Page 1

Service Guide
For safety and warranty information see
the page immediately after the schematics.
Publication Number 33220-90012 (order as 33220-90100 manual set)
Edition 2, March 2005
Copyright © 2003, 2005 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Agilent 33220A
20 MHz Function/
Arbitrary Waveform Generator
Page 2

Agilent 33220A at a Glance
The Agilent Technologies 33220A is a 20 MHz synthesized function
generator with built-in arbitrary waveform and pulse capabilities.
Its combination of bench-top and system features makes this function
generator a versatile solution for your testing requirements now and in
the future.
Convenient bench-top features
• 10 standard waveforms
• Built-in 14-bit 50 MSa/s arbitrary waveform capability
• Precise pulse waveform capabilities with adjustable edge time
• LCD display provides numeric and graphical views
• Easy-to-use knob and numeric keypad
• Instrument state storage with user-defined names
• Portable, ruggedized case with non-skid feet
Flexible system features
• Four downloadable 64K-point arbitrary waveform memories
• GPIB (IEEE-488), USB, and LAN remote interfaces are standard
• SCPI (Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments) compatibility
Note:
Unless otherwise indicated, this manual applies to all Serial
2
Numbers.
Page 3

The Front Panel at a Glance
1 Graph Mode/Local Key
2 On/Off Switch
3 Modulation/Sweep/Burst Keys
4 State Storage Menu Key
5 Utility Menu Key
6 Help Menu Key
7 Menu Operation Softkeys
8 Waveform Selection Keys
9 Manual Trigger Key (used for
Sweep and Burst only)
10 Output Enable/Disable Key
11
Knob
12
Cursor Keys
13
Sync Connector
14
Output Connector
Note: To get context-sensitive help on any front-panel key or menu softkey,
press and hold down that key.
3
Page 4

The Front-Panel Display at a Glance
Menu Mode
Numeric
Readout
Mode
Information
Trigger
Information
Softkey Labels
Units
Output
Status
Graph Mode
To enter or exit the Graph Mode, press the key.
Parameter
Name
Parameter
Value
Display
Icon
Signal
Ground
In Graph Mode, only one parameter label
is displayed for each key at one time.
4
Page 5

Front-Panel Number Entry
1. Use the keys below the knob to move the cursor left or right.
1. Key in a value as you would on a typical calculator.
You can enter numbers from the front-panel using one of two methods.
Use the knob and cursor keys to modify the displayed number.
2. Rotate the knob to change a digit (clockwise to increase).
Use the keypad to enter numbers and the softkeys to select units.
2. Select a unit to enter the value.
5
Page 6
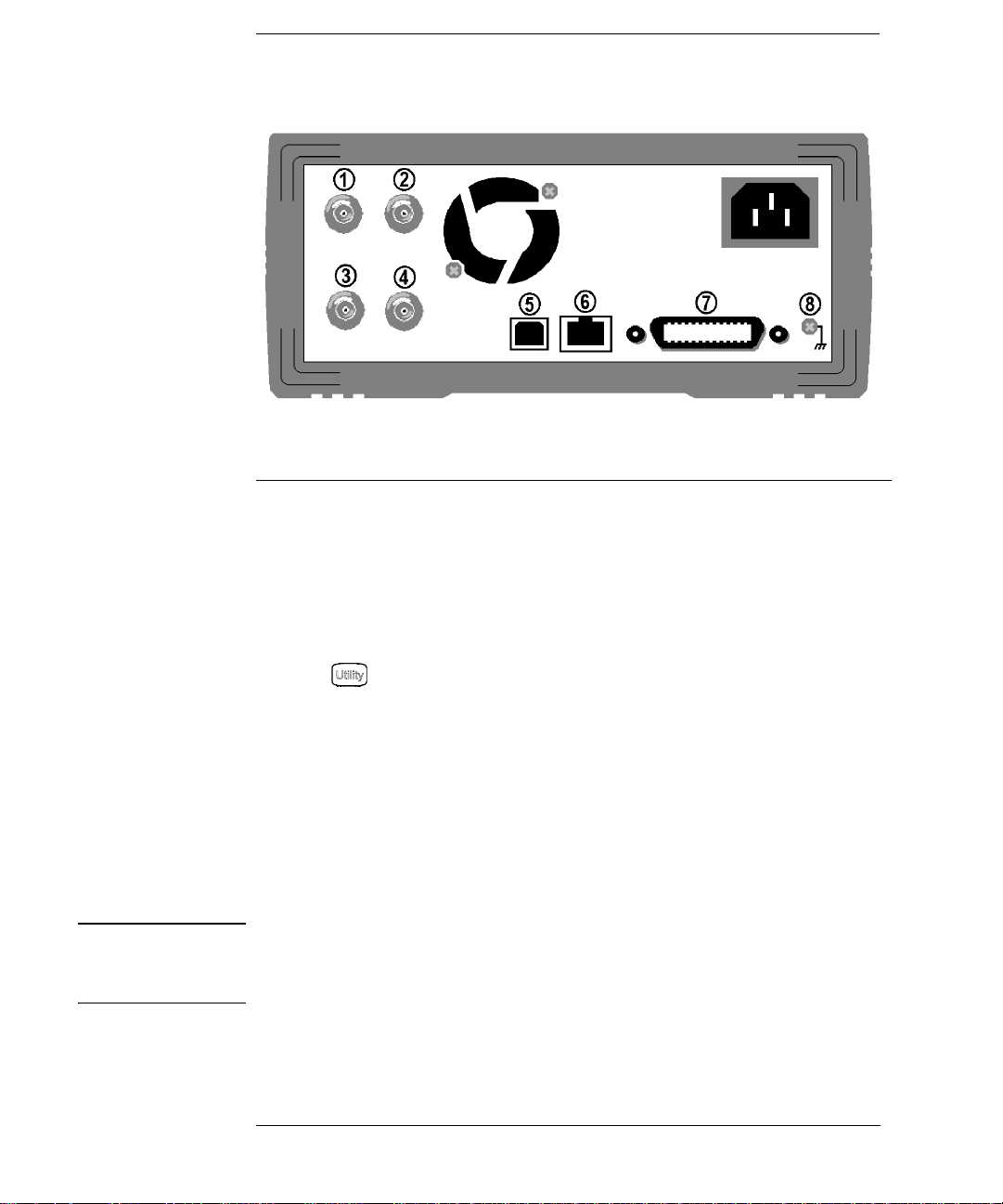
The Rear Panel at a Glance
1
External 10 MHz Reference Input Terminal
(Option 001 only)
2
Internal 10 MHz Reference Output Terminal
(Option 001 only)
3 External Modulation Input Terminal
Input: External Trig/ FSK / Burst Gate
4
Output: Trigger Output
.
.
5 USB Interface Connector
6 LAN Interface Connecto r
7 GPIB Interface Connector
8 Chassis Ground
Use the menu to:
• Select the GPIB address (see chapter 3).
• Set the network parameter s for the LAN interface (see chapter 3).
• Display the current network parameters (see chapter 3).
Note: The External and Internal 10 MHz Reference Terminals (1 and 2,
above) are present only if Option 001, External Timebase Reference, is
installed. Otherwise, the holes for these connectors are plugged.
WARNING For protection from electrical shock, the power cord ground must not be
defeated. If only a two-contact electrical outlet is available, connect the
instrument’s chassis ground screw (see above) to a good earth ground.
6
Page 7

In This Book
Specifications Chapter 1 lists the function generator’s specifications.
Quick Start Chapter 2 prepares the function generator for use and
helps you get familiar with a few of its front-panel features.
Front-Panel Menu Operation Chapter 3 introduces you to the frontpanel menu and describes some of the function generator’s menu features.
Calibration Procedures
and adjustment procedures for the
Theory of Operation Chapter 5 describes block and circuit level
theory related to the operation of the function generator.
Service Chapter 6 provides guidelines for returning your function
generator to Agilent Technologies for servicing, or for servicing it
yourself.
Replaceable Parts Chapter 7 contains a detailed parts list of the
function generator.
Backdating Chapter 8 describes the differences between this manual
and older issues of this manual.
Schematics Chapter 9 contains the function generator’s schematics and
component locator drawings.
You can contact Agilent T echnologies at one of the following telephone
numbers for warranty, service, or technical support information.
Chapter 4 provides calibration, verification,
function generator.
In the United States: (800) 829-4444
In Europe: 31 20 547 2111
In Japan: 0120-421-345
Or use our Web link for information on contacting Agilent worldwide.
www.agilent.com/find/assist
Or contact your Agilent Technologies Representative.
7
Page 8

8
Page 9

Contents
Chapter 1 Specifications 13
Chapter 2 Quick Start 19
To Prepare the Function Generator for Use 21
To Adjust the Carrying Handle 22
To Set the Output Frequency 23
To Set the Output Amplitude 24
To Set a DC Offset Voltage 26
To Set the High-Level and Low-Level Values 27
To Select “DC Volts” 28
To Set the Duty Cycle of a Square Wave 29
To Configure a Pulse Waveform 30
To View a Waveform Graph 31
To Output a Stored Arbitrary Waveform 32
To Use the Built-In Help System 33
To Rack Mount the Function Generator 35
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation 37
Front-Panel Menu Reference 39
To Select the Output Termination 41
To Reset the Function Generator 41
To Read the Calibration Information 42
To Unsecure and Secure for Calibration 43
To Store the Instrument State 46
To Configure the Remote Int erface 47
Contents
9
Page 10

Contents
Contents
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures 53
Agilent Technologies Calibration Services 55
Calibration Interval 55
Adjustment is Recommended 55
Time Required for Calibration 56
Automating Calibration Procedures 57
Recommended Test Equipment 58
Test Considerations 59
Performance Verification Tests 60
Internal Timebase Verification 64
AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Verification 65
Low Frequency Flatness Verification 66
0 dB Range Flatness Verification 67
+10 dB Range Flatness Verification 69
+20 dB Range Flatness Verification 71
Calibration Security 73
Calibration Message 75
Calibration Count 75
General Calibration/Adjus tment Procedure 76
Aborting a Calibration in Progress 77
Sequence of Adjustments 77
Self-Test 78
Frequency (Internal Timebase) Adjustment 79
Internal ADC Adjustment 80
Output Impedance Adjustment 81
AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Adjustment 83
Low Frequency Flatness Adjustment 85
0 dB Range Flatness Adjustments 86
+10 dB Range Flatness Adjustments 88
+20 dB Range Flatness Adjustment 90
Calibration Errors 93
10
Page 11

Chapter 5 Theory of Operation 95
Block Diagram 97
Power Supplies 100
Main Power Supply 100
Earth Referenced Power Supplies 101
Floating Power Supplies 102
Analog Circuitry 103
Waveform DAC and Filters 103
Squarewave Comparator 104
Square and P ulse Level Translator 104
Main Output Circuitry 106
System ADC 107
System DAC 108
Digital Circuitry 110
Synthesis IC and Waveform Memory 110
Timebase, Sync Output, and Relay Drivers 111
Main Processor 112
Front Panel 114
External Timebase (Option 001) 115
Contents
4
Contents
Chapter 6 Service 117
Operating Checklist 118
Types of Service Available 119
Repackaging for Shipment 120
Cleaning 120
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Precauti ons 121
Surface Mount Repair 121
Troubleshooting Hi nts 122
Self-Test Procedures 124
Disassembly 127
Chapter 7 Replaceable Parts 139
33220-66511 – Main PC Assembly 141
33220-66502 – Front-Panel PC Assembly 155
33220-66503 – External Timebase PC Assembly 156
33220A Chassis Assembly 158
Manufacturer List 159
11
Page 12

Contents
Contents
Chapter 8 Backdating 161
Chapter 9 Schematics 163
A1 Clocks, IRQ, RAM, ROM, and USB Schematic 165
A1 Front Panel Interface, LAN, GPIB, and Beeper Schematic 166
A1 Cross Guard, Serial Communications, Non-Volatile Memory, and
Trigger Schematic 167
A1 Power Distribution Schematic 168
A1 Synthesis IC and Wa veform RAM Schematic 169
A1 Timebase, Sync, and Relay Drivers Schematic 170
A1 System ADC Schematic 171
A1 System DAC Schematic 172
A1 Waveform DAC and Filters and Square Wave Comparator Schematic
173
A1 Square / Pulse Level Translation Schematic 174
A1 Gain Switching and Output Amplifier Schematic 175
A1 Earth Referenced Power Supply Schematic 176
A1 Isolated Power Supply S chematic 177
A2 Keyboard Scanner and Display Connector Schematic 178
A2 Key Control Schematic 179
A3 External Timebase Schematic 180
A1 Component Locator (top) 181
A1 Component Locator (bottom) 182
A2 Compone nt Locator 183
A3 Compone nt Locator 184
12
Page 13

