|2]:COMP
Long
:OUTPut[1|2]:COMPlement[:STATe]
Form Set & Query
Parameter
ON | OFF | 1 | 0
60

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
*RST value OFF
Description Use this command to switch the complement OUTPUTs on or off.
Example
:OUTP1:COMP ON
:OUTP2:COMP OFF
Switch on complement OUTPUT 1
Switch off complement OUTPUT 2
Command :CORR[1|2]:EDELay
Long
[:SOURce]:CORRection[1|2]:EDELay[:TIMe]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix
with engineering prefixes.
S
*RST value 0.0 s
Specified Limits –25.0 ns to +25.0 ns
Description Use this command to program the OUTPUT Deskew delay. This allows
you to deskew the OUTPUTS so that the zero-delay points of both
OUTPUT signals are the same at the device-under-test.
Example
:CORR1:EDEL 0NS
:CORR2:EDEL 5.18NS
Set OUTPUT 1 DESKEW to 0
Set OUTPUT 2 DESKEW to 5.18 ns
Command :CURR[1|2]
Long
[:SOURce]:CURRent[1|2][:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix
with engineering prefixes.
A
*RST value 20 mA (50 Ω into 50 Ω)
Specified Limits 3.8 V Outputs (50 Ω into short): max. 152 mA typical
3.0 V Outputs (50 Ω into short): max. 120 mA typical
61

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Value coupling
Amplitude = High – Low
Offset =
High – Low
2
Range coupling Offset
Description This command programs the amplitude current of the OUTPUT signal.
Note that to set the OUTPUT levels in terms of current, you first have to
execute the [:SOURce]:HOLD CURRent command to enable the
[:SOURce]:CURRent subsystem.
The available current range is limited by the specified voltage limits.
Example
Command :CURR[1|2]:OFFSet
Long
:HOLD CURR
:CURR1 75MA
[:SOURce]:CURRent[1|2][:LEVel][:IMMediate]:OFFSet
Enable CURRENT subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 amplitude to 75 mA
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix A with engineering prefixes.
*RST value 0.0 µA (50 Ω into 50 Ω)
Specified Limits 3.8 V Outputs (50 Ω into short): max. 152 mA typical
3.0 V Outputs (50 Ω into short): max. 120 mA typical
Value coupling
Amplitude = High – Low
Offset =
High – Low
2
Range coupling Amplitude
Description This command programs the offset current of the OUTPUT signal. Note
that to set the OUTPUT levels in terms of current, you first have to
62

SCPI Instrument Command List
execute the [:SOURce]:HOLD CURRent command to enable the
[:SOURce]:CURRent subsystem.
The available current range is limited by the specified voltage limits.
Example
:HOLD CURR
:CURR1:OFF 50MA
Enable CURRENT subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 offset to 50 mA
Command :CURR[1|2]:HIGH
Long
[:SOURce]:CURRent[1|2][:LEVel][:IMMediate]:HIGH
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix A with engineering prefixes.
*RST value +10 mA (50 Ω into 50 Ω)
Specified Limits 3.8 V Outputs (50 Ω into short): max. 152 mA typical
3.0 V Outputs (50 Ω into short): max. 120 mA typical
Value coupling
Programming Reference
Amplitude = High – Low
Offset =
High – Low
2
Range coupling Low-level
Description This command programs the High-level current of the OUTPUT signal.
Note that to set the OUTPUT levels in terms of current, you first have to
execute [:SOURCE]:HOLD CURRent command to enable the
[:SOURCE]:CURRent subsystem.
The available current range is limited by the specified voltage limits.
Example
:HOLD CURR
:CURR1:HIGH 150MA
Enable CURRENT subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 High-level to 150 mA
63

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :CURR[1|2]:LOW
Long
[:SOURce]:CURRent[1|2][:LEVel][:IMMediate]:LOW
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix
A
with engineering prefixes.
*RST value –10 mA (50 Ω into 50 Ω)
Specified Limits 3.8V Outputs (50 Ω into short): max. 152 mA typical
3.0V Outputs (50 Ω into short): max. 120 mA typical
Value coupling
Amplitude = High – Low
Offset =
High – Low
2
Range coupling High-level
Description This command programs the Low-level current of the OUTPUT signal.
Note that to set the OUTPUT levels in terms of current, you first have to
execute the
[:SOURce]:CURRent
[:SOURce]:HOLD CURRent
subsystem.
command to enable the
The available current range is limited by the specified voltage limits.
Example
:HOLD CURR
:CURR1:LOW 50 MA
Command :CURR[1|2]:LIM
Long
[:SOURce]:CURRent[1|2]:LIMit[:HIGH]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix
A
with engineering prefixes.
*RST value +10.0 mA
64
Enable CURRENT subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 Low-level to 50 mA

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Description Use this command to set/read the High-level current limit. If you switch
on current limiting, the High-level current cannot be set above the
programmed limit.
NOTE The current is NOT limited by the OUTPUT hardware, this is a software
limit.
Example
:HOLD CURR
:CURR1:LIM 50 MA
:CURR1:LIM:STAT ON
Enable CURRENT subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 High-level current limit to 50 mA
Switch on OUTPUT 1 limits
Command :CURR[1|2]:LIM:LOW
Long
[:SOURce]:CURRent[1|2]:LIMit:LOW
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix
with engineering prefixes.
A
*RST value –10.0 mA
Description Use this command to set/read the Low-level current limit. If you switch
on current limiting, the Low-level current cannot be set below the
programmed limit.
NOTE The current is NOT limited by the OUTPUT hardware, this is a software
limit.
Example
:HOLD CURR
:CURR1:LIM:LOW -50MA
:CURR1:LIM:STAT ON
Enable CURRENT subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 Low-level current limit to – 50mA
Switch on OUTPUT 1 limits
Command :CURR[1|2]:LIM:STAT
Long
[:SOURce]:CURRent[1|2]:LIMit:STATe
Form Set & Query
Parameter
ON | OFF | 1 | 0
65