1
1
Specifications
Page 14

1
Chapter 1 Specificat ions
Agilent 33220A Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator
Waveforms
Standard: Sine, Squa re, Ramp,
Built-in Arbitrary: Exponential rise,
Triangle, Pulse, Noise,
DC
Exponential fall,
Negative ramp,
Sin(x)/x, Cardiac.
Waveform Characteristics
Sine
Frequency: 1 µHz to 20 MHz,
Amplitude Flatness:
< 100 kHz 0.1 dB
100 kHz to 5 MHz 0.15 dB
5 MHz to 20 MHz 0.3 dB
Harmonic Distortion:
DC to 20 kHz -70 dBc -70 dBc
20 kHz to 100 kH z -65 dBc -60 dBc
100 kHz to 1 MHz -50 dBc -45 dBc
1 MHz to 20 MHz -40 dBc -35 dBc
Total Harmonic Distortion:
DC to 20 kHz 0.04%
Spurious (Non-Harmonic) Output:
DC to 1 MHz -70 dBc
1 MHz to 20 MHz -70 dBc +6 dB/octave
Phase Noise
(10 kHz offset): -115 dBc / Hz, typical
[1], [2]
[2], [3]
1 µHz resolution
(Relative to 1 kHz)
< 1 Vpp >
[2], [3]
[2], [4]
1 Vpp
Square
Frequency: 1 µHz to 20 MHz,
1 µHz resolution
Rise/Fall Time: < 13 ns
Overshoot: < 2%
Variable Duty Cycle: 20% - 80% (to 10 MHz)
40% - 60% (to 20 MHz)
Asymmetry (@ 50% Duty): 1% of period + 5 ns
Jitter (RMS): 1 ns + 100 ppm of
period
Ramp, Triangle
Frequency: 1 µHz to 200 kHz,
1 µHz resolution
Linearity: < 0.1% of peak output
Variable Symmetry: 0.0% to 100.0%
Pulse
Frequency: 500 µHz to 5 MHz,
1 µHz resolution
Pulse Width
(period < 10 s): 20 ns minimum,
10 ns resolution
Variable Edge Time: < 13 ns to 100 ns
Overshoot: < 2%
Jitter (RMS): 300 ps + 0.1 ppm of
period
Noise
Bandwidth: 10 MHz, typical
Arbitrary
Frequency: 1 µHz to 6 MHz,
1 µHz resolution
Waveform Length: 2 to 64 K points
Amplitude Resolution: 14 bits (including sign)
Sample Rate: 50 MSa/s
Minimum Rise/Fa ll Time: 35 ns, typical
Linearity: < 0.1% of peak output
Settling Time: < 250 ns to 0.5% of
final value
Jitter (RMS): 6 ns + 30 ppm
Non-volatile Memory: Four waveforms
14
Page 15

Chapter 1 Specifications
Agilent 33220A Function /Arbitrary Waveform Generator
1
Common Characteristics
Amplitude
Range:
Into 50 Ω: 10 mVpp to 10 Vpp
Into open circuit: 20 mVpp to 20 Vpp
Accuracy (at 1 kHz):
Units: Vpp, Vrms, dBm
Resolution: 4 digits
DC Offset
Range (peak AC + DC): ± 5 V into 50 Ω
Accuracy:
Resolution: 4 digits
[1], [2]
Main Output
Impedance: 50 Ω typical
Isolation: 42 Vpk maximum to
Protection: S hort-circuit prot ected,
Internal Frequency Reference
Accuracy:
[5]
± 10 ppm in 90 days,
External Frequency Reference (Option 001)
Rear Panel Input:
Lock Range: 10 MHz ± 500 Hz
Level: 100 mVpp to 5 Vpp
Impedance: 1 kΩ typical, AC
Lock Time: < 2 seconds
Rear Panel Output:
Frequency: 10 MHz
Level: 632 mVpp (0 dBm),
Impedance: 50 Ω typical, AC
[1], [2]
± 1% of setting
± 1 mVpp
±10 V into open circuit
± 2% of offset setting
± 0.5% of ampl. ± 2 mV
earth
overload automatically
disables main output
± 20 ppm in 1 year
coupled
typical
coupled
Phase Offset:
Range: +360 to -360 degrees
Resolution: 0.001 degrees
Accuracy: 20 ns
Modulation
AM
Carrier Waveforms: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Arb
Source: Internal/External
Internal Modulation: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Triangle, Noise, Arb
(2 mHz to 20 kHz)
Depth: 0.0% to 120.0%
FM
Carrier Waveforms: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Arb
Source: Internal/External
Internal Modulation: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Triangle, Noise, Arb
(2 mHz to 20 kHz)
Deviation: DC to 10 MHz
PM
Carrier Waveforms: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Arb
Source: Internal/External
Internal Modulation: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Triangle, Noise, Arb
(2 mHz to 20 kHz)
Deviation: 0.0 to 360.0 degrees
PWM
Carrier Waveforms : Pulse
Source: Internal/External
Internal Modulation: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Triangle, Noise, Arb
(2 mHz to 20 kHz)
Deviation: 0% to 100% of pulse
width
4
15
Page 16

1
Chapter 1 Specificat ions
Agilent 33220A Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator
FSK
Carrier Waveforms: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Source: Internal/External
Internal Modulation: 50% duty cycle square
External Modulation Input
Arb
(2 mHz to 100 kHz)
[6]
(for AM, FM, PM, PWM)
Voltage Range: ± 5 V full scale
Input Resistance: 5 kΩ typical
Bandwidth: DC to 20 kHz
Sweep
Waveforms: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Type: Linear or Logarithmic
Direction: Up or Down
Sweep Time: 1 ms to 500 s
Trigger: Single, External or
Marker Falling edge of Sync
Burst
Waveforms: Sine, Square, Ramp,
Type: Counted (1 to 50,000
Start/Stop Phas e: -360 to +360 degrees
Internal Period: 1 µs to 500 s
Gate Source: External Trigger
Trigger Source: Single, External, or
[7]
Arb
Internal
signal (programmable
frequency)
Triangle, Pulse, Noise,
Arb
cycles), Infinite, Gated
Internal
T rigger Cha rac teris ti cs
Trigger Input:
Input Level: TTL compatible
Slope: Rising or falling,
Pulse Width: > 100 ns
Input Impedance: > 10 kΩ, DC coupled
Latency: < 500 ns
Jitter (RMS) 6 ns (3.5 ns for Pulse)
Trigger Output:
Level: TTL compatible into
Pulse Width: > 400 ns
Output Impedance: 50 Ω, typical
Maximum Rate: 1 MHz
Fanout: <
selectable
>
1 kΩ
4 Agilent 33220As
Programming Times (typical)
Configuration Times
USB 2.0
Function
Change
Frequency
Change
Amplitude
Change
Select User
Arb
111 m s 111 ms 111 ms
1.5 ms 2.7 ms 1.2 ms
30 ms 30 ms 30 ms
124 ms 124 ms 123 ms
Arb Download Times (binary transfer)
USB 2.0
64 K points 96.9 ms 191.7 ms 336.5 ms
16 K points 24.5 ms 48.4 ms 80.7 ms
4 K points 7.3 ms 14.6 ms 19.8 ms
Download times do not include setup or output time.
LAN
(VXI-11)
LAN
(VXI-11)
GPIB
GPIB
16
Page 17

Chapter 1 Specifications
Agilent 33220A Function /Arbitrary Waveform Generator
1
General
Power Supply: CAT II
100 to 240 V
50/60 Hz (-5%, +10%)
100 to 120 V @
400 Hz (± 10%)
Power Consumption: 50 VA maximum
Operating Environment: IEC 61010
Pollution Degree 2
Indoor Location
Operating Temperature: 0 °C to 55 °C
Operating Humidity: 5% to 80% RH,
non-condensing
Operating Altitude: Up to 3000 meters
Storage Temperature: -30 °C to 70 °C
State Storage Memory: Power off state
automatically sav ed .
Four user-configurabl e
stored states.
Interface: GPIB, USB, and LAN
standard
Language: SCPI - 1993,
IEEE-488.2
Dimensions (W x H x D):
Bench T op: 261.1 mm by 103.8 mm
by 303.2 mm
Rack Mount: 212.8 mm by 88.3 mm
by 272.3 mm
Weight: 3.4 kg (7.5 lbs)
Safety Designed to: UL-1244, CSA 1010,
EN61010
EMC Tested to: MIL-461C, EN55011,
EN50082-1
Vibration and Shock: MIL-T-28800, Type III,
Class 5
Acoustic Noise: 30 dBa
Warm-up Time: 1 hour
@
Note: Specifications are subject to change
without notice. For the latest specifications,
go to the Agilent 33220A product page and
find the 33220A Datasheet.
www.agilent.com/find/33220A
This ISM device complie s w ith C ana di an ICES-001.
Cet appareil ISM est conforme à la norme NMB-001
du Canada.
N10149
________________
Footnotes:
1
Add 1/10th of output amplitude and offset
specification per
the range of 18
2
Autorange enabled.
3
DC offset set to 0 V.
4
Spurious output at low amplitude is
°C for operation outside
°C to 28 °C.
-75 dBm (typical).
5
Add 1 ppm / °C (average) for operation out-
side the range of 18
6
FSK uses trigger input (1 MHz maximum).
7
Sine and square waveforms above 6 MHz
°C to 28 °C.
are allowed only with an “infinite” burst
count.
4
17
Page 18

1
Product Dimensions
Chapter 1 Specifications
Agilent 33220A Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator
All dimensions are
shown in millimeters.
18
Page 19

2
2
Quick Start
Page 20

Quick Start
One of the first things yo u will want to do w ith your function ge nerator is
to become acquainted with the fro nt panel. We have w ri tten the exercises
in this chapter to prepare the instrument for use and help you get
familiar with some of its front-panel operations. This chapter is divided
into the following sections:
2
• To Prepare the Function Generator for Use, on page 21
• To Adjust the Carrying Handle, on page 22
• To Set the Output Frequency, on page 23
• To Set the Output Amplitude, on page 24
• To Set a DC Offset Voltage, on page 26
• To Set the High-Level and Low-Level Values, on page 21
• To Select “DC Volts”, on page 22
• To Set the Duty Cycle of a Square Wave, on page 29
• To Configure a Pulse Waveform, on page 30
• To View a Waveform Graph, on page 31
• To Output a Stored Arbitrary Waveform, on page 32
• To Use the Built-In Help System, on page 33
• To Rack Mount the Function Generator, on page 35
20
Page 21

Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Prepare the Function Generator for Use
To Prepare the Function Generator for Use
Power
Switch
1 Check the list of supplied items.
Verify that you have received the following items with your instrument.
If anything is missing, please contact your nearest Agilent Sales Office.
One power cord.
One User’s Guide.
This Service Guide.
One folded Quick Start Tutorial.
One folded Quick Reference Guide.
Certificate of Calibration.
Connectivity software on CD-ROM.
One USB 2.0 cable.
2 Connect the power cord and turn on the function generator.
The instrument runs a short power-on self test, which takes a few
seconds. When the instrument is ready for use it displays a message
about how to obtain help, along with the current GPIB address. The
function generator powers up in the sine wave function at 1 kHz with an
amplitude of 100 mV peak-to-peak (into a 50Ω termination).
the
Output
the key
connector
.
is disabled. To enable the Output
At power-on,
connector, press
2
4
If the function generator does not turn on, verify that the power cord is
firmly connected to the power receptacle on the rear p a ne l (t he po w er -line
voltage is automatically sensed at power-on). You should also make sure
that the function generator is connected to a power source that is energized
Then, verify that the function generator is turned on.
If the power-on self test fails, “Self-T est Failed” is displayed along with an
error code. See Chapter 6 for information on self-test error codes, and
for
instructions on returning the function generator to Agilent for service.
21
.
Page 22

Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Adjust the Carrying Handle
To Adjust the Carrying Handle
2
To adjust the position, grasp the handle by the sides and pull outward.
Then, rotate the handle to the desired position.
Retracted
Carrying
Position
Extended
22
Page 23

To Set the Output Frequency
Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Set the Output Frequency
At power-on, the function generator outputs a sine wave at 1 kHz with
an amplitude of 100 mV peak-to-peak (into a 50Ω termination).
The following steps show you how to change the frequency to 1.2 MHz.
1Press the “Freq” softkey.
The displayed frequency is either the power-on value or the frequency
previously selected. When you change functions, the same frequency is
used if the present value is valid for the new function. To set the
waveform period instead, press the Freq softkey again to toggle to the
Period softkey (the current selection is highlighted).
2 Enter the magnitude of the desired frequency.
Using the numeric keypad, enter the value “1.2”.
2
4
3 Select the desired units.
Press the softkey that corresponds to the desired units. When you select
the units, the function generator outputs a waveform with the displayed
frequency (if the output is enabled). For this example, press MHz
Note: Y
keys.
ou can also enter the desired value using the knob and cursor
.
23
Page 24

Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Set the Output Amplitude
To Set the Output Amplitude
2
At power-on, the function generator outputs a sine wave with an
amplitude of 100 mV peak-to-peak (into a 50Ω termination) .
The following steps show you how to change the amplitude to 50 mVrms.
1Press the “Ampl” softkey.
The displayed amplitude is either the power-on value or the amplitude
previously selected. When you change functions, the same amplitude is
used if the present value is valid for the new function. To set the amplitude
using a high level and low level, press the Ampl softkey again to toggle to
the HiLevel and LoLevel softkeys (the current selection is highlighted).
2 Enter the magnitude of the desired amplitude.
Using the numeric keypad, enter the value “50”.
3 Select the desired units.
Press the softkey that corresponds to the desired units. When you select
the units, the functio n ge ner ator out puts the wave form w ith the disp layed
amplitude (if the output is enabled). For this example, press mV
Note: Y
keys.
24
ou can also enter the desired value using the knob and cursor
RMS
.
Page 25
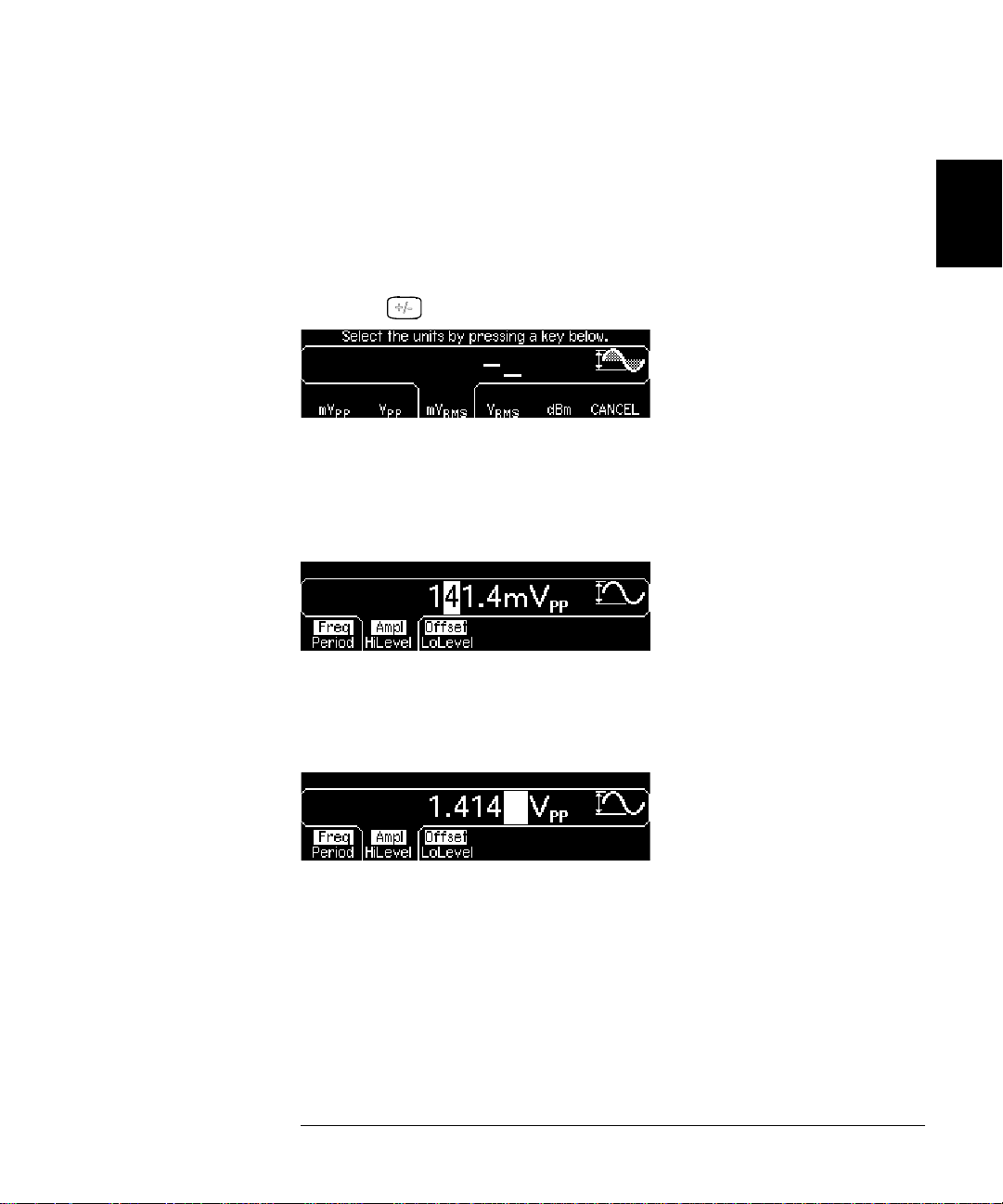
Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Set the Output Amplitude
You can easily convert the displayed amplitude from one unit to another.
For example, the following steps show you how to convert the amplitude
from Vrms to Vpp.
4 Enter the numeric entry mode.
Press the key to enter the numeric entry mode.
5 Select the new units.
Press the softkey that corresponds to the desired units. The displayed
value is converted to the new units. For this example, press the Vpp
softkey to convert 50 mVrms to its equivalent in volts peak-to-peak.
2
4
To change the displayed amplitude by decades, press the right-cursor
key to move the cursor to the units on the right side of the display.
Then, rotate the knob to increase or decrease the displayed amplitude
by decades.
25
Page 26

Chapter 2 Quick Start
T o Set a DC Offset Voltage
To Set a DC Offset Voltage
2
At power-on, the function generator outputs a sine wave with a dc offset
of 0 volts (into a 50Ω termination). The following steps show you how to
change the offset to –1.5 mVdc.
1Press the “Offset” softkey.
The displayed off set voltage is either the power-on value or the offset
previously selected. When you change functions, the same offset is used
if the present value is valid for the new function.
2 Enter the magnitude of the desired offset.
Using the numeric keypad, enter the value “–1.5”.
3 Select the desired units.
Press the softkey that corresponds to the desired units. When you select
the units, the functio n ge ner ator out puts the wave form w ith the disp layed
offset (if the output is enabled). For this example, press mV
Note: Y
keys.
26
ou can also enter the desired value using the knob and cursor
DC
.
Page 27
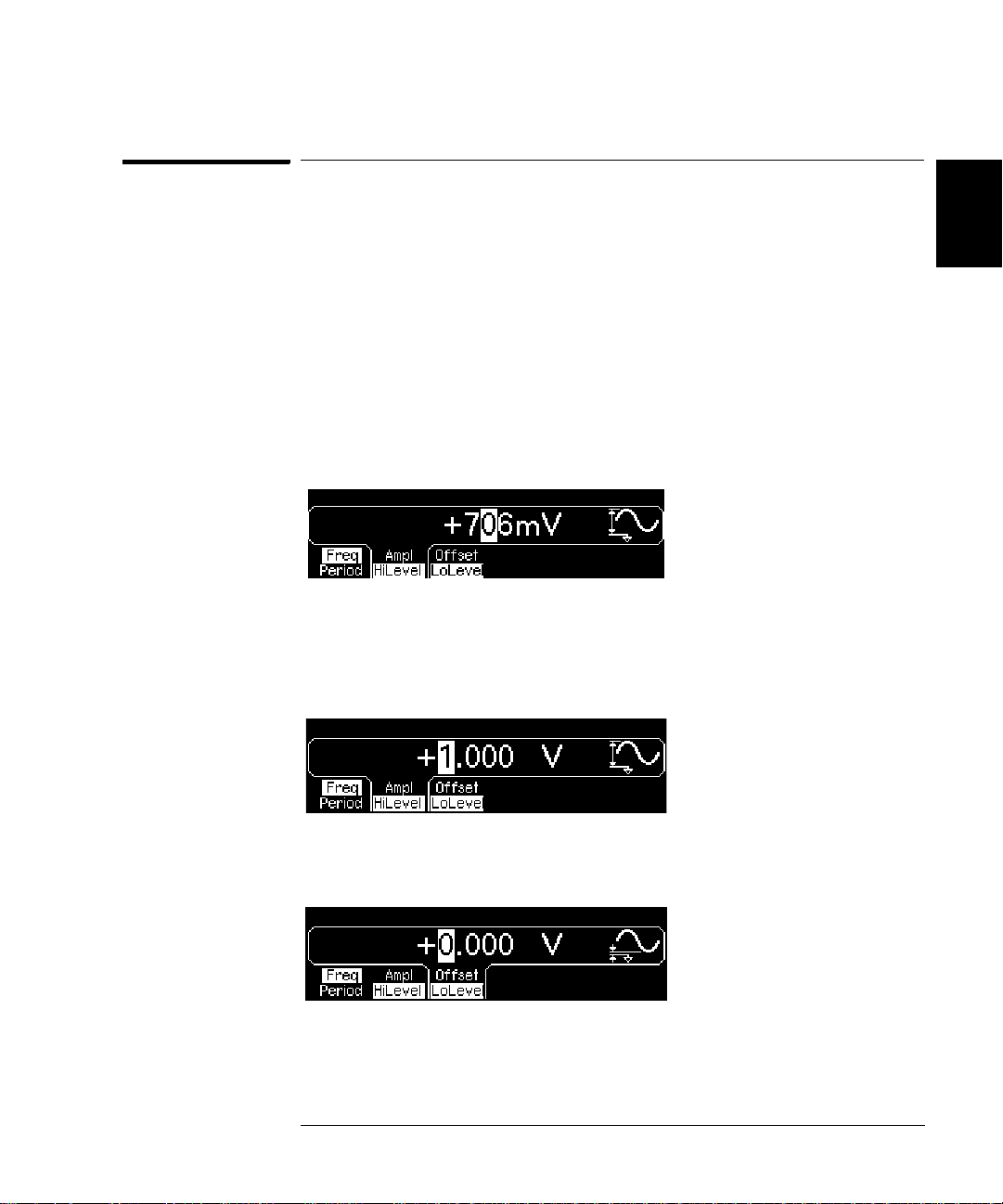
Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Set the High-Level and Low-Level Values
To Set the High-Level and Lo w-Level Values
You can specify a signal by setting its amplitude and dc offset values, as
described previously. Another way to set the limits of a signal is to
specify its high-level (maximum) and low-level (minimum) values. This
is typically convenient for digital applications. In the following example,
let's set the high-level to 1.0 V and the low-level to 0.0 V.
1 Press the "Ampl" softkey to select "Ampl".
2 Press the softkey again to toggle to "HiLevel".
Note that both the Ampl and Offset softkeys toggle together, to HiLevel
and LoLevel, respectively.
3 Set the "HiLevel" value.
Using the numeric keypad or the knob, select a value of "1.0 V". (If you
are using the keypad, you will need to select the unit, "V", to enter the
value.)
2
4
4 Press the "LoLevel" softkey and set the value.
Again, use the numeric keyp ad or the knob to enter a value of "0.0 V".
Note that these settings (high-level = "1.0 V" and low-level = "0.0 V") are
equivalent to setting an amplitude of "1.0 Vpp" and an offset of "500
mVdc".
27
Page 28

Chapter 2 Quick Start
T o Select “DC Volts”
To Select “DC Volts”
2
You can select the "DC Volts" feature from the “Utility” menu, and then
set a constant dc voltage as an "Offset" value. Let's set "DC Volts" = 1.0
Vdc.
1 Press and then select the DC On softkey.
The Offset value becomes selected.
2 Enter the desired voltage level as an "Offset".
Enter 1.0 Vdc with the numeric keypad or knob.
You can enter any dc voltage from -5 Vdc to +5 Vdc.
28
Page 29

Chapter 2 Quick Start
T o Set the Duty Cycle of a Square Wave
To Set the Duty Cycle of a Square Wave
At power-on, the duty cycle for square waves is 50%. You can adjust th e
duty cycle from 20% to 80% for output frequencies up to 10 MHz. The
following steps show you how to change the duty cycle to 30%.
1 Select the square wave function.
Press the key and then set the desired output frequency to any
value up to 10 MHz.
2Press the “Duty Cycle” softkey.
The displayed duty cycle is either the power-on value or the percentage
previously selected. Th e duty cycle represents the amount of time per
cycle that the square wave is at a high level (note the icon on the right
side of the display).
3 Enter the desired duty cycle.
Using the numeric keypad or the knob, select a duty cycle value of “30”.
The function generator adjusts the duty cy cle immediately and outputs a
square wave with the specified value (if the output is enabled).
2
4
29
Page 30

Chapter 2 Quick Start
T o Configure a Pulse Waveform
To Configure a Pulse Waveform
2
You can configure the function generator to output a pulse waveform
with variable pulse width and edge time. The following steps show you
how to configure a 500 ms pulse waveform with a pulse width of 10 ms
and edge times of 50 ns.
1 Select the pulse function.
Press the key to select the pulse function and output a pulse
waveform with the default parameters.
2 Set the pulse period.
Press the Period softkey and then set the pulse period to 500 ms.
3 Set the pulse width.
Press the Width softkey and then set the pulse width to 10 ms. The pulse
width represents the time from the 50% threshold of the rising edge to
the 50% threshold of the next falling edge (note the display icon).
4 Set the edge time for both edges.
Press the Edge Time softkey and then set the edge time for both the
rising and falling edges to 50 ns. The edge time represents the time from
the 10% threshold to the 90% threshold of each edge (note the display icon
30
).
Page 31