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
*RST value OFF
Description This command switches the output limits on or off. When you switch on
the output limits cannot program the output-levels beyond the
programmed limits, until you switch off the output-limits. The limits
apply whether you program High/Low levels or Amplitude/Offset levels.
NOTE
You can switch the limits on and off in both the
[:SOURce]:CURRent
and the [
:SOURce]:VOLTage
but the current and voltage limits are not enabled/ disabled
independently
. The voltage and current limits are always enabled/
disabled together.
Example
:HOLD CURR
:CURR1:LIM 50MA
:CURR1:LIM:LOW -50MA
:CURR1:LIM:STAT ON
Command :FREQ
Long
[:SOURce]:FREQuency[:CW][:FIXed]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter Suffix Hz with engineering prefixes, or MHZ for Megahertz.
*RST value 1.00 MHz
Specified limits HP 81131A: 1 kHz to 400 MHz
HP 81132A: 1 kHz to 660 MHz
Value coupling
Period =
1
Enable CURRENT subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 High-level current limit to 50 m
Set OUTPUT 1 LOW-level current limit to –50mA
Switch on OUTPUT 1 limits
Frequency
subsystems
Description Use this command to set/read the pulse frequency. Select the frequency
source for the pulse frequency using :TRIGger:SOURce. The currently
selected source is programmed by this command. Note that the specified
limits and available resolution depend on the selected source.
66

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
You cannot set the pulse frequency if you have selected the CLK IN
connector as the frequency source (:TRIG:SOUR EXT).
Example
:TRIG:SOUR INT
:FREQ 75MHz
Select internal PLL as pulse trigger
Set pulse frequency to 75 MHz
Command :FREQ:AUTO
Long
[:SOURce]:FREQuency[:CW][:FIXed]:AUTO
Form Event
Parameter ONCE
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to measure the frequency at the CLK IN connector. If
the CLK IN connector is the selected pulse frequency source, you can
then read the measured value with :FREQ?
Example
:TRIG:SOUR EXT2
:FREQ:AUTO ONCE
:FREQ?
Select ext CLK IN as pulse trigger
Measure frequency at CLK IN
Query pulse frequency
Command :HOLD
Long
[:SOURce]:HOLD
Form Set & Query
Parameter VOLTage | CURRent
*RST value VOLT
Description Use this command to enable either of the [:SOURce]:VOLTage or
[:SOURce]:CURRent subsystems.
You can control the signal levels of the instrument OUTPUTs in terms of
voltage or current.
67

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :PHAS[1|2]
Long
[:SOURce]:PHASe[1|2][:ADJust]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix
DEG
or
RAD
. A parameter without a suffix is interpreted as
*RST value 0.0
Specified limits 0 to 360° constrained by delay and period limits.
Value coupling
Phase
Delay =
360
Period
×
RAD
.
Functional
coupling
Programming the pulse phase also executes
PHASe
so that the pulse phase is held constant when the signal frequency
[:SOURce]:PULSe:HOLD
is changed.
Description Use this command to set/read the relative phase-delay of the output
signal. This is equivalent to setting an absolute or percentage pulse-delay
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DELay
with
.
If you want the phase delay to remain constant when the pulse period is
varied (rather than the absolute pulse delay) use
Example
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DELay[1|2]:HOLD PRATio
:PULS:DEL1 500NS
:PHAS2 180 DEG
:PULS:DEL1:HOLD TIM
:PULS:DEL2:HOLD PRAT
Set OUTPUT 1 delay to 500ns
Set OUTPUT 2 phase to 180
Hold OUTPUT 1 delay constant with varying perio
Hold OUTPUT 2 phase constant with varying period
.
°
Command :PULS:DCYC[1|2]
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DCYCle[1|2]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix PCT
*RST value 10.0% (derived from Width and Period)
d
68

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Specified limits 0.1 – 99.9%, depends on Width & Period.
Value coupling
Width =
Description Use this command to program the dutycycle of the pulse signal. If you
want to set an absolute pulse-width use
[:SOURce]:PULSe:WIDTh[1|2].
If you want the pulse dutycycle to remain constant when the pulse period
is varied (rather than the absolute pulse width use)
[:SOURce]:PULSe:HOLD[1|2] DCYCle
Example
Command :PULS:DEL[1|2]
Long
:PULS:DCYC1 25PCT
:PULS:HOLD1 DCYC
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DELay[1|2]
Duty Cycle
100
×
Period
Set OUTPUT 1 dutycycle to 25%
Hold dutycycle constant with varying period
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix S with engineering prefixes. You can change the default unit using
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DELay[1|2]:UNIT.
*RST value 0.0
Specified limits 0 to 3.00 µs
Value coupling
Phase =
Delay
× 360
Period
Delay% =
Description Use this command to set/read the pulse-delay. Delay is the time between
the start of the pulse period and the start of the leading-edge of the pulse.
If you want the pulse-delay to remain constant when the pulse period is
Delay
Period
× 100
69

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
varied (rather than the phase-delay) use
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DELay[1|2]:HOLD TIME.
Example
:PULS:DEL1 500NS
:PHAS2 180 DEG
:PULS:DEL1:HOLD TIME
:PULS:DEL2:HOLD PRAT
Set OUTPUT1 delay to 500 ns
Set OUTPUT 2 phase to 180
Hold OUTPUT 1 delay constant with
varying period
Hold OUTPUT 2 phase constant with
varying period
°
Command :PULS:DEL[1|2]:HOLD
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DELay[1|2]:HOLD
Form Set & Query
Parameter TIME | PRATio
*RST value TIME
Description Use this command to set/read the coupling between the pulse period and
the pulse-delay:
Example
TIME The absolute pulse-delay is held fixed when the pulse period is
PRATio The pulse phase-delay (delay as ratio of period) is held fixed
:PULS:DEL1 500ns
:PHAS2 180DEG
:PULS:DEL1:HOLD TIME
:PULS:DEL2:HOLD PRAT
varied (Pulse phase varies).
when the pulse period is varied. (Pulse-delay varies).
Command :PULS:DEL[1|2]:UNIT
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DELay[1|2]:UNIT
Form Set & Query
Parameter S | SEC | PCT | DEG | RAD
*RST value SEC
70
Set OUTPUT 1 delay to 500ns
Set OUTPUT 2 phase to 180°
Hold OUTPUT 1 delay constant with varying period
Hold OUTPUT 2 phase constant with varying period