To View a Wav e f o r m Graph
Chapter 2 Quick Start
To View a Waveform Graph
In the Graph Mode, you can view a graphical representation of the
current waveform parameters. The softkeys are listed in the same order
as in the normal display mode, and they perform the same functions.
However, only one label (for example, Freq or Period) is displayed for
each softkey at one time.
1 Enable the Graph Mode.
Press the key to enable the Graph Mode. The name of the
selected
parameter’s numeric value field are both highlighted.
2 Select the desired parame ter.
To select a specific parameter, note the softkey labels at the bottom of
the display.
• As in the normal disp lay mode , you can e dit numb ers using either the
parameter,
For example
numeric keypad or the knob and cursor keys.
shown in the up per-left corne r of the display, a nd the
, to select period, press the Period softkey.
currently
2
4
•
Param ete rs w h ic h n o rmally toggle wh en you press a key a se cond time
also toggle in the Graph Mode. Howev er, you can see on ly on e label
for each softkey at one time (for example, Freq or Period).
• To exit the Graph Mode, press again.
The key also serves as a key to restore front-panel control
after remote interface operation s.
31
Page 32

Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Output a Stored Arbitrary Waveform
To Output a Stored Arbitrary Waveform
2
There are five built-in arbitrary waveforms stored in non-volatile memory
The following steps show you how to output the built-in “exponential fall”
waveform
For information on creating a custom arbitrary waveform, refer to
“To Create and Store an Arbitrary Waveform” in the User’s Guide.
1 Select the arbitrary waveform function.
When you press the key to select the arbitrary waveform function,
a temporary message is displayed indicating which waveform is currently
selected (the default is “exponential rise”).
2 Select the active waveform.
Press the Select Wform softkey and then press the Built-In softkey to
select from the five built-in waveforms. Then press the Exp Fall softkey.
The waveform is output using the present settings for frequency,
amplitude, and offset unless you change them.
from the front panel.
.
The selected waveform is now assigned to the key. Whenever you
press this key, the selected arbitrary waveform is output. To quickly
determine which arbitrary waveform is currently selected, press .
32
Page 33

To Use the Built-In Help System
To Use the Built-In Help System
Chapter 2 Quick Start
The built-in help system is designed to provide context-sensitive
assistance on any front-panel key or menu softkey. A list of help topics
is also available to assist you with several front-panel operations.
1 View the help information for a function key.
Press and hold down the key. If the message contains
information than will fit on the di spla y, pre s s th e ↓ softkey or turn the
knob clockwise to view the remaining information.
Press DONE to exit Help.
2 View the help information for a menu softkey.
Press and hold down the Freq softkey.
information than will fit on the di spla y, pre s s th e ↓ softkey or rotate the
knob clockwise to view the remaining information.
If the message con tai ns
more
more
2
4
Press DONE to exit Help.
33
Page 34

2
Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Use the Built-In Help System
3 View the list of help topics.
Press the key to view the list of available help topi cs. To scroll
through the list, press the ↑ or ↓ softkey or rotate the knob. Select the
third topic “Get HELP on any key” and then press SELECT.
Press DONE to exit Help.
4 View the help information for displayed messages.
Whenever a limit is exceeded or an y other invali d config uration i s found,
the function generator will display a message. For example, if you enter
a value that exceeds the frequency limit for the selected function,
a message will be displayed. The built-in help system provides additional
information on the most recent message to be displayed.
Press the k ey, select the first top ic “
and then press SELECT.
Press DONE to exit Help.
Local Language Help: The built-in help system in available in multiple
languages. All messages, context-sensitive help, and help topics appear
in the selected language. The menu softkey labels and status line
messages are not translated.
To select the local language, press the key, press the System
softkey, and then press the Help In softkey. Select the desired language.
View the last message displayed”,
34
Page 35

Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Rack Mount the Function Generator
To Rack Mount the Function Generator
You can mount the Agilent 33220A in a standard 19-inch rack cabinet
using one of two optional kits available. Instructions and mounting
hardware are included with each rack-mounting kit. Any Agilent
System II instrument of the same size can be rack-mounted beside the
Agilent 33220A.
Note:
before rack-mounting the instrument.
T o remove the handle, rotate it to vertical and pull the ends outward.
Remove the carrying handle, and the front and rear rub ber bumpers
4
2
,
Front
To remove the rubber bumper, stretch a corner and then slide it off.
Rear (bottom view)
35
Page 36

2
Chapter 2 Quick Start
To Rack Mount the Function Generator
T o rack mount a single instrument, order adapter kit 5063-9240.
To rack mount two instruments side-by-side, order lock-link kit 5061-9694
and flange kit 5063-9212. Be sure to use the support rails in the rack cabinet.
Note: The lock-link kit works only for instruments of equal depth. If you
want to mount an Agilent 33220A and an instrument of a different depth
(for example, an Agilent 33250A) contact your Agilent Representative for
further information.
In order to prevent overheating, do not block the flow of air into or out of
the instrument. Be sure to allow enough clearance at the rear, sides, and
bottom of the instrument to permit adequate internal air flow.
36
Page 37

3
3
Front-Panel Menu Operation
Page 38

3
Front-Panel Menu Operation
This chapter introduces you t o the fro nt-pane l keys and menu oper ation.
This chapter does not give a deta iled descri ption of eve ry front-pa nel key
or menu operation. It does, however, give you an overview of the frontpanel menus and many front-panel operations. Refer to the Agilent
33220A User’s Guide for a complete discussion of the function generator’s
capabilities and operation.
• Front-Panel Menu Reference, on page 39
• To Select the Output Termination, on page 41
• To Reset the Function Generator, on page 41
• To Read the Calibration Information, on page 42
• To Unsecure and Secure for Calibration, on page 43
• To Store the Instrument State, on page 46
• To Configure the Remote Interface, on page 47
38
Page 39

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
Front-Panel Menu Reference
Front-Panel Menu Reference
This section gives an overview of the front-panel menus. The remainder
of this chapter contains examples of using the front-panel menus.
Configure the modulation p aramete rs for AM, F M, PM , FSK and PWM.
• Select the modulation type.
• Select an internal or external modulation source.
• Specify AM modulation depth, modulating frequency, and modulation shape.
Specify FM frequency deviation, modulating frequency, and modulation shape.
•
•
Specify PM phase deviation, modulating frequency, and modulation shape.
• Specify FSK “hop” frequency and FSK rate.
• Specify PWM deviation, modulating frequency, and modulation shape.
Configure the parameters for frequency sweep.
• Select linear or logarithmic sweeping.
• Select the start/stop frequencies or
• Select the time in seconds required to complete a sweep.
• Specify a marker frequency.
• Specify an internal or external trigger source for the sweep.
• Specify the slope (rising or falling edge) for an external trigger source.
• Specify the slope (rising or falling edge) of the “Trig Out” signal.
Configure the parameters for burst.
center/span frequencies.
4
3
• Select the triggered (N Cycle) or externally-gated burst mode.
• Select the number of cycles per burst (1 to 50,000, or Infinite).
• Select the starting phase angle of the burst (-360° to +360°).
• Specify the time from the start of one burst to the start of the next burst.
• Specify an internal or external trigger source for the burst.
• Specify the slope (rising or falling edge) for an external trigger source.
• Specify the slope (rising or falling edge) of the “Trig Out” signal.
39
Page 40

3
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
Front-Panel Menu Reference
Store and recall instrument states.
• Store up to four instrument states in non-volatile memory.
• Assign a custom name to each storage location.
• Recall stored instrument states.
• Restore all instrument settings to their factory default values.
• Select the instrument’s power-on configuration (last or factory default).
Configure system-related parameters.
• Generate a dc-only voltage level.
• Enable/disable the Sync signal which is output from the “Sync” connector.
• Select the output termination (1Ω to 10 kΩ, or Infinite).
• Enable/disable amplitude autoranging.
• Select the waveform polarity (normal or inverted).
• Select the GPIB address.
• Specify the LAN configuration (IP address and network configuration).
Select how periods and commas are used in numbe rs displayed on the front pa nel.
•
• Select the local language for front-panel messages and help text.
• Enable/disable the tone heard when an error is generated.
• Enable/disable the display bulb-saver mode.
• Adjust the contrast setting of the front-panel display.
• Perform an instrument self-test.
• Secure/unsecure the instrument for calibration and perform manual calibrations.
• Query the instrument’s firmware revision codes.
View the list of Help topics.
• View the last message displayed.
• View the remote command error queue.
• Get HELP on any key.
• How to generate a dc-only voltage level.
• How to generate a mo dulated waveform.
• How to create an arbitrary waveform.
• How to reset the instrument to its default state.
• How to view a waveform in the Graph Mode.
• How to synchronize multiple instruments.
• How to obtain Agilent Technical Support.
40
Page 41

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
To Select the Output Termination
To Select the Output Termination
The Agilent 33220A has a fixed series output impedance of 50 ohms to
the front-panel Output connector. If the actual load im pedance is
different than the value specified, the displayed amplitude and offset
levels will be incorrect. The load impedance setting is simply provided
as a convenience to ensure that the displayed voltage matches the
expected load.
1Press .
2 Navigate the menu to set the output termination.
Press the Output Setup softkey and then select the Load softkey.
4
3
3 Select the desired ou tput termination.
Use the knob or numeric keypad to select the desired load impedance or
press the Load softkey again to choose “High Z”.
To Reset the Function Generator
To reset the instrument to its factory default state, press and then
select the Set to Defaults softkey. Press YES to confirm the operation.
For a complete listing of the instrument’s power-on and reset conditions,
see “Agilent 33220A Factory Default Settings” in the User’s Guide.
41
Page 42

3
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
To Read the Calibration Information
To Read the Calibration Information
You can access the instrument’s calibration memory to read the
calibration count and calibration message.
Calibration Count You can query the instrument to determine how
many calibrations have been performed. Note that your instrument was
calibrated before it left the factory. When you receive your instrument,
read the count to determine its initial value. The count value increments
by one for each calibration point, and a complete calibration may
increase the value by many counts.
Calibration Message The instrument allows you to store one message
in calibration memory. Fo r example, you can s tore the d ate when the last
calibration was perfor med, the date wh en th e next calibrat ion is due , the
instrument’s serial number, or even the name and phone number of the
person to contact for a new calibration.
You can record a calibration message only from the remote interface
and only when the instrument is unsecured.
Y ou can read the message from either the front-panel or over the remote
interface. You can read the calibration message whether the instrument
is secured or unsecured.
1 Select the Cal Info interface.
Press and then select the Cal Info softkey from the “Test/Cal” menu.
The first line in the display shows th e calibration count.
The second line shows the calibration message.
The last line indicates the current version of the firmware.
The calibration info rmation will tim e-out and disappea r after a few sec onds.
Select the Cal Info softkey to show t he inf orma tio n agai n.
2 Exit the menu.
Press the DONE softkey.
42
Page 43

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
T o Unsecure and Secure for Calibration
To Unsecure and Secure for Calibration
This feature allows you to enter a security code to prevent accidental
or unauthorized adjustments of the instrument. When you first receive
your instrument, it is secured. Before you can adjust the instrument,
you must unsecure it by entering the correct security code.
• The security code is set to AT33220A when the instrument is shipped
from the factory. The security code is stored in non-volatile memory,
and does not change when power has been off, after a Factory Reset
(*RST command), or after an Instrument Preset (SYSTem:PRESet
command).
• The security code may contain up to 12 alphanumeric characters.
The first character must be a letter, but the remaining characters
can be letters, numbers, or an underscore ( _ ). You do not have to
use all 12 characters but the first character must always be a letter.
Note If you forget your security code, you can disable the security feature by
applying a temporary short inside the instrument as described in
“To Unsecure the Instrument Without the Security Code” on page 73.
4
3
43
Page 44

3
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
To Unsecure and Secure for Calibration
To Unsecure for Calibration
1 Select the Secure Code interface.
Press and then select the Test/Cal softkey.
2 Enter the Secure Code.
Use the knob to change the displayed character. Use the arrow keys to
move to the next character.
+
When the last character of the secure code is entered, the instrument
will be unsecured.
3 Exit the menu.
Press the DONE softkey.
44
Page 45

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
T o Unsecure and Secure for Calibration
To Secure After Calibration
1 Select the Secure Code interface.
Press and then select the Test/Cal softkey.
2Enter a Secure Code.
Enter up to 12 alphanumeric characters. The first character must be
a letter.
Use the knob to change the displayed character. Use the arrow keys to
move to the next character.
4
3
+
3 Secure the Instrument.
Select the Secure softkey.
4 Exit the menu.
Press the DONE softkey.
45
Page 46

3
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
T o Store the Instrument State
To Store the Instrument State
You can store the instrument state in one of four non-volatile storage
locations. A fifth storage location automatically holds the power-down
configuration of the instrument. When power is restored, the instrument
can automatically return to its state before power-down.
1 Select the desired storage location.
Press and then select the Store State softkey.
2 Select a custom name for the selected location.
If desired, you can assign a custom name to each of the four locations.
• The name can contain up to 12 characters. The first character
be a letter but the remaining characters can be letters, numbers
the underscore character (“_”).
• To add additional characters, press the right-cursor key until the
cursor is to the right of the existing name and then turn the knob.
• To delete all characters to the right of the cursor position, press .
• To use numbers in the name, you can enter them directly from the
numeric keypad. Use the de cimal point from the numeric keypad to
add the underscore character (“_”) to the name.
3 Store the instrument state.
Press the STORE STATE softkey. The instrument stores the selected
function, frequency, amplitude, dc offset, duty cycle, symmetry, as well
as any modulation parameters in use. The instrument does not store
volatile waveforms created in the arbitrary waveform function.
46
must
, or
Page 47