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Description Use this command to set/read the default units for the pulse-delay
parameter. The default unit of a parameter is the unit used when the
parameter is programmed to a value without a unit suffix.
Example
:PULS:DEL1:UNIT PCT
:PULS:DEL1 50
Set OUTPUT 1 delay unit to %
Set OUTPUT 1 delay to 50% of period
Command :PULS:HOLD[1|2]
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:HOLD[1|2]
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
WIDTh | DCYCle | TDELay
WIDTh
Description Use this command to set whether the pulse-width, the pulse-dutycycle or
the pulse trailing-edge delay is held constant when the pulse period is
changed.
Example
:PULS:DEL:HOLD1 TIME
:PULS:DEL 20NS
:PULS:HOLD1 DCYC
:PULS:DCYC 25PCT
Hold OUTPUT 1 delay fixed when frequency varies
Set OUTPUT 1 delay to 20ns
Hold OUTPUT 1 Dutycycle fixed when frequency
varies
Set OUTPUT 1 Dutycycle to 25%
Command :PULS:PER
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:PERiod
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter SuffixS with engineering prefixes.
*RST value 1 µs
Specified limits HP 81131A: 2.5 ns to 1 ms
HP 81132A: 1.5 ns to 1 ms
71

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Value coupling
Frequency =
1
Period
Description Use this command to set/read the pulse period. Select the pulse period
source using :TRIGger:SOURce. The currently selected source is
programmed by this command. Note that the specified limits and
available resolution depend on the selected source.
You cannot set the pulse period if you have selected the CLK IN
connector as the frequency source (:TRIG:SOUR EXT2).
Example
:TRIG:SOUR INT
:PULS:PER 25NS
Command :PULS:PER:AUTO
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:PERiod:AUTO
Form Event
Select internal PLL as pulse trigger
Set pulse frequency to 25 ns
Parameter ONCE
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to measure the period at the CLK IN connector. If the
CLK IN connector is the selected pulse period source, you can then read
the measured value with :PULS:PER?
Example
:TRIG:SOUR EXT2
:PULS:PER:AUTO ONCE
:PULS:PER?
Select ext CLK IN as pulse trigger
Measure period at CLK IN
Query pulse period
Command :PULS:TDEL[1|2]
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:TDELay[1|2]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter Suffix S with engineering prefixes.
72

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
*RST value 100 ns
Specified Limits HP 81131A: 1.25 ns to 999.9 µs
HP 81132A: 0.75 ns to 999.9 µs
Description Use this command to program the delay of the trailing-edge of the pulse
relative to the start of the pulse period. This is an alternative method of
programming the pulse-width.
Example
:PULS:DEL1 500NS
:PULS:DEL1:HOLD TIME
:PULS:TDEL1 750NS
Set OUTPUT 1 delay to 500 ns
Hold OUTPUT 1 delay constant with varying period
Set OUTPUT 1 trailing delay to 750 ns
Command :PULS:TRAN[1|2]:UNIT
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:TRANsition[1|2]:UNIT
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
S | SEC | PCT
SEC
Description Use this command to set the default units for the pulse transition-times.
The default unit is used when the parameter is programmed to a value
without a unit suffix.
Command :PULS:TRAN[1|2]
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:TRANsition[1|2][:LEADing]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffixS with engineering prefixes
*RST value 0.8 ns
Specified limits HP 81131A: 0.8 ns or 1.6 ns
Parameter
Trailing-edge = Leading-edge fixed coupled
coupling
73

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Description Use this command to set/read the transition-time of the pulse leading-
edge. Note that the leading and trailing edges of the pulse have to fit
within the defined pulse-width.
Example
:PULS:TRAN1 1.6NS
Set OUTPUT 1 leading edge to 1.6 ns
NOTE Selectable transition time is only available with HP 81131A.
Command :PULS:TRAN[1|2]:TRA
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:TRANsition[1|2]:TRAiling
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffixS with engineering prefixes.
*RST value 0.8 ns
Specified limits HP 81131A: 0.8 ns or 1.6 ns
Parameter
Trailing-edge = Leading-edge fixed coupled
coupling
Description Use this command to set/read the transition-time of the pulse trailing-
edge. Note that the leading and trailing edges of the pulse have to fit
within the defined pulse-width.
NOTE Selectable transition time is only available with HP 81131A.
Command :PULS:TRIG[1]:MODE
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:TRIGger[1]:MODE
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
CONTinuous | STARt
STARt
74

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Description Use this command to set/read the TRIGGER OUT generation mode in
pattern mode.
Command :PULS:TRIG[1]:POS
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:TRIGger[1]:POSition
Form Set & Query
Parameter
1 | 2 | 3 | 4
*RST value 1
Description Use this command to set/read the TRIGGER OUT position in pattern
mode. The specified value selects a segment number for the HP 81130A.
Command :PULS:TRIG[1]:VOLT
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:TRIGger[1]:VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate]
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
TTL | PECL | SYM | ECLG ND | ECLN2 V
TTL
Description Use this command to set/read the output levels at the TRIGGER OUT
connector.
Termination
Value High Level Low Level
TTL 2,5V 0V 0V 50
PECL 4,2V 3,3V 3,0V 50
SYM 0,5V –0.5V 0V 50
ECLGND –0,8V –1,7V 0V 50
ECLN2V –0,8V –1,7V –2,0V 50
Vol tage
Termination
Resistor
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
75

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :PULS:WIDT[1|2]
Long
[:SOURce]:PULSe:WIDTh[1|2]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix
S
with engineering prefixes
*RST value 100 ns
Specified Limits HP 81131A: 1.25 ns to 999.9 µs
HP 81132A: 0.75 ns to 999.9 µs
Description Use this command to program the width of the pulse signal. If you want
to set width as dutycycle use
[:SOURce]:PULSe:DCY Cle[1 |2]
.
If you want the pulse-width to remain constant when the pulse period is
varied (rather than the dutycycle) use
[:SOURce]:PULSe:HOLD[1|2 ]
WIDTh.
Example
:PULS:WIDT1 50NS
:PULS:HOLD1 WIDTH
Set OUTPUT 1 pulse width to 50 ns
Hold pulse-width constant with varying period
Command :ROSC:SOUR
Long
[:SOURce]:ROSCillator:SOURce
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
INTernal | EXTernal
INT
Description Use this command to set/read the reference source for the PLL. If you
select the external reference (CLK IN connector) you can choose to use a
1 MHz, 2 MHz, 5 MHz or 10 MHz reference signal using
:ROSC:EXT:FREQ.
INTernal Lock the PLL to its internal reference
EXTernal Lock the PLL to a reference signal at the CLK IN connector. The exter-
nal reference signal can be 1, 2, 5 or 10 MHz.
Example
:ROSC:SOUR EXT
:ROSC:EXT:FREQ 10 MHZ
Set external PLL reference (CLK IN)
Set expected PLL reference frequency
to 10 MHz
76

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :ROSC:EXT:FREQ
Long
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
*RST value 5 MHz
Specified limits 1 MHz, 2 MHz , 5 MHz or 10 MHz
Description Use this command to set/read the expected reference frequency for the
Example
Command :VOLT[1|2]
Long
[:SOURce]:ROSCillator:EXTernal:FREQuency
PLL at the CLK IN connector. The external reference can be a 1, 2, 5 or 10
MHz signal. Note that if you program any value other than the specified
values, the value will be set to the nearest of the specified values.
:ROSC:SOUR EXT
:ROSC:EXT:FREQ 10MHZ
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2][:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]
Set external PLL reference (CLK IN)
Set expected PLL reference frequency to 10 MHz
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffixV with engineering prefixes.
*RST value 1.00 V
Specified Limits HP 81131A: 0.10 Vpp to 3.80 Vpp
HP 81132A: 0.10 Vpp to 2.50 Vpp
Value coupling
High = Offset +
Amplitude
2
Low = Offset
–
Amplitude
2
Range coupling Offset
77

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Description This command programs the amplitude voltage of the OUTPUT signal.
Note that to set the OUTPUT levels in terms of voltage, you first have to
execute the [:SOURce]:HOLD VOLTage command to enable the
[:SOURce]:VOLTage subsystem.
The available voltage range is limited by the specified current limits.
Example
:HOLD VOLT
:VOLT1 2V
Enable VOLTAGE subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 amplitude to 2 V
Command :VOLT[1|2]:OFFSet
Long
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2][:LEVel][:IMMediate]:OFFSet
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix V with engineering prefixes.
*RST value 0.0 mV
Specified Limits HP 81131A: –1.95 V to 3.75 V
HP 81132A: –1.95 V to 2.95 V
Value coupling
High = Offset +
Amplitude
2
Low = Offset
–
Amplitude
2
Range coupling Amplitude
Description This command programs the offset voltage of the OUTPUT signal. Note
that to set the OUTPUT levels in terms of voltage, you first have to
execute the [:SOURce]:HOLD VOLTage command to enable the
[:SOURce]:VOLtage subsystem.
The available voltage range is limited by the specified current limits.
Example
:HOLD VOLT
:VOLT1:OFF -800MV
78
Enable VOLTAGE subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 offset to –800mV

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :VOLT[1|2]:HIGH
Long
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2][:LEVel][:IMMediate]:HIGH
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffixV with engineering prefixes.
*RST value 500 mV
Specified Limits HP 81131A: –1.90 V to 3.80 V
HP 81132A: –1.90 V to 2.50 V
Value coupling
Amplitude = High – Low
Offset =
High – Low
2
Range coupling Low-level
Description This command programs the High-level voltage of the OUTPUT signal.
Note that to set the OUTPUT levels in terms of voltage, you first have to
execute the
[:SOURce]:VOLTage
[:SOURce]:HOLD VOLTage
subsystem.
command to enable the
The available voltage range is limited by the specified current limits.
Example
:HOLD VOLT
:VOLT1:HIGH 2V
Command :VOLT[1|2]:LOW
Long
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2][:LEVel][:IMMediate]:LOW
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix
V
with engineering prefixes.
*RST value –500 mV
Specified Limits HP 81131A: –2.00 V to 3.70 V
Enable VOLTAGE subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 high level voltage to 2 V
79

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
HP 81132A: –2.00 V to 2.90 V
Value coupling
Amplitude = High – Low
Offset =
High – Low
2
Range coupling High-level
Description This command programs the Low-level voltage of the OUTPUT signal.
Note that to set the OUTPUT levels in terms of voltage, you first have to
execute the [:SOURce]:HOLD VOLTage command to enable the
[:SOURce]:VOLTage subsystem.
The available voltage range is limited by the specified current limits.
Example
:HOLD VOLT
:VOLT1:LOW 500MV
Command :VOLT[1|2]:LIM
Long
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit[:HIGH]
Enable VOLTAGE subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 low-level to 500mV
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix V with engineering prefixes.
*RST value +500 mV
Description Use this command to set/read the High-level voltage limit. If you switch
on voltage limiting, the High-level voltage cannot be set above the
programmed limit. Note that the voltage is NOT limited by the OUTPUT
hardware, this is a software limit.
Example
:HOLD VOLT
:VOLT1:LIM 2V
:VOLT1:LIM:STAT ON
Enable VOLTAGE subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 High-level limit to 2 V
Switch on OUTPUT 1 limits
80

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :VOLT[1|2]:LIM:LOW
Long
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:LOW
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffixV with engineering prefixes.
*RST value –500 mV
Description Use this command to set/read the Low-level voltage limit. If you switch
on voltage limiting, the Low-level voltage cannot be set below the
programmed limit. Note that the voltage is NOT limited by the OUTPUT
hardware, this is a software limit.
Example
:HOLD VOLT
:VOLT1:LIM:LOW 0V
:VOLT1:LIM:STAT ON
Enable VOLTAGE subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 Low-level voltage
Switch on OUTPUT 1 limits
Command :VOLT[1|2]:LIM:STAT
Long
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[1|2]:LIMit:STATe
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
ON | OFF | 1 | 0
OFF
Description This command switches the output limits on or off. When you switch on
the output limits cannot program the output-levels beyond the
programmed limits, until you switch off the voltage-limits. The limits
apply whether you program High/Low levels or Amplitude/Offset levels.
NOTE You can switch the limits on and off in both the
and the
[:SOURce]:VOLTage
subsystems but the current and voltage
[:SOURce]:CURRent
limits are not enabled/ disabled independently. The voltage and current
limits are always enabled/disabled together.
Example
:HOLD VOLT
:VOLT1:LIM 2V
:VOLT1:LIM:LOW 0V
:VOLT1:LIM:STAT ON
Enable VOLTAGE subsystem
Set OUTPUT 1 High level voltage limit to 2
Set OUTPUT 1 Low-level voltage limit to 0
Switch on OUTPUT 1 limits
V
81