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
To Configure the Remote Interface
To Configure the Remote Interface
The Agilent 33220A supports remote interface communication using a
choice of three interfaces: GPIB, USB, and LAN. All three interfaces are
"live" at power up. The instructions that follow tell how to conf igure y our
remote interface from the instrument front panel.
Note Connectivity software is provided with your instrument on CD-ROM to
enable communications over these interfaces. Install this software as
described in the instructions provided with the CD-ROM.
GPIB Configuration
You need only select a GPIB address.
1 Select the “I/O” menu.
Press and then press the
2 Select the GPIB address.
Use the knob and cursor keys or the numeric keypad to select a GPIB
address in the range 0 through 30 (the factory default is “10”).
The GPIB address is shown on the front-panel display at power-on.
3 Exit the menu.
I/O softkey.
4
3
Press the DONE softkey.
USB Configuration
The USB interface requires no front panel configuration parameters.
Just connect the Agilent 33220A to your PC with the appropriate USB
cable. The interface will self configure. Press the Show USB Id softkey in
the “I/O menu” to see the USB interface identification string. Both USB
1.1 and USB 2.0 are supported.
47
Page 48

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
To Configure the Remote Interface
LAN Configuration
There are several parameters that you may need to set to establish
network communication using the LAN interface. Primarily, you will
need to establish an IP address. You may need to contact your network
administrator for help in establishing communication with the LAN
interface.
1 Select the “I/O” menu.
3
Press and then press the
2 Select the “LAN” menu.
Press the
From this menu, you can select IP Setup to set an IP address and relat ed
parameters, DNS Setup to configure DNS, or Current Config to view the
current LAN configuration.
3 Establish an “IP Setup.”
To use the Agilent 33220A on the network, you must first establish an IP
setup, including an I P addre ss, and pos sib ly a su bnet mask and ga te way
address. Press the IP Setup softkey. By default, DHCP is set to On.
LAN softkey.
I/O softkey.
With DHCP On, an IP address will automatically be set by DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Pr otocol) when you connect the Agilent
33220A to the network, provided the DHCP server is found and is able to
do so. DHCP also automatically deals with the subnet mask and gateway
48
Page 49

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
To Configure the Remote Interface
address, if required. This is typically the easiest way to establish LAN
communication for your instrument. All you need to do is leave DHCP On.
However, if you cannot establ ish communicati on by means of DH CP, you
will need to manually set an IP address, and a subnet mask and gateway
address if they are in use. Follow these steps:
a. Set the “IP Address.” Press the softkey to select DHCP Off. The
manual selection softkeys appear an d the current IP address is
displayed:
Contact your network administrator for the IP address to use. All IP
addresses take the dot-notation form "nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn" where "nnn"
in each case is a byte value in the range 0 through 255. You can enter
a new IP address using the numeric keypad (not the knob). Just type
in the numbers and the period delimiters using the keypad. Use the
left cursor key as a backspace key. Do not enter leading zeros. For
further informa tion, s ee “More about IP Addre sses an d Dot No tatio n”
at the end of this section.
4
3
b. Set the “Subnet Mas k.” The subnet mask is required if your
network has been divided into subnets. Ask your network
administrator whether a subnet mask is needed, and for the correct
mask. Press the Subnet Mask softkey and enter the subnet mask in
the IP address format (using the keypad).
c. Set the “Default Gateway.” The gateway address is the address of
a gateway, which is a device that connects two networks. Ask your
network administrator whether a gate way is in use and for the
correct address. Press the Default Gateway softkey and enter the
gateway address in the IP address format (using the keypad).
d. Exit the “IP Setup” menu. Press DONE to return to the "LAN"
menu.
49
Page 50

3
Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
To Configure the Remote Interface
4 Configure the “DNS Setup” (optional).
DNS (Domain Name Service) is an Internet service that translates
domain names into IP addresses. Ask your network administrator
whether DNS is in use, and if it is, for the host name, domain name, and
DNS server address to use.
Start at the “LAN” menu.
Press the DNS Setup softkey to display the “Host Name” field.
a. Set the “Host Name.” Enter the host name. The host name is the
host portion of the domain name, which is translated into an IP
address. The host name is entered as a string using the knob and
cursor keys to select and change characters. The host name may
include letters, numbers, and dashes (“-”). You can use the keypad for
the numeric characters only.
Press to delete all characters to the right of the cursor position.
b. Set the “Domain Name.” Press the Domain Name softkey and enter
the domain name. The domain name is translated into an IP address.
The domain name is entered as a string using the knob and cursor
keys to select and change characters. The domain name may include
letters, numbers, dashes (“-”), and periods (“.“). You can use the
keypad for the numeric characters only.
Press to delete all characters to the right of the cursor position.
c. Set the “DNS Server” address. Press the DNS Server softkey and
enter the address of the DNS server in the IP address format (using
the keypad).
d. Exit the “DNS Setup” menu. Press DONE to return to the "LAN"
menu.
50
Page 51

Chapter 3 Front-Panel Menu Operation
To Configure the Remote Interface
5 View the current LAN configuration.
Press the Current Config soft key to view the current LAN configu ration.
To scroll through the configuratio n, use the ↑ and ↓ softkeys or rotate the
knob. Press DONE to return to the “LAN” menu.
6 Exit the menu.
Press DONE to exit each menu in turn, or p
menu directly.
More about IP Addresses and Dot Notation
Dot-notation addresses ("nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn" where "nnn" is a byte value)
such as IP addresses must be expressed with care. This is because
most web software on the PC will interpret byte values with leading zeros
as octal numbers. Thus, "255.255.020.011" is actually equivalent to the
decimal "255.255.16.9" rather than "255.255.20.11" because ".020" is
interpreted as "16" expressed in octal, and ".011" as "9". To avoid
confusion it is best to use only decimal expressions of byte values (0 to
255), with no leading zeros.
The Agilent 33220A assumes that all IP addresses and other dot-
notation addresses are expressed as decimal byte values, and strips all
leading zeros from these byte values. Thus, if you try to enter
"255.255.020.011" in the IP address field, it becomes "255.255.20.11" (a
purely decimal expression). You should enter exactly the same
expression, "255.255.20.11" in your PC web software to address the
instrument. Do not use "255.255.020.011"—the PC will interpret that
address differently due to the leading zeros.
ress
to exit the “Utility”
4
3
51
Page 52

3
52
Page 53

4
4
Calibration Procedures
Page 54

4
Calibration Procedures
This chapter contains procedures for verification of the instrument's
performance and adjustment (calibration). The chapter is divided into
the following sections:
• Agilent Technologies Calibration Services, on page 55
• Calibration Interval, on pag e 55
• Adjustment is Recommended, on page 55
• Time Required for Calibration, on page 56
• Automating Calibration Procedures, on page 57
• Recommended Test Equipment, on page 58
• Test Considerations, on page 59
• Performance Verification Tests, on page 60
• Internal Timebase Verification, on page 64
• AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Verification, on page 65
• Low Frequency Flatness Verification, on page 66
• 0 dB Range Flatness Verification, on page 67
• +10 dB Range Flatness Verification, on page 69
• +20 dB Range Flatness Verification, on page 71
• Calibration Security, on page 73
• Calibration Message, on page 75
• Calibration Count, on page 75
• General Calibration/Adjustment Procedure, on page 76
• Aborting a Calibration in Progress, on page 77
• Sequence of Adjustments, on page 77
•Self-Test, on page 78
• Frequency (Internal Timebase) Adjustment, on page 79
• Internal ADC Adjustment, on page 80
• Output Impedance Adjustment, on page 81
• AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Adjustment, on page 83
• Low Frequency Flatness Adjustment, on page 85
• 0 dB Range Flatness Adjustments, on page 86
• +10 dB Range Flatness Adjustments, on page 88
• +20 dB Range Flatness Adjustment, on page 90
• Calibration Errors, on page 93
54
Page 55

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Agilent Technologies Calibration Services
Closed-Case Electronic Calibration The instrument features closed-case
electronic calibration. No internal mechanical adjustments are required.
The instrument calculates correction factors based upon the input
reference value you set. The new correction factors are stored in nonvolatile memory until the next calibration adjus tment is performed. Nonvolatile EEPROM calibration memory does not change when power has
been off or after a remote interface reset.
4
Agilent Technologies Calibration Services
When your instrument is due for calibration, contact your local
Agilent Technologies Service Center for a low-cost recalibration.
The Agilent 33220A is supported on automated calibration systems
which allow Agilent to provide this service at competitive prices.
4
Calibration Interval
The instrument should be calibrated on a regular interval determined by
the measurement accuracy requirements of your application. A 1-year
interval is adequate for most applications. Accuracy specifications are
warranted only if adjustment is made at regular calibration intervals.
Accuracy specifications are not warranted beyond the 1-year calibration
interval. Agilent Technologies does not recommend extending calibration
intervals beyond 2 years for any application.
Adjustment is Recommended
Whatever calibration interval you select, Agilent Technologies
recommends that complete re-adjustment should always be performed
at the calibration interval. This will assure that the Agilent 33220A
will remain within specification for the next calibration interval.
This criteria for re-adjustment provides the best long-term stability.
Performance data measured using this method can be used to extend
future calibration intervals.
Use the Calibration Count (see page 75) to verify that all adjustments
have been performed.
55
Page 56

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Time Required for Calibration
Time Required for Calibration
The Agilent 33220A can be automa tically c alibrat ed under computer control.
With computer control you can perform the complete calibration
procedure and performance verification tests in approximately 30 minutes
once the instrument is warmed-up (see “Test Considerations” on page 59).
Manual adjustments and verifications, using the recommended test
equipment, will take appro x imat el y 2 hours .
START
4
Incoming
Verification?
NO
Perform
Adjustments
(approx 1 Hour)
Do Performance
Verification Tests
(approx 1 Hour)
DONE
YES
Do Performance
Verification Tests
(approx 1 Hour)
56
Page 57

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Automating Calibration Procedures
Automating Calibration Procedures
You can automate the complete verification and adjustment procedures
outlined in this chapter if you have access to programmable test
equipment. You can program the instrument configurations specified
for each test over the remote interface. You can then enter read-back
verification data into a test program and compare the results to the
appropriate test limit values.
You can also adjust the instrument from the remote interface. Remote
adjustment is similar to the local front-panel procedure. You can use a
computer to perform the adjustment by first selecting the required
function and range. The calibration value is sent to the instrument and
then the calibration is initiated over the rem ote interfac e. The instrument
must be unsecured prior to initiating the calibration procedure.
For further information on programming the instrument, see chapters
3 and 4 in the Agilent 33220A User’s Guide.
4
4
57
Page 58

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Recommended Test Equipment
Recommended Test Equipment
The test equipment recommended for the performance verification and
adjustment procedures is listed below. If the exact instrument is not
available, substitute calibration standards of equivalent accuracy.
Instrument Requirements Recommended Model Use*
4
Digital Multimeter
(DMM)
Power Meter 100 kHz to 100 MHz
Power Head 100 kHz to 100 MHz
Attenuator –20 dB Agilent 8491A Opt 020 Q, P, T
Frequency Meter accuracy: 0.1 ppm Agilent 53131A Opt 010
Oscilloscope** 500 MHz
Adapter N type (m) to BNC (m) N type (m) to BNC (m) Q, P, T
Cable BNC (m) to dual-banana (f) Agilent 10110B Q, P, T
ac volts, true rms, ac coupled
accuracy: ±0.02% to 1 MHz
dc volts
accuracy: 50 ppm
resolution: 100 µV
Resistance
Offset-compensated
accuracy: ±0.1Ω
1 µW to 100 mW (–30 dBm to +20 dBm)
accuracy: 0.02 dB
resolution: 0.01 dB
1 µW to 100 mW (–30 dBm to +20 dBm)
2 Gs/second
50Ω input termination
Agilent 3458A Q, P, T
Agilent E4418B Q, P, T
Agilent 8482A Q, P, T
Q, P, T
(high stability)
Agilent 54831B T
Cable (2 required) Dual banana (m) to dual banana (m) Agilent 11000-60001 Q, P, T
Cable RG58, BNC (m) to dual banana Agilent 11001-60001 Q, P, T
Cable RG58, BNC (m) to BNC (m) Agilent 8120-1840 Q, P, T
* Q = Quick Verification P = Performance Verification T = Troublesh ooting
** An oscilloscope is not required for calibration, only for troubleshooting.
58
Page 59

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Tes t Considerations
Test Considerations
For optimum performance, all procedures should comply with the
following recommendations:
• Assure that the calibration ambient temperature is stable and
between 21 °C and 25 °C (23 °C
• Assure ambient relative humidity is less than 80%.
• Allow a 1-hour warm-up period before verification or adjustment.
• Keep the measurement cables as short as possible, consistent with
the impedance requirements.
±2 °C).
4
• Use only RG-58 or equivalent 50
Ω cable.
4
59
Page 60