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :STATus:OPERation
This command tree accesses the OPERation status group. The
OPERation status group is not used by the instrument therefore this
command tree is redundant.
:STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?
:STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle
:STATus:OPERation:NTRansition
:STATus:OPERation:PTRansition
Command :STATus:PRESet
Long
:STATus:PRESet
Form Event
*RST value Not Applicable
Description This command
• Clears all status group event-registers
• Clears the error queue
• Presets the status group enable-, PTR-, and NTR-registers as follows:
Status Group Register Preset value
OPERation ENABle
QUEStionable ENABle
82
PTR
NTR
PTR
NTR
0000000000000000
0111111111111111
0000000000000000
0000000000000000
0111111111111111
0000000000000000

Command :STATus:QUEStionable
This command tree accesses the QUEStionable status group. The
QUEStionable status group contains warning bits for voltage, current,
time and frequency parameters. A warning occurs when the output signal
could be out of specification due to the combined specification
uncertainties of many parameters, although all parameters are set within
their individually specified limits. If a parameter is set outside its
specified limits an error is generated.
The following commands are used to access the registers within the
status group:
1. :STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt]?
Form
*RST value
Description
Query
Not Applicable
This command reads the event register in the QUEStionable status
group.
2. :STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Form
*RST value
Description
Query
Not Applicable
This command reads the condition register in the QUEStionable
status group.
Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
3. :STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle
Form
Parameter
*RST value
Specified
limits
Description
Set & Query
Numeric
Not affected by *RST
0 – 32767
This command sets or queries the enable register in the
QUEStionable status group.
4. :STATus:QUEStionable:NTRansition
Form
Parameter
*RST value
Specified
limits
Description
Set & Query
Numeric
Not applicable
0 – 32767
This command sets or queries the negative transition register in
the QUEStionable status group.
83

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
5. :STATus:QUEStionable:PTRansition
Form
Parameter
*RST value
Specified
limits
Description
Set & Query
Numeric
Not applicable
0 – 32767
This command sets or queries the positive transition register in the
QUEStionable status group.
Command :SYST:ERR?
Long
:SYSTem:ERRor?
Form Query
*RST value Not Applicable
Description Use this command to read the instrument error queue. The instrument
error queue can store up to 30 error codes on a first-in-first-out basis.
When you read the error queue, the error number and associated
message are put into the instrument's output buffer.
If the queue is empty, the value 0 is returned, meaning
No Error
. If the
queue overflows at any time, the last error code is discarded and
Example
replaced with
:SYS:ERR?
-350
meaning
Queue overflow
Query for errors
.
Output example:
-222 "Data out of range" overlap at output 1: Width>Period
The above message is an example of a customized description. Generic
descriptions are available in the SCPI 1995 Command Reference, items
21.8.4 to 21.8.11.
":SYST:WARN:STR?"
Send
. Alternatively, the HELP key shows the
current errors and warnings and their description on the instruments
display.
84

Command :SYST:KEY
Long
:SYSTem:KEY
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter suffix No suffix allowed
*RST value Not Applicable
Specified limits
No. Key Description
255 No key pressed (Query only)
0 DATA ENTRY 0
1 DATA ENTRY 1
2 DATA ENTRY 2
3 DATA ENTRY 3
4 DATA ENTRY 4
5 DATA ENTRY 5
6 DATA ENTRY 6
7 DATA ENTRY 7
8 DATA ENTRY 8
9 DATA ENTRY 9
10 DATA ENTRY .
11 DATA ENTRY
12 Cursor Up
13 Cursor Down
14 Cursor Left
15 Cursor Right
16
17
18
MAN
STORE
HELP
Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
+/–
85

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
No. Key Description
19
20
21 Softkey 1
22 Softkey 2
23 Softkey 3
24 Softkey 4
25
26
27
28
29 Modify Knob Left (counter-clockwise)
30 Modify Knob Right (clockwise)
SHIFT
MORE
NANO
MICRO/MEGA
MILLI/KILO
ENTER
Description In query form, this command reads the last key pressed. The buffer is
emptied by *RST and returns the value -1 when empty.
In set form, the command simulates pressing a key on the frontpanel.
Simulated key-press are also recorded as the last key pressed.
NOTE :SYST:KEY 19 sets the instrument to LOCAL mode.
1. In remote mode only the softkeys under the display and the SHIFT
(LOCAL) key are active. Since the instrument normally switches to
remote mode when any command is received, including
:SYSTem:KEY, simulating one of the other disabled keys has no
effect.
2. If you want to simulate full frontpanel operation, you must prevent
the instrument from entering remote mode by using the REN line of
the HP-IB to maintain local mode (LOCAL 7 in BASIC).
If you do this, the :SYSTem:KEY command is the only command which
works. Any other commands will be buffered in the instrument blocking
any further :SYSTem:KEY commands, until remote mode is enable.
86

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :SYST:PRES
Long
:SYSTem:PRESet
Form Same as *RST
Command :SYST:SEC
Long
:SYSTem:SECurity[:STATe]
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
ON|OFF
OFF
Description
CAUTION Do not switch on system security unless you are willing to erase the
instrument settings stored in the instrument. All instrument memories,
including the current setting, will be overwritten with the default settings
if you
• Switch off system security
• Switch the instrument off and on again
• If you accidentally switch on system security, and want to rescue the
settings stored in the instrument, store the settings on a memory card.
You can then recall them from the memory card later.
Use this command to switch on system security mode. Switch on system
security if you need to make sure that all instrument settings stored in
the instrument are erased automatically when the instrument is switched
off, or when security mode is switched off.
The instrument settings are erased by overwriting them with the default
settings.
System security mode is not available via the frontpanel. If you want to
erase all settings by hand:
1 SHIFT STORE 0 to RECALL the default settings from memory 0.
2 STORE 1, STORE 2 ,...,STORE 4 to store the defaults in memories 1 to 4.
87

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :SYST:SET
Long
:SYSTem:SET
Form Set & Query
Parameter Block data
*RST value Not applicable
Description In query form, the command reads a block of data containing the
instrument's complete set-up. The set-up information includes all
parameter and mode settings, but does not include the contents of the
instrument setting memories, the status group registers or the
:DISPlay[:WINDow][:STATe]
The data is in a binary format, not
ASCII, and cannot be edited.
In set form, the block data must be a complete instrument set-up read
using the query form of the command.
Command :SYST:VERS?
Long
:SYSTem:VERSion?
Form Query
*RST value "1992.0"
Description This command reads the SCPI revision to which the instrument
complies.
Command :SYST:WARN?
Long
:SYSTem:WARNing[:COUNt]?
Form Query
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to read the number of warnings which are currently
active. Note that the warning status of voltage, current, time and
frequency are also summarized by bits in the QUESTionable Status
register.
88

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :SYST:WARN:STR?
Long
:SYSTem:WARNing:STRing?
Form Query
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to read all the currently active warning messages. The
warning messages are concatenated to form a single string with a ; as
separator between the messages.
Command :SYST:WARN:BUFF?
Long
:SYSTem:WARNing:BUFFer?
Form Query
*RST value Not applicable
Description Use this command to read the maximum possible number of characters
which could be returned by
:SYST:WARN:STR?
if all warnings were
active.
Command :TRIG:COUN
Long
:TRIGger[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt]:COUNt
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
*RST value 1
Specified limits 1 to 65504
Description Use this command to set/read the number of trigger events (pulse
periods) to be generated for each arming event in pulse and burst mode
(in pattern mode the number of trigger events depends on the used
89

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
sequence). This corresponds to selecting the event mode on the MODE/
TRG screen:
PULSES
Set a trigger count of 1 so that a single pulse period is
generated for each arming event.
BURST of
Set a trigger count of 2 to 65504 so that a burst of 2 to 65504
pulse periods is generated for each arming event. Switch off
pattern mode so that a pulse is generated in each pulse
period. (
:DIG:PATT OFF
)
NOTE For a started burst this command will reduce the number of pulses on
channel 1 and channel 2 (:TRIGger:COUNt:PULSes[1|2]) to the value
set by :TRIGger:COUNt. Changes of the number of pulses on the
channels will increase the value to of :TRIGger:COUNt to reflect the
changes on the channels.
Examples To set STARTED BURST of 16 pulse periods and 6 Pulses at
Out1, the burst are started by a positive level at the EXT INPUT:
:ARM:SOUR EXT1
:ARM:MODE STAR
:ARM:SENS POS
:TRIG:COUN 16
:TRIG:COUN:PULS1 6
:TRIG:SOUR INT1
:DIG:PATT OFF
Set arming from EXT INPUT
Set started mode
Set arming on positive level
Burst length 16
Number of pulses at OUTPUT 1
Pulse period trigger from internal PLL.
Disable pattern operating mode
To set GATED PULSES Pulses at Out1, gated by a positive level at the
EXT INPUT:
:ARM:SOUR EXT1
:ARM:MODE GAT
:ARM:SENS POS
:TRIG:COUN 1
:TRIG:SOUR INT1
:DIG:PATT OFF
Set arming from EXT INPUT
Set arming on levels
Set arming on positive level 1 pulse period
Single pulse output mode
Pulse period trigger from internal PLL.
Disable pattern data
90

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Influence of :TRIGger:COUNt and :TRIGger:COUNt:PULSes[1|2] in
started burst mode:
:ARM:SOUR IMM
TRIG:COUN 1
:ARM:MODE STAR
:TRIG:COUN:PULS1 20
:TRIG:COUN 5
:TRIG:COUN:PULS1?
:TRIG:COUN?
:TRIG:COUN:PULS1 10
:TRIG:COUN?
:TRIG:COUN 20
:TRIG:COUN?
:TRIG:COUN 8
:TRIG:COUN:PULS1?
:TRIG:COUN 1
:TRIG:COUN:PULS1?
⇒
⇒
⇒
5
10
10
⇒
⇒
⇒
5
8
8
Set continuous mode
Set Pulse mode
Prepare started mode
Set number of pulses on channel 1 to 20
Set Burst mode with a length of 5 clocks,
the number of pulses on both channels
will be reduced to 5 if necessary.
Request number of pulses on channel 1
Request number of clock within the
started burst
Set number of pulses on channel 1 to 10
Request number of clocks within the
started burst
Set number of clocks within the started
burst to 20
Request the number of clocks with in
the started burst. The return value is 10,
because none of the channels will generate more than 10 pulses.
Set the number of clocks within the
started burst to 8.
Request the number of pulses on channel 1. The return value is 8, because the
number of clocks has been decreased to
a value less than the currently used
number of pulses on channel 1.
Set Pulse mode
Request the number of pulses on channel 1. The value stays unchanged, since
the instrument is no longer in started
burst mode.
91

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :TRIG:COUN:PULS[1|2]
Long
:TRIGger[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt]:COUNt:PULSes[1|2]
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
*RST value 2
Specified limits 2 to 65504
Description Use this command to set/read the number of pulses within a burst at
OUTPUT 1 or OUTPUT 2.
Examples To set
Out1
:ARM:SOUR EXT1
:ARM:MODE STAR
:ARM:SENS POS
:TRIG:COUN 16
:TRIG:COUN:PULS1 6
:TRIG:SOUR INT1
:DIG:PATT OFF
STARTED BURST of 16 pulse periods
, the burst is started by a positive level at the EXT INPUT:
Set arming from EXT INPUT
Set started mode
Set arming on positive level
Burst length 16
Set 6 pulses at OUTPUT 1
Pulse period trigger from internal PLL.
Disable pattern operating mode
6 Pulses at
and
Command :TRIG:LEV:TERM
Long
:TRIGger[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt]:LEVel:TERMination
Form Set & Query
Parameter Numeric
Parameter SuffixV with engineering prefixes.
*RST value 0.0 V
Specified Limits –2.1V to +3.3V
Description Use this command to program the termination voltage compensation of
the CLK IN connector.
Example
:TRIG:LEV:TERM 2.5V
Set CLK IN termination voltage to 2.5 V
92