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Performance Verification Tests
Performance Verification Tests
Use the Performance Verification Tests to verify the measurement
performance of the instrument. The performance verification tests use
the instrument’s specifications listed in the “Specifications” chapter
beginning on page 13.
You can perform three different levels of performance verification tests:
• Self-Test A series of internal verification tests that give high
confidence that the instrument is operational.
• Quick Verification A combination of the in ternal self-tests and
selected verification tests.
4
• Performance Verification Tests An extensive set of t es ts tha t a re
recommended as an acceptance test when you first receive the
instrument or after performing adjustments.
Self-Test
A brief power-on self-test occurs automatically whenev er you turn o n the
instrumen t. This limited test assures that the instrument is operational.
To perform a complete self-test:
1 Press on the front panel.
2 Select the Self Test softkey from the “Test/Cal” menu.
A complete description of the self-tests can be found in chapter 6.
The instrument will automatically perform the complete self-test
procedure when you release the key. The self-test will complete in
approximately 15 seconds.
• If the self-test is successful, “Self Test Passed” is displayed on the
front panel.
• If the self-test fails, “Self Test Failed” and an error number are
displayed.
If repair is required, see chapter 6, “Service,” for further details.
60
Page 61

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Performance V erification Tests
Quick Performance Check
The quick performance check is a combination of internal self-test and
an abbreviated performance test (specified by the letter Q in the
performance verification tests). This test provides a simple method to
achieve high confidence in the instrument's ability to functionally
operate and meet specifications. These tests represent the absolute
minimum set of performance checks recommended following any service
activity. Auditing the instrument’s performance for the quick check
points (designated by a Q) verifies performance for normal accuracy drift
mechanisms. This test does not check for abnormal component failures.
To perform the quick performance check, do the following:
1 Perform a complete self-test. A procedure is given on page 60.
4
2 Perform only the performance verification tests indicated with the
letter Q.
3 If the instrument fails the quick performance check, adjustment or
repair is required.
Performance Verification Tests
The performance verification tests are recommended as acceptance
tests when you first receive the instrument. The acceptance test results
should be compared against the specifications given in chapter 1.
After acceptance, you should repeat the performance verification tests at
every calibration interval.
If the instrument fails performance verification, adjustment or repair
is required.
Adjustment is recommended at every calibration interval. If adjustment
is not made, you must guard band, using no more than 80% of the
specifications listed in chapter 1, as the verification limits.
4
61
Page 62

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Performance Verification Tests
Special Note:
Amplitude and Flatness Verification Procedures
Measurements made during the AC Amplitude (high-impedance)
Verification procedure (see page 65 ) are used as refere nce measurements
in the flatness verification procedures (beginning on page 66). Additional
reference measurements and calculated references are used in the
flatness verification proc edures. Pho to-copy and use the table on page 6 3
to record these reference measurements and perform the calculations.
The flatness verificat ion proced ures use bo th a DMM and a Po wer Meter
to make the measurements. To correct the difference between the DMM
and Power Meter measurements, the Power Meter reference
measurement level is adjusted to set the 0.00 dB level to the DMM
measurement made at 1 kHz. The flatness error of the DMM at 100 KHz
is used to set the required 0.00 dB reference.
The instrument internally corrects the difference betwee n the high-Z
input of the DMM and the 50 Ω input of the Power Meter when setting
the output level.
The reference measurements must a lso be converted from Vrms (made
by the DMM) to dBm (made by the Power Meter).
The equation used for the conversion from Vrms (High-Z) to dBm
(at 50 Ω) is as follows:
Power (dBm) = 10 log(5.0 * V
Flatness measurements for the –10 db, –20d B, and –30 dB attenuator
ranges are verified as a part of the 0 dB verification procedure. No
separate verification procedure is given for these ranges.
rms
2
)
62
Page 63

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Performance V erification Tests
Amplitude and Flatness Verification Worksheet
1. Enter the following measurements (from procedure on page 65).
1kHz_0dB_reference = __________________________ Vrms
1kHz_10dB_reference = __________________________ Vrms
1kHz_20dB_reference = __________________________ Vrms
2. Calculate the dBm value of the rms voltages.
1kHz_0dB_reference_dBm ==10 * log(5.0 * 1kHz_0dB_reference
_______________ ___ ___ ___ __ dBm
1kHz_10dB_reference_dBm ==10 * log(5.0 * 1kHz_10dB_reference2)
__________________________ dBm
1kHz_20dB_reference_dBm ==10 * log(5.0 * 1kHz_20dB_reference
_______________ ___ ___ ___ __ dBm
3. Enter the following measurements (from the procedure on page 66).
100kHz_0dB_reference = __________________________ Vrms
100kHz_10dB_reference = __________________________ Vrms
2
)
2
)
4
4
100kHz_20dB_reference = __________________________ Vrms
4. Calculate the dBm value of the rms voltages.
100kHz_0dB_reference_dBm ==10 * log(5.0 * 100kHz _0dB_reference
__________________________ dBm
100kHz_10dB_reference_dBm ==10 * log(5.0 * 100kHz_10dB_reference
__________________________ dBm
100kHz_20dB_reference_dBm ==10 * log(5.0 * 100kHz_20dB_reference
__________________________ dBm
5. Calculate the offset values.
100kHz_0dB_offset ==100kHz_0dB_reference_dBm – 1kHz_0dB_reference_dBm
__________________________ dBm (use on page 67)
100kHz_10dB_offset ==100kHz_10dB_reference_dBm
__________________________ dBm (use on page 69)
100kHz_20dB_offset ==100kHz_20dB_reference_dBm – 1kHz_20dB_reference_dBm
__________________________ dBm (use on page 71)
2
)
2
)
2
)
– 1kHz_10dB_reference_dBm
63
Page 64

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Internal Timebase Verification
Internal Timebase Verification
This test verifies the output frequency accuracy of the instrument. All
output frequencies are derived from a single generated frequency.
1 Connect a frequency counter as shown below (the frequency counter
input should be terminated at 50 Ω).
2 Set the instrument to the output described in the table below and
measure the output frequency. Be sure the instrument output is enabled.
Agilent 33220A Measurement
Function Amplitude Frequency Nominal Error
Q Sine Wave 1.00 Vpp 10.000,000,0 MHz 10.000 MHz ± 200 Hz
*
The error is ± 100 Hz within 90 days of calibration, or ± 200 Hz within one year.
3 Compare the measured frequency to the test limits shown in the table.
64
*
Page 65

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Verification
AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Verification
This procedure checks the ac amplitude output accuracy at a frequency
of 1 kHz, and establishes reference measurements for the higher
frequency flatness verification procedures.
1 Set the DMM to measure Vrms Volts. Connect the DMM as shown below.
4
2 Set the instrument to each output described in the table below and
measure the output voltage with the DMM. Press to set the output
impedance to High–Z. Be sure the output is enabled.
Agilent 33220A Measurement
Output Setup Function Frequency Amplitude Nominal Error*
Q High Z Sine Wave 1.000 kHz 20.0 mVrms 0.020 Vrms ± 0.00091 Vrms
Q High Z Sine Wave 1.000 kHz 67.0 mVrms 0.067 Vrms ± 0.00138 Vrms
Q High Z Sine Wave 1.000 kHz 200.0 mVrms 0.200 Vrms ± 0.00271 Vrms
1
Q High Z Sine Wave 1.000 kHz 670.0 mVrms 0.670 Vrms
Q High Z Sine Wave 1.000 kHz 2.000 Vrms 2.0000 V r m s
Q High Z Sine Wave 1.000 kHz 7.000 Vrms 7.000 Vrms
Q High Z Square Wave 41.000 kHz 900.0 mVrms 0.900 Vrms ± 0.0100 Vrms
* Based upon 1% of setting ±1 mVpp (50 Ω); converted to Vrms for High–Z.
1
Enter the measured value on the worksheet (page 63) as 1kHz_0dB_reference.
2
Enter the measured value on the worksheet (page 63) as 1kHz_10dB_reference.
3
Enter the measured value on the worksheet (page 63) as 1kHz_20dB_reference.
4
Square wave amplitude accuracy is not specified. This measurement an d error
may be used as a guideline for typical operation.
± 0.00741 Vrms
2
± 0.0207 Vrms
3
± 0.0707 Vrms
3 Compare the measured voltage to the test limits shown in the table.
65
Page 66

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Low Frequency Flatness Verification
Low Frequency Flatness Verification
This procedure checks the AC amplitude flatness at 100 kHz using the
reference measurements recorded in the Amplitude and Flatness
Verification Worksheet. These measurements also establish an error
value used to set the powe r meter reference. The tra nsfer measu rements
are made at a frequency of 100 kHz using both the DMM and the power
meter.
1 Set the DMM to measure ac Volts. Connect the DMM as shown in the
figure on page 65.
2 Set the instrument to each output described in the table below and
measure the output voltage with the DMM. Press to set the output
impedance to High-Z. Be sure the output is enabled.
Agilent 33220A Measurement
Output Setup Function Frequency Amplitude Nominal Error
Q High Z Sine Wave 100.000 kHz 670.0 mVrms 0.670 Vrms
Q High Z Sine Wave 100.000 kHz 2.000 Vrms 2.000 Vrms
Q High Z Sine Wave 100.000 kHz 7.000 Vrms 7.000 Vrms
1
Enter the measured value on the worksheet (page 63) as
100kHz_0dB_reference.
2
Enter the measured value on the worksheet (page 63) as
1k00Hz_10dB_reference.
3
Enter the measured value on the worksheet (page 63) as
100kHz_20dB_reference.
1
± 0.0067 Vrms
2
± 0.020 Vrms
3
± 0.070 Vrms
3 Compare the measured voltage to the test limits shown in the table.
4 You have now recorded all the required measurements on the worksheet
(page 63). Complete the worksheet by making all the indicated
calculations.
66
Page 67

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
0 dB Range Flatness Verification
0 dB Range Flatness Verification
This procedure checks the high frequency ac amplitude flatness above
100 kHz on the 0dB attenuator range. (Flatness is relative to 1 kHz.)
1 Connect the power meter to measure the output amplitude of the
instrument as shown below.
4
4
2 Set up the function generator as follows:
• Output impedance: 50 Ω (press and select Output Setup).
•Waveform: Sine
• Frequency: 100 kHz
• Amplitude: 3.51 dBm
Make sure the output is enabled.
3 On the power meter, use the Relative Power function to set the current
reading as the reference value. This will allow you to compare future
measurement results in dB.
4 Set the power met er offset to equal the 100kHz_0dB_offset value
previously calculated. This sets the power meter to directly read the
flatness error specification relative to 1 kHz. 100kHz_0dB_offset is
calculated on the Amplitude and Flatness Verification Worksheet.
67
Page 68

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
0 dB Range Flatness Verification
5 Set the function generator to each output described in the table below
and measure the output amplitude with the power meter (the relative
measurement in dB).
Agilent 33220A Measurement
Output Setup Function Amplitude Frequency Nominal Error
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 100.000 kHz 0 dB ±0.1 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 200.000 kHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 500.000 kHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 2.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 3.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
4
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 4.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 5.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 8.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 10.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 12.500 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 14.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 16.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 17.500 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +3.51 dBm 20.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
6 Compare the measured output to the test limits shown in the table.
68
Page 69

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+10 dB Range Flatness Verification
+10 dB Range Flatness Verification
This procedure checks the high frequency ac amplitude flatness above
100 kHz on the +10dB attenuator range. (Flatness is relative to 1 kHz.)
1 Connect the power meter to measure the output amplitude of the
instrument as shown on page 67.
2 Set up the function generator as follows:
• Output impedance: 50 Ω (press and select Output Setup).
•Waveform: Sine
• Frequency: 100 kHz
• Amplitude: 13.00 dBm
Make sure the output is enabled.
3 On the power meter, use the Relative Power function to set the current
reading as the reference value. This will allow you to compare future
measurement results in dB.
4 Set the power met er offset to equal the 100kHz_10dB_offset value
previously calculated. This sets the power meter to directly read the
flatness error specification relative to 1 kHz. 100kHz_10dB_offset is
calculated on the Amplitude and Flatness Verification Worksheet.
4
4
69
Page 70

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+10 dB Range Flatness Verification
5 Set the instrument to each output described in the table below and
measure the output amplitude with the power meter (the relative
measurement in dB).
Agilent 33220A Measurement
Output Setup Function Amplitude Frequency Nominal Error
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 100.000 kHz 0 dB ±0.1 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 200.000 kHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 500.000 kHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 2.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 3.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
4
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 4.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 5.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 8.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.3 dB
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 10.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 12.500 MHz 0 dB ±0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 14.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 16.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 17.500 MHz 0 dB ±0.3 dB
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +13.00 dBm 20.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.3 dB
6 Compare the measured output to the test limits shown in the table.
70
Page 71