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
Command :TRIG:SOUR
Long
:TRIGger[:SEQuence[1] | :STARt]:SOURce
Form Set & Query
Parameter
*RST value
IMMediate | INTernal[1] | EXTernal2
INT
Description Use this command to select the pulse period source of the HP 81130A by
selecting the source of the pulse period trigger signal:
Pulse period sources set by
:TRIG:SOUR
Pulse period source :TRIG:SOURce
internal PLL
CLK IN
IMMediate | INTernal[1]
EXTernal2
93

Programming Reference
SCPI Instrument Command List
94

3
3Specifications
In this chapter you will find the specifications of the HP 81130A Pulse
Generator and its output modules HP 81131A and HP 81132A.
At the end of this chapter, “Pulse Parameter Definitions” on page 111
provides detailed information on the definition of the pulse parameters
used by the instrument.
NOTE
Warranted Performance
Specifications describe the instrument’s warranted performance. Nonwarranted values are described as typical. All specifications apply after a
30 minute warm-up phase with 50 Ohm source, a 50 Ohm load resistance
and separate channels. They are valid from 0 °C to 55 °C ambient
temperature.
95

Specifications
Declaration of Conformity
Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer
Safety Standard
EMC Standard
Supplementary
Information
Hewlett-Packard GmbH
Boeblingen Instruments Division
Herrenberger Str.110–140
D-71034 Boeblingen, Germany
We declare that the system:
HP 81100 Family of Pulse-/Data Generators
HP 81110 A 330/165 MHz Pulse/Pattern Generator
HP 81104 A 80 MHz Pulse Pattern Generator
HP 81101 A 50 MHz Pulse Pattern Generator
HP 81112 A 330 MHz , 3.5V Output Module
HP 81130 A * 400/660 MHz Puls-/Pattern Generator
HP 81131 A * 400 MHz , 3.5V Output Module
HP 81132 A * 660 MHz , 2.5V Output Module
conforms to the following standards:
IEC 1010-1:1990 +A1:1992 EN61010-1:1993
EN 55011:1991 / CISPR 11 Group 1, Class B
* EN 55011:1991 / CISPR 11 Group 1, Class A
EN 61000-4-2:1995 ESD: 4kVcd; 8 kVad;4kV c.p.
EN 61000-4-3:1995 Radiated Immunity: 3V/m 80%AM
ENV 50204: 1995 Radiated Immunity: 3V/m; 50%Dty
EN 61000-4-4:1995 Fast Transients/Bursts: 0.5kV, 1kV
EN 61000-4-5:1995 Surges: 1kVdiff; 2kV com.mode
EN 61000-4-6:1995 Conducted Immunity
EN 61000-4-8:1993 Power freq. magn. field 3A/m; 50Hz
IEC1000-4-11:1994 Voltage Dips and Interruptions
The product herewith complies with the requirements of the
•
Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC) and the
•
EMC Directive (89/336/EEC).
During the measurements against EN55011, the I/O ports were terminated with their
nominal impedance, the HP-IB connection was terminated with the cable HP 10833B.
When the product is connected to other devices, the user must ensure that the connecting
cables and the other devices are adequately shielded to prevent radiation.
Boeblingen, June 09th 1998 Wolfgang Fenske
Regulation Consultant
96

Specifications
HP 81130A Specifications
HP 81130A Specifications
General
Environmental Conditions
Operating temperature: 0°C to +55°C
Storage temperature: –40°C to +70°C
Humidity: 95% r.h. up to 40°C ambient temperature
Altitude: up to 2000 m
Installation: Category II
Pollution: Degree 2
EMC: conforms to EN50082-1, EN55011, Class A
Battery: Lithium, type CR2477-N
(HP part number 1420-0557)
Safety
IEC1010, CSA1010
Power requirements
100–240 Vac, ±10%, 50–60 Hz;
100–120 Vac, ±10%, 400 Hz
Power consumption: 300 VA max.
Maximum Dimensions (H x W x D)
89 mm x 426 mm x 521 mm
97

Specifications
HP 81130A Specifications
Weight
Net
8.5 kg Single Channel
9.2 kg Dual Channel
Shipping
13.8 kg Dual Channel
Recalibration period
1 year recommended
Warranty
3 years standard
Acoustic Noise Emission
For ambient temperature up to 30°C,
under normal operation and at the typical operator position:
LpA = 52 dB (5.9 bel) typical {47 dB (5.3 bel) at 23°C) typical}
Measured in accordance with ISO 7779/EN 27779.
98

Specifications
HP 81130A Specifications
Timing Specifications
The timing characteristics are measured at 50% amplitude at fastest
transitions in continuous mode and 50 Ω load impedance.
NOTE The HP 81130A is designed and recommended for an operation in the
frequency range of 170 kHz to 400/660 MHz. However it can be operated
in the extended range down to 1 kHz. Changes in specifications below
170 kHz are set in brackets [].
Period & Frequency
Period can also be entered as frequency.
Period & Frequency
Period range: 2.5 ns to 1 ms 1.5 ns to 1 ms
Frequency range: 1 kHz to 400.0 MHz 1 kHz to 660.0 MHz
Period/frequency
resolution:
Period accuracy
RMS-jitter:
(internal reference,
internal clock)
a
In burst mode the first period may be decreased by 150 ps.
HP 81130A with HP 81131A
a
:
4 digits, 2 ps best case
HP 81130A with HP 81132A
± 100 ppm [0.01%]
0.001% + 15 ps
Repeatability is typically four times better than accuracy.
99

Specifications
HP 81130A Specifications
Width
The width can be entered as absolute width, duty cycle, or trailing edge
delay.
Widt h
Width range: 1.25 ns to (period – 1.25 ns) 750 ps to (period – 750 ps)
Resolution: 4 digits, 2 ps best case [0.05% of period]
Accuracy:
Jitter: 0.001% + 15 ps
HP 81130A with HP 81131A
100 ppm ± 200 ps [± 0.06% of period]
±
HP 81130A with HP 81132A
Delay
Measured between trigger output and main output. Can be entered as
absolute delay, phase ° or % of period.
Delay
Variable delay range: 0 to 3.00 µs: independent of period
Resolution: 4 digits, 2 ps best case [0.05% of period]
Accuracy:
Jitter: 0.001% + 15 ps
Fixed Delay: 32 ns typ.
HP 81130A with HP 81131A
> 3.00 µs: 0 ns to 1 period
(0.01% + 100 ps) relative to the zero-delay
±
HP 81130A with HP 81132A
[±0.035% of period]
Deskew
Compensation for different cable delays.
Deskew
Range:
Resolution: 4 digits, 2 ps best case
HP 81130A with HP 81131A
HP 81130A with HP 81132A
25 ns
±
For frequencies >170 kHz only.
100