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+20 dB Range Flatness Verification
+20 dB Range Flatness Verification
This procedure checks the high frequency ac amplitude flatness above
100 kHz on the +20dB attenuator range. (Flatness is relative to 1 kHz.)
1 Connect the power meter to measure the output voltage of the
instrument as shown below.
4
4
Caution Most power meters will require an attenuator or special power head to
measure the +20 dB output.
2 Set up the function generator as follows:
• Output impedance: 50 Ω (press and select Output Setup).
•Waveform: Sine
• Frequency: 100 kHz
• Amplitude: 23.90 dBm
Make sure the output is enabled.
3 On the power meter, use the Relative Power function to set the current
reading as the reference value. This will allow you to compare future
measurement results in dB.
71
Page 72

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+20 dB Range Flatness Verification
4 Set the power met er offset to equal the 100kHz_20dB_offset value
previously calculated. This sets the power meter to directly read the
flatness error specification relative to 1 kHz. 100kHz_20dB_offset is
calculated on the Amplitude and Flatness Verification Worksheet.
5 Set the instrument to each output described in the table below and
measure the output amplitude with the power meter.
Agilent 33220A Measurement
Output Setup Function Amplitude Frequency Nominal Error
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 100.000 kHz 0 dB ± 0.1 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 200.000 kHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 500.000 kHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 2.000MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 3.000MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 4.000 MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 5.000MHz 0 dB ±0.15 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 8.000MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 10.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 12.500 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 14.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 16.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 17.500 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
Q 50 Ω Sine Wave +23.90 dBm 20.000 MHz 0 dB ± 0.3 dB
6 Compare the measured output to the test limits shown in the table.
72
Page 73

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Calibration Security
Calibration Security
This feature allows you to enter a security code to prevent accidental
or unauthorized adjustments of the instrument. When you first receive
your instrument, it is secured. Before you can adjust the instrument,
you must unsecure it by entering the correct security code.
See “To Unsecure and Secure for Calibration”, on pag e 43 for a proc edure
to enter the security code from the front panel. Use the CAL:SEC:STAT ON
command to enter the security code using the remote interface.
• The security code is set to AT33220A when the instrument is shipped
from the factory. The security code is stored in non-volatile memory,
and does not change when power has been off, after a Factory Reset
(*RST command), or after an Instrument Preset (SYSTem:PRESet
command).
• The security code may contain up to 12 alphanumeric characters.
The first character must be a letter, but the remaining characters
can be letters, numbers, or an underscore ( _ ). You do not have to
use all 12 characters but the first character must always be a letter.
Note If you forget your security code, you can disable the security feature by
applying a temporary short inside the instrument as described below.
To Unsecure the Instrument Without the Security Code
To unsecure the instrument without the correct security code, follow t he
steps below. See “To Unsecure and Secure for Calibration” on page 43.
See “Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Precautions” on page 121 before
beginning this procedure.
4
4
Note If you do not have a record of the security code, there are two codes you
may wish to try before you use the procedure below. First try AT33220A
(the factory default code). If that code does not work, you may wi sh to try
the single letter A as the security code. If someone has re-secured
calibration without entering a new code, the default code is the letter A.
1 Disconnect the power cord and all input connections.
2 Disassemble the instrume nt using the “Gene ral Dis assembl y Procedu re”
on page 128.
73
Page 74

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Calibration Security
3 Apply a temporary short between the two exposed metal pads on the
A1 assembly. The general location is shown in the figure below. On the
PC board, the pads are marked CAL ENABLE.
U101
U102
Pads
4 Apply power and turn on the instrument.
WARNING Be careful not to touch the power line connections or high voltages on the
power supply module. Power is present even if the instrument is turned
off.
5 The display will show the message “Calibration security has been
disabled”. The instrument is now unsecured.
6 Turn off the instrument and remove the power cord.
7 Reassemble the instrument.
Now you can enter a new security code, see “To Unsecure and Secure for
Calibration”, on page 43. Be sure you record the new security code.
74
Page 75

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Calibration Message
Calibration Message
The instrument allows you to store one message in calibration memory.
For example, you can store the date when the last calibration was
performed, the date when the next calibration is due, the instrument's
serial number, or even the name and phone number of the person to
contact for a new calibration.
You can record a calibration message only from the remote interface
and only when the instrument is unsecured. Use the CAL:STRING
<message> command.
You can read the message from either the front-panel or over the remote
interface. You can read the calibration message whether the instrument
is secured or unsecured. Reading the calibration message from the front
panel is described on “To Read the Calibration Information”, on page 42.
Use the CAL:STRING? query to read the message over the remote
interface.
4
4
Calibration Count
You can query the instrument to determine how many calibrations have
been performed. Note that your instrument was calibrated before it left
the factory. When you receive your instrument, read the count to
determine its initial value. The count value increments by one for each
calibration point, and a complete calibration may increase the value by
many counts. See “To Read the Calibration Information”, on page 42.
Use the CAL:COUNT? query to read the count over th e remote interface.
75
Page 76

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
General Calibration/Adjustment Procedure
General Calibration/Adjustment Procedure
The following procedure is the recommended method to complete an
instrument calibration. Th is procedure is an overview of the steps
required for a complete calibration. Additional details fo r each step in
this procedure are given in the appropriate sections of this chapter.
1 Read “Test Considerations” on page 59.
2 Unsecure the instrument for calibration (see page 73).
3 Perform the verification tests, beginning on page page 60, t o characterize
the instrument (incoming data).
4
4 Press on the front panel.
5 Select the “Test / Cal” menu.
6 Select Perform Cal.
7 Enter the Setup Number for the procedure bei ng per formed . The de fa ult
setup number is “1” and, from the front panel, the number will increment
as the procedures are performed.
8 Select BEGIN.
9 For setups that require an input, adjust the value shown in the display
to the measured value and select ENTER VALUE.
10 The setup will automatically advance to the next required value.
Note To cancel the adjustment procedure, select CANCEL STEP. The display
will return to the setup number entry.
11 When finished, select END CAL.
12 Secure the instrument against calibration.
13 Note the new security code and calibration count in the instrument’s
maintenance records.
76
Page 77

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Aborting a Calibration in Progress
Aborting a Calibration in Progress
Sometimes it may be necessary to abort a calibration after the procedure
has already been initiated. You can abort a calibration at any time by
turning off the power. When performing a calibration from the remote
interface, you can abort a calibration by issuing a remote interface device
clear message followed by a *RST.
The instrument stores calibration constants at the end of each
adjustment procedure. If you lose power, or otherwise abort an
adjustment in progress, you will only need to perform the interrupted
adjustment procedure again.
Caution If power is lost when the instrument is attempting to write new
calibration constants to EEPROM, you may l ose al l calibration constants
for the function. Typically, upon re-applying power, the instrument will
report error “-313, Calibration Memory Lost”.
4
4
Sequence of Adjustments
The adjustment sequence shown in the following sections of this chapter
is recommended to minimize the number of test equipment set-up and
connection changes.
You may perform individual adjustments as necessary. Setups 1 through 7
must be performed in order and must be performed before any other
setup procedure.
77
Page 78

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Self-Test
Self-Test
Self-Test is performed as the first step to ensure the instrument is in
working order before beginning any additional adjustments.
Note Be sure to follow the requirements listed in “Test Considerations” on
page 59 before beginning any adjustments.
1 Press on the front panel. Select Perform Cal on the “Test / Cal”
menu. Enter setup number “1” and select BEGIN.
Setup
4
1 Performs the Self-test. The Main Output is disabled during test.
2 If the instrument fails any self-test, you must repair the instrument
before continuing the adjustment procedures.
Note The self-test procedure takes approximately 15 seconds to complete.
78
Page 79

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Frequency (Internal Timebase) Adjustment
Frequency (Internal Timebase) Adjustment
The function generator stores a calibration constant that sets the VCXO
to output exactly 10 MHz.
1 Set the frequency counter resolution to better than 0.1 ppm and the
input termination to 50 Ω (if your frequency counter does not have a 50 Ω
input termination, you must provide an external termination). Make the
connections shown below.
4
4
2 Use a frequency counter to measure the output frequency for each setup
in the following table.
Nominal Signal
Setup Frequency Amplitude
2 <10 MHz 1 Vpp Output frequency is slightly less than 10MHz
3 >10 MHz 1 Vpp Output frequency is slightly more than 10MHz
4 ~10 MHz 1 Vpp Output frequency should be near 10MHz
5* 10 MHz 1 Vpp Output frequency should be 10MHz ±1ppm
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
3 Using the numerical keypad or knob, adjust the displayed frequency at
each setup to match the measured frequency. Select ENTER VALUE.
4 After performing setup 5:
a. If your calibration procedures require yo u to verify t he adjustment
just made, exit the calibration menu and perform “Internal
Timebase Verification”, on page 64.
b. If you are making all the adjustments and then verifying the
instrument’s performance, continue with the next procedure in
this chapter.
79
Page 80

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Internal ADC Adjustment
Internal ADC Adjustment
The function generator stores calibration constants related to the gain
and offset of the internal ADC. Setup 6 must always be performed
before any other adjustments are attempted. The internal ADC is then
used as a source for the calibration constants generated in setup 7.
1 Make the connections as shown below.
Modulation In
2 Set the DMM to display 5 1/2 digits and measure the dc value. Record
the measurement.
3 Enter the following setup and use the numeric keypad or knob to enter
the measured value of the dc source.
Nominal Signal
Setup DC level
6* ~1.1 Vdc ±10% Calibrates the internal ADC.
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
Note This setup requires approximately 15 seconds to complete.
4 Disconnect all cables from the rear panel Modulation In connector.
80
Page 81

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Output Impedance Adjustment
5 Enter and begin the following setup.
Setup
7* Self-calibration. The output is disabled.
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
6 There are no specific operational verification tests for setups 6 and 7
since the constants generated affect almost all behavior of the
instrument. Continue with the next adjustment procedure in this
chapter.
Output Impedance Adjustment
4
The function generator stores calibration constants for the output
impedance. The output impedance constants are generated with and
without the distortion filter and using all five attenuator paths.
1 Set the DMM to measure offset-compensated, four-wire Ohms. Set the
DMM to use 100 NPLC integration. Make the connections as shown
below.
4
81
Page 82

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Output Impedance Adjustment
2 Use the DMM to make a resistan ce measurement at the front panel
Output connector for each setup in the following table. The expected
measured value is approximately 50 Ω.
Setup
8* -30dB range
9* -20dB range
10* -10dB range
11* 0dB range
12* +10dB range
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
4
3 Using the numeric keypad or knob, adjust the displayed impedance at
each setup to match the measured impedance. Select ENTER VALUE.
4 There are no specific operational verification tests for Output
Impedance. Continue with the next adjustment procedure in this
chapter.
82
Page 83

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Adjustment
AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Adjustment
The function generator stores a calibration constant for each highimpedance attenuator path. The gain coefficient of each path is
calculated using tw o measurements; one with the waveform DAC at +
output and one with waveform DAC at – output. The setups, therefore,
must be performed in pairs.
1 Connect the DMM as shown below.
4
4
83
Page 84

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
AC Amplitude (high-impedance) Adjustment
2 Use the DMM to measure the dc vo ltage at the front-panel Output
connector for each setup in the following table.
Nominal Signal
Setup DC level
13 +0.015 V Output of -30dB range
14* -0.015 V Output of -30dB range
15 +0.05 V Output of -20dB range
16* -0.05 V Output of -20dB range
17 +0.15 V Output of -10dB range
18* -0.15 V Output of -10dB range
19 +0.50 V Output of 0dB ran ge
20* -0.50 V Output of 0dB range
21 +0.15 V Output of -10dB range (Amplifier In)
22* -0.15 V Output of -10dB range (Amplifier In)
23 +0.50 V Output of 0dB range (Amplifier In)
24* -0.50 V Output of 0dB range (Amplifier In)
25 +1.5 V Output of +10dB range (Amplifier In)
26* -1.5 V Output of +10dB range (Amplifier In)
27 +5 V Output of +20dB range (Amplifier In)
28* -5 V Output of +20dB range (Amplifier In)
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
3 Using the numeric keypad or knob, adjust the displayed voltage at each
setup to match the measured voltage. Select ENTER VALUE. (Entered
values are rounded to the nearest 100 µV).
4 After performing setup 28:
a. If your calibration procedures require yo u to verify t he adjust ment
just made, exit the calibration menu and perform “AC Amplitude
(high-impedance) Verification”, on page 65.
b. If you are making all the adjustments and then verifying the
instrument’s performance, continue with the ne xt procedure in
this chapter.
84
Page 85

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Low Frequency Flatness Adjustment
Low Frequency Flatness Adjustment
The Low Frequency Flatness adjustment calculates the flatness response
of 3 attenuator paths with the Elliptical filter and 2 attenuator paths
with the Linear Phase filter.
1 Set the DMM to measure Vrms. Make the connections sho wn on p age 8 3.
4
2 Use the DMM to measure t he out put volt age fo r each of the setups in t he
table below.
Nominal Signal
Setup Frequency Amplitude
29* 1 kHz 0.56 Vrms Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
30* 100 kHz 0.56 Vrms Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
31* 1 kHz 0.56 Vrms Flatness for 0dB, Linear Phase Filter
32* 100 kHz 0.56 Vrms Flatness for 0dB, Linear Phase Filter
33* 1 kHz 1.7 Vrms Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
34* 100 kHz 1.7 Vrms Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
35* 1 kHz 5.6 Vrms Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
36* 100 kHz 5.6 Vrms Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
37* 1 kHz 5.6 Vrms Flatness for +20dB, Linear Phase Filter
38* 100 kHz 5.6 Vrms Flatness for +20dB, Linear Phase Filter
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
3 Using the numeric keypad or knob, adjust the displayed voltage at each setu p
to match the measured voltage. Select ENTER VALUE.
4 After performing setup 38:
a. If your calibration procedures require yo u to verify t he adjustment
just made, exit the calib ration menu an d perfo rm “ Low F req uency
Flatness Verification”, on page 66.
b. If you are making all the adjustments and then verifying the
instrument’s performance, continue with the next procedure in
this chapter.
4
85
Page 86

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
0 dB Range Flatness Adjustments
0 dB Range Flatness Adjustments
1 Connect the power meter as shown on pag e 88.
2 Use the power meter to measure the output amplitude for each of the
setups in the table below.
Note Setup 39 establishes the power meter reference for all the remaining
setups in this table. You must always perform setup 39 before any of the
following setups.
Nominal Signal
Setup Frequency Amplitude
39* 100 kHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Power Meter Reference for 0dB Range
40* 200 kHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
41* 500 kHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
42* 1.5 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
43* 3 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
44* 4 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
45* 6 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
46* 8 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
47* 10.1 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
48* 12.5 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
49* 14.1 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
50* 16.1 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
51* 17.5 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
52* 19.9 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Elliptical Filter
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
This table is continued on the next page.
86
Page 87

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
0 dB Range Flatness Adjustments
Nominal Signal
Setup Frequency Amplitude
53* 200 kHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Linear Phase Filter
54* 500 kHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Linear Phase Filter
55* 1.5 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Linear Phase Filter
56* 3.0 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Linear Phase Filter
57* 4 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Linear Phase Filter
58* 6 MHz 0.28 Vrms 2 dBm Flatness for 0dB, Linear Phase Filter
59 0 dBm Setup not used for this instrument
60* 0 dBm Setup not used for this instrument
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
Note Setups 59 and 60 are not used in this instrument. From the front panel,
press the Enter softkey to advance the setup from 59 to 61. No number
entry is required .
3 Using the numeric keypad, adjust the displayed amplitude at each setup
to match the measured amplitude (in dBm). Then select ENTER VALUE.
Note In order to get dBm you must use the numeric keypad (not the knob) to
enter the number, and then select “dBm”.
4 After performing setup 58:
a. If your calibration procedures require yo u to verify t he adjustment
just made, exit the calibratio n menu and perform “0 dB Range
Flatness Verification”, on page 67.
b. If you are making all the adjustments and then verifying the
instrument’s performance, continue with the next procedure in
this chapter.
4
4
87
Page 88

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+10 dB Range Flatness Adjustments
+10 dB Range Flatness Adjustments
Note The Linear Phase path is not adjusted. It is approximated using the
other path’s va lu es .
1 Connect the powe r met er as sh o wn below.
2 Use a power meter to measure the output amplitude for each of the
setups in the table on the next page.
Note Setup 61 establishes the power meter reference for all the remaining
setups in this table. You must always perform setup 61 before any of the
following setups.
88
Page 89

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+10 dB Range Flatness Adjustments
Nominal Signal
Setup Frequency Amplitude
61* 100 kHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Power Meter Reference for +10dB Range
62* 200 kHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
63* 500 kHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
64* 1.5 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
65* 3 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
66* 4 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
4
67* 6 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
68* 8 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
69* 10.1 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
70* 12.5 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
71* 14.1 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
72* 16.1 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
73* 17.5 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
74* 19.9 MHz 0.9 Vrms 12 dBm Flatness for +10dB, Elliptical Filter
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
3 Using the numeric keypad, adjust the displayed amplitude at each setup
to match the measured amplitude (in dBm). Then select ENTER VALUE.
Note In order to get dBm you must use the numeric keypad (not the knob) to
enter the number, and then select “dBm”.
4 After performing setup 74:
a. If your calibration procedures require yo u to verify t he adjustment
just made, exit the calibratio n menu and perform “+10 dB Range
Flatness Verification”, on page 69.
b. If you are making all the adjustments and then verifying the
instrument’s performance, continue with the next procedure in
this chapter.
4
89
Page 90

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+20 dB Range Flatness Adjustment
+20 dB Range Flatness Adjustment
Caution Most power meters will require an attenuator (–20 dB) or special power
head to measure the +20 dB output.
Be sure to correct the measurements for the specifications of the
attenuator you use. For example, if the nominal attenuator value
is –20 dB at the specified frequency, you must add 20 dB to the power
meter reading before entering the value.
1 Make the connections as shown below:
2 Use the power meter to measure the output amplitude for each of the
setups in the table on the next page.
Note Setup 75 establishes the power meter reference for all the remaining
setups in this table. You must always perform setup 75 before any of the
following setups.
90
Page 91

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+20 dB Range Flatness Adjustment
Nominal Signal
Setup Frequency Amplitude
75* 100 kHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Power Meter Reference
76* 200 kHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
77* 500 kHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
78* 1.5 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
79* 3 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
80* 4 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
4
81* 6 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
82* 8 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
83* 10.1 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
84* 12.5 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
85* 14.1 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
86* 16.1 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
87* 17.5 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
88* 19.9 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Elliptical Filter
89* 200 kHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Linear Phase Filter
90* 500 kHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Linear Phase Filter
91* 1.5 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Linear Phase Filter
92* 3 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Linear Phase Filter
93* 4 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Linear Phase Filter
94* 6 MHz 2.8 Vrms 22 dBm Flatness for +20dB, Linear Phase Filter
* Constants are stored after completing this setup.
4
91
Page 92

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
+20 dB Range Flatness Adjustment
3 Using the numeric keypad, adjust the displayed amplitude at each setup
to match the measured amplitude (in dBm). Then select ENTER VALUE.
Note In order to get dBm you must use the numeric keypad (not the knob) to
enter the number, and then select “dBm”.
4 After performing setup 94:
a. If your calibration procedures require yo u to verify t he adjust ment
just made, exit the calibration menu and perform “+20 dB Range
Flatness Verification”, on page 71.
b. If you are making all the adjustments and then verifying the
instrument’s performanc e, verify the output specifications of the
instrument using the “Performance Verification Tests”, on page
60.
You have now completed the recommended adjus tment procedures.
Verification of the output specifications is recommended.
92
Page 93

Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Calibration Errors
Calibration Errors
The following errors are failures that may occur during a calibration.
System error messages are described in chapter 5 of the Agilent 33220A
User’s Guide. Self-test error messages are described beginning on
page 124.
701 Calibration error; security defeated by hardware jumper
The function generator’s calibration security feature has been disabled
by temporarily shorting the two “CAL ENABLE” pads on the internal
circuit board as described starting on page 73.
702 Calibration error; calibration memory is secured
A calibration cannot be performed when calibration memory is secured.
See “To Unsecure and Secure for Calibration”, on page 43 for a procedure
to enter the security code from the front panel. Use the CAL:SEC:STAT
ON command to enter the security code using the remote interface.
703 Calibration error; secure code provided was invalid
Invalid security code specified with the CAL:SEC:STAT ON command.
706 Calibration error; value out of range
You have entered a value that was unexpected by the calibration firmware.
For example, if a number is expected such a 50.XX ohms, and you enter
10 ohms, that number is outside the expected range of valid inputs.
707 Calibration error; signal input is out of range
Occurs during the ADC Adjustment, setup 6, if the 1 Volt input voltage is
too high. May also occur during self-calibration (setup 7), run self-test to
diagnose cause of problem.
707 707: Calibration error; cal edge time; rise time cal error
707: Calibration error; cal edge time; fall time cal error
707: Calibration error; cal edge time; default values loaded
Indicates a failure in the rise-time or fall-time circuitry has prevented
calibration. The edge-time was calibrated using default values, limiting
accuracy. Service is required to correct the problem and achieve design
accuracy for the rise and fall times.
4
4
93
Page 94

4
Chapter 4 Calibration Procedures
Calibration Errors
850 Calibration error; set up is invalid
You have selected an invalid calibration setup number with the CAL:SET
command.
851 Calibration error; set up is out of order
Certain calibrati on steps require a specif ic beginni ng and ending sequen ce.
You may not enter into the middle of a sequence of calibration steps.
94
Page 95

5
Theory of Operation
5
Page 96

Theory of Operation
This chapter provides descriptions of the circuitry shown on the
schematics in chapter 9.
• Block Diagram, on page 97
• Main Power Supply, on page 100
• Earth Referenced Power Supplies, on page 101
• Floating Power Supplies, on page 102
• Waveform DAC and Filters, on page 103
• Squarewave Comparator, on page 104
• Main Output Circuitry, on page 106
• System ADC, on page 107
•System DAC, on page 108
• Synthesis IC and Waveform Memory, on page 110
• Timebase, Sync Output, and Relay Drivers, on page 111
• Main Processor, on page 112
• Front Panel, on page 114
• External Timebase (Option 001), on page 115
5
96
Page 97

Chapter 5 Theory of Operation
Block Diagram
Block Diagram
The function generator’s circuits may be divided into three main
categories: power supplies, analog circuits, and digital circuits. The
instrument is further divided into floating and earth referenced
circuitry.
This discussion refers to the block diagram on page page 99.
The Main Processor U101 combines many instrument functions onto one
custom IC. It interfaces directly with the GPIB and LAN interfaces, and
through a controller chip with the USB interface. A 50 MHz crystal
oscillator provides the clock signal for U101 operations. A 24 MHz clock
is used for USB operations.
The Main Processor communicates with the Front Panel and performs
the keyboard scanning. Serial data is used to write to the display. The
cross-isolation communication with the Synthesis IC uses optically
isolated serial data links.
The Synthesis IC is a gate array and performs most of instrument
functions. This gate array has an on-board UART. A 50 MHz voltagecontrolled-oscillator provides the main clock for the Synthesis IC and the
Waveform DAC. The Synthesis IC implements clock generation, pulse
generation, DDS and modulation functions, and sets the output
waveform and function.
The system DAC outputs various control voltages that are multiplexed
into track and hold circuits. These output voltages are used to correct the
output waveform for v ario us offs ets, ri se time s, an d calibr ation va lues. If
present, the optional external timebase circuitry provides an input and
output for an external time base. A Sync Out signal is available at the
front panel.
4
5
Some of the output voltages are read back to the Synthesis IC via the
System ADC. Here, voltages from various circuits in the instrument are
multiplex ed with the Modulation IN signal and meas ured by the
Synthesis IC.
The 14–bit waveform DAC is loaded with data from the Synthesis IC.
The output is then fed through one of two filters before being buffered
and sent to the Main Output Circuitry.
97
Page 98

5
A portion of the output sine wave is squared by a comparator and used to
create a variable du ty c ycle si gn al us ed b y th e Synt hes is IC t o crea te t he
squarewave, pulse generator clock, and sync signals.
The squarewave DAC output is split into two opposite value signals and
applied to a multiplexer. The output of this multiplexer is a square wave
or pulse signal with the correct duty cycle. The rising edge and falling
edge of the signal are adjusted and the signal is buffered and sent to the
Main Output Circuit.
The Main Output circuit accepts one of two inputs; the sine/arb
waveform or the squarewave/pulse waveform. Once selected, the signal
can be applie d to one or bo th att e nua to r s and/or a +20 dB amplifier. The
attenuators and amplifier are used to create the requested output signal
amplitude.
The output is protected by a relay. When the relay is open, the
instrument can read the value of the Main Output Circuit. The output
relay is opened o n user co mmand, i f a cur rent ov erload is detected , or if a
voltage over–range condit io n is foun d.
Conventions Used on Schematics and in this Discussion
Major signal and control lines are marked with a name in uppercase.
If the name is followed by an * (for example, TRIG_SYNC*), the line
is inverted logic. If the name is followed by a lowercase e, (for example,
TRIGe), the line is t he ECL-level version of a TLL or CMOS signal.
98
Page 99

Chapter 5 Theory of Operation
Block Diagram
4
99
5
Page 100

Chapter 5 Theory of Operation
1
Main Power Supply
Power Supplies
The line input voltage is filtered and applied to the main power supply.
The main power supply provides all power to the instrument. S econdary
power supplies are contained on the main circuit board. The secondary
power supplies include both isolated and earth-referenced supplies.
5
+15V
+5V
+3.3V_ISO
+1.8V_ISO
–5V
–15V
+3.3V_ER
+1.8V_ER
10-240 Vac
Power
Switch
Line
Filter
Display Backlight
Main Supply
+12V
K1201
CCFL_ON
(from U101)
PWR_ON
Isolated
Power
Supplies
Earth
Referenced
Power
Supplies
FAN
A1 Power SuppliesFront Panel
Main Power Supply
The main power supply is a switching supply. No schematic is given for
this supply since it should b e replaced as a unit. The main power supply
provides an earth referenced +12 Volts to the A1 circuit board.
The +12 Volt supply is always active if line power is applied to the
instrument. Switching the instrument power switch only affects the A1
secondary po wer su p plie s.
100
 Loading...
Loading...