Specifications
HP 81130A Specifications
Transi t ion Times
Measured between 10% and 90% of amplitude, except for ECL levels (20%
and 80% of amplitude).
Tran si ti on Ti mes
Range:
Minimum transition:
At ECL levels: <450 ps < 350 ps (200 ps typ.)
HP 81130A with HP 81131A
800 ps or 1600 ps
(selectable)
600 ps for Vpp ≤ 1 V
≤
900 ps for Vpp > 1 V
≤
HP 81130A with HP 81132A
fixed
500 ps typ.
Digital Channel Add
In this mode, channel 1 and channel 2 are added and fed to channel 1
output. Channel 2 is still available.
101
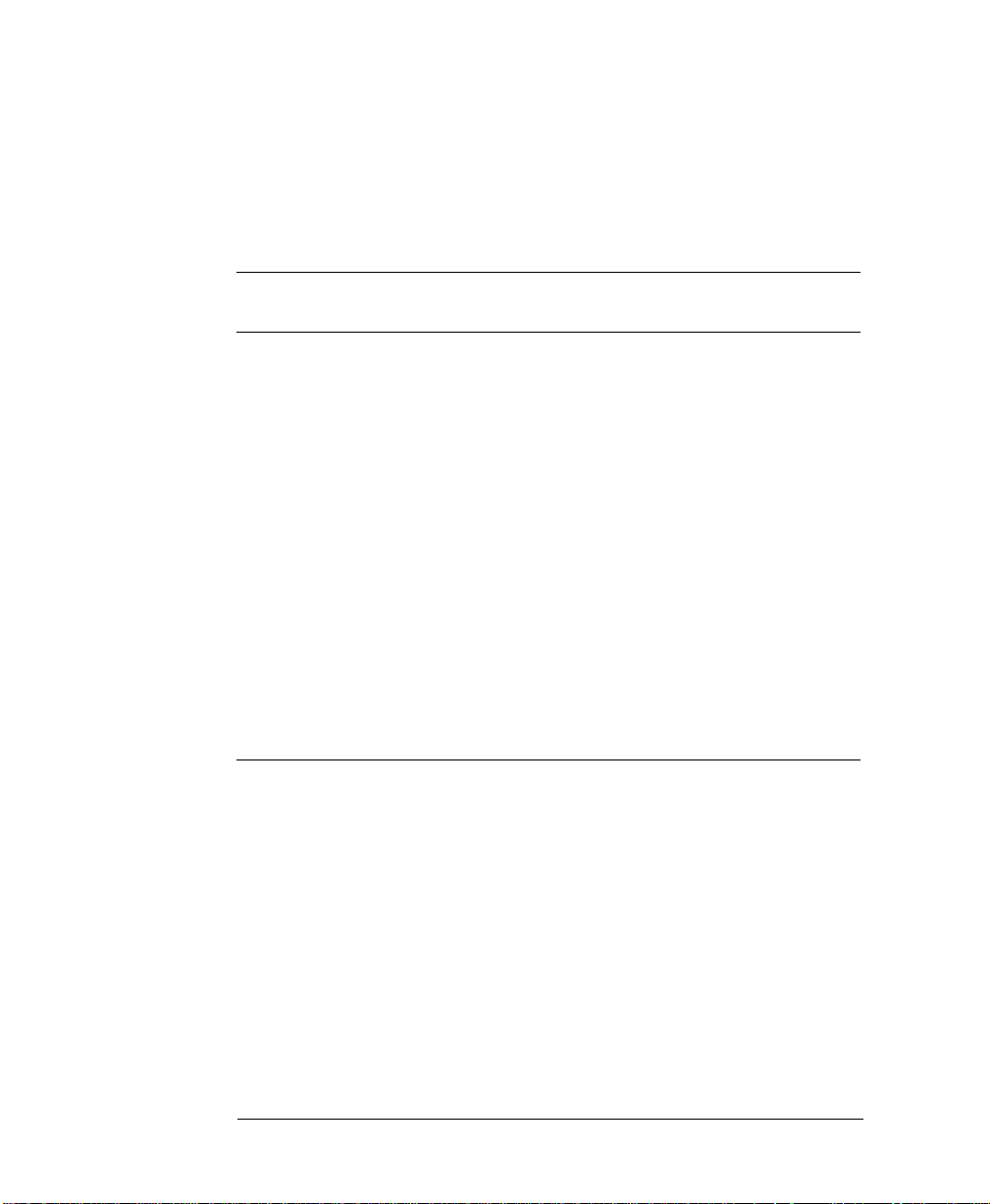
Specifications
HP 81130A Specifications
Main Output Level Specifications
Level parameters can be entered as high/low level in terms of voltage or
current or offset/amplitude.
Level
Specifications
Output impedance: 50 Ω ± 1% typ. 50 Ω ± 5% typ.
Max. external voltage: –2.2 V to +5.5 V –2.0 V to +4.0 V
Amplitude: 0.10 Vpp to 3.80 Vpp 0.10 Vpp to 2.50 Vpp
Level window: –2.00 V to +3.80 V –2.00 V to +3.00 V
Accuracy:
Limits: high and low level can be limited to protect the DUT
Resolution: 3 digits (10 mV best case)
Short circuit current: –80 mA to +152 mA –80 mA to +120 mA
Baseline noise: 4 mV RMS typ. 8 mV RMS typ.
Connectors: SMA(f) 3.5 mm
Overshoot/preshoot/
ringing:
Normal/inverted: differential outputs
ON/OFF: relays connect/disconnect output (HiZ)
HP 81130A with HP 81131A
(2% + 50 mV)
±
(5% +50 mV) of amplitude typ.
±
HP 81130A with HP 81132A
(5% + 50 mV)
±
102
 Loading...
Loading...